Project VISTAAR

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
IIT Madras has partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare on Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources). MoU signed between the Ministry and IIT Madras to integrate information about agricultural start-ups into the VISTAAR platform.
Key Highlights:
Project Objectives:
- Digitalisation of Agricultural Extension: To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the agricultural extension system through digital platforms.
- Access to Start-Up Innovations: Provide farmers easy access to over 12,000 start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors, connecting them to technological solutions and innovations.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Focus on making farming more sustainable and climate-resilient by promoting adoption of innovative technologies.
Key Features of VISTAAR:
- Integration of start-up data via IIT Madras' startup information platform and its incubatee, YNOS Venture Engine.
- Advisory services covering:
- Crop production
- Marketing
- Value addition
- Supply chain management
- Information on government schemes for agriculture, allied sectors, and rural development.
- Real-time, contextual, and accurate information to enhance decision-making and improve farming practices.
Significance of the Project:
- The platform will expand the outreach of agricultural extension services, providing support to farmers across India.
- It will ensure farmers access high-quality advisory services that are critical for improving productivity and income.
- Integration of start-up-driven innovations will aid in the adoption of climate-resilient farming practices.
- Timely and accurate information will empower farmers to make informed decisions and improve the efficiency of agricultural processes.
Impact on Farmers:
- Digitalisation will provide farmers with easier access to expert advice and resources, enhancing productivity.
- Improved access to government schemes ensures farmers can avail themselves of financial and technical support for development.
- The project aligns with national objectives of enhancing agriculture’s contribution to India’s economy and ensuring food security.
Operation Green Scheme

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The government’s flagship Operation Greens scheme, designed to stabilise crop prices and benefit farmers, has spent just 34 per cent of its allocated budget for 2024-25, according to a parliamentary report, even as onion farmers in Maharashtra reel from massive losses and potato shortages grip eastern states.
Key Highlights:
Overview:
- Launched: November 2018 under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana.
- Objective: Stabilize prices and improve farmers' income by enhancing the production and marketing of perishable crops, initially focusing on Tomato, Onion, and Potato (TOP).
- Expanded Scope (2021): Includes 22 perishable crops like mango, banana, ginger, apple, and shrimp.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI).
- Funding: Managed by the National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED).
Key Aims:
- Reduce price volatility in agricultural markets.
- Minimize post-harvest losses.
- Strengthen farm-to-market linkages.
- Enhance farmers’ earnings by stabilizing market prices.
- Promote value addition and food processing.
Scheme Components:
- Short-term Interventions:
- Subsidies on transportation (50%) and storage (50%) to protect farmers from distress sales.
- Price stabilization during periods of surplus or shortage.
- Long-term Interventions:
- Development of farm-gate infrastructure like cold storage and processing facilities.
- Strengthening production clusters and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Building efficient agri-logistics systems.
- Promoting food processing and value addition capacities.
Key Features:
- 50% subsidy on transportation and storage costs for eligible crops.
- Projects eligible for 50% subsidy (up to ?50 crore per project), and for FPOs, a 70% subsidy.
- Demand-driven funding based on applications, with no fixed crop or state-wise allocation.
Key Findings from Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) Report (2024):
- Underutilisation of Budget: Only 34% (?59.44 crore) of the allocated ?173.40 crore for 2024-25 spent by October 2024, leaving 65.73% unspent.
- Slow Implementation: Out of 10 targeted projects, only 3 were completed by October 2024.
- Limited Impact on Price Stabilization:
- Onion prices fell by nearly 50% in Maharashtra, despite the scheme's intent to stabilize prices.
- Potato shortages in states like Odisha and Jharkhand due to weather-induced production dips in West Bengal.
- Inconsistent Policies: Export bans and fluctuating export duties caused frustration among onion farmers, undermining the scheme’s effectiveness in ensuring fair prices.
Impact on Farmers:
- Price Stabilization: Despite the scheme’s aims, price fluctuations continue to affect farmers, especially in Maharashtra with the onion price crash.
- Post-Harvest Losses: The scheme aims to reduce wastage by building infrastructure like cold storage, but challenges remain in implementation.
- Market Linkages: Attempts to connect farmers and FPOs with retail markets have not yet yielded significant results.
Operational Challenges:
- The scheme faces challenges in fulfilling its dual mandate of ensuring fair prices for farmers while keeping consumer prices affordable.
- The slow utilization of funds and incomplete infrastructure projects raise concerns about the effectiveness of the program.
- Inconsistent policy decisions, like the export ban and imposition of export duties, have contributed to farmer discontent.
National Farmers' Day

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
National Farmers' Day, also known as Kisan Diwas, is celebrated annually on December 23rd to honor the vital contributions of Indian farmers and commemorate the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, India's fifth Prime Minister. A passionate advocate for rural development and farmers' welfare, Charan Singh's policies laid the foundation for several reforms aimed at uplifting the agrarian economy. His contributions continue to inspire government initiatives that prioritize the welfare of farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural growth and ensuring food security for the nation.
The Legacy of Chaudhary Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh was born on December 23, 1902, in Noorpur, Uttar Pradesh. His deep understanding of rural issues and commitment to improving farmers’ lives earned him the title of "Kisan Leader". Throughout his political career, he championed reforms such as the Debt Redemption Bill (1939), which alleviated the financial burdens of farmers, and the Land Holding Act (1960), which promoted fair distribution of agricultural land. He also advocated for Minimum Support Price (MSP), and his policies laid the groundwork for NABARD and other farmer-centric institutions.
Significance of Kisan Diwas
Kisan Diwas highlights the importance of agriculture in India’s economy and employment, with farmers constituting nearly 50% of the workforce. The day emphasizes the need for policies that address farmers' challenges such as climate change, financial constraints, and technological adoption. It also serves as a reminder of the necessity to empower farmers through innovative solutions, financial security, and sustainable farming practices.
Key Government Initiatives for Farmer Welfare
The Indian government has launched several schemes to address the challenges faced by farmers and support their socio-economic upliftment:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to mitigate financial risks due to crop loss.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY): A pension scheme for farmers to ensure long-term social security.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient fertilizer use and soil health by providing farmers with personalized soil health reports.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): These entities help farmers collectively access markets, reduce costs, and improve bargaining power.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Provides affordable credit to farmers, especially for agriculture-related activities.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Helps farmers access timely credit for agricultural purposes at concessional rates.
Significant Budget Allocations and New Schemes
The government has drastically increased its budget allocation to the agriculture sector. From Rs. 21,933.50 crore in 2013-14, the budget has risen to Rs. 1,22,528.77 crore for 2024-25, underlining the government's commitment to farmer welfare and sustainable agricultural development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme: This initiative, aimed at empowering Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs), supports the use of drones for agricultural purposes, including fertilizer and pesticide application, with 80% financial assistance.
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP): Enhances the quality and productivity of horticulture crops by ensuring disease-free planting material.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to modernize farming with digital infrastructure, including crop estimation surveys and e-agriculture platforms.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Encourages chemical-free, sustainable farming practices.
Farmers' Role in Nation-Building
India’s agricultural sector not only sustains the livelihoods of millions but also contributes significantly to the country's GDP. In FY 2023-24, agriculture contributed 17.7% to the Gross Value Added (GVA). With over 54% of the country's land dedicated to agriculture, farmers are critical to food security and rural development.
In 2023-24, India achieved a record foodgrain production of 332.2 million tonnes, illustrating the resilience of Indian farmers in ensuring food availability despite challenges like climate change.
7 New Schemes to Boost Farmer Income
- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, approved seven schemes to improve farmers’ lives and increase their incomes at a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 Crore.
1. Digital Agriculture Mission: based on the structure of Digital Public Infrastructure, Digital Agriculture Mission will use technology for improving farmers’ lives. The Mission has a total outlay of Rs 2,817 crores. It comprises two foundational pillars
1. Agri Stack
- Farmers registry
- Village land maps registry
- Crop Sown Registry
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- Geospatial data
- Drought/flood monitoring
- Weather/satellite data
- Groundwater/water availability data
- Modelling for crop yield and insurance
The Mission has provision for
- Soil profile
- Digital crop estimation
- Digital yield modelling
- Connect for crop loan
- Modern technologies like AI and Big Data
- Connect with buyers
- Bring new knowledge on mobile phones
2. Crop science for food and nutritional security: with a total outlay of Rs 3,979 crore. The initiative will prepare farmers for climate resilience and provide for food security by 2047. It has following pillars:
- Research and education
- Plant genetic resource management
- Genetic improvement for food and fodder crop
- Pulse and oilseed crop improvement
- Improvement of commercial crops
- Research on insects, microbes, pollinators etc.
3. Strengthening Agricultural Education, Management and Social Sciences: with a total outlay of Rs 2,291 Crore the measure will prepare agriculture students and researchers for current challenges and comprises the following
- Under Indian Council of Agri Research
- Modernising agri research and education
- In line with New Education Policy 2020
- Use latest technology … Digital DPI, AI, big data, remote, etc
- Include natural farming and climate resilience
4. Sustainable livestock health and production: with a total outlay of Rs 1,702 crore, the decision aims to Increase farmers income from livestock and dairy. It comprises the following
- Animal health management and veterinary education
- Dairy production and technology development
- Animal genetic resource management, production and improvement
- Animal nutrition and small ruminant production and development
5. Sustainable development of Horticulture: with a total outlay of Rs 1129.30 crore the measure is aimed at increasing farmers’ income from horticulture plants. It comprises the following
- Tropical, sub-tropical and temperate horticulture crops
- Root, tuber, bulbous and arid crops
- Vegetable, floriculture, and mushroom crops
- Plantation, spices, medicinal, and aromatic plants
6. Strengthening of Krishi Vigyan Kendra with an outlay of Rs 1,202 crore
7. Natural Resource Management with an outlay of Rs 1,115 crore
Digital Agriculture Mission

- 03 Sep 2024
Introduction
India's digital revolution has significantly transformed governance and service delivery in recent years by creating digital identities, secured payments and transactions. This progress has paved the way for a thriving digital ecosystem across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and retail, positioning India as a leader in citizen-centric digital solutions.
For a similar transformation of the Agriculture Sector, the Union Cabinet Committee, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the 'Digital Agriculture Mission' with a substantial financial outlay of Rs. 2,817 Crore, including a central government share of Rs. 1,940 Crore, on September 2, 2024.
The Digital Agriculture Mission is designed as an umbrella scheme to support various digital agriculture initiatives. These include creating Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), implementing the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), and supporting IT initiatives by the Central Government, State Governments, and Academic and Research Institutions.
The scheme is built on two foundational pillars:
- Agri Stack
- Krishi Decision Support System.
Additionally, the mission includes ‘Soil Profile Mapping’ and aims to enable farmer-centric digital services to provide timely and reliable information for the agriculture sector.
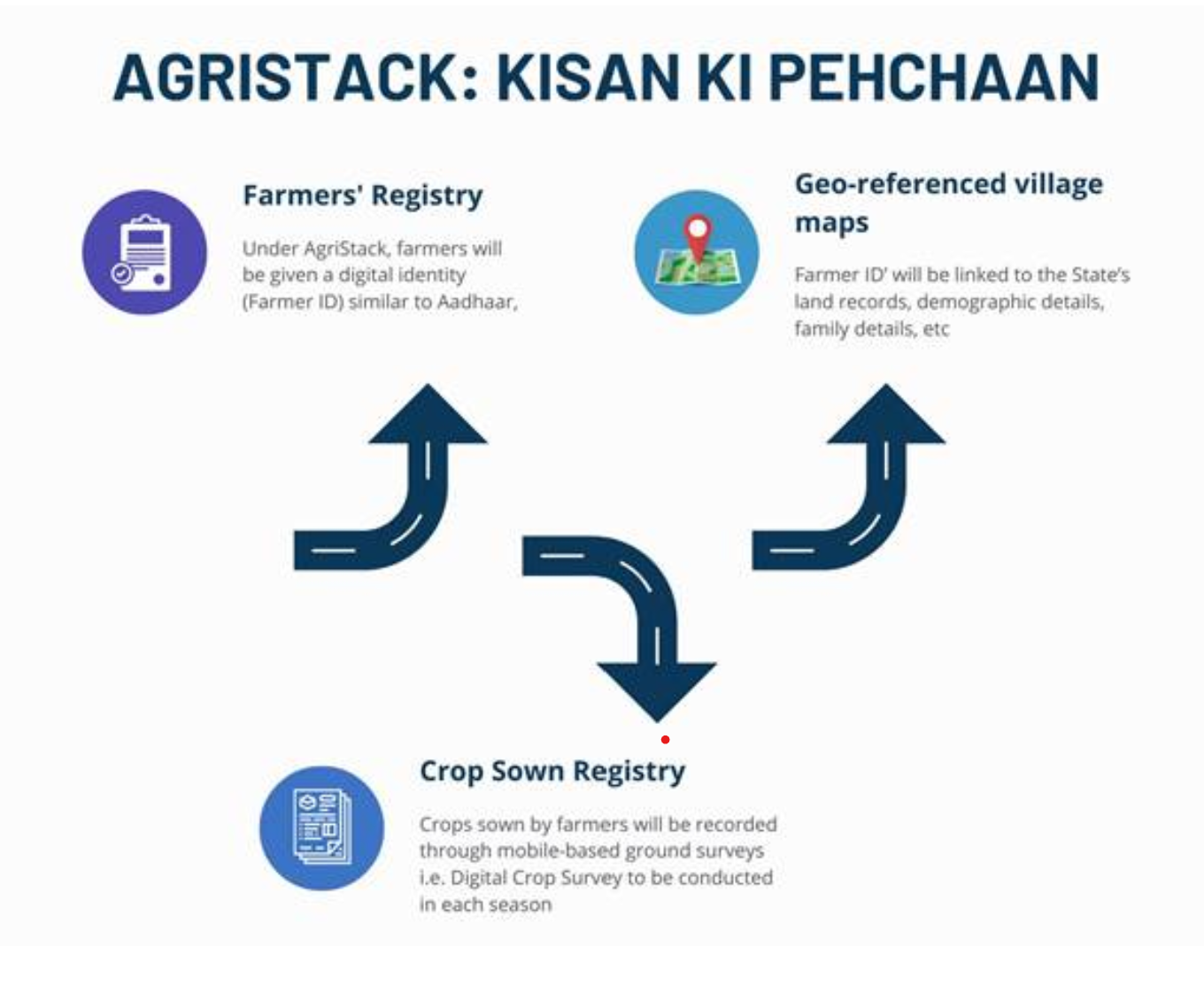
AgriStack: Kisan ki Pehchaan
AgriStack is designed as a farmer-centric Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to streamline services and scheme delivery to farmers. It comprises three key components:
1. Farmers' Registry
2. Geo-referenced village maps
3. Crop Sown Registry
- A crucial feature of AgriStack is the introduction of a 'Farmer ID', similar to Aadhaar card, serving as a trusted digital identity for farmers.
- These IDs, created and maintained by the State Governments/ Union Territories, will be linked to various farmer-related data, including land records, livestock ownership, crops sown, and benefits availed.
- The implementation of AgriStack is progressing through partnerships between the Central and State Governments, with 19 states having signed MoUs with the Ministry of Agriculture. Pilot projects have been conducted in six states to test the creation of Farmer IDs and the Digital Crop Survey.
- The six states include Uttar Pradesh (Farrukhabad), Gujarat (Gandhinagar), Maharashtra (Beed), Haryana (Yamuna Nagar), Punjab (Fatehgarh Sahib), and Tamil Nadu (Virudhnagar).
Key targets include:
- Creating digital identities for 11 crore farmers over three years (6 crore in FY 2024-25, 3 crore in FY 2025-26, and 2 crore in FY 2026-27)
- Launching the Digital Crop Survey nationwide within two years, covering 400 districts in FY 2024-25 and all districts in FY 2025-26
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- The Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) will integrate remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources into a comprehensive geospatial system.
3. Soil Profile Mapping
Under the mission, detailed soil profile maps on a 1:10,000 scale for approximately 142 million hectares of agricultural land have been envisaged, with 29 million hectares of soil profile inventory already being mapped.
- Further under the Digital Agriculture Mission, the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) will be used for crop-cutting experiments to provide precise yield estimates, enhancing agricultural production accuracy.
- The mission is expected to create direct and indirect employment in agriculture, providing opportunities for around 2,50,000 trained local youth and Krishi Sakhis.
- By leveraging modern technologies like data analytics, AI, and remote sensing, the mission will improve service delivery for farmers, including streamlined access to government schemes, crop loans, and real-time advisories.
Key Components of the Mission
The Digital Agriculture Mission focuses on grassroots implementation, targeting farmers as the primary beneficiaries. Some of the key benefits of the mission include:
- Digital authentication for accessing services and benefits, reducing paperwork and the need for physical visits.
- Enhanced efficiency and transparency in government schemes, crop insurance, and loan systems through accurate data on crop area and yield.
- Crop map generation and monitoring for better disaster response and insurance claims.
- Development of digital infrastructure to optimize value chains and provide tailored advisory services for crop planning, health, pest management, and irrigation.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 that the Government, in partnership with states, will implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture over the next three years.
- This initiative will cover farmers and their lands, with a digital crop survey for Kharif planned for 400 districts this year. The goal is to update registries with details of 6 crore farmers and their lands.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 had previously introduced the DPI for agriculture, which aims to provide comprehensive data on farmers, including demographic details, land holdings, and crops sown. The DPI will integrate with state and central digital infrastructures to offer a range of farmer-centric services, including information on livestock, fisheries, soil health, and available benefits.
Conclusion
- The Union Cabinet also approved six major schemes alongside the Digital Agriculture Mission, with a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 crore.
- These initiatives include Rs 3,979 crore for Crop Science aimed at ensuring food security and climate resilience by 2047, and Rs 2,291 crore for strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences to support students and researchers. Rs 1,702 crore is allocated for Sustainable Livestock Health and Production to boost incomes from livestock and dairy, while Rs 1,129.30 crore is designated for Sustainable Development of Horticulture to increase income from horticulture. Additionally, Rs 1,202 crore will be invested in strengthening Krishi Vigyan Kendra, and Rs 1,115 crore towards Natural Resource Management.
- These comprehensive approaches leverage digital technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in India's agricultural sector, potentially transforming the lives of millions of farmers across the country. By extending the digital revolution to agriculture, India aims to further solidify its position as a global leader in innovative, technology-driven solutions for critical sectors of the economy.
SPICED SCHEME

- 25 Sep 2024
In the News
The Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry has authorized the SPICED scheme (Sustainability in Spice Sector through Progressive, Innovative, and Collaborative Interventions for Export Development), which will run until 2025-26.
Overview
This initiative aims to expand the cultivation area and enhance the productivity of both small and large cardamom. It will also focus on improving the quality of spices for export through advancements in post-harvest processes and promoting value-added spice exports.
Key Objectives:
- Increase cardamom production and boost export potential.
- Improve post-harvest quality to meet export standards and ensure compliance with safety and quality regulations.
India holds the position of the largest producer, consumer, and exporter of spices globally.
Cardamom
Cardamom is sourced from the seeds of the Elettaria cardamomum plant (commonly known as green or true cardamom) and is a member of the ginger family. It is known for its unique, robust flavor that combines both spicy and sweet notes. There are two primary varieties: Small Cardamom and Large Cardamom.
Small Cardamom:
- Origin: Native to the evergreen forests of South India's Western Ghats.
- Major Producers: Primarily grown in Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Growing Conditions: Thrives in loamy soil with thick shade, requires temperatures between 10°C and 35°C, and needs 1500 to 4000 mm of annual rainfall.
Large Cardamom:
- Distribution: Mainly cultivated in the Sub-Himalayan regions of Northeast India, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Major Producers: Key production areas include Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and the Darjeeling district of West Bengal.
- Growing Conditions: Prefers high altitudes (600 to 2000 meters), with average rainfall of 3000-3500 mm, and temperatures ranging from 6°C to 30°C. Well-drained, loamy soils rich in organic matter are ideal.
About the Spices Board of India
Established in 1987 under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the Spices Board of India serves as the apex organization for the promotion and export of a diverse array of spices, including black pepper, both small and large cardamom, ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, cumin, and fenugreek. The Board was formed by merging the Cardamom Board (1968) and the Spices Export Promotion Council (1960). Its headquarters is located in Kochi, Kerala.
100 YEARS OF ICAR-NISA

- 23 Sep 2024
Overview:
The ICAR-National Institute of Secondary Agriculture (NISA), originally established in 1924 as the Indian Institute of Natural Resins and Gums in Ranchi, Jharkhand, marks its centenary this year. Renamed in 2022, it operates under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, focusing on enhancing the value of agricultural products.
Understanding Secondary Agriculture:
Secondary agriculture encompasses the transformation of primary agricultural products into higher-value commodities and includes activities such as:
- Beekeeping
- Poultry farming
- Agricultural tourism
This sector plays a crucial role in converting agricultural produce, residues, and by-products into valuable goods for various uses, including pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial applications. Examples of secondary agriculture practices include:
- Extracting vitamins from grains
- Producing oil from rice bran
- Making jaggery from sugarcane
- Cottage industries for jams and pickles
Growth Potential: The sector is poised for growth due to:
- Increasing consumer demand for value-added products like ready-to-eat meals.
- The need for innovative uses of renewable agro-bio resources.
- The significant availability of agricultural byproducts.
Significance of Secondary Agriculture:
- Environmental Sustainability: Proper utilization of crop residues can reduce waste and pollution.
- Enhanced Farmer Income: Activities like beekeeping and lac culture provide additional revenue streams for farmers.
- Value Addition: Processing agricultural products increases their shelf life and overall productivity.
- Promotion of Cottage Industries: Supports rural economies and fosters technology adoption.
Challenges Ahead: Despite its potential, secondary agriculture faces several hurdles:
- The industry for high-value products from agricultural byproducts, such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, is still emerging.
- Small landholdings complicate the collection of crop residues.
- Limited research on suitable technologies hampers development.
- There is a lack of awareness among farmers regarding the processing of agricultural waste.
Conclusion
As ICAR-NISA celebrates its 100th anniversary, it remains crucial in shaping the future of secondary agriculture in India, addressing both challenges and opportunities to enhance sustainability and farmer livelihoods.
Precision Farming
- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
The Centre is contemplating to earmark Rs 6,000 crore to promote precision farming, a modern approach that uses smart technology such as Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, drones and data analytics to boost production through maximal use of resources while minimising environmental impact.
Key Details:
- Union Ministry of Agriculture is planning a Smart Precision Horticulture Programme under the existing Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) scheme.
- It will cover 15,000 acres of land in five years from 2024-25 to 2028-29 and is expected to benefit about 60,000 farmers.
- At present, the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), launched during Covid-19, has provisions for financing infrastructure projects for smart and precision agriculture.
- Under AIF, individual farmers as well as farmers’ communities such as Farmer Producer Organization, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies and SHGs are eligible for loans with interest subvention of 3% for using technological solutions in farm practices. These practices include farm/ harvest automation; purchase of drones, putting up specialised sensors on field; use of blockchain and AI in agriculture; remote sensing and Internet of Things (IoT).
Positive impact
- Smart and precision agriculture maximises use of resources like water, fertilisers and pesticides to increase production quality and quantity, all while insulating farmers from vagaries of climate change and other uncertainties, besides ensuring sustainable farming.
Apart from offering financial support, the Centre is also considering collaborating with the Netherlands and Israel, where tech-based modern farming solutions are being used, through Centres of Excellences (CoEs). The number of CoEs is likely to be 100 in the next five years. Under Indo-Israel Agriculture Project, 32 CoEs have already been set up across 14 states.
The Centre has also set up 22 Precision Farming Development Centres (PFDCs) across the country to test new technologies and modify them according to local needs.
According to the Ministry, these 22 PFDCs are located across State/Central Agricultural Universities, ICAR Institutes and IITs in TN, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Haryana, Telangana, West Bengal, Ladakh, UP, Punjab, Gujarat, Uttrakhand, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Manipur and Assam. Besides, funds are released to states/UTs for projects involving use of AI and machine learning, under schemes like the National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture.
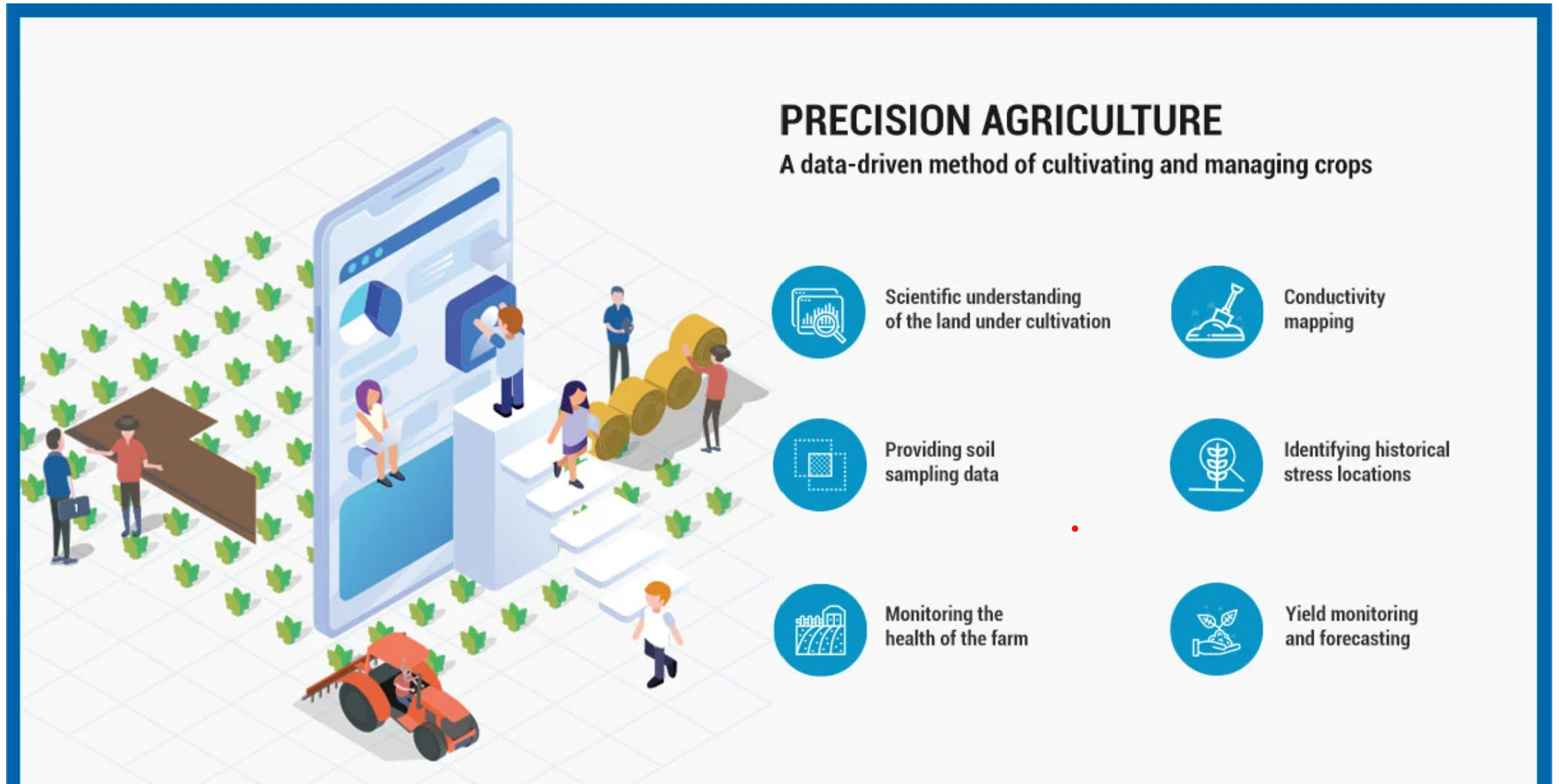
What is Precision Agriculture?
- Precision Agriculture is a farm management concept that revolves around the process of observing, measuring, and responding to various inter-and intra-field variability inputs for modern agriculture.
- Popular definitions of Precision Agriculture (PA) or Site-Specific Crop Management (SSCM) describe the term as a technology-enabled approach to farming management that observes, measures, and analyzes the needs of individual fields and crops.
- The goal of precision agriculture is to increase efficiency and productivity, reduce input costs, and improve environmental sustainability.
- Key Advantages:
- A refined set of cultivation practices and choice of crops based on the suitability of land
- Elimination of volatility and risk
- Waste management
- Reduced production costs
- Minimum environmental impact
- Optimized use of fertilizers
- Water management with optimized irrigation practices
- Improved soil health
Pink Bollworm Attack

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Haryana has seen an overall fall in acreage under cotton cultivation to 4.76 lakh hectares (lh) this kharif season from 6.65 lh in 2023. This has been accompanied by an increase in the area under rice from 15.20 lh to an all-time-high of 16.44 lh in the state.
Key Details:
- The reduction in the cotton area — also reported in neighbouring Rajasthan (from 7.91 lh to 5.13 lh) and Punjab (2.14 lh to 1 lh) — has been attributed mainly to PBW infestation.
- In May-June this year, at the time of sowing, the price of kapas (raw unginned cotton) averaged Rs 6,700-6,800 per quintal in Haryana mandis. This was against the average Rs 11,100-11,200 per quintal two years ago.
Pink Bollworm (PBW) Infestation:
- Impact: The pink bollworm has devastated cotton yields by attacking the bolls, which affects the weight and quality of the cotton. This pest has been particularly damaging since its appearance in 2017-18 and has caused significant losses in Haryana, Rajasthan, and Punjab.
- Spread: PBW spreads through the air and infected crop residues, which harbor larvae and spread to future crops. This infestation has led to a dramatic decrease in cotton acreage.
The spread of pink bollworm
- The pink bollworm first appeared in north India during the 2017-18 season in a few districts in Haryana and Punjab, primarily cultivating Bt cotton, and spread to Rajasthan by 2021.
- PBW primarily spreads through the air. Residue of infected crops, often left by farmers on the field to be used as fuel, can also harbour PBW larvae which can then infect future crops. Infected cotton seeds are another reason behind the pest’s spread.
Economic Impacts:
- Price Decline: The price of kapas (raw cotton) has dropped from Rs 11,100-11,200 per quintal to Rs 6,700-6,800, significantly impacting farmers’ profitability.
- Farmer Losses: Farmers like Shyam Sundar have reported substantial losses due to low yields and poor quality, leading them to switch to more profitable and reliable crops like paddy and guar.
Transition to Paddy
Water Requirements:
- Challenges: Paddy requires much more water compared to cotton. Farmers need to flood their fields, which is challenging in regions where groundwater is saline or limited.
- Current Practices: Despite the increased water requirements, some farmers have transitioned to paddy due to its potentially better economic returns, especially when paddy prices are relatively high.
Monsoon and Irrigation:
- Weather Dependence: The monsoon this year has been favorable, allowing some farmers to successfully grow paddy. However, reliance on monsoon and supplementary irrigation from tubewells is not sustainable in the long term.
Government and Expert Perspectives
Government Incentives:
- Subsidies: The Haryana government is offering incentives for farmers switching to alternative crops and using water-saving techniques like direct seeding of paddy.
- Support: While there is support available, the effectiveness and reach of these measures are mixed, and some farmers have faced issues with insurance claims and financial aid.
Expert Opinions:
- Temporary Solution: Experts caution that while switching to paddy may be a temporary solution, it is not sustainable long-term due to water scarcity and environmental concerns.
- Environmental Impact: Paddy cultivation contributes to higher carbon and methane emissions, which adds to the environmental challenges in the region.
Economic and Industry Implications
Cotton Industry Concerns:
- Reduced Production: Lower cotton production affects the entire supply chain, from textile manufacturers to cottonseed oil and meal producers.
- Potential Recovery: There is hope that reduced PBW infestation this year may lead to a recovery in cotton yields, but the extent of this recovery remains uncertain.
AgriSURE Fund and Krishi Nivesh Portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union agriculture minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan launched two initiatives — a fund aimed at boosting farm-sector startups, and a single-window portal to process investments — as part of a slew of measures being taken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government in its third term to bolster the farm economy.
Key Details:
- AgriSure is a ?750-crore fund established to support agricultural startups.
- Krishi Nivesh Nidhi is a portal designed to expedite the clearance of project proposals.
- Both initiatives aim to enhance farm incomes.
Awards for Credit Disbursal:
- Scheduled banks were recognized for their credit disbursals under the government’s agriculture infrastructure fund.
- First prize: State Bank of India (SBI).
- Second prize: HDFC Bank.
- Third prize: Canara Bank.
Significance of Agriculture Sector:
- Agriculture contributes 16% to India’s GDP.
- Farmers play a crucial role as both producers and consumers in the economy.
PM Modi’s Strategy to Double Farmers’ Incomes:
- The strategy includes:
- Increasing output.
- Reducing input costs.
- Ensuring profitable prices.
- Promoting crop diversification.
- Supporting natural farming.
- Enhancing value addition to crops.
Details of AgriSure Fund:
- Blended capital fund with a total corpus of ?750 crore:
- ?250 crore each from the Department of Agriculture and NABARD.
- ?250 crore to be raised from financial institutions.
- Managed by NabVentures, a subsidiary of NABARD.
- Provides both equity and debt support to startups and agripreneurs.
- Focuses on high-risk, high-impact activities within the agriculture value chain.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund:
- Mobilized projects worth ?78,000 crore with ?45,000 crore in financing so far.
- Expanded areas of coverage approved by the Union Cabinet on August 28.
- Aims to create durable farm assets, such as warehouses and processing plants.
- Can be used by agricultural produce marketing committees (APMCs) for market facility improvements.
Funding and Loan Details:
- Part of the ?20-lakh crore stimulus package introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Total funding of ?1 lakh crore over four years:
- ?10,000 crore for 2020-21.
- ?30,000 crore each for the subsequent three financial years.
- Provides medium-to-long term debt financing for rural projects.
- Interest subvention of 3% per annum on loans up to ?2 crore for seven years, with the government covering part of the interest.
Deda Method of Preserving Seeds

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
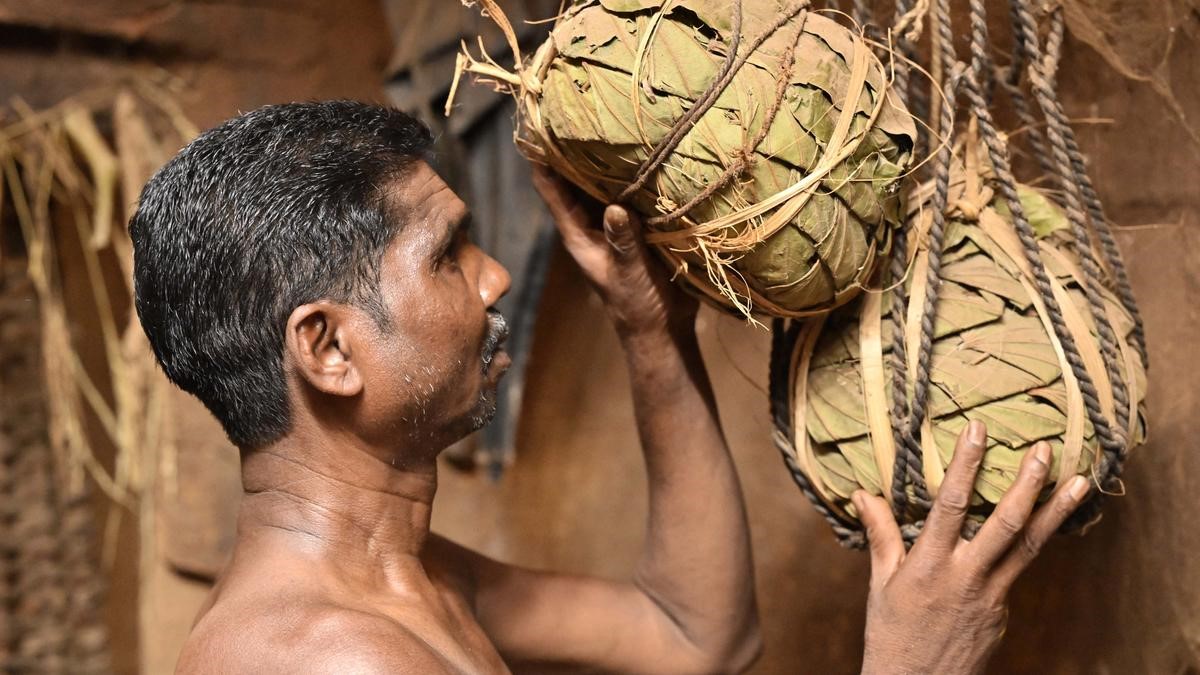
In his 50s, Madakam Unga, a Muria tribal farmer who migrated from Chhattisgarh and settled in the dense forests of the Godavari Valley, is still practising ‘deda’, a traditional method of preserving seeds that his ancestors handed over to his family.
What is the Deda Method?
- The Deda Method is an ancestral seed preservation technique passed down through generations.
- This unique method involves the use of natural materials to create a protective, airtight environment for the seeds, ensuring their viability for future planting.
Preservation Process:
- Seeds are packed tightly and wrapped in leaves to form a sturdy bundle resembling a boulder.
- The seed-filled leaf packages are then woven together with Siali leaves (Bauhinia vahlii), locally known as 'addakulu,' forming the distinctive deda structure.
- A deda consists of three layers:
- The innermost layer contains wood ash spread over Siali leaves.
- The ash is then covered with lemon leaves, creating a protective casing.
- Lastly, seeds are preserved within this casing and sealed, with each deda supporting up to 5kg of seeds.
Advantages:
- The Deda Method effectively protects seeds from pests and worms, ensuring their quality and viability.
- Seeds preserved using this technique can be used for cultivation for up to five years.
- This method is particularly useful for preserving the seeds of various pulses, such as green gram, red gram, black gram, and beans.
- By utilizing the Deda Method, farmers can maintain a reliable, diverse collection of seeds, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices and supporting long-term food security.
Facts About Muria Tribe:
- Location: The Muria tribe is found in the states of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Language: They speak Koya, a Dravidian language.
- Population and Status: In Andhra Pradesh, the Muria, also known as 'Gutti Koyas' by native tribes, are internally displaced people (IDPs) with a population of around 6,600.
- Cultural Practices: The Muria have a progressive outlook on marriage and life.
- A notable example is the Ghotul, a communal dormitory that provides an environment for Muria youth to explore and understand their sexuality.
Recognition: While most Gutti Koya belong to the Gond or Muria communities, which are recognized as Scheduled Tribes in Chhattisgarh, they lack such recognition in Telangana.
Hydroponic Farming

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the wake of evolving consumer preferences, India is at the forefront of an agricultural transformation, pivoting towards sustainable farming with an emphasis on health.
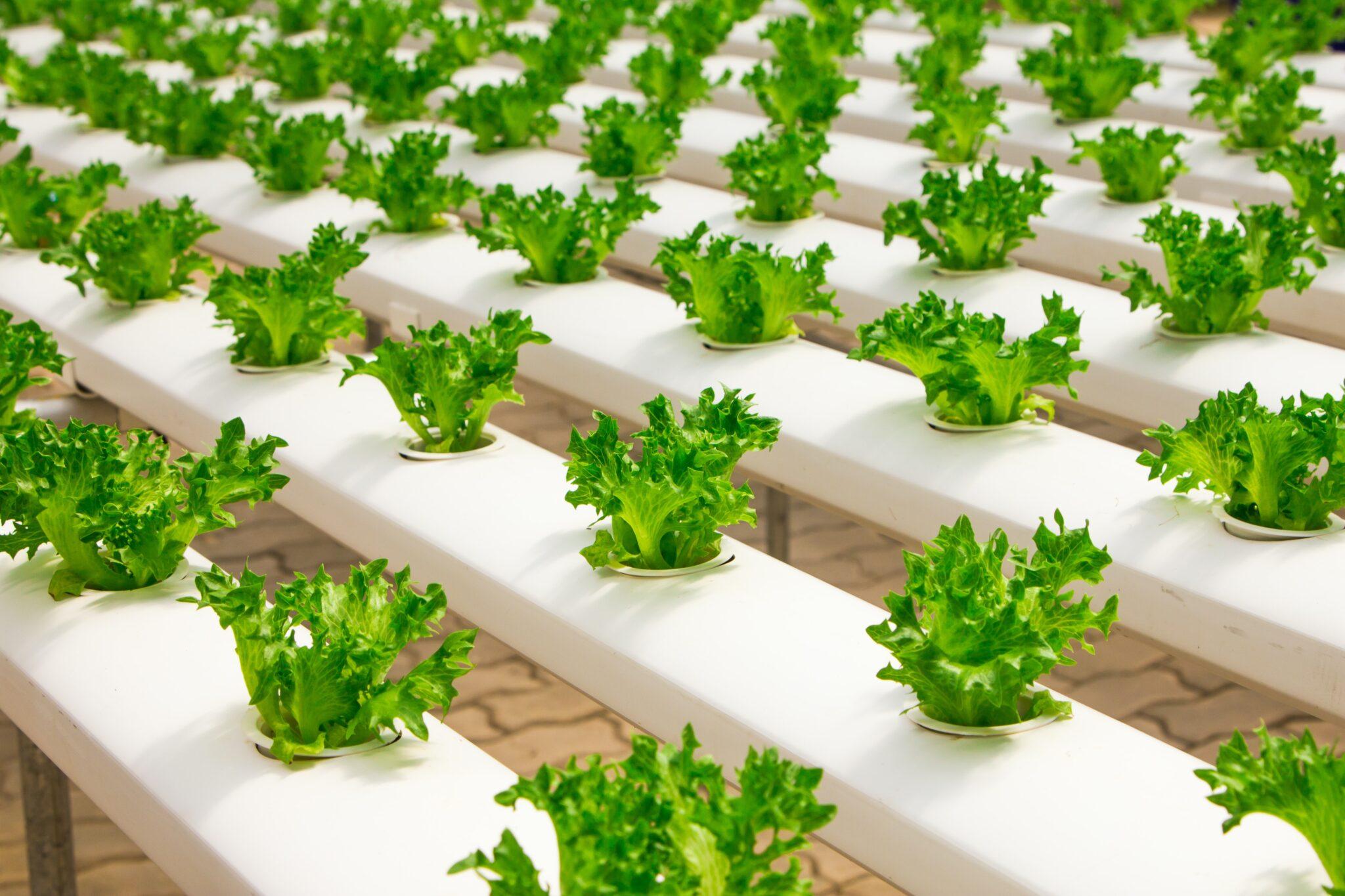
What is Hydroponics?
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, utilizing nutrient-rich water as the primary source of essential minerals and elements.
- The technique involves the circulation of nutrient-enriched water through a network of pipes or channels, directly supplying the roots of plants with the necessary nourishment for their growth and development.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Soilless Cultivation: Hydroponics eliminates the need for soil by providing an alternative substrate or a soil-like medium, such as rock wool, perlite, or vermiculite, to support the plants' roots.
- Nutrient Control: This technique enables precise control over the nutrient composition, concentration, and pH levels in the water, ensuring optimal nutrient availability for plants.
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponics recirculates and reuses water, significantly reducing water consumption compared to traditional soil-based farming.
- Space Optimization: Due to the compact nature of hydroponic systems, they can be used in urban areas, greenhouses, and indoor facilities, maximizing yield per unit area.
- Year-round Cultivation: With controlled environmental conditions, hydroponics allows for continuous cultivation, regardless of seasonal changes or weather fluctuations.
- Hydroponics provides a sustainable, efficient, and adaptable approach to agriculture, with potential benefits in resource conservation, food security, and sustainable urban food production.
Hydroponics in India:
- According to a report by Datamintelligence, India’s hydroponic market is poised for a remarkable growth trajectory, with a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.53% by 2027, outpacing the global industry’s estimated growth of 6.8%.
- This surge underscores the vast potential of hydroponics in meeting the rising demand for sustainable food produce, particularly in metros and tier 1 cities where health-conscious consumers are willing to pay a premium for fresh, safe, and sustainably grown products.
- This transformative shift is not just a response to changing consumer preferences for fresh produce but also an adaptation to the geographical and environmental challenges that face traditional farming methods.
Suitable Regions for Hydroponic Farming:
- Hydroponic farming presents a viable solution in regions where traditional farming faces significant barriers:
- Areas with Limited Water Supply: Hydroponics drastically reduces water usage, making it ideal for drought-prone areas.
- Rocky Regions: In places where the terrain is unsuitable for soil-based agriculture, hydroponics offers a practical alternative.
- Low Soil Fertility Areas: Hydroponics bypasses the need for fertile soil, allowing cultivation in regions with poor soil quality.
- Demand-Driven Areas: Regions with a high demand for fresh products are perfect for hydroponic farms, catering to health-conscious consumers in urban and semi-urban locales
The Edge with Hydroponic Farming in India:
- Hydroponic farming’s ascendancy in India is attributed to several compelling benefits, underpinned by technological advancements that lower operational costs and facilitate scalability:
- Versatility in Location: It enables agriculture in environments traditionally deemed unsuitable, such as deserts or cold climates.
- Controlled Conditions: Farmers have precise control over nutrients, pH, and the growing environment, optimizing plant health and yield.
- Resource Efficiency: The recycling of water and nutrients significantly cuts down on input costs and environmental impact.
- Enhanced Growth Rates: Increased oxygen availability accelerates plant growth, leading to quicker harvest cycles.
- Pest and Disease Reduction: By eliminating soil, hydroponics reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Higher Yields: The efficiency and controlled environment of hydroponic systems result in substantially higher crop yields.
- Labour and Maintenance Savings: The absence of weeding and traditional cultivation reduces labour requirements and costs.
- Improved Working Conditions: Elevating crops to a more accessible height improves ergonomics for farm workers, further reducing labour costs.
- No Need for Crop Rotation: Hydroponics eliminates the necessity for crop rotation, simplifying farm management.
- Reduced Transplant Shock: Plants grown hydroponically experience less stress when transplanted, enhancing survival rates.
Every village to have agricultural credit societies by 2027

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah Friday said that the Centre has decided to ensure formation of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027.
Context:
- Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah recently announced the Centre's commitment to establishing Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027, introducing 20 new activities to enhance their profitability.
- Emphasizing the significance of computerization in PACS, Shah highlighted its role in fostering development opportunities.
- He also inaugurated the National Cooperative Database and unveiled the 'National Cooperative Database 2023: A Report' to bridge existing gaps through comprehensive analysis.
- The database initiative progressed through three phases, including mapping approximately 2.64 lakh societies across agriculture, dairy, and fisheries sectors in the first phase.
- Subsequent phases involved data collection from various federations, banks, and mapping of the remaining 8 lakh primary cooperative societies in other sectors.
- The unveiling revealed over 8 lakh registered societies in the country, connecting more than 30 crore citizens.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)?
- PACS are grassroots cooperative credit societies, constituting the final tier in a three-tier cooperative credit system led by State Cooperative Banks (SCBs) at the state level.
- SCBs channel credit to District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) operating at the district level, which collaborate with PACS, directly serving farmers.
- PACS operate as cooperative entities, with individual farmers as members and elected office-bearers from within the community. Villages may host multiple PACS.
- These societies extend short-term and medium-term agricultural loans to farmers for various farming activities.
Number of PACS in India:
- Established since 1904, India currently boasts over 1,00,000 PACS nationwide, engaging a significant member base exceeding 13 crore farmers.
- However, operational PACS stand at only 63,000, indicating the need for enhanced functionality and outreach.
Why are PACS Appealing?
- PACS offer crucial last-mile connectivity, ensuring farmers have access to capital at the onset of agricultural activities.
- They streamline credit extension processes, providing farmers with timely financial support with minimal paperwork, unlike traditional banks known for cumbersome procedures.
- PACS simplify paperwork and administrative tasks, offering farmers collective strength and assistance from PACS office-bearers.
- Unlike individual interactions required with commercial banks, PACS enable farmers to navigate loan processes collectively, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Challenges Faced by PACS:
- Political influences often overshadow financial prudence within PACS, impacting loan recovery.
- Various committees have highlighted systemic issues within the cooperative system, including low member participation, lack of professionalism, inadequate governance, bureaucratic hurdles, and a workforce with aging and disengaged employees.
Centre increases Fair and Remunerative Prices of sugarcane

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs recently approved ?340/quintal as the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for the sugar season 2024-25 at a sugar recovery rate of 10.25%.
What is the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)?
- FRP was introduced by the government in 2009 by an amendment to the Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966.
- It replaced the Statutory Minimum Price (SMP) on the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) consultation.
- The FRP system assured timely payment to farmers, irrespective of the profit and loss to sugar mills.
- Further, the new system made it mandatory for sugar mills to pay the farmers within 14 days of delivery of sugarcane.
- Additionally, the FRP system introduced grading on the basis of sugar recovery rate from sugarcane wherein a premium was paid to the farmer on higher recovery and a reduction in rates on lower recovery.
- The FRP is based on the Rangarajan Committee report on reorganising the sugarcane industry.
Factors Considered for Announcing FRP:
-
- Cost of production of sugarcane
- Return to the growers from alternative crops and the general trend of prices of agricultural commodities
- Availability of sugar to consumers at a fair price
- The price at which sugar produced from sugarcane is sold by sugar producers
- Recovery of sugar from sugarcane
- The realisation made from the sale of by-products viz. molasses, bagasse and press mud or their imputed value
- Reasonable margins for the growers of sugarcane on account of risk and profits
Effect of the New FRP:
- Sugar production in India was hit hard in the October-December 2023 quarter as production fell by 11.21 million metric tonnes;
- It was 12 million in the same quarter the previous year.
- The increase in FRP is going to increase the cost for producers.
- The increased FRP will benefit over five crore sugarcane farmers in the country, however, the increase in production cost could affect end-consumers as well.
- Factors such as FRP hikes, akin to MSP, make it attractive to farmers but also increase prices in the local market as mills pass on that cost to consumers
