Z-Morh Tunnel
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Z-Morh Tunnel at Sonamarg, which has now been renamed the Sonamarg Tunnel.
Key Takeaways:
- A 6.4-km bi-directional tunnel with an approach road of 5.6 km, Z-Morh connects the Sonamarg health resort with Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- The tunnel has acquired its name for the Z-shaped road stretch that was previously at the place where the tunnel is being constructed.
- The Z-Morh project was initiated by the Border Roads Organisation in 2012. Although the BRO awarded the construction contract to Tunnelway Ltd, the project was subsequently taken over by National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Significance
Strategic Importance
- Connectivity: Provides all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh, ensuring year-round access.
- Military Significance:
- Critical for rapid deployment of Indian Armed Forces to Ladakh’s border areas, particularly in the context of tensions with Pakistan and China.
- Reduces dependence on air transport, lowering costs and increasing the longevity of the Indian Air Force’s aircraft.
- Adjacent Projects:
- Zojila Tunnel: An even more crucial project connecting Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion by December 2026 (extended to 2030). This will bypass the avalanche-prone Zojila Pass.
- Srinagar-Leh Highway: The Z-Morh Tunnel supports the key Srinagar-Leh route, which is important for defence logistics and trade.
Economic Significance
- Tourism:
- Sonamarg, known as the "Meadow of Gold," will benefit from year-round accessibility, boosting tourism.
- Local businesses that rely on seasonal tourist traffic will have consistent revenue flow.
- Trade and Agriculture:
- Reduced travel time and improved road safety will benefit farmers and traders, especially for those transporting goods between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Facilitates increased investment and economic growth in the region.
Broader Infrastructure Projects in Jammu & Kashmir
Several key infrastructure projects are contributing to regional development:
- Zojila Tunnel
- Cost: ?6,800 crore
- Length: 13 km tunnel, bypassing Zojila Pass.
- Completion: Expected by 2030.
- Strategic Importance: Provides all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
- Srinagar Semi-Ring Road
- Cost: ?2,919 crore
- Objective: Relieve traffic congestion in five districts, including Srinagar.
- Delay: New completion date is June 2025.
- Hydroelectric Power Projects:
- Ratle HE Project: 850 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar district.
- Kwar HE Project: 540 MW, in Kishtwar.
- Pakal Dul HE Project: 1,000 MW, on the Marusudar River, Kishtwar.
- Kiru HE Project: 624 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar.
- Strategic Relevance: These projects will enhance energy security and contribute to the region’s power grid.
Anji Khad Bridge

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Overview:
- The Anji Khad Bridge is India's first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Jammu and Kashmir’s Reasi district.
- It is a key part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project aimed at enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Kashmir and the rest of India.
- The bridge crosses the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab River, and is expected to transform regional transport, boost tourism, and promote economic growth.
Key Features:
- Dimensions:
- Total length: 725.5 meters.
- Main Pylon Height: 193 meters from the foundation, standing 331 meters above the riverbed.
- The bridge is designed for train speeds of up to 100 km/h and can withstand wind speeds of up to 213 km/h.
- Structure and Design:
- Asymmetrical cable-stayed design supported by 96 cables with varying lengths (82 to 295 meters).
- The structure includes:
- A 120-meter approach viaduct on the Reasi side.
- A 38-meter approach bridge on the Katra side.
- A 473.25-meter cable-stayed portion crossing the valley.
- A 94.25-meter central embankment linking the main bridge to the approach viaduct.
- Construction Techniques:
- Used advanced construction techniques such as DOKA Jump Form Shuttering, Pump Concreting, and Tower Crane Technique to enhance safety and reduce construction time by 30%.
- A 40-ton tower crane imported from Spain was employed for operations at great heights.
- The project utilized site-specific investigations by IIT Roorkee and IIT Delhi due to the region’s complex geological and seismic conditions.
- Engineering Challenges:
- The bridge had to be constructed in the difficult Himalayan terrain, with fragile geological features such as faults and thrusts.
- Seismic activity in the region required additional precautions in the design and construction process.
- Safety and Monitoring:
- Equipped with an integrated monitoring system that includes multiple sensors to ensure the structural health of the bridge during operation.
Importance and Impact:
- Connectivity: The bridge will significantly improve connectivity between Katra and Reasi, ensuring faster rail travel and linking the Kashmir Valley with the rest of India.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Expected to boost tourism and economic development by improving access to the region, attracting visitors, and facilitating smoother transportation of goods and services.
- Sustainability: The bridge's design ensures it remains safe under extreme weather conditions, offering long-term reliability for the Indian Railways network.
Collaboration and International Expertise:
- The design and supervision were handled by ITALFERR (Italy), with proof-checking conducted by COWI (UK).
- The project combines Indian engineering codes with Eurocodes, adhering to international standards for structural integrity.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
PM GatiShakti National Master Plan

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Prime Minister commended the completion of three years of the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, calling it a transformative initiative for India’s infrastructure development.
- Key Benefits: The plan enhances multimodal connectivity and improves efficiency across various sectors, contributing to logistics, job creation, and innovation.
Overview of PM GatiShakti National Master Plan
- Launch Date: October 2021
- Objective: A transformative initiative worth ?100 lakh crore aimed at revolutionizing India’s infrastructure over five years.
- Development Tool: Created as a Digital Master Planning tool by the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N).
- GIS Platform: Utilizes a dynamic Geographic Information System to integrate action plans from various ministries into a comprehensive database.
- Goals: Accelerate project completion, reduce timelines, and enhance India’s global competitiveness by addressing inter-ministerial challenges.
Key Features
- Digital Integration: A digital platform coordinating the efforts of 16 ministries for seamless infrastructure planning.
- Multi-Sector Collaboration: Incorporates initiatives from major programs like Bharatmala and Sagarmala.
- Economic Zones Development: Focuses on key areas such as textile clusters and pharmaceutical hubs to boost productivity.
- Technology Utilization: Employs advanced spatial planning tools and ISRO satellite imagery for data-driven project management.
Core Sectors Driving the Plan
- The National Master Plan is centered around seven primary sectors that enhance economic growth and connectivity, supported by sectors like energy transmission and social infrastructure.
Six Pillars of PM GatiShakti
- Comprehensiveness: Integrates various initiatives through a centralized portal, ensuring efficient planning.
- Prioritisation: Allows ministries to prioritize projects based on national importance and resource allocation.
- Optimisation: Identifies infrastructure gaps and selects the most efficient transportation routes.
- Synchronisation: Ensures coordinated efforts across ministries to avoid delays.
- Analytical Capabilities: Offers extensive data layers for improved spatial planning and decision-making.
- Dynamic Monitoring: Uses satellite imagery for real-time project tracking and adjustments.
Achievements of PM GatiShakti
- District-Level Expansion: Extended to 27 aspirational districts, with plans for 750 in the near future.
- Technological Integration: Enhanced real-time infrastructure planning using geospatial tools.
- Global Outreach: The GatiShakti tool showcased to 30 countries and highlighted at international conferences.
- Social Sector Benefits: Identified areas for new healthcare facilities and improved planning in various districts.
- Rural and Urban Development: Implemented projects for irrigation and city logistics in multiple states.
- Employment Initiatives: Utilized for setting up training institutes near industrial clusters.
All-India Reservoir Status
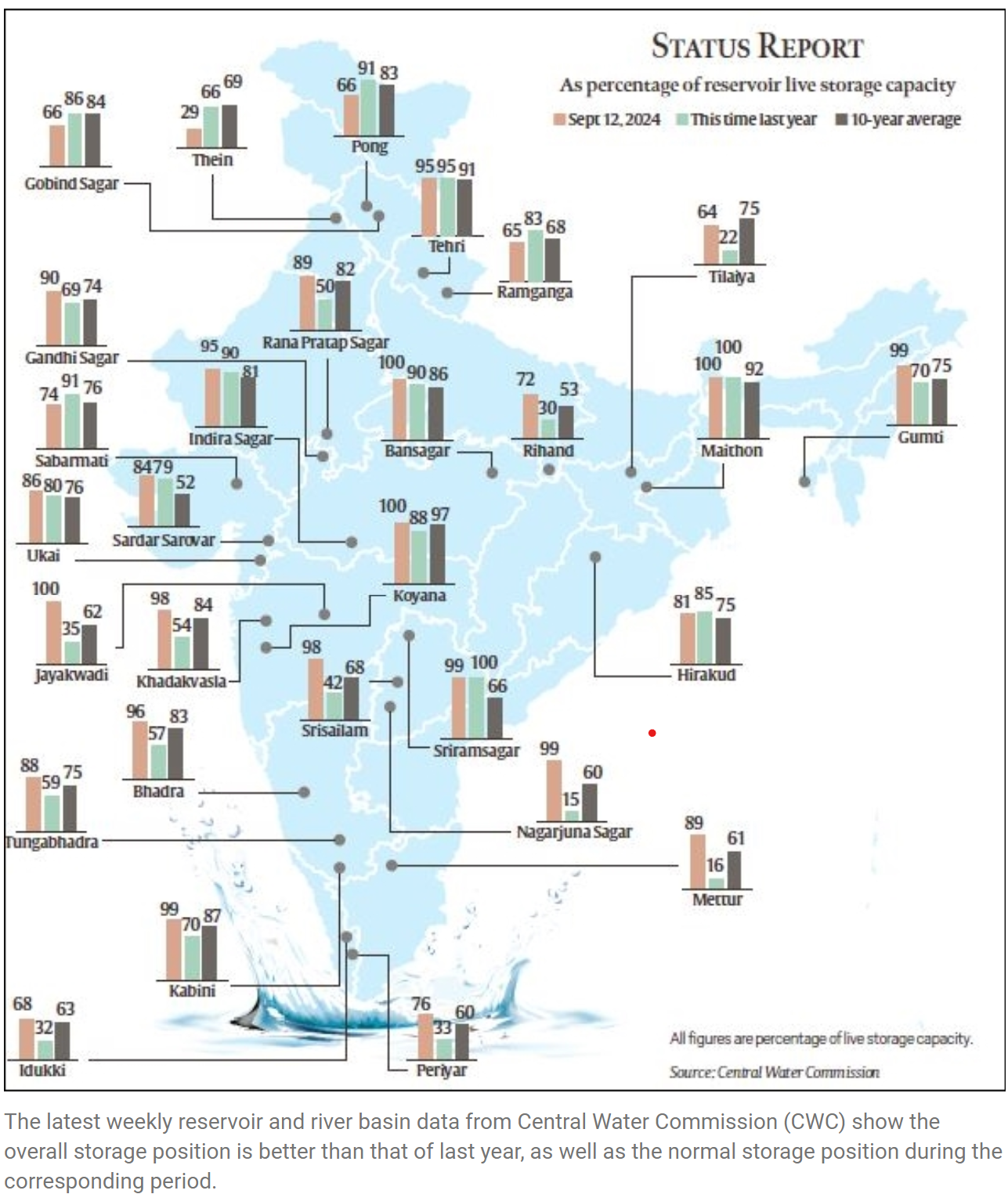
- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
The southwest monsoon has provided significant rainfall across India, with total precipitation at 836.7 mm as of September 12, marking an 8% surplus for this time of year. The Central Water Commission (CWC) reports that reservoir levels are notably higher compared to last year and the 10-year average.
All-India Reservoir Status
- Total Capacity: 180.852 billion cubic metres (BCM) across 155 reservoirs.
- Current Storage: 153.757 BCM, which is 85% of total capacity.
- Last Year Comparison: 119.451 BCM (66%) and 10-year average of 130.594 BCM.
Regional Reservoir Highlights:
- North: 11 reservoirs at 68% capacity (13.468 BCM). Storage is lower than last year (81%) and decadal average (82%). Himachal Pradesh and Punjab saw significant rainfall deficits.
- East: 25 reservoirs at 76% capacity (15.797 BCM), improved from last year's 58%. Despite deficits in Nagaland and Bihar, overall rainfall has supported reservoir levels.
- West: 50 reservoirs at 90% capacity (33.526 BCM), a marked increase from 75% last year. Heavy rainfall, particularly in Gujarat, has led to flooding but boosted water reserves.
- Central: 26 reservoirs at 89% capacity (42.808 BCM), better than last year's 76%. This region has enjoyed normal or above-average rainfall.
- South: 43 reservoirs at 88% capacity (48.158 BCM), significantly higher than 49% last year. Regions traditionally receiving less monsoon rain have also seen improvements.
Comparison to 2023
- Improved Storage: Notable increases in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, and several others.
- Stable: No change in Goa and Telangana.
- Declines: Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Uttarakhand show worse conditions compared to last year.
River Basin Status
Major river basins exhibit normal or above storage levels, including:
- Barak (98.72%)
- Krishna (94.53%)
- Cauvery (93.54%)
- Narmada (92.19%)
- Godavari (91.85%)
- Others range from 83% to 66%.
Overall, the 2024 monsoon has led to improved water storage conditions across much of India, benefiting numerous states while highlighting specific areas of concern.
PM Gram Sadak Yojana-IV

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the proposal of the Department of Rural Development for “Implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana - IV (PMGSY-IV) during FY 2024-25 to 2028-29”.
- The financial assistance is to be provided for the construction of 62,500 Kms road for providing new connectivity to eligible 25,000 unconnected habitations and construction/upgradation of bridges on the new connectivity roads. Total outlay of this scheme will be Rs. 70,125 crore.
Details of the Scheme:
The details of the approval given by the Cabinet are as follows:
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana -IV is launched for financial year 2024-25 to 2028-29. Total outlay of this scheme is Rs. 70,125 crore (Central Share of Rs. 49,087.50 crore and Sate Share of Rs. 21,037.50 crore).
- Under this scheme 25,000 unconnected habitations of population size 500+ in plains, 250+ in NE & Hill Sates/UTs, special category areas (Tribal Schedule V, Aspirational Districts/Blocks, Desert areas) and 100+ in LWE affected districts, as per Census 2011 will be covered.
- Under this scheme 62,500 Km of all-weather roads will be provided to unconnected habitations. Construction of required bridges along the alignment of the all-weather road will also be provided.
Benefits:
- 25,000 unconnected habitations will be provided all weather road connectivity.
- The all-weather roads will play the role of catalysts for the required socio-economic development and transformation of the remote rural areas. While connecting habitations, the nearby government educational, health, market, growth centers will be connected, as far as feasible, with the all-weather road for the benefit of the local people.
- The PMGSY -IV will incorporate international benchmarks and best practices under road constructions such as Cold Mix Technology and Waste Plastic, Panelled Cement concrete, Cell filled concrete, Full Depth Reclamation, use of construction waste and other wastes such as Fly Ash, Steel Slag, etc.
- PMGSY -IV road alignment planning will be undertaken through the PM Gati Shakti portal. The planning tool on PM Gati Shakti portal will also assist in DPR preparation.
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- PMGSY is a central government scheme launched in 2000 to provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected rural habitations.
- The scheme was originally a 100% centrally-sponsored initiative, but starting from the financial year 2015-16, the funding has been shared between the Central and State governments in a 60:40 ratio.
Good Digital Public Infrastructure
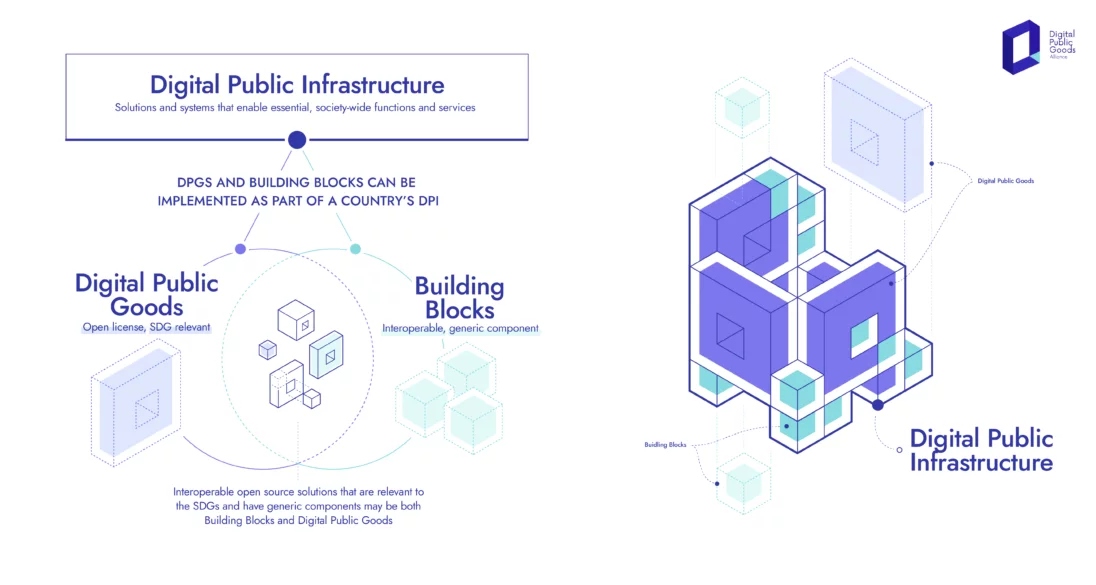
- 08 Sep 2024
Good digital public infrastructure (DPI) integrates technology with societal needs, ensuring that it is secure, scalable, and inclusive.
India’s achievement of over 80% financial inclusion in just six years has drawn international praise, particularly as a model for the Global South. This accomplishment underscores India’s success in achieving both digital and financial inclusion for over a billion people. Consequently, the G20 summit in New Delhi in 2023 highlighted the critical role of digital public infrastructure.
In response, India’s G20 task force has released a comprehensive report outlining a global strategy for DPI development. This positions India to support other nations in achieving digital sovereignty, financial inclusion, and self-reliance.
The evolving digital landscape is marked by a variety of stakeholders—including private enterprises, government bodies, non-profits, and think tanks—each working to advance their DPI solutions. This raises two key questions: How can we identify genuine and reliable DPIs from the plethora available? And what differentiates a “good DPI” from a “bad DPI”?
Identifying effective DPI involves assessing how well technology meets societal needs while ensuring security, scalability, and inclusivity. Authenticity and adherence to core principles are essential for evaluating DPIs.
The Citizen Stack Model
Citizen Stack, built upon the proven success of India Stack, emerges as a trusted ecosystem in digital infrastructure. India Stack, a robust digital platform, has demonstrated its effectiveness and security on a vast scale, serving over a billion citizens. This strong foundation enhances Citizen Stack’s credibility and reliability. Unlike DPI manufacturers, Citizen Stack functions as a regulatory body or auditor, certifying and authenticating DPIs to ensure they meet high standards of quality and security.
Citizen Stack’s approach is comprehensive, focusing on security, scalability, and inclusivity. The DPI platforms approved by Citizen Stack are designed to meet the diverse needs of large populations while maintaining stringent security measures to protect user data and privacy. As an auditor, Citizen Stack ensures that certified DPIs are dependable, secure, and beneficial to the public.
In an era of abundant digital solutions and promises, distinguishing genuinely reliable platforms is essential. Citizen Stack offers assurance as a gold standard for DPI solutions.
Guiding Principles of a “Good DPI”
Citizen Stack has established five core principles—referred to as sutras—that define a good DPI:
- Maintain Citizen Relationships: Ensure that digital infrastructure supports a fair relationship between citizens, the market, and the state, free from undue influence.
- Protect Empowerment and Privacy: Implement consent-based data sharing systems that prioritize individual empowerment and privacy.
- Prevent Monopolistic Lock-In: Ensure interoperability to avoid citizens being restricted by monopolistic entities.
- Combine Techno-Legal Regulation: Integrate technology with legal frameworks to govern ethical tech use, ensuring innovation while safeguarding security and societal rights.
- Foster Public-Private Innovation: Encourage collaboration between public and private sectors, while avoiding corporate dominance. The focus should be on public good rather than corporate monopolies, and technology should prevent exploitation by state or corporate actors.
International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI)

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Countries must build “resilient infrastructure” against natural disasters that are becoming more frequent and severe, said Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently.
About the Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI):
- The Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) is a global partnership comprising national governments, UN agencies and programs, multilateral development banks, private sector entities, and academic institutions.
- Established during the United Nations Climate Action Summit in 2019 in New York, CDRI is dedicated to addressing the challenges associated with building resilience in infrastructure systems and development processes.
Objectives:
- CDRI aims to enhance the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks, thereby promoting sustainable development.
- It seeks to expedite the development and retrofitting of resilient infrastructure to meet the imperatives of the Sustainable Development Goals, including universal access to basic services and fostering prosperity and decent work.
- Serving as an inclusive multi-stakeholder platform, CDRI is led and managed by national governments. It facilitates the exchange of knowledge on various aspects of infrastructure resilience.
- CDRI brings together diverse stakeholders to create mechanisms assisting countries in upgrading their capacities, systems, standards, regulations, and practices related to infrastructure development, tailored to their risk contexts and economic needs.
Membership:
- Since its inception, 39 countries, 7 international organizations, and 2 private sector organizations joined as members.
- International organizations include:
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- World Bank Group
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)
- European Union
- European Investment Bank, and
- The Private Sector Alliance for Disaster-Resilient Societies (ARISE)
- The CDRI is the second major coalition launched by India outside of the UN, the first being the International Solar Alliance.
Secretariat:
- CDRI's secretariat is based in New Delhi, India.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
iBUS, a digital infrastructure solutions company, said recently it has raised $200 million from the government-backed National Investment and Infrastructure Fund Limited (NIIF).
What is the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)?
- The National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) stands as a pioneering fund manager dedicated to investing in India's infrastructure and related sectors.
- Established in 2015, NIIF marks India's inaugural sovereign wealth fund (SWF), embodying a collaborative investment platform for both international and domestic investors.
Key Aspects of NIIF:
- Investment Mandate: NIIF operates with a mandate to deploy equity capital into domestic infrastructure projects, spanning greenfield, brownfield, and stalled ventures.
- Its investment horizon extends across diverse asset classes, including infrastructure, private equity, and other sectors, all aimed at delivering attractive risk-adjusted returns.
- Ownership and Independence: With 49% ownership by the Indian government, NIIF boasts over $4.9 billion in assets under management, solidifying its status as the nation's largest infrastructure fund.
- Despite its close ties with the government, NIIF maintains autonomy in its investment decisions, ensuring a professional and impartial approach to its operations.
- Professional Management: The fund is predominantly owned by institutional investors and managed by a proficient team with expertise in both investments and infrastructure.
- This professional oversight ensures the strategic deployment of capital and efficient management of investments.
- Regulatory Compliance: NIIF operates within the regulatory framework as an Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) registered with the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- It actively raises capital from a spectrum of domestic and international institutional investors, further bolstering its financial resources.
NIIF manages capital through four distinct funds:
- NIIF Master Fund: Focused on infrastructural projects such as roads, ports, airports, and power, it stands as India's largest infrastructure fund.
- NIIF Private Markets Fund: Invests in infrastructure and associated sectors through third-party managed funds.
- NIIF Strategic Opportunities Fund: Devoted to developing large-scale businesses and greenfield projects deemed strategically significant for the nation.
- India-Japan Fund: NIIF's bilateral initiative aimed at environmental preservation in India, with contributions from both the Indian government and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation.
- NIIF catalyzes fostering sustainable infrastructure development in India while facilitating fruitful collaborations between Indian and international stakeholders, exemplifying a robust model for investment-driven growth.
NHAI to start rolling out satellite-based tolling on national highways soon

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said in Parliament in February that the government plans to implement a new highway toll collection system based on the global navigation satellite system before the model code of conduct for the 2024 election kicks in.
What is the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)?
- GNSS refers to a constellation of satellites providing signals from space that transmit positioning and timing data to GNSS receivers.
- The receivers then use this data to determine location.
- Examples of GNSS include Europe’s Galileo, the USA’s GPS, Russia’s GLONASS and China’s BeiDou
How will the GNSS-Based Toll System work?
- The system will use an automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) system through cameras installed on highways and deduct tolls based on the distance traveled by a vehicle.
- The device monitors the movements while driving, accurately marking the entry and exit points on tolled segments. By analyzing travel distance, it computes the charges accordingly.
- This eliminates the uniformity of fixed tolls at booths, ensuring fairness for drivers traversing shorter distances.
Difference between FASTags and ANPR technology:
- FASTags streamline electronic toll payments at toll plazas equipped with scanners, enabling vehicles to pass through without stopping.
- Conversely, GNSS-based systems utilize ANPR technology to deduct tolls based on distance traveled, rendering traditional toll plazas unnecessary.
What are the Challenges?
- Detection of Non-Compliance: Without physical barriers, detecting non-compliant vehicles, such as those without an On-Board Unit (OBU) or engaging in fraudulent activities, poses a challenge.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying gantry-mounted Automatic Number-Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems along highways is essential for capturing violations and enforcing toll payments.
- License Plate Quality: The effectiveness of ANPR systems relies on the quality of license plates; subpar plates hinder accurate recognition and enforcement efforts.
- Data Privacy and Security: GNSS-based toll systems entail collecting and processing sensitive location data, necessitating robust privacy and security measures.
PM Modi Inaugurates 'Sudarshan Setu', India's Longest Cable-Stayed Bridge
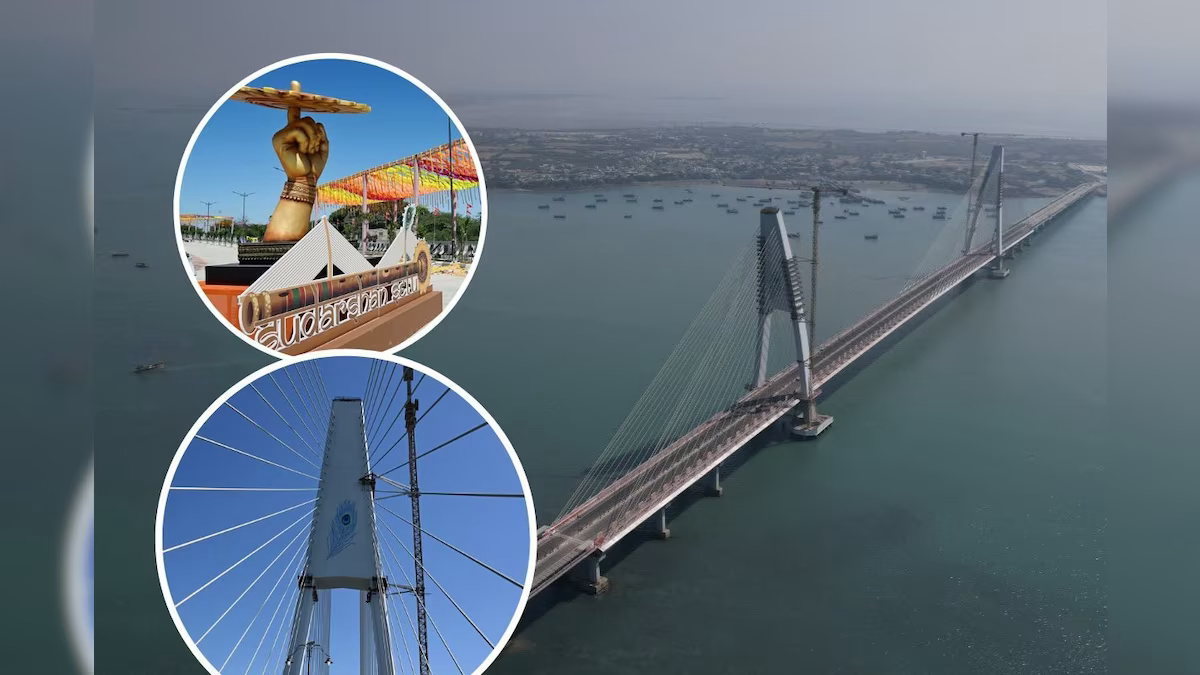

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently inaugurated the Sudarshan Setu, a four-lane cable-stayed bridge connecting Okha to Beyt Dwarka island in Gujarat.
About the Sudarshan Setu:
- 'Sudarshan Setu' is the country's longest cable-stayed bridge 2.32 km on the Arabian Sea connecting Beyt Dwarka island to mainland Okha in Gujarat's Devbhumi Dwarka district.
- It boasts a unique design, featuring a footpath adorned with verses from the Bhagavad Gita and images of Lord Krishna on both sides.
- It also has solar panels installed on the upper portions of the footpath, generating one megawatt of electricity.
- The 2.32 km bridge, including 900 metres of a central double-span cable-stayed portion and a 2.45 km long approach road, has been constructed at a cost of Rs 979 crore.
About Beyt Dwarka:
- Bet/Beyt (pronounced ‘Bait’ Dwarka also known as Shankhodara, is an island located near the shores of Okha which is situated around 30 km from Dwarka, in the Gulf of Kutch.
- It said that Lord Krishna resided here while Dwarka was his constitutional seat.
History:
- Bet Dwarka derived its name from the word ‘bet’ which translates to ‘gift’ and is believed that Lord Krishna received it from his friend Sudama.
- In the ancient epic, Mahabharata, Bet Dwarka is known by the name of ‘Antardvipa’ to which people of the Yadava clan needed to travel by boat.
- Explorations and excavations carried out under the sea have revealed the presence of settlements whose age can be traced back to the era of the Harappan civilisation and that of the Mauryan rule.
- In the later years, the region was under the administration of the Gaekwad clan of the state of Baroda.
- During the revolt of 1857, Vaghers attacked the region and captured it, but had to concede defeat in two years and return the region back to the Gaekwads.
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (PIB)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the continuation of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to be implemented under the Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund:
- This initiative operates as a Central Sector Scheme aimed at incentivizing investments from various entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSMEs, Farmer’s Producers Organizations (FPOs), and Section 8 companies.
- These investments are directed towards establishing infrastructure for:
- Dairy processing and value addition
- Meat processing and value addition
- Animal feed plants
Objectives:
- Facilitating the expansion of milk and meat processing capacity and diversification of products, thereby granting unorganized rural milk and meat producers greater access to organized markets.
- Enhancing price realization for producers and ensuring the availability of quality milk and meat products for domestic consumers.
- Promoting exports and elevating the sector's contribution to export revenue.
- Providing quality concentrated animal feed to cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry, ensuring balanced rations at affordable prices.
- The Government of India offers a 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, including a two-year moratorium, for loans covering up to 90% of the investment.
- These loans are accessible from scheduled banks, the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), NABARD, and NDDB.
- Notably, government entities and cooperatives are excluded from availing benefits under this scheme.
What is Animal Husbandry?
- Animal husbandry encompasses the controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, with a focus on enhancing desirable qualities through breeding.
- It serves as a vital branch of agriculture dedicated to animals raised for various purposes such as meat, fibre, milk, and other products.
- This involves day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the overall management of livestock.
- In India, animal husbandry plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of many farmers, offering significant self-employment opportunities, particularly for landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, and women.
- The sector contributes to providing affordable and nutritious food to millions of Indians through the production of meat, eggs, milk, and other essential items.
- Additionally, it serves as a valuable source of raw materials such as hides, skins, bones, blood, and fat.
- Animals are often regarded as the best insurance against natural calamities like drought, famine, and other adversities, providing a degree of stability to farmers in unpredictable conditions.
Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (Indian Express)
- 05 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Authorities from the Ministry of Union Housing and Urban Affairs have indicated that the initial installment of loans for supporting ongoing projects in tier-2 and tier-3 cities through the Urban Infrastructure Development Fund (UIDF) is expected to be released shortly.
Facts About:
The UIDF is created by utilizing the priority sector lending shortfall.
Objective:
- This fund serves as a resource for public agencies to develop urban infrastructure in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
Emphasis is placed on essential services such as sewage and solid waste management, water supply, sanitation, construction, and improvement of drainage systems, with a priority on projects that have a significant impact.
The National Housing Bank manages this fund.
It initially has a corpus of ?10,000 crore and is modeled after the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF).
States are encouraged to harness resources from the 15th Finance Commission's grants and existing schemes, while also considering user charges when accessing the UIDF.
Currently, it covers 459 tier-2 cities and 580 tier-3 cities.
UIDF Loans:
- nterest rate: Bank Rate minus 1.5%
- The loan principal is repayable in five equal annual installments within seven years from the draw date, including a two-year moratorium period.
- Interest payments are made on a quarterly basis.
