Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The rising incidence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) across the globe has become a concern for doctors, while early diagnosis is lacking, diagnosis in itself is challenging considering that other conditions could mimic IBD.
What is IBD?
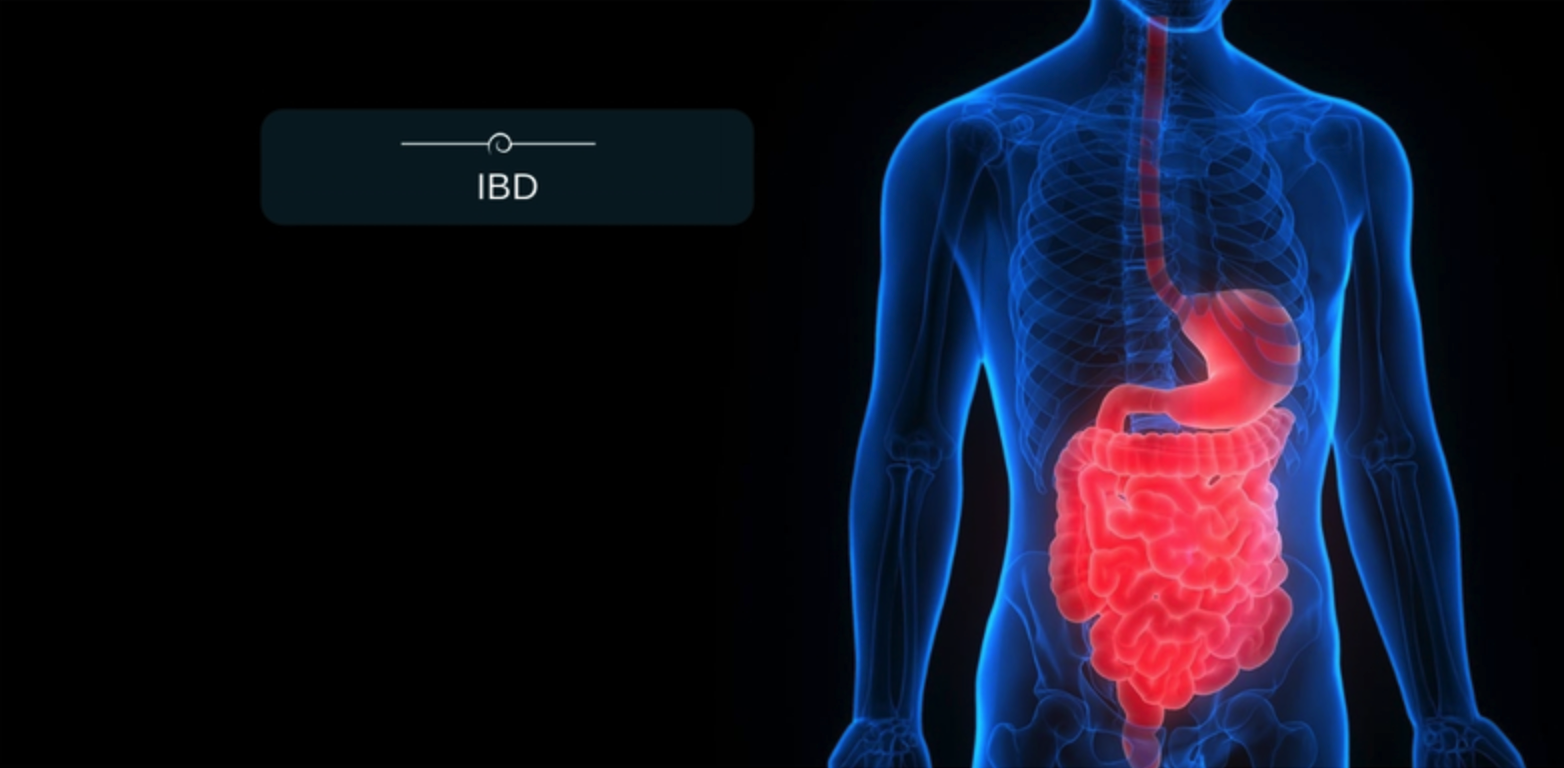
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a recurring and long-term (chronic) condition that affects the digestive tract.
- IBD causes inflammation of the stomach, small intestine, and colon.
- IBD is a progressive disease that can become worse over time and cause other damage if not properly diagnosed and treated.
- There are two types of IBD: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s disease: leads to inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, however, it commonly affects the end of the small intestine (the ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (the right colon).
- Crohn’s disease can also affect the entire thickness or alternating areas of the bowel wall.
- Ulcerative colitis: causes inflammation in the large intestine or colon.
- This form of IBD inflames the innermost lining of the colon and creates tiny open sores (ulcers).
- Crohn’s disease: leads to inflammation anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, however, it commonly affects the end of the small intestine (the ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (the right colon).
What causes IBD?
- The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but IBD is the result of a weakened immune system. Possible causes are:
- The immune system responds incorrectly to environmental triggers, such as a virus or bacteria, which causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- There also appears to be a genetic component.
- Someone with a family history of IBD is more likely to develop this inappropriate immune response.
Symptoms of IBD:
- Although Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are different conditions, IBD conditions have similar symptoms, such as:
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Rectal bleeding
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
How Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treated?
- While there is no curative treatment for IBD, it is managed through medication, dietary changes, and occasionally surgery.
- The treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, mitigate complications, prevent future flare-ups, and potentially promote the healing of inflamed intestines.
