Makaravilakku festival

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Kerala police deploy 5,000 personnel at Sabarimala ahead of Makaravilakku festival.
Key Highlights:
- Makaravilakku is a prominent annual Hindu festival held at the Sabarimala Temple in Kerala, dedicated to Lord Ayyappa.
- It marks the celestial event of the Sun entering Capricorn (Makaram Rashi) on Makara Sankranti.
- The festival is a culmination of the 41-day pilgrimage to Sabarimala, celebrated with devotion, discipline, and spiritual purification.
- Sabarimala is one of the largest pilgrimage sites globally, drawing 10-15 million devotees annually.
Location:
- The Sabarimala Temple is located on the Sabarimala hill in Pathanamthitta, Kerala, within the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
- It is surrounded by 18 hills and is located along the banks of the Pamba River.
Key Rituals:
- 41-Day Pilgrimage (Vratham): Devotees observe strict practices like celibacy, fasting, and wearing black or saffron attire to purify the body and soul.
- Makaravilakku (Makara Jyothi): A celestial light appears on Makara Sankranti, believed to be a divine manifestation of Lord Ayyappa.
- Thiruvabharanam Procession: On Makaravilakku day, sacred royal ornaments (Thiruvabharanam) are carried in a procession from the Pandalam Palace to the temple.
- Aarti at Ponnambalamedu: The Makaravilakku light is believed to emanate from camphor lit during the Aarti ritual at Ponnambalamedu, viewed three times from Sabarimala.
Festival Duration:
- The Makaravilakku festival lasts for seven days, starting on Makara Sankranti and concluding with the Guruthi offering, which propitiates the gods of the wilderness.
Significance of Makaravilakku:
- The festival symbolizes the merging of celestial and spiritual energies, highlighting devotion, purity, and self-discipline.
- Devotees chant the mantra "Swamiye Saranam Ayyappa," seeking blessings and protection from Lord Ayyappa.
- The event promotes equality, as all devotees wear simple black or blue attire and carry the sacred bundle, “Irumudi Kettu.”
Cultural and Religious Aspects:
- The festival is an important cultural and religious observance for millions of Hindus.
- Though previously believed to be a supernatural event, Makaravilakku now involves a ritual performed by the Malayaraya tribe, overseen by the Travancore Devaswom Board.
Prohibition on Women:
- The temple traditionally restricts women aged 10-50 from entering. This was challenged in 2018 when the Supreme Court ruled to lift the prohibition, although it remains a contentious issue.
Kilauea Volcano
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Kilauea volcano erupts on Hawaii's Big Island.
Location:
- Kilauea is located on the southeastern shore of Hawaii’s Big Island, within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park.
Type of Volcano:
- Active Shield Volcano – Kilauea is a shield volcano, meaning it has broad, gentle slopes due to the eruption of fluid lava, which flows easily across large areas. Its eruptions tend to be less explosive than those of other types of volcanoes, creating a relatively safe environment for research and tourism compared to more volatile volcanoes.
Key Features:
- Summit Caldera: Kilauea has a large caldera at its summit, Halema'uma'u, which is a major volcanic feature. The caldera formed from the partial collapse of the volcano after the eruption of large amounts of magma. The caldera spans around 3 miles in length and 2 miles in width, covering an area of over 4 square miles.
- Rift Zones: Kilauea has two active rift zones stretching to the east and southwest, which are areas where lava can erupt and spread across the island. These rift zones are responsible for much of the volcanic activity.
- Lava Flows: Over the last 1,000 years, Kilauea has covered 90% of its surface with lava flows, making it one of the most active volcanoes in the world. It is known for producing highly fluid lava, which allows the lava to travel long distances from the eruption site.
- Historical Activity: Kilauea has had near-continuous eruptions in modern history, particularly between 1983 and 2018, with 34 eruptions since 1952. The volcano has remained active with frequent eruptions, and its lava lake was visible at the summit until 1924.
- Mythological Significance: The volcano is considered the home of Pele, the Hawaiian goddess of fire, lightning, and volcanoes. The Halema'uma'u crater is especially sacred, as it is believed to be the goddess's dwelling place.
Why is Kilauea Significant?
- Active and Young: Kilauea is one of the youngest volcanic products of the Hawaiian hotspot, a series of volcanic islands formed by the movement of the Pacific plate over a stationary plume of hot material beneath the Earth’s crust.
- Continuous Eruptions: It has been erupting regularly, with the exception of a quiet period between 1924 and 1952. Its eruptions are a significant natural phenomenon that scientists and visitors closely monitor.
- Proximity to Mauna Loa: Kilauea is located near Mauna Loa, another active shield volcano. Together, these two volcanoes form a large volcanic region, and their slopes merge seamlessly, making this area home to two of the world's most active volcanoes.
Shield Volcanoes and Kilauea
- Shield Volcanoes: A shield volcano is characterized by its broad, gentle slopes. These slopes are formed by repeated eruptions of fluid basalt lava, which spreads easily over large areas. Unlike composite volcanoes, which have steep, conical shapes, shield volcanoes like Kilauea have a much wider, dome-like appearance.
- Low Explosivity: Eruptions from shield volcanoes are generally low in explosivity, and lava flows are typically slow-moving. However, explosive events can occur if water interacts with lava, but this is relatively rare in Kilauea's eruptions.
Kilauea's Current Activity
In December 2024, Kilauea began erupting again, continuing its pattern as one of the most active volcanoes in the world. This eruption has once again drawn attention to the ongoing volcanic activity on the Big Island of Hawaii, as the volcano regularly contributes to the reshaping of the island and its landscape.
Other Volcanoes in India:
While Kilauea is known for its active status, India also has volcanic features, although most are dormant or extinct:
- Barren Island (Andaman Islands) – India’s only active volcano.
- Narcondam (Andaman Islands) – A dormant volcano.
- Baratang (Andaman Islands) – Known for mud volcanoes.
- Deccan Traps (Maharashtra) – A vast volcanic plateau formed by ancient eruptions.
- Dhinodhar Hills (Gujarat) – Extinct volcano.
- Dhosi Hill (Haryana) – An ancient volcanic site with historical significance.
Hyperloop Technology
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s first hyperloop test track (410 meters) completed by Indian Railways, IIT-Madras’Avishkar Hyperloop team and TuTr (incubated startup) at IIT-M discovery campus, Thaiyur in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
India’s First Hyperloop Test Track:
- Location: IIT Madras’ Discovery Campus, Chennai.
- Collaboration: Indian Railways, IIT-Madras' Avishkar Hyperloop team, and TuTr Hyperloop (startup).
- Track Length: 410 meters.
- Test Speed: Initial successful test at 100 km/h; plans for 600 km/h in the next phase.
- Passenger Capacity: 40–100 passengers per pod, depending on design.
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Concept: A high-speed transport system using pods in low-pressure vacuum tubes, designed to achieve speeds similar to aircraft (up to 1,100 km/h).
- Working:
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Pods float on magnets, eliminating friction.
- Vacuum Tubes: Reduces air resistance for high-speed travel.
- Propulsion: Linear induction motors propel pods.
- Energy: Solar-powered, designed for zero emissions.
India’s Hyperloop Projects:
- Current Status:
- Successful testing of a 410-meter test track at IIT Madras.
- Ongoing feasibility studies for routes like Chennai Airport–Parandur, Mumbai–Pune, and Amritsar–Chandigarh.
- Phase 1 & 2: First phase involves a 11.5-kilometer track; future expansion to 100 km.
- Mumbai–Pune Corridor: Planned as India’s first full-scale Hyperloop system, aiming to reduce travel time from 3–4 hours to 25 minutes.
Benefits of Hyperloop:
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to 1,100 km/h (operational speed around 360 km/h).
- Efficiency: Reduces travel time, energy-efficient with reduced air resistance and friction.
- Sustainability: Powered by renewable energy (e.g., solar power), offering zero emissions.
- Point-to-Point Travel: No intermediate stops, making it more time-efficient.
Challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Expensive to build the vacuum tubes, stations, and supporting systems.
- Land Acquisition: Difficulty in acquiring land, especially in densely populated areas.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of a specific regulatory framework for such advanced transport systems.
- Technological Barriers: Complex engineering challenges, including development of maglev systems and vacuum seals.
Global Context:
- Origin: Concept proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
- Worldwide Adoption: Hyperloop is being explored globally, with projects in the U.S., UAE, and Europe.
GG Tau A System

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
GG Tau A System: Located about 489 light-years from Earth, this system is a triple-star setup that is between 1 to 5 million years old. This makes it an ideal system for studying the early stages of planetary formation.
Findings from the Discovery:
- Protoplanetary Disk: The system features a protoplanetary disk made of gas and dust, where new planets are forming. Researchers from NISER (National Institute of Science Education and Research), Odisha detected emissions from key molecules in the disk.
- Chemical Molecules: The molecules are frozen on tiny dust particles in the coldest regions of the disk (temperatures between 12 K and 16 K). These frozen molecules could serve as the building blocks for new planets.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Triple-Star Configuration: GG Tau A’s triple-star system is rare, and it has complex gravitational interactions among the three stars. This complicates how the gas and dust disk behaves and provides unique insights into planetary formation in multi-star systems.
- Study of Planet Formation: Traditionally, planets form around single stars or in binary systems. However, multi-star systems like GG Tau A present challenges for planet formation. Studying this system helps scientists understand how planets can form in more complex environments.
- Cold Conditions for Planet Formation: The study found that icy conditions in the disk are essential for the accumulation of materials that form planets. These low temperatures (below the freezing point of carbon monoxide) allow dust and gas particles to clump together, creating the foundation for exoplanets.
Broader Implications:
- Exoplanet Diversity: This research enhances our understanding of how planets form in different types of star systems, contributing to the study of exoplanets and their potential diversity across the universe.
- Astrophysics and Planetary Science: This discovery plays a crucial role in improving our knowledge of the early stages of planet formation, especially in complicated star systems like triple-star setups, which are rare but can provide valuable insights into how planetary systems evolve under unique conditions.
Research Tools:
- The team used advanced radio telescopes located in the Atacama Desert (Chile) to observe the emissions from the disk, highlighting the role of cutting-edge technology in space exploration and astronomical research.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
Proba-3 Mission

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
Europe's Proba-3 mission to arrive in India for launch aboard PSLV-XL by ISRO
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The Proba-3 mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), aims to observe the Sun’s corona by creating an artificial solar eclipse. This will allow continuous observation of the Sun’s faint outer atmosphere, which is typically only visible during a natural solar eclipse.
- Key Features:
- Artificial Solar Eclipse: The two spacecraft will fly in formation to maintain a shadow between them, enabling the uninterrupted observation of the solar corona.
- Formation Flying: The satellites must maintain a precise formation with an accuracy of one millimetre, equivalent to the thickness of a fingernail.
Mission Details
- Launch Date: Scheduled for December 4, 2024.
- Launch Location: Satish Dhawan Space Centre near Chennai, India.
- Launch Vehicle: The PSLV-XL rocket developed by ISRO will be used for the launch.
- Spacecraft Mass: The combined mass of the two spacecraft is 550 kg.
- Orbit: The spacecraft will be placed in a highly elliptical orbit with a maximum altitude of 60,000 km to facilitate the precise formation flying.
- This high altitude minimizes Earth’s gravitational pull and reduces the amount of propellant required to maintain their positions during the mission.
Mission Significance
- Solar Observation: The primary objective is to observe the Sun’s corona, which has been challenging to study due to its faintness. The artificial eclipse will allow continuous data collection on solar activity.
- Formation Flying: This technology will allow the two satellites to maintain autonomous flight with millimetre-level precision, which is a significant advancement in satellite formation control.
- Six-Hour Observation Windows: Each formation flying session will last for up to six hours, during which the satellites will observe the Sun's corona.
Technological and Scientific Contributions
- ASPIICS Instrument: The ASPIICS (AStronomical PIcture Camera for the Intense Corona of the Sun) will be the mission's primary instrument, developed by the Royal Observatory of Belgium. It will provide crucial data on solar activity and space weather.
- International Collaboration: The mission is a collaborative effort involving 14 ESA member states and various organizations across Europe.
- Mission Control: The mission will be managed from the ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Belgium, with significant pre-launch training and preparations already underway.
ISRO's Role and Historical Context
- Launch by ISRO: The Proba-3 mission will be ISRO’s first launch for ESA since 2001, marking an important milestone in India-Europe space cooperation.
- PSLV-XL Rocket: ISRO’s PSLV-XL rocket is known for its reliability and capability in deploying satellites into precise orbits. It is well-suited to carry the 550 kg Proba-3 duo into a highly elliptical orbit for the mission.
IMF retains India’s growth projection at 7% for FY25
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
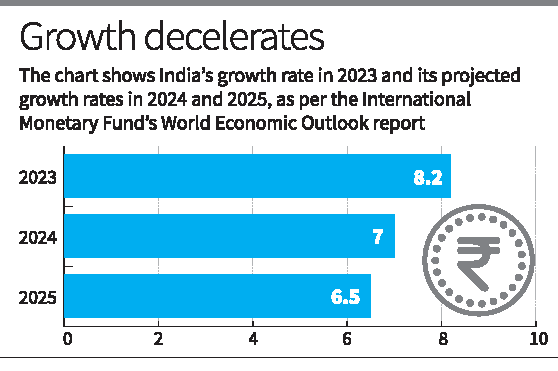
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised India's GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 7%, up by 20 basis points from its previous estimate of 6.8%.
- India’s Growth Projections:
- Current Fiscal Year (FY2024-25): India’s GDP growth is projected at 7%, unchanged from June 2024 estimates.
- Next Fiscal Year (FY2025-26): Growth expected at 6.5%.
- Growth Decline from FY2023 (8.2%): The slowdown is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand post-pandemic and the economy returning to its potential.
- Global Economic Growth:
- World Output: Projected global growth at 3.2% in both 2024 and 2025.
- Advanced Economies: U.S. GDP growth revised upward to 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
- Emerging Markets & Developing Economies: Growth revised upwards, largely due to stronger economic activity in Asia, with China and India being key contributors.
- Global Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Inflation Decline: Global inflation has decreased from its peak of 9.4% in Q3 2022 to 3.5% projected by end-2025.
- Inflation Outlook: Despite reductions in inflation, price pressures persist in some regions.
- Monetary Policy Tightening: IMF acknowledges challenges due to tight monetary conditions in several economies and their potential impacts on labor markets.
- Global Risks and Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating conflicts in West Asia (e.g., Lebanon) have increased geopolitical risks, potentially affecting commodity markets.
- Protectionism: Growing protectionist policies worldwide are a risk to global trade and economic stability.
- Sovereign Debt Stress: Debt burdens in several countries could become a source of instability.
- Weak Chinese Economy: Slower-than-expected recovery in China remains a significant concern for global economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Risks: Prolonged tight monetary policies in some countries could impact labor markets and economic recovery.
- IMF’s Policy Recommendations for Medium-Term Growth:
- Monetary Policy Neutrality: Countries should adopt a neutral monetary policy stance to balance growth and inflation control.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustment: Build fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy to ensure stability.
- Structural Reforms: Implement structural reforms to boost productivity and cope with challenges like aging populations, the climate transition, and the need for youth employment.
- India’s Economic Outlook - Key Drivers:
- Rural Consumption Growth: The upward revision of India's FY2024-25 GDP forecast to 7% is driven by improved consumption, especially in rural areas.
- Upward Revisions for 2023: The increased growth forecast also reflects positive carryover effects from India's 8.2% growth in 2023.
- Emerging Asia's Growth: The growth outlook for emerging Asia is supported by India and China, though long-term growth prospects for China are weaker (projected to slow to 3.3% by 2029).
- Global Economic Outlook:
- World Growth Projections: Global growth is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025.
- Diverging Growth Rates: Growth across economies is converging as output gaps close, particularly in advanced economies (e.g., U.S. labor market cooling, euro area recovery).
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 12 Sep 2024
In News:
- The Union Cabinet has approved a major expansion of the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) to cover all senior citizens aged 70 years and above.
- This change allows anyone in this age group to be eligible for health insurance, regardless of their income level.
- This expansion aims to address the healthcare needs of the elderly, who often face higher medical expenses as they age.
- By lifting income restrictions, the government is ensuring that more senior citizens can benefit from much-needed health coverage, which will help ease the financial burden of healthcare.
How does the scheme work?
- The AB PM-JAY now covers an additional 6 crore individuals from 4.5 crore families, focusing on seniors aged 70 and above. Each senior citizen will be given a health card, allowing them easy access to healthcare services under the scheme.
- The scheme provides Rs 5 lakh coverage annually per family. If there are multiple senior citizens in the same family, this coverage is shared among them. The scheme is particularly beneficial for nuclear families, where the financial burden on elderly members can be more difficult to manage.
Key details of the scheme for senior citizens above 70
- Eligibility - All senior citizens aged 70 and above are eligible for Rs 5 lakh health coverage, regardless of income or social status.
- Top-up coverage - For families already enrolled in Ayushman Bharat, senior members will receive an extra Rs 5 lakh top-up, which is solely for their use.
- Private insurance - Senior citizens with private health insurance can still take advantage of the scheme without any conflict with their existing coverage.
- Public health schemes - Seniors who are part of other public health schemes like the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Ex-Servicemen Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS), or Ayushman Central Armed Police Force (CAPF) will need to choose between their current insurance and the new Ayushman Bharat health coverage.
- New health cards - All eligible senior citizens will receive a separate health card, which will help them access the scheme’s benefits more efficiently.
Who pays for the coverage?
- The cost of this expanded coverage will be Rs 3,437 crore initially. State governments will bear 40% of the expenses, while the Centre will cover the remaining 60%. For states in hilly and northeastern regions, the Centre will fund 90% of the costs.
- As more senior citizens enrol, the costs may increase. Experts point out that covering elderly individuals often costs more than providing insurance for younger, economically weaker sections of society. However, the government is prepared to scale up the coverage based on demand.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
- AB PM-JAY launched in 2018, is a flagship program designed to offer affordable and accessible healthcare to millions of vulnerable families across India.
- The primary aim is to provide health insurance coverage up to ?5 lakhs per family annually for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- The scheme currently supports 55 crore individuals from 12.34 crore families throughout the country.
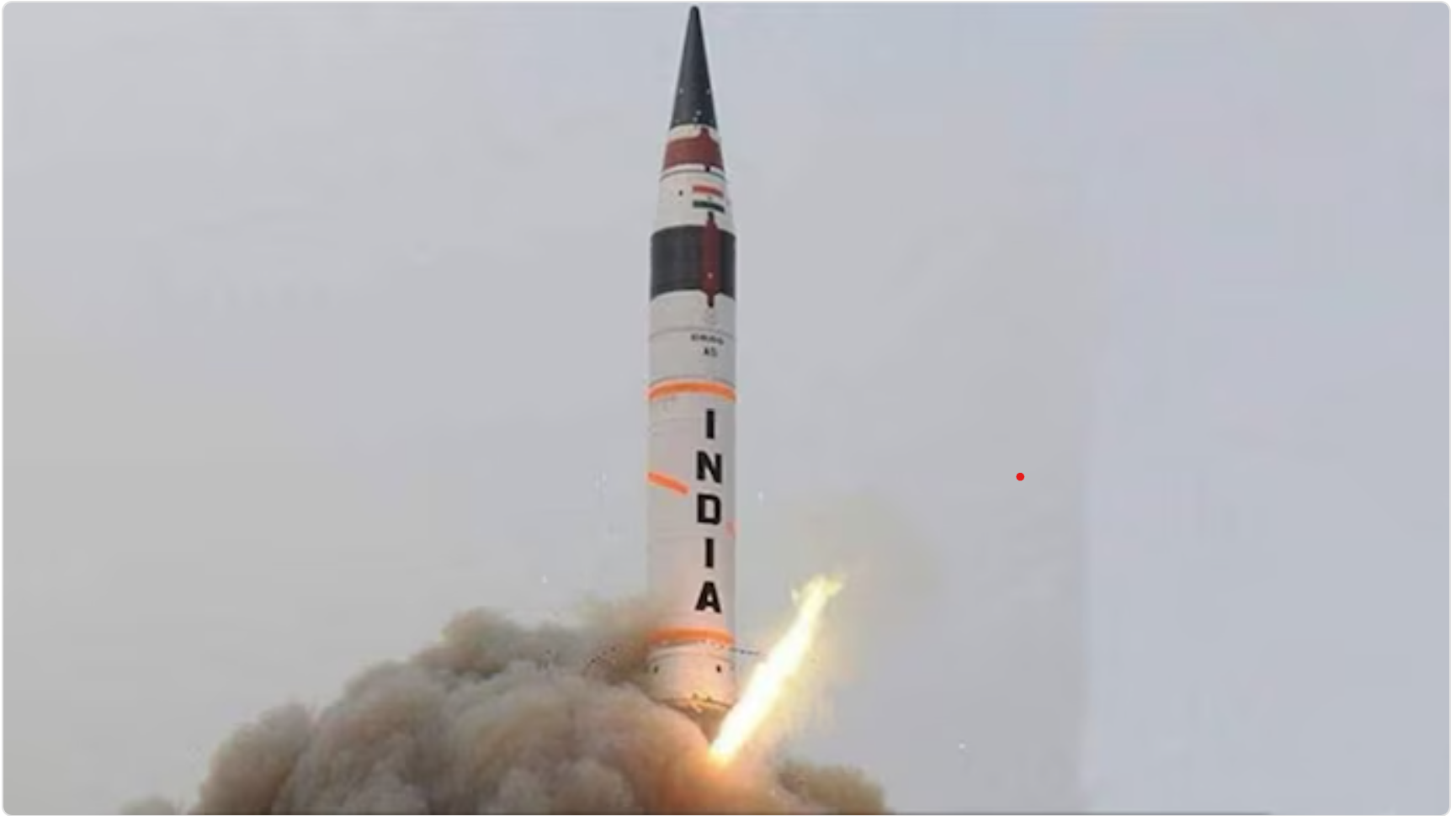
Agni-4 ballistic missile successfully test-fired in Odisha

- 09 Sep 2024
In News:
India successfully test-fired the Agni-4 ballistic missile from the Integrated Test Range in Chandipur, Odisha. The test, conducted by the Strategic Forces Command (SFC) under India's Nuclear Command Authority (NCA), demonstrated the missile's operational and technical capabilities.
Key Details:
- Missile Specifications:
- Range: The Agni-4 missile has a maximum range of 4,000 kilometers.
- Payload: It can carry a payload of up to 1,000 kilograms.
- Length: The missile is approximately 20 meters long.
- Launch Platform: It is designed for deployment on a road-mobile launcher, enhancing its flexibility and mobility.
- Historical Context:
- Previous Test (2012): In its earlier test in 2012, Agni-4 successfully covered over 3,000 kilometers within 20 minutes. This was noted as the longest-range mission achieved by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) at that time.
- Name Change: The Agni-4 was previously known as Agni-2 Prime.
- Development and Capabilities:
- Development: The Agni missiles, including the Agni-4, are developed by the DRDO, showcasing India's advancements in missile technology and strategic capabilities.
- Comparison with Agni-5: The Agni-4 is part of a series of Agni missiles that have progressively enhanced India's missile range and strike capabilities. The Agni-5 represents an even more advanced development in this series.
The successful test of Agni-4 underscores India's commitment to strengthening its strategic defense capabilities and maintaining its deterrence posture.
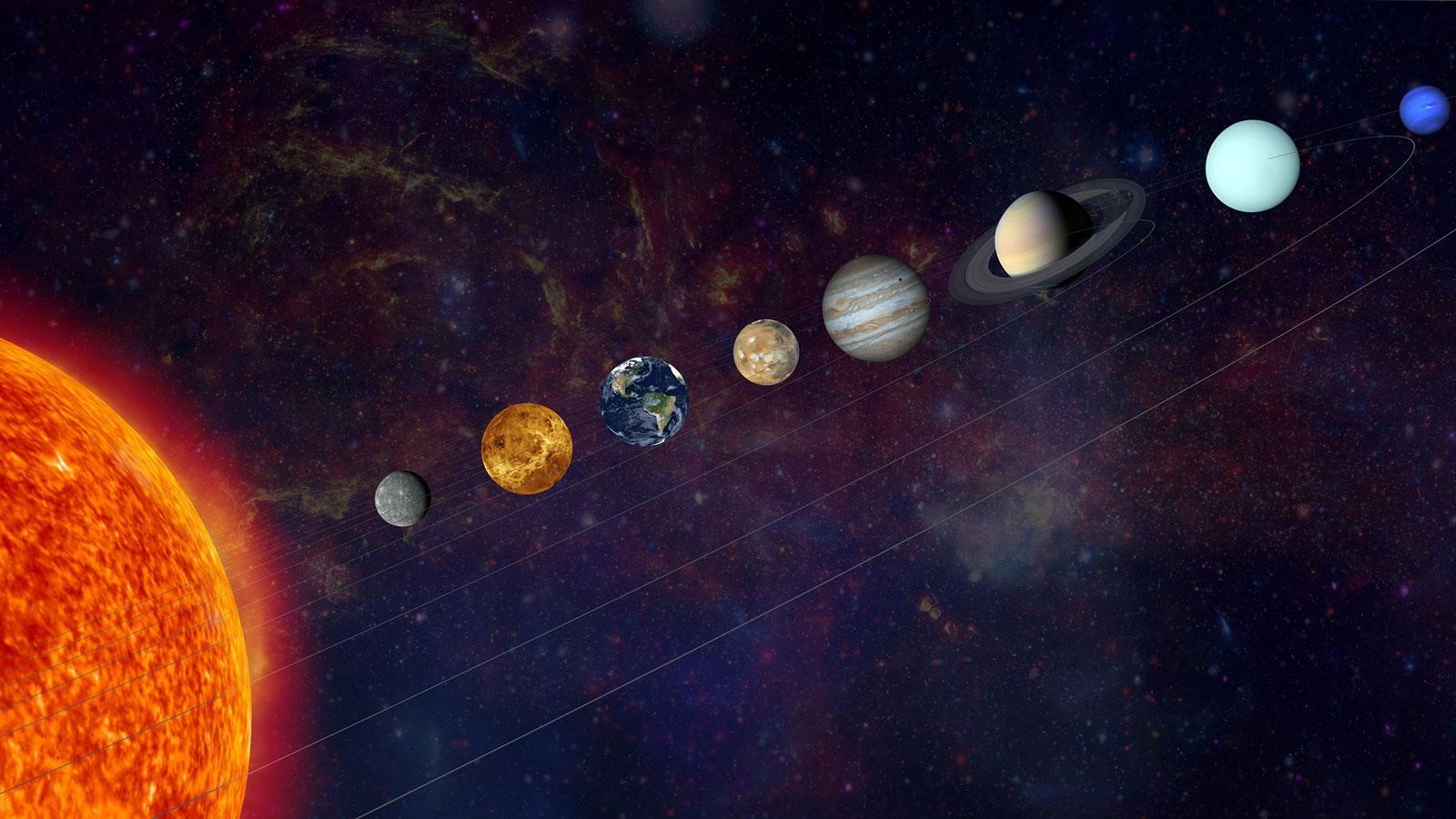
Planetary Alignment

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Next month, on June 3, there will be a planetary alignment that may actually allow you to witness six planets align in the sky.
What is a Planetary Alignment?
- Planetary alignment is a term used to describe the positioning of planets in the solar system such that they appear to be in a straight line or close to one when viewed from a specific vantage point, for us that's Earth.
- It is an astronomical event that happens when, by coincidence, the orbits of several of the planets of the Solar System bring them to roughly the same side of the Sun at the same time.
- This phenomenon is more an illusion of perspective rather than the planets being in a perfect line in space.
- It’s important to emphasise that the planets aren’t forming a straight line in space – that’s a much rarer astronomical event called a syzygy.
- However, because all the planets, including the Earth, orbit around the Sun in roughly the same orientation (moving in which we call the “Plane of the Ecliptic”), when they’re on the same side of the Sun as each other, they appear to form a line in the sky when we view them from Earth.”
- Planetary alignments are rather common within themselves, especially when two, three, or even four planets align in the sky.
- Five or more planets aligning, however, is less common.
- April 8, 2024, was the last time the planets were all in alignment.
Which planets will align?
- Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune will form a near-straight line, offering an extraordinary opportunity to witness this cosmic phenomenon.
Which planets will be visible?
- While six planets align, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye, due to their vast distance from Earth.
- Meanwhile, the Moon will also play a spoilsport as it distorts the visibility.
- Mercury and Jupiter will be tricky to see in the sky due to their proximity to the Sun in their orbit.
- However, Mars and Saturn will be visible to the naked eye, though very dim.
- Meanwhile, keen observers will need telescopes or high-powered binoculars to spot the distant planets Uranus and Neptune.
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
Tesla’s India entry gets boost as government approves new EV policy
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government announced a new electric vehicle (EV) policy recently that is expected to provide a major boost to Tesla's plans to start operations in India.
What is the Revised EV Policy Offering Tax Incentives?
- The Government of India has sanctioned a new initiative aimed at positioning India as a premier manufacturing hub, fostering the production of cutting-edge electric vehicles (EVs) within the nation.
- Crafted to entice investments from renowned global EV manufacturers, this policy seeks to provide Indian consumers access to state-of-the-art EV technology while bolstering the Make in India campaign.
- By cultivating a competitive environment among EV players, the policy endeavors to fortify the EV ecosystem, stimulating innovation and efficiency.
- Furthermore, it is anticipated to stimulate substantial production rates, capitalize on economies of scale, and drive down production costs, consequently curbing crude oil imports, narrowing trade imbalances, and mitigating urban air pollution, thereby fostering a healthier environment for all.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Minimum Investment Requirement: Companies are mandated to invest a minimum of Rs 4,150 Crores.
- Investment Ceiling: There is no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Manufacturing Timeline: Companies must establish manufacturing facilities in India within 3 years and commence commercial production of e-vehicles.
- Within 5 years, they should achieve 50% domestic value addition.
- Domestic Value Addition (DVA): Localization levels of 25% by the 3rd year and 50% by the 5th year are mandatory during manufacturing.
- Customs Duty: A customs duty of 15%, applicable to Completely Knocked Down (CKD) units, will be enforced for 5 years.
- Import Limits: Import of at most 8,000 EVs annually is permitted under this scheme, with provisions for carrying forward unutilized import quotas.
- Bank Guarantee Requirement: Investment commitments necessitate bank guarantees to cover the forgone customs duty.
EV Adoption in India:
- In 2023, electric vehicle sales in India surged by 49.25% year-on-year, surpassing 15 lakh units, as the Federation of Automobile Dealers' Association (FADA) reported.
- This notable increase follows a total sale of approximately 10 lakh units recorded in 2022, indicating a rapid growth trajectory.
- Factors contributing to this surge include improved product availability, escalating fuel prices, state subsidies, and incentives provided under the FAME-II Initiative.
What is the FAME-II Scheme?
- The FAME India scheme, initiated in 2015, serves as an incentive program aimed at accelerating the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, with its acronym standing for "Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles in India."
- In 2019, the Central government sanctioned Phase II of the FAME Scheme with a budgetary allocation of 10,000 Crore over three years, extending until March 31, 2024.
- The primary objective of Phase II is to stimulate demand by facilitating the deployment of 7000 e-Buses, 5 lakh e-3 Wheelers, 55,000 e-4 Wheeler Passenger Cars (including Strong Hybrid), and 10 lakh e-2 Wheelers, thereby fostering the growth of the electric vehicle ecosystem.
- Under the FAME-II scheme, nearly 2 lakh vehicles have received support, signifying a significant stride towards electric vehicle adoption in the country.
Government Initiatives to Promote EV Usage:
- Battery Swapping Policy: The Battery Swapping Policy offers an alternative approach wherein discharged batteries are exchanged for charged ones, enabling efficient charging without vehicle downtime.
- NITI Aayog has recently unveiled a draft battery-swapping policy, prioritizing metropolitan cities with populations exceeding 40 lakh for the establishment of battery-swapping networks in the initial phase.
- Switching to EVs: Central and State governments extend upfront subsidies to mitigate the overall costs associated with electric vehicles, incentivizing consumers to transition towards cleaner mobility options.
- E-AMRIT Portal: The e-AMRIT portal serves as a comprehensive platform, furnishing resources and support to facilitate the seamless transition to electric vehicles, thereby bolstering the nation's electrification agenda.
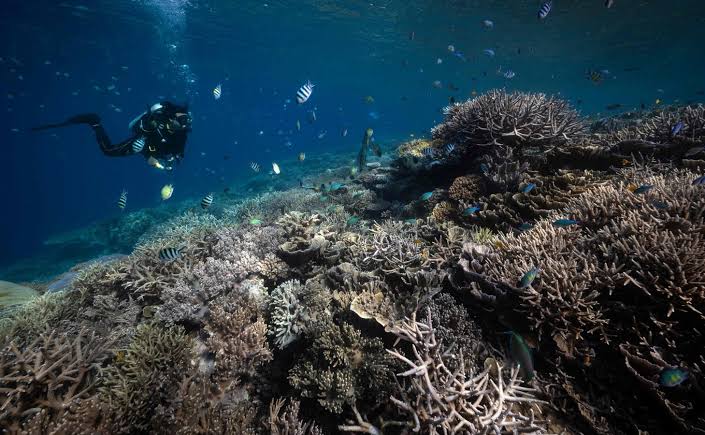
Exclusive-World on brink of fourth mass coral reef bleaching event- NOAA

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world stands on the brink of witnessing its fourth mass coral bleaching event, a phenomenon that threatens to hit vast expanses of tropical reefs, including significant portions of Australia's iconic Great Barrier Reef.
Key Findings from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
- Impending Fourth Mass Coral Bleaching Event: The world is on the brink of a fourth mass coral bleaching event, following those in 1998, 2010, and 2014.
- To classify as global, widespread bleaching must occur across three ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian.
- Impact of Previous Events: The last global mass coral bleaching event occurred from 2014 to 2017, resulting in the loss of nearly a third of the Great Barrier Reef's corals.
- Preliminary data indicates that approximately 15% of the world's reefs experienced significant coral die-offs during this event.
- Current Situation: This year is witnessing even more severe bleaching events, with the Caribbean experiencing its worst coral bleaching on record following the Northern Hemisphere summer last year.
- Link to Climate Phenomena: Coral bleaching is often associated with the naturally occurring El Niño climate phenomenon, which leads to warmer ocean waters.
- Climate Change Impact: The world recently experienced its first 12-month period with an average temperature exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- A temperature rise of 1.5°C is considered the tipping point for mass coral die-offs, with scientists estimating that 90% of the world's corals could be lost as a result.
About the Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals: Corals are animals known as polyps, which engage in a symbiotic relationship with tiny algae called zooxanthellae.
- These algae provide corals with food and oxygen, while corals offer them a safe habitat.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are limestone structures formed by thousands of tiny coral animals and are predominantly found in tropical climates.
Coral Bleaching and Its Concerns:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals are exposed to stressful conditions like high temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry, leading them to expel the zooxanthellae.
- Without these algae, corals lose their color and turn white, hence the term 'bleaching,' and cannot survive for long in this state.
- Recovery Potential: Despite its severity, coral bleaching doesn't necessarily mean the end of the reef; timely removal of stressors can facilitate the return of zooxanthellae and coral recovery.
- Ecological Importance: Coral reefs serve as habitats and food sources for numerous fish and marine species.
- They also offer coastal protection from erosion and storms and play a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Beyond their ecological functions, coral reefs represent stunning biodiversity and natural beauty, making their loss a tragic prospect for future generations.
- Impacts: When coral reefs suffer, so do the ecosystems and communities reliant on them, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of coral degradation.
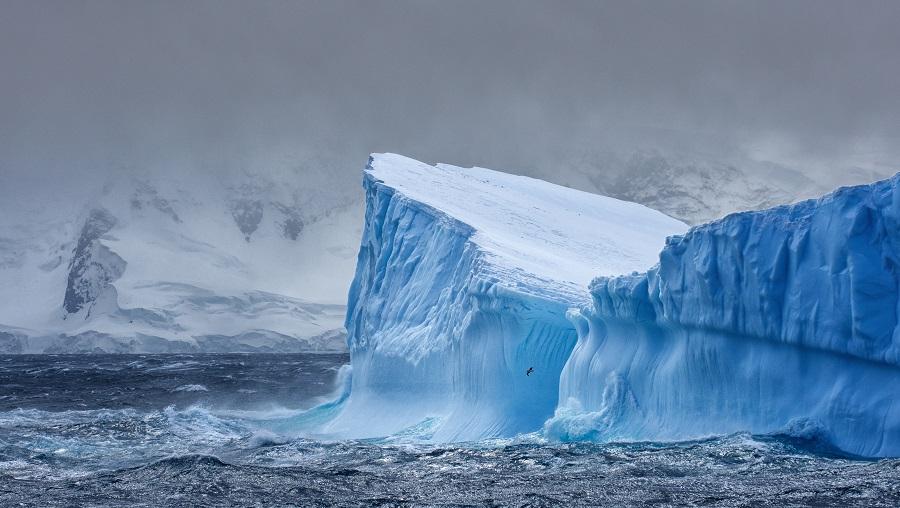
Doomsday Glacier has lost 50 billion tons of ice, melting began 80 years ago

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Antarctica's Doomsday Glacier, the world's widest glacier, has lost over 50 billion tons of ice and the melting rate is on the rise as the continent gets warmer.
What is Doomsday Glacier?
- The Thwaites Glacier (also known as Doomsday Glacier), a massive and world’s widest glacier is located in West Antarctica.
- The Doomsday nickname reflects the potential for catastrophic flooding if the glacier were to collapse completely.
- Scientists are particularly concerned about Thwaites Glacier because of its size and location.
- If it were to collapse or significantly retreat, it could lead to a more rapid flow of ice from the interior of West Antarctica into the ocean, contributing to rising sea levels.
- The collapse could lead to a 65 cm rise in global sea level.
- The ice loss in the region has been observed to be accelerating since the 1970s, however, so far it remained unclear as to when this retreat began.
- The significant glacial retreat began in the 1940s and the findings coincide with previous work that studied retreat on Pine Island Glacier and found glacial retreat began in the ‘40s as well.
- This change is not random nor specific to one glacier but It is part of a larger context of a changing climate.
Why Did the Melting Begin?
- The meeting was kicked off by an extreme El Nino climate pattern that warmed the west Antarctic, and since then the glacier has not been able to recover from the damage.
- It is significant that El Niño only lasted a couple of years, but the two glaciers, Thwaites and Pine Island remain in significant retreat.
- Once the system is kicked out of balance, the retreat is ongoing.
- The Doomsday Glacier's melting remains one of the most crucial events triggered and accelerated by climate change and could lead to the submergence of several coastal regions of the world.
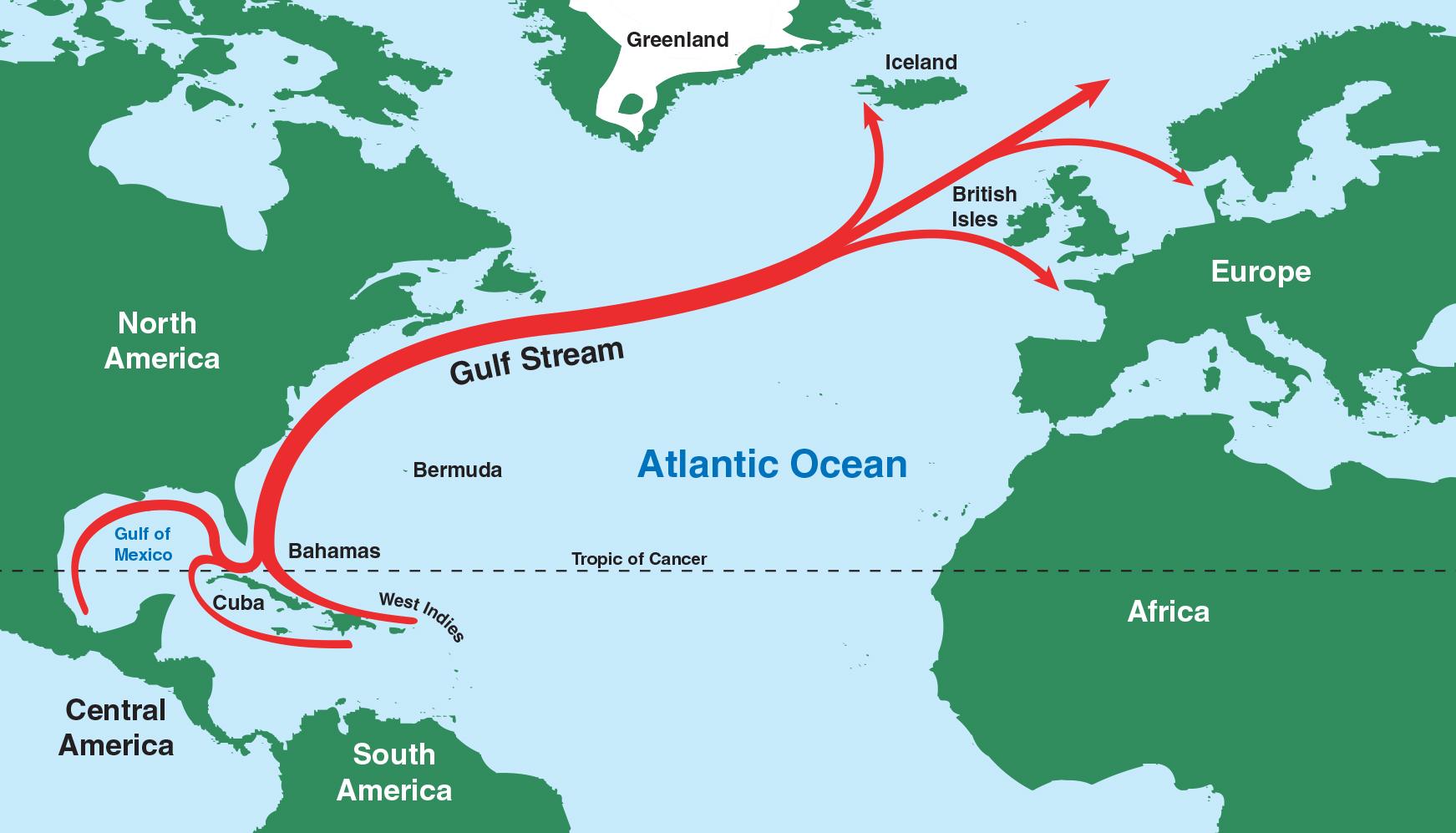
Melting Glaciers Threaten Gulf Stream Collapse by 2025 (India Today)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the world grapples with the escalating impacts of climate change, a recent study has sounded the alarm on the potential collapse of the Gulf Stream by 2025.
What is the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is a strong ocean current that brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico into the Atlantic Ocean.
- It extends all the way up the eastern coast of the United States and Canada.
What Causes the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is caused by a large system of circular currents and powerful winds, called an oceanic gyre.
- There are five oceanic gyres on Earth.
- The Gulf Stream is part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre.
- The ocean is constantly in motion, moving water from place to place via currents.
- The Gulf Stream brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico all the way up to the Norwegian Sea.
- As the warm water comes in, colder, denser water sinks and begins moving south—eventually flowing along the bottom of the ocean all the way to Antarctica.
How Does the Gulf Stream Impact Weather and Climate?
- This strong current of warm water influences the climate of the east coast of Florida, keeping temperatures there warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer than the other southeastern states.
- Since the Gulf Stream also extends toward Europe, it warms Western European countries as well.
- In fact, England is about the same distance from the equator as the cold regions of Canada, yet England enjoys a much warmer climate.
- If it weren’t for the warm water of the Gulf Stream, England would have a much colder climate.
How Long Have We Known About the Gulf Stream?
- We’ve known about the Gulf Stream for more than 500 years.
- In 1513, Spanish explorer Ponce de Leon noted that there was a strong current in this location.
- A few years later, Ponce de Leon’s ship pilot realized that the Gulf Stream could help speed up the sailing trip from Mexico to Spain.
- In the late 18th century, Benjamin Franklin became the first to chart out the path of the Gulf Stream on a map.
Stone Age Wall Discovered Beneath the Baltic Sea (India Today)
- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A megastructure found in the Baltic Sea may represent one of the oldest known hunting structures used in the Stone Age — and could change what’s known about how hunter-gatherers lived around 11,000 years ago.
About the Blinkerwall:
- The Blinkerwall is the oldest known megastructure crafted by humans in Europe.
- It is around a kilometre-long structure that lies hidden in the Bay of Mecklenburg, submerged under 21 metres of water.
- It consists of approximately 1,400 smaller stones intricately positioned to connect almost 300 larger boulders, some of which were deemed too massive for human groups to have manoeuvred.
- The total weight of the wall's stones exceeds 142 tonnes, making it improbable that natural processes, such as tsunamis or glacial movements, formed it.
- It likely dates back over 10,000 years, sinking beneath rising sea levels around 8,500 years ago.
- This positions it among the oldest known examples of hunting architecture globally and potentially designates it as the oldest man-made megastructure in Europe.
About the Baltic Sea:
- The Baltic Sea is a semi-enclosed inland sea situated in Northern Europe.
- As an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean, it stretches northward from the latitude of southern Denmark nearly to the Arctic Circle, acting as a divider between the Scandinavian Peninsula and the rest of continental Europe.
- With a coastline spanning approximately 8,000 km, the Baltic Sea is bordered by several countries, including Sweden, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Finland, Estonia, Germany, Denmark, and Russia.
- Covering an area of around 377,000 sq.km, the sea measures approximately 1,600 km in length and 193 km in width.
- It is linked to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal and to the North Sea's German Bight through the Kiel Canal, while it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Danish Straits.
- The Baltic Sea encompasses three significant gulfs: the Gulf of Bothnia to the north, the Gulf of Finland to the east, and the Gulf of Riga slightly to the south.
- Renowned as the world's largest brackish inland water body, the Baltic Sea exhibits lower water salinity levels compared to the World Oceans due to freshwater influx from the surrounding land and its shallow depth.
- More than 250 rivers and streams discharge into the Baltic Sea, with the Neva River being the largest among them.
- The sea boasts over 20 islands and archipelagos, with Gotland, located off the coast of Sweden, ranking as the largest island in the Baltic Sea.
Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative (India Today)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) recently introduced a scheme named 'Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad' (SSPCA).
About the Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative:
- The SSPCA Initiative, spearheaded by the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), aims to enhance the global competitiveness of Indian students in technical education.
- Crafted to provide financial backing to students aspiring to excel in international scientific events, the initiative offers a comprehensive support system.
Financial Assistance and Mentorship:
- Under the SSPCA scheme, individual students or student teams can avail themselves of travel grants to engage in international competitions.
- This assistance encompasses financial aid, mentorship, logistical support, and networking opportunities, empowering students to effectively represent India on the global stage.
- Financial aid extended by the AICTE scheme amounts to up to Rs 2 lakh per student, covering various expenses such as international and domestic travel, registration fees, visa applications, accommodation, airport taxes, travel insurance, and equipment costs associated with the competition.
Eligibility:
- Eligibility for the SSPCA initiative extends to students enrolled in diploma, B.E./B. Tech, integrated M. Tech, and M./M. Tech programs in AICTE-approved institutions.
- Each team of students is entitled to financial support under the scheme once during the course of their study.
About the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE):
- Established as the statutory body and national-level council for technical education in India, the AICTE has played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of technical education in the country.
- Founded in 1945 as an advisory body, it gained statutory status through an Act of Parliament in 1987.
Functions:
- The AICTE is responsible for granting approval for the establishment of new technical institutions, the introduction of new courses, and variations in intake capacity.
- It sets and upholds norms and standards for technical institutions to ensure quality development.
- Additionally, the AICTE promotes technical education through various schemes aimed at fostering innovation, faculty development, research and development, and inclusivity for women, the handicapped, and marginalized sections of society.
- Technical institutions under the AICTE's purview encompass a wide array of programs, including post-graduate, undergraduate, and diploma courses across multiple disciplines.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, the AICTE continues to be at the forefront of advancing technical education and innovation in India.
Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme (India Today)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, the Union Minister of Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship launched the EdCIL Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme.
About the Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme:
- The Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme ensures equitable access to high-quality educational systems by facilitating a seamless transition from secondary to higher education and providing financial support to meritorious students from Navodaya Vidyalayas who lack financial means.
- It embodies a holistic approach to empowerment, aiming to expand educational opportunities, especially for students from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
- The programme aims to secure assistance and funding from non-governmental partners and private sources, including CSR grants, national and international donors, and impact investors.
- Initially, the programme will benefit students in grades XI and XII studying in Navodaya Vidyalayas across the country.
- A dedicated fintech platform has been developed under Vidyanjali to disburse sponsorships to students through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- This platform plays a crucial role in data management, application processing, progress tracking, grant disbursement monitoring, fund utilization monitoring, generating impact reports for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), recognizing notable student achievements, and publicly acknowledging the support of funders, among other functions.
What is EdCIL?
- Educational Consultants India Limited (EdCIL) is the sole Public Sector Undertaking under the Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- Established on June 17, 1981, under the Companies Act, 1956, it holds the distinction of being categorized as a 'Mini Ratna Organisation' by the Government of India.
- EdCIL provides consultancy and technical services in various domains of education and human resource development, both domestically and globally.
- Its clientele includes numerous state and central government departments, public sector undertakings (PSUs), and autonomous bodies such as Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs), Kendriya Vidyalayas, and Navodaya Vidyalayas.
Hydrothermal System Beneath the Waters of Lake Rotorua in New Zealand's North Island (India Today)
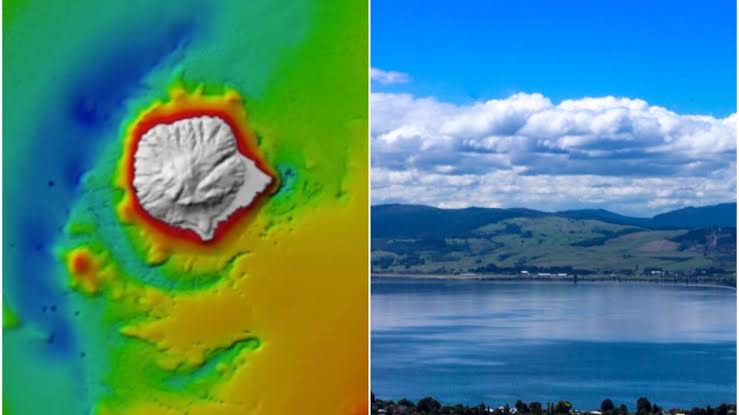

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
In a big revelation, scientists have unveiled a hidden hydrothermal system beneath the waters of Lake Rotorua, a site steeped in Maori legend and situated atop a dormant volcanic crater on New Zealand's North Island.
What are Hydrothermal Systems?
- Hydrothermal systems manifest in regions with intense heat, occurring both on continents near convergent plate boundaries and on the ocean floor in proximity to mid-ocean ridges.
- Three essential components—fluids, heat, and permeable rock structures—are crucial for their formation.
- Formation Dynamics:
- These systems are frequently situated near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates diverge, leading to the creation of new seafloor.
- Operational Mechanism:
- Hydrothermal systems initiate as seawater infiltrates fractures in the oceanic crust, gaining heat from the Earth's interior as it descends.
- Interacting with the oceanic crust, the seawater, reaching temperatures of 350-400 degrees Celsius, undergoes chemical modifications, extracting elements from the rocks.
- Despite the extreme pressure at ocean depths preventing boiling, this process generates hydrothermal fluid—a mixture of gasses and dissolved elements, including metals.
- Return to the Seafloor:
- The superheated fluid is ejected back to the seafloor and rapidly cools upon contact with near-freezing ocean bottom waters.
- Chimney-Like Deposits:
- Chemicals dissolved in the fluid precipitate at the vent, creating chimney-like deposits.
- These formations support unique deep-sea chemosynthetic communities—organisms relying on chemicals, not photosynthesis, to sustain their metabolism.
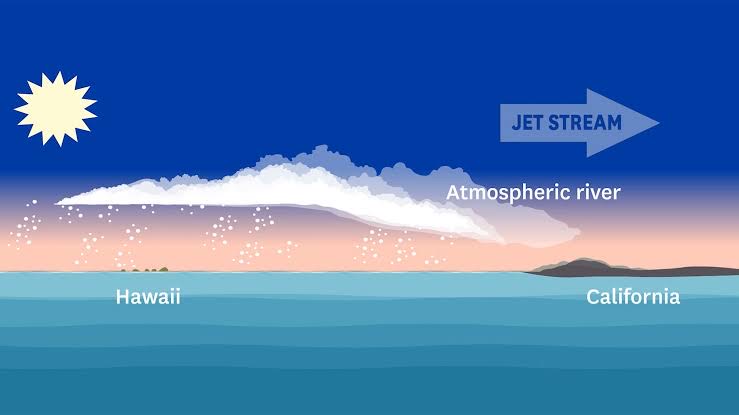
“Pineapple Express” Sweeps California, Atmospheric River Leaves State In Distress (India Today)
- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A strong and grievous atmospheric river storm is predicted to hit California during the later part of Saturday, leaving over another storm, which resulted in extreme flooding in the last week.
What is an Atmospheric River?
- Atmospheric rivers are long and relatively narrow bands of water vapor that form over an ocean and flow through the sky, transporting much of the moisture from the tropics to northern latitudes.
- They occur globally but are especially significant on the West Coast of the United States, where they create 30% to 50% of annual precipitation and are vital to water supplies but also can cause storms that produce flooding and mudslides.
- While they are an incredibly important source of rainfall, they can also bring flash flooding, mudslides, and landslides, sometimes killing people and destroying property.
- Formation: Formed by winds associated with cyclones, atmospheric rivers typically range from 250 miles to 375 miles (400 to 600 kilometers) in width and move under the influence of other weather.
- Many atmospheric river events are weak. But the powerful ones can transport extraordinary amounts of moisture.
- Studies have shown that they can carry seven to 15 times the average amount of water discharged daily by the Mississippi River.
- Forty-six atmospheric rivers made landfall in the U.S. West Coast during the water year 2023.
- Nine were categorized as strong, two were extreme and one was exceptional.
- California experienced extensive flooding and massive snowfall.
What Happens When an Atmospheric River Reaches Land?
- When the moisture-laden air moves over mountain ranges such as the Sierra Nevada along the California-Nevada line, the water vapor rises and cools, becoming heavy precipitation that falls as rain or snow.
- While traditional cold winter storms out of the north Pacific build the Sierra snowpack, atmospheric rivers tend to be warm.
- Snow may still fall at the highest elevations but rain usually falls on the snowpack at lower elevations.
- That can quickly prompt melting, runoff and flooding and decrease the snowpack needed for California’s water supply.
What is a Pineapple Express?
- It is a nickname for a strong atmospheric river in the tropical Pacific near Hawaii.
Where did the Term Atmospheric River Come From?
- The name came from research published in the 1990s by scientists Yong Zhu and Reginald E. Newell of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
US Approved Sale of 31 Predator Drones to India (India Today)
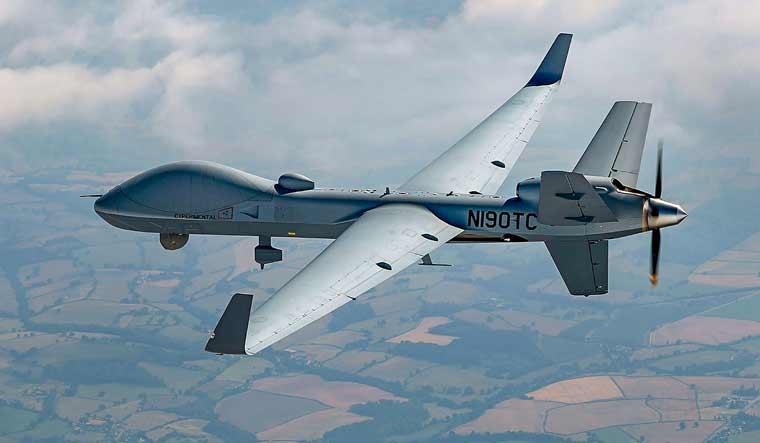

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant development that underscores the deepening strategic partnership between India and the United States, the US State Department has approved a landmark Foreign Military Sale to the Indian government.
News Summary:
- The US Defense Security Cooperation Agency has formally notified the US Congress regarding a potential military sale of MQ-9B SkyGuardian drones and associated equipment to the Government of India.
What is a Drone?
- Drones are aerial vehicles powered by various means, capable of autonomous flight or remote piloting, and can carry payloads, lethal or nonlethal, depending on the mission.
Key Features of MQ-9B SkyGuardian Drones:
- Designed for extended over-the-horizon flights lasting over 30 hours, facilitated by satellite connectivity.
- Incorporates advanced capabilities to safely operate in civilian airspace, facilitating joint operations with civil authorities for real-time situational awareness.
- Equipped with sophisticated maritime intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) systems, enabling real-time monitoring and patrolling both above and below the ocean's surface.
Significance of Drone Technology in Defense:
- Strategic Importance: Drones offer valuable intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities, providing real-time visuals and data to support decision-making processes.
- They also reduce risks to personnel and offer cost-effective alternatives to conventional manned aircraft.
- Tactical Advantages: Drones enable precision strikes with minimal collateral damage, enhance coordination and logistics in challenging terrains, and facilitate operations in remote or hostile environments.
Challenges Associated with Drones:
- Complex Airspace Management: The integration of drones into India's airspace necessitates a robust management framework to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Factors like strong winds can affect drone operations, highlighting the need for resilient systems capable of operating in varied environmental conditions.
- Privacy and Safety Concerns: There are concerns regarding the potential misuse of drones for breaching privacy and safety regulations, emphasizing the importance of stringent regulations and oversight mechanisms.
Closest-ever Sun photo captured by Solar Orbiter (India Today)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The European Space Agency's Solar Orbiter has captured the most detailed image of the Sun's full disc and outer atmosphere, the corona, to date.
What is the Solar Orbiter?
- Solar Orbiter is a Sun-observing satellite, equipped with 10 state-of-the-art science instruments, that aims to provide unprecedented insights into the workings of the Sun.
- It intends to conduct an in-depth study of both the Sun and the inner heliosphere, exploring the uncharted regions closest to our Solar System.
- A collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, it represents the most intricate scientific laboratory ever dispatched to study the Sun.
- Distinguished by its capability to capture images of the Sun from a closer vantage point than any preceding spacecraft, it also marks the first exploration of the Sun's previously uncharted polar regions.
- Launched on February 10, 2020, the mission unveiled its initial images in June of the same year.
- Following gravitational assist manoeuvres at Earth and Venus, it commenced full science operations in December 2021.
- Solar Orbiter actively orbits the Sun in an elliptical trajectory, with its closest point, the perihelion, located approximately 25 million miles (40 million kilometres) from the Sun—closer than the orbit of Mercury.
- In terms of instrumentation, it actively carries six remote-sensing instruments for observing the Sun and the solar corona, along with four in-situ instruments for measuring the solar wind, energetic particles, and electromagnetic fields.
- The mission actively aims to continue its scientific operations until at least 2027.
Is Halley’s Comet returning? (India Today)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The celestial calendar for 2023 is set to offer a spectacular show as the Orionid meteor shower is expected to rain down its greatest number of meteors on the mornings of October 21 and 22.
About the Orionid Meteor Shower:
- An annual celestial spectacle illuminating the night sky every October, the Orionid meteor shower is a captivating phenomenon with a fascinating origin.
- This cosmic event transpires as Earth traverses the remnants of debris left by Halley's Comet, officially designated as 1P/Halley.
- Halley's Comet, on a roughly 76-year orbit around the sun, sheds dust particles from its nucleus during each passage through the inner solar system.
- This process creates a distinctive trail of debris along its path.
- In late October each year, Earth intersects this celestial trail, giving rise to the mesmerizing display known as the Orionid meteor shower.
- Measuring about five by nine miles in size, Halley's Comet undergoes a remarkable transformation, losing between three to ten feet of material with each journey through the inner solar system.
- The resulting debris becomes the source of the Orionid meteors.
- This celestial event offers a visual treat for observers in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres, particularly during the post-midnight hours.
- It provides an opportunity to witness the graceful streaks of light as the meteors traverse the night sky.
What are Meteors?
- Meteors, often referred to as "shooting stars," are a captivating manifestation of meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at high speed and subsequently burning up.
- Meteor showers, occurring annually or at regular intervals, are linked to the Earth passing through the dusty debris trail left behind by a comet.
- In the case of the Orionid meteor shower, the meteors are named after the constellation Orion, close to where these luminous streaks appear in the sky.
- This annual celestial event not only captivates observers with its dazzling display but also serves as a reminder of the dynamic interactions between Earth and the celestial bodies that grace our cosmic neighbourhood.
New Artificial Intelligence System BTSbot Discovers Supernova (India Today)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international team led by Northwestern University has successfully created an artificial intelligence (AI) tool Bright Transient Survey Bot (BTSbot) that can detect, identify, and classify supernovae.
What is the Bright Transient Survey Bot (BTSbot)?
- The Bright Transient Survey Bot operates as a machine-learning algorithm, undergoing training with a vast dataset comprising over 1.4 million images from nearly 16,000 sources.
- Utilizing data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF), it successfully identified the recently discovered supernova named SN2023tyk.
- Functionality: The algorithm seamlessly automates the process of seeking potential supernovae across the night sky.
- In the case of SN2023tyk, it autonomously requested the supernova's spectrum from the Palomar Observatory.
- Subsequently, the Spectral Energy Distribution Machine (SEDM), another robotic telescope, performed comprehensive observations to obtain the source's spectrum.
- Advantages: This innovative system not only streamlines the entire workflow of searching, detecting, confirming, classifying, and announcing new supernovae but also eradicates human error, significantly enhancing the speed of the process.
- The Bright Transient Survey Bot showcases the potential of automated technology in advancing astronomical discoveries.
What is artificial intelligence?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the interdisciplinary field of computer science dedicated to developing algorithms and computational models that emulate human cognitive processes.
- Rooted in machine learning and advanced data analytics, AI aims to create systems capable of reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- AI involves the study and design of intelligent agents, encompassing areas like natural language processing, computer vision, and expert systems.
- It seeks to enhance machines' ability to learn from experience, adapt to new information, and perform tasks that traditionally necessitate human intelligence, fostering innovation across diverse domains, including healthcare, finance, and robotics.
A New Discovery: Unveiling an Underwater Mountain Range in the Southern Ocean (India Today)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have discovered an ancient underwater mountain range hidden within the world's strongest ocean current, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
Context:
- During a recent research expedition, scientists discovered a previously unknown mountain range deep beneath the Southern Ocean’s surface.
- Using state-of-the-art sonar technology, researchers were able to map out the underwater landscape with astonishing accuracy, revealing a vast range of peaks, ridges, and valleys.
- This newfound mountain range spans hundreds of miles and is estimated to be millions of years old.
- Geological Significance: This discovery holds immense importance for our understanding of the Earth’s geological history.
- The underwater mountain range provides key evidence of plate tectonics and the movement of Earth’s crust, as well as the formation of new landmasses.
- By studying the composition and structure of these underwater formations, scientists will be able to gain insights into the geological processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
- Moreover, the discovery raises intriguing questions about the relationship between underwater mountains and the surface landscapes they may be connected to.
- Researchers are eager to investigate whether similar mountain ranges exist on land and whether they share a common origin.
- Implications for Climate and Ecosystems: The newfound underwater mountain range also has significant implications for climate and marine ecosystems.
- These underwater peaks can act as barriers, influencing ocean currents and affecting nutrient distribution.
- Understanding the impact of these formations on ocean dynamics is crucial for predicting climate patterns and better managing marine resources.
- Additionally, these underwater mountains create a unique habitat for a diverse range of marine species.
- The ridges and valleys provide sheltered zones where marine life can thrive, with the potential for new species discoveries.
- Protecting these habitats will be critical in preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
About the Southern Ocean:
- The Southern Ocean, also referred to as the Antarctic Ocean is one of the Earth's five major ocean basins.
- Its formation traces back approximately 34 million years when Antarctica and South America underwent a gradual separation, resulting in the creation of the Drake Passage.
- This passage, situated between the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and South America, delineates the Southern Ocean from the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, encompassing their tributary seas surrounding Antarctica below the 60° S latitude.
- Physiography: The ocean floor structure features a continental shelf, typically less than 160 miles (about 260 km) wide, expanding to a maximum width exceeding 1,600 miles (2,600 km) near the Weddell and Ross seas.
- Renowned for its robust winds, intense storms, marked seasonal variations, and frigid temperatures, the Southern Ocean is predominantly influenced by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC).
- This current, the longest, strongest, and deepest-reaching on Earth, follows a clockwise circulation around the continent, surpassing all others in the volume of water it transports globally.
- Biodiversity: The Southern Ocean sustains diverse flora and fauna, with a majority of marine life relying on the nutrient-rich phytoplankton found in the Antarctic Convergence.
- Notable species include whales, penguins, orcas, and seals, contributing to the region's rich biodiversity.
Watermeal May Become an Essential Food for Astronauts (India Today)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists from Mahidol University in Thailand have been exploring the potential of watermeal, the smallest flowering plant on Earth, as a source of nutrition and oxygen for astronauts.
What is Watermeal?
- The Watermeal scientifically known as Wolffia, is often mistaken for algae, but they're actually the smallest flowering plants in the world!
- Its simplicity and rapid growth rate make it an ideal candidate for studying the effects of altered gravity on plant development.
- this tiny plant is aquatic, predominantly floating on the surface of water bodies.
- Because watermeal doesn’t have any roots, stems or leaves, it is basically just a sphere floating on a body of water.
- It's a prolific producer of oxygen through photosynthesis and belongs to the duckweed family (Lemnaceae).
- Each individual watermeal plant is extremely small, roughly the size of a pinhead.
- It has a simple, globular, and rootless structure, often appearing like minute green grains on the water.
- Watermeal thrives in quiet, nutrient-rich freshwater environments like ponds, lakes, and marshes.
- The plant is found globally, with a significant presence in Asia and Thailand.
- Watermeal is known to be a rich source of protein, making it a nutritious foodstuff.
- In Thailand, it has been part of the local diet for generations, appearing in dishes ranging from soups to salads.
Samudrayaan (IndiaToday)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
India's ambitious Samudrayaan project, aimed at exploring the deep ocean and its resources, is set to send three personnel to a depth of 6000 meters in a submersible vehicle.
About Samudrayaan Project:
- India's inaugural manned mission to delve into the depths of the ocean for exploration.
- Its primary objectives include studying deep ocean resources and conducting biodiversity assessments.
- The mission is designed to ensure minimal disturbance to the ecosystem, focusing solely on exploration.
- Part of the comprehensive Deep Ocean Mission aligned with the Central Government's Blue Economy policy.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) leads the implementation of this ambitious, multi-institutional endeavor.
What is the Blue Economy?
- Blue economy refers to the sustainable use of marine resources for exploration, economic growth, improved livelihoods, and transport while preserving the health of marine and coastal ecosystems.
- In India, the blue economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including shipping, tourism, fisheries, and offshore oil and gas exploration.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (India Today)
- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has reported a significant anthrax outbreak in Zambia, marking an alarming spread of the disease across nine out of the country's ten provinces.
What is anthrax?
- According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), anthrax is a highly infectious disease that is caused by the gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis.
- Although it affects animals like cows, sheep, and goats, humans can get sick if they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Anthrax is not contagious, which means we can't catch it from another person like the cold or flu.
Symptoms of anthrax:
- The disease manifests in three forms depending on the route of infection: cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and inhalational.
- Cutaneous anthrax, the most common form, presents with itchy bumps that develop into black sores, often accompanied by fever and muscle aches.
- Gastrointestinal anthrax resembles food poisoning initially but can escalate to severe abdominal pain and bloody diarrhoea.
- Inhalational anthrax, the deadliest form, starts with cold-like symptoms before progressing to severe respiratory distress and shock.
How is anthrax diagnosed?
- Anthrax can be diagnosed by identifying Bacillus anthracis in blood, skin lesions, or respiratory secretions through laboratory culture, PCR, or ELISA tests.
- While there is no specific test to determine exposure to anthrax, public health investigations play a crucial role in identifying potential cases.
Treatment for anthrax:
- Treatment for anthrax is available and includes antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, or levofloxacin.
- If diagnosed early, antibiotic treatment can cure most anthrax infections.
- In severe cases, hospitalisation and treatments like continuous fluid drainage and mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
- Vaccines are also available for both livestock and humans, although human vaccines are typically reserved for those at high occupational risk.
Millipede species (India Today)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent discovery, a previously unknown species of millipede was found dwelling beneath the city of Los Angeles, United States.
About Millipede Species:
- The recently discovered species belongs to the category of thread Millipedes.
- It measures approximately the length of a paperclip but is as slim as pencil lead.
- Scientifically identified as Illacme socal, this millipede is translucent and displays sinuous movements akin to a jellyfish tentacle.
- The creature's habitat lies about four inches beneath the ground, where it burrows and secretes distinctive chemicals, exhibiting unique behavior.
- Remarkably, this millipede is blind and relies on hornlike antennas extending from its head to navigate its surroundings.
What are Millipedes?
- Millipedes belong to the arthropod class Diplopoda, placing them in the same group as centipedes.
- These invertebrates exhibit a cylindrical or slightly flattened body structure.
- Despite their name, "millipede," which translates to "a thousand feet," these creatures do not actually have a thousand feet. However, they possess numerous legs on their bodies.
- The millipede's body is segmented, and each segment carries two sets of legs attached to the underside.
- Diet-wise, millipedes are detritivores, subsisting on dead organic matter found in the earth, such as damp wood pieces, decaying leaves, and other materials that are naturally present in their moist underground habitat.
Conjunctivitis (India Today)
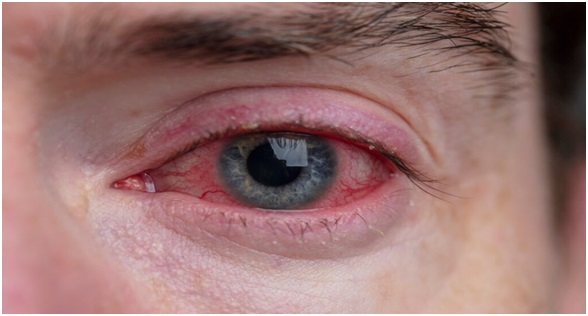
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
India has been witnessing a sharp increase in eye infections, specifically conjunctivitis. Amid heavy rainfall, Delhi and nearby areas have reported multiple cases of conjunctivitis.
About Conjunctivitis:
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as "pink eye," is an inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, which is the thin, clear tissue that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner surface of the eyelids. It can affect one or both eyes and is a highly contagious condition.
Causes of Conjunctivitis:
- Bacterial Infection: Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumoniae, can cause bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Viral Infection: Viruses, including adenoviruses, can lead to viral conjunctivitis. This form of conjunctivitis is highly contagious and is often associated with colds or respiratory infections.
- Allergies: Allergic conjunctivitis occurs due to an allergic reaction to substances like pollen, pet dander, dust mites, or certain medications.
- Irritants: Exposure to irritants like smoke, chemicals, or foreign objects in the eye can cause irritant conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis:
- Redness of the eyes
- Watery or thick, yellowish discharge from the eyes
- Itchiness or burning sensation in the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Crusty eyelids or lashes, especially in the morning (more common in bacterial conjunctivitis)
- Swelling of the conjunctiva
- Blurred vision
Treatment:
- The treatment of conjunctivitis depends on its underlying cause:
- Bacterial conjunctivitis: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments are commonly prescribed to treat bacterial infections.
- Viral conjunctivitis: Since it is caused by a virus, antibiotics won't work. The symptoms are often relieved with supportive measures like artificial tears, cold compresses, and good hygiene practices to prevent spreading.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: Avoiding allergens is essential. Antihistamine eye drops or oral medications can help alleviate symptoms.
- Irritant conjunctivitis: Removing the irritant and using artificial tears can help soothe the eyes.
Prevention:
- To prevent the spread of conjunctivitis, one should follow these measures:
- Frequent handwashing.
- Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes.
- Avoid sharing towels, pillowcases, or eye makeup with an infected person.
- Avoid close contact with individuals showing symptoms of conjunctivitis.
Project Naman (India Today)
- 06 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Army has initiated 'Project Naman,' which involves setting up centers to provide support and address concerns for veterans and the families of personnel who have made the ultimate sacrifice.
Facts About:
- Project Naman aims to create centers for veterans and the families of fallen personnel to provide assistance and address their concerns.
- The first center will be located in Delhi Cantonment.
- Named 'Naman,' these centers will include a Common Service Centre, offering various government-to-customer services.
- Additionally, they will assist in updating pensioners' accounts on the SPARSH portal for veterans, next of kin, and dependents.
