GEAPP and ISA Sign $100 Million Agreement for Solar Projects

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) signed a Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF) agreement with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to mobilize $100 million for funding high-impact solar energy projects. This collaboration is part of a wider effort to accelerate India's clean energy transition, bridge financing gaps, and enhance the country's energy systems. Along with this agreement, two other key initiatives were announced:
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition)
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge)
These programs aim to address energy transition challenges by fostering scalable, cost-efficient solutions, digitalizing utilities, and supporting innovations for sustainable energy.
Key Features:
- Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF):
- The MDTF aims to raise and deploy $100 million to finance impactful solar energy projects, with ISA driving the strategic direction.
- GEAPP’s Project Management Unit will provide governance, fundraising, and technical expertise to ensure project success.
- The collaboration emphasizes the importance of solar energy in achieving India's clean energy goals.
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition):
- Focuses on transforming grid systems by digitalizing grid assets and integrating them with smart sensors.
- Real-time data will help reduce transmission losses and facilitate Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) deployment, assisting in the integration of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) into the grid.
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge):
- A platform for identifying and scaling innovative solutions to accelerate the clean energy transition, especially within India's growing startup ecosystem.
- Focuses on supporting investable opportunities for energy transition solutions, building on the earlier success of ENTICE 1.0.
Global Impact of GEAPP:
GEAPP, launched with an initial commitment of $464 million, has already funded 130 projects across 40 countries. These projects have impacted over 50 million people, helping reduce 43 million tons of CO2 emissions. The collaboration with ISA is expected to deepen GEAPP's efforts in mobilizing capital to foster clean energy access and tackle climate change.
India’s Clean Energy Transition:
India has already extended electricity access to over 800 million people, but about 2.5% of households still remain unelectrified. Distributed renewable energy, especially solar energy, will play a pivotal role in reaching these underserved populations. India aims for 47 GW of battery energy storage systems by 2032, which will support grid stability and energy access.
Additional Initiatives and Impact:
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
- GEAPP has also supported India’s first commercial standalone BESS project, which will provide 24/7 power to over 12,000 low-income customers.
- The project is set to lower electricity tariffs by 55%, benefiting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Strategic Alliances:
- The partnership with ISA and the strategic initiatives like DUET and ENTICE 2.0 aim to further India’s climate and energy goals, bringing renewable energy solutions to underserved regions, and supporting the country's energy security.
Role of GEAPP and ISA:
- GEAPP works to mobilize financing, provide technical expertise, and ensure effective implementation of renewable energy projects globally.
- ISA focuses on solar energy solutions, and with this agreement, it seeks to enhance the solar energy capacity in its member countries, aligning with climate targets.
About GEAPP:
GEAPP is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, philanthropy, technology partners, and financial institutions. Its goal is to transition developing economies to clean energy while enhancing economic growth. It aims to:
- Reduce 4 gigatons of carbon emissions.
- Provide clean energy access to 1 billion people.
- Create 150 million new jobs globally.
Anji Khad Bridge

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Overview:
- The Anji Khad Bridge is India's first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Jammu and Kashmir’s Reasi district.
- It is a key part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project aimed at enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Kashmir and the rest of India.
- The bridge crosses the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab River, and is expected to transform regional transport, boost tourism, and promote economic growth.
Key Features:
- Dimensions:
- Total length: 725.5 meters.
- Main Pylon Height: 193 meters from the foundation, standing 331 meters above the riverbed.
- The bridge is designed for train speeds of up to 100 km/h and can withstand wind speeds of up to 213 km/h.
- Structure and Design:
- Asymmetrical cable-stayed design supported by 96 cables with varying lengths (82 to 295 meters).
- The structure includes:
- A 120-meter approach viaduct on the Reasi side.
- A 38-meter approach bridge on the Katra side.
- A 473.25-meter cable-stayed portion crossing the valley.
- A 94.25-meter central embankment linking the main bridge to the approach viaduct.
- Construction Techniques:
- Used advanced construction techniques such as DOKA Jump Form Shuttering, Pump Concreting, and Tower Crane Technique to enhance safety and reduce construction time by 30%.
- A 40-ton tower crane imported from Spain was employed for operations at great heights.
- The project utilized site-specific investigations by IIT Roorkee and IIT Delhi due to the region’s complex geological and seismic conditions.
- Engineering Challenges:
- The bridge had to be constructed in the difficult Himalayan terrain, with fragile geological features such as faults and thrusts.
- Seismic activity in the region required additional precautions in the design and construction process.
- Safety and Monitoring:
- Equipped with an integrated monitoring system that includes multiple sensors to ensure the structural health of the bridge during operation.
Importance and Impact:
- Connectivity: The bridge will significantly improve connectivity between Katra and Reasi, ensuring faster rail travel and linking the Kashmir Valley with the rest of India.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Expected to boost tourism and economic development by improving access to the region, attracting visitors, and facilitating smoother transportation of goods and services.
- Sustainability: The bridge's design ensures it remains safe under extreme weather conditions, offering long-term reliability for the Indian Railways network.
Collaboration and International Expertise:
- The design and supervision were handled by ITALFERR (Italy), with proof-checking conducted by COWI (UK).
- The project combines Indian engineering codes with Eurocodes, adhering to international standards for structural integrity.
Ramesh Chand Panel
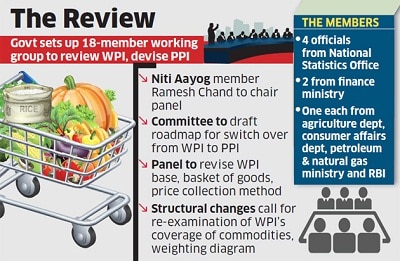
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India has formed an 18-member panel, headed by Ramesh Chand, a member of NITI Aayog, to revise the base year of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to 2022-23 from the current base year of 2011-12. The panel will also work on a roadmap for transitioning from WPI to the Producer Price Index (PPI).
Key Highlights:
Role and Mandates of the Panel:
- Revised Commodity Basket: The panel will recommend a new commodity basket for both WPI and PPI, reflecting structural changes in the economy.
- Review of Price Collection System: The panel will evaluate the current system for price collection and propose improvements.
- Computational Methodology: It will determine the computational methodology for both WPI and PPI to ensure accuracy in tracking price changes.
- The panel has been tasked with submitting its final report to the Office of the Economic Adviser at the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIT) within 18 months.
Understanding WPI vs. PPI:
- WPI (Wholesale Price Index) tracks the price of goods at the wholesale stage (i.e., goods sold in bulk to businesses), and excludes the service sector.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- Does not consider consumer-facing prices.
- Excludes services (about 55% of GDP).
- Can have double-counting bias due to multiple transactions before the final sale.
- Does not account for indirect taxes and may include export/import prices.
- Use: WPI helps in tracking bulk price movements between businesses, but doesn't fully represent consumer price inflation.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- PPI (Producer Price Index) tracks prices at various stages of production, considering both goods and services, and measures the average change in prices received by domestic producers.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
- Excludes indirect taxes (making it more accurate for price movement tracking).
- Includes services, unlike WPI, giving a broader view of price trends across the economy.
- More aligned with international standards (System of National Accounts).
- Reflects prices before consumer consumption, providing a business-oriented perspective of price trends.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
Why the Transition to PPI?
- The PPI is already used by major economies like the US, China, Germany, and Japan as it provides a more comprehensive measure of inflation from a producer’s perspective.
- It is expected to be a better indicator of inflationary trends in the overall economy, including both goods and services.
Challenges and Roadmap:
- The switch to PPI is complex, and the panel will need to ensure that the transition does not disrupt the current data collection and reporting systems. Both WPI and PPI will run concurrently until PPI stabilizes.
BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
In a significant move, the Indian Parliament passed the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024 on December 5, 2024, bringing much-needed reforms to the aviation sector. The Bill, which replaces the Aircraft Act of 1934, aims to streamline aviation regulations and improve the ease of doing business in the industry.
Key Highlights of the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024:
- Single-Window Clearance for Aviation Personnel: One of the major changes is the transfer of responsibility for the Radio Telephone Operator Restricted (RTR) certification from the Department of Telecom (DoT) to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This move consolidates the certification process under a single authority, making it easier for aviation personnel like pilots, engineers, and flight dispatchers to obtain their licenses.
- Regulation of Aircraft Design: The Bill not only retains provisions for regulating aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and repair, but also introduces new provisions to regulate aircraft design and the places where aircraft are designed.
- Enhanced Penalties for Violations: The Bill specifies severe penalties for violations, such as dangerous flying, carrying prohibited items (like arms or explosives), or littering near airports. Offenders may face imprisonment up to three years, fines up to ?1 crore, or both.
- Introduction of Second Appeal Mechanism: For the first time, the Bill introduces a second appeal process against decisions of regulatory bodies like the DGCA and BCAS, ensuring further scrutiny of decisions related to penalties.
- Improved Licensing Process: The shift of the RTR certification process from the DoT to DGCA aims to curb allegations of corruption associated with the previous system, where candidates often had to pay bribes to clear exams.
Organizational Setup and Authorities:
The Bill outlines the establishment of three key authorities under the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- DGCA: Responsible for civil aviation safety, licensing, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
- BCAS: Ensures aviation security and develops relevant security measures.
- AAIB: Investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
The central government retains supervision over these bodies, with the power to modify or review their orders.
Criticisms and Concerns:
- Lack of Autonomy for DGCA: The DGCA, unlike independent regulators in other sectors (such as telecom or insurance), operates under direct government supervision. The lack of clear qualifications, selection process, and tenure for the DGCA Director General has raised concerns about the regulator's independence.
- Unilateral Appointment of Arbitrators: The Bill empowers the government to unilaterally appoint an arbitrator in certain cases, which has been criticized for potentially violating the right to equality under Article 14 of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has previously ruled that such unilateral appointments may be unconstitutional.
- Discretionary Criminal Penalties: The central government is granted the discretion to impose criminal penalties for rule violations, which some argue could undermine the principle of separation of powers, as it is the legislature's role to define criminal offenses and penalties.
- Exclusionary Hindi Title: Some critics argue that the Hindi title of the Bill may alienate non-Hindi-speaking populations, which make up a significant portion of India’s demographic.
Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP)

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) launched the Global Strategic Preparedness, Readiness and Response Plan (SPRP) to tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:
- Tackle dengue and other Aedes-borne arboviruses (e.g., Zika, chikungunya).
- Reduce disease burden, suffering, and deaths globally.
- Background:
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Unplanned urbanization.
- Poor water, sanitation, and hygiene practices.
- Climate change.
- Increased international travel.
- An estimated 4 billion people at risk, projected to increase to 5 billion by 2050.
- Significant increase in dengue cases; 12.3 million reported by August 2023, nearly double the total from 2022.
- Rapid geographical spread of dengue due to:
- Global Impact:
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- South-East Asia.
- Western Pacific.
- Americas.
- Africa facing compounded health crises due to conflicts and disasters.
- Dengue endemic in over 130 countries, particularly affecting:
- Emergency Grade: WHO has graded the global dengue situation as grade 3, the highest emergency level.
- Key Components of SPRP:
- Emergency Coordination: Leadership and coordination activities for outbreak response.
- Collaborative Surveillance: Tools for early detection and control, including strengthened surveillance and epidemiological analysis.
- Community Protection: Engaging communities in local prevention and response measures.
- Safe and Scalable Care: Ensuring resilient health services for adequate patient care.
- Access to Countermeasures: Promoting research for better treatments and vaccines.
- Implementation Timeline: Over one year until September 2025, requiring US$ 55 million for health preparedness and response efforts.
- Alignment with Other Initiatives:
- Supports the Global Vector Control Response 2017-2030.
- Linked to the Global Arbovirus Initiative (2022) targeting mosquito-borne diseases.
- Call to Action:
- Encourages collaboration among government agencies, healthcare providers, and communities.
- Emphasizes the need for innovation and improved vector control strategies.
This plan aims to mobilize a coordinated response to the escalating threat of dengue and related diseases, emphasizing the role of all stakeholders in public health.
IBSA (INDIA, BRAZIL, SOUTH AFRICA) GROUPING

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant move for global security, the Foreign Ministers of the IBSA (India, Brazil, South Africa) grouping issued a strong declaration against terrorism during the 79th UN General Assembly in New York. This declaration condemned terrorism in all its forms and reaffirmed the collective responsibility of the international community to eliminate terrorist safe havens worldwide.
Key Points from the IBSA Declaration:
- Universal Threat: The ministers stressed that terrorism is a threat that transcends borders, cultures, and governments.
- Rule of Law: They emphasized that counter-terrorism efforts must adhere to international law, particularly the UN Charter and human rights laws, ensuring civil liberties are respected.
- International Framework: A call was made for establishing a comprehensive international counter-terrorism framework, with the United Nations at its core, to coordinate global efforts against terrorism.
- Cross-Border Security: The declaration highlighted the need for stringent actions against the movement of terrorists and the financing of terrorist networks, condemning groups like Al-Qaeda, ISIS/Daesh, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT), and Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM).
- Comprehensive Convention: A renewed commitment to accelerate the adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism at the UN was emphasized, aiming to create a unified legal framework for combating terrorism.
What is Operation Kawach, the new ‘war on drugs’ waged by Delhi Police?

- 05 Sep 2024
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, 'Operation Kawach' is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police.
In a major crackdown on the menace of drugs in the national capital, the Crime Branch of the Delhi Police conducted widespread raids, swooping down on over 100 locations across Delhi. Earlier, raids conducted during the intervening night of May 12 and 13 had led to the arrest of 31 drug offenders in 30 cases under the Narcotic-Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985.
As many as 12 bootleggers were also arrested in six cases of the Excise Act. The operation also saw the seizure of 957.5 grams of heroin, 57.8 kilograms of marijuana and 782 bottles of illicit liquor.
What is Operation Kawach?
Aimed at identifying and apprehending people involved in the trafficking and distribution of narcotics, ‘Operation Kawach’ is a joint initiative launched by the Crime Branch in coordination with all district units of the Delhi Police. The initiative aims to combat the harmful influence of drug addiction on youth and children and underscores the authorities’ commitment to safeguarding the well-being of young individuals and curbing the distribution of illicit substances in educational settings.
Operation Kawach is primarily intended to save the youth from the menace of drugs. Although the focus is to take stringent action on the supply side, it is also appealed to society to create awareness and reduce the demand of drugs. The parents, teachers and the social reformers are specially requested to sensitise the youth about the grave consequences of drug addiction.
Operation Kawach: The story so far
According to the official, the joint operations, which utilised a variety of resources such as undercover officers, surveillance, canine support and intelligence gathering, targetted both street-level dealers and high-level traffickers and have both ‘top-to-bottom’ and ‘bottom-to-top’ approaches to effectively counter drug trafficking in the national capital.
In this year, Delhi Police has arrested 534 narco-offenders in 412 NDPS cases. Around 35 kg of heroin/smack, 15 kg of cocaine, 1,500 kg of ganja, 230 kg of opium, 10 kg of charas and 20 kg of poppy have been recovered during these operations.
National Agriculture Market or eNAM (Financial Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
With more states opening up or facilitating trade of agricultural commodities on the electronic -National Agriculture Market (eNAM), a spurt in trading among various markets within the state as well as at the inter-state level is being witnessed.
What is the National Agriculture Market (eNAM)?
- eNAM is an online trading platform dedicated to agricultural commodities in India.
- Launched on April 14, 2016, it is wholly funded by the Government of India.
- The Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC), operating under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, takes the lead in implementing e-NAM
Objectives of eNAM:
- The primary goal is to enhance marketing opportunities for farmers by establishing a competitive and transparent price discovery system.
- It also facilitates online payment options for buyers, aiming to streamline the selling process for farmers.
Network and Structure:
- The NAM portal connects existing agricultural markets, including APMC/RMC market yards, sub-market yards, private markets, and unregulated markets.
- By creating a centralized online platform, e-NAM unifies agricultural markets nationwide for efficient commodity price discovery.
Key Features:
-
- Farmers can showcase products in nearby markets, allowing traders from any location to provide quotes.
- Single-window services encompass all APMC-related activities, including commodity details, buy-and-sell offers, and direct e-payment settlements to farmers' accounts.
- Facilitating Trade:
- eNAM allows traders, buyers, and commission agents to obtain licenses from state-level authorities without physical presence requirements.
- Quality standards and infrastructure for testing are harmonized in every market, including provision for Soil Testing Laboratories in selected mandis.
- Stakeholder Benefits:
- Designed for the collective benefit of farmers, mandis, traders, buyers, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and exporters.
- Stakeholder advantages include transparent online trading, real-time price discovery, reduced transaction costs, and availability of commodity prices on the e-NAM mobile app.
- Additional Benefits:
- Farmers receive details of commodity prices, quantity sold, and quality certification through SMS.
- The system promotes a more efficient supply chain and facilitates warehouse-based sales.
- Online payments are directly deposited into farmers' bank accounts, ensuring a seamless and secure financial transaction process.
NFRA to inspect Big 4, others in 2024 too (Financial Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is going to inspect the Big Four audit firms as well as other top auditors of large listed entities in 2024, an official familiar with the development told FE.
What is the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA)?
- The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is a statutory body and was constituted on 1st October 2018 by the Government of India under Sub Section (1) of section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- It is responsible for setting accounting standards in the country.
- The Punjab National Bank fraud prompted the government to establish an NFRA as the legal regulator for the auditing profession.
- Its mandate is to improve the quality and consistency of financial statements in the country and ensure that businesses and financial institutions disclose accurate and fair information.
- The National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) is located in New Delhi.
- The chairperson since March 2022 is Ajay Bhushan Pandey.
- The NFRA can probe listed as well as unlisted public companies.
- Companies must have a paid-up capital of ?500 crores and an annual turnover of ?1,000 crores.
Functions and Duties:
- As per Sub Section (2) of Section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013, the duties of the NFRA are to:
- Recommend accounting and auditing policies and standards to be adopted by companies for approval by the Central Government;
- Monitor and enforce compliance with accounting standards and auditing standards;
- Oversee the quality of service of the professions associated with ensuring compliance with such standards and suggest measures for improvement in the quality of service;
- Perform such other functions and duties as may be necessary or incidental to the aforesaid functions and duties.
Composition of the NFRA:
- As mandated by the Companies Act, NFRA is comprised of a chairperson appointed by the Central Government and a maximum of 15 members.
- The individuals selected for these roles must possess expertise in accountancy, auditing, finance, or law.
- Furthermore, they are required to declare to the Central Government that there is no conflict of interest or lack of independence in their appointment.
Membership Qualifications:
- All members, including the chairperson, who are in full-time employment, are prohibited from association with any audit firm (including related consultancy firms) during their term of office and for a period of two years after the completion of their term.
Powers of the NFRA:
- The NFRA has the same powers as the Civil Court.
- The NFRA has the authority to investigate matters of misconduct involving CAs and Chartered Accountants.
- It can impose a penalty of not less than ?1 lakh but not exceeding 5 times the fees collected.
- Also, the NFRA may also investigate and take action against individuals who violate the rules of professional conduct.
- It has the power to initiate investigations on its own and upon referral from the Central Government.
Indian Immunologicals rolls out indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine (Financial Express)
- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian Immunologicals Ltd (IIL), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) recently announced that it has launched India’s first indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine, Havisure.
About Havisure Vaccine:
- The vaccine is effective in preventing the disease and is recommended for children in routine immunization.
- It is a two-dose vaccine wherein the first dose is administered at above 12 months of age and the second dose is given at least after 6 months of the first dose.
- The vaccine is also recommended for individuals who are at risk of exposure or travel to the regions with high hepatitis A prevalence.
- In addition to this people with occupational risk of infection and suffering from chronic liver diseases also need Hepatitis A vaccination.
Key Facts About Hepatitis A:
- Hepatitis A is an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV).
- The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected (and unvaccinated) person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the faeces of an infected person.
- The disease is closely associated with unsafe water or food, inadequate sanitation, poor personal hygiene and unprotected sex.
- Unlike hepatitis B and C, hepatitis A does not cause chronic liver disease but it can cause debilitating symptoms and rarely fulminant hepatitis (acute liver failure), which is often fatal.
- Hepatitis A occurs sporadically and in epidemics worldwide, with a tendency for cyclic recurrences.
- Epidemics related to contaminated food or water can erupt explosively, such as the epidemic in Shanghai in 1988 that affected about 300,000 people.
- They can also be prolonged, affecting communities for months through person-to-person transmission.
- Hepatitis A viruses persist in the environment and can withstand food production processes routinely used to inactivate or control bacterial pathogens.
- Geographical distribution: Infection is common in low- and middle-income countries with poor sanitary conditions and hygienic practices, and most children (90%) have been infected with the hepatitis A virus before the age of 10 years, most often without symptoms.
- Transmission: The hepatitis A virus is transmitted primarily by the fecal-oral route; that is when an uninfected person ingests food or water that has been contaminated with the feces of an infected person.
- In families, this may happen through dirty hands when an infected person prepares food for family members.
- Waterborne outbreaks, though infrequent, are usually associated with sewage-contaminated or inadequately treated water.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of hepatitis A range from mild to severe and can include fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark-coloured urine and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin).
- Not everyone who is infected will have all the symptoms.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A.
- Recovery from symptoms following infection may be slow and can take several weeks or months.
- Prevention: Improved sanitation, food safety and immunization are the most effective ways to combat hepatitis A.
How do flights land safely despite fog and low visibility? The wizardry tech that makes it possible! (Financial Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the past few days, the Delhi airport has experienced chaos, resulting in over 100 flight delays, 10 flights being diverted, and some even cancelled due to low visibility caused by dense fog conditions affecting flying operations.
What is an Instrument Landing System?
- Fog, which is the suspension of water droplets near the ground, poses a considerable obstacle to aircraft operations during instances of reduced visibility.
- This atmospheric condition results in thick mist which hampers flight operations, necessitating the reliance on instruments like the “Instrument Landing System” (ILS) to navigate through the obscured surroundings.
- ILS is a standard International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) precision landing aid that is used to provide accurate azimuth (angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system) and descent guidance signals for guidance to flight for landing on the runway under adverse weather conditions.
- To put things in perspective, ILS operates in tandem with ground-based equipment and avionic components on the aircraft, providing precise guidance to pilots during the critical phases of approach and landing.
- The ILS guiding system helps planes land in low visibility with the help of radio signals and also sometimes high-intensity lighting arrays.
- Among the various categories of ILS, Category 3 (CAT III) is the most significant due to its capability to support landing operations in low visibility conditions, thereby enhancing flight safety and operational efficiency.
- At present, airports like Delhi, Amritsar, Jaipur, Lucknow, and Kolkata among others use CAT IIIB technology in India.
- However, the absence of pilots or the ILS technology can lead to massive delays and cancellations.
- Moreover, a lot of financial and logistics are required to operate the technology which is still a distant dream at many airports around the country.
How does this system work?
- Consisting of two main components—the localizer and the glide slope—the CAT safe system functions by transmitting radio signals that help pilots align their aircraft with the correct runway and maintain the appropriate descent path.
- The localizer ensures lateral alignment, guiding the aircraft along the correct azimuth toward the runway centerline.
- Simultaneously, the glide slope provides vertical guidance, aiding pilots in maintaining the proper descent angle for a safe landing.
- Together, these components create a reliable and accurate navigational reference, allowing pilots to execute precision landings even when external visibility is severely compromised.
- Notably, ILS-equipped runways are equipped with ground-based transmitters positioned at the end of the runway, emitting signals that are received by the aircraft’s onboard ILS receiver.
- As the aircraft approaches the runway, the pilot uses the visual and audible cues provided by the ILS to make real-time adjustments, ensuring that the aircraft remains aligned with the desired glide path.
- In essence, the technology significantly enhances aviation safety and operational reliability by enabling pilots to conduct precise landings even in conditions that would otherwise pose a considerable risk.
NHAI cracks down on multiple FASTags for a single vehicle, launches ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ program (Financial Express)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) announced on Monday (January 15) that FASTags with valid balances but incomplete KYC will be deactivated by banks after January 31, 2024.
What is the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ Program?
- In a bid to enhance the efficiency of the electronic toll collection system and facilitate seamless movement at toll plazas, NHAI has initiated the ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ program, discouraging the use of a single FASTag for multiple vehicles or linking multiple FASTags to a particular vehicle.
- NHAI encourages FASTag users to complete the ‘Know Your Customer’ (KYC) process for their latest FASTag, aligning with RBI guidelines.
- To prevent inconvenience, users must ensure KYC completion for their latest FASTag and discard all previously issued FASTags through their respective banks.
- The initiative aims to deactivate or blacklist previous tags after January 31, 2024.
- Ensuring seamless and comfortable journeys: The ‘One Vehicle, One FASTag’ initiative, coupled with the high penetration rate of FASTag at around 98% and over 8 crore users, is poised to streamline toll operations, ensuring efficient and comfortable journeys on national highways.
About FASTags:
- FASTag serves as an electronic toll collection system in India, administered by the NHAI.
- Utilising Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, it facilitates toll payments directly from the linked prepaid or savings account or directly from the toll owner.
- FASTag utilizes Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, allowing seamless toll payments while the vehicle is in motion.
- Windscreen Affixation: FASTag is affixed on the vehicle's windscreen, providing a hassle-free experience for customers to drive through toll plazas without the need to stop for payments.
- Automatic Deduction: Toll fares are automatically deducted from the linked account of the customer, ensuring a swift and cashless transaction.
- Vehicle Specific: Once affixed to a vehicle, FASTag becomes vehicle-specific, preventing transferability to another vehicle.
- Purchase from NETC Member Banks: FASTag can be conveniently purchased from any of the National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) Member Banks.
- Prepaid Account Recharge: In the case of linking FASTag to a prepaid account, customers need to recharge or top-up the tag based on their usage.
Govt’s ZED scheme for MSMEs hits 1 lakh certification milestone; check scheme’s details (Financial Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Zero Effect, Zero Defect scheme (ZED) by the MSME Ministry, which aims to encourage environmentally sustainable manufacturing practices among MSMEs, has achieved the 1 lakh certification milestone
What is the Zero Effect, Zero Defect (ZED) Scheme?
- Launched in October 2016 and revamped in April 2022, the ZED scheme offers certification for environmentally conscious manufacturing under three certification levels (gold, silver and bronze) classified according to 20 performance-based parameters such as quality management, timely delivery, process control, waste management, etc.
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to 75 per cent of the total cost of certification, with a maximum subsidy ceiling of Rs 50,000 along with up to Rs 2 lakh support for handholding/consultancy to achieve the next certification level.
- For technology upgradation, the scheme offers assistance of up to Rs 3 lakhs for moving towards zero effect solutions/pollution control measures/cleaner technology.
- MSMEs are charged Rs 10,000 for bronze certification, Rs 40,000 for silver certification, and Rs 90,000 for gold certification.
- In December 2023, the MSME Ministry made the ZED scheme free for women-led MSMEs.
- In addition, the government will now make a guaranteed payment of 100 per cent financial support for the certification cost under the scheme.
- The ZED certification is valid for three years and the MSME units are required to re-apply for the certificate as per the validity of the scheme.
- Currently, the scheme is applicable for manufacturing MSMEs only.
- The government hasn’t announced the scheme’s model for services MSMEs yet.
- The scheme is in line with the government’s plan to reduce the country’s CO2 emissions by 1 billion tons by 2030, reduce carbon intensity below 45 per cent by 2030 and finally make way for achieving a Net-Zero emission target by 2070.
- The ZED Certification envisages the promotion of Zero Defect Zero Effect (ZED) practices amongst MSMEs so as to:
- Encourage and enable MSMEs to manufacture quality products using the latest technology, and tools & to constantly upgrade their processes for the achievement of high quality and high productivity with the least effect on the environment.
- Develop an Ecosystem for ZED Manufacturing in MSMEs, to enhance competitiveness and enable exports.
- Promote the adoption of ZED practices and recognise the efforts of successful MSMEs.
- Encourage MSMEs to achieve higher ZED Certification levels through graded incentives.
- Increase public awareness of demanding Zero Defect and Zero Effect products through the MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification.
- Identify areas to improve upon, thereby assisting the Government in policy decisions and investment prioritization.
Painkiller Meftal could cause DRESS syndrome (Financial Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has recently issued a drug safety alert for doctors and patients about the use of the commonly used painkiller mefenamic acid, popularly sold under the brand name Meftal.
Context:
- The Pharma standard body, Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) in its preliminary analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) from the PvPI database revealed that Meftal can lead to Drug Reactions with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome.
- According to doctors, this syndrome causes a diverse array of clinical symptoms, anywhere from 2 to 8 weeks after initiating the offending drug.
What is DRESS syndrome?
- DRESS syndrome (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms) is an adverse reaction term that is currently used to describe a hypersensitivity reaction.
- Experts classify DRESS syndrome as a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- It is a serious drug reaction affecting the skin and other organs, with a mortality rate of up to 10%.
- It manifests when the immune system excessively responds to specific medications, leading to a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- This reaction can manifest with various symptoms across the body, including fever, abnormalities in blood, and inflammation of organs.
What are the symptoms of DRESS syndrome?
- Patients diagnosed with DRESS syndrome typically present with a rash, fever, and eosinophilia but can have a variety of symptoms including liver, lung, or kidney involvement.
- “DRESS syndrome should be suspected if a diffuse rash erupts and is accompanied by fever, facial edema, and enlarged lymph two to six weeks after starting a new high-risk medication.
How to treat DRESS Syndrome?
- The most important step to treat DRESS Syndrome is to stop the medication involved in the reaction, and sometimes, no further treatment is needed.
- Topical steroids can be given to treat the rash and in certain cases, further treatment is needed to protect the organs from damage, such as with steroids, which can be given either intravenously or orally.
- “Treatment with steroids can be needed for weeks or even months, and lab work is monitored carefully during this time.
- The average time to recovery is six to nine weeks.
Sindhudurg Fort (Financial Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is gearing up to showcase its operational prowess in a significant ‘Operational Demonstration’ scheduled for December 4, 2023, at Sindhudurg Fort in Maharashtra.
About Sindhudurg Fort:
- Sindhudurg Fort is a historically significant stronghold situated on an islet in the Arabian Sea, just off the coast of Maharashtra in western India.
- Positioned on Kurte Island near Malvan town in Sindhudurg District within the Konkan region of Maharashtra, this formidable fortress was commissioned and constructed under the reign of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj of the Maratha Empire in 1664.
- The primary objective behind its construction was to counteract the escalating influence of foreign colonizers, including English, Dutch, French, and Portuguese merchants, and to curb the rise of the Siddis of Janjira.
- The Bakhar (a form of historical narrative written in Marathi prose) written by Chitragupta aptly mentions this fort as the most invaluable asset to Shivaji Maharaj.
Key Features:
- The fort spans 48 acres and boasts fortified walls that are 29 feet high and 12 feet thick, extending for a distance of two miles.
- Guarding these walls are 52 bastions equipped with embrasures for cannons.
- Access to the fort is through the Dilli Darwaja, the main gate, uniquely designed to blend seamlessly with the walls and visible only from close quarters.
- The fort is surrounded by several smaller forts, including Padmagad, Rajkot, and Sarjekot.
- An intriguing feature within the fort is a slab bearing the handprint and footprint of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Additionally, a small temple dedicated to the Maratha King is situated within the fort's bounds
Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (Financial Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister announced the launch of two India-led initiatives: the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository and a Social Impact Fund aimed at promoting the development of Social Impact Fund to advance Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in the Global South during the Virtual G20 Leaders’ Summit on 22nd November 2023.
About the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository:
- It was developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It is an extensive resource center that combines knowledge and insights from G20 members and visiting countries.
- Its primary objective is to fill the knowledge gap in the decision-making processes and methodologies necessary for designing, constructing, deploying, and governing Digital Public Infrastructures (DPIs).
- The GDPIR presents information in a standardized format from countries and organizations that have successfully implemented DPIs on a large scale.
- This includes elements such as maturity scales, source codes (where available), and governance frameworks.
- Currently, the GDPIR showcases 54 DPIs from 16 countries.
- The DPIs from India featured in the GDPIR include
- Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), eSanjeevani, Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), DigiLocker, Umang, Co-WIN, Government e-marketplace, API Setu, Diksha, E-Hospital and Poshan Tracker etc.
What about the Social Impact Fund?
- The fund will financially support countries developing DPIs, providing “upstream technical and non-technical assistance”.
- The platform allows other governments, international organisations, and philanthropies to contribute to the fund too.
- India has pledged an initial commitment of $25 million (USD) to the fund.
Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) (Financial Express)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The AIM and NITI Aayog have recently introduced a new accelerator known as Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) aimed at providing support to startups in the circular economy sector in both Australia and India.
About Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE):
- RISE, a collaborative initiative between Australia’s national science agency (CSIRO), and Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), the Government of India’s flagship initiative for fostering innovation and entrepreneurship, is a dedicated accelerator.
- This program is designed to support startups and small to mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India and Australia focusing on circular economy technologies and solutions.
Key Highlights:
- Focus Themes: The RISE Accelerator targets startups in India and Australia engaged in circular economy technologies, specifically in:
- Climate Smart Agriculture
- Clean Energy
- Circular Economy and Waste Management, and
- Climate Smart Mobility.
- Nine-Month Program: Over the course of nine months, the RISE Accelerator aims to assist startups in navigating early steps in a new region, establishing connections with the right partners, customers, and talent, and building credibility to succeed in international markets.
- First Round Focus: In its initial round, the accelerator concentrates on supporting startups and SMEs involved in technologies and solutions related to waste and the circular economy.
- Financial Support: Participating startups have the opportunity to receive up to INR 40,00,000 in non-equity grants.
- Future Rounds: Subsequent rounds of the accelerator will shift focus to climate-smart agriculture, clean energy, and climate-smart mobility.
Bhoomi Rashi Portal is revolutionizing land acquisition for Highway projects – Here’s how (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari revealed in a recent statement to the Rajya Sabha that the Bhoomi Rashi portal is instrumental in expediting the development of highway infrastructure in India.
About the Bhoomi Rashi Portal:
- The acquisition of land was done manually before the year 2018. The data files were moved physically, leading to some limitations. This included delays in issuing notices, errors in land details, etc.
- To overcome the issues, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways came up with a system.
- It is known as “Bhoomi Rashi”.
- The portal came into force on 1st April 2018
- The system is digital and automates the whole land acquisition (LA) process.
- It made and still makes the LA process more transparent and error-free.
- The portal processes the notices at every stage on a real-time basis.
Key Objectives:
- Acceleration of Land Acquisition: The primary goal is to facilitate a quicker and more efficient land acquisition process for National Highways.
- Centralized Processing: Acting as a singular online platform, it consolidates the processing of land acquisition notifications, contributing to the swift development of highway infrastructure projects.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensures transparency and accountability throughout the land acquisition process.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Facilitates the electronic transfer of benefits directly to the accounts of the beneficiaries involved in the land acquisition.
Salient Features:
- Bilingual application with Hindi and English for easy usability
- Preparation of interface for adding basic details of the project, including land acquisition sanction details
- Preparation of interface for Land Acquisition locations. villages
- Preparation of Interface for Competent Authority for Land Acquisition (CALA) details. CALA is a revenue functionary of the State Government appointed for each NH Project.
- Interface for generating land acquisition notification
- Interface for land Details
- Interface for generation of notification: organisational email IDS for all those involved in the process flow to ensure smooth e-office management
- Interface for Objections and processing
- Interface for compensation determination and finalisation
- Interface for land owners and affected parties
- Interface for reports generation
The portal is seamlessly integrated with the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) of the Ministry of Finance, ensuring real-time deposit of compensation into the accounts of affected/interested individuals.
What is Land Acquisition?
- Land acquisition is the governmental process, whether at the state or union level, through which private land is procured for infrastructure development, urbanization, or industrialization.
- In exchange, the government provides appropriate compensation to the landowner based on market value and assumes responsibility for the rehabilitation and resettlement of those affected by the land acquisition.
MSME Ministry launches 3 sub-schemes under RAMP programme; makes ZED scheme free for women (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
MSME Minister Narayan Rane recently launched three sub-schemes under the ministry’s existing RAMP ((Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity) programme.
About the RAMP Programme:
- The Raising & Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) program, supported by the World Bank and inaugurated in 2022, is dedicated to enhancing the performance of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) across India.
Program Objectives:
- Market and Credit Access: Facilitate improved access to markets and credit for MSMEs.
- Institutional Strengthening: Enhance institutional and governance structures at both central and state levels.
- Center-State Collaborations: Foster improved linkages and partnerships between central and state entities.
- Delayed Payment Issues: Address challenges related to delayed payments within the MSME sector.
- Greening of MSMEs: Promote sustainable practices and the adoption of green technologies within MSMEs.
- The National MSME Council has been set up by the Ministry to work as an administrative and functional body of the RAMP Programme.
Sub Schemes under RAMP:
- MSME GIFT Scheme: Aims to support MSMEs in adopting green technology through interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance.
- MSE SPICE Scheme: Focuses on promoting circular economy projects, with credit subsidy mechanisms, aligning with the MSME sector's goal of achieving zero emissions by 2070.
- MSE ODR Scheme: A pioneering initiative leveraging modern IT tools and Artificial Intelligence to address delayed payment incidents for Micro and Small Enterprises.
- Implementing Agencies for Sub Schemes:
- MSME GIFT and MSME SPICE Schemes: Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- MSE ODR Scheme: National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI)
- These sub-schemes, under the RAMP umbrella, signify a comprehensive effort to fortify and propel the growth of MSMEs, incorporating technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Hard Currency (Financial Express)

- 21 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI) said in a statement that Conditions are not ripe to make INR a hard currency.
What is Hard Currency?
- Usually, developed countries issue hard currency, and this currency is easier to trade and receive funds from other countries or investors from other nations.
Key characteristics of hard currencies:
- Hard currency means a stable currency, and its value does not fluctuate much in the international markets.
- It makes hard money currency easily tradable.
- It is issued by a sound economy. Developed countries issue hard currency and it is accepted by all nations across the world.
- It is highly liquid and several countries prefer to accept hard currency instead of local currency as it has lesser fluctuations and can be easily converted to local currency.
- Hard currency is universally accepted and international investors have a sense of faith in hard currency for trading.
- Countries across the globe consider hard currency as a foreign currency reserve, further adding to its value.
- As hard currency is easily convertible and stable, it is widely used in international exchanges.
- The value of the hard currency does not change much in response to global events.
- When domestic currencies struggle, people start holding on to hard currencies to protect their wealth.
Examples of hard currencies:
- US dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese yen (JPY)
- British pound (GBP)
- Swiss franc (CHF) etc.
INS Sumedha (Financial Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In a strategic move as part of the Indian Navy’s mission-based deployment to West Africa and the Atlantic, INS Sumedha conducted a port call at Walvis Bay, Namibia recently.
About INS Sumedha:
- INS Sumedha is a Saryu-class, Naval Offshore Patrol Vessel (NOPV) of the Indian Navy.
- It is the third ship of the class to be commissioned and was built by Goa Shipyard Limited in India.
- The ship was commissioned in March 2014.
- INS Sumedha is designed to undertake a variety of missions, including fleet support operations, coastal and offshore patrolling, ocean surveillance, and monitoring of sea lines of communication and offshore assets.
- The ship is also capable of carrying out humanitarian assistance and disaster relief (HADR) operations.
- INS Sumedha has been deployed on a number of operational missions, including:
- Operation Kaveri, the evacuation of Indian citizens from Sudan in April 2023.
- The ship has also participated in a number of international exercises, including Exercise Bright Star 2023 in Egypt.
About Walvis Bay:
- Walvis Bay is a city on the coast of Namibia, in the Erongo Region.
- It is the second-largest city in Namibia, after Windhoek, and is the capital of the Erongo Region.
- It is a major port city, and is the main port for Namibia.
- The port is home to a number of shipping companies and is a major export center for Namibian goods, such as fish, minerals, and diamonds.
- Originally a German enclave during the colonial era, Walvis Bay became a vital part of Namibia after gaining independence in 1990.
- The official language of the city is English, but Afrikaans, German, and Portuguese are also spoken.
INDUS-X Initiative (Financial Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On the eve of the India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, the inaugural INDUS-X Investors Meet was held in New Delhi.
What is the INDUS X Initiative?
- The INDUS-X initiative, also known as the India-U.S. Defense Acceleration Ecosystem, was launched in June 2023 during the State Visit of the Prime Minister of India to the United States.
- Its primary objective is to expand the strategic technology partnership and defense industrial cooperation between the governments, businesses, and academic institutions of India and the United States.
- INDUS-X is envisioned as a defense innovation bridge, encompassing Joint Challenges, a Joint Innovation Fund, academia engagement, industry-startup connections, private sector investment in defense projects, mentorship by experts, and niche technology projects, among other initiatives.
- This collaborative effort holds the promise of ushering in a new era of defense innovation and cooperation between India and the United States.
About INDUS X Investors Meet:
- The first-ever INDUS-X Investors Event brought all the stakeholders including Startups, Investors, Incubators, and Industry from both sides under one roof to discuss the collaborative agendas and opportunities thereon.
- The event also had focused panel discussions with a select audience of 50 thought leaders, including start-ups, investors, government officials, and business leaders from the defence industry.
- The panel discussed ‘Investment Opportunities in the Defence Sector’, elaborating upon establishing a sustainable commercial foundation for defence collaboration and co-production.
- The INDUS-X Educational Series (Gurukul) was also launched during the event.
- The Gurukul initiative is aimed at helping innovators and startups to navigate the defence eco-system of the US and India.
Surat Diamond Bourse to create 150,000 jobs! Modi is confident ‘world’s largest office building’ will be a boon for artisans and businessmen (Financial Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the inauguration ceremony of the Surat diamond bourse in Gujarat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi revealed plans for the creation of 150,000 new jobs, emphasising the bourse’s role as a “one-stop shop” for artisans and businessmen.
About Surat Diamond Bourse:
- Established in February 2015 by the former Chief Minister of Gujarat, Smt. Anandiben Patel, the Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is a prominent diamond trade centre situated in DREAM (Diamond Research and Mercantile) city, Surat, Gujarat.
- Recognized as the "diamond city" due to its diamond industry, which processes 85 to 90% of the world's rough diamonds, the SDB stands as the world's largest diamond trading hub, spanning an expansive floor space of 660,000 square meters and surpassing The Pentagon as the largest office building globally.
- Themed around the 'panch tatva,' symbolizing the five elements of nature – air, water, fire, earth, and sky, the SDB is designed with thematic landscaping.
- As a global centre for both rough and polished diamond and jewellery trading, it unifies various facets of the diamond industry, including cutting, polishing, and trading activities, within its vast expanse.
- The Bourse features a state-of-the-art 'Customs Clearance House' for Import-Export, a Jewelry mall for retail jewellery business, and facilities for International Banking and Safe Vaults.
Importance of the SDB Project:
- The Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is set to accommodate a diverse range of diamond-related enterprises, encompassing the sale of both rough and polished diamonds, diamond manufacturing machinery, diamond planning software, diamond certificate firms, lab-grown diamonds, and more.
- Anticipated to be a major contributor to employment, the SDB is poised to generate substantial job opportunities.
- With an expected direct employment impact on over 1.5 lakh individuals across various roles within the diamond industry, it aims to bolster economic activity and livelihoods.
- Acknowledging its commitment to environmental responsibility, the complex has earned pre-certification as a green building by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC).
- This recognition is a testament to the SDB's implementation of eco-friendly and sustainable practices in its operations.
What is DREAM City?
- DREAM City, short for Diamond Research and Mercantile City, is an emerging business district located in Surat.
- Encompassing 810 hectares (2,000 acres) of land near Khajod, it follows the model of the Gujarat International Finance Tec (GIFT) City and Dholera Smart City near Ahmedabad.
- Envisioned as a comprehensive urban development, DREAM City is slated to feature office spaces, residential areas, and associated amenities.
- The project is under the purview of a special-purpose vehicle established by the Government of Gujarat.
- With an anticipated opening in 2030, DREAM City is poised to become Gujarat's third smart city, aligning with the state's commitment to fostering modern and sustainable urban environments.
State Bank of India (SBI) has raised its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) by up to 10 basis points for selected tenures (Financial Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
State Bank of India (SBI) on Friday hiked its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) on various tenures by 5-10 basis points (bps), a move that could make consumer loans, such as auto or home loans, more expensive for borrowers.
What is the Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR)?
- The MCLR, or Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate, represents the minimum lending rate below which a bank is not authorized to lend.
- This mechanism aims to facilitate the calculation of the minimum interest rate applicable to various types of loans offered by banks.
- Introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on April 1, 2016, the MCLR methodology serves to improve the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission and enhance transparency in the interest rate-setting process, replacing the earlier base rate structure established in July 2010.
- Calculation of MCLR: MCLR is internally determined by the bank, considering the remaining period for the loan repayment. This rate is closely tied to actual deposit rates and is calculated based on four key components:
- The marginal cost of funds
- Negative carry-on account of the cash reserve ratio
- Operating costs
- Tenor premium
- Under the MCLR framework, banks have the flexibility to offer loans at fixed or floating interest rates across all categories.
- The actual lending rates for various loan categories and tenors are determined by adding the components of spread to the MCLR.
- Consequently, the bank is restricted from lending at a rate lower than the MCLR for a specific maturity concerning all loans linked to that benchmark.
- Banks review and publish MCLRs for different maturities on a monthly basis.
- Certain loan rates, such as those for fixed-rate loans with tenors exceeding three years and special loan schemes offered by the government, remain unaffected by MCLR fluctuations.
Difference Between MCLR and Base Rate:
MCLR stands as a more evolved iteration of the base rate, presenting several distinctions between the two:
- Origin and Regulation: The base rate is the RBI-set minimum interest rate, and financial institutions cannot lend below this rate.
- MCLR, on the other hand, is an internal benchmarking system used by financial institutions, allowing them to set lending rates based on a predetermined spread.
- Cost Calculation: The base rate relies on the average cost of funds.
- MCLR is rooted in the marginal or incremental cost of money, providing a more dynamic reflection of the current cost scenario.
- Impact of RBI's Repo Rate: The base rate remains unaffected by changes in the RBI's repo rate.
- MCLR, however, is directly influenced by revisions in the repo rate, adjusting accordingly.
- Consideration Factors: The base rate typically considers the minimum rate of return or profit margin.
- In contrast, when determining the MCLR, factors such as the tenor premium are taken into account, resulting in a more nuanced rate-setting process.
Pralay Ballistic Missiles (Financial Express)
- 19 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Defense Ministry has recently approved the purchase of a regiment of Pralay tactical ballistic missiles for the Indian Army.
Facts About:
- Pralay is a quasi-ballistic surface-to-surface missile.
- It can strike targets at distances ranging from 150 to 500 kilometers.
- The missile can carry between 350 and 700 kilograms of high-grade explosives.
- Pralay is developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It uses a solid propellant rocket motor and incorporates advanced technologies.
- The missile features a state-of-the-art navigation and integrated avionics system.
- Pralay can alter its trajectory during mid-flight.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (Financial Express)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Presently, the Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) Samudra Prahari is on an international mission covering ASEAN countries.
Facts About:
- Samudra Prahari is an Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) specifically designed for pollution control purposes.
Key Highlights:
- It holds the distinction of being Southeast Asia's pioneering pollution control vessel.
- Equipped with cutting-edge Pollution Response and Control equipment for effectively managing oil spills within the Exclusive Economic Zone.
- Features tanks and inflatable barges for the storage of oil spills.
- Capable of seamless oil recovery operations with a substantial storage capacity of 500 KL.
- Designed to accommodate and operate a twin-engine Advanced Light Helicopter, along with the capability to handle and embark Chetak helicopters.
- Notable features encompass an integrated platform management system, power management system, high-powered external firefighting system, and an indigenous gun mount with firefighting capabilities.
- The vessel possesses unmanned machinery operation capabilities for enhanced efficiency.
Scrub Typhus and Leptospirosisa (Financial Express)
- 18 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Scrub Typhus claims 5 lives, while Leptospirosis spreads in Odisha; health authorities remain vigilant.
Facts About:
- Scrub typhus, caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi bacteria, is prevalent in Asia-Pacific regions, including India.
- It spreads via chigger mites in rural areas. Symptoms include high fever, headaches, muscle pain, and a distinctive rash, often leading to swollen lymph nodes.
- If untreated, it can cause severe complications affecting vital organs.
- Diagnosis relies on clinical symptoms and blood tests.
- Timely antibiotics like doxycycline or azithromycin are effective treatments.
- Preventive measures include protective clothing, insect repellent, and avoiding dense vegetation.
- Recent cases in Odisha, have prompted heightened health alerts and emphasize the importance of early detection and treatment, alongside public awareness efforts.
About Leptospirosis:
- Leptospirosis caused by the bacterium Leptospira interrogans, is a potentially fatal zoonotic disease and is common in warm, humid regions worldwide.
- Humans can contract it from infected animal urine, particularly rodents, cattle, pigs, and dogs.
- Symptoms include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Leptospirosis may occur in two phases, with the second phase being more severe and potentially causing kidney or liver failure, or meningitis.
- Antibiotics are effective in treating the disease, particularly when administered early.
- It's prevalent in both urban and rural areas, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures and public health awareness.
