Eighth Pay Commission

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union government has approved the constitution of the Eighth Pay Commission, benefiting 50 lakh central government employees and 65 lakh pensioners, including serving and retired defence personnel. The decision, taken ahead of the Delhi Assembly elections, aims to address long-standing demands from trade unions and employee organizations.
Key Features of the 8th Pay Commission
- Early Constitution: Although the Seventh Pay Commission's term ends in 2026, the early establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission ensures timely recommendations and implementation.
- Composition: The commission will have a Chairperson and two members, typically led by a retired Supreme Court judge.
- Terms of Reference (ToR):
- Revision of Pay: Recommend updates to salary structures and allowances.
- Addressing Pay Disparities: Resolve wage differences across various cadres.
- Market Parity: Align pay structures with industry standards.
- Pension and Retirement Benefits: Improve pension schemes and adjust them for inflation.
- Economic Impact Analysis: Assess how salary hikes contribute to economic growth.
- Stakeholder Consultations: Engage with governments and other stakeholders before finalizing recommendations.
Economic Implications of the 8th Pay Commission
- Employee Well-being: Higher wages will enhance the quality of life for government employees.
- Boost to Consumption: Increased salaries are expected to stimulate demand and support economic expansion.
- Ripple Effect on PSUs & States: Many public sector undertakings and state governments follow the central pay commission’s recommendations, potentially leading to wider economic benefits.
- Fiscal Considerations: The implementation of the Seventh Pay Commission in 2016-17 led to an expenditure increase of ?1 lakh crore. A similar rise in 2026-27 could impact fiscal space for capital expenditures.
Challenges and Concerns
- Implementation Delays: Past commissions have taken two years to submit recommendations, which could push implementation beyond 2027.
- Living Wage & Pension Issues: Existing formulas for minimum wage and pension calculations may need revision to reflect rising healthcare, education, and digital access costs.
- Financial Burden on the Exchequer: A significant increase in revenue expenditure could limit the government’s ability to invest in infrastructure and development projects.
Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
Section 479 of the BNSS 2023

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Centre urges states, UTs to ensure undertrial prisoner relief in jails.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The MHA has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to implement provisions of Section 479 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 to provide relief to undertrial prisoners (UTPs) in jails. This initiative aims to address issues such as long detention and overcrowding in prisons.
Key Provisions of Section 479 of BNSS, 2023
- Purpose: To offer relief to undertrial prisoners by mandating their release on bail or bond under specific conditions.
- Key Provisions:
- Subsection (1):
- Release on Bail: UTPs who have served half the maximum sentence for their offense (except offenses punishable by death or life imprisonment) are eligible for release on bail.
- Release on Bond for First-Time Offenders: First-time offenders, who have served one-third of the maximum sentence, are eligible for release on bond by the court.
- Subsection (3):
- Mandatory Application: It is the responsibility of the prison superintendent to apply to the concerned court for the release of eligible prisoners on bail or bond.
- Subsection (1):
- Superintendent’s Role:
- Prison superintendents are mandated to ensure timely applications for bail or bond are filed for eligible UTPs.
Implementation and Reporting
- MHA’s Advisory:
- On January 1, the MHA issued a letter to the Chief Secretaries, Director Generals, and Inspectors General of prisons in all states and UTs to ensure compliance with the provisions of Section 479 of BNSS.
- States and UTs were instructed to report the status of implementation in a prescribed format starting from January 1, 2025.
- Data to be Reported:
- First-Time UTPs: Number of first-time UTPs who have served one-third of their maximum sentence.
- Court Applications: Number of applications for bail filed by jail superintendents.
- Release on Bail: Number of UTPs released on bond or bail after meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Other UTPs: Number of UTPs who have completed half of their sentence, and the number of applications filed for their release.
- MHA’s Campaign:
- Launched on Constitution Day (November 26), this campaign encouraged states and UTs to identify eligible prisoners and file their bail applications, thus helping to reduce overcrowding in prisons and mitigate long-term detention.
Background and Context
- Why Section 479?
- Section 479 aims to reduce the prolonged detention of undertrials, some of whom may have already served significant portions of their maximum sentences. This will not only alleviate overcrowding in prisons but also expedite justice for prisoners who have spent extended periods in jail awaiting trial.
- Earlier MHA Initiatives:
- Prior to this directive, the MHA had issued an advisory on October 16, 2024, encouraging states and UTs to implement Section 479. A special push was also made during Constitution Day to move applications for the release of eligible prisoners.
- Expected Outcome:
- The measures are expected to significantly ease the challenges of overcrowded jails and provide timely relief to undertrials, especially first-time offenders. By enforcing these provisions, the government seeks to improve the judicial process for UTPs and contribute to a more effective and humane criminal justice system.
Open Data Kit (ODK) Toolkit

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has deployed the Open Data Kit (ODK) platform to enhance transparency in government spending and improve accountability in the delivery of government schemes.
- The toolkit is being used for designing, collecting, and managing data relevant to audits.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Enhance transparency in public spending.
- Improve accountability in government schemes and projects.
- Collect real-time beneficiary feedback to aid audit planning and identify areas needing additional review.
Key Features:
- End-to-end encryption: Ensures secure data management.
- Integration with CAG’s Operating System (OIOS): Facilitates seamless analysis and management of data.
- Multi-language support: Allows for surveys in multiple languages, making it more accessible to diverse beneficiaries.
- User-friendly interface: Simplifies the design and management of data collection processes for auditors.
Usage and Applications:
- Beneficiary surveys are a key tool for gathering data, helping CAG identify problem areas in government schemes.
- The ODK toolkit was recently deployed in audits of AIIMS institutions in Mangalagiri (Guntur) and Bibinagar (Hyderabad) to assess patient satisfaction and gather evidence for performance reviews.
Working Process:
- Surveys are designed on the ODK platform and deployed to beneficiaries.
- Data is collected in real-time and analyzed using the OIOS system to generate actionable insights for audits.
- Beneficiary feedback is used to evaluate scheme delivery and improve efficiency.
Significance:
- Facilitates data-driven decision-making in audits, ensuring that audits are more transparent and evidence-based.
- Improves the citizen-centric evaluation of government schemes by gathering direct feedback from beneficiaries.
- Enhances the performance review of key institutions like AIIMS, contributing to better service delivery.
- The introduction of the ODK toolkit is part of the CAG’s efforts to use digital tools for better governance and accountability in the public sector. This also aligns with the growing trend of using technology for governance and auditing.
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
PM CARES Fund Contributions and Utilization (2022-23)
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM CARES Fund) received Rs 912 crore in contributions during the financial year 2022-23 as donations continued to pour in even after the Covid pandemic.
Key Highlights:
Contributions Received:
- Total contributions in 2022-23: Rs 912 crore.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 909.64 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 2.57 crore.
Interest Income:
- Total interest income for 2022-23: Rs 170.38 crore.
- From regular accounts: Rs 154 crore.
- From foreign contributions account: Rs 16.07 crore.
Refunds and Additional Inflows:
- Rs 225 crore in refunds, including:
- Rs 202 crore refund from procurement of 50,000 ventilators for government hospitals.
Disbursements:
- Total disbursed in 2022-23: Rs 439 crore:
- Rs 346 crore for PM CARES for Children.
- Rs 91.87 crore for procurement of 99,986 oxygen concentrators.
- Rs 1.51 crore for refunds.
- Rs 24,000 for legal charges, and Rs 278 for bank and SMS charges.
Cumulative Contributions (2019-23):
- Rs 13,605 crore received from 2019-20 to 2022-23.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 13,067 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 538 crore.
- Interest income over these years: Rs 565 crore.
About PM CARES Fund:
Formation and Purpose:
- Established: March 27, 2020, as a Public Charitable Trust under the Registration Act, 1908.
- Purpose: To address emergencies like COVID-19, natural disasters, and man-made calamities. It also supports healthcare infrastructure and essential facilities.
Governance and Structure:
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister (ex-officio).
- Trustees: Defence, Home, and Finance Ministers (ex-officio).
- Additional Trustees: Appointed by the PM, serving on a non-profit basis (e.g., Justice K T Thomas (retd.) and Kariya Munda).
Tax Exemptions:
- Donations are eligible for 100% tax exemption under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Donations qualify as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The fund is exempt under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), allowing it to receive foreign donations.
Reassessment of Conjugal Visits in Delhi Prisons

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi government is reassessing the proposal to permit conjugal visits for prisoners, following the suspension of a similar initiative in Punjab.
- Delhi Chief Minister has sought further input from the Law Department and explored if similar schemes are implemented in other states.
Conjugal Visits - Definition & Context:
- Conjugal visits involve allowing prisoners to spend private time with their legal partners or spouses, including intimate relations, within prison premises.
- No national policy exists in India for conjugal rights of prisoners, leading to varied implementations across states.
Punjab’s Pilot Project - ‘Parivar Mulakat’:
- Ludhiana Central Jail introduced the 'Parivar Mulakat' programme in September 2022, allowing face-to-face meetings with family in designated rooms.
- The initiative was suspended shortly after its launch due to security concerns, particularly difficulty in conducting thorough body checks on visitors.
Challenges in Delhi:
- Overcrowded prisons in Delhi make it challenging to manage the logistical demands of conjugal visits, especially with up to 1,200 daily visitations.
- The Home Department has received proposals but no progress has been made over the past year.
Legal Precedents on Conjugal Rights:
- Punjab and Haryana High Court (2014) ruled that prisoners have a right to conjugal visits to facilitate procreation.
- Madras High Court (2018) allowed a life convict on parole for conjugal relations, and in 2023, a judge called for similar considerations for Tamil Nadu.
Human Rights Argument:
- Advocates argue that denying conjugal visits to prisoners violates basic human rights of both prisoners and their spouses, particularly those aged 21-50, who are often in sexually active years.
- Amit Sahni, a social activist, filed a PIL highlighting that most prisoners in Delhi are denied conjugal rights despite their eligibility.
Government’s Position:
- Delhi DG (Prisons) had argued that temporary leave such as parole and furlough serve the purpose of family ties, questioning the need for conjugal visits within prison.
Need for Legal Framework:
- Legal experts suggest the creation of a law and policy framework to regulate conjugal visits, ensuring clear guidelines for their implementation.
- S.D. Singh, a Supreme Court advocate, emphasized that conjugal visits should be legally recognized as a right, requiring formal legislation for consistent implementation.
Future Considerations:
- The Delhi government’s reassessment may lead to a policy that considers both human rights and security concerns in its decision on conjugal visits.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
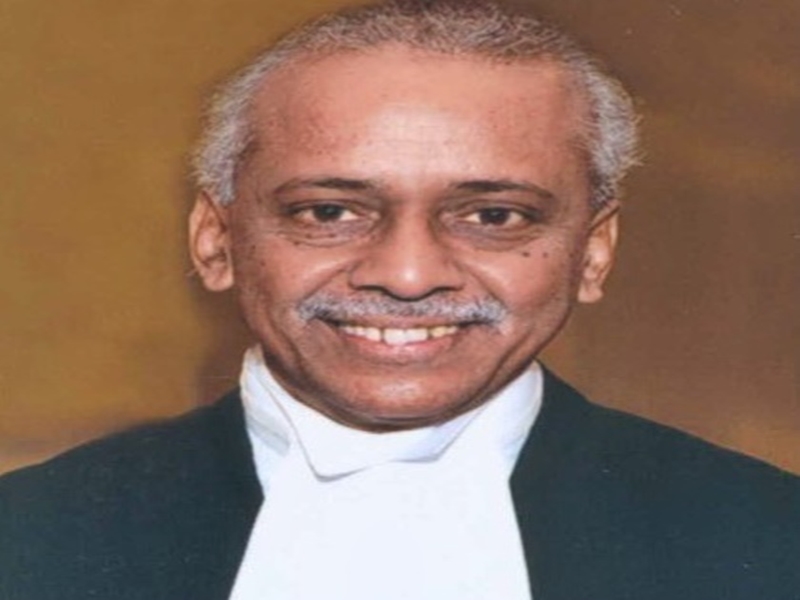

- 24 Dec 2024
In News
Justice V. Ramasubramanian, a retired Supreme Court judge, has been appointed as the new chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC). This decision was made by President Droupadi Murmu, and it comes following the completion of Justice Arun Kumar Mishra's tenure as NHRC chairperson in June 2023. After Justice Mishra's retirement, Vijaya Bharathi Sayani served as the acting chairperson. Alongside Justice Ramasubramanian, Priyank Kanoongo and Dr. Justice Bidyut Ranjan Sarangi (Retd.) have also been appointed as members of the commission.
Justice Ramasubramanian had been appointed a judge of the Supreme Court in September 2019 and retired in June 2023. His appointment to the NHRC is seen as a significant development for human rights advocacy and protection in India.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
Establishment and Legal Framework
- Formation Date: The NHRC was established on October 12, 1993, under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Paris Principles: It was created in alignment with the Paris Principles (1991), which were endorsed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, aimed at setting standards for national human rights institutions.
- Statutory Body: NHRC is a statutory body, meaning it is established by law, with a primary function to safeguard human rights in India.
Objectives
The NHRC's primary objective is to promote and protect human rights as defined in Section 2(1)(d) of the PHRA, which include fundamental rights such as:
- Right to Life
- Right to Liberty
- Right to Equality
- Right to Dignity
These rights are guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and are essential to the protection of individuals' freedoms and welfare.
Composition of NHRC
- Chairperson: A former Chief Justice of India or a former Supreme Court judge serves as the chairperson.
- Members:
- One former or sitting Supreme Court judge.
- One former or sitting Chief Justice of a High Court.
- Three members, with at least one woman, who have experience in human rights matters.
- Ex-Officio Members: The chairpersons of various National Commissions (e.g., SC/ST, Women, Minorities) and the Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities are also part of the NHRC.
Functions and Powers
The NHRC has several crucial functions and powers to ensure the protection and promotion of human rights:
- Inquiry into Human Rights Violations: The commission can inquire into violations of human rights by public servants or negligence in protecting rights.
- Recommendations: It can make recommendations on how to protect, promote, and effectively implement human rights within India.
- Review of Laws: NHRC assesses various laws, treaties, and international instruments related to human rights.
- Research and Awareness: It promotes research, publications, and awareness about human rights issues, including educating the public about their rights and safeguards.
- Inspection of Institutions: NHRC has the authority to visit and inspect institutions such as jails, detention centers, and other places of confinement to ensure the humane treatment of individuals.
72nd North Eastern Council (NEC) Plenary Session

- 23 Dec 2024
Overview:
The 72nd Plenary of the North Eastern Council (NEC), concluded in Agartala, Tripura, marking the second time the city hosted this significant event since 2008. The plenary featured a series of high-level discussions focused on accelerating development and addressing the socio-economic challenges of the North Eastern Region (NER), which includes Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura.
Key Highlights:
- Pre-Plenary Technical Sessions: Central ministries presented their developmental agendas for the NER, charting a path forward for the region's growth and addressing key challenges.
- Main Plenary:
- Presiding Officers: The session was chaired by the Union Home Minister and NEC Chairman, Shri Amit Shah, along with DoNER Minister, Shri Jyotiraditya M. Scindia, and Minister of State, Dr. Sukanta Majumdar.
- Participants: Governors, Chief Ministers, Chief Secretaries, Planning Secretaries, and high-ranking officials from all eight northeastern states will engage in strategic discussions to foster regional development.
- Agartala as Host:
- Agartala's selection as the venue signifies the evolving role of the city in regional development, as plenary sessions are usually held in Shillong and Guwahati.
- Significance of the NEC:
- The North Eastern Council (NEC), established in 1971, plays a pivotal role in the socio-economic development of the region. It was initially an advisory body but has evolved into a regional planning agency with a larger mandate.
- The NEC has contributed significantly to the development of critical infrastructure in the region, such as over 11,500 kilometers of roads, power generation through NEEPCO, and educational institutions like RIMS.
- Prime Minister's Vision for the NER:
- The Prime Minister’s vision for the region revolves around recognizing it as 'Ashta Lakshmi'—symbolizing immense potential and cultural richness. The NEC is central to realizing this vision through initiatives like the PM-DevINE scheme.
Key Achievements of the NEC:
- Over 11,500 kilometers of road construction, improving regional connectivity.
- Increased power generation capacity via projects managed by NEEPCO.
- Established institutions like the Regional Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) and others that cater to regional educational and technical needs.
Recent Focus and Shift in Governance:
- In the 72nd Plenary, the Union Home Minister highlighted a shift in the focus of police forces in northeastern states, urging them to focus not just on insurgency control but on ensuring the constitutional rights of citizens, reflecting a new governance phase in the region.
Parliamentary Standing Committee on Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (PSC) and MGNREGA
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) on Rural Development and Panchayati Raj highlighted several issues within the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS). The committee recommended reforms to address these challenges, especially concerning wage rates, workdays, payment systems, and infrastructure.
Key Challenges in MGNREGS Implementation:
- Wages Not Aligned with Inflation:
- MGNREGA wage rates have failed to keep pace with inflation, diminishing the purchasing power of rural workers. This discourages workers from completing the full 100 workdays.
- The wage guarantee of 100 days per household often falls short, especially during times of natural calamities or post-pandemic recovery.
- Revision of Permissible Works:
- The list of allowable work under MGNREGA is outdated and doesn't cover all rural needs, such as flood protection or land erosion management. Delayed revisions limit its effectiveness in addressing region-specific challenges.
- Delayed Payment of Wages:
- Issues like Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) glitches, inactive Aadhaar details, or frozen bank accounts often lead to delayed wage payments.
- The delay in wages undermines the scheme's goal of providing livelihood support.
- Unemployment Allowance:
- Those who apply for work but are not provided employment within 15 days are entitled to a daily unemployment allowance. However, this allowance is rarely paid, and when it is, the amounts are insufficient.
- Weak Social Audits:
- Social audits are a vital mechanism to ensure transparency and accountability. However, in the 2020-21 fiscal year, only 29,611 Gram Panchayats out of a total were audited, pointing to the weak social audit system.
- Lack of Ombudsman:
- Despite the provision for 715 ombudsmen, only 263 have been appointed. This reduces the oversight and accountability of the scheme.
Recommendations for MGNREGS Reform by the PSC:
- Revision of Wage Rates:
- Link MGNREGA wages to an inflation index, ensuring wages reflect the rising cost of living in rural areas.
- The base year (2009-2010) should be updated to align with current inflation trends.
- Increase Days of Work:
- The PSC recommended increasing the guaranteed workdays from 100 to 150 days. This will provide better livelihood security, especially in times of economic distress.
- Improvement in Payment Mechanisms:
- The committee recommended maintaining alternative payment systems alongside ABPS to prevent wage delays.
- A streamlined process should be put in place to ensure timely wage disbursement, reducing bureaucratic hurdles.
- National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS):
- The committee stressed the importance of training programs to help beneficiaries effectively use the NMMS.
- It also suggested retaining alternative attendance methods to avoid exclusion due to technological barriers. NMMS helps enhance transparency and accountability by tracking attendance and work progress.
- Sufficient Fund Allocation:
- The committee emphasized the need for adequate financial allocations for MGNREGS to make it more effective in providing livelihood security to rural households.
Additional Context and Statistics:
- In 2024-25, the average wage increase under MGNREGA was just Rs 28/day.
- The MGNREGA wage increase for 2023-24 ranged from 2%-10%.
- The Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labour (CPI-AL) is used to determine wage rates, although Dr. Nagesh Singh Committee (2017) recommended using the CPI Rural instead.
About the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (PSC):
- Established: August 5, 2004.
- Jurisdiction: The committee oversees the Ministry of Rural Development and the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- Composition: 31 members – 21 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha.
- Functions:
- Reviews Demands for Grants and reports.
- Examines Bills referred by the Speaker or Chairman.
- Reviews the annual reports of relevant ministries.
- Considers national policy documents.
About MGNREGA:
- Launched: 2005 by the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Objective: Provides 100 days of unskilled manual work at minimum wages for rural households annually.
- Key Features:
- Legal Guarantee: Work must be provided within 15 days of request.
- Unemployment Allowance: If work isn't provided within 15 days, beneficiaries are entitled to a daily allowance.
- Women-Focused: At least one-third of beneficiaries are women.
- Social Audits: Mandated by the Gram Sabha for all projects under the scheme.
One Nation, One Election
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The government has recently taken steps to implement "One Nation, One Election" by presenting two Constitution Amendment Bills in the Lok Sabha: the One Nation One Election – The Constitution 129th Amendment Bill 2024 and the Union Territories Laws Amendment Bill 2024.
Introduction to the Concept:
- Objective: Proposes synchronizing elections for Lok Sabha (national) and State Legislative Assemblies to be held on the same day.
- Purpose: Aims to reduce costs, minimize logistical challenges, and address governance disruptions caused by frequent elections.
- 2024 Report: The High-Level Committee Report on Simultaneous Elections, released in December 2024, outlines a roadmap for implementing this reform.
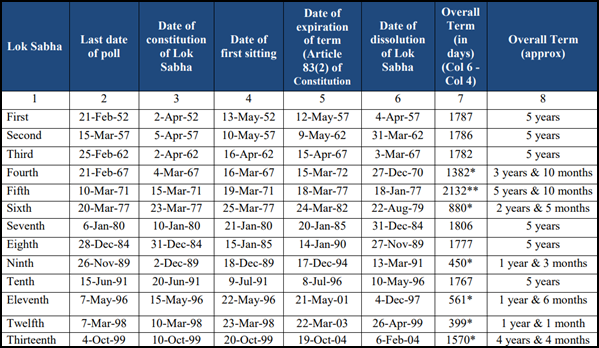
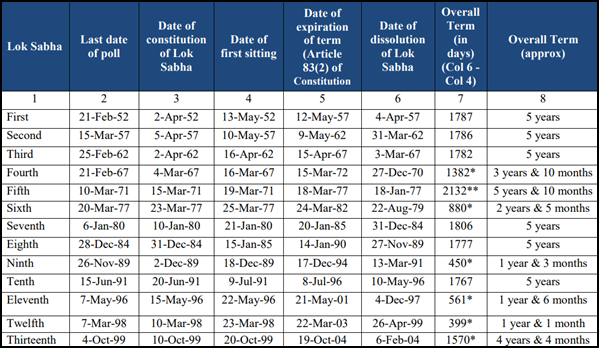
Historical Background:
- Previous Practice: From 1951 to 1967, Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections were conducted together.
- Disruptions: The practice was interrupted due to premature dissolutions and emergencies, leading to staggered elections across India.
High-Level Committee on Simultaneous Elections:
- Committee Formation: Headed by former President Ram Nath Kovind, formed on 2nd September 2023.
- Public Response: Over 21,500 responses, with 80% in favor.
- Political Party Responses: 32 political parties supported the idea, while 15 raised concerns about regional party marginalization.
- Expert Consultations: Majority of experts supported the reform, emphasizing resource optimization and reduced disruptions.
Committee Recommendations:
- Constitutional Amendments: Proposals to amend Articles 82A and 324A to enable simultaneous elections.
- Two-Phase Implementation:
- Phase 1: Synchronize elections for Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Include Municipalities and Panchayats within 100 days.
- Single Electoral Roll: Creation of a unified electoral roll and EPIC for all levels of elections, reducing duplication and errors.
Rationale for Simultaneous Elections:
- Governance Consistency: Reduces focus on election preparation, allowing more attention to developmental work.
- Prevents Policy Paralysis: Mitigates disruptions caused by the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) during frequent elections.
- Resource Optimization: Reduces the need for personnel and resources for election duties, allowing better allocation to governance tasks.
- Preserves Regional Party Relevance: Local issues remain prioritized, ensuring regional parties' concerns are heard.
- Equitable Political Opportunities: Encourages diversification and inclusivity within political parties.
- Financial Benefits: Reduces the financial burden of conducting multiple elections, enhancing economic efficiency.
Conclusion:
- The concept of "One Nation, One Election" is a significant reform aimed at streamlining India's electoral processes. With broad public and political support, it promises improved governance, cost savings, and better resource management in the future.
One Nation, One Election Bill
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The One Nation, One Election Bill has made significant progress in India, passing the Lok Sabha with 269 votes in favor and 198 votes against. The bill proposes the synchronization of elections for the Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and local bodies (Panchayats and Municipalities), aiming to streamline the electoral process, reduce costs, and enhance governance.
Key Updates:
- The bill has been approved by the Union Cabinet and will be reviewed by a Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC), whose report will be presented for further approval and discussion in Parliament.
- The process will unfold in two phases:
- Phase 1: Simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Synchronizing local body elections (Panchayats and Municipalities) within 100 days of the general elections.
Historical Context:
- 1951-1967: India previously conducted simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies until disruptions, such as premature dissolutions of assemblies, led to staggered elections after 1967.
- The One Nation One Election concept has been revived to address inefficiencies in the current system, especially the high cost of conducting frequent elections.
Advantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Cost Reduction: Synchronizing elections can significantly lower the financial burden by eliminating the need for multiple election cycles, reducing the deployment of resources like security personnel and election staff.
- Long-Term Governance Focus: Politicians can prioritize governance and policy implementation rather than election campaigning, fostering long-term stability.
- Increased Voter Turnout: Voter fatigue, caused by frequent elections, may reduce, leading to higher turnout as elections occur less often.
- Fairer Political Competition: Smaller regional parties could have a better chance to compete with larger national parties by reducing election-related costs.
- Efficient Use of Resources: Security forces and administrative resources can be deployed more effectively, avoiding the redundancy caused by multiple election cycles.
Disadvantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Synchronization Challenges: Aligning elections across a vast and diverse country like India, especially in states with unstable political situations, may prove difficult.
- Federalism Concerns: The implementation may require constitutional changes that could impact India's federal structure, potentially limiting the autonomy of states in election matters.
- Impact on Regional Issues: National issues could overshadow regional concerns, diluting the focus on state-specific matters.
- Challenges for Regional Parties: Larger national parties may dominate the electoral landscape, reducing the influence of regional parties and undermining the federal nature of the political system.
- Accountability Risks: Fixed terms without frequent elections might reduce public scrutiny of elected officials, affecting their accountability.
Constitutional Amendments Required:
The implementation of One Nation, One Election requires amendments to several key constitutional provisions:
- Article 83: Regarding the duration of the Lok Sabha, amendments are needed to synchronize the timing of dissolution.
- Article 85: Deals with the sessions and dissolution of Parliament, which needs to be aligned with the new system.
- Article 172: Pertains to the duration of State Legislatures, requiring amendments for synchronization.
- Article 174: Similar to Article 85, it governs the sessions and dissolution of State Legislatures, needing standardization.
Implementation Challenges:
- Logistical Complexity: Conducting simultaneous elections would require immense logistical coordination, including vast numbers of electronic voting machines and trained personnel.
- Political Accountability: Fixed terms may reduce the accountability that frequent elections bring, potentially leading to governance stagnation.
- Impact on Federalism: Amendments to the Constitution regarding state legislatures might face resistance from states concerned about their autonomy.
Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024 was passed in the Lok Sabha on December 20, 2024, aiming to enhance the functioning and autonomy of Indian Railways.
Key Provisions:
- Repeal of the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905: The Bill repeals the 1905 Act and incorporates its provisions into the Railways Act, 1989, simplifying the legal framework by reducing the need to refer to two separate laws.
- Statutory Backing for Railway Board: The Bill provides statutory backing to the Railway Board, which previously lacked such a legal mandate. It grants the Union government the authority to determine the number of members, their qualifications, terms, and conditions of service.
- Decentralization of Power: The Bill aims to decentralize decision-making, granting greater autonomy to regional railway zones. This shift will allow more independence in budgeting, infrastructure projects, and recruitment, addressing long-standing calls for improved regional empowerment.
- Independent Regulator: The Bill proposes the creation of an independent regulator for overseeing tariffs, safety, and private sector participation. This idea has been supported by previous expert committees to encourage greater competition and transparency in the sector.
- Fast-Tracking Infrastructure and Services: The Bill will streamline approvals for new train services and infrastructure projects, helping meet demands from underserved regions, particularly in states like Bihar.
Objectives:
- Modernization of the Legal Framework: By incorporating the provisions of the 1905 Act into the 1989 Act, the Bill aims to simplify and modernize the legal architecture governing the railways.
- Empowerment of Railway Zones: Autonomy for railway zones is seen as a key step towards improving efficiency and accountability in operations.
- Private Sector Participation: The establishment of an independent regulator is expected to promote private participation in the railway sector, aligning with international standards.
Historical Context:
- The Indian Railways Act, 1890 established the foundations for Indian Railways as a government entity, which was further refined with the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905.
- This Bill aligns with recommendations from previous committees, including the Sreedharan Committee (2014) and the Committee on Restructuring Railways (2015), which have called for greater decentralization and autonomy for railway zones, as well as an independent regulatory body.
Challenges and Proposed Reforms:
- Financial Sustainability: The railways face challenges such as high operating costs, particularly from salaries and pensions, and losses in the passenger segment. Suggestions to improve finances include rationalizing passenger fares, enhancing freight revenue, and attracting private investment in infrastructure.
- Efficient Freight Operations: The Bill also addresses concerns about network congestion, especially for freight operations, and aims to increase the competitiveness of freight transport by improving infrastructure and reducing cross-subsidies from passenger fares.
Recommendations of various Committees on reforming the Railways
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
Human Rights Day 2024

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
Human Rights Day 2024 celebrated every year on 10th December is dedicated to promote protection of fundamental rights and freedom of all individuals.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Promote and protect human rights and freedoms worldwide.
- Theme (2024): “Our Rights, Our Future, Right Now” – highlights the importance of immediate action to protect and uphold human rights globally.
Historical Significance:
- Commemorates: The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
- UN Resolution: Established by UN Resolution 423 (V) in 1950.
- First Observance: December 10, 1950.
- Father of Human Rights Day: Eleanor Roosevelt, for her pivotal role in drafting the UDHR.
Key Highlights:
- The UDHR:
- Adopted in 1948, it defines fundamental human rights for all individuals.
- Comprises 30 articles, addressing rights such as freedom, equality, and access to education, healthcare, and fair employment.
- Role of the UN: UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC): A body under the UN responsible for monitoring and promoting human rights worldwide, comprising 47 member states.
- Human Rights Day Focus in 2024:
- Emphasizes human rights education, particularly among the youth.
- Addresses emerging challenges like cybercrimes, AI impacts, and climate change.
- Reaffirms the importance of safeguarding human dignity globally.
Human Rights Declared by UDHR:
- Right to freedom and equality
- Right to life, liberty, and security
- Freedom from slavery and torture
- Right to recognition before the law
- Equal protection under the law
- Right to a fair trial
- Right to privacy and protection from attacks
- Right to work and fair employment
- Right to rest and leisure
- Right to education
- Right to an adequate standard of living
- Right to participate in government and cultural activities
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 celebrated the remarkable contributions of 45 Panchayats from across India for their role in driving sustainable and inclusive development in rural areas. The awards were presented on 11th December 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi, with President Smt. Droupadi Murmu and Union Minister of Panchayati Raj Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh (Lalan Singh) presiding over the event.
Key Highlights:
- Categories of Awards: The awards focus on rural governance, social inclusion, environmental sustainability, and the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP): Recognizes top-performing Gram Panchayats across 9 thematic areas like health, water, sanitation, and governance.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar: Awarded to the best Panchayats based on overall excellence across all LSDG themes.
- Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Honors Panchayats for contributions to renewable energy.
- Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Awarded to Panchayats achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
- Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar: Recognizes institutions supporting Panchayats in implementing LSDGs.
- Notable Achievements:
- Women’s Leadership: 42% of the award-winning Panchayats were led by women.
- States with Top Performers: States like Tripura, Odisha, and Maharashtra were prominently recognized for their achievements, especially in sustainability efforts like carbon neutrality and renewable energy adoption.
- Prize Distribution: A total of ?46 crore was awarded to the 45 winners, with funds directly transferred to their accounts.
Objectives:
The National Panchayat Awards aim to:
- Promote rural development through effective Panchayat governance.
- Encourage competition among Panchayats for improving public services and infrastructure.
- Recognize excellence in implementing sustainable development practices.
Key Themes of the Awards:
The awards are aligned with 9 LSDG themes that contribute to achieving 17 SDGs:
- Poverty-Free and Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean and Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just and Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 underscore the significant role of Panchayats in shaping rural India by focusing on inclusive and sustainable development. The awards also promote the importance of localized governance in achieving SDGs, encouraging other Panchayats to adopt best practices and contribute to India's overall development goals.
Reforms in Merchant Shipping

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The Government is preparing to introduce several significant bills aimed at driving much-needed reforms in the shipping industry. Key among them are the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 and the Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024, both of which promise to bring transformative changes to boost the sector.
Context and Need for Reforms:
- Outdated Framework: The Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, and the Coasting Vessels Act, 1838, fail to address the current needs of the shipping sector, particularly offshore vessels.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate regulation of offshore vessels, maritime training institutions, and welfare provisions for seafarers on foreign-flagged ships.
- Global Alignment: Need to align with international maritime conventions and modernize administration for competitiveness and better governance.
- Investment and Growth: Outdated laws hinder foreign investment and ease of doing business, necessitating a regulatory overhaul.
Key Features of the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Ease of Vessel Registration:
- Reduces ownership threshold for Indian entities from 100% to 51%, enabling NRIs, OCIs, and foreign entities to invest.
- Facilitates registration of vessels chartered by Indian entities under the "bareboat charter-cum-demise" system, promoting capital-deficient entrepreneurs.
- Temporary registration provisions for vessels destined for demolition, boosting India's ship recycling industry.
- Expansion of Vessel Scope:
- Broadens the definition of "vessel" to include all types of mechanized and non-mechanized crafts, such as submersibles, hydrofoils, and Mobile Offshore Units (MOUs).
- Ensures comprehensive regulatory oversight, particularly in the offshore sector, enhancing transparency and safety.
- Coastal Security:
- Strengthens coastal security by empowering authorities to issue instructions to all types of vessels, addressing vulnerabilities highlighted by incidents like the 26/11 Mumbai attacks.
- Marine Pollution Measures:
- Incorporates global standards like the MARPOL convention to address marine pollution.
- Introduces measures such as reducing sulphur content in marine fuel and banning single-use plastics on Indian ships.
- Launch of the ‘Swachh Sagar’ portal to ensure proper disposal of ship-generated waste.
- Seafarer Welfare:
- Expands welfare provisions to include Indian seafarers working on foreign-flagged ships, offering protections under the Maritime Labour Convention (MLC).
- Ensures better working conditions and safety standards for a growing workforce of Indian seafarers abroad.
- Maritime Training Regulations:
- Establishes a legal framework to regulate maritime training institutions, addressing the rise of unauthorized institutes post-liberalization.
- Ensures standardized, high-quality education and eliminates fraudulent practices.
Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Focus on Commercial Utilization of Coastal Waters:
- Distinguishes between the technical regulation of ships and the commercial utilization of Indian coastal waters.
- Aims to streamline licensing, operations, and coastal planning, enhancing the integration of inland and coastal shipping.
- Alignment with ‘Sagarmala’ Program: Supports the promotion of coastal shipping through better infrastructure and connectivity, in line with the government's ‘Sagarmala’ initiative, which boosts port connectivity and coastal trade.
International Conventions India Has Ratified:
- MARPOL: Focuses on preventing ship-based pollution.
- Maritime Labour Convention (MLC): Protects seafarers' rights and ensures fair working conditions.
- Bunker Convention: Addresses liability for oil pollution damage.
- Wreck Removal Convention: Mandates safe removal of shipwrecks.
- Civil Liability Convention: Establishes liability for oil pollution incidents.
Significance of the Reforms:
- Modernized Framework: Aligns India’s maritime laws with global standards for enhanced competitiveness.
- Economic Growth: Encourages foreign investment and entry into the shipping sector by removing regulatory barriers.
- Environmental Sustainability: Focus on combating marine pollution and ensuring sustainable shipping practices.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Strengthens coastal security and ensures stringent safety regulations for vessels.
- Seafarers’ Welfare: Extends benefits and protections to Indian seafarers working globally, ensuring better working conditions.
- Maritime Education: Provides a robust regulatory framework to ensure high-quality, standardized maritime training.
Community and Individual Forest Rights in Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR)

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Coimbatore District Collector, granted community and individual forest rights under the Forest Rights Act, 2006, to tribal settlements in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) on December 6, 2024.These rights were handed over to three tribal settlements and 14 families at a function in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
- Community Forest Rights:
- Three tribal settlements in ATR—Nagaroothu I, Nagaroothu II, and Chinnarpathi—were granted community rights.
- These rights allow the settlements to collect forest produce excluding timber, such as mango, amla, honey, tamarind, and grass for making brooms.
- Individual Forest Rights:
- Individual rights were granted to 14 families from the Old Sarkarpathy tribal settlement.
- The families had requested these rights for traditional cultivation practices passed down by their ancestors.
- The individual rights were approved after the recommendation of a sub-divisional committee and scrutiny by a district-level committee.
- About the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- Purpose: The FRA was enacted to address historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities and ensure their livelihood and food security.
- Key Provisions:
- Individual Rights: Self-cultivation, habitation, and in-situ rehabilitation.
- Community Rights: Access to grazing, fishing, water bodies in forests, and protection of traditional knowledge and customary rights.
- Eligibility: Rights can be claimed by any community or individual who has lived in the forest for at least three generations (75 years) before December 13, 2005.
- Critical Wildlife Habitats: The Act mandates that critical wildlife habitats in national parks and sanctuaries remain inviolate for wildlife conservation.
- Authorities Involved in Vesting Forest Rights:
- Gram Sabha: Initiates the process for determining the nature and extent of rights.
- Sub-Divisional Level Committee: Examines resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha.
- District Level Committee: Grants final approval for forest rights.
- Challenges with Forest Rights Implementation:
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- Arbitrary rejection of claims.
- Lack of deadlines for claims processing.
- Unaddressed rights of communities displaced by development projects.
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, at an altitude of 1,400 meters.
- Established as a tiger reserve in 2007, it is surrounded by multiple protected areas like the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Eravikulam National Park.
- Biodiversity in Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Habitats: The reserve contains wet evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, and unique habitats like montane grasslands and marshy grasslands.
- Flora: The reserve is home to around 2,500 species of angiosperms, including species like balsam, orchids, and wild relatives of cultivated crops such as mango, jackfruit, cardamom, and pepper.
- Fauna: It supports various wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, sambars, spotted deer, leopards, jackals, and jungle cats.
Development Initiatives for North East Region (NER)

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) was announced as a new Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding in the Union Budget 2022-23 with initial outlay of Rs.1500 crore.
PM-DevINE Scheme:
- Launched in 2022 as a Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding.
- Initial outlay: Rs. 1500 crore in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- Total outlay: Rs. 6600 crore for the period from FY 2022-23 to FY 2025-2026, approved by the Union Cabinet on 12 October 2022.
- Objectives:
- Fund infrastructure projects in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti.
- Support social development projects tailored to the felt needs of the NER.
- Enable livelihood opportunities for youth and women.
- Address development gaps in various sectors.
- 35 projects worth Rs. 4857.11 crore have been sanctioned under the scheme up to 30 November 2024, including 7 projects from the Union Budget 2022-23.
Industrialization Initiatives:
- North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS):
- Launched on 1 April 2017, ended on 31 March 2022.
- Aimed at promoting industrialization in the NER.
- UNNATI Scheme:
- Launched on 9 March 2024 for enhancing regional infrastructure and promoting industrial growth.
- Provides specific incentives to industries, including:
- Capital Investment Incentive.
- Capital Interest Subvention.
- Manufacturing & Services Linked Incentive.
Budgetary Allocation for NER Development:
- Non-exempt Union Ministries/Departments are mandated to allocate at least 10% of their annual Gross Budgetary Allocation towards NER development.
- Between 2019-20 and 2023-24, these Ministries/Departments have incurred Rs. 3,53,412 crore towards the development of NER.
Role of State Governments and Central Support:The Government of India supplements state efforts with various schemes to promote industrialization and infrastructure development in the NER.
The PM-DevINE scheme, along with initiatives like UNNATI and the allocation of substantial funds by the central government, aims to accelerate the holistic development of NER. These efforts focus on infrastructure, social development, and industrialization, with specific emphasis on youth and women empowerment, ensuring long-term growth and prosperity for the region.
BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
In a significant move, the Indian Parliament passed the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024 on December 5, 2024, bringing much-needed reforms to the aviation sector. The Bill, which replaces the Aircraft Act of 1934, aims to streamline aviation regulations and improve the ease of doing business in the industry.
Key Highlights of the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024:
- Single-Window Clearance for Aviation Personnel: One of the major changes is the transfer of responsibility for the Radio Telephone Operator Restricted (RTR) certification from the Department of Telecom (DoT) to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This move consolidates the certification process under a single authority, making it easier for aviation personnel like pilots, engineers, and flight dispatchers to obtain their licenses.
- Regulation of Aircraft Design: The Bill not only retains provisions for regulating aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and repair, but also introduces new provisions to regulate aircraft design and the places where aircraft are designed.
- Enhanced Penalties for Violations: The Bill specifies severe penalties for violations, such as dangerous flying, carrying prohibited items (like arms or explosives), or littering near airports. Offenders may face imprisonment up to three years, fines up to ?1 crore, or both.
- Introduction of Second Appeal Mechanism: For the first time, the Bill introduces a second appeal process against decisions of regulatory bodies like the DGCA and BCAS, ensuring further scrutiny of decisions related to penalties.
- Improved Licensing Process: The shift of the RTR certification process from the DoT to DGCA aims to curb allegations of corruption associated with the previous system, where candidates often had to pay bribes to clear exams.
Organizational Setup and Authorities:
The Bill outlines the establishment of three key authorities under the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- DGCA: Responsible for civil aviation safety, licensing, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
- BCAS: Ensures aviation security and develops relevant security measures.
- AAIB: Investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
The central government retains supervision over these bodies, with the power to modify or review their orders.
Criticisms and Concerns:
- Lack of Autonomy for DGCA: The DGCA, unlike independent regulators in other sectors (such as telecom or insurance), operates under direct government supervision. The lack of clear qualifications, selection process, and tenure for the DGCA Director General has raised concerns about the regulator's independence.
- Unilateral Appointment of Arbitrators: The Bill empowers the government to unilaterally appoint an arbitrator in certain cases, which has been criticized for potentially violating the right to equality under Article 14 of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has previously ruled that such unilateral appointments may be unconstitutional.
- Discretionary Criminal Penalties: The central government is granted the discretion to impose criminal penalties for rule violations, which some argue could undermine the principle of separation of powers, as it is the legislature's role to define criminal offenses and penalties.
- Exclusionary Hindi Title: Some critics argue that the Hindi title of the Bill may alienate non-Hindi-speaking populations, which make up a significant portion of India’s demographic.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
The Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, is once again in focus, albeit in a context in which its objectives are being ignored. Civil suits questioning the religious character of mosques at Varanasi and Mathura are progressing apace. These developments show that legislation freezing the status of places of worship is inadequate to stop Hindu claimants from making determined legal efforts to achieve their goal of replacing them with temples.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991:
- Objective: To preserve the religious character of places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947, and prevent changes in religious identity.
- Key Provisions:
- Section 3: Prohibits conversion of a place of worship from one religion to another.
- Section 4(1): Ensures the religious character remains unchanged from August 15, 1947.
- Section 4(2): Terminates ongoing or future legal proceedings seeking to alter the religious character of a place of worship.
- Exemptions:
- Ayodhya dispute: Exempted, allowing ongoing litigation.
- Ancient monuments & archaeological sites: Not covered by the Act.
- Already settled disputes or those agreed upon before the Act came into force.
- Penalties: Violators can face up to 3 years of imprisonment or fines.
- Criticism: The Act has been challenged for limiting judicial review, imposing a retrospective cutoff date, and restricting religious rights.
Recent Legal Disputes:
- Gyanvapi Mosque (Varanasi):
- Claim: Hindu worshippers assert the right to worship deities (e.g., Ma Sringar Gauri, Lord Vishweshwar) within the mosque premises.
- Legal Basis: Claim that the mosque was built over an ancient Hindu temple.
- Court's Ruling: The court allows the case to proceed, stating that the aim is to assert worship rights, not change the mosque’s status.
- Archaeological Survey: ASI report confirms the existence of a temple before the mosque’s construction.
- Key Legal Outcome: The Places of Worship Act does not bar these suits as they aim to ascertain the religious character of the site, not alter it.
- Shahi Idgah Mosque (Mathura):
- Claim: Hindu groups assert the mosque was built over Lord Krishna’s birthplace.
- Historical Context: The dispute was settled by a compromise in 1968, which was implemented in 1974, where part of the land was given to the mosque.
- Current Legal Dispute: New suits challenge the 1968 agreement as ‘fraudulent’ and seek the entire land to be transferred to the deity.
- Court's Ruling: The Act is not applicable as the 1968 agreement predates the 1991 Act, and the dispute pertains to the compromise, not the religious character.
- Shahi Jama Masjid (Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh):
- Claim: Allegation that the mosque was built over a Hindu temple (Hari Har Mandir).
- Survey Request: Petitioners seek a survey to verify the site’s historical and religious character.
- Legal Context: The mosque is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904.
Key Legal Interpretations:
- Court’s Role: Courts have ruled that the Places of Worship Act does not prohibit suits related to the religious character of a site if they are aimed at determining, not altering, that character.
- Interpretation of ‘Religious Character’: The Allahabad High Court stated that a structure can’t have dual religious character (both Hindu and Muslim), and the religious character of a place must be determined through evidence.
Political and Social Implications:
- Ongoing Controversy: The Gyanvapi and Mathura mosque disputes continue to fuel political and religious debates, as Hindu organizations seek to assert their claims, while mosque committees and Muslim groups resist changes.
- Public and Legal Attention: The legal and political landscape surrounding the Places of Worship Act remains contentious, with several legal suits challenging its applicability.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
At an event celebrating the National Sports Day, The Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour& Employment launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Empower retired athletes through career development.
- Provide tailored education, internships, and skill enhancement.
- Address the human resource gap in the sports sector.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Retired athletes aged 20-50 years.
- Winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- National/state-level medalists or participants in recognized competitions (e.g., National Sports Federations, Indian Olympic Association).
- Courses Offered (16 Courses):
-
- Strength & Conditioning Trainer
- Sports Nutritionist
- Sports Event Management
- Corporate Wellness Trainer
- Sports Masseur
- Sports Entrepreneurship
- Store Manager
- Fitness Centre Manager
- Physical Education Trainer
- Fitness Trainer
- Yoga Trainer
- Venue Supervisor
- Self-Defence Trainer
- Community Sports Trainer
- Camping & Trekking Guide
- Facility Caretaker
- Program Structure:
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12 and above
- Class 11 and below
- Hybrid learning mode:
- Self-paced learning via a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training and internships.
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Internship and Placement:
- Internships offered in sports organizations, competitions, training camps, and leagues.
- Post-course placement assistance and entrepreneurial guidance.
- Implementing Agency:Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) for the pilot phase.
- Importance:
- Provides sustainable career pathways for retired athletes.
- Utilizes the experience and skills of retired athletes to benefit future generations of athletes.
- Contributes to the growth of sports and nation-building.
- National Sports Day (29th August):
- Celebrated in honor of Major Dhyan Chand's birth anniversary.
- Promotes sports and physical fitness in India.
- Awards like Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna presented to honor excellence in sports.
Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The controversy surrounding the Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has intensified following claims that the mosque, built during the Mughal Emperor Babur's reign (1526–1530), was constructed over a Hindu temple, the Hari Har Mandir. This claim has led to legal battles and violent clashes, making it part of a broader series of disputes involving mosques built during the Mughal era, such as the Gyanvapi mosque in Varanasi and the Eidgah Masjid in Mathura.
Background and Legal Context:
The dispute began when a petition was filed in Sambhal's district court on November 19, 2024, claiming the Jama Masjid was built on the site of an ancient temple. The petitioners, led by Hari Shanker Jain, demanded a survey to ascertain the religious character of the site. This petition follows a pattern seen in similar cases in Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have raised similar claims about mosque sites. The court ordered a photographic and videographic survey of the mosque, which, initially carried out peacefully, later sparked violence on November 24 when the survey was accompanied by chanting crowds. This led to protests, stone pelting, and allegations of police firing, resulting in several deaths.
The Jama Masjid is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904, and is listed as a Monument of National Importance by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). This gives the case legal and cultural sensitivity, as it involves both national heritage and religious sentiments.
Historical and Architectural Context:
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal was constructed by Mir Hindu Beg, a general under Babur, in the early 16th century. It is one of three mosques commissioned by Babur, alongside those in Panipat and Ayodhya. The mosque is noted for its architectural style, which includes a large square mihrab hall, a dome, and arches, constructed using stone masonry and plaster. Some historians argue that the mosque might be a Tughlaq-era structure modified during Babur's reign. Locally, Hindu tradition holds that the mosque incorporates elements of a Vishnu temple, believed to be the site of Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu.
The Places of Worship Act, 1991:
The dispute has reignited debates about the Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, which mandates that the religious character of any place of worship as it existed on August 15, 1947, should be maintained, with the exception of the ongoing Babri Masjid dispute. The Act aims to prevent any further contests regarding religious sites, and Section 3 of the Act explicitly prohibits converting a place of worship into a site of a different religious denomination.
The petition filed in Sambhal seeks to alter the religious character of the mosque, directly contravening the Places of Worship Act. The petitioners have cited remarks by Supreme Court Justice D.Y. Chandrachud in 2022, suggesting that a survey to ascertain the religious character of a place might not violate the Act. This has led to petitions challenging the Act in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, Dhar, and now Sambhal.
The Legal and Social Implications:
The ongoing dispute over the Shahi Jama Masjid highlights the tension between historical narratives, legal frameworks, and communal harmony. The Supreme Court has intervened in the matter, temporarily halting further proceedings in the trial court, urging that the mosque's management committee approach the Allahabad High Court. The Court emphasized the importance of maintaining peace and harmony and cautioned against any actions that could escalate tensions.
The case underscores the challenges of balancing India's rich historical heritage with its diverse religious communities. As the legal process unfolds, the outcome of the Sambhal dispute could set significant precedents for how similar cases are handled in the future.
Conclusion:
The Sambhal mosque dispute, much like the Gyanvapi and Ayodhya cases, brings to the forefront the complex intersections of history, religion, and law. It also raises critical questions about the application of the Places of Worship Act and its implications for preserving India's pluralistic society. The outcome of this case, alongside the pending petitions in other states, will be crucial in shaping the future of religious site disputes in India.
Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
- It was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology, Earth Sciences, PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy, and Space, along with Shri V. Srinivas, the Secretary of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- This initiative, conceptualized by DARPG, aims to evaluate and rank central Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal mechanisms.
Key Aspects of GRAI 2023:
- Objective: GRAI 2023 was designed to provide a comparative assessment of Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal systems. It was created based on recommendations from the Parliamentary Standing Committee of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- Assessment Method: The index evaluates 89 Central Ministries and Departments across four dimensions:efficiency, feedback, domain&organisational Commitment
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Group A: Ministries/Departments with more than 10,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Group B: Ministries/Departments with 2,000 to 9,999 grievances (33 Ministries/Departments)
- Group C: Ministries/Departments with fewer than 2,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Top Performers:
- Group A: The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare topped the rankings.
- Group B: The Office of the Comptroller & Auditor General of India led.
- Group C: The Department of Investment & Public Asset Management ranked first.
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Analysis: GRAI 2023 includes an in-depth analysis of the root causes of effective grievance redressal for each Ministry/Department, presented in a color-coded, easily understandable format.
- Advancements: The report outlines a roadmap for improving grievance redressal, emphasizing:
- Utilization of advanced technologies such as AI and Machine Learning (ML) for predictive analytics and data analysis.
- The introduction of features like IGMS 2.0 and TreeDashboard within CPGRAMS.
- Improved training for Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs) and more rigorous audits to increase accountability.
- Expansion of CPGRAMS integration to local governments, enhancing the grievance redressal system across all levels of governance.
Commonwealth Secretariat recognized CPGRAMS as a best practice in grievance redressal at its meeting in April 2024.
Supreme Court Ruling on EVMs

- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The Supreme Court dismissed the PIL, remarking that EVMs are only questioned after electoral losses, not when elections are won. It emphasized that no evidence of tampering was found.
What Are EVMs and VVPATs?:
- EVMs: Electronic Voting Machines are used for conducting elections to the Parliament, state legislatures, and local bodies. They consist of two units: theControl Unit (operated by the polling officer) and the Ballot Unit (where voters cast their votes).
- VVPAT: The Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail enables voters to verify that their vote is recorded as cast. A slip is printed showing the candidate’s name, symbol, and serial number, visible for 7 seconds before being cut and stored in a sealed box.
Safeguards to Ensure EVM Integrity:
- Technical Safeguards:
- Microcontroller Security: EVMs use one-time programmable (OTP) microcontrollers, which cannot be altered after manufacturing.
- Standalone Operation: EVMs do not have wired or wireless connectivity, eliminating risks of remote tampering.
- Post-2013 Features: Advanced EVMs (M3) include tamper detection and mutual authentication protocols.
- Administrative Protocols:
- Randomized EVM Allocation: EVMs are randomly allocated to polling stations to avoid predetermined assignments.
- Mock Polls: Multiple mock polls are conducted to test the functionality of EVMs.
- Counting Procedures: EVMs are brought to counting tables under CCTV surveillance, and VVPAT slips are randomly cross-verified.
- Secure Storage: EVMs are stored under strict protocols, including double-lock systems, CCTV surveillance, and GPS-tracked transport.
Advantages of EVMs Over Ballot Papers:
- Elimination of Invalid Votes: EVMs ensure no invalid votes, a common problem with torn or mis-marked ballot papers.
- Prevention of Booth Capturing: EVMs restrict vote casting to 4 votes per minute, preventing fraudulent vote insertion.
- Accurate and Fast Counting: EVMs enable quick, error-free vote counting, reducing delays and human errors.
- Transparency: Voters can verify their votes through the VVPAT, and the vote count is displayed transparently without revealing candidate-wise results prematurely.
Evolution of EVMs in India:
- 1977: Concept of EVMs conceived.
- 1990: The Dinesh Goswami Committee recommended the use of EVMs.
- 2004: EVMs used nationwide in Lok Sabha elections.
- 2013: VVPAT was introduced to improve transparency.
- 2019: First nationwide use of EVMs backed by VVPAT.
E-Daakhil Portal
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
- The E-Daakhil portal was launched by the Department of Consumer Affairs to promote consumer rights and ensure timely justice.
- The portal was launched nationwide with its final rollout in Ladakh on 22nd November 2024, making it operational across all states and union territories of India.
Background and Purpose:
- Introduced in September 2020, the portal was developed in response to the Consumer Protection Act 2019, which aims to address emerging consumer concerns.
- Aimed at providing a hassle-free, inexpensive, and speedy mechanism for filing consumer complaints, especially post the COVID-19 pandemic.
- E-Daakhil is an online platform that simplifies the grievance redressal process, allowing consumers to file complaints remotely, without the need for physical presence.
Portal Features:
- User-friendly interface: Simple and intuitive, allowing consumers to file and track complaints online.
- Registration process: Users can register through OTP on their mobile or an activation link via email.
- Paperless and transparent: The entire process, from filing complaints to tracking the case status, is digital and transparent.
- Consumers can file complaints, pay fees, and monitor the progress of their cases from the comfort of their homes.
Success and Impact:
- By the end of 2023, E-Daakhil was available in 35 states and union territories; with Ladakh being the latest addition in November 2024.
- Over 2.81 lakh users have registered, and 1.98 lakh cases have been filed, of which 38,453 cases have been disposed of.
Future Developments:
- E-Jagriti: A new initiative that will further streamline the case filing, tracking, and management process, reducing delays and paperwork.
- E-Jagriti aims to improve communication between parties, ensuring faster dispute resolution.
Extension of Ban on ULFA

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) extended the ban on United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA) for five years under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967.
- The notification specifically includes all factions, wings, and front organizations associated with ULFA.
Reason for Extension:
- ULFA continues to pursue secessionist objectives (separation of Assam from India).
- The group is involved in criminal activities such as extortion, intimidation, and violent actions.
- ULFA has maintained links with other insurgent groups and continues to engage in illegal activities like the possession of arms and ammunition.
Peace Process:
- Pro-talks faction of ULFA, led by Arabinda Rajkhowa, signed a peace agreement with the central and Assam governments in December 2023.
- This faction has agreed to renounce violence, disband the organization, and join the democratic process.
- However, the hardline faction of ULFA, led by Paresh Baruah, remains active and continues its militant activities.
ULFA’s Formation and Objectives:
- ULFA was founded in 1979 with the goal of achieving the "restoration of Assam's sovereignty" through armed struggle.
- It has been a key player in the Assamese separatist movement for several decades.
Legal Framework:
- The UAPA (1967) empowers the government to declare an organization as unlawful or label individuals as terrorists if they engage in activities threatening India’s sovereignty, integrity, or promote terrorism and secession.
- The latest extension of the ban was made under Section 3(1) of UAPA.
Significance for Internal Security:
- This development is important for understanding insurgency and separatism in the Northeast and the government’s approach to national security and counterinsurgency.
- The ULFA issue highlights challenges in addressing regional insurgencies and the role of the UAPA in maintaining national integrity.
Socialist and Secular in Preamble

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
Supreme Court upholds ‘secular, socialist’ in Preamble of the Constitution.
Key Highlights of the Supreme Court Judgment
- Judgment Overview:
- Supreme Court's Ruling: The Court upheld the inclusion of the terms ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ in the Preamble of the Indian Constitution through the 42nd Amendment Act of 1976.
- Challenge: Petitioners, including BJP leader Subramanian Swamy, challenged the retrospective application of these terms, arguing they were not part of the original Preamble adopted in 1949.
- Court's Explanation:
- Socialist: The term represents a welfare state aimed at reducing inequality and ensuring social, political, and economic justice, but does not prescribe a specific economic policy (left or right).
- Secular: Denotes a state that treats all religions equally, ensuring religious freedom and neutrality in religious matters. It is linked to Articles 14, 15, and 16, which ensure equality and non-discrimination.
- Retrospective Application:The Court affirmed that Parliament’s amendment power under Article 368 extends to the Preamble, and the retrospective application of the terms was valid.
- Constitution as a ‘Living Document’:The Court emphasized that the Constitution is adaptable to societal changes and evolving needs. The inclusion of 'secular' and 'socialist' reflects India’s evolving democratic and social framework.
- Interpretation of Secularism and Socialism:
- Secularism in India refers to the state's neutral stance towards all religions, promoting religious harmony.
- Socialism signifies India’s commitment to ensuring equality of opportunity and promoting welfare policies, such as social justice and economic welfare.
Constitutional and Legal Framework
- Article 368: Grants Parliament the authority to amend the Constitution, including the Preamble. The Court affirmed that this power is unquestionable.
- Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973): Established the ‘basic structure doctrine,’ which means certain fundamental features of the Constitution cannot be altered. The inclusion of ‘secular’ and ‘socialist’ is in line with this basic structure.
- S.R. Bommai Case (1994): Reinforced the secular nature of the Indian state.
Preamble to the Constitution
- Definition: The Preamble is an introductory statement that outlines the fundamental values and goals of the Indian Constitution.
- Key Objectives: Justice (social, economic, political), Liberty (thought, expression, belief), Equality (status and opportunity), and Fraternity (national unity and dignity).
- Terms in the Preamble:
- Sovereign: India's independence in all matters.
- Socialist: Commitment to social justice and welfare.
- Secular: Equal respect for all religions.
- Democratic: Governance by the people, through elected representatives.
- Republic: Head of state elected, not hereditary.
42nd Amendment Act, 1976:
- Context: Introduced during the Emergency under Indira Gandhi's government.
- Key Changes: Added 'socialist' and 'secular' to the Preamble, revised 'Unity of the Nation' to 'Unity and Integrity of the Nation.'
- Significance: Strengthened constitutional values like inclusivity, equality, and justice.
Socialist and Secular Initiatives by Government
- Socialist Programs:
- MGNREGA: Rural employment guarantee.
- PDS: Food security system.
- Right to Education (RTE): Free, compulsory education.
- Housing Schemes: Awas Yojana for the economically weaker sections.
- Secular Programs:
- Minority Welfare: Scholarships and skill development.
- Religious Protection Laws: Protection of places of worship.
- Communal Violence Laws: Special courts for violence-related cases.
- Constitutional Safeguards: Equal rights for all religions under Articles 25-28.
Significance of the Supreme Court Judgment
- Reaffirmation of Constitutional Values: The inclusion of ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ reinforces India’s commitment to equality, justice, and democratic principles.
- Legitimacy of Amendments: Affirms Parliament's constitutional power to amend the Preamble.
- Evolving Interpretation: Recognizes that the Constitution must evolve in response to societal and political changes.
India's First Constitution Museum

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla and Union law minister Arjun Ram Meghwal inaugurated the country's first Constitution Museum at OP Jindal Global University in Sonipat.
Museum Features
- Centrepiece: A photolithographic copy of the Indian Constitution (one of 1,000 reproductions).
- 360-Degree Experience: A visual presentation that takes visitors through pre-Independence India.
- Multimedia Presentation: Chronologically details significant events leading to the drafting of the Constitution.
- Constituent Assembly Members:
- Nearly 300 sculptured busts of members who contributed to the making of the Constitution.
- Hologram of Dr. BR Ambedkar: Located in the mezzanine section, showcasing his philosophies through interactive displays.
- Art Installations:
- ‘We, The People of India’ by Rajesh P Subramanian: Represents unity in diversity.
- ‘Echoes of Liberty’ by Rahul Gautam: Combines constitutional manuscripts with contemporary design.
- ‘Triad of Unity’ by Harsha Durugadda: Symbolizes unity, justice, and sovereignty.
- ‘Insaaf Ki Devi’ by Nishant S Kumbhatil: Depicts Lady Justice, representing judicial impartiality.
- ‘Equality Before Law’ by Pradeep B Jogdand: Illustrates equality and justice principles.
- ‘Map’ by Deval Verma: Encourages visitors to reflect on value and beauty.
- ‘Freedom’ by KR Nariman: Pays tribute to the people who uphold constitutional values.
- ‘Founding Mothers’ by Rahul Gautam: Honors the 15 women members of the Constituent Assembly.
Accessibility for Disabled Persons

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Supreme Court of India delivered a significant ruling affirming that the right of persons with disabilities (PwDs) to access environments, services, and opportunities is a fundamental human right. The judgment was made in the case of RajiveRaturi vs. Union of India &Ors. and is based on a report submitted by the Centre for Disability Studies (CDS) at NALSAR University of Law.
Key Points of the Judgment:
- Social Model of Disability:
- The Court upheld the social model of disability, which focuses on societal changes to ensure the full inclusion and participation of PwDs.
- The model emphasizes removing social barriers and creating an inclusive environment that accommodates all disabilities.
- Challenges Faced by PwDs: The ruling highlighted various challenges faced by PwDs, as identified in the CDS NALSAR report:
- Accessibility Barriers: Significant gaps exist in accessibility measures across public spaces such as courts, prisons, schools, and public transport.
- Intersectionality & Compounded Discrimination: PwDs often face multiple layers of discrimination, such as caste, gender, and socio-economic status, which compound their marginalization.
- Inconsistent Legal Framework: The RPwD Act (2016) mandates mandatory compliance for accessibility standards, but Rule 15 under RPwD Rules (2017) only offers self-regulatory guidelines, which the Court found insufficient.
- Court's Analysis of Rule 15:
- The Court declared Rule 15(1) of the RPwD Rules, 2017, as ultra vires, meaning it is inconsistent with the mandatory compliance intended by the RPwD Act.
- The Court stressed the need for stronger legal and regulatory enforcement to ensure access for PwDs.
- Principles of Accessibility: The Court outlined several essential principles for achieving accessibility:
- Universal Design: Environments and services should be universally accessible to all, including PwDs.
- Comprehensive Inclusion: All types of disabilities, both visible and invisible, should be addressed.
- Assistive Technology Integration: Using technology to support PwDs in daily activities.
- Stakeholder Consultation: PwDs and disability advocacy groups must be consulted in planning and designing accessible spaces.
- Two-Pronged Approach:
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
- Ensure accessibility in existing infrastructure: Modify and update current institutions and services to become accessible.
- Design future infrastructure with accessibility in mind: Plan and build new spaces and services that are inclusive from the start.
- The Court recommended a two-pronged approach:
Legal and Policy Framework:
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016:
- The RPwD Act mandates various accessibility standards and provisions to protect and promote the rights of PwDs, in alignment with India’s obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), which India ratified in 2007.
- The Act defines a person with a benchmark disability as someone with at least 40% of a specified disability.
- International Obligations:
- The ruling reaffirmed the importance of Article 9 of the UNCRPD, which emphasizes the right of PwDs to access the physical environment, transport, and information and communication technologies.
- Government Initiatives: The judgment highlights several initiatives aimed at improving accessibility:
- Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan): A nationwide effort to make public spaces and services accessible to PwDs.
- Assistance for Aids and Appliances: Government schemes to provide PwDs with necessary aids and appliances.
- Unique Disability Identification Portal: A platform for PwDs to register and obtain a disability certificate.
Notable Judicial Precedents:
The Court referred to several previous rulings that recognized the right to accessibility:
- State of Himachal Pradesh v. Umed Ram Sharma (1986): The Court included the right to accessibility under the Right to Life (Article 21) of the Constitution.
- Disabled Rights Group v. Union of India (2017): The Court directed that educational institutions ensure reserved seats for PwDs.
Parliamentary Panel's Review on Mechanism to Curb Fake News

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Parliamentary Panel on Communications and Information Technology is reviewing mechanisms to curb fake news, following the Bombay High Court striking down a provision of the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules, 2021.
- The controversial provision allowed the government to identify and flag "fake news" on social media through its Fact Check Unit (FCU).
- The panel, led by BJP MP Nishikant Dubey, has summoned representatives from News Broadcasters and Digital Association and the Editors Guild of India to discuss the issue on November 21, 2024.
Issue with the Amended IT Rules:
- The IT Rules, 2021 were amended in April 2022 to include “government business” under the definition of fake news, expanding the scope of content flagged by the FCU.
- This amendment was challenged by media bodies and individuals like comedian Kunal Kamra, leading to the Bombay High Court striking it down in 2024.
- The court deemed the provisions unconstitutional, citing concerns about transparency and the potential misuse of power.
Types of Fake News:
- Misinformation: False information spread unintentionally.
- Disinformation: Deliberately false information meant to deceive and cause harm.
Status of Fake News in India:
- India as a major spreader of misinformation: The World Economic Forum's Global Risks 2024 report identifies disinformation as a significant short-term risk, with India as one of the largest consumers and producers of false information.
- Social Media Influence: Platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, and YouTube are widely used in India for news dissemination, making them a breeding ground for fake news.
- Spread of Political and Religious Misinformation: Fake news often serves political or religious agendas, leading to societal polarization and conflict.
Government Efforts to Combat Fake News:
- IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023: This amendment expanded the scope of "fake news" to include “government business” and gave the FCU the authority to flag misleading content.
- Press Information Bureau (PIB) Fact Check Unit: The PIB continues to run a fact-checking initiative, but it lacks the authority to remove flagged content from social media platforms.
- Digital Literacy Campaigns: Programs like Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) aim to improve digital literacy, especially in rural areas, to help citizens identify and avoid fake news.
CRS Mobile App
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union Home Minister Amit Shah launched the Civil Registration System (CRS) mobile app.
- The app aims to integrate technology with governance by making the registration of births and deaths more accessible, seamless, and hassle-free.
Key Features of the App:
- Anytime, Anywhere Registration: Citizens can register births and deaths from anywhere and at any time, in their State’s official language.
- The app is designed to significantly reduce the time required for registration, making it more efficient and convenient for users.
Legal and Policy Background:
- The Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Act, 2023 mandates that all births and deaths in India, occurring from October 1, 2023, must be digitally registered through the Centre’s portal: dc.crsorgi.gov.in.
- This move is part of the broader effort to digitize civil records and create a centralized database.
Benefits of Digital Registration:
- Digital Birth Certificates: The new system will issue digital birth certificates which will serve as a single document to prove the date of birth for various services, such as:
- Admission to educational institutions
- Applying for government jobs
- Marriage registration
- Centralized Database: The integration of birth and death data into a centralized database will help update critical records such as:
- National Population Register (NPR)
- Ration cards
- Property registration
- Electoral rolls
National Population Register (NPR) Integration:
- The data collected through the CRS app will assist in updating the National Population Register (NPR), which was first collected in 2010 and updated in 2015 through door-to-door enumeration.
- The NPR serves as the first step toward the creation of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) under the Citizenship Act, aimed at identifying Indian citizens.
New Disability Certificate Rules (RPwD Rules, 2024)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Rules, 2024, were amended by the Union Government in the wake of the Puja Khedkar controversy, where an IAS probationer was dismissed for alleged forgery in her disability and caste certificates.
- National Platform for the Rights of the Disabled (NPRD) has called for a rollback of the new rules, citing that they make the process of obtaining disability certificates more stringent and cumbersome.
Key Changes Under the New RPwD Rules, 2024
- Authority for Issuing Disability Certificates:
- Only a designated medical authority or a notified competent medical authority at the district level can issue disability certificates.
- NPRD had proposed that experts from non-profits also be authorized to carry out checks, but this suggestion was not accepted.
- Colour-Coded UDID Cards:
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- White (general disability)
- Yellow (moderate disability)
- Blue (severe disability with 80% or higher).
- The new rules introduce colour-coded UDID cards to represent levels of disability:
- Mandatory Online Applications:
- Applicants are now required to apply for disability certificates online, which could be problematic for individuals who lack access to the internet, smartphones, or are digitally illiterate.
- The NPRD has urged the government to retain the option for in-person applications.
- Extended Time for Certificate Issuance:
- The new rules extend the time for issuing disability certificates from one month to three months.
- Reapplication Requirement:
- If there is no action taken on an application for two years, the applicant will have to reapply, which the NPRD considers unacceptable, as it punishes disabled individuals for system failures.
NPRD's Concerns
- Regressive and Burdensome:NPRD believes the amendments are regressive, adding more hurdles for genuine persons with disabilities to access certificates, which are crucial for identification and entitlement to services.
- Lack of Accountability:The NPRD argues that the rules do not address the systemic issues highlighted by the Puja Khedkar case, such as the lack of accountability at various levels in the certification process.
- Online Application Issues:Many people from the disabled community may struggle with technical jargon used in online applications and may not have the resources to complete the process digitally.
- Delay in Issuance:Extending the time for issuing certificates to three months could create delays for those in urgent need of certification for services or entitlements.
New 'Lady Justice' Statue in the Supreme Court

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Chief Justice of India unveiled the ‘new lady justice’ statue in the Supreme Court premises that replaced the ‘original lady justice’. The new statue is clothed in a saree, has shed the blindfold and holds scales on one hand and the Indian Constitution on the other.
Symbolism of the New Statue
- Design:
- Clad in a saree, symbolizing Indian tradition.
- No blindfold, with open eyes, conveying that justice "sees" all equally.
- Holds the Indian Constitution in one hand and scales of justice in the other.
- Significance:
- Aimed at decolonization of the judiciary, replacing colonial symbols with representations that reflect India's identity and values.
- The open eyes represent that justice is not blind, addressing social diversity, discrimination, and constitutional provisions for upliftment of underprivileged sections.
- The Constitution in place of a sword symbolizes its supremacy in India’s legal system.
Historical Context of Lady Justice
- Origin:
- Rooted in Roman mythology; Justitia, the goddess of justice, symbolized by scales, sword, and a blindfold.
- Blindfold added in the Renaissance as a satire on corrupt legal systems but later reinterpreted as a symbol of impartiality, representing justice without bias, irrespective of wealth, power, or social status.
- Scales: Balance in weighing both sides before judgment.
- Sword: Authority and power of law, to protect and punish.
Rationale for Change in India
- Colonial Legacy:
- The 'lady justice' symbol became prominent during British rule, reflecting colonial influence in India's legal system.
- Decolonial Intent:
- The shift from Western attire (robe) to a saree connects the statue to Indian traditions.
- Open eyes emphasize that Indian justice is not blind and addresses social inequalities directly.
- The Constitution's prominence underscores its role as the supreme guiding document in the Indian legal system.
Current Judicial System Challenges
- Pending Cases:
- Over 5 crore cases are pending across courts in India.
- Supreme Court recently dismissed a petition for a three-year timeline to resolve the backlog, citing the overwhelming volume of cases.
- Urgent Reforms Needed:
- Finalize the Memorandum of Procedure:
- Still pending after 8 years; addresses transparency and accountability in judicial appointments.
- Representation in Judiciary:
-
- Backward classes, SCs, STs, and minorities are underrepresented in higher judiciary (less than 25%), and women are underrepresented (less than 15%).
- Appointments should reflect India's social diversity.
-
- Vacancies in Courts:
-
- High Courts operate at 60-70% strength, contributing to a massive case backlog of over 60 lakh cases.
- Lower courts have 4.4 crore pending cases; vacancies must be filled by states promptly.
- Priority for Constitutional Cases:
-
- Cases concerning the constitutional validity of laws and individual liberty should be prioritized by the judiciary.
Conclusion
- The new Lady Justice statue is not just a symbolic change but reflects a broader effort to realign India’s judiciary with its social and constitutional values.
- To ensure fair and prompt justice, there is an urgent need to address systemic delays, fill vacancies, and improve diversity in judicial appointments.
- Only then will the judiciary truly embody the principles of impartiality and justice, as represented by the new statue.
First Chief Minister of J&K UT Takes Charge
- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Omar Abdullah sworn in as J&K CM; Surinder Kumar Choudhary is Deputy CM
Key Highlights:
- Omar Abdullah’s Political Context:
- This marks Omar Abdullah's second term as Chief Minister, after his tenure in 2009.
- He becomes the first Chief Minister of Jammu and Kashmir after the region’s special status was revoked and it was reorganized as a Union Territory in 2019.
- Challenges as CM of a Union Territory:
- Omar Abdullah acknowledged the unique challenges of serving as Chief Minister in a Union Territory and expressed hope that J&K’s Union Territory status would be temporary.
- Public Service and Security Measures:
- In his first official instructions, Abdullah asked the Director General of Police (DGP) to avoid creating “green corridors” or traffic halts during his movements. He also requested the minimization of sirens and aggressive security gestures, emphasizing minimal public inconvenience.
- Legal Context:
- Oath of Office: As per Article 164(3) of the Indian Constitution, the Chief Minister and other ministers are sworn in by the Governor or Lieutenant Governor in Union Territories.
- Abdullah is the first CM of the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir post the abrogation of Article 370 and the transition of J&K from a state to a Union Territory in 2019.
- Revocation of President's Rule:
- President’s Rule (under Article 356) was revoked following the election results, signaling the restoration of a functioning elected government after direct central governance in the region.
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
Justice Sanjiv Khanna Appointed as Next Chief Justice of India, Will Assume Office on November 11
- Appointment:
- Justice Sanjiv Khanna has been appointed as the 51st Chief Justice of India by President Droupadi Murmu.
- He is set to take office on November 11, 2024, succeeding Chief Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, who is retiring on November 10, 2024.
- Tenure:
- Justice Khanna's tenure will be relatively short, lasting only six months, as he is scheduled to retire on March 13, 2025.
Career and Background
- Education and Early Career:
- Justice Khanna is a graduate of Delhi University’s Campus Law Centre.
- He enrolled as an advocate in 1983 and primarily practiced before the Delhi High Court.
- Prior to his elevation to the Delhi High Court in 2005, he served as the Senior Standing Counsel for the Income Tax Department and the standing counsel for civil matters for the Delhi government.
- Judicial Career:
- Supreme Court Appointment: Justice Khanna was appointed to the Supreme Court in January 2019, despite not having served as Chief Justice of a High Court. He was elevated over other senior judges from the Delhi High Court, such as Justices Rajendra Menon and Pradeep Nandrajog, whose names were initially recommended but not forwarded to the government.
- Key Contributions:
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- February 2024: Part of the five-judge bench that struck down the Electoral Bond Scheme as unconstitutional.
- 2023: Contributed to upholding the abrogation of Article 370 of the Constitution.
- 2023: Authored a ruling granting the Supreme Court the power to directly grant divorce under Article 142 on the grounds of "irretrievable breakdown of marriage."
- Justice Khanna has been part of several significant rulings, including:
- Administrative Role:
- Justice Khanna currently serves as the Executive Chairman of the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA).
Process of Appointment of Chief Justice of India (CJI)
- Seniority Principle: The CJI is typically the senior-most judge of the Supreme Court.
- Memorandum of Procedure (MoP): The Law Ministry requests a recommendation from the outgoing CJI for his successor.
- Presidential Appointment: After receiving the recommendation, the President of India formally appoints the new CJI.
- Tenure and Retirement: The CJI serves until the age of 65. Upon retirement, the senior-most judge becomes the next CJI.
- Merit and Integrity Considerations: In addition to seniority, merit and integrity play crucial roles in the selection process for the CJI.
Co-district Initiative

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
Assam has launched an innovative administrative initiative by inaugurating 21 'co-districts' as part of its Phase 1 rollout, which began on Friday and will extend into Saturday, ultimately introducing a total of 39 co-districts. This new structure replaces the previous system of 24 civil sub-divisions, aiming to bring governance closer to the citizens.
About the Co-District Initiative
- Structure: Co-districts serve as smaller administrative units within the larger district framework, each headed by an Assistant District Commissioner.
- Objective: This unique initiative, the first of its kind in India, seeks to enhance accessibility to governance and address administrative challenges faced by district administrations.
- Scope: The government plans to establish co-district offices in all 126 assembly constituencies in Assam.
Functions and Powers
The co-districts will handle a variety of important functions, including:
- Land Revenue Matters: Managing land-related issues and revenue collection.
- Development and Welfare Work: Overseeing development projects and welfare programs.
- Excise and Disaster Management: Addressing excise-related matters and coordinating disaster response efforts.
- Administrative Control: Co-districts will have authority over all departmental activities within their jurisdiction.
- Magisterial Powers: Commissioners will be empowered to issue permissions for events and manage other administrative tasks.
- Routine Administrative Tasks: Responsibilities include issuing ration cards, caste certificates, and land sale permissions.
Supreme Court of India

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
On August 31, 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the National Conference of District Judiciary at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi. This event marked the 75th anniversary of the Supreme Court of India, highlighted by the unveiling of a commemorative stamp and coin.
Supreme Court of India: History and Key Insights
The Origins of the Judiciary
- The concept of law, or Dharma, in ancient India was significantly influenced by the Vedas, which outlined rules of conduct and rituals in the Dharma Sutras. These texts addressed the duties of individuals and the rights of kings, forming the foundation of Hindu Law. The earliest systematic examination of jurisprudence can be found in Kautilya's Artha Sastra (circa 300 B.C.), particularly its third chapter, which discusses legal transactions and disputes.
Establishment of the Supreme Court
- The Regulating Act of 1773, enacted by the British Parliament, initiated the establishment of the Supreme Court of Judicature at Calcutta, with its Letters of Patent issued on March 26, 1774. This court had the authority to hear all complaints and lawsuits involving His Majesty’s subjects in Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa. Additional Supreme Courts were later established in Madras (1800) and Bombay (1823).
- The Indian High Courts Act of 1861 replaced these Supreme Courts with High Courts in various provinces, which became the highest judicial authorities until the Federal Court of India was created under the Government of India Act 1935. After India gained independence in 1947, the Supreme Court of India was formally established on January 26, 1950, with its inaugural session held on January 28, 1950.
- The Supreme Court's rulings are binding across India, and it possesses the power of judicial review to ensure that legislative and executive actions align with constitutional provisions and fundamental rights.
Structure and Functioning
- Initially, the Supreme Court operated for only a few hours each day and convened for 28 days a year. Today, it functions extensively, meeting approximately 190 days annually. The court was temporarily housed in the Parliament House before moving to its current location on Tilak Marg, New Delhi, in 1958.
- The court's architecture symbolizes justice, featuring a prominent dome and spacious corridors. It began with a Chief Justice and seven judges, with Parliament later increasing this number as the workload grew. Currently, the Supreme Court includes a Chief Justice and 30 judges.
Appointment and Qualifications of Judges
- Judges are appointed by the President of India, based on recommendations from a committee of senior judges (Collegium System). A candidate must be a citizen of India and have served as a High Court judge for at least five years or as an advocate for ten years. The age of retirement for judges is 65 years.
Judicial Independence and Removal
- Judicial independence is constitutionally protected. A Supreme Court judge can only be removed by the President on grounds of proven misbehavior or incapacity, following a resolution supported by a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Parliament.
Judicial Salaries and Provisions
- Judges’ salaries and pensions are defined by the Supreme Court Judges (Salaries and Conditions of Service) Act, 1958, and are charged to the Consolidated Fund of India.
Acting Chief Justice
- In the absence of the Chief Justice, the President appoints another judge as the Acting Chief Justice, as stipulated in Article 126.
Post-Retirement Opportunities
- While retired judges cannot practice law in India, they often serve in governmental roles, such as leading commissions. There have been calls for a "cool-off" period before such appointments.
Ad Hoc Judges
- Ad hoc judges may be appointed when necessary, and must meet the qualifications for Supreme Court judges. Retired judges can also be called back to serve temporarily.
Courts of Record
- Both the Supreme Court and High Courts are classified as courts of record, with the authority to punish for contempt as per Article 129.
Seat of the Supreme Court
- The Supreme Court is based in Delhi but can convene anywhere in India, with such decisions made by the Chief Justice in consultation with the President.
SUPREME COURT RULING ON CHILD SEXUAL EXPLOITATIVE MATERIAL: KEY HIGHLIGHTS

- 24 Sep 2024
Overview of the Ruling
- Date: Recent ruling by the Supreme Court of India.
- Context: Determined that viewing, downloading, storing, or distributing material involving child sexual exploitation constitutes a criminal offense under the POCSO Act and the Information Technology Act.
- Appeal Background: Decision overturned a Madras High Court ruling that deemed private viewing of such material non-criminal.
Terminology and Legislative Recommendations
- Terminology Change: Supreme Court advocates replacing “child pornography” with “Child Sexual Exploitative and Abuse Material” (CSEAM) to avoid trivialization of the crime.
- Amendment Call: Court urged Parliament to amend the POCSO Act and advised promulgating an ordinance for immediate effect.
Key Highlights of the Ruling
- Redefinition of Terminology: Emphasizes that "pornography" may imply consensual acts, misrepresenting the nature of child exploitation.
- Expansion of Section 15 of the POCSO Act:
- Possession Without Reporting: Individuals must delete or report any stored CSEAM; failure results in penalties.
- Intent to Transmit: Possessing CSEAM with intent to share, barring reporting, is punishable.
- Commercial Possession: Storing CSEAM for commercial purposes faces the strictest penalties.
- Concept of Inchoate Offenses: Classifies offenses related to CSEAM as preparatory actions towards further crimes.
- Redefinition of Possession:
- Includes "constructive possession," where individuals can be liable without direct physical possession.
- Watching CSEAM online without downloading can still be deemed possession.
- Educational Reforms:
- Court urged for comprehensive sex education to counter stigma and misconceptions.
- Curriculum should cover consent, healthy relationships, and respect for diversity.
- Awareness of the POCSO Act: Central and state governments are mandated to promote awareness, supported by the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR).
- Formation of Expert Committee: To develop programs for health and sex education while increasing POCSO awareness among children.
- Victim Support and Awareness: Emphasized the need for psychological support, counseling, and educational assistance for victims.
Status of Crimes Against Children
- Increasing Incidents: India leads in online child sexual abuse imagery, with 25,000 uploads reported from April to August 2024.
- Geographical Distribution: Major uploads identified in Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- Rising Cases: From 331 cases in 2017 to 781 in 2018, with 1,171 cases of inappropriate content dissemination reported in 2022.
Overview of the POCSO Act
- Purpose: Addresses sexual exploitation and abuse of children, defining a child as anyone under 18.
- Features:
- Gender-Neutral: Recognizes that both genders can be victims.
- Victim Confidentiality: Mandates protection of victims’ identities.
- Mandatory Reporting: Requires reporting of suspected abuse.
Gaps in Implementation
- Support Persons: Lack of designated support persons for victims; 96% of cases showed inadequate support during legal processes.
- POCSO Courts: Only 408 designated courts across 28 states as of 2022, leading to access issues.
- Special Prosecutors: Shortage of trained public prosecutors for POCSO cases.
Conclusion
- Call for Collaboration: Emphasizes the need for a coordinated approach involving educators, healthcare providers, and law enforcement to combat child sexual exploitation.
- Societal Responsibility: A shift in societal attitudes is essential for preventing victimization and ensuring recovery for victims.
KEY FINDINGS ON ATROCITIES AGAINST SCS AND STS (2022)
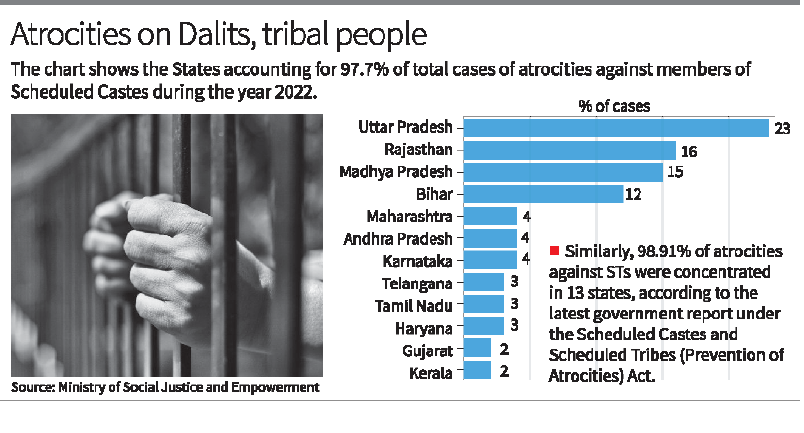
- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
According to the latest report under the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act by the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry, the majority of atrocities against Scheduled Tribes (STs) were also concentrated in 13 states, which reported 98.91% of all cases in 2022.
- Case Statistics:
- Total cases of atrocities against Scheduled Castes (SCs): 51,656
- Total cases against Scheduled Tribes (STs): 9,735
- 97.7% of SC cases and 98.91% of ST cases reported from 13 states.
- States with Highest Incidents:
- SCs:
- Uttar Pradesh: 12,287 cases (23.78%)
- Rajasthan: 8,651 cases (16.75%)
- Madhya Pradesh: 7,732 cases (14.97%)
- Other significant states: Bihar (6,799), Odisha (3,576), Maharashtra (2,706)
- STs:
- Madhya Pradesh: 2,979 cases (30.61%)
- Rajasthan: 2,498 cases (25.66%)
- Odisha: 773 cases (7.94%)
- Other significant states: Maharashtra (691), Andhra Pradesh (499)
- SCs:
- Charge Sheets and Investigations:
- SC-related cases: 60.38% resulted in charge sheets; 14.78% ended with final reports (false claims/lack of evidence).
- ST-related cases: 63.32% led to charge sheets; 14.71% concluded similarly.
- Pending investigations by end of 2022: 17,166 SC cases, 2,702 ST cases.
- Conviction Rates:
- Decline from 39.2% in 2020 to 32.4% in 2022.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies:
- Only 194 out of 498 districts in 14 states have established special courts for these cases.
- Lack of identified atrocity-prone areas in states like Uttar Pradesh despite high case numbers.
- Protection Cells:
- SC/ST protection cells established in multiple states and union territories.
Reasons for Atrocities Against SCs and STs
- Caste Prejudice: Deep-rooted hierarchies and social exclusion lead to violence.
- Land Disputes: Conflicts over land access among historically deprived SC/ST communities.
- Economic Marginalization: Limited access to education and resources heightens vulnerability.
- Power Imbalance: Dominant castes wield political and social influence, perpetuating discrimination.
- Inadequate Law Enforcement: Weak implementation of protective laws and bureaucratic bias hinder justice.
- Political Exploitation: Caste tensions are sometimes used for electoral gains.
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989
- Objective: Protect SCs and STs from caste-based violence and discrimination.
- Key Provisions:
- Defines various offences against SC/ST members, prescribing stricter punishments.
- Excludes anticipatory bail provisions for accused under the Act.
- Mandates establishment of special courts for speedy trials.
- Investigations must be conducted by senior police officers and completed within stipulated time frames.
- Recent Amendments:
- 2015: Enhanced protections for SC/ST women.
- 2019: Restored original provisions for arrest procedures following a Supreme Court ruling.
Recommendations for Improvement
- Strengthen Legal Framework: Establish more special courts and train personnel in sensitive handling of SC/ST cases.
- Improve Reporting Mechanisms: Enhance systems for victims to report atrocities without fear.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educate communities on SC/ST rights and legal protections.
- Targeted Interventions: Identify and address issues in atrocity-prone districts.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Implement frameworks for accountability and continuous improvement in addressing these issues.
- Collaborate with NGOs: Work with civil society to support victims and advocate for their rights.
One Nation, One Election

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union cabinet has recently approved the "One Nation, One Election" proposal, facilitating the conduct of simultaneous elections in India. This initiative follows a report submitted in March by a high-level committee chaired by former President Ram Nath Kovind, which unanimously recommended synchronizing Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections, along with local body polls, within 100 days.
What are Simultaneous Polls?
Simultaneous polls aim to align the timing of Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections across all states, thereby reducing the frequency of elections. Historically, simultaneous elections were held during the first four general election cycles (1952, 1957, 1962, and 1967), but this practice ended in 1959 after the dismissal of the Kerala government. Since then, due to premature dissolutions of various Assemblies, elections have been staggered. Currently, only four states—Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim—hold simultaneous elections with the Lok Sabha.
Arguments For and Against
Proponents argue that simultaneous elections can significantly reduce election-related costs, which amounted to approximately ?3,870 crore during the 2014 general elections. They also highlight that the Model Code of Conduct triggers twice in a five-year cycle, leading to extended periods of governance downtime.
Opponents caution that this approach may favor larger political parties with national reach, potentially sidelining smaller regional parties. A 2015 study found that the likelihood of a party winning both Lok Sabha and Assembly elections when held simultaneously is 77%, dropping to 61% if elections are spaced six months apart.
Implementation Process
The committee proposed a two-step implementation:
- Simultaneous Elections: Conduct elections for both the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies together.
- Synchronizing Local Elections: Hold elections for municipalities and panchayats within 100 days following the general elections.
Following the announcement of the "appointed date," the terms of all State Assemblies constituted after that date would end with the Lok Sabha's term. This could lead to most State governments not completing their five-year terms, even if they maintain a majority.
Required Constitutional Changes
Several amendments to the Constitution have been proposed:
- Introduction of Article 82A: This would require all Legislative Assemblies elected after the appointed date to conclude with the Lok Sabha’s term.
- Amendment of Article 327: Expanding Parliament's powers to include the conduct of simultaneous elections.
- Revisions to Articles 83 and 172: Defining the five-year term as the "full term" and any remaining period after premature dissolution as the "unexpired term."
- Introduction of Article 324A: Empowering Parliament to ensure that municipality and panchayat elections occur alongside general elections.
- Amendments for Union Territories: Ensuring that Assembly elections in Union Territories align with simultaneous elections.
- Single Electoral Roll: Proposing a common electoral roll for all elections, to be managed by the Election Commission of India (ECI).
State Ratification
Under Article 368, amending the Constitution may require ratification by state legislatures. The panel believes that syncing Assembly elections with Lok Sabha elections will not need state ratification, but amendments for a common electoral roll and synchronization of local elections will require cooperation from the states. The ruling BJP, currently in power in several states, will need to navigate upcoming Assembly elections in Haryana, Maharashtra, and Jharkhand to secure this support.
Conclusion
The "One Nation, One Election" initiative aims to streamline India's electoral process, potentially enhancing governance and reducing costs. However, its success depends on achieving political consensus and implementing necessary constitutional amendments, which will require collaboration among various political parties and state governments.
Fast-track special courts (FTSCs)

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
Fast-track special courts (FTSCs) are much more efficient than other courts in handling rape cases and those related to the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, a report released by the India Child Protection.
Key Details:
West Bengal's Performance
- West Bengal recorded less than a 2% disposal rate for rape and POCSO cases, the lowest in India.
- Only five out of 123 earmarked FTSCs are currently functioning in the state.
Overview of the India Child Protection (ICP)
- Established in 2005, the ICP is dedicated to combatting child sexual abuse and related crimes, including:
- Child trafficking
- Exploitation of children in the digital space
- Child marriage
Efficiency of FTSCs
- The ICP report titled "Fast Tracking Justice" highlighted that FTSCs disposed of 83% of cases in 2022, compared to 10% by conventional courts.
- As of August 2023, 755 out of 1,023 earmarked FTSCs were operational.
- Among these, 410 FTSCs are exclusively for POCSO cases.
Historical Context
- The FTSC scheme was launched by the Centre in October 2019, following a Supreme Court directive for ensuring the swift disposal of cases, related to rape and those coming under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Implemented by the Department of Justice, Ministry of Law and Justice.
Case Disposal Statistics
- FTSCs have disposed of 52% of the 4,16,638 rape and POCSO cases since the scheme's inception.
- Disposal rates improved from 83% in 2022 to 94% in 2023.
State-wise Disposal Rates
- Top Performing States:
- Maharashtra: 79.5%
- Punjab: 71.3%
- Kerala (Southern India): 69.5%
- Karnataka: 62.2%
- Tamil Nadu: 58.4%
- Lowest Performing States:
- West Bengal: 1.6%
- Jammu and Kashmir: 25%
- Meghalaya: 26.6%
- Delhi: 28.3%
Note: No data was available for Arunachal Pradesh, Ladakh, and Sikkim.
Need for Additional FTSCs
- The ICP report states that India needs at least 1,000 more FTSCs to manage the backlog effectively.
- The backlog of pending cases rose from 2,81,049 in 2020 to 4,17,673 by the end of 2022.
Advocacy for Reform
- Bhuwan Ribhu, a child rights activist, emphasized the urgent need for FTSCs to ensure justice for victims:
- Investment in the safety and security of women and children is crucial.
- All pending cases should be resolved within the next three years.
- Rehabilitation and compensation for victims should be prioritized.
- Time-bound policies for case disposal across all courts are necessary.
Funding and Resource Utilization
- The ICP report recommends optimizing the Nirbhaya Fund, created after the 2012 Delhi gang rape, to support additional FTSCs.
- There is currently ?1,700 crore unutilized, while the requirement for operationalizing new FTSCs is ?1,302 crore.
International Day of Democracy

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Karnataka marked the 'International Day of Democracy' by forming a 'historic' 2,500-km-long human chain as a symbol of equality, unity, fraternity, and participative governance. The massive human chain, which according to the Karnataka government will be the "world's longest", is being formed across the state from Bidar to Chamarajanagar, covering all 31 districts.
Key Highlights:
- Democracy Day is an annual celebration observed on September 15.
- The United Nations General Assembly established this day in 2007 to emphasise the global significance of democracy. It serves as a reminder that democracy is not merely a fixed condition, but an ongoing pursuit. It calls for active engagement from international organizations, nation-states, civil society and people to pursue the democratic idea.
International Day of Democracy History
- The International Day of Democracy was accredited by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) on November 8, 2007, by passing a resolution entitled “Support by United Nations system of efforts of governments to promote and consolidate new or restored democracies.”
- September 15 was chosen to coincide with the anniversary of the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s Universal Declaration on Democracy, which was adopted in Geneva on September 15, 1997.
- This declaration outlines the tenets of democracy proclaiming that democracy is “a system of government based on the freely expressed will of the people to determine their own political, economic, social and cultural systems and their full participation, through free and fair periodic elections, in the composition of their representative government.”
- After the Universal Declaration on Democracy, Qatar spearheaded the campaign to observe an International Day of Democracy at the United Nations.
- The first-ever International Day of Democracy was held in 2008.
International Day of Democracy Significance
- The International Day of Democracy evaluates global democracy, emphasising that it requires commitment and engagement from the international community, the national state governments, civil societies and individuals.
- The day also reminds the nations of the need to uphold the principles of democracy such as the freedom of speech enshrined in Article 19 of the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Black Coat Syndrome

- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
In her recent speech at the National Conference of District Judiciary, President Droupadi Murmu introduced the concept of 'black coat syndrome' to address the persistent issue of case delays in Indian courts. This term is intended to reflect the anxiety and reluctance that people experience when dealing with the judicial system, similar to the 'white coat syndrome' seen in medical settings.
Current Challenges in India's Judicial System
- Case Pendency: As of October 2023, there are over five crore cases pending across various levels of the judiciary in India. The current number of judges—20,580—falls short of effectively managing this caseload.
- Infrastructure Deficiencies: Many courts lack essential infrastructure and modern technology. For example, as of September 2023, 19.7% of district courts did not have separate toilets for women.
- Judicial Vacancies: There are notable vacancies in the judiciary. High courts have 347 unfilled positions out of a total of 1,114 sanctioned posts. Similarly, 5,300 out of 25,081 district judge positions are vacant.
- Gender Representation: The Supreme Court has three female judges, making up 9.3% of its bench. High courts have 103 female judges, representing 13.42%, while the district judiciary has a more balanced representation with 36.33% female judges.
Ongoing Initiatives to Address Judicial Challenges
- Technological Advancements:
- e-SCR (Electronic Supreme Court Reports): Provides digital access to Supreme Court judgments.
- Virtual Court System: Facilitates court proceedings through videoconferencing.
- eCourts Portal: Serves as a comprehensive platform for interaction among litigants, advocates, government bodies, and the public.
- National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG): Makes case statistics available at various levels for public and research use.
- Legal Reforms and Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR):
- National Mission for Justice Delivery and Legal Reforms (2011): Focuses on improving justice access by tackling delays and arrears.
- ADR Methods: Includes Lok Adalats, Gram Nyayalayas, and Online Dispute Resolution to expedite justice.
- Commercial Courts Act 2015: Enforces pre-institution mediation for commercial disputes.
- Fast Track Courts: Designed to speed up cases involving serious crimes, senior citizens, women, and children.
Strategies for Future Improvement
- Increasing Court Efficiency: The Chief Justice of India has stressed the need for courts to function beyond their current capacity of 71% to better align case disposal with new case inflows.
- Filling Judicial Positions: With 28% of district court positions vacant, a regularized recruitment schedule is suggested to address these gaps. Additionally, integrating judicial recruitment on a national scale is recommended to reduce regional biases.
- Enhancing Case Management: Establish District-Level Case Management Committees to better manage cases by reconstructing records and identifying priority cases. Encouraging pre-litigation dispute resolution can also help manage the case backlog.
- Adjusting Judicial Vacations: The 2003 Malimath Committee report proposed reducing vacation periods to help address the backlog of cases.
- Bridging Judiciary Gaps: Addressing the disparity between district courts and high courts is crucial to create a more cohesive and unified judicial system.
Govt dissolves Standing Committee on Statistics

- 10 Sep 2024
In News:
The recent dissolution of the 14-member Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) by the Union Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has sparked considerable controversy and debate. The committee, which was chaired by Pronab Sen, a renowned economist and former chief statistician of India, was reportedly disbanded after its members raised concerns about the delay in conducting the decennial census.
Key Points:
- Dissolution of the Committee:
- The SCoS, formed in July 2023, was responsible for advising the Union government on survey methodology and statistical frameworks. According to the experts the decision to dissolve the SCoS was due to an overlap in functions with the newly formed Steering Committee for National Sample Surveys.
- Concerns and Criticism:
- Dr. Pronab Sen and other committee members expressed concerns over the delay in conducting the census, which was due in 2021 but has yet to be carried out. The last census, conducted in 2011, is now outdated, impacting the accuracy of various statistical surveys.
- Members of the SCoS reportedly questioned the delay in census operations during their meetings, leading to speculation that their concerns may have contributed to the committee's dissolution.
- Formation of the New Steering Committee:
- The new Steering Committee for National Sample Surveys, chaired by Rajeeva Laxman Karandikar, was established following a recommendation by the National Statistical Commission (NSC). The roles of this new committee are said to overlap with those of the SCoS, which the Ministry cited as a reason for disbanding the latter.
Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS)
- The Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) was established by renaming and expanding the scope of the Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES), which was originally formed in December 2019.
- The SCES, with 28 members, was tasked with reviewing economic indicators related to the industrial sector, services sector, and labor force statistics, including datasets like the Periodic Labour Force Survey, the Annual Survey of Industries, and the Economic Census.
Current Structure and Members: The newly formed SCoS comprises 14 members, including:
- Four Non-Official Members
- Nine Official Members
- One Member Secretary
The committee's total membership can be extended up to 16 based on requirements.
Functions:
1. Review and Address Issues:
o The SCoS reviews the existing frameworks and addresses issues related to all surveys as presented by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI). This includes evaluating survey results and methodologies.
2. Advisory Role:
o It advises on various aspects of survey methodology, including sampling frames, sampling designs, and survey instruments. The committee is also responsible for finalizing the tabulation plans and results of surveys.
3. Data Collection and Production:
o The SCoS oversees the design and implementation of all data collection and production efforts. It ensures that data collected by MoSPI adheres to high standards of statistical quality and accuracy.
23rd Law Commission of India

- 06 Sep 2024
Constitution and Tenure:
- Notification and Term:
- The 23rd Law Commission of India was notified by the Union government on September 2, with effect from September 1.
- The commission will have a three-year term, concluding on August 31, 2027.
- The tenure of the previous Law Commission, chaired by former Karnataka High Court Chief Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi, ended on August 31.
Role and Importance of the Law Commission:
- Purpose:
- The Law Commission is a non-statutory body formed by the Union Ministry of Law and Justice through a gazette notification.
- Its role includes reviewing the functioning of laws, recommending the repeal of obsolete legislation, and providing recommendations on issues referred by the government.
- Composition:
- Typically chaired by a retired Supreme Court or High Court judge.
- Includes legal scholars and can also have serving judges.
- Impact:
- Over the years, 22 Law Commissions have submitted 289 reports.
- Their recommendations have influenced significant legislation, such as the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (CrPC), and the Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 (RTE Act).
Constitution of the 23rd Law Commission:
- Structure:
- The commission will consist of:
- A full-time chairperson.
- Four full-time members, including a member-secretary.
- Up to five part-time members.
- Ex officio members including the secretaries of the Legal Affairs and Legislative departments.
- The commission will consist of:
- Appointment and Remuneration:
- Chairperson and full-time members can be serving Supreme Court or High Court judges or other experts chosen by the government.
- The chairperson will receive a monthly salary of ?2.50 lakh, while members will receive ?2.25 lakh.
- The member-secretary must be an officer of the Indian Legal Service of the rank of Secretary.
- Serving judges appointed to the commission will serve until retirement or the end of the commission’s term, without additional remuneration.
Terms of Reference:
- Primary Tasks:
- Identify and recommend the repeal of obsolete or irrelevant laws.
- Create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for periodic review and simplification of existing laws.
- Identify laws that are misaligned with current economic needs and suggest amendments.
- Directive Principles and Reforms:
- Examine laws in light of Directive Principles of State Policy and suggest improvements and new legislation to achieve constitutional objectives.
- Address laws affecting the poor, conduct post-enactment audits of socio-economic legislation, and review judicial administration for responsiveness.
Previous Commission's Contributions:
- Reports and Recommendations:
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
- A report in April 2023 recommending retention of Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code (sedition law), with suggested amendments for clarity.
- A report recommending a new law to protect trade secrets.
- A report on simultaneous elections, though it was not submitted to the government before the commission’s chairperson assumed office as a Lokpal member.
- The 22nd Law Commission produced 11 reports, including:
Upcoming Focus:
- The 23rd Law Commission is expected to continue examining key issues, including the implementation of a uniform civil code, which was also considered by the 22nd Commission but whose recommendations remain unpublished.
Personality Rights

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Hollywood actress Scarlett Johansson has said she was “shocked” and “angered” to hear the voice of GPT-4o, OpenAI’s latest AI model, as it sounded “eerily similar” to her own voice.
What are Personality Rights?
- Personality rights or publicity rights are a subset of “celebrity rights” – a much broader term used to refer to certain rights enjoyed by celebrities.
- Besides personality rights, celebrities also have “privacy rights”, which include the right to be left alone.
- The name, voice, signature, images, or any other feature easily identified by the public are markers of a celebrity’s personality and are referred to as “personality rights.”
- These could include poses, mannerisms, or any other distinct aspect of their public persona.
- Several celebrities register aspects of their personalities as trademarks to use them commercially.
- For instance, footballer Gareth Bale trademarked the heart shape he makes with his hands as part of goal celebrations.
- The rationale behind such rights is that only the creator or owner of the unique features can gain commercial benefit from them.
- Therefore, unauthorised use could lead to revenue losses.
- In India, actors such as Rajnikanth, Anil Kapoor and Jackie Shroff have approached the courts over “personality rights” in India.
- Recently, the Delhi HC protected the personality and publicity rights of actor Jackie Shroff while restraining various e-commerce stores, AI chatbots, and social media from misusing Shroff’s name, image, voice, and likeness without his consent.
How are Personality Rights Protected in India?
- Although personality rights or their protection are not explicitly defined in Indian statutes, they usually fall under the right(s) to privacy and property.
- Concepts in intellectual property rights cases, such as passing off and deception, are usually applied in such cases while ascertaining if protection is warranted.
- Protection can be given through damages and injunctions.
After 10 years struggle, Mendha gets separate Panchayat status under Gramdan Act

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Maharashtra government recently notified Mendha, a village deep inside the forests of the state’s Gadchiroli district, as a separate Gram Panchayat under The Maharashtra Gramdan Act, 1964.
What is Gramdan?
- Gramdan is an expansion of the Bhoodan Movement started in 1951 by Aacharya Vinoba Bhave.
- ‘Bhoodan’ meant redistribution of land from bigger landowners to the landless.
- Under Gramdan, the entire village will put its land under a common trust.
- This way, the land will not be sold outside the village or to one who has not joined Gramdan in the village.
- But the landowners can continue to cultivate it and reap the benefits.
- The Movement paved the way for the protection of natural resources by giving equal rights and responsibilities to everyone in the community and empowering communities to move towards self-governance.
- Under the Act, at least 75 percent of landowners in the village should surrender land ownership to the village community for it to be declared as ‘gramdan’.
- Such land should at least be 60 percent of the village land. Five per cent of the surrendered land is distributed to the landless in the village for cultivation.
- Recipients of such land cannot transfer the same without the permission of the community.
- The rest remains with the donors.
- They and their descendants can work on it and reap the benefits.
- But they cannot sell it outside the village or to a village resident who has not joined Gramdan.
- Today, seven states in India have 3,660 Gramdan villages, the highest being in Odisha (1,309).
- The states are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- In September 2022, the Assam government repealed the Assam Gramdan Act, 1961 and Assam Bhoodan Act, 1965, bypassing The Assam Land and Revenue Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
- This, it said, was done to counter encroachment on donated lands in the state.
- Till that time, Assam had 312 Gramdan villages.
About Mendha’s Village Struggle:
- The village, comprising around 500 Gond Adivasis, has fought for its forests for years.
- It is popular as the first village in India to secure community forest rights (CFR), following the passing of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- Some 80 per cent of the area in the village is covered with dense forest.
- People here believe that land is not a private property but a collective resource that provides food and livelihood and should be saved and passed on to the next generation.
- All villagers in Mendha have surrendered their land, which is unique. In all other villages, only about 75-80 per cent of landowners had agreed to do so.
- The village fulfilled these conditions of the Act in 2013 and notified the district collector about its decision to implement the Act.
Amit Shah launches National Cooperative Database, to help in policy making
- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
Cooperation Minister Amit Shah on Friday launched the National Cooperative Database and stressed that it would help in policy making.
About National Cooperative Database (NCD):
- The National Cooperative Database (NCD) is an initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Cooperation, responding to the pressing need for a robust database to effectively capture essential information concerning India's extensive cooperative sector.
- Developed collaboratively with State Governments, National Federations, and stakeholders, the NCD is designed to promote a cooperative-centric economic model, offering a web-based digital dashboard for seamless data management.
- Acting as a centralized repository, the NCD aggregates data from cooperative societies, including National/State Federations, with information entered and authenticated by nodal officials at RCS/DRCS offices for cooperative societies and provided by various national/state federations for federations.
- The collected data encompasses diverse parameters, such as registered names, locations, membership numbers, sectoral details, operational areas, financial statements, audit statuses, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the cooperative landscape.
- Serving as a vital communication tool, the NCD facilitates efficient interaction between the Central Ministry, States/UTs, and Cooperative Societies, fostering collaboration and synergy within the cooperative sector.
- Key features and benefits of the NCD include single-point access, comprehensive and updated data, user-friendly interface, vertical and horizontal linkages, query-based reports and graphs, Management Information System (MIS) reports, data analytics, and geographical mapping capabilities.
Vaishnaw bats for further simplification of economic laws at ‘NITI for States’ platform launch

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union IT, Communications, and Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw Thursday stressed on the need to further simplify economic laws in a modern and relevant way at the launch of NITI Aayog’s ‘NITI for States’ platform.
About “NITI For States” Platform:
- It serves as a cross-sectoral knowledge hub envisioned to be a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Policy and Good Governance.
Key features include:
- A comprehensive repository comprising Best Practices, Policy documents, datasets, data profiles, and NITI publications across various sectors.
- Knowledge products spanning 10 sectors and two cross-cutting themes (Gender and Climate Change), such as Agriculture, Education, Energy, Health, Manufacturing, MSME, Tourism, Urban, and Water resources & WASH.
- An intuitive and user-friendly interface accessible via multiple devices, including mobile phones.
- The platform aims to catalyze digital governance transformation by providing government officials with contextualized, actionable knowledge and insights, thereby enhancing decision-making quality.
- It supports district collectors and block-level functionaries by granting access to innovative best practices from various States and Union Territories.
What is the Viksit Bharat Strategy Room?
- It serves as an interactive platform enabling users to visualize data, trends, best practices, and policies in an immersive manner, facilitating a comprehensive assessment of any problem statement.
- The platform features voice-enabled AI for user interaction and facilitates connectivity with multiple stakeholders through video conferencing.
- Designed as a plug-and-play model, it enables replication by states, districts, and blocks for widespread adoption.
- Collaboration with various government organizations by NITI Aayog includes:
- iGOT Karmayogi's "SAMARTH" online training modules accessible through the platform.
- Integration of NITI Aayog’s National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP) to provide access to government datasets.
- Support from the National E-Governance Division (NeGD) in developing the innovative Viksit Bharat Strategy Room.
- Multi-lingual support provided by Bhashini.
- Integration of PM Gatishakti BISAG-N team, with DPIIT support, to offer geospatial tools for Area Based Planning.
Minimum age to cast postal ballots hiked to 85 years

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the upcoming Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections, senior citizens who are 85 years and older will be able to opt for postal ballots as the government recently amended the rule to increase the eligibility from the current limit of 80 years and above.
News Summary:
- The government, in collaboration with the Election Commission, has introduced amendments to the Conduct of Election Rules (1961), specifically targeting the eligibility criteria for voting by postal ballot.
- Notably, the minimum age for senior citizens eligible for postal voting has been increased from 80 years to 85 years.
- Previously, Rule 27A of the Conduct of Election Rules had extended the postal ballot facility to senior citizens above 80 years, persons with disabilities, poll officers, and individuals diagnosed with COVID-19.
- This provision was first implemented during the 2020 Bihar assembly polls, coinciding with the onset of the pandemic.
- Despite the initial extension of postal voting rights to senior citizens aged 80 and above, a subsequent review by the Election Commission revealed that only a small fraction, approximately 2-3%, of eligible voters in this age group opted for postal ballots.
- The majority preferred to physically visit polling stations to cast their votes.
- Considering the statistics indicating that the total number of senior citizens above 80 years stands at 1.75 crore, with 98 lakh falling within the age range of 80-85 years, the government deemed it necessary to amend the existing rule.
- This adjustment reflects a nuanced approach aimed at ensuring efficient electoral processes while addressing the preferences and needs of elderly voters.
What is Postal Voting?
- Postal voting is only available to a specific group of voters.
- By retyping her choices on the ballot paper and returning it to the inspection officer before counting, a voter can remotely cast her ballot using this feature.
Who Can Avail This?
- Armed forces members such as those in the Army, Navy, and Air Force, armed police officers serving outside their home states, government workers stationed outside of India, and their wives are only eligible to vote by mail.
Features:
- Voters may use this service from any location outside of the designated constituency.
- This system makes it easier to create voter electoral roll data for services.
- It has two layers of security, making it a secure system:
- 1. Downloading the encrypted electronically transmitted postal ballot (ETPB) file requires an OTP (one-time password).
- 2. To decrypt, print, and deliver ETPB, a PIN is necessary.
- By sending postal ballots electronically to eligible service voters, this system addresses the time constraint associated with mailing postal ballots.
- The specific quick response code ensures confidentiality and prevents the duplication of cast ETPB.
Concerned Raised by Political Parties:
- Parties argue that allowing voters 65 and older to cast postal ballots violates voting confidentiality since many of the population lacks education and may ask for help from others at various points, ultimately identifying their chosen candidate.
- Their exposure to "administrative influence or influence by the government or the ruling party" also results from this.
Ex-SC Judge Justice AM Khanwilkar Appointed As Lokpal Chairperson

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nearly 19 months after he retired as a Supreme Court judge, Justice A M Khanwilkar was appointed the chairperson of the anti-corruption ombudsman Lokpal on Tuesday. The post fell vacant nearly two years ago.
Who is AM Khanwilkar?
- Justice Ajay Manikrao Khanwilkar was a Supreme Court judge between May 2016 and July 2022.
- He has also served as chief justice of the Madhya Pradesh High Court and the Himachal Pradesh High Court and as a judge of the Bombay High Court.
- Recently appointed as the Chairperson of the anti-corruption ombudsman Lokpal on Tuesday.
- The appointment came nearly two years after the post fell vacant.
- Khanwilkar was elected for the post following discussions by a high-level committee, which included:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi
- Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud
- Leader of the Opposition in Lok Sabha, Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury
- The Lokpal has been functioning without its permanent chief since the conclusion of Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose's term on May 27, 2022.
About Lokpal:
- The Lokpal is a statutory body established under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act of 2013.
- Its primary mandate is to investigate allegations of corruption against certain public officials and handle related matters.
- The organizational structure of Lokpal includes a chairperson and a maximum of eight members.
- The chairperson must be a former Chief Justice of India, a former Judge of the Supreme Court, or an eminent individual meeting specified eligibility criteria.
- Half of the maximum eight members are judicial members, who must be former Judges of the Supreme Court or former Chief Justices of High Courts.
- Additionally, a minimum of fifty percent of the members are drawn from SC/ST/OBC/minority backgrounds and include women.
How are Members Appointed?
- The President of India appoints the Chairperson and Members based on recommendations from a selection committee.
- This committee comprises the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Speaker of Lok Sabha, the Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, the Chief Justice of India or a nominated Judge, and one eminent jurist.
- Members serve a term of five years or until they reach 70 years of age, whichever comes first, starting from the date they assume office.
- The Chairperson receives salary, allowances, and other benefits equivalent to those of the Chief Justice of India.
- Similarly, Members receive salary, allowances, and other benefits equivalent to those of a Judge of the Supreme Court.
Jurisdiction:
- The Lokpal has the authority to investigate allegations of corruption against current or former Prime Ministers, Union Ministers, Members of Parliament, and officials from various levels of the Union Government categorized under Groups A, B, C, and D.
- Its jurisdiction extends to include chairpersons, members, officers, and directors of entities established by parliamentary acts or financed by the Union or State government, as well as any organization receiving foreign contributions exceeding Rs 10 lakh.
- However, there are exceptions regarding the Prime Minister's jurisdiction. The Lokpal cannot investigate allegations related to international relations, external/internal security, public order, atomic energy, and space. Moreover, complaints against the PM require approval from at least two-thirds of the Lokpal's members before initiation of an inquiry.
Powers of Lokpal:
- The Lokpal possesses the authority to oversee and issue directives to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
- Once the Lokpal has referred a case to the CBI, the investigating officer cannot be transferred without the Lokpal's approval.
- It holds the power to authorize the CBI to conduct search and seizure operations related to these cases.
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal is endowed with powers akin to those of a civil court.
- In specific circumstances, the Lokpal can confiscate assets, proceeds, receipts, and benefits obtained through corrupt means.
- It is empowered to recommend the transfer or suspension of public servants implicated in corruption allegations.
- The Lokpal can issue directives to prevent the destruction of records during the preliminary inquiry phase.
- As per Section 48 of the Act, the Lokpal is mandated to submit an annual report on its activities to the President, which is subsequently laid before both Houses of Parliament.
Ladakh: Centre agrees to examine demand for statehood, inclusion in Sixth Schedule of Constitution

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Centre has agreed to examine whether the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution can be implemented in Ladakh.
What is the Sixth Schedule?
- The Sixth Schedule under Article 244 provides for the formation of autonomous administrative divisions — Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) — that have some legislative, judicial, and administrative autonomy within a state.
- ADCs have up to 30 members with a term of 5 years and can make laws, rules and regulations with regard to land, forest, water, agriculture, village councils, health, sanitation, village- and town-level policing, inheritance, marriage and divorce, social customs and mining, etc.
- The Bodoland Territorial Council in Assam is an exception with more than 40 members and the right to make laws on 39 issues.
- The Sixth Schedule applies to the Northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram (three Councils each), and Tripura (one Council).
Why does Ladakh want to be part of the Sixth Schedule?
- There was much enthusiasm initially, mostly in Leh, after the August 5, 2019 decisions that created two new Union Territories.
- The Buddhist-dominated Leh district had long demanded UT status because it felt neglected by the erstwhile state government, which was dominated by politicians from Kashmir and Jammu.
- This development has sparked concerns among locals regarding potential challenges related to identity preservation, resource allocation, and administrative oversight.
- Also, the changed domicile policy in Jammu and Kashmir has raised fears in the region about its own land, employment, demography, and cultural identity.
- The UT has two Hill councils in Leh and Kargil, but neither is under the Sixth Schedule.
- Their powers are limited to the collection of some local taxes such as parking fees and allotment and use of land vested by the Centre.
- The Sixth Schedule empowers the Governor of the State to designate specific areas as administrative units within the Autonomous Districts and Autonomous Regions.
Can Ladakh be included in the Sixth Schedule?
- In September 2019, the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes recommended the inclusion of Ladakh under the Sixth Schedule, noting that the new UT was predominantly tribal (more than 97%), people from other parts of the country had been restricted from purchasing or acquiring land there, and its distinct cultural heritage needed preservation.
- Notably, no region outside the Northeast has been included in the Sixth Schedule.
- In fact, even in Manipur, which has predominantly tribal populations in some places, the autonomous councils are not included in the Sixth Schedule.
- Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh, which are totally tribal, are also not in the Sixth Schedule.
- “Ladakh’s inclusion in the Sixth Schedule would be difficult.
- The Constitution is very clear, the Sixth Schedule is for the Northeast.
- For tribal areas in the rest of the country, there is the Fifth Schedule.
- However, it remains the prerogative of the government — it can, if it so decides, bring a Bill to amend the Constitution for this purpose.
Eminent Jurist Senior Advocate Fali Nariman passes away

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, eminent jurist and senior advocate of the Supreme Court Fali S Nariman died at the age of 95.
Who was Fali S Nariman?
- Fali S Nariman was born on January 10, 1929, in Rangoon, then part of British India.
- He began his legal career by enrolling as an advocate of the Bombay High Court in November 1950.
- His stature grew, and he was designated as a senior advocate in 1961.
- In 1972, he moved to New Delhi to practise in the Supreme Court of India.
- In May 1972, Nariman assumed the role of additional solicitor-general of India; however, he resigned a day after the Emergency was imposed on June 26, 1975.
- He also served as the president of the International Council for Commercial Arbitration and chaired the Executive Committee of the International Commission of Jurists, Geneva, from 1995 to 1997.
- His son, Justice Rohinton F Nariman, formerly served as a judge on the Supreme Court.
- Nariman received the Padma Bhushan in January 1991 and in 2007 he was awarded the Padma Vibhushan.
What Were Some of Nariman's Landmark Cases?
- The Golak Nath case: In the historic judgement, the Supreme Court held that the Parliament cannot make a law which is capable of infringing the fundamental rights of citizens.
- It came up after two brothers in Punjab challenged the Constitution (17) Amendment Act, 1964, which came into effect by amending Article 31A of the Constitution. (This article deals with the acquisition of estates).
- Nariman, not only supported the petitioners but also appeared to argue on the issue representing the intervenors in the case.
- They argued that Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution under Article 368 did not include articles contained in Part III of the Constitution dealing with fundamental rights.
- Following the hearing of the case submitted in 1967, an eleven-judge bench agreed with the petitioner’s submissions pointing out that Article 13(2) states that Parliament cannot make a law which infringes fundamental rights.
- The Kesavananda Bharati case: The Kesavananda Bharati case is known for setting a benchmark in the Indian judiciary and had Nariman’s prompt representation in the SC.
- He assisted noted Advocate Nanabhoy Palkhivala in the famous case that led to the path-breaking judgement laying down the basic structure doctrine of the Constitution, clipping Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution.
- The 1973 verdict simultaneously gave the judiciary the authority to review any constitutional amendment on grounds of violation of the basic structure of the Constitution.
- The Bhopal Gas Tragedy case: In 1984, the Bhopal gas tragedy where 42 tons of toxic chemicals leaked from a pesticide plant owned by Union Carbide India Limited, resulting in thousands of deaths and environmental damage in the following years.
- The Supreme Court began hearing the case for compensation to the victims in 1988.
- Senior Advocate Nariman appeared, representing Union Carbide, and offered to pay a sum of 426 million dollars as compensation to the victims of the tragedy.
- In 1989, Union Carbide settled with the central government and agreed to pay 470 million dollars as compensation.
- The Cauvery Water Dispute case: Nariman represented Karnataka for over 30 years in the water-sharing dispute with Tamil Nadu.
- In 2016, the Supreme Court ordered the Karnataka government to release 6,000 cusecs (cubic feet per second) of water from September 21 to September 27.
- The Karnataka legislative assembly, however, passed a resolution stating that they did not have water to spare and chose to defy the court’s orders.
- Due to this non-compliance, Nariman refused to argue the case on behalf of the Karnataka government any further.
- On February 16, 2018, the court in its final judgement took note of Nariman’s stance on the issue and necessarily mentioned that Nariman had courageously lived up to the highest tradition of the Bar.
- The court then proceeded to reduce Karnataka’s annual water releases to 177.25 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) from 192 TMC.
- Disproportionate assets case against former Tamil Nadu Chief Minister J Jayalalithaa: AIADMK leader and former- Tamil Nadu CM Jayalalitha had been accused of misappropriating funds during her tenure between 1991 and 1995.
- A Sessions Court in Bangalore in September 2014 found that she had acquired property disproportionate to her known income and imposed a Rs 100 crore fine on her.
- This sentence was upheld by the Karnataka High Court a month later leading to an appeal at the Supreme Court.
- Nariman appeared on behalf of Jayalalitha in October 2014 and convinced the court to grant bail against executing the fine and suspend the sentence passed by the Sessions judge in Bangalore.
- The 1981 Second Judges case: The Supreme Court held that the primacy of the Chief Justice of India’s recommendation in judicial appointment and transfer can be turned down on cogent grounds by the government.
- However, the judicial discussions finally led to the creation of the collegium system of appointment of judges to constitutional courts in 1993, when the top court came out with its judgement in the second judge’s case.
- Nariman had stated that the advice given through consultation with the CJI must be seen as binding to protect the independence of the judiciary, as judges would be in a better position to determine the suitability and competence of candidates.
- In 1993, the nine-judge bench agreed with Nariman’s arguments and established the Supreme Court Collegium.
- The COVID-19 case: Nariman represented the Parsi community in its dispute over the protocol and standard operating procedure for handling of dead bodies of Parsi Zoroastrian COVID-19 victims under which metallic nets were to be installed above ‘Tower of Silence’ so that birds did not feed on the corpses and carry the killer virus elsewhere
