Makaravilakku festival

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Kerala police deploy 5,000 personnel at Sabarimala ahead of Makaravilakku festival.
Key Highlights:
- Makaravilakku is a prominent annual Hindu festival held at the Sabarimala Temple in Kerala, dedicated to Lord Ayyappa.
- It marks the celestial event of the Sun entering Capricorn (Makaram Rashi) on Makara Sankranti.
- The festival is a culmination of the 41-day pilgrimage to Sabarimala, celebrated with devotion, discipline, and spiritual purification.
- Sabarimala is one of the largest pilgrimage sites globally, drawing 10-15 million devotees annually.
Location:
- The Sabarimala Temple is located on the Sabarimala hill in Pathanamthitta, Kerala, within the Periyar Tiger Reserve.
- It is surrounded by 18 hills and is located along the banks of the Pamba River.
Key Rituals:
- 41-Day Pilgrimage (Vratham): Devotees observe strict practices like celibacy, fasting, and wearing black or saffron attire to purify the body and soul.
- Makaravilakku (Makara Jyothi): A celestial light appears on Makara Sankranti, believed to be a divine manifestation of Lord Ayyappa.
- Thiruvabharanam Procession: On Makaravilakku day, sacred royal ornaments (Thiruvabharanam) are carried in a procession from the Pandalam Palace to the temple.
- Aarti at Ponnambalamedu: The Makaravilakku light is believed to emanate from camphor lit during the Aarti ritual at Ponnambalamedu, viewed three times from Sabarimala.
Festival Duration:
- The Makaravilakku festival lasts for seven days, starting on Makara Sankranti and concluding with the Guruthi offering, which propitiates the gods of the wilderness.
Significance of Makaravilakku:
- The festival symbolizes the merging of celestial and spiritual energies, highlighting devotion, purity, and self-discipline.
- Devotees chant the mantra "Swamiye Saranam Ayyappa," seeking blessings and protection from Lord Ayyappa.
- The event promotes equality, as all devotees wear simple black or blue attire and carry the sacred bundle, “Irumudi Kettu.”
Cultural and Religious Aspects:
- The festival is an important cultural and religious observance for millions of Hindus.
- Though previously believed to be a supernatural event, Makaravilakku now involves a ritual performed by the Malayaraya tribe, overseen by the Travancore Devaswom Board.
Prohibition on Women:
- The temple traditionally restricts women aged 10-50 from entering. This was challenged in 2018 when the Supreme Court ruled to lift the prohibition, although it remains a contentious issue.
National Youth Day 2025

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 12, 2025, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated in the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2025, an event aimed at empowering India's youth and charting a roadmap for the nation's development. This occasion also coincided with the celebration of National Youth Day, marking the 163rd birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda, a renowned spiritual leader and social reformer who strongly believed in the transformative potential of India's youth.
Significance of National Youth Day
- Purpose:
- National Youth Day is celebrated to honor Swami Vivekananda's contributions, emphasizing the role of youth in nation-building.
- It promotes empowerment, leadership, and innovation among the youth.
- Year of First Celebration: 1985
- Key Theme (2025): "Arise, Awake, and Realize the Power You Hold"
Key Highlights from the Dialogue
- Goal of the Dialogue:
- Engaging youth in the decision-making process for a developed India by 2047.
- Empowering youth through platforms like quizzes, essay competitions, and thematic presentations.
- Ten Key Themes Discussed:
- Technology & Innovation
- Sustainability
- Women Empowerment
- Manufacturing & Agriculture
- Education and Skill Development
India’s Roadmap for 2047 (Viksit Bharat)
- Vision:
- Economic Power: India is moving toward becoming the third-largest economy.
- Strategic and Cultural Strength: India will have a robust economic, strategic, social, and cultural framework.
- Youth's Role: Innovation in technology, digital economy, space, and manufacturing will drive India’s growth.
- Key Projects and Targets:
- Target: Generating 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030.
- Net Zero Emissions for Railways: Set for 2030.
- Olympics: India aims to host the Olympics in the next decade.
- Space Power: Plans for a space station by 2035.
Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Challenge
- Objective:
- Engage youth in shaping ideas for a developed India.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is part of the Viksit Bharat Challenge.
- Stages of the Challenge:
- Viksit Bharat Quiz: Participation by 30 lakh youth.
- Essay Writing: Over 2 lakh essays on key developmental themes.
- State Rounds: Rigorous in-person competition to identify the top young leaders.
- Participant Categories:
- 1,500 from Viksit Bharat Challenge Track.
- 1,000 from Traditional Track (cultural and science innovation).
- 500 Pathbreakers (leaders in diverse sectors).
Achievements Under Government Benefiting Youth
- Educational Reforms:
- Increase in IITs, IIITs, IIMs, and AIIMS.
- Growth in the number of higher education institutions and their global rankings.
- Economic Growth:
- India's economy has grown to nearly $4 trillion.
- Infrastructure Investments: More than ?11 lakh crore allocated for infrastructure development.
- Employment Opportunities for Youth:
- Mudra Loans: ?23 lakh crore distributed to youth entrepreneurs.
- Startup Ecosystem: India is among the top three in global startups.
- PM Gati Shakti Mission: Facilitating logistics and infrastructure development, creating employment opportunities.
Future Outlook
- Youth as the Future Leaders of India:
- India’s Youth Power: Vital to achieving a developed nation by 2047.
- The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue is a platform for youth to voice their opinions and engage with policymakers.
- Role of Youth in India’s Transformation:
- Collective Responsibility: Every citizen's effort is essential for national goals.
- The vision of a Viksit Bharat hinges on the innovative contributions and ownership by young minds.
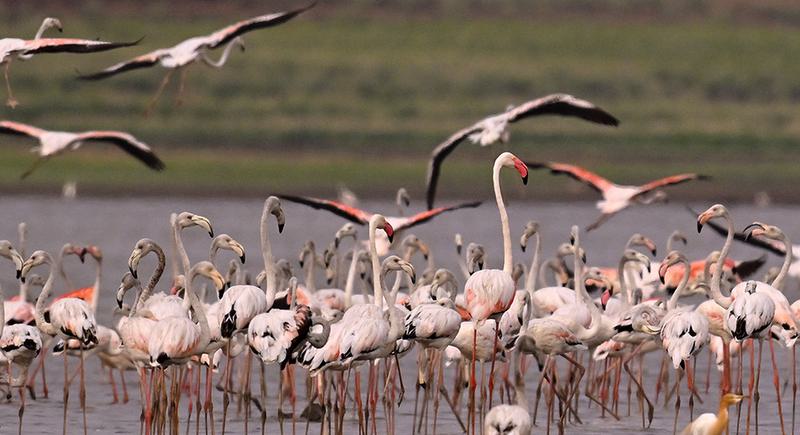
Flamingo Festival 2025

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
The Flamingo Festival 2025 took place at Sullurpeta, in Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. It celebrates the arrival of migratory birds, with a focus on flamingos, to the region's key bird habitats, including Pulicat Lake and Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary.
Key Highlights:
- Birdwatching: Over 200 bird species, including flamingos, are expected to flock to the region during this festival.
- Locations: The event spans across five locations:
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary
- B.V. Palem (Pulicat Lake)
- Atakanithippa
- Sri City
- Sullurpeta (site for cultural programs and stalls)
- Collaborations: In association with organizations like the Bombay Natural History Society.
- Focus on Local Community: Local residents of the eco-sensitive zone will be prioritized and supported.
Key Facts on Local Wildlife and Significance:
- Pulicat Lake:
- Location: On the Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu border, with 96% of the lake in Andhra Pradesh.
- Significance: The second-largest brackish water lake in India (after Chilika Lake in Odisha).
- Biodiversity: Critical habitat for migratory birds, including flamingos, and home to diverse flora and fauna.
- Economic Importance: Supports local fisheries and provides livelihood to nearby communities.
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: 20 km north of Pulicat Lake.
- Ecological Role: Largest breeding site in Southeast Asia for spot-billed pelicans.
- Biodiversity: 189 bird species, including painted storks and glossy ibises.
- Flora and Fauna: Features Barringtonia swamp forests and southern dry evergreen scrub, critical for biodiversity conservation.
- Symbiotic Relationship with Locals: Guano (bird droppings) from pelicans serves as a natural fertilizer for local agriculture, benefiting the farmers.
Flamingo Facts:
- Species: India hosts two flamingo species:
- Greater Flamingo (larger size, pale pink)
- Lesser Flamingo (smaller size, bright pink)
- Behavior: Nomadic and social birds, found in large flocks.
- Coloration: Flamingos' pink color comes from carotenoids in their diet, which are broken down and absorbed into their bodies.
Environmental & Economic Impact: The festival, apart from being a celebration of migratory birds, plays a vital role in:
- Eco-tourism development
- Biodiversity conservation
Local community engagement by highlighting sustainable tourism practices and supporting local livelihoods through eco-friendly initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
Toda Tribe

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional Modhweth festival marking the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- Celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- Held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and bountiful harvest.
- Participants perform a traditional dance outside the temple.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- Women are not part of the celebrations as per traditional customs.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- A pastoral tribe native to the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but stands out for its uniqueness among Dravidian languages.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve.
- Their territory is also recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices are based on a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as central deities.
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR)
- About:
- Established in 1986 as India’s first Biosphere Reserve.
- Located across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- India’s first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Tribal Groups in NBR:
- Home to several groups such as Adiyan, Aranadan, Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman, and Kurumbas.
- Ecological Significance:
- Represents the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones.
- Fauna:
- Home to species like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant, Nilgiri danio (freshwater fish), and Nilgiri barbare.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park, and Silent Valley.
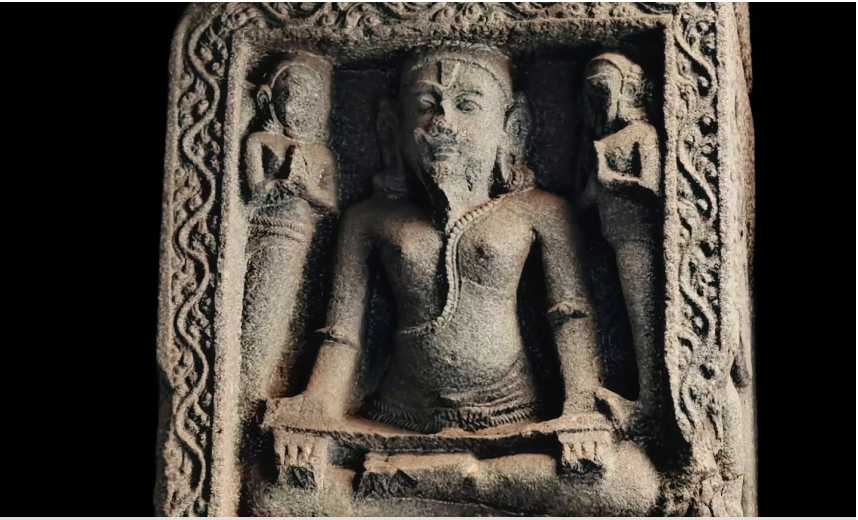
Saint Narahari Tirtha

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a remarkable discovery, a member of the Team of Research on Culture and Heritage (TORCH) has hit upon a three-foot idol of the 13th Century saint, Narahari T?rtha recently.
Key Highlights:
Birth and Early Life:
- Born circa 1243 CE in Chikakolu (modern-day Srikakulam, Andhra Pradesh).
- Hailing from an aristocratic family in the Gajapati Empire of Odisha.
Philosophical Influence:
- A prominent disciple of Madhvacharya, the founder of Dvaita philosophy (dualism).
- Narahari Tirtha played a key role in propagating Madhva's Vaishnavism in Eastern India, particularly in the Kalinga region (modern-day Odisha and Andhra Pradesh).
Role in Eastern Ganga Dynasty:
- Served as a minister in the Eastern Ganga Dynasty for over 30 years.
- Guided kings to align their governance with Sanatana Dharma and reformed temple administration.
- His contributions are documented in inscriptions at the Simhachalam and Srikurmam temples.
Religious and Cultural Contributions:
- Played a key role in spreading Vaishnavism and Dvaita philosophy.
- First to compose Devaranamas in Kannada, marking a significant cultural contribution.
- Contributed to the development of Yakshagana Bayalata (a dance-drama) and the classical dance form that evolved into Kuchipudi.
Writings and Intellectual Legacy:
- Authored 15 works, with two surviving texts: Gita Bhasya and Bhavaprakasika.
- His teachings and writings significantly impacted the Madhva tradition and regional literature.
Discovery of the Idol:
- A three-foot idol of Narahari Tirtha was discovered at Simhachalam Temple in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
- The idol depicts Narahari Tirtha holding a script on palm leaves, flanked by devotees.
Contributions to Temple and Education:
- Transformed the Simhachalam Temple into a renowned center for Vaishnavism.
- Played a crucial role in safeguarding sacred idols like Moolarama and Moola Sita for Madhvacharya.
Cultural and Artistic Legacy:
- Promoted regional art forms, helping establish Kuchipudi as a classical dance style in Andhra Pradesh.
- Advocated for Yakshagana Bayalata, a form of dance-drama popular in coastal Karnataka.
Honors and Recognition:
- Bestowed titles such as "Loka Surak?a?a Ati Nipu?a?" and "Yo Avati Kalinga Bhu Sambhav?n" for his contributions to philosophy and governance.
Final Resting Place:
- Narahari Tirtha was consecrated near Chakratirtha at Hampi on the banks of the Tungabhadra River after his death.
- His legacy continues to influence the temple traditions, especially in Puri Jagannath, strengthening the Madhva influence in Odisha.
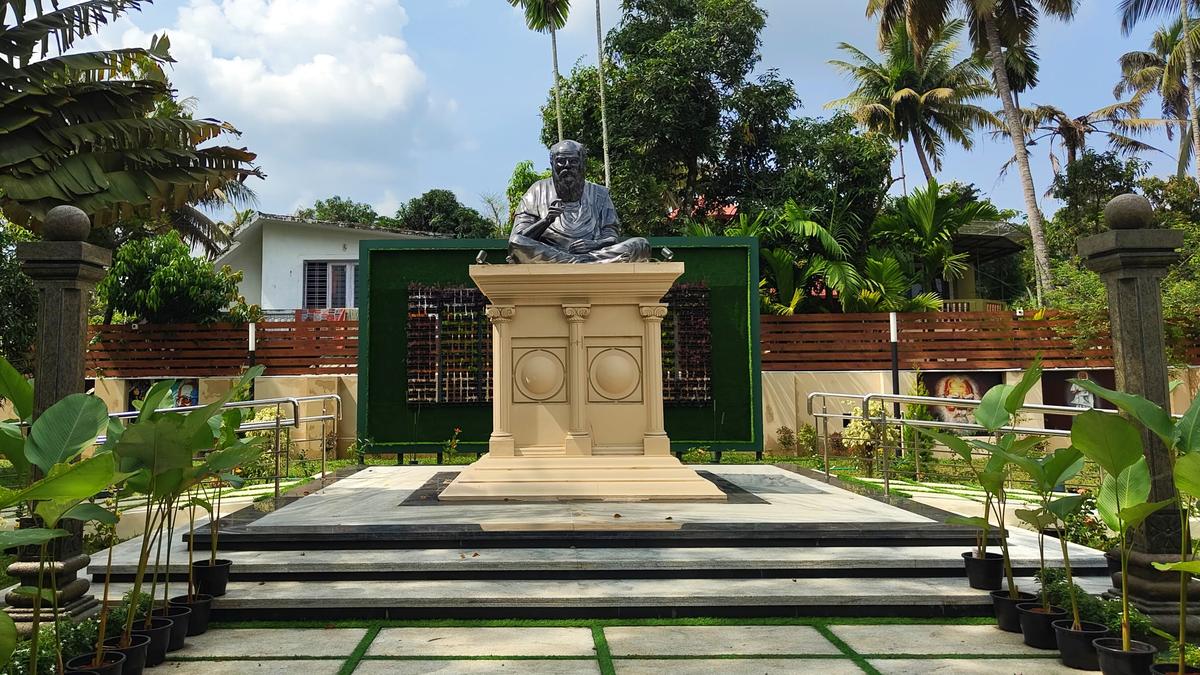
Thanthai Periyar Memorial

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
In a significant event for both Kerala and Tamil Nadu, Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan and Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin are set to reunite at Vaikom, to inaugurate the extensively renovated memorial dedicated to Tamil reformist E.V. Ramasami Naicker, popularly known as Thanthai Periyar. This marks a historic occasion over a year and a half after they jointly inaugurated the centenary celebrations of the Vaikom Satyagraha.
Key Highlights:
Memorial History and Significance:
- Established: January 1994
- Location: 70-cent property near Valiyakavala Junction, Vaikom
- Ownership: Tamil Nadu Government
- Periyar Statue: Installed in 1985 on 84 cents of land provided by Kerala government; remains the centerpiece.
- Historical Neglect: The memorial suffered from years of neglect before the renovation.
Role of Periyar in Vaikom Satyagraha:
- Vaikom Satyagraha (1924–1925):
- First organized movement for the rights of the ‘untouchable’ communities in India.
- Led by prominent leaders like T.K. Madhavan, K.P. Kesava Menon, and K. Kelappan.
- Periyar, alongside his wife Nagamma, joined the movement, seeking access to public roads leading to the Sri Mahadeva Temple in Vaikom.
- Periyar’s Contribution:
- Was imprisoned twice for his participation in the movement.
- Honored with the title Vaikom Veeran for his leadership.
- Impact: The movement played a crucial role in securing social equality for all sections of society.
Periyar’s Legacy:
- Self-Respect Movement: Founded by Periyar to promote social equality and eliminate caste-based discrimination.
- Dravidar Kazhagam: A political and social organization founded by Periyar, advocating for the rights of the Dravidian people.
- Father of the Dravidian Movement: Periyar’s philosophy and activism laid the foundation for the Dravidian political ideology and social reforms in Tamil Nadu.
Tamil Nadu's First Glass Bridge in Kanyakumari
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu inaugurated India’s first glass bridge over the sea in Kanyakumari, connecting the Thiruvalluvar Statue and the Vivekananda Rock Memorial.
- The bridge provides a safe and scenic walking route between these two iconic landmarks, eliminating the need for ferry trips.
Key Highlights:
- Dimensions and Design
- The bridge is 77 meters long and 10 meters wide, offering uninterrupted views of the sea from a unique vantage point.
- Designed to withstand marine conditions like corrosion and strong winds, ensuring durability and safety for visitors.
- Tourism Investment
- The bridge was built at a cost of ?37 crore, marking a significant investment in tourism infrastructure for Kanyakumari.
- This project aligns with the state’s vision to boost tourism and modernize amenities in the region.
- Significance as a Tourist Attraction
- The bridge is set to become a landmark tourist attraction, enhancing the visitor experience by providing a direct, scenic route between the two monuments.
- It is expected to play a pivotal role in boosting tourist footfall and the local economy.
About Thiruvalluvar Statue
- Location and Design
- The Thiruvalluvar Statue stands on a rock near the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanyakumari.
- It is a symbol of wisdom, officially named the Statue of Wisdom by the Tamil Nadu government.
- Physical Specifications
- The statue stands at a total height of 133 feet (41 meters), with the statue itself measuring 95 feet (29 meters) and the pedestal adding 38 feet (12 meters).
- Weight: The statue weighs approximately 7000 tonnes and is designed in a hollow structure.
About Vivekananda Rock Memorial
- Location and Significance
- Situated on a rock in the Laccadive Sea, around 500 meters from the mainland in Kanyakumari.
- The memorial commemorates Swami Vivekananda, who represented India’s spiritual legacy at the 1893 Parliament of World’s Religions in Chicago.
- Historical and Religious Importance
- The rock is believed to be the site where Swami Vivekananda attained enlightenment.
- It is also associated with goddess Kanyakumari, who is said to have prayed to Lord Shiva on this rock, with an imprint of her feet preserved there.
- Architectural Features
- The memorial incorporates diverse architectural styles, including the Sripada Mandapam and the Vivekananda Mandapam.
- A life-sized bronze statue of Swami Vivekananda is located at the memorial.
- The rock is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and Arabian Sea, where these three water bodies converge.
ASI Discovery at Srisailam Temple

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) uncovered ancient copper plates and gold coins at the Srisailam Temple in Andhra Pradesh, specifically in the Ghantamandapam area.
- The discovery includes 20 sets of copper plates, totaling 72 leaves, and various gold coins.
- The ASI's Epigraphy Branch in Mysore has completed the documentation of these findings, and the materials are being studied in detail.
Collaboration with Srisailam Devasthanam:
- In collaboration with the Srisailam Devasthanam, ASI plans to publish a book that will detail the findings and their historical significance.
- The book will be printed soon by Pragati Publications in Hyderabad.
Srisailam Temple Overview:
- The Srisailam Temple, also known as the Mallikarjuna Swamy Temple, is a prominent Hindu pilgrimage site in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is located in the Nallamala Hills, overlooking the Krishna River.
- The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva in the form of Mallikarjuna Swamy and Goddess Parvati as Bhramaramba Devi.
- It is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva and one of the Shakti Peethas, making it significant in both Shaivism and Shaktism.
Architectural Significance:
- The temple is built in the Dravidian style, featuring lofty towers and expansive courtyards, and is considered a prime example of Vijayanagara architecture.
- Historical references to the temple date back to the Satavahana period (2nd century AD), and the temple was further endowed by the Kakatiyas and Vijayanagara rulers.
Cultural and Religious Importance:
- The Srisailam Temple is unique for housing both a Jyotirlinga (Lord Shiva) and a Shakti Peetha (Goddess Bhramaramba), a rare combination not found at other temples.
- The great religious figure Adi Shankaracharya is believed to have visited the temple and composed the Sivananda Lahiri there.
Historical Context:
- The copper plates and inscriptions discovered are likely to provide valuable insights into the historical and cultural significance of the temple, as well as the region's ancient religious practices.
Re-emergence of the Dodo in Kashmir’s Papier Mâché Craft
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
Artisans in Srinagar, Kashmir, have revived the extinct dodo bird in papier mâché forms. These figurines are exported worldwide, particularly to Mauritius and Europe, ahead of the Christmas season. Over 50,000 dodo figurines have already been sent to international markets in 2024.
Key Highlights:
The Dodo:
- Scientific Name: Raphus cucullatus.
- Extinct Since: 1681, approximately 80 years after humans began interacting with them.
- Endemic to Mauritius: A flightless bird from the Indian Ocean island of Mauritius, a national symbol of the country.
- Extinction Causes: Overhunting and the introduction of invasive species like rats, pigs, and cats that preyed on their eggs.
- Physical Traits: Grey or brown plumage, about 3 feet tall, flightless and fearless.
Papier Mâché Craft in Kashmir:
- History: Practiced for over 600 years in Kashmir, introduced during the reign of King Zain-ul-Abidin (15th century).
- Techniques: Involves creating decorative objects using paper pulp, with traditional Persian motifs.
- Recent Addition of Dodo: The dodo was introduced to the papier mâché craft around two decades ago, likely by Mauritian tourists.
International Market and Demand:
- Mauritius: A significant market for the papier mâché dodo, as the bird is a national emblem of Mauritius.
- Europe: Exported to European countries during the Christmas season, contributing to the popularity of Kashmir’s handicrafts.
- Kashmir's Karkhanas: Local craft workshops in Srinagar are producing thousands of dodo figurines each season, with over 3,000 dodos produced this year.
Cultural and Economic Impact:
- Artisans' Contribution: Local artisans are helping keep the memory of the extinct dodo alive, while boosting Kashmir’s handicraft industry.
- Global Recognition: The dodo is now a sought-after item in global markets, linked to the traditional art of Kashmir.
- Kashmir Handicrafts: Several crafts from Kashmir, including papier mâché, have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags for their distinct cultural and regional significance.
ASI Decodes Sanskrit Inscription Found in Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK)

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
An ancient Sanskrit inscription found in Gilgit (PoK) was decoded by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
About the Inscription:
- Location:
- Gilgit (PoK): Written in Brahmi script, dating back to 4th century CE.
- Peshawar (Pakistan): Written in Sharada script, dating to 10th century CE.
- Details of Gilgit Inscription:
- Mentions Pushpasingha, who installed a Mahesvaralinga for the merit of his guru.
- Written in Brahmi script, which was prevalent during the 4th century CE.
- Religious Context: Indicates significant religious connection, particularly with Shaivism.
- Details of Peshawar Inscription:
- Fragmentary: Engraved on a slab.
- Written in Sharada characters (10th century CE).
- Mentions Buddhist Dharini (chants), particularly referring to Da (Dha) rini in line six.
- The inscription is partially damaged, and further details are unclear.
- Earlier Discoveries:
- This is not the first Sanskrit inscription decoded from Pakistan. In the past, Sanskrit inscriptions have been found in various parts of Pakistan.
- Swat Valley: Known for numerous Buddhist rock inscriptions in Sanskrit using Nagari script, which were part of the Gupta Empire (circa 240–550 CE).
- Religious and Cultural Implications:
- The Gilgit inscription provides evidence of Shaivism as a prominent religious practice in the region during the 4th century CE.
- The Peshawar inscription suggests Buddhist influences, particularly related to Buddhist chants and rituals.
- Swat Valley's Role: The inscriptions found here highlight its importance as a center of Buddhist learning and cultural exchange.
2023 National Tansen Samman

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
- The prestigious National Tansen Samman for 2023 was conferred upon Pt. Swapan Choudhary, a renowned tabla maestro from Kolkata, at the National Tansen Festival held in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
- Tansen Festival: This festival, renowned for its celebration of classical music, is organized annually in Gwalior, which is considered the music capital of Madhya Pradesh.
- Prize Details: As part of the honor, Pt. Swapan Choudhary was presented with an honorarium of five lakh rupees, a citation plaque, and a shawl-shriphal.
- About the Award:
- The National Tansen Samman was established in 1980 by the Madhya Pradesh government to recognize exceptional contributions to Indian classical music.
- It is named after Tansen, one of India's most celebrated classical musicians.
- The award is the highest national honor in the field of Indian classical music.
- Additional Award:
- Raja Mansingh Tomar Samman for 2023 was awarded to Sanand Nyas, an institution from Indore. This institution has been active for 35 years in the promotion of classical music, drama, and cultural festivals.
- Pt. Swapan Choudhary’s Remark: In response to receiving the honor, Pt. Choudhary expressed his gratitude and pride in joining the ranks of distinguished artists awarded the National Tansen Samman.
About Tansen: The Iconic Musician
- Legacy: Tansen, also known as Miyan Tansen, was a prominent Indian classical musician, composer, and vocalist. He is credited with popularizing several ragas and revolutionizing the Indian classical music tradition.
- Role at Akbar’s Court: Tansen was one of the Navaratnas (nine jewels) in the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He held the title of Mian, meaning "learned man," bestowed upon him by Akbar.
- Contributions:
- Tansen is famous for his compositions, including the introduction of notable ragas such as Miyan ki Malhar, Miyan ki Todi, and Darbari.
- He also improved the plucked rabab, which is of Central Asian origin, enhancing its role in Indian classical music.
- Historical Influence: Tansen's life and work are surrounded by extensive legend, and his contributions remain deeply influential in the development of Indian classical music today.
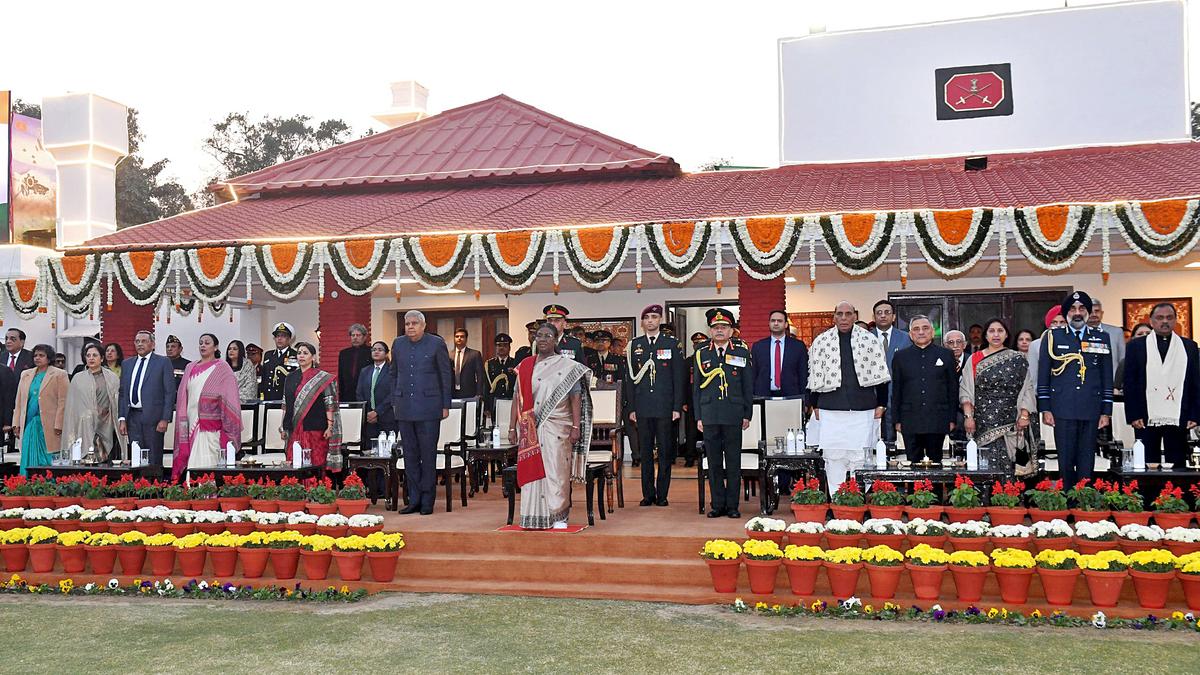
Vijay Diwas 2024

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 16, 2024, India commemorated Vijay Diwas, marking the 53rd anniversary of its victory in the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War. This day honors the bravery and sacrifices of Indian soldiers and the Mukti Bahini, whose collective efforts led to the creation of Bangladesh as an independent nation. On this occasion, leaders across India, paid heartfelt tributes to the fallen heroes who contributed to the victory, and to the enduring India-Bangladesh friendship.
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War culminated in the surrender of over 90,000 Pakistani soldiers, and India’s victory is celebrated as a defining moment in South Asian history.
The War’s Historical Context:
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War was a pivotal conflict between East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Pakistan (now Pakistan), leading to Bangladesh’s independence. It was a direct result of decades of social, political, and economic discrimination faced by East Pakistan, despite its larger population and contribution to Pakistan’s economy. Major events leading to the war included:
- Cultural and linguistic marginalization, with East Pakistan's Bengali language and identity being suppressed by the West.
- The 1970 elections that saw the Awami League, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, win a decisive victory in East Pakistan, but their demand for greater autonomy was rejected by West Pakistan.
- The violent crackdown by the Pakistani military in Operation Searchlight in March 1971, leading to widespread atrocities and a mass exodus of refugees into India.
India’s Role in the War:
India’s involvement in the conflict was initially cautious, but the refugee crisis—with over 10 million people fleeing to India—forced India to take action. India provided humanitarian aid and supported the Mukti Bahini, a guerrilla force of Bangladeshi fighters. On December 3, 1971, Pakistan’s preemptive airstrike on Indian military bases led to India's retaliation and full-scale military involvement, including air and naval operations.
India’s military, with assistance from the Mukti Bahini, launched a decisive campaign, ultimately leading to Pakistan’s surrender on December 16, 1971, and the creation of Bangladesh.
Vijay Diwas Observances:
- The 53rd Vijay Diwas celebrations at Fort William, Kolkata, saw a Bangladeshi delegation—including Mukti Joddhas (freedom fighters)—reflect on their memories of the war, highlighting India's crucial role in the liberation of Bangladesh.
- The event also featured a wreath-laying ceremony, military tattoo, and a salute to the shared sacrifice and friendship between India and Bangladesh.
The 1971 Surrender Painting and New Symbolism:
In an interesting development, the iconic 1971 surrender painting, depicting the surrender of Pakistani forces in Dhaka, was moved from the Army Chief’s lounge to the Manekshaw Centre. The painting was replaced by Karam Kshetra–Field of Deeds, a new artwork symbolizing India’s strategic and cultural heritage. This new piece incorporates elements like Lord Krishna’s chariot, Chanakya, and modern military assets, reflecting India’s military prowess and heritage.
Zakir Hussain
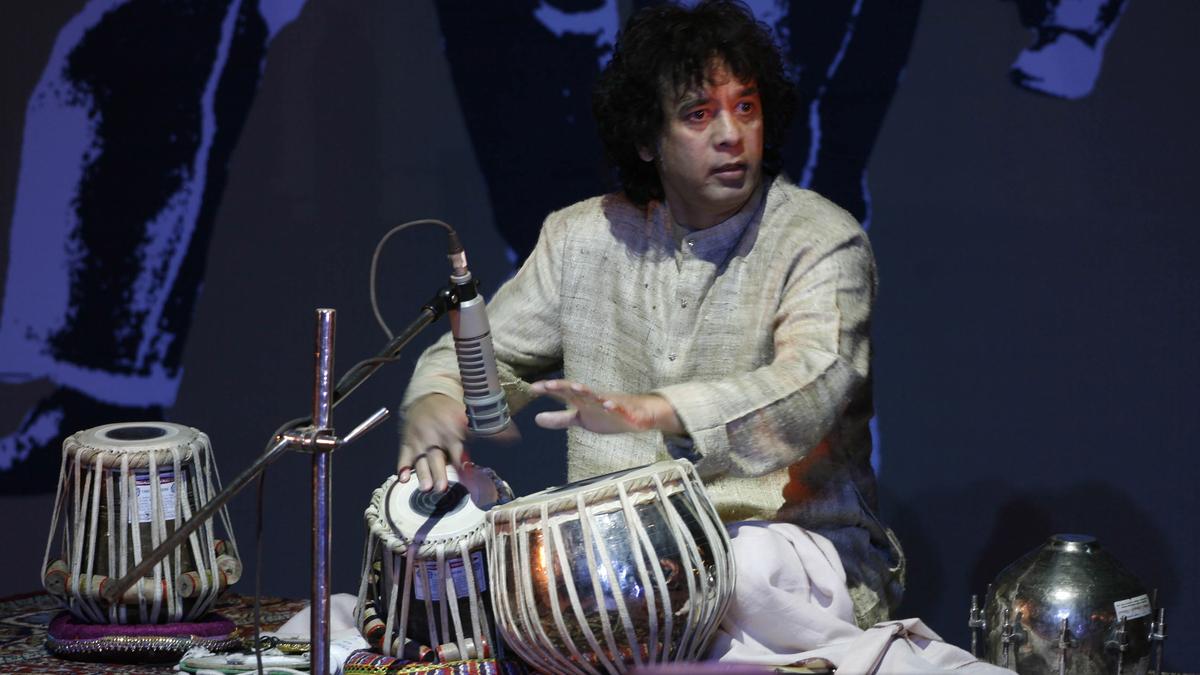

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Ustad Zakir Hussain, the legendary tabla virtuoso, passed away at the age of 73 due to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF).
Key Highlights:
- Career Highlights:
- Born on March 9, 1951, to Ustad Alla Rakha, a renowned tabla maestro.
- Began tabla training at age 7, with early guidance from his father.
- Co-founded Shakti in 1973 with John McLaughlin, blending Indian classical music with Western influences, pioneering world music.
- Worked with global artists, including George Harrison, John McLaughlin, and Mickey Hart.
- Awarded four Grammy Awards, including three at the 66th Grammy Awards (2024), and honored with the Padma Vibhushan in 2023.
- A visiting professor at Stanford and Princeton universities.
- Musical Style:
- Transformed the tabla from a background instrument into a dynamic, expressive solo performance.
- Known for his complex rhythms and spontaneous performances, making tabla accessible and glamorous.
- Emphasized the concept of "hazri" (attendance) in the court of music, seeing his music as an offering to a higher power.
- Cultural Influence:
- His music was a bridge between traditional Indian classical and contemporary global sounds, impacting audiences worldwide.
- Played a pivotal role in the cultural exchange of Indian classical music, gaining fans and respect across the globe.
- Participated in projects such as the Taj Mahal tea commercials and "Desh Raag", symbolizing unity and diversity in India.
What is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)?
- IPF is a chronic lung disease causing scarring of the lung tissue, leading to difficulty in breathing.
- Cause: The exact cause is unknown, hence termed "idiopathic" (unexplained).
- Risk Factors: Most common in older adults (over 50), men, and those with a history of smoking or viral infections.
About the Tabla:
- Structure: Composed of two drums—Tabla (right) and Bayan (left)—used primarily in Hindustani classical music.
- Material: Tabla has a wooden body, while Bayan can be made of clay or metal, both covered with animal skin and syahi paste.
- Role: Primarily accompanies vocal and instrumental performances, and is essential in various classical dance forms in northern India.
- Historical Note: Believed to have been invented by Amir Khusrau.
Prominent Tabla Players:
- Ustad Alla Rakha (father of Zakir Hussain).
- Zakir Hussain (himself).
- Shafat Ahmed and Samta Prasad.
Under the Sal Tree Theatre Festival

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
“Under the Sal Tree” Theatre Festival, held annually in Rampur, Assam, promotes eco-friendly and sustainable practices in theatre while showcasing rich cultural diversity.
Overview:
- Location: Rampur village, Goalpara district, Assam
- Organizer: Badungduppa Kalakendra, a social and cultural organization
- Founded: 1998 by Sukracharjya Rabha
- Festival Focus: Eco-friendly theatre practices, cultural diversity, and sustainability
Key Features
- Unique Setting: Open-air festival under Sal trees, with no artificial lighting or electric sound systems.
- Sustainability:
- No use of plastic.
- Carbon-neutral, with eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, straw, and cane.
- Performances in natural daylight, avoiding electric lights.
- International Participation: Theatre groups from countries like Poland, South Korea, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, North Korea, Bolivia, and Holland have performed.
- Cultural Celebration: Highlights indigenous art forms, languages, and traditions, e.g., Rabha and Bodo plays.
Festival Activities
- Performances:
- Includes plays like “Dadan Raja” (Rabha language play), “Kindhan Charithiram” (Tamil), and “Kisan Raj” (Hindi).
- Focus on themes such as societal change and resilience of farmers.
- Workshops & Community Projects: For performing artists, promoting artistic innovation and social impact.
- Anniversary Celebrations:
- 25th anniversary celebrated with special events and book releases, e.g., “Resonance: Echoing the Spirit of Badungduppa” and “Sukracharjya Rabha on the Back Stage”.
Impact & Legacy
- Theatre Movement: Celebrates art amidst nature, breaking geographical barriers despite the remote location.
- Founder’s Vision: Sukracharjya Rabha believed in the synergy between art and nature, aiming to bring social change through theatre.
- Local Involvement:
- 20 resident artists contribute to the festival’s success.
- Festival has become a major cultural attraction in Assam, drawing thousands of theatre enthusiasts.
Turner Prize

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
Jasleen Kaur, a 38-year-old Indian-origin Scottish artist, has won the prestigious Turner Prize 2024 for her exhibition "Alter Altar". This win highlights Kaur’s unique ability to weave together personal, political, and spiritual elements into a cohesive artistic expression. The exhibition explores themes such as plurality, migration, and cultural identity, drawing from Kaur’s own family history and experiences.
Exhibition Overview:
"Alter Altar," which was first showcased in Glasgow, features an array of everyday objects and cultural symbols, including:
- A vintage red Ford Escort covered in a large crocheted doily, symbolizing her father’s migrant aspirations.
- Worship bells, Irn-Bru orange resin, an Axminster carpet, and family photographs.
- Soundtracks, including music from Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan and Bob Marley, which reflect Kaur’s multicultural upbringing.
The exhibition blends these elements to examine migration, identity, and belonging. The jury, chaired by Alex Farquharson, Director of Tate Britain, praised Kaur’s ability to combine different voices through unexpected and playful material combinations, creating a visual and aural experience that evokes both solidarity and joy.
Personal and Political Reflection:
Kaur’s work reflects on the Sikh concept of Miri Piri, which represents the balance between the political and the spiritual. This duality is central to her exploration of cultural practices and the effects of violence, colonialism, and empire on these traditions. In her acceptance speech, Kaur also addressed political issues, calling for a ceasefire in Gaza and an end to institutional complicity in Israel's actions.
About the Turner Prize:
The Turner Prize, established in 1984, is one of the most prestigious awards in contemporary British art. It aims to recognize recent developments in British art. Kaur’s win is particularly significant as it marks the 40th anniversary of the award. Previous winners include renowned Indian-origin artists such as Anish Kapoor (1991).
International Abhidhamma Divas

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, International Abhidhamma Divas was celebrated at Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi, with PM Narendra Modi.
Key Details:
- India's Spiritual Legacy: Birthplace of Buddhism; site of Gautam Buddha's enlightenment.
- Sacred Sites: Veneration of locations like Bodh Gaya, symbolizing Buddha's journey and teachings.
- Core Teachings: Abhidhamma as a key philosophical component emphasizing mental discipline and self-awareness.
International Abhidhamma Divas
- Global Observation: Celebrates the significance of Abhidhamma in ethical conduct and mindfulness.
- Cultural Connection: Highlights India's role in preserving Buddhism and bridging ancient wisdom with contemporary practices.
Historical Background and Significance
- Commemoration: Marks Buddha’s descent from T?vati?sa to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur).
- Teaching Period: Buddha taught the Abhidhamma to deities for three months; linked to the end of the Rainy Retreat and the Pav?ra?? festival.
Teachings of Abhidhamma
- Systematic Analysis: Provides a detailed exploration of mind and matter, differing from Sutta Pi?aka.
- Specialized Vocabulary: Key terms include "citta" (consciousness), "cetasika" (mental factors), "r?pa" (materiality), and "nibb?na" (liberation).
- Textual Framework: Six core books of Abhidhamma Piñaka cover moral states, aggregates, and causal relationships.
- Key Treatise: The Paññh?na offers in-depth causal analysis, essential for practitioners’ understanding.
Modern Observance and Celebrations
- Significance of Pali: Recognition of Pali as a classical language; promoting India's Buddhist heritage.
- Participants: Gathering of ambassadors, monks, scholars from 14 countries; emphasizes Abhidhamma's relevance today.
- Program Highlights: Dhamma discourse, academic sessions on Abhidhamma’s significance, exhibitions on Pali's evolution and Buddha's teachings.
Classical Status of Pali Language
- Pali's Role: Sacred language for delivering Buddha's teachings; recognized as a Classical Language by India.
- Buddhist Canon: Major texts include the Tipitaka (Vinaya, Sutta, Abhidhamma Pitaka) and commentarial traditions.
- Literary Heritage: Jataka Kathas reflect shared moral values; status enhances Pali studies in education and research.
Significance
- Significance of Celebration: Abhidhamma Divas underscores efforts to preserve and promote Buddhism’s legacy.
- Revitalization of Buddhism: Fosters global engagement and appreciation for Buddha’s teachings, reaffirming India's role in Buddhist studies.
Thanjavur Veena
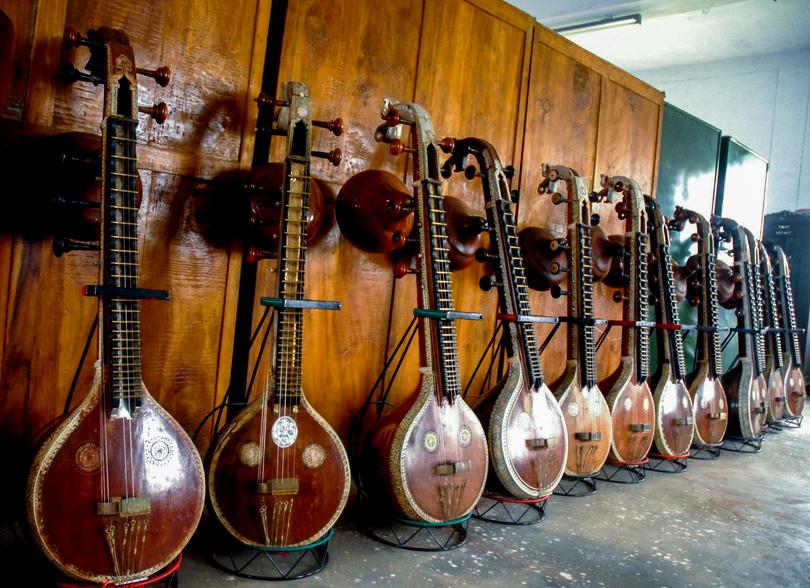

- 03 Sep 2024
In News:
The Thanjavur Veena has the distinction of being the first musical instrument in India to receive the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, highlighting its cultural and artistic significance. Here’s an overview of its features, types, and craftsmanship:
About Thanjavur Veena
- Construction:
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Ekantha Veena: Carved from a single block of wood.
- Sada Veena: Composed of three sections—resonator (kudam), neck (dandi), and head—with joints.
- The Thanjavur Veena is known for its unique construction, which comes in two main types:
- Design Features:
- The instrument features 24 fixed frets (mettu), enabling musicians to play a wide range of ragas.
- Traditionally made from the bark of the Jackfruit tree, the bark undergoes extensive testing to ensure quality and durability.
- Craftsmanship:
- The process of crafting a Thanjavur Veena can take 15-20 days, involving cutting, intricate carving, shaping, and assembly of the wood to form the integral parts of the instrument.
Types of Veena
The Thanjavur Veena is one of several types of veenas used in Indian classical music:
- Rudra Veena and Vichitra Veena: Predominantly used in Hindustani classical music.
- Saraswati Veena and Chitra Veena: Associated with Carnatic classical music, with the Saraswati Veena being unique to Thanjavur.
Cultural Significance
- The Saraswati Veena is particularly notable as it is often associated with Goddess Saraswati, the deity of learning and arts, who is frequently depicted holding a veena. This connection emphasizes the instrument's importance in Indian culture and music.
Battle of Saragarhi

- 13 Sep 2024
Why September 12 is Observed as Saragarhi Day:
- Historical Significance: The Battle of Saragarhi is considered one of the finest last stands in military history. On September 12, 1897, 21 soldiers of the 36th Sikh Regiment (now 4 Sikh) defended the fort against 8,000 Orakzai and Afridi tribal militants.
- 127th Anniversary: September 12 marks the 127th anniversary of this battle, which is now regarded as a legendary stand in global military history.
- The Battle: The 21 soldiers held the fort for seven hours despite being heavily outnumbered. They killed 200 militants and injured 600 before they were overwhelmed.
- Capt Amarinder Singh’s Account: In his book, he notes that the soldiers were aware of their certain death but chose to fight valiantly without surrendering, demonstrating unparalleled bravery.
What was Saragarhi and its Importance:
- Location and Role: Saragarhi was a communication tower between Fort Lockhart and Fort Gulistan in the North West Frontier Province (now Pakistan). It was crucial for linking these two forts, which housed a large number of British troops.
- Manning of Saragarhi: On that day, it was manned by only 21 soldiers from the 36th Sikh Regiment and a non-combatant, Daad, who performed odd jobs for the troops.
Details of the Battle:
- Initial Encounter: Around 9 am, the sentry spotted a large tribal army approaching, estimated between 8,000 and 15,000 strong.
- Communication: Sepoy Gurmukh Singh sent a Morse code message to Lt Col Houghton, requesting reinforcements. The response was to hold the position, as the supply route had been cut off.
- Challenges: The soldiers faced being outnumbered, limited ammunition (about 400 rounds per man), and communication issues. Sepoy Gurmukh Singh managed all heliograph communication tasks alone.
Key Figures:
- Havildar Ishar Singh: Leader of the defending troops, known for his bravery and independent nature. He was a respected and loved figure in his regiment.
- Sepoy Gurmukh Singh: The signalman who maintained communication during the battle, despite overwhelming challenges.
- Daad: The non-combatant who fought alongside the soldiers and killed five militants before being killed himself.
Recognition and Legacy:
- British Recognition: Queen Victoria awarded the 21 deceased soldiers the Indian Order of Merit (equivalent to the Victoria Cross), along with two ‘marabas’ (50 acres) and Rs 500 each.
- Current Observance: In 2017, the Punjab government declared September 12 as Saragarhi Day.
- Memorials: The Khyber Scouts regiment of the Pakistani army still mounts a guard at the Saragarhi memorial. The British built an obelisk with bricks from Saragarhi and commissioned gurdwaras at Amritsar and Ferozepur in honor of the martyrs. Shiromani Gurudwara Parbandhak Committee has named a hall after Saragarhi.
- Cultural Impact: The Battle of Saragarhi has inspired various media portrayals, including Akshay Kumar’s film Kesari.
Usha Mehta
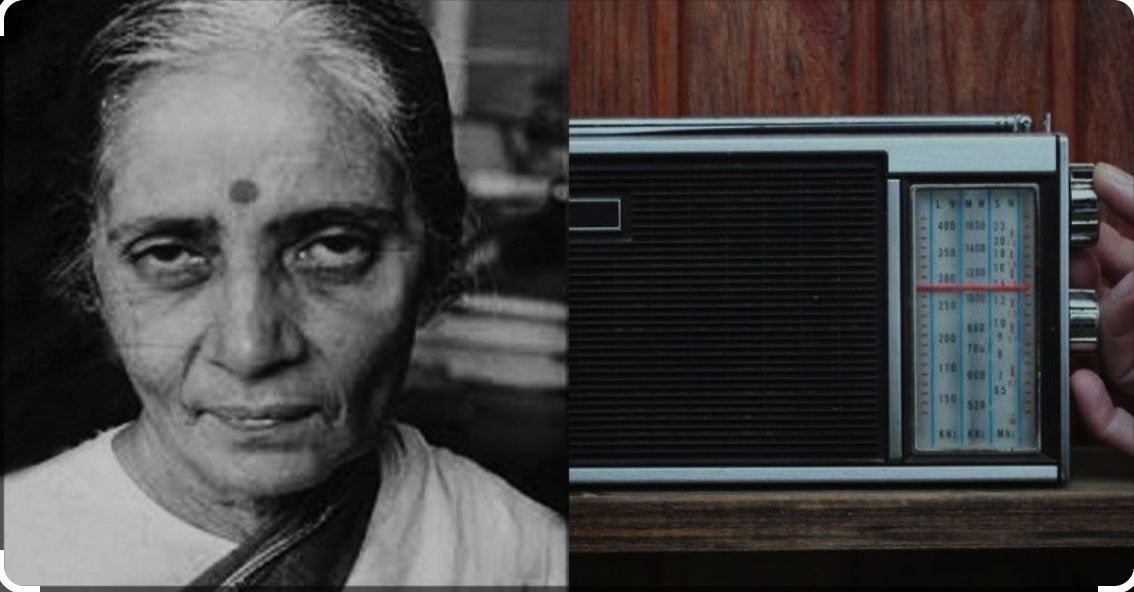

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent film has been launched, depicting the inspiring life story of Indian freedom fighter Usha Mehta.
About Usha Mehta:
- Born in 1920 in the village of Saras, near Surat in Gujarat, Usha Mehta, affectionately known as Ushaben, embodied the Gandhian principles of non-violence and civil disobedience from a young age.
Early Activism:
- At the tender age of eight in 1928, she participated in a protest march against the Simon Commission, demonstrating her early commitment to India's independence struggle.
- The Secret Congress Radio: In 1942, amidst the fervor of the Quit India Movement, Usha Mehta and her colleagues boldly established the Secret Congress Radio.
- This clandestine radio station played a pivotal role in connecting freedom movement leaders with the masses, ensuring the dissemination of crucial information, and maintaining the spirit of resistance against colonial rule.
Establishing an Underground Radio Station:
- With the outbreak of the War in 1939, the British government imposed stringent measures, including the suspension of all amateur radio licenses throughout the Empire.
- Operators were mandated to surrender their equipment to the authorities, under threat of severe repercussions for non-compliance.
Key Figures in the Operation:
- Usha Mehta, alongside Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, and Chandrakant Jhaveri, played instrumental roles in orchestrating the Congress Radio initiative, defying the ban on amateur radio broadcasting.
The Congress Radio Trial:
- The trial of the five accused individuals—Usha Mehta, Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, Chandrakant Jhaveri, and Nanak Gainchand Motwane, who facilitated crucial equipment—captivated public attention in Bombay.
- While Vithalbhai and Motwane were acquitted, Mehta, Babubhai, and Chandrakant faced severe sentences for their involvement.
Usha Mehta's Legacy:
- Following her release from Pune's Yerawada Jail in March 1946, Usha Mehta was lauded in nationalist circles as "Radio-ben," symbolizing her courageous defiance and commitment to the freedom struggle through underground broadcasting.
Independence, PhD, & Padma Vibhushan
- When India finally achieved independence in 1947, the British had divided the country into two parts – India and Pakistan, sending the region into chaos.
- The divide results in massive bloodshed with more than 10 million Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs seeking to find their home.
- Mehta was torn. “In a way, I was very happy, but sad at the same time because of partition.
- It was an independent India but a divided India,” she was quoted as saying in the book Freedom Fighters Remembered.
- She was away from active politics in independent India due to her ill health but continued to remain a staunch Gandhian till the very end.
- She penned the script for a documentary on Gandhi produced by her colleague at the radio station, and earned a PhD in Gandhian thought at the University of Bombay.
- She taught political science and ran the politics department at the university.
- She also taught at Wilson College for 30 years.
- She was also the president of the Gandhi Peace Foundation.
- In 1998, she was awarded India’s highest civilian honor, the Padma Vibhushan.
- She lived a simple life and never married or had children.
- She died on 11 August 2000 at the age of 80.
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) (DST Gov)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The study by ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute (ICAR-IVRI), Izatnagar, Bareilly has found the exact status of EEHV and its subtypes circulating among the Asian elephant population in India.
What is Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV)?
- Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus (EEHV) is responsible for one of the most devastating viral infectious diseases in elephants worldwide, especially young Asian elephants.
- EEHV is a double-stranded DNA virus that is classified in the family Herpesviridae.
- The mortality rate is very high (70-85%) and death occurs within a short period (2-4 days).
- In India, the incidence of EEHV-HD was first reported in 1997.
- 9 of 15 potential cases were confirmed from Southern India in wild free-ranging calves in Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu forest reserves, and Madras Zoo.
- Transmission of the disease: EEHV is mostly spread through mucosal secretions which include:
- Saliva, Breast milk, Nasal secretions, Trunk to trunk contacts etc
- The disease can only affect elephants and is not infectious to humans or other animals.
- Symptoms: Some elephants show symptoms such as reduced appetite, nasal discharge and swollen glands.
- Treatment: Treatment involves a combination of strategies such as antiviral therapy, aggressive fluid therapy to counter haemorrhaging, immuno-stimulant drugs like selenium and Vitamins C and E, as well as antipyretics and analgesics to manage fever.
- It's important to note that there is no definitive cure for herpesviruses in animals or humans since these viruses typically enter a latent state.
Scientists uncover seismic clues in Kopili Fault zone, advancing earthquake preparedness (PIB)
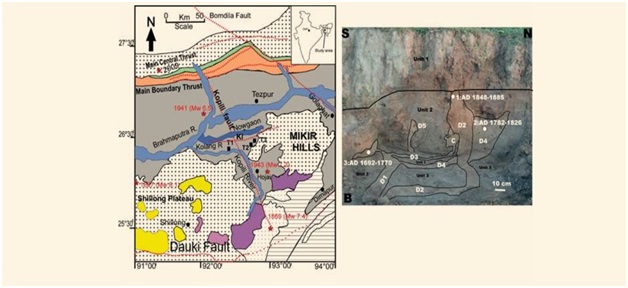
- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have detected seismogenic liquefaction characteristics within the dynamically active Kopili Fault (KF) zone.
About Kopili Fault Zone:
- The Kopili Fault extends from the western part of Manipur up to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- It covers a distance of about 400 km and is closer to the Himalayan Frontal Thrust.
- The Kopili fault bisects the Meghalaya Plateau and isolates the Mishmi block from the main part of the plateau.
- The Kopili fault is almost passing through the Kopili River.
- The river Kopili rises in the North Cachar Hills District in Borail Range at an altitude of 1525 meters.
- From a field study, it is observed that the Kopili Fault region is moving in the northeast direction at an average velocity of 28.397N mm/yr and 40.227E mm/yr.
- This region is characterized by heightened seismic activity, classified within the most critical Seismic Hazard Zone V.
- The geological dynamics are attributed to collisional tectonics, where the Indian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- The fault itself is a transpressional fracture, producing dextral strike-slip earthquakes in the lower crust.
- The Kopili fault zone, a tectonic depression filled by the alluvium of the Kopili River and its tributaries, has experienced numerous seismic events, notable among them being the 1869 earthquake (magnitude 7.8) and the 1943 earthquake (magnitude 7.3).
