Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also known as the Indian Nino, could potentially resurface for the second consecutive year during the latter part of 2024.
What is the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)?
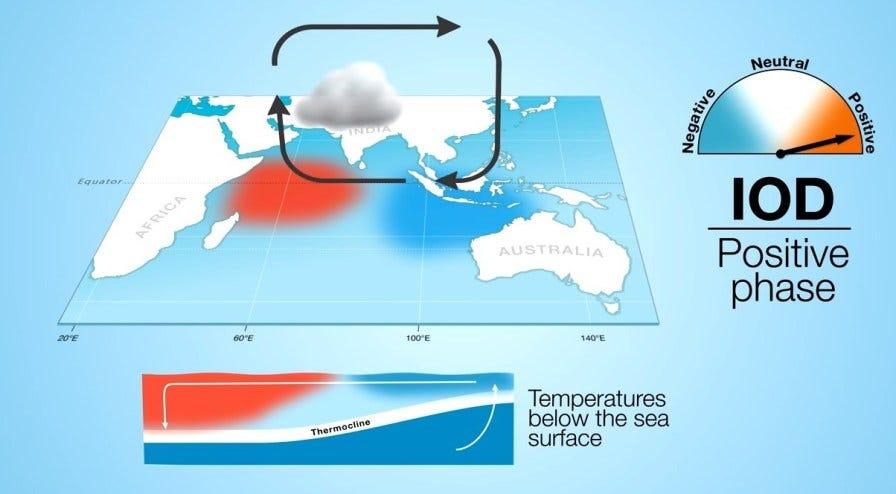
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is defined by the difference in the sea surface temperature between the two equatorial areas of the Indian Ocean – a western pole near the Arabian Sea (in western Indian Ocean) and an eastern pole closer to the Bay of Bengal (in eastern Indian Ocean).
- The IOD affects the climate of Southeast Asia, Australia and other countries that surround the Indian Ocean Basin.
- The Indian Monsoon is invariably influenced by the IOD.
- IOD is simply the periodic oscillation of sea surface temperatures, from ‘positive’ to ‘neutral’ and then ‘negative’ phases.
- If the sea surface temperature of the western end rises above normal (0.4°C) and becomes warmer than the eastern end, it leads to a positive IOD.
- This condition is favourable for the Indian Monsoon as it causes a kind of barrier in the eastern Indian Ocean and all the southwesterly winds blow towards the Indian sub-continent.
- Accordingly, the waters in the eastern Indian Ocean cool down, which tends to cause droughts in adjacent land areas of Indonesia and Australia.
- Conversely, during a negative IOD period, the waters of the tropical eastern Indian Ocean are warmer than water in the tropical western Indian Ocean.
- This results in increased rainfall over parts of southern Australia.
Effects on India:
- A positive IOD can boost India's southwest monsoon performance depending on its development timing.
- Example: In 2019, a strong IOD event improved a 30% rainfall deficit during the late monsoon season.
- Benefits for agriculture through recharging water sources and reservoirs.
- The development of IOD likely benefits India's agricultural sector, particularly in areas with precarious water storage levels.
Difference between El Nino and IOD:
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and the El Nino are independent climatic phenomena but often co-occur.
- Both IOD and El Nino result in changes in global wind patterns. To know about the change of wind patterns, click here.
- However, the cycle of IOD is shorter, while El Nino condition could last for even two years.
- IOD commences in the month of May and ends with the withdrawal of the Southwest Monsoon in the Indian sub-continent.
