PM Young Achievers’ Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM YASASVI)

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
With a vision of "Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas", the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has implemented the PM Young Achievers Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM-YASASVI).
- Objective of PM-YASASVI:
- The scheme aims to provide financial support and educational opportunities to students from Other Backward Classes (OBC), Economically Backward Classes (EBC), and Denotified Tribes (DNT).
- The goal is to help these students overcome financial barriers and pursue quality education, fostering a more inclusive and equitable society.
- Consolidation of Earlier Schemes:
- PM-YASASVI integrates multiple previous scholarship schemes:
- Dr. Ambedkar Post-Matric Scholarship for EBCs.
- Dr. Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs.
- This consolidation aims to streamline the process and increase the impact on vulnerable groups.
- Key Components of the Scheme:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: For students in Class 9-10 with annual family income below ?2.5 lakh. Provides ?4,000 annually.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: For students pursuing higher education, with academic allowances ranging from ?5,000 to ?20,000 based on course type.
- Top Class School Education: For meritorious students, offering ?1.25 lakh annually for students from OBC, EBC, and DNT categories in Classes 9-12.
- Top Class College Education: Covers tuition, living expenses, and educational materials for students in top institutions.
- Construction of Hostels for OBC Boys and Girls: Provides hostel facilities to socially and educationally backward students near government institutions.
- Scope and Financial Allocation (2023-24):
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: ?32.44 crore allocated to states and UTs for the year 2023-24, benefiting 19.86 lakh students.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: ?387.27 crore allocated for the year, benefiting 27.97 lakh students.
- Top Class School Education: ?6.55 crore for 2,602 students.
- Top Class College Education: ?111.18 crore for 4,762 students.
- Hostel Construction: ?14.30 crore allocated for the construction of hostels, accommodating 1,146 students.
- Key Benefits:
- Financial Assistance: Reduces the financial burden on students from marginalized communities, enabling them to continue their education without financial stress.
- Inclusive Education: Supports students from disadvantaged backgrounds, ensuring that they can access quality education from school through to higher education.
- Promotion of Merit: Focuses on meritorious students, ensuring that academic excellence is supported at all levels, from school to top-class institutions.
- Selection Process:
- The YASASVI Entrance Test (YET) is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) for candidate selection under the scheme.
- Eligible students must appear for this test, and the results determine scholarship awards.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- The scheme is open to OBC, EBC, and DNT students with a family income not exceeding ?2.5 lakh annually.
- Additional specific eligibility criteria may apply for different scholarships under the scheme.
- Application Process:
- Interested students can apply for scholarships via the National Scholarship Portal (scholarships.gov.in), which is the official platform for application submission.
National Water Awards 2023

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
The Hon’ble President of India Smt. Droupadi Murmu will confer the 5th National Water Awards 2023 on October 22nd 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi.
Organizing Body:
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Department: Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR)
- Purpose: To recognize and honor individuals, organizations, and bodies that have made significant contributions to water conservation and management.
Award Categories
- Best State
- Best District
- Best Village Panchayat
- Best Urban Local Body
- Best School or College
- Best Industry
- Best Water User Association
- Best Institution (other than school or college)
- Best Civil Society Organization
Winners
- Best State:
- 1st Prize: Odisha
- 2nd Prize: Uttar Pradesh
- 3rd Prize (joint): Gujarat & Puducherry
- Other Awards: Winners in the remaining categories have been recognized, with citations, trophies, and cash prizes provided in certain categories.
Objectives of the National Water Awards
- Promote Water Conservation: Raise awareness about the importance of water and encourage effective water usage practices.
- Recognize Efforts: Celebrate the work of individuals, institutions, and organizations contributing to the government’s vision of a ‘Jal Samridh Bharat’ (Water-rich India).
- National Campaign: Under the guidance of Hon’ble Prime Minister, the Ministry of Jal Shakti has been working to spread awareness on water management and conservation through extensive national campaigns.
History and Background
- The National Water Awards (NWAs) were launched in 2018 by the DoWR, RD & GR to foster awareness and action on water-related issues.
- Awards were given for 2019, 2020, and 2022, but there were no awards in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The awards aim to inspire best practices in water usage, conservation, and management across India, involving government bodies, industries, communities, and civil society.
Significance
- The National Water Awards serve as a platform to recognize the innovative initiatives taken by various stakeholders in addressing water challenges.
The awards contribute to furthering the government’s mission of achieving sustainable water management practices across the nation.
Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto.
About Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC):
- The Indian Historical Records Committee (IHRC) is a national forum established in 1919, comprising creators, custodians, and users of records.
- Its primary purpose is to advise the Government of India on matters related to record management and their utilization for historical research.
Secretariat:
- The National Archives of India, New Delhi, serves as the Secretariat for the IHRC, formerly known as the Indian Historical Records Committee since 1911.
Leadership and Membership:
- Led by the Union Minister of Culture, the IHRC consists of 134 members, including government agencies, government-appointed nominees, representatives from State/UT Archives, universities, and learning institutions.
- Over the years, the IHRC has convened 62 sessions.
Committee Structure: The IHRC operates with two adjunct bodies:
- Editorial Committee: Responsible for reviewing and approving papers based on archival sources for presentation at committee sessions.
- Standing Committee: Tasked with reviewing the implementation of committee recommendations and providing input on meeting agendas.
- The Secretary of the Ministry of Culture chairs the Standing Committee of IHRC.
- The Indian Historical Records Commission (IHRC) has adopted a new logo and motto recently.
- The logo signifies the theme and uniqueness of IHRC entirely.
- The pages in the shape of lotus petals represent IHRC as the resilient nodal institution for maintaining historical records.
- The Sarnath pillar in the middle represents India's glorious past.
- Brown as the colour theme reinforces the organization's mission of preserving, studying, and honouring India's historical records.
- The motto translates as "Where history is preserved for the future."
- The IHRC plays a vital role in identifying, collecting, cataloging, and maintaining historical documents, manuscripts other sources of historical information.
- By doing so the Commission ensures that valuable historical knowledge is conserved for future generations.
- The motto, therefore, reflects the Commission's commitment to ensuring the safeguarding of historical documents and making these accessible for the benefit of present and future generations.
Panchayat Development Index (PIB)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of State for Panchayati Raj recently informed Lok Sabha about the Panchayat Development Index.
About the Panchayat Development Index:
- The Panchayat Development Index serves as a comprehensive and versatile metric designed to actively evaluate the holistic advancement, efficacy, and ongoing progress of panchayats.
- This index actively considers a spectrum of socio-economic indicators and parameters, offering an actively nuanced understanding of the well-being and developmental status of local communities within the panchayat's jurisdiction.
- Objectives: The primary objective is to actively play a pivotal role in assessing performance and progress towards actively achieving Sustainable Development Goals at the grassroots level.
- An active component of this initiative is the Local Indicators Framework, which encompasses nine key themes for actively localising Sustainable Development Goals.
- These themes actively encompass creating poverty-free and thriving livelihoods, ensuring health and actively child-friendly environments, actively promoting water sufficiency, actively fostering clean and green spaces, actively developing self-sufficient infrastructure, actively establishing socially just and secure communities, actively promoting good governance, and actively creating women-friendly villages.
How Ranking Works?
- Ranks within the index are actively assigned based on scores, actively categorising panchayats into four grades.
- Those actively scoring below 40 percent are actively classified as Grade D,
- 40-60 percent as Grade C,
- 60-75 percent as Grade B
- 75-90 percent as Category A
- and those actively surpassing 90 percent are actively designated as A+.
- Significance of this Index: The significance of this index lies in its ability to actively offer valuable insights into areas requiring attention and improvement within rural areas under panchayat jurisdiction.
- It actively aids in identifying disparities, gauging the achievement of development goals, and actively crafting targeted policies and interventions to elevate the overall well-being and quality of life in rural communities.
Scientists uncover seismic clues in Kopili Fault zone, advancing earthquake preparedness (PIB)
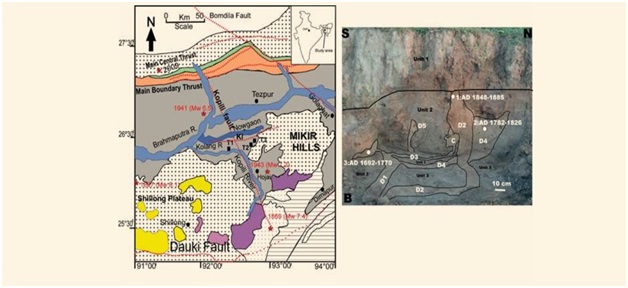
- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have detected seismogenic liquefaction characteristics within the dynamically active Kopili Fault (KF) zone.
About Kopili Fault Zone:
- The Kopili Fault extends from the western part of Manipur up to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- It covers a distance of about 400 km and is closer to the Himalayan Frontal Thrust.
- The Kopili fault bisects the Meghalaya Plateau and isolates the Mishmi block from the main part of the plateau.
- The Kopili fault is almost passing through the Kopili River.
- The river Kopili rises in the North Cachar Hills District in Borail Range at an altitude of 1525 meters.
- From a field study, it is observed that the Kopili Fault region is moving in the northeast direction at an average velocity of 28.397N mm/yr and 40.227E mm/yr.
- This region is characterized by heightened seismic activity, classified within the most critical Seismic Hazard Zone V.
- The geological dynamics are attributed to collisional tectonics, where the Indian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- The fault itself is a transpressional fracture, producing dextral strike-slip earthquakes in the lower crust.
- The Kopili fault zone, a tectonic depression filled by the alluvium of the Kopili River and its tributaries, has experienced numerous seismic events, notable among them being the 1869 earthquake (magnitude 7.8) and the 1943 earthquake (magnitude 7.3).
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) (PIB)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) has recently praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
About Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):
- The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body created by WHO and FAO of the United Nations with 188 member countries.
- It is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular session once a year alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO with all work subject to approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organizations.
- The Commission works in the six UN official languages.
- India has been a member of this commission since 1964.
- The 46th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was held from 27 November to 2 December (2023) in Rome, Italy.
- In the current session, India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millet, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet, and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
Kati Bihu (PIB)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Prime Minister, Narendra Modi recently extended best wishes on the auspicious occasion of KatiBihu to the people of Assam.
About Kati Bihu:
- Kati Bihu is an annual celebration observed in the state of Assam, signifying the relocation of rice saplings.
- The term "Kati" translates to cutting, representing the agricultural activity during this period.
- Also known as Kongali Bihu, with "Kongali" connoting a state of poverty, the festival holds cultural significance in Assam alongside two other Bihu festivals—Bhogali or Magh Bihu in January and Rongali or Bohag Bihu in April.
Significance:
- In this month, food resources are scarce, prompting people to celebrate by illuminating their homes with earthen lamps or candles.
- Lighting lamps near the Tulsi plant are a central aspect of the festival, signifying devotion and auspiciousness.
- People light a special lamp known as "Akash Banti" (Sky candle) in their paddy fields. Fueled by mustard oil, these lamps are elevated on bamboo poles.
- The belief prevails that the illuminated lamps guide the spirits of ancestors toward their heavenly abode.
Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” Portal Launched (PIB)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Development of the North-East Region virtually launched the “MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” portal at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi recently.
About Poorvottar Sampark Setu Portal:
- The Poorvottar Sampark Setu portal is a robust tool designed to streamline and improve the monitoring of Union Ministers' fortnightly visits to the North Eastern Region (NER)
Key features include:
- Insightful Dashboard: The portal offers a comprehensive dashboard presenting valuable insights and graphical information on state-wise/district-wise visits to NER by Union Ministers, serving as a centralized resource for stakeholders.
- Curated Minister List: It generates a curated list of Ministers eligible for nomination for visits to NER in the upcoming months, facilitating efficient planning.
- Online Tour Reporting: After their visit, Ministers can conveniently submit tour reports and recommendations online, streamlining the reporting process.
- Recommendation Analysis: MDoNER (Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region) can analyze and forward the received recommendations to respective line Ministries, Departments, and State Governments for prompt action.
- Summary Report Generation: The portal offers a one-click summary report generation feature, simplifying the overview of visits for effective decision-making.
What is the MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard?
- The MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard is a comprehensive platform integrating data from 112 schemes across 55 Departments and Ministries.
Its key benefits include:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Empowers stakeholders with data-driven insights for informed decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines operations, ensuring a seamless and efficient workflow.
- Centralized Monitoring: Provides a centralized hub for monitoring diverse schemes and initiatives.
- Policy-Level Decision Tool: Functions as a valuable tool for crafting policies based on robust data analysis.
- Information Integration: Integrates information seamlessly, fostering coherence and accessibility.
- Focused Monitoring: Keeps a vigilant eye on NER Aspirational districts, North East border districts, and the most backward districts in NER for targeted interventions.
INS Sumedha Visits Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (PIB)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Naval Ship INS Sumedha recently made a port visit at Lagos, Nigeria as part of its deployment to the Gulf of Guinea (GoG).
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is the third vessel among the indigenously crafted Saryu-class Naval Offshore Patrol Vessels (NOPV).
- Constructed and designed domestically, Goa Shipyard Limited played a pivotal role in the indigenous creation of INS Sumedha.
- The vessel officially joined the Indian Navy's fleet on March 7, 2014.
- Operational Base: A key asset of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet, INS Sumedha operates from its base in Visakhapatnam.
- Primary Functions: The vessel is tasked with a diverse range of functions, including EEZ surveillance, anti-piracy patrols, fleet support operations, maritime security provision to offshore assets, and execution of escort operations for high-value assets.
- Features:
- With a displacement of 2,230 tonnes, INS Sumedha boasts dimensions of 105 meters in length and 12.9 meters in beam.
- Equipped with a cutting-edge weapon and sensor package, the vessel ensures enhanced operational capabilities.
- Designed to carry an Advanced Light Combat Helicopter onboard, adding to its versatility in maritime operations.
- Powered by two of the largest diesel engines deployed in the Indian Navy, INS Sumedha attains a top speed of 25 knots.
- Featuring a remarkable range of 6,000 nautical miles (11,000 km) at 16 knots (30 km/h), the offshore patrol vessel is well-suited for prolonged missions and operations.
About the Gulf of Guinea:
- Location: Situated as the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Guinea is positioned off the western coast of the African continent.
- The Gulf lies at the confluence of the Prime Meridian and the Equator, specifically at 0°0’N and 0°0'E.
- Extent and Coastline: Encompassing an area of 2.3 million square kilometres, the Gulf features an extensive coastline stretching approximately 6,000 kilometres.
- Characterized by a narrow continental shelf, it boasts a distinctive coastal landscape.
- Oceanic Conditions: The Gulf of Guinea experiences warm tropical waters characterized by relatively low salinity, influenced by the inflow of rivers and high regional rainfall.
- Notable tributaries include the Volta and Niger rivers.
- Coastal Countries: 16 countries border the Gulf of Guinea, including Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Cote d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Republic of Congo, Guinea, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Gabon, Nigeria, Ghana, São Tomé and Principe, Togo, and Sierra Leone.
- Topography: The coastal region is predominantly low-lying, featuring mangrove swamps, marshes, and lagoons.
- Geological Significance: The Gulf's coastline bears a striking resemblance to the continental margin of South America, affirming the theory of continental drift.
- Holding over 35% of the world’s petroleum reserves, the Gulf of Guinea is a significant global repository of petroleum.
- Security Challenges: Regrettably, the Gulf of Guinea has gained notoriety as one of the world’s most perilous gulfs due to widespread piracy, significantly impacting West African countries and attracting international concern.
INS Beas to Be Upgraded (PIB)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Defence signed a contract on October 16, 2023, in New Delhi for the life Upgrade and Re-Powering of "INS Beas" with Kochi-based M/S Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) at an overall cost of Rs. 313.42 Cr.
Context:
- The INS Beas is gaining attention as the first Brahmaputra Class Frigate to undergo a transition from steam to diesel propulsion.
- The completion of its Mid-Life Upgrade and Re-Powering in 2026 is expected to result in the INS Beas joining the active fleet of the Indian Navy, equipped with a modernized weapon suite and upgraded combat capabilities.
About INS Beas:
- INS Beas (F37) stands as a Brahmaputra-class frigate within the Indian Navy, constructed at the Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE) in Kolkata.
- Commissioned on July 11, 2005, it is the second ship in the Indian Navy to carry this name, with the first being a Leopard-class frigate commissioned in 1960 and decommissioned in 1992.
- Role: Functioning as a versatile warship, INS Beas is proficient in various missions, encompassing anti-aircraft, anti-submarine, and anti-ship warfare.
- Additionally, it plays a crucial role in patrolling, surveillance, and safeguarding India's maritime interests.
- Features: The ship's design and construction are wholly Indian, derived from the modification of the Godavari-class frigate.
- With a displacement of about 3,850 tonnes, INS Beas boasts a length of 126 meters (413 feet) and a beam width of 14.5 meters (48 feet).
- Propulsion: Powered by 2 steam turbines, INS Beas demonstrates remarkable agility, capable of reaching speeds exceeding 30 knots during naval operations.
- Technology: Equipped with modern sensor suites and matching weapon systems, the ship embodies cutting-edge technology to enhance its operational capabilities.
Cabinet Approves Establishment of an Autonomous Body Mera Yuva Bharat (PIB)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, has approved the establishment of an autonomous body Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat).
About Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat):
- Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat), an autonomous body will benefit the youth in the age group of 15-29 years, in line with the definition of ‘Youth’ in the National Youth Policy.
- In the case of programme components specifically meant for adolescents, the beneficiaries will be in the age group of 10-19 years.
- It will help in Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and to make the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- It will be launched on 31st October 2023 on National Unity Day.
Objective:
- The primary objective of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) is to make it a whole of Government platform for youth development.
- With access to resources & connection to opportunities, youth would become community change agents and nation builders allowing them to act as the Yuva Setu between the Government and the citizens.
- It seeks to harness the immense youth energy for nation-building.
The establishment of Mera Yuva Bharat (MY Bharat) would lead to:
- Leadership Development in the Youth:
- Improve leadership skills through experiential learning by shifting from isolated physical interaction to programmatic skills.
- Investing more in youth to make them social innovators, and leaders in the communities.
- Setting the focus of the Government on youth-led development and making the Youth “active drivers” of development and not merely “passive recipients”.
- Better alignment between youth aspirations and community needs.
- Enhanced efficiency through Convergence of existing programmes.
- Act as a one-stop shop for young people and Ministries.
- Create a centralized youth database.
- Improved two-way communication to connect youth government initiatives and activities of other stakeholders that engage with youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem.
Why There is a Need for Such Initiative?
- India’s youth are to play a critical role in defining the future of the nation.
- There is a need to establish a new contemporary technology-led platform for the Government to engage with the present-day youth.
- Ensuring accessibility by creating a digital ecosystem
- Mera Yuva Bharat supported by a technology platform would help to increase the Youth outreach efforts of the Department of Youth Affairs.
SUGAM REC Mobile App for 54EC Bonds Investors (PIB)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, REC Limited, the Maharatna Central Public Sector Enterprise launched a SUGAM REC mobile application.
What is the SUGAM REC App?
- The SUGAM REC App caters exclusively to current and prospective investors in REC's 54EC Capital Gain Tax Exemption Bonds.
- Users can conveniently download e-bond certificates, apply for new investments, access essential forms for KYC updates, and connect with REC's Investor Cell through call, email, or WhatsApp.
What are 54EC Bonds?
- Also known as Capital Gain Bonds, these fixed-income instruments offer capital gains tax exemption under section 54EC.
- Investors can save on income tax for long-term capital gains by investing in these bonds within six months of the gain.
- With a fixed lock-in period of 5 years, the bonds can be held in either Physical or Demat form.
- Issued by government-managed institutions, they fund specific capital projects and derive their name from the relevant section of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Key Facts about REC Limited:
- A 'Maharatna' company under the Ministry of Power, Government of India.
- Registered with RBI as a non-banking finance company (NBFC), Public Financial Institution (PFI), and Infrastructure Financing Company (IFC).
- Established in 1969 to address severe drought and famine, focusing on energizing agricultural pump sets for irrigation and reducing reliance on monsoons.
- Provides long-term loans and financing products to State, Centre, and Private Companies for infrastructure asset creation.
- It is the nodal agency for initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (SAUBHAGAYA), Deen Dayal Upadhaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY), and National Electricity Fund (NEF) Scheme.
Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) (PIB)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, GoI is organizing the 19th Working Party on Data Collection and Statistics (WPDCS19) of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) from 28th November to 2nd December 2023.
About the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission:
- The Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for the management of tuna and tuna-like species in the Indian Ocean.
- It works to achieve this by promoting cooperation among its Contracting Parties (Members) and Cooperating Non-Contracting Parties in order to ensure the conservation and appropriate utilisation of fish stocks and encouraging the sustainable development of fisheries.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations adopted the Agreement for the Establishment of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission during its 105th Session in Rome on 25 November 1993.
- The Indian Ocean holds the position as the second-largest tuna fishery globally, making it a crucial focus for the IOTC.
- Currently, the IOTC boasts 31 contracting parties, including countries and two cooperating non-contracting parties, Liberia and Senegal.
- Membership is open to Indian Ocean coastal countries, countries or regional economic integration organizations that are UN members, countries that are members of UN special organizations, and countries involved in tuna fishing in the Indian Ocean.
- India is an active member of the IOTC, with its headquarters located in Victoria, Seychelles.
