Fast Track Immigration FTI-TTP

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India is launching the Fast Track Immigration Trusted Traveller Program (FTI-TTP) to streamline immigration at seven major airports.
Key Highlights:
- The initiative, inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, aims to enhance the travel experience for Indian nationals and Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) cardholders.
- This comes seven months after the programme was first introduced at Indira Gandhi International (IGI) Airport, New Delhi. The airports included in this initial phase are: Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Cochin and Ahmedabad
Objectives of FTI-TTP
- Provide seamless and secure immigration services.
- Reduce human intervention using automated e-gates.
- Align with the Viksit Bharat@2047 vision for modern infrastructure.
How the Programme Works
The FTI-TTP simplifies immigration with automated e-gates. Travellers must complete a one-time online registration to enroll. The process involves:
- Online Registration: Submit personal details and upload necessary documents via the official portal (https://ftittp.mha.gov.in).
- Biometric Submission: Fingerprints and facial images must be submitted at an airport or Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO).
- Immigration Clearance via E-Gates:
- Passengers scan their boarding passes and passports at e-gates.
- Biometrics are automatically verified.
- Upon authentication, the e-gate opens, granting clearance.
Validity: Registration is valid for five years or until the registered passport expires, whichever comes first.
Who is Eligible?
The first phase of the FTI-TTP is open to:
- Indian nationals.
- OCI cardholders aged between 12 and 70 years.
- Children aged 12-18 can register using their parents’ email/phone number.
- ECR (Emigration Check Required) passport holders are not eligible.
Documents Required for Registration
- Passport-sized photograph (as per Indian passport specifications).
- Scanned copy of passport (front and back pages).
- Proof of current address.
- OCI card details (if applicable).
Key Points to Note
- Registration may take up to a month due to verification by field agencies.
- Applications with incorrect or outdated information may be rejected.
- In case of passport loss or expiry, travellers must reapply and submit fresh biometrics.
- Passports must have at least six months’ validity at the time of applying.
- For support, travellers can reach out via email at india.ftittp-boi@mha.gov.in.
Implementation Phases
The FTI-TTP will be implemented in two phases:
- Phase 1: Covers Indian citizens and OCI cardholders.
- Phase 2: Will extend to foreign travellers.
- The programme will be expanded to 21 major airports across the country.
Comparison with Similar Global Programmes
Several countries have implemented similar fast-track immigration systems:
United States: Global Entry
- Introduced in 2008.
- Offers self-service kiosks for pre-approved travellers.
- Requires background checks and in-person interviews.
United Kingdom: Registered Traveller Service
- Launched in 2015.
- Allows frequent visitors from select countries, including India, to use e-gates.
- Requires visa eligibility or multiple prior visits.
European Union: Smart Borders Initiative
- Implemented in 2016, with full deployment expected by 2024.
- Pre-registers biometric data for faster processing at Schengen Area borders.
Australia: SmartGate
- Started in 2007 for Australian and New Zealand passport holders.
- Uses automated kiosks for identity verification via passport scans and photos.
Saudi Arabia: Smart Travel System
- Launched in 2019.
- Uses automated e-gates for faster immigration clearance.
- Expanding as part of Vision 2030 to improve travel experience, particularly for Hajj pilgrims.
Israel-Hamas Ceasefire and Hostage Release Deal
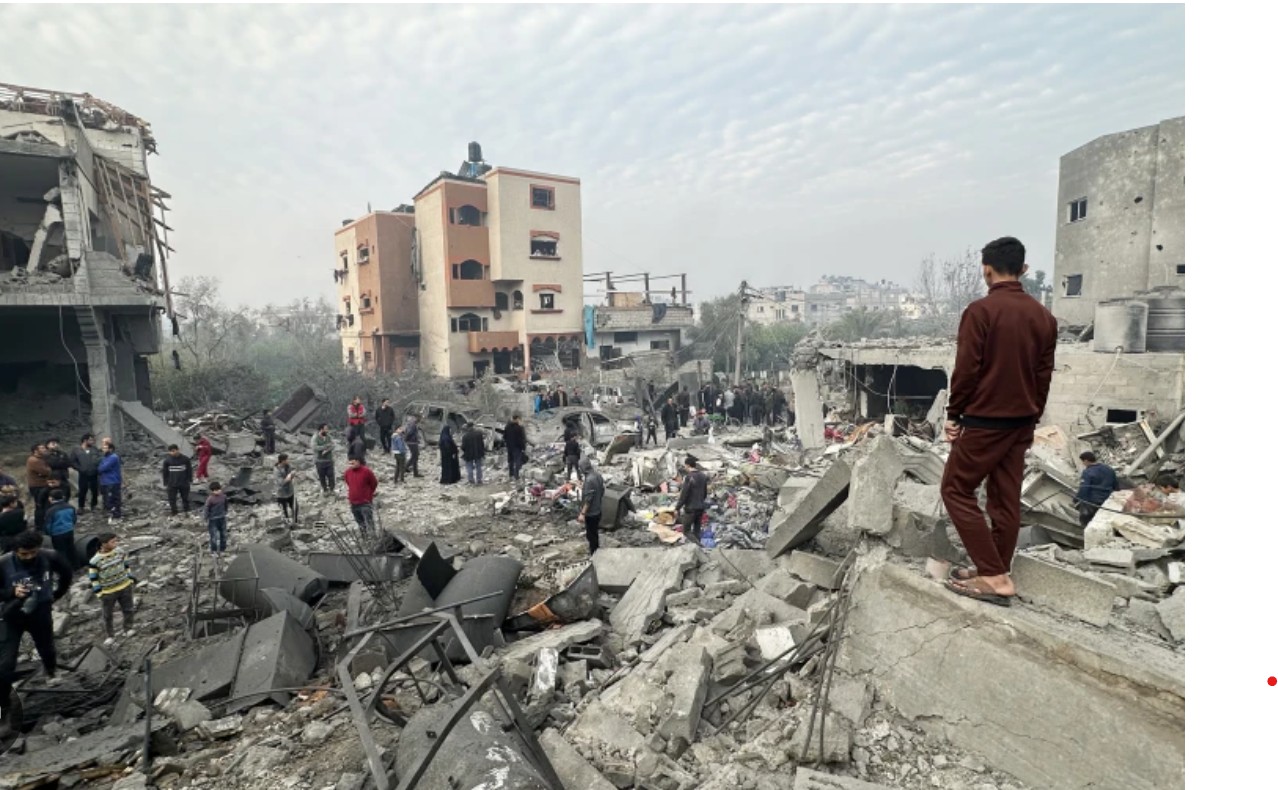

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Israel and Hamas have agreed on a Gaza ceasefire and hostage release deal after 15 months of war.
Key Highlights:
Ceasefire Agreement Details:
- Location: The deal was brokered in Doha, Qatar.
- Approval Process: The deal must be approved by Israel’s Cabinet to take effect.
- Mediators: The agreement was negotiated by Qatar, Egypt, and the United States, with their involvement ensuring the implementation of the deal.
Phases of the Deal:
- First Phase (42 Days):
- Release of 33 hostages by Hamas, including women, children, and elderly people.
- Hostage Exchange: Hostages will be exchanged for Palestinian prisoners in Israeli jails.
- Gaza Ceasefire and Withdrawal: Israeli forces will gradually withdraw from Central Gaza and move to the borders.
- Return of Displaced Palestinians: Displaced Palestinians will be allowed to return to Northern Gaza.
- Humanitarian Aid: 600 humanitarian aid trucks will be allowed into Gaza daily.
- Second Phase:
- Hostage Release: Negotiations will begin for the release of remaining hostages.
- Full Israeli Troop Withdrawal: Israel will fully withdraw its forces.
- Third Phase:
- Reconstruction of Gaza: Overseen by Egypt, Qatar, and the United Nations.
- Reopening of Border Crossings: For movement in and out of Gaza.
- Return of Hostage Bodies: Return of any bodies of hostages who died.
Background of the Israel-Hamas Conflict:
- Start: On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched an attack on Israel, called Operation Al-Aqsa Flood, causing significant casualties.
- Israeli Response: Israel launched Operation Iron Sword in retaliation.
- Casualties: The conflict resulted in 46,707 Palestinian deaths, mostly civilians, and 1,210 Israeli deaths.
About Gaza Strip:
- Location: A Palestinian enclave on the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Israel and Egypt.
- Administration: The Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas since 2006.
- Movement Restrictions: Israel controls air space and shoreline, imposing restrictions. Egypt controls one border and also restricts movement.
Gaza Truce Deal:
- Nature: A proposed ceasefire to end the ongoing conflict.
- Primary Parties: Israel and Hamas.
- Supporting Nations: United States, Qatar, and Egypt.
- Significance:
- Aims to stop fighting and address the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- Potential to influence regional stability and Israeli politics.
- Marks an important moment in U.S. diplomacy under the Biden administration.
India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) completes two years of remarkable success, driving mutual growth and showcasing the complementarity of both economies.
Key Achievements:
- Bilateral Merchandise Trade Surge:
- Trade increased from USD 12.2 billion (2020-21) to USD 26 billion (2022-23).
- Trade moderated slightly in 2023-24 to USD 24 billion, but exports from India to Australia grew by 14%.
- From April-November 2024, bilateral trade reached USD 16.3 billion.
- Preferential Import Utilization:
- Export utilization: 79%
- Import utilization: 84%
- Sectoral Growth:
- Textiles, chemicals, and agriculture sectors have seen significant growth.
- New export products: Gold studded with diamonds, turbojets.
- India’s imports: Metalliferous ores, cotton, wood products that fuel Indian industries.
- Geopolitical Strengthening:
- Enhanced relations in forums like Quad, Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI).
Key Features of the Agreement:
- Tariff Reductions:
- Australian goods: 85% tariff-free access to India (rising to 90% by 2026).
- Indian goods: 96% tariff-free access to Australia (rising to 100% by 2026).
- Access to Key Markets:
- India: Access to Australia's fast-growing market.
- Australia: Access to India's labor-intensive sectors like gems, jewelry, textiles, leather, furniture, food, agriculture.
- Services and IT:
- 135 sub-sectors covered in services.
- India gains market access in 103 sub-sectors with Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status in 31.
- Fast-tracked approval of medicines and elimination of double taxation for India's IT sector.
- Job Creation & Skill Exchange:
- Expected creation of 1 million jobs in India.
- Opportunities for Indian yoga teachers, chefs, and 100,000 students with post-study work visas.
Future Prospects:
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA): Builds on ECTA to advance bilateral trade, with 10 formal rounds and ongoing inter-sessional discussions.
- Trade Target: Aim to reach AUD 100 billion in trade by 2030.
- Global Economic Impact: Strengthening the partnership will contribute to a more resilient and dynamic global economy, with deeper economic integration between India and Australia.
UN Approves New AU Force to Combat Al-Shabaab in Somalia
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- On January 19, 2024, the UN Security Council approved a new African Union (AU) force in Somalia to counter the Al-Shabaab terrorist group.
- The resolution was supported by 14 of 15 members, with the US abstaining due to concerns about funding.
- The new force will replace the African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) after its mandate ends on December 31, 2024.
New Mission - AUSSOM:
- The new mission is named African Union Support and Stabilization Mission in Somalia (AUSSOM).
- AUSSOM will continue supporting Somali forces in stabilizing the nation and combating terrorism.
- The mission's objective is to enhance security and stability in Somalia, addressing the challenges posed by Al-Shabaab and ISIL.
Mandate and Operations:
- AUSSOM allows for the deployment of up to 12,626 personnel, including 1,040 police officers, until June 2025.
- The force will focus on counterterrorism, maintaining security, and assisting the Somali government in stabilizing the country.
Financing:
- A hybrid funding approach will be used:
- 75% of the mission’s costs will be covered by the UN, and 25% will come from African Union and partner countries.
- The US raised concerns about the UN's disproportionate funding of the mission, which led to its abstention from voting.
Contributing Countries:
- Egypt has announced its participation in the new force.
- Burundi and Ethiopia will not be contributing troops to AUSSOM.
- Ethiopia has its own ongoing disputes with Somalia, particularly regarding its maritime deal with the breakaway Somaliland region.
Background on Somalia's Challenges:
- Somalia has faced decades of civil war, an insurgency by Al-Shabaab, and recurring climate disasters.
- The country is one of the poorest in the world, and its internal conflicts are exacerbated by clannism, which has fragmented its political and social structure.
Historical Context of Peace Missions in Somalia:
- Previous UN peacekeeping missions in Somalia (1992-1995) faced significant failures, notably the Battle of Mogadishu and the failure to prevent the 1993 massacre.
- The rise of Al-Shabaab in the mid-2000s has further escalated the conflict, and the mission of AUSSOM aims to address these continuing threats.
The Role of Clannism:
- Clannism has hindered the establishment of a unified government in Somalia, with clan rivalries leading to a lack of national cohesion.
- Clannism refers to the prevalence of clan-centric politics, where allegiance to clan and sub-clan interests often takes precedence over national cohesion. In Somalia, the major clans are Darod, Hawiye, Dir, and Rahanweyn.
Importance of AUSSOM:
- AUSSOM represents a strategic shift in the international approach to stabilizing Somalia, relying more on African-led initiatives for peace and security in the region.
Global Peacekeeping Operations:
- The UN peacekeeping mission has been active globally, with over 1 million personnel deployed across 70+ operations.
- Success stories like Sierra Leone (1999-2005) and Liberia (2003-2018) demonstrate the potential impact of well-executed peace missions, but past failures like in Somalia (1992-1995) and Rwanda (1994) underline the challenges faced.
India’s Contribution:
- India has contributed significantly to UN peacekeeping missions, deploying over 253,000 personnel in 49 operations since 1948.
- India’s contributions to missions in Somalia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, and Sudan reflect its active role in global peacekeeping efforts.
Schengen Zone Membership

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the European Union (EU) cleared Bulgaria and Romania for full membership in the Schengen Zone, effective January 1, 2025. This marks the end of a 13-year wait for these Eastern European nations, which joined the EU in 2007.
Key Highlights:
- Schengen Integration: Until now, Bulgaria and Romania were partially integrated into the Schengen Zone, with air and sea travel without border checks since March 2024. However, land border controls were still in place due to Austria's objections, mainly due to concerns over migration and border security.
- Austria's Shift: Austria had blocked full entry for years but finally lifted its veto on December 9, 2024, after a border protection package was agreed upon. This package includes joint border guard deployment at the Bulgarian-Turkish border and temporary land border controls for six months.
Schengen Zone Details:
- What is the Schengen Zone?
- Created by the Schengen Agreement (1985) and the Schengen Convention (1990), it is the world’s largest area without internal border controls, allowing free movement across most EU countries and some non-EU countries. It currently includes 29 countries (25 EU states and 4 non-EU countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland).
- Key Features:
- Free Movement: Over 425 million people can travel freely within the zone without border checks.
- Uniform Visa Policy: Short-term stays of up to 90 days are allowed for tourists and business travelers from outside the Schengen Area.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: The Schengen Information System (SIS) facilitates security and border management by sharing critical data between countries.
- Temporary Border Controls: Countries can temporarily reintroduce border controls for security reasons, after notifying other member states and the European Commission.
Bulgaria and Romania
- Bulgaria:
- Capital: Sofia
- Location: Southeastern Europe, bordered by the Black Sea, Romania, Turkey, Greece, North Macedonia, and Serbia.
- Political System: Parliamentary Republic
- Romania:
- Capital: Bucharest
- Location: Bounded by Ukraine, Moldova, Black Sea, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Hungary.
- Political System: Semi-Presidential Republic
Implications of Full Schengen Membership:
- Security and Unity: Romania and Bulgaria's full integration into the Schengen Zone is seen as a boost to both EU security and unity. It solidifies the EU's commitment to free movement while enhancing border security across Europe.
- Impact on Migration: With Bulgaria and Romania’s full membership, the EU’s border management system will be more integrated, helping to address ongoing migration challenges.
Naseem-Al-Bahr 2024
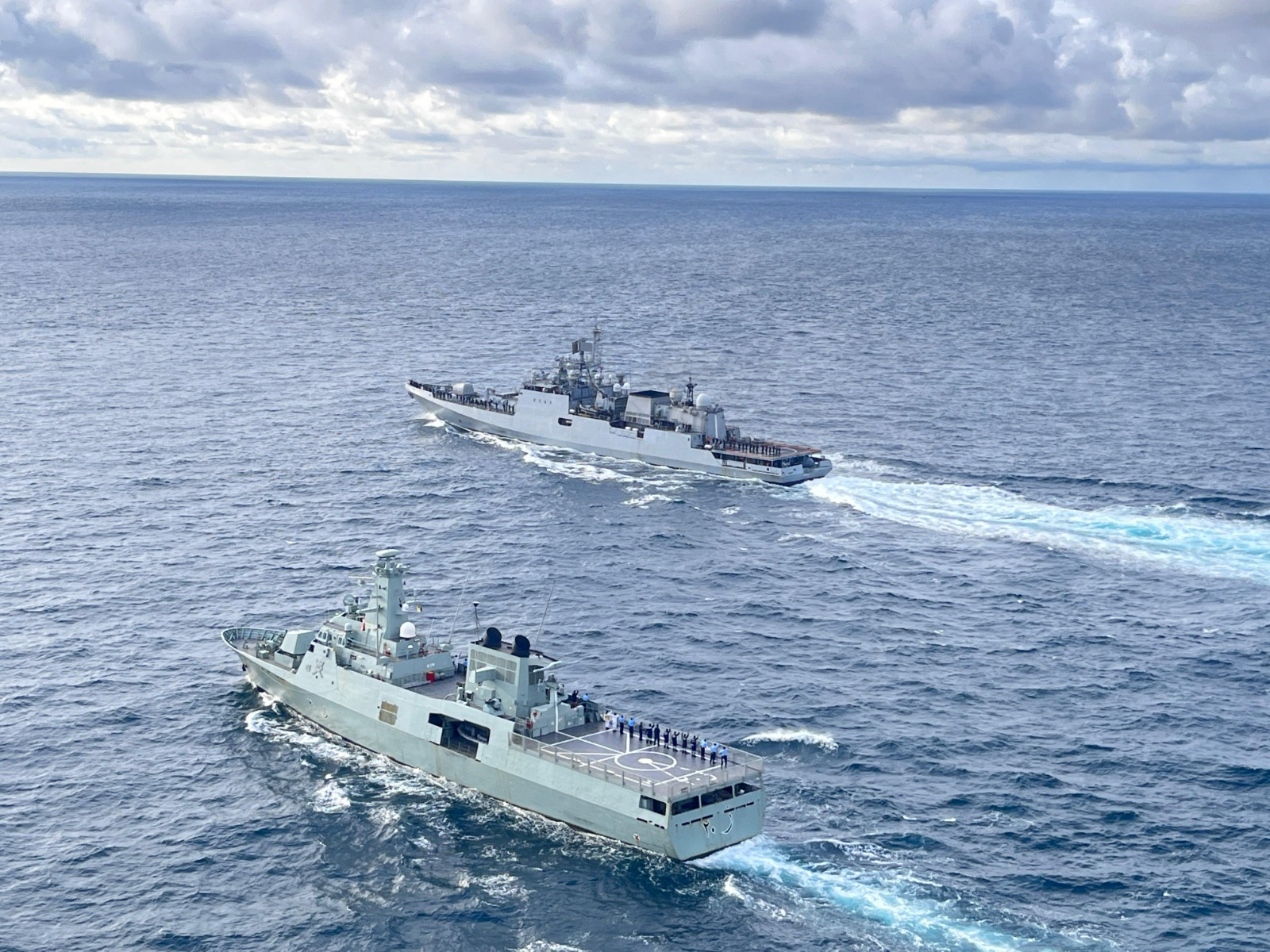

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
Indo-Oman bilateral naval exercise Naseem-Al-Bahr was held in Goa from October 2024.
Naseem-Al-Bahr Exercise Overview
- Indian and Omani Participants:
- Indian Navy: INS Trikand (warship) and Dornier Maritime Patrol Aircraft.
- Royal Navy of Oman: Vessel Al Seeb.
- Initiation: Launched in 1993, marking a long-standing strategic partnership between India and Oman.
- Structure: The exercise is conducted in two phases:
- Harbour Phase:
- Professional Interactions: Subject Matter Expert Exchanges (SMEE), planning conferences.
- Social & Sports Engagements: Informal activities to foster mutual understanding.
- Sea Phase:
- Naval Operations:
- Gun firings at surface inflatable targets.
- Close-range anti-aircraft firings.
- Replenishment at Sea Approaches (RASAPS).
- Helicopter Operations: INS Trikand’s helicopter performed cross-deck landings and Vertical Replenishment (VERTREP) with RNOV Al Seeb.
- Aircraft Support: Dornier aircraft provided Over-the-Horizon Targeting (OTHT) data to enhance operational coordination.
- Naval Operations:
- Harbour Phase:
Key Highlights of the 2024 Exercise
- Interoperability: The exercise focused on improving operational coordination and enhancing mutual understanding of naval practices.
- Cohesion: The Indian Navy Sea Riders embarked on RNOV Al Seeb to further strengthen the bilateral relationship.
Strategic Significance
- Strengthening Ties: Naseem-Al-Bahr reaffirms the strong strategic relationship between India and Oman.
- Regional Collaboration: This exercise exemplifies India's growing collaboration with like-minded nations in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Broader Defence Relations:
- Oman is the first GCC country to conduct such bilateral naval exercises with India.
- Both countries also engage in other defence exercises:
- Army: Al Najah.
- Air Force: Eastern Bridge.
Trade Relations Between India and Oman (2022):
- Oil: India is the second-largest market for Oman's crude oil exports, following China.
- Non-oil Exports: India is Oman's fourth-largest market for non-oil exports, after UAE, US, and Saudi Arabia.
- Imports: India is the second-largest source of Oman's imports, following the UAE.
- Ongoing Trade Agreement: Both nations are currently negotiating a trade agreement to further boost bilateral economic cooperation.
India’s Tripartite Agreement

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Nepal, India, and Bangladesh have signed a tripartite agreement to facilitate cross-border electricity trade, enabling Nepal to export surplus electricity to Bangladesh via India.
Key Details of the Agreement
- Export Period: The agreement allows for electricity exports from June 15 to November 15 each year.
- Initial Export Volume: In the first phase, Nepal will export 40 MW of hydroelectricity to Bangladesh through Indian territory.
- Electricity Rate: The fixed rate per unit of electricity is set at 6.4 cents.
- Projected Revenue: Nepal is expected to earn approximately $9.2 million annually from this trade.
This agreement aims to enhance regional cooperation in energy trade and support sustainable development in the participating countries.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar will attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Heads of Government meeting in Islamabad on October 15-16, 2023.
- This marks the first visit by an Indian External Affairs Minister to Pakistan since Sushma Swaraj in 2015.
Context of the Visit:
- The visit is primarily for the SCO meeting, reflecting India's focus on regional cooperation mechanisms.
- No bilateral meetings have been scheduled as of now, although Jaishankar's presence is based on "reciprocity" following Pakistan's participation in an earlier SCO meeting in India.
SCO Overview:
- Established on June 15, 2001, in Shanghai; evolved from the "Shanghai Five" formed in 1996.
- Original members included China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and later Uzbekistan.
- Current members: India, Pakistan, Iran, and others, with Afghanistan and Mongolia holding Observer Status.
Significance of the SCO:
- Focuses on security cooperation, primarily among Asian nations.
- Seen as an alternative to Western international frameworks, especially with heavyweights like Russia and China positioning against US influence.
- India's inclusion alongside Pakistan in 2017 reflects the geopolitical jostling between Russia and China.
Geopolitical Dynamics:
- While SCO promotes cooperation, underlying tensions remain, particularly between India and Pakistan, and India and China.
- The organization has limited tangible outcomes due to member states' rivalries and differing interests.
India's Objectives in SCO:
- Provides a platform for enhancing relations with Central Asian countries, addressing common security concerns.
- Involves participation in the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) to combat terrorism and drug trafficking.
India-Pakistan Relations:
- Jaishankar's visit is seen in light of ongoing tensions; India shares difficult relations with both China and Pakistan.
- India canceled a summit under its presidency last year, opting for a virtual format instead.
Implications for Regional Politics:
- The visit comes shortly after the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections, with potential implications for India-Pakistan ties.
- Despite attending the SCO meeting, there is little expectation of progress in the India-Pakistan peace process.
- Recent statements from the Indian government criticize Pakistan for hosting wanted individuals, reflecting ongoing diplomatic tensions.
Strategic Importance:
- Participation in SCO allows India to engage with key regional players, including Russia, China, and Central Asian leaders.
- The meeting serves as preparation for India's participation in upcoming BRICS discussions, emphasizing the interconnectedness of these groupings.
India-U.S. MoU on Critical Minerals Supply Chains
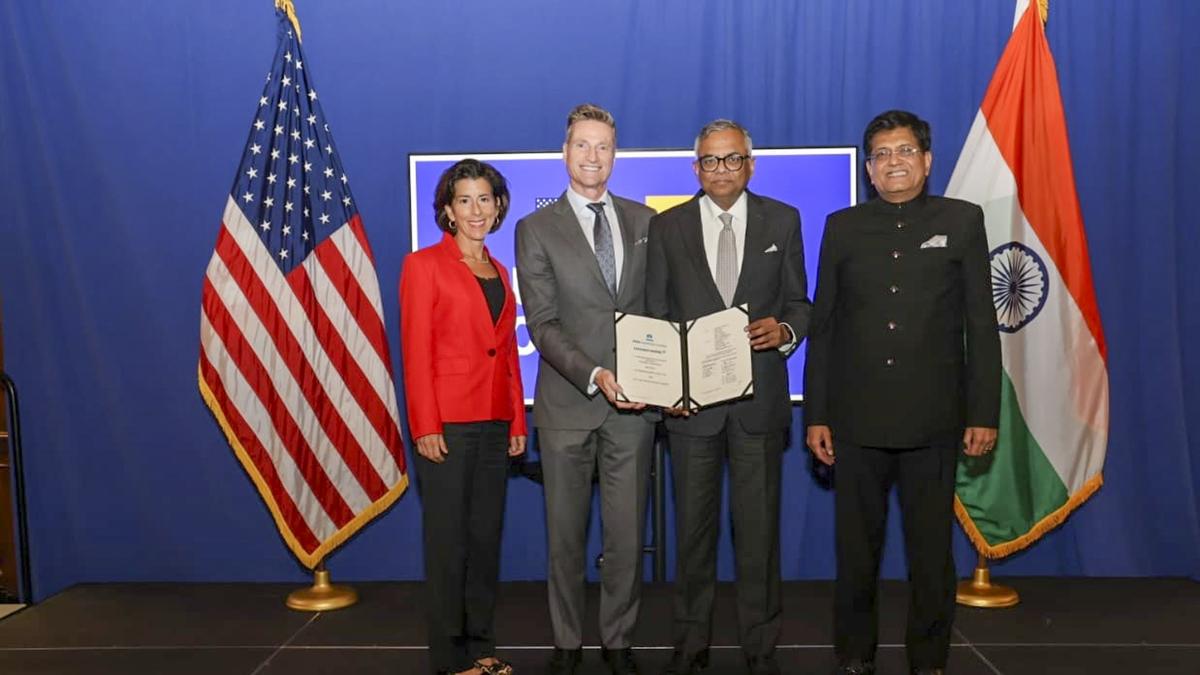

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
- The sixth Commercial Dialogue took place in Washington on October 4, 2024, led by Indian Union Minister of Commerce Piyush Goyal and U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo.
- MoU Signing: A day prior, the leaders signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) aimed at expanding and diversifying critical minerals supply chains to enhance resilience.
- Focus Areas:
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Exploration
- Extraction
- Processing and refining
- Recycling and recovery
- Identification of equipment, services, policies, and best practices for the development of U.S. and Indian critical minerals, covering:
- Context: This agreement follows China's export restrictions on gallium and germanium, critical for the semiconductor industry, and its ban on technology related to rare earth magnets and critical materials extraction.
- Strategic Goals:
- Promote open supply chains, technology development, and investment flows for green energy.
- Explore collaboration with other mineral-rich countries, particularly in Africa and South America.
- Progress on Semiconductor Supply Chains:
- Continued efforts to establish resilient semiconductor supply chains since the previous MoU.
- Completion of a "readiness assessment" by the U.S. Semiconductor Industry Association and India Electronics Semiconductor Association.
- Commitment to foster investments, joint ventures, and technology partnerships.
- Innovation Handshake: Success of roundtables in San Francisco and New Delhi aimed at enhancing innovation ecosystems and startup collaboration.
- Strategic Clean Energy Partnership: Discussions from the EIN Roundtable in March 2024 informed the U.S.-India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership meeting.
- IPEF Supply Chain Agreement: Significant progress noted in the IPEF ministerial meeting, focusing on semiconductors, chemicals, and critical minerals, particularly batteries and healthcare products.
- Future Collaborations:
- Focus on expanding U.S. Department of Commerce presence in India with approximately 70 Foreign Commercial Service staff.
- Plans for a U.S. trade mission to India in March 2025 aimed at supporting U.S. SMEs owned by underserved communities.
- Domestic Solar Manufacturing Protection: India reinstated the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) order to protect local solar PV module production against cheaper imports from China.
- Economic Context:
- The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights China's expanding manufacturing trade surplus and its restrictive actions affecting India's access to solar equipment.
- India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes have invested over $4.5 billion to bolster clean energy manufacturing but require additional policies to safeguard these investments.
USCIRF Report on India: Key Highlights

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), a Washington DC-based bipartisan U.S. federal government agency, has released a country update on India, flagging “collapsing religious freedom conditions”.
- Agency Overview:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is an independent, bipartisan U.S. federal commission established under the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Its primary functions include reviewing global religious freedom violations, providing policy recommendations to U.S. leaders, and publishing annual reports.
- Current Concerns:
- USCIRF's latest report indicates a “collapse” in religious freedom conditions in India, particularly worsening throughout 2024, especially around national elections.
- Legal and Policy Changes:
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- State-level anti-conversion and anti-terrorism laws.
- Implementation rules for the 2019 Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA).
- Passage of a State-level Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in Uttarakhand.
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- Violations and Incidents:
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Authorities have facilitated the construction of Hindu temples on former mosque sites.
- Increased attacks on religious minorities, particularly following the consecration of the Ayodhya temple in January 2024.
- Targeting of Religious Minorities:
- Arrests of Christians accused of forced conversions under anti-conversion laws.
- Anti-cow slaughter laws exploited by vigilante groups to target Muslims, Christians, and Dalits, often with little to no legal repercussions for perpetrators.
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Recommendations:
- USCIRF urges the U.S. State Department to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern” due to severe violations of religious freedom.
About USCIRF
- Composition: Comprised of nine commissioners appointed by the U.S. President or Congressional leaders, supported by non-partisan staff.
- Objective: To monitor and recommend actions on religious freedom violations aligned with international human rights standards.
Colombo Security Conclave (CSC)

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) recently marked a significant milestone with the signing of the Charter and the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the establishment of its Secretariat in Colombo. This initiative aims to strengthen regional security collaboration among member states.
Key Features of the Colombo Security Conclave
- Member States: The CSC comprises five member countries:
- India
- Bangladesh
- Sri Lanka
- Maldives
- Mauritius
Additionally, Seychelles participates as an observer nation.
- Core Objectives: The primary goal of the CSC is to enhance regional security by addressing transnational threats and challenges that are common concerns for member states. This includes a collaborative approach to ensure stability and safety in the region.
Origin and Evolution
- The CSC originated as the Trilateral for Maritime Security Cooperation, established through trilateral meetings among National Security Advisors (NSAs) and Deputy NSAs from India, Maldives, and Sri Lanka starting in 2011.
- The initiative faced a setback after 2014 due to heightened tensions between India and the Maldives.
- It was revived and rebranded as the CSC in 2020, expanding its membership to include Mauritius and, more recently, Bangladesh.
Structure and Cooperation
- The conclave facilitates interactions among NSAs and Deputy NSAs of member countries, fostering dialogue and cooperation on security matters.
- Cooperation under the CSC is organized around five key pillars:
- Maritime Safety and Security
- Countering Terrorism and Radicalization
- Combating Trafficking and Transnational Organized Crime
- Cybersecurity and Protection of Critical Infrastructure
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief
Permanent Secretariat
- The establishment of a permanent Secretariat in Colombo is expected to enhance coordination and streamline operations among member states, bolstering the efficacy of the CSC in addressing regional security issues.
INDIA TO SUPPORT TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO IN DEVELOPING UPI-LIKE PAYMENT SYSTEM

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- NPCI International Payments Limited (NIPL) has partnered with Trinidad and Tobago's Ministry of Digital Transformation to create a payment platform for person-to-person and person-to-merchant transactions.
- Modeling on UPI: The new digital payments system will be based on India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI), which is widely recognized as a leading digital payment solution.
- Role of NPCI: NIPL, a quasi-government body under the Reserve Bank of India, manages India’s retail payment systems, including UPI.
Previous Initiatives
- Global Expansion: Earlier in 2024, NIPL also committed to establishing digital payment systems in Peru and Namibia, leveraging the UPI model.
- Ongoing Talks: NIPL is exploring opportunities with additional countries in Africa and South America to assist in building their payment infrastructures.
Significance:
- UPI has emerged as a transformative force in India's financial landscape, registering nearly 15 billion transactions in August 2024, with an estimated value of USD 245 billion.
- This strategic partnership aims to empower Trinidad and Tobago to establish a reliable and efficient real-time payments platform for both person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) transactions, expanding digital payments in the country and fostering financial inclusion.
INDIA-UZBEKISTAN BILATERAL INVESTMENT TREATY (BIT)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
India and Uzbekistan signed the Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) aimed at boosting the confidence of investors of both the countries.
Key Highlights:
- Investor Protections:
- Assured Protection: The BIT guarantees protection for investors from both countries, aligning with international standards.
- Minimum Standards: It establishes a minimum standard of treatment and non-discrimination for investors.
- Dispute Resolution: An independent arbitration forum will be available for dispute settlement.
- Investment Safeguards:
- Protection from Expropriation: The treaty safeguards investments from unjust expropriation.
- Transparency and Compensation: Provisions are included for transparency and compensation for losses incurred.
- Regulatory Balance: While protecting investors, the treaty maintains a balance with the state's right to regulate, ensuring adequate policy space for both countries.
Economic Context
- Shared Commitment: The BIT reflects the commitment of both nations to foster economic ties and create a resilient investment environment.
- Expected Outcomes: It is anticipated that the treaty will facilitate increased bilateral investments, benefiting businesses and economies in India and Uzbekistan.
- Current Investment Landscape: As of August 2024, Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) from India to Uzbekistan stands at $20 million, with Indian investments notable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, amusement parks, automobile components, and hospitality.
India and Bilateral Investment Treaties
BITs are reciprocal agreements between two countries designed to promote and protect foreign private investments within each other's territories.
- Key Guarantees Established:
- National Treatment: Foreign investors are treated on par with domestic companies.
- Fair and Equitable Treatment: Investors receive treatment aligned with international law.
- Protection from Expropriation: Limits the ability of a country to seize foreign investments without appropriate compensation.
- Status of BITs in India
- Historical Context:
- Until 2015, India had signed BITs with 83 countries, with 74 currently in force. These agreements were based on the Indian Model BIT established in 1993.
- Revisions and Current Approach: In 2015, India revised its Model BIT text. Since then, India has:
- Signed new BITs/Investment Agreements with four countries.
- Entered negotiations with 37 countries/blocks for new agreements.
- Terminated older BITs with 77 countries, with only six remaining in force.
- Historical Context:
- Key Features of the Revised Model BIT
- Investor Protection:
- Provides robust protection for foreign investors in India and Indian investors abroad.
- Balances investor rights with government obligations.
- Investor Confidence:
- Enhances investor confidence by ensuring non-discriminatory treatment and a level playing field.
- Establishes an independent arbitration forum for dispute resolution.
- Investment Definition:
- Adopts an "enterprise"-based definition of investment to encompass various forms of investment.
- Dispute Settlement Provisions:
- Refined Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) provisions require investors to exhaust local remedies before seeking international arbitration.
- Limits arbitration tribunals to awarding monetary compensation only.
- Regulatory Authority Preservation:
- Excludes government procurement, taxation, subsidies, compulsory licenses, and national security from BIT coverage, ensuring the government retains regulatory authority.
- Investor Protection:
- Strategic Impact
- Preferred FDI Destination: The revised BIT aims to position India as a preferred destination for foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Protection of Outbound FDI: It also focuses on safeguarding outbound investments made by Indian entities.
ASIA POWER INDEX

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
In a major shift, India surpassed Japan to become the third-largest power in the Asia Power Index, reflecting its increasing geopolitical stature. This achievement is driven by India's dynamic growth, youthful population, and expanding economy, solidifying its position as a leading force in the region.
Key Factors Behind India’s Rise:
- Economic Growth: India has shown remarkable post-pandemic economic recovery, contributing to a 4.2-point rise in its Economic Capability. India’s massive population and strong GDP growth reinforce its standing as the world’s third-largest economy in PPP terms.
- Future Potential: India’s Future Resources score increased by 8.2 points, signalling a potential demographic dividend. Unlike its regional competitors, particularly China and Japan, India benefits from a youthful population that will continue to drive economic growth and labour force expansion in the coming decades.
- Diplomatic Influence: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership has garnered greater international recognition. India’s non-aligned strategic posture has allowed New Delhi to navigate complex international waters effectively. India ranked 6th in terms of diplomatic dialogues in 2023, reflecting its active engagement in multilateral forums.
- Further, India’s large population and economic capabilities offer it substantial promise. India’s score in Cultural Influence has also remained relatively strong, underpinned by its global diaspora and cultural exports.
- In addition, India’s role in multilateral diplomacy and security cooperation has been a point of emphasis. India's participation in dialogues, as well as its leadership in the Quad, has allowed it to play a significant role in regional security dynamics, albeit outside of formal military alliances.
Asia Power Index
- The Asia Power Index, launched by the Lowy Institute in 2018, is an annual measure of power dynamics in the Asia-Pacific region.
- It evaluates 27 countries across the Asia-Pacific, examining their ability to shape and respond to the external environment.
- The 2024 edition offers one of the most comprehensive assessments of power distribution in the region to date. Timor-Leste has been included for the first time, reflecting its growing importance in Southeast Asia.
- The Index focuses on both the material capabilities of states and the influence they exert on the international stage.
Criteria and Parameters of Power Measurement
Power in the Asia Power Index is divided into resource-based and influence-based determinants:
- Resource-Based Determinants:
- Economic Capability: The core economic strength of a country, measured through indicators like GDP at purchasing power parity (PPP), technological sophistication, and global economic connectivity.
- Military Capability: Evaluates conventional military strength based on defense spending, armed forces, weapon systems, and signature capabilities like long-range power projection.
- Resilience: The internal capacity to deter threats to state stability, including institutional robustness, geopolitical security, and resource security.
- Future Resources: Forecasts the future distribution of resources, including economic, military, and demographic factors projected for 2035.
- Influence-Based Determinants:
- Economic Relationships: The capacity to exercise leverage through trade, investment, and economic diplomacy.
- Defense Networks: The strength of alliances and partnerships, measured through military cooperation and arms transfers.
- Diplomatic Influence: The extent of a country's diplomatic reach, participation in multilateral forums, and foreign policy ambition.
- Cultural Influence: The ability to shape international public opinion through cultural exports, media, and people-to-people ties.
A country's overall power score is derived from a weighted average of these eight measures, encompassing 131 individual indicators. The results offer a nuanced understanding of how countries convert their resources into influence within the Asia-Pacific.
China test-fires an intercontinental ballistic missile into the Pacific Ocean
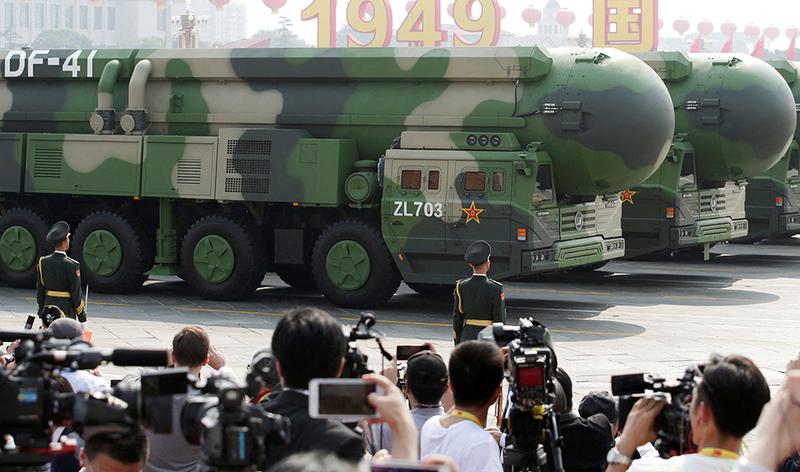

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
China stated that it test-launched an intercontinental ballistic missile, firing it into the Pacific Ocean in its first such exercise in decades.
- Launch Details:
- The missile carried a dummy warhead and fell into a designated area in the high seas.
- The specific flight path and landing location were not disclosed.
- Testing Objectives:
- The launch tested weapon performance and troop training levels, achieving its expected objectives.
- Historical Context:
- This is the first ICBM test over the Pacific Ocean in over 40 years.
- China's first ICBM, the DF-5, was test-fired in 1980.
- ICBM Specifications:
- The latest ICBM, likely the DF-41, has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilometers (7,400 to 9,300 miles), capable of reaching the US mainland.
- Strategic Messaging:
- Analysts interpret the test as a warning to the US, suggesting direct intervention in Taiwan could expose the American homeland.
- The test signals China's ability to engage multiple fronts simultaneously.
- Regional Tensions:
- Recent weeks have seen heightened tensions with Japan, the Philippines, and Taiwan due to military incursions and exercises.
- International Norms:
- There is a global expectation to notify nations of long-range missile launches to avoid miscalculations. China has limited agreements regarding this, primarily with Russia.
- Military Buildup:
- Under Xi Jinping, China has enhanced its nuclear capabilities and revamped the PLA’s Rocket Force.
- Recent satellite imagery indicates the construction of hundreds of ICBM silos in China’s deserts.
- Future Projections:
- As of 2023, China has over 500 operational nuclear warheads, projected to exceed 1,000 by 2030 according to the Pentagon.
- Implications of the Test:
- The ICBM test may be aimed at demonstrating military readiness despite recent corruption scandals within the Rocket Force.
About ICBMs:
- An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range ballistic missile system primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery. They are powerful and destructive weapons, capable of travelling vast distances at incredibly high speeds.
- Key features of ICBMs:
- Range: Range greater than 5,500 kilometres with maximum ranges varying from 7,000 to 16,000 kilometres.
- Speed: ICBMs can travel at speeds exceeding 20,000 kilometres per hour.
- Payload: Typically designed to carry nuclear warheads, though they could potentially be used to deliver other types of weapons, such as chemical or biological weapons.
- Deployment: ICBMs can be launched from silos underground, mobile launchers on land, or submarines at sea.
- Countries having operational ICBMs: Russia, United States, China, France, India, United Kingdom, Israel and North Korea.
INDO-PACIFIC ECONOMIC FRAMEWORK (IPEF)

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
India signed agreements within the US-led 14-member IPEF focused on a clean and fair economy.
- Objectives:
- Facilitate development, access, and deployment of clean energy and climate-friendly technologies.
- Strengthen anti-corruption measures and promote tax transparency among member countries.
- Clean Economy Agreement:
- Aims to accelerate energy security and mitigate greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Focuses on innovative methods to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote technical cooperation.
- Fair Economy Agreement:
- Seeks to create a transparent and predictable business environment to enhance trade and investment.
- Emphasizes information sharing, asset recovery facilitation, and strengthening cross-border investigations.
- Funding Mechanisms:
- IPEF offers platforms for technical assistance and concessional funding.
- IPEF Catalytic Capital Fund: Initial grant of $33 million aimed to catalyze $3.3 billion in private investments.
- PGI Investment Accelerator: Received $300 million from the US International Development Finance Corporation.
- Concerns Raised:
- Experts highlighted concerns over the secrecy of IPEF negotiations with limited public input.
- Expressed hope that India has not agreed to a non-derogation clause that could limit domestic regulatory flexibility for national projects.
- Potential Risks:
- Most standards discussed in IPEF are aligned with those in the US and OECD countries.
- India risks compliance pressures in future trade deals if it adopts these standards without adequate preparation.
- Strategic Importance of IPEF:
- Involves 14 member countries, focusing on economic cooperation through four key pillars: trade, supply chain resilience, clean economy, and fair economy.
- Represents 40% of the global economy and 28% of world trade, highlighting India's commitment to regional partnerships alongside the US, Japan, Australia, and other Indo-Pacific nations.
India-China Disengagement Along the LAC
- 18 Sep 2024
Overview of Disengagement Progress
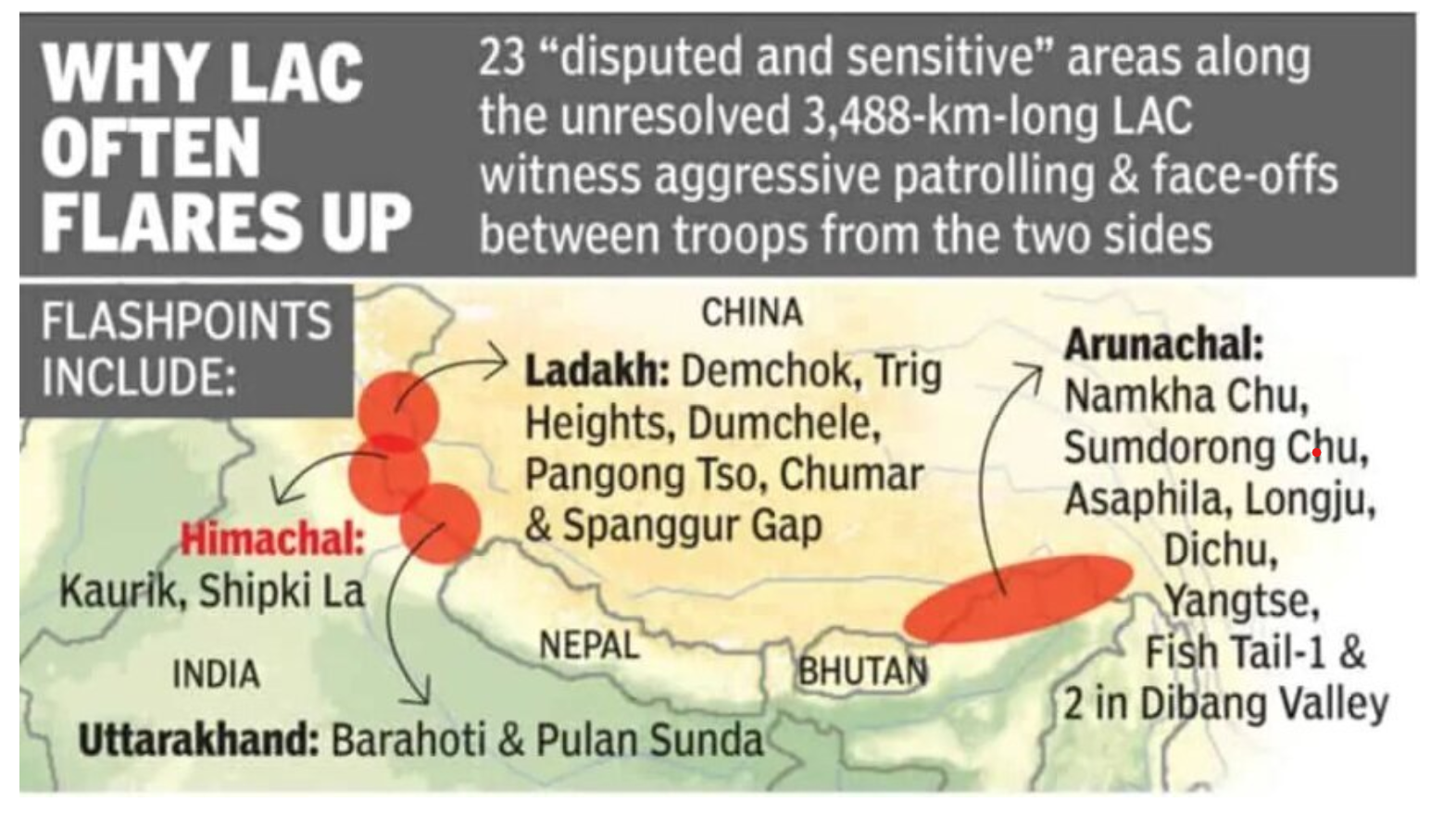
Recently, India’s External Affairs Minister announced that about 75% of the “disengagement problems” with China along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in Ladakh have been “sorted out.” However, notable areas such as Demchok and the Depsang plains have seen no progress toward resolution over the past two years.
Recent Developments on India-China Disengagement
Verified Disengagement
India and China have mutually agreed to and verified disengagement from five friction points, including:
- Galwan Valley
- Pangong Tso
- Gogra-Hot Springs
Despite this, issues in Demchok and Depsang remain unresolved.
Diplomatic Efforts
Recent high-level diplomatic interactions have facilitated the disengagement along the LAC. Key meetings include:
- India’s National Security Advisor Ajit Doval meeting Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi at the BRICS NSAs meeting in St Petersburg, Russia.
- Anticipation for further disengagement is linked to the upcoming BRICS Summit in October in Kazan, Russia, where leaders from both nations are expected to meet.
Significance of Disengagement
The 31st meeting of the Working Mechanism for Consultation & Coordination on India-China Border Affairs (WMCC) was described as “frank, constructive, and forward-looking.” Participants urged both parties to “narrow down the differences” and “find early resolution of the outstanding issues.” The phrase "narrow down the differences" marks a hopeful shift in the dialogue surrounding the border standoff.
Strategic Importance of Depsang Plains and Demchok
Depsang Plains
The Depsang Plains hold strategic significance due to the following reasons:
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA)’s control threatens India’s position over the Siachen Glacier, potentially encircling the Indian Army between China and Pakistan.
- A coordinated attack from both China and Pakistan would leave India’s military position on the Siachen Glacier vulnerable.
- The Indian Army identifies this region as particularly susceptible to mechanized warfare due to its flat terrain, which also offers direct access to Aksai Chin.
Demchok
Demchok is crucial for several reasons:
- It facilitates effective surveillance of Chinese movements and activities in the Aksai Chin region.
- It supports essential road and communication links that enable rapid military mobilization and logistical support.
Key Areas in the India-China Standoff
Pangong Lake Region
- This area frequently sees patrols from both India and China intersecting.
- The north bank of the lake is divided into eight "fingers," with India claiming territory up to Finger 8 and China disputing it down to Finger 4.
Demchok Region
- Recent reports indicated increased Chinese activity and heavy equipment movement.
Galwan River Basin
- Satellite imagery revealed Chinese tents near the Galwan River basin, suggesting incursions into traditionally held Indian territories.
Gogra Post
- A Chinese military buildup near the Gogra post has escalated tensions.
Daulat Beg Oldie (DBO)
- Chinese encroachments have been reported in the DBO sector, located on the Indian side.
- The DBO airstrip is critical for winter operations and reinforcements, accessible via the 255 km-long Darbuk-Shyok-DBO road.
India-Maldives Defence Talks

- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
- India and the Maldives held their first defence talks since India withdrew its military personnel early this year.
Significance of Talks:
- The dialogue is notable given recent tensions in bilateral relations. Relations soured after President Mohamed Muizzu's election on an "India Out" platform, leading to the withdrawal of Indian troops. The last defence cooperation dialogue was held in March 2023 under President Ibrahim Solih.
Discussion Topics:
-
- Expediting ongoing defence cooperation projects.
- Planning forthcoming bilateral military exercises.
- Enhancing high-level exchanges and capability development.
Context of Tensions:
-
- Mohamed Muizzu, who took office in November 2023, had called for the removal of Indian military personnel, a significant shift from the previous administration’s stance.
- India agreed to withdraw 80 military personnel between March and May 2024. Indian technical personnel now operate key equipment like helicopters and a Dornier aircraft in the Maldives.
Recent Developments:
-
- Maldives Foreign Minister Moosa Zameer visited India in May.
- President Muizzu attended PM Narendra Modi’s swearing-in ceremony in June.
- In August, Indian External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar visited the Maldives to reaffirm bilateral ties.
Historical Defence Cooperation:
-
- India gifted a Dornier aircraft to the Maldives in 2020 and a patrol vessel in 2019.
- India provided a coastal radar system last year and laid the foundation for the 'Ekatha Harbour' project, enhancing Maldivian Coast Guard capabilities.
Ongoing Projects:
-
- Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP) - a $500 million initiative financed by India.
- Building a new Coast Guard base at Uthuru Thilafalhu (UTF) atoll.
- India’s grant for High Impact Community Development Projects (HICDPs).
Strategic Importance:
-
- For Maldives: India is a key security partner and crisis responder, with historical assistance during emergencies (Operation Neer, Vaccine Maitri). Maldives seeks to restore Indian tourist numbers, vital for its economy.
- For India: The Maldives is crucial to India's Neighbourhood First Policy and Vision SAGAR. Its strategic location between major Indian Ocean chokepoints makes it a vital partner for maritime security and countering China's influence.
Recent Changes:
-
- The Muizzu government decided not to renew a 2019 MoU for hydrographic surveying with India, ending joint hydrographic surveys conducted under the pact.
Travel and Trade:
-
- Both countries benefit from an open skies arrangement and visa-free access for tourism, medical, and business purposes
The League of Arab States (LAS)/Arab League
- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Arab League called recently for a UN peacekeeping force in the "occupied Palestinian territories" at an international summit dominated by the war between Israel and Hamas.
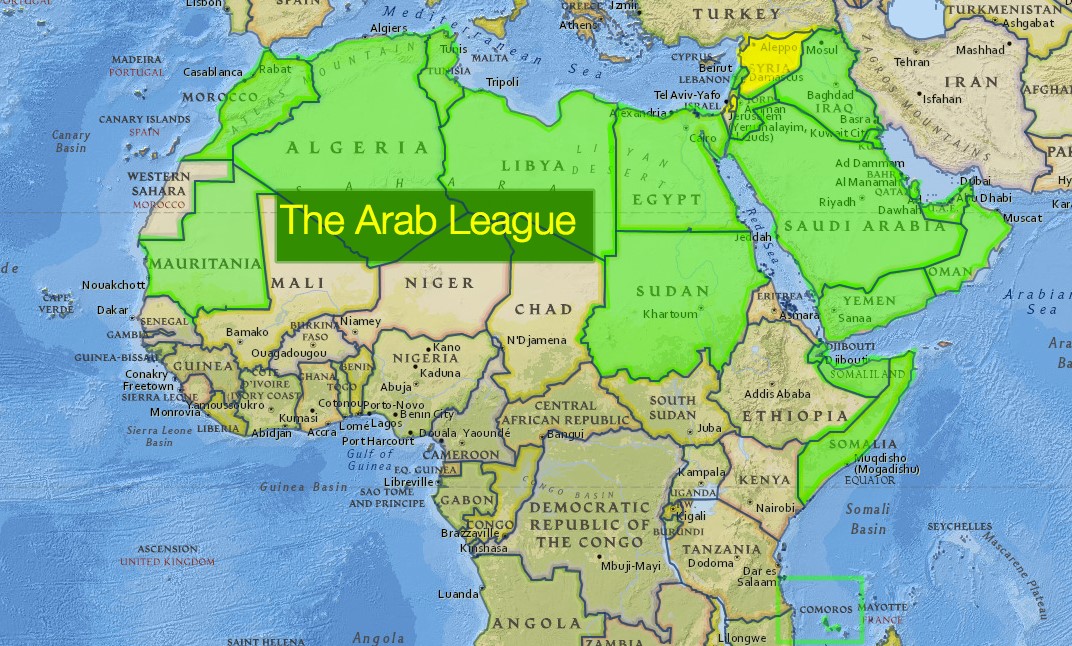
What is the Arab League?
- The League of Arab States was formed in Cairo on 22 March 1945 with six members: Egypt, Iraq, Transjordan (later renamed Jordan), Lebanon, Saudi Arabia and Syria, with Yemen joining on 5 May 1945.
- It currently has 22 member states; Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordon, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
- Four countries have been admitted as observers: Brazil, Eritrea, India and Venezuela.
- Each member state has one vote in the League Council, while decisions are binding only on those states that have voted for them.
- The official language of the Arab League and its 22 member states is Arabic.
- The league seeks to promote the political, social, and military interests of its members.
- The head of the league is known as the secretary-general.
- The secretary-general is appointed to a five-year term by a two-thirds majority of league members.
- Headquarters: Cairo, Egypt.
Goals:
- The overall aim of the league is to promote Arab interests.
- Its main goals are to strengthen and coordinate the political, cultural, economic, and social programs of its members and to try to settle disputes among them or between them and third parties.
- In 1950 the members also agreed to provide military support to help defend each other.
The Arab League Council:
- The League Council is the highest body of the Arab League and is composed of representatives of member states, typically foreign ministers, their representatives, or permanent delegates.
- Each member state has one vote.
- The Council meets twice a year, in March and September. Two or more members may request a special session if they desire.
- The general secretariat manages the daily operations of the league and is headed by the secretary-general.
- The general secretariat is the administrative body of the league, the executive body of the council, and the specialized ministerial councils.
International Criminal Court (ICC)

- 21 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
International Criminal Court (ICC) Chief Prosecutor recently announced that he has applied for arrest warrants against Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Defence Minister Yoav Gallant for crimes against humanity in the ongoing Gaza war.
What is the International Criminal Court (ICC)?
- The International Criminal Court (ICC) in The Hague (Netherlands) is a permanent global court established in 2002.
- The ICC was created as a result of the Rome Statute, a treaty established at a United Nations conference in Italy and signed in 1998 by 120 countries — giving the ICC its power.
- The ICC is independent of the United Nations (UN) but is endorsed by the UN General Assembly.
- It also maintains a cooperation agreement with the UN.
- It has the power to prosecute individuals and leaders for genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes.
- Unlike the International Court of Justice (ICJ), which is an organ of the UN, the ICC does not prosecute states.
The Court does not have universal jurisdiction:
- Its jurisdiction only applies to crimes committed by nationals of States Parties or Non-States Parties that have recognized its jurisdiction through declaration and crimes committed in such States.
- The Court may also exercise its jurisdiction for crimes that have been referred to it by the United Nations Security Council, in accordance with a resolution adopted under Chapter VII of the Charter of the United Nations.
The Court’s jurisdiction is governed by the principle of complementarity:
- It does not relieve States of their primary responsibility and only intervenes when the States have been unable or did not wish, to try crimes under their jurisdiction.
- The Court is not a United Nations body. However, it is part of the international system to fight against impunity and prevent and handle crises.
How is the ICC governed?
- The Rome Statute created three bodies:
- The International Criminal Court
- The Assembly of States Parties
- The Trust Fund for Victims
- The Assembly of States Parties (ASP) is made up of representatives of States Parties.
- It provides general guidelines while respecting the independence of the Court and makes decisions relating to how it operates (in particular by electing judges and the Prosecutor and by approving the ICC’s budget).
- The Trust Fund for Victims was created by the ASP to grant individual reparations to victims by executing reparations orders handed down by the Court.
- It also contributes to their rehabilitation through psychological and physical recovery and material support.
- The Fund has financed projects in Uganda, the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The International Criminal Court is made up of four bodies:
- The Presidency (made up of three judges) is responsible for external relations with States, organizes the Divisions’ judicial work and supervises the administrative work of the Registry;
- The Judicial Divisions – the Pre-Trial Division, the Trial Division and the Appeals Division – carry out judicial proceedings;
- The Office of the Prosecutor carries out preliminary analyses, investigations and prosecutions;
- The Registry carries out non-judicial activities related to safety, interpretation, information and outreach or support to lawyers for the defence and victims.
The recruitment process for judges at the ICC:
- Every three years, the ASP elects six new judges, a third of the 18 ICC judges, for a term of nine years.
- The candidates for the position of judge at the ICC are presented by the States Parties.
- The election of judges is governed by a unique procedure that aims to ensure, insofar as possible, that there is a balanced bench with regard to legal expertise, geographical representation and gender.
How does the International Criminal Court differ from the International Court of Justice?
International Criminal Court:
1. Part of the United Nations (UN)?
Ans. No, The International Criminal Court is independent but co-operates closely with the UN.
2. What is its aim?
Ans. To try individuals who are suspected of the crime of genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity or the crime of aggression.
3. Where is it located?
Ans. The Hague
International Court of Justice:
1. Part of the United Nations (UN)?
Ans. No, The International Court of Justice is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations.
2. What is its aim?
Ans. To settle legal disputes between states,and to advise the UN on legal questions.
3. Where is it located?
Ans. The Hague
Order of the Druk Gyalpo

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently received Bhutan’s highest civilian award, the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’, during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
What is the ‘Order of the Druk Gyalpo’ Award?
- The Order of the Druk Gyalpo, Bhutan's most prestigious civilian award, was recently conferred upon Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his two-day State visit to the neighboring nation.
- As the first foreign Head of Government to receive this esteemed accolade, Prime Minister Modi joins a select group of individuals honored for their exceptional contributions to Bhutanese society, service, integrity, and leadership.
- According to the ranking and precedence established within Bhutan's honor system, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo represents the pinnacle of lifetime achievement, taking precedence over all other orders, decorations, and medals.
- Prime Minister Modi received the award in recognition of his outstanding contributions to strengthening India-Bhutan relations and his dedicated service to the Bhutanese nation and its people.
- Past recipients of the Order of the Druk Gyalpo include:
- Her Majesty The Royal Queen Grandmother Ashi Kesang Choden Wangchuck in 2008
- His Holiness Je Thrizur Tenzin Dendup in 2008, and
- His Holiness Je Khenpo Trulku Ngawang Jigme Choedra in 2018.
- With Prime Minister Modi's recent addition to this esteemed list, the Order of the Druk Gyalpo continues to symbolize Bhutan's appreciation for remarkable individuals who significantly impact the country and its people.
Countries hope to bring BBNJ or High Seas treaty into force by 2025

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Blue Leaders High-Level Event on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction was held in Belgium on March 7, 2024, to urge nations to ratify a new treaty to protect the high seas from pollution, climate change and overfishing.
What is the BBNJ Treaty?
- The BBNJ Treaty, also referred to as the Treaty of the High Seas, is an international agreement aimed at conserving and sustainably managing marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, operating within the framework of the UNCLOS.
- These areas encompass the high seas beyond exclusive economic zones or national waters.
- It represents nearly half of the Earth's surface and is characterized by minimal regulation and understanding of their biodiversity, with only 1% currently under protection.
- Launched at the One Ocean Summit in February 2022, the High Ambition Coalition on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction seeks to unite various delegations involved in BBNJ negotiations toward a comprehensive and ambitious outcome.
- The negotiations focus on key elements agreed upon in 2015, including the conservation and sustainable use of marine genetic resources, area-based management tools such as marine protected areas, environmental impact assessments, and initiatives for capacity-building and technology transfer in marine science and management.
- India is yet to sign the treaty. However, it called on efforts for entry into force and implementation of the treaty at the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration held in September 2023.
The Importance of a Legally Binding Instrument for BBNJ:
- Biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction is crucial for ocean health, coastal communities' welfare, and global sustainability, constituting 95% of the ocean and offering essential ecological, economic, social, cultural, scientific, and food-security benefits.
- Despite their significance, these areas face escalating threats such as pollution, overexploitation, and the impacts of climate change, compounded by the anticipated rise in demand for marine resources in the future.
- Even the deep seafloors, considered one of the most inhospitable habitats, are experiencing the onset of extinction processes, with alarming statistics showing that 62% of assessed mollusc species are threatened, including critically endangered, endangered, and vulnerable species, while the International Seabed Authority permits deep sea mining contracts.
- It is imperative to establish a legally binding framework for managing and regulating biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, as over 60% of this resource in the global seas remains unmanaged and unprotected, necessitating comprehensive conservation measures.
India, and ASEAN discuss the review of the trade agreement

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India hosted the 3rd meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which focused on reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement at Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi from February 16th to 19th, 2024.
About the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- The Framework Agreement laid a sound basis for the establishment of an ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (FTA), which includes FTA in goods, services and investment.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization of ten Southeast Asian countries:
- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN's primary objectives are to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its member states.
- The organization operates on the principles of mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, and consensus-building. ASEAN's motto, "One Vision, One Identity, One Community," underscores its commitment to fostering unity and solidarity among Southeast Asian nations.
- Economically, ASEAN has made significant strides towards integration through initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and production base.
- This has facilitated trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
- Additionally, ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of issues, including security, environmental sustainability, cultural exchange, and disaster management.
