Cabinet Approves Establishment of ‘Third Launch Pad’ at ISRO's Sriharikota Facility

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, has approved the establishment of a Third Launch Pad (TLP) at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), located at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. This project marks a significant step in enhancing India’s space capabilities and will support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV) for ISRO’s evolving space exploration programs.
Key Features of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP will be built with an adaptable design, capable of supporting NGLV and LVM3 vehicles with semi-cryogenic propulsion. The launch pad will also serve as a standby for the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Sriharikota. This addition will help ISRO meet its growing launch capacity needs, particularly for future human spaceflight missions and space exploration projects. It will facilitate higher launch frequencies, thus boosting the Indian space ecosystem.
Implementation Strategy and Timeline
The Third Launch Pad is planned to be developed within 48 months (4 years), with the total cost pegged at ?3984.86 Crore. The development will involve maximized industry participation and will utilize existing infrastructure at the launch complex. The project will also leverage ISRO’s experience gained from establishing the earlier launch pads.
The Importance of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP is designed to support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV), a key part of ISRO’s vision for space exploration. The facility will not only accommodate heavier vehicles but will also ensure standby capacity for the Second Launch Pad (SLP). Its strategic location at Sriharikota ensures several advantages:
- Proximity to the Equator: This offers a substantial increase in payload capacity due to the additional push provided by the Earth's rotation.
- Safety and Accessibility: The site is free from major international maritime or airline routes, ensuring a safe flight path.
- Geographical Advantage: The launch pad is situated on the eastern coast, enabling launches in an easterly direction, maximizing the benefits of Earth’s rotational speed.
Future Plans for Indian Space Exploration
The establishment of the Third Launch Pad is crucial for the expanded vision of India’s space program, particularly in line with the Amrit Kaal period. ISRO aims to achieve ambitious milestones, such as the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and an Indian Crewed Lunar Landing by 2040. The NGLV will play a pivotal role in these plans, with features like:
- A three-stage vehicle and reusable first stage.
- Semi-cryogenic propulsion, using refined kerosene and liquid oxygen, which will increase payload capacity by three times at 1.5 times the cost of current vehicles.
The Role of Sriharikota in India’s Space Program
Sriharikota, the hub of ISRO’s launch operations, has been integral to India’s space exploration. Currently, the Indian Space Transportation Systems rely on two operational launch pads:
- First Launch Pad (FLP): Established over 30 years ago for PSLV and SSLV missions, FLP continues to support Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) launches.
- Second Launch Pad (SLP): Built primarily for GSLV and LVM3 vehicles, SLP also serves as a standby for PSLV. Over its 20 years of operation, SLP has supported several national missions, including Chandrayaan-3, and is preparing for the Gaganyaan missions.
Narasapur Crochet Lace Craft

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The Narasapur crochet lace craft, which has been a significant part of the cultural and economic fabric of the Godavari region in Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag. The GI tag, registered by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) on March 1, 2024, acknowledges that this unique craft is geographically linked to the West Godavari and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema districts in the Godavari region.
Key Details:
- Historical Background:
- The origins of the Narasapur crochet lace craft date back to 1844, when Macrae and his wife from Scotland introduced the lace-making technique to local women while they were associated with a Christian missionary in Dummugudem (now in Telangana).
- Over time, the craft became a crucial part of the region’s heritage and survived significant historical events like the Indian famine of 1899 and the Great Depression of 1929.
- Craftsmanship:
- The crochet lace is produced using thin threads and delicate crochet needles of varying sizes, resulting in intricate designs.
- The products made include doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bedspreads, table runners, and tablecloths, among others. These items are often exported to international markets like the US, UK, and France.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- The craft is predominantly carried out by women artisans, with over 15,000 women involved in its production. The GI tag is expected to revitalize the industry, especially after its stagnation due to the COVID-19 pandemic and competition from machine-made lace from China.
- The craft is also an important part of the Alankriti Lace Manufacturing Mahila Mutual Aided Co-operative Societies’ Federation Limited, which supports local women artisans and has revived operations at the Alankriti Lace Park in Narasapur.
- GI Tag Benefits:
- The Geographical Indication tag serves to protect the authenticity of the lace products, boost demand, and ensure better market recognition.
- It provides legal protection to the traditional craft, preventing unauthorized use of the term "Narasapur lace" by others and promoting the region's cultural heritage and economic growth.
- Future Outlook:
- With the GI tag, there is hope for increased demand for Narasapur lace products both in domestic and global markets, thus offering a fresh avenue for artisans to revive and sustain the craft.
- Alankriti Federation and other stakeholders are optimistic that the GI tag will significantly revitalize the local economy and empower women in the region.
Protected Planet Report 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Protected Planet Report 2024, released by UNEP-WCMC and IUCN, evaluates global progress toward achieving Target 3 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF). This target aims to conserve 30% of Earth's terrestrial, inland water, coastal, and marine areas by 2030.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Current Global Coverage
- Land and Inland Waters: 17.6% protected.
- Oceans and Coastal Areas: 8.4% protected.
- Progress since 2020: Minimal increase (<0.5% for both realms), equivalent to an area twice the size of Colombia.
- Remaining Challenges to Achieve Target 3 by 2030
- Land: An additional 12.4% of land area must be protected (equivalent to Brazil + Australia).
- Ocean: 21.6% more marine areas must be safeguarded (larger than the Indian Ocean).
- Key Gaps:
- Only 8.5% of protected areas on land are well-connected.
- Only one-fifth of the areas critical for biodiversity are fully protected.
- Biodiversity representation remains uneven, with some ecological regions having no protection at all.
- Governance and Effectiveness Issues
- Less than 5% of protected land and 1.3% of marine areas have management effectiveness assessments.
- Only 0.2% of protected land and 0.01% of marine areas have undergone equitable governance assessments.
- Indigenous governance covers less than 4% of protected areas despite Indigenous and traditional territories covering 13.6% of the terrestrial areas.
- Ocean Conservation Progress: Most progress is in national waters; however, areas beyond national jurisdiction (the high seas) remain underrepresented (<11% coverage).
- Data Deficiency: Insufficient data to measure biodiversity outcomes, equity, and governance in protected areas.
Importance of Target 3
- Biodiversity Benefits: Protected areas play a critical role in halting and reversing biodiversity loss.
- Ecosystem Services: These areas contribute to clean air, water, climate regulation, and food security.
- Cultural and Economic Significance: They uphold the rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities, ensuring equitable governance and sustainable resource use.
Key Recommendations
- Accelerate Conservation Efforts:
- Expand protected and conserved areas with a focus on biodiversity hotspots.
- Ensure areas are ecologically connected and effectively managed.
- Strengthen Indigenous and Local Contributions:
- Recognize and support the stewardship of Indigenous Peoples and local communities.
- Ensure their voices and knowledge systems are integrated into conservation planning.
- Improve Governance and Equity:
- Address gaps in equitable governance and include rights-based approaches.
- Global Cooperation:
- Increase international financing to developing nations for biodiversity conservation.
- Foster cross-border partnerships and support data-sharing initiatives.
- Enhance Data Availability:
- Collect and disseminate data on the effectiveness of protected areas and their biodiversity outcomes.
India’s Role and Strategy
- Commitment to KM-GBF: India updated its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) to align with the KM-GBF goals, aiming to protect 30% of natural areas by 2030.
- Focus on Restoration: Prioritizes the restoration of forests, rivers, and other ecosystems to maintain essential resources like clean air and water.
- Indigenous Participation: India emphasizes integrating Indigenous territories into its conservation framework.
Asset Recovery Interagency Network–Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP)

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- India, represented by the Directorate of Enforcement (ED), has joined the Steering Committee of the Asset Recovery Interagency Network-Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP).
- Leadership Role: India will assume the presidency of ARIN-AP and host the Annual General Meeting (AGM) in 2026, providing a platform for global cooperation in asset recovery and tackling economic crimes.
ARIN-AP Overview:
- Establishment: ARIN-AP is a multi-agency network formed to address the proceeds of crime across the Asia-Pacific region.
- Network Goals: Its mission is to facilitate cross-border collaboration in the areas of asset tracing, freezing, and confiscation.
- Membership: ARIN-AP includes 28 member jurisdictions and 9 observers, and operates as a key component of the Global CARIN Network (Camden Asset Recovery Inter-Agency Network).
- Functioning: ARIN-AP operates through a network of contact points that enable intelligence exchange among member agencies, promoting effective communication and coordination for asset recovery.
Significance of ARIN-AP's Work:
- Combating Economic Crimes: ARIN-AP enhances the efforts of law enforcement agencies in tracing and recovering assets linked to criminal activities, including both movable and immovable assets.
- Informal Exchange of Intelligence: The network allows for the informal exchange of intelligence between agencies, which often accelerates the identification and recovery of proceeds of crime. This can later lead to formal actions through bilateral or multilateral agreements.
- Global Impact: With over 100 jurisdictions in the broader CARIN Network, ARIN-AP plays a key role in global efforts to combat fugitive economic offenders and illicit financial flows.
India’s Contribution and Alignment with G-20 Priorities:
- India’s Leadership: India’s presidency in ARIN-AP will enhance its leadership in asset recovery, facilitating closer cooperation with regional and international law enforcement agencies.
- G-20 Alignment: This role aligns with India’s priorities under the G-20 framework, particularly focusing on the Nine-Point Agenda aimed at tackling fugitive economic offenders and improving asset recovery mechanisms.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
India’s Semiconductor Market Projected to Surpass $100 Billion by 2030
- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
India's semiconductor market is poised to exceed $100 billion by 2030, according to a report from the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association and Counterpoint Research. Currently valued at $45 billion in 2023, the market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 13%, driven by demand in mobile handsets and IT sectors, which together account for over 75% of revenues.
Key Highlights:
- Growth Drivers: The growth is supported by strong demand for electronics and government initiatives like the production-linked incentive scheme. Semiconductors are essential for various industries, including electronics, defense, healthcare, and automotive.
- Importance of Semiconductors: These materials, which include silicon and germanium, are crucial for electronic devices. They can conduct electricity under certain conditions, making them fundamental in transistors, integrated circuits, and devices like LEDs and solar cells.
- Global Context: The global semiconductor supply chain has shown vulnerabilities, particularly during the chip shortage of 2021. Major producers include Taiwan (44% market share), China (28%), South Korea (12%), the U.S. (6%), and Japan (2%). Countries are now focusing on building domestic chip industries to reduce dependency on a few key suppliers.
Factors Favoring India's Growth in Semiconductors:
- Skilled Workforce: India has a vast pool of STEM graduates, providing a skilled workforce for semiconductor manufacturing and design.
- Cost Advantage: Lower labor costs and efficient supply chains position India favorably for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Diversification: India is becoming a hub for back-end assembly and testing operations, with potential for front-end manufacturing.
- Government Support: Initiatives like Semicon India and the India Semiconductor Mission aim to create a robust semiconductor ecosystem, offering substantial fiscal incentives for companies.
Government Initiatives:
- Semiconductor Fab Scheme: Provides 50% project cost support for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Display Fab Scheme: Offers similar support for display manufacturing.
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme: Trains 85,000 engineers across academic and R&D institutions.
- Recent approvals for the establishment of semiconductor plants in Gujarat and Assam further bolster this initiative.
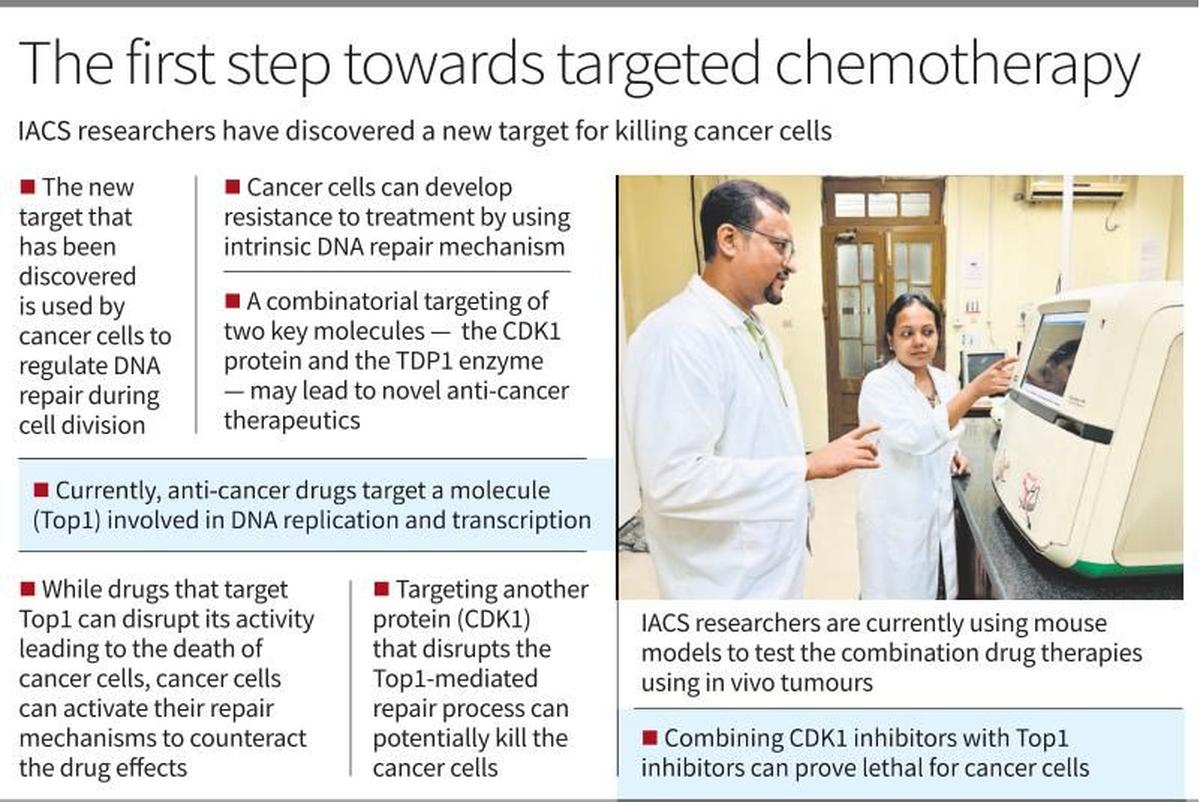
New Cancer Therapy Target
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
Net Direct Tax inflows increase by 16.1%

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
- Advance tax payments from corporates and personal taxpayers have risen by 22.6%, surpassing ?4.36 lakh crore. This increase is driven by a 39.2% rise in Personal Income Tax (PIT) receipts and an 18.2% uptick in corporate taxes.
Key Details:
- Overall net direct tax receipts have reached approximately ?9.96 lakh crore, reflecting a 16.1% increase, though this marks a slowdown from the 22.5% growth recorded as of August 11.
- As of September 17, corporate tax collections grew by 10.5%, while inflows from PIT increased by 18.9%.
- Securities Transaction Tax collections nearly doubled to ?26,154 crore, and refunds surged by 56.5% to ?2.05 lakh crore, according to data from the Income Tax Department.
- Personal taxes continue to outpace corporate taxes, contributing 51.7% of net direct tax receipts for the year.
- Gross tax collections, before accounting for refunds, have risen by 21.5%, totaling ?12.01 lakh crore.
Union Budget 2024-25: Corridor Projects for Bihar's Temples

- 18 Sep 2024
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2024-25 announced plans to develop corridor projects for the Vishnupad Temple at Gaya and the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar. These initiatives aim to enhance both temples as significant pilgrimage and tourist destinations, modeled after the successful Kashi Vishwanath Corridor. The temples are located approximately 10 kilometers apart and hold considerable cultural significance.
Key Facts About the Temples
Vishnupad Temple at Gaya
- Location: Situated on the banks of the Phalgu/Falgu River in Gaya district, Bihar.
- Deity: Dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
- Legend: Local mythology recounts that a demon named Gayasur sought the power to help others attain moksha (liberation). After misusing this power, he was subdued by Lord Vishnu, who left a footprint at the temple, symbolizing this event.
- Architectural Features: The temple stands about 100 feet tall and is supported by 44 pillars made from large gray granite blocks (Munger Black stone), joined with iron clamps. The octagonal shrine is oriented towards the east.
- Construction: Built in 1787 under Queen Ahilyabai Holkar's orders.
- Cultural Practices: The temple is especially significant during Pitra Paksha, a time for honoring ancestors, attracting many devotees. The Brahma Kalpit Brahmins, or Gayawal Brahmins, have served as traditional priests since ancient times.
Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya
- Historical Significance: Believed to be the location where Gautam Buddha attained enlightenment under the Mahabodhi Tree.
- Construction: Originally built by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC, with the current structure dating back to the 5th–6th centuries.
- Architectural Features: The temple complex includes the 50-meter-high Vajrasana (the Diamond Throne), the sacred Bodhi Tree, and six other sacred sites associated with Buddha's enlightenment. The site is surrounded by numerous ancient Votive stupas and is protected by circular boundaries.
- Sacred Sites:
- Bodhi Tree: A direct descendant of the original tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Animeshlochan Chaitya: Where Buddha spent the second week of meditation post-enlightenment.
- Ratnachakrama: Site of Buddha's third week after enlightenment.
- Ratnaghar Chaitya: Site of Buddha's fourth week after enlightenment.
- Ajapala Nigrodh Tree: Site of Buddha’s fifth week after enlightenment.
- Lotus Pond: Site of Buddha’s sixth week after enlightenment.
- Rajyatana Tree: Site of Buddha’s seventh week after enlightenment.
- Recognition: Designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2002, the Mahabodhi Temple attracts numerous national and international pilgrims, emphasizing its spiritual importance.
Other Tourist Attractions in Bihar
Additional notable tourist sites in Bihar include:
- Vishwa Shanti Stupa in Rajgir
- Nalanda
- Ancient city of Patliputra
- Valmiki Nagar Tiger Reserve in West Champaran
What is the Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP)?
The Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP) aims to upgrade religious sites into world-class destinations for spiritual and tourism purposes.
Agnibaan - SOrTeD: World’s First 3D-printed Rocket Engine
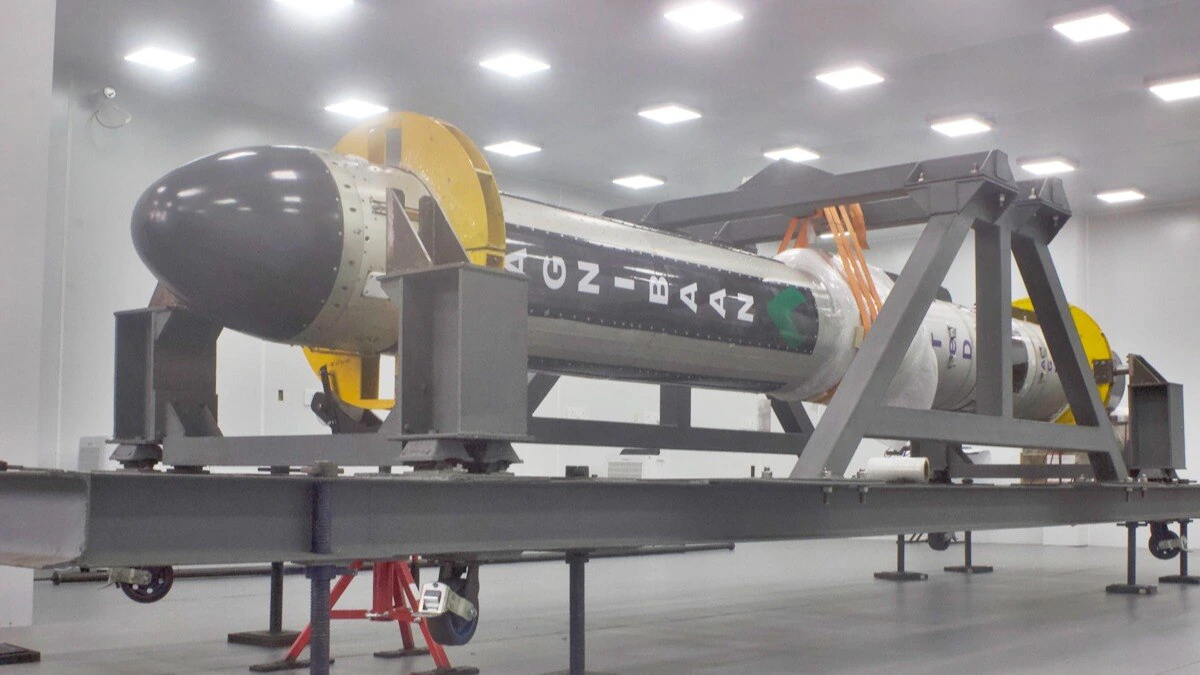

- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos on Thursday successfully launched its first sub-orbital test vehicle powered by the world’s first single-piece 3D-printed rocket engine, after calling off its launch at least four times previously.
What is Agnibaan - SOrTeD?
- Agnibaan SOrTeD is a sub-orbital technological demonstrator of the Agnibaan launch vehicle, manufactured by Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos.
- A sub-orbital launch reaches outer space but does not complete an orbit around Earth, intersecting the Earth's atmosphere or surface without becoming an artificial satellite or reaching escape velocity.
- This marks Agnikul’s fifth launch attempt since March 22. With this launch, AgniKul became the second private company to achieve a rocket launch in India, following Skyroot's successful flight in 2022.
Features:
- It is a customizable, two-stage launch vehicle capable of carrying up to 300 kg into an orbit approximately 700 km above Earth.
- Semi-Cryogenic Engine: Utilizes a combination of liquid and gaseous propellants, operating at temperatures higher than cryogenic engines but lower than traditional liquid rocket engines.
- Uses refined kerosene, which is lighter and can be stored at normal temperatures, allowing more propellant to be carried. When combined with liquid oxygen, kerosene provides higher thrust.
- The test flight aims to demonstrate in-house, homegrown technologies, gather crucial flight data, and ensure the optimal functioning of systems for AgniKul's orbital launch vehicle, Agnibaan.
- The rocket is designed for accessing both low and high-inclination orbits and is completely mobile, enabling launches from more than 10 ports.
Agnibaan Acheivments:
- World’s First 3D-Printed Engine: Agnibaan is the first rocket to use a 3D-printed engine.
- First Semi-Cryogenic Engine-Powered Rocket Launch: Pioneering the use of semi-cryogenic engines in rocket launches.
- India’s First Private Launchpad Rocket Launch: The first Indian rocket launch conducted from a private launchpad.
- Unique Engine Configuration: Powered by the only engine in India that uses both gas and liquid fuel (liquid oxygen/kerosene).
Significance:
- Typically, rocket engine parts are manufactured separately and assembled later.
- The 3D-printed manufacturing process is expected to lower launch costs and reduce vehicle assembly time, offering affordable launch services for small satellites.
About 3D Printing:
- 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, creates three-dimensional objects from digital models by adding material layer by layer.
- This process, which uses materials like plastic, composites, or bio-materials, allows for efficient and customized production, contrasting with traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Notable Examples of 3D Printing:
- Industry Applications: 3D printing is widely used in industries such as healthcare, automotive, and aerospace.
- Aerospace: In May, Relativity Space launched a test rocket made entirely from 3D-printed parts, standing 100 feet tall and 7.5 feet wide.
- However, the rocket experienced a failure shortly after takeoff.
- Healthcare: During the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, 3D printers were utilized to produce essential medical equipment, including swabs, face shields, masks, and parts for ventilators.
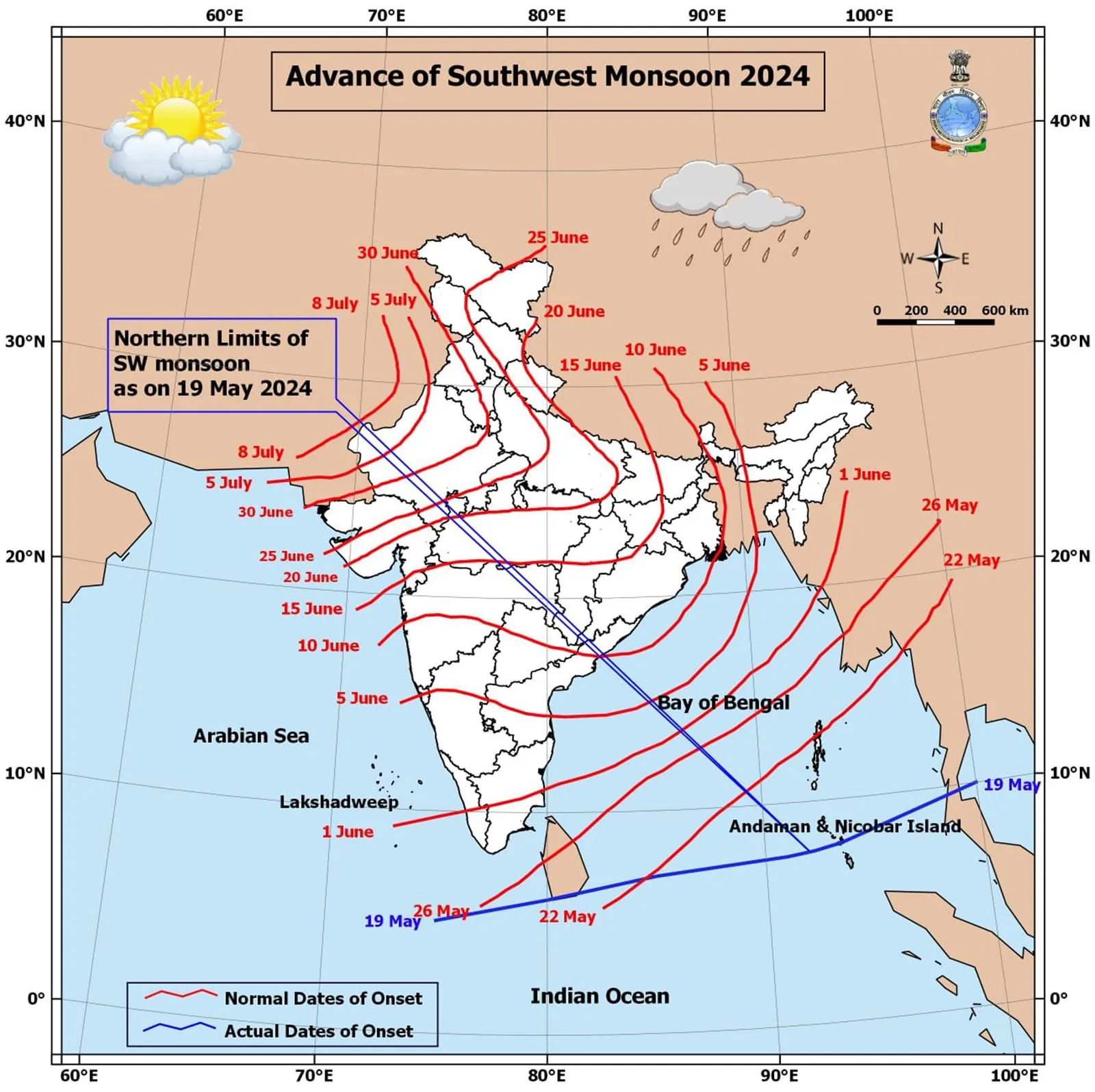
Onset of Monsoon
- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The southwest monsoon is progressing normally, and conditions are suitable for its onset on the Kerala coast in the next five days, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said on Monday (May 27).
What does the ‘onset of monsoon’ Mean?
- The onset of the monsoon over Kerala marks the beginning of the four-month, June-September southwest monsoon season over India, which brings more than 70% of the country’s annual rainfall.
- The onset of the monsoon is a significant day in India’s economic calendar.
- According to the IMD, the onset of the monsoon marks a crucial transition in the large-scale atmospheric and ocean circulations in the Indo-Pacific region, and the Department announces it only after certain defined and measurable parameters, adopted in 2016, are met.
Onset & Advance of Monsoon:
- Broadly, the IMD checks for the consistency of rainfall over a defined geography, its intensity, and wind speed.
- Rainfall: The IMD declares the onset of the monsoon if at least 60% of 14 designated meteorological stations in Kerala and Lakshadweep record at least 2.5 mm of rain for two consecutive days at any time after May 10. In such a situation, the onset over Kerala is declared on the second day, provided specific wind and temperature criteria are also fulfilled.
- The 14 enlisted stations are Minicoy, Amini, Thiruvananthapuram, Punalur, Kollam, Alappuzha, Kottayam, Kochi, Thrissur, Kozhikode, Thalassery, Kannur, Kasaragod, and Mangaluru.
- Wind field: The depth of westerlies, prevailing winds that blow from the west at midlatitudes — should be up to 600 hectopascals (1 hPa is equal to 1 millibar of pressure) in the area bound by the equator to 10ºN latitude and from longitude 55ºE to 80ºE.
- The zonal wind speed over the area bound by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-80ºE longitude should be of the order of 15-20 knots (28-37 kph) at 925 hPa.
- Heat: According to IMD, the INSAT-derived Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR) value (a measure of the energy emitted to space by the Earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere) should be below 200 watts per sq m (wm2) in the box confined by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-75ºE latitude.
- Northern Limit of Monsoon (NLM): Southwest monsoon normally sets in over Kerala around 1st June.
- It advances northwards, usually in surges, and covers the entire country around the 15th of July.
- The NLM is the northernmost limit of monsoon up to which it has advanced on any given day.
In general, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands start receiving monsoon rainfall between May 15 and May 20 every year, and it usually starts raining along the Kerala coast in the last week of May.
Gliese 12b
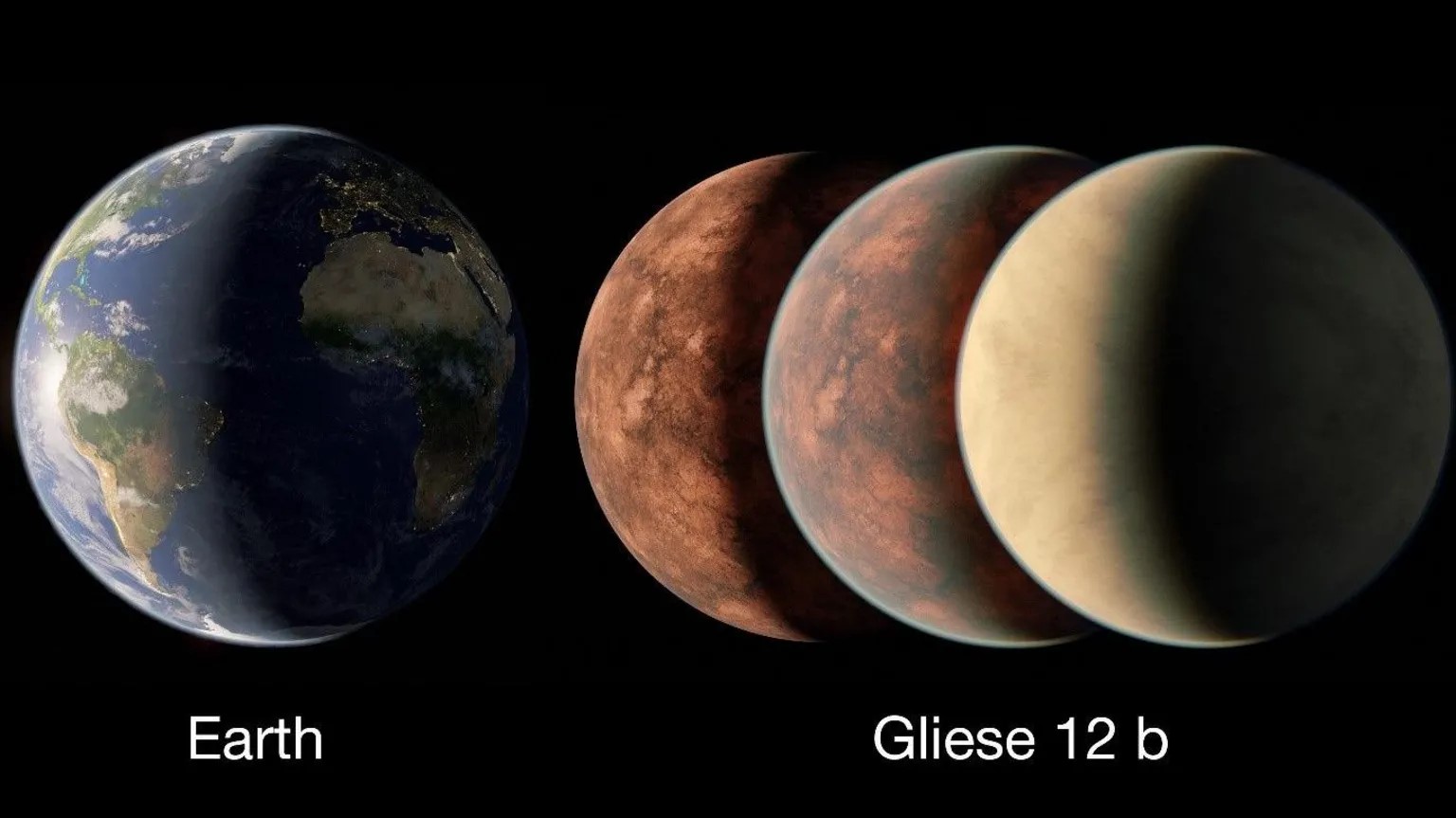

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered a new planet that they say could "potentially support human life."
What is Gliese 12b?
- Gliese 12 b is a rocky planet just 40 light-years away from Earth.
- It orbits around a star called Gliese 12, a cool red dwarf in the constellation Pisces.
- This star is only 27 per cent of the size of our sun, with about 60 per cent of its surface temperature.
- But it's this lower temperature that makes Gliese 12 b theoretically habitable for humans.
- Gliese 12 b is one of the few known rocky planets where humans could theoretically survive according to scientists.
- The planet was discovered by an international team, in collaboration with NASA and the European Space Agency, using data from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and ESA's Characterizing Exoplanet Satellite (CHEOPS).
- Gliese 12 b falls into this "Goldilocks zone," with an average temperature of 107 degrees Fahrenheit and a size somewhere between Venus and Earth.
- The researchers hope that by learning more about Gliese 12 b's atmosphere we may be able to answer questions about the evolution of our own solar system and other habitable planets.
About the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS):
- TESS is a NASA mission dedicated to discovering exoplanets around nearby bright stars.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral.
- TESS operates in a unique high Earth orbit with a period of 12 to 15 days.
- This orbit is designed to keep the telescope's view largely unobstructed by Earth and the Moon.
- The prime mission concluded on July 4, 2020, but TESS continues to operate on an extended mission.
- TESS has identified a wide range of exoplanets, from small rocky worlds to giant planets, highlighting the diversity of planetary systems in our galaxy.
- TESS uses the transit method to find exoplanets. It monitors stars for periodic dips in brightness, which occur when a planet crosses in front of the star along our line of sight.
- The size of the dip indicates the planet's diameter and the duration of the transit provides information about the planet's orbit.
- The transit method allows scientists to determine the diameter and orbital size of exoplanets.
- Orbits within certain ranges fall into the "habitable zone," where conditions may allow liquid water to exist on the surface of Earth-like worlds.
Sweet Sorghum

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Governments should be using their agriculture extension services to raise awareness among farmers, and consumers about the benefits & practical applications of sweet sorghum in people’s diet.
About Sweet Sorghum:
- Sweet sorghum is the most important millet crop occupying the largest area among the cereals next to rice.
- It is mainly grown for its grain and fodder.
- Alternative uses of sorghum include commercial utilization of grain in the food industry and utilization of stalk for the production of value-added products like ethanol, syrup jaggery and enriched bagasse as fodder and as a base material for cogeneration.
- Sweet sorghum has emerged as a supplementary crop to sugarcane in dry land pockets for the production of ethanol.
- The success rate is high because of the use of existing machinery available in the sugar factories and attached distilleries.
- The advantages of the crop are it can be grown with limited water and minimal inputs and it can be harvested in four months.
Climate and Soil:
- Sweet sorghum can be sown in June with the southwest monsoon, in September-October with the northeast monsoon (500-600 mm rainfall), or in summer with assured irrigation.
- The crop prefers moderate rainfall; excessive moisture or heavy rain after flowering can reduce sugar content.
- With irrigation, early sowing before June can prevent issues with heavy rains during flowering and grain maturation.
- Summer sowing may result in lower biomass and sugar yield. Sweet sorghum thrives in well-drained soils of medium depth (18" and above), with water requirements varying by soil type (red, black, laterite, and loamy).
Multiple Uses of Sweet Sorghum:
- Sweet sorghum is a versatile crop used for grain, animal feed, and sugary juice.
- Its grains are made into steamed bread, porridge, and beer, providing high nutritional value with proteins, carbohydrates, fibre, and essential minerals like potassium, calcium, sodium, and iron.
- Resilient in arid climates, sweet sorghum produces significant biomass, which, along with grains, serves as high-quality animal feed.
- The sugary juice from its stalks is used for bioethanol production, yielding more ethanol per hectare than maize, second only to sugarcane.
- Notably, sweet sorghum is drought-resistant, capable of dormancy during dry periods and resuming growth later.
- Its tolerance to low water, nitrogen inputs, salinity, and drought stress makes it ideal for arid regions, making it popular in the US, Brazil, and China.
India VIX

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India VIX, which is an indicator of the market’s expectation of volatility over the near term, surged past the 21 mark recently.
What is India VIX?
- India VIX is a volatility index computed by the NSE based on the order book of NIFTY Options.
- For this, the best bid-ask quotes of near and next-month NIFTY options contracts, which are traded on the F&O segment of NSE are used.
- India VIX indicates the investor’s perception of the market’s volatility in the near term i.e. it depicts the expected market volatility over the next 30 calendar days.
- The higher the India VIX values, the higher the expected volatility and vice versa, as per NSE.
- ‘VIX’ is a trademark of the CBOE, and Standard & Poor’s has granted a license to NSE, with permission from the CBOE, to use such a mark in the name of the India VIX and for purposes relating to the India VIX.
What is the Volatility Index?
- The Volatility Index, VIX or the Fear Index, is a measure of the market’s expectation of volatility over the near term.
- Volatility is often described as the ‘rate and magnitude of changes in prices’ and in finance often referred to as risk.
- Usually, during periods of market volatility, the market moves steeply up or down and the volatility index tends to rise.
- As volatility subsides, the Volatility Index declines.
- The Volatility Index is a measure of the amount by which an underlying index is expected to fluctuate in the near term, (calculated as annualised volatility, denoted in percentage e.g. 20 per cent) based on the order book of the underlying index options.
- The Chicago Board of Options Exchange (CBOE) was the first to introduce the volatility index for the US markets in 1993 based on S&P 100 Index option prices.
- In 2003, the methodology was revised and the new volatility index was based on S&P 500 Index options.
- Since its inception, it has become an indicator of how market practitioners think about volatility.
- Investors use it to gauge market volatility and base their investment decisions accordingly.
PS4 Engine

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully tested a liquid rocket engine made with the help of additive manufacturing technology — commonly known as 3D printing.
About PS4 Engine:
- ISRO has successfully conducted a long-duration test of its PS4 engine, re-designed for production using cutting-edge additive manufacturing (AM) techniques, also known in common parlance as 3D printing, and crafted in the Indian industry.
- The PS4 engine is the uppermost stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), comprising two Earth-storable liquid engines.
- The engine uses the earth-storable bipropellant combinations of Nitrogen Tetroxide as oxidiser and Mono Methyl Hydrazine as fuel in pressure-fed mode.
- It was developed by ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC).
- LPSC redesigned the engine making it amenable to the Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) concept thereby gaining considerable advantages.
- It was developed by ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC).
- The manufacturing of the engine was done by the Indian industry partner, Wipro 3D, and the engine was hot tested at ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu.
Why did ISRO use 3D printing to build the PS4 engine?
- The technology helped ISRO bring down the number of parts in the engine from 14 to a single piece.
- The space agency was able to eliminate 19 weld joints and saved 97% of the raw material.
- It also reduced the overall production time by 60%.
What is 3D Printing?
- 3D printing is a process that uses computer-created design to make three-dimensional objects layer by layer.
- It is an additive process, in which layers of a material like plastic, composites or bio-materials are built up to construct objects that range in shape, size, rigidity, and colour.
How is 3D printing done?
- To carry out 3D printing, one needs a personal computer connected to a 3D printer.
- All they need to do is design a 3D model of the required object on computer-aid design (CAD) software and press ‘print’.
- The 3D printer does the rest of the job.
- 3D printers construct the desired object by using a layering method, which is the complete opposite of the subtractive manufacturing processes.
- The (3D) printers act generally the same as a traditional inkjet printer in the direct 3D printing process, where a nozzle moves back and forth while dispensing a wax or plastic-like polymer layer-by-layer, waiting for that layer to dry, then adding the next level.
- It essentially adds hundreds or thousands of 2D prints on top of one another to make a three-dimensional object.
- Notably, these machines are capable of printing anything from ordinary objects like a ball or a spoon to complex moving parts like hinges and wheels.
- We can print a whole bike, handlebars, saddle, frame, wheels, brakes, pedals and chain–ready assembled, without using any tools.
- It’s just a question of leaving gaps in the right places.
Non-market Economy Status

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vietnam has been pushing the President Joe Biden administration to quickly change its “non-market economy” classification to “market economy”, in a bid to avoid high taxes imposed by the US on the goods imported from the Southeastern country.
Why does Vietnam Want to Get the ‘Market Economy’ Status?
- Vietnam has argued that in recent years it has implemented enough economic reforms that get its name off the non-market economies list.
- The country does meet a number of criteria for the status to be changed.
- For instance, Vietnam allows foreign investment, wages are determined by free negotiations between workers and management, and most of the means of production are not owned by the state.
- The change in status will also help Vietnam get rid of the anti-dumping duties, making its products more competitive in the US market.
- Vietnam’s Center for WTO and International Trade has said that the method of calculating anti-dumping duties is flawed as it causes “the dumping margin to be pushed up very high” and does not actually reflect the situation of Vietnamese companies.
About Non-market Economy Status:
- Non-market economy status refers to a designation applied to countries by international trade authorities, particularly the World Trade Organization (WTO), based on their economic structure and policies.
- In a non-market economy, the allocation of resources, production decisions, and pricing mechanisms are predominantly influenced by the government rather than by market forces.
- This can include state ownership of key industries, government intervention in setting prices, and restrictions on foreign investment and trade.
- For trade purposes, countries classified as non-market economies may face different treatment in anti-dumping investigations and trade disputes.
- This designation can affect how trade regulations and tariffs are applied to goods originating from these countries.
- The US designates a country as a non-market economy based on several factors which are:
- If the country’s currency is convertible
- If wage rates are determined by free bargaining between labour and management
- If joint ventures or other foreign investments are allowed whether the means of production are owned by the state; and
- If the state controls the allocation of resources and price and output decisions.
- Other factors like human rights are also considered.
- The non-market economy label allows the US to impose “anti-dumping” duties on goods imported from designated countries.
Market Economies:
- Market economies operate based on the interactions between consumers and businesses, guided primarily by the law of supply and demand, rather than by central government policies.
- Theoretical Foundation: Developed by classical economists like Adam Smith, David Ricardo, and Jean-Baptiste Say, market economies emphasize the role of free markets in allocating resources efficiently.
- Modern Market Economies: Often referred to as mixed economies, modern market economies may still involve some government interventions, such as price-fixing, licensing, quotas, and industrial subsidies, but the majority of decisions are market-driven.
- Examples include countries like India, the USA, and the UK, where market forces play a significant role in shaping economic activities.
What is Anti-dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a protectionist tariff that a domestic government imposes on foreign imports that it believes are priced below fair market value.
- In order to protect their respective economy, many countries impose duties on products they believe are being dumped in their national market; this is done with the rationale that these products have the potential to undercut local businesses and the local economy.
- While the intention of anti-dumping duties is to save domestic jobs, these tariffs can also lead to higher prices for domestic consumers.
- In the long term, anti-dumping duties can reduce the international competition of domestic companies producing similar goods.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO)–an international organization that deals with the rules of trade between nations–also operates a set of international trade rules, including the international regulation of anti-dumping measures.?
GOLDENE

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, researchers have created a free-standing sheet of gold (goldene) that is only one atom thick.
What Is Goldene?
- Goldene is an innovative, free-standing 2D metal with a thickness of just one atom.
- Created through a unique process, Goldene offers a wide range of potential applications in various industries, particularly in electronics and catalysis.
How is it created?
- Scientists first encapsulate an atomic monolayer of silicon between layers of titanium carbide.
- Gold is deposited on this structure, allowing the gold atoms to diffuse and replace the silicon atoms, creating a monolayer of trapped gold atoms.
- Using Murakami's reagent and a Japanese technique employed in forging katanas and high-quality knives, the titanium carbide layers are etched away, leaving a free-standing, one-atom-thick layer of gold.
Dimensions:
- Goldene sheets are approximately 100 nanometres thick, roughly 400 times thinner than the most delicate commercially available gold leaf.
Applications: Goldene's unique properties offer potential applications in various sectors:
- Electronics industry: Goldene's thinness and conductivity can enhance electrical components and circuitry.
- Carbon dioxide conversion: It can potentially aid in transforming carbon dioxide into useful products.
- Hydrogen-generating catalysis: Goldene could be utilized to efficiently produce hydrogen.
- Selective production of value-added chemicals: The material's properties enable the selective generation of chemicals for specific applications.
- Hydrogen production: It can contribute to the clean production of hydrogen.
- Water purification: Goldene could be implemented in water treatment technologies.
Significance:
- Goldene is an economically viable alternative to conventional, thicker gold structures, making it an appealing option for catalytic applications.
- Its unique characteristics position Goldene as a potentially revolutionary material for various industries.
Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Enacted on May 1, 2014, after decades of advocacy, the Street Vendors Act has achieved progress yet faces implementation challenges in safeguarding vendors' livelihoods.
About Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014:
- The Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014 was enacted to legitimize the rights of street vendors (SVs) and regulate their activities.
- It is implemented by respective States/UTs by framing Rules, schemes, Bye-laws and Plan for Street Vending as per provisions of the Act.
- It seeks to safeguard and manage street vending in urban areas, with State-level regulations and initiatives overseen by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) through the formulation of by-laws, urban planning, and regulatory measures.
- The Act clearly defines the roles and obligations of both vendors and various levels of government.
- One of the primary objectives of the Act is to ensure the inclusion of all "existing" vendors within designated vending zones by issuing vending certificates (VCs).
- It establishes Town Vending Committees (TVCs) as a mechanism for participatory governance, with street vendor representatives comprising 40% of the committee members, including a sub-representation of 33% for women SVs.
- These committees are tasked with overseeing the allocation of vending spaces and ensuring the representation of all existing vendors within vending zones.
- Moreover, the Act provides mechanisms for addressing grievances and disputes, proposing the establishment of Grievance Redressal Committees chaired by a civil judge or judicial magistrate.
- Additionally, it mandates that States/ULBs conduct surveys to identify street vendors at least once every five years, ensuring an updated understanding of the street vending landscape and facilitating effective regulatory measures.
Bambi Bucket

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an Indian Air Force MI 17 V5 helicopter, equipped with a Bambi Bucket, was deployed to combat the forest fires in Nainital district, Uttarakhand.
What is a Bambi Bucket?
- Bambi Bucket is a specialised aerial firefighting tool that has been in use since the 1980s.
- It is essentially a lightweight collapsible container that releases water from underneath a helicopter to targeted areas.
- The water is released by using a pilot-controlled valve.
- One of its key features is that it can be quickly and easily filled.
- The bucket can be filled from various sources, including a lake, river, pond, and swimming pool, which allows firefighters to swiftly refill it and return to the target area.
- Bambi Bucket is available in a variety of sizes and models, with capacities ranging from 270 liters to more than 9,840 liters.
How was the Bambi Bucket Invented?
- The Bambi Bucket was invented by Don Arney, a Canadian business, in 1982.
- Arney came up with the idea after he realised that the aerial firefighting water buckets in use at the time were not efficient and had a high failure rate.
- These water buckets were generally made of “solid fiberglass, plastic, or canvas with metal frames” and were “too rigid to fit inside the aircraft” and had to be “trucked to fire sites or flown in on the hook of a helicopter thereby slowing the aircraft down.
- Another issue was that the water dropped from these containers used to get dispersed into a spray thereby reducing impact.
- Bambi Bucket does not have these limitations.
- One, it can be stored within the helicopter until development.
- Two, it discharges a solid column of water, “resulting in a more accurate and effective water dump, less evaporation on the descent, and greater impact force.
- It was an instant success and began to be widely used for firefighting.
- Today, Bambi Bucket is used in more than 115 countries around the world by more than 1,000 helicopter operators.
Global Tiger Conservation Coalition

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At the Sustainable Finance for Tiger Landscapes Conference, Bhutan and the Tiger Conservation Coalition pledged to mobilize $1 billion for tiger conservation efforts.
About the Tiger Conservation Coalition:
- The Tiger Conservation Coalition is a group of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that have worked for many years with partners to conserve tigers.
- It brings together leading tiger biologists and experts in wildlife crime, human-wildlife coexistence, policy, finance, development, and communications with unprecedented alignment on achieving tiger conservation at scale.
- Its member organizations include the Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA), Fauna & Flora, the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), Panthera, TRAFFIC, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF).
- It is an independent group of organizations that combines and shares the vast knowledge, on-the-ground experience, and data of its members and partners to support Tiger Range Countries in developing and implementing effective approaches to tiger conservation.
- The Coalition was founded on strong relationships among eminent tiger experts already working together on major tiger assessments, including the latest assessment by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species released in 2022, and the forthcoming Green Status Assessment, and coalesced around a common vision for tiger recovery.
- By engaging national and local civil society organizations from the region, and continuing to support the Global Tiger Initiative Council and the Global Tiger Forum, the coalition aims to further strengthen partnerships and impactful outcomes for tigers.
- In January 2022, the Tiger Conservation Coalition released its vision for tiger recovery through 2034, the next Year of the Tiger.
- “Securing a Viable Future for the Tiger” presents a set of measurable goals and high-level strategic approaches to achieve the long-term presence of viable and ecologically functional populations of wild tigers.
- Its suggested actions, grounded in the latest science and results, would lead to increasing numbers of tigers secure in current and expanded protected habitats, with distribution and connectivity across their indigenous range.
- Tiger Conservation Coalition members co-developed Tiger Conservation Landscapes 3.0, an integrated habitat modeling system to measure and monitor changes in tiger habitat at range-wide, national, biome, and landscape scales in near real-time.
- This work serves as a model for objective, range-wide, habitat monitoring as countries work to achieve the goals laid out in the 30x30 agenda, the Sustainable Development Goals, and the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
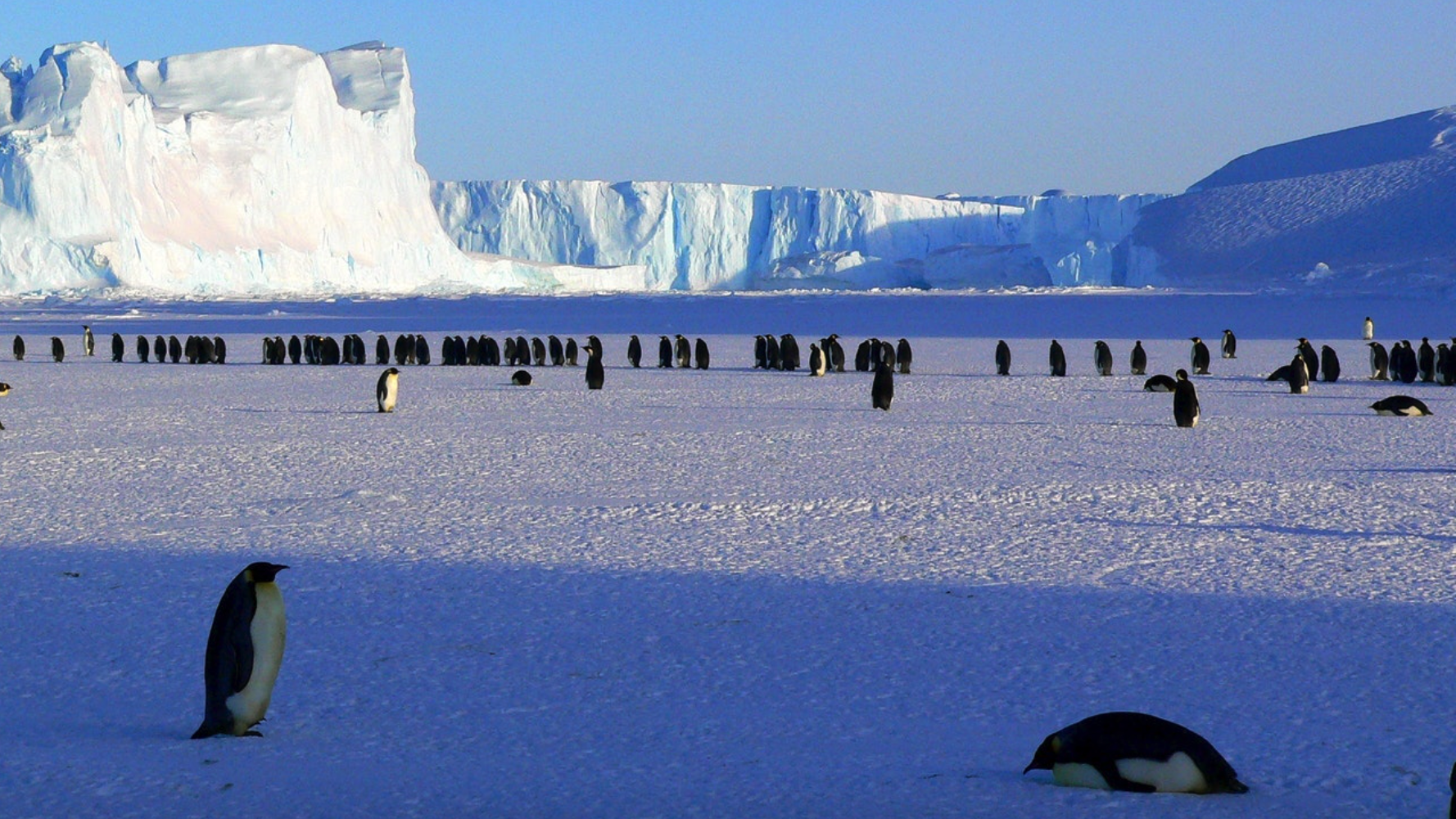
Tundra Ecosystem

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent study has warned that the warming planet may alter the characteristics of tundra environments and could transform them from carbon sinks to carbon sources.
About Tundra Ecosystem:
- The Tundra ecosystem is one of the unique ecosystems of the planet.
- The adverse climatic conditions of tundra regions like dry winds, meager precipitation, and extreme cold make it a unique and desert-like ecosystem with treeless fields.
- These harsh climatic conditions of the tundra region make the survival of plant and animal species quite severe.
Key Characteristics of Tundra Regions:
- Low Temperatures: Tundra areas experience frigid temperatures, ranging from -34 to -6 degrees Celsius (-30 to 20 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Short Growing Seasons: The tundra's summer growth period lasts merely 50 to 60 days, with sunlight persisting up to 24 hours a day.
- Permafrost: Below the surface lies a layer of permanently frozen soil, varying from a few inches to several feet thick.
- Minimal Precipitation: Despite being likened to deserts in terms of moisture, tundra regions receive low precipitation levels, primarily in the form of snow.
- Limited Biodiversity: Harsh conditions in the tundra support fewer plant and animal species compared to other biomes.
- Carbon Sink: Tundras serve as significant carbon storage areas due to the slow decomposition rates in their cold environments.
Types of Tundra:
- Arctic Tundra: Found north of the taiga belt in the far Northern Hemisphere, encompassing regions between the North Pole and the boreal forest, including parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, and Finland.
- Alpine Tundra: Prevails above the tree line in mountain ranges worldwide, such as the Rockies, the Andes, the Himalayas, and the Alps.
- Antarctic Tundra: Encompasses several sub-Antarctic islands and portions of the Antarctic continent.
Flora and Fauna:
- Flora: Common plant species in tundra regions include mosses, lichens, sedges, cotton grass, and birches.
- Fauna: Wildlife in tundra ecosystems includes Arctic foxes, snow geese, polar bears, and other cold-adapted species.
Thiruvalluvar

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Seeking to connect with the people of Tamil Nadu where his party is trying to gain a foothold, Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced that the BJP will work towards building Thiruvalluvar cultural centers all over the world.
Who was Thiruvalluvar?
- Thiruvalluvar, the author of the revered 'Thirukkural' or 'Sacred Couplets', remains a figure of historical debate.
- His exact period and religious affiliation are uncertain, with proposed dates ranging from the 3rd or 4th century CE to the 8th or 9th century.
- Various groups regard him as a Hindu sage, a Jain sage, or a Dravidian saint with no religious identifiers except his Dravidian heritage.
- Accounts of Thiruvalluvar's origins are diverse.
- In Edward Jewitt Robinson's 1873 book, 'Tamil Wisdom: Traditions Concerning Hindu Sages and Selections from their Writings', he described Thiruvalluvar as a "Pariah" with a mother from "the low class" and a possibly Brahmin father.
- According to this narrative, Thiruvalluvar was found in a grove near a Shiva temple in Mayilapur and was taken in by the wife of a high-ranking Velalan before being entrusted to a "Pariah family."
- Despite the ambiguity surrounding Thiruvalluvar's identity, his wisdom-laden verses in 'Thirukkural' continue to influence and inspire generations across religious and cultural divides.
Why does Thiruvalluvar matter?
- Thiruvalluvar, affectionately called Valluvar by Tamils, is revered as a cultural and moral icon across caste and religious lines.
- His 'Thirukkural', a compilation of 1,330 couplets, is an integral part of Tamil culture, comparable to the Bhagavad Gita or Ramayana in North Indian Hindu households.
- It serves as a foundational text for ethical living and tracing Tamil cultural roots.
- Beyond Tamil Nadu, Thiruvalluvar's wisdom is celebrated in the context of ancient India's rich philosophical heritage, emphasizing morality and ethics.
- His enduring influence is evident as successive Indian finance ministers reference his teachings in annual Budget speeches.
- However, competing claims to Thiruvalluvar's legacy have sparked controversy, such as the 2019 debate surrounding the BJP's depiction of him in saffron robes instead of traditional white garments.
- Despite these disputes, the profound impact of Thiruvalluvar's teachings continues to resonate across various cultures and languages, fostering unity and moral guidance.
Why Are Political Parties Asserting Thiruvalluvar's Legacy?
- Political parties, both national and regional, have long vied for ownership of Thiruvalluvar's legacy. For instance, the BJP, with a limited grassroots presence in Tamil Nadu, seeks to bolster its standing through the appropriation of Tamil saints and icons.
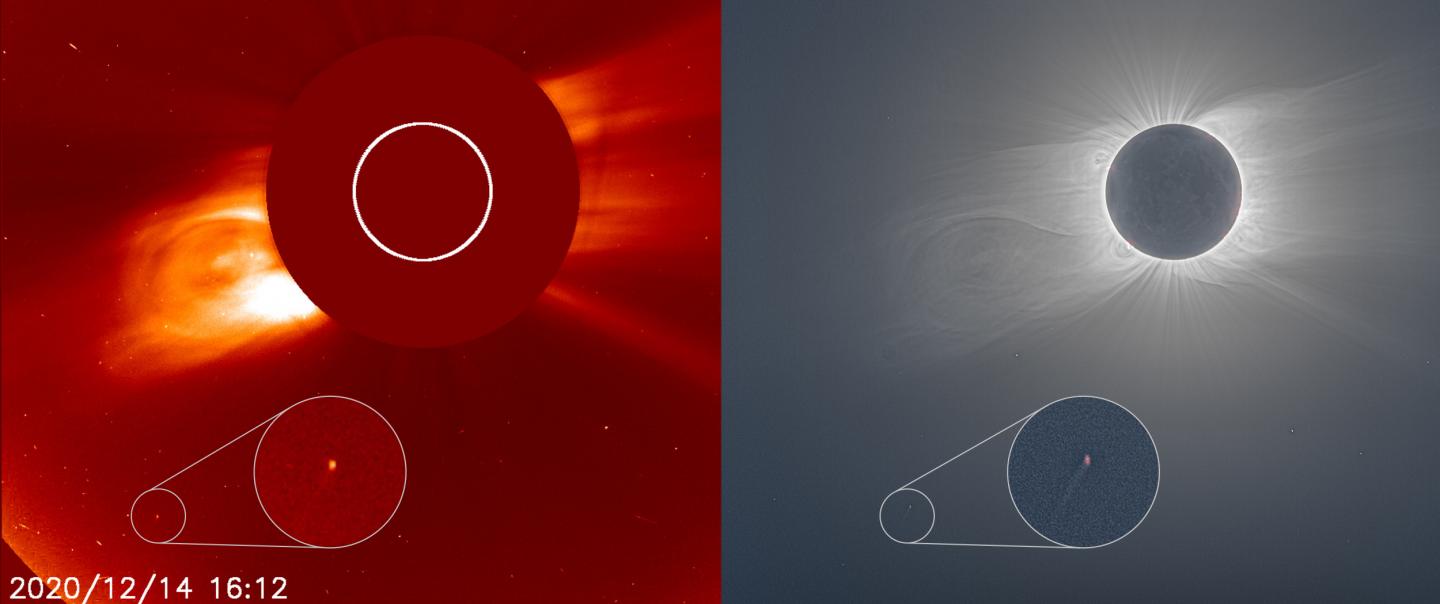
Sungrazing Comet
- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A tiny "sungrazer" comet was discovered, photographed, and destroyed during the recent total solar eclipse — all within 24 hours.
What is a Sungrazing Comet?
- Sungrazing comets are a special class of comets that come very close to the sun at their nearest approach, a point called perihelion.
- To be considered a sungrazer, a comet needs to get within about 850,000 miles from the sun at perihelion.
- Many come even closer, even to within a few thousand miles.
- Being so close to the sun is very hard on comets for many reasons.
- They are subjected to a lot of solar radiation which boils off their water or other volatiles.
- The physical push of the radiation and the solar wind also help form the tails. As they get closer to the sun, the comets experience extremely strong tidal forces or gravitational stress.
- In this hostile environment, many sungrazers do not survive their trip around the sun.
- Although they don't crash into the solar surface, the sun can destroy them anyway.
- Many sungrazing comets follow a similar orbit, called the Kreutz Path, and collectively belong to a population called the Kreutz Group.
- Close to 85% of the sungrazers seen by the SOHO satellite are on this orbital highway.
- Scientists think one extremely large sungrazing comet broke up hundreds, or even thousands, of years ago, and the current comets on the Kreutz Path are the leftover fragments of it.
- Comet Lovejoy, which reached perihelion on December 15, 2011, is the best-known recent Kreutz-group sungrazer.
- And so far, it is the only one that NASA's solar-observing fleet has seen survive its trip around the sun.
What is a Comet?
- A comet is a small celestial body made primarily of ice, dust, and rocky material that orbits the sun in an elongated path.
- When a comet approaches the sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, releasing dust and gas into a glowing coma, or halo, around the comet's nucleus.
- This glowing coma often forms a tail that stretches away from the sun due to the solar wind and radiation pressure.
- Comets are often referred to as "dirty snowballs" or "icy dirtballs" because of their composition.
- They are believed to be remnants from the early formation of the solar system and carry important information about its history.
- Comets can have highly elliptical orbits, sometimes taking thousands or even millions of years to complete a single orbit around the sun.
TSAT-1A Satellite

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
SpaceX successfully launched and deployed the TSAT-1A satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in partnership with Satellogic Inc.
About TSAT-1A Satellite:
- TSAT-1A is a groundbreaking optical sub-meter resolution Earth observation satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in collaboration with Latin American company Satellogic Inc.
- This collaboration began in late 2023, culminating in TSAT-1A's assembly at TASL's Assembly, Integration, and Testing (AIT) plant in Karnataka, India.
- Launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United States, via SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket, TSAT-1A has since garnered attention for its advanced capabilities and strategic significance.
Key Features of TSAT-1A:
- Sub-meter resolution imagery: TSAT-1A's primary strength lies in its ability to capture high-resolution military-grade imagery of Earth's surface, providing precision of less than one meter per pixel.
- Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging: This technology enables TSAT-1A to gather data across a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, offering a detailed and nuanced understanding of land, water, and other natural resources.
- Enhanced performance: TSAT-1A offers improved collection capacity, a wider dynamic range, and low-latency data delivery, ensuring efficient and reliable intelligence gathering.
Strategic Applications and Implications:
- Designed for use by Indian defense forces, TSAT-1A is set to play a pivotal role in discreet information gathering, with the potential for data-sharing among friendly nations.
- By enhancing defense forces' preparedness, response capabilities, and strategic decision-making, TSAT-1A represents a significant milestone in India's space industry and a potential game-changer in the realm of defense and security.
About SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket:
- The Falcon 9 is a partially reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX.
- Known for its reliable and safe transportation capabilities, Falcon 9 is primarily used to launch payloads and crew into Earth orbit.
- Since its first launch in 2010, Falcon 9 has made significant strides in the aerospace industry, becoming the first commercial rocket to launch humans to orbit in 2020 and maintaining a strong safety record with only one flight failure to date.
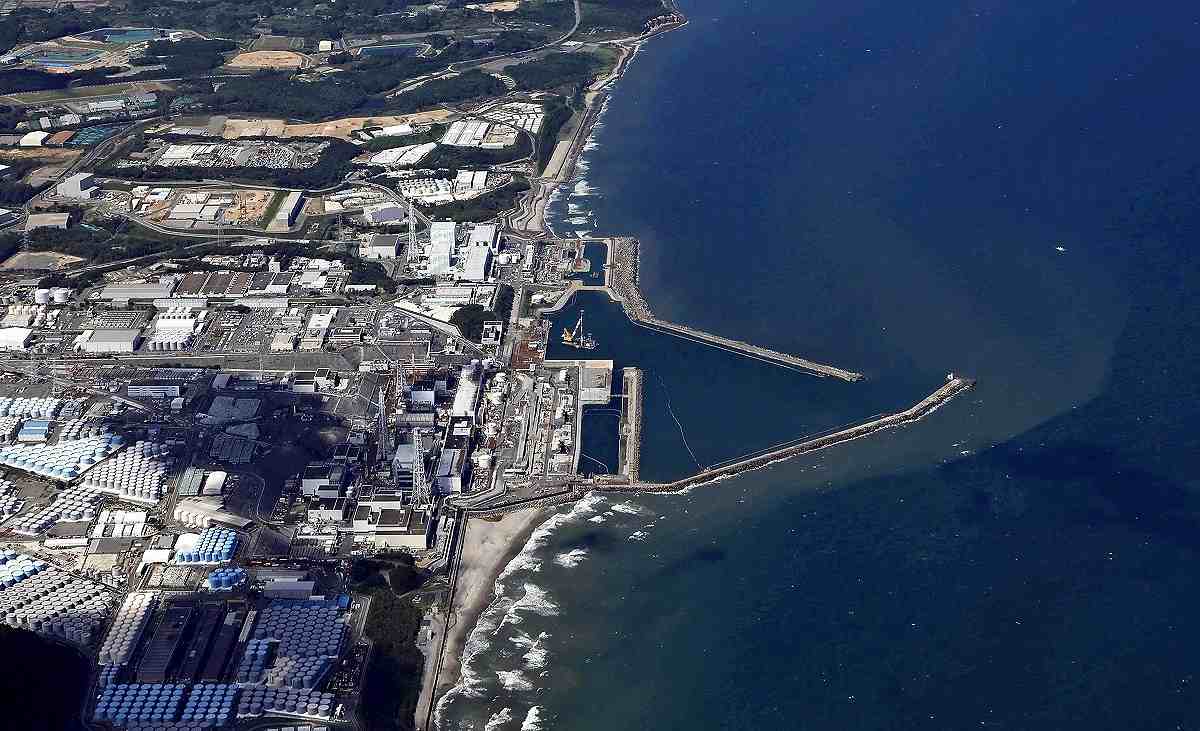
Fukushima Water Issue

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Japan announced that its experts have engaged in discussions with their Chinese counterparts to address Beijing's concerns regarding the release of treated radioactive wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea.
What is the Fukushima Water Issue?
- In 2021, the Japanese government unveiled plans to gradually discharge over one million tonnes of contaminated water from the Fukushima nuclear plant into the ocean over the next three decades.
- The contaminated water is a residual product of the devastating 2011 earthquake and tsunami that incapacitated the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, resulting in the release of radioactive materials.
- After more than ten years of storing this wastewater, Japan asserts that they are facing storage space limitations and contends that the treated water is now safe for release.
Concerns Surrounding the Fukushima Water Discharge:
- Tritium and Carbon-14: The water from Fukushima undergoes filtration via the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), effectively reducing most radioactive contaminants to acceptable safety levels, except tritium and carbon-14.
- While both emit low levels of radiation, consumption in large quantities could potentially pose risks.
- Insufficient Research: Scientists emphasize the need for further investigation into the potential impact of the water discharge on the ocean bed and marine ecosystems.
- The Pacific Islands Forum regional group has labeled the proposed plan as "another significant nuclear contamination disaster," citing ongoing challenges faced by its member nations due to past US nuclear testing.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF):
- The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including the formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations.
- It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia.
- It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
- The PIF secretariat is located in Suva, the capital of Fiji.
Nuclear Incidents:
- A nuclear and radiation incident denotes an occurrence that has resulted in significant repercussions for individuals, the environment, or the facility involved.
- These may entail fatal consequences for individuals, substantial releases of radioactivity into the environment, or reactor core meltdowns.
- Globally, there have been a total of 99 incidents at nuclear power plants.
- Fifty-seven of these incidents have transpired since the Chornobyl disaster, with the United States accounting for 57% of all nuclear-related incidents.
- Noteworthy nuclear power plant mishaps encompass:
- Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011)
- Chernobyl disaster (1986)
- Three Mile Island accident (1979), and
- The SL-1 accident (1961).
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
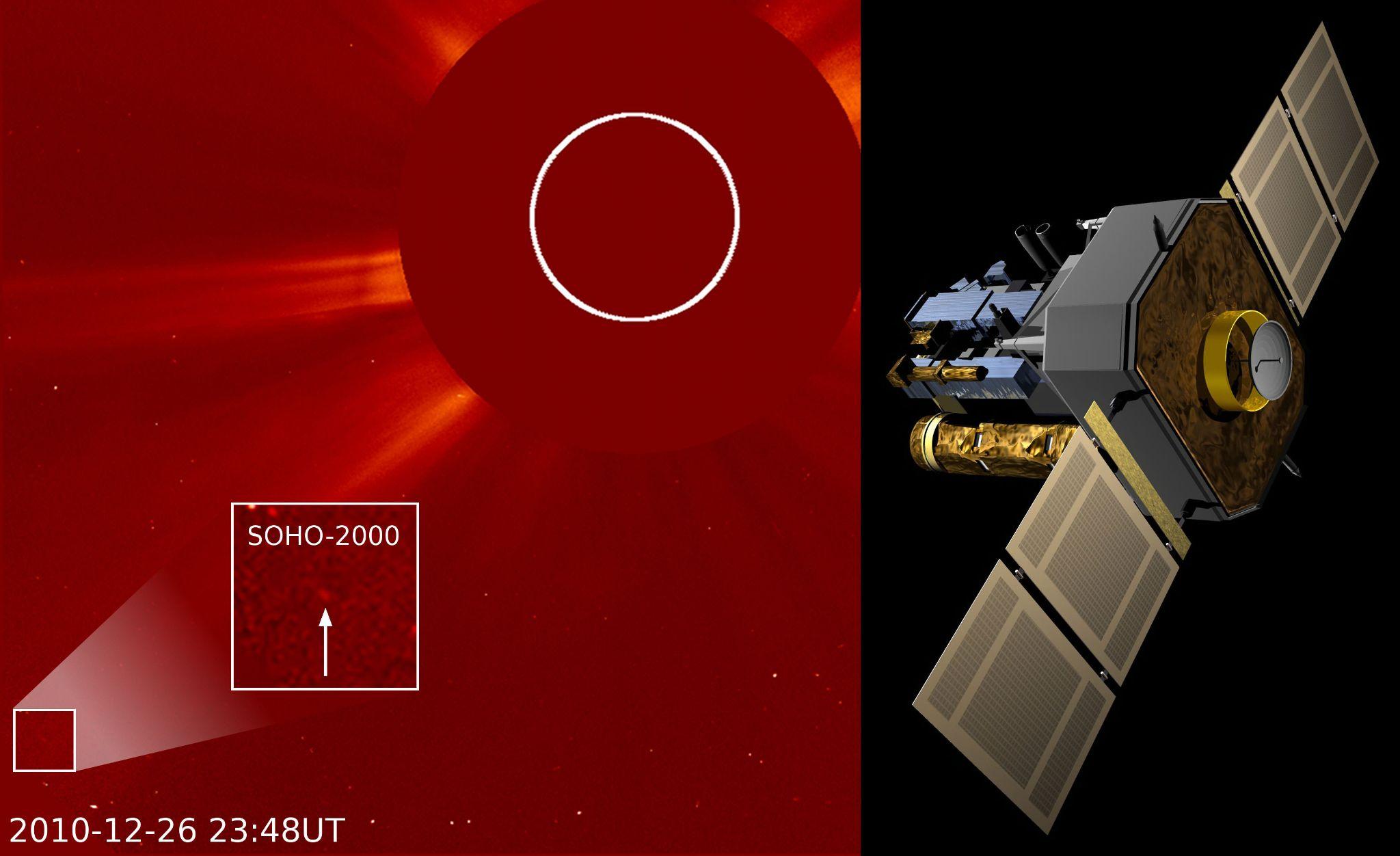
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
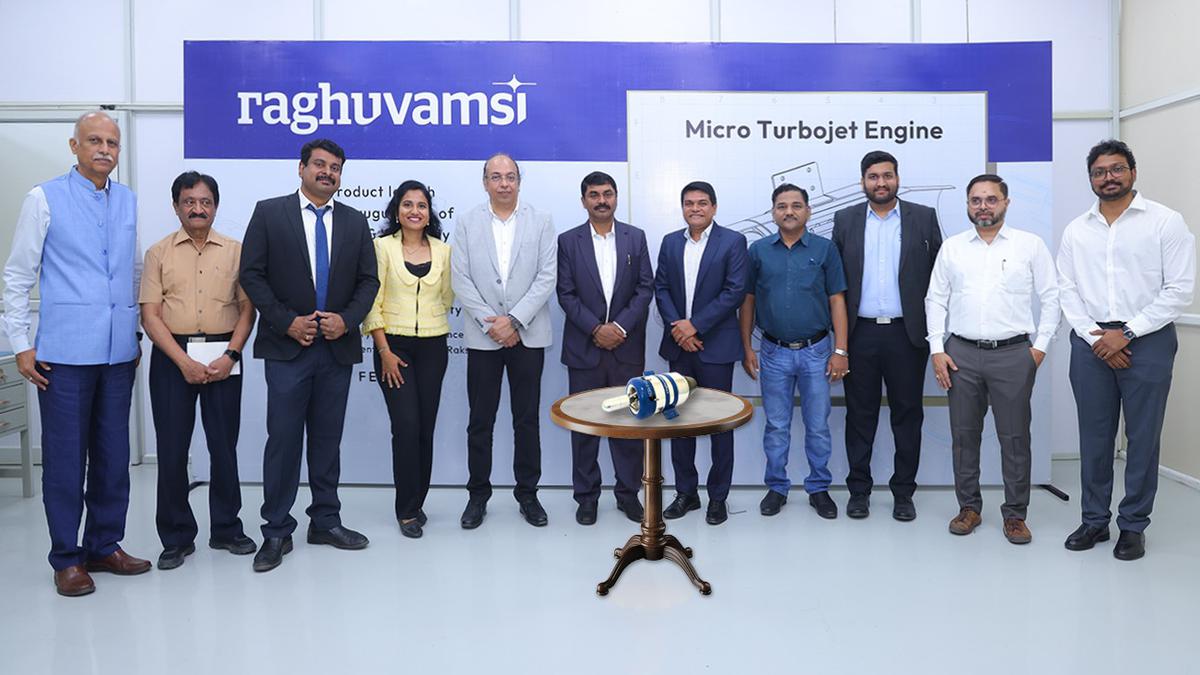
. First-of-its-kind Micro Turbojet Engine made in India

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A micro turbojet engine designed and developed indigenously by Hyderabad-based firm Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools with the support of the IIT Hyderabad has been unveiled.
Key Highlights of the Micro Turbojet Engine “INDRA RV25: 240N”:
- It is an indigenous micro turbojet engine made in India.
- Its primary focus is on serving unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones.
- Beyond UAVs, the engine exhibits versatile applications in air taxis, jetpacks, auxiliary power units, range extenders, and potential use in power generation for the future.
- Indigenous design and development: Engineered entirely in India by the Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools (RVMT) team of skilled engineers & supported by IIT, Hyderabad.
- A great demonstration of the potential of Industry-Academia partnership
- Self-reliance and autonomy: By reducing reliance on imported technologies, components, and expertise, the Micro Turbojet Engine contributes to India’s goal of achieving self-sufficiency in critical sectors, bolstering national security and economic resilience
- Empowering local manufacturing: The launch of the indigenous Micro Turbojet Engine not only drives technological innovation but also stimulates the growth of the domestic aerospace and defense manufacturing ecosystem, creating jobs and fostering economic growth.
What Is a Turbojet Engine and How Does It Work?
- Turbojet engines are jet engines that, like other jet engines, generate propulsion by discharging or expelling heated air.
- They feature a combustion chamber in which they burn fuel and air.
- As they burn this mixture, turbojet engines will discharge heated air.
- It can find turbojet engines in commercial airplanes, civilian airplanes, and military aircraft.
How Turbojet Engines Work?
- The process begins by drawing air through an intake.
- Turbojet engines feature an air intake, which is typically located near the front of the engine.
- Air will flow into this intake, at which point it will be redirected to the engine’s interior.
- After entering the engine, the air will become compressed.
- Turbojet engines feature a set of rotating blades. Known as compressors, these rotating blades are designed to compress the air.
- The next step in the process is combustion which involves the burning of fuel and air.
- Turbojet engines will inject fuel into the same combustion chamber where the compressed air is located.
- A spark will then ignite the mixture of fuel and compressed air, thereby generating hot, high-pressure exhaust gas.
- The exhaust gas generated by the combustion is expelled out the rear of the turbojet engine.
- This rearward expulsion allows for forward propulsion.
- As the exhaust gas is discharged out the rear of the turbojet engine, the airplane will be propelled forward.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference
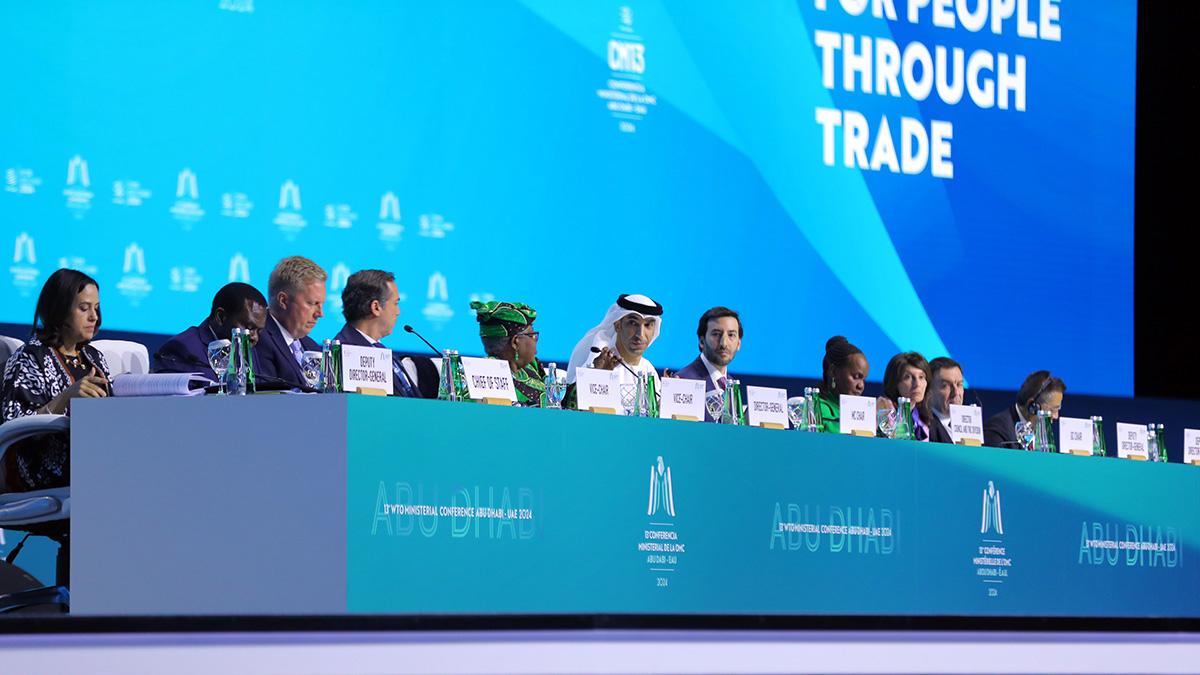

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
Cabinet approves Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for the period 2021-26

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of “Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)” with a total outlay of Rs. 4,100 crore for a period of 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
About the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP):
- The FMBAP Scheme is being implemented throughout the country for effective flood management, erosion control and anti-sea erosion and to help in maintaining peace along the border.
- The scheme benefits towns, villages, industrial establishments, communication links, agricultural fields, infrastructure etc. from floods and erosion in the country.
- The catchment area treatment works will help in the reduction of sediment load into rivers.
- The Scheme aims at the completion of the ongoing projects already approved under FMP.
The Scheme has two components:
- Under the Flood Management Programme (FMP) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 2940 crore, central assistance will be provided to State Governments for taking up critical works related to flood control, anti-erosion, drainage development and anti-sea erosion, etc.
- The pattern of funding to be followed is 90% (Centre): 10% (State) for Special Category States (8 North-Eastern States and Hilly States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and UT of Jammu & Kashmir) and 60% (Centre):40% (State) for General/ Non-Special Category States.
- Under the River Management and Border Areas (RMBA) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 1160 crore, flood control and anti-erosion work on common border rivers with neighbouring countries including hydrological observations and flood forecasting, and investigation & pre-construction activities of joint water resources projects (with neighbouring countries) on common border rivers will be taken up with 100% central assistance.
- The Scheme has the provision of incentivizing the States which implement flood plain zoning, recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Importance:
- While the primary duty of flood management lies with the State Governments, the Union Government actively promotes and advocates for the adoption of modern technology and innovative approaches.
- Additionally, projects executed under the RMBA component serve to safeguard critical installations of security agencies and border outposts situated along border rivers from the perils of floods and erosion.
- Furthermore, the scheme includes provisions for incentivizing states that implement flood plain zoning, a recognized and effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Will the ‘Paruveta Festival’ celebrated in Andhra’s Ahobilam get UNESCO recognition?

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
INTACH is striving to obtain UNESCO recognition for the yearly 'Paruveta' festival, emphasising its cultural significance.
About the Paruveta Festival:
- Paruveta Festival, also known as the 'mock hunting festival', is a celebrated tradition at the Sri Narasimha Swamy temple in Ahobilam, Andhra Pradesh.
- It stands out as a symbol of communal harmony, where devotees from various religious backgrounds, including Muslims, come together to offer prayers.
Origin and Significance:
- According to folklore, the festival commemorates Lord Vishnu's incarnation as Narasimha, who married Chenchulakshmi, a tribal girl, symbolising unity across different communities.
- The festival's rituals, typically observed during Vijayadashami or Sankranti, extend for a 'mandala' period of forty days in Ahobilam.
Activities and Customs:
- During the festival, the temple deity is carried to the 32 Chenchu tribal villages surrounding Ahobilam for forty days.
- The journey begins with a symbolic act where tribals shoot arrows at the deity's palanquin, signifying protection and reverence.
- Chenchus participated by undertaking 'Narasimha Deeksha', wearing yellow robes and Tulasi Mala, while observing celibacy.
- The temple staff reside in these villages throughout the festival, showcasing the tradition of a casteless society with no traces of untouchability.
Key Points about Chenchu Tribes:
- Geographic Distribution: Chenchu tribes primarily inhabit the hills of southern India, particularly in Andhra Pradesh.
- Additionally, Chenchu communities can be found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Orissa.
- Language and Communication: Their native language, known as Chenchu, belongs to the Dravidian language family.
- While many Chenchu individuals speak Telugu, their traditional language holds cultural significance.
- Livelihood and Occupation: Historically, Chenchu people pursued a nomadic lifestyle, relying on food gathering.
- However, due to factors such as agricultural expansion, many have transitioned to working as farmers or forest labourers.
- Housing and Settlements: Chenchu dwellings are typically hive-shaped structures constructed from wattle thatch, composed of interwoven poles, twigs, reeds, or branches.
- These houses reflect their traditional architectural style and are adapted to their environment.
- Social Structure: Chenchu society is organised into clans, which are extended family units, as well as local groups and individual families.
- They adhere to exogamous marriage practices, prohibiting unions within the same clan.
- Additionally, Chenchu kinship is patrilineal, tracing descent through male lineage.
BSNL floats Rs 65,000 crore tender for phase-III BharatNet project

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
BSNL, the state-owned telecommunications company, has initiated a tender process amounting to approximately Rs 65,000 crore for the implementation of the phase-III BharatNet project.
What is the BharatNet Phase III Project?
- The BharatNet phase-III project adopts a three-level architecture:
- Internet leased line bandwidth
- Middle-mile connectivity, and
- Last-mile connectivity
- It aims to involve village-level entrepreneurs or Udyamis in providing last-mile connectivity to households on a revenue-sharing basis.
- BSNL aims to provide 15 million home fibre connections over five years using the BharatNet Udyami model.
About BharatNet Project:
- The BharatNet Project is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world.
- It aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats across India in a phased manner.
- Its core objective is to ensure equitable access to broadband services for all telecom service providers, fostering the deployment of services like e-health, e-education, and e-governance in rural and remote areas.
- Initiated in 2011 and executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in 2012, the project operates in three phases.
- Phase I launched in 2011, focused on creating the National Optical Fibre Network, leveraging existing infrastructure and laying additional fibre to bridge connectivity gaps up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Phase II, approved in 2017, builds upon Phase I’s experiences, aligning with the Digital India vision.
- It adopts a flexible approach, integrating various media such as Optical Fibre Cable (OFC), Radio, and satellite to connect Gram Panchayats, utilizing models like State-led, Private Sector, and CPSU Models for implementation.
- Phase III, spanning from 2019 to 2023, aims to establish a robust, future-ready network with district-to-block fibre connectivity, featuring ring topology for redundancy.
- This comprehensive approach ensures the creation of a resilient and inclusive telecom infrastructure, facilitating socio-economic development in rural India.
Coal Ministry Hosts Industry Interaction on Coal Gasification (ET)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Coal has announced it will host an Industry Interaction on February 16, 2024, in Hyderabad to discuss the development of coal and lignite gasification projects across India.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a process where coal undergoes partial oxidation with air, oxygen, steam, or carbon dioxide to produce a fuel gas.
- This gas serves as an alternative to piped natural gas or methane for energy generation.
- Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) is a technique involving the conversion of coal into gas within the seam, extracted through wells.
- Production of Syngas: This process yields Syngas, a mixture primarily comprising methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas finds applications in producing fertilisers, fuels, solvents, and synthetic materials.
- Significance: In manufacturing, steel companies traditionally rely on costly imported coking coal. Syngas derived from coal gasification offers a cost-effective alternative.
- It is utilized in electricity generation, chemical feedstock production, and hydrogen-based applications like ammonia production and fueling a hydrogen economy.
Advantages of Coal Gasification:
- Coal gasification offers a solution to local pollution issues.
- It is deemed environmentally cleaner than direct coal combustion.
- Decreasing dependence on imported natural gas, methanol, ammonia, and other vital commodities, enhances energy security.
- This technology has the potential to mitigate environmental impacts by curbing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable approaches, aligning with India's global objectives for a more environmentally sustainable future.
Concerns Associated with Coal Gasification Plants?
- The main disadvantage of coal gasification is that it is an expensive process.
- The process can produce a number of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and mercury.
- The process produces a lot of ash, which can pollute the environment.
- The process uses a lot of water, which can lead to water shortages in areas where it is used.
8th Century Kotravai Sculpture from Pallava Period Discovered (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, archaeologists discovered an eighth-century Kotravai sculpture, an artefact that dates back to the Pallava period, near Ulundurpet, Tamil Nadu.
About the Kotravai Sculpture:
- Kotravai sculpture is made in a slab stone of five-feet height and four-feet width.
- The idol is depicted with eight hands, indicating its origin in the eighth century during the Pallava period.
- The sculpture depicts various elements such as chakkara, sword, bell, and abhaya mudra in the right hands.
- Conch, bow, shield, and Uru Mudhra are shown in the left side hands along with bangles in all hands.
- The presence of trishul (soolam) and lion (simmam) on the right side of head, and blackbuck (kavarimann) on the left side.
- Kotravai is portrayed standing on the head of a buffalo, with two guards on each side.
About the Pallava Dynasty:
- The Pallava Dynasty, a prominent power in South India, thrived from the 3rd to the 9th centuries.
- Their dominion encompassed the northern regions of Tamil Nadu, portions of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana, with Kanchipuram serving as their capital.
- The Pallavas were known for their patronage of Buddhism, Jainism, and Brahminical faith, as well as their support for music, painting, and literature.
- Origins: Initially vassals of the Andhra Satavahanas, the Pallavas gained autonomy following the latter's decline in Amaravati.
- Gradually expanding southward, they established their capital in Kanchipuram during the 4th century CE.
- Under the reigns of Mahendravarman I (571 - 630 CE) and Narasimhavarman I (630 - 668 CE), the Pallava realm experienced significant growth in wealth and power.
- According to the accounts of Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang, Bodhidharma, the founder of the Chan (Zen) school of Buddhism in China, was purportedly a prince of the Pallava empire.
- The Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang visited Kanchipuram, the capital of Pallavas, during the reign of Narasimha Varman I and lauded their benevolent governance.
Architectural Contributions of the Pallavas:
- The Pallava Dynasty is renowned for its patronage of Dravidian architecture, particularly temple construction.
- They played a pivotal role in the evolution from rock-cut architecture to stone temples.
- Their most celebrated architectural achievements can be found in Mahabalipuram, which flourished as a significant hub of art, architecture, and literature during Pallava rule.
- Narasimhavarman II commissioned notable structures such as the Kailasanatha Temple in Kanchipuram and the Shore Temple.
- Among these temples, Kailasanatha and Vaikuntaperumal stand out for their architectural excellence.
- The Vaikuntaperumal shrine, erected in the 8th century AD, is renowned for its intricate sculptures depicting Pallava history.
- Religion: The Pallavas embraced Shaivism, a predominant local religion, thereby aligning themselves with Dravidian cultural traditions.
Military Engagements and Decline of the Pallava Dynasty:
- Throughout their reign, the Pallavas engaged in persistent conflicts with both the Chalukya Dynasty to the north and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola and Pandyas to the south.
- The Pallavas faced ongoing battles with the Chalukyas of Badami and ultimately succumbed to the supremacy of the Chola kings in the 8th century CE.
- The ascent of the Rashtrakutas marked the decline of the Pallava Dynasty.
- In 897 AD, Vijayalaya, the Chola King, decisively defeated Aparajitavarman, the last Pallava King, thereby sealing the fate of the Pallava Dynasty.
Regulating India's Online Gaming Industry (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will act as a regulator for the online gaming sector rather than an industry-led self-regulatory organization (SRO).
What are Online Games?
- Online games refer to games that are played over some form of computer network, most often the Internet.
- Online games can range from simple text-based games to games incorporating complex graphics and virtual worlds populated by many players simultaneously.
Types of Online Gaming:
- e-Sports: Originally played offline or on gaming consoles, e-Sports now thrive in the online realm, featuring structured competitions among professional players or teams.
- Fantasy Sports: These games involve assembling virtual teams composed of real-life athletes from different sports teams.
- Points are earned based on the actual performance of these athletes, as seen in platforms like Dream11.
- Online Casual Games: These diversions can be skill-based, where success relies on mental or physical prowess, or chance-based, where outcomes are determined by random events, like dice rolls.
How Big is India's Online Gaming Industry?
- The online gaming sector in India is primarily nurtured by a burgeoning startup ecosystem, boasting a robust 27% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
- Projections suggest that the integration of AI and online gaming could contribute up to $300 billion to India's GDP by 2026-27.
- India leads the global charts in terms of the percentage of new paying users (NPUs) in gaming, soaring from 40% in 2020 to an anticipated 50% in 2021.
- Transactional gaming revenue witnessed a notable 26% surge in India, with the number of paying players escalating from 80 million in 2020 to 95 million in 2021, as per a FICCI report.
Challenges Confronting India's Online Gaming Sector:
- Regulatory Void: The absence of a regulatory framework poses challenges in implementing essential measures such as grievance redressal, player protection, data security, and curbing deceptive advertisements.
- Illegal Offshore Markets: Illicit offshore gambling and betting platforms pose threats to financial integrity and national security, with estimated annual tax losses to India amounting to $45 billion.
- Interstate Quandary: Varied state regulations on online gaming create inconsistencies, compounded by the Internet's borderless nature, making enforcement difficult.
- Societal Implications: The surge in online gaming raises concerns about addiction, mental health, financial fraud, and privacy breaches, warranting a comprehensive approach to address these issues.
The Problem of Self-Regulatory Bodies Under the IT Rules:
- The implementation of the IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 represented a significant stride in regulatory oversight.
- According to these rules, online real-money gaming platforms must obtain approval from a regulatory authority, while those not involving real money are exempt from such requirements.
- In April 2023, the government issued online gaming regulations and provided a three-month window for the industry to propose Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs).
- However, the proposals submitted were predominantly influenced by gaming companies and their industry associations, raising concerns about their ability to function as impartial regulatory bodies.
PM-SVANidhi Boosted the Annual Income of Street Vendors (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A study that evaluated the impact of the PM SVANidhi, a small working capital loan scheme for street vendors, has found that the first tranche of `10,000 led to an additional annual income of `23,460 for each beneficiary.
News Summary:
- Commissioned by the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the study was conducted by the Centre for Analytical Finance at the Indian School of Business (ISB) from January to June 2023.
- Although the report's findings will inform the Ministry's assessment of the PM SVANidhi scheme, it is not expected to be publicly released.
Key Findings of the Report:
- 94% of beneficiaries who received the initial Rs 10,000 loan reported using it for business investments, rising to 98% for those who received a second loan.
- The first loan contributed to an average additional monthly income of Rs 1,955, totalling Rs 23,460 over the one-year loan period.
- Approximately 13.9% of disbursed loans were categorized as non-performing assets (NPAs), indicating no payments for three months or more.
- Beneficiaries demonstrated a lower debt-to-income (DTI) ratio compared to typical small businesses, indicating high creditworthiness.
- Despite the PM SVANidhi program, there was limited improvement in street vendors accessing formal credit from other sources, with only 9% having loans from financial institutions.
What is PM SVANidhi?
- The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) stands as a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, launched on June 1, 2020.
- Its core aim is to extend accessible credit to street vendors, enabling them to revive their businesses and achieve self-reliance.
- The scheme is specifically tailored to empower street vendors, including hawkers, rehri walas, thelewala, and those operating in urban and peri-urban areas.
- PM SVANidhi facilitates eligible street vendors to obtain working capital loans devoid of collateral requirements.
- These loans, with a maximum cap of Rs. 10,000 and a one-year tenure, are intended to support vendors in procuring essential items, securing raw materials, and meeting their operational expenses.
- Furthermore, the scheme offers a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, promoting timely repayments and fostering financial discipline.
How Does PM SVANidhi Work?
- The PM SVANidhi scheme operates through a streamlined and accessible application process designed to maximize participation and outreach among street vendors.
- Vendors can apply for the scheme via a dedicated online portal or through Common Service Centers (CSCs) established nationwide.
- Once the application is submitted, it undergoes a brief verification process conducted by relevant authorities.
- Upon successful verification, the loan amount is directly transferred to the vendor's bank account.
- Vendors can then utilize the funds to revive their businesses, purchase inventory, and cover operational expenses.
Key Features and Benefits of PM SVANidhi:
- Affordable Credit: PM SVANidhi offers accessible working capital loans of up to Rs. 10,000 to street vendors, facilitating credit access without the need for collateral.
- Interest Subsidy: The scheme provides a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, incentivizing timely repayments and easing financial burdens.
- Digital Empowerment: PM SVANidhi promotes digital transactions and payments among street vendors, fostering adaptation to evolving business practices and enhancing financial literacy.
- Enhanced Livelihood: By availing of PM SVANidhi benefits, street vendors can improve their livelihoods, expand their businesses, and generate sustainable income for themselves and their families.
- Access to Social Security Schemes: Street vendors enrolled in PM SVANidhi are eligible for various social security schemes, including Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), providing financial coverage and protection during unforeseen events.
Conclusion
The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme stands as a beacon of hope for street vendors throughout India. By offering accessible credit, digital empowerment, and access to social security schemes, PM SVANidhi is propelling the advancement and prosperity of street vendors, empowering them to establish sustainable livelihoods. This groundbreaking initiative, with its manifold advantages and inspiring success stories, underscores the Government of India's dedication to fostering an inclusive and self-sufficient economy.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY) (PIB)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY), a sub-scheme under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana.
About Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana:
- Implemented as a Central Sector Sub-scheme within the broader framework of the PMMSY, this initiative aims to bolster the fisheries sector.
- Funding: With an estimated outlay of Rs. 6,000 crore, the scheme comprises 50% public finance, including contributions from the World Bank and the AFD, and the remaining 50% anticipated investment from beneficiaries and the private sector.
- Duration: Operational for four years from FY 2023-24 to FY 2026-27, spanning all States and Union Territories.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Fishers, Fish (Aquaculture) Farmers, Fish workers, Fish Vendors or such other persons directly engaged in the fisheries value chain.
- Micro and Small enterprises in the form of Proprietary Firms, Partnership Firms and Companies registered in India, Societies, Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), Cooperatives, Federations, Village Level Organizations like Self Help Groups (SHGs), Fish Farmers Producer Organizations (FFPOs) and Startups engaged in fisheries and aquaculture value chains.
- FFPOs also include Farmer's Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Any other beneficiaries that may be included by the Department of Fisheries, Gol as targeted beneficiaries.
Aims and objectives of PM-MKSSY:
- Gradual Formalization of the unorganized fisheries sector through self-registration of fishers, fish farmers and supportive workers under a National Fisheries Sector Digital Platform including the creation of work-based digital identities of fish workers for improved service delivery.
- Facilitating access to institutional financing fisheries sector micro and small enterprises.
- Providing a one-time incentive to beneficiaries for purchasing aquaculture insurance.
- incentivising fisheries and aquaculture microenterprises through performance grants for improving fisheries sector value-chain efficiencies including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
- Incentivising micro and small enterprises through performance grants for the adoption and expansion of fish and fishery product safety and quality assurance systems including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Lower House of Parliament recently passed the Finance Bill moved by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
Context:
- The Lok Sabha passed the Finance Bill, 2024 by voice vote recently.
- Also, the House passed the Appropriation Bill, granting authorization for government expenditures for four months in the upcoming fiscal year.
- The Appropriation Bill is a significant legislative measure that empowers the government to utilize public funds allocated in the annual budget.
- It serves to uphold accountability and transparency by necessitating parliamentary approval for expenditures and prevents unauthorized withdrawals from the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Furthermore, the lower house sanctioned the Rs 1.8 lakh crore budget for the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
What is a Finance Bill?
- The Finance Bill, classified as a Money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution, is an annual presentation in the Lok Sabha following the Union Budget announcement.
- It encapsulates the government's fiscal proposals concerning taxation, expenditure, and other financial affairs.
- Through this bill, the government submits its proposals for imposing new taxes, altering the existing tax framework, or extending the current tax structure beyond the approved period to Parliament.
- Accompanied by a Memorandum elucidating its provisions, the Finance Bill is exclusively introduced in the Lok Sabha, though amendments can be recommended by the Rajya Sabha.
- Approval from both houses of Parliament is requisite for the bill to become law, with a mandate for passage within 75 days of its introduction.
- While all Money Bills fall under the category of Financial Bills, not all Financial Bills qualify as Money Bills.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely focusing on tax proposals is classified as a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Bill addressing taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects is categorized as a Financial Bill.
- Thus, if a Bill entails government expenditure along with other matters, it is designated as a financial bill.
Highlights of the 2024 Finance Bill:
- Stability in Income Tax: With the impending general elections in April-May 2024, the bill prioritizes continuity by retaining the current tax framework for the fiscal year 2024-2025.
- Targeted Relief Measures: Incorporates slight tax concessions tailored to particular sectors or taxpayer groups.
- Promotion of Economic Expansion: Encompasses provisions aimed at fostering infrastructure enhancement, investment stimulation, and streamlining business operations.
- Fiscal Discipline: Pursues fiscal consolidation objectives through proposed strategies to manage expenditures or enhance revenue generation.
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
The Uttarakhand Cabinet on Sunday approved the final draft of the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) without any changes, a day before the state Assembly convenes for a special session to take up the Bill.
What is Uniform Civil Code (UCC)?
- A Uniform Civil Code signifies a unified legal framework for the entire country, applicable across all religious communities concerning personal matters like marriage, divorce, inheritance, and adoption.
- The objective is to replace the current fragmented personal laws that govern interpersonal relationships within different religious communities.
Constitutional Framework:
- Article 44 of the Constitution mandates the State to strive for a Uniform Civil Code applicable to all citizens.
- Positioned in Part-IV as a Directive Principle, Article 44, while not justiciable, serves as a fundamental governance guideline.
- These principles, outlined in Article 37, provide overarching ideas for the State to consider in policy formulation and law enactment.
Current Landscape of Personal Laws:
- In the Concurrent list of the Constitution, matters such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance fall under both Parliament and state legislature jurisdictions.
- Hindu personal laws have been codified into four parts since 1956, while Muslim laws, not codified per se, draw from religious texts.
- Christians, Zoroastrians, and Jews are governed by their own personal laws. Goa stands as an exception, following the Portuguese Civil Code.
Need for Uniform Civil Code:
- A UCC aims to establish equal status for all citizens, addressing the inconsistency and lack of uniformity in personal laws across different religions.
- This inconsistency, conflicting with Article 14's Equality before the Law guarantee, often results in gender disparities.
Challenges and Criticisms:
- While advocating equality, the UCC concept raises concerns about potential clashes with the Right to Freedom of Religion (Article 25).
- Critics argue that separate personal laws uphold the right to practice one's religion, particularly crucial for minorities.
- Striking a balance, the Law Commission's 2018 report suggests preserving diversity in personal laws while ensuring alignment with fundamental rights.
The Way Forward:
- Encouraging a progressive mindset through education, awareness, and sensitization is vital for understanding the spirit of the UCC.
- Simultaneously, discriminatory personal laws should be amended or abolished.
- The Law Commission recommends codifying different personal laws to derive universal principles prioritizing equity, rather than imposing a blanket Uniform Civil Code
Govt To Sell Bharat Rice At Rs 29/Kg in Retail Market (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will launch retail sales of Bharat Rice at ?29 per kg from next week to provide relief to consumers. It has also directed traders to disclose rice stock to control prices.
Context:
- The recent announcement by the Union government regarding the retail sale of rice at Rs 29 per kg through three cooperatives has garnered attention in the news.
- This initiative, known as 'Bharat Rice,' seeks to address the upward trend in rice prices.
- Over the past year, retail prices have surged by 14.5%, while wholesale prices have seen a 15.5% increase.
- This move aims to mitigate the impact of rising rice prices on consumers and ensure the affordability and accessibility of this staple food item.
Recent Developments:
- In response to escalating domestic rice prices and to ensure food security within the country, the Union government implemented measures in 2023.
- These included a ban on the export of white (non-basmati) rice and the imposition of a 20% export duty on par-boiled rice.
- The decision to restrict rice exports was driven by the need to stabilize domestic prices and guarantee an ample food supply for the nation.
- Experts predict that these restrictions are likely to remain in place until the upcoming general election scheduled for April-May 2024.
- Challenges in rice production during the 2023-24 kharif season, exacerbated by dry weather conditions attributed to El Nino, have further complicated the supply situation.
- Despite these trade limitations, local rice prices have remained firm, prompting government warnings to retailers.
Government Intervention:
- Union Food Secretary Sanjeev Chopra highlighted a 14.51% increase in retail rice prices over the past year.
- In response to rising rice prices, the government has mandated traders, wholesalers, retailers, and processors to report their rice and paddy stocks every Friday to manage food inflation and curb speculative activities.
- To counter inflationary pressures, the government has initiated the retail sale of 'Bharat Rice' to the general populace.
- Initially, 5 lakh tonnes of rice will be allocated for retail sale under this brand through agencies like NAFED, NCCF, and Kendriya Bhandar, priced at ?29 per kilogram in 5 kg and 10 kg bags.
- Furthermore, the Food Corporation of India (FCI) has ample stocks of good-quality rice available for sale to traders and wholesalers under the open market sales scheme at a reserve price of ?29 per kilogram.
Status of India’s Rice Exports:
- India holds the position of the world's largest rice exporter, accounting for 45% of the global rice market share.
- During April-May 2023, overall rice exports witnessed a notable increase of 21.1% compared to the previous fiscal year.
- Basmati rice exports in May 2023 alone surged by 10.86% compared to May 2022, reflecting a sustained upward trend.
- The export of non-Basmati rice has been steadily rising over the past three years, with Basmati rice exports in 2022-2023 surpassing the previous year's figures.
- Recent data provided by the government indicates a 15% increase in total rice exports (excluding broken rice) by August 17 compared to the corresponding period in the previous year.
- Regional Dynamics: Thailand anticipates a nearly 25% decrease in rice production for the 2023-2024 season, while Myanmar has halted raw rice exports.
- Similarly, rice availability is expected to be limited in Iraq and Iran.
- India annually exports more than 4 million tons of basmati - a premium long-grain variety famed for its aroma - to Iran, Iraq, Yemen, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and the United States, among others.
Three New Major Railway Corridors Announced Under PM GatiShakti in the Interim Budget 2024-25 (PIB)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Interim Budget for 2024-25 announcement for implementation of three Economic Railway Corridors identified under the PM GatiShakti for enabling multi-modal connectivity.
Context:
- The Interim Budget for 2024-25 has laid the groundwork for implementing three major Economic Railway Corridors under the PM GatiShakti initiative.
- This will enable multi-modal connectivity, including:
- Energy, mineral, and cement corridors
- Port connectivity corridors and
- High-traffic density corridors
Significance of the Three Corridors:
- Logistics Efficiency Boost: These Corridors serve as catalysts for enhancing logistics efficiency, thereby cutting down on the costs associated with rail transportation.
- By streamlining rail movements, they pave the way for smoother and more cost-effective logistics operations.
- Alleviating Rail Congestion: One of their primary roles is to alleviate congestion on heavily trafficked rail routes.
- By diverting some of the traffic to these designated Corridors, the strain on high-density rail networks is relieved, ensuring smoother and more reliable transportation across the board.
- Promoting Modal Shift: The Corridors play a pivotal role in encouraging a modal shift from road to rail and coastal shipping.
- By providing efficient rail connections and integrating coastal shipping options, they offer viable alternatives to traditional road transport, thereby reducing congestion on highways and minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Sustainability: A key benefit of these Corridors is the reduction of the carbon footprint associated with logistics operations.
- By promoting more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as rail and coastal shipping, they contribute to mitigating the environmental impact of freight movement, fostering sustainability in logistics practices.
About PM GatiShakti National Master Plan:
- The government of India initiated the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti National Master Plan to transform the nation's infrastructure.
- PM Modi launched the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP) on 13th October 2021, on the 75th Independence Day to provide multimodal connectivity infrastructure to various economic zones.
- The scheme is expected to smooth out the execution of projects across the nation and foster coordination between different ministries engaged with these projects.
Advantages of PM Gati Shakti:
- It lays out a centralised portal to unite the infrastructural initiatives of 16 central ministries and departments.
- Facilitates these ministries, gives a centralised transportation and logistics grid for smoother data flow and sped up project clearance.
- Large-scale infrastructure projects like UDAAN, expansion of the railway network, Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, and Bharat Net will be executed by the Gati Shakti master plan.
- The Gati Shakti master plan aims to create employment potential for a large number of individuals.
- The plan's three primary targets are smooth multimodal connectivity, enhanced prioritisation and optimal usage of resources to create capacities on time, and resolution of issues like standardisation, disjointed planning and clearances.
- The Gati Shakti mission aims to create world-class infrastructure in the country and foster logistical synergy across various modes of movement.
- The general objective of the drive is to increase competitiveness and economic development in India.
Expansion of Nano DAP (Indian Express)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, presenting the interim budget on (February 1), announced the expansion of the application of Nano DAP on various crops in all agro-climatic zones.
What is DAP?
- Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a fertilizer containing phosphorus and nitrogen, crucial nutrients for plant growth.
- Its chemical formula is (NH?)?HPO?. DAP is widely utilized in agriculture to offer plants a quick and easily accessible nutrient source.
- It ranks as the second most utilized fertilizer in India, following urea. Notably, DAP is rich in phosphorus (P), which plays a vital role in promoting root establishment and development.
- Application of DAP is typically done just before or at the time of sowing to ensure optimal plant growth and development.
What is Nano DAP?
- Nano DAP is an innovative liquid fertilizer formulation comprising nanoparticles of Diammonium Phosphate (DAP).
- Serving as a rich source of nitrogen and phosphorus, the two primary nutrients crucial for crop growth, Nano DAP offers unique advantages.
- Its small particle size, measuring less than 100 nm, coupled with a high surface area, facilitates easy absorption by plant leaves.
- This novel nano-formulation contributes to enhanced crop growth and yield, decreased environmental impact, and improved profitability for farmers.
Why Nano DAP?
- In addition to being more efficient than conventional DAP, Nano DAP has a few other benefits.
- First, it is more pocket-friendly than its conventional counterpart.
- A 500 ml bottle of Nano DAP, equivalent to a 50-kg bag of conventional DAP, is priced at only Rs 600 (compared to Rs 1,350 for the bag).
- Since the government provides significant subsidies on DAP, the adoption of a more inexpensive fertiliser will likely be a significant relief to the government’s subsidy burden.
- Second, for farmers, Nano DAP is also significantly more convenient.
- Simply put, 500 ml bottles are easier to transport, store, and use than 50kg bags.
- The fertiliser is sprayed on crops, with 250-500 ml of DAP, dissolved in water, required per spray, per acre.
- Most importantly, however, India currently imports significant quantities of fertiliser to meet domestic demand.
- The adoption of domestically-produced Nano DAP — produced in Kalol, Gujarat — is set to significantly reduce this import burden.
- This revolutionary step will not only take Indian agriculture forward in foodgrain production but it will also make India self-reliant in fertiliser production.
- The adoption of Nano DAP will help in achieving self-sufficiency in fertilisers and greatly benefit our farmers.
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (PIB)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the continuation of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to be implemented under the Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund:
- This initiative operates as a Central Sector Scheme aimed at incentivizing investments from various entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSMEs, Farmer’s Producers Organizations (FPOs), and Section 8 companies.
- These investments are directed towards establishing infrastructure for:
- Dairy processing and value addition
- Meat processing and value addition
- Animal feed plants
Objectives:
- Facilitating the expansion of milk and meat processing capacity and diversification of products, thereby granting unorganized rural milk and meat producers greater access to organized markets.
- Enhancing price realization for producers and ensuring the availability of quality milk and meat products for domestic consumers.
- Promoting exports and elevating the sector's contribution to export revenue.
- Providing quality concentrated animal feed to cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry, ensuring balanced rations at affordable prices.
- The Government of India offers a 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, including a two-year moratorium, for loans covering up to 90% of the investment.
- These loans are accessible from scheduled banks, the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), NABARD, and NDDB.
- Notably, government entities and cooperatives are excluded from availing benefits under this scheme.
What is Animal Husbandry?
- Animal husbandry encompasses the controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, with a focus on enhancing desirable qualities through breeding.
- It serves as a vital branch of agriculture dedicated to animals raised for various purposes such as meat, fibre, milk, and other products.
- This involves day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the overall management of livestock.
- In India, animal husbandry plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of many farmers, offering significant self-employment opportunities, particularly for landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, and women.
- The sector contributes to providing affordable and nutritious food to millions of Indians through the production of meat, eggs, milk, and other essential items.
- Additionally, it serves as a valuable source of raw materials such as hides, skins, bones, blood, and fat.
- Animals are often regarded as the best insurance against natural calamities like drought, famine, and other adversities, providing a degree of stability to farmers in unpredictable conditions.
Framework for Voluntary Carbon Market in Agriculture Sector (Down To Earth)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The central government recently launched a framework to promote voluntary carbon markets in the agriculture sector.
What are Carbon Markets?
- Carbon markets are trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought.
- Companies or individuals can use carbon markets to compensate for their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing carbon credits from entities that remove or reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- One tradable carbon credit equals one tonne of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas reduced, sequestered or avoided.
- When a credit is used to reduce, sequester, or avoid emissions, it becomes an offset and is no longer tradable.
Why are Carbon Markets Important?
- Scientists warn that 2°C of warming will be exceeded during the 21st century unless we achieve deep reductions in GHG emissions now.
- Effective action will require concerted and sufficient investment, knowing also that the costs of inaction will be far higher.
- The latest IPCC report finds all countries are falling way short, with financial flows three to six times lower than levels needed by 2030 – and even starker differences in some regions of the world.
- Many countries are turning to carbon markets as a key component in driving and financing the necessary transformation to tackle the climate crisis.
How Many Types of Carbon Markets Are There?
- There are broadly two types of carbon markets: compliance and voluntary.
- Compliance markets are created as a result of any national, regional and/or international policy or regulatory requirement.
- Voluntary carbon markets (VCM)– national and international – refer to the issuance, buying and selling of carbon credits, on a voluntary basis.
- The current supply of voluntary carbon credits comes mostly from private entities that develop carbon projects, or governments that develop programs certified by carbon standards that generate emission reductions and/or removals.
Importance of Establishing a VCM Framework in the Agricultural Sector:
- Emission Concerns: Agriculture in India contributes approximately 15% of the nation's greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the urgent need for mitigation strategies.
- Vulnerability: With around 50% of cultivated land being rainfed and more than 80% of farmers categorized as small or marginal, the sector is highly susceptible to the impacts of climate change.
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (2010): This initiative focuses on promoting adaptation measures such as agroforestry, micro irrigation, and soil health management, which not only reduce emissions but also offer opportunities for carbon sequestration.
- Additional Income Opportunities: Through the implementation of these practices, farmers can potentially generate additional income streams.
World's First 'Black Tiger Safari', to be Established in Odisha (TOI)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha is gearing up to provide an unparalleled experience to visitors through its upcoming black tiger safari, offering a rare glimpse into the lives of these majestic creatures in their natural habitat.
What are Black Tigers or Melanistic Tigers?
- Black tigers, also known as melanistic tigers, are a unique phenomenon resulting from a genetic condition called melanism.
- Melanism causes an increased production of melanin, a pigment responsible for hair, eye, and skin colouration, resulting in black or nearly black skin, feathers, or hair in animals.
- In Simlipal Tiger Reserve, many royal Bengal tigers belong to a distinct lineage characterized by higher-than-normal levels of melanin.
- These tigers exhibit black and yellow interspersed stripes on their coats, though they are not entirely black.
- Therefore, they are more accurately described as pseudo-melanistic.
- As per the 2022 All-India Tiger Estimation, 16 tigers were recorded in Similipal Tiger Reserve, out of which 10 were melanistic.
- However, ongoing tiger surveys conducted by the state government suggest that the actual number of royal Bengal tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve may be higher than reported by the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Factors Contributing to (Pseudo) Melanism:
- Research conducted by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) in Bengaluru indicates that a single mutation in the gene Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) is responsible for the enlargement or spreading of black stripes into the yellow background of black tigers.
- Genetic analyses and computer simulations suggest that Similipal's black tigers may have originated from a very small founding population of tigers and are likely inbred.
- Additionally, the isolation of tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve leads to breeding within the population, further contributing to the prevalence of melanism among these tigers.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal, which derives its name from the ‘Simul’ (Silk Cotton) tree, is a national park and a Tiger Reserve situated in the northern part of Orissa’s Mayurbhanj district.
- It spans an expansive area of 2,750 square kilometres (1,060 square miles), bordering Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is a key component of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which encompasses three protected areas:
- Similipal Tiger Reserve
- Hadagarh Wildlife Sanctuary, and
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary
- Biodiversity: Similipal is renowned for its rich biodiversity, boasting a diverse array of wildlife including the majestic Bengal tiger, the iconic Asian elephant, the formidable gaur, and the elusive chausingha.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves site since 2009, it stands as Asia's second-largest biosphere reserve, following the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat.
- Notably, Similipal Tiger Reserve holds the distinction of being the sole natural habitat in India for melanistic royal Bengal tigers, adding to its ecological significance.
Interim Budget 2024: Exporters seek higher allocation for MAI scheme (Business Standard)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the interim Budget 2024, exporters have urged the government to allocate funds worth $3.88 billion for the Market Access Initiative (MAI) scheme to promote Indian exports and help them hit the ambitious $2 trillion target by 2030.
What is the Market Access Initiatives (MAI) Scheme?
- The Market Access Initiative (MAI) Scheme is an Export Promotion Scheme envisaged to act as a catalyst to promote India’s exports on a sustained basis.
- The scheme is formulated on a focus product-focus country approach to evolve specific markets and specific products through market studies/surveys.
- Assistance would be provided to Export Promotion Organizations/Trade Promotion Organizations/National Level Institutions/ Research Institutions/Universities/Laboratories, Exporters etc., for enhancement of exports through accessing new markets or through increasing the share in the existing markets.
- Under the Scheme, the level of assistance for each eligible activity has been fixed.
- The following activities will be eligible for financial assistance under the Scheme:
- Marketing Projects Abroad
- Capacity Building
- Support for Statutory Compliances
- Studies
- Project Development
- Developing Foreign Trade Facilitation Web Portal
- To support Cottage and handicraft units
How does the MAI Scheme work?
- The scheme’s primary goal is to facilitate export growth by enabling entities to enter new markets or enhance their presence in existing markets.
- To accomplish this, the scheme provides predetermined levels of assistance for each eligible activity.
- By directing attention to key products and specific markets, the MAI Scheme serves as a catalyst for driving India’s export expansion in a sustainable and strategic manner.
Who is eligible to receive assistance under the MAI Scheme?
- Various entities are eligible to receive financial assistance under the MAI Scheme, including:
- Export promotion organizations
- Trade promotion organizations
- National level institutions
- Research institutions
- Universities
- Laboratories
- Individual exporters
- Start-ups
Who administers the MAI Scheme?
- The MAI Scheme is administered by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, through the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
From red ant chutney to black rice, the 7 Odisha products that have bagged GI tags (Indian Express)
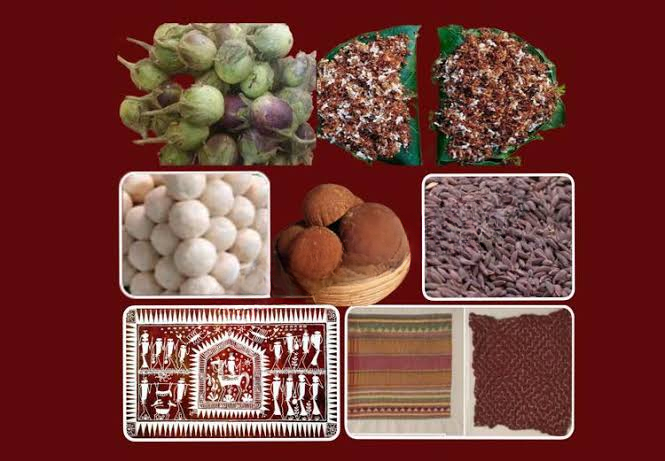

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Seven products from Odisha, ranging from the Similipal Kai chutney made with red weaver ants to the embroidered Kapdaganda shawl, have bagged the coveted Geographical Indication (GI) tag in recognition of their exclusivity to the state.
What is Geographical Indication (GI) Tag?
- Geographical Indications of goods refer to the place of origin of a product.
- Such tags are accorded as they convey an assurance of quality and distinctiveness, attributable to the fact of its origin in a specific geographical locality, region or country.
- In India, the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, awards GIs.
- A GI registration is given to an area, not a trader, but once a product gets the registration, traders dealing in the product can apply to sell it with the GI logo.
- Authorised traders are each assigned a unique GI number.
- If any unauthorised trader tries selling the product under that name, they can be prosecuted under The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- A marker of authentic products, the GI tags also help protect the interests of the local growers and artisans by preventing duplicity of the products and sale from unauthorised traders.
- Consumers, through the tags, can know which goods are certified.
The Seven Products and Their Distinctiveness:
- Kapdaganda shawl: Woven and embroidered by the women of the Dongria Kondh tribe, a particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) in the Niyamgiri hills in Odisha’s Rayagada and Kalahandi districts, the shawl reflects the rich tribal heritage of the Dongria Kondhs.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Green symbolises the mountains and hills, and yellow stands for peace and happiness.
- Red stands as the symbol of blood.
- The motifs in the shawls are mostly lines and triangles, believed to be a reflection of the importance of mountains for the community.
- The shawl is worn by both men and women and the Dongrias gift it to their family members as a token of love and affection.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Lanjia Saura Painting: The painting is also known as Idital. The artworks are famous for their beauty, aesthetics, ritualistic association and iconography.
- The art form belongs to the Lanjia Saura community, a PVTG largely residing in the Rayagada district.
- These paintings are in the form of exterior murals painted on the mud walls of homes.
- White paintings figure over a crimson-maroon background.
- It is believed that the Lanjia Sauras paint their walls with Idital artworks to show gratitude to their deities and forefathers, and also for the well-being of their community.
- Reflecting the love and affection of the primitive tribes for nature, they feature subjects like tribal humans, trees, animals, birds, the Sun and the Moon.
- Koraput Kala Jeera Rice: The black-coloured rice variety, also known as the ‘Prince of Rice’, is famous for its aroma, taste, texture and nutritional value.
- Tribal farmers of the Koraput region have preserved the rice variety for around 1,000 years.
- As the rice grains resemble cumin seeds, it is also called Kala Jeera. Consumption of the rice variety helps in increasing haemoglobin levels and improves metabolism in the body.
- The farmers and producers of Koraput Kala Jeera rice have followed the traditional knowledge and practices in cultivation.
- Similipal Kai chutney: The chutney made with red weaver ants is a traditional delicacy of the tribals in Odisha’s Mayurbhanj district.
- The ants are found in the forests of Mayurbhanj, including in the Similipal forests – Asia’s second-largest biosphere.
- Rich in medicinal and nutritional value, the chutney is believed to be a good source of nutrients like protein, calcium, zinc, vitamin B-12, iron, magnesium, potassium, etc.
- The tribals prepare the Kai chutney by grinding the ants manually on a Sil Batta or the grinding stone.
- Mayurbhanj’s tribals also earn their livelihood by selling the red ants and the chutney made from the ants.
- They believe that its consumption helps boost immunity and prevents diseases.
- Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal: Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal is known for its prickly thorns on the stems and the whole plant.
- The green and round fruits contain more seeds as compared to other genotypes.
- It is famous for its unique taste and relatively short quick cooking time. The plants are resistant to major insects and can be grown with minimal pesticide.
- It is being widely cultivated in Nayagarh district of the state.
- Odisha Khajuri Guda: Odisha’s “Khajuri Guda” or jaggery is a natural sweetener extracted from date palm trees and has its origin in the Gajapati district.
- Traditionally, the jaggery is prepared in a trapezoidal form called ‘Patali Gur’ and is organic by nature.
- It is dark brown and has a unique taste.
- Dhenkanal Magji: Dhenkanal Magji is a type of sweet made from cheese from buffalo milk, with distinct characteristics in terms of appearance, taste, flavour, shape, and size.
- It also has unique nutritional values that distinguish it from other cheese-based sweets.
- The sweet is prepared by draining moisture from the cheese and then frying it, finally forming balls from the mixture.
Cabinet clears PRITHVI initiative for ease of research in earth sciences (Indian Express)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government Friday approved an initiative that will give it the flexibility to pursue research and use funds allocated to five different sub-schemes related to earth sciences over a five-year period.
About the PRITHVI Scheme:
- The PRITHVI Scheme is an initiative by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) designed to deepen our understanding of the Earth and its essential indicators.
- With a substantial allocation of Rs 4,797 crore spanning 2021-26, this comprehensive initiative aims to significantly advance research, modeling, and service delivery in critical domains like weather, climate, oceans, and polar regions.
- The scheme amalgamates five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere and Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems and Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training, and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Collectively, these programs strive to deepen our comprehension of Earth's vital signs and translate scientific knowledge into practical services for the benefit of society, the environment, and the economy.
Objectives:
- A primary aim of PRITHVI is to enhance and sustain long-term observations across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth.
- This facilitates the recording and monitoring of vital signs and changes within the Earth System.
- The scheme places emphasis on developing predictive models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards while advancing our understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring polar regions and high seas is a significant aspect, targeting the discovery of new phenomena and resources.
- The scheme underscores the development of technology for exploring and sustainably harnessing oceanic resources for societal applications.
Implementation:
- Various components of the PRITHVI scheme are interdependent, executed in an integrated manner through the collective efforts of the institutes under the MoES.
Is Halley’s Comet returning? (India Today)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The celestial calendar for 2023 is set to offer a spectacular show as the Orionid meteor shower is expected to rain down its greatest number of meteors on the mornings of October 21 and 22.
About the Orionid Meteor Shower:
- An annual celestial spectacle illuminating the night sky every October, the Orionid meteor shower is a captivating phenomenon with a fascinating origin.
- This cosmic event transpires as Earth traverses the remnants of debris left by Halley's Comet, officially designated as 1P/Halley.
- Halley's Comet, on a roughly 76-year orbit around the sun, sheds dust particles from its nucleus during each passage through the inner solar system.
- This process creates a distinctive trail of debris along its path.
- In late October each year, Earth intersects this celestial trail, giving rise to the mesmerizing display known as the Orionid meteor shower.
- Measuring about five by nine miles in size, Halley's Comet undergoes a remarkable transformation, losing between three to ten feet of material with each journey through the inner solar system.
- The resulting debris becomes the source of the Orionid meteors.
- This celestial event offers a visual treat for observers in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres, particularly during the post-midnight hours.
- It provides an opportunity to witness the graceful streaks of light as the meteors traverse the night sky.
What are Meteors?
- Meteors, often referred to as "shooting stars," are a captivating manifestation of meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at high speed and subsequently burning up.
- Meteor showers, occurring annually or at regular intervals, are linked to the Earth passing through the dusty debris trail left behind by a comet.
- In the case of the Orionid meteor shower, the meteors are named after the constellation Orion, close to where these luminous streaks appear in the sky.
- This annual celestial event not only captivates observers with its dazzling display but also serves as a reminder of the dynamic interactions between Earth and the celestial bodies that grace our cosmic neighbourhood.
Is Pegasus spyware targeting journalists in India? (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amnesty International and Washington Post recently announced that it has found the presence of Pegasus spyware, sold only to governments, on two Indian journalists’ phones.
What is Pegasus Spyware, and How Does it Infiltrate Devices?
- Pegasus is a sophisticated form of malware, covertly designed to gather information without the user's knowledge.
- Developer: Developed by the Israeli security firm NSO Group.
- Objectives: Pegasus serves three primary purposes:
- Collecting historical data on a device discreetly.
- Continuously monitoring user activities and gathering personal information.
- Transmitting the collected data to third parties.
Infiltration Mechanisms:
- Pegasus utilizes "zero-click exploits," exploiting vulnerabilities in popular apps like iMessage and WhatsApp.
- Notably, zero-click exploits require no user interaction, differentiating them from typical cyberattacks.
- Network injection attacks are another method employed by Pegasus, where unsecured websites are used to infiltrate devices within milliseconds of the user's visit.
What is a Zero-click exploit?
- A zero-click exploit involves the installation of malicious software on a device without the device owner's consent.
- Notably, it does not require any action from the device owner to initiate or complete the installation.
Specific Exploit in the Recent Case with Indian Journalists:
- The particular exploit reportedly used in the incidents is known as BLASTPAST (previously identified as BLASTPASS), unfolding in two phases.
- Initial Phase: The attack aims to establish a connection with Apple HomeKit, a platform enabling users to control various smart devices on their network.
- The primary objective of this phase might be to assess how the device could be vulnerable to exploitation or to maintain visibility for potential future attacks.
- Second Phase: Malicious content is sent through the iMessage app to the target device.
- This stage is pivotal as it delivers the complete spyware payload, enabling extensive surveillance and data collection.
Chennai's Pallikaranai Wetlands Welcoming Migratory Bird Flocks (The Hindu)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
With over 150 garganeys, and several other species, including waders and raptors, flocking the Pallikaranai marshland, the curtain for the migratory season has been raised.
About Pallikaranai Marshland:
- Location: Pallikaranai marshland is a freshwater and partly saline wetland, located approximately 20 kilometres south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- The eastern border of the marsh is flanked by the Buckingham Canal.
- Rich Ecosystem: The diverse ecosystem of Pallikaranai supports an impressive array of wildlife, including 115 bird species, 10 mammals, 21 reptiles, 10 amphibians, 46 fish, nine molluscs, five crustaceans, and seven butterfly species.
- Notable Species: Among the diverse wildlife are noteworthy species such as the Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis), glossy ibis (Plegadis falcinellus), grey-headed lapwings (Vanellus cinereus), and Pheasant-tailed jacana (Hydrophasianus chirurgus).
- Biodiversity Significance: Beyond its biodiversity, the marshland serves a crucial role in flood prevention for Chennai, absorbing water during wet periods and releasing it during dry spells.
- Environmental Threats: Despite its ecological importance, the site faces threats from invasive non-native species, household sewage, urban wastewater, and periodic droughts.
- Ramsar Designation: Acknowledging its ecological significance, Pallikaranai marshland holds the status of being one of India's Ramsar sites, recognized for its importance in wetland conservation on an international scale.
Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission (HT)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Dr Aroh Barjatya, an Indian-origin scientist is set to lead the multi-institution NASA rocket mission on October 14.
About Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission:
- The APEP mission entails the launch of three rockets, each equipped with scientific instruments, to explore changes in the upper atmosphere during a solar eclipse, particularly during the critical phase of sudden light reduction.
- Mission Objective: To investigate alterations in the ionosphere induced by the abrupt decrease in sunlight during an eclipse, leading to the generation of waves in this atmospheric layer.
- Measurements will encompass changes in electric and magnetic fields, as well as variations in density and temperature.
- Launch Details: The launch site is the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, with a specific focus on studying the ionosphere's response during an eclipse.
- Potential Impact on Communications: NASA notes projections indicating a temperature and density reduction in the ionosphere during the eclipse, potentially causing disruptive wave disturbances that could affect GPS and satellite communications.
- Process: Rockets will be strategically positioned just beyond the path of annularity, where the Moon directly aligns with the Sun.
- Each rocket will deploy four compact scientific instruments designed to capture data on electric and magnetic fields, density, and temperature changes.
- NASA's primary objective is to achieve unprecedented simultaneous measurements from multiple ionospheric locations during a solar eclipse.
- Rationale for Rocket Selection: Sounding rockets were chosen for their precision in pinpointing and measuring specific regions of space.
- Their ability to investigate lower altitudes, inaccessible to satellites, makes them ideal for this mission.
- Sounding rockets offer precise data recording as they ascend and descend during suborbital flights, covering altitudes ranging from 45 to 200 miles (70 to 325 kilometres) above Earth's surface along their flight path.
Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently gave its approval for the three-year extension of fast-track courts that are specifically used to handle sexual offense cases.
About Fast Track Special Court (FTSC):
- The Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) initiative started in August 2019 as a centrally sponsored scheme to handle cases related to rape and the POCSO Act.
- Originally planned for one year, it got extended to March 2023, and now it's extended further until March 2026 with a financial allocation of Rs. 1952.23 crore from the Nirbhaya Fund.
- These specialized courts, totaling 761, including 414 exclusive POCSO Courts, operate across all States and Union Territories.
- The Department of Justice, Ministry of Law & Justice, oversees their implementation.
- The primary aim is to expedite justice, offering quick relief to victims and reinforcing the nation's commitment to ending sexual and gender-based violence.
- The expected outcomes of this scheme are significant.
- They include a substantial reduction in pending cases related to Rape & POCSO Act, providing swift access to justice for victims through improved facilities and expedited trials, and reducing the burden on the judicial system by managing the number of cases effectively.
Comet P12/Pons-Brooks (The Hindu)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Astronomers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have used the Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT) in Hanle, Ladakh, to photograph the Comet P12/Pons-Brooks.
About Comet P12/Pons-Brooks:
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is a Halley-type periodic comet that was first discovered by Jean-Louis Pons on July 12, 1812.
- It is nicknamed the 'Devil Comet' or likened to the 'Millennium Falcon' for its distinctive appearance.
- It has an orbital period of about 71.3 years.
- During its closest approach to the Sun or perihelion, the comet comes within about 0.78 astronomical units (AU) of the Sun, while at its furthest point, or aphelion, it is located at a distance of about 17.2 AU.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is also known for being the probable parent body causing the κ-Draconids meteor shower.
- It will make its return in 2024 and it is expected to reach its maximum brightness (potentially visible to the naked eye) during the month of April.
- With its closest approach occurring just a few days before a total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, it presents a unique opportunity for skywatchers to potentially view the comet during the eclipse.
- However, since the comet's brightness can be unpredictable, there is no guarantee it will be visible.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is currently in the constellation of Lyra Constellation.
Deepfakes (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government has warned top social media and internet companies that their platforms may be temporarily suspended and even be ordered blocked in case they are unable to tackle the menace of deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- The term "deepfake" combines the concepts of deep learning with the fabrication of content.
- Deepfakes involve the creation of synthetic images and audio using machine-learning algorithms, intending to disseminate misleading content by replacing a real person's appearance, voice, or both with artificially generated likenesses or voices.
- These manipulated creations can either depict nonexistent individuals or simulate real people engaging in actions or utterances they never did.
- Originating in 2017, the word "deepfake" emerged when a Reddit user named "deepfakes" shared explicit videos featuring celebrities.
- The process of crafting deepfakes utilizes machine learning models employing neural networks to manipulate visual and auditory elements.
- To generate a convincing deepfake video, creators train the neural network on extensive real footage of the targeted person, facilitating a realistic understanding of their appearance from various angles and lighting conditions.
- This trained network is then combined with computer graphics to overlay the person onto a different actor.
- Regrettably, this technology is increasingly exploited for malicious purposes, including scams, celebrity impersonation, election interference, social engineering, disinformation attacks, identity theft, and financial fraud.
- The distinguishing factor of deepfakes lies in their challenging detection due to their sophisticated nature.
Dwarf Planet Eris (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered the inside structure of the enigmatic dwarf planet Eris.
About Dwarf Planet Eris:
- This new dwarf planet is the largest object found in orbit around the sun since the discovery of Neptune and its moon Triton in 1846.
- It was discovered on Jan. 5, 2005, and It is larger than Pluto, discovered in 1930.
- Like Pluto, the new dwarf planet is a member of the Kuiper belt, a swarm of icy bodies beyond Neptune in orbit around the sun.
- Eris is named for the ancient Greek goddess of discord and strife.
- The surface of Eris is extremely cold, so it seems unlikely that life could exist there.
- With a radius of about 1,163 kilometers, Eris is about 1/5 the radius of Earth.
- Eris, like Pluto, is a little smaller than Earth's Moon.
- Eris takes 557 Earth years to make one trip around the Sun.
- As Eris orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 25.9 hours, making its day length similar to ours.
- Moons: Eris has a very small moon called Dysnomia.
- Dysnomia has a nearly circular orbit lasting about 16 days.
- Eris most likely has a rocky surface similar to Pluto.
- Atmosphere: The dwarf planet is often so far from the Sun that its atmosphere collapses and freezes, falling to the surface as snow.
- As it gets closest to the Sun in its faraway orbit, the atmosphere thaws.
Wasp-107b (TOI)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In its latest discovery, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has discovered a planet "Wasp-107b" where specks of sand fall as rain.
What is “Wasp-107b”?
- WASP-107b is a warm exoplanet with Neptune’s mass and Jupiter’s radius.
- This makes it ‘fluffy’ compared to the giant gas planets in our Solar System.
- This unusual size-to-mass ratio has given astronomers a unique opportunity to probe its atmosphere roughly 50 times deeper than more dense planets like Jupiter.
- This gas giant, often referred to as a "super-Neptune," holds several remarkable characteristics that set it apart from other known exoplanets.
Key Characteristics of WASP-107b:
- Size and Mass: WASP-107b is roughly the size of Jupiter, but with only about 12% of Jupiter's mass.
- This makes it one of the least dense exoplanets ever discovered.
- Orbit and Proximity: WASP-107b orbits its host star, WASP-107, very closely, completing an orbit in just 5.7 days.
- It is located about 200 light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo.
- Sand Rain: WASP-107b exhibits a unique water cycle similar to Earth's, but with a peculiar twist: instead of water droplets, the planet experiences sand rain.
- These sand grains, composed of silicates, rise from lower atmospheric levels and condense into clouds before falling back down.
- Atmosphere: WASP-107b possesses a puffy atmosphere, likely due to its low density.
- In 2018, scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope detected helium in its atmosphere, marking the first detection of this element in an exoplanet's atmosphere.
- Potential for Atmospheric Characterization: WASP-107b's large size and proximity to its star make it a promising target for future atmospheric characterization studies.
- Scientists hope to glean more insights into the composition and dynamics of its atmosphere.
INDUS-X Initiative (Financial Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On the eve of the India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, the inaugural INDUS-X Investors Meet was held in New Delhi.
What is the INDUS X Initiative?
- The INDUS-X initiative, also known as the India-U.S. Defense Acceleration Ecosystem, was launched in June 2023 during the State Visit of the Prime Minister of India to the United States.
- Its primary objective is to expand the strategic technology partnership and defense industrial cooperation between the governments, businesses, and academic institutions of India and the United States.
- INDUS-X is envisioned as a defense innovation bridge, encompassing Joint Challenges, a Joint Innovation Fund, academia engagement, industry-startup connections, private sector investment in defense projects, mentorship by experts, and niche technology projects, among other initiatives.
- This collaborative effort holds the promise of ushering in a new era of defense innovation and cooperation between India and the United States.
About INDUS X Investors Meet:
- The first-ever INDUS-X Investors Event brought all the stakeholders including Startups, Investors, Incubators, and Industry from both sides under one roof to discuss the collaborative agendas and opportunities thereon.
- The event also had focused panel discussions with a select audience of 50 thought leaders, including start-ups, investors, government officials, and business leaders from the defence industry.
- The panel discussed ‘Investment Opportunities in the Defence Sector’, elaborating upon establishing a sustainable commercial foundation for defence collaboration and co-production.
- The INDUS-X Educational Series (Gurukul) was also launched during the event.
- The Gurukul initiative is aimed at helping innovators and startups to navigate the defence eco-system of the US and India.
Missiles from rebel territory in Yemen miss a ship near key Bab el-Mandeb Strait, US official says (TOI)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Two missiles fired by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
Context:
- Two missiles fired from territory held by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the key Bab el-Mandeb Strait on Wednesday.
- An American warship also shot down a suspected Houthi drone flying in its direction during the incident.
- The ship was carrying Indian-manufactured jet fuel and was heading for either Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
- It was coming from Mangalore in southern India and had an armed security crew on board.
- The Houthis have carried out a series of attacks on vessels in the Red Sea and launched drones and missiles targeting Israel.
About Bab el-Mandeb Strait:
- The Bab-el-Mandeb is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa.
- It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait is a chokepoint between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East and is a strategic link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is one of the world's most important routes for global seaborne commodity shipments, particularly crude oil and fuel.
- The Perim Island divides the strait into two channels, of which the eastern is known as the Bab Iskender (Alexander's Strait), while the western is known as Dact-el-Mayun.
What is the Horn of Africa?
- The Horn of Africa, the world's fourth-largest peninsula, is located in Northeast Africa, extending eastwards from the African mainland and bordered by the Red Sea, Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean.
- Positioned equidistantly from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer, it encompasses diverse landscapes, including the Ethiopian Plateau, Ogaden desert, and Eritrean and Somalian coasts.
- The Horn of Africa includes the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- This region has experienced historical complexities, including imperialism, neo-colonialism, the Cold War, ethnic tensions, intra-African conflicts, poverty, disease, and famine.
In a monthly report, the IEA projected that India's oil product demand growth would slow to 2.5% next year from 4.1% in 2023. (ET)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA) said recently that the "explosive growth" in Indian oil product consumption may be coming to an end.
About International Energy Agency:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an autonomous intergovernmental organization founded in 1974 in Paris, France.
- Its primary focus revolves around energy policies, emphasizing economic development, energy security, and environmental protection, collectively known as the '3 E’s of IEA.'
- The IEA Clean Coal Centre is dedicated to providing independent information and analysis on making coal a cleaner energy source in line with UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Originating in response to the oil crisis of 1973-1974, the IEA's mandate has evolved to include tracking global energy trends, advocating sound energy policies, and fostering international energy technology cooperation.
- Mission: The IEA's mission is to ensure reliable, affordable, and clean energy for its member countries and beyond.
- Focus Areas: Key focus areas include energy security, economic development, environmental awareness, and global engagement.
- The IEA collaborates closely with non-member countries, particularly major producers and consumers, to find solutions to shared energy and environmental concerns.
- IEA’s Membership: The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
- It also includes eight association countries. Four countries are seeking accession to full membership, Chile, Colombia, Israel and Lithuania.
- A candidate country to the IEA must be a member country of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership Criteria:
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- These reserves, accessible to the government even if not directly owned, should be readily deployable to address disruptions in the global oil supply.
- Demand Restraint Program: Candidates are required to implement a demand restraint program aimed at reducing national oil consumption by up to 10%.
- Emergency Response Capability: Member countries must have legislation and organizational frameworks in place to operate Coordinated Emergency Response Measures (CERM) on a national basis.
- Transparent Reporting: Legislation and measures should be established to ensure that all oil companies under the jurisdiction of the candidate country promptly report information upon request.
- Collective Action Capability: Measures must be in place to guarantee the country's capability to contribute its share in collective actions initiated by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- India joined this organization in 2017 as an Associate member.
- However, in 2021, the International Energy Agency (IEA) invited India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, to become its full-time member.
- Major reports published by the IEA include the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report, World Energy Statistics, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, and the India Energy Outlook Report.
Navy plans to get undersea chariots, made in India, for special operations (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is planning to acquire indigenously made swimmer delivery vehicles — also known as underwater chariots and midget submarines — as part of efforts to modernise and strengthen the capabilities of its Marine Commandos (MARCOS) for special undersea operations.
News Summary:
- In a strategic move, the Indian Navy set to deploy domestically manufactured undersea chariots for specialized operations.
- These innovative vessels, designed to accommodate a crew of at least six, will be equipped with cutting-edge lithium-ion batteries for enhanced performance.
- The significant size of these undersea chariots opens up new possibilities, allowing divers to transport larger cylinders.
- This advancement translates to extended underwater missions, thereby amplifying operational capabilities in shallow waters.
- Moreover, the spacious design of these chariots facilitates the carriage of extra weaponry, providing the Navy with increased flexibility for diverse and complex operations.
- This development signifies a noteworthy stride in bolstering the Navy's underwater capabilities through indigenous technological advancements.
What are Chariots?
- Nearly all modern navies in the world use chariots, which are extremely specialized platforms.
- These self-propelled vehicles can be deployed from ships or submarines, tailored to their size and designated roles.
- Notably, during World War II, manned human torpedoes were commonly referred to as chariots.
- Functionality: Chariots prove invaluable for naval operations in shallow waters, offering a spectrum of missions.
- These include shallow-water surveillance, targeted assaults on adversary coastal installations, and even engagements with ships in harbours.
- Particularly advantageous is their ability to grant marine commandos access to areas close to adversary harbours—locations that submarines, constrained by shallow waters, may find challenging to reach.
- Furthermore, these chariots facilitate the efficient transportation of weapons and equipment to operational zones.
- Utilization in India: While detailed information on the swimmer delivery vehicles employed by the Indian Navy is not widely available, some sources suggest the utilization of Italian-made chariots for several years.
- Around 2012, recognizing the strategic importance of these platforms, the Ministry of Defence entrusted Hindustan Shipyard Limited with the construction of two such submarines, underscoring India's commitment to enhancing its maritime capabilities.
What are Marine Commandos (MARCOS)?
- The Marine Commandos, known by the acronym MARCOS and formally recognized as the Marine Commando Force (MCF), stand as the specialized forces within the Indian Navy entrusted with the execution of special operations.
- Established in February 1987, MARCOS possesses versatile capabilities to operate effectively across diverse environments, encompassing sea, air, and land.
- Over time, the force has accumulated valuable experience, earning an esteemed international reputation for its high level of professionalism.
- MARCOS routinely engage in specialized maritime operations in regions such as Jammu and Kashmir, navigating the Jhelum River and Wular Lake with precision and expertise.
PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Schemer (Indian Express)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry has recently announced a fresh target for its PM SVANidhi scheme, focusing on empowering street vendors.
About PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme:
- Launched on June 01, 2020, by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the PM SVANidhi Scheme aims to assist street vendors affected by the Covid-19 lockdown in reviving their livelihoods.
- As a micro-credit initiative, it provides street vendors with a collateral-free loan of Rs. 10,000 at a low-interest rate (below 12%) for one year, facilitating their financial recovery.
- Originally scheduled until March 2022, the scheme has now been extended till December 2024 with a focus on expanding the affordable loan corpus, encouraging digital transactions, and promoting holistic socio-economic development for street vendors and their families.
- Eligibility for the loan requires street vendors who were vending on or before March 24, 2020, and hold a certificate of vending issued by the Town Vending Committees (comprising local authorities and vendors) after conducting a survey.
- The scheme offers several benefits, including an interest subsidy of 7% per annum on timely loan repayment, no penalty on early repayment, cash back incentives up to Rs. 100 per month to promote digital transactions, and the possibility of credit limit escalation for prompt loan repayment.
- The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) serves as the implementation agency for the scheme, ensuring efficient delivery and monitoring of financial support to street vendors across the country.
Yak Churpi (TOI)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Arunachal Pradesh, a northeastern state, achieved a noteworthy milestone as the distinctive and culturally important yak milk product known as 'Yak Churpi' has received the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About 'Yak Churpi':
- Yak Churpi is a special dairy product crafted from the milk of the indigenous Arunachali yak breed.
- It's produced by Brokpas, tribal yak herders who migrate with their yaks to higher altitudes (above 10,000 ft) during summers and return to mid-altitude mountainous areas in winters.
- These exceptional yaks are primarily found in the West Kameng and Tawang districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Churpi is a naturally fermented dairy item with a high protein content.
- It plays a vital role in the diets of tribal communities living in the cold, mountainous regions of the state.
- It's often used as a vegetable substitute and is a common ingredient in vegetable and meat dishes, frequently enjoyed with rice.
- The GI tag for Yak Churpi has significant benefits, including the conservation of yaks and the improvement of the socio-economic status of yak herders.
- Arunachali yaks are unique in terms of their body characteristics, size, strain, and weight, making them the only registered yak breed in India.
SATELLITE INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (Indian Express)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Reliance Jio recently declared that it had effectively tested the first gigabit internet service in India, based on satellite technology.
Facts About:
- Satellite Internet operates in a way similar to satellite TV.
- It begins with an internet service provider launching satellites into space to orbit the Earth.
These satellites, placed in low- or high-Earth orbit, transmit a signal.
- A receiver dish, positioned in your home or business, captures this signal.
It should have an unobstructed view of the sky.
- You connect a modem to this dish to convert the received signal into usable internet connectivity.
- High-speed satellite internet is typically delivered through constellations of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- LEO satellites orbit the planet at altitudes ranging from 250 to 2,000 kilometers.
- Communication between these satellites and Earth occurs using radio waves.
Advantages of Satellite Internet:
- Satellite Internet is ideal for users residing in rural or remote areas, far from urban centers or cable/phone offices.
- It relies on a satellite dish for two-way communication and doesn't require telephone cables or lines.
- When compared to other internet options, satellite internet experiences fewer or minimal network outages.
e-Cabinet System (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Tripura inaugurated an e-cabinet system in Agartala, aimed at advancing digital infrastructure and enhancing the digitization of government services and information.
Facts About:
- The e-Cabinet system is a robust software portal designed for State Governments to facilitate electronic and online Cabinet meetings.
- It has been developed by the National Information Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY).
- Tripura is now the fourth state, and the second in the Northeast region, to implement the e-cabinet system, following in the footsteps of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Key Features:
- Enhances the utilization of technology in meetings and reduces paper consumption.
- Streamlines workflow activities for meetings, covering pre-meeting, during the meeting, and post-meeting phases.
- Offers a user-friendly interface designed for smart tablets, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Incorporates a secure push and pull mechanism to safeguard sensitive Cabinet matters.
- Establishes an institutional memory and knowledge repository, facilitating quick searches and retrieval of information.
- For virtual meetings, eCabinet seamlessly integrates with the Bharat VC solution of NIC.
Benefits and Impact of eCabinet:
- Substantial savings in paper, fuel, and manpower resources.
- Real-time data updates.
- Enhanced information accessibility, promoting coordinated actions.
- Improved decision-making processes and swift retrieval of meeting decisions and action taken.
- Enables virtual participation of Ministers in Cabinet proceedings.
Interbank Call Money Market (ET)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RBI is considering launching a pilot program for a central bank digital currency (CBDC) specifically designed for interbank borrowing or the call money market.
Facts About:
- The Interbank Call Money Market is a short-term financial market where big institutions borrow and lend money to each other at interbank rates, which are the interest rates banks charge when they borrow from one another.
- The loans in this market are very short, typically lasting only a week or less.
- These loans are often used by banks to meet their reserve requirements.
- It's not just banks that use this market; other participants can include financial institutions, mutual funds, large corporations, and insurance companies.
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) (LiveMint)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Taking advantage of the substantial number of written-off loans held by lenders and the government's recovery endeavors, ARCs are seizing the opportunity to acquire these loans.
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs):
- The Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) functions as a distinct financial institution that acquires Non Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions, facilitating the process of cleansing their balance sheets.
- This enables banks to focus on their core banking activities. Instead of expending time and effort pursuing defaulters, banks can opt to sell the troubled assets to ARCs at a mutually agreed-upon value.
Legal Basis:
- The establishment of ARCs in India is supported by the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- The SARFAESI Act streamlines the reconstruction of bad assets, avoiding the need for court intervention.
- Subsequently, numerous ARCs were established and registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which holds regulatory authority over these institutions.
Capital Needs for ARCs:
- Following the 2016 amendment to the SARFAESI Act, ARCs were mandated to possess a minimum Net Owned Fund of Rs. 2 crores. However, in 2017, the RBI increased this threshold to Rs. 100 crores.
- ARCs must maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) equivalent to 15% of their risk-weighted assets.
