Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has recently been renamed MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease), reflecting a shift in understanding of the disease's root causes and its broader implications.
Why the Name Change?
- The primary reason for renaming NAFLD to MASLD is to highlight the metabolic dysfunction as the primary cause of the disease.
- Previously, the term NAFLD focused on the absence of alcohol consumption, which inadvertently shifted attention away from the true contributors, like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- The term MASLD eliminates the stigma associated with "non-alcoholic," which may have misled people into thinking alcohol consumption was the only factor, even though metabolic issues are the central cause.
- The term MASLD shifts the focus towards metabolic dysfunction, making it easier for healthcare professionals to understand, diagnose, and treat the condition more effectively.
The Connection to Metabolic Dysfunction
- MASLD is strongly associated with metabolic issues such as abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, and high blood sugar. These metabolic problems are key contributors to liver fat accumulation.
- People with abdominal obesity are 2-3 times more likely to develop fatty liver disease. MASLD affects about 25% of the global population, and the rates increase significantly (up to 50-70%) in individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity.
- By focusing on metabolic dysfunction, MASLD encourages addressing the root causes rather than just the symptoms, offering a more effective approach to treatment and prevention.
How is MASLD Diagnosed?
Advancements in non-invasive diagnostic methods have improved the ability to diagnose MASLD more easily and accurately, including:
- FibroScan: A non-invasive, painless test to measure liver fat and stiffness, replacing the need for liver biopsy.
- MRI and Ultrasound Techniques: Reliable methods for assessing liver fat and scarring.
- Blood Tests: Common tests like ALT, AST, and GGT assess liver function. Researchers are also exploring new markers like CK-18 fragments and the ELF score (Enhanced Liver Fibrosis) to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Implications for Patient Care
The renaming of NAFLD to MASLD has important implications for patient care:
- Targeted Treatments: By focusing on the metabolic roots, treatments such as weight loss, blood sugar management, and cholesterol control can be prioritized. These interventions help reduce the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, liver failure, and cirrhosis.
- Earlier Diagnosis: MASLD encourages earlier recognition of the condition, which can lead to better management and improved long-term outcomes.
Prevention
Preventing MASLD involves avoiding foods that exacerbate liver fat buildup. Dr. Punit Singla, director at Marengo Asia Hospitals, emphasizes limiting or avoiding:
- Fast food, junk food, and processed foods
- Foods high in sugar, including red and processed meats
A healthier lifestyle with a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can significantly help prevent or manage MASLD.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
100-Day Intensified Nationwide TB Campaign

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
- Union Health Minister Shri JP Nadda launched a 100-day intensified TB campaign in Panchkula, Haryana, aimed at reducing TB incidence and mortality. The campaign will focus on 347 high-risk districts across India.
Key Highlights:
- Campaign Goals:
- Find and treat missing TB cases, especially in high-risk groups.
- Significantly reduce TB-related deaths.
- Focus Areas:
- The campaign is part of India’s larger goal to eliminate TB before the 2030 SDG deadline.
- Strategies include early detection and rapid treatment of TB patients.
- Historical Context:
- TB was once seen as a "slow death" and patients were isolated.
- In 2018, the Prime Minister set the vision to end TB before 2030.
- Recent Government Initiatives:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs network of 1.7 lakh centers helps in early TB detection.
- Increased diagnostic infrastructure: Laboratories increased from 120 in 2014 to 8,293 today.
- Introduction of new drug regimens: Shorter and more effective treatments have increased the treatment success rate to 87%.
- Ni-kshay Support: Rs 3,338 crore transferred to 1.17 crore TB patients via direct benefit transfer.
- Key Achievements:
- TB decline rate in India has increased from 8.3% (2015) to 17.7% today, surpassing the global average.
- TB-related deaths have dropped by 21.4% over the past decade.
- Private Sector Involvement:
- Mandatory notification of TB patients by private practitioners has led to an 8-fold increase in TB case notifications.
- 4Ts Approach for TB Elimination: Test, Track, Treat, and Technology (use of advanced tools for diagnosis and treatment).
- New Initiatives:
- Ni-kshay Vahaan: Mobile vans to detect and treat TB patients in remote areas.
- Launch of national guidelines for a new drug-resistant TB regimen (BPaLM), which is a 4-drug combination therapy for multi-drug-resistant TB.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana:
- Increase in nutritional support: Monthly support raised from Rs 500 to Rs 1000 per TB patient.
- The initiative also includes energy boosters for enhanced patient care.
- Mobile Diagnostics:
- Deployment of AI-enabled portable X-ray units and molecular tests to bring diagnostics closer to people, especially in remote areas.
- Monitoring and Data: Intensified data tracking via the Ni-kshay portal to provide timely updates to TB patients.
- Background of the Campaign:
- Part of the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- The 347 districts were selected based on indicators like death rates, presumptive TB examination rates, and incidence rates.
- Campaign Materials:
- Unveiling of Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) resources in regional languages.
- Honoring TB Champions and Ni-kshay Mitras during the event.
- Government’s Strategic Framework:
- India’s National Strategic Plan (NSP) for TB elimination (2017-2025).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign and Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- Tuberculosis (TB) Overview:
- TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and primarily affects the lungs, spreading through the air.
- Mortality rate has decreased from 28 per lakh (2015) to 23 per lakh (2022).
Disease X
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent outbreak reported in the first week of December 2024 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which has claimed over 400 lives and remains unclassified, has raised concerns that it could be an instance of Disease X.
What is Disease X?
- Definition: Disease X is a hypothetical, unidentified pathogen that has the potential to cause a global health crisis, either as an epidemic or pandemic.
- Origins: Could arise from zoonotic spillover (animal-to-human transmission), antimicrobial resistance, bioterrorism, or lab accidents.
- Severity: Predicted to be 20 times more lethal than SARS-CoV-2, with rapid transmission and significant mortality.
- Features: Represents unknown threats, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, or prions.
- Emergence Factors: Driven by deforestation, urbanization, climate change, and human-wildlife interactions.
Historical Context
- Conceptualization: The term was coined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2018, post the 2014–2016 Ebola outbreak, which revealed gaps in global health responses.
- Zoonotic Origins: Around 70% of emerging diseases since 1940 have zoonotic origins, linked to human encroachment on wildlife habitats.
WHO’s Priority Pathogen List
- Purpose: To focus global resources and attention on diseases with high epidemic or pandemic potential but lacking sufficient vaccines or treatments.
- Pathogens Listed: Includes Ebola, Marburg, Lassa fever, Nipah virus, Rift Valley fever, Zika virus, and Disease X.
- Criteria: These diseases have high mortality rates, potential for rapid spread, and inadequate preventive or therapeutic options.
Why Disease X is a Concern
- Unpredictability: Its emergence, transmission, and impact remain uncertain, making preparedness challenging.
- Globalization: Increased global travel and trade facilitate rapid spread of diseases across borders.
- Environmental Drivers: Climate change, urbanization, and deforestation disrupt ecosystems, bringing humans into closer contact with wildlife and pathogens.
Patterns in Emerging Diseases
- Zoonotic Spillover: The majority of emerging diseases originate from animals, with over 1.7 million undiscovered viruses in wildlife that could infect humans.
- Increased Outbreaks: Since the mid-20th century, the frequency of new diseases has risen, reflecting environmental, demographic, and global factors.
Challenges in Predicting Disease X
- Uncertainty: The vast pool of potential pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc.) makes it difficult to predict the exact nature, origin, or timing of Disease X.
- Environmental and Climatic Changes: Climate change reshapes disease transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases like malaria and dengue.
- Technological and Knowledge Gaps: Many pathogens that could cause pandemics are still unidentified. Genomic sequencing and AI are advancing but cannot fully predict Disease X.
Global Preparedness Initiatives
- WHO's Role: WHO’s priority pathogen list and Pandemic Treaty aim to ensure coordinated, global responses to future outbreaks.
- Pandemic Fund: Supports strengthening health systems, especially in low-income countries.
- mRNA Vaccine Hubs: Enhance vaccine production capacity, particularly in developing countries.
- Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI): Works on "prototype pathogen" platforms to create vaccines within 100 days of identifying a new disease.
Indian Initiatives for Disease Surveillance and Preparedness
- Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP): Tracks outbreaks, monitors trends, and strengthens the country’s epidemic preparedness.
- National Institute of Virology (NIV): Focuses on researching viral pathogens and zoonotic diseases.
- Biotech Initiatives: Indigenous vaccine development and diagnostic tools are crucial for combating future outbreaks.
- Emergency Response Fund: Allocates resources to support immediate pandemic response efforts.
Key Challenges in Tackling Disease X
- Prediction Complexity: The interactions between humans, animals, and the environment are too complex to predict the exact nature of Disease X.
- Health Disparities: Low- and middle-income countries often lack the infrastructure to effectively combat pandemics, making them more vulnerable.
- Climate Change: Alters transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases carried by vectors like mosquitoes.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Surveillance: Implementing real-time genomic sequencing and AI-driven tools for early outbreak detection.
- Global Cooperation: Promoting equitable sharing of vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments to ensure timely and efficient responses.
- Public Health Infrastructure: Invest in strengthening healthcare systems, especially in high-risk regions like the Congo Basin.
- Research and Development: Focus on universal vaccines, diagnostic tools, and prototype pathogen platforms that can be quickly adapted to new diseases.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
The Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, hosted a two-day Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) knowledge sharing workshop in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Event Overview:
- Two-day workshop hosted by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education.
- Focus areas: School-to-Work Transition and Strengthening the Assessment System.
- Key Objectives:
- To enhance school-to-work transitions.
- To discuss strengthening educational assessment systems.
- Align education with future workforce needs as per the National Education Policy 2020.
Day 1: School-to-Work Transition
Panel Discussions:
- Policy Frameworks:
- Role of National Education Policy 2020, National Curriculum Framework (NCF), and National Credit Framework (NCrF) in school-to-work transitions.
- Focus on integrating skill education into school curricula, fostering multidisciplinary learning, and continuous evaluation to meet industry standards.
- Emphasis on internships, apprenticeships, and flexible learning pathways.
- Curriculum Integration:
- Need for integrated efforts across departments and aligning curriculum with industry demands.
- Focus on strengthening 21st-century skills in CBSE schools.
- Career Counselling and Psychometric Analysis:
- Focus on using psychometric assessments for career counselling and preparing students for future work environments.
- Work-Based Learning:
- Discussed partnerships with industry for work-based learning.
- Effective collaborations between schools and industry for internships, placements, and best practices.
Day 2: Strengthening Assessment System
- Psychometric Analysis & Career Counselling:
- Smt. Idzes Angmo Kundan (Principal Secretary, Maharashtra) presented the 3 P approach to career choices: Personal Interest, Parental Approach, and Possible Opportunities.
- Enhancing Student Outcomes:
- Discussed improving student outcomes by strengthening assessment systems.
- Shared innovations in educational assessments.
- Highlighted innovative assessment practices for future education.
- VSK Implementation (Chhattisgarh):
- Discussed VSK modes, data analysis, and strategies for integrating assessment outcomes with learning objectives.
- Strengthening Assessment Cells:
- Advocated for the establishment of assessment cells.
- Discussed best practices and challenges in strengthening assessment cells across states.
World Food Day 2024

- 16 Oct 2024
In News:
World Food Day, observed annually on October 16, has its roots in the establishment of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) by the United Nations in 1945.
Significance: World Food Day emphasizes the critical need to address global hunger and promote resilient food systems capable of overcoming challenges like climate change and economic disparities.
Introduction
- Food is vital for life, health, and well-being.
- Despite sufficient global food production, millions lack access to nutritious food.
- World Food Day serves as a reminder of ongoing challenges in achieving food security.
History and Theme
- Origins: Established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 1945, officially recognized in 1979.
- First Celebration: Took place in 1981 with the theme "Food Comes First."
- 2024 Theme: "Right to Food for a Better Life and a Better Future," highlighting that food security is essential for dignity and health. It emphasizes the need for sustainable practices and equitable distribution.
India’s Commitment to Food Security
- India has made significant strides in combating hunger through various programs aimed at malnutrition and poverty alleviation.
- Key initiatives include:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): Provides subsidized food grains to 75% of the rural and 50% of the urban population, benefiting about 81 crore individuals.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY): Offers free food grains to approximately 81.35 crore beneficiaries, extending support during the COVID-19 pandemic for an additional five years.
- PM POSHAN Scheme: Aims to improve children's nutritional status in government schools with a budget of ?12,467.39 crores for 2024-25.
- Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY): Focuses on the most vulnerable populations, supporting over 8.92 crore individuals and empowering women.
- Rice Fortification: Distribution of fortified rice through the Public Distribution System has improved nutritional intake for millions.
- Price Stability Initiatives: The government manages price volatility of essential commodities using the Price Stabilization Fund (PSF) and ensures affordability through strategic product launches.
Global Recognition of Indian Cuisine
- The Indian Thali has been recognized for its nutritional and sustainable qualities by the WWF Living Planet Report.
- Its plant-based composition contributes to lower resource use and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- If globally adopted, India’s dietary patterns could significantly lessen the environmental burden.
Significance
- India’s comprehensive initiatives reflect its dedication to food security and improving citizens' quality of life.
- By enhancing agricultural productivity and supporting vulnerable populations, India makes strides towards eradicating hunger.
- On World Food Day, these efforts underline India's commitment to achieving Sustainable Development Goal 2: Zero Hunger, while serving as a model for global food security initiatives.
Jipmer Launches ‘Tele-MANAS’ Mental Health Helpline

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Jipmer (Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) has launched the "Tele-MANAS" (Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States) helpline, a toll-free service (14416) aimed at providing mental health support.
- This initiative is part of the National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP), launched by the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Purpose and Need:
- With an estimated 1 in 10 people in India suffering from mental illness, and about 1% experiencing severe conditions, the service addresses significant gaps in mental health access, particularly in rural and remote areas.
- The helpline aims to provide immediate support for issues such as anxiety, depression, and emotional distress.
Training and Operations:
- Jipmer will train qualified counsellors who will subsequently train additional counsellors to expand the reach of the service.
- Counselors will be available 24/7, including holidays, to ensure continuous support.
Support Structure:
- Trained counselors will serve as the first point of contact for individuals seeking help, providing responses, suggestions, and necessary referrals to advanced mental health facilities.
- Jipmer will supervise the program, ensuring regular retraining and maintaining service quality.
Integration with National Programs:
- The initiative is coordinated by the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), which acts as the National Apex Centre for the NTMHP.
- It includes a comprehensive information library on mental health and guidance for managing early signs of stress and emotional challenges.
Impact on Mental Health Services:
- The program aims to enhance the overall quality of mental health services across states and union territories in India, making them more accessible to a larger population.
- Emphasizes the importance of mental health as a public health priority.
Mpox Diagnostic Test

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
In an important move to improve global access to Mpox testing, the World Health Organization (WHO) has listed the first Mpox in vitro diagnostic under its Emergency Use Listing procedure.
- Context of Mpox Outbreak:
- Since January 2022, mpox has spread to 121 countries.
- By September 2024, there were 103,048 confirmed cases and 229 deaths.
- Diagnostic Test Approval:
- WHO approved Abbott Laboratories’ PCR diagnostic test, Alinity MPXV assay, for emergency use.
- This test detects mpox virus DNA from skin swabs, intended for trained lab personnel.
- Emergency Use Listing (EUL) Procedure:
- Allows WHO to expedite approval of unlicensed vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tests during public health emergencies.
- In August, WHO called for manufacturers to submit diagnostic tools to aid low-income countries.
- Current Testing Landscape:
- Limited testing capacity has hindered response, especially in Africa, where over 30,000 suspected cases were reported in 2024.
- 35 laboratories in India are now equipped to test suspected mpox cases.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis:
- Early detection facilitates timely treatment and control of the virus, essential in outbreak areas.
- Characteristics of the Alinity MPXV Assay:
- Utilizes real-time PCR to detect mpox virus (clade I/II) DNA from lesion materials.
- Designed for skilled laboratory personnel familiar with PCR techniques.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- WHO is reviewing three additional mpox diagnostic tests and negotiating with more companies to enhance availability.
- Efforts include addressing the spread of a new variant, clade Ib, which is affecting more women and children.
- Public Health Implications:
- Expanding access to diagnostics is vital for managing the mpox outbreak and protecting populations, particularly in underserved regions.
- WHO emphasizes the importance of quality-assured medical products in containing the virus spread.
Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) launched the Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP) to tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:
- Tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses (e.g., Zika, chikungunya).
- Reduce disease burden, suffering, and deaths globally.
- Background:
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Unplanned urbanization.
- Poor water, sanitation, and hygiene practices.
- Climate change.
- Increased international travel.
- An estimated 4 billion people at risk, projected to increase to 5 billion by 2050.
- Significant increase in dengue cases; 12.3 million reported by August 2023, nearly double the total from 2022.
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Global Impact:
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- South-East Asia.
- Western Pacific.
- Americas.
- Africa facing compounded health crises due to conflicts and disasters.
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- Emergency Grade: WHO has graded the global dengue situation as grade 3, the highest emergency level.
- Key Components of SPRP:
- Emergency Coordination: Leadership and coordination activities for outbreak response.
- Collaborative Surveillance: Tools for early detection and control, including strengthened surveillance and epidemiological analysis.
- Community Protection: Engaging communities in local prevention and response measures.
- Safe and Scalable Care: Ensuring resilient health services for adequate patient care.
- Access to Countermeasures: Promoting research for better treatments and vaccines.
- Implementation Timeline: Over one year until September 2025, requiring US$ 55 million for health preparedness and response efforts.
- Alignment with Other Initiatives:
- Supports the Global Vector Control Response 2017-2030.
- Linked to the Global Arbovirus Initiative (2022) targeting mosquito-borne diseases.
- Call to Action:
- Encourages collaboration among government agencies, healthcare providers, and communities.
- Emphasizes the need for innovation and improved vector control strategies.
This plan aims to mobilize a coordinated response to the escalating threat of dengue and related diseases, emphasizing the role of all stakeholders in public health.
Indian push needed to end AIDS as a global health threat by 2030: UNAIDS

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The UNAIDS Director recently highlighted the crucial role India plays in the global fight against HIV/AIDS, asserting that without its significant contributions, achieving the Sustainable Development Goal of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 is unlikely.
Understanding HIV/AIDS
- HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which diminishes the body's ability to combat infections and diseases.
- When HIV progresses to its most severe form, it is diagnosed as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), characterized by a severely compromised immune system, leading to life-threatening infections and cancers.
- The virus is transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids, including blood, semen, and breast milk. While there is currently no cure, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can effectively manage HIV and prevent its progression to AIDS.
India’s Progress in Combating HIV/AIDS
- From 2010 to 2023, India has made significant strides in reducing annual new HIV infections by 44%, surpassing the global average.
- Additionally, AIDS-related deaths in India have decreased by nearly 80% during the same period, also exceeding global trends. However, challenges persist, with approximately 68,000 new infections reported in 2023, translating to around 185 daily.
- The Global AIDS Strategy emphasizes the need for 80% of prevention services to be delivered by community-led organizations, which are essential for reaching key populations but require sufficient resources and support.
About UNAIDS
UNAIDS, established in 1996, coordinates global efforts to combat HIV/AIDS and supports those affected. Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations and works in collaboration with various global and national partners to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030.
Key aspects of UNAIDS include:
- Global Mandate: To coordinate responses, support countries in prevention and treatment, and advocate for human rights and equality in access to services.
- Targets: The "90-90-90" targets aimed for 2020 sought to ensure that 90% of people living with HIV were diagnosed, 90% of those diagnosed were on treatment, and 90% of those on treatment achieved viral suppression.
- Current Strategy: The 2021-2026 Global AIDS Strategy focuses on eliminating inequalities that drive HIV and aims to ensure that 30 million people are on treatment by 2025.
- Funding and Advocacy: Funded by governments, private foundations, and corporations, UNAIDS organizes key campaigns, including World AIDS Day, to raise awareness and promote advocacy.
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India

- 03 Sep 2024
Overview
India’s mental healthcare landscape is evolving, with increasing awareness and decreasing stigma around mental health issues. However, access to mental healthcare remains a significant challenge due to a shortage of professionals. Here are the key points:
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India
- Rising Demand: Shifts in societal attitudes have led to more individuals seeking mental health support. Awareness and willingness to access treatment have notably increased.
- Professional Shortage: Despite the rising demand, there are only 0.75 psychiatrists per one lakh population, far below the World Health Organization’s recommendation of three per lakh. As of the latest data, India has about 9,000 psychiatrists, while an estimated 36,000 are needed to meet the standard.
- Slow Workforce Growth: Approximately 1,000 psychiatrists enter the workforce annually, but with attrition and unemployment, it could take around 27 years to reach the WHO target without intervention.
- Comparative Analysis: India has one of the lowest psychiatrist-to-population ratios among BRICS nations, trailing only Ethiopia. However, it performs better than many South Asian countries.
Limitations of Current Data
- Outdated Survey: The data largely relies on the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted between 2015 and 2016, which is based on a limited sample size of around 40,000 people across 12 states.
- Narrow Focus: The NMHS primarily addressed specific mental illnesses and overlooked milder conditions, emotional issues, and vulnerable populations like prisoners and the homeless.
- Need for Updated Research: A second NMHS is scheduled for release next year, which may provide more comprehensive data and insights.
Improvements in Awareness and Attitudes
- Positive Attitudinal Shift: A study by the LiveLoveLaugh Foundation found significant improvements in how Indians perceive mental health. For instance, the percentage of people believing that individuals with mental illnesses can handle responsibilities rose from 32% in 2018 to 65% in 2021.
- Willingness to Seek Help: Over 90% of respondents in 2021 indicated they would seek treatment for themselves or support others in doing so, a substantial increase from 54% in 2018.
- Increased Awareness: Awareness of mental health issues has grown, with 96% of respondents in 2021 recognizing mental health compared to 87% in 2018.
Conclusion
While India is making strides in reducing stigma and increasing awareness around mental health, the critical shortage of mental health professionals poses a significant barrier to accessing timely care. Addressing this issue requires targeted policy interventions and incentives to boost the supply of mental health professionals and improve the overall infrastructure for mental healthcare in the country.
MARBURG VIRUS OUTBREAK IN RWANDA
- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Rwanda is currently facing an outbreak of Marburg virus disease (MVD), leading to six fatalities, primarily among healthcare workers.
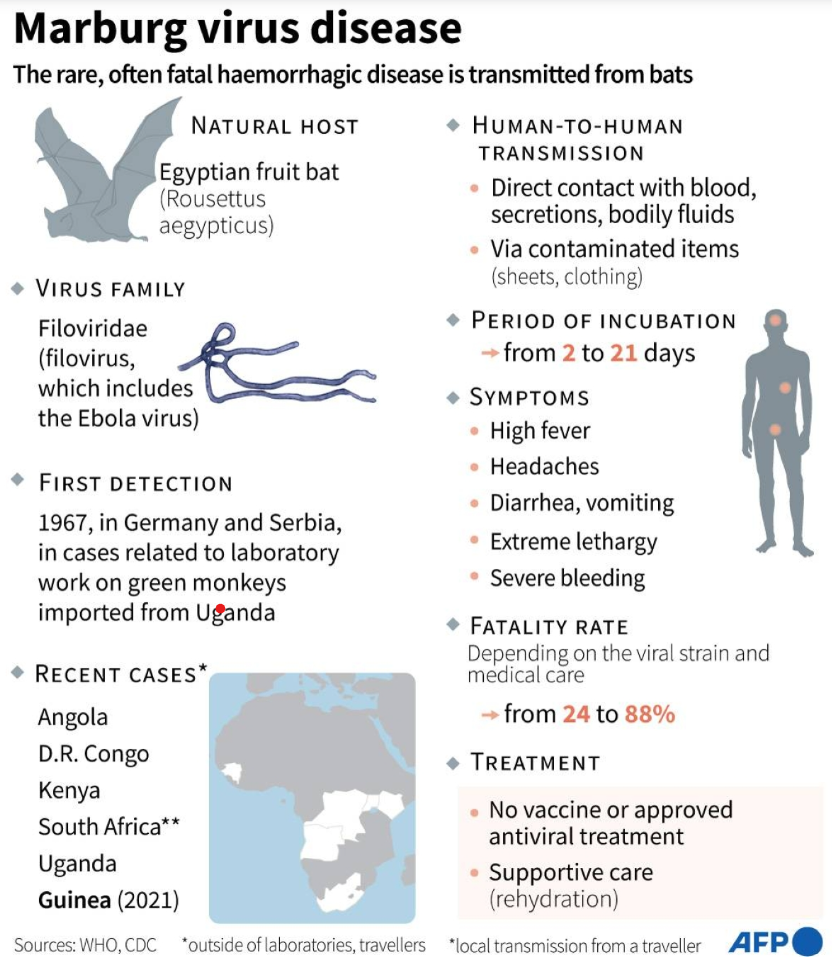
What is Marburg Virus Disease?
Marburg virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness first identified in 1967 in Germany. It is caused by the Marburg virus, which is primarily transmitted to humans through contact with infected animals, particularly fruit bats.
Current Situation in Rwanda
The ongoing outbreak has claimed six lives, most of whom were healthcare professionals. The Minister of Health has emphasized the need for heightened preventive measures and community vigilance.
Symptoms and Transmission
Common symptoms of MVD include high fever, severe headache, watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. The virus spreads through direct contact with the blood, secretions, and bodily fluids of infected individuals.
Available Treatments and Supportive Care
There is currently no specific treatment for Marburg virus disease. Supportive care, including symptom management and hydration, is critical, and early medical attention is essential for those exhibiting symptoms.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
To prevent the spread of MVD, individuals should:
- Practice good hygiene.
- Avoid contact with infected persons.
- Ensure thorough cooking of animal products.
- Use protective equipment when caring for sick patients.
Global Context and Pandemic Risk
While Marburg virus disease poses a significant mortality risk and can spread between humans, its pandemic potential is lower than that of more contagious viruses. Rapid containment efforts are essential to prevent wider outbreaks.
India’s Commitment to Social Determinants of Health at UNGA
- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, represented India at the G20 Joint Finance-Health Task Force meeting during the 79th UN General Assembly.
- Focus: The session emphasized the importance of investing in health and addressing social determinants of health (SDH) through initiatives like debt-for-health swaps.
Key Highlights:
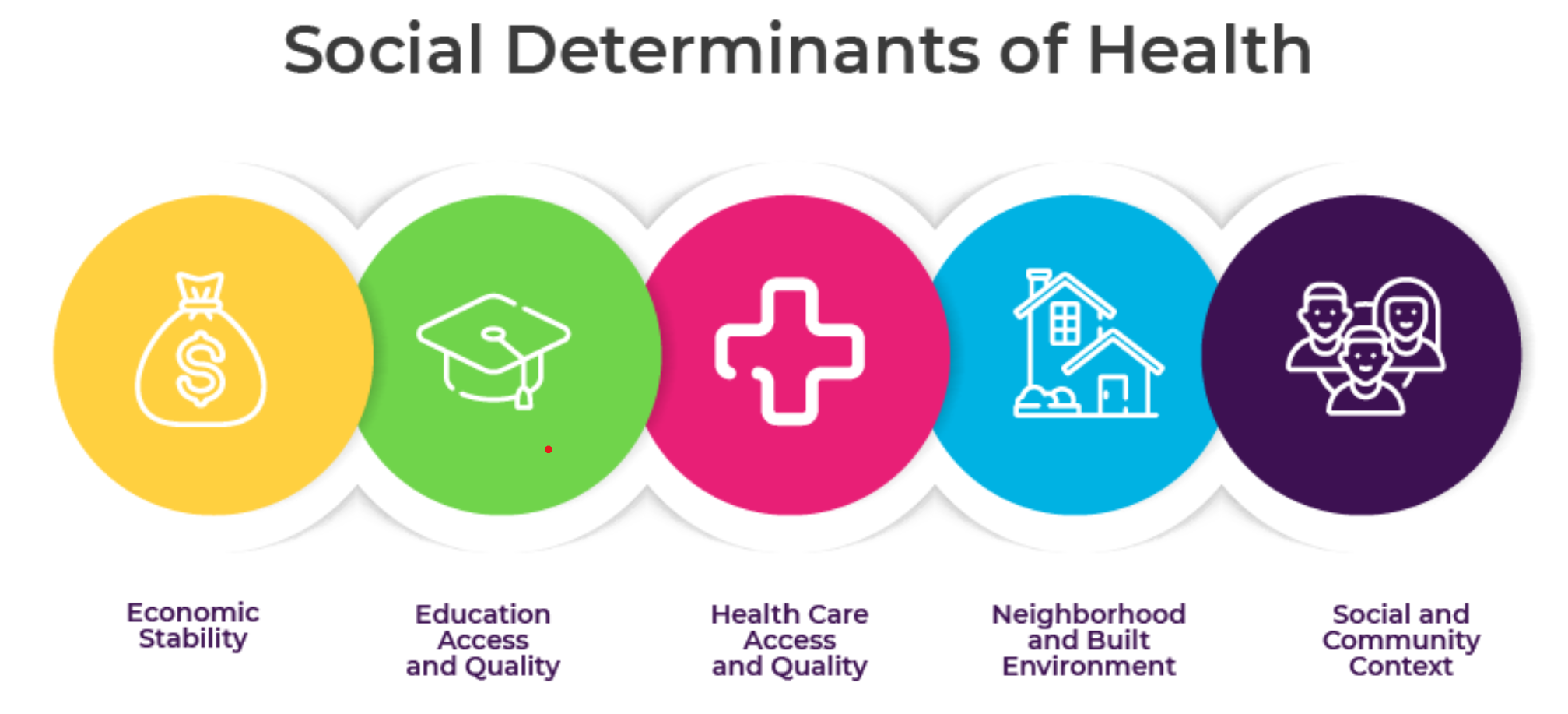
- Role of SDH: Underscored how social determinants such as housing, sanitation, water access, and income security are crucial for health investment priorities.
- Flagship Programs: India’s notable initiatives include:
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health insurance scheme.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Aiming for a cleaner India.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Ensuring water access for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Promoting housing for all.
- Impact of PM-JAY: Highlighted improvements in access to healthcare and outcomes, especially for non-communicable diseases.
Data and Policymaking
- Importance of Data: Stressed the need for enhanced data availability and standardization on SDH indicators to support effective policymaking.
- Unified Approach: Called for G20 nations to collaborate on data collection and analysis for better health systems globally.
Exploring Debt-for-Health Swaps
- Potential Mechanism: Discussed debt-for-health swaps as a means to relieve financial pressure while promoting health equity.
- Next Steps: Emphasized the need for stakeholder engagement and pilot programs to ensure effective implementation.
Conclusion
- Global Leadership: India reaffirmed its commitment to health equity through evidence-based policies and partnerships.
- Shared Vision: Advocated for a unified effort towards achieving “Health for All,” highlighting the significance of investments in social determinants of health.
About Social determinants of health (SDOH)
- SDOH are non-medical factors that affect a person's health, well-being, and quality of life. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age.
- SDOH also include the broader systems that shape everyday life, such as economic policies, social norms, and political systems.
- Some examples of SDOH include:
- Safe housing, transportation, and neighborhoods
- Racism, discrimination, and violence
- Education, job opportunities, and income
- Access to nutritious foods and physical activity opportunities
- Polluted air and water
- Language and literacy skills
POLITICAL DECLARATION ON ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
World leaders have officially adopted the Political Declaration on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) at the UN High-Level Meeting, highlighting the urgent need for coordinated global action to combat AMR, which claims 1.27 million lives annually. This declaration recognizes drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) as a critical component of the global AMR response, marking a significant moment in the fight against antimicrobial resistance.
Key Highlights of the Declaration
- DR-TB Priority: The declaration emphasizes the severe burden that DR-TB imposes on health systems, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), and the potential reversal of progress made against tuberculosis and the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Global Death Reduction Target: A target to reduce global deaths associated with AMR by 10% by 2030 and a funding goal of USD 100 million to help at least 60% of countries establish funded AMR plans by 2025.
- Support for Vulnerable Groups: Recognition of the socioeconomic challenges faced by those affected by AMR, affirming the need for integrated, person-centered healthcare, including support to reduce stigma.
- Independent Panel for Action: Agreement to establish an independent panel to provide evidence for actions against AMR by 2025.
Commitment to Action
The Stop TB Partnership applauds this commitment and urges UN Member States to provide necessary funding for implementing the declaration's commitments. The partnership aims to work closely with governments and civil society to translate these commitments into concrete actions.
Challenges of Antimicrobial Resistance
AMR poses a significant threat, particularly in LMICs, where it exacerbates existing healthcare challenges:
- Increased Infections: Medical facilities often become hotspots for treatment-resistant infections, making routine procedures riskier. In LMICs, about 11% of surgical patients experience infections.
- Lack of Resources: Access to clean water, proper diagnostics, and antimicrobial medicines is often limited, increasing vulnerability to drug-resistant infections.
- Impact of Conflicts: AMR complicates treatment in conflict zones, where drug-resistant infections spread rapidly among displaced populations, further emphasizing the need for peaceful resolutions.
Economic Implications of AMR
The economic case for addressing AMR is compelling:
- Without a stronger response, AMR could lead to an additional $412 billion in healthcare expenditures annually over the next decade, along with $443 billion in losses due to workforce participation and productivity declines.
- Implementing critical AMR interventions is considered a “best buy,” with a potential return of $7 to $13 for every dollar invested.
AYUSHMAN BHARAT DIGITAL MISSION (ABDM)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) have been created in the past three years under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM). The digital healthcare mission marked its three-year anniversary.
Key Highlights:
- Launch Date: September 27, 2021.
- Vision: Establish a robust digital health infrastructure to enhance healthcare accessibility, efficiency, and transparency.
- Duration: A transformative three-year journey aimed at revolutionizing India’s digital healthcare ecosystem.
Objectives and Background
- Alignment with National Health Policy: The mission stems from the National Health Policy (2017), emphasizing accessibility and the integration of digital technologies.
- Building Blocks:
- National Health Stack (2018) introduced unique health identifiers and verified registries.
- National Digital Health Blueprint (2019) provided guidance for implementing ABDM.
Key Features of ABDM
- Unique Health Identifier (ABHA ID): Assigns a unique ID to every individual for managing health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): Comprehensive database of healthcare professionals across all systems of medicine.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): Repository of public and private health facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies.
- Health Information Exchange and Consent Manager (HIE-CM): Allows secure access and sharing of health records based on informed consent.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Facilitates the discovery and delivery of health services.
- National Health Claims Exchange (HCX): Standardizes the insurance payment process for quicker claims.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensures confidentiality and security of health-related information in compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Interoperability: Enables seamless data exchange among stakeholders, supported by key gateways (HIE-CM, NHCX, UHI).
- Transparency: Offers individuals access to both public and private health services, ensuring transparent pricing and accountability.
Key Initiatives
- Scan and Share: QR-code based OPD registration reduces wait times and improves data accuracy.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Financial incentives to encourage participation in the ABDM ecosystem, launched on January 1, 2023.
- Microsites for Private Sector Adoption: Operationalized 106 microsites to facilitate ABDM adoption among private providers.
- End-to-End ABDM Adoption Pilot: Aimed at digitizing healthcare facilities across India, with 131 selected for participation.
Achievements
- Health Accounts Creation: Over 67 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) established, linking 42 crore health records.
- Ecosystem Participation: Involvement of 236 private entities and leading public institutions, enhancing interoperability.
- Healthcare Facility Registration: 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals registered.
Moving Towards Transformation
- Collaborations: Partnerships with IIT Kanpur and Maharashtra University of Health Sciences to drive digital health education and public goods development.
- Training Initiatives: Introduction of a WhatsApp Chatbot for stakeholder training on digital health practices.
- Digital Health Standards: Launched by the National Accreditation Board of Hospitals to promote digital health technology adoption.
- Integration of eSwasthya Dham Portal: Extends ABDM benefits to Char Dham Yatris.
Vision for the Future
ABDM aims to create a seamless digital health ecosystem, ensuring every Indian citizen has access to their health records through a unique ABHA ID. The initiative includes:
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS): Aids healthcare professionals in improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
QUAD CANCER MOONSHOT

- 23 Sep 2024
In News:
The Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative is a significant collaborative effort among the Quad countries—India, the United States, Australia, and Japan—aimed at combating cancer through innovative strategies. The initiative focuses on key areas such as preventing and detecting cancer, improving treatment, and alleviating the disease's impact on patients and families.
Key Highlights of the Quad Cancer Moonshot Initiative:
- Focus Areas:
- Cervical Cancer Screening: Enhancing access to screening programs.
- HPV Vaccination: Increasing vaccination rates against HPV, which is the leading cause of cervical cancer.
- Patient Treatment: Improving treatment protocols and accessibility for cancer patients.
- India’s Contributions:
- Financial Commitment: India has pledged $10 million to support the WHO’s Global Initiative on Digital Health, aimed at enhancing digital health technologies for cancer care in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Material Support: India will provide cervical cancer screening kits, detection tools, and HPV vaccines valued at $7.5 million to bolster healthcare initiatives in the region.
- AI-based Protocols: Development of AI-driven treatment protocols to improve care delivery for cancer patients.
- Capacity Building: India aims to enhance radiotherapy services and overall cancer prevention strategies in the Indo-Pacific.
This initiative represents a strong commitment to fostering international collaboration in healthcare, particularly in the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer. By empowering communities with accessible tools and resources, the Quad countries aim to significantly reduce the burden of cancer in the region.
Nipah viral infection

- 17 Sep 2024
In News:
- The district administration has imposed restrictions on social gatherings and made masks mandatory in Malappuram district after a 24-year-old man from Naduvath, near Wandoor, died from the Nipah viral infection.
- Five wards in Tiruvali and Mampad grama panchayats have been declared containment zones. Schools, colleges, madrasas, anganwadis and cinema halls in these zones will remain closed until further notice.
What is Nipah?
- Nipah is a viral infection that mainly affects animals such as bats, pigs, dogs and horses.
- It is known to cause infection in humans when they come in contact with saliva, urine, or faecal matter of infected animals — by eating fruits that have been bitten into by the animals or scaling trees were the bats live.
- It can also be transmitted human to human through close contact, but this is not the most common route of transmission.
- The case fatality ratio of Nipah can be extremely high at 40 to 75%. To compare, even at the peak of the Covid-19 pandemic, the case fatality ratio (CFR) – proportion of people who die among those who test positive – remained at around 3%.
What are the symptoms of Nipah?
People with Nipah start showing symptoms around four to 14 days after getting infected. The infection causes fever, headache, cough, sore throat and difficulty breathing. In later stages, the infection can also lead to brain swelling or encephalitis, leading to confusion, drowsiness, and seizures. With encephalitis, people can go into coma within 24 to 48 hours.
How does the Nipah monoclonal antibody work?
The monoclonal antibody binds with the part of the viral envelope that attaches to the human cells to gain entry. Given early in the disease, it prevents the virus from entering more and more cells, thereby stopping its proliferation and severe disease.
The monoclonal antibody has to be administered in the early stages of the disease, before encephalitis sets in.
India first imported 20 doses of the monoclonal antibodies — enough for ten patients — from a laboratory in Australia’s University of Queensland during the 2018 outbreak. Another 20 doses were requested last year. The monoclonal antibody has so far been used in 14 individuals globally and none of them died.
What can be done to protect yourself?
Usually, Nipah outbreaks are localised, meaning people from the rest of the country are not at risk of the infection at present. People from areas where cases are detected should refrain from coming in close contact with the family members and other contacts of the two case. With the infection transmitted by fruit bats, the government also suggests precautions like washing the fruits and peeling them before consumption. Fruits with signs of bat bites should be discarded. And, palm sap or juice must be boiled before consumption.
World Health Assembly 2024

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Assembly will convene from May 27 to June 1 to discuss amendments to the International Health Regulations, aimed at improving the ability of countries to respond to public health emergencies and prepare a potential new pandemic agreement.
What is the World Health Assembly?
- The World Health Assembly is the decision-making body of the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations (UN) agency dedicated to promoting the global population's health and access to the highest levels of healthcare provision.
- Its main functions are to determine WHO's policies, elect the Organization's Director-General, supervise financial policies, and review and approve the proposed WHO budget.
- Delegates from WHO member states come together at an annual assembly held at the UN headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, to focus on a specific healthcare agenda created by the organization's Executive Board.
- The Executive Board comprises 34 technically qualified members, each elected for a three-year term.
- They meet every year in January to agree on the agenda and any resolutions that will be put before the World Health Assembly for consideration.
- Now in its 76th session, the theme for this year’s event is “Health For All: 75 Years of Improving Public Health”.
What does the Assembly do?
- Delegates at the annual World Health Assembly discuss the Executive Board's policy agenda for the coming year and decide which health goals and strategies will guide the WHO's public health work.
- Other functions include voting to appoint the organization's Director-General to serve a five-year term.
- Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus holds the post currently, having been re-elected in 2022 to serve a second term as head of the world's leading public health agency.
Why is it important?
- Since its inauguration, the Assembly has presided over WHO policies that have helped eradicate deadly diseases like smallpox and the poliovirus and helped foster international collaborations to develop and distribute vaccines for diseases like malaria and COVID-19.
About International Health Regulations (IHR):
- First adopted by the World Health Assembly (WHA) in 1969, the IHR was last revised in 2005. These regulations aim to maximize collective efforts in managing public health events while minimizing disruptions to travel and trade.
- The IHR has 196 State Parties, including all 194 WHO Member States, plus Liechtenstein and the Holy See.
- The IHR provide a comprehensive legal framework that outlines countries' rights and obligations in managing public health events and emergencies with the potential to cross borders.
- The regulations introduce crucial safeguards to protect the rights of travellers and others, covering the treatment of personal data, informed consent, and non-discrimination in the application of health measures.
- Legally Binding Instrument: As an instrument of international law, the IHR is legally binding on 196 countries.
Heatstroke

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Health Ministry has issued standardised guidelines for confirming heatstroke and heat-related deaths in the country.
What is a Heatstroke?
- Heatstroke, also known as sunstroke, is a medical emergency resulting from the body overheating due to exposure to high temperatures and humidity or prolonged physical exertion in hot conditions.
- Individuals experiencing heat exhaustion may exhibit symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and increased heart rate.
Criteria for Heatstroke:
- Heatstroke is characterized by body temperatures of 40°C (104°F) or higher, accompanied by delirium, seizures, or coma, posing a potentially fatal condition.
Heatstroke Deaths in India:
- According to analysis of data from the National Crime Records Bureau, over 11,000 people in India died due to heatstroke between 2012 and 2021.
Government Initiatives:
- The Health Ministry released a National Action Plan on Heat-Related Illness in July 2021, outlining strategies to address health challenges posed by heat waves.
- The India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) aims to mitigate heat impacts by ensuring sustainable cooling and thermal comfort for all by 2037-38.
First Aid Measures for Heatstroke:
-
- Move the affected person to a cool, shaded area.
- Offer water or a rehydrating drink if the person is conscious.
- Fan the person to promote cooling.
- Seek medical attention if symptoms worsen, persist, or if the person loses consciousness.
- Avoid giving alcohol, caffeine, or carbonated beverages.
- Apply a cool, wet cloth to the person's face or body.
- Loosen clothing to improve ventilation.
Key Points from the Guidelines:
- Rationale for the Guidelines: Between 2013 and 2022, there was an 85% increase in estimated annual heat-related mortality compared to 1991–2000, driven by global warming and changing demographics.
- Without significant adaptation progress, annual heat-related deaths could surge by 370% by mid-century if global temperatures continue to rise towards 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
- In light of these projections, enhancing our understanding and surveillance of heat-related health issues is imperative.
Preparation and Authorship:
- The guidelines were developed by the National Programme on Climate Change and Human Health (NPCCHH) in collaboration with the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC).
Objective:
- The guidelines aim to assist hospitals in identifying criteria for categorizing deaths as heat-related or due to heat stroke, promoting evidence-based medical decision-making.
Autopsy Considerations:
- Decisions regarding autopsy should be based on factors such as the circumstances of death, the age of the deceased, and available resources.
- Where feasible, collecting blood, urine, etc., for toxicological examination is recommended, contingent on the condition of the body.
Challenges in Diagnosing Heat-Related Deaths
- Diagnosing heat-related deaths post-mortem presents several challenges, including:
- Frequently unavailable pre-terminal or terminal body temperatures.
- Non-specific autopsy findings vary based on the duration of survival after heat exposure.
- Reliance on-scene investigation for diagnosing hyperthermia, a condition resulting from the body's inability to regulate heat.
- Consideration of circumstances of death and exclusion of alternative causes.
- It's noted that autopsies are not mandatory for heat-related deaths.
Widal Blood Test

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Widal test's tendency to produce inaccurate results is clouding the understanding of India's typhoid burden, leading to increased costs, and exacerbating antimicrobial resistance risks.
What is the Widal Blood Test?
- A Widal test is a serological diagnostic test for typhoid fever.
- It helps evaluate the level of antibodies produced by the body in response to the Salmonella bacterial infection that causes typhoid fever in patients.
- Widal blood test is also known as a typhoid blood test report, as it is widely used for diagnosing typhoid fever.
- The symptoms of typhoid fever may be similar to those of other diseases, which can make the diagnosis of typhoid difficult without proper testing.
- Typhoid fever is a severe illness caused by a bacterium called Salmonella Typhi.
- This bacterium affects the gastrointestinal system and causes a range of symptoms such as high fever, diarrhoea or constipation, headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, weight loss, and red spots.
- The bacteria usually enter the body through contaminated food or water.
- Typhoid requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications such as severe intestinal perforation or bleeding.
- The Widal blood test is a quick and easy serological test that can help confirm or rule out whether a fever is due to a typhoid infection.
- Typically, typhoid symptoms appear within 6 to 30 days of exposure to the bacterial infection.
- The Widal test is designed to detect antibodies against O (somatic) and H (flagellar) antigens that cause the infection and typhoid fever.
- Infection through these antigens produces specific antibodies in response.
- The Widal blood test analyses the interaction between these two antigens and the antibodies produced in the patient's body through a blood sample.
- Detecting the presence of these antibodies in the Widal blood test indicates a bacterial infection.
- However, it has several limitations and has been phased out in many countries due to its potential for inaccuracy.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) advises against relying heavily on the Widal Test because various factors can influence its results.
- For example, a single positive result does not definitively confirm an active typhoid infection and a negative result does not necessarily rule it out.
- Additionally, obtaining an accurate diagnosis requires testing at least two serum samples taken 7-14 days apart, which can be time-consuming and often impractical.
- In areas with a continuous high burden of typhoid, baseline antibody levels may already be elevated, complicating the interpretation of results without knowing the appropriate cut-off values.
- Furthermore, cross-reactivity with antibodies produced against other infections or vaccinations can lead to false positives.
- Prior antibiotic therapy can also impact antibody levels, resulting in false negatives.
- Despite its accessibility and historical significance, the Widal Test's limitations emphasize the need for more accurate and reliable diagnostic methods for typhoid fever.
West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)
- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Each organ transplant case will receive a distinctive National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) ID assigned to both the donor and the recipient.
Highlights of the News:
- The Union Health Ministry has mandated the cessation of commercial organ transactions, particularly those involving foreign nationals, and emphasized the need for stringent oversight by local authorities.
- For deceased donor transplants, a NOTTO-ID is required for organ allocation, while in living donor transplants, the ID must be generated within 48 hours post-surgery through the NOTTO website by the hospital.
What is the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)?
- NOTTO is a national organization established under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
It serves as the central coordinating hub for:
- Organ and tissue procurement and distribution.
- Maintaining a registry of organ and tissue donation and transplantation activities across the country.
NOTTO comprises two divisions:
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network:
- Acts as the primary center for nationwide coordination of organ and tissue procurement, distribution, and registry.
- Established in accordance with the Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011.
- National Biomaterial Centre (National Tissue Bank):
- This center focuses on filling the gap between demand and supply while ensuring quality assurance in tissue availability.
- The Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011 has expanded NOTTO's scope to include tissue donation and registration of tissue banks.
Activities performed by NOTTO include:
-
- Coordinating tissue procurement and distribution
- Donor tissue screening
- Tissue removal and storage
- Tissue preservation
- Laboratory screening of tissues
- Tissue tracking
- Sterilization
- Record maintenance
- Data protection and confidentiality
- Quality management in tissues
- Patient information on tissues
- Developing guidelines, protocols, and standard operating procedures
- Training and assistance in registering other tissue banks
CoViNet
- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a global network of laboratories to identify and monitor potentially novel coronaviruses that could emerge shortly.
What is CoViNet?
- The Coronavirus Network (CoViNet) is a global collaboration of laboratories with expertise in human, animal, and environmental coronavirus surveillance.
- This network aims to identify and monitor potential new coronaviruses that could emerge and impact public health worldwide.
- To enhance pandemic preparedness, CoViNet will expand its scope to include animal health and environmental surveillance, as well as timely risk assessments.
- This will allow the World Health Organization (WHO) to develop more informed policies and protective measures against future viral outbreaks.
- CoViNet will also play a pivotal role in building and supporting laboratory capacities in low- and middle-income countries to monitor MERS-CoV and other emerging coronaviruses of public health importance.
- By fostering knowledge exchange and capacity building, CoViNet aims to strengthen the global response to coronavirus threats.
- Furthermore, data generated through CoViNet's efforts will guide the work of the WHO's Technical Advisory Groups on Viral Evolution (TAG-VE) and Vaccine Composition (TAG-CO-VAC). These groups rely on cutting-edge research and surveillance data to inform public health policies and vaccination strategies.
- With 36 laboratories from 21 countries across all six WHO regions, CoViNet currently encompasses a wide range of expertise and resources.
- Three Indian institutions, namely, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology in Pune, and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, proudly represent the country in this global network dedicated to coronavirus surveillance and preparedness.
About the World Health Organization (WHO):
- The World Health Organization (WHO) stands as a paramount global health authority, dedicated to promoting health, preventing diseases, and improving healthcare systems worldwide.
- Established in 1948, WHO operates as a specialized agency of the United Nations, with its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It collaborates with governments, international organizations, and civil society to address pressing health challenges and provide guidance and support to countries in need.
- WHO's mandate encompasses a wide array of health-related issues, including infectious diseases, non-communicable diseases, mental health, maternal and child health, and environmental health.
- Through research, policy development, and technical assistance, WHO plays a vital role in shaping health policies, setting standards, and coordinating responses to health emergencies such as pandemics and natural disasters.
- With a mission to ensure the highest attainable level of health for all people, WHO continues to lead efforts in global health governance, advocacy, and capacity-building, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable world.
Post-Vaccination Immunity
- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent review revealed that only a handful of vaccines offer durable protection lasting beyond 20 years.
About Post-vaccination immunity:
Mechanism:
- The fundamental immunological process involves the production of memory B cells in lymph nodes, providing long-term protection against diseases.
- These memory B cells recognize antigens delivered by vaccines, prompting the production of potent antibodies upon encountering similar antigens from foreign objects like viruses, effectively eliminating infections.
- T cell support is essential for the activation of memory B cells, thus vaccines stimulating T cells are capable of inducing their production.
- Notably, certain vaccines, such as polysaccharide typhoid and pneumococcal vaccines, may not prompt the production of B cells.
- To extend the duration of immunity conferred by memory B cells, frequent boosters may be necessary, ranging from six months to several years.
- However, the presence of memory B cells alone does not guarantee protection, as the effectiveness of vaccines in triggering their production varies.
- Long-lasting plasma cells (LLPCs) migrate from lymph nodes to the bone marrow, where they may persist for decades, constituting a crucial aspect of vaccine-induced immunity.
- Every vaccine aims to generate LLPCs in the bone marrow for lifelong protection, with vaccines like those for measles and rubella known to stimulate LLPC production.
- Notably, some potent vaccines, such as mRNA COVID-19 shots, may not effectively activate LLPCs in the bone marrow.
- For vaccines to confer long-term protection, they must generate both memory B cells and LLPCs in the bone marrow, with variations in vaccine effectiveness in producing these cells explaining differences in their durability.
Hepatitis B
- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Public knowledge and awareness about Hepatitis B, a deadly disease that can cause end-stage liver cirrhosis and liver cancer, is dismal in India, according to a new study conducted by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi.
What is Hepatitis B?
- It is a severe liver infection that can lead to liver damage, cancer, and death.
- The virus spreads through contact with an infected person's blood or bodily fluids.
- One can get hepatitis B through sexual contact, sharing needles or other drug-injection equipment, or from mother to child during childbirth.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is a severe viral infection of the liver that can cause inflammation and scarring.
- Symptoms include fatigue, fever, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice.
Causes of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- HBV is found in the blood and body fluids of an infected person. It can spread through contact with fluids, such as:
- Blood, through needle sharing or accidental needle sticks
- Contact with body fluids, such as saliva, etc.
- Sexual contact with someone who has HBV
- From a mother to a child through childbirth
- Hepatitis B can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as:
- Sharing personal items like toothbrushes or razors with someone who has HBV
- Getting a tattoo or body piercing with contaminated equipment
Types of Hepatitis B:
- There are three main types of hepatitis B: acute, chronic, and carriers.
- Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after exposure to the virus. It is the most common type of hepatitis B in children.
- Chronic hepatitis B is a long-term illness that can lead to serious health problems, including liver failure and liver cancer.
- Carriers of hepatitis B have the virus in their blood but do not show any symptoms.
Treatment for Hepatitis B
- Several medications can help treat hepatitis B.
- These include antiviral drugs, which can help reduce the amount of virus in the body, and immunomodulators, which can help boost the immune system to better fight the virus.
- If the liver is damaged, one may also need medication to help protect it from further damage.
- HBIG (Hepatitis B Immuno Globulin) is one of the best ways to treat hepatitis B.
- Adults who have been exposed to hepatitis should get HBIG and vaccination as soon as possible, preferably within 24 hours but not later than 14 days after the exposure.
Prevention of Hepatitis B:
- The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated.
- The vaccine is given as a series of shots.
- The first shot is usually given at birth; the rest at 1–2 months old, 6–18 months old, and 4–6 years old.
- If one was not vaccinated as a child, they can receive the vaccines as an adult.
Haemodialysis
- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Findings from a nationwide private hemodialysis network show that there is a variation in the survival of patients receiving hemodialysis in India depending on various factors, and stress on the need to standardize dialysis care across centers.
What is Hemodialysis?
- Haemodialysis, also known as dialysis, is a medical procedure that helps individuals with kidney failure by removing waste products and excess fluid from their blood.
- This procedure essentially performs the functions of the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste and maintaining the body's electrolyte balance.
Key points about hemodialysis:
- Process: During hemodialysis, a patient's blood is circulated through a machine with a semipermeable membrane, called a dialyzer or an artificial kidney.
- The dialyzer filters out waste products, such as urea and creatinine, and excess fluid from the blood, which is then discarded, while essential components are returned to the patient's bloodstream.
- Access: To perform hemodialysis, a patient typically requires vascular access, which is a surgically created connection between an artery and a vein, usually in the arm.
- This connection allows for the efficient flow of blood from the patient to the dialysis machine and back.
- Duration: Haemodialysis treatment typically lasts for around 3-5 hours and is performed several times per week, depending on the patient's needs and kidney function.
- Indications: Haemodialysis is prescribed for patients with end-stage kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), who need immediate intervention while waiting for a kidney transplant or when a transplant is not a suitable option.
- Side effects: Some common side effects of hemodialysis include low blood pressure, muscle cramps, itching, and fatigue.
- Complications such as infection, access problems, and blood clotting may also occur, but these risks can be minimized with proper medical supervision and management.
- In summary, hemodialysis is a life-sustaining treatment for patients with kidney failure, offering a means to maintain their health and well-being despite the loss of kidney function.
Health ministers of 11 African countries commit to end malaria deaths

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a historic gathering in Cameroon’s capital Yaoundé, African health ministers, global malaria partners, funding agencies, scientists, civil society organizations and other principal malaria stakeholders pledged to end malaria deaths, especially given the tools and systems available.
What is the Yaounde Declaration?
- The Yaounde Declaration was endorsed by health ministers from 11 African nations with the highest malaria burden, aiming to expedite efforts to eliminate malaria-related deaths.
- Signed during the Yaoundé conference, co-hosted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of Cameroon, the declaration underscores a collective commitment to combat malaria.
- The signatory countries include Burkina Faso, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania, together accounting for approximately 70% of the global malaria burden.
- Commitments entail stronger leadership and increased domestic funding for malaria control programs, leveraging data technology, adhering to updated technical guidance, and intensifying efforts at national and sub-national levels.
- Ministers pledged augmented health sector investments to fortify infrastructure, personnel, and program implementation, fostering multi-sectoral collaboration, and cultivating partnerships for funding, research, and innovation.
- Signatories affirmed their resolute dedication to hasten malaria mortality reduction and to ensure mutual accountability for the declaration's outlined commitments.
Current Status of Malaria:
- Between 2019 and 2022, global malaria cases increased from 233 million to 249 million, with Africa experiencing a substantial rise from 218 million to 233 million cases, highlighting the continent as the epicenter of the malaria crisis.
- The 11 African countries represented at the conference bear the highest burden of malaria infections and deaths.
Progress and Challenges:
- Despite some progress, malaria incidence has only declined by 7.6% and mortality by 11.3%, falling short of the African Union’s interim goals.
- Only seven out of 46 member states have achieved a 40% reduction in malaria incidence or mortality.
- Urgent action is imperative to bridge a financial gap of $1.5 billion to sustain basic malaria services, especially for vector control.
- Additional funding of $5.2 billion annually for progress towards elimination and $11 billion for climate adaptation in the health sector is crucial to avert significant surges in cases and deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations like children and pregnant women.
An initiative to improve nutrition in adolescent girls using Ayurveda under Mission Utkarsh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The project for anemia control under Mission Utkarsh will be a joint public health initiative by the Ministries of Ayush and Women and Child Development and will be launched in five aspirational districts first as a pilot project.
About Mission Utkarsh:
- Mission Utkarsh was launched in January 2022, a new initiative of “rapid improvement of selected Districts” to improve.
- Under this mission, 15 central ministries and departments are working to bring select key performance indicators in bottom districts to the state and national average.
- Over 94,000 adolescent girls between the age group of 14-18 years registered under Poshan Tracker at approximately 10,000 Anganwadi Centres will benefit in 12 12-month periods of the program.
- The coordinating agency for the project will be the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS).
- Classical Ayurveda medicines (Drakshavaleha and Punarnavadi mandoor) for better nutrition to improve the health of the anemic adolescent girls will be provided for a period of 3 months.
- These five districts are Dhubri in Assam, Bastar in Chhattisgarh, Paschimi Singhbhum in Jharkhand, Gadchiroli in Maharashtra, and Dholpur in Rajasthan.
- Building research capacity through training, conferences, workshops, and seminars with the active participation of researchers of integrative healthcare would be enhanced.
What is Anaemia?
- According to WHO, anemia occurs when there is a lower-than-normal count of red blood cells or a reduced hemoglobin concentration within them, crucial for oxygen transport throughout the body.
Symptoms
- This condition leads to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath due to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common nutritional cause, although deficiencies in folate, vitamins B12 and A can also contribute.
- Chronic diseases like kidney or liver disease, cancer, and genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia further exacerbate anemia.
Significance:
- Anaemia has significant implications, particularly affecting vulnerable populations like pregnant women and children under five, impacting reproductive health and reducing work capacity, thus posing an economic burden.
Anaemia in India:
- India faces a substantial anemia burden, with recent surveys indicating alarming prevalence rates among women aged 15-49 and children aged six months to five years, highlighting the urgent need for public health interventions.
India gets desi Garbhini GA2 for evaluation of foetal growth
- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Specifically tailored to address the unique characteristics of foetal growth within the Indian population, India has finally got its locally made ‘Garbhini-GA2’, a groundbreaking Artificial Intelligence model.
What is Garbhini-GA2?
- The Garbhini-GA2 model, developed as part of the DBT India initiative (GARBH-Ini) program by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad, addresses the challenge of accurately estimating foetal age (gestational age, GA) in the Indian population, particularly in the second and third trimesters.
- Unlike existing formulas designed for Western populations, Garbhini-GA2 accounts for variations in foetal growth specific to the Indian context, significantly reducing estimation errors by nearly threefold.
- This innovative model is crucial for ensuring precise prenatal care and determining accurate delivery dates, thereby enhancing maternal and foetal health outcomes.
- Garbhini-GA2 marks a milestone as the first late-trimester GA estimation model validated using Indian population data, offering a tailored approach to foetal age determination that is essential for effective maternal healthcare."
About Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI):
- THSTI, an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Science and Technology, was founded in 2009 in Faridabad, Haryana, with a core commitment to advancing research beyond mere discovery.
- By fostering collaboration among diverse teams in medicine, science, and technology, THSTI leverages translational expertise to drive clinical research and innovation.
- In addition to its core mission, THSTI plays a pivotal role in fostering social innovation and entrepreneurial endeavors, particularly in the domain of maternal and child healthcare.
Race to the global eradication of Guinea worm disease nears the finish line
- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world is on the brink of a public health triumph as it closes in on eradicating Guinea worm disease. There were more than 3.5 million cases of this disease in the 1980s, but according to the WHO, they dwindled to 14 cases in 2021, 13 in 2022, and just six in 2023.
What is Guinea Worm Disease?
- Dracunculiasis is also called guinea worm disease (GWD).
- It is an infection caused by a parasite called Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm).
- This parasite is an organism that survives by deriving nutrients and feeding off another organism.
- GWD spreads through drinking contaminated water.
- It is presently eradicated in most parts of the world but is still seen in remote parts of Africa and some remote rural areas in the world where there is no access to clean drinking water.
- GWD is considered endemic in three African countries, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Mali.
- In recent years, a few cases of GWD in animals, especially dogs, have been reported in developed countries as well.
- GWD is a serious condition, that causes debilitating pain and complications, affecting the quality of life
Symptoms:
- People infected with Guinea worm don’t typically have any symptoms until about a year after they're first infected.
- It’s not until the worm is about to erupt from the skin that people start to feel sick.
- What that happens, the symptoms of Guinea worm disease can include Fever, Nausea and vomiting, Diarrhoea, Shortness of breath, Burning, itching, pain, and swelling where the worm is in the body (often the legs and feet) and Blister where the worm breaks through the skin.
Impact:
- Guinea worm disease isn’t often deadly, but it can cause serious complications, lifelong disabilities, and financial hardship for those involved.
- The pain involved is often so intense that it’s difficult for people to work, go to school, or care for themselves or others.
- This lasts an average of 8.5 weeks, though lifelong disability is common.
Dracunculiasis Treatment:
- There is no vaccine or drug developed to prevent or treat this disease.
- The only means available is the management of the disease which is removing the whole worm and caring for the wound caused by it and avoiding infection in the process or exposure to the guinea worm larvae at all costs, especially by avoiding contaminated drinking water and stagnant water sources.
- Without proper treatment, wounds caused by the worm can become infected by bacteria, leading to sepsis, septic arthritis, and contractures (when joints lock and deform).
- In some cases, these infections become life-threatening.
WHO launches digital health platform agreed upon in India’s G20 presidency

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Achieving one of the three priority areas agreed upon during India’s G20 presidency in 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) recently launched the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) virtually, a platform for sharing knowledge and digital products among countries.
About Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH):
- The Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) is a network managed by the World Health Organization (WHO), dedicated to enhancing and coordinating efforts for country-led digital health transformation through collaborative partnerships and knowledge sharing.
- It was launched by the WHO and the Government of India during the G20 Health Ministerial Meeting in Gandhinagar.
- Functioning as a platform for inter-country knowledge exchange and digital product dissemination, GIDH strives to achieve several key objectives through collective action:
- Assess and prioritise countries' requirements for sustainable digital health transformation.
- Enhance the alignment of digital health resources and address unfunded priorities at the country level.
- Facilitate the accelerated attainment of the strategic objectives outlined in the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025.
- Promote capacity building and synergize efforts to support local development, maintenance, and adaptation of digital health technologies to evolving needs.
- Comprising four primary components, GIDH operates as a network of networks:
- Country Needs Tracker: Tracks and prioritises country-specific digital health requirements.
- Country Resource Portal: Provides a comprehensive map of available digital health resources within each country.
- Transformation Toolbox: Shares quality-assured digital tools to support country-led digital health initiatives.
- Knowledge Exchange: Facilitates the exchange of insights and best practices among member countries.
- GIDH extends support to countries in three fundamental ways:
- By attentively addressing their needs
- By fostering resource alignment to prevent fragmentation, and
- By offering access to quality-assured digital products.
- Membership in GIDH is open to all institutions actively involved in the digital health domain.
What is Digital Health?
- Digital health denotes the utilisation of technology, encompassing mobile devices, software applications, and various digital tools, to enhance health outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery.
- Essentially, it represents an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of technology and healthcare, integrating a diverse array of concepts and innovations.
- This encompasses a broad spectrum of technologies and services, spanning telemedicine, electronic health records, wearable devices, health information exchange, and more.
- Examples of notable digital health initiatives include India’s CoWIN platform and UNICEF's RapidPro and FamilyConnect programs.
- RapidPro, UNICEF’s real-time information platform, serves as a foundational component in its digital health portfolio.
- FamilyConnect, another UNICEF initiative, delivers targeted, lifecycle-based messages via SMS to various recipients, including pregnant women, new mothers, and heads of households.
India Initiatives on Digital Health:
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM): Designed to establish a comprehensive national digital health ecosystem featuring unique health IDs, electronic health records (EHRs), and a platform for health data exchange.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): Aims to develop a digital infrastructure for the Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM), incorporating health registries, electronic claim processing, and telemedicine services.
- E-Sanjeevani Telemedicine Platform: Enables virtual consultations between healthcare providers and patients nationwide, enhancing access to medical care.
- Jan Arogya Setu App and CoWIN Platform: Offers access to healthcare services, facilitates appointment scheduling, and disseminates COVID-19-related information.
- Digital Aarogya Mitra (DAM): Implements a community health worker program utilising technology for data collection and community-based health interventions.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Guinea (WHO)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea's Health Ministry has officially notified them of a diphtheria outbreak.
What is Diphtheria?
- Diphtheria, an extremely contagious and infectious disease, instigates severe inflammation in the nose, throat, and trachea (windpipe).
- This ailment is caused by strains of bacteria known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produce a potent toxin responsible for the onset of illness.
Causes:
- The bacterial infection spreads through various means, including respiratory droplets emitted during coughing or sneezing.
- Transmission can also occur through contact with infected open sores or ulcers. The bacteria's toxin is the primary culprit behind the illness.
Symptoms:
- Manifesting 2-5 days post-infection, symptoms of diphtheria encompass a thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, a sore throat, hoarseness, swollen glands in the neck, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, fever, chills, and fatigue.
- If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can lead to damage to the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Infection and Spread:
- Diphtheria bacteria thrive on person-to-person transmission, emphasizing respiratory droplets as a common mode of contagion.
- Skin infections are possible but seldom result in severe disease.
Treatment:
- Combatting diphtheria involves a dual-pronged approach:
- Antitoxin (Anti-diphtheritic Serum): This neutralizes bacterial toxins and is specifically employed for respiratory system infections. The antitoxin acts on toxins that haven't bound with cells and tissues.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Penicillin): These medications eradicate the bacteria, preventing further spread. Antibiotics are effective against both the respiratory system and skin infections caused by diphtheria.
Union Health Minister Launches MedTech Mitra Platform to Empower Medical Technology Innovators (NewsOnAir)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Health Minister Dr Mansukh Mandaviya has launched MedTech Mitra - a strategic initiative to empower MedTech innovators and advance healthcare solutions.
What is the MedTech Mitra Portal?
- The MedTech Mitra portal is an online platform designed to support medtech innovators by assisting in clinical evaluation, regulatory facilitation, and the adoption of new products in the medical technology sector.
- This collaborative initiative is overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), operating under the direction/guidance of NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission.
Significance:
- In conjunction with recent policies and incentive schemes, such as the medical devices policy and the production-linked incentive scheme, the MedTech Mitra platform aims to catalyze growth in the medical devices sector and promote domestic manufacturing.
- These initiatives seek to foster the indigenous development of affordable and high-quality MedTech devices and diagnostics, thereby significantly reducing the sector's reliance on imports.
- The platform is envisioned to streamline the innovation process and facilitate research and development for emerging start-ups, ensuring a smoother journey from concept to product.
- By offering comprehensive guidance, including support for animal and clinical trials, the platform aims to bridge gaps for startups and promote ease of innovation.
- The MedTech Mitra portal is poised to foster collaborations between engineers, scientists, and clinicians, addressing a previously existing gap in partnerships within the sector.
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) serves as the apex institution in India responsible for formulating, coordinating, and advancing biomedical research.
- With a primary mandate to conduct, coordinate, and implement medical research for societal benefit, ICMR is dedicated to translating medical innovations into tangible products and processes, subsequently integrating them into the public health system.
- Financial support for ICMR is provided by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) (NewsOnAir)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Health Authority (NHA) has recently declared the extension of its Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) until the 31st of December 2023.
About Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS):
- Launched in December 2022, the DHIS became effective from 1st January 2023.
- The scheme is implemented by the National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Its primary objectives include giving a further impetus to digital health transactions across the country through the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
Salient Features of DHIS:
- The scheme offers incentives of up to four crore rupees, determined by the number of digital health records created and linked to patients' Ayushman Bharat Health Account numbers.
- Incentives are extended to hospitals, diagnostic labs, and providers of digital health solutions, including Hospital/Health Management Information Systems (HMIS) and Laboratory Management Information Systems (LMIS).
- Health facilities (hospitals and diagnostic labs) registered with the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission's Health Facility Registry (HFR) and meeting the specified eligibility criteria can avail of the incentives.
Benefits of DHIS:
- Incentives for Digitization: Healthcare facilities and Digital Solution Companies participating in the scheme can earn incentives to cover expenses related to digitization.
- Enhanced Efficiency in Healthcare Delivery: DHIS streamlines the healthcare process, eliminating hassles in registration, appointment scheduling, consultations, IPD admission, discharge, and more.
- Robust Digital Health Ecosystem: The scheme contributes to the development of a strong digital health ecosystem, encompassing various levels of healthcare facilities.
- Improved Quality of Care: DHIS facilitates evidence-based, accessible, and high-quality healthcare services, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
