GQ-RCP Platform
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have developed a technology for targeted better detection of HIV-genome derived G-Quadruplex (GQ).
Key Features of the GQ-RCP Platform
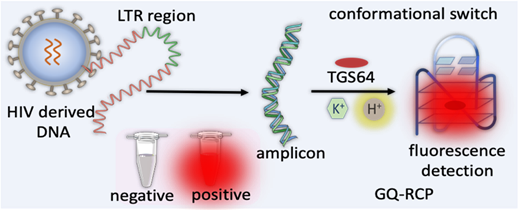
- Technology: GQ Topology-Targeted Reliable Conformational Polymorphism (GQ-RCP) platform developed by Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR).
- Detection Mechanism: Uses a fluorometric test to detect HIV-derived GQ DNA through reverse transcription and amplification.
- Advantage: Increases diagnostic reliability by reducing false positives associated with non-specific DNA probes.
- Process: pH-mediated transition of double-stranded DNA into GQ conformation for targeted detection.
- Flexibility: Initially designed for SARS-CoV-2, now adapted for HIV diagnosis.
About HIV
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) attacks the immune system, specifically CD4 cells, weakening the body's ability to fight infections.
- Transmission: Spread through bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- AIDS: Without treatment, HIV progresses to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), where the immune system becomes severely damaged.
- Management: No cure; managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which controls viral replication.
Current HIV Situation in India
- Prevalence: As of 2021, ~2.4 million people living with HIV in India, with a 0.22% adult prevalence rate.
- Demographic Distribution: High prevalence among female sex workers (2.61%) and injecting drug users (5.91%). Women represent 39% of HIV-positive population.
- High-Prevalence States: Northeastern states have the highest prevalence (e.g., Mizoram - 2.70%) and southern states (e.g., Andhra Pradesh - 0.67%).
Government Initiatives on HIV
- National AIDS Control Program (NACP): Launched in 1992, aims for prevention, treatment, and care.
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focus on awareness, blood safety, and surveillance.
- Phase II (1999-2006): Expanded interventions for high-risk populations.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Increased targeted interventions and civil society involvement.
- Phase IV (2012-2021): Focused on integration of HIV services into public health systems.
- Phase V (2021-2026): Aim to reduce new infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2026.
- Legislative Framework: The HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Act (2017) ensures the rights of people living with HIV and access to treatment without discrimination.
- International Support: India receives support from UNAIDS, WHO, the World Bank, and foundations like Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
