Makaravilakku festival

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Kerala police deploy 5,000 personnel at Sabarimala ahead of Makaravilakku festival.
Key Highlights:
- Makaravilakku is a prominent annual Hindu festival held at the Sabarimala Temple in Kerala, dedicated to Lord Ayyappa.
- It marks the celestial event of the Sun entering Capricorn (Makaram Rashi) on Makara Sankranti.
- The festival is a culmination of the 41-day pilgrimage to Sabarimala, celebrated with devotion, discipline, and spiritual purification.
- Sabarimala is one of the largest pilgrimage sites globally, drawing 10-15 million devotees annually.
Location:
- The Sabarimala Temple is located on the Sabarimala hill in Pathanamthitta, Kerala, within the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
- It is surrounded by 18 hills and is located along the banks of the Pamba River.
Key Rituals:
- 41-Day Pilgrimage (Vratham): Devotees observe strict practices like celibacy, fasting, and wearing black or saffron attire to purify the body and soul.
- Makaravilakku (Makara Jyothi): A celestial light appears on Makara Sankranti, believed to be a divine manifestation of Lord Ayyappa.
- Thiruvabharanam Procession: On Makaravilakku day, sacred royal ornaments (Thiruvabharanam) are carried in a procession from the Pandalam Palace to the temple.
- Aarti at Ponnambalamedu: The Makaravilakku light is believed to emanate from camphor lit during the Aarti ritual at Ponnambalamedu, viewed three times from Sabarimala.
Festival Duration:
- The Makaravilakku festival lasts for seven days, starting on Makara Sankranti and concluding with the Guruthi offering, which propitiates the gods of the wilderness.
Significance of Makaravilakku:
- The festival symbolizes the merging of celestial and spiritual energies, highlighting devotion, purity, and self-discipline.
- Devotees chant the mantra "Swamiye Saranam Ayyappa," seeking blessings and protection from Lord Ayyappa.
- The event promotes equality, as all devotees wear simple black or blue attire and carry the sacred bundle, “Irumudi Kettu.”
Cultural and Religious Aspects:
- The festival is an important cultural and religious observance for millions of Hindus.
- Though previously believed to be a supernatural event, Makaravilakku now involves a ritual performed by the Malayaraya tribe, overseen by the Travancore Devaswom Board.
Prohibition on Women:
- The temple traditionally restricts women aged 10-50 from entering. This was challenged in 2018 when the Supreme Court ruled to lift the prohibition, although it remains a contentious issue.
Kilauea Volcano
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Kilauea volcano erupts on Hawaii's Big Island.
Location:
- Kilauea is located on the southeastern shore of Hawaii’s Big Island, within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park.
Type of Volcano:
- Active Shield Volcano – Kilauea is a shield volcano, meaning it has broad, gentle slopes due to the eruption of fluid lava, which flows easily across large areas. Its eruptions tend to be less explosive than those of other types of volcanoes, creating a relatively safe environment for research and tourism compared to more volatile volcanoes.
Key Features:
- Summit Caldera: Kilauea has a large caldera at its summit, Halema'uma'u, which is a major volcanic feature. The caldera formed from the partial collapse of the volcano after the eruption of large amounts of magma. The caldera spans around 3 miles in length and 2 miles in width, covering an area of over 4 square miles.
- Rift Zones: Kilauea has two active rift zones stretching to the east and southwest, which are areas where lava can erupt and spread across the island. These rift zones are responsible for much of the volcanic activity.
- Lava Flows: Over the last 1,000 years, Kilauea has covered 90% of its surface with lava flows, making it one of the most active volcanoes in the world. It is known for producing highly fluid lava, which allows the lava to travel long distances from the eruption site.
- Historical Activity: Kilauea has had near-continuous eruptions in modern history, particularly between 1983 and 2018, with 34 eruptions since 1952. The volcano has remained active with frequent eruptions, and its lava lake was visible at the summit until 1924.
- Mythological Significance: The volcano is considered the home of Pele, the Hawaiian goddess of fire, lightning, and volcanoes. The Halema'uma'u crater is especially sacred, as it is believed to be the goddess's dwelling place.
Why is Kilauea Significant?
- Active and Young: Kilauea is one of the youngest volcanic products of the Hawaiian hotspot, a series of volcanic islands formed by the movement of the Pacific plate over a stationary plume of hot material beneath the Earth’s crust.
- Continuous Eruptions: It has been erupting regularly, with the exception of a quiet period between 1924 and 1952. Its eruptions are a significant natural phenomenon that scientists and visitors closely monitor.
- Proximity to Mauna Loa: Kilauea is located near Mauna Loa, another active shield volcano. Together, these two volcanoes form a large volcanic region, and their slopes merge seamlessly, making this area home to two of the world's most active volcanoes.
Shield Volcanoes and Kilauea
- Shield Volcanoes: A shield volcano is characterized by its broad, gentle slopes. These slopes are formed by repeated eruptions of fluid basalt lava, which spreads easily over large areas. Unlike composite volcanoes, which have steep, conical shapes, shield volcanoes like Kilauea have a much wider, dome-like appearance.
- Low Explosivity: Eruptions from shield volcanoes are generally low in explosivity, and lava flows are typically slow-moving. However, explosive events can occur if water interacts with lava, but this is relatively rare in Kilauea's eruptions.
Kilauea's Current Activity
In December 2024, Kilauea began erupting again, continuing its pattern as one of the most active volcanoes in the world. This eruption has once again drawn attention to the ongoing volcanic activity on the Big Island of Hawaii, as the volcano regularly contributes to the reshaping of the island and its landscape.
Other Volcanoes in India:
While Kilauea is known for its active status, India also has volcanic features, although most are dormant or extinct:
- Barren Island (Andaman Islands) – India’s only active volcano.
- Narcondam (Andaman Islands) – A dormant volcano.
- Baratang (Andaman Islands) – Known for mud volcanoes.
- Deccan Traps (Maharashtra) – A vast volcanic plateau formed by ancient eruptions.
- Dhinodhar Hills (Gujarat) – Extinct volcano.
- Dhosi Hill (Haryana) – An ancient volcanic site with historical significance.
Agni-4 ballistic missile successfully test-fired in Odisha

- 09 Sep 2024
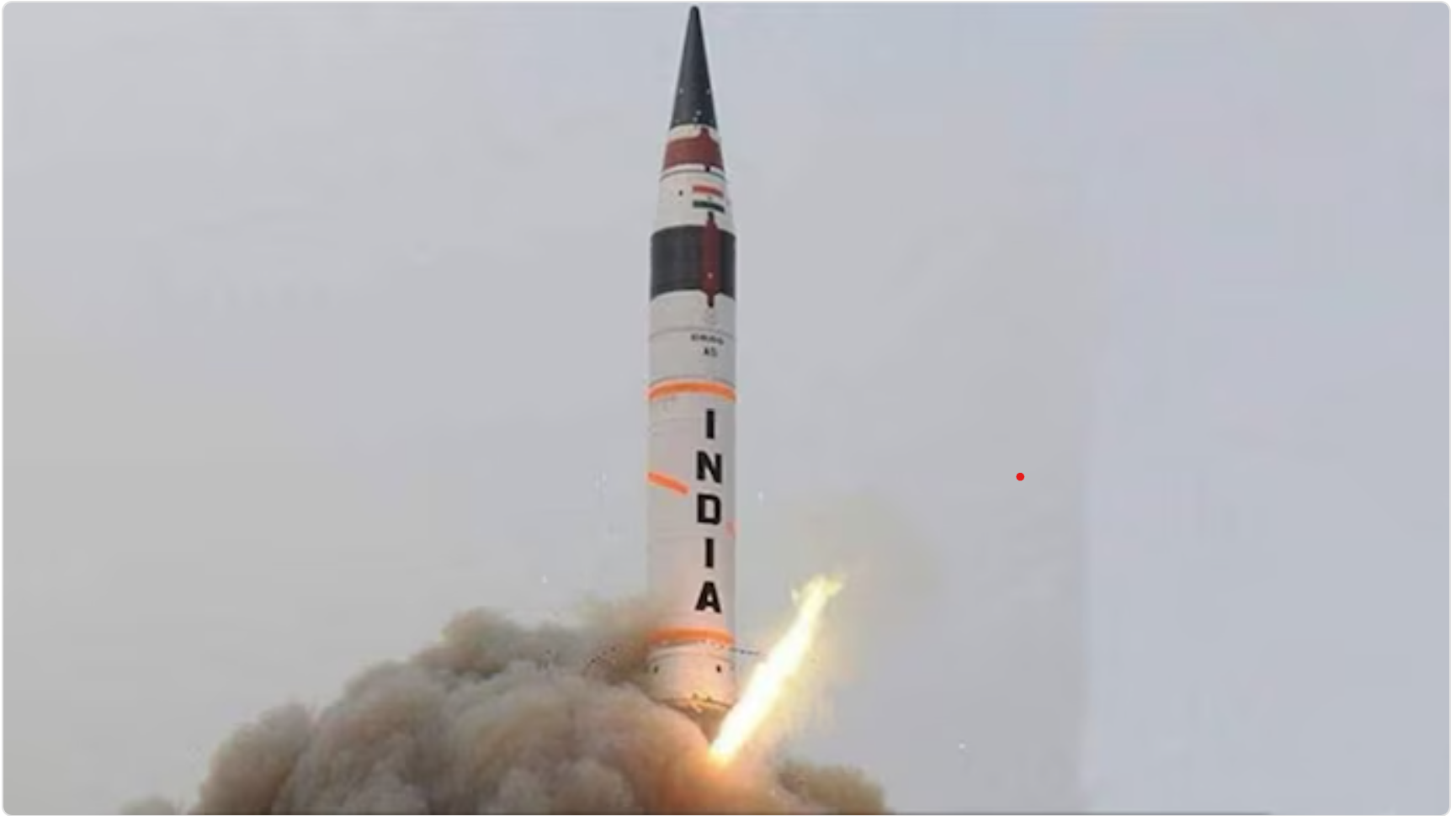
In News:
India successfully test-fired the Agni-4 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range in Chandipur, Odisha. The test, conducted by the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) under India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA), demonstrated the missile's operational and technical capabilities.
Key Details:
- Missile Specifications:
- Range: The Agni-4 missile has a maximum range of 4,000 kilometers.
- Payload: It can carry a payload of up to 1,000 kilograms.
- Length: The missile is approximately 20 meters long.
- Launch Platform: It is designed for deployment on a road-mobile launcher, enhancing its flexibility and mobility.
- Historical Context:
- Previous Test (2012): In its earlier test in 2012, Agni-4 successfully covered over 3,000 kilometers within 20 minutes. This was noted as the longest-range mission achieved by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) at that time.
- Name Change: The Agni-4 was previously known as Agni-2 Prime.
- Development and Capabilities:
- Development: The Agni missiles, including the Agni-4, are developed by the DRDO, showcasing India's advancements in missile technology and strategic capabilities.
- Comparison with Agni-5: The Agni-4 is part of a series of Agni missiles that have progressively enhanced India's missile range and strike capabilities. The Agni-5 represents an even more advanced development in this series.
The successful test of Agni-4 underscores India's commitment to strengthening its strategic defense capabilities and maintaining its deterrence posture.
Tesla’s India entry gets boost as government approves new EV policy
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government announced a new electric vehicle (EV) policy recently that is expected to provide a major boost to Tesla's plans to start operations in India.
What is the Revised EV Policy Offering Tax Incentives?
- The Government of India has sanctioned a new initiative aimed at positioning India as a premier manufacturing hub, fostering the production of cutting-edge electric vehicles (EVs) within the nation.
- Crafted to entice investments from renowned global EV manufacturers, this policy seeks to provide Indian consumers access to state-of-the-art EV technology while bolstering the Make in India campaign.
- By cultivating a competitive environment among EV players, the policy endeavors to fortify the EV ecosystem, stimulating innovation and efficiency.
- Furthermore, it is anticipated to stimulate substantial production rates, capitalize on economies of scale, and drive down production costs, consequently curbing crude oil imports, narrowing trade imbalances, and mitigating urban air pollution, thereby fostering a healthier environment for all.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Minimum Investment Requirement: Companies are mandated to invest a minimum of Rs 4,150 Crores.
- Investment Ceiling: There is no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Manufacturing Timeline: Companies must establish manufacturing facilities in India within 3 years and commence commercial production of e-vehicles.
- Within 5 years, they should achieve 50% domestic value addition.
- Domestic Value Addition (DVA): Localization levels of 25% by the 3rd year and 50% by the 5th year are mandatory during manufacturing.
- Customs Duty: A customs duty of 15%, applicable to Completely Knocked Down (CKD) units, will be enforced for 5 years.
- Import Limits: Import of at most 8,000 EVs annually is permitted under this scheme, with provisions for carrying forward unutilized import quotas.
- Bank Guarantee Requirement: Investment commitments necessitate bank guarantees to cover the forgone customs duty.
EV Adoption in India:
- In 2023, electric vehicle sales in India surged by 49.25% year-on-year, surpassing 15 lakh units, as the Federation of Automobile Dealers' Association (FADA) reported.
- This notable increase follows a total sale of approximately 10 lakh units recorded in 2022, indicating a rapid growth trajectory.
- Factors contributing to this surge include improved product availability, escalating fuel prices, state subsidies, and incentives provided under the FAME-II Initiative.
What is the FAME-II Scheme?
- The FAME India scheme, initiated in 2015, serves as an incentive program aimed at accelerating the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, with its acronym standing for "Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles in India."
- In 2019, the Central government sanctioned Phase II of the FAME Scheme with a budgetary allocation of 10,000 Crore over three years, extending until March 31, 2024.
- The primary objective of Phase II is to stimulate demand by facilitating the deployment of 7000 e-Buses, 5 lakh e-3 Wheelers, 55,000 e-4 Wheeler Passenger Cars (including Strong Hybrid), and 10 lakh e-2 Wheelers, thereby fostering the growth of the electric vehicle ecosystem.
- Under the FAME-II scheme, nearly 2 lakh vehicles have received support, signifying a significant stride towards electric vehicle adoption in the country.
Government Initiatives to Promote EV Usage:
- Battery Swapping Policy: The Battery Swapping Policy offers an alternative approach wherein discharged batteries are exchanged for charged ones, enabling efficient charging without vehicle downtime.
- NITI Aayog has recently unveiled a draft battery-swapping policy, prioritizing metropolitan cities with populations exceeding 40 lakh for the establishment of battery-swapping networks in the initial phase.
- Switching to EVs: Central and State governments extend upfront subsidies to mitigate the overall costs associated with electric vehicles, incentivizing consumers to transition towards cleaner mobility options.
- E-AMRIT Portal: The e-AMRIT portal serves as a comprehensive platform, furnishing resources and support to facilitate the seamless transition to electric vehicles, thereby bolstering the nation's electrification agenda.
