INDIA JOINS THE INTERNATIONAL BIG CAT ALLIANCE (IBCA)
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
India formally joined the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on April 9, 2023, during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- Objective: The IBCA aims to conserve the world's seven big cat species: tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, cheetah, jaguar, and puma, focusing on their protection and natural habitats.
- Founding Members: India joins Nicaragua, Eswatini, and Somalia as founding members of the IBCA, which will collaborate with 24 countries and nine organizations.
- Headquarters: The IBCA will be headquartered in India, facilitating efforts to protect big cats and their ecosystems.
Purpose and Goals of IBCA
- Conservation Focus: The alliance addresses common challenges in the protection of the seven big cats, promoting sustainable resource use and tackling climate change.
- Collaboration and Support: The IBCA will provide a platform for member nations to share knowledge, expertise, and support recovery efforts in potential habitats.
- Mobilization of Resources: The alliance aims to mobilize financial and technical resources for effective conservation strategies based on global experiences.
Background and Evolution
- Inception: PM Modi proposed an international initiative against poaching and illegal wildlife trade in 2019, advocating for collaboration among tiger range countries.
- Extension of Project Tiger: The IBCA serves as an extension of India's long-standing commitment to wildlife protection, initially exemplified by the launch of Project Tiger in 1973.
Big Cat Species Overview
- Tiger (Endangered)
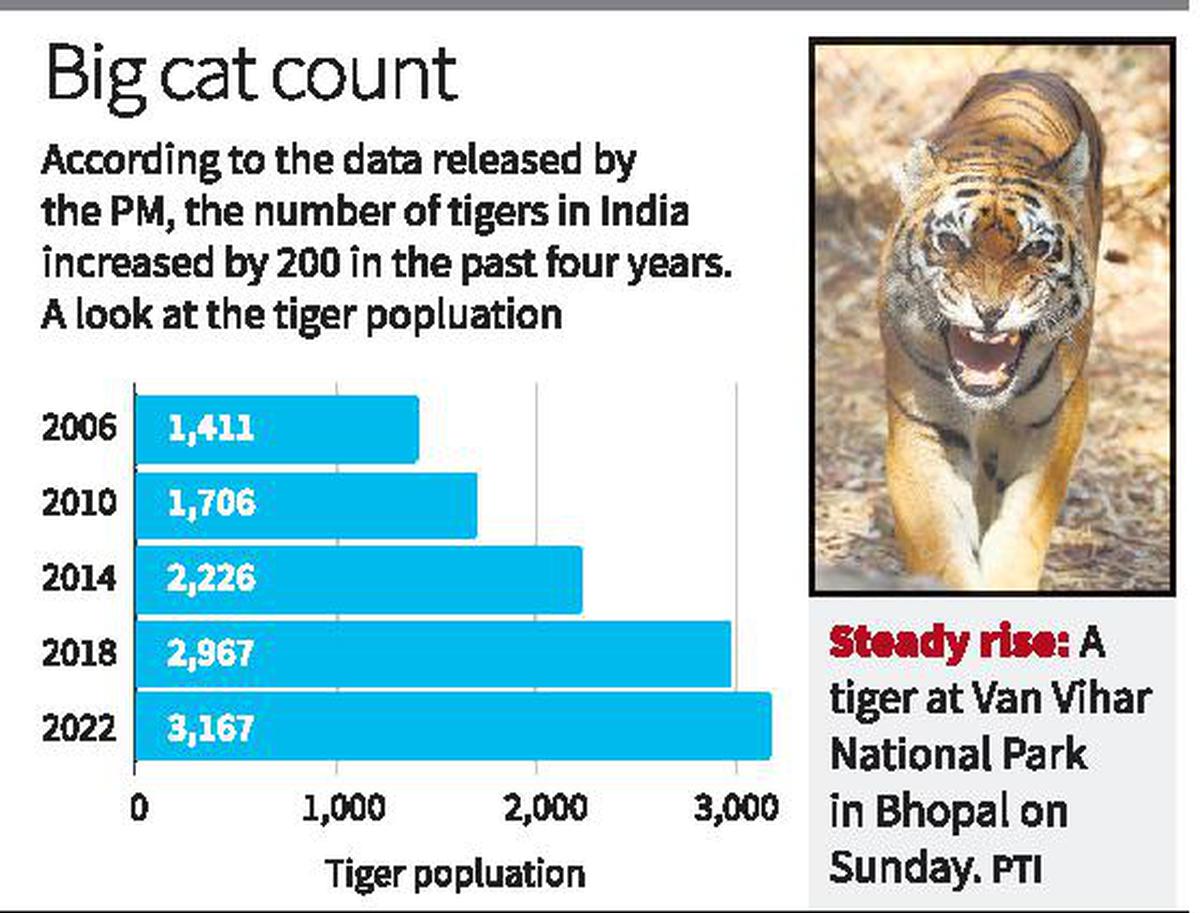
- Population: Approx. 3,167 in India, accounting for over 75% of the global population.
- Threats: Habitat loss, poaching, and climate change impacting their territory.
- Lion (Vulnerable)
- Population: Estimated 700 in India.
- Threats: Habitat reduction and targeted poaching.
- Leopard (Near Threatened)
- Population: Around 13,000 in India, with approximately 250,000 globally.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
- Snow Leopard (Vulnerable)
- Population: 400-700 in India, with global estimates of 4,000-6,500.
- Threats: Poaching, habitat loss, and human disturbances.
- Cheetah (Vulnerable)
- Population: Declined to less than 7,000 globally; declared extinct in India in 1952.
- Threats: Habitat loss, climate change, and illegal trafficking.
- Jaguar (Near Threatened)
- Population: Approximately 173,000 globally, primarily in South America.
- Threats: Deforestation, illegal hunting, and habitat fragmentation.
- Puma (Near Threatened)
- Population: Estimated 50,000, experiencing a decline.
- Threats: Habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict.
Future Initiatives
- Translocation Efforts: Following successful cheetah translocations from Namibia and South Africa, India plans to explore similar initiatives for other big cats.
- Global Cooperation: The IBCA will strengthen conservation efforts by working with a broader network of range countries to combat poaching and promote habitat preservation.
