India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
IMEC is an important initiative that can add to India's maritime security and faster movement of goods between Europe and Asia, said Union Minister of Commerce & Industry at the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) India-Mediterranean Business Conclave 2024 in New Delhi.
Key Details:
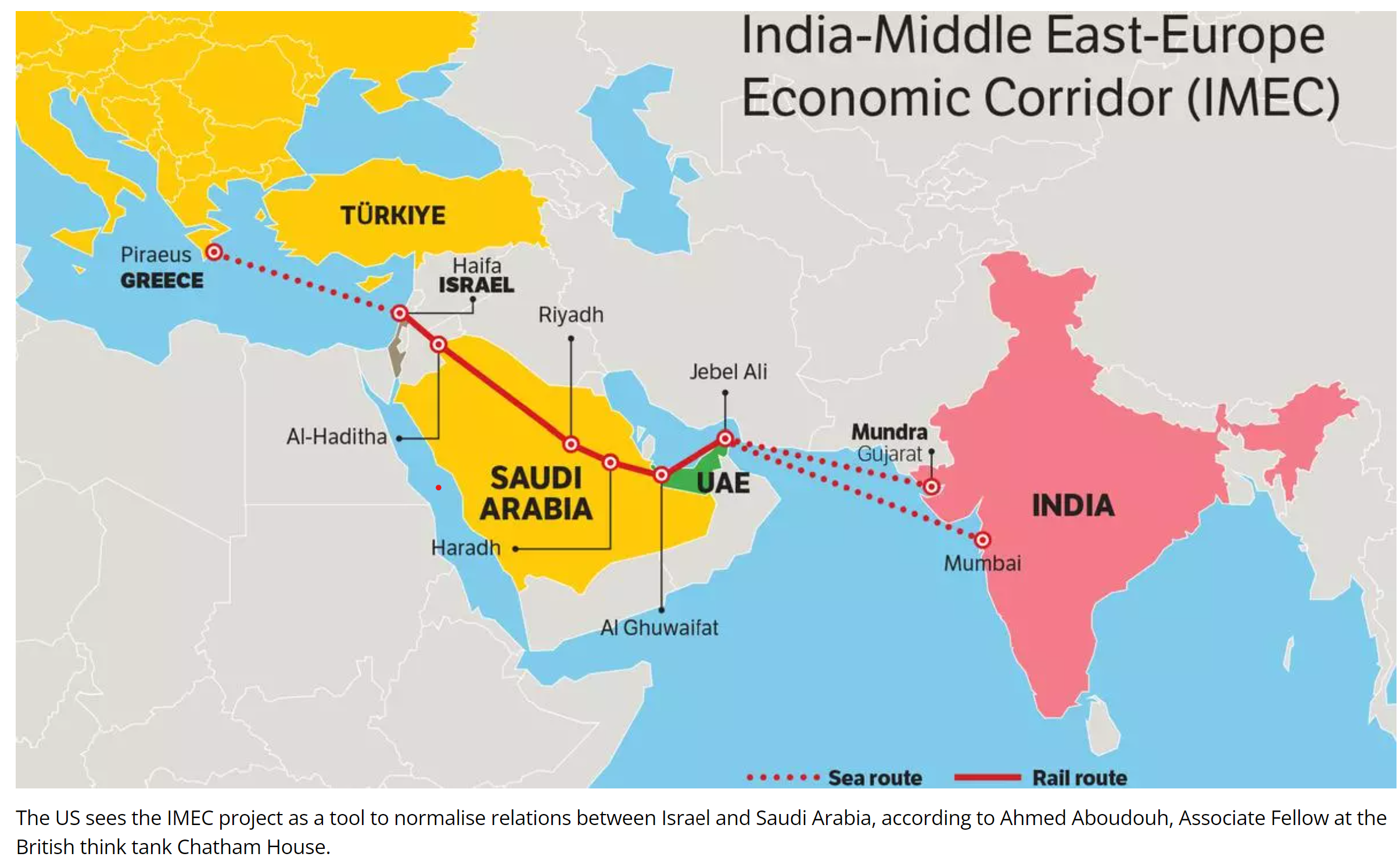
- Corridors:
- East Corridor: Connects India to the Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Links the Gulf to Europe.
- Components:
- Railroad: Provides a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network.
- Ship-to-Rail Networks: Integrates road, sea, and rail transport routes.
- Road Transport: Complements the overall transport infrastructure.
- Expected Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Enhances transit efficiency and reduces costs.
- Economic Unity: Promotes economic integration and job creation.
- Environmental Impact: Lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transformative Integration: Connects Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Additional Features:
- Infrastructure: Includes laying cables for electricity and digital connectivity, and pipes for clean hydrogen export.
- Implementation:
- MoU Commitments: Participants will collaboratively address technical design, financing, legal, and regulatory aspects.
- Action Plan: A meeting is planned within 60 days to develop an action plan with specific timetables.
Geoeconomic Perspective
- Economic Integration and Interdependence:
- Prosperity Through Integration: IMEC aims to foster trade and investment among India, the Middle East, and Europe, potentially leading to mutual prosperity and regional stability.
- Building Bridges: Aligns with the liberal international order by promoting economic interdependence to reduce tensions and create shared interests.
- Support from Major Powers: Backed by the US, Europe, and India, signaling a strong commitment to economic ties and regional stability.
- Economic Potential:
- Infrastructure and Trade Routes: Enhances infrastructure and trade routes, boosting economic activity, trade volumes, and investment opportunities.
- Regional Development: Promotes job creation and development in economically disadvantaged areas along the corridor.
Geopolitical Perspective
- Strategic Rivalry with China:
- Countering the BRI: IMEC is seen as a strategic counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), offering an alternative aligned with US, European, and Indian interests.
- Regional Influence: Aims to limit China’s influence in the Middle East and South Asia by establishing a competing corridor.
- Geopolitical Alliances:
- Aligning Interests: Involves strategic partnerships among the US, Europe, and India, reflecting concerns about China’s global strategy and shifting power dynamics.
- Rivalry and Competition: The IMEC could be viewed as a global positioning move, responding to China’s growing influence and securing strategic interests.
Reasons for Joining the IMEC
- Economic Enhancement:
- Boosts Indo-Gulf Relations: Enhances trade and economic ties with the Arab Gulf, addressing infrastructure gaps.
- Regional Connectivity: Links India with key partners like Israel and Jordan, boosting economic opportunities.
- Strategic Trade Routes:
- Alternative Routes: Complements existing routes like Chabahar Port and INSTC, connecting India to southern Eurasia.
- Bypassing Choke Points: Offers a shorter route to Eastern Mediterranean and Western Europe, avoiding strategic choke points.
- Energy and Trade Opportunities:
- Access to Resources: Provides potential access to Eastern Mediterranean gas fields.
- Trade Bloc Connectivity: Links India with the EU and GCC, opening up growth opportunities.
- Geopolitical Aspirations:
- Global Power Ambitions: Supports India’s goal to enhance global influence and integrate with eastern and western neighbors.
- Economic Growth: Leverages economic integration to support development and influence.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Economic Integration: Facilitates infrastructure creation for increased trade volumes and regional stability.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Financial Express)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Presently, the Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) Samudra Prahari is on an international mission covering ASEAN countries.
Facts About:
- Samudra Prahari is an Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) specifically designed for pollution control purposes.
Key Highlights:
- It holds the distinction of being Southeast Asia's pioneering pollution control vessel.
- Equipped with cutting-edge Pollution Response and Control equipment for effectively managing oil spills within the Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Features tanks and inflatable barges for the storage of oil spills.
- Capable of seamless oil recovery operations with a substantial storage capacity of 500 KL.
- Designed to accommodate and operate a twin-engine Advanced Light Helicopter, along with the capability to handle and embark Chetak helicopters.
- Notable features encompass an integrated platform management system, power management system, high-powered external firefighting system, and an indigenous gun mount with firefighting capabilities.
- The vessel possesses unmanned machinery operation capabilities for enhanced efficiency.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Indian EXpress)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of India recently declared the start of a massive economic corridor connecting India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Facts About:
- The project involves India, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, the European Union, France, Italy, Germany, and the US.
- Its goal is to boost trade between these countries, especially in energy products.
- The IMEC has two parts:
An Eastern Corridor linking India to the Gulf region and
A Northern Corridor connecting the Gulf region to Europe.
- It includes railways, ship-rail transit, and road routes.
- This corridor will have a railway, an electricity cable, a hydrogen pipeline, and a high-speed data cable.
- In the future, it will play a big role in connecting India, West Asia, and Europe economically.
- This rail and shipping corridor is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment (PGII).
- Why is it important?
- It will increase prosperity by enhancing energy and digital communications flow among these nations.
- The project will also address the infrastructure needs of developing countries in terms of growth.
