Global Hunger Index 2024
- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
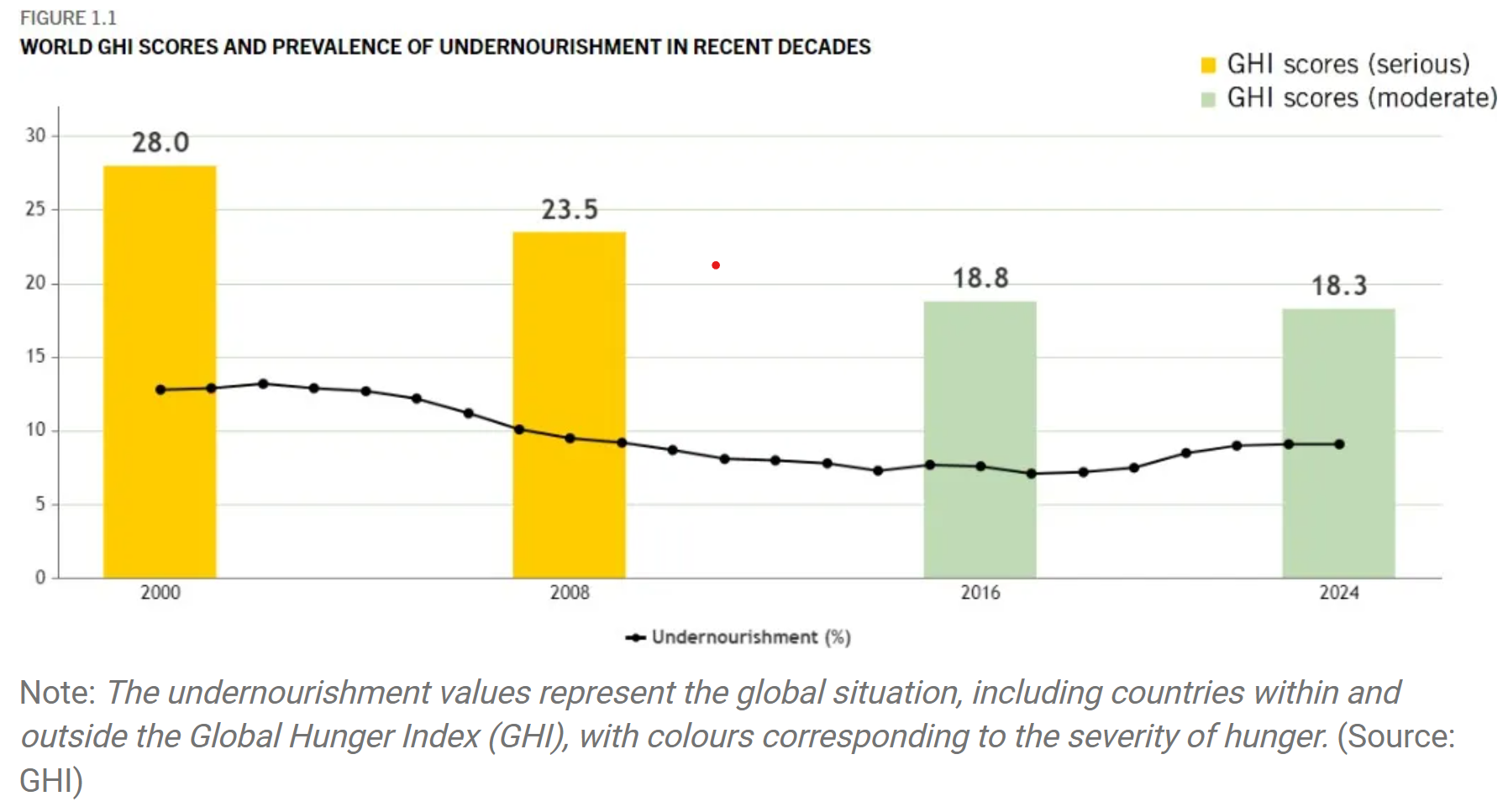
The 2024 Global Hunger Index (GHI) emphasizes food as a fundamental human right, alongside air and water.
Key Highlights:
- Current Crisis: Despite adequate food production globally, around 350 million people face extreme hunger, with 49 million on the brink of famine.
- Statistics: Over 820 million people are chronically undernourished, and malnutrition claims the lives of five million children under five each year.
Top 10 Countries Most Affected by Hunger (2024)
- Somalia: GHI Score 44.1 (GHI 2000: 63.3)
- Yemen: GHI Score 41.2 (GHI 2000: 41.6)
- Chad: GHI Score 36.4 (GHI 2000: 50.5)
- Madagascar: GHI Score 36.3 (GHI 2000: 42.3)
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: GHI Score 34.9 (GHI 2000: 47.2)
- Haiti: GHI Score 34.3 (GHI 2000: 39.8)
- Niger: GHI Score 34.1 (GHI 2000: 53.1)
- Liberia: GHI Score 31.9 (GHI 2000: 48.0)
- Central African Republic: GHI Score 31.5 (GHI 2000: 48.0)
- Korea (DPR): GHI Score 31.4 (GHI 2000: 43.7)
India's Position
- Ranking: India ranks 105th in the GHI 2024, categorized as having a "serious" hunger situation.
- GHI Score: India’s score stands at 27.3, showing some improvement from a score of 38.4 in 2000 (previously classified as "alarming").
Key Concerns in India
- Undernourishment: 13.7% of the population is undernourished.
- Child Stunting: 35.5% of children under five are stunted.
- Child Wasting: 18.7% of children under five experience wasting.
- Child Mortality: 2.9% of children do not survive to age five.
Global Hunger Index (GHI):
A tool measuring hunger across countries based on four indicators:
-
- Undernourishment
- Child Wasting
- Child Stunting
- Child Mortality
- Data Sources: The GHI is based on data from credible organizations like the FAO, WHO, and UNICEF, as well as government surveys.
Hunger Indicators Explained
- Undernourishment: Reflects the overall food access situation.
- Child Wasting: Indicates acute malnutrition; a critical health issue.
- Child Stunting: Reflects chronic malnutrition; significant public health concern.
- Child Mortality: Represents the most severe consequence of hunger.
The 2024 GHI report reveals that while progress has been made in addressing hunger globally, significant challenges remain, particularly in countries like India and the most affected nations. Addressing these issues is crucial for achieving the goal of zero hunger by 2030.
