Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) of NITI Aayog, in partnership with New Shop (India’s largest 24/7 convenience retail chain), launched the initiative EmpowHER Biz – Sapno Ki Udaan under the Award to Reward (ATR) program. This program aims to empower women entrepreneurs by providing them with the skills, resources, and mentorship needed to succeed in the organized retail sector. The collaboration seeks to create a robust retail ecosystem that supports women in overcoming barriers such as societal biases, limited access to financing, and a lack of mentorship.
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Target Participants: The program will select 50 women aged 18-35 through an online application process. Women from Delhi NCR, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat will be considered.
- Top 20 Participants: The 20 best candidates will receive a 100% waiver on New Shop franchise fees, enabling them to operate their own retail businesses with reduced financial barriers.
- Program Objective: Equip women entrepreneurs with skills such as retail management, digital tools, financial literacy, and business development. Participants will also receive valuable mentorship to help them grow and scale their businesses.
- Focus on Retail: The initiative focuses on empowering women within the organized retail sector, creating a sustainable ecosystem that fosters growth and development for female entrepreneurs.
About Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP):
- Incubation & Transition: Established in 2018, WEP was incubated within NITI Aayog and transitioned into a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) in 2022.
- Purpose: WEP aims to empower women entrepreneurs by addressing challenges like information asymmetry and providing essential support in key areas such as:
- Access to Finance
- Market Linkages
- Training & Skilling
- Mentoring & Networking
- Compliance & Legal Assistance
- Business Development Services
- Collaboration: WEP partners with over 30 public and private sector organizations to develop scalable and impactful programs. Since 2023, the Award to Reward initiative offers a framework for stakeholders to create impactful programs for women entrepreneurs.
About New Shop:
- Business Model: New Shop operates over 200 round-the-clock convenience retail stores in high-density areas, including highways and gas stations. The company plans to expand into airports, railway stations, and other mass transit hubs.
- Franchising Vision: By 2030, New Shop aims to empower over 10,000 entrepreneurs in India through its franchising model. The partnership with WEP seeks to help women entrepreneurs access this growth opportunity.
Program Outcomes:
- Mentorship & Training: Participants will be mentored and trained on key aspects such as retail management, business development, and digital tools.
- Franchise Opportunity: Top participants will gain access to New Shop’s franchising ecosystem, providing them a ready-made business opportunity with lower entry barriers.
- Financial Assistance: The program will also provide financial resources to the women, helping them build their businesses with greater ease.
Open Data Kit (ODK) Toolkit

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has deployed the Open Data Kit (ODK) platform to enhance transparency in government spending and improve accountability in the delivery of government schemes.
- The toolkit is being used for designing, collecting, and managing data relevant to audits.
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Enhance transparency in public spending.
- Improve accountability in government schemes and projects.
- Collect real-time beneficiary feedback to aid audit planning and identify areas needing additional review.
Key Features:
- End-to-end encryption: Ensures secure data management.
- Integration with CAG’s Operating System (OIOS): Facilitates seamless analysis and management of data.
- Multi-language support: Allows for surveys in multiple languages, making it more accessible to diverse beneficiaries.
- User-friendly interface: Simplifies the design and management of data collection processes for auditors.
Usage and Applications:
- Beneficiary surveys are a key tool for gathering data, helping CAG identify problem areas in government schemes.
- The ODK toolkit was recently deployed in audits of AIIMS institutions in Mangalagiri (Guntur) and Bibinagar (Hyderabad) to assess patient satisfaction and gather evidence for performance reviews.
Working Process:
- Surveys are designed on the ODK platform and deployed to beneficiaries.
- Data is collected in real-time and analyzed using the OIOS system to generate actionable insights for audits.
- Beneficiary feedback is used to evaluate scheme delivery and improve efficiency.
Significance:
- Facilitates data-driven decision-making in audits, ensuring that audits are more transparent and evidence-based.
- Improves the citizen-centric evaluation of government schemes by gathering direct feedback from beneficiaries.
- Enhances the performance review of key institutions like AIIMS, contributing to better service delivery.
- The introduction of the ODK toolkit is part of the CAG’s efforts to use digital tools for better governance and accountability in the public sector. This also aligns with the growing trend of using technology for governance and auditing.
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
PM CARES Fund Contributions and Utilization (2022-23)
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM CARES Fund) received Rs 912 crore in contributions during the financial year 2022-23 as donations continued to pour in even after the Covid pandemic.
Key Highlights:
Contributions Received:
- Total contributions in 2022-23: Rs 912 crore.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 909.64 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 2.57 crore.
Interest Income:
- Total interest income for 2022-23: Rs 170.38 crore.
- From regular accounts: Rs 154 crore.
- From foreign contributions account: Rs 16.07 crore.
Refunds and Additional Inflows:
- Rs 225 crore in refunds, including:
- Rs 202 crore refund from procurement of 50,000 ventilators for government hospitals.
Disbursements:
- Total disbursed in 2022-23: Rs 439 crore:
- Rs 346 crore for PM CARES for Children.
- Rs 91.87 crore for procurement of 99,986 oxygen concentrators.
- Rs 1.51 crore for refunds.
- Rs 24,000 for legal charges, and Rs 278 for bank and SMS charges.
Cumulative Contributions (2019-23):
- Rs 13,605 crore received from 2019-20 to 2022-23.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 13,067 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 538 crore.
- Interest income over these years: Rs 565 crore.
About PM CARES Fund:
Formation and Purpose:
- Established: March 27, 2020, as a Public Charitable Trust under the Registration Act, 1908.
- Purpose: To address emergencies like COVID-19, natural disasters, and man-made calamities. It also supports healthcare infrastructure and essential facilities.
Governance and Structure:
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister (ex-officio).
- Trustees: Defence, Home, and Finance Ministers (ex-officio).
- Additional Trustees: Appointed by the PM, serving on a non-profit basis (e.g., Justice K T Thomas (retd.) and Kariya Munda).
Tax Exemptions:
- Donations are eligible for 100% tax exemption under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Donations qualify as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The fund is exempt under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), allowing it to receive foreign donations.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On Good Governance Day, commemorating the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for various departments, launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative. This initiative is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign, which aims to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) at the grassroots level by enhancing the capacity and competence of elected representatives and officials.
Objective of the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
The initiative seeks to strengthen PRIs by providing innovative tools and frameworks for capacity building and participatory governance. It will focus on equipping local leaders and officials with the necessary knowledge and tools to make effective decisions and implement sustainable development initiatives. Piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, it uses e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to address knowledge gaps and improve service delivery at the local level. This program aligns with the government's mission to decentralize governance and promote citizen-centric and equitable development across rural India.
Other Key Initiatives Launched on Good Governance Day
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform Dashboard: A new dashboard on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, which empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators to monitor progress in capacity-building efforts. The enhanced dashboard includes customizable views, robust data filtering tools, and insights to optimize decision-making, marking the introduction of the 1600th e-learning course. This development is part of the Mission Karmayogi initiative to strengthen the civil service through continuous learning.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: The CPGRAMS Annual Report provided a review of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS). This platform has been instrumental in resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually, leveraging advanced technologies and multilingual support. The report also highlighted the implementation of the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI), which has improved transparency, accountability, and the efficiency of public service delivery.
- Single Simplified Pension Application Form: A new digital pension system was launched, combining nine separate pension forms into a single, streamlined application. This digital transformation integrates e-HRMS with Bhavishya, reducing processing time and ensuring timely pension disbursement with real-time tracking and Aadhaar-based e-signatures. This system enhances the user experience for pensioners, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Compendium of Pension Related Instructions 2024: Dr. Singh introduced a comprehensive Compendium of updated rules, procedures, and guidelines related to pensions. This document serves as a reference for pensioners and administrative personnel, ensuring clarity in the pension process and aligning with the government's vision of simplifying and streamlining pension systems.
Good Governance Day 2024 (Sushasan Diwas)
- Observed on: December 25 annually, marking the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1924–2018).
- Introduced in 2014: By the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Purpose: To honor Vajpayee's contribution and promote good governance practices in India.
- Objective of Good Governance Day:
- Promote Government Accountability: Ensuring government actions and services are transparent and citizens benefit equally.
- Instill Good Governance Values: Encourages civil servants to practice effective and responsible governance.
- Bridge the Gap: Between citizens and the government through active participation.
- Theme for 2024: "India’s Path to a Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens through Good Governance and Digitalisation."
eShram-One Stop Solution

- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
- The ‘eShram-One Stop Solution’ will be launched on 21 October 2024 by the Union Minister of Labour & Employment and Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Objective: To provide easy access to various social security and welfare schemes for unorganized workers in India.
Key Features
- Mediator Platform: The eShram-One Stop Solution will act as an intermediary to facilitate the integration of multiple government schemes for unorganized workers, ensuring efficient access to services and support.
- Information Integration: It will integrate data on beneficiaries across various social security and welfare programs meant for unorganized workers, providing a single point of access.
- Target Group: Aimed at unorganized workers, including daily wage earners, migrants, and others who do not have regular formal employment.
Benefits
- Awareness & Accessibility: The platform will make unorganized workers aware of various government schemes tailored to their needs, helping them access benefits more easily.
- Effective Scheme Implementation: The eShram-One Stop Solution will aid in the identification and implementation of welfare schemes for faster saturation and coverage.
Integration with Existing Schemes
- 12 Integrated Schemes: Currently, 12 social security schemes from different ministries/departments have already been mapped with eShram.
eShram’s Progress So Far
- Launch: eShram was launched on 26 August 2021.
- Achievements: Over 30 crore unorganized workers have been enrolled, highlighting the widespread impact and popularity of the initiative among the target population.
Karmayogi Saptah – National Learning Week

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the ‘Karmayogi Saptah’ - National Learning Week on 19th October at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Context:
- The National Learning Week is a key event in the ongoing Mission Karmayogi initiative, aimed at building a civil service rooted in Indian ethos with a global outlook.
- Objective:
- To promote capacity building for civil servants through competency-linked learning.
- To align civil servants with national goals and foster a "One Government" approach.
- About National Learning Week (NLW):
- Largest learning event for civil servants, focused on individual and organizational growth.
- Encourages lifelong learning and continuous professional development.
- Provides fresh impetus to the Mission Karmayogi initiative, launched in September 2020, aimed at a future-ready, citizen-centric civil service.
- Learning Targets for Karmayogis:
- Each civil servant (Karmayogi) must complete at least 4 hours of competency-linked learning during the week.
- Learning opportunities include:
- Role-based modules on iGOT (Integrated Government Online Training platform).
- Webinars, public lectures, and policy masterclasses by prominent experts.
- Focus on improving skills for citizen-centric service delivery.
- Workshops & Seminars:
- Ministries, departments, and organizations organized domain-specific workshops and seminars.
- The goal is to enhance skills and knowledge, fostering better public service delivery.
- Outcomes:
- Strengthened alignment of civil servants with national priorities and goals.
- Enhanced individual competencies to better address citizen needs.
- A stronger commitment to continuous learning within the civil service.
Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS)

- 18 Oct 2024
In News:
The Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, hosted a two-day Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) knowledge sharing workshop in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Event Overview:
- Two-day workshop hosted by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education.
- Focus areas: School-to-Work Transition and Strengthening the Assessment System.
- Key Objectives:
- To enhance school-to-work transitions.
- To discuss strengthening educational assessment systems.
- Align education with future workforce needs as per the National Education Policy 2020.
Day 1: School-to-Work Transition
Panel Discussions:
- Policy Frameworks:
- Role of National Education Policy 2020, National Curriculum Framework (NCF), and National Credit Framework (NCrF) in school-to-work transitions.
- Focus on integrating skill education into school curricula, fostering multidisciplinary learning, and continuous evaluation to meet industry standards.
- Emphasis on internships, apprenticeships, and flexible learning pathways.
- Curriculum Integration:
- Need for integrated efforts across departments and aligning curriculum with industry demands.
- Focus on strengthening 21st-century skills in CBSE schools.
- Career Counselling and Psychometric Analysis:
- Focus on using psychometric assessments for career counselling and preparing students for future work environments.
- Work-Based Learning:
- Discussed partnerships with industry for work-based learning.
- Effective collaborations between schools and industry for internships, placements, and best practices.
Day 2: Strengthening Assessment System
- Psychometric Analysis & Career Counselling:
- Smt. Idzes Angmo Kundan (Principal Secretary, Maharashtra) presented the 3 P approach to career choices: Personal Interest, Parental Approach, and Possible Opportunities.
- Enhancing Student Outcomes:
- Discussed improving student outcomes by strengthening assessment systems.
- Shared innovations in educational assessments.
- Highlighted innovative assessment practices for future education.
- VSK Implementation (Chhattisgarh):
- Discussed VSK modes, data analysis, and strategies for integrating assessment outcomes with learning objectives.
- Strengthening Assessment Cells:
- Advocated for the establishment of assessment cells.
- Discussed best practices and challenges in strengthening assessment cells across states.
Co-district Initiative

- 05 Oct 2024
In News:
Assam has launched an innovative administrative initiative by inaugurating 21 'co-districts' as part of its Phase 1 rollout, which began on Friday and will extend into Saturday, ultimately introducing a total of 39 co-districts. This new structure replaces the previous system of 24 civil sub-divisions, aiming to bring governance closer to the citizens.
About the Co-District Initiative
- Structure: Co-districts serve as smaller administrative units within the larger district framework, each headed by an Assistant District Commissioner.
- Objective: This unique initiative, the first of its kind in India, seeks to enhance accessibility to governance and address administrative challenges faced by district administrations.
- Scope: The government plans to establish co-district offices in all 126 assembly constituencies in Assam.
Functions and Powers
The co-districts will handle a variety of important functions, including:
- Land Revenue Matters: Managing land-related issues and revenue collection.
- Development and Welfare Work: Overseeing development projects and welfare programs.
- Excise and Disaster Management: Addressing excise-related matters and coordinating disaster response efforts.
- Administrative Control: Co-districts will have authority over all departmental activities within their jurisdiction.
- Magisterial Powers: Commissioners will be empowered to issue permissions for events and manage other administrative tasks.
- Routine Administrative Tasks: Responsibilities include issuing ration cards, caste certificates, and land sale permissions.
NAMASTE programme

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
A recent government survey has shed light on the demographics of workers engaged in the hazardous cleaning of urban sewers and septic tanks across India. This initiative, part of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment's NAMASTE programme, highlights significant disparities within this labor sector.
Key Findings
- Community Representation: An overwhelming 91.9% of the 38,000 workers profiled belong to marginalized communities:
- Scheduled Castes (SC): 68.9%
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 14.7%
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): 8.3%
- General Category: 8%
- Mortality Rates: Between 2019 and 2023, at least 377 individuals died while performing hazardous cleaning tasks, underscoring the dangers associated with this work.
The NAMASTE Programme
- Objective: The NAMASTE programme aims to mechanize sewer work to prevent fatalities linked to manual cleaning. It seeks to transition workers into safer, more sustainable roles as "sanipreneurs" by providing safety training, equipment, and capital subsidies.
- Background: This programme replaces the earlier Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS), focusing on the more technical aspects of hazardous cleaning rather than manual scavenging.
- Namaste is a Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) as a joint initiative of the MoSJE and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The Scheme has been approved with an outlay of Rs. 360 crore for four years from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- NAMASTE aims to achieve the following outcomes:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- All sanitation work is performed by skilled workers
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- Sanitation workers are collectivized into SHGs and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers (SSWs) have access to alternative livelihoods
- Strengthened supervisory and monitoring systems at national, state and ULB levels to ensure enforcement and monitoring of safe sanitation work
- Increased awareness amongst sanitation services seekers (individuals and institutions) to seek services from registered and skilled sanitation workers
Progress and Coverage
- Implementation: Since the scheme's inception, 3,326 urban local bodies (ULBs) have begun profiling workers, with many reporting minimal or no workers engaged in hazardous cleaning.
- Data Collection: The government is gathering data from over 3,000 ULBs across 29 states and union territories to better understand the scope and risks associated with this labor.
Good Digital Public Infrastructure
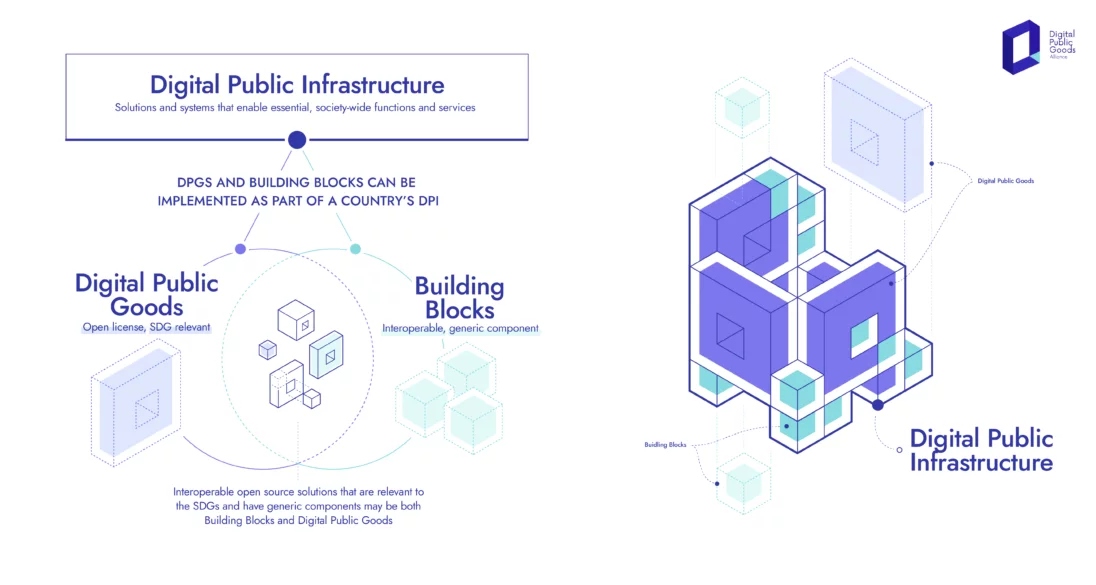
- 08 Sep 2024
Good digital public infrastructure (DPI) integrates technology with societal needs, ensuring that it is secure, scalable, and inclusive.
India’s achievement of over 80% financial inclusion in just six years has drawn international praise, particularly as a model for the Global South. This accomplishment underscores India’s success in achieving both digital and financial inclusion for over a billion people. Consequently, the G20 summit in New Delhi in 2023 highlighted the critical role of digital public infrastructure.
In response, India’s G20 task force has released a comprehensive report outlining a global strategy for DPI development. This positions India to support other nations in achieving digital sovereignty, financial inclusion, and self-reliance.
The evolving digital landscape is marked by a variety of stakeholders—including private enterprises, government bodies, non-profits, and think tanks—each working to advance their DPI solutions. This raises two key questions: How can we identify genuine and reliable DPIs from the plethora available? And what differentiates a “good DPI” from a “bad DPI”?
Identifying effective DPI involves assessing how well technology meets societal needs while ensuring security, scalability, and inclusivity. Authenticity and adherence to core principles are essential for evaluating DPIs.
The Citizen Stack Model
Citizen Stack, built upon the proven success of India Stack, emerges as a trusted ecosystem in digital infrastructure. India Stack, a robust digital platform, has demonstrated its effectiveness and security on a vast scale, serving over a billion citizens. This strong foundation enhances Citizen Stack’s credibility and reliability. Unlike DPI manufacturers, Citizen Stack functions as a regulatory body or auditor, certifying and authenticating DPIs to ensure they meet high standards of quality and security.
Citizen Stack’s approach is comprehensive, focusing on security, scalability, and inclusivity. The DPI platforms approved by Citizen Stack are designed to meet the diverse needs of large populations while maintaining stringent security measures to protect user data and privacy. As an auditor, Citizen Stack ensures that certified DPIs are dependable, secure, and beneficial to the public.
In an era of abundant digital solutions and promises, distinguishing genuinely reliable platforms is essential. Citizen Stack offers assurance as a gold standard for DPI solutions.
Guiding Principles of a “Good DPI”
Citizen Stack has established five core principles—referred to as sutras—that define a good DPI:
- Maintain Citizen Relationships: Ensure that digital infrastructure supports a fair relationship between citizens, the market, and the state, free from undue influence.
- Protect Empowerment and Privacy: Implement consent-based data sharing systems that prioritize individual empowerment and privacy.
- Prevent Monopolistic Lock-In: Ensure interoperability to avoid citizens being restricted by monopolistic entities.
- Combine Techno-Legal Regulation: Integrate technology with legal frameworks to govern ethical tech use, ensuring innovation while safeguarding security and societal rights.
- Foster Public-Private Innovation: Encourage collaboration between public and private sectors, while avoiding corporate dominance. The focus should be on public good rather than corporate monopolies, and technology should prevent exploitation by state or corporate actors.
After 10 years struggle, Mendha gets separate Panchayat status under Gramdan Act

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Maharashtra government recently notified Mendha, a village deep inside the forests of the state’s Gadchiroli district, as a separate Gram Panchayat under The Maharashtra Gramdan Act, 1964.
What is Gramdan?
- Gramdan is an expansion of the Bhoodan Movement started in 1951 by Aacharya Vinoba Bhave.
- ‘Bhoodan’ meant redistribution of land from bigger landowners to the landless.
- Under Gramdan, the entire village will put its land under a common trust.
- This way, the land will not be sold outside the village or to one who has not joined Gramdan in the village.
- But the landowners can continue to cultivate it and reap the benefits.
- The Movement paved the way for the protection of natural resources by giving equal rights and responsibilities to everyone in the community and empowering communities to move towards self-governance.
- Under the Act, at least 75 percent of landowners in the village should surrender land ownership to the village community for it to be declared as ‘gramdan’.
- Such land should at least be 60 percent of the village land. Five per cent of the surrendered land is distributed to the landless in the village for cultivation.
- Recipients of such land cannot transfer the same without the permission of the community.
- The rest remains with the donors.
- They and their descendants can work on it and reap the benefits.
- But they cannot sell it outside the village or to a village resident who has not joined Gramdan.
- Today, seven states in India have 3,660 Gramdan villages, the highest being in Odisha (1,309).
- The states are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- In September 2022, the Assam government repealed the Assam Gramdan Act, 1961 and Assam Bhoodan Act, 1965, bypassing The Assam Land and Revenue Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
- This, it said, was done to counter encroachment on donated lands in the state.
- Till that time, Assam had 312 Gramdan villages.
About Mendha’s Village Struggle:
- The village, comprising around 500 Gond Adivasis, has fought for its forests for years.
- It is popular as the first village in India to secure community forest rights (CFR), following the passing of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- Some 80 per cent of the area in the village is covered with dense forest.
- People here believe that land is not a private property but a collective resource that provides food and livelihood and should be saved and passed on to the next generation.
- All villagers in Mendha have surrendered their land, which is unique. In all other villages, only about 75-80 per cent of landowners had agreed to do so.
- The village fulfilled these conditions of the Act in 2013 and notified the district collector about its decision to implement the Act.
Amit Shah launches National Cooperative Database, to help in policy making
- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
Cooperation Minister Amit Shah on Friday launched the National Cooperative Database and stressed that it would help in policy making.
About National Cooperative Database (NCD):
- The National Cooperative Database (NCD) is an initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Cooperation, responding to the pressing need for a robust database to effectively capture essential information concerning India's extensive cooperative sector.
- Developed collaboratively with State Governments, National Federations, and stakeholders, the NCD is designed to promote a cooperative-centric economic model, offering a web-based digital dashboard for seamless data management.
- Acting as a centralized repository, the NCD aggregates data from cooperative societies, including National/State Federations, with information entered and authenticated by nodal officials at RCS/DRCS offices for cooperative societies and provided by various national/state federations for federations.
- The collected data encompasses diverse parameters, such as registered names, locations, membership numbers, sectoral details, operational areas, financial statements, audit statuses, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the cooperative landscape.
- Serving as a vital communication tool, the NCD facilitates efficient interaction between the Central Ministry, States/UTs, and Cooperative Societies, fostering collaboration and synergy within the cooperative sector.
- Key features and benefits of the NCD include single-point access, comprehensive and updated data, user-friendly interface, vertical and horizontal linkages, query-based reports and graphs, Management Information System (MIS) reports, data analytics, and geographical mapping capabilities.
Vaishnaw bats for further simplification of economic laws at ‘NITI for States’ platform launch

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union IT, Communications, and Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw Thursday stressed on the need to further simplify economic laws in a modern and relevant way at the launch of NITI Aayog’s ‘NITI for States’ platform.
About “NITI For States” Platform:
- It serves as a cross-sectoral knowledge hub envisioned to be a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Policy and Good Governance.
Key features include:
- A comprehensive repository comprising Best Practices, Policy documents, datasets, data profiles, and NITI publications across various sectors.
- Knowledge products spanning 10 sectors and two cross-cutting themes (Gender and Climate Change), such as Agriculture, Education, Energy, Health, Manufacturing, MSME, Tourism, Urban, and Water resources & WASH.
- An intuitive and user-friendly interface accessible via multiple devices, including mobile phones.
- The platform aims to catalyze digital governance transformation by providing government officials with contextualized, actionable knowledge and insights, thereby enhancing decision-making quality.
- It supports district collectors and block-level functionaries by granting access to innovative best practices from various States and Union Territories.
What is the Viksit Bharat Strategy Room?
- It serves as an interactive platform enabling users to visualize data, trends, best practices, and policies in an immersive manner, facilitating a comprehensive assessment of any problem statement.
- The platform features voice-enabled AI for user interaction and facilitates connectivity with multiple stakeholders through video conferencing.
- Designed as a plug-and-play model, it enables replication by states, districts, and blocks for widespread adoption.
- Collaboration with various government organizations by NITI Aayog includes:
- iGOT Karmayogi's "SAMARTH" online training modules accessible through the platform.
- Integration of NITI Aayog’s National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP) to provide access to government datasets.
- Support from the National E-Governance Division (NeGD) in developing the innovative Viksit Bharat Strategy Room.
- Multi-lingual support provided by Bhashini.
- Integration of PM Gatishakti BISAG-N team, with DPIIT support, to offer geospatial tools for Area Based Planning.
Worldwide Governance Indicators (Indian Express)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Chief Economic Adviser recently expressed worry about credit rating agencies using the World Bank's Worldwide Governance Indicators to assess ratings, particularly for developing countries.
About Worldwide Governance Indicators:
- The Worldwide Governance Indicators is based on a long-standing research programme of The World Bank.
- It was first established in 1996 to measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries.
- These aggregate indicators are derived from over 30 individual data sources produced by a variety of survey institutes, think tanks, non-governmental organizations, international organizations, and private sector firms.
- The indicators capture six key dimensions of governance including:
- Voice and Accountability
- Political Stability and Absence of Violence
- Government Effectiveness
- Regulatory Quality
- Rule of Law
- Control of Corruption
- According to The World Bank, corruption is the single greatest obstacle to economic and social development.
About The World Bank:
- The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries around the world.
- Its goals are to reduce poverty and support development.
- It helps by offering a growing range of free tools, research, and knowledge to help people address the world’s development challenges, for instance, comprehensive, downloadable indicators about development in countries around the globe.
