PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, launched the PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31 dedicated to Indian Sign Language (ISL) on December 6, 2024, in New Delhi.
Channel Purpose and Vision:
- Objective: To bridge the communication gap between the hearing-impaired and hearing populations by promoting ISL.
- Significance: Channel 31 aims to unlock talent and ensure equal opportunities for all, making society more inclusive and progressive.
- ISL's Role: Pradhan emphasized the importance of alternative communication methods like ISL, which ensures that individuals with hearing impairments have equal access to education, employment, and societal participation.
Government's Focus on Inclusivity:
- Legal Framework: Pradhan highlighted the expansion of recognized disabilities from 7 to 21, making the legal framework more comprehensive.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The policy focuses on inclusive education, with particular attention to Children with Special Needs (CwSN). The NEP promotes the standardization of ISL and its inclusion in educational curricula.
- Employment and Cultural Expression: ISL is not only essential for communication but also contributes to cultural expressions like dance and drama. Pradhan emphasized that learning ISL would open employment opportunities and allow individuals to express themselves fully.
Importance of Channel 31:
- The launch of Channel 31 aligns with India’s commitment to ensuring equal rights and access to education, as enshrined in the Constitution.
- Pradhan urged for widespread adoption of ISL, ensuring that more people learn the language to better support the hearing-impaired community.
PM e-Vidya Initiative:
- Launch Date: PM e-Vidya was launched as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan on May 17, 2020, to bridge the digital divide and ensure inclusive education.
- Key Components:
- DIKSHA: A national platform providing e-content for all grades.
- DTH TV Channels: Initially started with 12 channels, now expanded to 200, offering supplementary education in multiple languages.
- SWAYAM: A platform for online courses and MOOCs for both school and higher education.
- Community Radio & Podcasts: These platforms are used for wider educational outreach, especially in rural and remote areas.
- e-Content for Teachers: Interactive videos and resources aimed at enhancing teacher education.
Channel Content:
- Channel 31 will provide 24x7 educational content for children with hearing impairments, teachers, and other stakeholders.
- The content will include school curricula, career guidance, skill training, mental health support, and promotion of ISL as a subject.
- The content will be available on YouTube, increasing its reach and accessibility.
Parliamentary Panel's Review on Mechanism to Curb Fake News

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Parliamentary Panel on Communications and Information Technology is reviewing mechanisms to curb fake news, following the Bombay High Court striking down a provision of the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules, 2021.
- The controversial provision allowed the government to identify and flag "fake news" on social media through its Fact Check Unit (FCU).
- The panel, led by BJP MP Nishikant Dubey, has summoned representatives from News Broadcasters and Digital Association and the Editors Guild of India to discuss the issue on November 21, 2024.
Issue with the Amended IT Rules:
- The IT Rules, 2021 were amended in April 2022 to include “government business” under the definition of fake news, expanding the scope of content flagged by the FCU.
- This amendment was challenged by media bodies and individuals like comedian Kunal Kamra, leading to the Bombay High Court striking it down in 2024.
- The court deemed the provisions unconstitutional, citing concerns about transparency and the potential misuse of power.
Types of Fake News:
- Misinformation: False information spread unintentionally.
- Disinformation: Deliberately false information meant to deceive and cause harm.
Status of Fake News in India:
- India as a major spreader of misinformation: The World Economic Forum's Global Risks 2024 report identifies disinformation as a significant short-term risk, with India as one of the largest consumers and producers of false information.
- Social Media Influence: Platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, and YouTube are widely used in India for news dissemination, making them a breeding ground for fake news.
- Spread of Political and Religious Misinformation: Fake news often serves political or religious agendas, leading to societal polarization and conflict.
Government Efforts to Combat Fake News:
- IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023: This amendment expanded the scope of "fake news" to include “government business” and gave the FCU the authority to flag misleading content.
- Press Information Bureau (PIB) Fact Check Unit: The PIB continues to run a fact-checking initiative, but it lacks the authority to remove flagged content from social media platforms.
- Digital Literacy Campaigns: Programs like Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) aim to improve digital literacy, especially in rural areas, to help citizens identify and avoid fake news.
RBI's Recent Monetary Policy Review
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) maintained its benchmark interest rate at 6.5% for the 10th consecutive monetary policy review since April 2023. The policy stance was shifted to “neutral,” indicating potential for a future rate cut.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Overview
- The decision to keep interest rates unchanged was supported by a majority of five out of six members of the MPC, which convened for three days starting October 7.
- The change in policy stance from “withdrawal of accommodation” to “neutral” was unanimously agreed upon.
Focus Areas
- The MPC emphasized the need for a durable alignment of inflation with targets while supporting economic growth.
- Macroeconomic parameters for inflation and growth were described as well balanced.
Inflation Insights
- A moderation in headline inflation is expected to reverse in September, likely remaining elevated due to adverse base effects.
- Retail inflation was below the central bank’s median target of 4% in July and August.
Growth Projections
- The RBI maintained its 7.2% GDP growth projection and a 4.5% average inflation estimate for 2024-25, with risks evenly balanced.
- Second-quarter inflation projection was revised down to 4.1% from 4.4%, while a rise to 4.8% is expected for the October to December quarter.
Domestic Growth and Investment
- Domestic growth remains robust, with private consumption and investment growing together.
- This growth has provided the RBI with the capacity to prioritize inflation control to achieve the 4% target.
Risks to Inflation
The Governor highlighted that unexpected weather events and escalating geopolitical conflicts pose significant upside risks to inflation.
Global Electricity Review 2024

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In 2023, India overtook Japan to become the world’s third-highest producer of solar power, according to a report by international energy analytics agency Ember recently.
About Global Electricity Review 2024:
- The Global Electricity Review is published by Ember, a leading climate and energy think tank focused on accelerating the global transition to clean energy.
- The Global Electricity Review 2024 offers an in-depth analysis of the global electricity landscape in 2023.
- Drawing from a vast dataset encompassing 80 countries representing 92% of global electricity demand, and historical data from 215 countries, the report provides a robust and comprehensive examination of the current state of the electricity sector.
- The report's objective is to evaluate the progress made in transitioning the world's electricity systems towards cleaner, low-carbon sources, with a focus on limiting global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Key Findings from the Report:
- Record Solar Energy Generation: Solar energy accounted for a record 5.5% of global electricity in 2023, solidifying its position as the fastest-growing electricity source for the nineteenth consecutive year.
- Renewables Surge: Renewable sources accounted for 30% of global electricity, marking a significant increase from 19% in 2000. Solar and wind power drove this expansion, with low-carbon sources contributing to nearly 40% of global electricity generation in 2023.
- Fossil Fuel Decline Forecast: The report predicts a decline in fossil fuel generation in 2024 and beyond, indicating a possible peak in global fossil fuel production in 2023.
- China's Dominance: China emerged as a significant contributor to renewable energy, accounting for 51% of the global solar generation increase and 60% of new global wind generation in 2023.
India-Specific Insights from the Report:
- India's Rise in Solar Generation: In 2023, India surpassed Japan to become the world's third-largest solar power generator, climbing from its ninth position in 2015.
- While India's installed solar capacity ranks fifth globally, its rapid growth demonstrates significant progress in harnessing solar energy.
- Share of Solar Energy in India's Electricity Mix: India generated 5.8% of its electricity from solar energy in 2023.
- This substantial contribution highlights the increasing role of solar power in meeting the country's energy demands.
- India's Contribution to Global Solar Growth: India experienced the world's fourth-largest surge in solar generation in 2023, adding 18 TWh to its capacity.
- Alongside China, the United States, and Brazil, India accounted for 75% of global solar growth in that year.
- Solar Generation Growth Since 2015: Global solar generation in 2023 was six times higher than in 2015, with India witnessing a remarkable seventeen-fold increase.
- India's Renewable Energy Target: India has committed to tripling its renewable capacity by 2030, aiming for 500 GW of installed renewable energy capacity.
- This ambitious target will require a significant acceleration in annual capacity additions.
'Egg Shell Skull' Rule

- 30 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Underlining that the state and central consumer courts incorrectly applied the ‘eggshell skull’ legal principle, the Supreme Court recently restored the compensation of Rs 5 lakhs awarded by the district consumer forum in a medical negligence case.
What is the ‘Eggshell Skull’ Rule?
- The eggshell skull rule is a common law principle applied in civil litigation.
- Essentially, when the offender would be liable for all injuries that might be intensified due to the peculiar conditions of the injured person that the offender might not have known.
- Simply put, the defendant would be held responsible for injuries caused to a person when he hit him on the head, even if the victim had a particularly delicate skull or an ‘eggshell’ for a skull.
- A person who has an eggshell skull would be more severely impacted by an act, which an otherwise “normal person” would be able to withstand.
- The rule is applied for claiming an enhanced compensation, for damage that is more than what could have been ordinarily anticipated to be caused by the defendant.
Origin of the ‘Eggshell Skull’ Rule:
- The 'eggshell skull' rule, also known as the 'thin skull rule,' is a legal doctrine that holds a defendant liable for all consequences resulting from their negligent or intentional actions, even if the victim's pre-existing vulnerability worsens the outcome.
- The rule's origins can be traced back to an 1891 US case, Vosburg v. Putney, in which a boy kicked another's shin without knowing about his prior injury, leading to complications.
- The Wisconsin Supreme Court held that the defendant was responsible for the subsequent harm, even though he did not intend to cause such severe damage.
- A similar case in England a decade later involved a pregnant woman who experienced severe shock and gave birth to a disabled child after a horse van was negligently driven into a public house where she worked.
- The King's Bench upheld the principle that defendants are liable for the harm caused to victims, regardless of pre-existing vulnerabilities.
- The eggshell skull rule has been applied in various legal cases across different jurisdictions, emphasizing that defendants are accountable for the consequences of their actions, even when victims' unique vulnerabilities contribute to more significant harm.
What was the Jyoti Devi Medical Negligence Case?
- In 2005, Jyoti Devi underwent an appendix removal surgery in Himachal Pradesh, India.
- However, her abdominal pain persisted, leading to a four-year ordeal and multiple hospital visits.
- Eventually, doctors discovered that a 2.5 cm needle had been left in her abdomen during the initial surgery, requiring another operation to remove it.
- Jyoti sought compensation for medical negligence and was initially awarded Rs 5 lakhs by the district consumer forum.
- The hospital appealed, leading to the state consumer forum reducing the compensation to Rs. 1 lakh, and the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) increasing it to Rs. 2 lakhs.
What did the SC Rule?
- The Supreme Court (SC) restored the original Rs 5 lakh compensation, criticizing the lower compensation amounts as "paltry" and "unjust."
- The SC ruled that the 'eggshell skull' rule did not apply in Jyoti's case since there was no evidence of a pre-existing vulnerability or medical condition that contributed to her suffering.
- The court cited two factors for increasing the compensation: Jyoti's prolonged pain over five years and the decade-long legal battle she endured.
Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI)

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) is preparing to defend the government’s human rights processes at a meeting in Geneva this week, where a decision on whether India’s human rights body will retain its “A status” is expected to be made.
About Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI):
- The Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) is a representative body of National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) from across the world.
- It assists in the establishment and strengthening of independent and effective NHRIs, which meet the international standards set out in the Paris Principles.
- GANHRI encourages joint activities and cooperation among NHRIs, organises international conferences, liaises with the United Nations and other international organisations, assists NHRIs under threat, and assists governments in establishing NHRIs.
- The Asia Pacific Forum of National Human Rights Institutions (APF) and other member institutions continue to make a significant contribution to the operations and human rights initiatives of GANHRI.
- The organisation is incorporated as a non-profit organisation under Swiss law.
- Its Statute, adopted in March 2009, sets out its objectives and how it operates.
Membership:
- NHRIs that comply fully with the Paris Principles – and which have been granted 'A status' by GANHRI – are eligible to become voting members of GANHRI and to hold governance positions.
- NHRIs that only partially comply with the Paris Principles – and which have been granted 'B status' by GANHRI – can participate in meetings of GANHRI but are not eligible to vote or to hold governance positions.
Bureau:
- The operations of GANHRI are managed by its Bureau, which is comprised of representatives from each of the four regional groupings:
- Africa, the Americas, Europe, and the Asia Pacific.
- Each regional grouping is represented by elected representatives from four 'A status' NHRIs.
- The APF is currently represented on the GANHRI Bureau by Australia, India, Korea, and Qatar.
- A key role of the Bureau is to assess applications for membership in the ICC.
- It also reviews and determines the accreditation status of NHRIs, following a recommendation from the Sub-Committee on Accreditation.
- In addition, the Bureau collaborates with the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), in particular the National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Unit, to facilitate the participation of NHRIs in the United Nations Human Rights Council.
- Bureau meetings are usually held twice a year; the first is in conjunction with the first quarter session of the UN Human Rights Council and the second is in conjunction with one of the NHRI regional network's meetings.
- A meeting is also held in conjunction with the bi-annual International Conference.
International Conference:
- The International Conference involves NHRIs, as well as representatives of United Nations agencies, international organisations, and civil society.
- The purpose of the International Conference is to strengthen cooperation between NHRIs, to discuss human rights issues of shared concern, and to ensure follow-up at the national level.
- The International Conference is held every two years, alternating between Europe, the Americas, Africa, and the Asia Pacific.
Officials:
- The positions of GANHRI Chairperson and Secretary are served on a rotational basis by representatives nominated by the four regional coordinating committees: Europe, Africa, the Americas, and the Asia Pacific.
- The current GANHRI Chairperson is Maryam Abdullah Al Attiyah, Chairperson of the National Human Rights Committee of Qatar (NHRC), representing the Asia Pacific region.
- The current GANHRI Secretary is Amina Bouayach, Chairperson of the National Human Rights Council of Morocco (CNDH), representing the African region.
Secretariat:
- The National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Unit of OHCHR acts as the GANHRI secretariat.
- GANHRI has a permanent representative in Geneva to support and facilitate the participation of NHRIs in the UN Human Rights Council and its human rights mechanisms.
Bridge Fuel

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Natural gas has been called a ‘bridge fuel’ for countries looking to transition away from coal and oil dependency, and as they pursue a pathway towards renewables and electrification.
What is Bridge Fuel?
- Bridge fuel is a widely recognized term for fuels that aim to meet society's energy needs while minimizing environmental impacts during the transition to a clean, renewable energy economy.
- The primary objective of bridge fuels is to replace current fossil-fuel-dependent energy sources and pave the way for a greenhouse gas emission-free future.
- Natural gas is often considered a bridge fuel due to its lower greenhouse gas emissions during combustion compared to other fossil fuels.
- However, an ideal bridge fuel should also contribute to national energy independence and reduce pollution-related costs.
- Bridge fuels play a crucial role in balancing current energy demands with the long-term goal of achieving a sustainable, renewable energy landscape.
What is Natural Gas and How is it Formed?
- Natural gas, a non-renewable fossil fuel, is a mixture of hydrocarbon-rich gases.
- This colorless, odorless gas consists primarily of methane (70-90%), with smaller amounts of ethane and propane.
- Possible impurities include carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitrogen.
- Natural gas formation dates back millions to hundreds of millions of years ago when layers of organic matter (such as plants, animals, and diatoms) accumulated on land and ocean floors.
- Over time, these layers were buried under sediment and rock. Intense pressure and heat transformed this carbon and hydrogen-rich material into coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Today, natural gas reserves are found deep within the Earth's crust, often alongside other hydrocarbon deposits like coal and crude oil.
- The extraction, processing, and utilization of natural gas play a critical role in meeting global energy demands while transitioning towards cleaner, renewable energy sources.
Applications of Natural Gas:
- Natural gas undergoes processing and conversion into cleaner fuels for various applications.
- During processing, several valuable by-products like propane, ethane, butane, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen are extracted for further use.
Key uses of natural gas include:
- Generating electricity and heat, serving as a primary energy source for power plants.
- In compressed form (CNG), it fuels vehicles, providing a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline or diesel.
- Powering boilers and air conditioning systems for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
- Manufacturing fertilizers, particularly ammonia, support the agricultural sector.
- As a cleaner fossil fuel, natural gas has a lower environmental impact than coal, emitting 50% less CO2.
- This makes it a critical component in the global shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly energy solutions.
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Eight years after Parliament passed the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs is in the process of reviewing the functioning of the Act, including by holding regular meetings with homebuyers and setting up a data collection unit within the Ministry.
What Is Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)?
- The Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 is an act of the Parliament of India that strives to protect home buyers and helps escalate the investment made in the real estate industry.
- It was established under this Act to regulate the real estate sector.
- Additionally, it acts as the adjudicating body for faster dispute resolution related to the real estate industry.
The Primary Objectives of the Act:
- Ensuring Transparency: Promoting transparency in the real estate sector regarding the sale of flats, apartments, plots, buildings, or any real estate project.
- Establishing Dispute Resolution: Setting up an adjudicating mechanism to swiftly resolve disputes.
- Protecting Buyer Interests: Safeguarding the interests of buyers/allottees in the real estate domain.
- Building Trust: Fostering trust between buyers and promoters by leveraging regulatory authority.
- Furthermore, the Act mandates that Real Estate Regulatory Authorities establish and maintain a web portal containing pertinent details of all registered real estate projects for public access.
Reasons for RERA Implementation:
- The introduction of RERA was necessitated by challenges faced by the Indian real estate sector since 2012, including factors such as unemployment, recession, low rental yield, inventory pile-up, and ambiguous tax and arbitration frameworks.
Projects Covered by RERA:
- RERA covers commercial and residential projects, including plotted developments, that exceed 500 square meters or comprise more than 8 units.
- Additionally, projects lacking a Completion Certificate prior to the Act's commencement are subject to its provisions.
Benefits of RERA Implementation:
- Standardization: RERA ensures uniformity in the real estate sector concerning aspects like carpet areas and common areas, thereby preventing malpractices such as alterations in layout, area, agreements, and specifications.
- It also mandates disclosure of details regarding brokers, architects, and contractors.
- Timely Delivery: Developers are obligated to adhere to scheduled delivery timelines for office spaces or homes.
- Failure to comply may result in stringent penalties or imprisonment for the developer.
- Regulatory Compliance: RERA mandates obtaining clearance from government departments before the sale of any residential or commercial property.
- Financial Transparency: Developers are required to maintain separate bank accounts for each project, enhancing financial transparency and accountability.
- Warranty Protection: Buyers are empowered to report any structural defects in the building to the developer within one year of possession, with the developer obligated to rectify them free of charge.
Challenges Associated with RERA:
- Limited Scope: The regulations of RERA do not extend to ongoing projects or those stalled due to clearance issues, potentially leaving certain projects outside its jurisdiction.
- Approval Delays: Delays in approval and clearance from government agencies may impede the timely completion and delivery of real estate projects, affecting both developers and buyers.
- Exemption for Small Developers: Small-scale developers overseeing projects smaller than 500 square meters are exempt from RERA's provisions, and registration with the regulatory authority is not compulsory for them.
- Project Launch Delays: Projects cannot be launched without necessary clearances, which may result in delays in the commencement of new projects.
Hume’s Empathic Voice Interface (EVI)

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI startup Hume unveiled a new voice interface yesterday that the company claims is “the first conversational AI with emotional intelligence.
What is an Empathic Voice Interface (EVI)?
- Empathic Voice Interface (EVI) by Hume, a New York-based research lab and technology company, is the world’s first emotionally intelligent voice AI.
- It accepts live audio input and returns both generated audio and transcripts augmented with measures of vocal expression.
- By processing the tune, rhythm, and timbre of speech, EVI unlocks a variety of new capabilities, like knowing when to speak and generating more empathic language with the right tone of voice.
- These features enable smoother and more satisfying voice-based interactions between humans and AI, opening new possibilities for personal AI, customer service, accessibility, robotics, immersive gaming, VR experiences, and much more.
- Developers can now seamlessly integrate EVI into various applications using Hume’s API, offering a unique voice interface experience.
EVI boasts several distinctive empathic capabilities:
- Human-Like Tone: EVI responds with tones resembling human expressions, enhancing the conversational experience.
- Responsive Language: It adapts its language based on the user’s expressions, addressing their needs effectively.
- State-of-the-Art Detection: EVI uses the user’s tone to detect the end of a conversation turn accurately, ensuring seamless interactions.
- Interruption Handling: While it stops when interrupted, EVI can effortlessly resume from where it left off.
- Self-Improvement: EVI learns from user reactions to continuously improve and enhance user satisfaction over time.
- In addition to its empathic features, EVI offers fast, reliable transcription and text-to-speech capabilities, making it versatile and adaptable to various scenarios.
- It seamlessly integrates with any Language Model Library (LLM), adding to its flexibility and utility.
What is an AI with Emotional Intelligence and How Can it be Used?
- Artificial Intelligence with emotional intelligence, also known as affective computing or emotion AI, refers to the integration of emotional awareness and intelligence into AI systems, enabling them to recognize, understand, and respond to human emotions.
- This capability draws inspiration from the concept of emotional intelligence in humans, which involves perceiving and managing emotions in both oneself and others.
- The development of emotionally intelligent AI involves leveraging advanced techniques in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to enable AI systems to recognize emotions in facial expressions, speech, and text.
- These systems can adapt their responses based on recognized emotions, creating more empathetic and nuanced interactions between humans and AI.
Potential applications of AI with emotional intelligence include:
- Healthcare: Emotion-sensitive AI could help detect depression, anxiety, or other mental health issues by analyzing speech patterns, facial expressions, or social media posts.
- Education: AI systems could adapt to individual students' emotions, providing customized support and facilitating better learning experiences.
- Customer Service: Emotion AI could enable businesses to respond more appropriately to customer emotions, improving customer satisfaction and fostering long-term loyalty.
- Entertainment: Affective computing could make games and other entertainment experiences more immersive and engaging by adapting to users' emotions in real-time.
Devin AI, an AI software engineer, can handle coding projects end-to-end

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a US-based startup Cognition has unveiled an AI-powered tool, Devin, which it calls the “world’s first fully autonomous AI software engineer”.
What is Devin?
- Devin is a super-smart computer program created by a company called Cognition.
- It's like having a clever assistant for software engineering tasks.
- With just a simple instruction, Devin can write code, build websites, and make software all on its own.
- But Devin isn't trying to replace human engineers, instead, it's meant to work together with them to make their jobs easier.
- The special feature of Devin is its ability to think ahead and solve tricky problems.
- It can learn from its mistakes and keep getting better over time.
- Plus, it has all the tools that a human engineer needs, like a way to write code and browse the internet.
- Devin has been tested against other AI programs, and it did way better, solving almost 14 out of 100 problems compared to just under 2 for others.
- So, in simple terms, Devin is like a super-smart assistant that helps engineers do their work faster and better, without taking their jobs away.
How does Devin work?
- Devin works by using advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to understand and execute tasks related to software engineering.
- When given a prompt or instruction, Devin analyzes the request and uses its vast database of knowledge and problem-solving techniques to generate code, design websites, or develop software.
- One of Devin's key features is its ability to think ahead and plan complex tasks.
- It can make thousands of decisions based on the given task and learn from its mistakes to improve its performance over time.
- Devin also has access to essential tools like a code editor and web browser, enabling him to complete tasks from start to finish.
- It can learn new technologies, tackle a wide range of engineering challenges, and even train its own AI models.
- Additionally, Devin can collaborate with human engineers in real time, providing updates, accepting feedback, and contributing to design choices.
- Overall, Devin works by harnessing the power of AI to automate routine tasks, streamline workflows, and empower engineers to focus on more complex problems.
- By combining human expertise with machine intelligence, Devin represents a significant advancement in software engineering technology.
India to restart Penicillin G manufacture
- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will start manufacturing the common antibiotic Penicillin G later this year, three decades after the country’s last plant shut down, Union health minister Mansukh Mandaviya announced last week.
What is Penicillin G?
- Penicillin G serves as a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) utilized in the production of various common antibiotics.
- Its molecular formula is C16H18N2O4S.
- Penicillin G (potassium or sodium) is an FDA-approved antibacterial medication primarily indicated for treating severe bacterial infections like pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, syphilis, among others.
- This natural penicillin antibiotic is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly due to limited oral absorption.
- Additionally, Penicillin G may be employed in certain instances as prophylaxis against susceptible organisms.
Why did Penicillin Manufacturing Stopped in India?
- The discontinuation of Penicillin G production in India, along with numerous other active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), resulted from the influx of cheaper Chinese products driven by subsidies.
- Torrent Pharma in Ahmedabad was the final plant to halt Penicillin G production, with at least five companies, including Torrent, manufacturing the antibiotic in the country during the 1990s.
- In the early 1990s, India boasted nearly 2,000 API manufacturers, while approximately 10,000 units produced formulations. However, the allure of cheaper Chinese alternatives grew, particularly with the relaxation of customs rules during the country's economic liberalization.
- The Drug Prices Control Order, which imposed price caps on essential medicines, further incentivized companies to opt for cheaper imported products.
- While India previously sold Penicillin G for around Rs 800 per kg, China drastically reduced prices to nearly Rs 400 per kg, rendering domestic manufacturing economically unviable.
Why the Delay in Restarting Production?
- Lack of Urgency: Despite awareness within the industry and government about the decline in API production in India due to the availability of cheaper alternatives globally, there was limited emphasis on restarting domestic production.
- The supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic highlighted the need for self-reliance, prompting the government to launch initiatives like the PLI scheme to bolster domestic manufacturing.
- High Initial Investment: API manufacturing, particularly for fermented compounds like Penicillin G, entails significant upfront costs.
- Establishing a production facility requires substantial capital investment, with companies often needing several years to break even.
- Dominance of China: China has emerged as a dominant supplier, significantly expanding its manufacturing capacity over the past three decades.
- Competing with Chinese prices would necessitate substantial investments in larger facilities.
What's the Impact of PLI Schemes?
- Reduction in API Imports: Since the implementation of the PLI scheme, there has been a notable decrease in API imports.
- For instance, the import dependency for paracetamol, which was previously two-thirds of the required volume, has now halved.
- Incentive Structure: The PLI scheme offers incentives structured as follows:
- 20% support for the first four years, gradually reducing to 15% in the fifth year and 5% in the sixth year for eligible sales of fermentation-based bulk drugs like antibiotics, enzymes, and hormones such as insulin.
- Chemically synthesized drugs receive a 10% incentive for six years on eligible sales.
Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay, the unsung feminist freedom fighter in the history of India
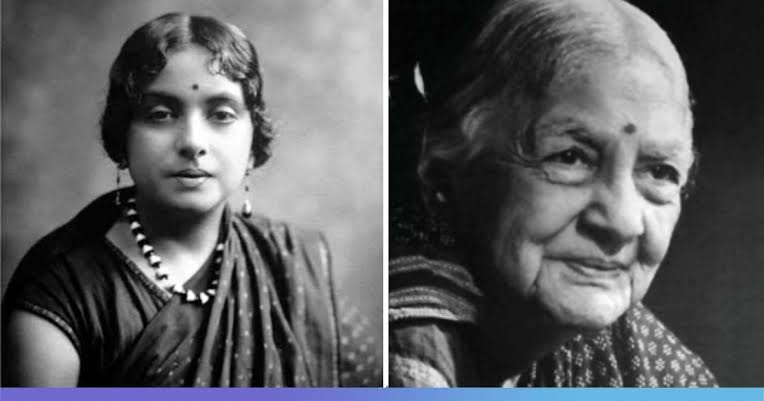

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Post-Independence, the revival of the crafts sector began with Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay who strongly championed the handicrafts movement for the role it could play in social and economic upliftment.
About Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay:
- Kamaladevi was born in April 1903 in a liberal Chitrapur Saraswat Brahmin family in Mangalore (now Mangaluru).
- She completed her primary education at the local St Ann’s Convent.
- Growing up in a land with a rich cultural heritage, especially of the music and dance form Yakshagana, she developed a taste for traditional art forms.
- After her father’s untimely death, Kamaladevi moved to her maternal uncle’s house.
- There, she met renowned freedom fighters, including Gopalkrishna Gokhale, Srinivasa Shastri, Ramabai Ranade and Annie Besant.
- Kamaladevi was married off at the age of 14 and widowed two years later.
- Unperturbed by these life events, she joined Queen Mary’s College in Madras (now Chennai) for higher studies.
- There, she met Sarojini (Chattopadhyay) Naidu’s brother Harindranath Chattopadhyay which led to their wedlock.
- However, their marriage ended over incompatibility issues and this, too, created history – Kamaladevi was the first legal divorce granted through an Indian court of law.
- Kamaladevi played a prominent role in political reforms and India’s freedom struggle.
- She was the first woman to contest the Madras provincial elections.
- Though she lost by a narrow margin, she got recognition and was appointed secretary of the All-India Women’s Conference.
- She joined Indian National Congress in 1927 and was elected to the All-India Congress Committee within a year.
- During the Salt March to Dandi, she convinced Gandhi to give women equal opportunity to be in the forefront of the march.
- Later, she joined Seva Dal and trained women activists.
- However, the British government banned Seva Dal and threw Kamaladevi into jail.
- There, she contracted jaundice. Having experienced the pathetic condition of the prison hospital, she built a hospital for inmates upon release.
- Kamaladevi got attracted to socialism and took up the problems of laborers and peasants.
- During World War II, she visited America and met several political activists, mostly blacks, and shared with them India’s non-violent approach to freedom struggle.
- The British got wind of her activism and banned her from returning to India.
- Unmoved, Kamaladevi continued on her journey, visiting South Africa, China, Japan and Vietnam.
- Kamaladevi was inarguably the embodiment of women’s empowerment.
- She was an advocate of female sexual freedom and birth control.
- Her remarriage after widowhood and legal divorce from her second marriage were symbolic of her self-empowerment.
- She acted in many films (a Kannada film, too) when the film industry was not considered a respectable place for women.
- Indeed, Kamaladevi’s immense travel and experiences shaped her as a secular, socialist world citizen.
- Such were her ideals that led to her building the city of Faridabad to rehabilitate some 50,000 craftsmen who moved to India from Pakistan during Partition.
- Post-independence, she helped revive Indian handicrafts and built institutions for a ‘New India’-- to name a few, the National School of Drama, Bharatiya Natya Sangha, Lady Irwin College, Sangeet Natak Academy, Central Cottage Industries Emporium, World Craft Council, Craft Council of India, and the Delhi Craft Council.
- Kamaladevi was a prolific writer, too and wrote 18 books altogether, touching upon women’s issues, Indian handicrafts and her foreign visits.
- She published her autobiography, “Inner Recesses, Outer Spaces: Memoir” (1986).
- She received several awards in recognition of her public service, like Padma Bhushan and Padma Vibhushan, the Ramon Magsaysay Award and the UNESCO Award.
- She died in Mumbai on October 29, 1988, aged 85.
Bengaluru's Rameshwaram cafe blast puts the spotlight on IEDs

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
At least nine people were injured after an explosion at the bustling Rameshwaram Cafe in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area recently, possibly by an improvised explosive device (IED).
What is Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs)?
- An Improvised Explosive Device (IED) refers to a makeshift explosive device constructed and deployed unorthodoxly or improvised.
- These devices are typically crafted using commonly available materials, including explosives, triggers, and containers, often to cause destruction, injury, or death.
- IEDs can vary widely in design and complexity, ranging from simple pipe bombs to more intricate devices incorporating timers, remote controls, or even cellular communication for activation.
- IEDs can be deployed using a vehicle, carried, placed, or thrown by a person, delivered in a package, or concealed on the roadside.
- Due to their adaptable nature, IEDs are commonly used by insurgents, terrorists, and other malicious actors to carry out attacks against both military and civilian targets.
- Their unpredictable nature and often concealed placement make them particularly challenging for security forces to detect and mitigate.
- Efforts to counter IED threats involve a combination of technological advancements, intelligence gathering, and counterinsurgency strategies aimed at identifying and neutralizing these devices before they can cause harm.
Types of IEDs:
- Vehicle-Borne IEDs: Among the most destructive forms of IEDs are those concealed within vehicles. These can be driven to specific locations and detonated, causing massive explosions capable of levelling buildings.
- Suicide Bombings: Suicide bombings involve individuals strapping IEDs to their bodies, becoming human carriers of destruction. This method inflicts maximum damage in densely populated areas.
- Package IEDs: Package IEDs are small devices hidden in innocuous-looking packages. They are often placed in public spaces, targeting unsuspecting victims.
Methods of IED Initiation:
- Remote Control: IEDs can be remotely triggered using various methods, such as cell phones or radio signals, allowing attackers to maintain a safe distance from the explosion.
- Pressure Activation: Pressure-sensitive IEDs detonate when a certain amount of pressure is applied, making them lethal traps for those who inadvertently trigger them.
- Timers: IEDs can also be equipped with timers, which delay the explosion to occur at a specific time, further complicating detection and prevention.
The Devastating Impact of IEDs:
- The aftermath of IED explosions is often catastrophic, leading to loss of life, severe injuries, and widespread damage to infrastructure.
- The psychological impact on survivors and affected communities can be long-lasting.
Detection Technologies and Challenges:
- Detection technologies such as (Metal Detectors, X-ray and Imaging Scanners, Explosive Trace Detection (ETD), and Sniffer Dogs) play a critical role in countering the threat of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), but they also face numerous challenges due to the evolving nature of these devices.
India, and ASEAN discuss the review of the trade agreement

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India hosted the 3rd meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which focused on reviewing the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement at Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi from February 16th to 19th, 2024.
About the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- The Framework Agreement laid a sound basis for the establishment of an ASEAN-India Free Trade Area (FTA), which includes FTA in goods, services and investment.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
About ASEAN:
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN is an intergovernmental organization of ten Southeast Asian countries:
- Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- ASEAN's primary objectives are to promote political and economic cooperation and regional stability among its member states.
- The organization operates on the principles of mutual respect, non-interference in internal affairs, and consensus-building. ASEAN's motto, "One Vision, One Identity, One Community," underscores its commitment to fostering unity and solidarity among Southeast Asian nations.
- Economically, ASEAN has made significant strides towards integration through initiatives like the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and production base.
- This has facilitated trade, investment, and economic development within the region.
- Additionally, ASEAN serves as a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of issues, including security, environmental sustainability, cultural exchange, and disaster management.
Banks to conduct periodic performance reviews of empanelled advocates to fast-track cases in DRTs

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Banks will conduct periodical reviews of the performance of empanelled advocates at debt recovery tribunals (DRTs) and rationalise the cases assigned to them based on performance.
What is the Debt Recovery Tribunal?
- Debt Recovery Tribunal is a quasi-judicial body formed under the Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions (RDDBFI) Act, 1993 to facilitate recovery of loans by banks and financial institutions to the customers.
- It was introduced as a response to the growing issue of Non-performing Assets (NPAs) and the need for a dedicated mechanism to resolve disputes related to debt recovery.
- These tribunals were instituted to offer a swifter and more effective alternative to traditional civil courts for the resolution of matters concerning debt recovery by banks and financial institutions.
- Its Appellate Tribunal is the Debt Recovery Appellate Tribunal (DRAT).
- Under Section 22 of the RDDBFI Act, 1993, both DRT and DRAT are mandated to adhere to the principles of natural justice, and proceedings before them are deemed to be judicial.
Jurisdiction of Debt Recovery Tribunal:
- They are empowered to adjudicate cases brought forth by banks, financial institutions, and related entities seeking the recovery of outstanding amounts.
- DRTs preside over matters surpassing a designated monetary threshold, and their rulings carry the weight of civil court decrees.
- The scope of DRT jurisdiction encompasses a broad spectrum of financial claims, encompassing loans, advances, and financial aid extended by banks and financial institutions.
Powers of DRT:
- Under Section 22(2) of the RDDBFI Act, 1993, the DRT possesses the following powers:
- Summoning individuals and compelling them to testify under oath.
- Demanding the disclosure and presentation of documents.
- Accepting evidence through affidavits.
- Issuing commissions to examine witnesses or documents.
- Revisiting its rulings.
- Rejecting applications due to default or adjudicating them in absentia.
- Revoking any order of dismissal stemming from default or any order passed in absentia.
- Addressing any other matters stipulated by regulations.
- The organisational framework of the Debt Recovery Tribunal:
- DRTs fall under the purview of the Ministry of Finance and operate akin to judicial courts.
- Each DRT is helmed by a Presiding Officer, who must hold qualifications equivalent to that of a District Judge.
- The Presiding Officer is appointed for a tenure of five years or until reaching the age of 62, whichever comes first.
- Appointment of the Presiding Officer is vested in the Central Government.
- At present, 39 DRTs and 5 DRATs are functioning across the country.
- Each DRT and DRAT are headed by a Presiding Officer and a Chairperson respectively.
Revised Guidelines for Community Radio Stations (ET)

- 14 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
With a view to ensuring the growth of the community radio sector, the Union government on Tuesday increased the advertising time for community radio stations as well as the tariff rate for advertisements.
What are Community Radio Stations (CRSs?
- Community radio stations (CRSs) are low-power radio stations with a coverage area of approximately a 10-15 km radius, depending on the area’s geography, which is meant to be set up and operated by local communities.
- They offer a platform where content is disseminated in localized dialects and regional languages.
- Local, context-specific issues are raised and discussed in these stations in local idioms.
- India's first community radio station (CRS) was inaugurated on the campus of Anna University in 2004.
- Currently, there are 481 CRSs in India.
About the Revised Policy Guidelines:
- Under the revised policy, the government has permitted any eligible organisation functional in multiple districts to set up a maximum of six community radio stations in different districts.
- The advertising time for community radio stations has been increased from seven minutes per hour to 12 minutes per hour, while the rate of advertisement has been hiked from Rs 52 to Rs 74 per 10 seconds, the guidelines stated.
- The policy also fixed the validity of the letter of intent issued to an organisation to one year, with a buffer of three months to the applicant for any unforeseen circumstances.
- The revised policy guidelines are expected to fuel the growth of the community radio sector.
- The guidelines stated that the licensee would set up an advisory and content committee comprising members of the local community, with 50 per cent representation for women.
RISC-V Technology (The Hindu)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Chip designer Qualcomm said on Tuesday it is partnering with Alphabet's Google to make wearable devices like smartwatches using chips based on RISC-V technology.
What is RISC-V Technology?
- RISC-V technology, colloquially pronounced as "risk five," stands as a pioneering open-source initiative in computer architecture.
- Functioning as an open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), it serves as the foundation for crafting customized processors tailored to various end applications.
- Positioned as the fifth generation of processors rooted in the Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) philosophy, RISC-V originated as a project at UC Berkeley.
- Initially conceived for academic purposes, it has since matured into a robust standard now overseen by RISC-V International.
- RISC-V operates as an open-standard architecture, with its definition shaped collaboratively by member companies associated with RISC-V International—a global nonprofit organization steering the ISA.
- This collaborative approach fosters innovation and design freedom among member companies, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in processor technology.
- At its core, RISC-V features a concise set of instructions upon which all software designs run.
- This streamlined architecture empowers designers to tailor and construct processors in alignment with the specific requirements of their intended applications.
Key Advantages:
- The merits of RISC-V extend beyond its technical specifications. Its open-standard nature facilitates industry-wide collaboration and innovation, enabling diverse stakeholders to contribute to the evolution of processor technology.
- Moreover, the entire RISC-V architecture is subject to scrutiny in the public domain, mitigating concerns related to back doors and concealed channels.
Applications:
- RISC-V finds application across a broad spectrum of industries, including wearables, industrial processes, Internet of Things (IoT), home appliances, smartphones, automotive systems, high-performance computing (HPC), and data centres.
- Its versatility makes it a compelling choice for diverse technological landscapes, showcasing its adaptability and efficacy across various domains.
Nitrogen-9 Nucleus (Indian Express)

- 20 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers have found "compelling evidence" supporting the existence of the uncommon nitrogen-9 isotope. This discovery challenges previous interpretations and provides a fresh perspective on subatomic structures.
About Nitrogen-9 Nucleus:
- Nitrogen-9 is a radioactive isotope of nitrogen.
- This means that it is unstable and will eventually decay into a different isotope of nitrogen or a different element.
- It is considered unusual because it has an uncommon combination of seven protons and two neutrons (7:2) in its atomic nucleus.
- This creates an unusually high ratio of protons to neutrons.
- Generally, elements have a balanced ratio for stability, but Nitrogen-9’s high proton content makes it less stable, challenging the conventional stability thresholds.
- This oddity raises questions about its existence in this state and how it maintains stability, introducing complexity to our understanding of atomic nuclei.
- The reason for nitrogen-9's short half-life is that the strong force, which is responsible for holding nuclei together, is not strong enough to overcome the Coulomb repulsion between the positively charged protons in the nitrogen-9 nucleus.
- The discovery of nitrogen-9 is a major breakthrough in our understanding of nuclear physics.
- It showed that nuclei with very high proton-to-neutron ratios can exist, even if they are only for a very short time.
- This discovery has led to new research into the limits of nuclear stability and the role of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in holding nuclei together.
What is an Isotope?
- An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in its atomic nucleus.
- This variance in neutron count results in different atomic masses for isotopes of the same element.
- Isotopes of an element share similar chemical properties but may exhibit differences in physical properties, such as stability and radioactivity.
SARAS AAJEEVIKA MELA (PIB)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The popular SARAS Mela Gurugram was recently inaugurated by the Union Minister of State for Rural Development, Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution.
Facts About:
- SARAS Mela is a women empowerment initiative by the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihoods Mission of the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD)
- It’s aim is to bring the rural women self-help group members under one platform where they can showcase their skills, sell their products and build connections with potential market players at fair prices.
- The organisation trains women in different livelihood craftsmanship skills and gives them a platform to market their products.
- Their stalls are entirely free, and all their expenses, including their stay, are borne by the Mela organising committee.
- The SARAS Mela is organised by the National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR).
- Saras Melas are regularly organised across India throughout the year.
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The revised guidelines were issued for the Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for the North East Region (PM-DevINE).
Facts About:
- PM-DevINE, was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 to address development gaps in the North Eastern Region (NER).It was approved by the Cabinet for the remaining four years of the 15th Finance Commission from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The new Scheme is a Central Sector Scheme and will be implemented by the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER).
- The PM-DevINE Scheme will have an outlay of Rs.6,600 crore for the four year period from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- An Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC) will be established, tasked with various functions under the scheme.
Objectives of PM-DevINE
- Fund infrastructure convergently, in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti;
- Support social development projects based on felt needs of the NER;
- Enable livelihood activities for youth and women;
- Fill the development gaps in various sectors.
Functions of Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC)
- It assesses initial project proposals based on quality, viability, and socio-economic impact, working alongside representatives from relevant Indian Government Ministries/Departments and State Governments.It then recommends project selection from among these proposals.
- The EIMC proposes effective monitoring and evaluation methods, which may involve on-site inspections through third-party agencies.
- The committee also devises mechanisms for the operation and maintenance of PM-DevINEprojects, aiming to ensure their sustainability.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=194206
NavIC to link to Aadhaar enrolment devices (The Hindu)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Department of Space (DoS) has told the Parliamentary Committee of Science and Technology that the Navigation with Indian Constellation or (NavIC) is going to be integrated into Aadhaar enrolment devices.
Facts About:
About the merger:
- Need: Currently the Aadhaar enrolment kits that are used to collect and verify personal details are linked to Global Positioning system (GPS).
- The DoS has conducted successful field trials and is providing technical expertise for the finalisation of procurement specifications for the devices.
- Overall, the integration of NavIC into Aadhaar enrolment devices will enhance navigation accuracy and provide better disaster management capabilities.
- Significance:
- NavIC’s integration will enhance the accuracy and reliability of these devices.
Aadhaar authentication process:
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has been created, with the mandate of providing a Unique Identity (Aadhaar) to all Indian residents.
- The UIDAI provides online authentication using demographic and biometric data.
- Aadhaar authentication is the process involves Aadhaar Number, along with other attributes, including biometrics, is submitted online to the Aadhaar system for its verification on the basis of information or data or documents available with it.
- During the authentication transaction, the resident’s record is first selected using the Aadhaar Number and then the demographic/biometric inputs are matched against the stored data which was provided by the resident during enrolment/update process.
How NavIC will ensure data protection?
- NavIC offers two services:
- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and;
- Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- These two services are provided in both L5 (1176.45 MHz) and S band (2498.028 MHz).
- NavIC coverage area includes India and a region up to 1,500 km beyond the Indian boundary.
- Newer satellites will have an additional band called L1 that will be compatible with civilian use.
Present NavIC uses:
- The National Disaster Management Agency (NDMA) was already utilising NavIC as an alert dissemination system for major natural disasters like landslips, earthquakes, floods, and avalanches.
- The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information System (INCOIS) relies on NavIC to broadcast cyclones, high waves, and tsunamis alert messages to fishermen venturing into the deep sea.
Organizations working with NavIC data:
- NavIC standards were set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Telecom Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI), Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC), Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), and Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM), International Electrotechnical Committee (IEC), and International Standards Organisation (ISO).
Concerns with GPS or other global systems:
- Threat to data security and sovereignty: System like GPS and GLONASS are operated by defence agencies of the respective nations.
- Breach of personal information: It is possible that the civilian service can be degraded or denied.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/indian-gps-navic-to-link-to-aadhaar-enrolment-devices/article67181022.ece
River Devika Rejuvenation Project (PIB)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Science & Technology sheds light on the progress of the River Rejuvenation Project, Devika. This initiative, inspired by the Namami Ganga campaign, aims to safeguard the sacred Devika River’s purity and health.
Facts About:
Comprehensive Waste Management:
- Focus on Liquid Waste Management.
- Creation of a network of pipes and manholes connecting households.
- Objective: Efficient disposal of liquid waste, preventing pollution, and preserving the sanctity of the river.
Complementary Solid Waste Management:
- Encompasses responsible collection, disposal, and management of solid waste.
- Essential to prevent environmental degradation and maintain river and surrounding health.
Financial Allocation Breakdown:
- Project investment exceeds Rs 190 crores.
- Allocation shared between Central and Union Territory (UT) at a 90:10 ratio.
Empowering Communities through PRIs:
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) pivotal for grassroots project success.
- PRIs’ involvement enhances community engagement, fosters ownership, and promotes sustainable development practices.
Devika River:
- Originates from Suddha Mahadev temple in Jammu and Kashmir’s Udhampur district.
- Flows through western Punjab (now Pakistan) where it merges with the Ravi River.
Cultural Significance:
- Revered by Hindus as sister of the Ganga River.
- Devika River believed to be a manifestation of Goddess Parwati, benefiting the people of MaderDesha (areas between river Ravi and Chenab).
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1946187
Revised manufacturing rules for drug firms (Indian Express)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently the center government directed all pharmaceutical companies in the country to implement the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Facts About:
Directions by the Government:
- Larger companies with a turnover of over Rs 250 crore have been asked to implement the changes within six months.
- The medium and small-scale enterprises with turnover of less than Rs 250 crore have been asked to do so within a year.
About Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP):
- Quality Management: It is a set of guidelines and quality management principles which ensure pharmaceutical products, as well as other products in the food and healthcare industries, are consistently produced and controlled to meet quality standards appropriate for their intended use.
- Aspects Include: It covers all aspects of the manufacturing process, including the premises, equipment, personnel, materials, production, quality control, documentation, and storage of finished products.
Need for the Improved Standards:
- To match up with the Global Standards: Implementation of the new norms will bring the Indian industry on par with global standards.
- Only 2,000 of the 10,500 drug manufacturing units in the country at present meet global standards, being WHO-GMP certified.
- The improved standards will ensure that pharmaceutical companies follow standard processes, quality control measures, and do not cut corners, improving the quality of medicines available in India as well as sold in the global market.
- To improve Indian Products Image: There have been a string of incidents where other countries have reported alleged contamination in India-manufactured syrups, eye-drops, and eye ointments.
- The deaths of 70 children in the Gambia, 18 children in Uzbekistan, three persons in the United States, and six deaths in Cameroon have been linked to these products.
- To rectify the Deficiencies: A risk-based inspection of 162 manufacturing units by the government found several deficiencies — incoming raw materials not being tested before use, product quality not being reviewed , absence of quality failure investigation, infrastructure deficiency to prevent cross-contamination, faulty design of manufacturing and testing areas, missing qualified professionals, and poor documentation.
- To Provide a Structure to the Draft: Implementation of the revised good manufacturing practices (GMP) as listed in the 2018 draft schedule M of the drugs and cosmetics rules.
Major Changes & Significance:
- Standard & Reliable Quality: The revised GMP guidelines focus on quality control measures, proper documentation, and IT backing to maintain quality of medicines produced.
- Review & Validation: It introduces pharmaceutical quality systems, quality risk management, product quality review and validation of equipment.
- Thorough Investigation: Carrying regular quality reviews of all its products, verify consistency of the quality and the processes, thorough investigation of any deviation or suspected defect and implementation of any preventive actions.
- Evaluation of Changes: It also suggests a change control system to evaluate all changes that may affect the production or quality of the product.
- Maintenance of Stability & Required Conditions:The companies will also be needed to mandatorily maintain the drugs in a stability chamber, set the proper temperature and humidity, and carry out an accelerated stability test as well.
- Data Safety & Security: The guidelines also state that companies should have GMP-related computerized systems, which ensure that there is no tampering of data related to the processes.
- In case sensitive data is entered manually to the system, there will be additional checks to validate the accuracy of the data. Backups would also be created to ensure there is no loss of data.
Conclusion:
The step taken is a required and desirable one. Instituting the same quality across the industry will give confidence to regulators from other countries and will improve the quality of drugs in the domestic markets.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/revised-manufacturing-rules-for-drug-firms-what-changes-and-why-8879305/
