QS World Future Skills Index 2025

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The QS World Future Skills Index 2025, released by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS), evaluates countries' readiness to meet the evolving demands of the global job market. It assesses nations based on skill development, education, and economic transformation, highlighting their preparedness for emerging technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and sustainability.
India’s Performance in the Index:
- Overall Ranking: India is ranked 25th globally, categorizing it as a “Future Skills Contender.”
- Future of Work Category: India ranked 2nd, only behind the United States, reflecting its preparedness for AI, digital, and green jobs.
- Economic Transformation: India scored 58.3, the lowest among the top 30 countries, reflecting challenges in innovation and sustainability.
- Skills Fit: India received a score of 59.1, the weakest among the top 30 nations, indicating a gap between workforce skills and industry requirements.
- Academic Readiness: India’s education system is struggling to keep pace with employer demands, necessitating curriculum reforms and stronger academia-industry collaboration.
Key Findings from the Report:
Strengths:
- Digital Readiness: India has demonstrated strong capabilities in integrating digital talent into the workforce.
- Youth Advantage: A large, young population provides a demographic dividend for sustained economic growth.
- Startup Ecosystem: India’s startup culture and government initiatives support technological advancement and innovation.
Weaknesses:
- Higher Education-Industry Gap: Mismatch between education and employer requirements, particularly in AI, green skills, and entrepreneurship.
- Limited R&D Investment: India’s research and development spending is 0.6% of GDP, far below the global average of 2.7%.
- Low Innovation in Sustainability: India scored 15.6 out of 100, ranking poorly in future-oriented innovation for sustainability.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) estimates a 29 million skilled workforce gap in critical sectors such as healthcare, semiconductor manufacturing, and AI.
- Low Employability Rates: Only 25% of management professionals, 20% of engineers, and 10% of graduates meet global employability standards.
- Higher Education Accessibility: Many students face difficulties in accessing quality tertiary education, particularly in skill-intensive fields.
Opportunities for Growth:
- Leverage Demographic Dividend: India can capitalize on its young workforce to dominate skill-based industries while other nations struggle with aging populations.
- Policy Support:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on modular education and reskilling initiatives.
- ULLAS Program: Aims to expand lifelong learning and skill development.
- Technological Integration: Advancements in AI and digital learning can help modernize academic curricula and improve job readiness.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Enhancing Academia-Industry Collaboration: Universities should prioritize problem-solving, entrepreneurship, and creativity to align education with employer needs.
- Increasing R&D Investment: Raising spending on research and development to promote innovation and sustainability.
- Expanding Access to Education: Bridging regional disparities in tertiary education through flexible and modular learning.
- Strengthening Policy Implementation: Ensuring effective execution of skilling programs to reduce the workforce-employability gap.
Commissioning of Three Indian Naval Combatants

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
In a major boost to India’s maritime defense capabilities, three frontline warships—INS Nilgiri, INS Surat, and INS Vaghsheer—were commissioned into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai. This marks a significant step in India's self-reliance in defense manufacturing and strengthens its presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
INS Nilgiri: Project 17A Stealth Frigate
INS Nilgiri is the lead ship of the Project 17A class, an advanced version of the Shivalik-class frigates, designed for multi-mission capabilities in blue-water operations.
Key Features:
- Advanced stealth technology reducing radar and infrared signatures.
- Equipped with supersonic surface-to-surface missiles, Medium Range Surface-to-Air Missiles (MRSAM), upgraded 76 mm guns, and rapid-fire close-in weapon systems.
- Versatile roles in anti-surface, anti-air, and anti-submarine warfare.
- Constructed using integrated modular design for faster assembly.
- Other ships in this class—Himgiri, Taragiri, Udaygiri, Dunagiri, and Vindhyagiri—are under construction at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE).
INS Surat: Project 15B Stealth Destroyer
INS Surat is the fourth and final guided missile destroyer under Project 15B, following INS Visakhapatnam, INS Mormugao, and INS Imphal. It represents an upgraded version of the Kolkata-class destroyers.
Key Features:
- AI-Enabled Operations: First Indian warship integrated with artificial intelligence solutions for enhanced combat efficiency.
- High-Speed Capability: Can exceed speeds of 30 knots (56 km/h).
- Advanced Armament: Equipped with modern surface-to-air and anti-ship missiles, torpedoes, and sophisticated network-centric warfare sensors.
- Strategic Role: Acts as a high-speed, maneuverable warship with increased strike capability and endurance.
Project 15B was initiated in 2011, with ships named after major Indian cities to symbolize national unity. These destroyers serve as critical assets in naval operations, ensuring dominance in maritime warfare.
INS Vaghsheer: Project 75 Scorpene-Class Submarine
INS Vaghsheer is the sixth and final Kalvari-class submarine built under Project 75, designed for stealth and versatile naval operations.
Key Features:
- Scorpene-Class Design: Developed in collaboration with the French Naval Group.
- Diesel-Electric Propulsion: Silent and highly maneuverable, making it one of the world’s most advanced attack submarines.
- Mission Capabilities: Specializes in anti-surface warfare, anti-submarine warfare, intelligence gathering, and special operations.
- Weapons Systems: Armed with wire-guided torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and state-of-the-art sonar systems.
The Kalvari-class submarines continue India's legacy of submarine warfare, named after decommissioned Soviet-origin Foxtrot-class submarines post-Independence.
LEADS 2024 Report

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
- Launch of the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report and the Logistics Excellence, Advancement, and Performance Shield (LEAPS) 2024 awards in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of LEADS 2024 Report:
- Evaluate logistics performance across Indian states and union territories.
- Provide actionable insights for logistics reforms to foster competitive federalism.
- Assess logistics infrastructure, services, regulatory environment, and sustainability efforts.
- Performance Evaluation:
Region Achievers Fast Movers Aspirers
Coastal States Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu Andhra Pradesh, Goa Kerala, West Bengal
Landlocked States Haryana, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand
North-Eastern States Assam, Arunachal Pradesh Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura Manipur
Union Territories Chandigarh, Delhi Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Ladakh
Lakshadweep, Puducherry
- Key Remarks:
- Action Plans for Better Logistics: States should develop regional and city-level logistics plans, including for last-mile connectivity, to attract investments.
- Green Logistics: Advocate for sustainable logistics practices to ensure environmentally responsible growth.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Encourage PPPs to promote multi-modal hubs and streamline logistics infrastructure.
- Technological Integration: Push for the adoption of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics to enhance efficiency in logistics operations.
- Skill Development & Gender Inclusivity: Focus on workforce inclusivity and skill development to boost sectoral growth. Promote gender diversity in logistics.
- LEAD Framework: Urge logistics sectors to embrace the LEAD framework (Longevity, Efficiency, Accessibility, Digitalisation) for transformation.
- LEAD Framework and Recommendations:
- Longevity, Efficiency, and Effectiveness: Improve long-term logistics strategies.
- Accessibility and Accountability: Ensure better reach and transparent logistics practices.
- Digitalisation: Enhance digital transformation across logistics processes.
- About LEADS:
- Full Form: Logistics Ease Across Different States.
- Launched: 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Purpose: To assess and improve logistics infrastructure and services across Indian states and UTs.
- Methodology: Based on over 7,300 responses from a pan-India survey and inputs from over 750 stakeholder consultations.
- LEAPS 2024 Awards: Recognized excellence in the logistics sector across categories such as air, rail, road, maritime freight service providers, startups, MSMEs, and educational institutions.
- PM GatiShakti Course: Launched a 15-hour online course on “PM GatiShakti Concept for Efficient Infrastructure Planning and National Development”, hosted on iGOT Karmayogi platform and UGC SWAYAM portal.
- Logistics Cost Framework Report: Unveiled a report on the logistics cost framework, aiming to accurately estimate logistics costs in India through a hybrid methodology, incorporating both EXIM and domestic cargo data.
- Significance of LEADS:
- Provides critical insights into logistics performance, helping States and UTs to improve infrastructure, services, and regulatory practices.
- Plays a key role in India's vision of becoming a $32 trillion economy by 2047 by improving logistics efficiency, sustainability, and global competitiveness.
Rabbit Fever
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Tularemia, commonly known as "rabbit fever," is a rare but highly infectious bacterial disease caused by Francisella tularensis. Though uncommon, it can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. Over recent years, cases of tularemia have been on the rise in the United States, drawing attention to the broader environmental and epidemiological factors influencing the disease’s spread.
Rising Incidence of Tularemia
Between 2011 and 2022, the United States saw a 56% increase in the annual average incidence of tularemia infections compared to the previous decade, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vulnerable populations include children aged 5 to 9, older men, and individuals of American Indian or Alaska Native descent. The increasing number of reported cases highlights the growing concern over this disease, despite its rarity.
Transmission Pathways
Tularemia is primarily transmitted through:
- Direct Contact with Infected Animals: Common carriers include rabbits, hares, and rodents, particularly those infected with Francisella tularensis. This presents a risk for individuals working closely with wildlife, such as hunters.
- Insect Bites: Ticks, especially in regions with high tick populations, and deer flies can spread the disease.
- Contaminated Food or Water: Consuming undercooked meat from infected animals or untreated water can lead to infection.
- Inhalation of Contaminated Dust or Droplets: This is a potential risk in agricultural or laboratory settings and can result in pulmonary tularemia.
Contributing Factors to the Rise in Cases
Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of tularemia:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are increasing tick activity and extending breeding seasons, allowing the bacteria to spread more easily.
- Habitat Encroachment: Deforestation and increased human interaction with wildlife are amplifying exposure to infected animals.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Advances in surveillance and testing methods have made it easier to detect tularemia, leading to more reported cases.
Early Symptoms and Diagnosis
Tularemia symptoms can vary depending on the route of infection. Symptoms typically appear 3 to 5 days post-exposure and may include:
- Sudden high fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Chills, fatigue, and body aches
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially near the site of infection (e.g., under the arms or in the groin)
There are four primary forms of tularemia:
- Ulceroglandular: Characterized by skin ulcers and swollen lymph nodes.
- Glandular: Swollen lymph nodes without ulcers.
- Pneumonic: Lung infection, often resulting from inhalation.
- Typhoidal: A more systemic form, with symptoms like fever and abdominal pain.
Differentiating tularemia from other conditions such as flu, pneumonia, or lymphadenitis is key for diagnosis. A skin ulcer or swollen lymph nodes in individuals with recent exposure to wildlife or ticks is a critical diagnostic clue.
Treatment and Prognosis
Tularemia is treatable with antibiotics. First-line treatment includes streptomycin or gentamicin, while doxycycline or ciprofloxacin may be used for milder cases. Treatment typically lasts 10 to 21 days, and when initiated promptly, the disease has a high recovery rate and minimal complications. However, untreated cases can lead to chronic infections, lung abscesses, pneumonia, or severe sepsis, with mortality rates of 1-2% under treatment. Untreated severe cases can result in mortality rates between 30% and 60%.
Tularemia in India: A Potential Concern?
Tularemia is extremely rare in India, mainly due to the country's differing ecological conditions and limited interaction with the primary reservoirs of Francisella tularensis. However, awareness remains crucial, especially for individuals traveling to endemic regions or working in wildlife settings. Despite its rarity in India, the rising global incidence and changing environmental factors warrant continued vigilance.
Pegasus Spyware

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
For the first time, a court in the US has held Israel’s NSO Group liable for its intrusive spyware Pegasus, which could set up a measure of accountability for the company that it has, for long, allegedly downplayed.
Overview:
- Pegasus is a spyware developed by the Israeli company NSO Group.
- It has been used for surveillance, allegedly targeting journalists, activists, politicians, and government officials across the world, including India.
Recent Legal Developments:
- US Court Ruling (2024):
- A US court held NSO Group liable for using Pegasus to surveil 1,400 WhatsApp users, including 300 from India.
- NSO Group violated the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the California Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA).
- The ruling may revive debates on the accountability of spyware use and its implications on privacy.
Use of Pegasus in India:
- Targeted Individuals (2021):
- 300 Indian numbers allegedly targeted, including journalists, politicians, Union Ministers, and civil society members.
- High-profile targets included opposition leaders, constitutional authorities, and activists.
- Government Denial:
- The Indian government denied involvement, stating allegations lacked substance.
- In Parliament, IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw rejected claims, asserting India’s surveillance laws prevent unauthorized surveillance.
- NSO Group Response:
- NSO Group denied the allegations, calling them “false and misleading” and citing doubts about the sources.
Investigations and Legal Actions:
- Supreme Court Inquiry:
- The Supreme Court appointed a committee of technical experts in 2021 to investigate claims.
- August 2022 Report: Found no conclusive evidence of spyware use on examined devices but noted lack of cooperation from the government.
- State-Level Investigations:
- West Bengal: Set up a Commission of Inquiry into Pegasus surveillance, later halted by the Supreme Court.
- Andhra Pradesh: The issue became political, with allegations that the previous government used Pegasus to monitor opposition figures.
Pegasus Spyware Features:
- Capability: Can hack iOS and Android devices to collect data, record conversations, capture photos, and access app data.
- Exploitation Method: Uses zero-day vulnerabilities to exploit iOS and Android devices covertly.
- Invisibility: Operates without user knowledge, often only detected through signs like browser closings after phishing links are clicked.
Controversial Use of Pegasus:
- Global Use: Though intended for fighting terrorism and crime, Pegasus has been misused for spying on journalists, politicians, human rights activists, and opposition leaders.
- India Specifics:
- Pegasus Project: Targeted Indian citizens, including activists, journalists, and politicians.
- Amnesty International: Confirmed use of Pegasus to target Indian phones.
India's Legal Framework for Surveillance:
- Telecommunications Act (2023): Empowers the government to control telecom services during emergencies, but requires authorization for lawful interceptions.
- IT Act (2000): Allows the government to monitor, intercept, or decrypt information through computer resources under certain conditions.
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act (2023): Aims to protect personal data, including provisions on surveillance, data breaches, and rights of individuals over their data.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns:
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- Surveillance infringes on the right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Freedom of speech and expression (Article 19) may be curtailed, with surveillance being used to suppress dissent.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Surveillance often occurs without judicial or parliamentary oversight, leading to potential executive overreach.
- Inability to Seek Legal Remedies:
- Citizens targeted by surveillance cannot challenge it due to lack of awareness, undermining constitutional rights.
- Executive Overreach and Suppression of Free Expression:
- Pegasus revelations have raised concerns about surveillance targeting constitutional functionaries, suppressing free speech, and stifling open discourse.
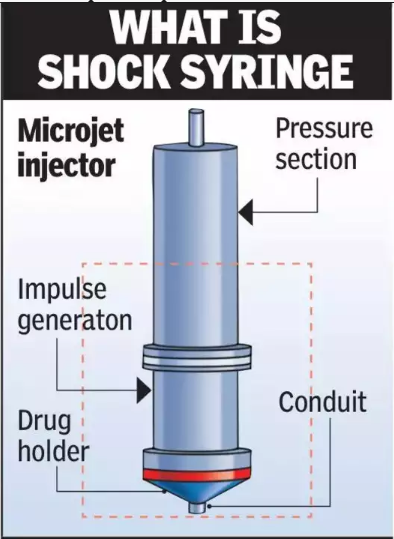
IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
How the Shock Syringe Works:
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) Mission
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission, a key milestone in India’s space capabilities. The mission will deploy two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into a 740 km orbit using the PSLV-C60 rocket. SpaDeX aims to demonstrate the technology for satellite docking, a critical component for future space missions such as lunar exploration and the development of India's own space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
Key Objectives of SpaDeX Mission:
- Primary Objective: To demonstrate the rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft (SDX01 and SDX02) autonomously.
- Secondary Objectives: Include testing electric power transfer between the docked spacecraft, composite spacecraft control, and post-docking payload operations.
The mission will see the two spacecraft gradually approach each other, performing a series of maneuvers, starting at a 20 km distance and closing to millimeter-scale distances before docking. Once docked, they will execute secondary tasks, such as scientific payload operations, using advanced technologies including high-resolution cameras, multi-spectral payloads, and radiation monitors.
Technological Innovations:
- Docking Mechanism: An indigenous, motor-driven, low-impact, androgynous docking system with capture, extension/retraction, and rigidization mechanisms. Both spacecraft are equipped with identical docking systems to simplify operations.
- Advanced Sensors: The spacecraft will use a Laser Range Finder (LRF), Proximity & Docking Sensors (PDS), and Rendezvous Sensors for precise distance measurement and to guide the docking process.
- Inter-Satellite Communication: The spacecraft will employ autonomous inter-satellite links (ISL) for real-time communication and data sharing.
- RODP Processor: This system, based on GNSS, ensures accurate position and velocity determination for the spacecraft during the docking procedure.
Significance of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Technological Milestone: SpaDeX positions India as the fourth country, after the US, Russia, and China, to develop space docking technology.
- Space Exploration: The successful demonstration will facilitate future space exploration, including Chandrayaan-4 and interplanetary missions.
- Modular Space Infrastructure: Space docking is essential for building multi-modular space stations, which allows the construction of large structures in space and enhances flexibility for future missions.
- Satellite Servicing: Docking enables satellite servicing, including repairs, refueling, and upgrades, which increases the operational lifespan of satellites.
SpaDeX Mission for India’s Space Station:
The SpaDeX mission is a crucial step towards India’s plans for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). This will be India’s first modular space station, designed to conduct advanced scientific research, including in life sciences and medicine. BAS is expected to begin operations by 2035, and the development of docking technology is pivotal for its assembly and operation.
Mission Launch Details:
The PSLV-C60 rocket is set to launch the SpaDeX mission from Sriharikota. The mission is a demonstration of India's growing space capabilities and its indigenous technologies, including the Bharatiya Docking System (BDS).
Challenges and Technological Requirements:
The docking process requires extremely precise maneuvering, as the two spacecraft will be traveling at speeds of 28,800 km/h and must reduce their relative velocity to just 0.036 km/h before docking. This level of precision is crucial for future missions involving spacecraft servicing, crew transfers, and the construction of space infrastructure like BAS.
In addition to the docking demonstration, SpaDeX will carry 24 academic and startup payloads aboard the PSLV’s fourth stage, POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4), offering a valuable platform for microgravity research.
Future Prospects:
The success of SpaDeX will pave the way for more complex missions, such as India’s lunar and Mars exploration programs, the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and international collaborations in satellite servicing and space infrastructure.
Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program

- 21 Dec 2024
On December 20, 2024, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $350 million policy-based loan aimed at expanding India's manufacturing sector and improving the resilience of its supply chains. This loan is part of the Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program.
Key Points:
- Loan Agreement Signatories:
- Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), Ministry of Finance, Government of India
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- SMILE Program:
- Goal: Strengthen the logistics ecosystem to enhance India's manufacturing sector and improve supply chain resilience.
- Structure: The program includes two subprograms focusing on strategic reforms in logistics and infrastructure development.
- Key Features of the SMILE Program:
- Strengthening Multimodal Infrastructure: Enhances logistics infrastructure at the national, state, and city levels.
- Standardization: Improves warehousing and other logistics assets to attract private sector investment.
- External Trade Logistics: Enhances efficiencies in external trade logistics.
- Smart Systems: Adopts systems for efficient, low-emission logistics to promote sustainability.
- Expected Outcomes:
- Cost Reduction & Efficiency: Strategic reforms will reduce logistics costs and improve efficiency.
- Job Creation: Infrastructure development and reforms are expected to generate substantial employment opportunities.
- Gender Inclusion: The program promotes gender inclusion through economic growth initiatives.
- Impact on India’s Economy:
- The transformation of India’s logistics sector will enhance the competitiveness of the manufacturing sector and drive sustainable economic growth.
About the Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- Headquarters: Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines.
- Established: December 19, 1966.
- Members: 69 countries, including both regional (e.g., India, China) and non-regional (e.g., USA, Japan) members.
- Function: ADB promotes social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific, providing loans, grants, and technical assistance for development projects.
- Key Shareholders:
- Japan: 15.57%
- USA: 15.57%
- India: 6.32%
- China: 6.43%
- Australia: 5.77%
Black holes in Webb data allay threat to cosmology’s standard model

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched almost three years ago, has provided unprecedented insights into the early universe. Astronomers were surprised to find large, fully-developed galaxies when the universe was only 400-650 million years old, a timeframe previously thought to be too early for such structures.
The Challenge to the Standard Model:
- Cosmological Expectations: According to the standard model of cosmology, the first stars formed around 100-200 million years after the Big Bang, and galaxies began to form within the first billion years.
- Unexpected Findings: JWST observations seemed to show that galaxies were already large and well-formed much earlier than expected, raising questions about the timeline of galaxy formation.
New Study's Contribution:
- The Study: A study published in the Astrophysical Journal in August 2024, examined JWST data from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science (CEERS) Survey. They focused on galaxies from 650 to 1,500 million years after the Big Bang.
- Key Findings: One explanation for the unexpected size and number of early galaxies is that these galaxies formed stars much more efficiently than those in the modern universe. This could account for the larger-than-expected galaxies.
The Role of Black Holes:
- Impact of Black Holes: The study also explored the presence of black holes at the centers of early galaxies. These black holes, which emit significant light, were previously unaccounted for in the star mass estimations of galaxies. When the researchers removed the light from black holes (referred to as "little red dots"), they found that the galaxies were not as massive as initially thought.
- Correction to Previous Estimates: This adjustment in calculations helped align the data with the standard model of cosmology, sparing it from a major revision.
Implications for the Standard Model:
- Star Formation Efficiency: The study suggests that extreme conditions in the early universe, including abundant gas and less disruptive stellar events, could explain the higher efficiency of star formation.
- Cosmology's Stability: Despite earlier challenges to the standard model, the new findings support its predictions, showing that more efficient star formation and the role of black holes could explain the rapid growth of galaxies in the early universe.
Future Research Directions:
- Expanding Data Sets: The team plans to incorporate more data from JWST to study even earlier galaxies, which could help refine our understanding of galaxy formation in the early universe.
- Further Observations: As the team continues to explore galaxies from even earlier periods (around 400 million years after the Big Bang), they aim to strengthen their findings and provide further evidence to either support or challenge the current cosmological models.
RBI's Stance on De-dollarisation and Risk Diversification

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
- Governor Shaktikanta Das clarified that India is not pursuing "de-dollarisation," but rather aiming to diversify risk in trade. Measures like local currency trade agreements and Vostro accounts are intended to reduce reliance on the US dollar without eliminating it entirely.
- Objective: The goal is to de-risk India's trade, not to fully replace the dollar, especially amidst rising geopolitical tensions.
Key Highlights:
Vostro Accounts and Local Currency Trade:
- Vostro Accounts: These accounts, held by foreign banks in Indian rupees, facilitate transactions in local currencies, helping mitigate the risks of dollar dependency.
- International Currency Trade: By promoting trade in local currencies, the RBI seeks to reduce exposure to fluctuations in the dollar's value. However, these efforts have faced challenges due to India’s limited international presence in goods and services trade.
Gold Purchases by Central Banks:
- Surge in Gold Purchases: Global central banks, including the RBI, have significantly increased gold holdings. India added 27 tonnes in October 2024 alone, the largest increase among central banks.
- Motivations for Gold: The surge in gold buying reflects growing concerns about geopolitical risks, including the Ukraine war, and the potential for secondary sanctions. Gold is seen as a safe haven asset that diversifies reserves away from the US dollar.
Decline in Dollar Dominance:
- Global Shift: The share of the US dollar in global reserves has been gradually declining, partly due to the rise of the Chinese yuan. Central banks are increasingly turning to gold and alternative currencies as part of a diversification strategy.
- Impact on Emerging Markets: Countries like India are particularly motivated to reduce reliance on the dollar due to geopolitical tensions and economic vulnerabilities linked to the dollar’s dominance.
India’s Domestic Currency Trade Initiatives:
- Trade with Russia and UAE: India is actively exploring trade in domestic currencies with countries like Russia and the UAE to reduce dependence on the dollar. However, these efforts have faced slow uptake due to India’s trade deficit with most countries except the US.
- Challenges in Adoption: Despite efforts to internationalize the rupee, high transaction costs and lack of sufficient demand for rupee-based trade are significant barriers.
BRICS and Shared Currency Discussions:
- Geopolitical Complexity: BRICS nations, due to their geographical and economic diversity, have discussed the possibility of a shared currency, but no consensus has been reached.
- Reluctance Toward Yuan: India has resisted using the Chinese yuan for transactions, particularly for Russian oil imports, despite the yuan’s growing acceptance. This reflects India’s desire to maintain economic sovereignty and avoid over-reliance on a single currency.
Regional Implications of Dollar Volatility:
- Neighbourhood Impact: Countries like Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan have experienced significant financial distress due to declining dollar reserves and surging oil prices, exacerbated by the Ukraine war.
- India’s Resilience: India’s strong dollar reserves have helped it maintain economic stability, but the country remains cautious of dollar volatility, particularly as oil prices rise.
Conclusion:
- Strategic Balance: India’s approach reflects a strategic balance of mitigating risks while ensuring global trade stability. The RBI’s emphasis on gold accumulation and pushing for rupee-based trade demonstrates a desire to reduce exposure to the dollar, but challenges like trade deficits and high transaction costs still hinder the full realization of these goals.
- Economic Sovereignty: Through these measures, India seeks to safeguard its economic sovereignty and financial stability in an increasingly unpredictable global economy.
INS Jatayu, India’s new naval base in Lakshadweep

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On Wednesday (March 6), Naval Detachment Minicoy will be commissioned as INS Jatayu, an upgraded naval base, marking an important milestone in the Indian Navy’s resolve to incrementally augment security infrastructure at the strategic Lakshadweep Islands.
About INS Jatayu Naval Base:
- The existing Naval Detachment Minicoy, which is under the operational command of the Naval Officer-in-Charge (Lakshadweep), will be commissioned as INS Jatayu.
- A naval detachment has administrative, logistics, and medical facilities.
- INS Jatayu will be upgraded to a naval base with additional infrastructure such as an airfield, housing, and personnel, after obtaining the requisite environmental and other clearances.
- The fragile ecology of the island may pose challenges for the construction but there are plans to construct a new airfield that will be capable of operating both military and civil aircraft.
Significance of INS Jatayu?
- The basing of an independent naval unit with requisite infrastructure and resources will enhance its overall operational capability in the islands.
- The establishment of the base is in line with the government’s focus on comprehensive development of the islands.
- The base will enhance its operational reach, facilitate its anti-piracy and anti-narcotics operations in the western Arabian Sea, and augment its capability as the first responder in the region.
- With the commissioning of INS Jatayu, the Indian Navy will add to its strength on the western seaboard.
- The proposed airfield will allow operations for a range of aircraft, including P8I maritime reconnaissance aircraft and fighter jets, and extend the Navy’s reach and operational surveillance capabilities at a time when India is seeking to counter the growing Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean Region.
- This has an immediate bearing at a time when India’s relations with the Maldives have come under strain since the election of the pro-China President Mohamed Muizzu.
About the Lakshadweep Islands:
- Lakshadweep, ‘a hundred thousand islands’ in Sanskrit and Malayalam, is an archipelago of 36 islands located between 220 km and 440 km from Kochi.
- The islands, only 11 of which are inhabited, have a total area of only 32 sq km.
- The Lakshadweep are part of a chain of coralline islands in the Indian Ocean that includes Maldives to the south, and the Chagos archipelago farther beyond, to the south of the equator.
- Given their location in the Indian Ocean, the Lakshadweep are of huge strategic importance to India.
- Minicoy straddles vital Sea Lines of Communications (SLOCs) — the world’s main maritime highways — including the Eight Degree Channel (between Minicoy and Maldives) and the Nine Degree Channel (between Minicoy and the main cluster of Lakshadweep islands).
- In consequence, the Lakshadweep Islands are also vulnerable to marine pollution.
