RBI tweaks norms related to the Regulatory Sandbox scheme

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank recently tweaked guidelines for the Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme under which participating entities will have to comply with digital personal data protection norms.
About the Regulatory Sandbox Scheme:
- The Regulatory Sandbox scheme denotes a controlled regulatory environment where new products or services can undergo live testing.
- Functioning as a "safe space" for businesses, regulators may offer certain relaxations for testing purposes within this environment.
- It serves as a structured platform for regulators to engage with the industry and develop regulations that foster innovation and enable the delivery of cost-effective financial products.
- The scheme holds potential as a tool for creating dynamic regulatory environments that adapt to emerging technologies through evidence-based learning.
Objectives:
- Offering innovative technology-led entities an opportunity for limited-scale testing of new products or services, potentially involving regulatory relaxations before broader implementation.
- At its core, the Regulatory Sandbox is a formal program allowing market participants to test new products, services, or business models in live settings, under appropriate oversight.
- Proposed financial services under the scheme should leverage new or emerging technology to address consumer needs or offer benefits.
- The overarching goal is to promote responsible innovation in financial services, enhance efficiency, and deliver consumer benefits.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the 'Enabling Framework for Regulatory Sandbox' in August 2019 after extensive consultations.
- The updated framework mandates compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act of 2023 for sandbox entities.
- Furthermore, the timeline for various stages of the Regulatory Sandbox process has been extended from seven to nine months.
- Fintech companies, including startups, banks, financial institutions, and other entities providing support to financial services businesses, are among the target applicants for entry into the Regulatory Sandbox.
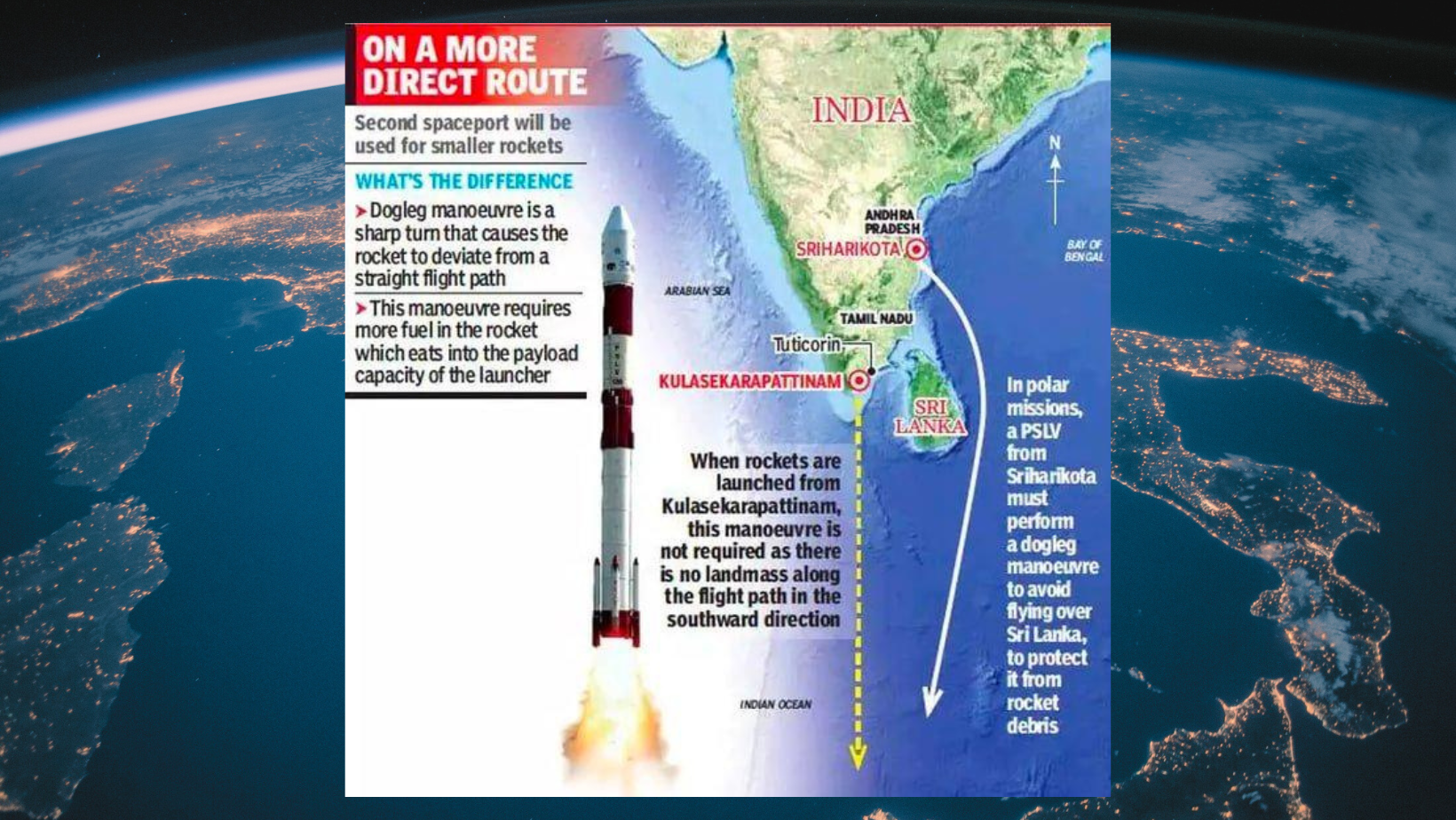
PM Modi lays stone for India’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam
- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the country’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam in Tuticorin district recently.
About Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport:
- The Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport is a forthcoming space launch facility located in Kulasekarapattinam, a coastal village near the temple town of Tiruchendur in Thoothukudi district, southern Tamil Nadu.
- It will become the second operational spaceport in India after the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, established in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, in 1971, and will feature two launch pads.
- The primary focus of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport will be to facilitate the commercial launch of Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs).
- Spanning 2,350 acres, the spaceport will comprise 35 essential facilities, including a launch pad, rocket integration facilities, ground range and checkout facilities, and a mobile launch structure (MLS) equipped with checkout computers.
- With the capability to launch up to 24 satellites annually using a mobile launch structure, it offers a strategic advantage by enabling direct southward launches over the Indian Ocean, thus conserving fuel for small rocket launches.
- This stands in contrast to the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, where launching into a polar orbit necessitates additional fuel due to the curved trajectory required to avoid crossing landmasses, particularly Sri Lanka.
- The estimated cost of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport project is Rs. 986 crore.
About the Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs):
- The SSLV, or Small Satellite Launch Vehicle, is a three-stage launch vehicle characterized by three solid propulsion stages and a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) serving as a terminal stage.
- Measuring 2 meters in diameter and 34 meters in length, the SSLV boasts a lift-off weight of 120 tonnes.
- Designed for versatility, the SSLV can effectively launch a 500kg satellite into a 500 km planar orbit.
- Notable features of the SSLV include its cost-effectiveness, rapid turnaround time, ability to accommodate multiple satellites, feasibility for launch-on-demand, and minimal infrastructure requirements.
New waste management technology could improve life in rural India

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new waste management technology that allows pyrolysis at a community level could help rural Indians cut indoor air pollution, improve soil health, and generate clean power, a recent study has claimed.
What is BioTRIG?
- BioTRIG represents a novel waste management technology centered around pyrolysis, poised to mitigate indoor air pollution, enhance soil quality, and foster clean energy generation across rural India.
- This community-oriented pyrolysis system is ingeniously crafted to utilize locally generated waste, offering a sustainable solution tailored to village environments.
- The innovative process yields three valuable by-products: bio-oil, syngas, and biochar fertilizer, presenting multifaceted benefits for rural communities, from cleaner energy sources to enhanced agricultural productivity.
- Moreover, the self-sustaining nature of BioTRIG enables the utilization of syngas and bio-oil to fuel subsequent pyrolysis cycles, with excess electricity catering to local energy needs, fostering self-reliance and sustainability.
- By harnessing the clean-burning properties of bio-oil and the soil-enriching qualities of biochar, BioTRIG empowers rural households to transition away from traditional cooking fuels while concurrently enhancing agricultural resilience and carbon sequestration efforts.
Significance:
- Computer simulations indicate that the BioTRIG system holds the potential to significantly mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from communities, potentially reducing them by nearly 350 kg of CO2-eq per capita per year.
- This projection underscores a noteworthy positive influence on both climate emissions and public health.
- The BioTRIG technology could mark a paradigm shift in waste management practices and energy generation methods within rural India, promising transformative benefits for communities.
What is Pyrolysis?
- Pyrolysis is a transformative chemical recycling method that disassembles residual organic matter into its fundamental molecular components.
- This innovative process entails confining the waste within an oxygen-deprived enclosure and subjecting it to temperatures exceeding 400 degrees Celsius.
Education Minister launches SWAYAM Plus platform

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Dharmendra Pradhan recently launched the ‘SWAYAM Plus’ platform to offer courses developed collaboratively with the industry.
About the SWAYAM Plus Platform:
- SWAYAM is a Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platform providing educational opportunities by bringing the best teaching and learning resources to everyone.
- Operated by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-Madras, this platform aims to extend educational opportunities to both traditional students and working professionals, aligning with the provisions of the NEP 2020 for flexible entry and exit points in education.
- By enabling individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, SWAYAM Plus empowers them to enhance their skills and career prospects, thus contributing to India's knowledge economy.
Objectives and features:
- SWAYAM Plus primarily focuses on achieving the following:
- Building an ecosystem for all stakeholders in professional and career development, including learners, course providers, industry, academia, and strategic partners;
- Enabling a mechanism that provides credit recognition for high?quality certifications and courses offered by the best industry and academia partners;
- Reaching a large learner base by catering to learning across the country, with a focus on reaching learners from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas and Offering employment-focused courses, based on learner needs – across chosen disciplines with options to learn through resources in vernacular languages.
- Enhanced employability: SWAYAM Plus empowers individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, enhancing skills and career prospects.
- Industry partnerships: Courses are tailored to industry requirements in collaboration with industry leaders.
Key features:
- Multilingual content, AI guidance, credit recognition, and pathways to employment are prominent features.
Implementation and reach:
- SWAYAM Plus aims to offer high-quality courses with credit recognition, reaching learners nationwide, especially from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas.
Value-added services:
- Value-added services like mentorship, scholarships, and job placements will be provided, creating a digital ecosystem for upskilling and reskilling at all education levels.
- SWAYAM, launched in 2017, had enrolled 72 lakh learners by 2023.
- Now, in line with the NEP 2020, SWAYAM Plus will incorporate courses tailored to industry requirements, developed in collaboration with industry leaders like L&T, Microsoft, and CISCO.
European Parliament adopts nature restoration law

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Parliament recently adopted the first European Union (EU) law to restore degraded ecosystems across the 27-nation political and economic bloc.
About the Nature Restoration Law:
- The Nature Restoration Law is hailed as a significant stride toward rejuvenating Europe’s natural habitats, with a staggering 81% currently classified as being in poor health.
- It sets a pioneering example for global emulation, emphasizing the criticality of safeguarding and revitalizing our natural environment for the welfare of forthcoming generations.
Objectives:
- This legislation aims to rejuvenate ecosystems, habitats, and species across the European Union's (EU) terrestrial and marine domains, fostering the enduring recuperation of diverse and robust nature.
- Additionally, it endeavors to contribute to the EU's climate mitigation and adaptation objectives while fulfilling international commitments.
- These directives aspire to encompass a minimum of 20% of the EU's land and marine territories by 2030, with the ultimate goal of restoring all ecosystems in need by 2050.
Specific Targets:
- Wetlands, forests, grasslands, rivers, lakes, heath & scrub, rocky habitats, and dunes: The objective is to enhance and restore biodiverse habitats on a large scale, fostering the recovery of species populations through habitat improvement and expansion.
- Pollinating Insects: The target is to reverse the decline of pollinator populations by 2030, aiming for a positive trajectory in pollinator numbers.
- Forest Ecosystems: The aim is to promote an upward trend in standing and fallen deadwood, varied aged forests, forest connectivity, common forest bird populations, and organic carbon reserves.
- Urban Ecosystems: The objective is to achieve zero net loss of green urban spaces by 2030 and expand the total area covered by green urban spaces by 2040 and 2050.
- Agricultural Ecosystems: The goal is to bolster grassland butterfly and farmland bird populations, increase organic carbon reserves in cropland mineral soils, and augment the proportion of agricultural land featuring diverse landscape characteristics.
About the European Union (EU):
- The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 European countries that collaborate on various issues, including trade, security, and environmental protection.
- Founded after World War II to promote peace and economic cooperation, the EU has evolved into a complex organization with its own institutions, laws, and currency (the euro).
- It operates on the principles of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, with the European Commission, European Parliament, and European Council among its key decision-making bodies.
- The EU's single market allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people across member states, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
- Additionally, the EU plays a prominent role in global affairs, advocating for multilateralism, sustainable development, and climate action.
Scientists are closer to creating a reference genome for Indians; 10,000 samples sequenced already

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Government’s ambitious Genome India initiative achieved a significant milestone Tuesday as researchers completed sequencing 10,000 healthy genomes from different regions of the country, representing 99 distinct populations.
News Summary:
- The Department of Biotechnology has announced the successful completion of India's '10,000 genome' project, aimed at establishing a comprehensive reference database of whole-genome sequences within the country.
- This milestone marks the creation of a detailed genetic map of India, offering significant potential for both clinicians and researchers in diverse fields.
- With India emerging as the largest genetic laboratory globally, this rich dataset is poised to catalyze advancements in the country's biology sector.
- Notably, India's bio-economy has witnessed remarkable growth, expanding from $10 billion in 2014 to over $130 billion in 2024, signaling a promising trajectory for future development.
- The entirety of the genomic dataset will be housed at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC), serving as a valuable digital resource for research purposes.
- Established in 2022, the IBDC represents India's sole indigenous databank, eliminating the need for Indian researchers to rely on foreign servers for hosting biological datasets.
What is Genome Sequencing?
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the exact order of the building blocks (nucleotides) that make up an organism's entire DNA, or genome.
- It's like reading the complete instruction manual for life, containing the information needed to create and maintain an organism.
Applications of Genome Sequencing:
- Healthcare: Doctors can diagnose diseases with greater accuracy, personalize treatments, and uncover the causes of rare conditions.
- Agriculture: Scientists can engineer crops with desired traits like disease resistance and improved yield, while breeders select animals with specific characteristics.
- Forensics: DNA profiling aids criminal investigations and paternity testing.
- Conservation: Studying the genetic diversity of endangered species helps with conservation efforts while analyzing invasive species' origins aids in controlling their spread.
What is the Human Genome Project (HGP)?
- Initiated in 1990, the Human Genome Project aimed to elucidate the entire sequence of the human genome.
- In 2023, the project culminated in the release of the latest version of the complete human genome, boasting a mere 0.3% error margin.
- Enabled by the Human Genome Project, whole-genome sequencing facilitates the examination of an individual's genome to uncover deviations from the average human genome.
- These deviations, or mutations, offer insights into an individual's susceptibility to diseases, their responsiveness to specific stimuli, and other pertinent genetic attributes.
About the Genome India Project:
- The Genome India Project stands as a pioneering initiative approved by the Department of Biotechnology, geared towards gene mapping.
- This project sets out with the ambitious objective of compiling an exhaustive repository documenting genetic diversity across the Indian populace.
- At its core, the endeavor seeks to conduct genome sequencing for more than 10,000 individuals spanning various geographic and ethnic backgrounds within India, ultimately laying the groundwork for a standardized reference genome specific to the Indian demographic.
Significance of the Genome India Project:
- Unveiling Unique Genetic Variants: The Genome India Project holds the key to unraveling genetic variants exclusive to India’s diverse population, enabling tailored drug formulations and therapeutic interventions.
- For instance, mutations like MYBPC3, linked to premature cardiac arrest and prevalent in 4.5% of Indians, underscore the necessity of region-specific genetic insights, contrasting with global rarity.
- Similarly, the discovery of the LAMB3 mutation, causing a severe skin disorder and impacting nearly 4% of the population around Madurai, emphasizes the localized genetic complexities absent in global databases.
- Comprehensive Database for India's Population: With a colossal population exceeding 1.3 billion, India boasts a mosaic of over 4,600 distinct population groups, many practicing endogamy.
- This vast demographic diversity underscores the need for a comprehensive genetic database tailored to India's populace, crucial for identifying and addressing disease-causing mutations prevalent within specific groups.
- Unlike extrapolating findings from global datasets, the Genome India Project provides precise genetic insights essential for Indian-centric healthcare strategies.
African leaders demand financial systems reform; launch ‘Africa Club’ at 37th African Union Summit
- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, during the 37th African Union Summit, member countries initiated the formation of the Africa Club.
What is the Africa Club?
- The Africa Club is an alliance of African Multilateral Financial Institutions, established at the African Union summit, designed to enhance Africa's influence in the global financial system.
- The initiative aims to align its operations with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the African Union's Agenda 2063, fostering innovative financial instruments, facilitating debt management discussions, and promoting collaborative efforts to address the specific needs of African nations.
- Its membership comprises key institutions such as the African Export-Import Bank, Trade and Development Bank, Africa Finance Corporation, African Reinsurance Corporation, African Trade and Investment Development Insurance, Shelter Afrique Development Bank, and ZEP – RE (PTA Reinsurance Co).
About the African Union:
- The African Union is a continental organization consisting of 55 member states across the African continent, established on May 26, 2001, in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
- The AU's objectives include promoting peace, security, and stability on the continent, accelerating political and socioeconomic integration, defending the sovereignty and territorial integrity of member states, and advancing sustainable development.
- It serves as a platform for African countries to coordinate their efforts in various fields, including governance, human rights, economic development, infrastructure, health, education, and culture.
- The AU's structures include the Assembly of Heads of State and Government, the Executive Council, the Pan-African Parliament, the African Court of Justice and Human Rights, and various specialized technical committees and organs.
- Through its initiatives and programs, the AU works towards realizing the vision of an integrated, prosperous, and peaceful Africa, driven by its citizens and representing a dynamic force in the global arena.
Google unveils Genie AI which can create video games from text and image prompts

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Google DeepMind unveiled Genie, a novel model capable of creating interactive video games based solely on textual or image prompts.
What is Genie AI?
- Genie is a foundation world model that is trained on videos sourced from the Internet.
- The model can “generate an endless variety of playable (action-controllable) worlds from synthetic images, photographs, and even sketches.”
- It is the first generative interactive environment that has been trained in an unsupervised manner from unlabelled internet videos.
- When it comes to size, Genie stands at 11B parameters and consists of a spatiotemporal video tokenizer, an autoregressive dynamics model, and a simple and scalable latent action model.
- These technical specifications let Genie act in generated environments on a frame-by-frame basis even in the absence of training, labels, or any other domain-specific requirements.
What does Genie do?
- Genie is a new kind of generative AI that enables anyone – even children – to dream up and step into generated worlds similar to human-designed simulated environments.
- It can be prompted to generate a diverse set of interactive and controllable environments although it is trained on video-only data.
- It is a breakthrough as it makes playable environments from a single image prompt.
- According to Google DeepMind, Genie can be prompted with images it has never seen.
- This includes real-world photographs, and sketches, allowing people to interact with their imagined virtual worlds.
- When it comes to training, they focus more on videos of 2D platformer games and robotics.
- Genie is trained on a general method, allowing it to function on any type of domain, and it is scalable to even larger Internet datasets.
Why is it Important?
- The standout aspect of Genie is its ability to learn and reproduce controls for in-game characters exclusively from internet videos.
- This is noteworthy because internet videos do not have labels about the action that is performed in the video, or even which part of the image should be controlled.
- It allows you to create an entirely new interactive environment from a single image.
- This opens up many possibilities, especially new ways to create and step into virtual worlds.
- With Genie, anyone will be able to create their own entirely imagined virtual worlds.
First Pey Jal Survekshan Awards to be conferred by President on 5th March

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
President Droupadi Murmu will present the first Pey Jal Survekshan Awards on the 5th of next month in New Delhi.
About the Pey Jal Survekshan Awards:
- The Pey Jal Survekshan Awards feature a prestigious lineup of 130 accolades, spotlighting outstanding contributions in the realm of water management.
- The awards span various categories, including the Pey Jal Gold, Silver, and Bronze City Awards, with each tier symbolizing excellence in specific population segments (ranging from 1 to 10 Lakh, 10 to 40 Lakh, and more than 40 Lakh).
- In addition to these, commendations are also extended for commendable efforts in areas such as Best Water Body, Sustainability Champion, Reuse Champion, Water Quality, City Saturation, and the prestigious AMRUT 2.0 Rotating Trophy of the Year.
Comprehensive Evaluation Parameters:
- Embracing a multifaceted approach, the evaluation criteria encompass a wide array of parameters, including accessibility, coverage, water quality maintenance at treatment facilities and household levels, sustainability practices ensuring the health of water bodies, adoption of SCADA/flowmeters, and efficient reuse of treated wastewater.
- Cities are meticulously graded using a star rating system, ranging from 5 stars to No star, meticulously reflecting their performance across these pivotal benchmarks.
- Ensuring Water Purity and Transparency: The Pey Jal Survekshan reinforces the assurance of clean water through rigorous independent NABL lab testing at both the source and consumer ends.
- Leveraging advanced technological tools such as GIS-enabled web portals, geo-tagging, and infrastructure mapping, the survey captures precise and transparent data, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Enhancing Urban Governance and Citizen Engagement: Anticipated to serve as a catalyst for urban local body (ULB) decision-making processes, the outcomes of the Pey Jal Survekshan are poised to elevate service delivery standards while fostering active citizen participation.
- By nurturing a sense of ownership and disseminating knowledge on water conservation and optimal utilization, the awards endeavor to empower communities toward sustainable water management practices.
What is the AMRUT Mitra initiative?
- The AMRUT Mitra initiative is geared towards active engagement of women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in urban water management, recognizing women as pivotal stakeholders and highlighting their vital role in household water governance.
- Tasked with executing AMRUT 2.0 projects, the Mitras will undertake various responsibilities, including billing, collection, leak detection, plumbing, water quality monitoring, and infrastructure upkeep.
- At its core, AMRUT Mitra seeks to cultivate a sense of ownership among women, fostering inclusivity and diversity in traditionally male-dominated domains while ensuring equitable access to safe drinking water and addressing gender disparities.
- Expected outcomes encompass the empowerment of women SHGs, socio-economic upliftment, alignment with AMRUT 2.0 objectives, heightened community awareness, and the establishment of a blueprint for future endeavors.
An initiative to improve nutrition in adolescent girls using Ayurveda under Mission Utkarsh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The project for anemia control under Mission Utkarsh will be a joint public health initiative by the Ministries of Ayush and Women and Child Development and will be launched in five aspirational districts first as a pilot project.
About Mission Utkarsh:
- Mission Utkarsh was launched in January 2022, a new initiative of “rapid improvement of selected Districts” to improve.
- Under this mission, 15 central ministries and departments are working to bring select key performance indicators in bottom districts to the state and national average.
- Over 94,000 adolescent girls between the age group of 14-18 years registered under Poshan Tracker at approximately 10,000 Anganwadi Centres will benefit in 12 12-month periods of the program.
- The coordinating agency for the project will be the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS).
- Classical Ayurveda medicines (Drakshavaleha and Punarnavadi mandoor) for better nutrition to improve the health of the anemic adolescent girls will be provided for a period of 3 months.
- These five districts are Dhubri in Assam, Bastar in Chhattisgarh, Paschimi Singhbhum in Jharkhand, Gadchiroli in Maharashtra, and Dholpur in Rajasthan.
- Building research capacity through training, conferences, workshops, and seminars with the active participation of researchers of integrative healthcare would be enhanced.
What is Anaemia?
- According to WHO, anemia occurs when there is a lower-than-normal count of red blood cells or a reduced hemoglobin concentration within them, crucial for oxygen transport throughout the body.
Symptoms
- This condition leads to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath due to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common nutritional cause, although deficiencies in folate, vitamins B12 and A can also contribute.
- Chronic diseases like kidney or liver disease, cancer, and genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia further exacerbate anemia.
Significance:
- Anaemia has significant implications, particularly affecting vulnerable populations like pregnant women and children under five, impacting reproductive health and reducing work capacity, thus posing an economic burden.
Anaemia in India:
- India faces a substantial anemia burden, with recent surveys indicating alarming prevalence rates among women aged 15-49 and children aged six months to five years, highlighting the urgent need for public health interventions.
RBI Allows Lending And Borrowing Govt Securities

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to deepen the bond market, the Reserve Bank of India on Wednesday issued guidelines for lending and borrowing in government securities.
What are Government Securities?
- Government securities, also known as G-Secs, refer to the debt instruments issued by the government to finance its fiscal requirements.
- These securities are backed by the government’s guarantee of repayment and are considered risk-free investments.
- They are an integral part of the fixed-income market and are traded on the government securities market.
- Government securities serve as a means for the government to raise funds from the public to meet its expenditure needs, bridge budget deficits, and fund developmental projects.
- Investors who purchase these securities lend money to the government in return for regular interest payments and the principal amount at maturity.
- These securities come in mainly two categories:
- Short-Term: Often known as “Treasury Bills,” these have initial maturities of less than a year.
- Long-Term: Typically referred to as Government Bonds or Dated Securities, these have an original maturity of one year or more.
- In India, the Central Government issues both treasury bills and bonds or dated securities while the State Governments issue only bonds or dated securities, which are called State Development Loans (SDLs).
Treasury Bills (Short-Term G-Secs)
- Treasury Bills, commonly known as T-Bills, are short-term government securities with a maturity period of less than one year.
- They are issued at a discount to their face value and are highly liquid instruments.
- T-Bills serve as a mechanism for the government to efficiently manage its short-term funding requirements.
Dated Securities (Long-Term G-Secs)
- Dated Securities are long-term government securities with a fixed maturity period, typically 5 to 40 years.
- They pay regular interest to investors, known as coupon payments, and return the principal amount at maturity.
- Dated Securities are vital for financing long-term projects and meeting government borrowing needs.
Centre approves interest-free loans to FCV tobacco growers in Andhra Pradesh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Central Government has approved a 10 thousand rupees interest-free Loan to the Flue Cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco growers in Andhra Pradesh.
What is Flue Cured Tobacco?
- There are three types of tobacco curing methods traditionally used: Air-Cured, Fire-Cured, and Flue-Cured.
- Each of the different curing methods results in a tobacco product that is distinguishable by both its nicotine content and its aroma.
Flue-Cured:
- Flue-curing tobacco is raised with a low level of nitrogen and harvested by priming method.
- Harvested leaves are strung on sticks which are then stacked into to flue curing barn.
- The barn is artificially heated.
- Green leaves should be loaded in the upper half of the barn and the lighter ones in the lower half.
- The three steps are Yellowing, Fixing the color, and Drying.
Grading:
- After curing, leaves are graded by sorting leaves into uniform lots according to body, color, and degree of blemish or damage.
- The most important elements of quality in FCV tobacco are color, texture, size, blemish, strength, even burning with white ash, and agreeable flavor.
Why is Tobacco Cured?
- To create smoking tobacco, the tobacco leaves need to be cured, or dried out.
- The wet, green tobacco leaves of a tobacco plant initially contain too much moisture to catch fire.
- They also have a higher chlorophyll content.
- By releasing a certain amount of chlorophyll from the leaves during the drying-out process, the natural tannins come out giving the smoked tobacco its flavor and scent.
- The curing process makes the leaf dry enough to smoke while increasing the sugar and natural tannins found in each leaf to create the sweetly aromatic and mild taste tobacco is known for.
Key Characteristics of Flue-cured Tobacco:
-
- Produces primarily cigarette tobacco
- Contains a high sugar content
- Contains medium to high levels of nicotine
- Rich in natural tannins which creates its distinct mild and slightly sweet flavor and aroma
- FCV tobacco is mainly produced in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka in India.
India gets desi Garbhini GA2 for evaluation of foetal growth
- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Specifically tailored to address the unique characteristics of foetal growth within the Indian population, India has finally got its locally made ‘Garbhini-GA2’, a groundbreaking Artificial Intelligence model.
What is Garbhini-GA2?
- The Garbhini-GA2 model, developed as part of the DBT India initiative (GARBH-Ini) program by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad, addresses the challenge of accurately estimating foetal age (gestational age, GA) in the Indian population, particularly in the second and third trimesters.
- Unlike existing formulas designed for Western populations, Garbhini-GA2 accounts for variations in foetal growth specific to the Indian context, significantly reducing estimation errors by nearly threefold.
- This innovative model is crucial for ensuring precise prenatal care and determining accurate delivery dates, thereby enhancing maternal and foetal health outcomes.
- Garbhini-GA2 marks a milestone as the first late-trimester GA estimation model validated using Indian population data, offering a tailored approach to foetal age determination that is essential for effective maternal healthcare."
About Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI):
- THSTI, an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Science and Technology, was founded in 2009 in Faridabad, Haryana, with a core commitment to advancing research beyond mere discovery.
- By fostering collaboration among diverse teams in medicine, science, and technology, THSTI leverages translational expertise to drive clinical research and innovation.
- In addition to its core mission, THSTI plays a pivotal role in fostering social innovation and entrepreneurial endeavors, particularly in the domain of maternal and child healthcare.
. First-of-its-kind Micro Turbojet Engine made in India
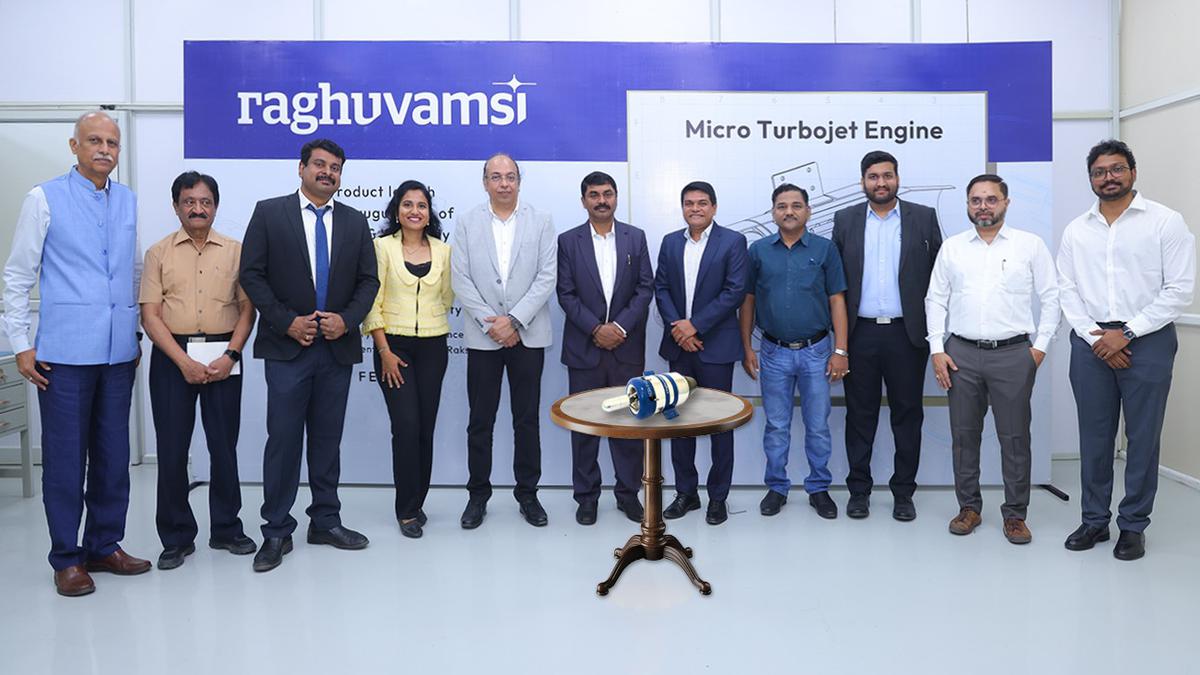

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A micro turbojet engine designed and developed indigenously by Hyderabad-based firm Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools with the support of the IIT Hyderabad has been unveiled.
Key Highlights of the Micro Turbojet Engine “INDRA RV25: 240N”:
- It is an indigenous micro turbojet engine made in India.
- Its primary focus is on serving unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones.
- Beyond UAVs, the engine exhibits versatile applications in air taxis, jetpacks, auxiliary power units, range extenders, and potential use in power generation for the future.
- Indigenous design and development: Engineered entirely in India by the Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools (RVMT) team of skilled engineers & supported by IIT, Hyderabad.
- A great demonstration of the potential of Industry-Academia partnership
- Self-reliance and autonomy: By reducing reliance on imported technologies, components, and expertise, the Micro Turbojet Engine contributes to India’s goal of achieving self-sufficiency in critical sectors, bolstering national security and economic resilience
- Empowering local manufacturing: The launch of the indigenous Micro Turbojet Engine not only drives technological innovation but also stimulates the growth of the domestic aerospace and defense manufacturing ecosystem, creating jobs and fostering economic growth.
What Is a Turbojet Engine and How Does It Work?
- Turbojet engines are jet engines that, like other jet engines, generate propulsion by discharging or expelling heated air.
- They feature a combustion chamber in which they burn fuel and air.
- As they burn this mixture, turbojet engines will discharge heated air.
- It can find turbojet engines in commercial airplanes, civilian airplanes, and military aircraft.
How Turbojet Engines Work?
- The process begins by drawing air through an intake.
- Turbojet engines feature an air intake, which is typically located near the front of the engine.
- Air will flow into this intake, at which point it will be redirected to the engine’s interior.
- After entering the engine, the air will become compressed.
- Turbojet engines feature a set of rotating blades. Known as compressors, these rotating blades are designed to compress the air.
- The next step in the process is combustion which involves the burning of fuel and air.
- Turbojet engines will inject fuel into the same combustion chamber where the compressed air is located.
- A spark will then ignite the mixture of fuel and compressed air, thereby generating hot, high-pressure exhaust gas.
- The exhaust gas generated by the combustion is expelled out the rear of the turbojet engine.
- This rearward expulsion allows for forward propulsion.
- As the exhaust gas is discharged out the rear of the turbojet engine, the airplane will be propelled forward.
PM Modi Inaugurates 'Sudarshan Setu', India's Longest Cable-Stayed Bridge
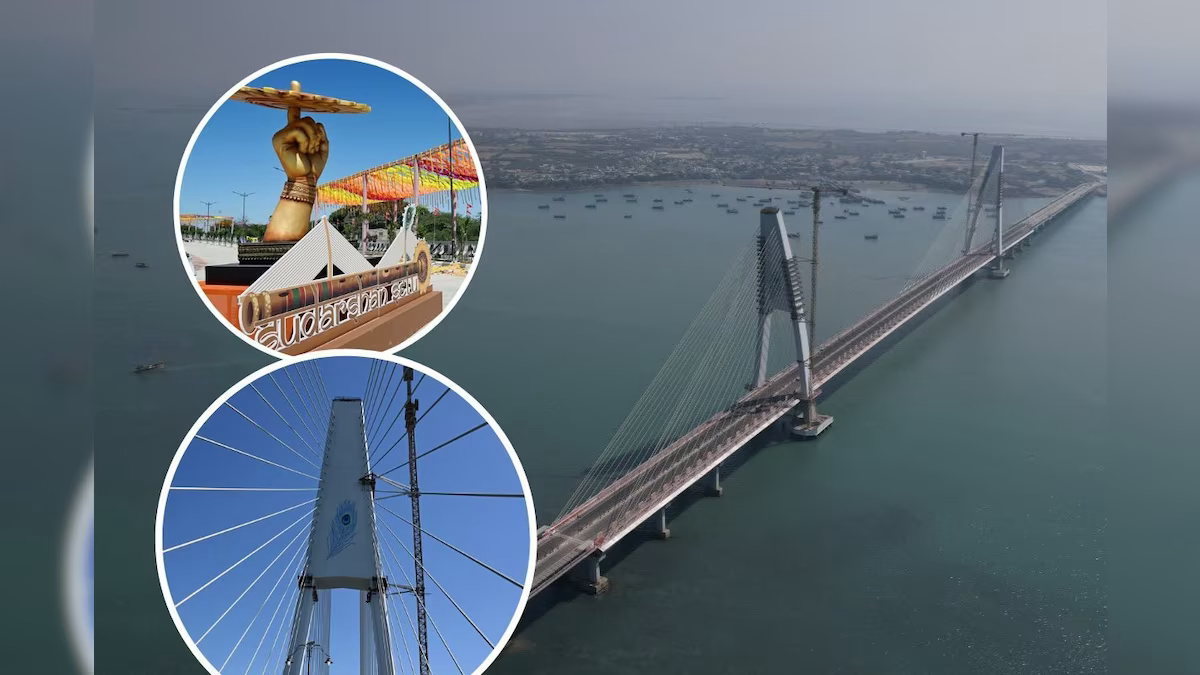

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently inaugurated the Sudarshan Setu, a four-lane cable-stayed bridge connecting Okha to Beyt Dwarka island in Gujarat.
About the Sudarshan Setu:
- 'Sudarshan Setu' is the country's longest cable-stayed bridge 2.32 km on the Arabian Sea connecting Beyt Dwarka island to mainland Okha in Gujarat's Devbhumi Dwarka district.
- It boasts a unique design, featuring a footpath adorned with verses from the Bhagavad Gita and images of Lord Krishna on both sides.
- It also has solar panels installed on the upper portions of the footpath, generating one megawatt of electricity.
- The 2.32 km bridge, including 900 metres of a central double-span cable-stayed portion and a 2.45 km long approach road, has been constructed at a cost of Rs 979 crore.
About Beyt Dwarka:
- Bet/Beyt (pronounced ‘Bait’ Dwarka also known as Shankhodara, is an island located near the shores of Okha which is situated around 30 km from Dwarka, in the Gulf of Kutch.
- It said that Lord Krishna resided here while Dwarka was his constitutional seat.
History:
- Bet Dwarka derived its name from the word ‘bet’ which translates to ‘gift’ and is believed that Lord Krishna received it from his friend Sudama.
- In the ancient epic, Mahabharata, Bet Dwarka is known by the name of ‘Antardvipa’ to which people of the Yadava clan needed to travel by boat.
- Explorations and excavations carried out under the sea have revealed the presence of settlements whose age can be traced back to the era of the Harappan civilisation and that of the Mauryan rule.
- In the later years, the region was under the administration of the Gaekwad clan of the state of Baroda.
- During the revolt of 1857, Vaghers attacked the region and captured it, but had to concede defeat in two years and return the region back to the Gaekwads.
Ladakh: Centre agrees to examine demand for statehood, inclusion in Sixth Schedule of Constitution

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Centre has agreed to examine whether the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution can be implemented in Ladakh.
What is the Sixth Schedule?
- The Sixth Schedule under Article 244 provides for the formation of autonomous administrative divisions — Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) — that have some legislative, judicial, and administrative autonomy within a state.
- ADCs have up to 30 members with a term of 5 years and can make laws, rules and regulations with regard to land, forest, water, agriculture, village councils, health, sanitation, village- and town-level policing, inheritance, marriage and divorce, social customs and mining, etc.
- The Bodoland Territorial Council in Assam is an exception with more than 40 members and the right to make laws on 39 issues.
- The Sixth Schedule applies to the Northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram (three Councils each), and Tripura (one Council).
Why does Ladakh want to be part of the Sixth Schedule?
- There was much enthusiasm initially, mostly in Leh, after the August 5, 2019 decisions that created two new Union Territories.
- The Buddhist-dominated Leh district had long demanded UT status because it felt neglected by the erstwhile state government, which was dominated by politicians from Kashmir and Jammu.
- This development has sparked concerns among locals regarding potential challenges related to identity preservation, resource allocation, and administrative oversight.
- Also, the changed domicile policy in Jammu and Kashmir has raised fears in the region about its own land, employment, demography, and cultural identity.
- The UT has two Hill councils in Leh and Kargil, but neither is under the Sixth Schedule.
- Their powers are limited to the collection of some local taxes such as parking fees and allotment and use of land vested by the Centre.
- The Sixth Schedule empowers the Governor of the State to designate specific areas as administrative units within the Autonomous Districts and Autonomous Regions.
Can Ladakh be included in the Sixth Schedule?
- In September 2019, the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes recommended the inclusion of Ladakh under the Sixth Schedule, noting that the new UT was predominantly tribal (more than 97%), people from other parts of the country had been restricted from purchasing or acquiring land there, and its distinct cultural heritage needed preservation.
- Notably, no region outside the Northeast has been included in the Sixth Schedule.
- In fact, even in Manipur, which has predominantly tribal populations in some places, the autonomous councils are not included in the Sixth Schedule.
- Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh, which are totally tribal, are also not in the Sixth Schedule.
- “Ladakh’s inclusion in the Sixth Schedule would be difficult.
- The Constitution is very clear, the Sixth Schedule is for the Northeast.
- For tribal areas in the rest of the country, there is the Fifth Schedule.
- However, it remains the prerogative of the government — it can, if it so decides, bring a Bill to amend the Constitution for this purpose.
IGNCA’s ‘language atlas’ to shine a light on India’s linguistic diversity

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts, an autonomous body under the Union Culture Ministry, proposes to conduct a linguistic survey across the country to create a ‘Language Atlas’ of India.
About the Language Atlas of India:
- The Language Atlas of India traces its roots back to the seminal Linguistic Survey of India (LSI) conducted by Sir George Abraham Grierson, which was first published in 1928.
- Since its inception, the linguistic landscape of India has undergone significant transformations, necessitating a comprehensive reevaluation.
- The proposed linguistic survey aims to capture the myriad languages and dialects prevalent across the country, acknowledging the dynamic nature of linguistic diversity.
- It seeks to document not only the languages and dialects actively spoken but also those that have faced extinction or are teetering on the brink of disappearance.
- Engaging a wide array of stakeholders, including the Ministries of Culture, Education, Tribal Affairs, Home, Social Justice and Empowerment, and Development of the North East Region, the survey endeavours to be inclusive and representative of diverse language communities.
- Phased Approach: The Detailed Project Report (DPR) advocates for a structured approach, commencing with state-wise data collection followed by regional assessments.
- Furthermore, the proposal advocates for the preservation of linguistic heritage through the digital archiving of audio recordings encompassing the linguistic richness of the nation.
- Significance: Languages serve as conduits of communication and repositories of cultural heritage, encapsulating local wisdom, traditions, narratives, and medicinal knowledge.
- For instance, many indigenous communities possess indigenous knowledge of medicinal plants and herbs, which are transmitted through generations via their native languages, emphasizing the intrinsic link between language and cultural preservation.
About the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA):
- Established in 1987 as an autonomous institution under the aegis of the Ministry of Culture, the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA) serves as a pivotal hub for research, academic endeavours, and dissemination within the realm of the arts.
- Governance Structure: Operating with a Board of Trustees, the IGNCA convenes regularly to provide overarching guidance and direction for its multifaceted activities.
- Under the stewardship of a Chairman, the Executive Committee, composed of select Trustees, oversees the operational facets of the centre.
- Integral Role in Project Mausam: Embracing its role as a research unit, the IGNCA actively contributes to Project Mausam, a collaborative initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Culture in partnership with the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), New Delhi.
- Project Mausam endeavours to explore the intricate tapestry of cultural routes and maritime landscapes that historically linked diverse regions along the Indian Ocean littoral, fostering connections between coastal centres and their hinterlands.
- Engagement in the Vedic Heritage Portal: In alignment with its commitment to cultural heritage preservation, the IGNCA embarks on a project dedicated to designing and developing a Vedic Heritage Portal, under the auspices of the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- This portal serves as a digital platform aimed at elucidating the profound messages encapsulated within the Vedas, contributing to the dissemination of ancient wisdom and knowledge.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
Analysis of Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23 Report

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The per capita monthly household expenditure more than doubled in 2022-23 as compared to 2011-12, according to the latest study by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO).
Context:
- As per the 2022-23 report, rising inequality between the top and bottom of the pyramid.
- Urban and rural households register higher expenditure, spending less on food items.
- New methodology and questionnaire used in Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2022-23.
About the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO):
- The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) comes under the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation headed by a Director General.
- It is responsible for the conduct of large-scale sample surveys in diverse fields on an All-India basis.
- Primarily data are collected through nationwide household surveys on various socio-economic subjects, Annual Survey of Industries (ASI), etc.
- Besides these surveys, NSSO collects data on rural and urban prices and plays a significant role in the improvement of crop statistics through supervision of the area enumeration and crop estimation surveys of the State agencies.
- It also maintains a frame of urban area units for use in sample surveys in urban areas.
The NSSO has four Divisions:
- Survey Design and Research Division (SDRD): This Division, located at Kolkata, is responsible for the technical planning of surveys, formulation of concepts and definitions, sampling design, designing of inquiry schedules, drawing up of tabulation plans, and analysis and presentation of survey results.
- Field Operations Division (FOD): The Division, with its headquarters at Delhi/Faridabad, is responsible for the collection of primary data for the surveys undertaken by NSS.
- Data Processing Division (DPD): The Division, with its headquarters at Kolkata is responsible for sample selection, software development, processing, validation and tabulation of the data collected through surveys.
- Survey Coordination Division (SCD): This Division, located in New Delhi, coordinates all the activities of different Divisions of NSS.
- It also brings out the bi-annual journal of NSS, titled “Sarvekshana”, and organizes National Seminars on the results of various Socio-economic surveys undertaken by NSS.
Key Insights From the 2022-23 Survey:
- Evolution of Food Expenditure: Over the past two decades, there has been a notable shift in spending patterns on food in India.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2022-23, both urban and rural households witnessed a gradual decline in the share of expenditure allocated to food.
- This period marks the first instance where food expenditure has dropped to below 50% in rural India and below 40% in urban India.
- Changing Dietary Preferences: The composition of food consumption has also undergone significant changes.
- Cereals and pulses have seen a reduction in their share of overall food consumption expenditure, while spending on milk has surged, surpassing that on cereals and pulses combined.
- In a noteworthy shift, the average Indian now spends more on fruits and vegetables than on food grains.
- Furthermore, expenditure on animal proteins like eggs, fish, and meat has shown a growing trend, indicating a preference for animal-based proteins over plant-based ones.
- Rise in Processed Food Consumption: There has been an observed increase in the share of expenditure allocated to processed foods, beverages, and purchased cooked meals.
- This trend aligns with the Engel Curve hypothesis, suggesting that as incomes rise, households allocate a smaller proportion of their spending to food and tend to prefer superior items over inferior ones.
- Closing Rural-Urban Consumption Gap: Consumption growth in rural areas has outpaced that in urban areas, leading to a narrowing of the rural-urban consumption divide.
- If this trend continues, it could potentially lead to parity in urban and rural incomes and consumption patterns in the future.
- Challenges in Inflation Calculation: The findings of the latest Household Consumption Expenditure (HCE) Survey underscore the need to review the inflation basket.
- The current Consumer Price Index (CPI)-based inflation calculation, established in 2012, may not accurately reflect contemporary consumption patterns.
- For instance, the disparity between the weightage assigned to cereals in the CPI basket and actual expenditure on cereals by rural households highlights the need for recalibration.
- Insights on Poverty Reduction: According to NITI Aayog CEO B V R Subrahmanyam, the latest survey indicates a reduction in poverty to five per cent nationwide.
- Both rural and urban areas are witnessing increased prosperity, as evidenced by rising per capita monthly expenditure.
- Demand for Legal Guarantee to MSP: While there is a demand for a legal guarantee to Minimum Support Price (MSP) for 23 crops, including food grains and sugarcane, the survey data suggests that the growth in the farm sector is being primarily driven by livestock, fisheries, and horticulture crops.
- This poses a pertinent question regarding the promotion of production: should the focus be on crops outside the MSP purview, such as milk, fish, poultry products, fruits, and vegetables, given their growing consumption trends?
BharatGPT Unveils Hanooman, a New Suite of Indic Generative AI Models

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the BharatGPT group, led by IIT Bombay along with seven other elite Indian engineering institutes announced that it would launch its first ChatGPT-like service next month.
What is Hanooman?
- Hanooman is a series of large language models (LLMs) that can respond in 11 Indian languages like Hindi, Tamil, and Marathi, with plans to expand to more than 20 languages.
- It is unveiled by Seetha Mahalaxmi Healthcare (SML) in partnership with the IIT Bombay-led BharatGPT ecosystem.
- The BharatGPT group, which is backed by Reliance Industries.
- Hanooman has been designed to work in four fields, including health care, governance, financial services, and education.
- According to BharatGPT, the series isn’t just a chatbot but It is a multimodal AI tool, which can generate text, speech, videos and more in multiple Indian languages.
- One of the first customised versions is VizzhyGPT, an AI model fine-tuned for healthcare using reams of medical data.
- The size of these AI models ranges from 1.5 billion to a whopping 40 billion parameters.
Are There Any Other Indian Language Models?
- Apart from BharatGPT, a host of different startups like Sarvam and Krutrim, backed by prominent VC investors such as Lightspeed Venture Partners and billionaire Vinod Khosla’s fund, are also building AI models customised for India
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
- Large language models use deep learning techniques to process large amounts of text.
- They work by processing vast amounts of text, understanding the structure and meaning, and learning from it.
- LLMs are ‘trained’ to identify meanings and relationships between words.
- The greater the amount of training data a model is fed, the smarter it gets at understanding and producing text.
- The training data is usually large datasets, such as Wikipedia, OpenWebText, and the Common Crawl Corpus.
- These contain large amounts of text data, which the models use to understand and generate natural language.
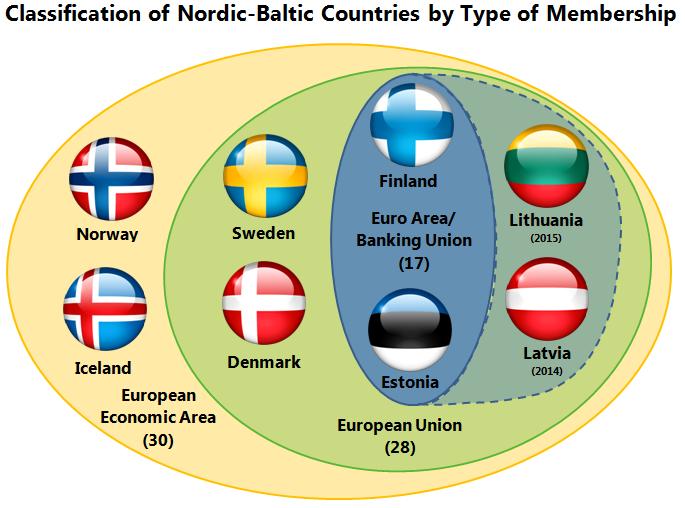
The NB8 visit to India focuses on cooperation and trust
- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar hosted the India-Nordic-Baltic meeting on the sidelines of the ongoing Raisina Dialogue 2024 recently.
What are the Nordic-Baltic Countries?
- The Nordic-Baltic countries, also known as the NB8, are a group of Northern European countries that share historical, cultural, and geopolitical ties.
- The group includes
- Nordic countries of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, and
- Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- These countries collaborate on various regional issues, such as security, economy, environment, and culture, and often work together within international organisations and forums.
- The term "Nordic-Baltic" highlights the close relationship and cooperation between these neighbouring states in the Baltic Sea region.
India's Relations with NB8 Countries:
- India's collaboration with NB8 nations is broadening, exemplified by initiatives like the India-Denmark Green Strategic Partnership, the India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy, and cooperation on sustainability and ICT with Finland, including the 'LeadIT' (Leadership for Industry Transition) initiative with Sweden.
- Cooperation extends across various sectors, including innovation, green transition, maritime affairs, healthcare, intellectual property rights, emerging technologies, space exploration, and artificial intelligence.
- Trade and investment between the NB8 region and India are on a steady rise, reflecting deepening economic ties.
- Moreover, the security dynamics of the Nordic-Baltic region and the Indo-Pacific are intertwined, underlining the interconnectedness of regional security challenges.
Significance of NB8:
- The NB8 nations embody advanced economies characterised by their outward orientation, emphasis on innovation, complementarity, and seamless integration into the European Common Market, the world's largest single market area.
- The Baltic states, in particular, stand out as pioneers in IT, digitization, cyber technology, and green innovations, showcasing their leadership in these critical domains.
- Moreover, all NB8 members share a steadfast commitment to democracy and human rights, serving as advocates for an international order grounded in principles of multilateralism and adherence to international law.
NB8 Proposals for India:
- In light of the Ukraine conflict and its ripple effects on global food and energy security, supply chains, macro-financial stability, inflation, and growth, the NB8 seeks to collaborate with India in the following ways:
- Recognizing Shared Challenges: In an increasingly interconnected world, challenges such as the Ukraine conflict, global health crises, climate-related events, and geopolitical tensions affect us all.
- Acknowledging these shared challenges underscores the necessity for collaborative efforts to address them effectively.
- Embracing a Positive Agenda: There is an urgent imperative to pivot towards a more positive agenda for global cooperation.
- Leveraging our mutual commitment to the multilateral system, the NB8 proposes to enhance dialogue and cooperation on issues that are paramount to India's priorities and those of other global partners.
PM Modi unveils of Sant Ravidas statue in Varanasi on 647th birth anniversary

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently said that the present government is taking forward the teachings and ideals of Sant Ravidas while following the mantra of ‘Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas, Sabka Vishwas aur Sabka Prayas’.
Who is Guru Ravidas?
- Guru Ravidass (also Ravidas, Rohidas and Ruhidas in eastern India) was a North Indian Guru mystic of the bhakti movement who was active in the 15th century CE.
- Venerated in the region of Uttar Pradesh as well as the Indian state of Maharashtra, his devotional songs and verses made a lasting impact upon the bhakti movement.
- He is often given the honorific Guru.
- He was a socio-religious reformer, a thinker, a theosophist, a humanist, a poet, a traveller, a pacifist and a spiritual figure before whom even head-priests of Benaras lay prostrate to pay homage.
- His birthday comes every year at Puran Mashi in the month of Magh.
- His mother’s name was Mata Kalsi and his father’s name was Baba Santokh Dass.
- Guru Ravidass was born into a humble family which was considered untouchable as per the social order prevailing at that time in Hindu society.
- He spearheaded the fight against man-made discrimination based on caste, colour or creed and preached the lofty ideas of socialism, secularism, equality and fraternity.
- He taught the lessons of universal brotherhood, tolerance, and the message of loving your neighbour, which got more importance in today’s world.
- Guru Ravidass fulfilled Guru Nanak Dev’s request by donating old manuscripts, which contained a collection of Guru Ravidass’s verses and poems.
- The earliest collection of these poems is available in Sri Guru Granth Sahib.
- It was compiled by Guru Arjan Dev, the fifth Guru of the Sikhs.
- There are 41 verses of Guru Ravidass in the Sikh Holy Book, Guru Granth Sahib.
- Meera Bai, a revered figure in Hindu spiritualism, is said to have considered Guru Ravidas as her spiritual Guru.
- It is said that Guru Ravidass disappeared from the world, leaving behind only his footprints.
- Some believe that Guru Ravidass lived in Banaras during his last days, dying a natural death at the age of 126 years.
Govt amends electricity rules to speed up new connections, promote EVs and solar PV systems
- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the government amended the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules 2020, allowing consumers to now obtain separate electricity connections for charging their electric vehicles, and reducing the time period for obtaining a new electricity connection.
Context:
- The Government of India has recently approved the amendments to the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020.
- According to the Union Minister for Power and New & Renewable Energy, Shri R. K. Singh, these amendments aim to expedite the process of obtaining new electricity connections.
- Encompassing various facets including billing, grievance redressal, compensation, and timeframes for new connections, these rules are designed to streamline consumer experiences.
- Moreover, they extend support to prosumers engaged in renewable energy generation.
- The amendments, as highlighted by the Minister, are poised to enhance consumer empowerment, fostering a more consumer-centric electricity ecosystem.
Major Amendments to the Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020:
- Streamlining Rooftop Solar Installation: Amendments exempt the requirement for technical feasibility studies for rooftop solar systems up to 10 kW capacity.
- For systems exceeding 10 kW, the timeframe for feasibility studies has been condensed from twenty to fifteen days, with automatic approval if deadlines are missed.
- Commissioning timelines for distribution licensees have been shortened from thirty to fifteen days.
- Dedicated Connections for Electric Vehicle Charging: Consumers can now secure separate electricity connections for charging Electric Vehicles (EVs), aligning with national emission reduction targets and Net Zero aspirations by 2070.
- Accelerated Connection Processes: New electricity connection timelines have been slashed from seven to three days in metropolitan areas, from fifteen to seven days in other municipal areas, and from thirty to fifteen days in rural regions.
- Exceptions apply in rural hilly terrains, maintaining the existing thirty-day period.
- Enhanced Consumer Rights in Residential Complexes: Residents in cooperative housing societies and residential colonies gain the option of individual or single-point connections, decided through transparent ballots conducted by Distribution Companies.
- Tariff parity is ensured between single-point and individual connections.
- Prompt Meter Installation for Complaints: Distribution licensees are mandated to install additional metres within five days of receiving complaints to verify consumption for a minimum of three months, enhancing consumer confidence and billing accuracy.
First moon-landing by private company
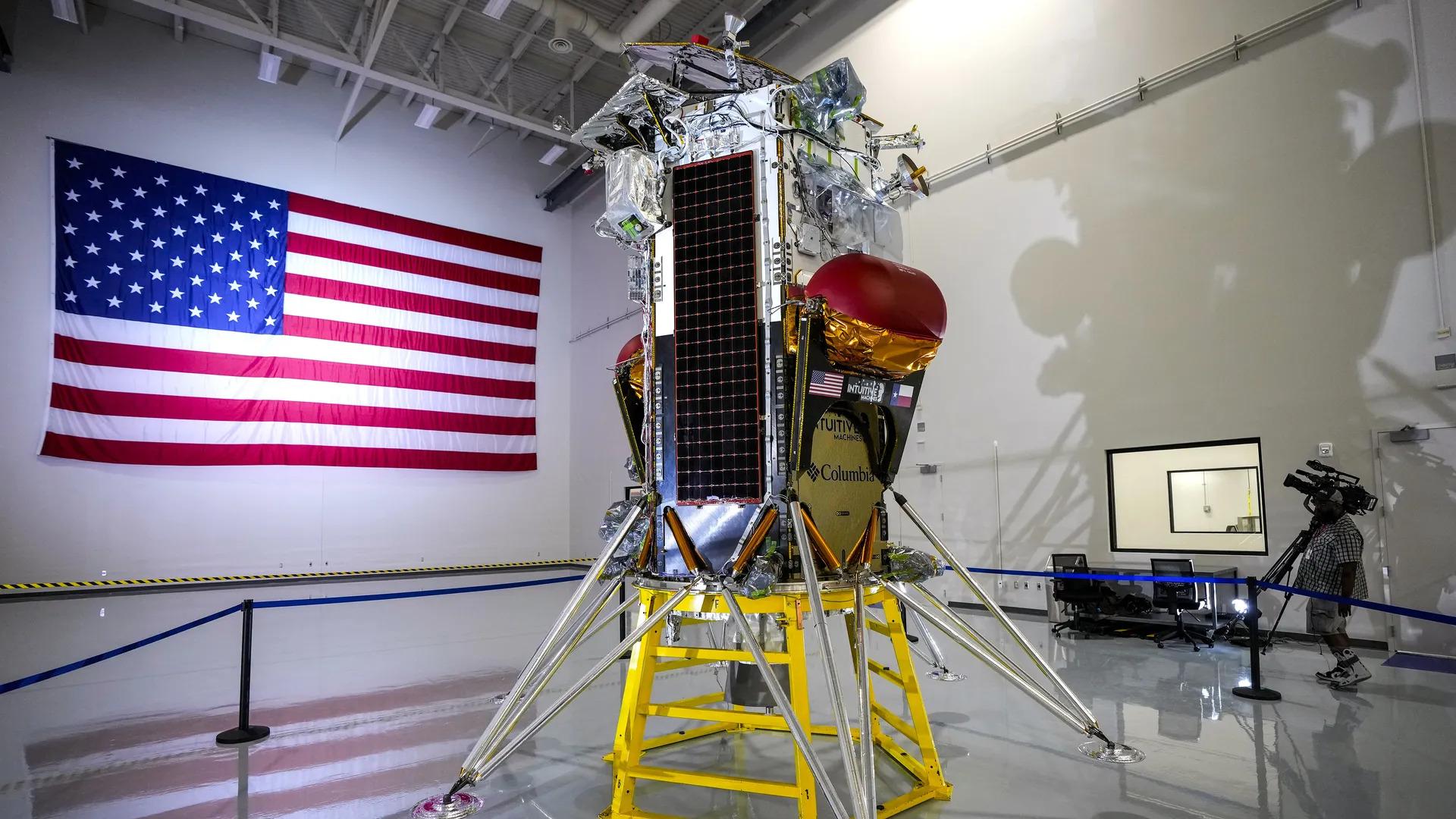

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fifty-two years after the last successful Apollo mission, a US-made spacecraft landed on the Moon recently which also marks the arrival of private space companies on the lunar surface.
What is Odysseus Lunar Exploration?
- Odysseus is a spacecraft built by Intuitive Machines, embarked on its journey from Earth aboard a Falcon 9 rocket by SpaceX recently.
- Intuitive Machines, headquartered in Houston, USA, boasts a decade-long legacy in space exploration endeavours.
- Loaded with six NASA payloads, Odysseus set its course for the Moon.
- Its lander module, Nova-C, achieved the milestone of landing in the Moon's south pole region, following Chandrayaan-3's similar feat last year.
- This marks the third successful moon-landing event in under a year, alongside Chandrayaan-3 and Japan's SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon).
Mission Objectives:
- The primary aim of the lunar lander is to assess the environmental conditions at the Moon's south pole.
- This assessment holds significant importance as NASA gears up for a crewed mission in September 2026 with Artemis III.
- Before sending astronauts to this area, NASA seeks to gather crucial data, including insights into water presence and accessibility, to inform mission planning.
Funding:
- Under the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, NASA allocated $118 million to Intuitive Machines for this mission.
- CLPS has engaged at least 14 private companies to ferry NASA payloads to the Moon, fostering a collaborative environment aimed at nurturing the private space industry's capabilities in lunar exploration technology and science.
The Significance of Odysseus:
- Advancing Long-Term Lunar Presence: Odysseus' successful landing heralds a transformative phase in lunar exploration, aiming to establish infrastructure and a technological ecosystem capable of sustaining extended human presence.
- Diverging from Past Lunar Missions: In contrast to the moon landings of the 1960s and 1970s spearheaded by the US and the Soviet Union, Odysseus' mission focuses on leveraging lunar resources for sustained exploration.
- While historic moon landings were remarkable feats, technological limitations of the time hindered the immediate utilisation of lunar resources such as mining.
- Supporting US Commitment to Moon Exploration via Artemis Program: Odysseus' touchdown aligns with the US commitment to rekindle lunar exploration through the ambitious Artemis program.
- This endeavour transcends mere lunar landing missions, aiming to establish essential infrastructure and a thriving lunar economy conducive to comprehensive exploration.
- Unlocking Lunar Potential as a Gateway to Deep Space: By laying the groundwork for lunar infrastructure and economic activity, missions like Odysseus pave the way for leveraging the Moon as a springboard for deeper space exploration, offering nations unprecedented opportunities for cosmic discovery.
Kiru Hydropower Corruption Case: CBI Searches J&K Ex-Governor Satya Pal Malik’s Premises

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The CBI conducted searches at the premises of former Jammu and Kashmir governor Satya Pal Malik and 29 other locations recently in connection with alleged corruption in the Rs 2,200-crore Kiru Hydropower project.
What are the Corruption Allegations Surrounding the Kiru Hydel Project?
- During his tenure as the governor of Jammu and Kashmir from August 23, 2018, to October 30, 2019, Satya Pal Malik claimed that he was offered a Rs 300-crore bribe to approve two files, one of which pertained to the project.
- In 2022, the J&K government requested a CBI investigation into alleged misconduct, previously highlighted by Satya Pal Malik, in the awarding of two government contracts.
- Concerns have been raised regarding the award of civil works, particularly to Patel Engineering Ltd, a prominent infrastructure and construction company established in 1949.
- The CBI has initiated action against the former CVPPPL chairman, MD, and Directors, as well as Patel Engineering.
- According to the FIR, an inquiry by the J&K Anti-Corruption Bureau and the Power Department had been conducted.
- The FIR alleges non-compliance with e-tendering guidelines in the awarding of civil works for the project.
- Additionally, accusations of substandard work and failure to employ local youth have been levelled against the hydel project.
What is the Kiru Hydel Power Project?
- The 624MW Kiru hydroelectric project is being developed as a run-of-river scheme in the Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir, a union territory in India.
- Location of the Kiru project: The Kiru hydropower project is being built along the Chenab River near the villages of Patharnakki and Kiru, approximately 42 km from Kishtwar.
- It will be located between the Kirthai II hydroelectric project to its upstream and the Kwar hydroelectric project to its downstream.
- The project is being developed by the Chenab Valley Power Projects (CVPPPL) joint venture (JV) between:
- National Hydroelectric Power (NHPC, 49%)
- Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development (JKSPDC, 49%) and
- The Power Trading Corporation (PTC, 2%)
- The Ministry of Environment Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) awarded environmental clearance for the hydroelectric project in 2016 while the foundation stone was laid in February 2019.
- The project is being constructed at an estimated cost of Rs 4,287 crore and is expected to start commercial operations in July 2025.
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the investment in the project in March 2019.
- Apart from helping address the energy demand across northern India and the state’s rural areas, it could aid small-scale and cottage industries.
Advantages of the Kiru Hydroelectric Power Project:
- This project aims to alleviate the energy shortage in Northern India while also enhancing the transportation, education, healthcare, and road infrastructure in the area.
- By bringing electricity to rural communities, the project will lessen the reliance of residents on alternative energy sources.
- The heightened power availability will foster the growth of small-scale and cottage industries, generating employment opportunities and revenue for the local populace.
What is a Run-of-river Project?
- Run-of-river hydropower is a facility that channels flowing water from a river through a canal or penstock to spin a turbine.
- Typically a run-of-river project will have little or no storage facility.
- Run-of-river provides a continuous supply of electricity (base load), with some flexibility of operation for daily fluctuations in demand through water flow that is regulated by the facility.
Race to the global eradication of Guinea worm disease nears the finish line
- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world is on the brink of a public health triumph as it closes in on eradicating Guinea worm disease. There were more than 3.5 million cases of this disease in the 1980s, but according to the WHO, they dwindled to 14 cases in 2021, 13 in 2022, and just six in 2023.
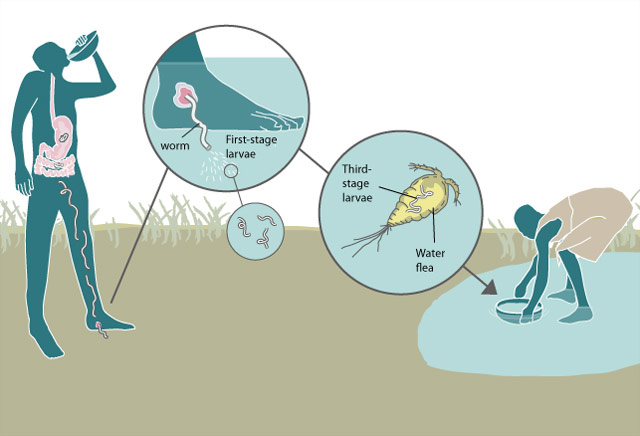
What is Guinea Worm Disease?
- Dracunculiasis is also called guinea worm disease (GWD).
- It is an infection caused by a parasite called Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm).
- This parasite is an organism that survives by deriving nutrients and feeding off another organism.
- GWD spreads through drinking contaminated water.
- It is presently eradicated in most parts of the world but is still seen in remote parts of Africa and some remote rural areas in the world where there is no access to clean drinking water.
- GWD is considered endemic in three African countries, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Mali.
- In recent years, a few cases of GWD in animals, especially dogs, have been reported in developed countries as well.
- GWD is a serious condition, that causes debilitating pain and complications, affecting the quality of life
Symptoms:
- People infected with Guinea worm don’t typically have any symptoms until about a year after they're first infected.
- It’s not until the worm is about to erupt from the skin that people start to feel sick.
- What that happens, the symptoms of Guinea worm disease can include Fever, Nausea and vomiting, Diarrhoea, Shortness of breath, Burning, itching, pain, and swelling where the worm is in the body (often the legs and feet) and Blister where the worm breaks through the skin.
Impact:
- Guinea worm disease isn’t often deadly, but it can cause serious complications, lifelong disabilities, and financial hardship for those involved.
- The pain involved is often so intense that it’s difficult for people to work, go to school, or care for themselves or others.
- This lasts an average of 8.5 weeks, though lifelong disability is common.
Dracunculiasis Treatment:
- There is no vaccine or drug developed to prevent or treat this disease.
- The only means available is the management of the disease which is removing the whole worm and caring for the wound caused by it and avoiding infection in the process or exposure to the guinea worm larvae at all costs, especially by avoiding contaminated drinking water and stagnant water sources.
- Without proper treatment, wounds caused by the worm can become infected by bacteria, leading to sepsis, septic arthritis, and contractures (when joints lock and deform).
- In some cases, these infections become life-threatening.
Earth’s early evolution: Fresh insights from rocks formed 3.5 billion years ago
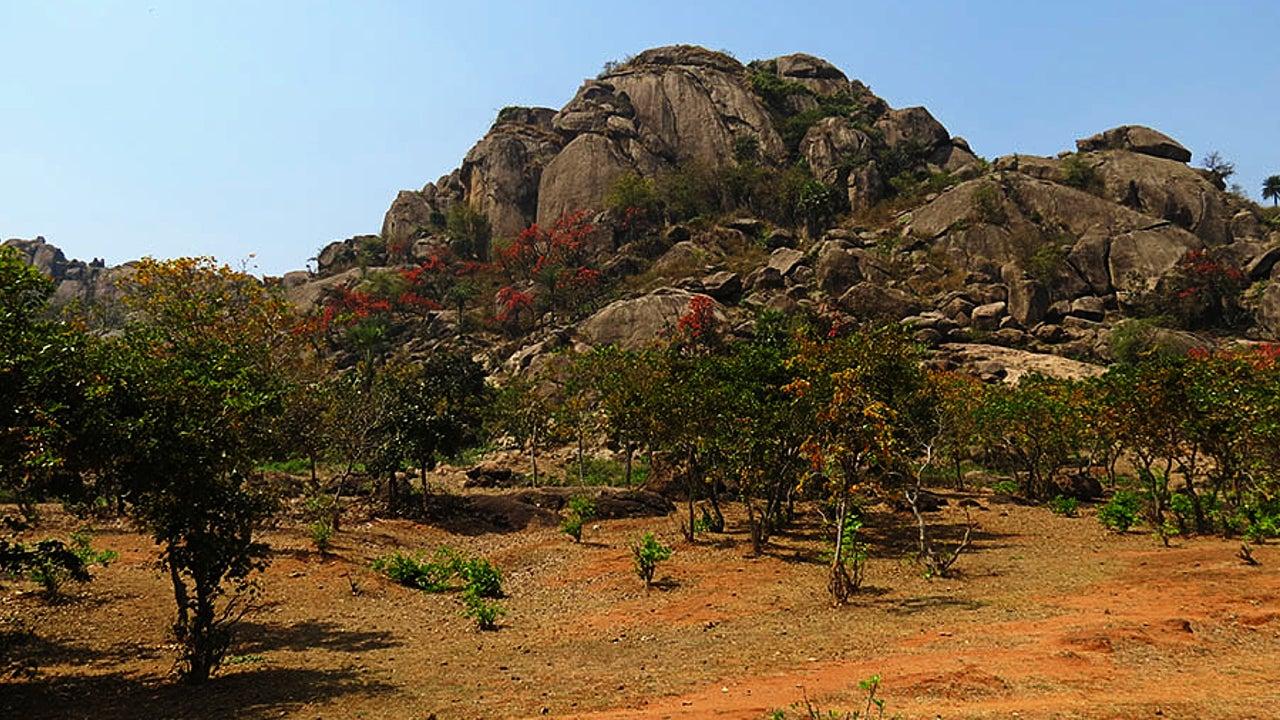

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exploring ancient cratons such as the Singhbhum Craton in India, alongside similar formations in South Africa and Australia, provides unparalleled insights into the early stages of our planet's development, reaching back approximately 3.5 billion years.
What is Singhbhum Craton?
- The Singhbhum Craton encompasses a vast expanse of rugged terrain, primarily spanning regions in Jharkhand and Odisha, situated between the Chhota Nagpur plateau and the Eastern Ghats.
- Dating back approximately 3.5 billion years, this ancient segment of the Earth's crust offers valuable insights into early geological processes.
- Its oldest rock formations consist predominantly of volcanic and sedimentary rocks, referred to as greenstone successions.
- Greenstones are characterised by submarine volcanic rocks with minor sedimentary components.
- Geologically akin to greenstone belts in South Africa's Barberton and Nondweni regions and the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia, these areas experienced extensive submarine mafic volcanic activity, rich in magnesium oxide, between 3.5 and 3.3 billion years ago, with preserved features like pillowed lava and komatiites.
Significance:
- The Singhbhum Craton sheds light on early tectonic activities during the Archaean era, enhancing our understanding of the Earth's formative stages.
- Its distinctive geological characteristics, particularly the presence of greenstone belts, yield invaluable data on surface and atmospheric processes crucial for theorising about early habitable conditions and the emergence of life on Earth.
What are Cratons?
- A craton is a stable and ancient part of Earth's lithosphere that has experienced long-term tectonic and geomorphic stability.
- It is considered to be the nucleus of a continent and is characterised by its thick and cold lithosphere.
- Cratons can undergo destruction, which is defined as a geological process resulting in the loss of craton stability due to changes in its physical and chemical properties.
- The mechanisms responsible for craton destruction include oceanic plate subduction, rollback and retreat of subducting plates, stagnation and dehydration of subducting plates in the mantle transition zone, melting of the mantle caused by dehydration of stagnant slabs, non-steady flow in the upper mantle induced by melting, and changes like the lithospheric mantle.
- Craton destruction can lead to crustal thinning, surface uplift, and the concentration of mineral deposits.
Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY)

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Social Justice and Empowerment, being the Nodal Department for the welfare of senior citizens, develops and implements programmes and policies for these groups in close collaboration with State Governments, Non-Governmental Organisations and civil society.
About the Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme to improve the quality of life of the Senior Citizens.
- The project is implemented by the Department of Social Justice and Empowerment.
Aims and Objectives:
- The main objective of the Scheme is to improve the quality of life of Senior Citizens by providing basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care and entertainment opportunities and by encouraging productive and active ageing through providing support for capacity building of State/ UT Governments/Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs)/Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) / local bodies and the community at large.
The components of the AVYAY Scheme are as under:-
-
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC)
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC)
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY)
- Elderline – National Helpline for Senior Citizens
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE)
- Geriatric Caregivers Training
Components of the AVYAY Scheme:
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC): Grant aid is provided to Non-Governmental/ Voluntary Organizations for running and maintenance of Senior Citizens' Homes (old age homes), continuous care homes, etc.
- Facilities like shelter, nutrition, medicare and entertainment are provided free of cost to indigent senior citizens.
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC): Grant in aid is released to States/ UTs for the creation of a pool of trained Geriatric Caregivers for senior citizens, for carrying a special drive for Cataract Surgeries for Senior Citizens and State Specific Activities for the welfare of senior citizens, especially who are indigent in the States/UTs.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY): To provide for senior citizens, suffering from any age-related disability/infirmity such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth and loco-motor disabilities.
- The eligible senior citizens under this component are those who are in the BPL Category or have monthly income up to Rs.15000/.
- Generic and non-generic devices are distributed to the senior citizens through the camps.
- Elderline: National Helpline for Senior Citizens (14567): The Ministry has set up the National Helpline for Senior Citizens to provide free information, Guidance, Emotional Support and field intervention in cases of abuse and rescues.
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE): To promote out-of-the-box and innovative solutions for commonly faced problems, innovative start-ups are identified and encouraged to develop products, processes and services for the welfare of the elderly under this initiative.
- The initiative is implemented through IFCI Venture Capital Funds Ltd. (Investment Manager).
- Geriatric Caregivers Training: To bridge the gap in supply and increasing demand in the field of geriatric caregivers and also to create a cadre of professional caregivers in the field of geriatrics.
- The component is implemented through the National Institute of Social Defence and at present 3,180 geriatric caregivers have been trained.
In a first, CERN scientists carry out laser cooling of Positronium

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a first, an international team of physicists from the Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved a breakthrough by demonstrating the laser cooling of Positronium.
About Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS):
- AEgIS is an experiment at the Antiproton Decelerator facility at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research).
- It is a collaboration of physicists from a number of countries in Europe and from India.
- In 2018, AEgIS demonstrated the first pulsed production of antihydrogen atoms, by interacting pulse-produced positronium (an atom consisting of only an electron and a positron) with cold, trapped antiprotons.
- The primary scientific goal of the Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) is the direct measurement of the Earth's gravitational acceleration, g, on antihydrogen.
What is Positronium?
- Positronium is a bound state system of a positron and an electron, similar to the hydrogen atom, where an electron orbits around a proton.
- In the case of positronium, the positron and the electron orbit around their common centre of mass.
- The system is unstable, and the two particles eventually annihilate each other, releasing two or more gamma ray photons.
- Positronium has two possible states:
- The singlet state (para-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are antiparallel and the system has a shorter lifetime, and
- The triplet state (ortho-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are parallel, and the system has a longer lifetime.
- Positronium has been studied extensively in experimental and theoretical physics because it provides a simple system for testing quantum electrodynamics (QED) and for studying the properties of matter and antimatter.
- It also has potential applications in fields such as material science, plasma physics, and astrophysics.
What is Antimatter?
- Antimatter shares similarities with ordinary matter, except for its opposite electric charge.
- Often referred to as "mirror" matter, antimatter pairs with ordinary matter particles.
- For example, while an electron possesses a negative charge, its antimatter counterpart is a positron, which carries a positive charge and has the same mass as an electron.
- Positrons, antiprotons, and antineutrons are the antimatter counterparts of electrons, protons, and neutrons, respectively, collectively known as antiparticles.
- These antiparticles can combine to form anti-atoms and theoretically could lead to the formation of antimatter regions within our universe.
- However, the coexistence of matter and antimatter is short-lived due to their tendency to annihilate upon contact, resulting in the release of substantial energy in the form of gamma rays or elementary particles.
- Antimatter, like matter, emerged during the Big Bang.
- Scientists have produced antimatter particles through high-speed collisions in large particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider operated by CERN outside Geneva.
- Additionally, antiparticles are sporadically generated throughout the universe through natural processes.
Eminent Jurist Senior Advocate Fali Nariman passes away

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, eminent jurist and senior advocate of the Supreme Court Fali S Nariman died at the age of 95.
Who was Fali S Nariman?
- Fali S Nariman was born on January 10, 1929, in Rangoon, then part of British India.
- He began his legal career by enrolling as an advocate of the Bombay High Court in November 1950.
- His stature grew, and he was designated as a senior advocate in 1961.
- In 1972, he moved to New Delhi to practise in the Supreme Court of India.
- In May 1972, Nariman assumed the role of additional solicitor-general of India; however, he resigned a day after the Emergency was imposed on June 26, 1975.
- He also served as the president of the International Council for Commercial Arbitration and chaired the Executive Committee of the International Commission of Jurists, Geneva, from 1995 to 1997.
- His son, Justice Rohinton F Nariman, formerly served as a judge on the Supreme Court.
- Nariman received the Padma Bhushan in January 1991 and in 2007 he was awarded the Padma Vibhushan.
What Were Some of Nariman's Landmark Cases?
- The Golak Nath case: In the historic judgement, the Supreme Court held that the Parliament cannot make a law which is capable of infringing the fundamental rights of citizens.
- It came up after two brothers in Punjab challenged the Constitution (17) Amendment Act, 1964, which came into effect by amending Article 31A of the Constitution. (This article deals with the acquisition of estates).
- Nariman, not only supported the petitioners but also appeared to argue on the issue representing the intervenors in the case.
- They argued that Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution under Article 368 did not include articles contained in Part III of the Constitution dealing with fundamental rights.
- Following the hearing of the case submitted in 1967, an eleven-judge bench agreed with the petitioner’s submissions pointing out that Article 13(2) states that Parliament cannot make a law which infringes fundamental rights.
- The Kesavananda Bharati case: The Kesavananda Bharati case is known for setting a benchmark in the Indian judiciary and had Nariman’s prompt representation in the SC.
- He assisted noted Advocate Nanabhoy Palkhivala in the famous case that led to the path-breaking judgement laying down the basic structure doctrine of the Constitution, clipping Parliament’s power to amend the Constitution.
- The 1973 verdict simultaneously gave the judiciary the authority to review any constitutional amendment on grounds of violation of the basic structure of the Constitution.
- The Bhopal Gas Tragedy case: In 1984, the Bhopal gas tragedy where 42 tons of toxic chemicals leaked from a pesticide plant owned by Union Carbide India Limited, resulting in thousands of deaths and environmental damage in the following years.
- The Supreme Court began hearing the case for compensation to the victims in 1988.
- Senior Advocate Nariman appeared, representing Union Carbide, and offered to pay a sum of 426 million dollars as compensation to the victims of the tragedy.
- In 1989, Union Carbide settled with the central government and agreed to pay 470 million dollars as compensation.
- The Cauvery Water Dispute case: Nariman represented Karnataka for over 30 years in the water-sharing dispute with Tamil Nadu.
- In 2016, the Supreme Court ordered the Karnataka government to release 6,000 cusecs (cubic feet per second) of water from September 21 to September 27.
- The Karnataka legislative assembly, however, passed a resolution stating that they did not have water to spare and chose to defy the court’s orders.
- Due to this non-compliance, Nariman refused to argue the case on behalf of the Karnataka government any further.
- On February 16, 2018, the court in its final judgement took note of Nariman’s stance on the issue and necessarily mentioned that Nariman had courageously lived up to the highest tradition of the Bar.
- The court then proceeded to reduce Karnataka’s annual water releases to 177.25 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) from 192 TMC.
- Disproportionate assets case against former Tamil Nadu Chief Minister J Jayalalithaa: AIADMK leader and former- Tamil Nadu CM Jayalalitha had been accused of misappropriating funds during her tenure between 1991 and 1995.
- A Sessions Court in Bangalore in September 2014 found that she had acquired property disproportionate to her known income and imposed a Rs 100 crore fine on her.
- This sentence was upheld by the Karnataka High Court a month later leading to an appeal at the Supreme Court.
- Nariman appeared on behalf of Jayalalitha in October 2014 and convinced the court to grant bail against executing the fine and suspend the sentence passed by the Sessions judge in Bangalore.
- The 1981 Second Judges case: The Supreme Court held that the primacy of the Chief Justice of India’s recommendation in judicial appointment and transfer can be turned down on cogent grounds by the government.
- However, the judicial discussions finally led to the creation of the collegium system of appointment of judges to constitutional courts in 1993, when the top court came out with its judgement in the second judge’s case.
- Nariman had stated that the advice given through consultation with the CJI must be seen as binding to protect the independence of the judiciary, as judges would be in a better position to determine the suitability and competence of candidates.
- In 1993, the nine-judge bench agreed with Nariman’s arguments and established the Supreme Court Collegium.
- The COVID-19 case: Nariman represented the Parsi community in its dispute over the protocol and standard operating procedure for handling of dead bodies of Parsi Zoroastrian COVID-19 victims under which metallic nets were to be installed above ‘Tower of Silence’ so that birds did not feed on the corpses and carry the killer virus elsewhere
Cabinet approves Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for the period 2021-26

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of “Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)” with a total outlay of Rs. 4,100 crore for a period of 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
About the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP):
- The FMBAP Scheme is being implemented throughout the country for effective flood management, erosion control and anti-sea erosion and to help in maintaining peace along the border.
- The scheme benefits towns, villages, industrial establishments, communication links, agricultural fields, infrastructure etc. from floods and erosion in the country.
- The catchment area treatment works will help in the reduction of sediment load into rivers.
- The Scheme aims at the completion of the ongoing projects already approved under FMP.
The Scheme has two components:
- Under the Flood Management Programme (FMP) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 2940 crore, central assistance will be provided to State Governments for taking up critical works related to flood control, anti-erosion, drainage development and anti-sea erosion, etc.
- The pattern of funding to be followed is 90% (Centre): 10% (State) for Special Category States (8 North-Eastern States and Hilly States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and UT of Jammu & Kashmir) and 60% (Centre):40% (State) for General/ Non-Special Category States.
- Under the River Management and Border Areas (RMBA) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 1160 crore, flood control and anti-erosion work on common border rivers with neighbouring countries including hydrological observations and flood forecasting, and investigation & pre-construction activities of joint water resources projects (with neighbouring countries) on common border rivers will be taken up with 100% central assistance.
- The Scheme has the provision of incentivizing the States which implement flood plain zoning, recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Importance:
- While the primary duty of flood management lies with the State Governments, the Union Government actively promotes and advocates for the adoption of modern technology and innovative approaches.
- Additionally, projects executed under the RMBA component serve to safeguard critical installations of security agencies and border outposts situated along border rivers from the perils of floods and erosion.
- Furthermore, the scheme includes provisions for incentivizing states that implement flood plain zoning, a recognized and effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Will the ‘Paruveta Festival’ celebrated in Andhra’s Ahobilam get UNESCO recognition?

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
INTACH is striving to obtain UNESCO recognition for the yearly 'Paruveta' festival, emphasising its cultural significance.
About the Paruveta Festival:
- Paruveta Festival, also known as the 'mock hunting festival', is a celebrated tradition at the Sri Narasimha Swamy temple in Ahobilam, Andhra Pradesh.
- It stands out as a symbol of communal harmony, where devotees from various religious backgrounds, including Muslims, come together to offer prayers.
Origin and Significance:
- According to folklore, the festival commemorates Lord Vishnu's incarnation as Narasimha, who married Chenchulakshmi, a tribal girl, symbolising unity across different communities.
- The festival's rituals, typically observed during Vijayadashami or Sankranti, extend for a 'mandala' period of forty days in Ahobilam.
Activities and Customs:
- During the festival, the temple deity is carried to the 32 Chenchu tribal villages surrounding Ahobilam for forty days.
- The journey begins with a symbolic act where tribals shoot arrows at the deity's palanquin, signifying protection and reverence.
- Chenchus participated by undertaking 'Narasimha Deeksha', wearing yellow robes and Tulasi Mala, while observing celibacy.
- The temple staff reside in these villages throughout the festival, showcasing the tradition of a casteless society with no traces of untouchability.
Key Points about Chenchu Tribes:
- Geographic Distribution: Chenchu tribes primarily inhabit the hills of southern India, particularly in Andhra Pradesh.
- Additionally, Chenchu communities can be found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Orissa.
- Language and Communication: Their native language, known as Chenchu, belongs to the Dravidian language family.
- While many Chenchu individuals speak Telugu, their traditional language holds cultural significance.
- Livelihood and Occupation: Historically, Chenchu people pursued a nomadic lifestyle, relying on food gathering.
- However, due to factors such as agricultural expansion, many have transitioned to working as farmers or forest labourers.
- Housing and Settlements: Chenchu dwellings are typically hive-shaped structures constructed from wattle thatch, composed of interwoven poles, twigs, reeds, or branches.
- These houses reflect their traditional architectural style and are adapted to their environment.
- Social Structure: Chenchu society is organised into clans, which are extended family units, as well as local groups and individual families.
- They adhere to exogamous marriage practices, prohibiting unions within the same clan.
- Additionally, Chenchu kinship is patrilineal, tracing descent through male lineage.
Unauthorised online lending apps high on the FSDC scanner

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fresh measures to curb unauthorised online lending apps’ operations could be on the anvil, following deliberations on the issue at the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) chaired by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman recently.
About the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC):
- The Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) is a high-level body established by the Government of India in 2010 to address macroeconomic and financial stability issues.
- Although not a statutory body, it operates under the Financial Stability Division of the Department of Economic Affairs within the Ministry of Finance.
Background:
- In response to the global financial crisis of 2008, recommendations were made by the Raghuram Rajan Committee for the creation of a centralised regulatory body to oversee India's financial system.
- The establishment of FSDC reflects India's proactive approach to enhance preparedness for future financial challenges.
Composition:
- Chaired by the Union Finance Minister, the council comprises key stakeholders including the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), finance and economic affairs officials, regulatory body chairpersons, and other relevant authorities.
- The Secretary of the Department of Economic Affairs serves as the council's secretary.
Responsibilities:
- FSDC is entrusted with the task of promoting financial stability, coordinating policy responses to systemic risks, and fostering the development of India's financial sector.
Concerns and Future Directions:
- Concerns have been raised about potential encroachment on the autonomy of sectoral regulators due to FSDC's leadership by the Union Finance Minister.
- To address this, it's crucial to safeguard the independence of regulatory bodies and establish clear guidelines to ensure effective coordination without undermining regulatory authority.
What is Digital Lending?
- Digital lending refers to the process of accessing credit online, facilitated through web platforms or mobile applications.
- This approach leverages technology across various stages of the lending process, including customer acquisition, credit assessment, approval, fund disbursement, recovery, and customer service.
Key Features:
- Utilises technology for end-to-end lending operations, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
- Offers flexibility in credit options and facilitates swift transactions, appealing to modern borrowers.
- Prominent examples include Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) schemes, which provide short-term financing for purchases, allowing consumers to defer immediate payments.
Drivers of Growth:
- Increased adoption is driven by widespread smartphone usage and the convenience of online transactions.
- Flexibility in credit offerings and simplified application processes contribute to the popularity of digital lending platforms.
- BNPL services, in particular, cater to consumers seeking deferred payment options for purchases and services.
Centre increases Fair and Remunerative Prices of sugarcane

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs recently approved ?340/quintal as the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for the sugar season 2024-25 at a sugar recovery rate of 10.25%.
What is the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)?
- FRP was introduced by the government in 2009 by an amendment to the Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966.
- It replaced the Statutory Minimum Price (SMP) on the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) consultation.
- The FRP system assured timely payment to farmers, irrespective of the profit and loss to sugar mills.
- Further, the new system made it mandatory for sugar mills to pay the farmers within 14 days of delivery of sugarcane.
- Additionally, the FRP system introduced grading on the basis of sugar recovery rate from sugarcane wherein a premium was paid to the farmer on higher recovery and a reduction in rates on lower recovery.
- The FRP is based on the Rangarajan Committee report on reorganising the sugarcane industry.
Factors Considered for Announcing FRP:
-
- Cost of production of sugarcane
- Return to the growers from alternative crops and the general trend of prices of agricultural commodities
- Availability of sugar to consumers at a fair price
- The price at which sugar produced from sugarcane is sold by sugar producers
- Recovery of sugar from sugarcane
- The realisation made from the sale of by-products viz. molasses, bagasse and press mud or their imputed value
- Reasonable margins for the growers of sugarcane on account of risk and profits
Effect of the New FRP:
- Sugar production in India was hit hard in the October-December 2023 quarter as production fell by 11.21 million metric tonnes;
- It was 12 million in the same quarter the previous year.
- The increase in FRP is going to increase the cost for producers.
- The increased FRP will benefit over five crore sugarcane farmers in the country, however, the increase in production cost could affect end-consumers as well.
- Factors such as FRP hikes, akin to MSP, make it attractive to farmers but also increase prices in the local market as mills pass on that cost to consumers
WHO launches digital health platform agreed upon in India’s G20 presidency

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Achieving one of the three priority areas agreed upon during India’s G20 presidency in 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) recently launched the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) virtually, a platform for sharing knowledge and digital products among countries.
About Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH):
- The Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) is a network managed by the World Health Organization (WHO), dedicated to enhancing and coordinating efforts for country-led digital health transformation through collaborative partnerships and knowledge sharing.
- It was launched by the WHO and the Government of India during the G20 Health Ministerial Meeting in Gandhinagar.
- Functioning as a platform for inter-country knowledge exchange and digital product dissemination, GIDH strives to achieve several key objectives through collective action:
- Assess and prioritise countries' requirements for sustainable digital health transformation.
- Enhance the alignment of digital health resources and address unfunded priorities at the country level.
- Facilitate the accelerated attainment of the strategic objectives outlined in the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025.
- Promote capacity building and synergize efforts to support local development, maintenance, and adaptation of digital health technologies to evolving needs.
- Comprising four primary components, GIDH operates as a network of networks:
- Country Needs Tracker: Tracks and prioritises country-specific digital health requirements.
- Country Resource Portal: Provides a comprehensive map of available digital health resources within each country.
- Transformation Toolbox: Shares quality-assured digital tools to support country-led digital health initiatives.
- Knowledge Exchange: Facilitates the exchange of insights and best practices among member countries.
- GIDH extends support to countries in three fundamental ways:
- By attentively addressing their needs
- By fostering resource alignment to prevent fragmentation, and
- By offering access to quality-assured digital products.
- Membership in GIDH is open to all institutions actively involved in the digital health domain.
What is Digital Health?
- Digital health denotes the utilisation of technology, encompassing mobile devices, software applications, and various digital tools, to enhance health outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery.
- Essentially, it represents an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of technology and healthcare, integrating a diverse array of concepts and innovations.
- This encompasses a broad spectrum of technologies and services, spanning telemedicine, electronic health records, wearable devices, health information exchange, and more.
- Examples of notable digital health initiatives include India’s CoWIN platform and UNICEF's RapidPro and FamilyConnect programs.
- RapidPro, UNICEF’s real-time information platform, serves as a foundational component in its digital health portfolio.
- FamilyConnect, another UNICEF initiative, delivers targeted, lifecycle-based messages via SMS to various recipients, including pregnant women, new mothers, and heads of households.
India Initiatives on Digital Health:
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM): Designed to establish a comprehensive national digital health ecosystem featuring unique health IDs, electronic health records (EHRs), and a platform for health data exchange.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): Aims to develop a digital infrastructure for the Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM), incorporating health registries, electronic claim processing, and telemedicine services.
- E-Sanjeevani Telemedicine Platform: Enables virtual consultations between healthcare providers and patients nationwide, enhancing access to medical care.
- Jan Arogya Setu App and CoWIN Platform: Offers access to healthcare services, facilitates appointment scheduling, and disseminates COVID-19-related information.
- Digital Aarogya Mitra (DAM): Implements a community health worker program utilising technology for data collection and community-based health interventions.
Malta becomes the 119th member of the International Solar Alliance

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Malta became the 119th country to join the International Solar Alliance recently.
About the International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is an alliance of more than 120 signatory countries that aims to reduce the dependence on non-renewable sources of energy like fossil fuels.
- Currently, 118 countries are signatories to the ISA Framework Agreement.
- The ISA is an action-oriented, member-driven, collaborative platform for increased deployment of solar energy technologies as a means for bringing energy access, ensuring energy security, and driving energy transition in its member countries.
- The platform strives to develop and deploy cost-effective and transformational energy solutions powered by the sun to help member countries develop low-carbon growth trajectories, with a particular focus on delivering impact in countries categorised as Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and the Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- The ISA was conceived as a joint effort by India and France to mobilise efforts against climate change through the deployment of solar energy solutions.
- It was conceptualised on the sidelines of the 21st Conference of Parties (COP21) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) held in Paris in 2015.
Role of India:
- As a founding member, India holds a pivotal position within the alliance, serving both as a host nation and a major contributor to achieving its objectives.
- The ISA marks a historic milestone as the first international organisation to establish its secretariat in India.
- With a target of generating 100 GW of solar energy by 2022, India's commitment represents a significant portion of the ISA's overall goal.
Recent Developments:
- The ISA was granted Observer Status by the UN General Assembly, fostering closer collaboration between the alliance and the United Nations to advance global energy growth and development.
- The approval of the 'Solar Facility' by the ISA introduces a payment guarantee mechanism aimed at incentivizing investments in solar projects, further driving progress towards sustainable energy initiatives.
India contributes $1 million to fund combating poverty and hunger

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India has contributed 1 million US Dollars to the Poverty and Hunger Alleviation Fund established by India, Brazil, and South Africa, IBSA.
What is the IBSA Fund?
- Established in 2004 and operational since 2006, the IBSA Fund embodies the collaborative efforts of India, Brazil, and South Africa.
- Contributing one million dollars annually each, the IBSA countries unite in a spirit of partnership to champion Southern-led, demand-driven projects in developing nations.
- With a focus on identifying replicable and scalable initiatives, the fund aims to address pressing development challenges in recipient countries.
- Supported projects align with partner countries' national priorities and international development agendas, including the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The fund's objectives encompass diverse areas such as promoting food security, combating HIV/AIDS, and expanding access to safe drinking water, among others, to advance sustainable development.
- To date, the IBSA Fund has allocated USD 50.6 million, funding 45 projects across 37 countries in the Global South.
- The United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC) fulfils the roles of Fund Manager and Secretariat for the IBSA Fund.
What is IBSA?
- IBSA stands for the India, Brazil, and South Africa Dialogue Forum, a unique platform that unites three major democracies and significant economies from diverse continents, collectively addressing common challenges.
- Formally established as the IBSA Dialogue Forum during a historic meeting of the Foreign Ministers from India, Brazil, and South Africa in Brasilia on June 6, 2003, the forum's inception was marked by the issuance of the Brasilia Declaration.
- To date, five IBSA Leadership Summits have been convened, with the 5th Summit held in Pretoria on October 18, 2011.
- In 2021, India held the chairmanship of IBSA under the theme "Democracy for Demography and Development."
- On March 2, 2023, Brazil assumed the rotating presidency of the India, Brazil, South Africa Dialogue Forum (IBSA), further advancing the forum's collaborative agenda.
Global leaders converge in Delhi for Raisina Dialogue 2024

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ninth edition of the Raisina Dialogue will be held from today till Friday (February 23) in New Delhi.
What is the Raisina Dialogue?
- The Raisina Dialogue is India’s premier conference on geopolitics and geoeconomics committed to addressing the most challenging issues facing the global community.
- Every year, leaders in politics, business, media, and civil society converge in New Delhi to discuss the state of the world and explore opportunities for cooperation on a wide range of contemporary matters.
- The Dialogue is structured as a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral discussion, involving heads of state, cabinet ministers and local government officials, who are joined by thought leaders from the private sector, media and academia.
- The conference is hosted by the Observer Research Foundation in partnership with the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India.
- This effort is supported by a number of institutions, organisations and individuals, who are committed to the mission of the conference.
- The theme of the 2024 edition is “Chaturanga: Conflict, Contest, Cooperate, Create”.
- During the three-day conference, the participants will engage with each other over six “thematic pillars”. These include:
- Tech Frontiers: Regulations & Realities
- Peace with the Planet: Invest & Innovate
- War & Peace: Armouries & Asymmetries
- Decolonising Multilateralism: Institutions & Inclusion
- The Post 2030 Agenda: People & Progress; and
- Defending Democracy: Society & Sovereignty.
After 30 years, Buddha relics travel to Thailand

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Four of the 20 relics of Lord Buddha preserved at the National Museum are being taken to Thailand for a month-long exposition beginning recently, in a rare trip abroad for the delicate antiquities recovered more than a century ago.
About the Relics of Lord Buddha:
- The relics of Lord Buddha and his disciples Arahata Sariputra and Arahata Maudgalayana are known as the ‘Kapilvastu Relics.’
- The relics date back to around the 4th or 5th Century BC.
- They were found in Bihar’s Piprahwa — a site that is believed to be the ancient city of Kapilvastu.
- Piprahwa today is located in Uttar Pradesh’s Siddharthnagar district.
- The relics were discovered by a team of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) officials in the 1970s.
- The ASI conducted excavations at Piprahwa from 1971-77 under the supervision of the archaeology director KM Srivastava.
History:
- Lord Buddha achieved Mahaparinirvana at the age of 80 in Kushinagar.
- The Mallas of Kushinagara cremated his body with ceremonies befitting a ‘Universal King’ (‘cakravartin’).
- His holy relics, from the funeral pyre, were collected, divided and given by Brahmin priest Dhona of Kushinagar to kings and priests.
- The eight shares were distributed among Ajatashatru of Magadha, the Licchavis of Vaishali, the Sakyas of Kapilavastu, Mallas of Kushinagar, Bullies of Allakappa, the Mallas of Pava, the Koliyas of Ramagrama and a Brahmana of Vethadipa.
- The sacred relics were commemorated in eight different stupas.
- Two more stupas came into existence, one over the urn in which the relics had been collected and one over the embers.
- Thus, stupas erected over the bodily relics of Buddha (Saririka-stupas) are the earliest surviving Buddhist shrines.
- It is stated that Ashoka (circa 272-232 BC), being an ardent follower of Buddhism, opened up seven of these eight stupas, and collected a major portion of the relics for enshrinement within innumerable stupas built by him to popularise Buddhism and spread dharma.
- In 1898, the discovery of an inscribed casket by William Claxton Peppé, a British colonial engineer and an estate manager at a Buddhist stupa site at Piprahwa, was an epoch-making incident.
- The inscription on the lid referred to the relics of Buddha and his community.
- The bone relics present in the stone coffer were presented to King Rama V of Thailand.
- The relics were further divided into three shares and gifted to Thailand, Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
- In Thailand, the holy relic has been enshrined in a chedi on the top of Suwanbanphot, Bangkok.
- Every year, during the Loi Krathong Festival, there is a seven-day and seven-night celebration, which has become a tradition to worship the Buddha’s relics.
La Nina impacted air quality in India in the winter of 2022
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new study suggests that monsoon rainfall over India, which is strongly influenced by El Niño and La Niña events—alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean impacting global weather may also affect air quality in the country.
Key Findings of the New Study on the Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- According to the researchers at the National Institute of Advanced Studies (Bengaluru) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (Pune), the strong influence of El Niño and La Niña events on monsoon rainfall over India, driven by the alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean, with far-reaching effects on global weather patterns.
- Remarkably, this study marks the first time that air quality in Indian cities has been directly linked to a La Niña event, suggesting an indirect connection to climate change, which intensifies the severity of El Niño and La Niña occurrences.
- Traditionally, northern Indian cities, notably Delhi, face elevated concentrations of PM2.5 pollutants from October to January.
- However, the winter of 2022 witnessed a notable deviation from this trend, with northern cities experiencing cleaner air than usual, while western and southern cities like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Chennai saw worsened air quality.
- Specifically, Delhi observed a 10% reduction in PM2.5 concentrations, contrasted with a 30% increase in Mumbai and a 20% rise in Bengaluru.
- The researchers, investigating this anomaly, identified the potent effects of the La Niña event, notably stronger than typical occurrences, leading to significant changes in wind circulation patterns over India.
- This impact became pronounced in the third year of La Niña, suggesting a cumulative effect that may amplify over time.
- While La Niña events are associated with improved air quality in northern India, the study emphasizes the need for further research to understand the potential impacts of El Niño events, which may produce contrasting effects on air quality across the country.
What are El Niño and La Niña?
- El Niño refers to a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Similarly, a La Niña occurs when the band of water spreads east to west and is cooler.
- Both phenomena affect the weather worldwide and can have drastic effects on economies that depend on rainfall.
- Together, El Niño and La Niña make up a cyclical process called the El Niño Southern Oscillation.
- An El Niño year creates a global warming crisis in miniature because the warm water spreading across the tropical Pacific releases a large amount of heat into the atmosphere.
- El Niño: El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, El Niño events often correlate with below-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to drought conditions in some regions, affecting agriculture and water resources.
- El Niño can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing warmer temperatures during El Niño events.
- La Niña: La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, La Niña events often correlate with above-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to increased precipitation in some regions, potentially causing flooding, while other areas may experience drought conditions.
- La Niña can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing cooler temperatures during La Niña events.
Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- Altering Wind Patterns: During the winter of 2022, the typical north-westerly winds, carrying agricultural pollutants from Punjab and Haryana towards Delhi and the Gangetic plains, were disrupted.
- Instead, wind circulation shifted to a north-south direction, diverting pollutants away from Delhi.
- Consequently, pollutants bypassed Delhi, travelling over Rajasthan and Gujarat towards southern regions.
- Modifying Local Wind Circulation near Mumbai: In Mumbai, the local wind circulation, which alternates between land-to-sea and sea-to-land flows every few days, experienced prolonged unidirectional winds.
- This sustained wind pattern prevented the dispersal of pollutants from the city, leading to their accumulation within Mumbai's atmosphere throughout the winter of 2022.
- These changes in wind patterns, influenced by La Niña, significantly impacted air quality dynamics in India, highlighting the intricate relationship between climate phenomena and regional atmospheric conditions.
Gold Hunt by Villagers Reveals Ancient Harappan Settlement in Gujarat

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The newly discovered Harappan settlement at Lodrani village in the Kutch region of Gujarat has sparked widespread interest in the fascinating remains of this ancient civilisation, making it an important site for archaeological exploration and research.
Features of Harappan site Morodharo:
- Morodharo is a fortified settlement of the Harappan era, with the fortification measuring 102 m to the west and 58 m north to the south.
- The thickness of the wall is 3.3 m on average.
- Morodhara has a 10x10 m platform on the southwest side and a well on the northeast side.
- Burial cairns have been found at Morodharo.
- A cairn is an intentionally constructed mound of stones, typically created for marking a location or serving as a burial mound.
- Harappan pottery with perforated jar sherds, reserved slipware and terracotta cakes have also been unearthed.
- All these items have a striking resemblance to those found in Dholavira.
About Harappan Civilization:
- The Harappan civilization, also known as the Indus Valley civilization was South Asia's first urban civilization, flourishing concurrently with Mesopotamia and Egypt.
- It encompassed the most extensive territory, covering approximately 800,000 square kilometres, compared to its contemporaries.
- Prominent cities during the Harappan period included Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro in present-day Pakistan, along with Dholavira, Lothal, and Surkotada in Gujarat, India, among others.
- Urban planning in Harappan cities followed a meticulous grid layout, with streets intersecting at right angles, dividing the cities into neat rectangular blocks.
- The streets and alleys were deliberately designed for efficient movement, accommodating carts and pedestrians, often featuring covered drains alongside.
- For defence and security, the cities were enclosed by sturdy walls made of mud bricks, shielding against intruders and natural calamities.
- Each city was structured into an elevated citadel and a lower town, with the former housing monumental structures like granaries and administrative buildings.
- Residential areas comprised multi-story brick houses clustered around courtyards, some equipped with private wells and well-ventilated bathrooms.
- A sophisticated drainage system ensured efficient waste disposal, with individual house drains connected to street-level drainage networks.
- Granaries and storage facilities were strategically positioned to manage surplus agricultural yields, reflecting advanced urban planning and resource management.
India, and ASEAN discuss the review of the trade agreement

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India hosted the 3rd meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which focused on reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement at Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi from February 16th to 19th, 2024.
About the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- The Framework Agreement laid a sound basis for the establishment of an ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (FTA), which includes FTA in goods, services and investment.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization of ten Southeast Asian countries:
- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN's primary objectives are to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its member states.
- The organization operates on the principles of mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, and consensus-building. ASEAN's motto, "One Vision, One Identity, One Community," underscores its commitment to fostering unity and solidarity among Southeast Asian nations.
- Economically, ASEAN has made significant strides towards integration through initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and production base.
- This has facilitated trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
- Additionally, ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of issues, including security, environmental sustainability, cultural exchange, and disaster management.
BSNL floats Rs 65,000 crore tender for phase-III BharatNet project

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
BSNL, the state-owned telecommunications company, has initiated a tender process amounting to approximately Rs 65,000 crore for the implementation of the phase-III BharatNet project.
What is the BharatNet Phase III Project?
- The BharatNet phase-III project adopts a three-level architecture:
- Internet leased line bandwidth
- Middle-mile connectivity, and
- Last-mile connectivity
- It aims to involve village-level entrepreneurs or Udyamis in providing last-mile connectivity to households on a revenue-sharing basis.
- BSNL aims to provide 15 million home fibre connections over five years using the BharatNet Udyami model.
About BharatNet Project:
- The BharatNet Project is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world.
- It aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats across India in a phased manner.
- Its core objective is to ensure equitable access to broadband services for all telecom service providers, fostering the deployment of services like e-health, e-education, and e-governance in rural and remote areas.
- Initiated in 2011 and executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in 2012, the project operates in three phases.
- Phase I launched in 2011, focused on creating the National Optical Fibre Network, leveraging existing infrastructure and laying additional fibre to bridge connectivity gaps up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Phase II, approved in 2017, builds upon Phase I’s experiences, aligning with the Digital India vision.
- It adopts a flexible approach, integrating various media such as Optical Fibre Cable (OFC), Radio, and satellite to connect Gram Panchayats, utilizing models like State-led, Private Sector, and CPSU Models for implementation.
- Phase III, spanning from 2019 to 2023, aims to establish a robust, future-ready network with district-to-block fibre connectivity, featuring ring topology for redundancy.
- This comprehensive approach ensures the creation of a resilient and inclusive telecom infrastructure, facilitating socio-economic development in rural India.
Hundred years ago, Satyendra Nath Bose changed physics forever
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In 2024, we commemorate the centenary of Bose's pivotal discovery of the precise equations governing the behaviour of collections of photons, fundamental particles of light.
About Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Satyendra Nath Bose (1894-1974) was an eminent Indian physicist renowned for his pioneering contributions to theoretical physics, notably in the realms of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics.
- His groundbreaking research laid the groundwork for Bose-Einstein statistics and the theoretical elucidation of Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Bose's profound insights not only advanced the understanding of fundamental physics but also played a pivotal role in refining the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
- His visionary work eventually paved the way for significant discoveries in particle physics, including the identification of the Higgs Boson, colloquially referred to as the "God Particle."
Major Contributions of Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Foundation of Bose-Einstein Statistics and Bosons: In 1924, Bose formulated a revolutionary explanation for Planck's law of black-body radiation using quantum mechanics principles, introducing the concept of "Bose-Einstein statistics."
- This theory delineates the behaviour of particles known as "bosons," characterized by integer spin.
- Bose-Einstein statistics elucidate how bosons, such as photons and atoms, preferentially occupy the same quantum state, a behaviour distinct from fermions governed by the Pauli exclusion principle.
- This groundbreaking work laid the groundwork for understanding particle behaviour at low temperatures and foretold the existence of the Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Prediction of Bose-Einstein Condensate: Bose's collaboration with Einstein in statistical mechanics led to the theoretical prediction of the Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), a revolutionary concept in quantum physics.
- According to Bose-Einstein statistics, at ultra-low temperatures approaching absolute zero, bosons can congregate in the lowest energy state, forming a condensed state.
- Often dubbed the "fifth state of matter," BEC occurs when bosons lose sufficient energy to coalesce into a single quantum state, creating a cohesive "super-particle" cloud.
- Experimental confirmation of Bose-Einstein condensation in 1995, decades after Bose's theoretical proposal, garnered Eric Cornell, Carl Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001.
- Together with Meghnad Saha, he published the first English translation of Einstein’s papers on general relativity.
- His dedication to research and scientific integrity earned him numerous accolades, including the Padma Vibhushan and the Fellowship of the Royal Society.
Banks to conduct periodic performance reviews of empanelled advocates to fast-track cases in DRTs

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Banks will conduct periodical reviews of the performance of empanelled advocates at debt recovery tribunals (DRTs) and rationalise the cases assigned to them based on performance.
What is the Debt Recovery Tribunal?
- Debt Recovery Tribunal is a quasi-judicial body formed under the Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions (RDDBFI) Act, 1993 to facilitate recovery of loans by banks and financial institutions to the customers.
- It was introduced as a response to the growing issue of Non-performing Assets (NPAs) and the need for a dedicated mechanism to resolve disputes related to debt recovery.
- These tribunals were instituted to offer a swifter and more effective alternative to traditional civil courts for the resolution of matters concerning debt recovery by banks and financial institutions.
- Its Appellate Tribunal is the Debt Recovery Appellate Tribunal (DRAT).
- Under Section 22 of the RDDBFI Act, 1993, both DRT and DRAT are mandated to adhere to the principles of natural justice, and proceedings before them are deemed to be judicial.
Jurisdiction of Debt Recovery Tribunal:
- They are empowered to adjudicate cases brought forth by banks, financial institutions, and related entities seeking the recovery of outstanding amounts.
- DRTs preside over matters surpassing a designated monetary threshold, and their rulings carry the weight of civil court decrees.
- The scope of DRT jurisdiction encompasses a broad spectrum of financial claims, encompassing loans, advances, and financial aid extended by banks and financial institutions.
Powers of DRT:
- Under Section 22(2) of the RDDBFI Act, 1993, the DRT possesses the following powers:
- Summoning individuals and compelling them to testify under oath.
- Demanding the disclosure and presentation of documents.
- Accepting evidence through affidavits.
- Issuing commissions to examine witnesses or documents.
- Revisiting its rulings.
- Rejecting applications due to default or adjudicating them in absentia.
- Revoking any order of dismissal stemming from default or any order passed in absentia.
- Addressing any other matters stipulated by regulations.
- The organisational framework of the Debt Recovery Tribunal:
- DRTs fall under the purview of the Ministry of Finance and operate akin to judicial courts.
- Each DRT is helmed by a Presiding Officer, who must hold qualifications equivalent to that of a District Judge.
- The Presiding Officer is appointed for a tenure of five years or until reaching the age of 62, whichever comes first.
- Appointment of the Presiding Officer is vested in the Central Government.
- At present, 39 DRTs and 5 DRATs are functioning across the country.
- Each DRT and DRAT are headed by a Presiding Officer and a Chairperson respectively.
Key aspect in poll bond case still alive: Money Bill route

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court struck down the electoral bonds scheme as unconstitutional recently, it saved one aspect of the challenge for another day and a larger bench – the issue of the government using the money Bill route to bring in the laws that introduced the electoral bonds.
News Summary:
- A recent ruling by a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court invalidated the electoral bonds scheme, citing it as unconstitutional.
- However, the court reserved one aspect of the challenge for further review by a larger bench – specifically, the government's use of the money Bill route to enact the laws introducing the electoral bonds.
The Supreme Court highlighted that:
- The examination of introducing these amendments through a money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution was not addressed.
- The interpretation of Article 110 of the Constitution has been referred to a seven-judge Bench and remains pending judicial review.
What are Money Bills?
- According to Article 110, a money Bill encompasses provisions related to taxes, government borrowing, and expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India, among other financial matters.
- Article 109 outlines the process for the passage of such Bills, granting predominant authority to the Lok Sabha in their enactment.
- The Speaker is responsible for certifying a Bill as a Money Bill, with the Speaker's decision being final.
- In the past seven years, the government has utilised the money Bill route to introduce various legislations, notably including the Aadhaar Act, 2016, and the Finance Act, 2017.
Other Instances of Government Utilising Money Bill Route:
- Several significant legislations have been enacted by the government through the money Bill route, including:
- The Finance Acts of 2016 and 2018, introduced amendments to the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act, of 2010.
- The Tribunals Reforms Act was passed as a money Bill in 2017.
- The rigorous amendments to the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) in 2022, alongside the enactment of the Aadhaar Act in 2018.
- The Supreme Court has upheld the validity of the PMLA amendments and the legality of the Aadhaar Act.
- Notably, Chief Justice of India Chandrachud dissented in the five-judge bench decision that upheld the Aadhaar Act, criticising the government's use of the money Bill route as a subversion of the Constitution.
- However, these laws may still face scrutiny and potential invalidation if the court determines that they were enacted through improper procedure, namely, utilising the money Bill route.
Difference Between Money Bills and Financial Bills:
- While every Money Bill is categorised as a Financial Bill, not every Financial Bill qualifies as a Money Bill.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely dedicated to tax proposals is deemed a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Financial Bill may include provisions on taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects.
- The Compensatory Afforestation Fund Bill, 2015, which establishes funds under the Public Account of India and states, serves as an example of a Financial Bill.
The process for passing these two types of bills varies considerably.
-
- The Rajya Sabha lacks the authority to reject or amend a Money Bill.
- Following passage by the Lok Sabha, Money Bills are referred to the Rajya Sabha for recommendations.
- Within 14 days, the Rajya Sabha must return the Bill to the Lok Sabha with its suggestions, which are not binding.
- Should the Lok Sabha reject the recommendations, the Bill is considered passed by both Houses in its original form from the Lok Sabha.
- If the Rajya Sabha fails to provide recommendations within 14 days, the same outcome applies.
- However, both Houses of Parliament must approve a Financial Bill.
- While an ordinary Bill can originate in either House, a Money Bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha, per Article 117(1).
- Moreover, only on the President's recommendation can anyone introduce or propose Money Bills in the Lok Sabha.
- Amendments related to reducing or abolishing any tax are exempt from requiring the President's recommendation.
- The essential conditions for a Financial Bill to attain Money Bill status are that it must solely originate in the Lok Sabha, not the Rajya Sabha, and must be introduced upon the President's recommendation.
INCOIS, ISRO to study rip currents for safer beaches

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) have embarked on a project to continuously monitor and issue operational forecast alerts of rip currents.
What is a Rip Current?
- Rip currents are channelled currents of water flowing away from shore at surf beaches.
- They typically extend from near the shoreline, through the surf zone and past the line of breaking waves. (The surf zone is the area between the high tide level on the beach to the seaward side of breaking waves.)
Formation of Rip Currents:
- Rip currents form when waves break near the shoreline, piling up water between the breaking waves and the beach.
- One of the ways this water returns to sea is to form a rip current, a narrow stream of water moving swiftly away from shore, often perpendicular to the shoreline.
Size of the Rip Currents:
- Rip currents can be as narrow as 10 or 20 feet in width though they may be up to ten times wider.
- The length of the rip current also varies.
- Rip currents begin to slow down as they move offshore, beyond the breaking waves, but sometimes extend for hundreds of feet beyond the surf zone.
Speed of the Rip Current:
- Rip current speeds can vary. Sometimes they are too slow to be considered dangerous.
- However, under certain wave, tide, and beach-shape conditions the speeds can quickly become dangerous.
Are All Rip Currents Dangerous?
- Rip currents are present on many beaches every day of the year, but they are usually too slow to be dangerous to beachgoers.
- However, under certain wave, tide, and beach-shape conditions they can increase to dangerous speeds.
- The strength and speed of a rip current will likely increase as wave height and wave period increase.
How Do Rip Currents Result in the Drowning of Swimmers?
- Drowning deaths occur when people pulled offshore are unable to keep themselves afloat and swim to shore.
- This may be due to any combination of fear, panic, exhaustion, or lack of swimming skills.
- Rip currents are the greatest surf zone hazard to all beachgoers. They can sweep even the strongest swimmer out to sea.
- Rip currents are particularly dangerous for weak and non-swimmers.
ISRO’s ‘Naughty Boy’ Rocket Launches INSAT-3DS (Indian Express)
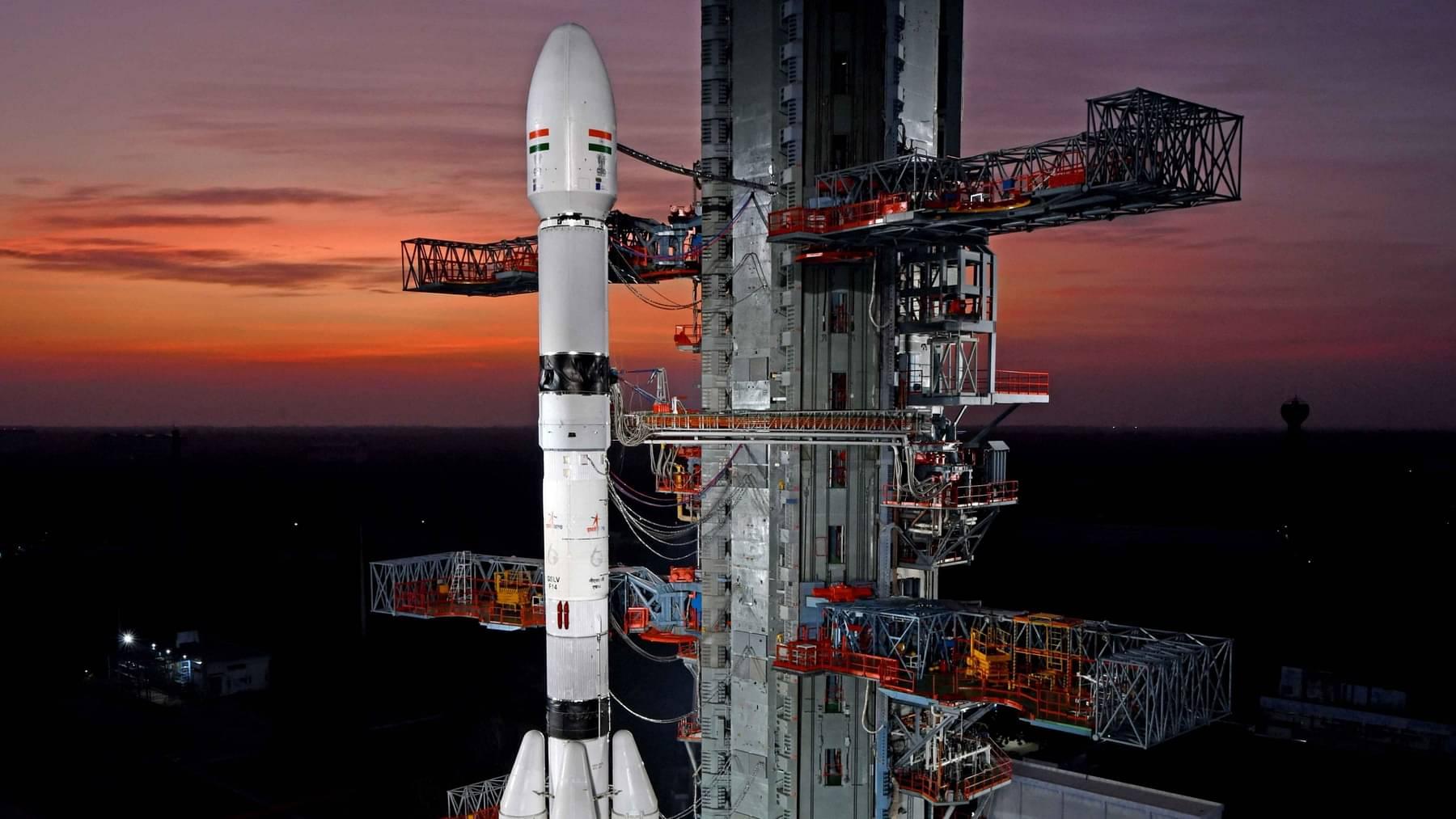

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently launched its weather satellite INSAT-3DS board spacecraft Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) F14, nicknamed the ‘naughty boy’ for its spotty record.
What is the GSLV-F14?
- The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), standing at a height of 51.7 metres, is a three-stage launch vehicle with a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes.
- First stage: Its first stage (GS1) features a solid propellant (S139) motor with 139 tons of propellant and four earth-storable propellant stages (L40) strapons, each carrying 40 tons of liquid propellant.
- Second Stage: The second stage (GS2) also utilises an earth-storable propellant system with a 40-ton propellant load.
- Third Stage: The third stage (GS3) is equipped with a cryogenic system containing 15 tons of propellant, consisting of liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
- GSLV-F14 serves as a versatile launch vehicle, capable of deploying various types of spacecraft for communication, navigation, earth resource surveys, and other specialised missions.
GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission Overview and Key Goals:
- INSAT-3DS Satellite marks a significant advancement in the Third Generation of Meteorological Satellite series from Geostationary Orbit, with substantial contributions from Indian industries.
- Fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), the mission aims to enhance meteorological services, complementing the existing capabilities of INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR satellites.
Key Objectives:
- Earth Observation and Oceanic Monitoring: Utilise various spectral channels to monitor Earth's surface, conduct oceanic observations, and assess environmental conditions critical for meteorology.
- Atmospheric Parameter Profiling: Provide vertical profiles of essential meteorological parameters within the atmosphere, enhancing our understanding of atmospheric dynamics.
- Data Collection and Dissemination: Facilitate the collection and dissemination of data from Data Collection Platforms (DCPs), ensuring timely access to crucial meteorological information.
- Satellite Aided Search and Rescue (SAR) Services: Enable Satellite Aided Search and Rescue services, enhancing emergency response capabilities through advanced satellite technology.
Significance of the GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission:
- The launch of INSAT-3DS holds a lot of significance for India's space agency as it is equipped to provide extremely accurate weather forecast information by studying the surface of the ocean, also being helpful in disaster prevention.
- The GSLV has encountered challenges in the past, with four out of 15 launches facing setbacks, contrasting with the higher success rates of ISRO's PSLV and LVM-3.
- The success of this mission is critical, especially considering the upcoming launch of the Earth observation satellite, NISAR, later this year, a collaborative effort between NASA and ISRO.
- INSAT-3DS, with a mission lifespan of 10 years, will assume the roles of INSAT-3D (2013) and INSAT-3DR (2016), which have reached the end of their operational lives.
- This mission will enhance meteorological forecasting capabilities, enabling better prediction of extreme weather events like thunderstorms, providing visibility assessments for aviation, and facilitating research on forest fires, smoke, snow cover, and climate dynamics.
OpenAI launches Sora (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
OpenAI has unveiled a new generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) model that can convert a text prompt into video, an area of GenAI that was thus far fraught with inconsistencies.
What is OpenAI's Sora?
- Sora is an AI model developed by OpenAI –– built on past research in DALL·E and GPT models –– and is capable of generating videos based on text instructions.
- It can also animate a static image, transforming it into a dynamic video presentation.
- Sora can create full videos in one go or add more to already created videos to make them longer.
- It can produce videos up to one minute in duration, ensuring high visual quality and accuracy.
- Sora can generate complex scenes with various characters, precise actions, and detailed backgrounds.
- Not only does the model understand the user's instructions, but it also interprets how these elements would appear in real-life situations.
- The model has a deep understanding of language, enabling it to accurately interpret prompts and generate compelling characters that express vibrant emotions.
- Sora can also create multiple shots within a single generated video that accurately portrays characters and visual style.
Limitations:
- Despite its impressive capabilities, OpenAI acknowledges certain limitations in the current iteration of Sora.
- The model may encounter challenges in accurately simulating complex physics within scenes, leading to potential discrepancies in cause-and-effect scenarios.
- For instance, while depicting a person taking a bite out of a cookie, Sora may struggle to consistently render a corresponding bite mark on the cookie in subsequent frames.
RBI Put Restraints on a Certain Card Network (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has ordered a certain card network to stop “unauthorised payments” made using business cards.
What is a Card Network?
- Card networks connect banks, merchants, and customers (card users) to one another so that transactions can be carried out smoothly and securely.
- Card networks are operating in the background every time a customer uses her card to make a payment.
- There are five authorised card networks in India:
- Visa
- Mastercard
- RuPay
- Diners Club, and
- American Express
Reasons Behind the RBI Order:
- Payments to Non-Card-Accepting Entities: The network facilitated card payments from corporations for commercial transactions, transferring the funds to non-card-accepting recipients via IMPS, RTGS, or NEFT without proper authorization, violating the Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act, 2007.
- Non-Adherence to KYC Requirements: Additionally, the RBI expressed concerns regarding non-compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) norms in these transactions.
What are the RBI’s Concerns?
- Under Section 4 of the PSS Act, such a payment system requires authorisation, which had not been obtained in this case.
- There were two other concerns as well.
- First, the intermediary in such an arrangement pooled a large amount of funds into an account that was not a designated account under the PSS Act.
- Second, transactions processed under this arrangement did not comply with the ‘originator and beneficiary information’ requirements, as stipulated under the ‘Master Direction on KYC’ issued by the RBI.
- Steps taken by the RBI: The RBI has instructed the card network to suspend all such arrangements until further notice.
- However, regular usage of business credit cards remains unaffected.
Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Researchers have now, for the first time, detected the presence of water molecules on the surface of an asteroid using the data from NASA's now-retired SOFIA airborne observatory.
About Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA):
- SOFIA is a powerful, general-purpose infrared observatory used to study the birth of new stars, planetary nebulae and supernova remnants, the atmospheres of Solar System objects, and many more.
- Earth’s atmosphere protects us from harmful radiation, but it also blocks a lot of light useful for astronomy.
- For that reason, NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) built the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) to fly aboard a modified commercial aircraft capable of flying above 99% of the light-blocking atmosphere.
- SOFIA is carried aboard an aeroplane capable of flying at an altitude of 13 kilometres, higher than 99% of the infrared-absorbing atmosphere.
- First flown in 2007, SOFIA provided the first measurements of Pluto’s atmosphere, mapped the dust and magnetic fields around black holes, and provided a wealth of information about star-forming nebulae.
- The telescope consists of a 2.5-meter (8.2-foot) mirror and a suite of scientific instruments including:
- Photometers to measure the brightness of sources
- Spectrometers to split the light into its component wavelengths, and
- A polarimeter to measure the polarisation of light caused by dust particles.
- Astronomer Gerard Kuiper is best known for his prediction of the Kuiper Belt of icy outer Solar System bodies, but in 1965, he used a high-flying NASA aeroplane to study Venus in infrared light, pioneering the use of aircraft for astronomy.
- SOFIA is Kuiper’s spiritual descendant, built on a larger scale and using a dedicated aeroplane.
- The SOFIA telescope is carried by a Boeing 747SP (“special purpose”) designed for long-duration flights.
- The aeroplane was modified in several ways, including a large opening on the side of the telescope.
- To operate under these conditions, SOFIA is lightweight and built to withstand mechanical vibrations and turbulence from air flowing across the opening in the side of the aeroplane.
- The aeroplane is capable of ten-hour flights, with flight paths chosen to keep ahead of the sunrise and maximise the amount of darkness.
- SOFIA achieved full operational capability in 2014 and prematurely ended in 2022 after operating for 12 years.
India initiates Anti-Dumping Probe into Solar Glass Imports from China and Vietnam (TOI)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has launched an anti-dumping investigation into the import of solar glass from China and Vietnam following a complaint from domestic players.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff levied on imports from foreign countries when their prices are lower than the fair market value of similar goods in the domestic market.
- It's implemented by governments to counteract the practice of "dumping," where foreign goods are sold at unfairly low prices in the domestic market, posing a threat to local businesses.
- The primary objective of anti-dumping duty is to safeguard domestic industries from unfair competition and restore fair trade practices.
- This measure is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to address instances where dumping causes genuine harm to domestic industries.
- To impose anti-dumping duties, governments must provide evidence of dumping, quantify its extent in terms of costs, and demonstrate the resulting injury or threat to domestic markets.
- While aimed at protecting local industries, anti-dumping duties can sometimes lead to increased prices for consumers within the country.
About Countervailing Duty (CVD):
- Countervailing duty (CVD) is a type of tariff imposed by a government to offset the adverse effects of import subsidies on domestic producers.
- It serves as an import tax applied by the importing country on subsidised products from abroad.
- CVD is imposed to address situations where foreign governments provide subsidies to their producers, lowering the cost of their goods and potentially disrupting fair competition.
- To prevent the influx of subsidised products into their markets, importing countries levy CVD, effectively neutralising the price advantage enjoyed by these imports.
- The imposition of CVD is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to help maintain fair trade practices among its member countries.
Difference Between Anti-dumping Duty and Countervailing Duty:
- Anti-dumping duty is enacted to safeguard domestic markets from the harmful effects of low-priced foreign goods, while CVD targets products benefiting from government subsidies, resulting in artificially low prices.
- The amount of Anti-dumping duty is determined by the margin of dumping, whereas CVD is calculated based on the subsidy value granted to foreign goods.
Melting Glaciers Threaten Gulf Stream Collapse by 2025 (India Today)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the world grapples with the escalating impacts of climate change, a recent study has sounded the alarm on the potential collapse of the Gulf Stream by 2025.
What is the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is a strong ocean current that brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico into the Atlantic Ocean.
- It extends all the way up the eastern coast of the United States and Canada.
What Causes the Gulf Stream?
- The Gulf Stream is caused by a large system of circular currents and powerful winds, called an oceanic gyre.
- There are five oceanic gyres on Earth.
- The Gulf Stream is part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre.
- The ocean is constantly in motion, moving water from place to place via currents.
- The Gulf Stream brings warm water from the Gulf of Mexico all the way up to the Norwegian Sea.
- As the warm water comes in, colder, denser water sinks and begins moving south—eventually flowing along the bottom of the ocean all the way to Antarctica.
How Does the Gulf Stream Impact Weather and Climate?
- This strong current of warm water influences the climate of the east coast of Florida, keeping temperatures there warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer than the other southeastern states.
- Since the Gulf Stream also extends toward Europe, it warms Western European countries as well.
- In fact, England is about the same distance from the equator as the cold regions of Canada, yet England enjoys a much warmer climate.
- If it weren’t for the warm water of the Gulf Stream, England would have a much colder climate.
How Long Have We Known About the Gulf Stream?
- We’ve known about the Gulf Stream for more than 500 years.
- In 1513, Spanish explorer Ponce de Leon noted that there was a strong current in this location.
- A few years later, Ponce de Leon’s ship pilot realized that the Gulf Stream could help speed up the sailing trip from Mexico to Spain.
- In the late 18th century, Benjamin Franklin became the first to chart out the path of the Gulf Stream on a map.
Coal Ministry Hosts Industry Interaction on Coal Gasification (ET)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Coal has announced it will host an Industry Interaction on February 16, 2024, in Hyderabad to discuss the development of coal and lignite gasification projects across India.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a process where coal undergoes partial oxidation with air, oxygen, steam, or carbon dioxide to produce a fuel gas.
- This gas serves as an alternative to piped natural gas or methane for energy generation.
- Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) is a technique involving the conversion of coal into gas within the seam, extracted through wells.
- Production of Syngas: This process yields Syngas, a mixture primarily comprising methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas finds applications in producing fertilisers, fuels, solvents, and synthetic materials.
- Significance: In manufacturing, steel companies traditionally rely on costly imported coking coal. Syngas derived from coal gasification offers a cost-effective alternative.
- It is utilized in electricity generation, chemical feedstock production, and hydrogen-based applications like ammonia production and fueling a hydrogen economy.
Advantages of Coal Gasification:
- Coal gasification offers a solution to local pollution issues.
- It is deemed environmentally cleaner than direct coal combustion.
- Decreasing dependence on imported natural gas, methanol, ammonia, and other vital commodities, enhances energy security.
- This technology has the potential to mitigate environmental impacts by curbing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable approaches, aligning with India's global objectives for a more environmentally sustainable future.
Concerns Associated with Coal Gasification Plants?
- The main disadvantage of coal gasification is that it is an expensive process.
- The process can produce a number of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and mercury.
- The process produces a lot of ash, which can pollute the environment.
- The process uses a lot of water, which can lead to water shortages in areas where it is used.
The Global Pulses Conference (The Hindu)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Global Pulses Conference, an annual meeting of pulses producers, processors and traders, suggested that India augment the production of pulses to meet the nutritional requirements.
About the Global Pulses Confederation (GPC):
- The Global Pulses Confederation (GPC) serves as a global representative body for the pulse industry.
- Stakeholders: It encompasses various stakeholders within the pulse industry, such as growers, researchers, traders, government entities, processors, and consumers.
- Headquarters: The GPC is based in Dubai and operates under the licensing of the Dubai Multi Commodity Centre (DMCC).
- The Global Pulses Conference, held annually, took place in New Delhi this year.
Key Observations from the Conference:
- Self-Sufficiency Target: India aims to achieve self-sufficiency in pulses production by 2027, having already attained this status in chickpeas and various other pulse crops, with minor gaps remaining in pigeon peas and black gram.
- Decadal Growth: Pulse production has witnessed a significant 60% growth, increasing from 171 lakh tonnes in 2014 to 270 lakh tonnes in 2024.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): The government has guaranteed farmers a minimum support price set at 50% above the actual cost of production, ensuring lucrative returns on investment.
- Current MSP rates reflect remarkable increases, such as 117% in masoor, 90% in moong, and substantial hikes in chana dal, toor, and urad compared to a decade ago.
- Government Initiatives: Efforts include the introduction of new seed varieties and the expansion of tur and black gram cultivation to bolster production.
- Importance of Pulse Crops: Pulse cultivation not only enriches soil health but also provides nutritional benefits, particularly for smallholding farmers.
- Improved cultivation practices promise widespread benefits for all stakeholders involved.
Status of Pulse Production in India:
- Production Trends: Over the past decade, pulse production in India has surged by 60%, escalating from 171 lakh tonnes in 2014 to 270 lakh tonnes in 2024.
- Global Standing: India boasts the distinction of being the world's largest producer, consumer, and importer of pulses. It contributes 25% to global production, consumes 27% of the world's total, and imports 14%.
- Agricultural Landscape: Pulses occupy approximately 20% of the foodgrain area in India and contribute 7-10% to the nation's total foodgrain production.
- Cultivation Seasons: While pulses are cultivated in both Kharif and Rabi seasons, Rabi pulses account for over 60% of the total production.
- Variety Distribution: Among pulse varieties, Gram leads the production, comprising roughly 40% of the total output, followed by Tur/Arhar at 15-20%, and Urad/Black Matpe and Moong each contributing approximately 8-10%.
- Self-Sufficiency: India has achieved self-sufficiency in chickpeas (chana) and various other pulse crops, with minor shortfalls, observed only in pigeon peas (tur) and black gram.
DoT Unveils 'Sangam: Digital Twin' Initiative (TOI)

- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications has introduced the 'Sangam: Digital Twin' initiative, which aims to transform infrastructure planning and design through innovation and the integration of advanced technologies.
What is Sangam: Digital Twin initiative?
- Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling monitoring, simulation, and analysis for adaptive outcomes.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' consists of two stages:
- The first is exploratory for creative exploration, and
- The second is for the practical demonstration of specific use cases, creating a future blueprint for collaboration in future infrastructure projects.
- The initiative aligns with advancements in communication, computation and sensing over the past decade, fostering a collaborative approach to reshape infrastructure planning and design.
- 'Sangam: Digital Twin' integrates 5G, IoT, AI, AR/VR, AI native 6G, Digital Twin and next-gen computational technologies to break silos and promote a whole-of-nation approach.
- The new initiative aims to transform ideas into solutions, bridging the gap between conceptualisation and realisation, and fostering advancements in infrastructure.
- Sangam encourages a holistic approach to innovation, uniting stakeholders to harness unified data and collective intelligence.
- It is aimed at creating an ecosystem that maximises the value of technological advancements for development.
- Sangam aims to demonstrate the practical implementation of innovative infrastructure planning solutions, providing a model framework for collaboration and a future blueprint for scaling successful strategies in future projects.
- The platform also offers a blog for pre-registered participants to connect, share insights, and engage in discussions.
Significance of Digital Twins:
- Facilitates remote monitoring, making it applicable for use in hazardous operations.
- Enhances predictive capabilities, assisting in making informed policy decisions.
- Improves operational efficiency, thereby ensuring the maintenance of output quality.
- Assists in urban planning by generating various simulations and forecasts.
The Schengen Area in Europe (The Hindu)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kosovo recently achieved visa-free entry to the Schengen zone in Europe, the world's largest area of unrestricted movement. Now, citizens of Kosovo can visit the Schengen zone as tourists for up to 90 days within 180 days.
Why Kosovo's Schengen Application Was Delayed for Years?
- Despite the European Commission's clearance of Pristina's readiness to address issues like illegal migration and corruption in 2018, Kosovo faced prolonged delays in obtaining Schengen visa-free status.
- The primary obstacle stemmed from opposition from various EU members who did not acknowledge Kosovo's unilateral declaration of independence from Serbia in 2008.
- Moreover, Kosovo lacks legal statehood recognition from the UN and is not acknowledged by key global players like Russia and China.
What is the Schengen Zone?
- The Schengen Zone is an area that encompasses much of Europe and enables visa-free and border-free travel within it.
- The Schengen zone is named after the Schengen Agreement, which was signed in 1985 in Schengen, Luxembourg.
- The Schengen Zone acts as a single jurisdiction that allows travellers to cross borders without stopping for any border checks and therefore enables those who live close to international borders to come and go with ease.
- It currently includes 27 countries in Europe, though not all are members of the European Union.
- The exceptions are Norway, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, and Iceland.
- Croatia, an EU member since 2013, joined Schengen in 2023, while Romania and Bulgaria, EU members since 2007, will gain partial Schengen entry from 31 March 2024.
Is Admission to Schengen Mandatory for EU Members?
- When the Schengen agreement took effect in 1995, only seven of the entire 15-member union at the time joined the passport-free area.
- Today, 23 of the 27 EU states are part of the passport-free zone, excluding Cyprus, Romania, Bulgaria and Ireland.
- The Schengen area comprises 27 countries, including four non-EU members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Switzerland and Norway.
- It is important not to confuse the status of the four countries with the recent entry of Kosovo and the other five western Balkan entrants which are not counted among the Schengen 27 members.
What are the Advantages of the EU’s Border-free Policy?
- For nationals of any country, the benefit is the freedom to travel with a single Schengen visa to other European nations within the borderless area.
- For EU states, the Visa-free borderless travel, alongside the single currency adopted by 20 EU countries, is the most visible symbol of European integration.
What are the Challenges Faced by the Schengen Region?
- The Schengen region faced significant challenges, particularly during the Eurozone sovereign debt crisis of the past decade.
- The influx of migrants from conflict areas in Africa and West Asia, coupled with the rise of anti-immigrant sentiments fueled by far-right populist parties in Europe, added strain to the region.
- At one point, there were discussions within the EU about potentially excluding Mediterranean border countries from the Schengen Area, as some individual states considered reintroducing border controls unilaterally.
8th Century Kotravai Sculpture from Pallava Period Discovered (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, archaeologists discovered an eighth-century Kotravai sculpture, an artefact that dates back to the Pallava period, near Ulundurpet, Tamil Nadu.
About the Kotravai Sculpture:
- Kotravai sculpture is made in a slab stone of five-feet height and four-feet width.
- The idol is depicted with eight hands, indicating its origin in the eighth century during the Pallava period.
- The sculpture depicts various elements such as chakkara, sword, bell, and abhaya mudra in the right hands.
- Conch, bow, shield, and Uru Mudhra are shown in the left side hands along with bangles in all hands.
- The presence of trishul (soolam) and lion (simmam) on the right side of head, and blackbuck (kavarimann) on the left side.
- Kotravai is portrayed standing on the head of a buffalo, with two guards on each side.
About the Pallava Dynasty:
- The Pallava Dynasty, a prominent power in South India, thrived from the 3rd to the 9th centuries.
- Their dominion encompassed the northern regions of Tamil Nadu, portions of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana, with Kanchipuram serving as their capital.
- The Pallavas were known for their patronage of Buddhism, Jainism, and Brahminical faith, as well as their support for music, painting, and literature.
- Origins: Initially vassals of the Andhra Satavahanas, the Pallavas gained autonomy following the latter's decline in Amaravati.
- Gradually expanding southward, they established their capital in Kanchipuram during the 4th century CE.
- Under the reigns of Mahendravarman I (571 - 630 CE) and Narasimhavarman I (630 - 668 CE), the Pallava realm experienced significant growth in wealth and power.
- According to the accounts of Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang, Bodhidharma, the founder of the Chan (Zen) school of Buddhism in China, was purportedly a prince of the Pallava empire.
- The Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang visited Kanchipuram, the capital of Pallavas, during the reign of Narasimha Varman I and lauded their benevolent governance.
Architectural Contributions of the Pallavas:
- The Pallava Dynasty is renowned for its patronage of Dravidian architecture, particularly temple construction.
- They played a pivotal role in the evolution from rock-cut architecture to stone temples.
- Their most celebrated architectural achievements can be found in Mahabalipuram, which flourished as a significant hub of art, architecture, and literature during Pallava rule.
- Narasimhavarman II commissioned notable structures such as the Kailasanatha Temple in Kanchipuram and the Shore Temple.
- Among these temples, Kailasanatha and Vaikuntaperumal stand out for their architectural excellence.
- The Vaikuntaperumal shrine, erected in the 8th century AD, is renowned for its intricate sculptures depicting Pallava history.
- Religion: The Pallavas embraced Shaivism, a predominant local religion, thereby aligning themselves with Dravidian cultural traditions.
Military Engagements and Decline of the Pallava Dynasty:
- Throughout their reign, the Pallavas engaged in persistent conflicts with both the Chalukya Dynasty to the north and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola and Pandyas to the south.
- The Pallavas faced ongoing battles with the Chalukyas of Badami and ultimately succumbed to the supremacy of the Chola kings in the 8th century CE.
- The ascent of the Rashtrakutas marked the decline of the Pallava Dynasty.
- In 897 AD, Vijayalaya, the Chola King, decisively defeated Aparajitavarman, the last Pallava King, thereby sealing the fate of the Pallava Dynasty.
Alaskapox Claims One Life in US (TOI)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
An elderly man has died from Alaskapox, the first known fatality from the recently discovered virus.
What is Alaskapox?
- Alaskapox is caused by orthopoxvirus, a family of brick-shaped viruses that can infect both animals and humans, leading to skin lesions or pox.
- The virus was first identified in a woman living near Fairbanks, Alaska, and has since been primarily detected in small mammals like red-backed voles and shrews.
- However, domestic pets such as dogs and cats may also be carriers of the virus.
What are the symptoms of Alaskapox?
- Symptoms of Alaskapox include the development of one or more bumps or pustules on the skin, accompanied by joint or muscle pain and swollen lymph nodes.
- While the majority of the seven known human cases in Alaska over the past nine years have experienced mild illnesses that were resolved without intervention, the virus poses a greater threat to individuals with weakened immune systems.
How is Alaskapox Transmitted?
- Transmission of Alaskapox is believed to occur through direct contact with infected animals.
- Unlike some of its orthopoxvirus relatives, there have been no documented instances of Alaskapox spreading from person to person.
- Though it's not clear how Alaskapox is transmitted, researchers say that it may be zoonotic meaning it can jump from animals to humans.
PM Modi addresses World Government Summit 2024 in Dubai (MEA)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Modi attended the World Government Summit 2024 as guest of honour in Dubai recently.
What is the World Governments Summit?
- The World Governance Summit serves as a worldwide platform committed to shaping the trajectory of government initiatives across the globe.
- This annual gathering takes place in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, convening leaders and experts from various sectors.
- Each year, the Summit sets the agenda for the forthcoming era of governance, emphasising the utilisation of innovation and technology to address pressing global challenges.
- Since its establishment in 2013, the Summit has been steadfast in its mission to influence the evolution of governmental practices and foster a brighter future for humanity.
World Governance Summit Organization:
- The World Governance Summit Organization operates as an impartial, nonprofit entity with a global reach, dedicated to influencing the future landscape of governance.
- Headquartered in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the organisation serves as a nexus for collaboration and idea exchange among governmental and non-governmental stakeholders.
- 2024 Summit: Dubai, United Arab Emirates
- Theme - 'Shaping Future Governments'
Key Highlights of PM Modi's Speech:
- Streamlining Government Operations: The Prime Minister addressed the evolving landscape of governance, emphasising India's adoption of transformative reforms under the ethos of "Minimum Government, Maximum Governance.”
- Human-Centred Governance: Drawing from India's experience leveraging digital technology for welfare, inclusivity, and sustainability, he advocated for a human-centred approach to governance.
- He highlighted India's focus on people's participation, last-mile delivery, and women-led development to foster an inclusive society.
- Need for Global Collaboration: Given the interconnected nature of the world, the Prime Minister stressed the importance of governments collaborating and learning from each other to tackle future challenges effectively.
- Model of Governance: Highlighting the current imperative, the Prime Minister underscored the necessity for governance to be inclusive, technologically adept, transparent, and environmentally sustainable.
- He outlined priorities such as Ease of Living, Justice, Mobility, Innovation, and Business in public service delivery.
- India's Climate Change Commitment: Reaffirming India's unwavering commitment to climate change action, he urged people to join Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) to foster a sustainable world.
- Leadership Role of India: The Prime Minister elaborated on India's leadership role, particularly as the chair of G-20, highlighting efforts to address global challenges and elevate development concerns of the Global South.
- He advocated for reforming multilateral institutions to give greater voice to the Global South in decision-making processes.
- India as a Global Partner: Emphasising India's commitment to global progress, he reiterated India's role as a "Vishwa Bandhu" (friend of the world), pledging continued contributions to global advancement.
China Moves its Nationals into its Vacant ‘Defence Villages’ Along LAC (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Chinese nationals have started occupying several of their model “Xiaokang” border defence villages across India’s north-eastern borders which the country has been building along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) since 2019.
News Summary:
- Chinese activity has been observed in several villages situated on its side of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) opposite the Lohit Valley and the Tawang sector of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Over the past five years, China has been undertaking the construction of 628 "well-off villages" along India's borders with the Tibet Autonomous Region, encompassing regions like Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The precise purpose of these villages remains ambiguous, although the structures are believed to serve as "dual-use infrastructure," serving both civilian and military functions.
What is the Line of Actual Control (LAC)?
- The LAC serves as the boundary separating areas under Indian administration from those under Chinese administration.
- However, it is not a formally agreed-upon boundary, lacking delineation on maps or physical demarcation on the ground.
- India views the LAC as approximately 3,488 km in length, while China's perspective estimates it to be around 2,000 km.
- The LAC is segmented into three sectors: the eastern sector covering Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim, the middle sector spanning Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, and the western sector in Ladakh.
- India's official boundary line, as depicted on maps released by the Survey of India, encompasses both Aksai Chin and Gilgit-Baltistan, diverging from the LAC.
- Consequently, the LAC does not coincide with India's claim line.
- For China, the LAC generally aligns with its claim line, except in the eastern sector, where it asserts control over the entire territory of Arunachal Pradesh, which it regards as South Tibet.
Dispute over the LAC and Controversy Surrounding Claim Lines in Ladakh:
- India disputes the validity of the Line of Actual Control (LAC), asserting that it is a construct devised by China.
- The Chinese demarcation appears as a series of disconnected points on a map, lacking a clear and consistent delineation.
- India contends that the line should exclude territorial gains made through aggression in 1962 and instead reflect the positions as of September 8, 1962, before the Chinese incursion.
- This ambiguity in the Chinese definition of the LAC leaves room for China to pursue incremental changes on the ground through military actions, as evidenced by the clash in the Galwan Valley between the Indian Army and the Chinese PLA in 2020.
- Aksai Chin, located in the Ladakh region of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, was not part of British India, despite being under British Empire control.
- As a result, while the eastern boundary was clearly defined in 1914 with the signing of the Shimla Agreement on the McMahon Line by British India, the western boundary in Ladakh remained unresolved.
- These historical maps, still officially recognized today, formed the basis of engagements with China, ultimately culminating in the 1962 War.
Infrastructure Development along the LAC:
- Consistently, China has enhanced its existing infrastructure along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), focusing on improving connectivity through mountain passes, constructing roads, bridges, and model villages.
- Additionally, China has been constructing infrastructure, including border villages, within Bhutanese territory.
- Over the past three to four years, India has intensified efforts to bolster its border infrastructure, encompassing initiatives to enhance forward connectivity, establish alternative routes to the LAC, and connect remote areas.
- India's Vibrant Villages program aims to modernise 663 border villages, providing them with essential amenities in the initial phase.
- Notably, 17 of these villages located along the borders with China in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh have been earmarked for development as pilot projects under this program.
- Moreover, significant progress is underway on three major highways in Arunachal Pradesh:
- The Trans-Arunachal Highway
- The Frontier Highway, and
- The East-West Industrial Corridor Highway.
Stone Age Wall Discovered Beneath the Baltic Sea (India Today)
- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A megastructure found in the Baltic Sea may represent one of the oldest known hunting structures used in the Stone Age — and could change what’s known about how hunter-gatherers lived around 11,000 years ago.
About the Blinkerwall:
- The Blinkerwall is the oldest known megastructure crafted by humans in Europe.
- It is around a kilometre-long structure that lies hidden in the Bay of Mecklenburg, submerged under 21 metres of water.
- It consists of approximately 1,400 smaller stones intricately positioned to connect almost 300 larger boulders, some of which were deemed too massive for human groups to have manoeuvred.
- The total weight of the wall's stones exceeds 142 tonnes, making it improbable that natural processes, such as tsunamis or glacial movements, formed it.
- It likely dates back over 10,000 years, sinking beneath rising sea levels around 8,500 years ago.
- This positions it among the oldest known examples of hunting architecture globally and potentially designates it as the oldest man-made megastructure in Europe.
About the Baltic Sea:
- The Baltic Sea is a semi-enclosed inland sea situated in Northern Europe.
- As an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean, it stretches northward from the latitude of southern Denmark nearly to the Arctic Circle, acting as a divider between the Scandinavian Peninsula and the rest of continental Europe.
- With a coastline spanning approximately 8,000 km, the Baltic Sea is bordered by several countries, including Sweden, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Finland, Estonia, Germany, Denmark, and Russia.
- Covering an area of around 377,000 sq.km, the sea measures approximately 1,600 km in length and 193 km in width.
- It is linked to the White Sea via the White Sea Canal and to the North Sea's German Bight through the Kiel Canal, while it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Danish Straits.
- The Baltic Sea encompasses three significant gulfs: the Gulf of Bothnia to the north, the Gulf of Finland to the east, and the Gulf of Riga slightly to the south.
- Renowned as the world's largest brackish inland water body, the Baltic Sea exhibits lower water salinity levels compared to the World Oceans due to freshwater influx from the surrounding land and its shallow depth.
- More than 250 rivers and streams discharge into the Baltic Sea, with the Neva River being the largest among them.
- The sea boasts over 20 islands and archipelagos, with Gotland, located off the coast of Sweden, ranking as the largest island in the Baltic Sea.
Farmers’ Protest 2.0 and MSP Demand (The Hindu)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's Farmers are back on the streets yet again, demanding guarantees on Minimum Support Prices, work on the Swaminathan Committee report, Electricity amendment bill, and debt waiver.
Why are Farmers Protesting?
- Farmers have demanded MSP assurance across all crops, implementing Swaminathan Commission recommendations, debt relief, pensions for farmers, and withdrawing cases against past protestors.
- Advocacy for India's exit from WTO and free-trade agreements are also demands that have been put forth by the farmers.
What is the Minimum Support Price (MSP)?
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) is the lowest rate at which government procurement agencies buy crops from farmers.
- It shields farmers from market fluctuations, offering stability and income security.
- MSP is crucial for ensuring fair prices for farmers and is determined by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), considering factors like production costs, market trends, and demand-supply dynamics.
- Established in 1965, CACP operates under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- After the CACP submits its recommendations, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by the Prime Minister of India, makes the final decision on MSP levels.
Which Crops are Covered Under MSP?
- Kharif crops such as Paddy, Jowar, Bajra, Ragi, Maize, Arhar, Moong, Urad, Cotton, Groundnut, Sunflower Seed, Soybean, and Sesamum.
- Rabi crops such as Wheat, Barley, Gram, Masur, Rapeseeds & Mustard, Safflower, and Toria.
- Additionally, MSP is announced for Copra, De-husked Coconut, and Jute, and Fair Remunerative Prices are declared for Sugarcane.
How is MSP Calculated?
- The Minimum Support Price (MSP) is calculated by considering both the explicit and implicit costs incurred by farmers.
- Explicit costs cover expenses like chemicals, fertilisers, seeds, and hired labour, while implicit costs include factors such as family labour and rent.
- These variables are represented by A2, FL, and C2.
- A2 refers to the expenses for inputs like chemicals, fertilisers, seeds, and hired labour for crop growth, production, and maintenance.
- A2 + FL includes both actual and implicit costs, such as family labour.
- C2 incorporates A2 + FL along with fixed capital assets and rent paid by farmers.
- Additionally, the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) takes into account various other factors:
- Cost of cultivation per hectare and crop costs in different regions.
- Cost of production per quintal and regional differences.
- Market prices of relevant crops and their fluctuations.
- Other production and labour costs, along with associated changes.
- Prices of commodities bought or sold by farmers and any fluctuations.
- Information on product supply, including area, yield, production, imports, exports, and stocks with public agencies or industries.
- Demand information across regions, including total and per capita consumption, processing industry trends, and capacity.
What Changes Did the Swaminathan Formula Propose?
- The National Commission on Farmers, chaired by agricultural scientist M S Swaminathan, in 2004, submitted a report to the government in 2006, suggesting that the solution to the farm crisis was to provide remunerative prices to the farmer.
- The commission recommended that the MSP should be 1.5 times the farmers’ input costs.
- For the calculation of input costs, however, the Swaminathan Commission laid down a different formula.
- Along with the paid-out cost (A2) and the imputed value of family labour (FL), also included the interest on the value of owned capital assets, rent paid for leased-in land, or the rental value of owned land (C2).
- Key difference:
- The government sets MSP at 1.5 times the Cost of Production (CoP), where Cop is A2+FL.
- The Swaminathan Commission, however, suggests that CoP should be based on C2, proposing the 'C2+50 per cent' formula for setting MSP.
National Generic Document Registration System (PIB)
- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Secretary, Department of Land Resources, rolled out the National Generic Document Registration System (NDGRS) throughout Assam along with the launch of Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) seeding of geo-referenced Cadastral Maps.
About National Generic Document Registration System:
- The Department of Land Resources has developed the National Generic Document Registration System (NGDRS) as part of the Digital India Land Records Modernisation Programme (DILRMP).
- As many as 28 States / UTs have adopted the NGDRS for Land Records.
- The NGDRS application is developed by the National Informatics Centre, Pune.
- It is a common, generic application developed for registration departments across the country under the One Nation One Software initiative.
Objectives of NGDRS:
- With technology being one of the major enablers, it is ensured that registrations and delivery of documents to the parties happen faster in comparison to the conventional methods. The broad level objectives are:
- One Nation One Software
- Generic platform for registration of properties and document across the country
- Citizen empowerment by enabling property valuation and online document submission
- A single platform of all the stakeholders in registration process
Features of NGDRS:
- It is a nationwide registration department application that is generic, standardised, and adaptable.
- Sub-registrars, citizens, and apex users from registration departments are the intended users of this program.
- NGDRS makes it easier for states to set up state-specific instances and customise the program to meet their needs.
- With its comprehensive user interface for document and property registration, the program makes it possible for citizens to continue with online land purchases.
- They are able to determine the circle rate for land, determine the type of land, and value properties based on current rates.
- The inability to transact in properties that are prohibited—such as government, tribal, mortgaged, etc.—helps them eventually determine where and what kind of land to purchase.
- After that, clients may schedule appointments in advance, apply online for document submission, and make quick payments.
- Purchasers of real estate only need to make one visit to the sub-registrar's office, and that should be during the final registration and signing process.
What is ULPIN?
- It is the distinct blockchain ID, and the land parcel's ULPIN from BhuNaksha allows for a unique identification.
- Every land parcel has a unique 14-digit alphanumeric identification number, often known as the AADHAR or fingerprint for land.
- The identification relies on georeferenced cadastral maps and is based on the land parcel's longitude and latitude.
- ULPIN has the following advantages: it guarantees transaction uniqueness, maintains current spatial records, connects property transactions, shares land record data across departments and financial institutions, and gets rid of fraudulent transactions.
Revised Guidelines for Community Radio Stations (ET)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
With a view to ensuring the growth of the community radio sector, the Union government on Tuesday increased the advertising time for community radio stations as well as the tariff rate for advertisements.
What are Community Radio Stations (CRSs?
- Community radio stations (CRSs) are low-power radio stations with a coverage area of approximately a 10-15 km radius, depending on the area’s geography, which is meant to be set up and operated by local communities.
- They offer a platform where content is disseminated in localized dialects and regional languages.
- Local, context-specific issues are raised and discussed in these stations in local idioms.
- India's first community radio station (CRS) was inaugurated on the campus of Anna University in 2004.
- Currently, there are 481 CRSs in India.
About the Revised Policy Guidelines:
- Under the revised policy, the government has permitted any eligible organisation functional in multiple districts to set up a maximum of six community radio stations in different districts.
- The advertising time for community radio stations has been increased from seven minutes per hour to 12 minutes per hour, while the rate of advertisement has been hiked from Rs 52 to Rs 74 per 10 seconds, the guidelines stated.
- The policy also fixed the validity of the letter of intent issued to an organisation to one year, with a buffer of three months to the applicant for any unforeseen circumstances.
- The revised policy guidelines are expected to fuel the growth of the community radio sector.
- The guidelines stated that the licensee would set up an advisory and content committee comprising members of the local community, with 50 per cent representation for women.
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) (DST)
- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) have pioneered a novel method for directly synthesising CNTs on glass substrates at a temperature of 750 °C.
What are Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)?
- A carbon nanotube is a small cylindrical carbon structure made out of graphene.
- The tube comprises hexagonal structures.
- Despite their very small size, carbon nanotubes are very strong.
- Carbon nanotubes are also known as “Buckytubes” because they resemble R. Buckminster Fuller’s geodesic domes.
- They are pivotal in advancing modern technology by showcasing extraordinary properties.
- Applications: They have found applications in diverse fields, including rechargeable batteries, flexible electronics, aerospace, transparent electrodes, touch screens, supercapacitors, and medicine.
- Recent Developments: The experiment employs the Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition Technique (PECVD), in which a spiral-shaped fused hollow cathode source is specifically constructed to create plasma.
- This novel method avoids the requirement for high temperatures and does not require a transition metal catalyst.
Why is It Necessary?
- Metal catalysts (Fe, Co, and Ni) and high temperatures (~1000 0C) are needed for conventional CNT production procedures.
- Concerns about biocompatibility arise with these catalysts for possible biomedical uses.
- A fascinating area of nanotechnology, the removal of these catalysts from CNTs presents a huge financial hurdle, underscoring the urgent need for cleaner, more sustainable CNT synthesis techniques.
- Clean CNTs that can be used in biomedical settings, optoelectronics, and energy studies may now be produced.
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) (Earth Org)
- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The circulation of the Atlantic Ocean, a key component in global climate regulation, is “on route” to a tipping point, according to a new study, which describes the findings as “bad news for the climate system and humanity.”
What is Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)?
- The ocean’s water is constantly circulated by currents.
- Tidal currents occur close to shore and are influenced by the sun and moon and the surface currents are influenced by the wind.
- However, other, much slower currents that occur from the surface to the seafloor are driven by changes in the saltiness and ocean temperature, a process called thermohaline circulation.
- These currents are carried in a large "global conveyor belt," which includes the AMOC.
- AMOC stands for Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation.
- The AMOC circulates water from north to south and back in a long cycle within the Atlantic Ocean.
- This circulation brings warmth to various parts of the globe and also carries nutrients necessary to sustain ocean life.
- The circulation process begins as warm water near the surface moves toward the poles (such as the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic), where it cools and forms sea ice.
- As this ice forms, salt is left behind in the ocean water.
- Due to the large amount of salt in the water, it becomes denser, sinks down, and is carried southwards in the depths below.
- Eventually, the water gets pulled back up towards the surface and warms up in a process called upwelling, completing the cycle.
- The entire circulation cycle of the AMOC, and the global conveyor belt, is quite slow.
- It takes an estimated 1,000 years for a parcel (any given cubic meter) of water to complete its journey along the belt.
- Even though the whole process is slow on its own, there is some evidence that the AMOC is slowing down further.
Is the AMOC Slowing Down?
- As our climate continues to change, there is a possibility that the AMOC will slow down, or come to a complete stop.
- While research shows it is weakening over the past century, whether or not it will continue to slow or stop circulating completely remains uncertain.
- If the AMOC does continue to slow down, however, it could have far-reaching climate impacts.
- For example, if the planet continues to warm, freshwater from melting ice at the poles would shift the rain belt in South Africa, causing droughts for millions of people.
What Would Happen if AMOC Failed?
- AMOC acts as a sort of "switch" for the climate, particularly in Europe and the northern hemisphere.
- It would result in less precipitation in regions like Europe, North America, China, and certain regions of Russia in Asia, as well as widespread cooling throughout the northern hemisphere.
- The Amazon rainforest might become dry and drought-prone as a result of the extra heat brought on by a collapsing AMOC, and it might even become a savannah state.
- In certain areas, monsoon development and rainfall might be impeded by a slowing in AMOC.
- There might be less rainfall in the Sahel (the West African monsoon area), less summer monsoon circulation in South Asia and India, and more winter storms in Europe.
- The summer monsoon circulation over the Indian subcontinent and the sea level pressure gradient are both weakened by a weakening of the land-sea heat gradient.
India's retail inflation moderates to 5.10 per cent in January (The Hindu)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's retail inflation has eased to 5.10% on an annual basis, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation.
What is Retail Inflation or CPI-based Inflation?
- Retail inflation, also known as Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation tracks the change in retail prices of goods and services which households purchase for their daily consumption.
- CPI is released by The National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- To measure inflation, we estimate how much CPI has increased in terms of percentage change over the same period the previous year.
- If prices have fallen, it is known as deflation (negative inflation).
- The Central Bank (RBI) pays very close attention to this figure in its role of maintaining price stability in the economy.
- The CPI monitors retail prices at a certain level for a particular commodity; and price movement of goods and services at rural, urban and all-India levels.
- The change in the price index over a period of time is referred to as CPI-based inflation or retail inflation.
- Generally, CPI is used as a macroeconomic indicator of inflation, as a tool by the central bank and government for inflation targeting and for inspecting price stability, and as a deflator in the national accounts.
- CPI also helps understand the real value of salaries, wages, and pensions, the purchasing power of the nation’s currency, and regulating rates.
- CPI, one of the most important statistics to ascertain economic health, is generally based on the weighted average of the prices of commodities.
- It basically gives an idea of the cost of the standard of living.
- CPI specifically identifies periods of deflation or inflation for consumers in their day-to-day living expenses.
- If there is inflation (when goods and services cost more) the CPI will rise over a period of time.
- If the CPI drops, that means there is deflation or a steady reduction in the prices of goods and services.
How is CPI calculated (CPI formula)?
- To calculate CPI, multiply 100 by the fraction of the cost price of the current period and the base period.
- CPI formula: (Price of the basket in current period / Price of the basket in base period) x 100
Odisha’s Gupteswar Forest Is Now A Biodiversity Heritage Site (TOI)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Gupteswar forest in the Koraput district of Odisha has been officially declared the fourth biodiversity heritage site (BHS) in the state.
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)?
- A Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) is a unique ecosystem with rich biodiversity that is designated for special protection and conservation.
- These sites are typically declared by individual states or local bodies under the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, of 2002, in India.
Who can Declare BHS?
- Under Section 37 of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 the State Government in consultation with local bodies may notify areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS).
- The ‘Biodiversity Heritage Sites’ (BHS) are unique ecosystems having rich biodiversity comprising of any one or more of the following components:
- The richness of wild as well as domesticated species or intra-specific categories.
- High endemism.
- Presence of rare and threatened species, keystone species, and species of evolutionary significance.
- Wild ancestors of domestic/cultivated species or their varieties.
- Past pre-eminence of biological components represented by fossil beds and having significant cultural, ethical or aesthetic values are important for the maintenance of cultural diversity, with or without a long history of human association with them.
- “The creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them.
- The purpose of declaring BHS is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation of such sites.”
The main objectives of declaring an area as a BHS are:
- To conserve biological diversity, including genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and species diversity.
- To protect habitats of rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- To promote sustainable use of biodiversity.
- To maintain cultural diversity and traditional knowledge associated with biodiversity.
- To raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) of India:
Revival of Weimar Triangle (The Hindu)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The governments of Poland, France and Germany vowed Monday to make Europe a security and defence power with a greater ability to back Ukraine, amid concerns that former U.S. President Donald Trump might return to the White House and allow Russia to expand its aggression on the continent.
What is the Weimar Triangle?
- The Weimar Triangle is a regional alliance of three European countries:
- France
- Germany
- Poland
- It was established in 1991 in the German city of Weimar, with the aim of promoting cooperation between the three countries on cross-border and European issues.
- The Weimar Triangle is not a formal organization, but rather a platform for dialogue and cooperation.
- The three countries hold regular summits, typically at the level of heads of state or government, and their foreign ministers also meet frequently.
- The Weimar Triangle also includes cooperation between parliaments, militaries, scientists, and cultural institutions.
Significance of the Weimar Triangle:
- The Weimar Triangle has played a significant role in European integration.
- It helped to support Poland's emergence from communism and its accession to the European Union in 2004.
- In recent years, the Weimar Triangle has taken on a renewed importance as Europe has faced a number of challenges, including the Ukraine crisis and the rise of populism.
- The three countries have worked together to promote stability and cooperation in Europe.
Some of the key areas of cooperation between the Weimar Triangle countries:
- Security: The three countries cooperate on a range of security issues, including defence, counterterrorism, and cybersecurity.
- Economy: The Weimar Triangle countries are major trading partners, and they work together to promote economic growth and integration.
- Energy: The three countries are working together to develop a more secure and sustainable energy supply.
- Climate change: The Weimar Triangle countries are committed to combating climate change and have pledged to meet the targets of the Paris Agreement.
- Culture: The three countries have a rich cultural heritage, and they work together to promote cultural exchange and understanding.
Greening India's Wastelands with Agroforestry (GROW) Report and Portal (DD News)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog recently unveiled the Greening and Restoration of Wasteland with Agroforestry (GROW) report and portal, aiming to bolster efforts in environmental conservation and sustainable land use across India.
About the Greening India's Wastelands with Agroforestry (GROW) Portal:
- The "Greening and Restoration of Wasteland with Agroforestry (GROW)-Suitability Mapping" portal offers universal access to state and district-level data.
- Hosted on the Bhuvan website, the GROW initiative aligns with national commitments to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030 and create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent.
- Led by NITI Aayog, the initiative involved collaboration from various institutions and utilized advanced technologies like remote sensing and GIS to assess agroforestry suitability across all Indian districts.
- Through thematic datasets, the project developed an Agroforestry Suitability Index (ASI) for national-level prioritization of greening and restoration projects.
- Based on analysis of five remote sensing-derived thematic layers - land use, wasteland, slope, water proximity, and soil organic content - the system provides information on areas suitable for agroforestry across India.
- It classifies areas as highly suitable, moderately suitable, and less suitable for agroforestry.
- Key features include generating district-level information on wasteland areas suitable for agroforestry, area prioritization regimes, live maps, area analysis-statistic reports, and an interactive mode/tool for flexibility in handling weights based on local conditions/needs.
Government Emphasis on Agroforestry in Budget Allocation:
- The Union Budget for the fiscal year 2022-23 has underscored the promotion of agroforestry and private forestry as a priority.
- Recognizing the critical goods and services provided by agroforestry, the budget aligns with the country's commitment to sustainable land use practices.
India's Agroforestry Leadership and Global Alignments:
- As the seventh-largest country globally, India faces challenges such as increased build-up areas, degraded land, and imbalanced resources.
- Approximately 16.96% of the Total Geographical Area (TGA) is a wasteland, necessitating transformation for productive use.
- India's pioneering National Agroforestry Policy, initiated in 2014, aims to enhance productivity, profitability, and sustainability through agroecological land use systems.
- Agroforestry aligns with global commitments, including the Paris Agreement, Bonn Challenge, UN Sustainable Development Goals, United Nations Convention on Combating Desertification (UNCCD), Doubling Farmers Income, Green India Mission, and more.
- India's proactive stance in promoting agroforestry contributes significantly to these international efforts, fostering a sustainable and resilient future.
Floor Test in the Bihar Legislative Assembly (Indian Express)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar's coalition government with the Bhartiya Janata Party (BJP) on Monday won a crucial trust vote in the Bihar Assembly.
What is a Floor Test?
- A floor test (also called a ‘trust vote’) is held in legislative bodies, to find out whether the government that is suspected to have lost the majority still retains the confidence of the House.
- This is done through a vote among the members.
- When the House is in session, it is the Speaker who can call for a floor test but when the Assembly is not in session, the Governor’s residuary powers under Article 163 allow him to call for a floor test.”
- Further, “In 2020, the Supreme Court, in Shivraj Singh Chouhan & Ors versus Speaker, Madhya Pradesh Legislative Assembly & Ors, upheld the powers of the Speaker to call for a floor test if there is a prima facie view that the government has lost its majority.”
What Happens During a Floor Test?
- In case the majority held by the government is questioned, the leader of the party which claims to have the majority has to move a vote of confidence and prove a majority among those present and voting.
- The CM moves a motion seeking a vote of confidence, on which MLAs who are present in the House vote.
- If the majority of members vote in favour, the government survives;
- If the CM loses the vote, the government has to resign.
- This happens both in Parliament and the state Legislative Assemblies.
- Voting can be conducted by either a voice vote, in which MLAs respond to the motion verbally.
- Voting electronically involves the casting of votes by pressing a button, after which the numbers for each side are displayed on a board.
- In a physical division of votes, lawmakers cast votes in a ballot box, which are then counted.
- Also in situations when there are differences within a coalition government, the Governor can ask the Chief Minister to prove majority in the house.
- There is another test, the Composite Floor Test, which is conducted only when more than one person stakes a claim to form the government.
- When the majority is not clear, the governor might call for a special session to see who has the majority.
- The majority is counted based on those present and voting.
- This can also be done through a voice vote where the member can respond orally or through division voting.
- Some legislators may be absent or choose not to vote.
- In division vote, voting can be done through electronic gadgets, ballots or slips.
- The person who has the majority will form the government.
- In case of a tie, the speaker can also cast his vote under Article 100 of the constitution.
Regulating India's Online Gaming Industry (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will act as a regulator for the online gaming sector rather than an industry-led self-regulatory organization (SRO).
What are Online Games?
- Online games refer to games that are played over some form of computer network, most often the Internet.
- Online games can range from simple text-based games to games incorporating complex graphics and virtual worlds populated by many players simultaneously.
Types of Online Gaming:
- e-Sports: Originally played offline or on gaming consoles, e-Sports now thrive in the online realm, featuring structured competitions among professional players or teams.
- Fantasy Sports: These games involve assembling virtual teams composed of real-life athletes from different sports teams.
- Points are earned based on the actual performance of these athletes, as seen in platforms like Dream11.
- Online Casual Games: These diversions can be skill-based, where success relies on mental or physical prowess, or chance-based, where outcomes are determined by random events, like dice rolls.
How Big is India's Online Gaming Industry?
- The online gaming sector in India is primarily nurtured by a burgeoning startup ecosystem, boasting a robust 27% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
- Projections suggest that the integration of AI and online gaming could contribute up to $300 billion to India's GDP by 2026-27.
- India leads the global charts in terms of the percentage of new paying users (NPUs) in gaming, soaring from 40% in 2020 to an anticipated 50% in 2021.
- Transactional gaming revenue witnessed a notable 26% surge in India, with the number of paying players escalating from 80 million in 2020 to 95 million in 2021, as per a FICCI report.
Challenges Confronting India's Online Gaming Sector:
- Regulatory Void: The absence of a regulatory framework poses challenges in implementing essential measures such as grievance redressal, player protection, data security, and curbing deceptive advertisements.
- Illegal Offshore Markets: Illicit offshore gambling and betting platforms pose threats to financial integrity and national security, with estimated annual tax losses to India amounting to $45 billion.
- Interstate Quandary: Varied state regulations on online gaming create inconsistencies, compounded by the Internet's borderless nature, making enforcement difficult.
- Societal Implications: The surge in online gaming raises concerns about addiction, mental health, financial fraud, and privacy breaches, warranting a comprehensive approach to address these issues.
The Problem of Self-Regulatory Bodies Under the IT Rules:
- The implementation of the IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 represented a significant stride in regulatory oversight.
- According to these rules, online real-money gaming platforms must obtain approval from a regulatory authority, while those not involving real money are exempt from such requirements.
- In April 2023, the government issued online gaming regulations and provided a three-month window for the industry to propose Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs).
- However, the proposals submitted were predominantly influenced by gaming companies and their industry associations, raising concerns about their ability to function as impartial regulatory bodies.
NAL Successfully Tested High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) at Challakere, Karnataka (TOI)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from city-based National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), a Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) lab, achieved a breakthrough by successfully testing an unmanned aerial vehicle called High-Altitude Pseudo Satellite (HAPS) at Chitradurga's Challakere in Karnataka.
News Summary:
- National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has achieved a milestone with the successful testing of an unmanned aerial vehicle known as the High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS) in Challakere, Karnataka.
- This innovative system, measuring 5 meters in length with an impressive 11-meter wingspan and weighing 23 kg, soared to an altitude of approximately 3 km and maintained its position for an impressive duration of eight hours.
- A comprehensive series of tests is slated, with the ultimate goal of developing a full-fledged aircraft boasting a remarkable 30-meter wingspan comparable to a Boeing 737 by the year 2027.
- This advanced craft is anticipated to ascend to an impressive altitude of 23 km and remain airborne for a remarkable period of at least 90 days.
- NAL's ambitious agenda includes the design and construction of various components essential for the HAPS, including propellers, battery management systems, carbon-composite airframes, flight-control systems, and high-powered electric motors capable of withstanding extreme temperature variations.
- Additionally, in a separate endeavour, a Bengaluru-based private company recently conducted the inaugural test flight of a solar-powered, long-endurance drone, achieving an impressive flight duration of 21 hours.
About High Altitude Pseudo-Satellite (HAPS):
- Since the 1990s, numerous global initiatives have been undertaken to explore the potential applications of High Altitude Pseudo Satellites, also known as High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS).
- Positioned above 20 km altitude in the stratosphere, these unmanned aircraft are designed for exceptionally long-duration flights, spanning months or even years.
- HAPS encompass various aircraft types, including airplanes, airships, and balloons.
Benefits/Advantages of HAPS:
- These solar-powered vehicles bridge the gap between unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) operating in lower altitudes and traditional satellites in space.
- They offer a wide array of applications, including telecommunications, emergency/public safety communications, intelligent transportation systems, maritime surveillance, environmental monitoring, and land border control.
- Compared to ground-based communication networks, HAPS can cover larger areas with minimal interference and facilitate data transfer between satellites and ground-based telecom networks.
- Unlike traditional satellites, which are costly to construct and launch, HAPS are more cost-effective and easier to deploy.
- It has both military and civilian applications, including intelligence, surveillance, telecommunication, and disaster response.
- The technology offers lower latency and can connect to multiple ground stations.
Significance for India:
- In India, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) announced in 2022 its collaboration with a startup company to develop a "futuristic" high-altitude pseudo satellite.
- Given India's extensive land borders stretching approximately 15,000 km and a coastline spanning 7,500 km, securing these borders is paramount, necessitating diverse solutions.
- Hovering at the Earth's atmospheric edge, HAPS offer valuable services for efficient border surveillance, tracking enemy movements deep into territories or seas, and conducting round-the-clock missions.
- Equipped with advanced optical and infrared cameras, state-of-the-art sensors, and other sophisticated technology, these aerial platforms are ideal for border patrolling, target tracking, maritime surveillance, navigation, and even missile detection.
- China's Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), a state-owned aerospace and defense conglomerate, has been actively developing various HAPS platforms for surveillance purposes.
- In 2018, it successfully tested the solar-powered Morning Star drone, renowned for its prolonged airborne endurance.
What Is Nazool Land Which Is At The Heart Of Haldwani Violence? (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Violence erupted in Uttarakhand’s Haldwani district recently after the administration conducted a demolition drive at the site of a mosque and madrasa, allegedly on Nazool land, killing five and injuring many more.
What is Nazool Land?
- Nazool land is owned by the government but most often not directly administered as state property.
- The state generally allots such land to any entity on lease for a fixed period, between 15 and 99 years.
- In case the lease term is expiring, one can approach the authority to renew the lease by submitting a written application to the Revenue Department of the local development authority.
- The government is free to either renew the lease or cancel it — taking back Nazool land.
- In almost all major cities of India, Nazool land has been allotted to different entities for a variety of different purposes.
How did Nazool Land Emerge?
- During British rule, kings and kingdoms which opposed the British frequently revolted against them, leading to several battles between them and the British Army.
- Upon defeating these kings in battle, the British would often take their land away from them.
- After India gained Independence, the British vacated these lands.
- But with kings and royals often lacking proper documentation to prove prior ownership, these lands were marked as Nazool land — to be owned by the respective state governments.
How Does the Government Use Nazool Land?
- The government generally uses Nazool land for public purposes like building schools, hospitals, Gram Panchayat buildings, etc.
- Several cities in India have also seen large tracts of land denoted as Nazool land used for housing societies, generally on lease.
- Very often, the state does not directly administer Nazool land but rather leases it to different entities.
- While several states have brought in government orders for framing rules for Nazool land, The Nazool Lands (Transfer) Rules, 1956 is the law mostly used for Nazool land adjudication.
New Education Policy Taking Forward Swami Dayanand’s Vision (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Education Policy 2020 is taking forward the vision of social reformer Swami Dayanand Saraswati, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said recently.
Who was Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati?
- Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati, born on February 12, 1824, in Tankara, Gujarat, was a pioneering social reformer.
- He established the Arya Samaj in 1875 with the aim of addressing prevailing social injustices.
Religious and Social Reforms:
- Rejection of Idolatry and Ritualism: Dayanand Saraswati staunchly opposed idol worship and ritualistic practices, advocating instead for the worship of a formless, attributeless God as outlined in the Vedas.
- Shuddhi Movement: He initiated the Shuddhi Movement to reclaim individuals who had converted to religions like Islam or Christianity, aiming to reintegrate them into Hinduism.
- Back to Vedas: Recognizing the importance of Vedic wisdom, he spearheaded a movement to revive the teachings of the Vedas, emphasizing their relevance in modern society.
- Women’s Rights: Dayanand Saraswati championed women’s rights, advocating for their education and equal participation in social and religious spheres alongside men.
- Opposition to Child Marriage and Sati: He vehemently opposed practices like child marriage and sati, viewing them as detrimental to society and antithetical to Vedic principles.
Educational Reforms:
- Dayanand Saraswati established several Gurukuls to impart Vedic knowledge to his followers and empower them to disseminate this wisdom further.
- Influenced by his philosophy and vision, his disciples founded the Dayanand Anglo Vedic (DAV) College Trust and Management Society following his demise in 1883.
- The first DAV High School was founded in Lahore on June 1, 1886, under the leadership of Mahatma Hans Raj.
Literary Contributions:
- Dayanand Saraswati's philosophical ideas are encapsulated in his notable works like "Satyartha Prakash" and "Veda Bhashya," shedding light on his vision for Hindu reform.
- His thoughts were further disseminated through the journal "Arya Patrika," which he edited, reflecting his philosophical convictions.
Arya Samaj:
- Founded by Dayanand Saraswati in Bombay in 1875, the Arya Samaj, meaning "society of the nobles," aimed to reform Hinduism by steering it away from superstition.
- With the motto "Krinvanto Vishwam Aryam" meaning "Make this world noble," the Samaj advocated for a return to the true essence of Hinduism, rejecting ritualistic practices like idol worship, pilgrimage, and animal sacrifice.
- In the 1880s, the Samaj actively supported widow remarriage, promoting social reforms aligned with its principles.
- The Arya Samaj's influence extends beyond India, with active branches worldwide.
PM-SVANidhi Boosted the Annual Income of Street Vendors (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A study that evaluated the impact of the PM SVANidhi, a small working capital loan scheme for street vendors, has found that the first tranche of `10,000 led to an additional annual income of `23,460 for each beneficiary.
News Summary:
- Commissioned by the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the study was conducted by the Centre for Analytical Finance at the Indian School of Business (ISB) from January to June 2023.
- Although the report's findings will inform the Ministry's assessment of the PM SVANidhi scheme, it is not expected to be publicly released.
Key Findings of the Report:
- 94% of beneficiaries who received the initial Rs 10,000 loan reported using it for business investments, rising to 98% for those who received a second loan.
- The first loan contributed to an average additional monthly income of Rs 1,955, totalling Rs 23,460 over the one-year loan period.
- Approximately 13.9% of disbursed loans were categorized as non-performing assets (NPAs), indicating no payments for three months or more.
- Beneficiaries demonstrated a lower debt-to-income (DTI) ratio compared to typical small businesses, indicating high creditworthiness.
- Despite the PM SVANidhi program, there was limited improvement in street vendors accessing formal credit from other sources, with only 9% having loans from financial institutions.
What is PM SVANidhi?
- The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) stands as a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, launched on June 1, 2020.
- Its core aim is to extend accessible credit to street vendors, enabling them to revive their businesses and achieve self-reliance.
- The scheme is specifically tailored to empower street vendors, including hawkers, rehri walas, thelewala, and those operating in urban and peri-urban areas.
- PM SVANidhi facilitates eligible street vendors to obtain working capital loans devoid of collateral requirements.
- These loans, with a maximum cap of Rs. 10,000 and a one-year tenure, are intended to support vendors in procuring essential items, securing raw materials, and meeting their operational expenses.
- Furthermore, the scheme offers a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, promoting timely repayments and fostering financial discipline.
How Does PM SVANidhi Work?
- The PM SVANidhi scheme operates through a streamlined and accessible application process designed to maximize participation and outreach among street vendors.
- Vendors can apply for the scheme via a dedicated online portal or through Common Service Centers (CSCs) established nationwide.
- Once the application is submitted, it undergoes a brief verification process conducted by relevant authorities.
- Upon successful verification, the loan amount is directly transferred to the vendor's bank account.
- Vendors can then utilize the funds to revive their businesses, purchase inventory, and cover operational expenses.
Key Features and Benefits of PM SVANidhi:
- Affordable Credit: PM SVANidhi offers accessible working capital loans of up to Rs. 10,000 to street vendors, facilitating credit access without the need for collateral.
- Interest Subsidy: The scheme provides a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, incentivizing timely repayments and easing financial burdens.
- Digital Empowerment: PM SVANidhi promotes digital transactions and payments among street vendors, fostering adaptation to evolving business practices and enhancing financial literacy.
- Enhanced Livelihood: By availing of PM SVANidhi benefits, street vendors can improve their livelihoods, expand their businesses, and generate sustainable income for themselves and their families.
- Access to Social Security Schemes: Street vendors enrolled in PM SVANidhi are eligible for various social security schemes, including Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), providing financial coverage and protection during unforeseen events.
Conclusion
The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme stands as a beacon of hope for street vendors throughout India. By offering accessible credit, digital empowerment, and access to social security schemes, PM SVANidhi is propelling the advancement and prosperity of street vendors, empowering them to establish sustainable livelihoods. This groundbreaking initiative, with its manifold advantages and inspiring success stories, underscores the Government of India's dedication to fostering an inclusive and self-sufficient economy.
7th Indian Ocean Conference 2024 (The Hindu)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
During the inauguration of the Indian Ocean Conference in Perth, Sri Lankan President Ranil Wickremesinghe highlighted the escalating concerns of smaller countries in the region regarding the militarization of the Indian Ocean and the increasing "great power rivalry."
What is the Indian Ocean Conference (IOC)?
- The Indian Ocean Conference (IOC) is an annual international event that centres on the geopolitical, economic, and strategic significance of the Indian Ocean region.
- It serves as a platform for policymakers, scholars, business leaders, and civil society representatives to discuss security, trade, and cooperation within the Indian Ocean area.
- Established in 2016, the conference's first edition took place in Singapore.
- Notably, the 6th IOC convened in Dhaka, Bangladesh, in 2023.
- Organized by the India Foundation in collaboration with various regional organizations, the IOC facilitates dialogue and collaboration on key issues impacting the Indian Ocean region.
Key Points from EAM Jaishankar’s Speech:
- Addressing Challenges in the Indian Ocean: Jaishankar highlighted the spectrum of challenges in the Indian Ocean, ranging from threats to maritime traffic like piracy and terrorism to concerns about international law, freedom of navigation, and sovereignty.
- He emphasized the interconnected nature of transnational and non-traditional threats, including those arising from illegal activities.
- Concerns about Grey Areas: Expressing concern about grey areas, Jaishankar noted that some issues, such as those related to climate change and natural disasters, are increasingly visible.
- He also discussed disruptive events and their impact, along with the consequences of distant crises like fuel and food shortages.
- Additionally, unsustainable debt, opaque lending practices, and unviable projects are affecting countries in the region.
- Structural Challenges of Globalization: Jaishankar discussed the structural challenges inherent in the current form of globalization, emphasizing over-concentrations in manufacturing and technology.
- He highlighted the importance of dispersing production across different geographies, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, and emphasized the need for reliable and resilient supply chains.
- Additionally, he noted the significance of trust and transparency in the digital era and the emergence of artificial intelligence.
- Drivers of the Future: Jaishankar underscored the importance of focusing on drivers of the future, such as digital technology, electric mobility, green hydrogen, and sustainable shipping, for a sustainable future.
About the Indian Ocean Region (IOR):
- The Indian Ocean Region (IOR) comprises the Indian Ocean and its adjacent territories, including coastal states and islands.
- Extending from the African coast in the west to the Australian coast in the east, and from the Arabian Peninsula and the Persian Gulf in the north to the southern coast of Sri Lanka and Australia in the south, the IOR covers approximately 70.6 million square kilometres, making it the world's third-largest ocean.
Significance of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR):
- Geopolitical Importance: Positioned as a major transit route for global trade, the IOR facilitates the transportation of vital commodities, including oil and gas.
- It hosts critical chokepoints like the Strait of Malacca and the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa.
- Economic Importance: Boasting several rapidly developing economies like India, China, and various Southeast Asian nations, the IOR is rich in natural resources, attracting substantial foreign investment.
- With 64% of the global population and 60% of the global GDP, the region plays a significant role in the global economy.
- Security Importance: The IOR is a region of paramount security significance, confronting challenges such as terrorism, piracy, and maritime security threats.
- It has witnessed heightened military activity from major powers like the US, India, and China in recent times.
- Environmental Importance: Home to diverse marine ecosystems like coral reefs and mangrove forests, the IOR supports biodiversity and sustains local communities.
- However, it faces environmental risks due to climate change, including rising sea levels and more frequent extreme weather events.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of RBI (The Hindu)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has prudently opted to persist with its objective of ‘ensuring that inflation progressively aligns to the target’ by keeping benchmark interest rates unchanged, and sticking with its stance of ‘withdrawal of accommodation’.
About the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC):
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), chaired by its Governor.
- The RBI shall organise at least four meetings of the Monetary Policy Committee in a year.
- Established under Section 45ZB of the RBI Act, 1934, the government forms this six-member committee.
Composition of MPC:
- Comprising six members, three are from the RBI, while the remaining members are appointed by the Government of India.
- Members include the RBI Governor (Chairperson), the RBI Deputy Governor responsible for monetary policy, one official nominated by the RBI Board, and three members proposed by the Government of India (chaired by the Cabinet Secretary).
- MPC members serve a single four-year term and are not eligible for reappointment.
Functions:
- The primary responsibility of the MPC is to determine the benchmark policy interest rate (repo rate) to manage inflation within the prescribed target level.
- The current mandate of the committee is to maintain annual consumer price index (CPI) inflation at 4% within a band of +/- 2% until March 31, 2026.
Earth System Model (HT)
- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology is developing a first-for-India Earth System Model to improve climate forecasts and predict climate impacts.
What is an Earth System Model (ESM)?
- An Earth System Model (ESM) is a complex computer program that simulates the interactions between the various components of our planet's climate system, including the atmosphere, oceans, land, ice, and biosphere.
- These models are crucial for understanding past, present, and future climate trends, and are used for purposes like:
- Improving weather forecasts: By accounting for intricate interactions between different parts of the Earth system, ESMs can potentially lead to more accurate weather predictions, particularly for longer-term forecasts.
- Predicting climate change impacts: By simulating different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions and other influencing factors, ESMs can project how climate change might affect specific regions and aspects like temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise.
- Informing adaptation and mitigation strategies: With insights into potential climate impacts, policymakers and individuals can make informed decisions about adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change.
India's Earth System Model:
- Recognizing the importance of such models, India is currently developing its first-ever indigenous Earth System Model, led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR).
- An amount of ?192.28 crores has been sanctioned under the Monsoon Convection, Clouds and Climate Change (MC4) sub-scheme to develop the climate forecasting system
- This project, funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, aims to:
- Enhance forecast accuracy: The model will incorporate advanced features to improve the reliability of weather forecasts, particularly for monsoons that are crucial for India's agriculture.
- Facilitate long-term climate studies: By simulating various climate scenarios, the model will provide valuable insights into potential future climate changes affecting India.
- Predict climate impacts: This model will help assess the risks and potential impacts of climate change on various sectors like agriculture, water resources, and coastal ecosystems.
- The project is expected to be completed by 2025 and is believed to be a significant step towards improving India's understanding and preparedness for the challenges posed by climate change.
About the Monsoon Convection, Clouds, and Climate Change (MC4) Sub-Scheme:
- The MC4 initiative aims to enhance our understanding of monsoonal precipitation changes and their implications in a warming climate by enhancing observational databases and climate models.
- Its overarching objective is to refine our understanding of the interactions between monsoon dynamics, clouds, aerosols, precipitation, and the water cycle within a changing climate context.
The nodal ministry overseeing this effort is the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
What is an Earth System Model (ESM)?
- An Earth System Model (ESM) is a complex computer program that simulates the interactions between the various components of our planet's climate system, including the atmosphere, oceans, land, ice, and biosphere.
- These models are crucial for understanding past, present, and future climate trends, and are used for purposes like:
- Improving weather forecasts: By accounting for intricate interactions between different parts of the Earth system, ESMs can potentially lead to more accurate weather predictions, particularly for longer-term forecasts.
- Predicting climate change impacts: By simulating different scenarios of greenhouse gas emissions and other influencing factors, ESMs can project how climate change might affect specific regions and aspects like temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise.
- Informing adaptation and mitigation strategies: With insights into potential climate impacts, policymakers and individuals can make informed decisions about adapting to and mitigating the effects of climate change.
India's Earth System Model:
- Recognizing the importance of such models, India is currently developing its first-ever indigenous Earth System Model, led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and the Centre for Climate Change Research (CCCR).
- An amount of ?192.28 crores has been sanctioned under the Monsoon Convection, Clouds and Climate Change (MC4) sub-scheme to develop the climate forecasting system
- This project, funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, aims to:
- Enhance forecast accuracy: The model will incorporate advanced features to improve the reliability of weather forecasts, particularly for monsoons that are crucial for India's agriculture.
- Facilitate long-term climate studies: By simulating various climate scenarios, the model will provide valuable insights into potential future climate changes affecting India.
- Predict climate impacts: This model will help assess the risks and potential impacts of climate change on various sectors like agriculture, water resources, and coastal ecosystems.
- The project is expected to be completed by 2025 and is believed to be a significant step towards improving India's understanding and preparedness for the challenges posed by climate change.
About the Monsoon Convection, Clouds, and Climate Change (MC4) Sub-Scheme:
The MC4 initiative aims to enhance our understanding of monsoonal precipitation changes and their implications in a warming climate by enhancing observational databases and climate models.
- Its overarching objective is to refine our understanding of the interactions between monsoon dynamics, clouds, aerosols, precipitation, and the water cycle within a changing climate context.
- The nodal ministry overseeing this effort is the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
Preamble to the Constitution of India (Indian Express)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently wondered if the Preamble to the Constitution could have been amended while retaining the date when the Constitution was adopted.
Background:
- In historical context, the Preamble underwent a solitary amendment in December 1976 via the 42nd Constitutional Amendment during the Indira Gandhi Government.
- This amendment introduced two modifications: replacing "unity of the nation" with "unity and integrity of the nation," and inserting "socialist" and "secular" between "sovereign" and "democratic."
- Initially, the Preamble described India as a "sovereign, democratic republic."
- Notably, the Supreme Court affirmed in the Kesavananda Bharati case that the Preamble constitutes an integral component of the Constitution, subject to Parliament's amending authority, provided the fundamental structure remains intact.
About the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
- The Preamble to the Constitution of India draws inspiration primarily from the 'Objective Resolution' penned by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1946.
- It serves as a concise introduction, outlining the foundational principles and aspirations of the nation. Key components include:
- Source of Constitutional Authority: It affirms that the Constitution derives its authority from the people of India.
- Nature of the Indian State: It declares India as a Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic, and Republican Polity.
- Objectives of the Constitution: It articulates Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity as the core objectives.
- Adoption Date: It designates November 26, 1949, as the date of adoption.
- Significance:
- Acts as a guiding framework for interpreting the Constitution and formulating laws.
- Defines the national aspirations and goals.
- Highlights the importance of fundamental rights and values for all citizens.
- Fosters a sense of national unity and identity.
Is the Preamble a Part of the Constitution of India?
- In the Berubari Union Case of 1960, the Supreme Court stated that the Preamble is not a formal part of the Constitution.
- However, it acknowledged that the Preamble provides insight into the intentions of the Constitution makers, thus aiding in interpreting any ambiguities within the Constitution.
- The Kesavananda Bharati Case of 1973 marked a reversal of this stance.
- The Supreme Court declared the Preamble as an intrinsic part of the Constitution, attributing it significant interpretive value.
- It emphasized that the Preamble plays a crucial role in understanding the spirit and objectives of the Constitution, guiding the interpretation of its provisions.
- In the LIC of India Case of 1995, the Supreme Court reiterated that the Preamble is indeed an integral component of the Constitution.
- However, it clarified that while the Preamble holds symbolic importance and helps in understanding the Constitution's essence, it cannot be directly enforced as a law in Indian courts.
Can the Preamble be Amended?
- An essential debate revolves around whether the Preamble can undergo amendments under Article 368.
- In the Kesavananda Bharati Case of 1973, the Supreme Court established that the Preamble constitutes a fundamental aspect of the Constitution and is therefore amenable to amendments.
- However, any such amendment must adhere to the principle that the 'Basic Structure' of the Constitution remains untouched.
Polygamy in India: Insights and debates surrounding Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly recently passed the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill, 2024 after a two-day discussion. The Bill brings uniformity in personal laws, governing things such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance, across communities in the state (excluding tribals).
What is Polygamy?
- Polygamy involves the practice of having multiple spouses simultaneously, which can include either wives or husbands.
- It manifests in two primary forms:
- Polygyny, where a man is married to several women concurrently, and
- Polyandry, where a woman is married to multiple men concurrently.
Who can have "multiple wives"?
- Under Hindu law, which applies to Hindus, Sikhs, Jains, and Buddhists, the practice of polygamy is prohibited.
- Individuals governed by Hindu law can face criminal proceedings under Sections 494 and 495 of the Indian Penal Code.
- The Special Marriage Act, as well as Christian and Parsi laws, also outlaw bigamy.
- However, the Shariat Protection Act exempts Muslims in India from the ban on polygamy.
- Additionally, due to the protection granted to cultural practices of scheduled tribes, polygynous marriages can be found in tribal groups across northeastern states, Odisha, Telangana, and other regions.
- Courts have had to face cases where a man converted to Islam from other religions to marry a second wife.
- While the Supreme Court, in its 1994 Sarla Mudgal verdict, declared that conversion solely for a second marriage is invalid, the Law Commission reports from 1961 and 2009 have emphasized the need to clarify the legal position of the "second wife" in a converted Muslim marriage and address the rights of any children born from such a union.
What does the data say?
- Government data on polygamy can be obtained from two main sources — the decadal census and the National Family Health Survey (NFHS). Both have certain limitations.
- The census does not directly collect data on polygamy.
- Rather its incidence is inferred from the difference in the number of married men and the number of married women in the country.
- More married women than men point to the prevalence of situations where men have married more than once.
- Rather its incidence is inferred from the difference in the number of married men and the number of married women in the country.
What does the census data say?
- According to the census of 2011, there are 28.65 crore married men in India, compared to 29.3 crore married women.
- The difference between the two numbers — 65.71 lakh — can be explained either by the incidence of polygamy or men going abroad.
- The highest discrepancy in the population of married men and women can be found among Hindus (who make up the largest number of Indians), followed by Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Sikhs, and Buddhists.
- However, when compared to their respective shares in the total population, Muslims and Christians report the greatest difference.
What does NFHS data say?
- The NFHS-5 showed the prevalence of polygamy (the percentage of women who reported their husbands had other wives) was highest among Christians (2.1%), followed by Muslims (1.9%), and Hindus (1.3%), looking at religion.
- Overall, Scheduled Tribes reported the highest incidence at 2.4%.
- A June 2022 study by the International Institute of Population Sciences (IIPS) showed that polygynous marriages (one man married to more than one woman at a time) have decreased from 1.9% in 2005-06 to 1.4% in 2019-21, among the whole population.
- Buddhists, who reported a 3.8% incidence of polygyny in 2005-06, saw the sharpest dip of 65.79% to 1.3% in 2019-21.
- The incidence of polygyny in the total population fell by 26.31%.
Constitutional Perspective and Supreme Court's Insights:
- India, as a secular state, upholds the principle of equality among religions, ensuring that no religion holds superiority or inferiority over another.
- The Indian Constitution guarantees fundamental rights to all citizens, and any legislation conflicting with these rights is considered unconstitutional.
- Article 13 of the Constitution invalidates any law inconsistent with Part III of the Constitution.
- Article 14 ensures equal treatment and protection under the law for every individual within India's territory.
- In a 2021 verdict, the Supreme Court highlighted India's recognition of a plural legal system, allowing different religious communities to abide by distinct 'personal laws.'
- However, these personal laws must adhere to constitutional validity and morality, ensuring they do not infringe upon Articles 14, 15, and 21 of the Constitution.
Bharat Ratna for former PMs Charan Singh and PV Narasimha Rao, scientist Swaminathan (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union government on February 9, 2024, announced former Prime Ministers Chaudhary Charan Singh, P.V. Narasimha Rao and agriculture scientist M.S. Swaminathan will be honoured with the country’s highest civilian honour, the Bharat Ratna posthumously.
News Summary:
- The government recently conferred the Bharat Ratna for former Prime Ministers Chaudhary Charan Singh and PV Narasimha Rao and agricultural scientist MS Swaminathan, who is known for his leading role in India's 'Green Revolution', posthumously.
- Earlier, the government had announced Bharat Ratna, for veteran BJP politician LK Advani and socialist icon and former Bihar Chief Minister Karpoori Thakur.
Who was PV Narasimha Rao?
- Pamulaparthi Venkata Narasimha Rao (28 June 1921 – 23 December 2004) was a lawyer and a towering Congress leader in undivided Andhra Pradesh, who became the 9th prime minister of India.
- He ruled the country between 1991 and 1996.
- In 1991, when India was facing a foreign reserves crisis, Narasimha Rao's government brought about three big-ticket economic reforms -- globalisation, liberalisation and privatisation.
- PV Narasimha Rao was the first person from South India to become the prime minister of India.
- He was born in a Telugu Niyogi Brahmin family in the Laknepalli village of Narsampet mandal, Warangal.
- The district is currently in Telangana.
- He was a freedom fighter who took part in Hyderabad's Vande Mataram movement in the late 1930s.
- After Independence, PV Narasimha Rao became a full-time politician.
- He was elected as an MLA for the first time in 1957.
- Till 1971, he assumed many ministerial positions in the state government. He became the chief minister of Andhra Pradesh in 1971.
- He was known as an Indira Gandhi loyalist and supported her in 1969 when the Congress vertically split into two parts.
- Rao also served as a member of parliament from Andhra Pradesh and handled home, defence and foreign affairs portfolios as a central minister.
- In 1991, he had almost retired, however, he came back to active politics after the assassination of Congress President and Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi's assassination.
- He was also the first Congress PM outside the Nehru-Gandhi family.
- He broke several conventions as the prime minister.
- He appointed economist Manmohan Singh as his finance minister.
- Together, they brought about economic reforms.
Who was Chaudhary Charan Singh?
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was born in a middle-class farmer family in Meerut in 1902.
- He started his political career with the Congress.
- He was first elected to the Uttar Pradesh assembly in 1937 from Chhaprauli and later got re-elected in 1946, 1952, 1962 and 1967.
- Chaudhary Charan Singh was appointed as a parliamentary secretary in Govind Ballabh Pant's government in 1946.
- He worked in several departments before being appointed a cabinet minister for justice and information in 1951.
- In 1967, he quit the Congress and became the chief minister of Uttar Pradesh for the first time after being elected as the leader of the Sanyukta Vidhayak Dal coalition.
- He became the chief minister for the second time in 1970.
- In 1979 after the Jana Sangh (BJP's predecessor) pulled out of the 18-month-old Morarji Desai-led Janata Party government.
- Congress (I) decided to extend support to Chaudhary Charan Singh who took oath as prime minister on July 28, 1979.
- But before he could prove his majority in the Lok Sabha, Indira Gandhi withdrew support to his government and Singh resigned.
- He continued to remain as caretaker PM till January 14, 1980.
Who was MS Swaminathan?
- M.S. Swaminathan is an eminent Indian agricultural scientist and geneticist hailed as the "Father of the Green Revolution" in India.
- Born on August 7, 1925, Swaminathan's groundbreaking research and advocacy have significantly contributed to India's agricultural development and food security.
- He played a crucial role in introducing high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice, which revolutionized agricultural productivity in the country during the 1960s and 1970s.
- Swaminathan has received numerous awards and honours for his contributions to agriculture and sustainable development, and he continues to be a leading voice in global efforts to address food security and environmental sustainability.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY) (PIB)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY), a sub-scheme under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana.
About Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana:
- Implemented as a Central Sector Sub-scheme within the broader framework of the PMMSY, this initiative aims to bolster the fisheries sector.
- Funding: With an estimated outlay of Rs. 6,000 crore, the scheme comprises 50% public finance, including contributions from the World Bank and the AFD, and the remaining 50% anticipated investment from beneficiaries and the private sector.
- Duration: Operational for four years from FY 2023-24 to FY 2026-27, spanning all States and Union Territories.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Fishers, Fish (Aquaculture) Farmers, Fish workers, Fish Vendors or such other persons directly engaged in the fisheries value chain.
- Micro and Small enterprises in the form of Proprietary Firms, Partnership Firms and Companies registered in India, Societies, Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), Cooperatives, Federations, Village Level Organizations like Self Help Groups (SHGs), Fish Farmers Producer Organizations (FFPOs) and Startups engaged in fisheries and aquaculture value chains.
- FFPOs also include Farmer's Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Any other beneficiaries that may be included by the Department of Fisheries, Gol as targeted beneficiaries.
Aims and objectives of PM-MKSSY:
- Gradual Formalization of the unorganized fisheries sector through self-registration of fishers, fish farmers and supportive workers under a National Fisheries Sector Digital Platform including the creation of work-based digital identities of fish workers for improved service delivery.
- Facilitating access to institutional financing fisheries sector micro and small enterprises.
- Providing a one-time incentive to beneficiaries for purchasing aquaculture insurance.
- incentivising fisheries and aquaculture microenterprises through performance grants for improving fisheries sector value-chain efficiencies including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
- Incentivising micro and small enterprises through performance grants for the adoption and expansion of fish and fishery product safety and quality assurance systems including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
What is a White Paper in Economics? Types and Main Purpose (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented a “white paper” on the Indian economy in Parliament recently.
What is a White Paper?
- A White Paper is a report, guide, research-based paper or formal government document that presents expert analysis about a topic or solution to a problem, or policy proposals, often bound in white covers.
- They have been used historically to introduce new policies or legislation and gauge public reaction to government initiatives, schemes or policies.
Types of White Paper:
- There are three types of white paper Economic White Paper, Budget White Paper, and Policy White Paper.
- Economic White Paper: It contains an analysis of the current state of the economy and talks about the challenges, and opportunities it faces.
- The paper also contains the government’s plans and strategies to address the issues.
- Budget White Paper: A Budget White Paper contains government budgetary priorities, spending schemes, revenue sources, and fiscal projections among other issues.
- Policy White Paper: A Policy White Paper talks about a specific policy, scheme or program of the government to address a particular issue or problem in the economy.
- Economic White Paper: It contains an analysis of the current state of the economy and talks about the challenges, and opportunities it faces.
What is the use of White Paper?
- The purpose of a white paper on the economy is to inform the public, Parliament, and stakeholders about a government's policy, vision, goals, plans, and actions being taken to safeguard the economic interests of the country.
- The document can also be used as a tool for consultation and feedback, as it invites comments and suggestions from various parties on the proposed policies or programs.
- A white paper can also influence public opinion and shape the political debate on economic issues.
Key Insights from the White Paper on the Indian Economy and its Objectives:
- The comprehensive 58-page document is structured into three primary segments.
- Section 1 delves into the macroeconomic landscape during the UPA's 10-year tenure.
- Section 2 presents an overview of various corruption scandals that occurred under the UPA administration.
- Section 3 outlines the strategies employed by the NDA to revitalize the economy.
Objectives of the white paper presented by FM:
- To elucidate the governance, economic, and fiscal challenges inherited by the NDA government upon assuming office in 2014.
- To shed light on the policies and initiatives undertaken by the NDA government since 2014 to rejuvenate the economy.
- To stimulate a more informed discourse on the significance of national interest and fiscal responsibility in governance, transcending political expediency.
Most Important Claims in the White Paper:
- The UPA era was marred by policy missteps and corruption scandals, notably non-transparent auctions of public resources like coal and telecom spectrum.
- In the aftermath of the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, the UPA's pursuit of high economic growth undermined macroeconomic stability, leading to challenges such as high inflation and fiscal deficit.
- Capital expenditure as a percentage of total expenditure declined significantly during the UPA tenure, impeding infrastructure development and economic growth.
- The White Paper highlights improvements under the NDA, including lower inflation rates and enhanced efficacy of schemes like Jan Dhan and Swachh Bharat Mission.
- The NDA government's proactive measures have steered the economy away from crisis, positioning India as one of the top global contributors to growth.
- Overall, the White Paper underscores the NDA's efforts to address economic challenges and foster sustainable growth in India.
What Insights Can We Draw from the Above Assertions?
- Examining the economic performance spanning two decades, especially in consecutive terms, presents a formidable challenge due to the multitude of factors influencing both the economy and its measurement methodologies.
- For example, the significant fluctuations in domestic inflation during the latter years of the UPA administration can largely be attributed to the volatile cost of crude oil.
- During FY12 to FY14, crude oil prices fluctuated between $111 and $105 per barrel, significantly impacting inflation rates. Subsequently, oil prices declined to $84 in FY15 and further to $46 in FY16.
- While the NDA government has achieved noteworthy milestones such as the implementation of GST and IBC, the white paper fails to acknowledge shortcomings within the economy.
- Notably, it overlooks critical issues such as unemployment, and the absence of a formal measure of poverty since 2011 is not addressed.
Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) (The Hindu)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Karnataka is currently facing challenges posed by the spread of Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), also recognized as monkey fever.
What is KFD?
- The disease was first noticed in the Kysanur Forest area of Sorab Taluk in Shivamogga district in 1956 and was named after the region.
- It is also known as monkey fever, as monkeys also get infected.
- The death of a monkey serves as a warning of a KFD outbreak.
- The scientists concluded that the virus (Flaviviridae virus family) must have been present in the forests of the Malnad region.
- It became active due to ecological changes.
- The disease spreads through ticks.
- Primates that come in contact with infective ticks contract the disease.
- Human beings who visit the forest area either for livelihood, to graze cattle, or to collect firewood contract the disease.
- Normally, the transmission begins from late November to June.
- It peaks between December and March, according to studies.
- A blood test is done to identify if someone has KFD.
Symptoms:
- Symptoms start to appear three to eight days after the bite, of an infective tick.
- The common symptoms are:
- Fever
- Redness of the eyes
- Severe headache, and
- Body pain
- Three to four days after the onset of initial symptoms, the patient may have gastrointestinal symptoms.
- In severe cases, bleeding from the nose is noted.
Treatment:
- There is no specific treatment, doctors handle the symptoms and monitor the vitals daily.
- An attempt to use a vaccine was given up after studies showed it to be ineffective.
- The ICMR is said to be in consultation with Indian Immunologicals for the development of a vaccine.
About 400 Smart Cities Mission Projects are Likely to Miss June 30 Deadline (Indian Express)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Housing and Urban Affairs Secretary Manoj Joshi told the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Housing and Urban Affairs that Some projects under the Smart Cities Mission would not be able to meet the June 30 deadline and the respective state governments would be responsible for completing them thereafter.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Approximately 400 Smart City Mission (SCM) projects are facing challenges in meeting the extended deadline of June 2024, according to a recent report by the Parliamentary committee.
- These projects, being implemented by around ten cities under the Center's flagship SCM, are at risk of not being completed within the timeframe.
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) has granted a second extension to the Smart Cities Mission, giving it until June 2024 to finalize pending work.
- However, if these projects are not completed by then, the respective state governments will be responsible for completing them at their own expense.
- The role of the ministry extends beyond merely transferring funds; it also involves overseeing project execution and ensuring successful completion.
- Despite the challenges, the ministry has emphasized that there will be no further extensions to the mission.
- Delays have been attributed to various factors, including difficulties in relocating local populations, legal hurdles such as land procurement issues, frequent turnover of smart cities' CEOs, and delays in projects requiring coordination with other government entities.
- In light of these challenges, the committee has proposed extending the Smart Cities Mission to Tier-2 cities located within 50-100 km of capital cities and tourist destinations.
- Additionally, the committee has highlighted the importance of protecting privacy rights, especially given the extensive deployment of surveillance technology like CCTV cameras and Integrated Command and Control Centers across all 100 cities involved in the mission.
What is the Smart Cities Mission (SCM)?
- The Smart Cities Mission (SCM) was initiated on 25th June 2015, to foster urban centers that offer essential infrastructure and a sustainable, clean environment.
- Through a competitive process spanning from 2016 to 2018, 100 cities were selected for development as Smart Cities, each receiving five years from their selection to complete designated projects.
- Administered as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), the program entails financial support from the Central Government amounting to Rs. 48,000 crores over five years, equating to an average of Rs. 100 crore per city per year, matched by an equivalent contribution from the State or Urban Local Body (ULB).
- Guided by six core principles, the Smart Cities initiative aims to enhance the quality of life for residents through the implementation of innovative solutions, fostering economic growth, and addressing social, economic, physical, and institutional aspects of urban development. It prioritizes sustainable and inclusive progress, endeavouring to establish scalable models that can serve as beacons for other cities aspiring for advancement.
- Financing for the Smart Cities Mission entails shared responsibilities between the Central Government, state governments, and ULBs, requiring equal contributions for project implementation.
- As of December 1, 2023, significant progress has been made, with 6,419 projects worth Rs. 1,25,105 crore completed out of a total of 7,970 projects valued at Rs. 1,70,400 crore.
- An additional 1,551 projects worth Rs. 45,295 crore are currently in progress, though certain cities, particularly those in the North-Eastern and Himalayan regions, as well as small Union Territories, face challenges in keeping pace.
- Budget allocations for the Smart Cities proposal have seen adjustments, with a reduction in the outlay from Rs. 7,634 crores to Rs. 7,535 crores in the revised budget for 2023-24, and a further decrease to Rs. 2,236 crores for the 2024-25 fiscal year.
Prithvi Vigyan Scheme to Bolster Earth Science Research Approved by Cabinet (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet has approved a Rs 4,797 crore research scheme to boost and maintain research momentum in the fields of ocean, atmospheric and polar sciences.
What is PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI)?:
- The PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI) will be an umbrella scheme spearheaded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences to help continue many of the ongoing research projects covering the period from 2021 to 2026.
- This scheme encompasses five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training and Outreach (REACHOUT)
- The principal objectives of the comprehensive PRITHVI Scheme are as follows:
- Enhancing and maintaining long-term observations across the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere to monitor critical indicators of the Earth System and its changes.
- Developing modelling systems to comprehend and forecast weather patterns, ocean dynamics, and climate-related hazards, while advancing the understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring the polar and high seas regions to uncover new phenomena and resources.
- Innovating technology for the exploration and sustainable utilization of oceanic resources benefits society at large.
- Translating insights from Earth systems science into services that contribute to societal well-being, environmental preservation, and economic prosperity.
- This scheme is poised to foster the development of integrated, multidisciplinary earth science research and innovative initiatives across various institutes under the MoES umbrella.
Significance of the PRITHVI Scheme:
- Under the PRITHVI Scheme, the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) plays a pivotal role in delivering vital services concerning weather, climate, oceanography, coastal conditions, hydrology, seismology, and natural hazards.
- These services play a crucial role in issuing forecasts, warnings, and alerts for a wide array of natural disasters, including tropical cyclones, floods, tsunamis, and earthquakes.
- By facilitating disaster preparedness and risk mitigation, they contribute significantly to safeguarding lives and property.
- Earth System Sciences encompass a comprehensive study of the interconnected components of the Earth, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere, along with their intricate interactions.
- The PRITHVI Scheme is designed to address these components comprehensively, enhancing our understanding of Earth System Sciences and delivering dependable services for the nation's benefit.
- Through integrated research and development endeavours across diverse MoES institutes, the scheme is poised to tackle major challenges in weather forecasting, climate science, oceanography, cryospheric studies, and seismology.
- These efforts aim to explore sustainable methods for harnessing both biological and non-biological resources, ensuring responsible utilization of our planet's resources.
Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative (India Today)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) recently introduced a scheme named 'Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad' (SSPCA).
About the Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative:
- The SSPCA Initiative, spearheaded by the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), aims to enhance the global competitiveness of Indian students in technical education.
- Crafted to provide financial backing to students aspiring to excel in international scientific events, the initiative offers a comprehensive support system.
Financial Assistance and Mentorship:
- Under the SSPCA scheme, individual students or student teams can avail themselves of travel grants to engage in international competitions.
- This assistance encompasses financial aid, mentorship, logistical support, and networking opportunities, empowering students to effectively represent India on the global stage.
- Financial aid extended by the AICTE scheme amounts to up to Rs 2 lakh per student, covering various expenses such as international and domestic travel, registration fees, visa applications, accommodation, airport taxes, travel insurance, and equipment costs associated with the competition.
Eligibility:
- Eligibility for the SSPCA initiative extends to students enrolled in diploma, B.E./B. Tech, integrated M. Tech, and M./M. Tech programs in AICTE-approved institutions.
- Each team of students is entitled to financial support under the scheme once during the course of their study.
About the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE):
- Established as the statutory body and national-level council for technical education in India, the AICTE has played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of technical education in the country.
- Founded in 1945 as an advisory body, it gained statutory status through an Act of Parliament in 1987.
Functions:
- The AICTE is responsible for granting approval for the establishment of new technical institutions, the introduction of new courses, and variations in intake capacity.
- It sets and upholds norms and standards for technical institutions to ensure quality development.
- Additionally, the AICTE promotes technical education through various schemes aimed at fostering innovation, faculty development, research and development, and inclusivity for women, the handicapped, and marginalized sections of society.
- Technical institutions under the AICTE's purview encompass a wide array of programs, including post-graduate, undergraduate, and diploma courses across multiple disciplines.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, the AICTE continues to be at the forefront of advancing technical education and innovation in India.
World Sustainable Development Summit 2024 (TERI)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar inaugurated the World Sustainable Development Summit in New Delhi recently in the presence of Prime Minister of Guyana Mark Phillips.
About the World Sustainable Development (WSDS) Summit:
- The WSDS Summit, organized annually by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), stands as a flagship event in the realm of sustainable development.
- Instituted in 2001, the Summit series boasts a distinguished legacy spanning over two decades, dedicated to advancing 'sustainable development' as a universally embraced objective.
- Distinguished as the sole independently convened international summit on sustainable development and environment originating from the Global South, the WSDS endeavours to forge enduring solutions for the global community.
- It achieves this by convening the world's foremost leaders and intellectuals on a singular platform.
- The upcoming WSDS 2024 marks the 23rd edition of this significant summit, revolving around the theme 'Leadership for Sustainable Development and Climate Justice'.
Key Facts about The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI):
- TERI stands as a premier think tank committed to conducting research aimed at fostering sustainable development in India and across the Global South.
- Established in 1974 as an information centre focusing on energy issues, TERI expanded its scope to encompass multifaceted research, policy analysis, consultancy, and implementation initiatives.
- TERI's research endeavours, commencing in the late 1980s, are rooted in its steadfast belief that the efficient utilization of energy and sustainable management of natural resources are indispensable for developmental progress.
- Across various sectors, TERI concentrates its efforts on:
- Promoting the efficient utilization of resources
- Enhancing access to and adoption of sustainable practices and inputs
- Mitigating environmental and climate impacts
- TERI's headquarters are located in New Delhi, serving as a hub for its diverse activities and initiatives.
Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Lower House of Parliament recently passed the Finance Bill moved by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
Context:
- The Lok Sabha passed the Finance Bill, 2024 by voice vote recently.
- Also, the House passed the Appropriation Bill, granting authorization for government expenditures for four months in the upcoming fiscal year.
- The Appropriation Bill is a significant legislative measure that empowers the government to utilize public funds allocated in the annual budget.
- It serves to uphold accountability and transparency by necessitating parliamentary approval for expenditures and prevents unauthorized withdrawals from the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Furthermore, the lower house sanctioned the Rs 1.8 lakh crore budget for the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
What is a Finance Bill?
- The Finance Bill, classified as a Money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution, is an annual presentation in the Lok Sabha following the Union Budget announcement.
- It encapsulates the government's fiscal proposals concerning taxation, expenditure, and other financial affairs.
- Through this bill, the government submits its proposals for imposing new taxes, altering the existing tax framework, or extending the current tax structure beyond the approved period to Parliament.
- Accompanied by a Memorandum elucidating its provisions, the Finance Bill is exclusively introduced in the Lok Sabha, though amendments can be recommended by the Rajya Sabha.
- Approval from both houses of Parliament is requisite for the bill to become law, with a mandate for passage within 75 days of its introduction.
- While all Money Bills fall under the category of Financial Bills, not all Financial Bills qualify as Money Bills.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely focusing on tax proposals is classified as a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Bill addressing taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects is categorized as a Financial Bill.
- Thus, if a Bill entails government expenditure along with other matters, it is designated as a financial bill.
Highlights of the 2024 Finance Bill:
- Stability in Income Tax: With the impending general elections in April-May 2024, the bill prioritizes continuity by retaining the current tax framework for the fiscal year 2024-2025.
- Targeted Relief Measures: Incorporates slight tax concessions tailored to particular sectors or taxpayer groups.
- Promotion of Economic Expansion: Encompasses provisions aimed at fostering infrastructure enhancement, investment stimulation, and streamlining business operations.
- Fiscal Discipline: Pursues fiscal consolidation objectives through proposed strategies to manage expenditures or enhance revenue generation.
Extending the Retirement Age of Supreme Court and High Court Judges (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has told a parliamentary panel that extending the retirement age of Supreme Court and High Court judges based on their performance may not be practical.
Key Insights from the Report on Judicial Processes and Reform:
- On August 07, 2023, the Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, and Law and Justice, chaired by Mr. Sushil Kumar Modi, presented its findings.
- Among its significant findings and recommendations, the Committee emphasized the necessity of raising the retirement age for judges.
- They highlighted the importance of aligning this age with advancements in medical sciences and increased life expectancy.
- At present, Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) judges retire at 65 and 62 years, respectively.
- The Committee proposes amending relevant Articles (124 and 217) of the Constitution to extend these retirement ages.
- The retirement age of the High Court Judges was increased from 60 to 62 years, after the 15th constitutional Amendment according to section 4 of the Constitutional Act 1963.
- Furthermore, the Committee suggests implementing a system of appraisal by the SC Collegium to assess judges' performance and health conditions, as well as the quality and quantity of judgments delivered, before extending their tenure.
Debate Regarding the Retirement Age for Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) Judges:
- Retiring SC judges have frequently reflected on their time in office, often feeling that their tenure didn't allow them sufficient opportunity to make meaningful contributions to the judiciary.
- In 2022, former Chief Justice of India (CJI) N.V. Ramana engaged in a dialogue with Justice Stephen Breyer of the US Supreme Court, who chose to retire at age 83 after serving for 27 years.
- Expressing his views, CJI Ramana, who was scheduled to retire after 8.5 years on the SC bench, remarked that 65 seemed 'too early an age for retirement.'
- Despite this, CJI Ramana's tenure surpassed that of most other SC judges.
- Among the current 32 Judges of the SC, only CJI Chandrachud, and Justices J.B. Pardiwala, K.V. Viswanathan, and Dipankar Datta are expected to exceed the 8-year mark.
- These judges represent a minority who surpass the average tenure of sitting SC judges, which stands at 5.4 years.
Why is the Government Resistant to Elevating the Retirement Age for SC and HC Judges?
- The government asserts that raising the retirement age for Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) judges might lead to potential issues of favouritism.
- They argue that such a move would grant excessive authority to the SC Collegium, potentially diminishing parliamentary oversight in evaluating judges for tenure extensions.
- Additionally, the government expresses concerns that this change could subject judges to external pressures, compromising their ability to maintain impartiality.
- Moreover, they highlight the strain it would place on the already limited human resources within the Judiciary and the Executive involved in the appointment process.
Additional Insights from the Report on Judicial Processes and Reform:
- Establishment of Regional SC Benches: The Committee highlighted the challenge faced by litigants from distant regions due to the centralized nature of the Supreme Court in Delhi.
- They proposed leveraging Article 130 to create regional benches in four or five locations.
- These regional benches would handle appellate matters, while constitutional issues would remain under Delhi's jurisdiction.
- Enhancing Social Diversity in Judicial Appointments: Recognizing a diversity deficit in the higher judiciary, the Committee pointed out the low representation of marginalized communities.
- They noted that since 2018, only a small percentage of High Court judges belonged to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- To address this, the Committee recommended that the Supreme Court and High Court Collegiums prioritize the nomination of women and candidates from marginalized communities, including minorities.
- Implementation of Mandatory Asset Declaration: While constitutional functionaries and government servants are obligated to declare their assets annually, judges are exempt from this requirement.
- The Committee urged the central government to enact legislation mandating higher judiciary judges to disclose their assets and liabilities each year to the appropriate authority.
- Revision of Vacation Practices in SC and HCs: The Committee observed that simultaneous vacations for the entire court contribute to case backlog and inconvenience for litigants.
- They proposed a staggered vacation system, wherein judges take leave at different times throughout the year, to mitigate this issue.
- Publication of Annual Reports by HCs: Presently, only a few High Courts publish annual reports, unlike the Supreme Court, which regularly issues its report.
- The Committee recommended that the Department of Justice collaborate with the Supreme Court to ensure that all High Courts prepare and publish their annual reports, promoting transparency and accountability in judicial operations.
Rajya Sabha passes Bills to add PVTGs of Odisha, A.P. in ST lists (Indian Express)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
The Rajya Sabha recently passed two Bills, which seek to modify the list of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
News Summary:
- The Rajya Sabha recently approved the Constitution (STs) Order Amendment Bill 2024 and the Constitution (SCs and STs) Order Amendment Bill 2024, introduced by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- This development paves the path for the inclusion of numerous new communities in the Scheduled Tribes (STs) list of Odisha, along with the incorporation of synonyms and phonetic variations of existing tribes in the ST lists of both Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
About the Legislation:
- The recently passed bills introduced notable changes to the Scheduled Tribes (STs) lists of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh, particularly focusing on the inclusion of seven Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), a subset of STs, with four additions in Odisha and three in Andhra Pradesh.
- In Odisha, the PVTGs added include:
- Pauri Bhuyan and Paudi Bhuyan as synonyms of the Bhuyan tribe.
- Chuktia Bhunjia as a synonym of the Bhunjia tribe.
- Bondo as a sub-tribe of the Bondo Poraja tribe.
- Mankidia as a synonym for the Mankirdia tribe.
- In Andhra Pradesh, the PVTGs added are:
- Bondo Porja and Khond Porja as synonyms of the Porja tribe.
- Konda Savaras as a synonym for the Savaras tribe.
- These additions mark a significant step as these groups, belonging to PVTGs, have been included in the scheduled list after 75 years of independence.
Additional Changes:
- Apart from these additions, the bills also facilitated changes in Odisha's ST list, including the relocation of two entries, Tamadia and Tamudia, from the Scheduled Castes list to the Scheduled Tribes list.
- Furthermore, synonyms, phonetic variations, and sub-tribes of at least eight existing communities in Odisha's ST list were added through the bill.
- Expanding Odisha's ST list, the bills introduced two new entries:
- The Muka Dora community (and synonyms) in undivided Koraput District, which comprises Koraput, Nowrangapur, Rayagada, and Malkangiri districts.
- The Konda Reddy (and synonyms) community.
Who are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), as defined by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA), comprise 75 distinct tribal communities in India.
- These groups are characterized by:
- Pre-agriculture level of technology,
- Stagnant or declining population trends,
- Extremely low literacy rates, and
- Subsistence level of economy.
- PVTGs were identified as a separate category based on the recommendations of the 1961 Dhebar Commission. Initially, there were 52 PVTGs, and over time, the list has expanded to include 75 groups across 18 states and Union Territories.
- According to data from the MoTA and the 2011 Census, Odisha has the largest population of PVTGs, with 8.66 lakh individuals, followed by Madhya Pradesh with 6.09 lakh and Andhra Pradesh (including Telangana) with 5.39 lakh.
- Overall, the total PVTG population exceeds 40 lakh, with Odisha's Saura community being the largest PVTG, numbering 5.35 lakh individuals.
SAMARTH Centers (PIB)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, the Minister of State for Heavy Industries informed the Lok Sabha about SAMARTH Centres.
About SAMARTH Centres:
- The Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) centers are established under the Scheme for "Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector."
- These centers play a crucial role in assisting Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) by providing workforce training and raising awareness about Industry 4.0 technologies through:
- Organizing seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events on Industry 4.0.
- Conducting training sessions to create awareness about Industry 4.0.
- Offering consultancy services (including in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics) and providing incubation support to start-ups, including MSMEs.
Key Highlights of the Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector Scheme:
- Initiated by the Ministry of Heavy Industries, this scheme aims to address technological obsolescence and improve access to quality industrial infrastructure and common facilities.
- Phase I of the scheme was launched in November 2014, focusing on skill development, infrastructure enhancement, and technology development in the Capital Goods Sector.
- Phase II, commenced on January 25, 2022, aims to amplify the impact created by Phase I by fostering a strong and globally competitive capital goods sector, contributing at least 25% to the manufacturing sector.
Components of the Scheme:
- Identification of Technologies through Technology Innovation Portals.
- Establishment of four New Advanced Centres of Excellence and augmentation of Existing Centres of Excellence.
- Promotion of skilling in the Capital Goods Sector, including the creation of qualification packages for skill levels 6 and above.
- Establishment of four Common Engineering Facility Centres (CEFCs) and augmentation of existing CEFCs.
- Augmentation of Existing Testing and Certification Centres.
- Establishment of ten Industry Accelerators for Technology Development.
Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PIB)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
PACS have been allowed by the Government to operate Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras (PMBJK) under the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Pariyojana of Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers (GOI).
About Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras:
- Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendras are established as part of the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana, initiated by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers in November 2008.
Objective:
- The primary objective is to ensure the availability of quality medicines at affordable prices for all segments of society, particularly the economically disadvantaged, thereby reducing out-of-pocket healthcare expenses.
- These Kendras offer generic drugs that are equivalent in quality and efficacy to expensive branded drugs but are available at significantly lower prices.
- All essential therapeutic medicines are stocked in Jan Aushadhi Stores, along with allied medical products commonly found in chemist shops, enhancing the viability of operating a Jan Aushadhi store.
- The Pharmaceutical & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI), established under the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Government of India, with the support of all Central Public Sector Undertakings (CPSUs), coordinates the procurement, supply, and marketing of generic drugs through the PMBKs.
Eligibility to Open a Jan Aushadhi Kendra:
- State Governments, reputable NGOs, trusts, private hospitals, charitable institutions, doctors, unemployed pharmacists, and individual entrepreneurs are eligible to apply for establishing a new Jan Aushadhi Kendra.
- Applicants are required to employ a Bachelor of Pharmacy (B Pharma) or Diploma in Pharmacy (D Pharma) degree holder as a pharmacist in their proposed store.
The Nagoya Protocol (Down To Earth)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Cameroon, a central African country recently adopted the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing.
About the Nagoya Protocol:
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilisation (the Protocol) is a globally binding agreement designed to fulfill the access and benefit-sharing obligations outlined in the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- Adopted in Nagoya, Japan, in October 2010, the Protocol came into effect on October 12, 2014, following the deposit of the fiftieth instrument of ratification.
- It establishes a transparent legal framework to ensure the fair and equitable distribution of benefits derived from the use of genetic resources, a key objective of the CBD.
Benefits of the Protocol:
- It provides researchers with a structured framework to access genetic resources for biotechnological research and development while ensuring a fair share of benefits derived from their utilization.
- Indigenous and local communities stand to benefit from the recognition and protection of traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources.
Scope of the Protocol:
- The Protocol covers genetic resources within the scope of the CBD and addresses the benefits arising from their utilization.
- Additionally, it encompasses traditional knowledge linked to genetic resources covered by the CBD and the benefits derived from its utilization.
Key Facts about the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- With 196 contracting parties, the CBD is the most comprehensive binding international agreement for conserving nature and sustainably managing natural resources.
- Opened for signing at the UN Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, the CBD aims to conserve biological diversity, ensure its sustainable use, and promote the fair and equitable sharing of benefits.
- The CBD covers biodiversity across ecosystems, species, and genetic resources.
- The Conference of the Parties (COP) serves as the highest decision-making body of the Convention, with the Secretariat based in Montreal, Canada.
- To further CBD objectives, two internationally binding agreements were adopted: the Cartagena Protocol in 2000, regulating the transboundary movement of living modified organisms, and the Nagoya Protocol in 2010, facilitating access to genetic resources and the equitable sharing of benefits.
Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme (India Today)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, the Union Minister of Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship launched the EdCIL Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme.
About the Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme:
- The Vidyanjali Scholarship Programme ensures equitable access to high-quality educational systems by facilitating a seamless transition from secondary to higher education and providing financial support to meritorious students from Navodaya Vidyalayas who lack financial means.
- It embodies a holistic approach to empowerment, aiming to expand educational opportunities, especially for students from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
- The programme aims to secure assistance and funding from non-governmental partners and private sources, including CSR grants, national and international donors, and impact investors.
- Initially, the programme will benefit students in grades XI and XII studying in Navodaya Vidyalayas across the country.
- A dedicated fintech platform has been developed under Vidyanjali to disburse sponsorships to students through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- This platform plays a crucial role in data management, application processing, progress tracking, grant disbursement monitoring, fund utilization monitoring, generating impact reports for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), recognizing notable student achievements, and publicly acknowledging the support of funders, among other functions.
What is EdCIL?
- Educational Consultants India Limited (EdCIL) is the sole Public Sector Undertaking under the Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- Established on June 17, 1981, under the Companies Act, 1956, it holds the distinction of being categorized as a 'Mini Ratna Organisation' by the Government of India.
- EdCIL provides consultancy and technical services in various domains of education and human resource development, both domestically and globally.
- Its clientele includes numerous state and central government departments, public sector undertakings (PSUs), and autonomous bodies such as Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs), Kendriya Vidyalayas, and Navodaya Vidyalayas.
India to sign 78 bn deal to extend Qatar LNG imports (Indian Express)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India and Qatar are likely to ink a deal recently to extend the supply of 7.5 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) of liquefied natural gas (LNG) for another 20 years beyond 2028.
Context:
- India wants to increase the share of natural gas in its primary energy mix to 15 per cent by 2030 from a little over 6 per cent at present.
- The country already depends on LNG imports to meet around half of its gas demand, and as demand grows, imports of the natural gas are also set to grow.
- World’s largest exporter of LNG, Qatar, accounts for over half of India’s imports.
- India imported a total of 19.85 million tonnes of LNG in 2022-23 (FY23), of which 10.74 million tonnes, or 54 per cent, came from Doha.
- India’s total imports from Qatar in FY23 were valued at $16.81 billion, of which LNG imports alone were worth $8.32 billion, or 49.5 per cent of the overall imports from Doha.
- Natural gas is seen as a significantly cleaner alternative to conventional petroleum fuels like diesel and petrol and is usually cheaper than crude oil.
- For India, which has an import dependency of over 85 per cent in the case of crude oil, natural gas is seen as more affordable as well as a transition fuel in the country’s energy transition pathway.
Trade Relationship Dynamics between India and Qatar:
- In the trade relationship between India and Qatar, there exists a significant trade imbalance favoring Qatar.
- Qatar stands as India's largest source of liquefied natural gas (LNG), which is gas cooled to liquid form for sea transportation.
Import Dependency on Gas:
- India's import reliance on natural gas stands at around 50%, with a governmental focus on increasing gas consumption likely leading to further import escalation in the future.
- Petronet LNG, India's primary LNG importer, holds a long-term contract with Qatar for importing 8.5 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) of LNG. Moreover, Qatar's gas holds a substantial share in India's LNG procurements from the spot market.
Demand for Natural Gas in India:
- India has set an ambitious target to elevate the share of natural gas in its primary energy mix to 15% by 2030, up from slightly over 6% at present.
- This aspiration is poised to drive a rapid surge in LNG imports in the upcoming years. Natural gas is perceived as a notably cleaner alternative to traditional petroleum fuels like diesel and petrol, and often comes at a lower cost than crude oil.
- Given India's over 85% import dependency on crude oil, gas emerges as both more economically viable and a smoother transition fuel in the energy transformation trajectory.
Trade Dynamics: India's Import from Qatar and Export to Qatar
- In FY 2022-23, India's total imports from Qatar amounted to $16.81 billion, with LNG imports constituting $8.32 billion of the total.
- While Indian LNG importers are endeavoring to diversify their sources, reducing heavy reliance on Qatar may take considerable time.
- On the export front, India's exports to Qatar were valued at only $1.97 billion in FY 2022-23, encompassing cereals, copper articles, iron and steel articles, vegetables, fruits, spices, and processed food products.
Global LNG Market Trends:
- The global LNG market currently leans towards sellers, especially following Russia's invasion of Ukraine, which disrupted Russian natural gas supplies to Europe.
- This disruption triggered a surge in LNG spot cargo prices globally.
- Unlike term contracts, spot LNG market prices are subject to higher volatility, with prices rising steeply in times of tight supply and falling sharply during a supply glut.
Future Outlook of the LNG Market:
- Industry experts predict a shift in the global LNG market dynamics over the next few years, transitioning into a buyer's market due to the surge in new LNG export projects.
- A buyer's market arises when there is an excess supply of goods or services compared to demand, granting buyers more negotiating leverage.
- Despite this anticipated shift, it may take several years for this scenario to materialize, with a substantial portion of new LNG export capacity expected to originate from Qatar itself.
International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (DownToEarth)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Experts from The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) called for ‘bold action’ and ‘urgent finance’ to prevent collapse of nature in High Mountain Asia on February 5, 2024, in the Nepalese capital of Kathmandu.
About the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD):
- The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) is an intergovernmental knowledge and learning center dedicated to serving the communities of the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region.
- Established and inaugurated on December 5, 1983, its mission is to generate and share knowledge that informs regional policy and action, attracting investments to facilitate the transition to greener, more inclusive, and climate-resilient development.
Membership and Governance:
- ICIMOD's member countries include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Its highest governing body is the Board of Governors, composed of representatives from each member country and independent members nominated by the ICIMOD Support Group based on their professional expertise and experience.
Functions and Objectives:
- The center serves the HKH region by generating and sharing information and knowledge to address critical mountain-related challenges.
- It bridges scientific research with policy formulation and practical on-the-ground implementation.
- Furthermore, ICIMOD provides a regional platform for experts, planners, policymakers, and practitioners to exchange ideas and perspectives, facilitating sustainable mountain development.
- Headquarters of ICIMOD is in Kathmandu, Nepal.
Key Facts about the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) Region:
- The Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region spans 3,500 km across eight countries, from Afghanistan in the west to Myanmar in the east.
- It serves as the source of ten major Asian river systems, including the Amu Darya, Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, and others.
- The HKH region plays a vital role in providing water, ecosystem services, and livelihoods to the people living within its boundaries.
Israel discovers 6-million-year-old giant underwater canyon of Messinian Event (TOI)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Israel Geological Survey announced recently that Israeli geologists discovered a huge underwater canyon on the bottom of the Eastern Mediterranean that was formed about 6 million years ago.
What is Messinian Event?
- The Messinian Event, also referred to as the Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC).
- It marks a significant geological occurrence during which the Mediterranean Sea experienced a cycle of partial or near-complete desiccation, making it one of the most severe ecological crises in Earth's history.
- This event unfolded approximately 6 million years ago (MYA) and persisted until around 5.3 MYA.
- The process began with the severance of the connection between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
- This disconnection resulted from a combination of reduced sea levels globally and the collision of the European and African plates, causing the land to rise.
- Consequently, the Mediterranean experienced significant evaporation, as its evaporation rate exceeded its precipitation rate.
- Without a substantial influx of water from the Atlantic, the sea began to evaporate rapidly.
- During this period, a vast underground canyon formed, with rivers cutting deep into the basin floor, creating a canyon much larger than the Grand Canyon, reaching depths of up to 2,000 meters (6562 feet).
- As the Mediterranean water evaporated, salt deposits, primarily composed of Halite and Gypsum, accumulated on the basin floor, some reaching depths of 800 meters (2,500 feet).
- Despite the rapid evaporation, salt deposition did not keep pace, resulting in an increase in water salinity.
- The heightened salinity levels made the Mediterranean inhospitable to marine life, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
- Eventually, the sea dried up almost entirely, culminating in the Zanclean flood when the Atlantic Ocean reclaimed the basin.
What is Deep-sea Canyon?
- Deep-sea canyons, such as those formed during the Messinian Event, are steep valleys carved into the seafloor of the continental slope, extending onto the continental shelf.
- These canyons vary in size and shape and have been sculpted by various erosional processes, including river flows during periods of low sea levels, mudslides, debris flows, and turbidity currents.
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 (Indian Express)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre on Monday introduced a Bill that would enable it to prescribe the norms for nominating chairpersons of State Pollution Control Boards, exempt certain industrial units from restrictions, and decriminalize “minor offenses” related to water pollution.
News Summary:
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 has been introduced in the Rajya Sabha.
- It is applicable to Himachal Pradesh and Rajasthan, with the potential to extend to other states through resolutions under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- The Bill empowers the Centre to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions and issue guidelines related to industry establishment.
About Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024:
- Enacted in 1974, the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act aimed to prevent and control water pollution, establishing penal provisions for non-compliance.
Rationale for the Amendment:
- The Amendment Bill underscores the importance of democratic governance, emphasizing trust in people and institutions. It addresses the outdated regulations leading to a trust deficit.
Key Amendments Proposed:
- The Amendment Bill seeks to modernize the existing penal provisions, replacing imprisonment with fines for minor violations. This move aligns with the principles of Ease of Living and Ease of Doing Business.
Major Features of the Amendment Bill:
- The Bill proposes several key changes, including:
- Prescribing the process for nominating the chairman of the State Pollution Control Board by the Central Government.
- Granting the Central government authority to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions on new outlets and discharges.
- Issuing guidelines on matters related to the establishment of industries by the Central government.
- Decriminalizing minor offenses and substituting them with monetary penalties.
- Specifying the adjudication process for penalties by officers of appropriate rank.
- Outlining penalties for non-compliance with regulations regarding new outlets, discharges, and sewage.
- Allocation of penalty amounts to the Environmental Protection Fund established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Mera Gaon, Meri Dharohar (MGMD)(PIB)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Government of India has decided to map and document all villages under Mera Gaon, Meri Dharohar (MGMD) Programme.
About the Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar Programme:
- The Mera Gaon Meri Dharohar (MGMD) programme is a nationwide initiative led by the Ministry of Culture, launched on July 27, 2023, under the National Mission on Cultural Mapping.
- Its primary aim is to compile detailed information about the life, history, and cultural essence of Indian villages and make this data accessible to both virtual and real-time visitors.
Key Components and Categories:
- Under the MGMD, information is collected across seven broad categories, including:
- Arts and Crafts Village
- Ecologically Oriented Village
- Scholastic Village Linked with Textual and Scriptural Traditions of India
- Epic Village linked with Ramayana, Mahabharata, and/or Puranic legends and oral epics
- Historical Village linked with Local and National History
- Architectural Heritage Village
- Any other distinctive characteristic, such as fishing village, horticulture village, shepherding village, etc.
Objectives:
- The primary objective of the project is to culturally map India's 6.5 lakh villages across 29 States and 7 Union Territories on a comprehensive virtual platform.
- Through MGMD, individuals will have the opportunity to immerse themselves in India's diverse and vibrant cultural heritage.
Core Ideals and Benefits:
- The fundamental aim of the project is to foster appreciation for India's rich cultural traditions, thereby promoting economic growth, social harmony, and artistic development in rural communities. The programme is envisioned as a catalyst for showcasing and preserving India's cultural diversity.
Financial Outlay and Scheme Components:
- A financial outlay of Rs. 353.46 Crore has been approved under the scheme of Financial Assistance for Promotion of Art and Culture, comprising eight scheme components:
- Financial Assistance to Cultural organizations with National Presence
- Cultural Function & Production Grant (CFPG)
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Cultural Heritage of the Himalayas
- Financial Assistance for the Preservation & Development of Buddhist/Tibetan Organization
- Financial Assistance for Building Grants including Studio Theatres
- Financial Assistance For Allied Cultural Activities
- Scheme for Safeguarding the Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Through these components, the programme aims to provide comprehensive support for the preservation and promotion of India's rich cultural heritage.
National Agriculture Market or eNAM (Financial Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
With more states opening up or facilitating trade of agricultural commodities on the electronic -National Agriculture Market (eNAM), a spurt in trading among various markets within the state as well as at the inter-state level is being witnessed.
What is the National Agriculture Market (eNAM)?
- eNAM is an online trading platform dedicated to agricultural commodities in India.
- Launched on April 14, 2016, it is wholly funded by the Government of India.
- The Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC), operating under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, takes the lead in implementing e-NAM
Objectives of eNAM:
- The primary goal is to enhance marketing opportunities for farmers by establishing a competitive and transparent price discovery system.
- It also facilitates online payment options for buyers, aiming to streamline the selling process for farmers.
Network and Structure:
- The NAM portal connects existing agricultural markets, including APMC/RMC market yards, sub-market yards, private markets, and unregulated markets.
- By creating a centralized online platform, e-NAM unifies agricultural markets nationwide for efficient commodity price discovery.
Key Features:
-
- Farmers can showcase products in nearby markets, allowing traders from any location to provide quotes.
- Single-window services encompass all APMC-related activities, including commodity details, buy-and-sell offers, and direct e-payment settlements to farmers' accounts.
- Facilitating Trade:
- eNAM allows traders, buyers, and commission agents to obtain licenses from state-level authorities without physical presence requirements.
- Quality standards and infrastructure for testing are harmonized in every market, including provision for Soil Testing Laboratories in selected mandis.
- Stakeholder Benefits:
- Designed for the collective benefit of farmers, mandis, traders, buyers, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and exporters.
- Stakeholder advantages include transparent online trading, real-time price discovery, reduced transaction costs, and availability of commodity prices on the e-NAM mobile app.
- Additional Benefits:
- Farmers receive details of commodity prices, quantity sold, and quality certification through SMS.
- The system promotes a more efficient supply chain and facilitates warehouse-based sales.
- Online payments are directly deposited into farmers' bank accounts, ensuring a seamless and secure financial transaction process.
INS Sandhayak - the Indian Navy’s First Survey Vessel Large (SVL) Ship (TOI)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Defense minister Rajnath Singh commissioned survey vessel INS Sandhayak into the Indian Navy at the Naval Dockyard recently.
About INS Sandhayak:
- INS Sandhayak stands as the first unit in a series of four Survey Vessel (Large) ships under construction at Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- Its primary mission is to conduct thorough coastal and deep-water Hydrographic Surveys, focusing on Port and Harbour approaches, navigational channels, and routes.
- The operational scope extends to maritime limits, encompassing the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and extended continental shelf.
Features:
-
- The vessel is equipped to gather oceanographic and geophysical data, serving the needs of both defense and civil applications.
- In a secondary role, it provides limited defense capabilities and can function as a hospital ship during wartime or emergencies.
- Cutting-Edge Technology:
-
- Equipped with advanced hydrographic tools, including a Data Acquisition and Processing System, Autonomous Underwater Vehicle, Remotely Operated Vehicle, DGPS Long-range positioning systems, and Digital side-scan sonar.
- Performance Specifications:
-
- Powered by two diesel engines, INS Sandhayak boasts a speed capability exceeding 18 knots.
- With a length of 110 meters and a displacement of 3400 tons, the vessel maintains an indigenous content exceeding 80 per cent by cost.
- Historical Continuity:
-
- This ship has been re-incarnated in its current form from the previous Sandhayak, decommissioned in 2021.
Hydrothermal System Beneath the Waters of Lake Rotorua in New Zealand's North Island (India Today)
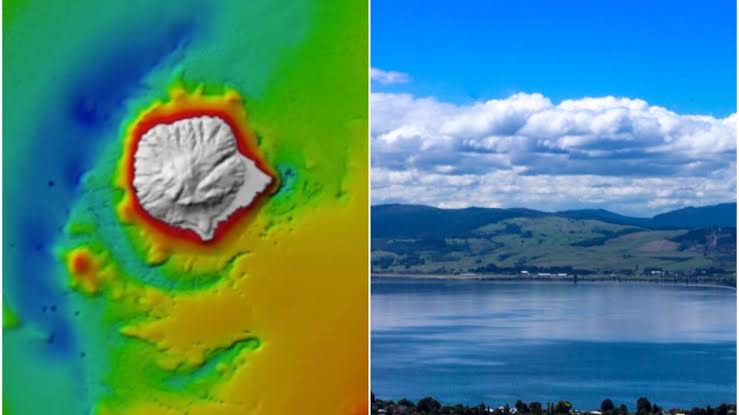

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
In a big revelation, scientists have unveiled a hidden hydrothermal system beneath the waters of Lake Rotorua, a site steeped in Maori legend and situated atop a dormant volcanic crater on New Zealand's North Island.
What are Hydrothermal Systems?
- Hydrothermal systems manifest in regions with intense heat, occurring both on continents near convergent plate boundaries and on the ocean floor in proximity to mid-ocean ridges.
- Three essential components—fluids, heat, and permeable rock structures—are crucial for their formation.
- Formation Dynamics:
- These systems are frequently situated near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates diverge, leading to the creation of new seafloor.
- Operational Mechanism:
- Hydrothermal systems initiate as seawater infiltrates fractures in the oceanic crust, gaining heat from the Earth's interior as it descends.
- Interacting with the oceanic crust, the seawater, reaching temperatures of 350-400 degrees Celsius, undergoes chemical modifications, extracting elements from the rocks.
- Despite the extreme pressure at ocean depths preventing boiling, this process generates hydrothermal fluid—a mixture of gasses and dissolved elements, including metals.
- Return to the Seafloor:
- The superheated fluid is ejected back to the seafloor and rapidly cools upon contact with near-freezing ocean bottom waters.
- Chimney-Like Deposits:
- Chemicals dissolved in the fluid precipitate at the vent, creating chimney-like deposits.
- These formations support unique deep-sea chemosynthetic communities—organisms relying on chemicals, not photosynthesis, to sustain their metabolism.
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
The Uttarakhand Cabinet on Sunday approved the final draft of the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) without any changes, a day before the state Assembly convenes for a special session to take up the Bill.
What is Uniform Civil Code (UCC)?
- A Uniform Civil Code signifies a unified legal framework for the entire country, applicable across all religious communities concerning personal matters like marriage, divorce, inheritance, and adoption.
- The objective is to replace the current fragmented personal laws that govern interpersonal relationships within different religious communities.
Constitutional Framework:
- Article 44 of the Constitution mandates the State to strive for a Uniform Civil Code applicable to all citizens.
- Positioned in Part-IV as a Directive Principle, Article 44, while not justiciable, serves as a fundamental governance guideline.
- These principles, outlined in Article 37, provide overarching ideas for the State to consider in policy formulation and law enactment.
Current Landscape of Personal Laws:
- In the Concurrent list of the Constitution, matters such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance fall under both Parliament and state legislature jurisdictions.
- Hindu personal laws have been codified into four parts since 1956, while Muslim laws, not codified per se, draw from religious texts.
- Christians, Zoroastrians, and Jews are governed by their own personal laws. Goa stands as an exception, following the Portuguese Civil Code.
Need for Uniform Civil Code:
- A UCC aims to establish equal status for all citizens, addressing the inconsistency and lack of uniformity in personal laws across different religions.
- This inconsistency, conflicting with Article 14's Equality before the Law guarantee, often results in gender disparities.
Challenges and Criticisms:
- While advocating equality, the UCC concept raises concerns about potential clashes with the Right to Freedom of Religion (Article 25).
- Critics argue that separate personal laws uphold the right to practice one's religion, particularly crucial for minorities.
- Striking a balance, the Law Commission's 2018 report suggests preserving diversity in personal laws while ensuring alignment with fundamental rights.
The Way Forward:
- Encouraging a progressive mindset through education, awareness, and sensitization is vital for understanding the spirit of the UCC.
- Simultaneously, discriminatory personal laws should be amended or abolished.
- The Law Commission recommends codifying different personal laws to derive universal principles prioritizing equity, rather than imposing a blanket Uniform Civil Code
“Pineapple Express” Sweeps California, Atmospheric River Leaves State In Distress (India Today)
- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A strong and grievous atmospheric river storm is predicted to hit California during the later part of Saturday, leaving over another storm, which resulted in extreme flooding in the last week.
What is an Atmospheric River?
- Atmospheric rivers are long and relatively narrow bands of water vapor that form over an ocean and flow through the sky, transporting much of the moisture from the tropics to northern latitudes.
- They occur globally but are especially significant on the West Coast of the United States, where they create 30% to 50% of annual precipitation and are vital to water supplies but also can cause storms that produce flooding and mudslides.
- While they are an incredibly important source of rainfall, they can also bring flash flooding, mudslides, and landslides, sometimes killing people and destroying property.
- Formation: Formed by winds associated with cyclones, atmospheric rivers typically range from 250 miles to 375 miles (400 to 600 kilometers) in width and move under the influence of other weather.
- Many atmospheric river events are weak. But the powerful ones can transport extraordinary amounts of moisture.
- Studies have shown that they can carry seven to 15 times the average amount of water discharged daily by the Mississippi River.
- Forty-six atmospheric rivers made landfall in the U.S. West Coast during the water year 2023.
- Nine were categorized as strong, two were extreme and one was exceptional.
- California experienced extensive flooding and massive snowfall.
What Happens When an Atmospheric River Reaches Land?
- When the moisture-laden air moves over mountain ranges such as the Sierra Nevada along the California-Nevada line, the water vapor rises and cools, becoming heavy precipitation that falls as rain or snow.
- While traditional cold winter storms out of the north Pacific build the Sierra snowpack, atmospheric rivers tend to be warm.
- Snow may still fall at the highest elevations but rain usually falls on the snowpack at lower elevations.
- That can quickly prompt melting, runoff and flooding and decrease the snowpack needed for California’s water supply.
What is a Pineapple Express?
- It is a nickname for a strong atmospheric river in the tropical Pacific near Hawaii.
Where did the Term Atmospheric River Come From?
- The name came from research published in the 1990s by scientists Yong Zhu and Reginald E. Newell of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Multidimensional Poverty in India (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, In her Interim Budget speech, the Union Finance Minister informed that nearly 25 crore people have been raised from multi-dimensional poverty in the last 10 years.
What is Multidimensional Poverty?
- Multidimensional Poverty refers to the complex nature of poverty, where individuals or communities experience various simultaneous disadvantages.
- These may include inadequate health, malnutrition, limited access to clean water and electricity, substandard living conditions, and limited educational or employment opportunities.
- Merely focusing on income as a poverty indicator fails to fully grasp the depth and breadth of deprivation experienced by individuals.
- Multidimensional Poverty recognizes that poverty encompasses more than just economic factors; it encompasses a range of dimensions that impact well-being and quality of life.
- This approach to measuring poverty incorporates not only income or consumption levels but also considers deprivations in education and access to essential infrastructure.
- The international poverty line, set at $2.15 per day (in 2017 purchasing power parity terms) by the World Bank, serves as a benchmark for evaluating monetary value but is complemented by a broader assessment of various dimensions of deprivation.
What is the Global Multidimensional Poverty Index?
- The Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) serves as a vital tool for assessing acute multidimensional poverty in over 100 developing nations.
- Published collaboratively by the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) and the UNDP's Human Development Report Office, it provides a comprehensive framework for tracking deprivation across three key dimensions and ten indicators.
- This index operates on a scale from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating greater levels of poverty.
- According to MPI methodology, individuals experiencing deprivation in a third or more of the weighted indicators are classified as "MPI poor."
India's Progress and Comparison:
- According to the 2023 Global MPI report, India successfully uplifted 415 million people out of poverty between 2005-06 and 2019-21, marking a significant achievement in poverty alleviation efforts.
- India is among 25 nations that have effectively halved their global MPI values within 15 years.
Comparison with India's National MPI:
- In addition to the global MPI, India has its own National Multidimensional Poverty Index.
- Published by NITI Aayog, India's MPI incorporates two additional indicators:
- Maternal health (under the health dimension) and
- Bank account ownership (under the standard of living dimension).
- This modification aligns the MPI with India's specific national priorities, offering a nuanced understanding of poverty dynamics within the country.
GHAR (GO Home and Re-Unite) Portal for Restoration and Repatriation of Child (PIB)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Women and Child Development developed the “Track Child Portal”, which enables tracking of the missing and found children in all States/UTs including Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, North Eastern States and Jharkhand.
What is the GHAR Portal?
- National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has developed and launched the portal GHAR - Go Home and Reunite, with the sole purpose of restoration and repatriation of children.
- The GHAR portal has been developed to digitally monitor and track the restoration and repatriation of children.
- Here's how the portal can help strayed children go home and reunite with their families:
- The portal digitally tracks and monitors children who are in the juvenile justice system and have to be repatriated to another country, state or district.
- It allows the digital transfer of cases of children to the Juvenile Justice Board/Child Welfare Committee of the state concerned.
- It will help in speedy repatriation of children.
- Where there is a requirement for a translator/interpreter/expert, a request will be sent to the state government concerned.
- Child welfare committees and district child protection officers can ensure proper restoration and rehabilitation of children by digitally monitoring the progress of the case of the child.
- A checklist format will be provided in the forms so that the children who are being hard to repatriate or children who are not getting their entitled compensation or other monetary benefits can be identified.
- A list of government-implemented schemes will be provided so that at the time of restoration the Child Welfare Committees can link the child with the schemes to strengthen the family and ensure that the child remains with his/her family.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development is administering the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 (JJ Act, 2015) (as amended in 2021) and the Rules thereunder, to ensure the safety, security, dignity and well-being of children.
- The Act provides for the protection of children in need of care and protection and those in conflict with the law by catering to their basic needs through care, protection, development, treatment and social reintegration.
- Under the JJ Act, 2015, the Child Welfare Committees have been empowered to make decisions regarding the children in need of care and protection for the children’s best interest.
- They are also mandated to monitor the functioning of the Child Care Institutions (CCIs).
- Similarly, under section 106 of the JJ Act, 2015, every state government has to constitute a District Child Protection Unit (DCPU) for every district to take up matters relating to children to ensure the implementation of the JJ Act, 2015 and its rules thereunder.
- To ensure effective coordination in child safety, protection and development, District Magistrates have been made the heads of DCPUs.
- DMs have been empowered to review the functioning of DCPUs and CWCs at regular intervals to ensure prompt decisions as per provisions of the JJ Act and Rules are taken by these bodies, keeping in mind the best interests of the children.
: Law Commission of India (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 22nd Law Commission of India led by Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi has recommended that the offense of criminal defamation should be retained in the new criminal laws.
About the Law Commission of India:
- The Law Commission of India is a non-statutory body, constituted by the Government of India from time to time.
- The commission's function is to research and advise the government on legal reform, and is composed of legal experts, and headed by a retired judge.
- The commission is established for a fixed tenure and works as an advisory body to the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- The first Law Commission was established during colonial rule in India by the East India Company under the Charter Act of 1833 and was presided over by Lord Macaulay.
- After that, three more commissions were established in British India.
- The first Law Commission of independent India was established in 1955 for a three-year term.
- Since then, twenty-one more commissions have been established.
- The 22nd Law Commission has been notified with effect from 21st February 2020 for a term of 3 years.
- Cabinet approves the extension of the term of the 22nd Law Commission of India up to 31st August 2024.
- Justice Rituraj Awasthi (Former Chief Justice of the Karnataka HC) was appointed as the chairperson of the current 22nd Law Commission.
- The last chairman of the 21st Law Commission was retired Supreme Court judge Justice B.S. Chauhan.
The Responsibilities of the Law Commission:
- Identification of laws which are no longer relevant and recommending the repeal of obsolete and unnecessary enactments;
- Suggesting enactment of new legislations as may be necessary to implement the Directive Principles and to attain the objectives set out in the Preamble of the Constitution;
- Considering and conveying to the Government its views on any subject relating to law and judicial administration that may be specifically referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Considering the requests for providing research to any foreign countries as may be referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Preparing and submitting to the Central Government, from time to time, reports on all issues, matters, studies and research undertaken by it and recommending such reports for effective measures to be taken by the Union or any State; and
- Performing such other functions as may be assigned to it by the Central Government from time to time.
Govt To Sell Bharat Rice At Rs 29/Kg in Retail Market (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will launch retail sales of Bharat Rice at ?29 per kg from next week to provide relief to consumers. It has also directed traders to disclose rice stock to control prices.
Context:
- The recent announcement by the Union government regarding the retail sale of rice at Rs 29 per kg through three cooperatives has garnered attention in the news.
- This initiative, known as 'Bharat Rice,' seeks to address the upward trend in rice prices.
- Over the past year, retail prices have surged by 14.5%, while wholesale prices have seen a 15.5% increase.
- This move aims to mitigate the impact of rising rice prices on consumers and ensure the affordability and accessibility of this staple food item.
Recent Developments:
- In response to escalating domestic rice prices and to ensure food security within the country, the Union government implemented measures in 2023.
- These included a ban on the export of white (non-basmati) rice and the imposition of a 20% export duty on par-boiled rice.
- The decision to restrict rice exports was driven by the need to stabilize domestic prices and guarantee an ample food supply for the nation.
- Experts predict that these restrictions are likely to remain in place until the upcoming general election scheduled for April-May 2024.
- Challenges in rice production during the 2023-24 kharif season, exacerbated by dry weather conditions attributed to El Nino, have further complicated the supply situation.
- Despite these trade limitations, local rice prices have remained firm, prompting government warnings to retailers.
Government Intervention:
- Union Food Secretary Sanjeev Chopra highlighted a 14.51% increase in retail rice prices over the past year.
- In response to rising rice prices, the government has mandated traders, wholesalers, retailers, and processors to report their rice and paddy stocks every Friday to manage food inflation and curb speculative activities.
- To counter inflationary pressures, the government has initiated the retail sale of 'Bharat Rice' to the general populace.
- Initially, 5 lakh tonnes of rice will be allocated for retail sale under this brand through agencies like NAFED, NCCF, and Kendriya Bhandar, priced at ?29 per kilogram in 5 kg and 10 kg bags.
- Furthermore, the Food Corporation of India (FCI) has ample stocks of good-quality rice available for sale to traders and wholesalers under the open market sales scheme at a reserve price of ?29 per kilogram.
Status of India’s Rice Exports:
- India holds the position of the world's largest rice exporter, accounting for 45% of the global rice market share.
- During April-May 2023, overall rice exports witnessed a notable increase of 21.1% compared to the previous fiscal year.
- Basmati rice exports in May 2023 alone surged by 10.86% compared to May 2022, reflecting a sustained upward trend.
- The export of non-Basmati rice has been steadily rising over the past three years, with Basmati rice exports in 2022-2023 surpassing the previous year's figures.
- Recent data provided by the government indicates a 15% increase in total rice exports (excluding broken rice) by August 17 compared to the corresponding period in the previous year.
- Regional Dynamics: Thailand anticipates a nearly 25% decrease in rice production for the 2023-2024 season, while Myanmar has halted raw rice exports.
- Similarly, rice availability is expected to be limited in Iraq and Iran.
- India annually exports more than 4 million tons of basmati - a premium long-grain variety famed for its aroma - to Iran, Iraq, Yemen, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and the United States, among others.
Three New Major Railway Corridors Announced Under PM GatiShakti in the Interim Budget 2024-25 (PIB)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Interim Budget for 2024-25 announcement for implementation of three Economic Railway Corridors identified under the PM GatiShakti for enabling multi-modal connectivity.
Context:
- The Interim Budget for 2024-25 has laid the groundwork for implementing three major Economic Railway Corridors under the PM GatiShakti initiative.
- This will enable multi-modal connectivity, including:
- Energy, mineral, and cement corridors
- Port connectivity corridors and
- High-traffic density corridors
Significance of the Three Corridors:
- Logistics Efficiency Boost: These Corridors serve as catalysts for enhancing logistics efficiency, thereby cutting down on the costs associated with rail transportation.
- By streamlining rail movements, they pave the way for smoother and more cost-effective logistics operations.
- Alleviating Rail Congestion: One of their primary roles is to alleviate congestion on heavily trafficked rail routes.
- By diverting some of the traffic to these designated Corridors, the strain on high-density rail networks is relieved, ensuring smoother and more reliable transportation across the board.
- Promoting Modal Shift: The Corridors play a pivotal role in encouraging a modal shift from road to rail and coastal shipping.
- By providing efficient rail connections and integrating coastal shipping options, they offer viable alternatives to traditional road transport, thereby reducing congestion on highways and minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Sustainability: A key benefit of these Corridors is the reduction of the carbon footprint associated with logistics operations.
- By promoting more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as rail and coastal shipping, they contribute to mitigating the environmental impact of freight movement, fostering sustainability in logistics practices.
About PM GatiShakti National Master Plan:
- The government of India initiated the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti National Master Plan to transform the nation's infrastructure.
- PM Modi launched the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP) on 13th October 2021, on the 75th Independence Day to provide multimodal connectivity infrastructure to various economic zones.
- The scheme is expected to smooth out the execution of projects across the nation and foster coordination between different ministries engaged with these projects.
Advantages of PM Gati Shakti:
- It lays out a centralised portal to unite the infrastructural initiatives of 16 central ministries and departments.
- Facilitates these ministries, gives a centralised transportation and logistics grid for smoother data flow and sped up project clearance.
- Large-scale infrastructure projects like UDAAN, expansion of the railway network, Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, and Bharat Net will be executed by the Gati Shakti master plan.
- The Gati Shakti master plan aims to create employment potential for a large number of individuals.
- The plan's three primary targets are smooth multimodal connectivity, enhanced prioritisation and optimal usage of resources to create capacities on time, and resolution of issues like standardisation, disjointed planning and clearances.
- The Gati Shakti mission aims to create world-class infrastructure in the country and foster logistical synergy across various modes of movement.
- The general objective of the drive is to increase competitiveness and economic development in India.
Expansion of Nano DAP (Indian Express)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, presenting the interim budget on (February 1), announced the expansion of the application of Nano DAP on various crops in all agro-climatic zones.
What is DAP?
- Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a fertilizer containing phosphorus and nitrogen, crucial nutrients for plant growth.
- Its chemical formula is (NH?)?HPO?. DAP is widely utilized in agriculture to offer plants a quick and easily accessible nutrient source.
- It ranks as the second most utilized fertilizer in India, following urea. Notably, DAP is rich in phosphorus (P), which plays a vital role in promoting root establishment and development.
- Application of DAP is typically done just before or at the time of sowing to ensure optimal plant growth and development.
What is Nano DAP?
- Nano DAP is an innovative liquid fertilizer formulation comprising nanoparticles of Diammonium Phosphate (DAP).
- Serving as a rich source of nitrogen and phosphorus, the two primary nutrients crucial for crop growth, Nano DAP offers unique advantages.
- Its small particle size, measuring less than 100 nm, coupled with a high surface area, facilitates easy absorption by plant leaves.
- This novel nano-formulation contributes to enhanced crop growth and yield, decreased environmental impact, and improved profitability for farmers.
Why Nano DAP?
- In addition to being more efficient than conventional DAP, Nano DAP has a few other benefits.
- First, it is more pocket-friendly than its conventional counterpart.
- A 500 ml bottle of Nano DAP, equivalent to a 50-kg bag of conventional DAP, is priced at only Rs 600 (compared to Rs 1,350 for the bag).
- Since the government provides significant subsidies on DAP, the adoption of a more inexpensive fertiliser will likely be a significant relief to the government’s subsidy burden.
- Second, for farmers, Nano DAP is also significantly more convenient.
- Simply put, 500 ml bottles are easier to transport, store, and use than 50kg bags.
- The fertiliser is sprayed on crops, with 250-500 ml of DAP, dissolved in water, required per spray, per acre.
- Most importantly, however, India currently imports significant quantities of fertiliser to meet domestic demand.
- The adoption of domestically-produced Nano DAP — produced in Kalol, Gujarat — is set to significantly reduce this import burden.
- This revolutionary step will not only take Indian agriculture forward in foodgrain production but it will also make India self-reliant in fertiliser production.
- The adoption of Nano DAP will help in achieving self-sufficiency in fertilisers and greatly benefit our farmers.
US Approved Sale of 31 Predator Drones to India (India Today)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a significant development that underscores the deepening strategic partnership between India and the United States, the US State Department has approved a landmark Foreign Military Sale to the Indian government.
News Summary:
- The US Defense Security Cooperation Agency has formally notified the US Congress regarding a potential military sale of MQ-9B SkyGuardian drones and associated equipment to the Government of India.
What is a Drone?
- Drones are aerial vehicles powered by various means, capable of autonomous flight or remote piloting, and can carry payloads, lethal or nonlethal, depending on the mission.
Key Features of MQ-9B SkyGuardian Drones:
- Designed for extended over-the-horizon flights lasting over 30 hours, facilitated by satellite connectivity.
- Incorporates advanced capabilities to safely operate in civilian airspace, facilitating joint operations with civil authorities for real-time situational awareness.
- Equipped with sophisticated maritime intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) systems, enabling real-time monitoring and patrolling both above and below the ocean's surface.
Significance of Drone Technology in Defense:
- Strategic Importance: Drones offer valuable intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities, providing real-time visuals and data to support decision-making processes.
- They also reduce risks to personnel and offer cost-effective alternatives to conventional manned aircraft.
- Tactical Advantages: Drones enable precision strikes with minimal collateral damage, enhance coordination and logistics in challenging terrains, and facilitate operations in remote or hostile environments.
Challenges Associated with Drones:
- Complex Airspace Management: The integration of drones into India's airspace necessitates a robust management framework to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Factors like strong winds can affect drone operations, highlighting the need for resilient systems capable of operating in varied environmental conditions.
- Privacy and Safety Concerns: There are concerns regarding the potential misuse of drones for breaching privacy and safety regulations, emphasizing the importance of stringent regulations and oversight mechanisms.
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (PIB)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the continuation of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to be implemented under the Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund:
- This initiative operates as a Central Sector Scheme aimed at incentivizing investments from various entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSMEs, Farmer’s Producers Organizations (FPOs), and Section 8 companies.
- These investments are directed towards establishing infrastructure for:
- Dairy processing and value addition
- Meat processing and value addition
- Animal feed plants
Objectives:
- Facilitating the expansion of milk and meat processing capacity and diversification of products, thereby granting unorganized rural milk and meat producers greater access to organized markets.
- Enhancing price realization for producers and ensuring the availability of quality milk and meat products for domestic consumers.
- Promoting exports and elevating the sector's contribution to export revenue.
- Providing quality concentrated animal feed to cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry, ensuring balanced rations at affordable prices.
- The Government of India offers a 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, including a two-year moratorium, for loans covering up to 90% of the investment.
- These loans are accessible from scheduled banks, the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), NABARD, and NDDB.
- Notably, government entities and cooperatives are excluded from availing benefits under this scheme.
What is Animal Husbandry?
- Animal husbandry encompasses the controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, with a focus on enhancing desirable qualities through breeding.
- It serves as a vital branch of agriculture dedicated to animals raised for various purposes such as meat, fibre, milk, and other products.
- This involves day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the overall management of livestock.
- In India, animal husbandry plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of many farmers, offering significant self-employment opportunities, particularly for landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, and women.
- The sector contributes to providing affordable and nutritious food to millions of Indians through the production of meat, eggs, milk, and other essential items.
- Additionally, it serves as a valuable source of raw materials such as hides, skins, bones, blood, and fat.
- Animals are often regarded as the best insurance against natural calamities like drought, famine, and other adversities, providing a degree of stability to farmers in unpredictable conditions.
Improved Fiscal Resilience Amid Modest Tax Buoyancy (Indian Express)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government’s aim to restrict the fiscal deficit to 5.8 per cent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) as against 5.9 per cent budgeted earlier for the financial year and the push to restrict the fiscal deficit target to below 4.5 per cent by 2025-26 rides on the back of a strong buoyancy in tax revenues.
What is Tax Buoyancy?
- Tax buoyancy elucidates the correlation between fluctuations in government tax revenue growth and changes in Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- This concept underscores the intrinsic link between the government's tax earnings and economic expansion.
- Essentially, as the economy accelerates, government tax revenue experiences a corresponding increase.
- Tax buoyancy delineates the responsiveness of tax revenue growth to alterations in GDP, signifying its sensitivity to economic fluctuations.
- A buoyant tax exhibits a revenue surge without necessitating a rise in tax rates, contingent upon factors such as the tax base's magnitude, tax administration efficiency, and the simplicity and rationality of tax structures.
- Typically, direct taxes demonstrate higher buoyancy, being more responsive to GDP growth rates.
What is Tax Elasticity?
- Tax elasticity, akin to tax buoyancy, refers to variations in tax revenue consequent to changes in tax rates.
- For instance, assessing how tax revenue fluctuates when the government reduces corporate income tax from 30 percent to 25 percent illustrates tax elasticity.
- This concept underscores the dynamic relationship between tax rates and revenue generation, reflecting the degree of responsiveness of tax revenue to alterations in tax rates.
About the Laffer Curve:
- The Laffer Curve, pioneered by economist Arthur Laffer in 1974, illustrates the interplay between tax rates and government tax revenue collection.
- This economic theory posits that tax rates exceeding a certain threshold diminish tax revenue by disincentivizing workforce participation.
- It suggests the existence of an optimal tax rate that maximizes total tax revenue.
- By visually depicting the inverse relationship between tax rates and tax revenue, the Laffer Curve highlights the complexities of tax policy and the importance of balancing tax rates to achieve revenue optimization.
RBI Action Against Paytm Payments Bank (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently barred Paytm Payments Bank from offering all its core services — including accounts and wallets — from March, effectively crippling the company’s business.
News Summary
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has directed Paytm Payment Bank to halt accepting money in any customer account, including wallets and prepaid instruments like FASTags, from March 1.
- This action comes due to ongoing non-compliance and significant supervisory concerns highlighted by the RBI.
What Does the RBI Directive Include?
- Barred Services: Paytm Payment Bank is prohibited from offering most of its essential services.
- Account Closure: Paytm cannot accept deposits or top-ups after February 29, and nodal accounts of its parent company, One97 Communications, and Paytm Payments Services, must be terminated by February 29.
- Transaction Settlement: All pending transactions and nodal accounts initiated by February 29 must be settled by March 15.
- Customer Withdrawals: Customers are permitted to freely withdraw or use the money from their Paytm accounts, including savings and current accounts, prepaid instruments, FASTags, etc., within their available balance.
Reasons Behind the Action:
- Ongoing Scrutiny: Paytm Payment Bank has been under RBI scrutiny since 2018.
- Compliance Concerns: While specifics were not disclosed, it's believed the action stems from RBI's concerns about KYC compliance and IT-related issues.
- Data Security: RBI is cautious about safeguarding depositors' money and protecting data.
- Concerns arose when Paytm Payment Bank and its parent company lacked sufficient barriers to prevent unauthorized access to data by China-based entities with indirect stakes in the parent company.
What is a Payments Bank?
- Payment banks function similarly to traditional banks but on a smaller scale and without engaging in credit risk.
- Established based on recommendations from the Nachiket Mor Committee, their primary objective is to promote financial inclusion by providing banking and financial services to underserved areas, including migrant workers, low-income households, and small entrepreneurs.
Legal Framework and Features:
- Registered as public limited companies under the Companies Act 2013 and licensed under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act 1949, payments banks operate under various regulations such as the Banking Regulation Act 1949, RBI Act 1934, and Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999.
Key features include:
- Differentiation: Payments banks are distinct from universal banks and operate on a smaller scale.
- Capital Requirement: The minimum paid-up equity capital for payment banks is set at 100 crores, with promoters required to contribute at least 40% during the first five years of operation.
- Permissible Activities: Payments banks can accept deposits up to Rs. 2,00,000, invest in government securities to meet statutory liquidity requirements and provide various banking services such as remittance, mobile payments, ATM/debit cards, and net banking.
- Additionally, they can serve as banking correspondents for other banks.
- Limitations: Payments banks are restricted from issuing loans and credit cards, accepting time deposits or NRI deposits, and establishing subsidiaries for non-banking financial activities.
Blue Economy 2.0 (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Interim Budget presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on (February 1) stressed environment-friendly development through the promotion of a ‘blue economy’.
What are the Proposals in the Interim Budget Regarding the Blue Economy?
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced plans to launch a scheme focusing on restoration, adaptation measures, coastal aquaculture, and mariculture, adopting an integrated and multi-sectoral approach.
- Restoration and adaptation measures aim to preserve ocean health during economic activities, while aquaculture involves farming aquatic plants and animals, and mariculture focuses on rearing marine creatures in saltwater.
- Additionally, five integrated aqua parks will be established, and the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) will be strengthened to increase aquaculture productivity, double exports to Rs 1 lakh crore, and create 55 lakh employment opportunities in the near future.
What is the Blue Economy?
- While the term blue economy can simply refer to economic activities related to the sea and the coasts, it is generally understood to have an element of sustainability in it.
- Thus, the European Commission defines it as “all economic activities related to oceans, seas and coasts.
- It covers a wide range of interlinked established and emerging sectors”; the World Bank says the blue economy is the “sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of ocean ecosystems.”
- For a country like India, with a long coastline, diversity in terms of fish and other ocean produce, and multiple tourism opportunities, the blue economy is highly significant.
Does India Have a Blue Economy Policy?
- The blue economy 2.0. a draft policy framework on India’s Blue Economy was first released in July 2022.
- The policy document contained “key recommendations on National Accounting Framework for Blue Economy and Ocean Governance, Coastal Marine Spatial Planning and Tourism Priority, Marine Fisheries, Aquaculture and Fish Processing.
- Manufacturing, Emerging Industries, Trade, Technology, Services and Skill Development, Logistics, Infrastructure and Shipping, Coastal and Deep-Sea Mining and Offshore Energy and Security, Strategic Dimensions and International Engagement.”
- When the G20 summit was hosted in New Delhi under India’s presidency, the Comptroller & Auditor General of India (CAG) chaired the Engagement Group for Supreme Audit Institutions (SAls) of the member countries in June 2023. Two priorities for the SAI20 deliberations were blue economy and responsible Artificial Intelligence.
CBSE Proposes New Plan For Class 10 & 12 (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
CBSE is reported to have proposed significant changes to the academic framework for secondary and higher secondary education, including a shift from studying two languages to three in Class 10, with the requirement that at least two must be native Indian languages.
Key Highlights of the Proposal:
Proposed Changes for Class 10:
- Transition from studying two languages to three, with a stipulation that at least two must be native Indian languages.
- Potential requirement for students to pass in 10 subjects, contrasting with the current mandate of five.
Proposed Changes for Class 12:
- Shift to studying two languages instead of one, with the condition that at least one must be a native Indian language.
- Introduction of a necessity to clear examinations in six subjects for high school graduation, up from the existing requirement of five.
The objective behind the Proposed Changes:
- These modifications are part of CBSE's broader initiative to implement a national credit framework in school education, addressing the absence of a formalized credit system in the standard curriculum.
Academic Year and National Learning Hours:
- According to the CBSE plan, an academic year will comprise 1200 notional learning hours, equivalent to earning 40 credits.
- Notional learning denotes the specified time required for an average student to achieve set outcomes.
- This encompasses both academic learning at school and non-academic or experiential learning outside of it.
Storage of Earned Credits:
- The scheme of studies has been adjusted to outline teaching hours and credits earned for each subject.
- These earned credits will be digitally stored in the Academic Bank of Credits, accessible through a linked Digilocker account.
What is the National Credit Framework (NCrF)?
- The draft NCrF was introduced by the Union Ministry of Education (MoE) in 2022, based on recommendations from an inter-ministerial committee.
- It serves as a guideline for schools, colleges, and universities to adopt the credit system, marking the inclusion of the entire school education system under its purview.
- Previously, only the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) followed a credit system, but the NCrF extended its coverage to include skill and vocational education.
Proposed Benefits of NCrF for Various Stakeholders:
- Students:
- Facilitates multidisciplinary education with flexible curricula.
- Eliminates distinctions between different streams like arts, science, social sciences, and commerce.
- Rewards students with credits for academic, skill, and experiential learning.
- Expands core learning to encompass both foundational and cognitive aspects.
- Institutions:
- Fosters collaboration between institutions.
- Simplifies and standardizes credit mechanisms.
- Emphasizes research and innovation.
- Utilizes institutional infrastructure efficiently.
- Government:
- Expected to increase student enrollment rates.
- Complements India's demographic dividend, aiming to become the Skill Capital of the World.
- Industry:
- Enables students to acquire NSQF-approved foundational skills from the industry, enhancing employability.
- Allows for quick educational upgradation and up-skilling through micro-credentials.
Significance of NCrF:
- Aligns with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 by integrating academic and vocational domains for flexibility and mobility.
- Facilitates re-entry into the education system for students who have dropped out.
- Promotes Recognition of Prior Learning, acknowledging skills acquired informally through various means.
Enforcement Directorate (ED) Arrests Jharkhand CM in a Corruption Case (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently Jharkhand CM Hemant Soren was arrested by the officials of the Enforcement Directorate (ED) in the land scam case.
News Summary:
- Jharkhand CM Hemant Soren became the third state chief minister to be arrested after the Enforcement Directorate took him into custody in a money laundering case.
- Before Hemant Soren, his father Shibu Soren and Madhu Koda were arrested.
- He was arrested in a case related to an illegal change of ownership of land in Jharkhand.
What is the Enforcement Directorate (ED)?
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) is a multi-disciplinary agency tasked with investigating money laundering offenses and violations of foreign exchange laws.
- It operates under the Department of Revenue within the Ministry of Finance and upholds strict compliance with the Constitution and laws of India.
Structure:
- Headquarters: Located in New Delhi, the ED is headed by the Director of Enforcement.
- Regional Offices: The agency has five regional offices situated in Mumbai, Chennai, Chandigarh, Kolkata, and Delhi, each overseen by Special Directors of Enforcement.
- Recruitment: Officers are recruited directly and transferred from other investigative agencies, comprising personnel from the Indian Revenue Services (IRS), Indian Police Services (IPS), and Indian Administrative Services (IAS), including roles such as Income Tax officers, Excise officers, Customs officers, and police officials.
- Tenure: Typically, officers serve a two-year term, extendable to five years with three annual extensions.
- Amendments to the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946, and the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) Act, 2003, enable the government to extend the tenure of directors for one year after completing their initial two-year terms.
Functions:
- COFEPOSA: Empowered by the Conservation of Foreign Exchange and Prevention of Smuggling Activities Act, 1974 (COFEPOSA), the ED can initiate cases of preventive detention related to violations of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA): This civil law aims to regulate external trade and payments, with the ED responsible for investigating suspected contraventions, adjudicating cases, and imposing penalties.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA): Enacted to combat money laundering, the ED is tasked with tracing assets derived from crime proceeds, attaching property, and prosecuting offenders through Special Courts.
- Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA): Introduced to address economic offenders seeking refuge abroad, the ED enforces this law by attaching properties of fugitives and confiscating assets, thereby deterring offenders from evading Indian law.
5 Wetlands Added to The Global List of Wetlands of International Importance under Ramsar Convention (TOI)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of World Wetlands Day, five more wetlands in India got the tag of international importance under the Ramsar Convention, making it the fourth largest country in terms of the number of sites on the list.
About the New Ramsar sites:
- The five newly added Indian sites in the list are Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu, and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve and Aghanashini Estuary in Karnataka.
- In India, Tamil Nadu continues to have the maximum number of Ramsar sites (16) followed by Uttar Pradesh (10).
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu): Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary is one of the largest inland wetlands of Tamil Nadu and is a significant source of groundwater recharge for the area.
- Water from the wetland is utilized by the villagers for cultivating crops such as paddy, sugar cane, cotton, corn, and split red gram.
- Karaivetti has one of the largest congregations of waterbirds in the State of Tamil Nadu.
- The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu): The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest derives its name from the Tamil word, "Solai", which means ‘tropical rainforest’.
- The ‘Sholas’ are found in the upper reaches of the Nilgiris, Anamalais, Palni hills, Kalakadu, Mundanthurai and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- These forested wetlands serve as habitats for the globally endangered Black-chinned Nilgiri Laughing thrush (Strophocincla cachinnans), Nilgiri Blue Robin (Myiomela major), and vulnerable Nilgiri Wood-pigeon (Columba elphinstonii).
- As many as 14 out of 26 endemic bird species of the Western Ghats are found in these wetlands.
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve (Karnataka): Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve is a human made Village Irrigation Tank built centuries back and is spread over an area of 98.76ha.
- It is an ecologically important wetland, rich in biodiversity, comprising over 210 species of plants, mammal species, reptiles, birds etc.
- It supports more than 1% of the biogeographic population of Painted Stork and Black-headed Ibis.
- Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka): Aghanashini Estuary is formed at the confluence of the Aghanashini River with the Arabian Sea.
- The brackish water of the Estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
- The wetland also provides livelihoods to families by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production.
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve (??Karnataka): Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, is a human-made wetland with an area of nearly 50 hectares which was constructed to store rainwater for irrigation purposes.
- The wetland harbors two vulnerable species, namely the Common pochard and River tern and four near-threatened species, namely the Oriental Darter Black-headed Ibis Woolly-necked Stork and Painted Stork.
- It is also one of the largest wintering grounds for the Bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in Southern India.
- The wetland is a designated Important Bird Area (IBA) and is also listed as a priority area for conservation in India.
What is the Ramsar Convention?
- The Ramsar Convention was signed on 2nd February 1971 to preserve the ecological character of their wetlands of international importance.
- It is named after Ramsar, the Iranian city where the treaty was signed in 1971, and places chosen for conservation under it are given the tag ‘Ramsar site’.
- The World Wetlands Day, celebrated on 2 February to raise global awareness about the importance of wetlands for human prosperity and a healthy planet.
