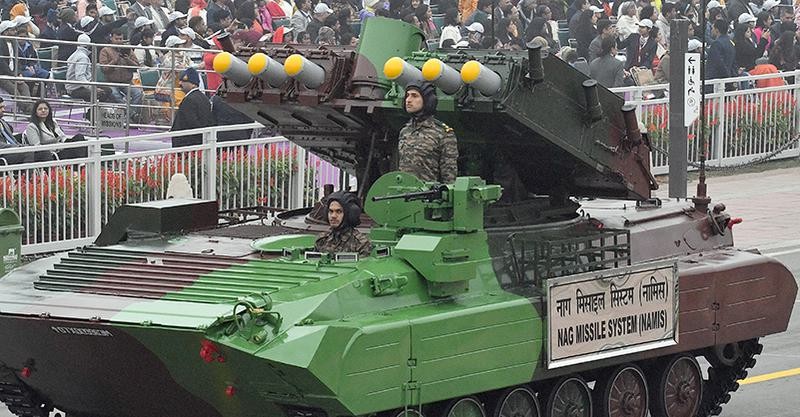
Nag Mark-2

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
UN Approves New AU Force to Combat Al-Shabaab in Somalia
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- On January 19, 2024, the UN Security Council approved a new African Union (AU) force in Somalia to counter the Al-Shabaab terrorist group.
- The resolution was supported by 14 of 15 members, with the US abstaining due to concerns about funding.
- The new force will replace the African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) after its mandate ends on December 31, 2024.
New Mission - AUSSOM:
- The new mission is named African Union Support and Stabilization Mission in Somalia (AUSSOM).
- AUSSOM will continue supporting Somali forces in stabilizing the nation and combating terrorism.
- The mission's objective is to enhance security and stability in Somalia, addressing the challenges posed by Al-Shabaab and ISIL.
Mandate and Operations:
- AUSSOM allows for the deployment of up to 12,626 personnel, including 1,040 police officers, until June 2025.
- The force will focus on counterterrorism, maintaining security, and assisting the Somali government in stabilizing the country.
Financing:
- A hybrid funding approach will be used:
- 75% of the mission’s costs will be covered by the UN, and 25% will come from African Union and partner countries.
- The US raised concerns about the UN's disproportionate funding of the mission, which led to its abstention from voting.
Contributing Countries:
- Egypt has announced its participation in the new force.
- Burundi and Ethiopia will not be contributing troops to AUSSOM.
- Ethiopia has its own ongoing disputes with Somalia, particularly regarding its maritime deal with the breakaway Somaliland region.
Background on Somalia's Challenges:
- Somalia has faced decades of civil war, an insurgency by Al-Shabaab, and recurring climate disasters.
- The country is one of the poorest in the world, and its internal conflicts are exacerbated by clannism, which has fragmented its political and social structure.
Historical Context of Peace Missions in Somalia:
- Previous UN peacekeeping missions in Somalia (1992-1995) faced significant failures, notably the Battle of Mogadishu and the failure to prevent the 1993 massacre.
- The rise of Al-Shabaab in the mid-2000s has further escalated the conflict, and the mission of AUSSOM aims to address these continuing threats.
The Role of Clannism:
- Clannism has hindered the establishment of a unified government in Somalia, with clan rivalries leading to a lack of national cohesion.
- Clannism refers to the prevalence of clan-centric politics, where allegiance to clan and sub-clan interests often takes precedence over national cohesion. In Somalia, the major clans are Darod, Hawiye, Dir, and Rahanweyn.
Importance of AUSSOM:
- AUSSOM represents a strategic shift in the international approach to stabilizing Somalia, relying more on African-led initiatives for peace and security in the region.
Global Peacekeeping Operations:
- The UN peacekeeping mission has been active globally, with over 1 million personnel deployed across 70+ operations.
- Success stories like Sierra Leone (1999-2005) and Liberia (2003-2018) demonstrate the potential impact of well-executed peace missions, but past failures like in Somalia (1992-1995) and Rwanda (1994) underline the challenges faced.
India’s Contribution:
- India has contributed significantly to UN peacekeeping missions, deploying over 253,000 personnel in 49 operations since 1948.
- India’s contributions to missions in Somalia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, and Sudan reflect its active role in global peacekeeping efforts.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Madhav Gadgil, an Indian ecologist, received the UN Environment Programme (UNEP)'s Champions of the Earth Award in 2024.
- The Champions of the Earth Award is UNEP’s highest environmental honor, recognizing individuals, organizations, and governments for significant contributions to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Contributions of Madhav Gadgil:
- Work in Western Ghats:
- Gadgil is recognized for his seminal work in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive region in India, which is a global biodiversity hotspot.
- He chaired the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), formed by the Indian government to assess the impacts of population pressure, climate change, and development on the region.
- Recommendations by WGEEP:
- Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA): Recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats range as an ESA.
- The WGEEP suggested dividing the Western Ghats into three Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ) based on environmental sensitivity.
- Development Restrictions: Proposed a ban on activities like mining, quarrying, thermal power plants, and large-scale hydropower projects in the most sensitive zones (ESZ-1).
- Governance Recommendations: Suggested a bottom-to-top governance approach, beginning with Gram Sabhas, and the creation of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority (WGEA) for effective management.
- Impact of Gadgil’s Work:
- His research and recommendations have played a crucial role in shaping environmental policy and public opinion in India.
- The UNESCO World Heritage status for the Western Ghats in 2012 was a significant step in global recognition of the region’s ecological importance.
About the Champions of the Earth Award:
- History & Significance:
- Established in 2005, the award recognizes trailblazers working towards addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- Since its inception, it has honored 122 laureates who have shown outstanding leadership in environmental conservation.
- 2024 Awardees:
- Madhav Gadgil (India) – for his work on the Western Ghats.
- Sonia Guajajara (Brazil) – for advocacy for Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
- Amy Bowers Cordalis (USA) – for her work in Indigenous rights and ecosystem restoration.
- Gabriel Paun (Romania) – for defending Europe’s old growth forests from illegal logging.
- Lu Qi (China) – for contributions to afforestation and combating desertification.
- SEKEM (Egypt) – for advancing sustainable agriculture.
Key Facts about UNEP:
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Established in 1972, UNEP is a leading global authority on environmental issues.
- UNEP aims to address climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution through scientific research, policy support, and public advocacy.
- UNEP is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya and works closely with 193 Member States to tackle the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
Digital Population Clock

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bengaluru's first digital population clock was inaugurated at the Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC) on November 8, 2024.
- The initiative is collaboration between ISEC and the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
Purpose:
- The clock provides real-time population estimates for Karnataka and India.
- It aims to enhance awareness about population dynamics and provide accurate demographic data for research and policy analysis.
Key Features:
- Real-time Updates:
- Karnataka’s population is updated every 1 minute and 10 seconds.
- India’s population updates every 2 seconds.
- Precision:
- The clock operates with satellite connections for real-time, accurate data updates.
- It functions autonomously with integrated components, ensuring continuous and precise tracking.
- Location: The clock is prominently displayed at the entrance of ISEC.
- National Expansion: Similar digital population clocks are being installed in 18 Population Research Centres across India by MoHFW.
Significance:
- Awareness: The clock serves as a visual tool to highlight the rapid pace of population growth and its implications for sustainable development.
- Research and Analysis: The clock is part of a broader effort to improve demographic studies and inform policy-making.
- Census Data Research Workstation:
- ISEC has introduced a new research workstation, supported by MoHFW, for in-depth demographic analysis.
- The facility is equipped with advanced software for studying population trends and supporting academic research.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
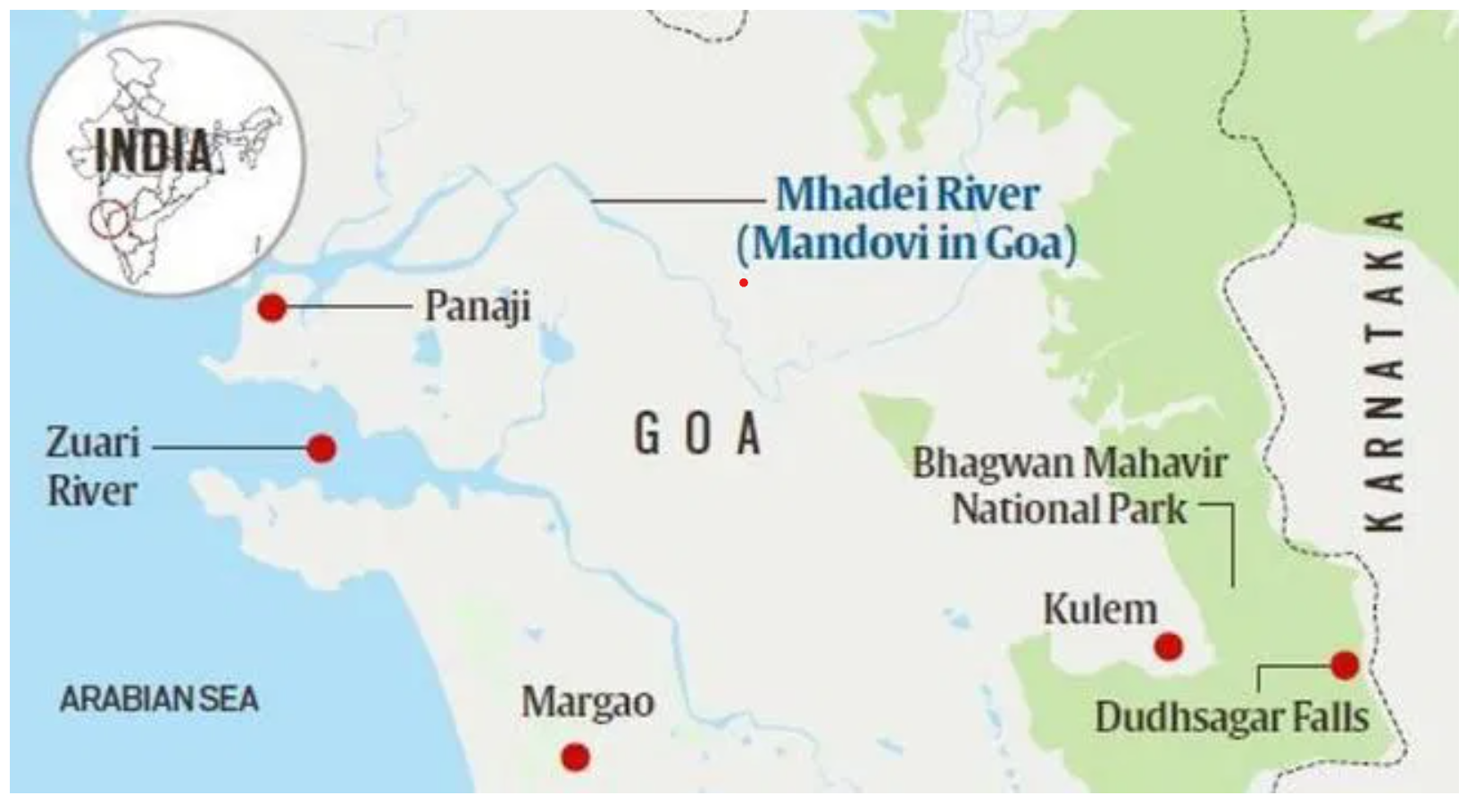
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
Location and Geography:
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
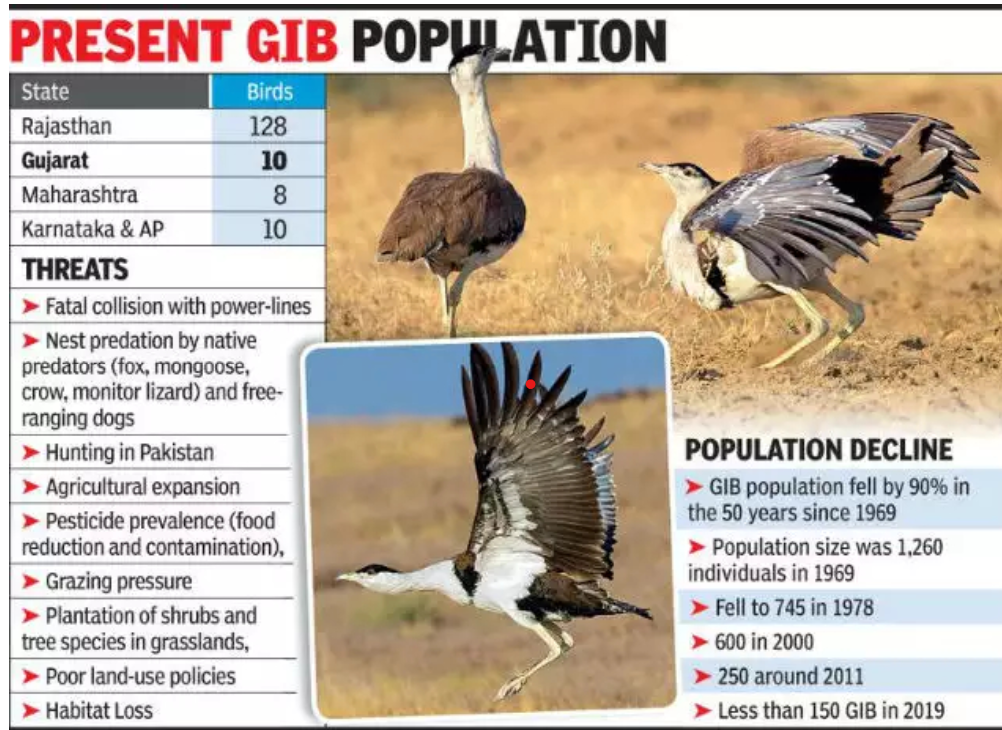
- 25 Oct 2024
A critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (GIB) chick was successfully born through artificial insemination (AI) at a breeding center in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, marking a crucial step in efforts to save the species.
Endangered Status:
- The Great Indian Bustard is classified as critically endangered with fewer than 150 individuals left in the wild in India.
- About 90% of these birds are found in the desert areas of Rajasthan, with smaller populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Main Threats to the Species:
- Habitat Loss: The primary threat is the loss of habitat, which is often perceived as wasteland and is diverted for infrastructure projects like roads and development.
- Slow Reproductive Rate: The bustard’s low reproductive rate exacerbates its risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts: Bustard Recovery Program
- In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched the Bustard Recovery Program to focus on captive breeding and creating a sustainable environment for the reintroduction of GIBs into the wild.
- A dedicated GIB breeding center was set up at the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, as part of this initiative.
- Protection Status of GIB:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- It is also the state bird of Rajasthan, emphasizing its importance in the region’s biodiversity.
World Energy Outlook 2024

- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Energy Agency's (IEA) World Energy Outlook 2024 offers an in-depth analysis of global energy trends, emphasizing the shift towards clean energy, growing energy demand, and the effects of geopolitical conflicts.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Growth:
- India was the fastest-growing major economy in 2023 with a 7.8% growth rate.
- On track to become the world’s third-largest economy by 2028.
- Surpassed China in 2023 to become the most populous country globally, despite a fertility rate below replacement level.
- Energy Demand Surge:
- India is projected to experience the highest increase in energy demand over the next decade.
- By 2035, India’s total energy demand is expected to rise by 35%, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increased living standards.
- Urbanization and Infrastructure Growth:
- Over 12,000 cars are expected to be added to Indian roads daily by 2035.
- Built-up space is set to increase by over 1 billion square meters annually, surpassing the total built space of South Africa.
- Industrial Expansion:
- Iron and steel production is expected to grow by 70% by 2035.
- Cement output is set to increase by 55%.
- Air conditioner stock to grow more than 4.5 times, with electricity demand from cooling expected to exceed Mexico’s total consumption in 2035.
- Energy Supply & Coal:
- India’s electricity generation capacity is projected to nearly triple to 1,400 GW by 2035.
- Coal remains a dominant energy source despite growth in renewables:
- Coal-fired power capacity will increase by 60 GW by 2030.
- Coal will continue to account for over 30% of electricity generation even as solar PV expands.
- By 2035, coal use in industries like steel and cement will grow by 50%.
- Renewable Energy & Clean Tech:
- India is on track to become a global leader in renewable energy, with a nearly 3x increase in electricity generation capacity.
- The country is expected to have the world’s third-largest installed battery storage capacity by 2030.
- By 2030, low-emission energy sources (solar, wind, nuclear) are expected to generate over 50% of India’s electricity.
- Electric Vehicles & Oil Demand:
- The rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to peak India’s oil demand by the 2030s, reducing reliance on oil for transportation.
- Oil demand for transport will decline as EVs proliferate, though demand for oil in other sectors (e.g., petrochemicals) will continue.
- Net Zero Target:
- India aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
- By 2035, clean energy generation could be 20% higher than current policy projections, thanks to electric mobility, hydrogen use, and improved energy efficiency.
- CO2 emissions are projected to be 25% lower than under the Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS).
- Policy Support:
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- PM-KUSUM scheme for solar energy in agriculture.
- National Solar Mission.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme to boost domestic solar PV manufacturing.
- India’s clean energy goals are backed by government initiatives, such as:
- Global Energy Trends:
- Geopolitical Risks: Global energy security remains affected by geopolitical tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine conflict, Middle East tensions).
- Energy Transition: Global shift toward clean energy, with solar and wind power investments accelerating.
- Oil & Gas Surplus: Oil and LNG supply expected to increase, putting downward pressure on prices by the late 2020s.
- Electric Mobility: EVs projected to account for 50% of new car sales by 2030.
- Energy Efficiency: Despite efforts, global targets for doubling energy efficiency by 2030 are unlikely to be met with current policies.
IEA Overview:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) provides analysis and policy advice on energy security, economic development, and environmental sustainability.
- Established in 1974, it now includes 31 member countries and 13 association countries, including India.
- Major publications: World Energy Outlook, India Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report.
THAAD Missile Defence System

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
The US pledged its THAAD missile defence system as well as several troops to Israel after Iran warned the country to not get involved.
In a new boost to Israeli forces, the United States will send a Terminal High Altitude Area Defence battery (THAAD) and troops to Israel amid its ongoing offensive against the Hezbollah.
THAAD battery:
- The Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system (THAAD) is an American anti-ballistic missile defence system. It can shoot down short, medium and intermediate range missiles in it's sphere.
- The THAAD has a “hit to kill” approach which blasts missiles as they before they enter their target zone during their descent.
- The THAAD was developed by the US after their experience of Iraq's Scud missile attacks during the Persian Gulf War in 1991. Out of a total of 88 Scud missiles, Iraq fired 42 into Israel and 46 into Saudi Arabia, killing many American soldiers in barracks as well.
- The first proposal for the THAAD was submitted to the US Defence Ministry in 1987 and a series of tests resulting in failures, finally led to a successful version in 1999.
- In 2008, the US deployed an early missile warning radar, a part of the THAAD system to Israel. Similar deployments were also made in 2012 and 2019, aiding Israel's ability to emerge as a military power in the Middle East.
Caracal

- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Gujarat government has recently announced plans to establish a Caracal Breeding and Conservation Center in the Chadva Rakhal area of Kutch, with a budget of ?10 crore.
About the Caracal
- The caracal, known locally as "siya gosh" (meaning "black ear" in Persian), is a reclusive and primarily nocturnal feline celebrated for its agility and remarkable skill in catching birds mid-flight.
- In terms of nesting, caracals typically utilize abandoned porcupine burrows or rock crevices for denning and are often found with their young hidden among dense vegetation. They tend to live in small groups, and their elusive behavior makes them hard to spot in the wild.
Habitat and Distribution
Caracals inhabit various environments, including woodlands, savannahs, and scrub forests. In India, suitable habitats are found in regions such as Kutch, the Malwa Plateau, the Aravalli hills, and Bundelkhand. This species is also present in numerous countries across Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia.
Threats to Survival
The caracal faces significant threats from extensive hunting, illegal wildlife trade, and the destruction of its natural habitats.
Conservation Status
According to the IUCN, the caracal is classified as "Least Concern." In India, it is protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
International Day of Democracy

- 16 Sep 2024
In News:
Karnataka marked the 'International Day of Democracy' by forming a 'historic' 2,500-km-long human chain as a symbol of equality, unity, fraternity, and participative governance. The massive human chain, which according to the Karnataka government will be the "world's longest", is being formed across the state from Bidar to Chamarajanagar, covering all 31 districts.
Key Highlights:
- Democracy Day is an annual celebration observed on September 15.
- The United Nations General Assembly established this day in 2007 to emphasise the global significance of democracy. It serves as a reminder that democracy is not merely a fixed condition, but an ongoing pursuit. It calls for active engagement from international organizations, nation-states, civil society and people to pursue the democratic idea.
International Day of Democracy History
- The International Day of Democracy was accredited by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) on November 8, 2007, by passing a resolution entitled “Support by United Nations system of efforts of governments to promote and consolidate new or restored democracies.”
- September 15 was chosen to coincide with the anniversary of the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s Universal Declaration on Democracy, which was adopted in Geneva on September 15, 1997.
- This declaration outlines the tenets of democracy proclaiming that democracy is “a system of government based on the freely expressed will of the people to determine their own political, economic, social and cultural systems and their full participation, through free and fair periodic elections, in the composition of their representative government.”
- After the Universal Declaration on Democracy, Qatar spearheaded the campaign to observe an International Day of Democracy at the United Nations.
- The first-ever International Day of Democracy was held in 2008.
International Day of Democracy Significance
- The International Day of Democracy evaluates global democracy, emphasising that it requires commitment and engagement from the international community, the national state governments, civil societies and individuals.
- The day also reminds the nations of the need to uphold the principles of democracy such as the freedom of speech enshrined in Article 19 of the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
AgriSURE Fund and Krishi Nivesh Portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union agriculture minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan launched two initiatives — a fund aimed at boosting farm-sector startups, and a single-window portal to process investments — as part of a slew of measures being taken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government in its third term to bolster the farm economy.
Key Details:
- AgriSure is a ?750-crore fund established to support agricultural startups.
- Krishi Nivesh Nidhi is a portal designed to expedite the clearance of project proposals.
- Both initiatives aim to enhance farm incomes.
Awards for Credit Disbursal:
- Scheduled banks were recognized for their credit disbursals under the government’s agriculture infrastructure fund.
- First prize: State Bank of India (SBI).
- Second prize: HDFC Bank.
- Third prize: Canara Bank.
Significance of Agriculture Sector:
- Agriculture contributes 16% to India’s GDP.
- Farmers play a crucial role as both producers and consumers in the economy.
PM Modi’s Strategy to Double Farmers’ Incomes:
- The strategy includes:
- Increasing output.
- Reducing input costs.
- Ensuring profitable prices.
- Promoting crop diversification.
- Supporting natural farming.
- Enhancing value addition to crops.
Details of AgriSure Fund:
- Blended capital fund with a total corpus of ?750 crore:
- ?250 crore each from the Department of Agriculture and NABARD.
- ?250 crore to be raised from financial institutions.
- Managed by NabVentures, a subsidiary of NABARD.
- Provides both equity and debt support to startups and agripreneurs.
- Focuses on high-risk, high-impact activities within the agriculture value chain.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund:
- Mobilized projects worth ?78,000 crore with ?45,000 crore in financing so far.
- Expanded areas of coverage approved by the Union Cabinet on August 28.
- Aims to create durable farm assets, such as warehouses and processing plants.
- Can be used by agricultural produce marketing committees (APMCs) for market facility improvements.
Funding and Loan Details:
- Part of the ?20-lakh crore stimulus package introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Total funding of ?1 lakh crore over four years:
- ?10,000 crore for 2020-21.
- ?30,000 crore each for the subsequent three financial years.
- Provides medium-to-long term debt financing for rural projects.
- Interest subvention of 3% per annum on loans up to ?2 crore for seven years, with the government covering part of the interest.
First Drug to Treat Common, Lethal Liver Disease Gets US Nod
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals Inc.’s drug Rezdiffra gained the first US approval to treat a potentially deadly liver disease that affects millions worldwide, succeeding in an area where some bigger rivals have failed.
What is Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)?
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver.
- NASH (or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) is a type of NAFLD that can damage the liver.
- NASH occurs when the fat buildup in the liver leads to inflammation (hepatitis) and scarring.
- NASH can be life-threatening, as it can cause liver scarring (called cirrhosis) or liver cancer.
- It is estimated that 3% to 5% of the global population is affected by NASH, though the disease is considered to be underdiagnosed.
Who gets NASH?
- The condition may be hereditary.
- If a person has family members who have had NASH or NAFLD, they are at risk.
- Additionally, having certain health conditions may increase a person’s risk of developing NASH. These include:
- Being overweight or obese.
- Having high cholesterol or high triglyceride levels.
- Having type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or prediabetes.
What are the signs and symptoms of NASH?
- NASH is known as a “silent” disease because many people present with few or no symptoms.
- However, some people will experience tiredness, pain, and discomfort in the upper right part of the abdomen.
How is NASH diagnosed?
- Diagnosing NASH can be challenging because symptoms may not be noticeable until the disease progresses.
- Healthcare providers typically suspect NASH based on abnormal blood or liver test results or imaging showing liver fat.
- Confirmation requires a liver biopsy, an invasive procedure with risks and expenses, involving taking a small liver sample for microscopic examination.
How is NASH treated?
- To manage NASH, losing weight is often recommended as it can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and scarring.
- This involves losing around 3% to 5% of body weight by limiting fats and sugars in the diet.
- Heavy alcohol use should also be avoided to prevent further liver damage.
- If NASH progresses to cirrhosis, treatment may involve medications, medical procedures, or even a liver transplant.
- Currently, there are no approved medications specifically for treating NASH, but ongoing research aims to develop new treatments.
Earth System Model (HT)
- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology is developing a first-for-India Earth System Model to improve climate forecasts and predict climate impacts.
What is an Earth System Model (ESM)?
- An Earth System Model (ESM) is a complex computer program that simulates the interactions between the various components of our planet's climate system, including the atmosphere, oceans, land, ice, and biosphere.
- These models are crucial for understanding past, present, and future climate trends, and are used for purposes like:
- Improving weather forecasts: By accounting for intricate interactions between different parts of the Earth system, ESMs can potentially lead to more accurate weather predictions, particularly for longer-term forecasts.
- Predicting climate change impacts: By simulating different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions and other influencing factors, ESMs can project how climate change might affect specific regions and aspects like temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise.
- Informing adaptation and mitigation strategies: With insights into potential climate impacts, policymakers and individuals can make informed decisions about adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change.
India's Earth System Model:
- Recognizing the importance of such models, India is currently developing its first-ever indigenous Earth System Model, led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR).
- An amount of ?192.28 crores has been sanctioned under the Monsoon Convection, Clouds and Climate Change (MC4) sub-scheme to develop the climate forecasting system
- This project, funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, aims to:
- Enhance forecast accuracy: The model will incorporate advanced features to improve the reliability of weather forecasts, particularly for monsoons that are crucial for India's agriculture.
- Facilitate long-term climate studies: By simulating various climate scenarios, the model will provide valuable insights into potential future climate changes affecting India.
- Predict climate impacts: This model will help assess the risks and potential impacts of climate change on various sectors like agriculture, water resources, and coastal ecosystems.
- The project is expected to be completed by 2025 and is believed to be a significant step towards improving India's understanding and preparedness for the challenges posed by climate change.
About the Monsoon Convection, Clouds, and Climate Change (MC4) Sub-Scheme:
- The MC4 initiative aims to enhance our understanding of monsoonal precipitation changes and their implications in a warming climate by enhancing observational databases and climate models.
- Its overarching objective is to refine our understanding of the interactions between monsoon dynamics, clouds, aerosols, precipitation, and the water cycle within a changing climate context.
The nodal ministry overseeing this effort is the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
What is an Earth System Model (ESM)?
- An Earth System Model (ESM) is a complex computer program that simulates the interactions between the various components of our planet's climate system, including the atmosphere, oceans, land, ice, and biosphere.
- These models are crucial for understanding past, present, and future climate trends, and are used for purposes like:
- Improving weather forecasts: By accounting for intricate interactions between different parts of the Earth system, ESMs can potentially lead to more accurate weather predictions, particularly for longer-term forecasts.
- Predicting climate change impacts: By simulating different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions and other influencing factors, ESMs can project how climate change might affect specific regions and aspects like temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise.
- Informing adaptation and mitigation strategies: With insights into potential climate impacts, policymakers and individuals can make informed decisions about adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change.
India's Earth System Model:
- Recognizing the importance of such models, India is currently developing its first-ever indigenous Earth System Model, led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR).
- An amount of ?192.28 crores has been sanctioned under the Monsoon Convection, Clouds and Climate Change (MC4) sub-scheme to develop the climate forecasting system
- This project, funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, aims to:
- Enhance forecast accuracy: The model will incorporate advanced features to improve the reliability of weather forecasts, particularly for monsoons that are crucial for India's agriculture.
- Facilitate long-term climate studies: By simulating various climate scenarios, the model will provide valuable insights into potential future climate changes affecting India.
- Predict climate impacts: This model will help assess the risks and potential impacts of climate change on various sectors like agriculture, water resources, and coastal ecosystems.
- The project is expected to be completed by 2025 and is believed to be a significant step towards improving India's understanding and preparedness for the challenges posed by climate change.
About the Monsoon Convection, Clouds, and Climate Change (MC4) Sub-Scheme:
The MC4 initiative aims to enhance our understanding of monsoonal precipitation changes and their implications in a warming climate by enhancing observational databases and climate models.
- Its overarching objective is to refine our understanding of the interactions between monsoon dynamics, clouds, aerosols, precipitation, and the water cycle within a changing climate context.
- The nodal ministry overseeing this effort is the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
Rare Golden Tiger takes a stroll in Assam’s Kaziranga National Park, video stuns people (HT)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
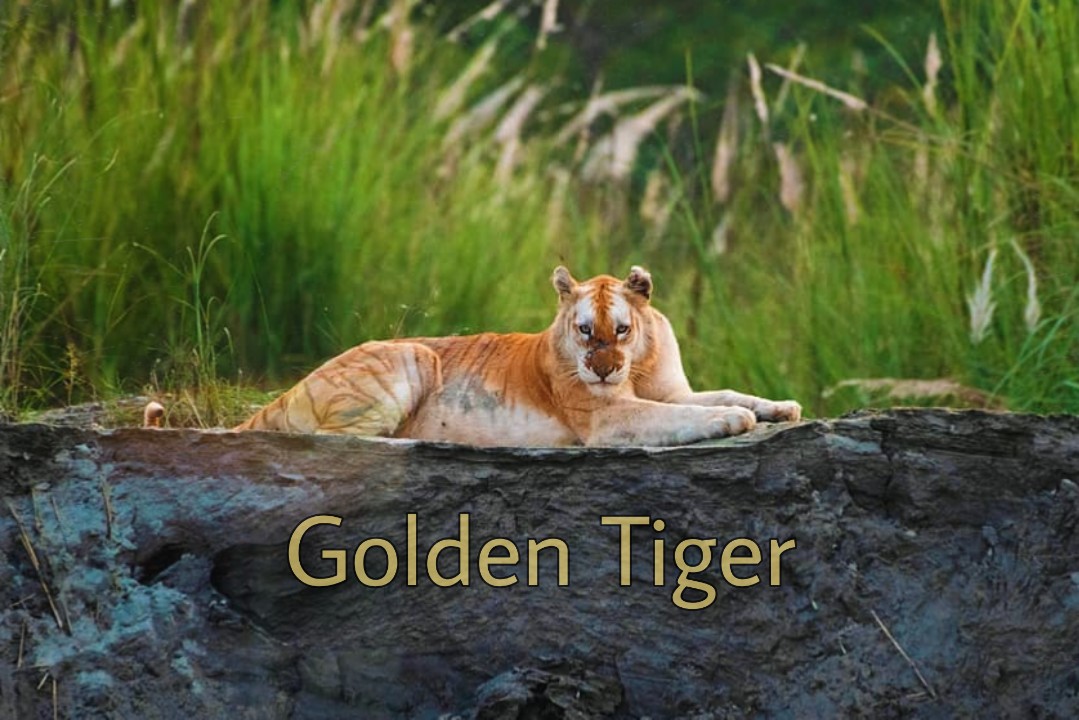
A rare golden tiger was recently spotted in Kaziranga National Park taking a stroll and is the only known golden big cat in India.
What is a Golden Tiger?
- A Golden Tiger, also called a Golden Tabby Tiger, is a Bengal tiger with a unique colour variation caused by a recessive gene.
- The tiger looks golden because it has a mutation or a genetic variant.
- Basically, tigers have three colours: black, orange and white.
- In the Golden Tiger, the black colour is missing and it is slightly faded.
- The golden colouring of these tigers comes from a recessive trait called 'wideband,' affecting how black pigments are produced during hair growth.
- Golden tigers are not a distinct subspecies but rather a product of genetic diversity among Bengal tigers.
- They are extremely rare in the wild and even more so in captivity.
About Kaziranga National Park:
- Kaziranga National Park lies partly in the Golaghat District and partly in the Nagaon District of Assam.
- It is the oldest park in Assam and covers an area of 430 sq km along the river Brahmaputra on the North and the Karbi Anglong hills on the South.
- The National Highway 37 passes through the park area and tea estates, hemmed by table-top tea bushes.
- Kaziranga National Park a world heritage site is famous for the Great Indian one-horned rhinoceros, the landscape of Kaziranga is of sheer forest, tall elephant grass, rugged reeds, marshes & shallow pools.
- It was declared a National Park in 1974.
- It is one of the last areas in eastern India undisturbed by a human presence.
- It is inhabited by the world's largest population of one-horned rhinoceroses, as well as many mammals, including tigers, elephants, panthers and bears, and thousands of birds.
- Vegetation: Due to the difference in altitude between the eastern and western areas of the park, mainly four main types of vegetation’ like alluvial inundated grasslands, alluvial savanna woodlands, tropical moist mixed deciduous forests, and tropical semi-evergreen forests.
- Flora: Kumbhi, Indian gooseberry, cotton tree, and elephant Apple are among the famous trees that can be seen in the park.
- Fauna: The forest region of Kaziranga Park is home to the world’s largest population of Indian Rhinoceros.
- Other animals that can be seen in the elephant grass, marshland and dense tropical moist broadleaf forests of Kaziranga are Hoolock Gibbon, Tiger, Leopard, Indian Elephant, Sloth Bear, Wild water buffalo, swamp deer, etc.
- Also in this park the good number of migratory bird species from Central Asia.
- With the increase in tiger population every year, the government authorities declared Kaziranga a Tiger Reserve in the year 2006.
PM Modi announces solar roof-top scheme for one crore households (HT)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Monday announced the 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana' under which one crore households will get rooftop solar across the nation.
What is 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana'?
- The scheme aims to equip one crore poor to middle-class households with rooftop solar panels in a bit to provide electricity from solar energy.
- The scheme would not only reduce the electricity bill of the poor and middle class but would also make India self-reliant in the energy sector.
- Rooftop solar panels are the photovoltaic panels installed on the roof of a building which is connected to the main power supply unit.
- Thus, it reduces the consumption of grid-connected electricity and saves electricity costs for the consumer.
- In a solar rooftop system, there is only an upfront capital investment and minimal cost for maintenance.
- Under this scheme, one crore households will get solar rooftops.
- Moreover, it will offer additional income for surplus electricity generation.
- The consumer can choose any vendor on the national portal and after installation, the subsidy is sent directly to the bank account of the consumer.
- The Pradhanmantri Suryodaya Yojana is a new scheme but very similar to the previously announced Rooftop Solar Programme in 2014.
- The previous scheme had aimed to produce 40,000 megawatts (MW) or 40 gigawatts (GW) of solar power by 2022.
India's Advancements in Solar Energy:
- At the end of last year, 2023, India’s solar power generation stood at 73.31 GW, up from 2022’s 63.3 GW.
- However, rooftop solar power generation only stands at around 11.08 GW as of December 2023.
- The total solar power generated in the nation, Rajasthan leads the pack with 18.7 GW while Gujarat follows with 10.5 GW.
- However, when talking about rooftop solar power, Gujarat is at peak position — with 2.8 GW — followed by Maharashtra at 1.7 GW.
- India has more than 300 million households and an average of 300 sunny days each year, which has tremendous potential for rooftop solar installations in residential spaces.
- However, experts note that despite several measures, India’s rooftop solar power generation is not where it should be, listing reasons for the situation.
- The primary reason for rooftop solar not becoming popular is that it is still an expensive option for many.
- There is also a lack of awareness.
Importance of Solar Power to India:
- Harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity is important to India for multiple reasons.
- If India wants to achieve its aim of becoming net zero by 2070, it has to look towards the sun.
- In fact, at COP26, in November 2021, India committed to meet 50 per cent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030.
- For these aims to be met, India has to harness the full capacity of the sun.
- Moreover, India’s share of global energy demand is predicted to double to 11 per cent in 2040, making it imperative to enhance energy security and self-sufficiency in power generation without increasing environmental costs.
- This increase in power demand is likely to increase India’s reliance on coal, oil and natural gas as a source of energy.
- However, additional imports of oil and increased domestic production of coal will not only fall short of energy demand but will also entail economic and environmental costs.
- The expansion of solar power units and increased reliance on solar power allow India to enhance energy security in the face of rising demand.
- Furthermore, India is already facing depleting groundwater levels, owing to which the nation must shift its energy resources away from water.
: In a first, India set to chair, and host UNESCO's World Heritage Committee session in Delhi (HT)

- 09 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a historic development, India is poised to chair and host UNESCO's World Heritage Committee session in New Delhi from July 21 to 31 this year, the Permanent Representative of India to UNESCO.
About the World Heritage Committee:
- The World Heritage Committee operates as a subsidiary of the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- Its primary responsibilities encompass executing the World Heritage Convention, determining the utilization of the World Heritage Fund, and disbursing financial assistance in response to requests from States Parties.
- The committee holds authoritative decision-making power regarding the inscription of properties on the World Heritage List, scrutinizes reports on the conservation status of listed properties, and prompts States Parties to rectify mismanagement issues.
- Additionally, it plays a pivotal role in determining the inclusion or removal of properties on the List of World Heritage in Danger.
- Structure:
- Comprising representatives from 21 States Parties elected by their General Assembly, the Committee operates with members serving six-year terms.
- However, many state parties opt for a four-year term voluntarily, allowing other state parties an opportunity to participate on the committee.
- Bureau of the World Heritage Committee:
- The Bureau, consisting of seven state parties elected annually by the Committee, includes a Chairperson, five Vice-Chairpersons, and a Rapporteur.
- This body is responsible for coordinating the Committee's activities, determining meeting schedules, and organizing the agenda.
What is UNESCO?
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) stands as a specialized agency within the United Nations (UN), dedicated to fostering global peace and security through collaborative efforts in education, arts, sciences, and culture.
- Established in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation, UNESCO boasts a membership of 193 states and 11 associate members, along with partnerships in the non-governmental, intergovernmental, and private sectors.
- The organization is headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris.
- UNESCO's foundational mission is to promote peace, sustainable development, and human rights by fostering cooperation and dialogue among nations.
- It pursues this overarching goal through five primary program areas: Education, Natural Sciences, Social/Human Sciences, Culture, and Communication/Information.
- The governance of UNESCO lies in the hands of the General Conference, comprising member states and associate members, convening biannually to establish the agency's programs and budget.
- The General Conference also elects members of the Executive Board, responsible for managing UNESCO's initiatives.
- Every four years, the Director-General is appointed by the General Conference to serve as the chief administrator of UNESCO.
- India has been a founding member of UNESCO, having ratified UNESCO’s Constitution on 4th November 1946.
Bhimashankar Temple (HT)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Tensions escalated at the Bhimashankar temple recently as a dispute unfolded between two groups of religious leaders, referred to as pujaris, regarding the leadership of the puja ceremony, leading to a brawl.
Bhimashankar Temple Overview:
- The Bhimashankar Temple is an ancient Hindu shrine dedicated to Lord Shiva, located amidst the Sahyadri hills in the Pune District of Maharashtra.
- Recognized as one of the 12 holy Jyotirlinga shrines in India, it holds immense spiritual significance.
- In recent times, it has gained additional importance as it was designated a "Wildlife Sanctuary," forming part of the Western Ghats and serving as the source of the Bhima River.
Historical Significance:
- Constructed around the 13th century, the temple is a testament to the craftsmanship of Vishwakarma sculptors.
- Subsequent enhancements, including the addition of spires (shikhara) by Maratha Empire statesman Nana Phadnavis in the 18th century, contribute to its historical evolution.
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, the Maratha ruler, is believed to have played a role in fostering worship at the temple through his endowments.
Architectural Marvel:
- A blend of old and new structures in the Nagara style of architecture, the Bhimashankar Temple boasts spacious courtyards, intricate wall carvings, and imposing pillars.
- The sanctum, or Garbhgriha, houses the sacred Jyotirlinga, positioned at a lower level. The Swayambhoo, a self-emanated Shiv Linga, holds a central place in the Sanctum Sanctorum.
- Exquisite mythological carvings adorn the massive pillars and doorframes, depicting divine figures and sacred symbols.
- Additionally, the temple encompasses an ancient shrine dedicated to Lord Shani, considered auspicious by devotees, and features the revered Nandi statue at its entrance.
What are Jyotirlingas?
- Jyotirlingas are shrines where Lord Shiva is worshipped in the form of a Jyotirlingam, representing different manifestations of the deity.
- Among the 12 main Jyotirlingas in India, Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga is one.
- Each of these sacred shrines is named after its presiding deity and holds unique spiritual significance for devotees across the country:
- Somnath Jyotirlinga in Gir, Gujarat
- Mallikarjuna Jyotirlinga in Srisailam, Andhra Pradesh
- Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga in Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh
- Omkareshwar Jyotirlinga in Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh
- Baidyanath Jyotirlinga in Deoghar, Jharkhand
- Bhimashankar Jyotirlinga in Maharashtra
- Ramanathaswamy Jyotirlinga in Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu
- Nageshwar Jyotirlinga in Dwarka, Gujarat
- Kashi Vishwanath Jyotirlinga in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh
- Trimbakeshwar Jyotirlinga in Nasik, Maharashtra
- Kedarnath Jyotirlinga in Rudraprayag, Uttarakhand
- Ghrishneshwar Jyotirlinga in Aurangabad, Maharashtra
New Plant Species Curcuma kakchingense Discovered in Manipur (HT)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
In a remarkable botanical discovery, a team of researchers from the Department of Life Sciences at Manipur University and Kwaklei and Khonggunmelei Orchids Pvt. Ltd. has unveiled a hitherto unknown plant species named "Curcuma kakchingense."
About Curcuma Kakchingense:
- Recently identified flowering plant species in Manipur, belong to the Zingiberaceae family.
- Member of the angiospermic family Zingiberaceae, which includes well-known plants like turmeric, gingers, and cardamom.
- Plant Characteristics: Robust plant reaching a height of eight feet, characterized by large terminal inflorescence.
- Natural Habitat: Thrives along the banks of the Sekmai River in the Kakching District of Manipur.
- Resemblance to Other Species: Bears a striking resemblance to local "Yaingung" (Curcuma longa) and Curcuma phrayawan from Thailand.
- Distinguished by lemon-yellow rhizomes with a notably bitter taste.
- IUCN Red List Classification: Classified as "Data Deficient" (DD) under the IUCN Red List category.
Importance of Curcuma Plants:
- Culinary and Traditional Uses: Various Curcuma species, including turmeric (Curcuma longa), play a vital role in cuisines, traditional medicines, spices, and dyes.
- Biological Activities: Curcumin and curcuminoids found in Curcuma species are nontoxic polyphenolic compounds with diverse biological activities.
- Pharmacological Properties: Essential oil of Curcuma species possesses pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancerous, anti-diabetic, and anti-microbial effects.
- Versatile Applications: Widely utilized in cosmetics, perfumes, and as ornamental plants, contributing to various industries and daily life.
Hailstorms Damage Apple Orchards in Kulgam, Shopian (HT)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A hailstorm in the evening caused massive damage to the crops and fruits in south Kashmir’s Kulgam and Shopian districts. Residents said the hailstorm damaged the apple fruit which was ready for harvesting.
What are Hailstorms?
- Hail, a solid form of rain composed of ice balls or lumps, leads to the formation of hailstorms when they descend to the ground.
- Typically lasting around 15 minutes, these storms can inflict injuries and damage to structures, vehicles, and more, particularly prevalent in midlatitude regions.
- Hailstorms occasionally coincide with other severe weather phenomena such as cyclones and tornadoes.
- The size of hailstones varies widely, ranging from small pellets under 1/4 inch to larger stones measuring several inches in diameter.
- Conditions: Conditions conducive to hailstorm occurrence involve the presence of highly developed Cumulonimbus clouds, massive anvil-shaped formations observed during thunderstorms that can reach heights of up to 65,000 feet.
- Strong updrafts, or ascending air currents within these clouds, and high concentrations of supercooled liquid water are essential elements.
- Formation of Hail: Hail formation begins with a water droplet lifted by an updraft inside a thundercloud.
- As it ascends, supercooled water droplets adhere to its surface, creating layers of ice.
- With continued ascent, the hail embryo grows by accumulating more supercooled particles until gravity pulls it down.
- Large hailstones often display alternating layers of clear and opaque ice due to irregular rates of freezing during their development.
New Toad Species Discovered in Dampa Tiger Reserve of Mizoram (HT)

- 12 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A group of scientists from India and the United Kingdom have discovered a new species of toads, the third of a genus found only in a very narrow area in northeast India.
About the Recently Discovered Toad Species:
- This newfound toad species, belonging to the bufoides genus, marks the third identified within a limited area in northeast India.
- Distinguished by its interdigital webbing, unique colouration, skin tuberculation, and the existence of ovoid, tuberculated, and depressed parotid glands, this species adds to the diversity of its genus.
- The preceding species from the same genus, Bufoides meghalayanus and Bufoides kempi, were previously identified in the region of Meghalaya.
- In recognition of its discovery and to honour the significant contributions of the renowned herpetologist S. Bhupathy, this new species has been aptly named after him.
About the Dampa Tiger Reserve:
- Situated in the Lushai Hills on the western side of Mizoram, the Dampa Tiger Reserve holds significance for its unique features.
- Establishment: Designated as a tiger reserve in 1994 under the Project Tiger initiative.
- Geographical Boundaries: Bordered on the west by the Chittagong hill tracts (Sazek hill range) of Bangladesh.
- The terrain is characterized by hills, with elevations ranging from 49 to 1095 meters above mean sea level.
- Prominent peaks include Chhawrpialtlang (1095m), Dampatlang (869m), and Pathlawilunglentlang (780m).
- Vegetation Diversity: Encompassing tropical evergreen to semi-evergreen forests, the reserve boasts a diverse range of vegetation.
- River Systems: Drained by the Khawthlangtuipui River in the west and the Teirei River in the east, with tributaries like Keisalam, Seling, and Aivapui flowing through the reserve.
- Fauna: Diverse mammalian species inhabit the reserve, including Hoolock Gibbon, Rhesus Macaque, Assamese Macaque, Pig-Tailed Macaque, Stump-Tailed Macaque, and Phayre’s Leaf Monkey.
- Flora: The reserve boasts a rich flora, featuring species such as Dipterocarpus turbinatus, Dipterocarpus marcocarpus, Terminalia myriocarpa, and Michelia champaca, among others.
New Ensign for the Indian Air Force (HT)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Indian Air Force (IAF) Chief Air Chief Marshal (ACM) Vivek Ram Chaudhari on Sunday unveiled a new Ensign for the force, as it marked its 91st anniversary, by the inclusion of the Air Force Crest in the top right corner of the Ensign, towards the fly side.
About the Indian Air Force (IAF) Ensign:
- The new IAF Ensign exclusively incorporates the IAF Crest, featuring distinctive elements that symbolize the spirit and ethos of the Indian Air Force.
Key Elements:
- IAF Crest: The crest prominently showcases the national symbol, the Ashoka Lion, atop, with "Satyamev Jayate" in the Devanagari script beneath.
- Himalayan Eagle: Positioned below the Ashoka Lion, a Himalayan eagle with outstretched wings symbolizes the formidable fighting spirit of the IAF.
- Light Blue Ring: Encircling the Himalayan eagle, a light blue ring bears the words "Indian Air Force."
- IAF Motto: Derived from the Bhagavad Gita, the motto "Nabha Sparsham Deeptam" (touching the sky with glory) is inscribed in golden Devanagari below the eagle.
- The IAF crest serves as a powerful symbol of inspiration and encouragement.
Variations:
- IAF has adopted various crests for commands, squadrons, and other establishments, all adhering to a standard frame featuring the formation sign and a motto at the foot.
Historical Evolution:
- British Era: During the British era, the IAF was known as the Royal Indian Air Force, and its ensign featured the Union Jack and the RIAF roundel.
- Post-Independence: The current IAF Ensign, created post-independence, replaces the Union Jack with the Indian tricolour and the RAF roundels with the IAF tri-colour roundel in the lower right canton.
Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission (HT)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Dr Aroh Barjatya, an Indian-origin scientist is set to lead the multi-institution NASA rocket mission on October 14.
About Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission:
- The APEP mission entails the launch of three rockets, each equipped with scientific instruments, to explore changes in the upper atmosphere during a solar eclipse, particularly during the critical phase of sudden light reduction.
- Mission Objective: To investigate alterations in the ionosphere induced by the abrupt decrease in sunlight during an eclipse, leading to the generation of waves in this atmospheric layer.
- Measurements will encompass changes in electric and magnetic fields, as well as variations in density and temperature.
- Launch Details: The launch site is the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, with a specific focus on studying the ionosphere's response during an eclipse.
- Potential Impact on Communications: NASA notes projections indicating a temperature and density reduction in the ionosphere during the eclipse, potentially causing disruptive wave disturbances that could affect GPS and satellite communications.
- Process: Rockets will be strategically positioned just beyond the path of annularity, where the Moon directly aligns with the Sun.
- Each rocket will deploy four compact scientific instruments designed to capture data on electric and magnetic fields, density, and temperature changes.
- NASA's primary objective is to achieve unprecedented simultaneous measurements from multiple ionospheric locations during a solar eclipse.
- Rationale for Rocket Selection: Sounding rockets were chosen for their precision in pinpointing and measuring specific regions of space.
- Their ability to investigate lower altitudes, inaccessible to satellites, makes them ideal for this mission.
- Sounding rockets offer precise data recording as they ascend and descend during suborbital flights, covering altitudes ranging from 45 to 200 miles (70 to 325 kilometres) above Earth's surface along their flight path.
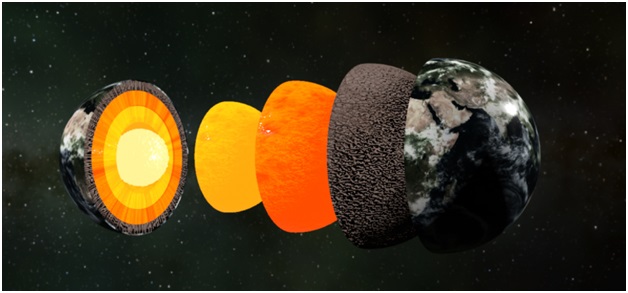
The E Prime Layer (HT)
- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an international team of scientists found a new mysterious layer called the E prime layer on the outer part of the Earth's core.
About the E Prime Layer:
- Before, it was thought that there's only a small exchange of materials between the Earth's core and mantle.
- However, experiments showed that when water reaches the boundary between the core and mantle, it reacts with silicon in the core and creates silica.
Development of this Layer:
- New research proposes that over billions of years, tectonic plates carrying surface water transported it deep into the Earth.
- When this water reaches about 1,800 miles below the surface at the core-mantle boundary, it triggers significant chemical changes, affecting the core's structure.
- Scientists observed that under high pressure, subducted water chemically reacts with core materials.
- This reaction forms a hydrogen-rich, silicon-depleted layer on the outer core, resembling a film.
- Silica crystals produced in this process rise and mix into the mantle, impacting the overall composition.
- Changes in the liquid metallic layer could potentially lead to reduced density and altered seismic characteristics, consistent with anomalies detected by seismologists.
Importance of this Discovery:
- This finding deepens researchers' understanding of the Earth's internal workings, revealing a more extensive and complex global water cycle than previously known.
- The altered core layer has significant implications for the interconnected geochemical processes that link surface water cycles with the deep metallic core.
What is ROV ‘Daksh’? (HT)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Defence Research Development Organisation's robotics team utilized the Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Daksh to aid in the ongoing rescue operations during the Uttarakhand tunnel collapse.
What is ROV Daksh?
- Daksh is a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), designed by the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) for the recovery of unexploded bombs.
- It can negotiate various hurdles in an urban setting and can also be utilised to survey and monitor nuclear and chemical contamination levels.
- 90% of its components are indigenous.
- It has ladder climbing abilities and can function for three continuous hours, with the capability to operate over distances exceeding 100 to 500 meters.
- It serves the bomb disposal units (BDU) of an army, police, and paramilitary forces, aiding in handling IEDs and other dangerous substances.
- Its manipulator arm can handle hazardous objects weighing up to 20kg from 2.5 meters and 9kg from 4 meters away.
- Daksh demonstrates the ability to climb stairs and maneuver steep slopes, with durable rubber wheels capable of withstanding blast impacts.
- It is equipped with multiple cameras, IED handling tools, nuclear biological chemical (NBC) reconnaissance systems, a master control station (MCS), and a shotgun.
- The equipment is specifically designed for use on a motorized pan-tilt platform, which can help reach the risky terrain.
Vadhavan Port (HT)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Vadhavan Port Project Ltd. (VPPL) has started the procedures to build a port with an estimated cost of ?76,220 crore. Public hearings are expected to commence in the coming months.
About Vadhavan Port:
- The Vadhavan Port is a proposed deep-sea port to be located in Palghar District, Maharashtra.
- It is expected to be one of the largest ports in the world, with a capacity to handle over 20 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) of containers per year.
- The port is being developed by a joint venture between the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) and the Maharashtra Maritime Board (MMB).
- The Vadhavan Port is being designed as a "green port" with a focus on sustainability.
- The port will use renewable energy sources and implement energy efficiency measures.
- The port will also have a dedicated waste management system to minimize environmental impact.
- It is expected to be operational by 2040 and is a critical project for India's economic growth and development.
- The Vadhavan Port is expected to be a major boost to the Indian economy.
- It will create thousands of jobs and attract billions of dollars in investment.
- The port will also help to reduce congestion at the JNPA, which is currently India's busiest container port.
- The Vadhavan Port is a major infrastructure project that is expected to have a significant impact on India's economy and society.
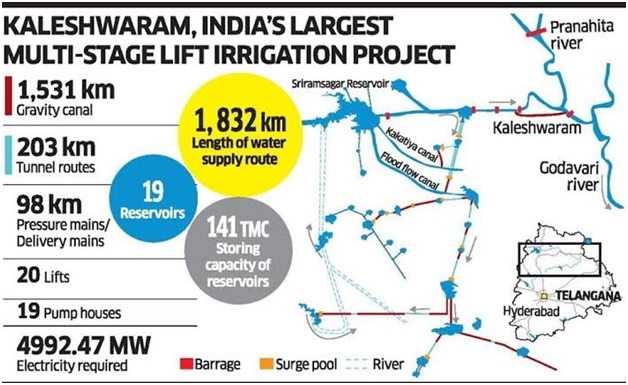
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) (HT)
- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A controversy over alleged engineering lapses in the ?1 lakh crore Kaleshwaram lift irrigation project on the Godavari river triggered an electoral slugfest in poll-bound Telangana.
About Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP):
- Location: The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) is situated at Kaleshwaram village in Telangana, along the Godavari River.
- Confluence Point: It is located at the confluence of the Pranhita and Godavari Rivers.
- At this confluence, the Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga rivers also meet, forming the seventh-largest drainage basin in the subcontinent.
- Originally called Pranahita-Chevella project in erstwhile Andhra Pradesh, it was redesigned, extended and renamed as Kaleshwaram project in Telangana in 2014.
- KLIP is known as the world's largest multi-stage and multi-purpose lift irrigation project.
- A significant feature of KLIP includes a series of underground and surface water pumping stations, claimed to be the world's largest of their kind.
- This lift irrigation system stretches over 300 kilometers and moves large volumes of water from rivers or reservoirs to be distributed through channels and additional reservoirs before reaching the next stations.
- Objective: The project's goal is to provide water to 45 lakh acres of land in Telangana for irrigation and drinking water.
- KLIP started in 2016 and will utilise approximately 283 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) of water from the Godavari River to serve 13 districts in Telangana.
World Food India 2023 (HT)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated that India's food diversity benefits investors worldwide as he inaugurated the second edition of "World Food India 2023" at Bharat Mandapam in Delhi recently.
What is World Food India 2023?
- World Food India 2023 provides a gateway of access to the Indian food market, promoting collaborations between domestic and foreign investors.
- It is organized by India's Ministry of Food Processing Industries in New Delhi from November 3rd to 5th.
- Objective: It aims to exhibit India's rich food culture and attract global investments in the food processing sector.
- The event brings together manufacturers, producers, investors, policymakers, and organizations from around the world involved in the food industry.
- Key Areas of Focus: The event is focused on leveraging millets as a superfood, positioning India as a global hub for food processing, unlocking growth potential in strategic segments, establishing an efficient ecosystem, and promoting sustainable development.
- India's Vision: This event aligns with India's vision to become a global leader in the food processing industry, highlighting the country's production, consumption, and export potential across various food sectors.
- India is taking steps to create an inclusive and sustainable ecosystem, attract foreign investment, and improve the ease of doing business in the food processing sector.
- Notably, the first edition of World Food India took place in 2017.
- India is a global leader in the production of various agricultural products, such as milk, bananas, mangoes, papayas, guavas, ginger, okra, and buffalo meat.
- It also ranks second in the production of rice, wheat, potatoes, garlic, and cashew nuts.
- Moreover, the United Nations has declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets (IYM 2023) with the goal of increasing millet production and consumption worldwide.
Voyager 2 Spacecraft (HT)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
NASA’'s Voyager 2 spacecraft, which is venturing through space between stars, faces communication problems due to antenna misalignment. .
About Voyager 2 Spacecraft:
- Voyager 2 is an iconic interplanetary spacecraft launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, with the primary objective of exploring the outer planets of our solar system.
- It is part of the Voyager program, and along with its twin, Voyager 1, it has provided invaluable insights into the distant regions of our cosmic neighborhood.
- The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of scientific instruments to study various aspects of the planets it encounters, including their atmospheres, magnetic fields, and planetary surfaces.
- Voyager 2 successfully conducted close flybys of Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1986, and Neptune in 1989, becoming the first and only spacecraft to visit these four giant gas planets.
- Beyond its initial mission, Voyager 2 continues to be operational and remains in communication with Earth, traveling at an impressive speed of approximately 34,000 miles per hour (55,000 kilometers per hour).
- It has since left the heliosphere, the region influenced by the Sun's magnetic field, and entered interstellar space, becoming the second human-made object to do so after Voyager 1.
- Throughout its journey, Voyager 2 has provided a wealth of data and discoveries about the outer planets and their moons, as well as valuable information about the space environment outside the solar system.
- It has captured breathtaking images of planetary systems, revealing the beauty and complexity of the outer planets and their fascinating moons.
- The spacecraft continues to be a remarkable testament to human ingenuity and curiosity as it ventures farther into the cosmos, providing us with an enduring legacy of exploration and knowledge about our celestial neighbors.
Basohli Pashmina is Recognized with GI Tag (HT)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Basohli Pashmina, a traditional craft with over a century of history from the Kathua district in Jammu and Kashmir, has been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Basohli Pashmina:
- Basohli Pashmina is renowned for its exceptional softness, fineness, lightweight quality, insulation, and durability.
- Pashmina products include shawls, mufflers, blankets, and baskets.
- Pashmina is a premium variety of cashmere, obtained from the fine undercoat of the Changthangi mountain goats.
- These goats are found on the Changthang Plateau in Tibet and parts of Ladakh.
- The Changpa people, who are nomads living on the Changthang plateau of Tibet, are traditional producers of pashmina wool.
