Magnetofossils
- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
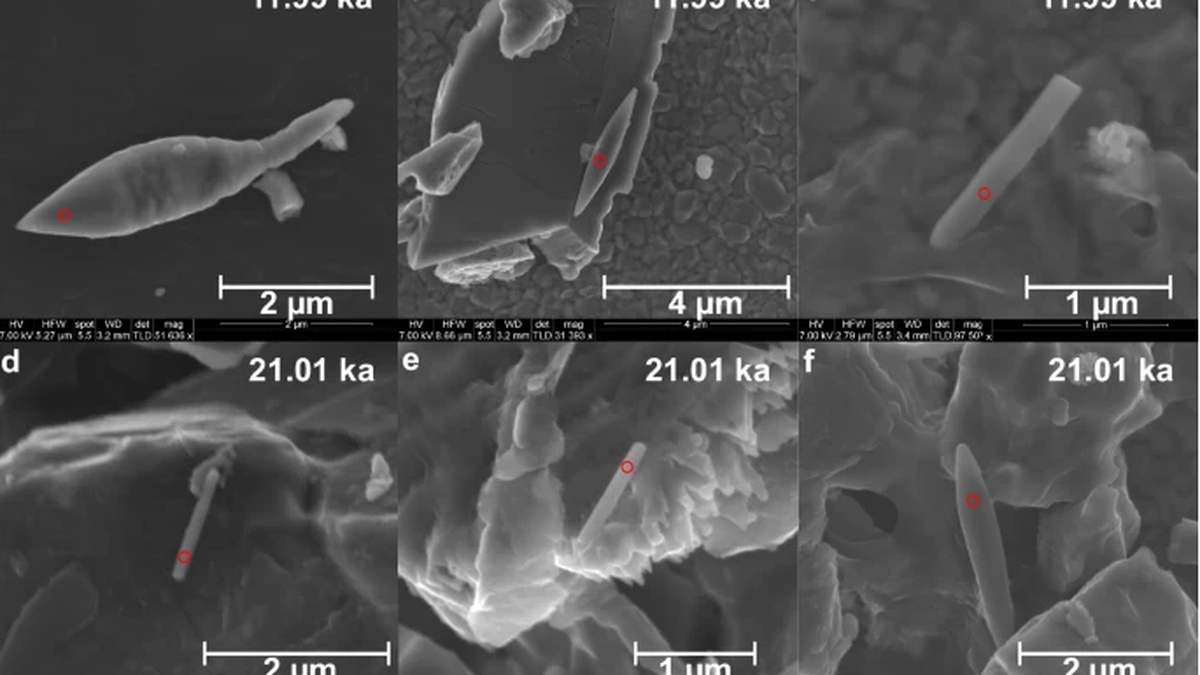
In the depths of the Bay of Bengal, scientists have discovered a 50,000-year-old sediment — a giant magnetofossil and one of the youngest to be found yet.
What are Magnetofossils?
- Magnetofossils represent the fossilized remnants of magnetic particles originated by magnetotactic bacteria, also referred to as magnetobacteria, encapsulated within the geological archives.
About Magnetotactic Bacteria:
- Magnetotactic bacteria, predominantly prokaryotic microorganisms, possess the unique ability to align themselves in alignment with Earth's magnetic field.
- These organisms were traditionally believed to utilize the Earth's magnetic field as a navigational aid to locate environments with optimal oxygen levels.
- Comprising distinctively structured particles abundant in iron, these bacteria harbor small sacs that function akin to a compass.
- Magnetotactic bacteria synthesize minute crystals composed of iron-rich minerals such as magnetite or greigite, facilitating their navigation amidst fluctuations in oxygen concentrations within their aquatic habitats.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Sediment Composition: The sediment core, measuring three meters in length and extracted from the southwestern Bay of Bengal, primarily comprised "pale green silty clays."
- Foraminifera Abundance: Researchers observed abundant benthic and planktic foraminifera, which are single-celled organisms characterized by shells found near the seabed and freely floating in water.
- Oxygen Concentration: At depths ranging from approximately 1,000 to 1,500 meters, the Bay of Bengal exhibited notably low oxygen levels.
- Analysis of the sediment sample confirmed fluctuations in monsoon activity, as evidenced by the presence of magnetic mineral particles from distinct geological periods.
- Role of Rivers: Rivers such as the Godavari, Mahanadi, Ganga-Brahmaputra, Cauvery, and Penner, which discharge into the Bay of Bengal, played a pivotal role in magnetofossil formation.
- Nutrient Supply: The nutrient-rich sediment transported by these rivers supplied reactive iron, which, combined with organic carbon in the suboxic conditions of the Bay of Bengal, created a conducive environment for magnetotactic bacteria growth.
- Impact of Oceanographic Processes: Factors such as freshwater discharge from rivers and oceanographic phenomena like eddy formation influenced the oxygen content in these waters, distinguishing them from other low-oxygen zones.
- Persistence of Suboxic Conditions: The presence of magnetofossils indicated the prolonged persistence of suboxic conditions in the Bay of Bengal, fostering an environment conducive to the proliferation of magnetotactic bacteria.
