Eighth Pay Commission

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union government has approved the constitution of the Eighth Pay Commission, benefiting 50 lakh central government employees and 65 lakh pensioners, including serving and retired defence personnel. The decision, taken ahead of the Delhi Assembly elections, aims to address long-standing demands from trade unions and employee organizations.
Key Features of the 8th Pay Commission
- Early Constitution: Although the Seventh Pay Commission's term ends in 2026, the early establishment of the Eighth Pay Commission ensures timely recommendations and implementation.
- Composition: The commission will have a Chairperson and two members, typically led by a retired Supreme Court judge.
- Terms of Reference (ToR):
- Revision of Pay: Recommend updates to salary structures and allowances.
- Addressing Pay Disparities: Resolve wage differences across various cadres.
- Market Parity: Align pay structures with industry standards.
- Pension and Retirement Benefits: Improve pension schemes and adjust them for inflation.
- Economic Impact Analysis: Assess how salary hikes contribute to economic growth.
- Stakeholder Consultations: Engage with governments and other stakeholders before finalizing recommendations.
Economic Implications of the 8th Pay Commission
- Employee Well-being: Higher wages will enhance the quality of life for government employees.
- Boost to Consumption: Increased salaries are expected to stimulate demand and support economic expansion.
- Ripple Effect on PSUs & States: Many public sector undertakings and state governments follow the central pay commission’s recommendations, potentially leading to wider economic benefits.
- Fiscal Considerations: The implementation of the Seventh Pay Commission in 2016-17 led to an expenditure increase of ?1 lakh crore. A similar rise in 2026-27 could impact fiscal space for capital expenditures.
Challenges and Concerns
- Implementation Delays: Past commissions have taken two years to submit recommendations, which could push implementation beyond 2027.
- Living Wage & Pension Issues: Existing formulas for minimum wage and pension calculations may need revision to reflect rising healthcare, education, and digital access costs.
- Financial Burden on the Exchequer: A significant increase in revenue expenditure could limit the government’s ability to invest in infrastructure and development projects.
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
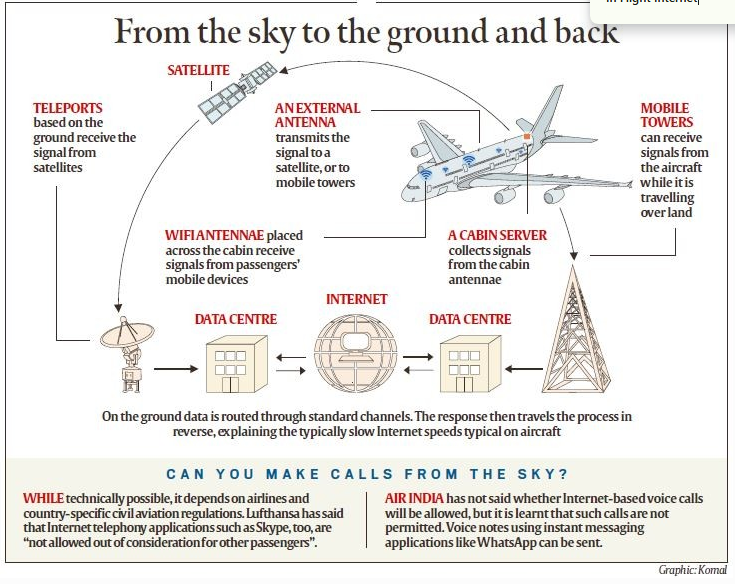
Connectivity Technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
Lighthouse Tourism in India

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
Lighthouse tourism in India is rapidly emerging as an exciting and profitable segment of the country's travel and tourism industry. India's coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers, is home to 204 lighthouses, many of which are being transformed into vibrant tourist destinations, celebrating both India's rich maritime history and its natural beauty.
Key Highlights:
- Historical and Scenic Appeal: Lighthouses in India are often located in breathtaking coastal or island locations, offering panoramic sea views and access to surrounding natural beauty. Some of these structures are centuries old and are situated near significant cultural landmarks or UNESCO World Heritage Sites, adding cultural depth to the visitor experience.
- Economic Growth: As part of the broader Maritime India Vision (MIV) 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, the Government of India is keen to transform these historic lighthouses into hubs of economic activity. By developing infrastructure, creating new tourism-related jobs, and fostering local entrepreneurship, lighthouse tourism aims to benefit coastal communities and boost India's tourism economy. As of 2023-24, 75 lighthouses across 10 states have been equipped with modern amenities, attracting 16 lakh visitors—a 400% increase from previous years.
- Government Initiatives:
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- The 1st Indian Lighthouse Festival, “Bharatiya Prakash Stambh Utsav”, was inaugurated on 23rd September, 2023 by the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal and Goa Chief Minister, Shri Pramod Sawant at the historic Fort Aguada in Goa.
- The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held in Odisha. Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, was also joined by Odisha Chief Minister, Mohan Charan Majhi. Shri Sonowal dedicated two new lighthouses at Chaumuck (Balasore) and Dhamra (Bhadrak) and emphasized empowering coastal communities to preserve and promote lighthouses as part of India’s rich maritime heritage.
- Sagarmala Programme: This government initiative integrates infrastructure development with sustainable practices, ensuring that the growth of lighthouse tourism benefits local communities while preserving the environment.
- Tourism Infrastructure: The government has invested ?60 crore in enhancing these sites, providing facilities like museums, parks, amphitheaters, and more to enrich the visitor experience.
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- Sustainable Development: The Indian government places a strong emphasis on eco-friendly tourism. This includes integrating lighthouses into broader coastal circuits and launching digital awareness campaigns to attract domestic and international tourists.
- Community Empowerment and Employment: Lighthouse tourism has already created direct and indirect employment, from hospitality to transportation, local handicrafts, and artisan work, with more than 500 jobs being generated. Local communities are being trained to offer skills in hospitality and tourism services.
Future Plans:
- Skill Development: Programs are being introduced to equip local people with the necessary skills to cater to the tourism industry.
- Sustainable Practices: Eco-friendly practices will continue to be emphasized to protect coastal ecosystems.
- Integration with Coastal Circuits: Lighthouses will become key points of interest in broader coastal tourism itineraries, further enhancing their appeal to tourists.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)

- 24 Dec 2024
In News
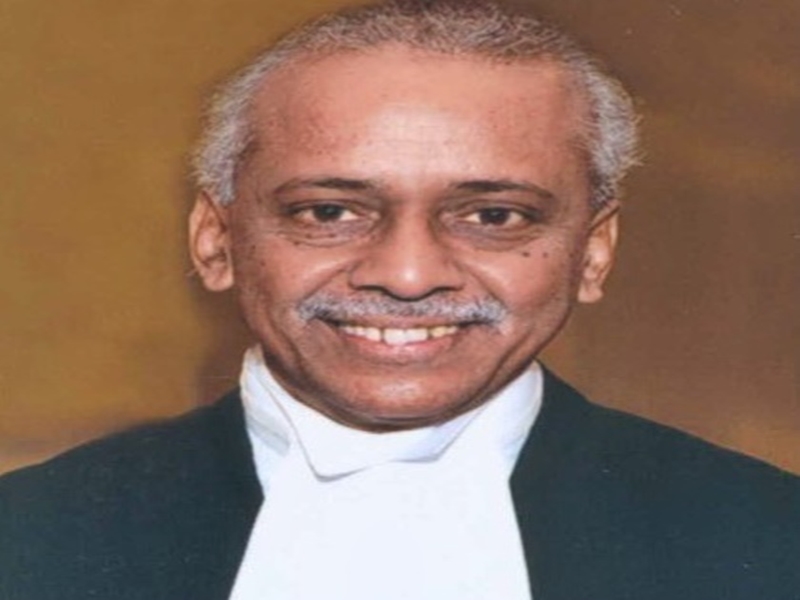
Justice V. Ramasubramanian, a retired Supreme Court judge, has been appointed as the new chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC). This decision was made by President Droupadi Murmu, and it comes following the completion of Justice Arun Kumar Mishra's tenure as NHRC chairperson in June 2023. After Justice Mishra's retirement, Vijaya Bharathi Sayani served as the acting chairperson. Alongside Justice Ramasubramanian, Priyank Kanoongo and Dr. Justice Bidyut Ranjan Sarangi (Retd.) have also been appointed as members of the commission.
Justice Ramasubramanian had been appointed a judge of the Supreme Court in September 2019 and retired in June 2023. His appointment to the NHRC is seen as a significant development for human rights advocacy and protection in India.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
Establishment and Legal Framework
- Formation Date: The NHRC was established on October 12, 1993, under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Paris Principles: It was created in alignment with the Paris Principles (1991), which were endorsed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, aimed at setting standards for national human rights institutions.
- Statutory Body: NHRC is a statutory body, meaning it is established by law, with a primary function to safeguard human rights in India.
Objectives
The NHRC's primary objective is to promote and protect human rights as defined in Section 2(1)(d) of the PHRA, which include fundamental rights such as:
- Right to Life
- Right to Liberty
- Right to Equality
- Right to Dignity
These rights are guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and are essential to the protection of individuals' freedoms and welfare.
Composition of NHRC
- Chairperson: A former Chief Justice of India or a former Supreme Court judge serves as the chairperson.
- Members:
- One former or sitting Supreme Court judge.
- One former or sitting Chief Justice of a High Court.
- Three members, with at least one woman, who have experience in human rights matters.
- Ex-Officio Members: The chairpersons of various National Commissions (e.g., SC/ST, Women, Minorities) and the Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities are also part of the NHRC.
Functions and Powers
The NHRC has several crucial functions and powers to ensure the protection and promotion of human rights:
- Inquiry into Human Rights Violations: The commission can inquire into violations of human rights by public servants or negligence in protecting rights.
- Recommendations: It can make recommendations on how to protect, promote, and effectively implement human rights within India.
- Review of Laws: NHRC assesses various laws, treaties, and international instruments related to human rights.
- Research and Awareness: It promotes research, publications, and awareness about human rights issues, including educating the public about their rights and safeguards.
- Inspection of Institutions: NHRC has the authority to visit and inspect institutions such as jails, detention centers, and other places of confinement to ensure the humane treatment of individuals.
Wroughton’s Free-Tailed Bat

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
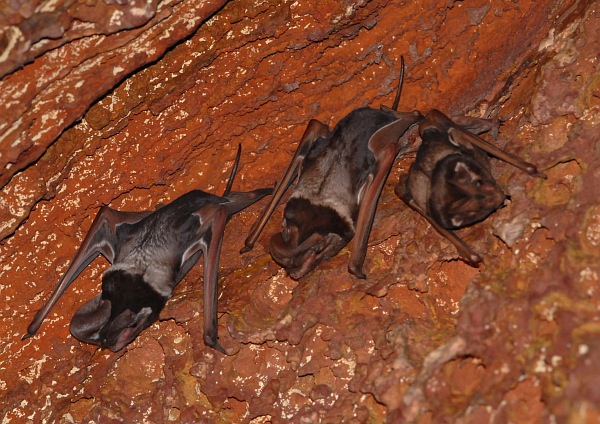
Wroughton’s free-tailed bat, a highly rare species of molossus bat, has been spotted at the Delhi Development Authority (DDA)’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park, marking a unique sighting.
Key Highlights:
- Species Overview: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni) is a rare species of molossus bat, notable for its powerful flight and ecological importance in controlling insect populations and assisting in pollination.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Listed as "Data Deficient".
- Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily found in the Western Ghats, with a single known breeding colony.
- Small colonies in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and a solitary individual sighted in Cambodia.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Large in size, with huge ears extending beyond the muzzle.
- Bicoloured velvet fur.
- Noted for powerful flying capabilities, enabling long-distance foraging.
- Ecological Role:
- Regulates insect populations.
- Known for assisting in pollination.
- Habitat:
- Roosts in caves, or dark, damp, and slightly warm places, typically in moderate-sized colonies.
- Significance of the Delhi Sighting:
- The sighting at Yamuna Biodiversity Park is significant for Delhi, marking a rare occurrence in the region.
- Delhi's bat species: The city is home to about 14 bat species, with four species, including the Indian false vampire and Egyptian free-tailed bat, considered locally extinct.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Two decades of ecological restoration have created specialized niches in the area, aiding species rewilding and ecological balance.
- The Aravalli Biodiversity Park in Gurugram now serves as the only known roosting site for the Blyth’s horseshoe bat in Delhi NCR.
- Additional Notes:
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat was considered critically endangered until 2000 due to its limited known population. However, the discovery of populations in other regions has led to a reclassification to "Data Deficient".
- Despite being discovered over a century ago, much about the bat's feeding ecology remains unknown.
Desert Knight Air Combat Exercise

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
India, France and UAE recently kicked off a major air combat exercise called “Desert Knight” over the Arabian Sea, strengthening trilateral defence cooperation and enhancing military interoperability amid the ongoing geopolitical churn.
Key Highlights:
- What It Is: A trilateral air combat exercise aimed at improving military interoperability and enhancing combat readiness among the participating nations.
- Nations Involved: India, France, and the UAE.
- Location: Conducted over the Arabian Sea, approximately 350-400 km southwest of Karachi.
- Aim of the Exercise:
- To strengthen trilateral defence cooperation among the three nations.
- To enhance combat skills and military interoperability of the air forces involved.
- Details of the Exercise:
- Duration: The exercise lasts for three days.
- The exercise involves large force engagement and intensive combat maneuvers in a realistic operational environment.
- Aircraft Involved:
- India: Deployed Sukhoi-30MKIs, Jaguars, IL-78 mid-air refuellers, and AEW&C (Airborne Early Warning and Control) aircraft from bases like Jamnagar.
- France: Deployed Rafale jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
- UAE: Deployed F-16 jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
Strategic Significance:
- The exercise is part of India’s efforts to build military interoperability with nations in the Persian Gulf region and strengthen defence ties with France and the UAE.
- Enhances combat readiness and strengthens cooperation against both traditional and non-traditional threats.
- Reflects the geopolitical shift and growing military cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, especially in the context of China’s expansionist activities.
- Trilateral Framework: India, France, and the UAE launched a trilateral framework in 2022, focusing on areas like defence, technology, energy, and environment.
- Previous Exercises: In addition to Desert Knight, the countries also conducted their first trilateral maritime exercise in June 2023 to enhance cooperation in maritime security.
Broader Defence Relations:
- India-France: Long-standing strategic partnership with regular joint exercises like Shakti (army), Varuna (navy), and Garuda (air force).
- India-UAE: The defence relationship has grown significantly in recent years, with regular professional exchanges, combat exercises, and staff talks. India participates in the Desert Flag exercise at Al Dhafra airbase annually.
Human Rights Day 2024

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
Human Rights Day 2024 celebrated every year on 10th December is dedicated to promote protection of fundamental rights and freedom of all individuals.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Promote and protect human rights and freedoms worldwide.
- Theme (2024): “Our Rights, Our Future, Right Now” – highlights the importance of immediate action to protect and uphold human rights globally.
Historical Significance:
- Commemorates: The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
- UN Resolution: Established by UN Resolution 423 (V) in 1950.
- First Observance: December 10, 1950.
- Father of Human Rights Day: Eleanor Roosevelt, for her pivotal role in drafting the UDHR.
Key Highlights:
- The UDHR:
- Adopted in 1948, it defines fundamental human rights for all individuals.
- Comprises 30 articles, addressing rights such as freedom, equality, and access to education, healthcare, and fair employment.
- Role of the UN: UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC): A body under the UN responsible for monitoring and promoting human rights worldwide, comprising 47 member states.
- Human Rights Day Focus in 2024:
- Emphasizes human rights education, particularly among the youth.
- Addresses emerging challenges like cybercrimes, AI impacts, and climate change.
- Reaffirms the importance of safeguarding human dignity globally.
Human Rights Declared by UDHR:
- Right to freedom and equality
- Right to life, liberty, and security
- Freedom from slavery and torture
- Right to recognition before the law
- Equal protection under the law
- Right to a fair trial
- Right to privacy and protection from attacks
- Right to work and fair employment
- Right to rest and leisure
- Right to education
- Right to an adequate standard of living
- Right to participate in government and cultural activities
Community and Individual Forest Rights in Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR)

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Coimbatore District Collector, granted community and individual forest rights under the Forest Rights Act, 2006, to tribal settlements in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) on December 6, 2024.These rights were handed over to three tribal settlements and 14 families at a function in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
- Community Forest Rights:
- Three tribal settlements in ATR—Nagaroothu I, Nagaroothu II, and Chinnarpathi—were granted community rights.
- These rights allow the settlements to collect forest produce excluding timber, such as mango, amla, honey, tamarind, and grass for making brooms.
- Individual Forest Rights:
- Individual rights were granted to 14 families from the Old Sarkarpathy tribal settlement.
- The families had requested these rights for traditional cultivation practices passed down by their ancestors.
- The individual rights were approved after the recommendation of a sub-divisional committee and scrutiny by a district-level committee.
- About the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- Purpose: The FRA was enacted to address historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities and ensure their livelihood and food security.
- Key Provisions:
- Individual Rights: Self-cultivation, habitation, and in-situ rehabilitation.
- Community Rights: Access to grazing, fishing, water bodies in forests, and protection of traditional knowledge and customary rights.
- Eligibility: Rights can be claimed by any community or individual who has lived in the forest for at least three generations (75 years) before December 13, 2005.
- Critical Wildlife Habitats: The Act mandates that critical wildlife habitats in national parks and sanctuaries remain inviolate for wildlife conservation.
- Authorities Involved in Vesting Forest Rights:
- Gram Sabha: Initiates the process for determining the nature and extent of rights.
- Sub-Divisional Level Committee: Examines resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha.
- District Level Committee: Grants final approval for forest rights.
- Challenges with Forest Rights Implementation:
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- Arbitrary rejection of claims.
- Lack of deadlines for claims processing.
- Unaddressed rights of communities displaced by development projects.
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, at an altitude of 1,400 meters.
- Established as a tiger reserve in 2007, it is surrounded by multiple protected areas like the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Eravikulam National Park.
- Biodiversity in Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Habitats: The reserve contains wet evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, and unique habitats like montane grasslands and marshy grasslands.
- Flora: The reserve is home to around 2,500 species of angiosperms, including species like balsam, orchids, and wild relatives of cultivated crops such as mango, jackfruit, cardamom, and pepper.
- Fauna: It supports various wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, sambars, spotted deer, leopards, jackals, and jungle cats.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
Narasapur Crochet Lace Craft

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The Narasapur crochet lace craft, which has been a significant part of the cultural and economic fabric of the Godavari region in Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag. The GI tag, registered by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) on March 1, 2024, acknowledges that this unique craft is geographically linked to the West Godavari and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema districts in the Godavari region.
Key Details:
- Historical Background:
- The origins of the Narasapur crochet lace craft date back to 1844, when Macrae and his wife from Scotland introduced the lace-making technique to local women while they were associated with a Christian missionary in Dummugudem (now in Telangana).
- Over time, the craft became a crucial part of the region’s heritage and survived significant historical events like the Indian famine of 1899 and the Great Depression of 1929.
- Craftsmanship:
- The crochet lace is produced using thin threads and delicate crochet needles of varying sizes, resulting in intricate designs.
- The products made include doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bedspreads, table runners, and tablecloths, among others. These items are often exported to international markets like the US, UK, and France.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- The craft is predominantly carried out by women artisans, with over 15,000 women involved in its production. The GI tag is expected to revitalize the industry, especially after its stagnation due to the COVID-19 pandemic and competition from machine-made lace from China.
- The craft is also an important part of the Alankriti Lace Manufacturing Mahila Mutual Aided Co-operative Societies’ Federation Limited, which supports local women artisans and has revived operations at the Alankriti Lace Park in Narasapur.
- GI Tag Benefits:
- The Geographical Indication tag serves to protect the authenticity of the lace products, boost demand, and ensure better market recognition.
- It provides legal protection to the traditional craft, preventing unauthorized use of the term "Narasapur lace" by others and promoting the region's cultural heritage and economic growth.
- Future Outlook:
- With the GI tag, there is hope for increased demand for Narasapur lace products both in domestic and global markets, thus offering a fresh avenue for artisans to revive and sustain the craft.
- Alankriti Federation and other stakeholders are optimistic that the GI tag will significantly revitalize the local economy and empower women in the region.
PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
The National Achievement Survey (NAS), a nationwide survey meant to assess students’ learning progress, will be held on December 4 this year under a new name – PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024. This year’s assessment involves a few changes from the last round in 2021.
Overview of PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024:
- New Name: The National Achievement Survey (NAS) is now rebranded as the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan 2024.
- Date: The survey will be held on December 4, 2024.
- Purpose: To assess students’ learning achievements across India.
- Organizing Bodies: Spearheaded by NCERT and CBSE.
What Does the Survey Assess?
- Assessment Focus: Evaluates students’ learning outcomes in various subjects.
- Survey Methodology: Uses multiple-choice questions to assess a sample of students.
- Target Groups: Students from government, government-aided, and private schools across every district in India.
History of NAS and PARAKH:
- NAS History: Conducted every three years since 2001 to capture learning progress.
- Involvement of Classes:
- 2001-2014: Included Classes 3, 5, and 8.
- 2014-15: Class 10 was introduced.
- 2017 and 2021: Covered Classes 3, 5, 8, and 10.
- Report Cards: Provides national, state, and district-level performance data.
Changes in 2024 Survey (PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan):
- Targeted Classes:
- Class 3 (End of foundational stage)
- Class 6 (End of preparatory stage)
- Class 9 (End of middle stage)
- Exclusion of Class 10: Unlike previous years, Class 10 students are not part of this year's assessment.
- Subjects Assessed:
- Class 3 & 6: Language, Mathematics, and The World Around Us (Concepts of Science, Social Science, and Environmental Education).
- Class 9: Language, Mathematics, Science, and Social Science.
Alignment with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020:
- NEP Structure: Aligns with the NEP 2020 framework, categorizing educational stages:
- Class 1-2: Foundational stage
- Class 3-5: Preparatory stage
- Class 6-8: Middle stage
- Class 9-12: Secondary stage
- The shift to Class 6 and 9 for this year’s survey matches the NEP's stage-wise educational framework.
Key Differences in 2024 Assessment:
- Survey Scale: In 2024, 75,565 schools and 22.9 lakh students from 782 districts will participate.
- 2021 Assessment Data:
- The 2021 survey revealed a drop in learning outcomes post-COVID-19.
- Class 3 students showed a performance below the national average in all states.
- Class 5: Only Punjab and Rajasthan had scores above the national average.
PARAKH's Role:
- PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) was established in 2023 as the National Assessment Centre to oversee such achievement surveys.
- Mandate: One of PARAKH’s primary roles is to organize national surveys like the PARAKH RashtriyaSarvekshan.
Significance of the Survey:
- Data Utilization: The survey helps in shaping educational policies based on real-time data on student learning levels.
- Competency-Based Assessment: This year’s survey is focused on competency-based assessments, aligning with the goals of NEP 2020.
- Policy and Planning: The data helps in designing interventions to address regional or subject-wise disparities in education quality.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
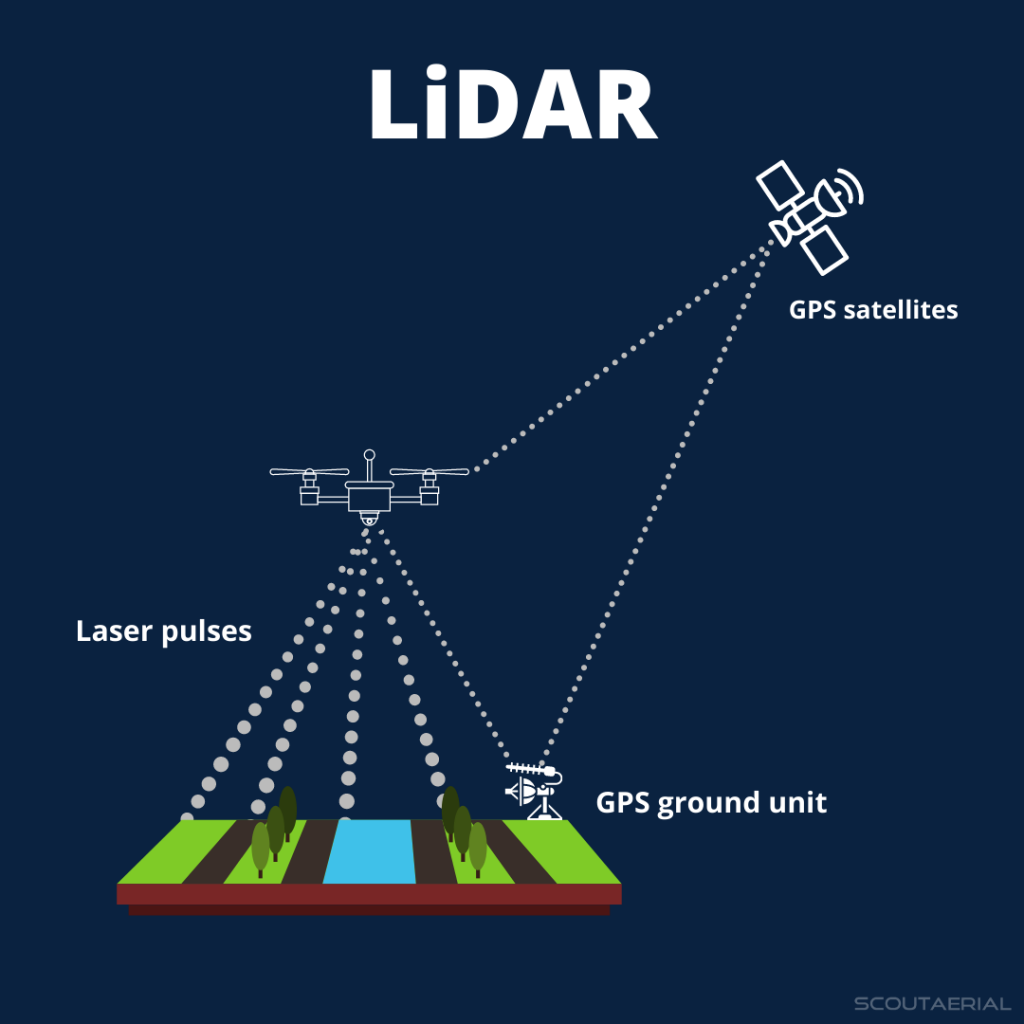
What is LiDAR?
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held with the aim of promoting lighthouse tourism and celebrating India’s maritime legacy.
Strategic Importance of the Lighthouse Projects
- The Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW) has invested significantly in developing lighthouses as tourist hubs. The festival marks a concerted effort to integrate tourism with the preservation of these iconic structures.
- Lighthouse tourism has witnessed a remarkable increase of over 400% in visitor numbers since 2014, as part of India's broader vision to promote the blue economy.
-
- From just 4 lakh visitors in 2014, the footfall surged to 16 lakh in 2023-24, with over 9 lakh tourists already in the first half of FY 2024-25.
-
Key Projects and Announcements at the Festival
- New Lighthouses: The announcement of the two new lighthouses at Chaumuck and Dhamra along Odisha’s coastline is significant for enhancing coastal infrastructure and promoting maritime tourism in the state.
- Kalwan Reef Lighthouse: Located in Jamnagar, Gujarat, this lighthouse is part of a broader effort to enhance maritime navigation and heritage conservation along India’s western coastline.
- Development of Coastal Communities: Highlighted the importance of empowering coastal communities, particularly those living around lighthouses, to preserve and promote these structures as national cultural icons. These communities are expected to play a crucial role in lighthouse preservation, as well as in tourism and local economic development.
- Paradip Port Initiatives: Additionally, major infrastructure projects at Paradip Port, such as a stacker-cum-reclaimer and a flyover bridge, were inaugurated to further bolster the port’s capabilities and enhance its role in maritime logistics. The Sagarmala Programme also continues to transform Paradip Port into a mega port with a projected handling capacity of 500 MTPA by 2047.
Economic and Employment Impact
The development of 75 iconic lighthouses across 9 coastal states and one Union Territory is not only aimed at tourism development but also focuses on job creation. As of 2024:
- More than 150 direct jobs and 500 indirect jobs have been created in sectors such as hospitality, transportation, and local crafts, driven by the increasing footfall at these tourist destinations.
- The creation of modern amenities at these lighthouses, such as museums, amphitheaters, and children’s parks, has helped in transforming lighthouses into multifaceted tourism hubs that attract both domestic and international tourists.
Collaborative Efforts for Preservation and Promotion
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encouraging collaboration between the government, local communities, and private stakeholders to develop and maintain lighthouses as sustainable tourist destinations.
- National Framework: A central association will be created to manage coastal societies surrounding lighthouses, enabling local communities to actively participate in their preservation, protection, and promotion.
- Cultural Integration: The event also underscored the need for integrating cultural heritage with tourism development, using the lighthouses as platforms to showcase local art, cuisine, and history.
National Florence Nightingale Awards 2024
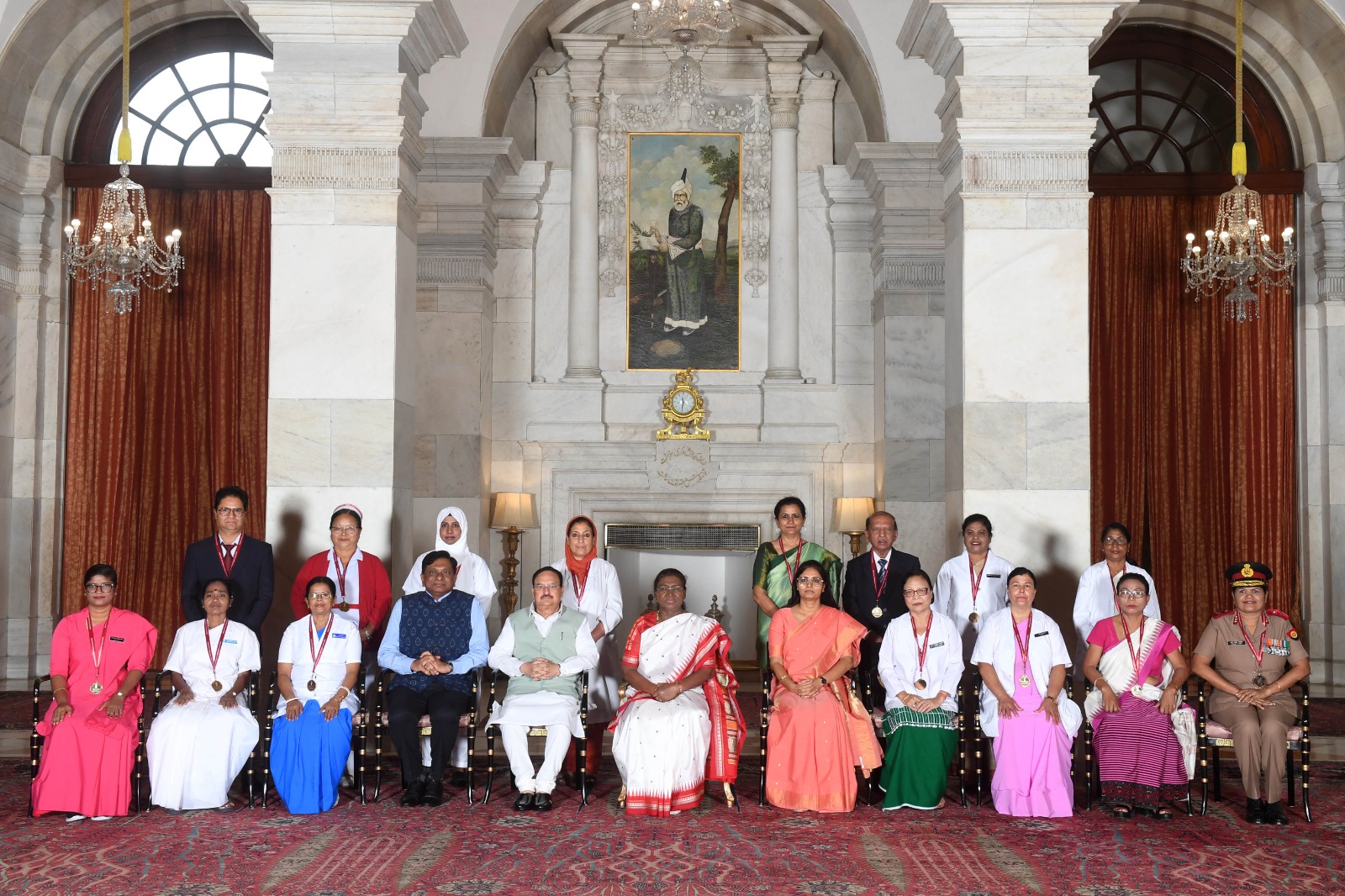

- 15 Sep 2024
In News:
President Droupadi Murmu honored 15 exemplary nursing professionals with the National Florence Nightingale Awards 2024, recognizing their extraordinary healthcare service.
Key Details:
- The National Florence Nightingale Award was instituted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India in the year 1973 as a mark of recognition for the meritorious services rendered by the nurses and nursing professionals to the society.
- A total of 15 awards are given in the category of registered auxiliary nurses and midwife, registered nurses and midwife and registered lady visitor, the statement said.
- The award is given to outstanding nursing personnel employed in central, states and Union territories and voluntary organisations.
- The nurse in her/his regular job in the hospital or community settings, educational or administrative setting is eligible for the national award.
- Each award consists of a Certificate of Merit, a cash award of ? 1,00,000 and a medal.
A Legacy of Florence Nightingale
- The National Florence Nightingale Awards, are named in honor of Florence Nightingale, the founder of modern nursing.
- Nightingale’s pioneering work during the Crimean War laid the foundation for professional nursing, and her relentless efforts in promoting hygiene and compassionate care revolutionized healthcare practices worldwide.
- In her honor, International Nurses Day is celebrated every year on May 12, her birthday.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024

- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of State for Women and Child Development, launched the Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024 in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh on 1st September,2024.
Key Highlights:
- As part of the 7th Rashtriya POSHAN Maah, awareness programs are being organized at various levels.
- Under the ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services) Project, complementary feeding activities were conducted at Anganwadi Centres (AWC) Paduck Bagicha, South Andaman.
- Also, at AWC, Champin Nancowrie, Nicobar district (Andaman & Nicobar) under the ICDS Tribal initiative, local food items and nutrition sources were displayed.
- These efforts aim to further the Prime Minister's vision of a ‘Suposhit Bharat’ by conducting diverse large-scale activities, harnessing the potential of Gram Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah:
- The programme is annually celebrated in the month of September, with a different theme each year, primarily focusing on addressing malnutrition by ensuring convergence of various nutrition-related schemes and programmes.
- The objective of the Poshan Maah is to ensure community mobilisation and bolster people’s participation for addressing malnutrition amongst young children, and women and to ensure health and nutrition for everyone.
Poshan Abhiyaan:
- POSHAN Abhiyan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme For Holistic Nourishment) focuses on advancing nutritional outcomes for children under six years, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- To cultivate widespread awareness about nutrition at each stage of life, it is celebrated annually as Poshan Maah (1st—30th September) and Poshan Pakhwada (fortnight of March).
- POSHAN Abhiyan (National Nutrition Month) aims to strengthen efforts to end hunger and malnutrition.
- It focuses to improving the nutritional outcomes among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers by focusing on prenatal care, diet, and optimal breastfeeding.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development plans month-long activities under Poshan Maah, focusing on issues such as the hygiene and sanitation, anaemia prevention, maternal and infant health, among others.
- There are outreach programmes, identification drives, camps, and fairs with a special focus on pregnant and lactating women, children below six years, and adolescent girls in order to realise the vision of ‘Swasth Bharat’.
New Light-based Tool to Detect Viral Infections

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A viral infection can stress cells and change their shapes and sizes. Researchers have built a tool to detect these changes.
About the new Tool:
- A team of researchers has developed an innovative method to detect viral infections in cells using only light and principles of high-school physics.
- The key insight is that viral infections can stress cells, causing changes in their shapes, sizes, and other features.
- As the infection progresses and the body becomes diseased, these changes become more pronounced.
- The researchers have found a way to translate these cellular changes into recognizable patterns that can indicate whether a cell is uninfected, virus-infected, or dead.
- For example, virus-infected cells tend to be elongated and have clearer boundaries compared to uninfected cells.
- By analyzing the patterns of light interacting with cells, this method can non-invasively differentiate between uninfected, virus-infected, and dead cells.
- This approach has the potential to revolutionize viral disease diagnosis and monitoring, providing a simple, cost-effective, and powerful tool for detecting viral infections at the cellular level.
Significance:
- This light-based approach to detecting viral infections offers several significant advantages over the current standard methods:
- Accuracy: The new light-based technique can detect viral infections with equal or even greater accuracy compared to existing standard methods that rely on chemical reagents.
- Cost-effectiveness: The equipment required for this new method costs only around one-tenth of the $3,000 (approximately Rs 2.5 lakh) needed for the standard chemical-based approach, making it a far more affordable option, especially for resource-constrained settings.
- Rapid results: The light-based method can identify virus-infected cells in just about two hours, significantly faster than the 40 hours required by the current standard method.
- This time efficiency can be crucial in situations where rapid detection is essential, such as during a virulent disease outbreak.
- Early detection: By enabling the early detection of viral infections at the cellular level, this new technique could prove invaluable in containing the spread of highly contagious viral diseases, such as a severe influenza outbreak.
What are Viruses?
- Viruses are microscopic organisms capable of infecting various hosts such as humans, plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi.
- Structurally, they consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protective shell called a capsid, with some viruses also possessing an envelope.
- Unable to reproduce independently, viruses rely on host cells to replicate by utilizing the cell's machinery.
- Common types include influenza viruses, human herpesviruses, coronaviruses, human papillomaviruses, enteroviruses, flaviviruses, orthopoxviruses, and hepatitis viruses.
- Viruses are responsible for causing illnesses such as flu, the common cold, and COVID-19.
Wildlife Corridors

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To revive the population of tigers in Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR) — the lone tiger reserve in the Maharashtra western region — the state’s forest department will soon translocate tigers from Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR) in Chandrapur district.
What are Wildlife Corridors?
- Corridors are essentially habitats and pathways that connect wildlife populations, which are fragmented by human settlements and infrastructure works.
- They are crucial for the long-term survival of the tiger population as they help guard against localised extinctions and ensure the exchange of gene flow, which helps in population diversity.
- Tigers have large home ranges and often travel long distances in search of mates and food.
- In doing so, they make use of these wildlife corridors and cross several human-dominated landscapes.
- The role played by corridors in conservation is a well-established one and has been incorporated into policy decisions as well.
- Mitigation measures such as underpasses, and wildlife crossings are now routinely ordered to safeguard tigers and other wildlife in projects where linear infrastructure projects fragment habitats.
- Litigation, advocacy, and policymaking have all contributed to this.
- The construction of an overpass on the National Highway- 7 to protect the migratory route of tigers underneath between the Kanha and Pench Tiger Reserves is one instance of embedding mitigation measures to protect corridors.
- Tigers routinely use the space beneath the elevated stretch of the highway to cross the forests.
- In 2014-15, the National Tiger Conservation Authority and Wildlife Institute of India (WII) mapped 32 major tiger corridors in the country across four broad tiger landscapes – Shivalik Hills and Gangetic plains, Central India and Eastern Ghats, Western Ghats, and the North East Hills.
Is Translocation the Best Approach for Tiger Recovery?
- Tiger translocation projects have been undertaken in India since 2008.
- Sariska Tiger Reserve, in 2008, and Panna Tiger Reserve, in 2009, have witnessed successful tiger reintroduction and translocation projects.
- There have also been failures and shelving of reintroduction plans, like in the case of Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha, which was the country’s first inter-state translocation project.
- However, before choosing translocation, other available options such as habitat improvement, prey augmentation, strengthening of tiger corridors, and vigilance improvement should be assessed.
- Even after translocations, one must ensure that corridors are strengthened and they are free of major disturbances.
- This will ensure the dispersal of tigers to other source population areas.
Diplomatic Passport

- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
After allegations of sexual abuse by Janata Dal (Secular) MP Prajwal Revanna came to light, the politician fled to Germany on a diplomatic passport.
What is a Diplomatic Passport?
- Diplomatic passports are issued to people holding diplomatic status or deputed by the Government of India for official duty abroad.
- Unlike normal passports, which are valid for 10 years and have a dark blue cover, diplomatic passports are valid for five years or less and have maroon covers.
- Diplomatic passports, also known as 'Type D' passports.
- A diplomatic passport has 28 pages.
- Holders of such passports are entitled to certain privileges and immunities as per international law, including immunity from arrest, detention, and certain legal proceedings in the host country.
Issuing Authority:
- The Ministry of External Affairs’s (MEA) Consular, Passport & Visa Division issues diplomatic passports (‘Type D’ passports) to people falling in broadly five categories:
- Those with diplomatic status;
- Government-appointed individuals travelling abroad for official business;
- Officers working under the branches A and B of the Indian Foreign Service (IFS), normally at the rank of Joint Secretary and above; and
- Relatives and immediate family of officers employed in IFS and MEA.
- Select individuals who are authorised to undertake official travel on behalf of the government”.
- The MEA issues visa notes to government officials going abroad for an official assignment or visit.
What are the Benefits of Having a Diplomatic Passport?
- Official identification: The diplomatic passport serves as an official identification document for individuals representing the Indian government on diplomatic missions.
- It helps in establishing their identity and official status.
- Diplomatic immunity: Diplomatic passport holders are typically entitled to certain privileges and immunities as per international law.
- This includes immunity from arrest, detention, and certain legal proceedings in the host country, safeguarding their ability to perform official duties without hindrance.
- Visa facilitation: Diplomatic passports often enjoy certain privileges when it comes to visa facilitation.
- Many countries offer expedited visa processing or waive visa requirements altogether for diplomatic passport holders, simplifying travel arrangements for official purposes.
- Access to diplomatic channels: The diplomatic passport grants access to diplomatic channels and services provided by Indian embassies, consulates, and other diplomatic missions worldwide.
- This includes assistance with consular services, protection, and support while abroad.
- Priority services: Diplomatic passport holders may receive priority services at airports and during immigration procedures.
- This can include dedicated immigration counters or expedited security and customs clearance, saving time during travel.
- Official representation: The diplomatic passport signifies the official representation of the Indian government and confers a sense of authority and credibility while dealing with international counterparts, foreign officials, and diplomatic communities.
Can Diplomatic Passports be Revoked?
- According to The Passports Act, 1967, the passport authority may cancel a passport or travel document, with the previous approval of the Central government.
- The passport authority can impound or revoke a passport if the authority believes that:
- The passport holder or travel document is in wrongful possession
- If the passport was obtained by the suppression of material information or based on wrong information provided by the individual
- If it is brought to the notice of the passport authority that the individual has been issued a court order prohibiting his departure from India or has been summoned by the court.
- A diplomatic passport can be revoked upon orders from a court during proceedings with respect to an offence allegedly carried out by the passport holder before a criminal court.
Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI)

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) is preparing to defend the government’s human rights processes at a meeting in Geneva this week, where a decision on whether India’s human rights body will retain its “A status” is expected to be made.
About Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI):
- The Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) is a representative body of National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) from across the world.
- It assists in the establishment and strengthening of independent and effective NHRIs, which meet the international standards set out in the Paris Principles.
- GANHRI encourages joint activities and cooperation among NHRIs, organises international conferences, liaises with the United Nations and other international organisations, assists NHRIs under threat, and assists governments in establishing NHRIs.
- The Asia Pacific Forum of National Human Rights Institutions (APF) and other member institutions continue to make a significant contribution to the operations and human rights initiatives of GANHRI.
- The organisation is incorporated as a non-profit organisation under Swiss law.
- Its Statute, adopted in March 2009, sets out its objectives and how it operates.
Membership:
- NHRIs that comply fully with the Paris Principles – and which have been granted 'A status' by GANHRI – are eligible to become voting members of GANHRI and to hold governance positions.
- NHRIs that only partially comply with the Paris Principles – and which have been granted 'B status' by GANHRI – can participate in meetings of GANHRI but are not eligible to vote or to hold governance positions.
Bureau:
- The operations of GANHRI are managed by its Bureau, which is comprised of representatives from each of the four regional groupings:
- Africa, the Americas, Europe, and the Asia Pacific.
- Each regional grouping is represented by elected representatives from four 'A status' NHRIs.
- The APF is currently represented on the GANHRI Bureau by Australia, India, Korea, and Qatar.
- A key role of the Bureau is to assess applications for membership in the ICC.
- It also reviews and determines the accreditation status of NHRIs, following a recommendation from the Sub-Committee on Accreditation.
- In addition, the Bureau collaborates with the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), in particular the National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Unit, to facilitate the participation of NHRIs in the United Nations Human Rights Council.
- Bureau meetings are usually held twice a year; the first is in conjunction with the first quarter session of the UN Human Rights Council and the second is in conjunction with one of the NHRI regional network's meetings.
- A meeting is also held in conjunction with the bi-annual International Conference.
International Conference:
- The International Conference involves NHRIs, as well as representatives of United Nations agencies, international organisations, and civil society.
- The purpose of the International Conference is to strengthen cooperation between NHRIs, to discuss human rights issues of shared concern, and to ensure follow-up at the national level.
- The International Conference is held every two years, alternating between Europe, the Americas, Africa, and the Asia Pacific.
Officials:
- The positions of GANHRI Chairperson and Secretary are served on a rotational basis by representatives nominated by the four regional coordinating committees: Europe, Africa, the Americas, and the Asia Pacific.
- The current GANHRI Chairperson is Maryam Abdullah Al Attiyah, Chairperson of the National Human Rights Committee of Qatar (NHRC), representing the Asia Pacific region.
- The current GANHRI Secretary is Amina Bouayach, Chairperson of the National Human Rights Council of Morocco (CNDH), representing the African region.
Secretariat:
- The National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Unit of OHCHR acts as the GANHRI secretariat.
- GANHRI has a permanent representative in Geneva to support and facilitate the participation of NHRIs in the UN Human Rights Council and its human rights mechanisms.
Bambi Bucket

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an Indian Air Force MI 17 V5 helicopter, equipped with a Bambi Bucket, was deployed to combat the forest fires in Nainital district, Uttarakhand.
What is a Bambi Bucket?
- Bambi Bucket is a specialised aerial firefighting tool that has been in use since the 1980s.
- It is essentially a lightweight collapsible container that releases water from underneath a helicopter to targeted areas.
- The water is released by using a pilot-controlled valve.
- One of its key features is that it can be quickly and easily filled.
- The bucket can be filled from various sources, including a lake, river, pond, and swimming pool, which allows firefighters to swiftly refill it and return to the target area.
- Bambi Bucket is available in a variety of sizes and models, with capacities ranging from 270 liters to more than 9,840 liters.
How was the Bambi Bucket Invented?
- The Bambi Bucket was invented by Don Arney, a Canadian business, in 1982.
- Arney came up with the idea after he realised that the aerial firefighting water buckets in use at the time were not efficient and had a high failure rate.
- These water buckets were generally made of “solid fiberglass, plastic, or canvas with metal frames” and were “too rigid to fit inside the aircraft” and had to be “trucked to fire sites or flown in on the hook of a helicopter thereby slowing the aircraft down.
- Another issue was that the water dropped from these containers used to get dispersed into a spray thereby reducing impact.
- Bambi Bucket does not have these limitations.
- One, it can be stored within the helicopter until development.
- Two, it discharges a solid column of water, “resulting in a more accurate and effective water dump, less evaporation on the descent, and greater impact force.
- It was an instant success and began to be widely used for firefighting.
- Today, Bambi Bucket is used in more than 115 countries around the world by more than 1,000 helicopter operators.
Nephrotic Syndrome
- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the heels of recent news reports on how keratin-based hair-straightening products containing glycolic acid derivatives led to severe kidney injury in women, researchers from Kerala have reported a series of cases wherein, the use of fairness creams has been linked to nephrotic syndrome.
What is Nephrotic Syndrome?
- Nephrotic syndrome causes scarring or damage to the filtering part of the kidneys (glomeruli).
- This causes too much protein to be lost from the blood into the urine.
People with nephrotic syndrome often have:
-
- Low levels of protein in the blood (hypoalbuminemia)
- Very high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria)
- Swelling (edema), especially around the eyes, feet, and hands
- High cholesterol
What causes nephrotic syndrome?
- Nephrotic syndrome results from damage to the kidneys' glomeruli.
- These are the tiny blood vessels that filter waste and excess water from the blood and send them to the bladder as urine.
- The glomeruli keep protein in the body. When they are damaged, protein leaks into the urine.
- Healthy kidneys allow less than 1 gram of protein to spill into the urine in a day.
- In nephrotic syndrome, the glomeruli let 3 grams or more of protein leak into the urine during 24 hours.
- Nephrotic syndrome may happen with other health problems, such as kidney disease caused by diabetes and immune disorders.
- It can also develop after damage from viral infections.
- The cause of nephrotic syndrome is not always known.
What are the symptoms of nephrotic syndrome?
- The symptoms of nephrotic syndrome include:
- Swelling or edema, typically in the ankles, feet, or legs
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight gain
- Foamy urine
Treatment:
- The treatment of nephrotic syndrome varies depending on its cause.
- However, it typically includes medications to treat the underlying cause, as well as changes in diet.
- Dietary changes that might help in treating nephrotic syndrome include Source:
- limiting sodium
- eating less protein
- reducing the intake of saturated fat and cholesterol
Complications of nephrotic syndrome:
- Serious complications of nephrotic syndrome include kidney failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Dialysis may be needed if kidney failure develops which can happen in extreme cases.
Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA)

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) Asia Pacific, in collaboration with other environmental organizations, has called on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to take decisive action in response to plastic pollution.
About Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA):
- The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) is an alliance of over 1,000 grassroots groups, NGOs, and individuals working towards a transition from a linear, extractive economy to a circular system.
- GAIA's primary objective is to create a world that prioritizes people's right to a safe and healthy environment, free from toxic pollution and resource depletion.
- GAIA envisions a just, zero-waste world where communities' rights are respected, and ecological limits are acknowledged. To achieve this vision, the alliance focuses on:
- Eliminating Incineration: GAIA advocates for alternatives to incineration and promotes waste management practices that protect the environment and public health.
- Promoting Zero Waste: The alliance supports the adoption of zero-waste strategies, emphasizing waste reduction, reuse, and recycling to conserve resources and reduce pollution.
- Addressing Plastic Pollution: GAIA recognizes the global plastic pollution crisis and works on initiatives to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable alternatives.
- Mitigating Climate Change: GAIA advocates for climate-friendly waste management practices, emphasizing the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions from waste disposal.
What is Incineration?
- Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves burning hazardous materials at high temperatures to destroy contaminants.
- This process takes place in an "incinerator," a furnace specifically designed to safely burn hazardous materials within a combustion chamber.
- Various types of hazardous materials can be treated through incineration, including soil, sludge, liquids, and gases.
- While incineration effectively destroys many harmful chemicals such as solvents, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pesticides, it does not destroy metals like lead and chromium.
- Modern incinerators are equipped with air pollution control mechanisms, such as fabric filters, scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators.
- These technologies help remove fly ash and gaseous contaminants generated during the incineration process, mitigating its environmental impact.
- Despite its benefits in waste treatment, incineration remains a topic of debate due to concerns about residual pollutants and the potential for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women)

- 18 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
According to a recent report by UN Women, six months into the war, Gaza is facing a humanitarian crisis disproportionately impacting women and girls.
What is UN Women?
- Founded in 2010 by the United Nations General Assembly as part of the UN reform agenda.
- Merges resources and mandates to create a more significant impact on gender equality and women's empowerment.
- Serves as a global advocate for women and girls, addressing their needs and accelerating progress.
Key Roles:
- Supports intergovernmental bodies like the Commission on the Status of Women in developing policies, global standards, and norms for gender equality.
- Assists member states in implementing these standards and offers technical and financial support upon request.
- Builds effective partnerships with civil society organizations.
- Leads and coordinates the UN system's work on gender equality while promoting accountability through regular monitoring of progress.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Works globally to realize the SDGs for women and girls.
- Promotes women's equal participation in all aspects of life.
Country-level Support:
- Collaborates with government and non-governmental partners in countries that request assistance.
- Helps implement policies, laws, services, and resources to advance gender equality.
Grant-making Funds:
- Fund for Gender Equality: Provides grants to support innovative, high-impact programs by government agencies and civil society groups.
- UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women: Finances initiatives that address violence against women and girls.
Commission on the Status of Women (CSW):
- A global policy-making body focused on gender equality and women's advancement.
- Operates as a functional commission of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
Information and Advocacy:
- Regularly provides information on women's rights issues to the General Assembly, ECOSOC, and the Security Council.
- Maintains the UN Secretary-General's database on violence against women, tracking measures taken by UN Member States and organizations.
- UN Women plays a vital role in advancing gender equality and women's empowerment worldwide by providing crucial support, resources, and advocacy through its various initiatives and collaborations.
B virus

- 17 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A 37-year-old man wounded by a wild monkey in Hong Kong is in intensive care suffering from infection with B virus.
What is B virus?
- B virus, also known as herpes B virus or Macacine herpesvirus 1 (McHV-1), is a type of herpesvirus found in macaque monkeys, particularly rhesus macaques.
- While asymptomatic in these animals, it can cause severe neurological complications, including encephalitis, in humans if transmitted through bites, scratches, or contact with infected bodily fluids.
Is B virus infection fatal??
- B virus infections in humans are rare but potentially fatal, with symptoms ranging from fever and headache to neurological dysfunction and death.
- Of the 50 cases reported in the US, 21 have died.
- Prompt treatment with antiviral medication is essential if exposure to B virus occurs, and preventive measures are crucial for individuals working with or handling macaques.
How does it spread??
- The transmission of this virus among humans is rare.
- So far, only one case of human-to-human transmission has been recorded.
What are the symptoms of B virus infection??
- Disease onset typically occurs within 1 month of exposure, although the actual incubation period can be as short as 3–7 days.
- The common symptoms seen during the infection are:
- Fever, headache, myalgia, and localized neurologic symptoms (e.g., pain, numbness, itching) might occur near the wound site.
- Lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain also can occur.
Treatment:
- The treatment for B virus includes providing antiviral medications.
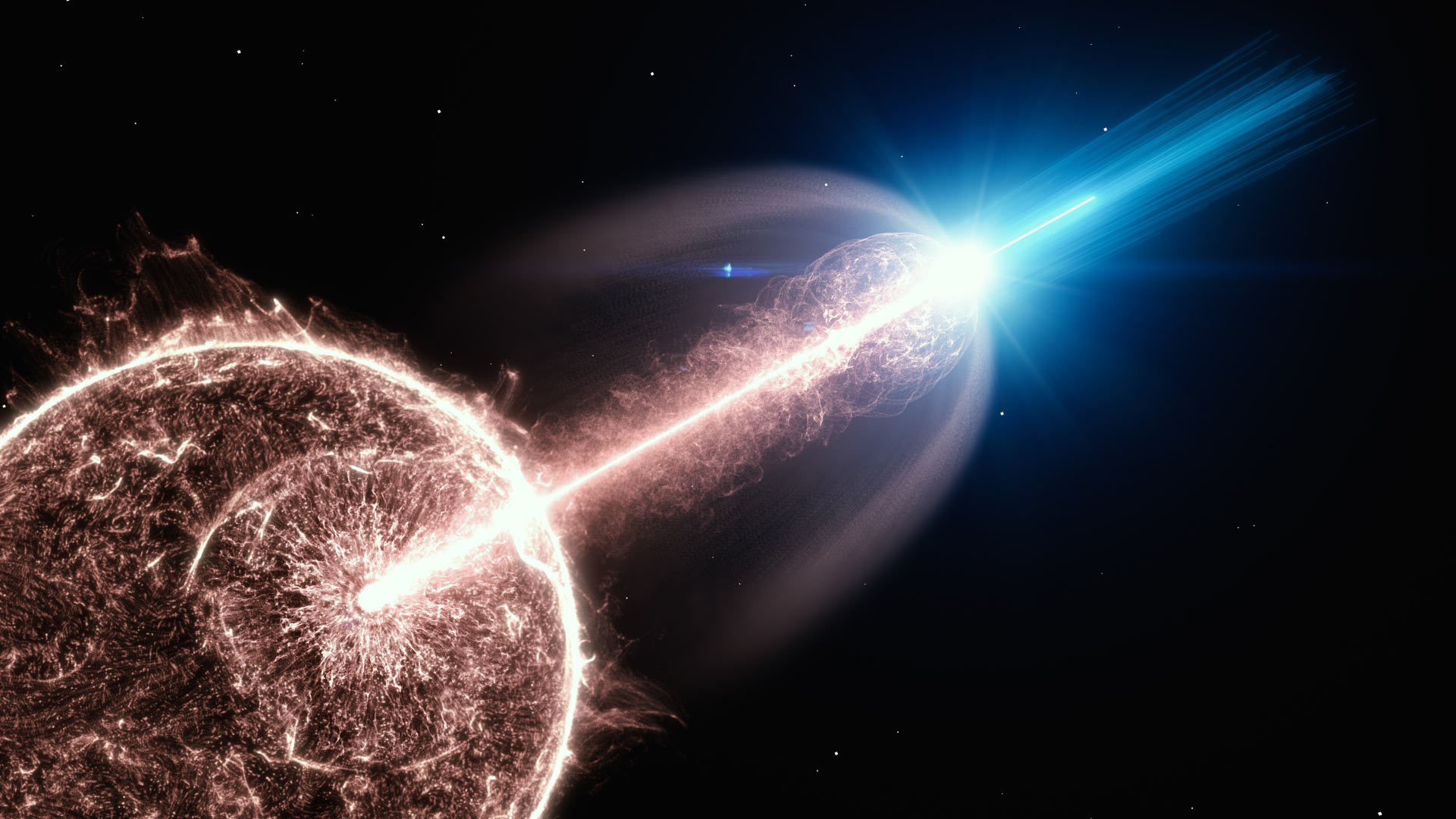
GRB 221009A - Gamma-ray Bursts (GRBs)

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Northwestern University recently confirmed that the brightest gamma-ray burst ever recorded, GRB 221009A, was caused by the collapse and explosion of a massive star.
About GRB 221009A:
- GRB 221009A, also known as Swift J1913.1+1946, is the brightest gamma-ray burst ever detected, estimated to be ten times brighter than the previous record holder.
- The burst itself lasted around seven minutes, but its effects were observable for over ten hours.
- GRB 221009A originated from a galaxy estimated to be 2.4 billion light-years away, yet it was powerful enough to influence Earth's atmosphere.
- This exceptionally bright burst emitted across a vast range of the electromagnetic spectrum, providing a unique opportunity for scientists to study this rare phenomenon in detail.
- The cause of the burst is attributed to the collapse of a massive star, but scientists are still investigating why it was so much brighter than other gamma-ray bursts.
What are Gamma-ray Bursts?
- Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are the most powerful explosions in the universe.
- These brief flashes of high-energy light result from some of the universe's most explosive events, including the birth of black holes and collisions between neutron stars.
- Lasting a few milliseconds to several minutes, GRBs can be hundreds of times brighter than an average supernova, making them as luminous as a million trillion suns.
- Thus, when a GRB erupts, it briefly becomes the brightest source of electromagnetic radiation in the observable universe.
- Gamma Ray Bursts are difficult to study because they are so short-lived.
- They were first detected by the Vela satellites, which were designed to detect nuclear tests during the Cold War.
- It was only years after their detection that they were declassified.
- The location of gamma-ray bursts within their host galaxy and their surrounding environment informs us as to the formation and evolution of the progenitor system, providing insight into stellar evolution and star formation across the age of the universe.
What causes a gamma-ray burst?
- The cause of a gamma-ray burst depends on how long it lasts.
- GRBs that last less than two seconds are caused by the merger of two neutron stars or the merger of a neutron star and a black hole.
- Longer GRBs, which can last hours, are triggered when a massive star collapses and births a black hole.
- In both cases, GRBs result from jets of particles accelerated to around 99.9% of the speed of light.
How powerful are gamma-ray bursts?
- In just a few seconds, a gamma-ray burst can emit as much energy as the sun will put out over its entire 9 billion-year lifetime
Do gamma-ray bursts happen in the Milky Way?
- GRBs seem to be most closely associated with galaxies that are in the midst of intense star formation, a period that our galaxy seems to have matured out of 2 billion to 3 billion years ago.
- However, the Milky Way is filled with the supernova remnants that mark the deaths of massive stars, indicating that our galaxy was once home to GRBs.
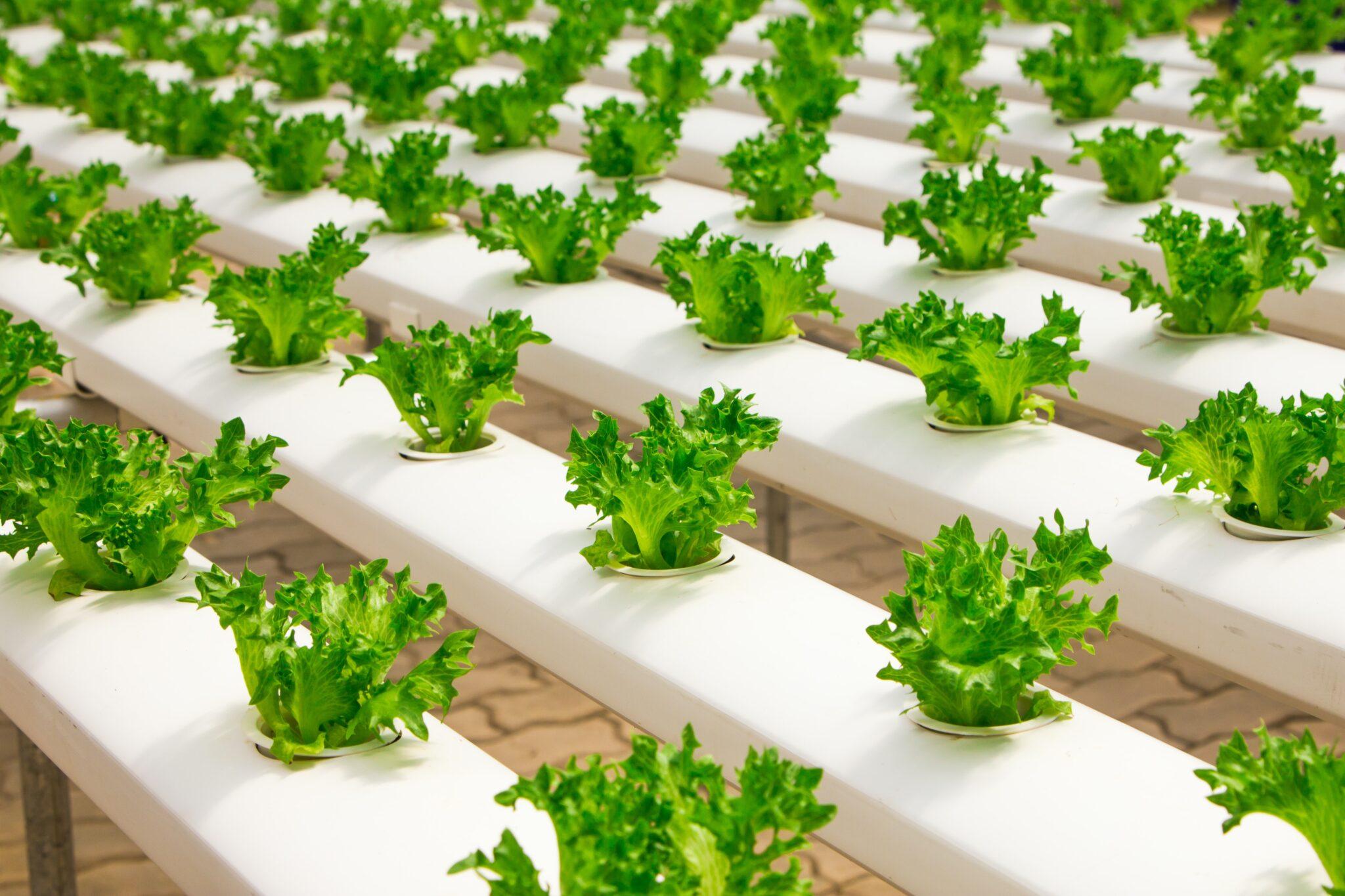
Hydroponic Farming

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the wake of evolving consumer preferences, India is at the forefront of an agricultural transformation, pivoting towards sustainable farming with an emphasis on health.
What is Hydroponics?
- Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, utilizing nutrient-rich water as the primary source of essential minerals and elements.
- The technique involves the circulation of nutrient-enriched water through a network of pipes or channels, directly supplying the roots of plants with the necessary nourishment for their growth and development.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Soilless Cultivation: Hydroponics eliminates the need for soil by providing an alternative substrate or a soil-like medium, such as rock wool, perlite, or vermiculite, to support the plants' roots.
- Nutrient Control: This technique enables precise control over the nutrient composition, concentration, and pH levels in the water, ensuring optimal nutrient availability for plants.
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponics recirculates and reuses water, significantly reducing water consumption compared to traditional soil-based farming.
- Space Optimization: Due to the compact nature of hydroponic systems, they can be used in urban areas, greenhouses, and indoor facilities, maximizing yield per unit area.
- Year-round Cultivation: With controlled environmental conditions, hydroponics allows for continuous cultivation, regardless of seasonal changes or weather fluctuations.
- Hydroponics provides a sustainable, efficient, and adaptable approach to agriculture, with potential benefits in resource conservation, food security, and sustainable urban food production.
Hydroponics in India:
- According to a report by Datamintelligence, India’s hydroponic market is poised for a remarkable growth trajectory, with a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.53% by 2027, outpacing the global industry’s estimated growth of 6.8%.
- This surge underscores the vast potential of hydroponics in meeting the rising demand for sustainable food produce, particularly in metros and tier 1 cities where health-conscious consumers are willing to pay a premium for fresh, safe, and sustainably grown products.
- This transformative shift is not just a response to changing consumer preferences for fresh produce but also an adaptation to the geographical and environmental challenges that face traditional farming methods.
Suitable Regions for Hydroponic Farming:
- Hydroponic farming presents a viable solution in regions where traditional farming faces significant barriers:
- Areas with Limited Water Supply: Hydroponics drastically reduces water usage, making it ideal for drought-prone areas.
- Rocky Regions: In places where the terrain is unsuitable for soil-based agriculture, hydroponics offers a practical alternative.
- Low Soil Fertility Areas: Hydroponics bypasses the need for fertile soil, allowing cultivation in regions with poor soil quality.
- Demand-Driven Areas: Regions with a high demand for fresh products are perfect for hydroponic farms, catering to health-conscious consumers in urban and semi-urban locales
The Edge with Hydroponic Farming in India:
- Hydroponic farming’s ascendancy in India is attributed to several compelling benefits, underpinned by technological advancements that lower operational costs and facilitate scalability:
- Versatility in Location: It enables agriculture in environments traditionally deemed unsuitable, such as deserts or cold climates.
- Controlled Conditions: Farmers have precise control over nutrients, pH, and the growing environment, optimizing plant health and yield.
- Resource Efficiency: The recycling of water and nutrients significantly cuts down on input costs and environmental impact.
- Enhanced Growth Rates: Increased oxygen availability accelerates plant growth, leading to quicker harvest cycles.
- Pest and Disease Reduction: By eliminating soil, hydroponics reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Higher Yields: The efficiency and controlled environment of hydroponic systems result in substantially higher crop yields.
- Labour and Maintenance Savings: The absence of weeding and traditional cultivation reduces labour requirements and costs.
- Improved Working Conditions: Elevating crops to a more accessible height improves ergonomics for farm workers, further reducing labour costs.
- No Need for Crop Rotation: Hydroponics eliminates the necessity for crop rotation, simplifying farm management.
- Reduced Transplant Shock: Plants grown hydroponically experience less stress when transplanted, enhancing survival rates.
India Abstains from UNHRC Resolution on Gaza Ceasefire

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently abstained on a resolution at the Human Rights Council that called on Israel for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza.
India's Voting Pattern on Israel-Palestine Issues at the UNHRC:
- India's stance on the Israel-Palestine conflict has been reflected in its voting behavior at the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC).
- While India has voted in favor of resolutions criticizing Israel for human rights violations, occupation of the Syrian Golan, and affirming Palestinian self-determination, it has also abstained from certain resolutions.
- In a significant development, India abstained from a resolution calling for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza and an arms embargo on Israel.
- This decision followed instances of violence, including the killing of aid workers and airstrikes.
- India's abstention is believed to be in line with its previous votes on resolutions involving "accountability."
- India's approach indicates its belief that both parties should be held accountable for their actions.
- As a result, it refrains from supporting resolutions that single out one side for condemnation.
- By taking a balanced stance, India aims to promote peace and stability in the region while advocating for the rights of all parties involved.
About the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is an inter-governmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2006.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, the council serves as a key platform for addressing human rights issues globally.
- The High Commissioner for Human Rights serves as the principal human rights official within the UN system.
- The council convenes three times annually to address human rights violations worldwide.
Membership:
- Comprising 47 member states, the council is responsible for promoting and safeguarding human rights across the globe.
- Member states are elected individually via secret ballot by a majority vote of the General Assembly.
- The election of members occurs within geographical groups to ensure equitable representation.
Tenure:
- Council members serve for a term of three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after two consecutive terms.
The UNHRC's primary functions include:
- Promoting universal respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms.
- Addressing violations of human rights, including gross and systematic violations.
- Developing international human rights law and making recommendations to the UN General Assembly.
- Conducting investigations into alleged human rights abuses through special rapporteurs and working groups.
- Reviewing the human rights records of all UN member states through the Universal Periodic Review process.
Agni-Prime Ballistic Missile

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has successfully flight-tested the new generation ballistic missile Agni-Prime from the APJ Abdul Kalam Island off the coast of Odisha.
About Agni-Prime Missile:
- Agni-P or Agni-Prime is a new generation nuclear-capable medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) developed by the DRDO that incorporates technological advances from Agni-IV and Agni-V and is considered a successor for Agni-I and Agni-II missiles in the operational service of the SFC.
- Agni-Prime, with a strike range of 1,000 to 2,000 km, has significant upgrades, which include composite motor casing, maneuverable reentry vehicle (MaRV), improved propellants, and navigation and guidance systems.
- It is a two-stage, surface-to-surface, road-mobile, and solid-fueled missile that is transported by a truck and launched via a canister.
- It is a ballistic missile with a dual redundant navigation and guidance system.
Features:
- Although Agni-Prime looks similar to Agni-III, the weight is reduced by half.
- Agni-P will replace older generation missiles such as Prithvi-II (350 km), Agni-II (2,000 km), Agni-III (3,000 km), and Agni-4 (4,000 km) ballistic missiles.
- Agni-Prime incorporates upgrades such as propulsion systems, composite rocket motor casings, and advanced navigation and guidance systems.
- Along with Agni-V, Agni-P will provide India with stronger deterrence against countries such as China and Pakistan.
- While Agni-V brings all of China within its strike range, Agni-P seems to have been developed to counter Pakistan's forces.
- Agni-P is developed to achieve maximum maneuverability against missile defense systems and higher accuracy for precision strikes.
What is a Ballistic Missile and why is it named so?
- A Ballistic missile follows a ballistic flight path - which comprises three phases of flight.
- In the first phase or the boost phase, the solid-fuel rocket engine propels the missile upwards and it has to rapidly gain velocity and altitude, by knifing through the densest parts of the earth's atmosphere.
- The second and unpowered phase of flight happens in the upper reaches of the earth's atmosphere or in space, where the missile travels along its pre-determined path, but without the power of its engines.
- It is known as the coast phase or mid-course phase and during this time, it travels along a horizontal path.
- During the coasting, the missile is either in space or the upper atmosphere, where it faces minimal resistance or drag.
- In the third and final phase or the terminal phase, the missile descends and gets back into the earth's atmosphere and flies towards its target, while being guided by its on-board systems.
Project Akashteer

- 05 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Army has started the induction of control and reporting systems under ‘Project Akashdeer’ to bolster its air defense capabilities.
What is 'Project Akashteer'?
- 'Project Akashteer' is a cutting-edge initiative designed to automate air defense control and reporting processes by digitizing them.
- Developed by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) as part of the 'Atmanirbhar Bharat' initiative, this project is poised to significantly enhance the operational efficiency and integration of the Army's air defense mechanisms.
- By integrating radar and communication systems at all levels into a unified network, 'Akashteer' aims to deliver an unprecedented level of situational awareness and control.
- This will enable swift engagement of hostile targets, significantly reduce the risk of fratricide, and ensure the safety of friendly aircraft in contested airspace.
- A noteworthy aspect of 'Akashteer' is its emphasis on mobility and resilience.
- The system's control centers, designed to be vehicle-based and mobile, can maintain operational capabilities even in challenging communication environments.
- The system will facilitate the achievement of complete automation of air defense operations and significantly enhance the air defense posture of India.
- The induction of the systems has commenced in the Indian Army's Corps of Army Air Defense, marking a significant move towards enhancing India's defense capabilities and technology absorption.
How it will help India's air defense system?
- The 'Akashteer Command and Control Systems will significantly enhance India's air defense capabilities in several ways:
- Efficiency and Integration: By digitizing Air Defence Control and Reporting processes, 'Akashteer' will usher in unprecedented levels of efficiency and integration.
- This will enable the Indian Army to respond swiftly to hostile threats while minimizing the risk of friendly fire incidents.
- Situational Awareness: 'Akashteer' integrates radar and communication systems into a unified network, providing the Indian Army with unprecedented situational awareness.
- This will enable them to detect and engage hostile targets more effectively, ensuring the safety of friendly aircraft in contested airspace.
- Mobility and Resilience: The system's vehicle-based and mobile Control Centers are designed to maintain operational capabilities even in challenging communication environments.
- This ensures that the Indian Army can operate effectively in diverse terrain and under adverse conditions.
- Automation: Overall, the deployment of 'Akashteer' signifies a leap towards complete automation of air defense operations.
- This will enhance the Indian Army's ability to defend its airspace, ensuring a safer and more secure future for the country.
- The Indian Army has declared 2024 as the 'Year of Technology Absorption' and is undertaking various initiatives to induct niche technology and systems into its inventory.
- The induction of 'Akashteer' control centers is one of the major milestones achieved by the Army on its path to transformation to meet the current and futuristic requirements of complex air defense operations.
Wadge Bank
- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
While India 'gave away' rights to Katchatheevu, in a subsequent pact, it secured sovereign rights in Wadge Bank near Kanyakumari.
What is Wadge Bank?
- Wadge Bank is a 10,000 square kilometer submarine plateau, of the sea south of Kanyakumari that is rich in biodiversity and considered India’s richest fishery resource.
- Wadge Bank, located near Cape Comorin, is home to more than 60 species of ornamental fish and other oceanic animals.
- It is a productive coastal area where three seas meet and tides create a rich fishing ground from May to October.
- Moreover, it is an invaluable treasure that indigenous people and communities depend on for food and resources, and is important to their culture.
How did India get control of the Wadge Bank?
- Wadge Bank came to India as part of the second of the two accords signed with Sri Lanka in the 1970s.
- Following the 1974 agreement under which Prime Minister Indira Gandhi ‘gave away’ Katchatheevu island to Sri Lanka, New Delhi, and Colombo signed another pact in 1976 under which the former bought Wadge Bank.
- On March 23, 1976, India and Sri Lanka signed the agreement on the maritime boundary in the Gulf of Mannar and the Bay of Bengal as part of which it was agreed that the Wadge Bank “lies within the exclusive economic zone of India, and India shall have sovereign rights over the area and its resources”.
- In the general description of Wadge Bank annexed with the treaty shared with the United Nations, it is described as “outside the territorial waters of India”.
- The Wadge Bank near Kanyakumari is rich in biodiversity and considered India’s richest fishery resource.
- As per the 1976 pact, Sri Lankan fishermen can’t engage in activities here.
- ??But at the request of Sri Lanka and as a gesture of goodwill, India agreed that Lankan fishing vessels licensed by the Government of India could fish in Wadge Bank for three years from its establishment as an exclusive economic zone of India with the stipulation that only six such vessels can fish and their catch cannot exceed 2,000 tonnes in a year.
- And, again at the request of the Sri Lankan government, India agreed to provide Colombo with 2,000 tonnes of fish of the quality, species, and at the price mutually agreed by the two sides for five years after the Lankans stopped fishing at the Wadge Bank.
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KOSO)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since ancient times, seafarers, mathematicians, astronomers, and physicists have all diligently studied and tracked the Sun and its phenomena, with the establishment of the Madras Observatory by the British East India Company in 1792 marking a pioneering effort in this region.
About Kodaikanal Solar Observatory:
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory is a solar observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru.
- It is on the southern tip of the Palani Hills 4 kilometers from Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu).
- The Government of India separated Astrophysics from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in April 1971.
- From solar data recorded on basic photographic plates or films, the 125-year-old KoSO boasts a mammoth digital repository containing 1.48 lakh digitized solar images of 10 terabytes.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots) and thousands of other images of the Sun recorded every day since the start of the 20th century.
- KoSO is the only observatory offering high-resolution digitized images for such a long period (with coverage of more than 75 percent).
- Today, it houses a spectrum of advanced instruments like the H-alpha telescope to perform full disc imaging, a White light Active Region Monitor (WARM) with calcium and sodium filters to make full disc simultaneous observations of the photosphere and chromosphere layers of the Sun, a solar tunnel telescope and more.
Links to the Great Drought:
- Scanty rainfall over south India during the winter monsoon of 1875 triggered one of the worst droughts the country had experienced till then.
- Multiple failed crops over the famine-stricken peninsular India killed 12.2 to 29.3 million people across the Madras and Mysore Provinces during 1875-1877.
- India, along with China, Egypt, Morocco, Ethiopia, southern Africa, Brazil, Columbia, and Venezuela, suffered concurrent multi-year droughts during 1876-1878, later named the Great Drought, and an associated global famine that killed nearly 50 million.
- The drought was thought to be due to multiple reasons:
- Solar activity
- Cool Pacific Ocean conditions followed by a record-breaking El Nino (1877-1878)
- Strong Indian Ocean Dipole and
- Warm North Atlantic Ocean conditions.
Solar Physics Observatory in Palani Hills:
- Established in response to the British Raj's acknowledgment of solar activity's link to India's weather patterns, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory, also known as the Indian Solar Observatory, was founded to conduct systematic studies on solar phenomena and their correlation with Indian meteorology.
- Located in Kodaikanal, selected for its favorable atmospheric conditions after careful consideration by Charles Michie Smith (a Professor of Physics at the Madras Christian College), the observatory was officially sanctioned by the Government of India in August 1893 and inaugurated by Lord Wenlock (the then Governor of Madras) in 1895.
- Commencing systematic observations in 1901, it merged with the Madras Observatory, enriching its instrumentation.
- Notable discoveries ensued, including the identification of the Evershed Effect.
- Over time, the observatory expanded its research domains to encompass cosmic rays, radio astronomy, and ionospheric physics, among others, solidifying its status as a pioneering institution in the field of astrophysics.
- Notably, it initiated solar radio observations in 1952, marking a significant milestone in Indian solar research.
- Despite the closure of contemporaneous observatories, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory has endured, continuing to contribute to our understanding of the Sun and its effects on Earth's climate and space weather.
Why Study the Sun?
- Being the primary source of energy, life on Earth is supported by the Sun.
- Any change on the solar surface or its periphery could significantly affect the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Powerful solar storms and solar flares can be potentially harmful to Earth’s satellite-based operations, power grids, and navigational networks.
- The KoSO (Kodaikanal Solar Observatory), which has been imaging the Sun for over a century now, has a rich repository of data.
- This is extremely useful not only to reconstruct the Sun’s historic past but also to link its behavioral changes to better understand and predict its future and its impact on life on Earth and Space weather.
Fukushima Water Issue

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Japan announced that its experts have engaged in discussions with their Chinese counterparts to address Beijing's concerns regarding the release of treated radioactive wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea.
What is the Fukushima Water Issue?
- In 2021, the Japanese government unveiled plans to gradually discharge over one million tonnes of contaminated water from the Fukushima nuclear plant into the ocean over the next three decades.
- The contaminated water is a residual product of the devastating 2011 earthquake and tsunami that incapacitated the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, resulting in the release of radioactive materials.
- After more than ten years of storing this wastewater, Japan asserts that they are facing storage space limitations and contends that the treated water is now safe for release.
Concerns Surrounding the Fukushima Water Discharge:
- Tritium and Carbon-14: The water from Fukushima undergoes filtration via the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), effectively reducing most radioactive contaminants to acceptable safety levels, except tritium and carbon-14.
- While both emit low levels of radiation, consumption in large quantities could potentially pose risks.
- Insufficient Research: Scientists emphasize the need for further investigation into the potential impact of the water discharge on the ocean bed and marine ecosystems.
- The Pacific Islands Forum regional group has labeled the proposed plan as "another significant nuclear contamination disaster," citing ongoing challenges faced by its member nations due to past US nuclear testing.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF):
- The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including the formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations.
- It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia.
- It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
- The PIF secretariat is located in Suva, the capital of Fiji.
Nuclear Incidents:
- A nuclear and radiation incident denotes an occurrence that has resulted in significant repercussions for individuals, the environment, or the facility involved.
- These may entail fatal consequences for individuals, substantial releases of radioactivity into the environment, or reactor core meltdowns.
- Globally, there have been a total of 99 incidents at nuclear power plants.
- Fifty-seven of these incidents have transpired since the Chornobyl disaster, with the United States accounting for 57% of all nuclear-related incidents.
- Noteworthy nuclear power plant mishaps encompass:
- Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011)
- Chernobyl disaster (1986)
- Three Mile Island accident (1979), and
- The SL-1 accident (1961).
Usha Mehta

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent film has been launched, depicting the inspiring life story of Indian freedom fighter Usha Mehta.
About Usha Mehta:
- Born in 1920 in the village of Saras, near Surat in Gujarat, Usha Mehta, affectionately known as Ushaben, embodied the Gandhian principles of non-violence and civil disobedience from a young age.
Early Activism:
- At the tender age of eight in 1928, she participated in a protest march against the Simon Commission, demonstrating her early commitment to India's independence struggle.
- The Secret Congress Radio: In 1942, amidst the fervor of the Quit India Movement, Usha Mehta and her colleagues boldly established the Secret Congress Radio.
- This clandestine radio station played a pivotal role in connecting freedom movement leaders with the masses, ensuring the dissemination of crucial information, and maintaining the spirit of resistance against colonial rule.
Establishing an Underground Radio Station:
- With the outbreak of the War in 1939, the British government imposed stringent measures, including the suspension of all amateur radio licenses throughout the Empire.
- Operators were mandated to surrender their equipment to the authorities, under threat of severe repercussions for non-compliance.
Key Figures in the Operation:
- Usha Mehta, alongside Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, and Chandrakant Jhaveri, played instrumental roles in orchestrating the Congress Radio initiative, defying the ban on amateur radio broadcasting.
The Congress Radio Trial:
- The trial of the five accused individuals—Usha Mehta, Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, Chandrakant Jhaveri, and Nanak Gainchand Motwane, who facilitated crucial equipment—captivated public attention in Bombay.
- While Vithalbhai and Motwane were acquitted, Mehta, Babubhai, and Chandrakant faced severe sentences for their involvement.
Usha Mehta's Legacy:
- Following her release from Pune's Yerawada Jail in March 1946, Usha Mehta was lauded in nationalist circles as "Radio-ben," symbolizing her courageous defiance and commitment to the freedom struggle through underground broadcasting.
Independence, PhD, & Padma Vibhushan
- When India finally achieved independence in 1947, the British had divided the country into two parts – India and Pakistan, sending the region into chaos.
- The divide results in massive bloodshed with more than 10 million Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs seeking to find their home.
- Mehta was torn. “In a way, I was very happy, but sad at the same time because of partition.
- It was an independent India but a divided India,” she was quoted as saying in the book Freedom Fighters Remembered.
- She was away from active politics in independent India due to her ill health but continued to remain a staunch Gandhian till the very end.
- She penned the script for a documentary on Gandhi produced by her colleague at the radio station, and earned a PhD in Gandhian thought at the University of Bombay.
- She taught political science and ran the politics department at the university.
- She also taught at Wilson College for 30 years.
- She was also the president of the Gandhi Peace Foundation.
- In 1998, she was awarded India’s highest civilian honor, the Padma Vibhushan.
- She lived a simple life and never married or had children.
- She died on 11 August 2000 at the age of 80.
Earth’s early evolution: Fresh insights from rocks formed 3.5 billion years ago
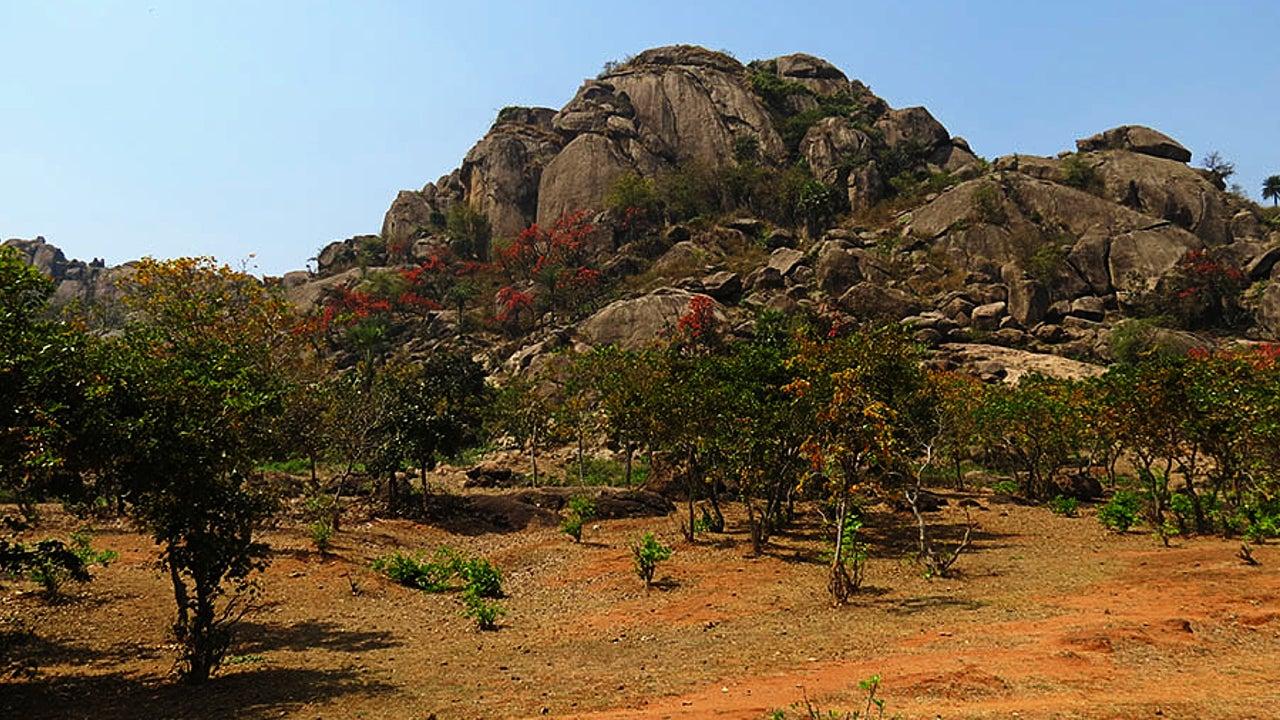

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exploring ancient cratons such as the Singhbhum Craton in India, alongside similar formations in South Africa and Australia, provides unparalleled insights into the early stages of our planet's development, reaching back approximately 3.5 billion years.
What is Singhbhum Craton?
- The Singhbhum Craton encompasses a vast expanse of rugged terrain, primarily spanning regions in Jharkhand and Odisha, situated between the Chhota Nagpur plateau and the Eastern Ghats.
- Dating back approximately 3.5 billion years, this ancient segment of the Earth's crust offers valuable insights into early geological processes.
- Its oldest rock formations consist predominantly of volcanic and sedimentary rocks, referred to as greenstone successions.
- Greenstones are characterised by submarine volcanic rocks with minor sedimentary components.
- Geologically akin to greenstone belts in South Africa's Barberton and Nondweni regions and the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia, these areas experienced extensive submarine mafic volcanic activity, rich in magnesium oxide, between 3.5 and 3.3 billion years ago, with preserved features like pillowed lava and komatiites.
Significance:
- The Singhbhum Craton sheds light on early tectonic activities during the Archaean era, enhancing our understanding of the Earth's formative stages.
- Its distinctive geological characteristics, particularly the presence of greenstone belts, yield invaluable data on surface and atmospheric processes crucial for theorising about early habitable conditions and the emergence of life on Earth.
What are Cratons?
- A craton is a stable and ancient part of Earth's lithosphere that has experienced long-term tectonic and geomorphic stability.
- It is considered to be the nucleus of a continent and is characterised by its thick and cold lithosphere.
- Cratons can undergo destruction, which is defined as a geological process resulting in the loss of craton stability due to changes in its physical and chemical properties.
- The mechanisms responsible for craton destruction include oceanic plate subduction, rollback and retreat of subducting plates, stagnation and dehydration of subducting plates in the mantle transition zone, melting of the mantle caused by dehydration of stagnant slabs, non-steady flow in the upper mantle induced by melting, and changes like the lithospheric mantle.
- Craton destruction can lead to crustal thinning, surface uplift, and the concentration of mineral deposits.
ISRO’s ‘Naughty Boy’ Rocket Launches INSAT-3DS (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently launched its weather satellite INSAT-3DS board spacecraft Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) F14, nicknamed the ‘naughty boy’ for its spotty record.
What is the GSLV-F14?
- The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), standing at a height of 51.7 metres, is a three-stage launch vehicle with a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes.
- First stage: Its first stage (GS1) features a solid propellant (S139) motor with 139 tons of propellant and four earth-storable propellant stages (L40) strapons, each carrying 40 tons of liquid propellant.
- Second Stage: The second stage (GS2) also utilises an earth-storable propellant system with a 40-ton propellant load.
- Third Stage: The third stage (GS3) is equipped with a cryogenic system containing 15 tons of propellant, consisting of liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
- GSLV-F14 serves as a versatile launch vehicle, capable of deploying various types of spacecraft for communication, navigation, earth resource surveys, and other specialised missions.
GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission Overview and Key Goals:
- INSAT-3DS Satellite marks a significant advancement in the Third Generation of Meteorological Satellite series from Geostationary Orbit, with substantial contributions from Indian industries.
- Fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), the mission aims to enhance meteorological services, complementing the existing capabilities of INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR satellites.
Key Objectives:
- Earth Observation and Oceanic Monitoring: Utilise various spectral channels to monitor Earth's surface, conduct oceanic observations, and assess environmental conditions critical for meteorology.
- Atmospheric Parameter Profiling: Provide vertical profiles of essential meteorological parameters within the atmosphere, enhancing our understanding of atmospheric dynamics.
- Data Collection and Dissemination: Facilitate the collection and dissemination of data from Data Collection Platforms (DCPs), ensuring timely access to crucial meteorological information.
- Satellite Aided Search and Rescue (SAR) Services: Enable Satellite Aided Search and Rescue services, enhancing emergency response capabilities through advanced satellite technology.
Significance of the GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission:
- The launch of INSAT-3DS holds a lot of significance for India's space agency as it is equipped to provide extremely accurate weather forecast information by studying the surface of the ocean, also being helpful in disaster prevention.
- The GSLV has encountered challenges in the past, with four out of 15 launches facing setbacks, contrasting with the higher success rates of ISRO's PSLV and LVM-3.
- The success of this mission is critical, especially considering the upcoming launch of the Earth observation satellite, NISAR, later this year, a collaborative effort between NASA and ISRO.
- INSAT-3DS, with a mission lifespan of 10 years, will assume the roles of INSAT-3D (2013) and INSAT-3DR (2016), which have reached the end of their operational lives.
- This mission will enhance meteorological forecasting capabilities, enabling better prediction of extreme weather events like thunderstorms, providing visibility assessments for aviation, and facilitating research on forest fires, smoke, snow cover, and climate dynamics.
Rare Golden Tiger takes a stroll in Assam’s Kaziranga National Park, video stuns people (HT)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
A rare golden tiger was recently spotted in Kaziranga National Park taking a stroll and is the only known golden big cat in India.
What is a Golden Tiger?
- A Golden Tiger, also called a Golden Tabby Tiger, is a Bengal tiger with a unique colour variation caused by a recessive gene.
- The tiger looks golden because it has a mutation or a genetic variant.
- Basically, tigers have three colours: black, orange and white.
- In the Golden Tiger, the black colour is missing and it is slightly faded.
- The golden colouring of these tigers comes from a recessive trait called 'wideband,' affecting how black pigments are produced during hair growth.
- Golden tigers are not a distinct subspecies but rather a product of genetic diversity among Bengal tigers.
- They are extremely rare in the wild and even more so in captivity.
About Kaziranga National Park:
- Kaziranga National Park lies partly in the Golaghat District and partly in the Nagaon District of Assam.
- It is the oldest park in Assam and covers an area of 430 sq km along the river Brahmaputra on the North and the Karbi Anglong hills on the South.
- The National Highway 37 passes through the park area and tea estates, hemmed by table-top tea bushes.
- Kaziranga National Park a world heritage site is famous for the Great Indian one-horned rhinoceros, the landscape of Kaziranga is of sheer forest, tall elephant grass, rugged reeds, marshes & shallow pools.
- It was declared a National Park in 1974.
- It is one of the last areas in eastern India undisturbed by a human presence.
- It is inhabited by the world's largest population of one-horned rhinoceroses, as well as many mammals, including tigers, elephants, panthers and bears, and thousands of birds.
- Vegetation: Due to the difference in altitude between the eastern and western areas of the park, mainly four main types of vegetation’ like alluvial inundated grasslands, alluvial savanna woodlands, tropical moist mixed deciduous forests, and tropical semi-evergreen forests.
- Flora: Kumbhi, Indian gooseberry, cotton tree, and elephant Apple are among the famous trees that can be seen in the park.
- Fauna: The forest region of Kaziranga Park is home to the world’s largest population of Indian Rhinoceros.
- Other animals that can be seen in the elephant grass, marshland and dense tropical moist broadleaf forests of Kaziranga are Hoolock Gibbon, Tiger, Leopard, Indian Elephant, Sloth Bear, Wild water buffalo, swamp deer, etc.
- Also in this park the good number of migratory bird species from Central Asia.
- With the increase in tiger population every year, the government authorities declared Kaziranga a Tiger Reserve in the year 2006.
PM Modi announces solar roof-top scheme for one crore households (HT)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Monday announced the 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana' under which one crore households will get rooftop solar across the nation.
What is 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana'?
- The scheme aims to equip one crore poor to middle-class households with rooftop solar panels in a bit to provide electricity from solar energy.
- The scheme would not only reduce the electricity bill of the poor and middle class but would also make India self-reliant in the energy sector.
- Rooftop solar panels are the photovoltaic panels installed on the roof of a building which is connected to the main power supply unit.
- Thus, it reduces the consumption of grid-connected electricity and saves electricity costs for the consumer.
- In a solar rooftop system, there is only an upfront capital investment and minimal cost for maintenance.
- Under this scheme, one crore households will get solar rooftops.
- Moreover, it will offer additional income for surplus electricity generation.
- The consumer can choose any vendor on the national portal and after installation, the subsidy is sent directly to the bank account of the consumer.
- The Pradhanmantri Suryodaya Yojana is a new scheme but very similar to the previously announced Rooftop Solar Programme in 2014.
- The previous scheme had aimed to produce 40,000 megawatts (MW) or 40 gigawatts (GW) of solar power by 2022.
India's Advancements in Solar Energy:
- At the end of last year, 2023, India’s solar power generation stood at 73.31 GW, up from 2022’s 63.3 GW.
- However, rooftop solar power generation only stands at around 11.08 GW as of December 2023.
- The total solar power generated in the nation, Rajasthan leads the pack with 18.7 GW while Gujarat follows with 10.5 GW.
- However, when talking about rooftop solar power, Gujarat is at peak position — with 2.8 GW — followed by Maharashtra at 1.7 GW.
- India has more than 300 million households and an average of 300 sunny days each year, which has tremendous potential for rooftop solar installations in residential spaces.
- However, experts note that despite several measures, India’s rooftop solar power generation is not where it should be, listing reasons for the situation.
- The primary reason for rooftop solar not becoming popular is that it is still an expensive option for many.
- There is also a lack of awareness.
Importance of Solar Power to India:
- Harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity is important to India for multiple reasons.
- If India wants to achieve its aim of becoming net zero by 2070, it has to look towards the sun.
- In fact, at COP26, in November 2021, India committed to meet 50 per cent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030.
- For these aims to be met, India has to harness the full capacity of the sun.
- Moreover, India’s share of global energy demand is predicted to double to 11 per cent in 2040, making it imperative to enhance energy security and self-sufficiency in power generation without increasing environmental costs.
- This increase in power demand is likely to increase India’s reliance on coal, oil and natural gas as a source of energy.
- However, additional imports of oil and increased domestic production of coal will not only fall short of energy demand but will also entail economic and environmental costs.
- The expansion of solar power units and increased reliance on solar power allow India to enhance energy security in the face of rising demand.
- Furthermore, India is already facing depleting groundwater levels, owing to which the nation must shift its energy resources away from water.
How the new Education Ministry guidelines will affect the coaching institutes (HT)

- 20 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Taking cognisance of coaching centres charging exorbitant fees from students, promoting unhealthy competition and stress among students, and a rise in student suicides and other malpractices, a set of new guidelines were released by the Education Ministry.
Guidelines for Registration and Regulation of Coaching Centers 2024:
- The guidelines define a 'coaching centre' as an establishment providing coaching for study programs, competitive exams, or academic support to more than 50 students at the school, college, and university levels, established, run, or administered by any person.
Key aspects of the guidelines include:
- Registration Process: Coaching centres must apply for registration within their local jurisdiction, adhering to specified forms, fees, and document requirements.
- Each branch of a coaching centre is considered a separate entity, requiring individual registration.
- Marketing Standards: Coaching centres are prohibited from making misleading promises or guarantees regarding ranks or marks.
- Transparency is mandated, with centres required to maintain an updated website containing detailed information.
- Student Enrollment: Students below the age of 16 are not permitted for enrolment, and entry is allowed only after the completion of secondary school examinations.
- Fee Structure: Tuition fees must be fair, with detailed receipts provided.
- A comprehensive prospectus must include information on courses, duration, facilities, fees, and refund procedures. Any fee increase during the course is prohibited.
- Exit Policy: Pro-rata refunds are mandated within 10 days for mid-course withdrawals.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Coaching centres must allocate a minimum of one square meter per student.
- Compliance with fire safety and building codes is essential, along with proper electrification, ventilation, lighting, security measures, and medical assistance.
- Study Hours: Classes should not coincide with school hours, and weekly off for students and tutors is mandatory.
- Class sizes must align with a healthy teacher-student ratio.
- Mental Wellbeing: Centers should establish mechanisms for immediate intervention and counselling for students in distress.
- Complaint Mechanism: Students, parents, or tutors/employees can file complaints, to be resolved within thirty days by the competent authority or an inquiry committee.
- Penalties: Penalties for violations include ?25,000 for the first offence, ?1 lakh for the second, and registration revocation for subsequent breaches.
Article 30 Not Intended To Ghettoise Minorities, Minority Institution Can Include Others In Administration: Supreme Court In AMU Case Hearing (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent observation, the Supreme Court, headed by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud, highlighted that the right granted to religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer their educational institutions under Article 30(1) of the constitution was not intended to "ghettoise" them.
What is Article 30 of the Indian Constitution?
- Article 30 of the Indian Constitution states the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.
- It says: “All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.”
When was Article 30 adopted?
- Article 30 was adopted on December 8, 1948.
Features of Article 30 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 30 of the Indian constitution consists of provisions that safeguard various rights of the minority community in the country keeping in mind the principle of equality as well.
- Article 30(1) says that all minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- Article 30(1A) deals with the fixation of the amount for the acquisition of property of any educational institution established by minority groups.
- Article 30(2) states that the government should not discriminate against any educational institution on the ground that it is under the management of a minority, whether based on religion or language while giving aid.
The debate around Article 30:
- On December 8, 1948, the Constituent Assembly debated the need for imparting primary education in one's mother tongue.
- One of the members of the Assembly moved an amendment to restrict the scope of this article to linguistic minorities.
- He argued that a secular state should not recognise minorities based on religion.
- Another member of the Assembly proposed to guarantee linguistic minorities the fundamental right to receive primary education in their language and script.
- He was concerned about the status of minority languages, even in regions which had a significant minority population.
- The Constituent Assembly rejected the proposals.
What is Article 29 of the Indian Constitution?
- Both Article 29 and Article 30 guarantee certain rights to minorities.
- Article 29 protects the interests of minorities by making a provision that any citizen/section of citizens having a distinct language, script or culture has the right to conserve the same.
- Article 29 mandates that no discrimination would be done on the grounds of religion, race, caste, language or any of them.
Concept of Minority in the Indian Constitution:
Religious minorities:
- While Article 30 and Article 29 of the Constitution do not specify 'minorities' in India, it is classified into religious minorities and linguistic minorities.
Religious Minorities in India:
- The basic ground for a community to be nominated as a religious minority is the numerical strength of the community.
- For example, in India, Hindus are the majority community.
- As India is a multi-religious country, it becomes important for the government to conserve and protect the religious minorities of the country.
- Section 2, clause (c) of the National Commission of Minorities Act, declares six communities as minority communities. They are:
- Muslims
- Christians
- Buddhists
- Sikhs
- Jains and
- Zoroastrians (Parsis)
Linguistic Minorities:
- A class or group of people whose mother language or mother tongue is different from that of the majority groups is known as the linguistic minority.
- The Constitution of India protects the interests of these linguistic minorities.
Autonomous systems becoming the preferred choice in Order of Battle for nations across the globe: Navy Chief (The Hindu)

- 10 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Chief of Naval Staff Admiral R Hari Kumar officially initiated the maiden indigenously produced Drishti 10 'Starliner' Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for the Indian Navy.
What is Drishti 10 Starliner UAV?
- Drishti 10 Starliner Unmanned Aerial Vehicle is an advanced intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) platform, developed by Adani Defence and Aerospace, and represents a significant leap forward in India’s defence technology.
- The Drishti 10 Starliner boasts an impressive 36 hours of endurance and a substantial 450 kg payload capacity.
- It stands out as the only all-weather military platform certified with NATO’s STANAG 4671 (standardized agreement 4671) for airworthiness, allowing it to operate in both segregated and unsegregated airspace.
- The UAV is equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, an extended endurance of 36 hours, and advanced communication capabilities.
- Its incorporation of new-age technologies such as Automatic Take Off and Landing (ATOL) positions it as a formidable asset.
- Notably, this UAV is a home-assembled version of the Hermes-900 MALE UAV, featuring an impressive 70% indigenous content.
- A notable feature of the Drishti 10 'Starliner' is its low maintenance demands, contributing to cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
- This quality enhances operational readiness, minimizing downtime and optimizing deployment opportunities.
- The Drishti 10 is outfitted with cutting-edge communication systems, encompassing satellite communication and Line-of-Sight (LOS) data links, guaranteeing dependable and secure data transmission.
What is Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)?
- A drone, also referred to as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), is an aircraft that operates without a human pilot, crew, or passengers on board.
- UAVs are integral components of unmanned aircraft systems, comprising a ground-based controller and a communication system linked with the UAV.
Drones are categorized based on their weight, adhering to existing regulations:
- Nano: Equal to or less than 250 grams
- Micro: Between 250 grams and 2 kilograms
- Small: From 2 kilograms to 25 kilograms
- Medium: Between 25 kilograms and 150 kilograms
- Large: Exceeding 150 kilograms
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module Retraces Steps to Earth Orbit (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have brought the Propulsion Module (PM) of the Chandrayaan-3 mission , which initially brought the Vikram lander to within 100 km of the Moon's surface before detaching and executing a historic controlled descent on August 23, back into Earth orbit.
What is a Propulsion Module in Chandrayaan-3?
- The Propulsion Module is a rectangular component of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft, equipped with solar panels for power.
- Its primary purpose was to transport the Lander module to the lunar polar circular orbit and facilitate its separation.
- Following separation, the SHAPE payload within the Propulsion Module was activated.
- Initially intended for a three-month operation during the mission, the ISRO announced on December 4th that the Chandrayaan-3's Propulsion Module had been manoeuvred out of lunar orbit.
- Placed high above Earth for an additional mission, the module is currently sustained by residual fuel.
- This bonus mission will showcase technologies crucial for future lunar sample retrieval, according to ISRO.
- As of now, the ISRO has not disclosed its plans for the spacecraft once it depletes its fuel.
Importance of Propulsion Module's Return to Earth's Orbit:
- ISRO highlighted the key achievements resulting from the return manoeuvres conducted on the Propulsion Module (PM) in connection to upcoming missions:
- Planning and executing the trajectory and manoeuvres for the return journey from the Moon to Earth.
- Developing a software module for planning such manoeuvres, along with its initial validation.
- Planning and executing a gravity-assisted flyby around a planet or celestial body.
- Preventing uncontrolled crashing of the PM onto the Moon's surface at the end of its life, aligning with the requirement of avoiding debris creation.
What is Chandrayaan-3 Mission?
Sindhudurg Fort (Financial Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is gearing up to showcase its operational prowess in a significant ‘Operational Demonstration’ scheduled for December 4, 2023, at Sindhudurg Fort in Maharashtra.
About Sindhudurg Fort:
- Sindhudurg Fort is a historically significant stronghold situated on an islet in the Arabian Sea, just off the coast of Maharashtra in western India.
- Positioned on Kurte Island near Malvan town in Sindhudurg District within the Konkan region of Maharashtra, this formidable fortress was commissioned and constructed under the reign of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj of the Maratha Empire in 1664.
- The primary objective behind its construction was to counteract the escalating influence of foreign colonizers, including English, Dutch, French, and Portuguese merchants, and to curb the rise of the Siddis of Janjira.
- The Bakhar (a form of historical narrative written in Marathi prose) written by Chitragupta aptly mentions this fort as the most invaluable asset to Shivaji Maharaj.
Key Features:
- The fort spans 48 acres and boasts fortified walls that are 29 feet high and 12 feet thick, extending for a distance of two miles.
- Guarding these walls are 52 bastions equipped with embrasures for cannons.
- Access to the fort is through the Dilli Darwaja, the main gate, uniquely designed to blend seamlessly with the walls and visible only from close quarters.
- The fort is surrounded by several smaller forts, including Padmagad, Rajkot, and Sarjekot.
- An intriguing feature within the fort is a slab bearing the handprint and footprint of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Additionally, a small temple dedicated to the Maratha King is situated within the fort's bounds
Diphtheria Outbreak in Guinea (WHO)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea's Health Ministry has officially notified them of a diphtheria outbreak.
What is Diphtheria?
- Diphtheria, an extremely contagious and infectious disease, instigates severe inflammation in the nose, throat, and trachea (windpipe).
- This ailment is caused by strains of bacteria known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produce a potent toxin responsible for the onset of illness.
Causes:
- The bacterial infection spreads through various means, including respiratory droplets emitted during coughing or sneezing.
- Transmission can also occur through contact with infected open sores or ulcers. The bacteria's toxin is the primary culprit behind the illness.
Symptoms:
- Manifesting 2-5 days post-infection, symptoms of diphtheria encompass a thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, a sore throat, hoarseness, swollen glands in the neck, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, fever, chills, and fatigue.
- If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can lead to damage to the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Infection and Spread:
- Diphtheria bacteria thrive on person-to-person transmission, emphasizing respiratory droplets as a common mode of contagion.
- Skin infections are possible but seldom result in severe disease.
Treatment:
- Combatting diphtheria involves a dual-pronged approach:
- Antitoxin (Anti-diphtheritic Serum): This neutralizes bacterial toxins and is specifically employed for respiratory system infections. The antitoxin acts on toxins that haven't bound with cells and tissues.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Penicillin): These medications eradicate the bacteria, preventing further spread. Antibiotics are effective against both the respiratory system and skin infections caused by diphtheria.
Amazon River Hits Lowest Levels in a Century Amid Drought in Brazil (Business Standard)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Amazon River fell to its lowest level in over a century on Monday at the heart of the Brazilian rainforest as a record drought upended the lives of hundreds of thousands of people and damaged the jungle ecosystem.
About the Amazon River:
- The Amazon River holds the distinction of being the world's largest river in terms of both water volume and width.
- Length and Course: Spanning an impressive 6,400 kilometres, it is the second-longest river globally, surpassed only by the Nile.
- Originating high in the Andes Mountains, the river courses its way eastward through vast rainforests and lowlands before reaching its culmination at the northeastern coast of Brazil, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Dynamic Width: During the dry season, the Amazon River exhibits a width ranging from 4 to 5 kilometres, expanding significantly to 50 kilometres in certain areas during the wet season.
- Unparalleled Drainage Area: The Amazon boasts the largest drainage area globally, with its watershed spanning across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Bolivia.
- Approximately two-thirds of the Amazon's mainstream and the majority of its basin lie within the borders of Brazil.
- Water Discharge and Global Impact: With a staggering water discharge of 300,000 cubic meters per second into the Atlantic Ocean, the Amazon contributes one-fifth of the total freshwater volume entering the world's oceans.
- This immense water flow plays a pivotal role in regulating global oxygen and carbon cycles.
- Extensive Tributaries: Featuring over 1,100 tributaries, including seventeen exceeding 1,500 kilometres in length, notable contributors include the Rio Negro, the Madeira River, and the Xingu River.
- Environmental Significance: The Amazon Rainforest, constituting approximately half of the Earth's remaining rainforest, stands as the largest repository of biological resources.
- Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," the Amazon plays a crucial role in maintaining the planet's oxygen and carbon balance.
‘Dunki’ and immigration: How the first modern passports came to be (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The recently released Shah Rukh Khan’s movie ‘Dunki’ is said to be based on the ‘donkey route’ or ‘donkey flight’ that lakhs of Indians take to reach countries like the US, the UK or some other European countries.
What is a Donkey Journey?
- Dunki is the Punjabi idiom that means to "hop from place to place", according to the Migration Policy Institute (MPI).
- It is a colloquial term for "donkey flights" or the "donkey flights method", which is a dangerous illegal immigration technique involving crossing a country's borders through a backdoor route via multiple stops in other countries.
How does the donkey flight method or dunki work?
- The desire for a higher quality of life has given rise to an industry driven by "agents" who charge exorbitant fees to help smuggle people to the country of their choice.
- Some agents may even run legitimate businesses while offering this dangerous option.
- The agents can offer various services, from fake papers to help through otherwise legal migration processes to smuggling people through ship containers.
Which countries are most targeted using the Dunki method?
- While donkey flight can be used to enter any country, the US, Canada, and the UK are some of the most popular destinations undertaken by Indian immigrants.
- According to a report, between February 2019 and March 2023, as many as 149,000 Indians were detained for attempting to enter the US illegally.
- Of this, most of those detained were from Gujarat and Punjab.
Risks involved in the dunki method:
- Dunki comes with tremendous risks, including the risk of capture, imprisonment, and deportation.
- When facilitated by an agent, the system is highly exploitative.
- Many sell off their assets, including ancestral land, to pay these agents.
- Agents may also withhold people's passports or other important documents to extort more money and assets.
- Moreover, smuggled migrants are also more vulnerable to becoming victims of other crimes during the smuggling process.
- The terrains of the places through which immigrants may have to travel pose a range of risks, including harsh weather conditions, rugged terrains, and access to basic resources like food and water.
- It must be noted that migrant smuggling is not the same as human trafficking.
- However, these crimes may sometimes interlink, adding another layer of risk for those engaging in illegal immigration.
About Passports:
- Rooted in history, passports trace back to mentions in the Hebrew Bible and structured systems in nations like France and the UK.
- The evolution into modern passports was catalyzed by the British Nationality and Status of Aliens Act in 1914, introducing features such as photographs and distinctive characteristics.
- The League of Nations' 1920 conference sought to standardize passport regulations, contributing to the establishment of a common British system.
- During the 1920s, the United States linked immigration laws to passports, imposing limitations on inflows.
- Despite initial reservations, passports have persisted as an integral element of contemporary citizenship.
- Indian Passports: The initiation of issuing Indian passports dates back to the First World War (1914-1918) through the Defence of India Act, as mandated by the British government for travel.
Deepfakes (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government has warned top social media and internet companies that their platforms may be temporarily suspended and even be ordered blocked in case they are unable to tackle the menace of deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- The term "deepfake" combines the concepts of deep learning with the fabrication of content.
- Deepfakes involve the creation of synthetic images and audio using machine-learning algorithms, intending to disseminate misleading content by replacing a real person's appearance, voice, or both with artificially generated likenesses or voices.
- These manipulated creations can either depict nonexistent individuals or simulate real people engaging in actions or utterances they never did.
- Originating in 2017, the word "deepfake" emerged when a Reddit user named "deepfakes" shared explicit videos featuring celebrities.
- The process of crafting deepfakes utilizes machine learning models employing neural networks to manipulate visual and auditory elements.
- To generate a convincing deepfake video, creators train the neural network on extensive real footage of the targeted person, facilitating a realistic understanding of their appearance from various angles and lighting conditions.
- This trained network is then combined with computer graphics to overlay the person onto a different actor.
- Regrettably, this technology is increasingly exploited for malicious purposes, including scams, celebrity impersonation, election interference, social engineering, disinformation attacks, identity theft, and financial fraud.
- The distinguishing factor of deepfakes lies in their challenging detection due to their sophisticated nature.
Risk weight (LiveMint)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Spooked by the strong growth in unsecured loans to consumers, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has increased the cost of funds for banks and non-bank financial companies (NBFCs), by increasing the risk weight of such loans.
What are Risk Weights?
- Every rupee lent by the bank is a cost or has an implication on its capital position.
- Depending on the nature of the loan and the inherent risk associated with it, risk weights are attributed.
- Banks have to ensure that their capital is enough to cover these risk-weighted assets.
- Total assets as disclosed in the financials and total risk-weighted assets are different things.
- Each asset class has varying risk weights.
- For instance, risk weights for home loans could range from 50 percent to 75 percent, for gold loans it is 75 percent.
- Corporate loans are charged 100 percent given the risk they carry.
How do they affect borrowers?
- Lower the risk weight, and lower the rate of interest. This is the thumb rule.
- Therefore, risk weights impact borrowers indirectly and are felt through the pricing of loans.
- For instance, home loans have the lowest interest rate among retail products because lower risk weights allow banks to pass on the advantage of capital consumption.
- Personal loans and credit cards have the highest interest rate because of their tenure and charge on capital.
Bhoomi Rashi Portal is revolutionizing land acquisition for Highway projects – Here’s how (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari revealed in a recent statement to the Rajya Sabha that the Bhoomi Rashi portal is instrumental in expediting the development of highway infrastructure in India.
About the Bhoomi Rashi Portal:
- The acquisition of land was done manually before the year 2018. The data files were moved physically, leading to some limitations. This included delays in issuing notices, errors in land details, etc.
- To overcome the issues, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways came up with a system.
- It is known as “Bhoomi Rashi”.
- The portal came into force on 1st April 2018
- The system is digital and automates the whole land acquisition (LA) process.
- It made and still makes the LA process more transparent and error-free.
- The portal processes the notices at every stage on a real-time basis.
Key Objectives:
- Acceleration of Land Acquisition: The primary goal is to facilitate a quicker and more efficient land acquisition process for National Highways.
- Centralized Processing: Acting as a singular online platform, it consolidates the processing of land acquisition notifications, contributing to the swift development of highway infrastructure projects.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensures transparency and accountability throughout the land acquisition process.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Facilitates the electronic transfer of benefits directly to the accounts of the beneficiaries involved in the land acquisition.
Salient Features:
- Bilingual application with Hindi and English for easy usability
- Preparation of interface for adding basic details of the project, including land acquisition sanction details
- Preparation of interface for Land Acquisition locations. villages
- Preparation of Interface for Competent Authority for Land Acquisition (CALA) details. CALA is a revenue functionary of the State Government appointed for each NH Project.
- Interface for generating land acquisition notification
- Interface for land Details
- Interface for generation of notification: organisational email IDS for all those involved in the process flow to ensure smooth e-office management
- Interface for Objections and processing
- Interface for compensation determination and finalisation
- Interface for land owners and affected parties
- Interface for reports generation
The portal is seamlessly integrated with the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) of the Ministry of Finance, ensuring real-time deposit of compensation into the accounts of affected/interested individuals.
What is Land Acquisition?
- Land acquisition is the governmental process, whether at the state or union level, through which private land is procured for infrastructure development, urbanization, or industrialization.
- In exchange, the government provides appropriate compensation to the landowner based on market value and assumes responsibility for the rehabilitation and resettlement of those affected by the land acquisition.
Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A dominant tiger named Bajrang said to have sired at least 50 cubs during his lifetime, recently died in a territorial fight with another powerful tiger, Chhota Matka, in the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR).
About Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve is the oldest and largest National Park in the Chandrapur district of Maharashtra.
- It is one of India's 47 project tiger reserves existing in India.
- The total area of the tiger reserve is 1,727 Sq.km, which includes the Tadoba National Park, created in the year 1955.
- The Andhari Wildlife Sanctuary was formed in the year 1986 and was amalgamated with the park in 1995 to establish the present Tadoba Andheri Tiger Reserve.
- The word 'Tadoba' is derived from the name of God "Tadoba" or "Taru," which is praised by local tribal people of this region, and "Andhari" is derived from the name of the Andhari river that flows in this area.
- Tadoba is presently home to more than 115 tigers, which is one of the highest in India.
- The vegetation of Tadoba forest is of Southern tropical dry deciduous type and is spread on around 626 sq. km.
- Teak is the prominent tree species in the forest.
- The Tadoba Tiger Reserve is rich in flora and fauna
- Flora: Some of the famous and widely seen flora of this park include Teak, Ain, Bija, Bamboo, Black Plum, and many others.
- Fauna: Tigers, Indian leopards, Sloth bears, Gaur, Nilgai, Striped Hyena, Spotted Deer, Barking Deer, Marsh Crocodile, etc.
Aurora (Indian Express)

- 10 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, NASA shared this incredible image of an aurora taken from the International Space Station.
What is Aurora?
- An aurora is a natural light display that shimmers in the sky.
- They are only visible at night, and usually only appear in lower polar regions.
- Auroras come in colors like blue, red, yellow, green, and orange.
- They're mostly visible near the Arctic and Antarctic Circles, known as the aurora borealis and aurora australis, respectively.
- These natural light shows occur when the solar wind from the sun meets Earth's magnetic field, creating a beautiful halo of light around the poles.
- This collision between solar wind ions and Earth's atmosphere atoms leads to stunning auroras.
- Their color depends on altitude and the atoms involved.
- Red comes from oxygen ions higher up, while the familiar green-yellow hues arise from interactions at lower altitudes.
- Sometimes, reddish and bluish tints appear, created by ions colliding with nitrogen atoms.
- The most active auroras happen when the solar wind is strongest, affected by solar weather changes, which follow an 11-year cycle.
- Equinoxes and magnetic storms can cause auroras to be seen even in mid-latitudes, affecting communication signals and occasionally causing disruptions.
- Auroras are a natural spectacle, painted by the collision of solar wind and Earth's atmosphere, creating these dancing lights in the night sky.
Full-blown late blight attack damages potato crops in Punjab (Indian Express)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Days after the experts from Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) had cautioned farmers against the late blight disease attack on potato crop, the worst fears of the potato farmers have come true.
About Late Blight Disease:
- Late Blight disease is attributed to the fungus Phytophthora infestans and stands as a significant threat to potato crops, potentially causing rapid failures if appropriate control measures are not implemented.
- Common in humid regions with specific temperature conditions, this disease manifests with initial symptoms of small, light to dark green, circular to irregular water-soaked spots.
- In cool, moist weather, these spots rapidly expand into large, dark brown or black lesions, often exhibiting a greasy appearance.
- A pale green to yellow border typically surrounds these lesions.
- The spread of Late Blight is facilitated by infected tubers and soil, acting as a primary source of infection.
- Infected tubers play a crucial role in the disease's persistence from one crop to another. Airborne infection occurs through sporangia.
- Effective control measures involve the prompt destruction of infected crop residue in the field to prevent the disease from spreading to nearby areas.
Diseases Caused by Bacteria on Potato Crops:
- Ring Rot
- Brown Rot
Diseases Caused by Fungi on Potato Crops:
- Late Blight
Diseases Caused by Virus on Potato Crops:
- Leaf Roll
- Mosaic
Palamu Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A recently captured image in the Palamu Tiger Reserve (PTR) reveals a new tiger, distinct from the one caught earlier this year.
About Palamau Tiger Reserve:
- The Palamau Tiger Reserve is located on the western side of Latehar district on the Chhotanagpur plateau in Jharkhand.
- It is one of the first 9 tiger reserves established in the country at the inception of ‘Project Tiger’, in the year 1973 in India and the only one in the state of Jharkhand.
- This reserve forms a part of the Betla National Park.
- The total area of the Tiger Reserve is 1129.93 sq. km
- It is the first reserve in the world in which a tiger census was carried out as a pugmark count, as early as 1932 under the supervision of J.W. Nicholson.
- The Palamau Tiger Reserve is very important for its biodiversity.
- The project area is constituted mainly of Sal forests, mixed deciduous forests, and bamboo groves.
- The reserve zone is the watershed area for 3 important rivers Koel, Burha, and Auranga.
India joins the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for flying wing technology in tailless configuration (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully carried out a flight trial of the Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator, an indigenous high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) from the Aeronautical Test Range, Chitradurga in Karnataka.
About the Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator:
- The Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator is a domestically developed high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) crafted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)’s Aeronautical Development Establishment.
- Its inaugural flight took place in July 2022, marking significant progress in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems, real-time integration, hardware-in-loop simulation, and an advanced Ground Control Station.
- The project team successfully optimized avionic systems, integration processes, and flight operations, culminating in the seventh and final flight in the ultimate configuration.
- Constructed with a complex arrowhead wing platform, the UAV prototype utilizes a lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- A noteworthy feature is the autonomous landing capability, eliminating the need for ground radars, infrastructure, or a pilot.
- This unique capability demonstration allows take-off and landing from any runway with surveyed coordinates.
- This technology demonstrator has been developed for India's secretive stealth combat drone called Ghatak.
- The successful flight in a tailless configuration has propelled India into the prestigious group of nations that have perfected the controls for the Flying wing configuration
Indian Joins Elite Club:
- With this flight in the tailless configuration, India has joined the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for the flying wing technology.
- These flight tests led to achievements in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems; integrated real-time and hardware-in-loop simulation, and a state-of-the-art Ground Control Station, informed the DRDO.
Aatmanirbharta
- The DRDO team had optimised the avionic systems, integration and flight operations towards the successful seventh flight in the final configuration.
- The aircraft prototype, with a complex arrowhead wing platform, is designed and manufactured with lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- Also, the composite structure, impregnated with fibre interrogators for health monitoring, is a showcase of ‘Aatmanirbharta’ in aerospace technology.
World Food India 2023 (HT)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated that India's food diversity benefits investors worldwide as he inaugurated the second edition of "World Food India 2023" at Bharat Mandapam in Delhi recently.
What is World Food India 2023?
- World Food India 2023 provides a gateway of access to the Indian food market, promoting collaborations between domestic and foreign investors.
- It is organized by India's Ministry of Food Processing Industries in New Delhi from November 3rd to 5th.
- Objective: It aims to exhibit India's rich food culture and attract global investments in the food processing sector.
- The event brings together manufacturers, producers, investors, policymakers, and organizations from around the world involved in the food industry.
- Key Areas of Focus: The event is focused on leveraging millets as a superfood, positioning India as a global hub for food processing, unlocking growth potential in strategic segments, establishing an efficient ecosystem, and promoting sustainable development.
- India's Vision: This event aligns with India's vision to become a global leader in the food processing industry, highlighting the country's production, consumption, and export potential across various food sectors.
- India is taking steps to create an inclusive and sustainable ecosystem, attract foreign investment, and improve the ease of doing business in the food processing sector.
- Notably, the first edition of World Food India took place in 2017.
- India is a global leader in the production of various agricultural products, such as milk, bananas, mangoes, papayas, guavas, ginger, okra, and buffalo meat.
- It also ranks second in the production of rice, wheat, potatoes, garlic, and cashew nuts.
- Moreover, the United Nations has declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets (IYM 2023) with the goal of increasing millet production and consumption worldwide.
Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) 'Prachand' (The Hindu)

- 01 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Army's Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) Prachand has conducted the first-ever day-and-night firing of 20 mm turret guns and 70 mm missiles.
About Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) 'Prachand':
- The LCH is the only assault helicopter in the world that has the ability to land and take off at 5,000 meters while carrying a sizable payload of fuel and weaponry.
- The helicopter features a frame and landing gear that are largely crash-proof, and it uses material that absorbs radar waves to reduce its radar signature.
- For protection against nuclear, biological, and chemical (NBC) emergencies, a pressurised compartment is available.
- The helicopter is protected from enemy radars and infrared seekers of enemy missiles by a countermeasure dispensing mechanism.
- LCH is powered by two French-origin Shakti engines manufactured by the HAL.
- The helicopter will be equipped with Helina missiles, the air force version of which is called Dhruvastra.
- It is capable of combat duties such as enemy air defence destruction, counter-insurgency warfare, combat search and rescue, anti-tank, and counter-surface force operations.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which is marking its 75th anniversary? (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Seventy-five years ago on Sunday, the UN General Assembly approved the Universal Declaration of Human Rights at a meeting in Paris – laying one of the foundation stones of the international order that emerged following the horrors of World War II.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)?
- On 10 December 1948, during a session in Paris, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously endorsed the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), marking a pivotal moment in shaping the post-World War II international order.
- The UDHR emerged as a response to wartime atrocities and aimed to establish a shared understanding of the fundamental rights and freedoms inherent to all individuals.
- A concise yet impactful document, the declaration comprises a preamble and 30 articles that delineate essential rights and freedoms.
- These 30 articles encompass a comprehensive spectrum of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Emphasizing their universality, these rights are deemed applicable to all individuals, irrespective of nationality, ethnicity, gender, religion, or any other status.
- While not legally binding, the UDHR has functioned as a guiding force inspiring the development of international human rights law.
Key Features:
- Preamble: The preamble elucidates the reasons behind adopting the declaration, underscoring the inherent dignity and the equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family.
- Articles: The UDHR articulates 30 articles outlining a wide array of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights. Examples of these rights include:
- The right to life, liberty, and security of person.
- The right to freedom of religion, expression, and assembly.
- The right to work and education.
- The right to an adequate standard of living.
- The declaration asserts that "all are equal before the law" and emphasizes the entitlement of everyone to "a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal."
- It also affirms the right of "everyone to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution.
Achievements of UNDHR:
- The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UNDHR) is acknowledged for its significant impact, having served as the inspiration and foundation for over 70 human rights treaties at both global and regional levels, as noted by the United Nations.
- It played a pivotal role in inspiring movements such as decolonization, the anti-apartheid movement, and various struggles for freedom worldwide, including those related to gender, LGBTIQ+ rights, and opposition against racism.
What is the Current Situation?
- As the 75th anniversary is commemorated, human rights face challenges amid conflicts such as the Israel-Hamas war, Russia's actions in Ukraine, internal strife in Myanmar and Sudan, and numerous other global situations.
- UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has remarked that the Universal Declaration has been frequently misused and abused, exploited for political gain, and often ignored by those who should uphold it.
- Contrastingly, Amnesty International asserts that the declaration serves as living proof that a global vision for human rights is attainable and can be realized.
- Despite instances of neglect or exploitation, the declaration remains relevant, and the world is encouraged to recognize its successes while learning from its failures.
Hematene (PIB)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
A new and remarkably efficient optical limiter has been developed by researchers, utilizing a novel 2D material known as 'hematene.'
- About Hematene:
- Nanoflakes of a material called hematene extracted from iron ore have been found capable of withstanding and acting as a shield from high laser intensities.
- Hence it could be used to make devices called optical limiters that can protect sensitive optical equipment from light-induced damage.
- Radiation from laser sources is highly concentrated and powerful and can be detrimental to sensitive equipment such as sensors, detectors, and other optical devices.
- When the input intensity increases optical limiters control the amount of light that passes through, thereby preventing damage to the optical component.
- These devices are often useful in laser technologies, military, telecommunications, aircraft, and scientific research in several ways.
- The MESO (Materials for Energy Storage and Optoelectronic Devices) Group of the Department of Physics, Sanatana Dharma College, Alappuzha, in collaboration with the Ultrafast and Nonlinear Optics Lab of the Raman Research Institute, Bangalore, has come up with a new and highly efficient optical limiter using a novel 2D material, ‘hematene’.
- They found that 2D nanoflakes of hematene, a material extracted from iron ore or hematite are capable of withstanding very high laser intensities, and they exhibited excellent optical limiting of green laser light (532 nm) while maintaining a high linear transmission (about 87%) for low-intensity light.
- The nanoflakes of lateral dimensions less than 10 nm, prepared by applying ultrasonic waves to hematite in a liquid medium ( facile exfoliation process) for a definite period to exfoliate the 2D nanoflakes of hematene were also found to be highly stable after year-long storage under ambient conditions, indicating tremendous potential as an optical limiter for futuristic applications.
- This research work carried out at SD College using the instrumentation facility procured through the Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure (FIST) programme of the Department of Science and Technology (DST) programme, was recently published in ACS Applied Optical Materials.
BlueWalker 3 Satellite (The Hindu)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international team of scientists has recently published a paper that explains how the prototype BlueWalker 3 satellite has affected the field of astronomy.
About the BlueWalker 3 satellite:
- The BlueWalker 3 satellite is a prototype that's part of a constellation owned by AST SpaceMobile.
- Launched in September 2022, it's notable for being one of the brightest objects in the night sky, even outshining the brightest stars.
- This satellite represents the largest-ever commercial communications array in low-Earth orbit, specifically designed to directly communicate with cellular devices at 5G speeds using 3GPP standard frequencies.
- Interestingly, the satellite operates at wavelengths close to those observed by radio telescopes, which could potentially interfere with radio astronomy.
LOWER SUBANSIRI HYDROELECTRIC POWER PROJECT (HT)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Lower Subansiri Hydro Electric Power project in Assam encountered a major problem when a significant landslide completely blocked its sole operational diversion tunnel, causing a substantial interruption in water flow through the river.
Facts About:
- This is the country's biggest hydroelectric project to date.
It is a run-of-river project on the Subansiri River.
- The Project is situated close to North Lakhimpur, which marks the boundary between Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- Capacity: 2000 MW.
- Up to 7.4 billion kWh of electricity will be produced there each year.
- Along with building a concrete gravity dam rising 116 meters above the riverbed, the project also entails building a surface powerhouse.
The dam will be 284 meters in length.
- The powerhouse is situated in the Subansiri district of Arunachal Pradesh, whereas the dam is situated in the Dhemaji district of Assam.
- It is being developed by the state-owned National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC).
- Finance: A term loan was used to finance 30% of the project's debt in addition to 70% equity.
- The budgetary support provided by the central government is a component of the equity component.
RASHTRIYA GOKUL MISSION (Down to Earth)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Rashtriya Gokul Mission is actively supporting the promotion of the Gir indigenous cow breed.
Facts About:
- It is being implemented for the development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- With a budget of Rs. 2400 crore, the program is also carried out under the general Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojna from 2021 to 2026.
- The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying is the nodal ministry.
Mission Objectives:
- To use cutting-edge technologies to raise milk production and sustainably improve the productivity of cows.
- To spread the practice of breeding bulls with high genetic merit.
- To increase the breeding network's strength and provide farmers with doorstep artificial insemination services to increase the coverage of artificial insemination.
- To encourage the scientific, all-encompassing rearing of native cattle and buffalo as well as conservation.
Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (PIB)
- 22 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian Government recently introduced a new set of National Awards for achievements in science, technology, and innovation called the "Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar."
Facts About:
The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is an award that recognizes outstanding contributions in the fields of science, technology, and innovation in India.
It's one of the highest honors in these fields.
Who can receive the awards?
- Scientists, technologists, and innovators, whether in government or private sectors, who have made significant breakthroughs in their respective fields.
- People of Indian origin living abroad who have made exceptional contributions benefiting Indian communities.
The awards are given in four categories:
- Vigyan Ratna (VR): Lifetime achievements in science and technology.
- Vigyan Shri (VS): Distinguished contributions in science and technology.
- Vigyan Yuva-Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (VY-SSB): Young scientists under 45 years old who've made exceptional contributions.
- Vigyan Team (VT): Teams of three or more scientists, researchers, or innovators who've excelled in their field.
The awards cover 13 domains, including Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Mathematics & Computer Science, Earth Science, Medicine, Engineering, Agriculture, Environment, Technology & Innovation, Atomic Energy, Space Science, and more.
Overnight Index Swap )Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Indian overnight index swap (OIS) rates have surged to their highest levels in a span of 10 months. This increase has been attributed to offshore payments and the triggering of stop-loss orders.
Facts About:
- An Overnight Index Swap (OIS) is a financial tool that involves exchanging returns from a fixed-rate asset for a predetermined daily overnight reference rate index for an agreed-upon duration.
- The primary goal of OIS is to mitigate interest rate risk, specifically the risk linked to changes in the overnight lending rate.
- An OIS rate is computed daily, and it is based on the average interest rate that institutions with loans tied to the overnight rate have paid for that particular day.
How does an OIS Operate:
- OIS instruments enable financial institutions to exchange the interest rates they are currently paying, all without the need to refinance or alter the terms of their existing loans.
- In a typical overnight index swap arrangement, one financial institution swaps an overnight (floating) interest rate, while the other swaps a fixed short-term interest rate.
- To initiate the swap, both institutions agree to maintain their loan obligations as usual.
- However, at the end of an agreed-upon timeframe, the institution that ends up paying less interest will compensate the other institution for the difference.
New Spider Species (HT)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In recent discoveries, two new spider species, named Palpimanus Godawan and Palpimanus Maldhok, were identified within the conservation areas of Rajasthan Desert National Park and Solapur.
Facts About:
- These two spider species, Godawan and Maldhok, have been named in tribute to the local name of the Great Indian Bustard.
Features of these Spiders:
- These spiders are quite reserved and tend to seek shelter under rocks or in crevices when they feel disturbed.
- They exhibit a maroon coloration, a distinctive characteristic shared with the other two recognized species within the Palpimanidae genus.
- Being ground-dwelling creatures, they possess relatively robust bodies, which restricts their ability to disperse in the typical spider fashion through ballooning or shooting webs to move from place to place.
- They tend to remain within a limited area.
Global Symposium on Farmers' Rights (NewsOnAir)
- 13 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
President Droupadi Murmu recently launched the First Global Symposium on Farmers' Rights in New Delhi.
Facts About:
- Location: ICAR Convention Centre, National Agricultural Science Centre, New Delhi. from September 12 to 15, 2023.
- Historical Background: The concept of hosting the inaugural GFSR was proposed by the Government of India during the Ninth Session of the Governing Body (GB9) of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (International Treaty) in September 2022.
This proposal received approval from the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization).
- Organized by: The Secretariat of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (International Treaty) under the umbrella of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) based in Rome.
- Hosted by: The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India, in collaboration with the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights (PPVFR) Authority, Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), and ICAR-National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR).
- Objective: The primary aim is to address crucial issues concerning farmers' rights and their pivotal role in global food security and agriculture.
- Distinguished scientists and experts from 59 countries around the world will participate.
- They will engage in discussions on how to acknowledge and compensate the significant contributions made by local and indigenous communities, as well as farmers from all corners of the world, in preserving and advancing plant genetic resources (PGR).
Wide Field Survey Telescope (HT)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
In September, China plans to launch the Wide Field Survey Telescope (WFST).
Facts About:
This telescope is the largest time-domain survey facility in the Northern Hemisphere.
Its main goals are as follows:
- To explore and continuously monitor dynamic astronomical events and conduct research in the field of time-domain astronomy.
- To detect faint and distant celestial signals, including those from galaxies beyond our Milky Way and galaxy clusters.
- To search for planets or their moons in the Kuiper Belt and beyond.
- To track and study a comprehensive list of one million solar system objects, providing a detailed view of the solar system's history and evolution.
The WFST is positioned at the Lenghu astronomical observation base in Qinghai Province, northwest China.
- This location, with an average altitude of approximately 4,000 meters, offers ideal conditions for observing the night sky, thanks to its clear skies, stable atmosphere, dry climate, and minimal artificial light pollution.
- It's widely recognized as one of the finest observatory sites across the Eurasian continent.
The WFST project commenced in July 2019, a result of collaboration between the University of Science and Technology of China and the Purple Mountain Observatory under the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Meningococcal Disease (HT)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The state of Virginia in the United States has issued a caution regarding a widespread outbreak of meningococcal disease.
Facts About:
Meningococcal disease is a rare but severe bacterial infection that causes inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
The two primary forms are meningitis and septicemia, both potentially life-threatening within hours.
Causes:
- This disease is caused by Neisseria meningitidis bacteria. Approximately 1 in 10 people carry these bacteria in their nose and throat without illness, but sometimes they can cause meningococcal disease.
Transmission:
- Transmission occurs through respiratory and throat secretions, like saliva, but usually requires close or prolonged contact. It's less contagious than the common cold or flu.
Symptoms:
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, stiff neck, photophobia (sensitivity to light), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a distinctive rash.
Treatment:
- Meningococcal disease is treated with antibiotics, and additional therapies may be necessary, such as oxygen therapy, medications for low blood pressure, and skin treatments, including surgery.
Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23 (PIB)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Air Force (IAF) contingent departed to participate in Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23, scheduled to be held at Cairo (West) Air Base, Egypt, from 27 August to 16 September 2023.
Facts About:
- It is a biennial multilateral tri-service exercise.
- This multinational exercise was launched in 1980 as part of the US-brokered peace treaty between Egypt and Israel.
- This is the first time that IAF is participating in Ex BRIGHT STAR-23.
- Participating countries: United States of America, Saudi Arabia, Greece and Qatar.
- The Indian Air Force contingent will consist of five MiG-29, two IL-78, two C-130 and two C-17 aircraft.
- Personnel from the IAF's Garud Special Forces, as well as those from the Numbers 28, 77, 78 and 81 Squadrons, will be participating in the exercise.
- Objective: To practice planning and execution of joint operations. Besides leading to the formation of bonding across borders, such interactions also provide a means to further strategic relations between participating nations.
- India and Egypt have had an exceptional relationship and deep cooperation wherein the two jointly undertook the development of aero-engine and aircraft in the 1960s, and training of Egyptian pilots was done by Indian counterparts.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1955399
RIGHT TO REPAIR (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In recent years, several states in the U.S. have enacted ‘right to repair’ laws.
Facts About:
- It refers to government measures that forbid manufacturers to impose barriers that deny consumers the ability to repair consumer products.
- The sectors identified for the right to repair include farming equipment, mobile phones/tablets, consumer durables, and automobiles/automobile equipment.
- Government has launched a unified portal, https://righttorepairindia.gov.in, to onboard leading brands and reliable third-party technicians to provide easy access to overhauling services.
- The portal has on boarded leading brands such as Apple, Samsung, Honda, Kent RO Systems, Havells, Hewlett Packard, and Hero MotoCorp.
- The portal seeks to streamline trade between original equipment manufacturers and third-party sellers.
- The right to repair has been recognized in many countries across the globe, including the USA, UK, and European Union.
Significance of Right to repair for India:
- Lowering costs for consumers: By providing access to third-party technicians, the right to repair can reduce costs for consumers who may not be able to afford expensive repairs or replacement devices.
- Reducing electronic waste: India is one of the largest generators of electronic waste in the world, and the right to repair can help reduce e-waste by extending the lifespan of electronic devices and appliances.
- Supporting small businesses: The right to repair can also support small businesses that provide repair services, by creating a level playing field with manufacturers who may have previously had a monopoly on repairs.
- Empowering consumers: By giving consumers the ability to repair their own devices or choose where to have them repaired, the right to repair empowers consumers to make informed choices and take control of their own devices.
- Promoting transparency and collaboration: The right to repair framework aims to build a consumer-centric ecosystem that promotes transparency and collaboration between manufacturers, sellers, and consumers.
Challenges associated with implementing right to repair in India
- Limited Access to Information: Many manufacturers do not provide adequate information to consumers about repair options or how to repair devices, which can make it difficult for consumers to exercise their right to repair.
- Lack of Awareness: Consumers lack awareness about their rights to repair and the benefits of repairing their devices leading to a lack of demand for repair services, limiting the growth of the repair industry.
- Opposition from manufacturers: Some manufacturers may oppose the right to repair, arguing that it could compromise their intellectual property rights or lead to safety concerns making it difficult to pass legislation or regulations to support the right to repair.
- Limited availability of spare parts: The availability of spare parts is often limited in India, particularly for older or less common models of devices makes it difficult for repair technicians to perform repairs or for consumers to find reliable repair services.
- Lack of regulatory mechanism: Currently, there is no comprehensive regulation in India that governs the right to repair which can lead to confusion among consumers and repair technicians about their rights and responsibilities, and may limit the growth of the repair industry.
Way Forward:
Many countries around the world have been attempting to pass effective ‘right to repair’ laws. But the movement has faced tremendous resistance from tech giants such as Apple and Microsoft over the years.
The New York legislation is a reminder that it is time to not only acknowledge the right to repair of consumers but also respond to the corresponding rights of the manufacturers. This warrants some expedited policy changes to recognise the ‘right to repair’, be it through amendments in the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 or through a separate law.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-the-right-to-repair-movement-7400287/
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) (Indian Express)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) recently addressed the Manipur DGP, urging the filing of an FIR against three individuals.
About the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR):
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
Composition of NCPCR:
- This commission has a chairperson and six members of which at least two should be women.
- All of them are appointed by Central Government for three years.
- The maximum age to serve in commission is 65 years for Chairman and 60 years for members.
Functions and responsibilities of NCPCR:
- Examine and assess current safeguards for child rights and propose effective implementation strategies.
- Submit periodic reports to the central government on the efficacy of these safeguards.
- Conduct investigations into child rights violations and recommend legal action when appropriate.
- Raise awareness about child rights and available safeguards through diverse channels, such as publications, media, and seminars.
- Conduct inspections of institutions housing children, including juvenile homes, and suggest remedial measures if required.
- Investigate complaints and proactively address issues related to child rights deprivation, violation, and non-implementation of protective laws.
