Cabinet Approves Establishment of ‘Third Launch Pad’ at ISRO's Sriharikota Facility

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Cabinet, has approved the establishment of a Third Launch Pad (TLP) at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), located at Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. This project marks a significant step in enhancing India’s space capabilities and will support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV) for ISRO’s evolving space exploration programs.
Key Features of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP will be built with an adaptable design, capable of supporting NGLV and LVM3 vehicles with semi-cryogenic propulsion. The launch pad will also serve as a standby for the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Sriharikota. This addition will help ISRO meet its growing launch capacity needs, particularly for future human spaceflight missions and space exploration projects. It will facilitate higher launch frequencies, thus boosting the Indian space ecosystem.
Implementation Strategy and Timeline
The Third Launch Pad is planned to be developed within 48 months (4 years), with the total cost pegged at ?3984.86 Crore. The development will involve maximized industry participation and will utilize existing infrastructure at the launch complex. The project will also leverage ISRO’s experience gained from establishing the earlier launch pads.
The Importance of the Third Launch Pad
The TLP is designed to support the Next Generation Launch Vehicles (NGLV), a key part of ISRO’s vision for space exploration. The facility will not only accommodate heavier vehicles but will also ensure standby capacity for the Second Launch Pad (SLP). Its strategic location at Sriharikota ensures several advantages:
- Proximity to the Equator: This offers a substantial increase in payload capacity due to the additional push provided by the Earth's rotation.
- Safety and Accessibility: The site is free from major international maritime or airline routes, ensuring a safe flight path.
- Geographical Advantage: The launch pad is situated on the eastern coast, enabling launches in an easterly direction, maximizing the benefits of Earth’s rotational speed.
Future Plans for Indian Space Exploration
The establishment of the Third Launch Pad is crucial for the expanded vision of India’s space program, particularly in line with the Amrit Kaal period. ISRO aims to achieve ambitious milestones, such as the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and an Indian Crewed Lunar Landing by 2040. The NGLV will play a pivotal role in these plans, with features like:
- A three-stage vehicle and reusable first stage.
- Semi-cryogenic propulsion, using refined kerosene and liquid oxygen, which will increase payload capacity by three times at 1.5 times the cost of current vehicles.
The Role of Sriharikota in India’s Space Program
Sriharikota, the hub of ISRO’s launch operations, has been integral to India’s space exploration. Currently, the Indian Space Transportation Systems rely on two operational launch pads:
- First Launch Pad (FLP): Established over 30 years ago for PSLV and SSLV missions, FLP continues to support Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) launches.
- Second Launch Pad (SLP): Built primarily for GSLV and LVM3 vehicles, SLP also serves as a standby for PSLV. Over its 20 years of operation, SLP has supported several national missions, including Chandrayaan-3, and is preparing for the Gaganyaan missions.
Pink Fire Retardant

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
As wildfires continue to rage across Southern California, authorities are deploying pink fire retardant from aircraft to help combat the blazes. Despite its widespread use, concerns over its effectiveness and environmental risks have surfaced in recent years.
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- Fire retardant is a chemical mixture designed to slow down or extinguish wildfires. The most commonly used product in the U.S. is Phos-Chek, a brand of retardant.
- Phos-Chek primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry (salts like ammonium polyphosphate), which helps the retardant stay longer and resist evaporation, unlike water.
Purpose and Visibility
- Fire retardants are sprayed ahead of fires to coat vegetation, reducing oxygen and preventing flames from spreading.
- Color is added to the fire retardant, often bright pink, to improve visibility. This ensures firefighters can track its spread and create effective fire lines, helping protect lives and property.
Manufacturer
- Perimeter Solutions manufactures Phos-Chek, which is used for aerial fire suppression efforts.
Effectiveness of Pink Fire Retardant
Limited Effectiveness
- The use of fire retardants like Phos-Chek is not always effective across different wildfire conditions.
- Aerial retardants depend on environmental conditions like terrain, slope, and weather for optimal effectiveness.
- Researchers, including Forest Service scientists, suggest that retardant effectiveness is more limited under changing climate conditions.
- Climate change is narrowing the window of opportunity for using aerial retardants, reducing their impact.
Uncertainty in Impact
- The effectiveness of fire retardants is hard to quantify. Multiple firefighting methods are used simultaneously, making it difficult to attribute wildfire suppression success solely to the retardant.
Environmental Concerns of Pink Fire Retardant
Toxicity and Pollution
- Phos-Chek contains toxic metals such as chromium and cadmium, both of which are harmful to humans and the environment.
- Chromium and cadmium are linked to serious health issues, including cancer and liver/kidney diseases.
- Aquatic life is particularly vulnerable to these toxins, as the chemicals can enter waterways, causing extensive damage to ecosystems.
Impact on Rivers and Streams
- The use of pink fire retardant has raised concerns regarding the contamination of rivers and streams.
- A study by the University of Southern California (USC) in 2024 estimated that 850,000 pounds of toxic chemicals have been released into the environment since 2009 due to fire retardant use.
Growing Use and Pollution
- From 2009 to 2021, over 440 million gallons of retardant were applied across U.S. lands.
- During this period, an estimated 400 tons of heavy metals were introduced into the environment, further exacerbating the pollution levels.
Financial and Practical Concerns
High Cost and Inefficiency
- The cost of deploying fire retardant is significant. Aerial firefighting operations require substantial resources, including planes, helicopters, and large quantities of retardant.
- Environmental experts argue that using fire retardant from planes is ineffective and expensive, especially in light of the growing environmental concerns.
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
Study Methodology:
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
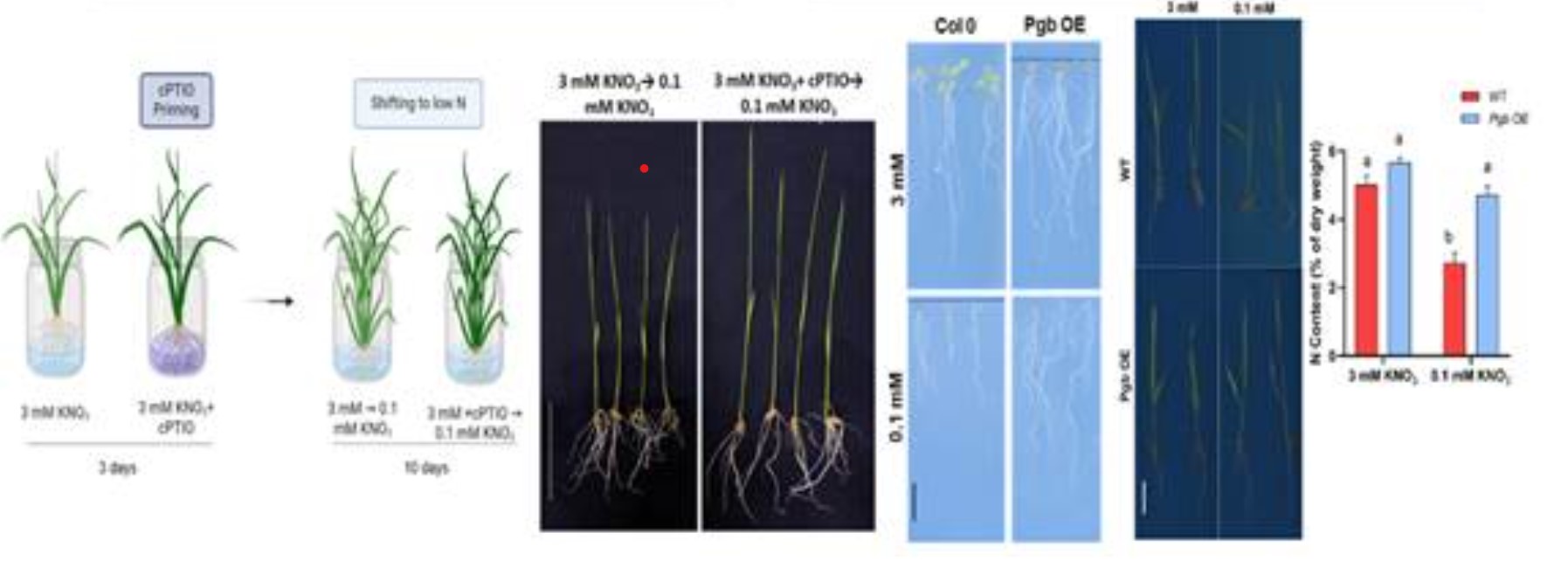
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
Toda Tribe

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Toda tribe, one of the oldest Dravidian ethnic groups in the Nilgiris Hills of Tamil Nadu, celebrated their traditional Modhweth festival marking the New Year.
What is the Modhweth Festival?
- About:
- Celebrated annually on the last Sunday of December or the first Sunday of January.
- Held at the Moonpo temple in Muthanadu Mund village, Nilgiri district.
- The Moonpo temple features a unique vertical spire with a thatched roof and a flat stone on top, making it one of the last Toda temples of its kind in the Nilgiris.
- Rituals and Celebrations:
- Prayers are offered to the deity, Thenkish Amman, for good health, rains, and bountiful harvest.
- Participants perform a traditional dance outside the temple.
- Unique Customs:
- Toda youth showcase their strength and masculinity by lifting a greased boulder weighing around 80 kg.
- Women are not part of the celebrations as per traditional customs.
What is the Toda Tribe?
- About:
- A pastoral tribe native to the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu.
- Classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) in Tamil Nadu.
- The Toda language is Dravidian but stands out for its uniqueness among Dravidian languages.
- Significance:
- Toda lands are part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO International Biosphere Reserve.
- Their territory is also recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Religion and Beliefs:
- Their religious practices are based on a pantheon of gods, with Tökisy (goddess) and Ön (god of the underworld) as central deities.
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR)
- About:
- Established in 1986 as India’s first Biosphere Reserve.
- Located across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
- India’s first biosphere reserve under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- Tribal Groups in NBR:
- Home to several groups such as Adiyan, Aranadan, Kader, Kurichian, Kuruman, and Kurumbas.
- Ecological Significance:
- Represents the confluence of Afro-tropical and Indo-Malayan biotic zones.
- Fauna:
- Home to species like Nilgiri tahr, Nilgiri langur, gaur, Indian elephant, Nilgiri danio (freshwater fish), and Nilgiri barbare.
- Protected Areas in NBR:
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park, and Silent Valley.
Chhattisgarh’s Link between Forest Ecosystem and Green GDP

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
In a first, the Chhattisgarh state has introduced an innovative plan that connects the ecosystem services of its forests with the Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP).
Key Highlights:
Chhattisgarh's Green GDP Initiative:
- First State in India to link forest ecosystem services with Green GDP.
- Forests cover 44% of Chhattisgarh's land area, playing a vital role in climate change mitigation.
- Key forest products (tendu leaves, lac, honey, medicinal plants) contribute significantly to the rural economy.
Green GDP:
- Definition: An adjustment of traditional GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and ecosystem degradation.
- Formula:
- Green GDP = Net Domestic Product (NDP) − (Cost of Resource Depletion + Ecosystem Degradation)
- NDP = GDP − Depreciation of Produced Assets.
Importance of Green GDP:
- Traditional GDP overlooks the environmental cost, treating activities like deforestation as economic gains.
- Green GDP adjusts for sustainability, ensuring long-term economic growth aligns with environmental preservation.
Global Context & Initiatives:
- SEEA (System of Environmental-Economic Accounting): Developed by the UN to track economic-environment relationships.
- WAVES: World Bank initiative integrating natural capital into national economic accounts.
- Bhutan’s GNH: Emphasizes ecological sustainability in development.
Benefits of Green GDP for Chhattisgarh:
- Promotes sustainable development by integrating economic and environmental goals.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forests help absorb CO2, playing a key role in carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supports sustainable use of resources, preserving ecosystems.
- Cultural Integration: Acknowledges forests' cultural and spiritual importance to local tribal communities (e.g., sacred groves).
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Valuing Ecosystem Services: Includes clean air (CO? absorption), water conservation, and biodiversity.
- Eco-tourism Promotion: Developing jungle safaris and national parks, boosting local employment.
- Scientific Assessments: Employing experts to quantify forest contributions to the economy.
Challenges of Green GDP Framework:
- Valuation Complexity: Difficult to assign monetary value to non-market environmental benefits like biodiversity.
- Data Gaps: Lack of comprehensive data on environmental degradation and resource usage.
- Implementation: Requires significant changes in accounting systems and policymaking.
- Forest Definition: Plantations like oil palm may be counted as forests, misleading environmental assessments.
- Political Resistance: States may manipulate data to secure funding, prioritizing plantations over natural forests.
- Local Integration: Difficulties in involving local bodies like Panchayats due to literacy and awareness gaps.
Future of Green GDP:
- Sustainable Resource Use: Encourages responsible consumption and production, aligning with SDG 12.
- Climate Action: Contributes to the reduction of fossil fuel reliance and promotes renewable energy, aligning with SDG 13.
- Green Investments: Stimulates green technologies and industries, fostering sustainable economic growth (SDG 8).
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
Five years after the COVID pandemic, China is experiencing a surge in HMPV cases, particularly in children under 14 years of age
Key Highlights:
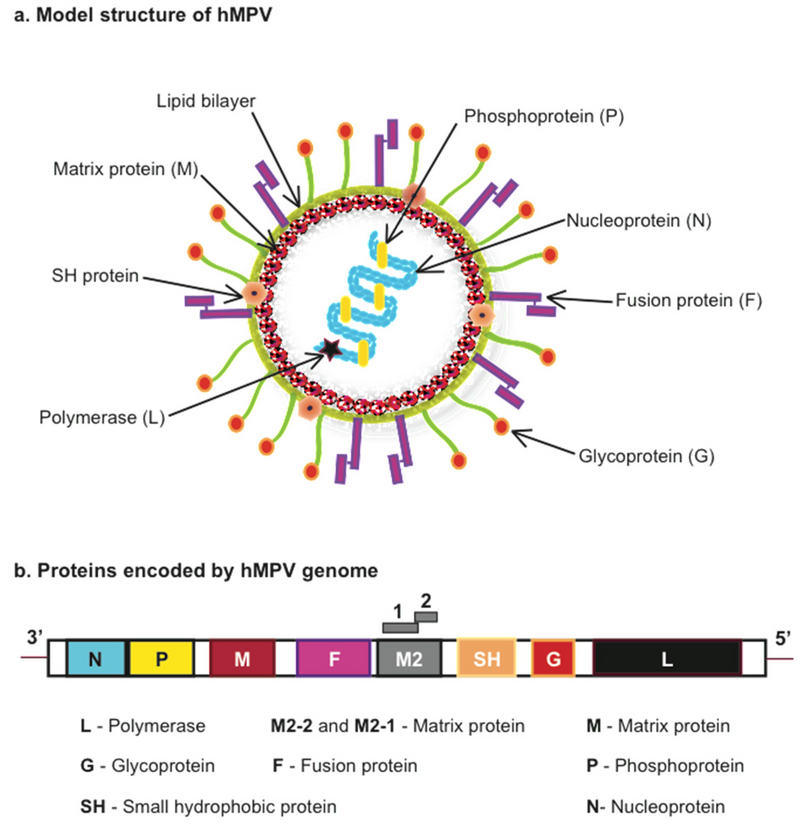
- What is HMPV?
- A respiratory virus from the Pneumoviridae family, discovered in 2001.
- Causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, similar to the common cold or flu.
- Origin and Discovery:
- Identified in the Netherlands in 2001 through genomic sequencing of respiratory samples.
- Risk Groups:
- Children under 5 years, especially infants.
- Elderly individuals (65+).
- Immunocompromised persons and those with chronic respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma).
- Symptoms:
- Common: Cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat.
- Severe: Wheezing, shortness of breath, potentially leading to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Incubation Period: 3-6 days.
- Transmission:
- Spread via droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact (e.g., handshakes, hugs).
- Contaminated surfaces, touching face after contact.
- Treatment:
- No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine available.
- Symptom management: hydration, rest, OTC medications for fever and congestion.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization (oxygen therapy, IV fluids).
- Diagnosis:
- NAATs (Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests): Detect viral genetic material.
- Antigen-based immunoassays: For severe cases or outbreaks.
- Complications:
- Can lead to bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, or COPD flare-ups.
- Risk of ear infections (otitis media) in some cases.
- Prevention:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Physical Distancing: Avoid close contact, wear masks in crowded settings.
- Caution for Vulnerable Groups: Extra care for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Global Situation:
- China: Experiencing a rise in HMPV cases, particularly among children under 14 years.
- India: No reported cases yet, but monitoring the situation closely.
Key Facts:
- HMPV is a winter virus commonly seen in colder months (winter and early spring).
- Estimated 10%-12% of respiratory illnesses in children are caused by HMPV.
- The virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, alongside respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles, and mumps.
No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV; antibiotics are ineffective.
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has recently been renamed MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease), reflecting a shift in understanding of the disease's root causes and its broader implications.
Why the Name Change?
- The primary reason for renaming NAFLD to MASLD is to highlight the metabolic dysfunction as the primary cause of the disease.
- Previously, the term NAFLD focused on the absence of alcohol consumption, which inadvertently shifted attention away from the true contributors, like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- The term MASLD eliminates the stigma associated with "non-alcoholic," which may have misled people into thinking alcohol consumption was the only factor, even though metabolic issues are the central cause.
- The term MASLD shifts the focus towards metabolic dysfunction, making it easier for healthcare professionals to understand, diagnose, and treat the condition more effectively.
The Connection to Metabolic Dysfunction
- MASLD is strongly associated with metabolic issues such as abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, and high blood sugar. These metabolic problems are key contributors to liver fat accumulation.
- People with abdominal obesity are 2-3 times more likely to develop fatty liver disease. MASLD affects about 25% of the global population, and the rates increase significantly (up to 50-70%) in individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity.
- By focusing on metabolic dysfunction, MASLD encourages addressing the root causes rather than just the symptoms, offering a more effective approach to treatment and prevention.
How is MASLD Diagnosed?
Advancements in non-invasive diagnostic methods have improved the ability to diagnose MASLD more easily and accurately, including:
- FibroScan: A non-invasive, painless test to measure liver fat and stiffness, replacing the need for liver biopsy.
- MRI and Ultrasound Techniques: Reliable methods for assessing liver fat and scarring.
- Blood Tests: Common tests like ALT, AST, and GGT assess liver function. Researchers are also exploring new markers like CK-18 fragments and the ELF score (Enhanced Liver Fibrosis) to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Implications for Patient Care
The renaming of NAFLD to MASLD has important implications for patient care:
- Targeted Treatments: By focusing on the metabolic roots, treatments such as weight loss, blood sugar management, and cholesterol control can be prioritized. These interventions help reduce the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, liver failure, and cirrhosis.
- Earlier Diagnosis: MASLD encourages earlier recognition of the condition, which can lead to better management and improved long-term outcomes.
Prevention
Preventing MASLD involves avoiding foods that exacerbate liver fat buildup. Dr. Punit Singla, director at Marengo Asia Hospitals, emphasizes limiting or avoiding:
- Fast food, junk food, and processed foods
- Foods high in sugar, including red and processed meats
A healthier lifestyle with a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can significantly help prevent or manage MASLD.
The ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Its Evolution

- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The ‘no-detention’ policy was a significant part of India’s education reforms under the Right to Education (RTE) Act of 2009. This policy aimed to prevent the detention or expulsion of students until the completion of elementary education (Classes 1-8), with a focus on reducing dropout rates and ensuring every child receives at least basic education. However, the policy has been contentious, with arguments both for and against its implementation.
What was the ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Why Was It Introduced?
The RTE Act (2009) made education free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 14, under Article 21A of the Constitution. Section 16 of the Act specifically prohibited the detention or expulsion of students in elementary education (Classes 1-8). The rationale was to prevent the demotivation and fear of failure that might cause children to drop out of school, especially those from marginalized backgrounds. By promoting automatic progression through grades, the policy aimed to ensure that no child was left behind due to academic struggles.
Key to this system was Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE), which assessed students on a holistic basis, beyond just formal exams, encouraging learning through regular feedback and assessments.
Amendments to the RTE Act (2017 and 2019)
In 2017, a Bill was introduced to amend the RTE Act, following concerns about the effectiveness of the ‘no-detention’ policy. The amended policy allowed for regular exams in Classes 5 and 8. If students failed, they would be given a re-examination within two months. If they still did not meet promotion criteria, detention could be enforced. This amendment empowered the Centre and states to decide whether to detain students in these grades.
The amendment came after criticism of the original policy for promoting students without sufficient learning progress. States like Madhya Pradesh and Punjab argued that no-detention was leading to poor academic performance, and called for a return to the traditional system of promoting students based on examination results.
Arguments for and Against the No-Detention Policy
Arguments for No-Detention:
- Reduced Dropout Rates: The policy helped ensure students, especially from disadvantaged backgrounds, continued in school without the fear of failure, leading to a drop in dropout rates.
- Holistic Development: It encouraged a child-centric learning approach where students were assessed on their overall development rather than just exam performance.
- Social Inclusivity: By promoting students regardless of performance, it was hoped that education would be more inclusive, preventing marginalization of students from lower socio-economic backgrounds.
Arguments Against No-Detention:
- Decline in Learning Outcomes: The policy led to a lack of motivation for students to perform academically. Without the accountability of exams, many students became less serious about their studies.
- Low Teacher Accountability: With automatic promotion, teachers had less incentive to ensure quality learning, leading to an overall dip in teaching standards.
- Impact on Educational Standards: Data indicated a decline in learning levels in government schools, as students were passed through the system without mastering the required skills.
In 2015, the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE) conducted a study suggesting that more flexibility was needed in the policy, allowing schools to retain students who were significantly behind. However, there were differing views within the committee. Some members argued that detention had no proven benefits, and that the real issue was the poor quality of the education system itself.
In 2016, the TSR Subramanian Committee on the New Education Policy suggested continuing the no-detention policy until Class 5, citing evidence of reduced dropout rates and increased enrollment. However, other states pushed for scrapping it due to concerns over declining educational standards.
The Shift Toward Scrapping the No-Detention Policy
By 2019, the RTE Act was amended to give states the discretion to hold back students in Classes 5 and 8, if they failed to meet the promotion criteria. This change came after state feedback that the no-detention policy was having adverse effects on learning outcomes and teacher accountability.
In 2024, the Ministry of Education took further steps to formalize this shift by introducing new rules under the RTE Act Amendment. Students failing to meet the promotion criteria in Classes 5 and 8 will be given additional instruction and an opportunity for a re-examination. If they still fail, they can be detained, with specialized guidance provided to help them catch up.
Which States Continue or Scrapped the No-Detention Policy?
The decision to maintain or scrap the policy varies across states and union territories:
- States Retaining No-Detention Policy: Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, among others, continue to implement the no-detention policy, citing its role in minimizing dropouts and promoting inclusivity.
- States That Have Scrapped the Policy: Delhi, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, West Bengal, and Gujarat have already discarded the policy, opting for examinations and re-examinations in Classes 5 and 8 to ensure better academic accountability.
Why the Controversy?
The debate over the no-detention policy hinges on balancing academic accountability with social inclusivity. Supporters argue that it ensures children from marginalized communities receive their full elementary education, while opponents point to the decline in learning standards, especially in government schools, as a major issue.
In summary, while the no-detention policy was introduced with the noble aim of reducing school dropouts and ensuring every child completed at least elementary education, its effectiveness has been questioned due to concerns over declining learning outcomes. The recent changes represent a shift towards better accountability and quality in education, while still ensuring that children receive additional support before being detained.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
Dark Comets

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Dark comets are a newly identified class of celestial objects that challenge our traditional understanding of comets and asteroids. Unlike regular comets, these objects exhibit characteristics that blur the lines between comets and asteroids, leading astronomers to closely study their nature, origin, and significance.
Discovery and Background
The first hint of dark comets appeared in 2016, when asteroid 2003 RM exhibited strange orbital deviations that suggested it might be a comet in disguise. NASA further fueled this interest in 2017 when it discovered ‘Oumuamua, an interstellar object that entered our Solar System. Though initially classified as an asteroid, its erratic motion and lack of a visible tail led scientists to consider it a dark comet. Since then, several more objects with similar characteristics have been discovered, and astronomers now identify these objects as a new class—dark comets.
Characteristics of Dark Comets
- Appearance: Dark comets do not exhibit the brilliant, glowing tails typically associated with comets. Instead, they resemble asteroids, appearing as faint points of light in space. Unlike bright comets, they do not have a visible coma (a cloud of gas and dust) or a tail, making them much harder to detect.
- Size: Dark comets are typically small, ranging from a few meters to a few hundred meters in diameter. Due to their small size, there is less surface area for material to escape, preventing the formation of the iconic tails seen in traditional comets.
- Orbital Path: These objects follow elongated, elliptical orbits. While some of them travel close to the Sun, they can also venture to the outer reaches of the Solar System, far beyond Pluto, and even into the Oort Cloud—the distant region where long-period comets are believed to originate.
- Spin and Gas Dispersion: Dark comets often rotate rapidly, dispersing gas and dust in all directions. This rapid spin contributes to their invisibility, as the gas and dust are scattered evenly, making it more difficult for astronomers to detect their presence.
- Composition: The composition of dark comets may also play a role in their lack of visibility. Over time, the materials that form the bright tails of comets may be depleted, especially for older objects. As a result, dark comets may not release enough gas to produce a visible coma or tail.
Types of Dark Comets
There are two main categories of dark comets:
- Inner Dark Comets: These are smaller objects that reside closer to the Sun and typically travel in nearly circular orbits. They are often just a few meters in size, with less surface area for gas and dust to escape.
- Outer Dark Comets: These larger objects, measuring over 100 meters in diameter, travel in highly eccentric orbits, similar to Jupiter-family comets. These dark comets follow elliptical paths that bring them close to the Sun and then send them back toward the outer reaches of the Solar System.
Importance of Studying Dark Comets
Dark comets may hold critical clues about the early Solar System and the formation of Earth. Studying these objects can provide insights into the origins of water on Earth, as well as the ingredients necessary for life. Their unique composition and orbits also offer potential for understanding the processes that led to the formation of planets.
Recent Discoveries and Advancements
Astronomers recently discovered 10 new dark comets with the help of the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) on a large telescope in Chile. The DECam, designed to study distant galaxies and stars, has enabled researchers to detect these faint objects by analyzing images of the night sky. Further progress is expected with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory, which will feature the largest digital camera ever built. This new instrument will allow astronomers to capture more detailed images of the night sky and detect fainter objects, potentially doubling or even tripling the number of known dark comets in the next decade.
Key Facts:
- Dark comets lack the characteristic glowing tails of typical comets, instead resembling asteroids.
- They exhibit erratic motions and follow elliptical orbits, often extending beyond Pluto and into the Oort Cloud.
- They are typically small (a few meters to hundreds of meters wide) and spin rapidly.
- The first dark comet was identified in 2016, with more discoveries made in the years since.
- The Dark Energy Camera (DECam) in Chile has been instrumental in detecting these elusive objects, with a new Vera C. Rubin Observatory expected to further enhance detection in the future.
- Studies suggest that between 0.5% and 60% of Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) could be dark comets, many originating from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
At an event celebrating the National Sports Day, The Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour& Employment launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Empower retired athletes through career development.
- Provide tailored education, internships, and skill enhancement.
- Address the human resource gap in the sports sector.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Retired athletes aged 20-50 years.
- Winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- National/state-level medalists or participants in recognized competitions (e.g., National Sports Federations, Indian Olympic Association).
- Courses Offered (16 Courses):
-
- Strength & Conditioning Trainer
- Sports Nutritionist
- Sports Event Management
- Corporate Wellness Trainer
- Sports Masseur
- Sports Entrepreneurship
- Store Manager
- Fitness Centre Manager
- Physical Education Trainer
- Fitness Trainer
- Yoga Trainer
- Venue Supervisor
- Self-Defence Trainer
- Community Sports Trainer
- Camping & Trekking Guide
- Facility Caretaker
- Program Structure:
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12 and above
- Class 11 and below
- Hybrid learning mode:
- Self-paced learning via a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training and internships.
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Internship and Placement:
- Internships offered in sports organizations, competitions, training camps, and leagues.
- Post-course placement assistance and entrepreneurial guidance.
- Implementing Agency:Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) for the pilot phase.
- Importance:
- Provides sustainable career pathways for retired athletes.
- Utilizes the experience and skills of retired athletes to benefit future generations of athletes.
- Contributes to the growth of sports and nation-building.
- National Sports Day (29th August):
- Celebrated in honor of Major Dhyan Chand's birth anniversary.
- Promotes sports and physical fitness in India.
- Awards like Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna presented to honor excellence in sports.
26 Rafale-Marine Jets

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- Deal for 26 Rafale-M jets nearing completion, with final formalities expected to be completed by January 2025.
- These jets are designed for naval operations and will be deployed on INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- Rafale-M Features: Multi-role, advanced avionics, AESA radar, and armaments like Meteor, MICA, SCALP, EXOCET.
- Three Scorpene Submarines: Additional three Scorpene-class submarines to be procured from France.
- These are part of a repeat order to Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), with five of the earlier six already inducted into service.
Nuclear Capabilities:
- INS Arighaat: Successfully fired a Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), marking a significant milestone for India's nuclear deterrence.
- Indigenous Nuclear Attack Submarine (SSN): India’s first indigenous SSN expected by 2036-37.
Strategic Maritime Engagement:
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR): Active monitoring of maritime activities, especially of China's PLA Navy and Chinese research vessels.
- Pakistan Navy Expansion: Acknowledged Pakistan’s efforts to become a 50-ship Navy, including the acquisition of 8 Chinese submarines. Indian Navy is adapting its plans to address this.
Nuclear Submarine Program (SSBN):
- INS Arihant: Conducted multiple deterrence patrols.
- INS Arighaat: Ongoing trials including the recent K4 SLBM test, with a range of 3,500 km.
Naval Vision 2047:
- Navy Chief released Vision 2047 document, outlining the future direction and growth of the Indian Navy.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements:
- Participation in various bilateral and multilateral exercises, including RIMPAC 2024 (Hawaii) and Russian Federation Navy’s Raising Day (St. Petersburg).
Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)was held in New Delhi, India, hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This annual event brings together meteorologists, earth scientists, and satellite data users to discuss advancements in satellite technology for weather and climate monitoring.
Key Facts:
- Objective:
- Promote Satellite Observations: Highlight the importance of satellite data for meteorology and climatology.
- Advance Remote Sensing Science: Foster advancements in satellite technology and its application in weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
- Encourage Collaboration: Facilitate dialogue between satellite operators and users to enhance the use of satellite data across the Asia-Oceania region.
- Discuss Future Plans: Update on the current status and future plans of international space programs.
- Engage Young Scientists: Encourage the involvement of young researchers in satellite science and meteorology.
- Participants:
- Around 150 participants from various countries, including key international space organizations like WMO, NASA, ESA, JAXA, and other meteorological and space entities.
- The conference will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on satellite data application.
- Significance of the Conference:
- Regional Cooperation: AOMSUC promotes stronger cooperation between countries in the Asia-Oceania region, addressing shared challenges in meteorology and satellite data usage.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances satellite data utilization for more accurate weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and climate monitoring.
- Disaster Risk Management: Strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events, improving disaster preparedness and response.
- Capacity Building: Offers training and workshops for local meteorologists, boosting the capacity of countries to use satellite data effectively for weather forecasting and climate services.
- Data Sharing: Encourages collaboration in satellite data sharing, facilitating better access to meteorological data across national borders.
- History of AOMSUC:The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China in 2010. Since then, the conference has been held annually in various Asia-Oceania locations and has become a leading event for the meteorological community.
Flexible UG Degree Completion Norms

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) has approved new guidelines for undergraduate (UG) degree completion, offering flexibility in the duration of academic programs.
Key Details:
- Two Options for Degree Completion:
- Accelerated Degree Programme:Students with exceptional academic performance or those completing additional credits can graduate earlier than the standard duration.
- Extended Degree Programme:Students facing personal, financial, or academic challenges can extend the time for degree completion without facing penalties.
- Objective:
- Enhance flexibility and a student-centric approach to higher education.
- Address challenges like balancing education with personal or professional commitments.
- Institutional Autonomy:Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) can implement these options based on available infrastructure and academic resources.
- Recognition of Flexibility:Degrees completed earlier or later will be treated on par with those completed within the standard duration.
- Alignment with Global Trends:This initiative aligns with global educational trends towards flexible learning paths.
- Support for Interdisciplinary Studies:The new regulations are expected to benefit students pursuing interdisciplinary studies or professional courses.
- NEP 2020 Alignment:The move is in line with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which promotes learner-centric education and skill development.
- Impact:The decision is likely to provide more options for students, making higher education more accessible and tailored to individual needs.
Ngada Festival

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
The Rengma Naga tribe concluded a two-day celebration of the Ngada festival-cum-Mini Hornbill Festival at the Tseminyu RSA ground in Nagaland.
Ngada Festival Overview:
- Celebration: It is an annual celebration observed by the Rengma Naga tribe, marking the end of the agricultural cycle.
- Duration: Typically, an eight-day festival, it is celebrated towards the end of November.
- Significance: It is a festival of thanksgiving, joy, and cultural unity, with a focus on gratitude for the harvest and remembrance of departed souls.
Cultural and Ritual Aspects:
- Rituals: The festival involves rituals for protection from misfortunes, such as fire and evil spirits, as well as prayers for peace and prosperity in the community.
- Agricultural Link: The festival is celebrated after the harvest season, symbolizing the end of the agricultural cycle and the beginning of the storage of crops.
- Official Announcement: The village priest announces the start of the festival, and preparations begin shortly after.
Importance of Ngada:
- Gratitude for the Harvest: The festival is a celebration of the hard work of the agricultural year and the bountiful harvest.
- Cultural Identity: The festival serves as a vital reminder of the Rengma Naga’s cultural heritage and traditions, helping to preserve them for future generations.
- Symbol of Unity: It fosters cultural unity and strengthens community bonds within the tribe.
Tribal Demographics:
- Population: The Rengma Naga tribe has a population of around 62,951 in Nagaland and 22,000 in Assam (according to the 2011 Census of India).
- Ethnic Identity: The Rengmas belong to the Tibeto-Burman ethnic group and identify themselves as Njong or Injang.
Historical and Cultural Background:
- Migration: It is believed that the Rengmas, along with other Naga tribes, migrated from Southeast Asia, crossing the Yunnan Mountain ranges, and eventually settled in the upper Burma region.
- Slavery: Historically, slavery was practiced among the Rengmas, with slaves known as menugetenyu and it sakesa. However, by the time the British arrived, slavery was in decline, and no Rengma tribespeople were known to be slaves.
Economy:
- Agricultural Lifestyle: The Rengma Naga are primarily agriculturalists, relying on Jhum cultivation (shifting cultivation) and wet rice cultivation.
- Crops Grown: They grow staple crops like paddy, along with seasonal crops and fruits.
Religion:
- Traditional Beliefs: Traditionally, the Rengma Naga worship supernatural beings.
- Christianity: Today, most of the Rengma tribe has converted to Christianity.
Nayi Chetna 3.0 – PahalBadlaav Ki

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan launches the third edition of ‘Nayi Chetna – PahalBadlaav Ki’ a month-long national campaign against gender-based violence in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) under the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Led by: DAY-NRLM’s extensive Self-Help Group (SHG) network.
- Aim of the Campaign: Raise awareness and encourage grassroots-level action to combat gender-based violence.
- Campaign Slogan: “EkSaath, EkAwaaz, HinsaKeKhilaaf” (United Voice Against Violence).
- Approach:
- Adopts a "whole-of-government" approach with collaboration from 9 key ministries:
-
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Department of School Education and Literacy
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Department of Justice
- Key Objectives:
- Raise awareness about all forms of gender-based violence.
- Mobilize communities to demand accountability and action.
- Facilitate access to timely intervention and support systems.
- Empower local institutions to take action against violence.
- Goals for Nayi Chetna 3.0:
- Generate widespread awareness about gender-based violence.
- Foster collective action at the grassroots level.
- Drive convergence among government ministries and community stakeholders.
- Create a sustainable and informed movement for gender equality and women’s empowerment.
Narasapur Crochet Lace Craft

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The Narasapur crochet lace craft, which has been a significant part of the cultural and economic fabric of the Godavari region in Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag. The GI tag, registered by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) on March 1, 2024, acknowledges that this unique craft is geographically linked to the West Godavari and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema districts in the Godavari region.
Key Details:
- Historical Background:
- The origins of the Narasapur crochet lace craft date back to 1844, when Macrae and his wife from Scotland introduced the lace-making technique to local women while they were associated with a Christian missionary in Dummugudem (now in Telangana).
- Over time, the craft became a crucial part of the region’s heritage and survived significant historical events like the Indian famine of 1899 and the Great Depression of 1929.
- Craftsmanship:
- The crochet lace is produced using thin threads and delicate crochet needles of varying sizes, resulting in intricate designs.
- The products made include doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bedspreads, table runners, and tablecloths, among others. These items are often exported to international markets like the US, UK, and France.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- The craft is predominantly carried out by women artisans, with over 15,000 women involved in its production. The GI tag is expected to revitalize the industry, especially after its stagnation due to the COVID-19 pandemic and competition from machine-made lace from China.
- The craft is also an important part of the Alankriti Lace Manufacturing Mahila Mutual Aided Co-operative Societies’ Federation Limited, which supports local women artisans and has revived operations at the Alankriti Lace Park in Narasapur.
- GI Tag Benefits:
- The Geographical Indication tag serves to protect the authenticity of the lace products, boost demand, and ensure better market recognition.
- It provides legal protection to the traditional craft, preventing unauthorized use of the term "Narasapur lace" by others and promoting the region's cultural heritage and economic growth.
- Future Outlook:
- With the GI tag, there is hope for increased demand for Narasapur lace products both in domestic and global markets, thus offering a fresh avenue for artisans to revive and sustain the craft.
- Alankriti Federation and other stakeholders are optimistic that the GI tag will significantly revitalize the local economy and empower women in the region.
6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee Meeting
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The 6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee and related meetings for discussions on the review of the AITIGA were held recently in Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Key Negotiation Areas
- 8 Sub-Committees under the AITIGA Joint Committee discussed:
- Market access, rules of origin, SPS measures, standards and technical regulations.
- Customs procedures, economic and technical cooperation, trade remedies, and legal and institutional provisions.
- 5 Sub-Committees met physically during this round of negotiations.
Progress in Discussions
- Textual Discussions: Sub-Committees made progress in discussions on various provisions.
- Tariff Negotiations: Initial steps towards initiating tariff negotiations were covered.
High-Level Meetings Leading to AITIGA Review
- 21st ASEAN-India Economic Ministers Meeting: Held in September 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
- 21st ASEAN-India Summit: Held in October 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
Both meetings urged the Joint Committee to expedite negotiations and aim for the conclusion of the review in 2025.
Bilateral Meetings
- ASEAN delegates held separate bilateral meetings with Thailand and Indonesia to discuss bilateral trade issues.
- Indian and ASEAN Chief Negotiators met to align on the ongoing issues and future steps.
India's Review Demands
- Request for Review: India sought a review of AITIGA (implemented in 2010), citing disproportionate trade benefits favoring ASEAN countries.
- India’s Objectives:
- Enhanced Market Access: India pushed for ASEAN countries, especially Vietnam, to commit to greater market-opening for Indian goods.
- Stricter Rules of Origin (ROO): India requested more stringent ROO provisions to prevent Chinese goods from entering India via ASEAN countries at preferential rates.
Trade Relationship and Economic Impact
- Bilateral Trade:
- Total trade with ASEAN reached USD 121 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Trade during April-October 2024 was USD 73 billion, marking a 5.2% growth.
- Trade Deficit: India’s trade deficit with ASEAN widened from USD 4.98 billion in FY 2010-11 to USD 38.4 billion in 2023-24.
- ASEAN accounts for 11% of India’s global trade.
Future Outlook
- The next meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee is scheduled for February 2025 in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The review process aims to further enhance sustainable trade between India and ASEAN countries.
11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus)

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
The 11th ADMM-Plus held in Vientiane, Laos saw Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh engage in discussions with his counterparts from the United States, Japan, and the Philippines.
Focus: The talks centered on strengthening defence partnerships, regional security, and enhancing cooperation among Indo-Pacific nations.
ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- Platform for Dialogue: The ADMM-Plus is a key platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners—Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- Establishment: The inaugural ADMM-Plus was held in HàN?i, Vietnam on 12 October 2010.
- Annual Meetings: Since 2017, the ADMM-Plus has met annually to enhance dialogue and cooperation amidst an increasingly complex regional security environment.
Objectives:
- Capacity Building: To aid ASEAN members in addressing shared security challenges.
- Promote Trust and Transparency: Enhance mutual trust and confidence between ASEAN and partner nations.
- Regional Peace and Stability: Focus on cooperation in defence and security to counter transnational security challenges.
- ASEAN Security Community: Contribute to realizing the ASEAN Security Community, as per the Bali Concord II, aiming for peace, stability, democracy, and prosperity in the region.
- Vientiane Action Programme: Facilitate ASEAN's efforts towards a peaceful, secure, and prosperous ASEAN with outward-looking relations with Dialogue Partners.
Know Your Medicine (KYM) App

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, has launched a nationwide appeal to strengthen the fight against doping in sports, urging athletes, coaches, and the entire sporting community to embrace the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India's ‘Know Your Medicine (KYM)’ app.
Introduction to KYM App
- Launch: The app was launched by Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, to combat doping in sports.
- Developer: National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) India.
- Purpose: To prevent inadvertent doping by allowing athletes to check whether a medicine contains substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Key Features of the KYM App
- Medicine Verification: The app enables athletes to verify if any medicine or its ingredients contain banned substances listed by WADA.
- Image and Audio Search: Unique search features help users easily search for specific sport-related information.
- Customizable Search: Users can select their sport category and receive relevant, sport-specific information.
- User-Friendly: Designed for athletes, coaches, and sports professionals to quickly verify medicines and ensure clean competition.
Importance of KYM App
- Supporting Clean Sports: The app promotes a fair and ethical sporting culture by reducing the risk of inadvertent doping.
- Integrity of Sports: Helps athletes avoid penalties or bans due to accidental doping, maintaining the integrity of the competition.
- Accessible Information: Provides easy access to information regarding medicines that may contain banned substances, which is crucial for athletes' health and careers.
NADA India's Mission
- Anti-Doping Awareness: The KYM app is part of NADA India’s broader initiative to educate athletes and raise awareness about the dangers of doping.
- Goal: To promote dope-free sports and ensure that athletes and coaches are equipped with the tools needed for compliance with anti-doping regulations.
NADA India: Background and Functions
- Established: NADA India was set up in November 2005 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Mission: To serve as the independent Anti-Doping Organization for India, aiming to create a doping-free sporting environment.
- Key Functions:
- Implementing Anti-Doping Code: Ensuring compliance with the World Anti-Doping Code among all sports organizations in India.
- Dope Testing Program: Coordinating a national dope testing program with stakeholders across various sports.
- Promoting Research and Education: Encouraging research on anti-doping and educating athletes on the importance of staying clean.
- Adopting Best Practices: Ensuring the implementation of high-quality standards for anti-doping programs.
Impact and Significance
- Preventing Doping: The KYM app helps prevent inadvertent doping incidents by providing athletes with the necessary tools to check their medicines.
- Supporting Athletes: It provides athletes with a reliable way to avoid banned substances in over-the-counter medications, thus safeguarding their careers.
- National and International Compliance: Supports India’s commitment to complying with international anti-doping norms, contributing to a global effort to maintain fairness in sports.
World Diabetes Day 2024
- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- World Diabetes Day is observed on November 14th each year to raise awareness about diabetes, its prevention, and management.
- It was created by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Significance: Commemorates the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting, who co-discovered insulin in 1922 alongside Charles Best.
- Theme (2024): "Access to Diabetes Care: Empowering Better Health for All".
History:
- Established in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and World Health Organization (WHO).
- Recognized as a global observance by the UN in 2006.
- Activities: Awareness campaigns, health check-ups, educational seminars, and lighting of Blue Circle Monuments worldwide as a symbol of unity in the fight against diabetes.
Global Diabetes Data (2022):
- Total Diabetic Adults: 828 million globally.
- India's Share: 212 million (approximately 25% of global cases).
- Other Countries:
-
- China: 148 million.
- USA: 42 million.
- Pakistan: 36 million.
- Indonesia: 25 million.
- Brazil: 22 million.
Risk Factors for Diabetes:
- Global Factors: Obesity and poor diets are key contributors.
- India-Specific Factors: Dietary habits, lack of exercise, and socio-economic disparities contribute significantly to the high prevalence.
Untreated Cases:
- Global untreated cases (2022): 445 million (59% of diabetics globally).
- India untreated cases (2022): 133 million (64 million men, 69 million women).
- Complications: Untreated diabetes leads to severe health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and premature death.
Types of Diabetes:
- Diabetes Mellitus: The most common type of diabetes, characterized by issues with insulin production or its efficient use.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
- Autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
- Primarily affects children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes (T2D):
- Insulin resistance combined with reduced insulin production.
- Often linked to lifestyle factors like obesity and physical inactivity.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- Occurs in pregnant women, leading to high blood sugar.
- Typically resolves after childbirth.
- Diabetes Insipidus:
- Imbalance of water regulation due to inadequate secretion or response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
- Leads to excessive urination and dehydration.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Frequent urination.
- Excessive thirst and hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Blurred vision.
- Fatigue.
- Slow-healing wounds.
Role of Insulin in Managing Diabetes:
- Function of Insulin: A hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood glucose levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells.
- In Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin injections or pumps are essential for survival.
- In Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin or oral medications may be prescribed alongside lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise.
Government Initiatives in India:
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS): Focuses on awareness, early diagnosis, and management of diabetes.
- National Health Policy (2017): Aims to reduce premature deaths from non-communicable diseases by 25% by 2025.
- Ayushman Bharat – Health and Wellness Centres: Provides free screenings and consultations for diabetes and other non-communicable diseases.
- Eat Right Movement: Promotes healthier dietary habits to combat obesity and reduce diabetes risks.
- School Health Programs: Aims to educate children on healthy lifestyles to prevent the early onset of Type 2 diabetes.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
Protected Planet Report 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Protected Planet Report 2024, released by UNEP-WCMC and IUCN, evaluates global progress toward achieving Target 3 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF). This target aims to conserve 30% of Earth's terrestrial, inland water, coastal, and marine areas by 2030.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Current Global Coverage
- Land and Inland Waters: 17.6% protected.
- Oceans and Coastal Areas: 8.4% protected.
- Progress since 2020: Minimal increase (<0.5% for both realms), equivalent to an area twice the size of Colombia.
- Remaining Challenges to Achieve Target 3 by 2030
- Land: An additional 12.4% of land area must be protected (equivalent to Brazil + Australia).
- Ocean: 21.6% more marine areas must be safeguarded (larger than the Indian Ocean).
- Key Gaps:
- Only 8.5% of protected areas on land are well-connected.
- Only one-fifth of the areas critical for biodiversity are fully protected.
- Biodiversity representation remains uneven, with some ecological regions having no protection at all.
- Governance and Effectiveness Issues
- Less than 5% of protected land and 1.3% of marine areas have management effectiveness assessments.
- Only 0.2% of protected land and 0.01% of marine areas have undergone equitable governance assessments.
- Indigenous governance covers less than 4% of protected areas despite Indigenous and traditional territories covering 13.6% of the terrestrial areas.
- Ocean Conservation Progress: Most progress is in national waters; however, areas beyond national jurisdiction (the high seas) remain underrepresented (<11% coverage).
- Data Deficiency: Insufficient data to measure biodiversity outcomes, equity, and governance in protected areas.
Importance of Target 3
- Biodiversity Benefits: Protected areas play a critical role in halting and reversing biodiversity loss.
- Ecosystem Services: These areas contribute to clean air, water, climate regulation, and food security.
- Cultural and Economic Significance: They uphold the rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities, ensuring equitable governance and sustainable resource use.
Key Recommendations
- Accelerate Conservation Efforts:
- Expand protected and conserved areas with a focus on biodiversity hotspots.
- Ensure areas are ecologically connected and effectively managed.
- Strengthen Indigenous and Local Contributions:
- Recognize and support the stewardship of Indigenous Peoples and local communities.
- Ensure their voices and knowledge systems are integrated into conservation planning.
- Improve Governance and Equity:
- Address gaps in equitable governance and include rights-based approaches.
- Global Cooperation:
- Increase international financing to developing nations for biodiversity conservation.
- Foster cross-border partnerships and support data-sharing initiatives.
- Enhance Data Availability:
- Collect and disseminate data on the effectiveness of protected areas and their biodiversity outcomes.
India’s Role and Strategy
- Commitment to KM-GBF: India updated its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) to align with the KM-GBF goals, aiming to protect 30% of natural areas by 2030.
- Focus on Restoration: Prioritizes the restoration of forests, rivers, and other ecosystems to maintain essential resources like clean air and water.
- Indigenous Participation: India emphasizes integrating Indigenous territories into its conservation framework.
21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) Meeting

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) meeting was held from November 5 to 6, 2024, at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- The meeting focused on strengthening defence ties between India and the US, covering a wide range of topics aimed at improving military cooperation.
Key Areas of Discussion
- Capacity Building: The meeting discussed initiatives for enhancing defence capacity through training exchanges, joint exercises, and sharing best practices.
- Defence Industrial Cooperation: Both countries explored opportunities for collaborative defence industrial ventures and technology sharing.
- Joint Exercises: The advancement of joint military exercises was highlighted to boost readiness against both conventional and hybrid threats.
- Strategic Objectives: The meeting aimed to enhance interoperability between the two countries' armed forces, enabling more effective joint operations.
Commitment to Strengthen Indo-US Defence Ties
- Strategic Partnership: Both nations reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening the Indo-US defence partnership, recognizing the shared challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Focus on Regional Security: The discussions underscored the importance of ensuring regional security and global stability in the face of emerging threats.
The Role of the MCG
- Purpose: The MCG forum serves as a key platform for enhancing strategic and operational defence collaboration between India and the US.
- Long-term Goals: The MCG aims to build mutual defence capabilities, counter emerging threats, and ensure the security of both nations and the wider region.
Kodo Millet

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Kodo millet is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections in India. It is one of the 'hardiest crops, drought tolerant with high yield potential and excellent storage properties,' according to researchers
Background on Kodo Millet:
- Kodo millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum), also known as Kodra or Varagu, is a hardy, drought-tolerant crop widely grown in India, especially in Madhya Pradesh.
- It is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections of India and is used to make various dishes like idli, dosa, and rotis.
- Kodo millet is valued for its high yield, nutritional benefits (rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants), and storage properties.
Incident in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- 10 elephants from a herd of 13 died over three days in Madhya Pradesh’s Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve.
- The cause of death was suspected to be mycotoxins associated with kodo millet, particularly Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), which is toxic to animals.
Historical Cases of Kodo Poisoning:
- The first human cases of kodo poisoning were reported in 1922 in the Indian Medical Gazette.
- Animals, including elephants, have also been affected by kodo millet consumption, with documented deaths as early as 1983.
- Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), a mycotoxin, was identified as the cause of kodo poisoning in the 1980s.
Why Does Kodo Millet Become Poisonous?
- Kodo millet is grown in dry and semi-arid regions and is vulnerable to fungal infections, particularly Ergot fungus, which produces CPA.
- When the crop encounters rainfall during maturing and harvesting, fungal infection can lead to "poisoned kodo," known locally as 'Matawna Kodoo' or 'Matona Kodo'.
- The mycotoxins in the infected millet are stable and resistant to standard food processing techniques.
Impact of Mycotoxins on Animals:
- Symptoms of poisoning: Vomiting, giddiness, unconsciousness, rapid pulse, cold extremities, limb tremors.
- Nervous and cardiovascular systems are primarily affected, causing liver dysfunction, heart damage, and gastrointestinal issues.
- In severe cases, consumption of infected kodo millet can cause death due to cardiovascular collapse and organ failure.
- Similar symptoms of depression and loss of mobility were observed in animal studies, including in mice.
Solution to Kodo Toxicity:
- Biocontrol agents (organisms that fight harmful pathogens) can help reduce fungal growth and mycotoxin production in kodo millet.
- Good agricultural practices: Sorting, proper storage in airtight containers, and avoiding moisture exposure during threshing can minimize contamination.
- Post-harvest management: Removing infected grains is crucial to preventing the spread of the disease.
Detection of Mycotoxins in Kodo Millet:
- Challenges: Mycotoxins are often undetectable by sight, and traditional methods like chromatography are time-consuming.
- Rapid detection tools: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), lateral flow assays (LFAs), and biosensors offer faster, on-site methods for detecting mycotoxins in kodo millet.
Asset Recovery Interagency Network–Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP)

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- India, represented by the Directorate of Enforcement (ED), has joined the Steering Committee of the Asset Recovery Interagency Network-Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP).
- Leadership Role: India will assume the presidency of ARIN-AP and host the Annual General Meeting (AGM) in 2026, providing a platform for global cooperation in asset recovery and tackling economic crimes.
ARIN-AP Overview:
- Establishment: ARIN-AP is a multi-agency network formed to address the proceeds of crime across the Asia-Pacific region.
- Network Goals: Its mission is to facilitate cross-border collaboration in the areas of asset tracing, freezing, and confiscation.
- Membership: ARIN-AP includes 28 member jurisdictions and 9 observers, and operates as a key component of the Global CARIN Network (Camden Asset Recovery Inter-Agency Network).
- Functioning: ARIN-AP operates through a network of contact points that enable intelligence exchange among member agencies, promoting effective communication and coordination for asset recovery.
Significance of ARIN-AP's Work:
- Combating Economic Crimes: ARIN-AP enhances the efforts of law enforcement agencies in tracing and recovering assets linked to criminal activities, including both movable and immovable assets.
- Informal Exchange of Intelligence: The network allows for the informal exchange of intelligence between agencies, which often accelerates the identification and recovery of proceeds of crime. This can later lead to formal actions through bilateral or multilateral agreements.
- Global Impact: With over 100 jurisdictions in the broader CARIN Network, ARIN-AP plays a key role in global efforts to combat fugitive economic offenders and illicit financial flows.
India’s Contribution and Alignment with G-20 Priorities:
- India’s Leadership: India’s presidency in ARIN-AP will enhance its leadership in asset recovery, facilitating closer cooperation with regional and international law enforcement agencies.
- G-20 Alignment: This role aligns with India’s priorities under the G-20 framework, particularly focusing on the Nine-Point Agenda aimed at tackling fugitive economic offenders and improving asset recovery mechanisms.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
What is LiDAR?
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
Introduction to Innovative Cancer Detection Technique
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
- Scientists have developed an ultrasound-based technique for detecting cancer, aiming to replace traditional biopsies, which are invasive and painful.
- Promising Alternative: The method uses high-energy ultrasound to release biomarkers (RNA, DNA, and proteins) from cancerous tissue into the bloodstream, allowing for early cancer detection with minimal discomfort.
- Presented at Acoustical Society Conference: The technique was discussed at the joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and Canadian Acoustical Association in May 2024.
Traditional Cancer Detection vs. New Ultrasound Approach
- Current Gold Standard - Biopsy: Traditionally, cancer is diagnosed using biopsies, where a tissue sample is extracted using a needle from suspected cancerous areas. Although effective, biopsies are invasive, painful, and carry some risks.
- Ultrasound as a Non-Invasive Alternative: The new method involves using high-frequency ultrasound waves to break off cancerous tissue into droplets, which are then released into the bloodstream. The biomarkers in the droplets can be analyzed for cancerous mutations.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: This ultrasound-based technique increases the levels of genetic and vesicle biomarkers in blood samples by over 100 times, enabling the detection of cancers and specific mutations that are otherwise undetectable in blood.
Key Findings of the Research
- Single Cancer Cell Detection: The technique allows for the detection of a single cancer cell in blood samples. It works by passing ultrasound waves through isolated blood samples, which break apart circulating cancer cells, releasing biomarkers into the blood.
- Cost-Effective: Traditional methods for detecting circulating cancer cells are costly (e.g., the ‘CellSearch’ test costs $10,000). In contrast, this ultrasound method can detect cancer with a much lower cost, around $100 (?8,400).
- Potential for Early Diagnosis: The research shows promise for detecting cancer at an early stage, even before symptoms appear, using blood samples.
Challenges and Next Steps
- Need for Large-Scale Clinical Trials: While the technique shows potential, large cohort studies involving diverse patient groups across different geographies and ethnicities are needed to validate the approach.
- Long-Term Study for Effectiveness: Further research is required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the technique across various cancer types and to determine the ideal biomarker thresholds for early detection.
- Regulatory Approval and Commercialization: If the clinical trials yield positive results, the method could be commercially available in approximately five years, following regulatory approval.
Understanding Cancer and Its Types
- Cancer Definition: Cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body.
- Types of Cancer:
- Carcinoma: Cancer originating in epithelial cells (e.g., breast, lung, prostate cancer).
- Sarcoma: Affects connective tissues like bones and muscles.
- Leukemia: Affects blood-forming tissues, leading to abnormal white blood cell production.
- Lymphoma: Begins in immune cells, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Melanoma: Cancer of pigment-producing skin cells.
- Key Differences Between Normal and Cancer Cells:
- Cancer cells grow uncontrollably and evade immune detection.
- Cancerous cells accumulate chromosomal abnormalities, unlike normal cells, which follow regulated growth patterns.
Chenchu Tribe

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
The Chenchus of Penukumadugu have lived in the dense Nallamala forests for centuries, their existence intertwined with the wilderness around them. However, their inability to keep up with the relentless pace of modernisation has led to dwindling work opportunities under the MGNREGA.
Chenchu Tribe Overview
- Location: Primarily in the dense Nallamala forests, Andhra Pradesh (AP).
- Tradition: Historically hunter-gatherers, now relying on subsistence farming.
- Vulnerable Status: Classified as one of the 12 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in Andhra Pradesh due to low literacy, stagnant population growth, and limited access to development.
- Livelihood: Dependent on forest resources (Non-Timber Forest Produce - NTFP) and agricultural labor.
Impact of MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme)
- MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project: Launched in 2009 to address specific needs of the Chenchus, such as physical strength, food insecurities, and cultural practices.
- Before Discontinuation: Provided 180 days of work per person annually, which helped Chenchus access regular income, improving food security and living conditions.
- Post-Discontinuation (2022):
- The project was integrated into a nationwide MGNREGS framework, reducing workdays to the standard 100 days per household.
- Consequences: Many Chenchus stopped engaging with MGNREGS due to bureaucratic hurdles (Aadhaar and bank linkage), reduced job days, and irregular wage payments.
- Only 1,500 out of 4,000 enrolled households currently participate in MGNREGS work.
Key Issues Post-MGNREGS Reform
- Aadhaar & Bank Account Challenges:
- Lack of literacy and digital skills makes the Aadhaar-based system intimidating.
- Many Chenchus are excluded from PDS and health benefits due to missing or unlinked Aadhaar cards.
- Absence of mobile phones and access to banks makes wage disbursement difficult.
- Irregular Payments & Trust Issues:
- The shift to bank payments has created trust issues, as many Chenchus are illiterate and cannot verify wage deposits.
- Distance from banks (up to 30 km) adds to the difficulty in accessing payments.
Forest Rights and Wildlife Conservation
- Forest Dependency: The Chenchus continue to depend on the forest for food and livelihood, but increasing restrictions due to wildlife conservation (e.g., Nagarjuna-Srisailam Tiger Reserve) have further curtailed their access to forest produce.
- Forest Rights Act (FRA): Many Chenchus have land pattas under the FRA but lack resources or support to utilize their land effectively due to the discontinuation of MGNREGS.
Government and Policy Response
- PVTG Initiatives: Various government initiatives like PM PVTG Mission, Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra, and Janjatiya Gaurav Divas aim to uplift PVTGs, but their impact remains limited without proper implementation of specialized support programs like the MGNREGS Chenchu Special Project.
IMF retains India’s growth projection at 7% for FY25
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised India's GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 7%, up by 20 basis points from its previous estimate of 6.8%.
- India’s Growth Projections:
- Current Fiscal Year (FY2024-25): India’s GDP growth is projected at 7%, unchanged from June 2024 estimates.
- Next Fiscal Year (FY2025-26): Growth expected at 6.5%.
- Growth Decline from FY2023 (8.2%): The slowdown is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand post-pandemic and the economy returning to its potential.
- Global Economic Growth:
- World Output: Projected global growth at 3.2% in both 2024 and 2025.
- Advanced Economies: U.S. GDP growth revised upward to 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
- Emerging Markets & Developing Economies: Growth revised upwards, largely due to stronger economic activity in Asia, with China and India being key contributors.
- Global Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Inflation Decline: Global inflation has decreased from its peak of 9.4% in Q3 2022 to 3.5% projected by end-2025.
- Inflation Outlook: Despite reductions in inflation, price pressures persist in some regions.
- Monetary Policy Tightening: IMF acknowledges challenges due to tight monetary conditions in several economies and their potential impacts on labor markets.
- Global Risks and Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating conflicts in West Asia (e.g., Lebanon) have increased geopolitical risks, potentially affecting commodity markets.
- Protectionism: Growing protectionist policies worldwide are a risk to global trade and economic stability.
- Sovereign Debt Stress: Debt burdens in several countries could become a source of instability.
- Weak Chinese Economy: Slower-than-expected recovery in China remains a significant concern for global economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Risks: Prolonged tight monetary policies in some countries could impact labor markets and economic recovery.
- IMF’s Policy Recommendations for Medium-Term Growth:
- Monetary Policy Neutrality: Countries should adopt a neutral monetary policy stance to balance growth and inflation control.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustment: Build fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy to ensure stability.
- Structural Reforms: Implement structural reforms to boost productivity and cope with challenges like aging populations, the climate transition, and the need for youth employment.
- India’s Economic Outlook - Key Drivers:
- Rural Consumption Growth: The upward revision of India's FY2024-25 GDP forecast to 7% is driven by improved consumption, especially in rural areas.
- Upward Revisions for 2023: The increased growth forecast also reflects positive carryover effects from India's 8.2% growth in 2023.
- Emerging Asia's Growth: The growth outlook for emerging Asia is supported by India and China, though long-term growth prospects for China are weaker (projected to slow to 3.3% by 2029).
- Global Economic Outlook:
- World Growth Projections: Global growth is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025.
- Diverging Growth Rates: Growth across economies is converging as output gaps close, particularly in advanced economies (e.g., U.S. labor market cooling, euro area recovery).
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- 19 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has sanctioned three pilot projects under the National Green Hydrogen Mission to explore the use of green hydrogen in steel production.
- The initiative aims to demonstrate safe and efficient hydrogen-based steelmaking processes, validate their technical feasibility, and evaluate economic viability for low-carbon steel production.
- Objectives of the Scheme:
- Identify and test advanced technologies for utilizing green hydrogen in the steel sector.
- Demonstrate safe and secure operation of hydrogen-based steel production.
- Validate technical and economic feasibility, contributing to decarbonization of iron and steel manufacturing.
- Pilot Project Components:
-
- 100% Hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) using vertical shaft furnaces.
- Hydrogen use in Blast Furnace to reduce coal/coke consumption.
- Hydrogen injection in vertical shaft-based DRI units.
-
- Sanctioned Pilot Projects:
- Matrix Gas and Renewables Ltd
- Capacity: 50 tons per day (TPD).
- Consortium Partners: Gensol Engineering Ltd, IIT Bhubaneswar, Metsol AB (Sweden).
- Simplex Castings Ltd
- Capacity: 40 TPD.
- Consortium Partners: BSBK Pvt. Ltd., Ten Eight Investment, IIT Bhilai.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Capacity: 3,200 TPD (Ranchi).
- Financial Support:
- Total Government Funding: ?347 crore for the three projects.
- These pilot projects are expected to be commissioned within the next three years and may serve as a blueprint for scaling up such technologies in India.
- About the National Green Hydrogen Mission:
- Launched: January 4, 2023.
- Total Budget: ?19,744 crore (up to FY 2029-30).
- Primary Goal: Establish India as a global hub for green hydrogen production and export while fostering decarbonization in sectors like steel, mobility, and energy.
- Key Features of the Mission:
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Supports domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and promotes the production and use of green hydrogen.
- Expected Outcomes by 2030:
- Green Hydrogen Production: At least 5 million metric tons (MMT) annually.
- Renewable Energy: Addition of 125 GW in renewable energy capacity.
- Investment: Over ?8 lakh crore in green hydrogen technologies.
- Employment: Creation of 6 lakh jobs.
- Reduction in Fossil Fuel Imports: Savings of over ?1 lakh crore.
- GHG Emissions Reduction: Avoidance of nearly 50 MMT of annual greenhouse gas emissions.
- SIGHT (Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition):
- Phase-wise Implementation:
- Phase I (2022-26): Focus on demand creation and initial deployment in existing hydrogen-using sectors (like steel and mobility).
- Phase II (2026-30): Expansion to new sectors with a push toward commercialization of green hydrogen.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission aims to significantly decarbonize India’s steel sector and other industries by leveraging hydrogen technology. With ?347 crore allocated for pilot projects in steelmaking, the initiative sets the stage for scalable, low-carbon steel production, contributing to India's clean energy transition and supporting its goal to become a global leader in green hydrogen.
India’s Semiconductor Market Projected to Surpass $100 Billion by 2030
- 17 Oct 2024
In News:
India's semiconductor market is poised to exceed $100 billion by 2030, according to a report from the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association and Counterpoint Research. Currently valued at $45 billion in 2023, the market is projected to grow at an annual rate of 13%, driven by demand in mobile handsets and IT sectors, which together account for over 75% of revenues.
Key Highlights:
- Growth Drivers: The growth is supported by strong demand for electronics and government initiatives like the production-linked incentive scheme. Semiconductors are essential for various industries, including electronics, defense, healthcare, and automotive.
- Importance of Semiconductors: These materials, which include silicon and germanium, are crucial for electronic devices. They can conduct electricity under certain conditions, making them fundamental in transistors, integrated circuits, and devices like LEDs and solar cells.
- Global Context: The global semiconductor supply chain has shown vulnerabilities, particularly during the chip shortage of 2021. Major producers include Taiwan (44% market share), China (28%), South Korea (12%), the U.S. (6%), and Japan (2%). Countries are now focusing on building domestic chip industries to reduce dependency on a few key suppliers.
Factors Favoring India's Growth in Semiconductors:
- Skilled Workforce: India has a vast pool of STEM graduates, providing a skilled workforce for semiconductor manufacturing and design.
- Cost Advantage: Lower labor costs and efficient supply chains position India favorably for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Supply Chain Diversification: India is becoming a hub for back-end assembly and testing operations, with potential for front-end manufacturing.
- Government Support: Initiatives like Semicon India and the India Semiconductor Mission aim to create a robust semiconductor ecosystem, offering substantial fiscal incentives for companies.
Government Initiatives:
- Semiconductor Fab Scheme: Provides 50% project cost support for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Display Fab Scheme: Offers similar support for display manufacturing.
- Chips to Startup (C2S) Programme: Trains 85,000 engineers across academic and R&D institutions.
- Recent approvals for the establishment of semiconductor plants in Gujarat and Assam further bolster this initiative.
New Cancer Therapy Target
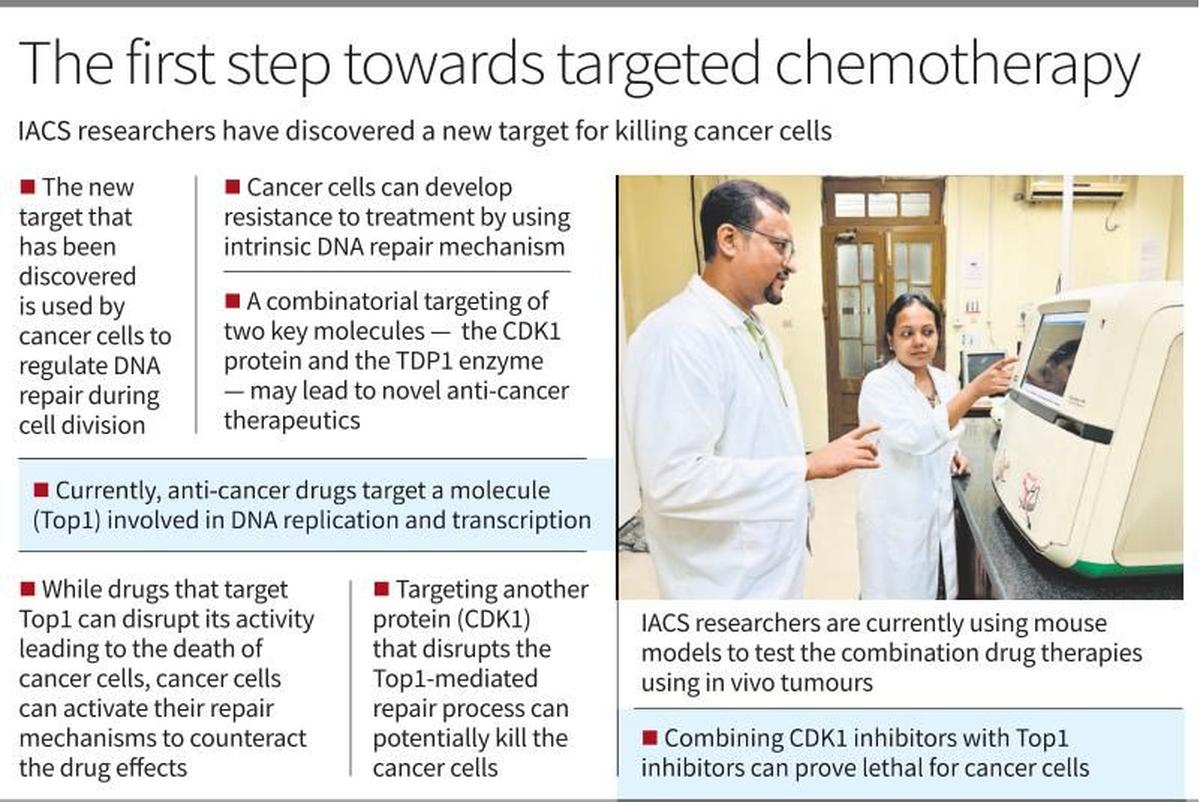
- 11 Oct 2024
In News:
Scientists have identified a promising new target for cancer treatment by activating a DNA repair enzyme called TDP1. This approach suggests a combination therapy that could serve as a potential precision medicine for patients resistant to current treatments.
- Current Treatment Limitations:
- Existing anticancer drugs (e.g., Camptothecin, Topotecan, Irinotecan) target Topoisomerase 1 (Top1), essential for DNA replication and transcription.
- Cancer cells frequently develop resistance to these single-agent therapies, necessitating alternative treatment strategies.
- Research Insights:
- Conducted by scientists at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS), Kolkata, under the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The study focused on how cancer cells repair DNA during cell division and respond to chemotherapy targeting Top1.
- Key Findings:
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1)
- Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1)
- CDK1 regulates the DNA repair process, while TDP1 helps cancer cells survive by repairing drug-induced Top1 damage.
- The research, published in The EMBO Journal 2024, highlights two critical proteins:
- Mechanism of Action:
- TDP1 repairs Top1 that is trapped during the S phase of DNA replication.
- The role of TDP1 during the mitotic phase was previously unknown; CDK1 phosphorylates TDP1, enhancing its repair capabilities.
- Phosphorylation is crucial for efficient DNA repair, allowing cancer cells to withstand Top1-targeted chemotherapy.
- Potential for Combination Therapy:
- Targeting both CDK1 and TDP1 could help overcome drug resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
- Suggested use of CDK1 inhibitors (e.g., avotaciclib, alvocidib) alongside Top1 inhibitors may disrupt DNA repair and halt the cell cycle, increasing cancer cell mortality.
- Research Implications:
- Phosphorylation of TDP1 by CDK1 is essential for managing DNA damage in cancer cells.
- Inhibiting CDK1 may induce chromosome instability, effectively targeting cancer cells.
- The combination of CDK1 and Top1 inhibitors aims to enhance cancer treatment effectiveness.
- Future Directions:
- Identifying CDK1 and TDP1 as potential targets paves the way for developing new cancer therapies that inhibit DNA repair mechanisms.
- Further studies using animal models are ongoing to validate this innovative approach for precision medicine in treating resistant cancers.
RBI's Recent Monetary Policy Review
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) maintained its benchmark interest rate at 6.5% for the 10th consecutive monetary policy review since April 2023. The policy stance was shifted to “neutral,” indicating potential for a future rate cut.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) Overview
- The decision to keep interest rates unchanged was supported by a majority of five out of six members of the MPC, which convened for three days starting October 7.
- The change in policy stance from “withdrawal of accommodation” to “neutral” was unanimously agreed upon.
Focus Areas
- The MPC emphasized the need for a durable alignment of inflation with targets while supporting economic growth.
- Macroeconomic parameters for inflation and growth were described as well balanced.
Inflation Insights
- A moderation in headline inflation is expected to reverse in September, likely remaining elevated due to adverse base effects.
- Retail inflation was below the central bank’s median target of 4% in July and August.
Growth Projections
- The RBI maintained its 7.2% GDP growth projection and a 4.5% average inflation estimate for 2024-25, with risks evenly balanced.
- Second-quarter inflation projection was revised down to 4.1% from 4.4%, while a rise to 4.8% is expected for the October to December quarter.
Domestic Growth and Investment
- Domestic growth remains robust, with private consumption and investment growing together.
- This growth has provided the RBI with the capacity to prioritize inflation control to achieve the 4% target.
Risks to Inflation
The Governor highlighted that unexpected weather events and escalating geopolitical conflicts pose significant upside risks to inflation.
44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses

- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
India Participates in 44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses
Key Contributions:
- Nutrient Reference Values:
- Advocated for reference values for ages 6 to 36 months.
- Suggested combining NRV-R values by averaging those for 6-12 months and 12-36 months.
- This proposal was accepted by the committee.
- Probiotic Guidelines:
- Emphasized the need to update FAO/WHO probiotic guidelines, which are two decades old.
- Highlighted the lack of international harmonization in probiotic regulations affecting global trade.
- Committee agreed to revisit guidelines and requested FAO and WHO to conduct a literature review on probiotics.
- Discussion on Sweetness Assessment:
- Disagreed with the EU’s sensory testing proposal for carbohydrate sources in Follow-up Formula, citing lack of scientific validation.
- Supported by USA, Canada, and others; this led to the committee discontinuing the topic for now.
- Noted that ISO 5495 or other methods could be used in the absence of harmonized methods.
- Delegation:
- Included representatives from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Advocated for various food safety, consumer health, and trade-related issues.
- Outcome:
- India’s suggestions were officially incorporated into the final report, significantly influencing global food safety and nutrition standards.
- Additional Announcements:
- FAO/WHO plans for a Joint Statement on Healthy Diet Principles.
- Updates on reviewing benefits and risks of Alternative Animal Source Foods (A-ASFs).
- FAO introduced a new “Food and Diet” domain on its FAOSTAT database.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 02 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour & Employment, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme on the occasion of National Sports Day in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
This programme aims to empower retired athletes by equipping them with essential career skills and knowledge, enhancing their employability and enabling them to contribute meaningfully to the sports ecosystem.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Retired athletes aged 20 to 50 years.
- Achievements:
- Must be winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- Alternatively, must have been national or state medallists or participants in competitions recognized by:
- National Sports Federations
- Indian Olympic Association
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
Programme Structure
- Levels: Two tiers based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12th and above
- Class 11th and below
- Learning Mode: A hybrid approach, combining:
- Self-paced online learning through a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training for practical skill development.
Lead Institute
- Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) will oversee the implementation and administration of the programme.
Support and Opportunities
- Placement Assistance: Comprehensive guidance for job placements in relevant sectors.
- Entrepreneurial Guidance: Support for athletes looking to start their own ventures in sports or related fields.
- Internships: Opportunities for hands-on experience in:
- Sports organizations
- Competitions
- Training camps
- Leagues
Implementation and Benefits
- Self-Paced Learning: Flexibility for participants to manage their learning schedules effectively.
- On-Ground Training: Hands-on practical sessions aimed at enhancing skills relevant to various career paths.
- Evaluation and Certification: Participants will be assessed and awarded a certificate upon successful completion, adding value to their career prospects.
The RESET Programme not only recognizes the achievements of retired athletes but also empowers them to leverage their experiences in new and impactful ways, fostering a robust sports ecosystem in India.
ETURNAGARAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
A rare collision of two cyclones has led to significant environmental impact, including the flattening of thousands of trees within the sanctuary.
Key Details:
- Location: Situated in the Mulugu district of Telangana, near the borders of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh. Approximately 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- Establishment: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Nizam government of Hyderabad.
- Area: Covers around 806 square kilometers.
Geographic Features
Rivers:
- Dayyam Vagu: A significant water source that divides the sanctuary into two parts.
- Godavari River: Flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
Flora
- Vegetation: Dense tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Key Species: Includes teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia trees, creating a lush habitat.
Fauna
- Wildlife: Home to diverse species such as:
- Mammals: Tiger, leopard, panther, wolf, wild dogs, jackals, sloth bear, chousingha, blackbuck, nilgai, sambar, spotted deer, and four-horned antelope.
- Reptiles: Notable for its population of mugger crocodiles and snakes, including cobras, pythons, and kraits.
Cultural Significance
- Temple: The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
India’s Commitment to Social Determinants of Health at UNGA
- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, represented India at the G20 Joint Finance-Health Task Force meeting during the 79th UN General Assembly.
- Focus: The session emphasized the importance of investing in health and addressing social determinants of health (SDH) through initiatives like debt-for-health swaps.
Key Highlights:
- Role of SDH: Underscored how social determinants such as housing, sanitation, water access, and income security are crucial for health investment priorities.
- Flagship Programs: India’s notable initiatives include:
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health insurance scheme.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Aiming for a cleaner India.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Ensuring water access for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Promoting housing for all.
- Impact of PM-JAY: Highlighted improvements in access to healthcare and outcomes, especially for non-communicable diseases.
Data and Policymaking
- Importance of Data: Stressed the need for enhanced data availability and standardization on SDH indicators to support effective policymaking.
- Unified Approach: Called for G20 nations to collaborate on data collection and analysis for better health systems globally.
Exploring Debt-for-Health Swaps
- Potential Mechanism: Discussed debt-for-health swaps as a means to relieve financial pressure while promoting health equity.
- Next Steps: Emphasized the need for stakeholder engagement and pilot programs to ensure effective implementation.
Conclusion
- Global Leadership: India reaffirmed its commitment to health equity through evidence-based policies and partnerships.
- Shared Vision: Advocated for a unified effort towards achieving “Health for All,” highlighting the significance of investments in social determinants of health.
About Social determinants of health (SDOH)
- SDOH are non-medical factors that affect a person's health, well-being, and quality of life. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age.
- SDOH also include the broader systems that shape everyday life, such as economic policies, social norms, and political systems.
- Some examples of SDOH include:
- Safe housing, transportation, and neighborhoods
- Racism, discrimination, and violence
- Education, job opportunities, and income
- Access to nutritious foods and physical activity opportunities
- Polluted air and water
- Language and literacy skills
GlobE Network

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- India was elected to the 15-member GlobE Steering Committee on September 26, 2024, in a plenary session in Beijing. The election involved a multistage voting process.
- Role and Significance:
- India will play a vital role in shaping the global agenda on corruption and asset recovery.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) highlighted India's expertise in combating corruption as a significant asset for the GlobE Network.
- About the GlobE Network:
- The Global Operational Network of Anti-Corruption Law Enforcement Authorities (GlobE Network) is a G-20 initiative, supported by India since 2020.
- Officially launched on June 3, 2021, during a UN General Assembly session against corruption.
- Currently comprises 121 member countries and 219 member authorities.
- Governance Structure:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) serves as the central authority for India within the GlobE Network.
- Indian member authorities include the CBI and the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
- The Steering Committee consists of one chair, one vice-chair, and 13 members providing leadership and direction.
- Functionality and Objectives:
- The GlobE Network facilitates the sharing of best practices, criminal intelligence, and strategy development among international agencies to combat corruption.
- It is supported by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), which provides secretariat services.
- G-20 Presidency Initiatives:
- During India’s G-20 Presidency in 2023, two high-level principles for combating corruption were adopted, emphasizing the use of the GlobE Network to enhance global cooperation.
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION 2.0

- 24 Sep 2024
Mission Overview:
- Launched on October 1, 2021, as the second phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Aims for "Garbage-Free Status" in all urban areas by 2026.
- Focuses on 100% source segregation, door-to-door waste collection, and scientific waste management.
Legacy Waste Issues:
- Legacy waste consists of improperly collected and stored solid waste, often found in landfills and abandoned sites.
- Approximately 15,000 acres of prime land are buried under nearly 16 crore tonnes of legacy waste in India.
- The mission seeks to convert legacy dumpsites into green zones and establish scientific landfills to manage untreated waste.
Current Progress:
- Of 2,424 identified dumpsites (each with over 1,000 tonnes of waste), only 470 have been fully remediated (16% reclaimed).
- 1,224 sites are under ongoing remediation, while 730 remain untouched.
- Out of 28,460 acres of affected land, 4,552 acres have been reclaimed, with 23,908 acres still to be addressed.
State Performance:
- Tamil Nadu: 837 acres reclaimed (42% of its total dumpsite area).
- Gujarat: Leads in percentage, reclaiming 75% of its landfill area (698 out of 938 acres).
Financial Aspects:
- Central assistance of ?3,226 crore has been approved for remediation efforts.
- States and Union Territories must provide a matching share to access these funds.
Challenges:
- Legacy waste management involves complexities such as radiological characterization, leachate management, and fire control.
- Current municipal solid waste generation in India is around 150,000 tonnes per day.
Historical Context:
- The original Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-U 1.0) launched on October 2, 2014, focused on making urban areas Open Defecation Free (ODF).
Net Direct Tax inflows increase by 16.1%

- 19 Sep 2024
In News:
- Advance tax payments from corporates and personal taxpayers have risen by 22.6%, surpassing ?4.36 lakh crore. This increase is driven by a 39.2% rise in Personal Income Tax (PIT) receipts and an 18.2% uptick in corporate taxes.
Key Details:
- Overall net direct tax receipts have reached approximately ?9.96 lakh crore, reflecting a 16.1% increase, though this marks a slowdown from the 22.5% growth recorded as of August 11.
- As of September 17, corporate tax collections grew by 10.5%, while inflows from PIT increased by 18.9%.
- Securities Transaction Tax collections nearly doubled to ?26,154 crore, and refunds surged by 56.5% to ?2.05 lakh crore, according to data from the Income Tax Department.
- Personal taxes continue to outpace corporate taxes, contributing 51.7% of net direct tax receipts for the year.
- Gross tax collections, before accounting for refunds, have risen by 21.5%, totaling ?12.01 lakh crore.
Union Budget 2024-25: Corridor Projects for Bihar's Temples

- 18 Sep 2024
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2024-25 announced plans to develop corridor projects for the Vishnupad Temple at Gaya and the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar. These initiatives aim to enhance both temples as significant pilgrimage and tourist destinations, modeled after the successful Kashi Vishwanath Corridor. The temples are located approximately 10 kilometers apart and hold considerable cultural significance.
Key Facts About the Temples
Vishnupad Temple at Gaya
- Location: Situated on the banks of the Phalgu/Falgu River in Gaya district, Bihar.
- Deity: Dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
- Legend: Local mythology recounts that a demon named Gayasur sought the power to help others attain moksha (liberation). After misusing this power, he was subdued by Lord Vishnu, who left a footprint at the temple, symbolizing this event.
- Architectural Features: The temple stands about 100 feet tall and is supported by 44 pillars made from large gray granite blocks (Munger Black stone), joined with iron clamps. The octagonal shrine is oriented towards the east.
- Construction: Built in 1787 under Queen Ahilyabai Holkar's orders.
- Cultural Practices: The temple is especially significant during Pitra Paksha, a time for honoring ancestors, attracting many devotees. The Brahma Kalpit Brahmins, or Gayawal Brahmins, have served as traditional priests since ancient times.
Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya
- Historical Significance: Believed to be the location where Gautam Buddha attained enlightenment under the Mahabodhi Tree.
- Construction: Originally built by Emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century BC, with the current structure dating back to the 5th–6th centuries.
- Architectural Features: The temple complex includes the 50-meter-high Vajrasana (the Diamond Throne), the sacred Bodhi Tree, and six other sacred sites associated with Buddha's enlightenment. The site is surrounded by numerous ancient Votive stupas and is protected by circular boundaries.
- Sacred Sites:
- Bodhi Tree: A direct descendant of the original tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Animeshlochan Chaitya: Where Buddha spent the second week of meditation post-enlightenment.
- Ratnachakrama: Site of Buddha's third week after enlightenment.
- Ratnaghar Chaitya: Site of Buddha's fourth week after enlightenment.
- Ajapala Nigrodh Tree: Site of Buddha’s fifth week after enlightenment.
- Lotus Pond: Site of Buddha’s sixth week after enlightenment.
- Rajyatana Tree: Site of Buddha’s seventh week after enlightenment.
- Recognition: Designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2002, the Mahabodhi Temple attracts numerous national and international pilgrims, emphasizing its spiritual importance.
Other Tourist Attractions in Bihar
Additional notable tourist sites in Bihar include:
- Vishwa Shanti Stupa in Rajgir
- Nalanda
- Ancient city of Patliputra
- Valmiki Nagar Tiger Reserve in West Champaran
What is the Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP)?
The Pilgrim Corridor Project (PCP) aims to upgrade religious sites into world-class destinations for spiritual and tourism purposes.
India Status Report on Road Safety 2024
- 18 Sep 2024
In News:
The "India Status Report on Road Safety 2024," prepared by the TRIP Centre at IIT Delhi, highlights India's slow progress in reducing road accident fatalities and emphasizes the need for a tailored approach to road safety.
Key Findings:
- Road Safety Analysis:
- The report analyzes road safety data from FIRs across six states and evaluates compliance with Supreme Court directives on road safety.
- There are significant disparities in road traffic death rates among states, with motorcyclists and truck-related fatalities being notably high.
- Road traffic injuries remain a critical public health issue, with little progress in reducing fatalities. Many states are unlikely to meet the UN goal of halving traffic deaths by 2030.
- Health Impact:
- In 2021, road traffic injuries ranked as the 13th leading cause of death in India and the 12th leading cause of health loss (measured in Disability-Adjusted Life Years, or DALYs). Six states listed road traffic injuries among their top 10 health loss causes.
- Crash Surveillance Deficiencies:
- India lacks a national crash-level database, relying on police station records, which are often incomplete and inaccurate. This hampers effective public policy and intervention strategies.
- State Performance:
- There is a threefold variation in per capita death rates across states. Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and Chhattisgarh have the highest rates, while West Bengal and Bihar have the lowest.
- Pedestrians, cyclists, and motorized two-wheeler riders are the most common accident victims, with trucks accounting for a large share of accidents.
- Helmet usage is low, especially in rural areas, and basic traffic safety measures are inadequate across many states.
- Global Comparison:
- India's road safety governance is starkly lagging compared to developed nations. By 2021, Indians were 600% more likely to die in road accidents compared to their counterparts in countries like Sweden.
Recommendations for Improvement
- National Database: Establish a comprehensive, publicly accessible database for fatal crashes to enhance understanding of risks and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Scaled Interventions: Prioritize road safety measures at both Central and State levels, tailored to the specific challenges of each region.
- Public Awareness and Safety: Increase public awareness of road safety measures, particularly helmet usage, and improve trauma care facilities.
- Infrastructure Audit: Conduct thorough audits of National and State Highways to identify safety gaps and implement necessary improvements.
By implementing these recommendations, India can take meaningful steps toward improving road safety and reducing fatalities.
Agnibaan - SOrTeD: World’s First 3D-printed Rocket Engine
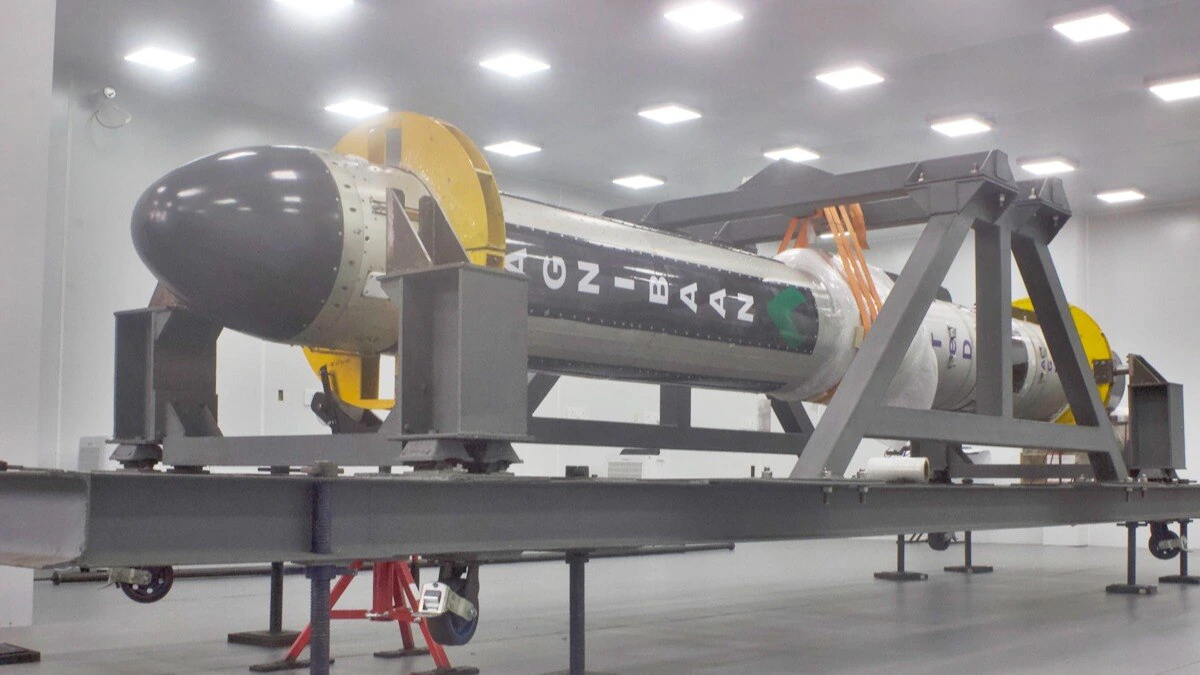

- 31 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos on Thursday successfully launched its first sub-orbital test vehicle powered by the world’s first single-piece 3D-printed rocket engine, after calling off its launch at least four times previously.
What is Agnibaan - SOrTeD?
- Agnibaan SOrTeD is a sub-orbital technological demonstrator of the Agnibaan launch vehicle, manufactured by Indian space startup Agnikul Cosmos.
- A sub-orbital launch reaches outer space but does not complete an orbit around Earth, intersecting the Earth's atmosphere or surface without becoming an artificial satellite or reaching escape velocity.
- This marks Agnikul’s fifth launch attempt since March 22. With this launch, AgniKul became the second private company to achieve a rocket launch in India, following Skyroot's successful flight in 2022.
Features:
- It is a customizable, two-stage launch vehicle capable of carrying up to 300 kg into an orbit approximately 700 km above Earth.
- Semi-Cryogenic Engine: Utilizes a combination of liquid and gaseous propellants, operating at temperatures higher than cryogenic engines but lower than traditional liquid rocket engines.
- Uses refined kerosene, which is lighter and can be stored at normal temperatures, allowing more propellant to be carried. When combined with liquid oxygen, kerosene provides higher thrust.
- The test flight aims to demonstrate in-house, homegrown technologies, gather crucial flight data, and ensure the optimal functioning of systems for AgniKul's orbital launch vehicle, Agnibaan.
- The rocket is designed for accessing both low and high-inclination orbits and is completely mobile, enabling launches from more than 10 ports.
Agnibaan Acheivments:
- World’s First 3D-Printed Engine: Agnibaan is the first rocket to use a 3D-printed engine.
- First Semi-Cryogenic Engine-Powered Rocket Launch: Pioneering the use of semi-cryogenic engines in rocket launches.
- India’s First Private Launchpad Rocket Launch: The first Indian rocket launch conducted from a private launchpad.
- Unique Engine Configuration: Powered by the only engine in India that uses both gas and liquid fuel (liquid oxygen/kerosene).
Significance:
- Typically, rocket engine parts are manufactured separately and assembled later.
- The 3D-printed manufacturing process is expected to lower launch costs and reduce vehicle assembly time, offering affordable launch services for small satellites.
About 3D Printing:
- 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, creates three-dimensional objects from digital models by adding material layer by layer.
- This process, which uses materials like plastic, composites, or bio-materials, allows for efficient and customized production, contrasting with traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Notable Examples of 3D Printing:
- Industry Applications: 3D printing is widely used in industries such as healthcare, automotive, and aerospace.
- Aerospace: In May, Relativity Space launched a test rocket made entirely from 3D-printed parts, standing 100 feet tall and 7.5 feet wide.
- However, the rocket experienced a failure shortly after takeoff.
- Healthcare: During the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, 3D printers were utilized to produce essential medical equipment, including swabs, face shields, masks, and parts for ventilators.
New Light-based Tool to Detect Viral Infections

- 30 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A viral infection can stress cells and change their shapes and sizes. Researchers have built a tool to detect these changes.
About the new Tool:
- A team of researchers has developed an innovative method to detect viral infections in cells using only light and principles of high-school physics.
- The key insight is that viral infections can stress cells, causing changes in their shapes, sizes, and other features.
- As the infection progresses and the body becomes diseased, these changes become more pronounced.
- The researchers have found a way to translate these cellular changes into recognizable patterns that can indicate whether a cell is uninfected, virus-infected, or dead.
- For example, virus-infected cells tend to be elongated and have clearer boundaries compared to uninfected cells.
- By analyzing the patterns of light interacting with cells, this method can non-invasively differentiate between uninfected, virus-infected, and dead cells.
- This approach has the potential to revolutionize viral disease diagnosis and monitoring, providing a simple, cost-effective, and powerful tool for detecting viral infections at the cellular level.
Significance:
- This light-based approach to detecting viral infections offers several significant advantages over the current standard methods:
- Accuracy: The new light-based technique can detect viral infections with equal or even greater accuracy compared to existing standard methods that rely on chemical reagents.
- Cost-effectiveness: The equipment required for this new method costs only around one-tenth of the $3,000 (approximately Rs 2.5 lakh) needed for the standard chemical-based approach, making it a far more affordable option, especially for resource-constrained settings.
- Rapid results: The light-based method can identify virus-infected cells in just about two hours, significantly faster than the 40 hours required by the current standard method.
- This time efficiency can be crucial in situations where rapid detection is essential, such as during a virulent disease outbreak.
- Early detection: By enabling the early detection of viral infections at the cellular level, this new technique could prove invaluable in containing the spread of highly contagious viral diseases, such as a severe influenza outbreak.
What are Viruses?
- Viruses are microscopic organisms capable of infecting various hosts such as humans, plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi.
- Structurally, they consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protective shell called a capsid, with some viruses also possessing an envelope.
- Unable to reproduce independently, viruses rely on host cells to replicate by utilizing the cell's machinery.
- Common types include influenza viruses, human herpesviruses, coronaviruses, human papillomaviruses, enteroviruses, flaviviruses, orthopoxviruses, and hepatitis viruses.
- Viruses are responsible for causing illnesses such as flu, the common cold, and COVID-19.
Onset of Monsoon
- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The southwest monsoon is progressing normally, and conditions are suitable for its onset on the Kerala coast in the next five days, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) said on Monday (May 27).
What does the ‘onset of monsoon’ Mean?
- The onset of the monsoon over Kerala marks the beginning of the four-month, June-September southwest monsoon season over India, which brings more than 70% of the country’s annual rainfall.
- The onset of the monsoon is a significant day in India’s economic calendar.
- According to the IMD, the onset of the monsoon marks a crucial transition in the large-scale atmospheric and ocean circulations in the Indo-Pacific region, and the Department announces it only after certain defined and measurable parameters, adopted in 2016, are met.
Onset & Advance of Monsoon:
- Broadly, the IMD checks for the consistency of rainfall over a defined geography, its intensity, and wind speed.
- Rainfall: The IMD declares the onset of the monsoon if at least 60% of 14 designated meteorological stations in Kerala and Lakshadweep record at least 2.5 mm of rain for two consecutive days at any time after May 10. In such a situation, the onset over Kerala is declared on the second day, provided specific wind and temperature criteria are also fulfilled.
- The 14 enlisted stations are Minicoy, Amini, Thiruvananthapuram, Punalur, Kollam, Alappuzha, Kottayam, Kochi, Thrissur, Kozhikode, Thalassery, Kannur, Kasaragod, and Mangaluru.
- Wind field: The depth of westerlies, prevailing winds that blow from the west at midlatitudes — should be up to 600 hectopascals (1 hPa is equal to 1 millibar of pressure) in the area bound by the equator to 10ºN latitude and from longitude 55ºE to 80ºE.
- The zonal wind speed over the area bound by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-80ºE longitude should be of the order of 15-20 knots (28-37 kph) at 925 hPa.
- Heat: According to IMD, the INSAT-derived Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR) value (a measure of the energy emitted to space by the Earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere) should be below 200 watts per sq m (wm2) in the box confined by 5-10ºN latitude and 70-75ºE latitude.
- Northern Limit of Monsoon (NLM): Southwest monsoon normally sets in over Kerala around 1st June.
- It advances northwards, usually in surges, and covers the entire country around the 15th of July.
- The NLM is the northernmost limit of monsoon up to which it has advanced on any given day.
In general, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands start receiving monsoon rainfall between May 15 and May 20 every year, and it usually starts raining along the Kerala coast in the last week of May.
Gliese 12b

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered a new planet that they say could "potentially support human life."
What is Gliese 12b?
- Gliese 12 b is a rocky planet just 40 light-years away from Earth.
- It orbits around a star called Gliese 12, a cool red dwarf in the constellation Pisces.
- This star is only 27 per cent of the size of our sun, with about 60 per cent of its surface temperature.
- But it's this lower temperature that makes Gliese 12 b theoretically habitable for humans.
- Gliese 12 b is one of the few known rocky planets where humans could theoretically survive according to scientists.
- The planet was discovered by an international team, in collaboration with NASA and the European Space Agency, using data from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and ESA's Characterizing Exoplanet Satellite (CHEOPS).
- Gliese 12 b falls into this "Goldilocks zone," with an average temperature of 107 degrees Fahrenheit and a size somewhere between Venus and Earth.
- The researchers hope that by learning more about Gliese 12 b's atmosphere we may be able to answer questions about the evolution of our own solar system and other habitable planets.
About the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS):
- TESS is a NASA mission dedicated to discovering exoplanets around nearby bright stars.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral.
- TESS operates in a unique high Earth orbit with a period of 12 to 15 days.
- This orbit is designed to keep the telescope's view largely unobstructed by Earth and the Moon.
- The prime mission concluded on July 4, 2020, but TESS continues to operate on an extended mission.
- TESS has identified a wide range of exoplanets, from small rocky worlds to giant planets, highlighting the diversity of planetary systems in our galaxy.
- TESS uses the transit method to find exoplanets. It monitors stars for periodic dips in brightness, which occur when a planet crosses in front of the star along our line of sight.
- The size of the dip indicates the planet's diameter and the duration of the transit provides information about the planet's orbit.
- The transit method allows scientists to determine the diameter and orbital size of exoplanets.
- Orbits within certain ranges fall into the "habitable zone," where conditions may allow liquid water to exist on the surface of Earth-like worlds.
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Meeting 2024

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Treaty on Intellectual Property, Genetic Resources and Associated Traditional Knowledge was adopted at the Diplomatic Conference held under the aegis of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) at its headquarters in Geneva recently.
What is the WIPO Meeting 2024?
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Meeting 2024 focuses on final-stage negotiations for a proposed treaty on intellectual property, genetic resources, and associated traditional knowledge.
- The aim is to protect the rights of communities that conserve genetic resources and hold traditional knowledge of their use.
- The main goal of the treaty is to enhance the efficacy, transparency, and quality of the patent system regarding genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- It aims to prevent patents for non-novel or non-inventive inventions and ensure proper disclosure of genetic resources and traditional knowledge in patent applications.
Key challenges in the negotiations:
- Key challenges include reaching a consensus on mandatory disclosure requirements, addressing biopiracy, deciding on the inclusion of DSI in the treaty, and defining traditional knowledge.
- Countries like the United States, Japan, and South Korea generally oppose mandatory disclosure requirements, adding complexity to the negotiations.
What are genetic resources and traditional knowledge associated?
- Genetic resources are genetic material of actual or potential value found in plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- These resources are essential in fields like agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
- Traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources refers to the knowledge, practices, and innovations of indigenous and local communities, developed and passed down through generations.
- This knowledge is often related to the use and conservation of genetic resources.
What is Biopiracy?
- Biopiracy refers to the unauthorized use and patenting of genetic resources and traditional knowledge without proper compensation or acknowledgement to the communities that developed and conserved them.
- The treaty seeks to address biopiracy by requiring the disclosure of genetic resources and traditional knowledge in patent applications and aligning with international agreements like the Nagoya Protocol.
What is Digital sequence information (DSI)?
- Digital sequence information (DSI) refers to the digital representation of genetic material.
- The treaty currently excludes DSI from its scope, which is a point of contention as it affects the management and protection of genetic resources.
- Including DSI in the treaty is under debate to ensure comprehensive protection.
Outcomes and Significance of this Meeting:
- Expected outcomes include finalizing the treaty's text, agreeing on substantive intellectual property provisions, and administrative issues.
- Once finalized, the treaty will be open for signature and aims to provide a robust framework for protecting genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- The treaty also aims to protect the rights of indigenous and local communities by ensuring they receive fair compensation and recognition for their genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- It also promotes the sustainable use and conservation of these resources, benefiting both global and local communities.
- The treaty has broader implications for international intellectual property law, biodiversity conservation, and the rights of indigenous and local communities.
- It aims to balance the interests of patent holders with the need to protect and sustainably use genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
India’s Role:
- India plays a significant role in the negotiations by advocating for strong disclosure requirements and a clear definition of traditional knowledge.
- India's participation helps ensure that the treaty provides sufficient policy space for countries to maintain their current stronger disclosure requirements under national laws.
Sweet Sorghum

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Governments should be using their agriculture extension services to raise awareness among farmers, and consumers about the benefits & practical applications of sweet sorghum in people’s diet.
About Sweet Sorghum:
- Sweet sorghum is the most important millet crop occupying the largest area among the cereals next to rice.
- It is mainly grown for its grain and fodder.
- Alternative uses of sorghum include commercial utilization of grain in the food industry and utilization of stalk for the production of value-added products like ethanol, syrup jaggery and enriched bagasse as fodder and as a base material for cogeneration.
- Sweet sorghum has emerged as a supplementary crop to sugarcane in dry land pockets for the production of ethanol.
- The success rate is high because of the use of existing machinery available in the sugar factories and attached distilleries.
- The advantages of the crop are it can be grown with limited water and minimal inputs and it can be harvested in four months.
Climate and Soil:
- Sweet sorghum can be sown in June with the southwest monsoon, in September-October with the northeast monsoon (500-600 mm rainfall), or in summer with assured irrigation.
- The crop prefers moderate rainfall; excessive moisture or heavy rain after flowering can reduce sugar content.
- With irrigation, early sowing before June can prevent issues with heavy rains during flowering and grain maturation.
- Summer sowing may result in lower biomass and sugar yield. Sweet sorghum thrives in well-drained soils of medium depth (18" and above), with water requirements varying by soil type (red, black, laterite, and loamy).
Multiple Uses of Sweet Sorghum:
- Sweet sorghum is a versatile crop used for grain, animal feed, and sugary juice.
- Its grains are made into steamed bread, porridge, and beer, providing high nutritional value with proteins, carbohydrates, fibre, and essential minerals like potassium, calcium, sodium, and iron.
- Resilient in arid climates, sweet sorghum produces significant biomass, which, along with grains, serves as high-quality animal feed.
- The sugary juice from its stalks is used for bioethanol production, yielding more ethanol per hectare than maize, second only to sugarcane.
- Notably, sweet sorghum is drought-resistant, capable of dormancy during dry periods and resuming growth later.
- Its tolerance to low water, nitrogen inputs, salinity, and drought stress makes it ideal for arid regions, making it popular in the US, Brazil, and China.
Planetary Alignment

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Next month, on June 3, there will be a planetary alignment that may actually allow you to witness six planets align in the sky.
What is a Planetary Alignment?
- Planetary alignment is a term used to describe the positioning of planets in the solar system such that they appear to be in a straight line or close to one when viewed from a specific vantage point, for us that's Earth.
- It is an astronomical event that happens when, by coincidence, the orbits of several of the planets of the Solar System bring them to roughly the same side of the Sun at the same time.
- This phenomenon is more an illusion of perspective rather than the planets being in a perfect line in space.
- It’s important to emphasise that the planets aren’t forming a straight line in space – that’s a much rarer astronomical event called a syzygy.
- However, because all the planets, including the Earth, orbit around the Sun in roughly the same orientation (moving in which we call the “Plane of the Ecliptic”), when they’re on the same side of the Sun as each other, they appear to form a line in the sky when we view them from Earth.”
- Planetary alignments are rather common within themselves, especially when two, three, or even four planets align in the sky.
- Five or more planets aligning, however, is less common.
- April 8, 2024, was the last time the planets were all in alignment.
Which planets will align?
- Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune will form a near-straight line, offering an extraordinary opportunity to witness this cosmic phenomenon.
Which planets will be visible?
- While six planets align, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye, due to their vast distance from Earth.
- Meanwhile, the Moon will also play a spoilsport as it distorts the visibility.
- Mercury and Jupiter will be tricky to see in the sky due to their proximity to the Sun in their orbit.
- However, Mars and Saturn will be visible to the naked eye, though very dim.
- Meanwhile, keen observers will need telescopes or high-powered binoculars to spot the distant planets Uranus and Neptune.
Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The ONDC Startup Mahotsav was held in New Delhi recently in collaboration between the Startup India initiative and the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC).
About the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC):
- The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is a network based on open protocol and will enable local commerce across segments, such as mobility, grocery, food order and delivery, hotel booking and travel, among others, to be discovered and engaged by any network-enabled application.
- The platform aims to create new opportunities, curb digital monopolies support micro, small and medium enterprises and small traders and help them get on online platforms.
- It is an initiative of the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Features of ONDC:
- ONDC, a UPI of e-commerce, seeks to democratise digital or electronic commerce, moving it from a platform-centric model to an open network.
- Through ONDC, merchants will be able to save their data to build credit history and reach consumers.
- The proposed government-backed platform aims to create a level playing field for e-commerce behemoths such as Amazon, Flipkart, and offline traders who have been crying foul at the unfair trade practices of these e-tailers.
- The platform will also be compliant with the Information Technology Act, 2000 and designed for compliance with the emerging Personal Data Protection Bill.
- In this system, ONDC plans to enable sellers and buyers to be digitally visible and transact through an open network, regardless of what platform or application they use.
- It will also empower merchants and consumers by breaking silos to form a single network to drive innovation and scale, transforming all businesses from retail goods, food to mobility.
- The new framework aims at promoting open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and open network protocols independent of any specific platform.
- It is expected to digitise the entire value chain, standardise operations, promote inclusion of suppliers, derive efficiencies in logistics and enhance value for consumers.
- According to the government's official statement, ONDC shall take all measures to ensure confidentiality and privacy of data in the network.
- ONDC shall not mandate the sharing of any transaction-level data by participants with ONDC.
- It will work with its participants to publish anonymised aggregate metrics on network performance without compromising on confidentiality and privacy.
- Presently, ONDC is in its pilot stage and the government has set up a nine-member advisory council, including Nandan Nilekani from Infosys and National Health Authority CEO R S Sharma, on measures needed to design and accelerate the adoption of ONDC.
World Telecommunication and Information Society Day

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
To commemorate the World Telecommunication and Information Society Day, C-DOT, the premier Telecom R&D Centre of the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) celebrates and announces special Initiatives “NIDHI” & “STAR Program” for the development of indigenous telecom solutions & technologies.
What is World Telecommunication and Information Society Day?
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) is celebrated every year in May to honour the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) on May 17, 1969.
- The day can be traced back to commemoration of the two significant events in the history of global communication.
- World Telecommunication and Information Society Day (WTISD) commemorates two significant events in the history of global communication.
- Firstly, it marks the founding of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 1865, when the first International Telegraph Convention was signed.
- Followed by, in November 2005, the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) called upon the United Nations General Assembly to also declare May 17th as World Information Society Day.
- And then in 2006, the ITU Plenipotentiary Conference in Antalya, Turkey, agreed to combine the two events as World Telecommunication and Information Society Day.
- This year’s World Telecommunications and Information Society Day 2024 focuses on the theme, “Digital Innovation for Sustainable Development,” underlying how digital innovation may help link everyone and create sustainable prosperity for all.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- Established in 1865, it is the oldest among the UN’s 15 specialized agencies.
- ITU is responsible for allocating global radio spectrum and satellite orbits, developing technical standards to ensure network interconnectivity, and improving ICT access for underserved communities.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, ITU is part of the UN Development Group and operates 12 regional offices worldwide.
- It functions as an intergovernmental public-private partnership with 193 member states and around 800 sector members. India, a member since 1952, was re-elected to the ITU Council for the 2019-2022 term.
Deda Method of Preserving Seeds

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In his 50s, Madakam Unga, a Muria tribal farmer who migrated from Chhattisgarh and settled in the dense forests of the Godavari Valley, is still practising ‘deda’, a traditional method of preserving seeds that his ancestors handed over to his family.
What is the Deda Method?
- The Deda Method is an ancestral seed preservation technique passed down through generations.
- This unique method involves the use of natural materials to create a protective, airtight environment for the seeds, ensuring their viability for future planting.
Preservation Process:
- Seeds are packed tightly and wrapped in leaves to form a sturdy bundle resembling a boulder.
- The seed-filled leaf packages are then woven together with Siali leaves (Bauhinia vahlii), locally known as 'addakulu,' forming the distinctive deda structure.
- A deda consists of three layers:
- The innermost layer contains wood ash spread over Siali leaves.
- The ash is then covered with lemon leaves, creating a protective casing.
- Lastly, seeds are preserved within this casing and sealed, with each deda supporting up to 5kg of seeds.
Advantages:
- The Deda Method effectively protects seeds from pests and worms, ensuring their quality and viability.
- Seeds preserved using this technique can be used for cultivation for up to five years.
- This method is particularly useful for preserving the seeds of various pulses, such as green gram, red gram, black gram, and beans.
- By utilizing the Deda Method, farmers can maintain a reliable, diverse collection of seeds, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices and supporting long-term food security.
Facts About Muria Tribe:
- Location: The Muria tribe is found in the states of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Language: They speak Koya, a Dravidian language.
- Population and Status: In Andhra Pradesh, the Muria, also known as 'Gutti Koyas' by native tribes, are internally displaced people (IDPs) with a population of around 6,600.
- Cultural Practices: The Muria have a progressive outlook on marriage and life.
- A notable example is the Ghotul, a communal dormitory that provides an environment for Muria youth to explore and understand their sexuality.
Recognition: While most Gutti Koya belong to the Gond or Muria communities, which are recognized as Scheduled Tribes in Chhattisgarh, they lack such recognition in Telangana.
India VIX

- 16 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India VIX, which is an indicator of the market’s expectation of volatility over the near term, surged past the 21 mark recently.
What is India VIX?
- India VIX is a volatility index computed by the NSE based on the order book of NIFTY Options.
- For this, the best bid-ask quotes of near and next-month NIFTY options contracts, which are traded on the F&O segment of NSE are used.
- India VIX indicates the investor’s perception of the market’s volatility in the near term i.e. it depicts the expected market volatility over the next 30 calendar days.
- The higher the India VIX values, the higher the expected volatility and vice versa, as per NSE.
- ‘VIX’ is a trademark of the CBOE, and Standard & Poor’s has granted a license to NSE, with permission from the CBOE, to use such a mark in the name of the India VIX and for purposes relating to the India VIX.
What is the Volatility Index?
- The Volatility Index, VIX or the Fear Index, is a measure of the market’s expectation of volatility over the near term.
- Volatility is often described as the ‘rate and magnitude of changes in prices’ and in finance often referred to as risk.
- Usually, during periods of market volatility, the market moves steeply up or down and the volatility index tends to rise.
- As volatility subsides, the Volatility Index declines.
- The Volatility Index is a measure of the amount by which an underlying index is expected to fluctuate in the near term, (calculated as annualised volatility, denoted in percentage e.g. 20 per cent) based on the order book of the underlying index options.
- The Chicago Board of Options Exchange (CBOE) was the first to introduce the volatility index for the US markets in 1993 based on S&P 100 Index option prices.
- In 2003, the methodology was revised and the new volatility index was based on S&P 500 Index options.
- Since its inception, it has become an indicator of how market practitioners think about volatility.
- Investors use it to gauge market volatility and base their investment decisions accordingly.
Rat-Hole Mining

- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
A one-member panel appointed by the High Court of Meghalaya to handle coal-related issues has flagged the lack of progress in restoring the environment damaged by rat-hole coal mining in the northeastern State.
What is Rat-hole Mining?
- Coal reserves are concentrated in Eastern India, spanning states such as Telangana, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal, with significant deposits also found in the North-Eastern regions like Assam and Meghalaya.
- However, commercial mining isn't prevalent in the North-East due to unsuitable terrain and the nature of coal deposits.
- Open mining faces additional challenges, and the coal in this region often contains high sulfur content, reducing energy efficiency and classifying it as low-quality coal.
- A rat-hole mine involves digging of very small tunnels, usually only 3-4 feet deep, in which workers, more often children, enter and extract coal.
- Once the pits are dug, miners descend using ropes or bamboo ladders to reach the coal seams.
- The coal is then manually extracted using primitive tools such as pickaxes, shovels, and baskets.
- A major portion of these employees are children, who are preferred because of their thin body shape and ease of accessing depths.
- This practice has become very popular in Meghalaya.
- Here there are majorly hilly terrains, which make coal mining very difficult.
- Also, digging a big hole is very difficult because a big hole demands pillars and support.
- Since it’s a good opportunity to extract coal from there for big as well as local investors, because it involves less investment and good returns, people are drawn towards this dangerous business.
- The practice is to not make any professional tunnels, install pillars, and ensure safety measures, but to just dig a small tunnel and put children and labour to work.
- Rat-hole mining is primarily practised only in Meghalaya.
- Such cases are not witnessed in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh because the coal seems to be thick in Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh while in Meghalaya coal seems to be very thin.
- So, economically it is not a good idea to do open mining, and therefore, they prefer rat-hole mining.
Types of rat-hole mining:
- The rat-hole mining is broadly of two types.
- In the side-cutting procedure, narrow tunnels are dug on the hill slopes and workers go inside until they find the coal seam.
- In the other type of rat-hole mining, called box-cutting, a rectangular opening is made, varying from 10 to 100 sqm, and through that a vertical pit is dug, 100 to 400 feet deep.
- Once the coal seam is found, rat-hole-sized tunnels are dug horizontally through which workers can extract the coal.
Environmental and Safety Concerns:
- Since rat-hole mining is illegal, it is practised behind closed doors, and therefore, no one is ready to invest in infrastructure development.
- Coal is stored near rivers because of a shortage of space which leads to pollution around water bodies.
- The water in the Kopili River (which flows through Meghalaya and Assam) has turned acidic.
- The entire roadsides in and around mining areas are for piling coal.
- This is a major source of air, water and soil pollution.
- Off-road movement of trucks and other vehicles in the area causes further damage to the ecology of the area.
- Due to rat-hole mining, during the rainy season, water gets flooded into the mining areas resulting in the death of many workers due to suffocation and hunger.
- If water has seeped into the cave, the worker can enter only after the water is pumped out.
- Also, the mines are typically unregulated, lacking safety measures such as proper ventilation, structural support, or safety gear for the workers.
When Was It Banned?
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned rat-hole mining in 2014 and retained the ban in 2015.
- The ban was on grounds of the practice being unscientific and unsafe for workers.
- The NGT order bans not only rat-hole mining but all “unscientific and illegal mining.”
- But orders of the Tribunal have been violated without exception since The State Government has failed to check illegal mining effectively.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)

- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 4th joint committee meeting for the review of AITIGA (ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement) was held in Putrajaya, Malaysia recently.
About ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
- Though this represented a decline from US$97 billion in 2018-19 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, it was an increase from US$81.3 billion in the 2017-18 financial year.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products and it does not apply to trade in services.
- ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
About the Association of the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
- The Association of the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a geopolitical and economic organization established to accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development among its ten (10) member states.
- It also aims to promote peace and stability in the region, active collaboration and mutual assistance on matters of common interest, Southeast Asian studies, and maintain close and beneficial cooperation with other regional and international organizations.
- It was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration by the founding members of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Brunei Darussalam then joined in 1984, Viet Nam in 1995, Lao PDR and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999, making up the current 10 Member States of ASEAN.
- The ASEAN Secretariat was set up in February 1976 and is based in Jakarta, Indonesia.
PS4 Engine

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully tested a liquid rocket engine made with the help of additive manufacturing technology — commonly known as 3D printing.
About PS4 Engine:
- ISRO has successfully conducted a long-duration test of its PS4 engine, re-designed for production using cutting-edge additive manufacturing (AM) techniques, also known in common parlance as 3D printing, and crafted in the Indian industry.
- The PS4 engine is the uppermost stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), comprising two Earth-storable liquid engines.
- The engine uses the earth-storable bipropellant combinations of Nitrogen Tetroxide as oxidiser and Mono Methyl Hydrazine as fuel in pressure-fed mode.
- It was developed by ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC).
- LPSC redesigned the engine making it amenable to the Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) concept thereby gaining considerable advantages.
- It was developed by ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC).
- The manufacturing of the engine was done by the Indian industry partner, Wipro 3D, and the engine was hot tested at ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu.
Why did ISRO use 3D printing to build the PS4 engine?
- The technology helped ISRO bring down the number of parts in the engine from 14 to a single piece.
- The space agency was able to eliminate 19 weld joints and saved 97% of the raw material.
- It also reduced the overall production time by 60%.
What is 3D Printing?
- 3D printing is a process that uses computer-created design to make three-dimensional objects layer by layer.
- It is an additive process, in which layers of a material like plastic, composites or bio-materials are built up to construct objects that range in shape, size, rigidity, and colour.
How is 3D printing done?
- To carry out 3D printing, one needs a personal computer connected to a 3D printer.
- All they need to do is design a 3D model of the required object on computer-aid design (CAD) software and press ‘print’.
- The 3D printer does the rest of the job.
- 3D printers construct the desired object by using a layering method, which is the complete opposite of the subtractive manufacturing processes.
- The (3D) printers act generally the same as a traditional inkjet printer in the direct 3D printing process, where a nozzle moves back and forth while dispensing a wax or plastic-like polymer layer-by-layer, waiting for that layer to dry, then adding the next level.
- It essentially adds hundreds or thousands of 2D prints on top of one another to make a three-dimensional object.
- Notably, these machines are capable of printing anything from ordinary objects like a ball or a spoon to complex moving parts like hinges and wheels.
- We can print a whole bike, handlebars, saddle, frame, wheels, brakes, pedals and chain–ready assembled, without using any tools.
- It’s just a question of leaving gaps in the right places.
Non-market Economy Status

- 10 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Vietnam has been pushing the President Joe Biden administration to quickly change its “non-market economy” classification to “market economy”, in a bid to avoid high taxes imposed by the US on the goods imported from the Southeastern country.
Why does Vietnam Want to Get the ‘Market Economy’ Status?
- Vietnam has argued that in recent years it has implemented enough economic reforms that get its name off the non-market economies list.
- The country does meet a number of criteria for the status to be changed.
- For instance, Vietnam allows foreign investment, wages are determined by free negotiations between workers and management, and most of the means of production are not owned by the state.
- The change in status will also help Vietnam get rid of the anti-dumping duties, making its products more competitive in the US market.
- Vietnam’s Center for WTO and International Trade has said that the method of calculating anti-dumping duties is flawed as it causes “the dumping margin to be pushed up very high” and does not actually reflect the situation of Vietnamese companies.
About Non-market Economy Status:
- Non-market economy status refers to a designation applied to countries by international trade authorities, particularly the World Trade Organization (WTO), based on their economic structure and policies.
- In a non-market economy, the allocation of resources, production decisions, and pricing mechanisms are predominantly influenced by the government rather than by market forces.
- This can include state ownership of key industries, government intervention in setting prices, and restrictions on foreign investment and trade.
- For trade purposes, countries classified as non-market economies may face different treatment in anti-dumping investigations and trade disputes.
- This designation can affect how trade regulations and tariffs are applied to goods originating from these countries.
- The US designates a country as a non-market economy based on several factors which are:
- If the country’s currency is convertible
- If wage rates are determined by free bargaining between labour and management
- If joint ventures or other foreign investments are allowed whether the means of production are owned by the state; and
- If the state controls the allocation of resources and price and output decisions.
- Other factors like human rights are also considered.
- The non-market economy label allows the US to impose “anti-dumping” duties on goods imported from designated countries.
Market Economies:
- Market economies operate based on the interactions between consumers and businesses, guided primarily by the law of supply and demand, rather than by central government policies.
- Theoretical Foundation: Developed by classical economists like Adam Smith, David Ricardo, and Jean-Baptiste Say, market economies emphasize the role of free markets in allocating resources efficiently.
- Modern Market Economies: Often referred to as mixed economies, modern market economies may still involve some government interventions, such as price-fixing, licensing, quotas, and industrial subsidies, but the majority of decisions are market-driven.
- Examples include countries like India, the USA, and the UK, where market forces play a significant role in shaping economic activities.
What is Anti-dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a protectionist tariff that a domestic government imposes on foreign imports that it believes are priced below fair market value.
- In order to protect their respective economy, many countries impose duties on products they believe are being dumped in their national market; this is done with the rationale that these products have the potential to undercut local businesses and the local economy.
- While the intention of anti-dumping duties is to save domestic jobs, these tariffs can also lead to higher prices for domestic consumers.
- In the long term, anti-dumping duties can reduce the international competition of domestic companies producing similar goods.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO)–an international organization that deals with the rules of trade between nations–also operates a set of international trade rules, including the international regulation of anti-dumping measures.?
Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM)

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India is working with like-minded countries to promote regulated tourism in Antarctica as a steady increase in the number of tourists threatens to harm the fragile ecology in the White Continent.
About the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting:
- The Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) is the annual meeting of the Parties to the 1959 Antarctic Treaty.
- The meeting serves as a platform for the exchange of information, discussion of common interests, and promotion of the principles and purposes of the Antarctic Treaty.
- The first ATCM was held in 1961, and initially occurred every other year, though the frequency has since increased.
- During the ATCM, representatives of the member countries address various issues related to Antarctica, such as environmental protection, scientific research, and tourism regulation.
- Key agenda items include strategic planning for sustainable management of Antarctica and its resources, policy, legal, and institutional operations, and biodiversity prospecting.
- The ATCM is organized by the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and was established in 2004.
- The Secretariat is responsible for facilitating communication and information exchange among the parties involved in the Antarctic Treaty System.
- In recent years, the ATCM has been hosted by various countries, with India hosting the 46th meeting in 2024.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India, through the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) and the Secretariat of the Antarctic Treaty will jointly organise the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM 46) from 20 to 30 May 2024 at the Lulu Bolgatty International Convention Centre (LBICC) in Kochi, India.
What is the Antarctic Treaty?
- The Antarctic Treaty is an international agreement that aims to preserve and protect the Antarctic continent and its surrounding waters for scientific research and peaceful purposes.
- Signed on December 1, 1959, by 12 countries, the treaty came into effect on June 23, 1961.
- The treaty establishes Antarctica as a natural reserve devoted to scientific research, and it designates the area south of 60°S latitude as a region free of military and nuclear activities.
Key aspects of the treaty include:
-
- Freedom of scientific research and exploration, with cooperation among signatory nations
- Exchange of scientific information and personnel between treaty member nations
- Prohibition of military activities, such as the establishment of military bases or weapons testing
- Prohibition of nuclear explosions and disposal of radioactive waste
- Acknowledgement that no new territorial claims can be made on the continent
- Designation of Antarctica as a "Special Conservation Area" to protect its ecosystems and native species
- Currently, 54 countries have ratified the Antarctic Treaty, and 29 of these countries have Consultative Party status.
- Consultative Parties have the right to participate in decision-making processes related to the management and governance of the Antarctic region, while Non-Consultative Parties are encouraged to engage in scientific research and exchange information.
- On 12 September 1983, India became the fifteenth Consultative Member of the Antarctic Treaty.
- It participates in the decision-making process along with the other 28 Consultative Parties to the Antarctic Treaty.
- India’s first Antarctic research station, Dakshin Gangotri, was established in 1983.
- At present, India operates two year-round research stations: Maitri (1989) and Bharati (2012).
- The permanent research stations facilitate Indian Scientific Expeditions to Antarctica, which have been ongoing annually since 1981.
- In 2022, India enacted the Antarctic Act, reaffirming its commitment to the Antarctic Treaty.
West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA)

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists utilized a CRISPR-Cas9 tool to restore vision in individuals, including adults and children, afflicted with congenital blindness termed Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA).
What is Leber Congenital Amaurosis?
- Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) is a rare genetic eye disorder where affected infants experience severe vision loss or blindness at birth.
- The condition results from the impaired function of light-gathering cells (rods and cones) in the retina.
Prevalence and Cause:
- LCA affects approximately one in 40,000 people.
- It is caused by a gene mutation that disrupts the proper function of the CEP290 protein, which is critical for vision.
Recent Development:
- Scientists have employed CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology to develop a novel therapy called EDIT-101.
- In a clinical trial called "BRILLIANCE," participants received a single dose of EDIT-101.
- The treatment involves cutting out the mutation in the CEP290 gene and replacing it with healthy DNA, restoring the normal function of the CEP290 protein and allowing the retina to detect light.
- This groundbreaking approach offers a promising treatment for individuals affected by LCA.
What is CRISPR-Cas9?
- CRISPR-Cas9 is a unique technology that enables geneticists and medical researchers to edit parts of the genome by removing, adding or altering sections of the DNA sequence.
- It is currently the simplest, most versatile and precise method of genetic manipulation.
How does CRISPR-Cas9 work?
- The CRISPR-Cas9 system operates through two primary molecules:
- Cas9, an enzyme often likened to "molecular scissors," which can precisely cut both strands of DNA at a designated location in the genome.
- Guide RNA (gRNA), a segment of RNA containing a specific pre-designed sequence (about 20 bases long) within a longer RNA scaffold.
- The scaffold binds to DNA, while the pre-designed sequence guides Cas9 to the intended genomic location, ensuring accurate DNA cleavage.
- The guide RNA is tailored to identify and bind to a particular sequence in the DNA, with RNA bases that complement those of the target DNA sequence.
- This specificity ensures that the guide RNA binds solely to the target sequence and avoids other genomic regions.
- Once bound, Cas9 cuts across both DNA strands at the targeted location.
- Subsequently, the cell's repair mechanisms recognize the DNA damage and attempt to rectify it.
- Scientists exploit this DNA repair process to introduce alterations to one or more genes within the genome of a selected cell.
FLiRT

- 07 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
There’s a new group of COVID-19 variants within the Omicron JN.1 lineage “which have demonstrated increased transmissibility and immune resistance” recently detected in the United States.
What is the New Covid-19 Variant FLiRT?
- FLiRT variants are sub-lineages of the Omicron COVID-19 variant.
- Detected in the United States, this variant group has been named Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) FLiRT variant KP.2 and is a spinoff of JN.1.11.1.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), FLiRT has led to increased hospitalisation rates, although it has not significantly raised mortality rates.
- Its primary impact is on the upper respiratory tract.
- The rapid emergence and diversification of the JN.1 variant and its descendant, KP.2, which shows significant alterations in spike (S) protein structure and increased resistance to existing vaccines, underscore the necessity for further research to understand the implications for public health and vaccine development.
Where does the name come from?
- The letters of FLiRT variation are derived from the technical names of the mutations:
- F and L are included in one, and R and T which is included in another.
What are the emerging symptoms?
- Symptoms associated with FLiRT are similar to those of other Omicron subvariants, including sore throat, cough, fatigue, nasal congestion, runny nose, headache, muscle aches, fever, and possible loss of taste and smell
Transmissibility:
- This variant is highly transmissible and can impact immunity and overall health.
- This variant spreads via respiratory droplets of the person to others or touching infected surfaces such as faucets, furniture, elevator buttons, and kitchen countertops, or coming in close contact with the person who is sick with this variant
Is there a concern for India?
- Currently, there are no reported cases of FLiRT variants in India, and our immunity is acquired.
- Thus far, no new vaccine is recommended.
China’s Chang’e-6 Mission

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, China launched its second mission to the far side of the Moon. If successful, it will be the world’s first mission to bring back samples from the part of the Moon that the Earth never gets to see.
What is Chang’e-6 Mission?
- China's Chang'e-6 spacecraft launched recently, on a mission to collect samples from the far side of the Moon.
- The mission aims to grab samples containing material ejected from the lunar mantle and thus provide insight into the history of the Moon, Earth, and Solar System.
- It is a 53-day-long mission. After reaching the Moon’s orbit, the mission’s orbiter will circle the natural satellite while its lander will descend into the 2,500-kilometre-wide South Pole-Aitken basin on the lunar surface.
- The impact that created the basin, among the largest in the history of the solar system, is thought to have dug up material from the lunar mantle.
- If that material can be retrieved, scientists can learn more about the history of the Moon’s insides.
- After collecting samples through scooping and drilling, the lander will launch an ascent vehicle, which will transfer the samples to the orbiter’s service module.
- This module will then return to the Earth.
- China is the only country to achieve a soft landing on the far side of the Moon.
- In 2019, its Chang’e-4 mission landed on the region and explored the Moon’s Von Karman crater with the help of a rover.
Why is the Far Side of the Moon Important?
- The Moon’s far side is often referred to as the dark side because it cannot be seen from the Earth, not because it does not catch the Sun’s rays.
- The Moon is tidally locked with the Earth and therefore, we see only one side of the Moon, also known as the near side.
- The far side has been under the spotlight in recent years as it is very different from the near side.
- It has a thicker crust, more craters and fewer maria, or plains where lava once flowed.
- Examining the samples from the far side can help scientists solve mysteries about the origin and evolution of the Moon — till now, scientists have only been able to analyse samples from the near side.
- The far-side samples can also give answers to the longstanding question: why is it different from the near side?
- Going to the far side, getting samples and doing different kinds of geophysical measurements is really important to figuring out this really long, long-standing mystery.
GOLDENE

- 06 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, researchers have created a free-standing sheet of gold (goldene) that is only one atom thick.
What Is Goldene?
- Goldene is an innovative, free-standing 2D metal with a thickness of just one atom.
- Created through a unique process, Goldene offers a wide range of potential applications in various industries, particularly in electronics and catalysis.
How is it created?
- Scientists first encapsulate an atomic monolayer of silicon between layers of titanium carbide.
- Gold is deposited on this structure, allowing the gold atoms to diffuse and replace the silicon atoms, creating a monolayer of trapped gold atoms.
- Using Murakami's reagent and a Japanese technique employed in forging katanas and high-quality knives, the titanium carbide layers are etched away, leaving a free-standing, one-atom-thick layer of gold.
Dimensions:
- Goldene sheets are approximately 100 nanometres thick, roughly 400 times thinner than the most delicate commercially available gold leaf.
Applications: Goldene's unique properties offer potential applications in various sectors:
- Electronics industry: Goldene's thinness and conductivity can enhance electrical components and circuitry.
- Carbon dioxide conversion: It can potentially aid in transforming carbon dioxide into useful products.
- Hydrogen-generating catalysis: Goldene could be utilized to efficiently produce hydrogen.
- Selective production of value-added chemicals: The material's properties enable the selective generation of chemicals for specific applications.
- Hydrogen production: It can contribute to the clean production of hydrogen.
- Water purification: Goldene could be implemented in water treatment technologies.
Significance:
- Goldene is an economically viable alternative to conventional, thicker gold structures, making it an appealing option for catalytic applications.
- Its unique characteristics position Goldene as a potentially revolutionary material for various industries.
Eta Aquariid Meteor Shower

- 04 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Eta Aquariid meteor shower, which has been active since April 15, will peak on May 4 and 5.
About Eta Aquariid Meteor Shower:
- The Eta Aquariids are a meteor shower associated with Halley's Comet.
- The shower is visible from about April 19 to about May 28 each year with peak activity on or around May 5.
- It is formed when Earth passes through the orbital plane of the famous Halley’s Comet, which takes about 76 years to orbit the Sun once.
- It seems to be originating from the Aquarius constellation, hence ‘Eta Aquariid’.
- The Eta Aquariid meteor shower is known for its rapid speed.
- This makes for long, glowing tails which can last up to several minutes.
- About 30 to 40 Eta Aquarid meteors can be seen per hour during the peak of the meteor shower if observed from the Southern Hemisphere.
- The number decreases to about 10 meteors per hour if being viewed in the Northern Hemisphere.
- This is due to the location of the “radiant” — the position in the sky where the meteor shower seems to come from.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, Eta Aquarid meteors most often appear as ‘Earthgrazers’ long meteors that appear to skim the surface of the Earth.
- In the South, however, they can be seen higher up in the sky and hence are more visible.
What are Comets?
- Comets are frozen leftovers from the formation of our solar system, some 4.6 billion years ago.
- They are composed of dust, rock and ice and orbit around the Sun in highly elliptical orbits which can, in some cases, take hundreds of thousands of years to complete.
- Billions of them are theorised to be orbiting the Sun beyond Neptune, in the Kuiper Belt and even more distant Oort cloud.
- Comets come in different sizes, although most are roughly 10 km wide.
- However, as they come closer to the Sun, comets “heat up and spew gases and dust into a glowing head that can be larger than a planet.
- This material also forms a tail that stretches millions of miles.
How are Meteor Showers Related to Comets?
- Meteors are simply grains of dust or rock that burn up as they enter the Earth’s atmosphere.
- This burning also creates a brief tail.
- Since most meteors are tiny they completely burn up in Earth’s atmosphere. However, once in a while, a large enough meteor passes through and hits the ground (at which time it is called a meteorite), often causing significant damage.
- A meteor shower can be observed when Earth passes through the clouds of dust left behind in a comet’s orbital plane.
- The sky lights up with small and large meteor tails as the debris left behind by the comet interacts with Earth’s atmosphere.
Ajrakh from Kutch

- 02 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The recent addition of Ajrakh from Kutch to the list of GI-tagged fabrics is a proud moment for India's rich textile heritage.
What is Ajrakh?
- The Ajrakh fabric is a traditional hand-block printing technique that originated in Kutch, Gujarat.
- It uses natural dyes and intricate patterns to create beautiful textiles, which are then used to make sarees, dupattas, stoles, and other garments.
- The unique feature of Ajrakh is its use of geometric patterns and rich earthy colours like indigo, madder, and mustard.
- This fabric has been an integral part of the Kutchi culture for centuries and has now gained recognition on a global level with its GI tag.
What is a GI tag?
- The GI tag is a certification that identifies a product as originating from a specific geographical location and possessing unique qualities due to that region's traditional knowledge and expertise.
- It not only adds value to the product but also protects it from imitation or misuse.
- Ajrakh's GI tag was granted by the Geographical Indications Registry after a long process of documentation and verification of its origin and production techniques.
Some other Indian textiles have received similar recognition.
- Banarasi Silk: The luxurious Banarasi silk sarees from Varanasi have been coveted by women all over the world for their exquisite designs and fine quality.
- This fabric has been granted a GI tag for its uniqueness in design, weaving technique, and use of pure silk and zari.
- The intricate designs of Banarasi silk sarees, inspired by Mughal and Persian art, make them stand out in the sea of Indian textiles.
- Chanderi Fabric: Chanderi, a small town in Madhya Pradesh, is known for its delicate and lightweight fabric.
- Chanderi sarees and suits are made from a combination of cotton and silk, giving them a sheer and lustrous appearance.
- This fabric has been granted a GI tag for its traditional handloom weaving technique, which dates back to the 13th century.
- The motifs used in Chanderi fabrics are inspired by nature and are intricately woven using golden zari.
- Kanjeevaram Silk: The Kanjeevaram sarees from Tamil Nadu are famous for their vibrant colours, fine silk, and intricate zari work.
- This fabric has been granted a GI tag for its traditional weaving technique that uses three shuttles to weave the body, border, and pallu of the saree separately and then join them together.
- The rich gold zari work on Kanjeevaram sarees makes them a must-have in every Indian woman's wardrobe.
- Kota Doria: One of the many varieties of sari clothing produced in Muhammadabad Gohna, Mau in Uttar Pradesh and the surrounding area, as well as in Kota, Rajasthan, is kota doria.
- Pure cotton and silk are used to make sarees, which are adorned with square-like designs called khats.
- Since these sarees were woven in Mysore, they were originally known as Masuria.
- The GI tag was given to Kota Doria in July 2005. Kota Doria cotton sarees are regarded as the lightest in India because of their transparency and low weight.
- Odisha Ikat: One type of ikat, which is a resist dyeing method, comes from Odisha and is called Orissa Ikat.
- It is sometimes referred to as "Bandha of Orissa" and has been an Orissan product since 2007.
- To produce the design on the loom before weaving, the warp and weft threads are tie-dyed.
Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Enacted on May 1, 2014, after decades of advocacy, the Street Vendors Act has achieved progress yet faces implementation challenges in safeguarding vendors' livelihoods.
About Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014:
- The Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014 was enacted to legitimize the rights of street vendors (SVs) and regulate their activities.
- It is implemented by respective States/UTs by framing Rules, schemes, Bye-laws and Plan for Street Vending as per provisions of the Act.
- It seeks to safeguard and manage street vending in urban areas, with State-level regulations and initiatives overseen by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) through the formulation of by-laws, urban planning, and regulatory measures.
- The Act clearly defines the roles and obligations of both vendors and various levels of government.
- One of the primary objectives of the Act is to ensure the inclusion of all "existing" vendors within designated vending zones by issuing vending certificates (VCs).
- It establishes Town Vending Committees (TVCs) as a mechanism for participatory governance, with street vendor representatives comprising 40% of the committee members, including a sub-representation of 33% for women SVs.
- These committees are tasked with overseeing the allocation of vending spaces and ensuring the representation of all existing vendors within vending zones.
- Moreover, the Act provides mechanisms for addressing grievances and disputes, proposing the establishment of Grievance Redressal Committees chaired by a civil judge or judicial magistrate.
- Additionally, it mandates that States/ULBs conduct surveys to identify street vendors at least once every five years, ensuring an updated understanding of the street vending landscape and facilitating effective regulatory measures.
Bambi Bucket

- 27 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, an Indian Air Force MI 17 V5 helicopter, equipped with a Bambi Bucket, was deployed to combat the forest fires in Nainital district, Uttarakhand.
What is a Bambi Bucket?
- Bambi Bucket is a specialised aerial firefighting tool that has been in use since the 1980s.
- It is essentially a lightweight collapsible container that releases water from underneath a helicopter to targeted areas.
- The water is released by using a pilot-controlled valve.
- One of its key features is that it can be quickly and easily filled.
- The bucket can be filled from various sources, including a lake, river, pond, and swimming pool, which allows firefighters to swiftly refill it and return to the target area.
- Bambi Bucket is available in a variety of sizes and models, with capacities ranging from 270 liters to more than 9,840 liters.
How was the Bambi Bucket Invented?
- The Bambi Bucket was invented by Don Arney, a Canadian business, in 1982.
- Arney came up with the idea after he realised that the aerial firefighting water buckets in use at the time were not efficient and had a high failure rate.
- These water buckets were generally made of “solid fiberglass, plastic, or canvas with metal frames” and were “too rigid to fit inside the aircraft” and had to be “trucked to fire sites or flown in on the hook of a helicopter thereby slowing the aircraft down.
- Another issue was that the water dropped from these containers used to get dispersed into a spray thereby reducing impact.
- Bambi Bucket does not have these limitations.
- One, it can be stored within the helicopter until development.
- Two, it discharges a solid column of water, “resulting in a more accurate and effective water dump, less evaporation on the descent, and greater impact force.
- It was an instant success and began to be widely used for firefighting.
- Today, Bambi Bucket is used in more than 115 countries around the world by more than 1,000 helicopter operators.
Bathymetry

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Scientists from the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) recently conducted a study of the bathymetry, or ocean floor, in the Indian Ocean.
What is Bathymetry?
- Bathymetry is a technique dedicated to mapping the depths of water bodies, that is, it is the measurement and representation of the topography of the bottom of rivers, seas, and oceans.
- In addition to measuring depth, this study also includes identifying underwater relief and creating three-dimensional maps of the sea floor.
- The word “bathymetry” comes from the Greek "bathýs", meaning deep, and "metron", meaning measure.
- Bathymetry allows for obtaining information about the physical characteristics of the sea floor, such as seamounts, mountain ranges, valleys, abyssal plains, and underwater canyons.
How is Bathymetry Performed?
- To carry out bathymetry, specific equipment is used, such as multibeam sonar (MultiBeam Echosounder), IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), and high-precision positioning systems (via satellite with RTK correction).
- Multibeam sonar emits sound pulses toward the sea floor and measures the time it takes for the sound to return to the sensor after being reflected by submerged surfaces.
- Based on this sound return time and knowledge of the exact position of the vessel and its attitude (roll, pitch, yaw), it is possible to calculate the depth at a given point.
- The bathymetry service generates charts, blueprints, and digital models (2D and 3D) of the sea floor.
- LiDAR sensors, on the other hand, are used to detect data through beams of light above the waterline, mapping slopes, rockfills, and channel walls.
- The fusion of bathymetry data with Lidar data allows the three-dimensional construction of the environment in very high resolution.
- Allowing the client to plan or verify works and/or assets in the region of interest.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- Established in 1999, the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) under the Ministry of Earth Science, Govt of India.
- It is mandated to provide ocean information and advisory services to a broad spectrum of users through sustained ocean observations and constant improvements through systematic and focused research.
- The activities include data services, consultancy, and capacity development.
- HQ: Hyderabad
- INCOIS is a permanent member of the Indian delegation to the IOC of UNESCO and a founding member of the Indian Ocean Global Ocean Observing System (IOGOOS) and the Partnership for Observing the Oceans (POGO).
Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS)

- 26 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The United States has confirmed providing long-range Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) to Ukraine to aid its war effort against Russia.
What is the ATACMS System?
- The Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) is one of the most potent missile systems built by US-based arms manufacturer Lockheed Martin.
- This is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system.
- Its biggest strengths are the long-range of attack, the ability to fire cluster munitions, and the weapon system’s mobility.
- Range: There is a mid-range version of the ATACMS, called Block 1, and a long-range version, Block 1A.
- ATACMS Block 1 has a range of 165 kilometres. Ukraine was provided these systems last year and used them to attack targets in October.
- ATACMS Block 1A, on the other hand, has a maximum range of 300 km. However, this depends on the kind of munition the missile carries.
- With such a range, the long-range ATACMS Block 1A is capable of striking targets well beyond the range of existing Army cannons, rockets, and other missiles.
- Mobility: ATACMS missiles are fired from the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) platforms. Both of these launching systems are highly mobile automatic systems.
Why Ukraine can’t use ATACMS to Target Russian Territories?
- Despite territories deep inside Russia now being within the range of the ATACMS, Ukraine cannot use it to hit targets in these locations.
- Ukraine has committed to only use the weapons inside Ukraine, not in Russia.
- The US administration has made it clear that the weapons cannot be used to hit targets inside Russia.
- The Biden administration is concerned that if Ukraine strikes deep into Russian territory, it will anger Moscow and escalate the conflict.
Microsoft Phi-3-Mini

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A few days after Meta unveiled its Llama 3 Large Language Model (LLM), Microsoft recently unveiled the latest version of its ‘lightweight’ AI model – the Phi-3-Mini.
What is Phi-3-Mini?
- Phi-3 refers to a series of language models developed by Microsoft, with Phi-3-mini being a notable addition.
- Phi-3-mini is a 3.8 billion parameter language model trained on 3.3 trillion tokens, designed to be as powerful as larger models while being small enough to be deployed on a phone.
- Despite its compact size, Phi-3-mini boasts impressive performance, rivaling that of larger models such as ChatGPT-3.5.
- Furthermore, Phi-3-mini can be quantized to 4 bits, occupying approximately 1.8GB of memory, making it suitable for deployment on mobile devices.
- The model’s training data, a scaled-up version of the one used for Phi-2, is composed of heavily filtered web data and synthetic data, contributing to its remarkable capabilities.
Advantages and Challenges of Phi-3-Mini:
- Phi-3-mini exhibits strengths in its compact size, impressive performance, and the ability to be deployed on mobile devices.
- Its training with high-quality data and chat-finetuning contribute to its success. This allows it to rival larger models in language understanding and reasoning.
- However, the model is fundamentally limited by its size for certain tasks.
- It cannot store extensive “factual knowledge,” leading to lower performance on tasks such as TriviaQA.
- Nevertheless, efforts to resolve this weakness are underway, including augmentation with a search engine and exploring multilingual capabilities for Small Language Models.
- Safety: Phi-3-mini was developed with a strong emphasis on safety and responsible AI principles, in alignment with Microsoft’s guidelines.
- The approach to ensuring safety involved various measures such as safety alignment in post-training, red-teaming, and automated testing.
- It also involved evaluations across multiple categories of responsible AI (RAI) harm.
How is Phi-3-Mini Different From LLMs?
- Phi-3-mini is the Small Language Model (SLM). Simply, SLMs are more streamlined versions of large language models.
- When compared to Large Language Model (LLM), smaller AI models are also cost-effective to develop and operate, and they perform better on smaller devices like laptops and smartphones.
- SLMs are great for “resource-constrained environments including on-device and offline inference scenarios.
- Such models are good for scenarios where fast response times are critical, say for chatbots or virtual assistants.
- Moreover, they are ideal for cost-constrained use cases, particularly with simpler tasks.
- While LLMs are trained on massive general data, SLMs stand out with their specialisation.
- Through fine-tuning, SLMs can be customised for specific tasks and achieve accuracy and efficiency in doing them.
- Most SLMs undergo targeted training, demanding considerably less computing power and energy compared to LLMs.
- SLMs also differ when it comes to inference speed and latency.
- Their compact size allows for quicker processing and their cost makes them appealing to smaller organisations and research groups.
Ross Ice Shelf

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
New research has found a "missing piece of the puzzle" of West Antarctic Ice Sheet melt, revealing that the collapse of the ice sheet in the Ross Sea region can be prevented—if we keep to a low-emissions pathway.
About Ross Ice Shelf:
- The Ross Ice Shelf is a floating mass of land-ice, with a front between 15 and 50 meters high. ?
- It is the largest ice shelf in Antarctica.
- Situated in the Ross Sea, it extends off the coast into the ocean, covering an impressive 487,000 square kilometers, roughly the size of France.
- Despite its vast surface area, only 10% of the ice shelf is visible above the water, mostly concealed beneath hundreds of meters of ice.
- The thickness of the Ross Ice Shelf varies significantly, ranging from about 100 meters to several hundred meters at its thickest points near the areas where the shelf connects to the Antarctic continent.
- The formation of the Ross Ice Shelf is the result of snow accumulation and compaction over time, which ultimately transforms into ice.
- It is continuously fed by glaciers draining from both the East and West Antarctic Ice Sheets, creating a balance as new ice is added while existing ice is removed through melting at the base and calving at the front.
- This massive ice shelf plays a critical role in stabilizing the Antarctic ice sheet.
About the Ross Sea:
- Location and Size: The Ross Sea is a vast, remote bay located just 320 km from the South Pole, positioned south and slightly east of New Zealand.
- It covers an area of approximately 370,000 square miles (960,000 square km), making it the largest polar marine ecosystem in the world.
- The sea's dynamics are significantly shaped by the coastal East-Wind Drift, which establishes a vast clockwise gyre, complemented by deepwater upwelling phenomena.
- Notably, it holds the distinction of being Antarctica's first protected area, serving as a habitat for a plethora of penguin species and numerous whale species.
- Depth: Despite its vast size, the Ross Sea is relatively shallow, with an average depth of approximately 530 meters.
- Historical Exploration: The sea is named after British explorer Sir James Clark Ross, who first visited the area in 1841 during his expedition to Antarctica.
- The Ross Sea's importance to both the scientific community and global conservation efforts cannot be overstated, as it provides valuable insights into the effects of climate change on polar ecosystems.
Global Tiger Conservation Coalition

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
At the Sustainable Finance for Tiger Landscapes Conference, Bhutan and the Tiger Conservation Coalition pledged to mobilize $1 billion for tiger conservation efforts.
About the Tiger Conservation Coalition:
- The Tiger Conservation Coalition is a group of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that have worked for many years with partners to conserve tigers.
- It brings together leading tiger biologists and experts in wildlife crime, human-wildlife coexistence, policy, finance, development, and communications with unprecedented alignment on achieving tiger conservation at scale.
- Its member organizations include the Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA), Fauna & Flora, the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), Panthera, TRAFFIC, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF).
- It is an independent group of organizations that combines and shares the vast knowledge, on-the-ground experience, and data of its members and partners to support Tiger Range Countries in developing and implementing effective approaches to tiger conservation.
- The Coalition was founded on strong relationships among eminent tiger experts already working together on major tiger assessments, including the latest assessment by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species released in 2022, and the forthcoming Green Status Assessment, and coalesced around a common vision for tiger recovery.
- By engaging national and local civil society organizations from the region, and continuing to support the Global Tiger Initiative Council and the Global Tiger Forum, the coalition aims to further strengthen partnerships and impactful outcomes for tigers.
- In January 2022, the Tiger Conservation Coalition released its vision for tiger recovery through 2034, the next Year of the Tiger.
- “Securing a Viable Future for the Tiger” presents a set of measurable goals and high-level strategic approaches to achieve the long-term presence of viable and ecologically functional populations of wild tigers.
- Its suggested actions, grounded in the latest science and results, would lead to increasing numbers of tigers secure in current and expanded protected habitats, with distribution and connectivity across their indigenous range.
- Tiger Conservation Coalition members co-developed Tiger Conservation Landscapes 3.0, an integrated habitat modeling system to measure and monitor changes in tiger habitat at range-wide, national, biome, and landscape scales in near real-time.
- This work serves as a model for objective, range-wide, habitat monitoring as countries work to achieve the goals laid out in the 30x30 agenda, the Sustainable Development Goals, and the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
As Asia is warming faster than the global average, it is witnessing more extreme weather, climate, and water-related events than any other region across the world.
Highlights of the State of the Climate in Asia 2023 Report:
- The 2023 State of the Climate in Asia Report, spearheaded by the World Meteorological Organization, sheds light on significant climate trends and events across the continent:
- In 2023, Asia witnessed 79 extreme climate events, affecting over nine million individuals, making it the most disaster-affected region.
- Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide soared to unprecedented levels in 2022.
- Oceans have absorbed approximately a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted annually into the atmosphere since 1960, resulting in record-high ocean heat content in 2023.
- Tropical cyclone activity over the North Indian Ocean surpassed the average.
- 2023 marked Asia's second-highest mean temperature on record, with Japan and Kazakhstan experiencing record warmth.
- Glacial retreat accelerated in 2023, particularly in the East Himalayas and Central Asia's Tian Shan mountains, due to elevated temperatures and arid conditions.
About the World Meteorological Organisation:
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations with a membership of 193 member states and territories.
- It is the UN system's authoritative voice on the state and behavior of the Earth's atmosphere, its interaction with the oceans, the climate it produces, and the resulting distribution of water resources.
- WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization, the roots of which were planted at the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23 March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences a year later.
- The Secretariat, headquartered in Geneva, is headed by the Secretary-General.
- Its supreme body is the World Meteorological Congress.
Crystal Maze-2 Missile

- 24 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Air Force achieved a milestone by successfully test-firing an air-launched ballistic missile, ROCKS or Crystal Maze 2, capable of hitting targets over 250 kilometers away.
About Crystal Maze-2 Missile:
- Crystal Maze 2 missile also known as ROCKS is an advanced air-launched missile developed by Israel, designed for precision strikes on high-value targets.
- This missile is capable of engaging heavily fortified positions from long distances, ensuring minimal collateral damage.
- It is renowned for its accuracy and reliability in combat scenarios, making it a preferred choice for missions requiring surgical precision.
- The missile’s integration into various platforms enhances its operational flexibility and effectiveness in diverse combat environments.
Features:
- Crystal 2 operates effectively in GPS-denied areas and can breach regions secured by air defense systems.
- This system allows for the choice between penetration or blast fragmentation warheads, making it suitable for targeting both surface and heavily fortified underground facilities.
- With a striking distance of over 250 kilometers, it offers versatility with options for either penetration or blast fragmentation warhead, ensuring the destruction of above-ground or well-protected underground targets.
- India is currently developing the Crystal Maze 2 missile.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) has successfully conducted tests on this missile and aims to procure it in large numbers under the Make in India initiative.
- This move highlights India’s dedication to achieving self-sufficiency in defense manufacturing.
Netzah Yehuda Battalion

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The US government may soon sanction a battalion of the Israeli Defence Forces (IDF) over alleged human rights violations, marking the first such move in the history of the two countries’ relations.
What is the Netzah Yehuda Battalion?
- The Netzah Yehuda battalion was set up in 1999 to accommodate the religious beliefs of ultra-Orthodox Jews and other religious nationalist recruits in the army.
- It was established to facilitate military service for these communities, accommodating their religious observances by scheduling prayer and study times, and restricting their interactions with female soldiers.
- The battalion is historically stationed in the occupied West Bank region and faces intense scrutiny for allegedly committing human rights violations against Palestinians.
- Netzah Yehuda came on the radar of United States agencies after the death of an elderly Palestinian-American man, who was detained by the battalion.
What is the Unit Accused Of?
- The United States called for a criminal investigation after Netzah Yehuda soldiers were accused of being involved in the death of a 78-year-old Palestinian-American, Omar Assad, who died of a heart attack in 2022 after he was detained and was later found abandoned at a building site.
- A Palestinian autopsy found Assad died from a stress-induced heart attack brought on by being manhandled.
- The case attracted unusual attention because of his dual nationality, his age, and a demand by the U.S. State Department for an investigation into his death.
- There have been several other incidents in recent years, some captured on video, in which Netzah Yehuda soldiers were accused of, or charged with, abusing Palestinian detainees.
- The battalion primarily operated in the West Bank before it was moved out of the territory in late 2022 after U.S. criticism.
- The unit has recently been serving in Gaza.
Tundra Ecosystem

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent study has warned that the warming planet may alter the characteristics of tundra environments and could transform them from carbon sinks to carbon sources.
About Tundra Ecosystem:
- The Tundra ecosystem is one of the unique ecosystems of the planet.
- The adverse climatic conditions of tundra regions like dry winds, meager precipitation, and extreme cold make it a unique and desert-like ecosystem with treeless fields.
- These harsh climatic conditions of the tundra region make the survival of plant and animal species quite severe.
Key Characteristics of Tundra Regions:
- Low Temperatures: Tundra areas experience frigid temperatures, ranging from -34 to -6 degrees Celsius (-30 to 20 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Short Growing Seasons: The tundra's summer growth period lasts merely 50 to 60 days, with sunlight persisting up to 24 hours a day.
- Permafrost: Below the surface lies a layer of permanently frozen soil, varying from a few inches to several feet thick.
- Minimal Precipitation: Despite being likened to deserts in terms of moisture, tundra regions receive low precipitation levels, primarily in the form of snow.
- Limited Biodiversity: Harsh conditions in the tundra support fewer plant and animal species compared to other biomes.
- Carbon Sink: Tundras serve as significant carbon storage areas due to the slow decomposition rates in their cold environments.
Types of Tundra:
- Arctic Tundra: Found north of the taiga belt in the far Northern Hemisphere, encompassing regions between the North Pole and the boreal forest, including parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, and Finland.
- Alpine Tundra: Prevails above the tree line in mountain ranges worldwide, such as the Rockies, the Andes, the Himalayas, and the Alps.
- Antarctic Tundra: Encompasses several sub-Antarctic islands and portions of the Antarctic continent.
Flora and Fauna:
- Flora: Common plant species in tundra regions include mosses, lichens, sedges, cotton grass, and birches.
- Fauna: Wildlife in tundra ecosystems includes Arctic foxes, snow geese, polar bears, and other cold-adapted species.
National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)
- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Each organ transplant case will receive a distinctive National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) ID assigned to both the donor and the recipient.
Highlights of the News:
- The Union Health Ministry has mandated the cessation of commercial organ transactions, particularly those involving foreign nationals, and emphasized the need for stringent oversight by local authorities.
- For deceased donor transplants, a NOTTO-ID is required for organ allocation, while in living donor transplants, the ID must be generated within 48 hours post-surgery through the NOTTO website by the hospital.
What is the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO)?
- NOTTO is a national organization established under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
It serves as the central coordinating hub for:
- Organ and tissue procurement and distribution.
- Maintaining a registry of organ and tissue donation and transplantation activities across the country.
NOTTO comprises two divisions:
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network:
- Acts as the primary center for nationwide coordination of organ and tissue procurement, distribution, and registry.
- Established in accordance with the Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011.
- National Biomaterial Centre (National Tissue Bank):
- This center focuses on filling the gap between demand and supply while ensuring quality assurance in tissue availability.
- The Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011 has expanded NOTTO's scope to include tissue donation and registration of tissue banks.
Activities performed by NOTTO include:
-
- Coordinating tissue procurement and distribution
- Donor tissue screening
- Tissue removal and storage
- Tissue preservation
- Laboratory screening of tissues
- Tissue tracking
- Sterilization
- Record maintenance
- Data protection and confidentiality
- Quality management in tissues
- Patient information on tissues
- Developing guidelines, protocols, and standard operating procedures
- Training and assistance in registering other tissue banks
BFI Biome Virtual Network Program

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) has joined the Blockchain for Impact (BFI) Biome Virtual Network Program to accelerate transformative healthcare solutions through biomedical innovation.
About BFI Biome Virtual Network Program:
- The BFI-Biome Virtual Network Program is a pioneering initiative uniting incubators and research institutes under a single umbrella.
- This fosters collaborations among the stakeholders in the translational pipeline, the process of transforming research discoveries into real-world applications.
- Through this program, BFI will allocate over 200,000 USD over the course of three years, leveraging C-CAMP’s expertise to develop essential programs for healthcare-based startups.
- C-CAMP being an organization to foster deep science research and innovation for societal impact, the goals and mandates of both partners naturally align and complement each other.
- The partnership is expected to blur disciplinary boundaries in approaching biotech R&D, promote cross-integration of expertise and infrastructure, and provide multidisciplinary insights into need identification, problem-solving, and solution implementation.
What is C-CAMP?
- Centre for Cellular And Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) is an initiative of the Dept of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, with a mandate to be an enabler of cutting edge Life Science Research and Innovation.
- C-CAMP is also a member of the Bangalore Life Sciences Cluster (BLiSC).
- It facilitates Bioscience Research and Entrepreneurship by providing Research, Development, Training, and Services in state-of-the-art Technology Platforms.
- As a part of C-CAMP's mandate of promoting entrepreneurship and innovation, C-CAMP has created and fostered an entrepreneur-friendly culture in and around the Academic/Research environment through its involvement in Seed Funding Schemes for Startups, Entrepreneur Mentorship program, and Bio-Incubation facility.
- It has established State-Of-The-Art Platform Technologies which are essential requirements for success and leadership in the field of Life Sciences.
- C-CAMP allows Investigators to use Techniques as tools and not be limited by Technological barriers while pursuing challenging scientific questions.
World Earth Day 2024

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
On World Earth Day 2024, a global network promoting local food and traditional cooking has called for practical measures to cut down on plastic use in the food chain and to safeguard the environment.
About World Earth Day:
- World Earth Day, also known as International Mother Earth Day, is a globally recognized event dedicated to raising awareness and promoting the sustainability of our planet.
- Earth Day is celebrated on April 22 in the United States and on either April 22 or the day the spring equinox occurs throughout the rest of the world.
- Theme: The theme for World Earth Day 2024 is “Planet vs Plastics”.
- The theme aims to bring attention to the serious issue of plastic pollution and how it harms nature.
Earth Day History:
- The origin of Earth Day can be traced back to 1970.
- The idea behind the event originated from Gaylord Nelson, a US senator, and Denis Hayes, a Harvard student.
- They were both deeply disturbed by the deteriorating environment in the United States and the massive January 1969 oil spill in Santa Barbara, California.
- Deeply disturbed by the environmental impacts, Gaylord Nelson wanted to infuse the energy of student protests into an emerging public consciousness about air and water pollution.
- He recruited Denis Hayes, a young activist, to manage the campus teach-ins and to scale the idea of environment conservation to a broader public.
- They choose April 22, a weekday between Spring Break and Final Exams, to increase student participation.
- Its immediate success was evident with a massive turnout of 20 million people across the US.
- By 1990, Earth Day became a global event transcending national borders.
Earth Day Significance:
- Earth Day symbolizes the need to protect our mother nature.
- The day encourages every individual to think about environmental conservation and act accordingly.
- It speaks about the need to reduce carbon footprints, conserve natural resources, and protect wildlife and natural habitats.
- The day also serves as a platform to advocate for policy changes that can have a positive impact on the environment.
Ethylene Oxide
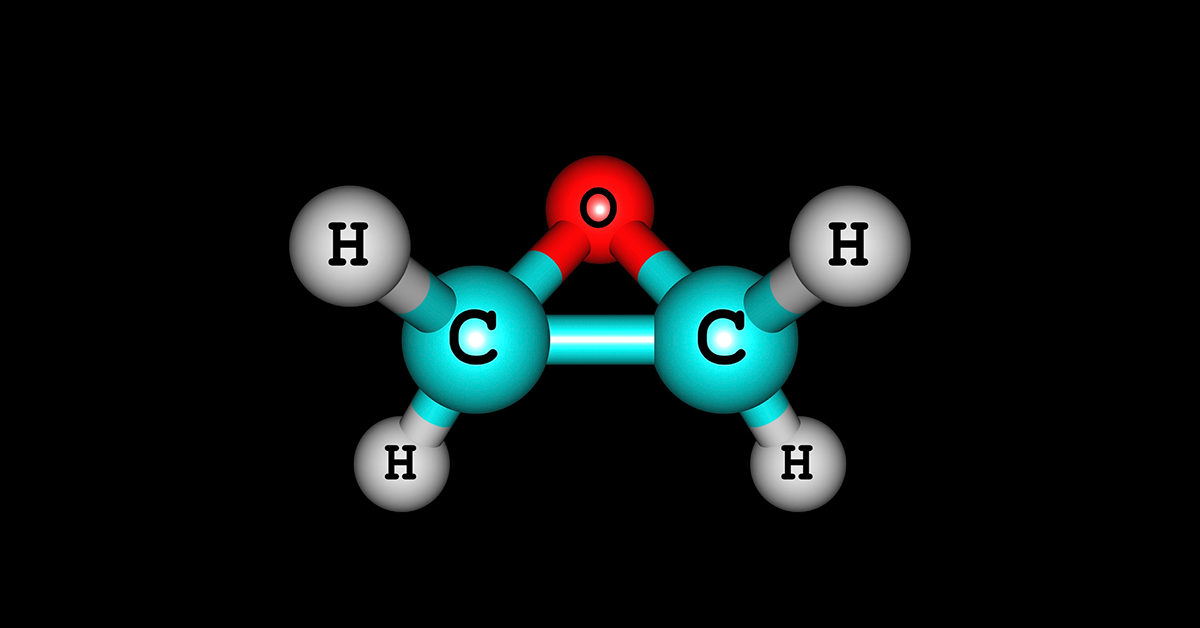
- 20 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Singapore Food Agency (SFA) has issued a recall on Indian spice brand Everest’s fish curry masala after detecting an ‘excessive’ amount of ethylene oxide–a pesticide–in it.
What is Ethylene Oxide?
- Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a slightly sweet odor and It dissolves easily in water.
- It is widely used in various industries due to its versatile properties.
- Its primary applications include the production of other chemicals, such as ethylene glycol for antifreeze and polyester, as well as the sterilization of medical equipment.
- It also has minor applications in agriculture.
- In this sector, it's used as a fumigant to control insect pests in stored agricultural goods, such as food commodities, to protect them from infestation.
- This usage makes up less than 1% of its applications, and it is combined with other gases to minimize potential toxicity to humans and the environment.
- While ethylene oxide plays a significant role in many industrial processes, it also poses health risks to those exposed to it.
- Potential health effects range from mild symptoms like headaches, nausea, and respiratory issues, to more severe problems such as cancer and reproductive harm.
- To minimize exposure risks, industries and facilities that use ethylene oxide are subject to environmental regulations and required to implement safety measures.
- These measures include emission-reducing and monitoring devices, on-site testing, site-specific operating parameters, and regular reporting and record-keeping.
- Despite these precautions, workers in factories that produce or use ethylene oxide, as well as people living near these facilities, may still face potential health risks.
How Do Pesticides Harm Our Bodies if Present in Food?
- Pesticides, designed to ward off unwanted organisms in agriculture, can pose extensive risks to human health if they find their way into our food chain.
- Even a brief exposure to some of them can cause acute poisoning and symptoms, including diarrhea, dehydration, and skin irritation.
- Some insecticides like Resmethrin, Cypermethrin, and Fenvalerate have been connected to chronic health issues, which include reproductive complications, immune system disruption, pores, and skin infection, and interference with the endocrine system.
- Even low-level exposure over the years can cause critical health implications.
How Long-term Issues Can be Combated?
- Some steps can be taken to mitigate the risks associated with pesticides and ethylene oxide exposure.
- It’s critical to prevent the runoff of insecticides into storm drains, which can contaminate water sources.
- While using insecticides, it’s essential to consider the characteristics of the application site to minimize unintended exposure.
- Attention to the geological factors and groundwater depth can prevent pesticide seepage into water reservoirs.
- By implementing these measures and maintaining strict regulations, we can minimize the health risks posed by these chemical substances.
Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA)

- 19 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) Asia Pacific, in collaboration with other environmental organizations, has called on the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to take decisive action in response to plastic pollution.
About Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA):
- The Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives (GAIA) is an alliance of over 1,000 grassroots groups, NGOs, and individuals working towards a transition from a linear, extractive economy to a circular system.
- GAIA's primary objective is to create a world that prioritizes people's right to a safe and healthy environment, free from toxic pollution and resource depletion.
- GAIA envisions a just, zero-waste world where communities' rights are respected, and ecological limits are acknowledged. To achieve this vision, the alliance focuses on:
- Eliminating Incineration: GAIA advocates for alternatives to incineration and promotes waste management practices that protect the environment and public health.
- Promoting Zero Waste: The alliance supports the adoption of zero-waste strategies, emphasizing waste reduction, reuse, and recycling to conserve resources and reduce pollution.
- Addressing Plastic Pollution: GAIA recognizes the global plastic pollution crisis and works on initiatives to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable alternatives.
- Mitigating Climate Change: GAIA advocates for climate-friendly waste management practices, emphasizing the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions from waste disposal.
What is Incineration?
- Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves burning hazardous materials at high temperatures to destroy contaminants.
- This process takes place in an "incinerator," a furnace specifically designed to safely burn hazardous materials within a combustion chamber.
- Various types of hazardous materials can be treated through incineration, including soil, sludge, liquids, and gases.
- While incineration effectively destroys many harmful chemicals such as solvents, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pesticides, it does not destroy metals like lead and chromium.
- Modern incinerators are equipped with air pollution control mechanisms, such as fabric filters, scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators.
- These technologies help remove fly ash and gaseous contaminants generated during the incineration process, mitigating its environmental impact.
- Despite its benefits in waste treatment, incineration remains a topic of debate due to concerns about residual pollutants and the potential for contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Thiruvalluvar

- 16 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Seeking to connect with the people of Tamil Nadu where his party is trying to gain a foothold, Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced that the BJP will work towards building Thiruvalluvar cultural centers all over the world.
Who was Thiruvalluvar?
- Thiruvalluvar, the author of the revered 'Thirukkural' or 'Sacred Couplets', remains a figure of historical debate.
- His exact period and religious affiliation are uncertain, with proposed dates ranging from the 3rd or 4th century CE to the 8th or 9th century.
- Various groups regard him as a Hindu sage, a Jain sage, or a Dravidian saint with no religious identifiers except his Dravidian heritage.
- Accounts of Thiruvalluvar's origins are diverse.
- In Edward Jewitt Robinson's 1873 book, 'Tamil Wisdom: Traditions Concerning Hindu Sages and Selections from their Writings', he described Thiruvalluvar as a "Pariah" with a mother from "the low class" and a possibly Brahmin father.
- According to this narrative, Thiruvalluvar was found in a grove near a Shiva temple in Mayilapur and was taken in by the wife of a high-ranking Velalan before being entrusted to a "Pariah family."
- Despite the ambiguity surrounding Thiruvalluvar's identity, his wisdom-laden verses in 'Thirukkural' continue to influence and inspire generations across religious and cultural divides.
Why does Thiruvalluvar matter?
- Thiruvalluvar, affectionately called Valluvar by Tamils, is revered as a cultural and moral icon across caste and religious lines.
- His 'Thirukkural', a compilation of 1,330 couplets, is an integral part of Tamil culture, comparable to the Bhagavad Gita or Ramayana in North Indian Hindu households.
- It serves as a foundational text for ethical living and tracing Tamil cultural roots.
- Beyond Tamil Nadu, Thiruvalluvar's wisdom is celebrated in the context of ancient India's rich philosophical heritage, emphasizing morality and ethics.
- His enduring influence is evident as successive Indian finance ministers reference his teachings in annual Budget speeches.
- However, competing claims to Thiruvalluvar's legacy have sparked controversy, such as the 2019 debate surrounding the BJP's depiction of him in saffron robes instead of traditional white garments.
- Despite these disputes, the profound impact of Thiruvalluvar's teachings continues to resonate across various cultures and languages, fostering unity and moral guidance.
Why Are Political Parties Asserting Thiruvalluvar's Legacy?
- Political parties, both national and regional, have long vied for ownership of Thiruvalluvar's legacy. For instance, the BJP, with a limited grassroots presence in Tamil Nadu, seeks to bolster its standing through the appropriation of Tamil saints and icons.
Precautionary Principle

- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The precautionary principle is becoming an established guideline for policymakers tackling environmental problems according to British environmentalist Norman Myers
What is the Precautionary Principle?
- The Precautionary Principle serves as a foundational concept in policymaking, advocating for the adoption of proactive measures to mitigate potential risks to public health or the environment:
- Proactive Risk Management: The principle legitimizes the implementation of preventative measures in situations where there are uncertainties regarding the extent of harm posed by certain activities or policies.
- Rather than waiting for conclusive scientific evidence, decision-makers are encouraged to take preemptive action to prevent serious or irreversible damage.
- Scientific Uncertainty: It acknowledges that in cases where scientific certainty is lacking, waiting for conclusive evidence before taking action may result in significant harm.
- Therefore, the principle emphasizes the importance of not using the absence of full scientific certainty as a justification for delaying necessary measures to prevent environmental degradation or protect public health.
- Risk-Averse Approach: By advocating for precautionary action, even in the absence of absolute certainty about potential harm, the principle prioritizes safety and prudence.
- It underscores the importance of erring on the side of caution to safeguard against potential risks, thus emphasizing a preventive rather than reactive approach.
- International Recognition: Originating in the 1970s, the Precautionary Principle has gained international recognition and has been enshrined in various international treaties and conventions related to environmental protection.
- It has been incorporated into the legal frameworks of organizations such as the European Union and has influenced decisions on issues ranging from climate change to biodiversity conservation.
- Application in Policy: The principle has influenced the development of laws and regulations worldwide, shaping policies related to endangered species, climate change, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Notably, it has played a significant role in determining the European Union's stance on GMOs and has been integral to the formulation of EU environmental law.
- The Precautionary Principle emphasizes the importance of taking proactive measures to address potential risks, particularly in situations where scientific evidence is uncertain but the potential consequences are significant.
- It embodies a proactive and risk-aware approach to policymaking, intending to prevent harm and promote sustainable development.
About Jim Corbett National Park:
- Jim Corbett National Park, named after the renowned naturalist and conservationist Jim Corbett, is situated in Uttarakhand's Nainital district.
- As the oldest national park in India, it was initially established as Hailey National Park in 1936 to protect the endangered Bengal tiger.
- The park is an integral part of the larger Corbett Tiger Reserve, with the Patli Dun Valley forming its core area.
- The Ramganga River flows through the park, contributing to its diverse ecosystem.
- Not only is it known for its rich biodiversity, but also for being the first area to come under the Project Tiger initiative in 1973.
Hubble Tension
- 15 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
One of the biggest mysteries in cosmology is the ‘Hubble tension’, the puzzle that the expansion of the Universe we see today doesn’t match what we think it should be from looking at the early cosmos.
What is Hubble Tension?
- The Hubble tension refers to a puzzling disagreement between two methods of measuring the universe's expansion rate, represented by the Hubble constant (H0).
- The Hubble constant describes how fast galaxies move away from each other due to cosmic expansion.
- Researchers employ two primary approaches to estimate H0: the cosmic distance ladder and analysis of the cosmic microwave background (CMB).
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
- CMB constitutes a ubiquitous sea of photons, remnants of the Big Bang's aftermath.
- Scientists scrutinize CMB for temperature variations and employ intricate trigonometric techniques to analyze its large-scale properties.
- This analysis culminates in an estimation of cosmic expansion at approximately 68 (km/s)/Mpc.
Cosmic Distance Ladder:
- This method facilitates the measurement of distances to celestial objects spanning various proximity ranges.
- Notably, Cepheid variable stars, which exhibit predictable luminosity fluctuations over time, serve as crucial distance indicators.
- By gauging the brightness of Cepheid variables, researchers can infer their distances, leading to an estimation of H0 around 73 (km/s)/Mpc.
Discrepancy and Hubble Tension:
- The utilization of these two distinct measurement methods yields slightly divergent values for H0, resulting in the emergence of the Hubble tension.
Significance of the Hubble Tension:
- The presence of the Hubble tension suggests potential implications, including unexplored physical phenomena or systematic errors in measurement techniques.
- Resolving this tension is imperative to enhance our comprehension of the universe's expansion dynamics and the fundamental laws governing it.
Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)

- 13 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A contentious recent decision by the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi), permitting carbon offsetting for Scope 3 emissions of businesses with SBTi-based climate targets, has stirred controversy and skepticism.
About Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi):
- The Science-based Targets Initiative (SBTi) is a global movement launched post the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement to mobilize companies in combating climate change.
- SBTi supports businesses in their decarbonization projects, ensuring compatibility with limiting global temperature rise to 1.5C° and achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
- Backed by a scientific method, SBTi verifies company objectives are aligned with COP21 goals.
- SBTi was initiated by four international organizations:
- United Nations Global Compact (UNGC)
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
- Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP)
- World Resource Institute (WRI)
- The primary objective of SBTi is to guide businesses in setting greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction targets that align with the Paris Agreement, are scientifically valid, and contribute significantly to reducing global emissions.
To determine a 1.5C° trajectory compatibility, SBTi uses science-based targets that account for the following factors:
-
- A carbon budget focused on achieving the 1.5C° global warming limit.
- GHG emission scenarios from the IPCC or the IEA.
- Emission allocation method: emission intensity reduction, absolute emission reduction, or emission intensity convergence toward a sector-specific reference level
- Through this methodology, companies can establish clear and science-based GHG reduction targets, effectively contributing to global emission reduction efforts.
SBTi's Net Zero objective:
- In October 2021, SBTi introduced its "Net Zero" benchmark, challenging committed companies to achieve long-term reduction targets up to carbon neutrality.
The Net Zero goal builds upon the initial SBT approach and focuses on four essential components:
-
- Short-term targets: To align with the 1.5°C objective, companies must set targets for reducing their total emissions (Scopes 1, 2, and 3) within a maximum of 5 to 10 years.
- Long-term objectives: Alongside short-term targets, Net Zero requires companies to define long-term goals compatible with limiting global warming to 1.5°C and achieve them by 2050 (or 2040 for the energy sector).
- Carbon finance for short-term contributions: Companies are encouraged to invest in external carbon sequestration or avoidance projects by purchasing carbon credits, complementing their GHG reduction efforts. SBTi prioritizes sequestered emissions over avoided emissions, considering the latter's carbon credits less reliable.
- Neutralization: As the final stage in reaching carbon neutrality, companies must minimize residual emissions and then offset them through carbon sequestration actions.
- The SBTi movement has rapidly gained international recognition for its rigor, reliability, and the credibility of the people behind it.
- Several thousand companies of all sizes have rapidly adopted the scientific approach it promotes. To date, nearly 6,800 companies worldwide have signed up to the SBTi.
Sungrazing Comet
- 12 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A tiny "sungrazer" comet was discovered, photographed, and destroyed during the recent total solar eclipse — all within 24 hours.
What is a Sungrazing Comet?
- Sungrazing comets are a special class of comets that come very close to the sun at their nearest approach, a point called perihelion.
- To be considered a sungrazer, a comet needs to get within about 850,000 miles from the sun at perihelion.
- Many come even closer, even to within a few thousand miles.
- Being so close to the sun is very hard on comets for many reasons.
- They are subjected to a lot of solar radiation which boils off their water or other volatiles.
- The physical push of the radiation and the solar wind also help form the tails. As they get closer to the sun, the comets experience extremely strong tidal forces or gravitational stress.
- In this hostile environment, many sungrazers do not survive their trip around the sun.
- Although they don't crash into the solar surface, the sun can destroy them anyway.
- Many sungrazing comets follow a similar orbit, called the Kreutz Path, and collectively belong to a population called the Kreutz Group.
- Close to 85% of the sungrazers seen by the SOHO satellite are on this orbital highway.
- Scientists think one extremely large sungrazing comet broke up hundreds, or even thousands, of years ago, and the current comets on the Kreutz Path are the leftover fragments of it.
- Comet Lovejoy, which reached perihelion on December 15, 2011, is the best-known recent Kreutz-group sungrazer.
- And so far, it is the only one that NASA's solar-observing fleet has seen survive its trip around the sun.
What is a Comet?
- A comet is a small celestial body made primarily of ice, dust, and rocky material that orbits the sun in an elongated path.
- When a comet approaches the sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, releasing dust and gas into a glowing coma, or halo, around the comet's nucleus.
- This glowing coma often forms a tail that stretches away from the sun due to the solar wind and radiation pressure.
- Comets are often referred to as "dirty snowballs" or "icy dirtballs" because of their composition.
- They are believed to be remnants from the early formation of the solar system and carry important information about its history.
- Comets can have highly elliptical orbits, sometimes taking thousands or even millions of years to complete a single orbit around the sun.
Higgs Boson

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Peter Higgs, the eminent theoretical physicist who first proposed the idea of what we now know as the “Higgs Boson,” died at the age of 94 on April 8.
What is the Higgs Boson?
- Particles make up everything in the universe but they did not have any mass when the universe began.
- They all sped around at the speed of light, according to the European Council for Nuclear Research (CERN).
- CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Research, is where the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is located, and it's where the discovery of the Higgs Boson was made in 2012 through experiments conducted at the LHC.
- Everything we see like planets, stars, and life, emerged after particles gained their mass from a fundamental field associated with the particle known as the Higgs boson.
- The particle has a mass of 125 billion electron volts making it 130 times bigger than a proton?, according to CERN.
- Interestingly, the subatomic particles known as bosons are named after Indian Physicist Satyendra Nath Bose.
How does the Higgs Boson Work?
- The Higgs boson is a fundamental component of a theory formulated by Higgs and colleagues in the 1960s to elucidate how particles acquire mass.
- According to this theory, a pervasive Higgs energy field permeates the universe.
- As particles traverse this field, they interact with and draw in Higgs bosons, which congregate around the particles in varying quantities.
- Likewise, envision the universe akin to a party: less prominent guests can swiftly traverse the room without notice, while more popular guests attract clusters of people (the Higgs bosons), thus decelerating their movement through the room.
- Similarly, particles navigating the Higgs field experience a comparable phenomenon.
- Certain particles attract larger assemblies of Higgs bosons, and the more Higgs bosons a particle draws in, the greater its mass becomes.
Why is the Higgs Boson Called the “God Particle?”
- The Higgs boson is popularly known as the "God Particle".
- The name originated from Nobel Prize-winning physicist Leon Lederman's book on the particle which he titled the "Goddamn Particle", owing to frustration over how difficult it was to detect.
- However, his publishers changed the name to "The God Particle", which often draws ire from religious communities.
Who was Peter Higgs?
- Born in UK's Newcastle upon Tyne in 1929, Mr Higgs studied at King's College in London and has taught at the University of Edinburgh since the 1950s.
- Described as a modest man who published only a few scientific papers, he disliked his sudden fame calling it "a bit of a nuisance", even cringing when the term "Higgs boson" was used.
- Even as a lifelong atheist, he disliked the name "God particle".
- In 2013, Higgs and Francois Englert won the Physics Nobel Prize for their work on the particle which was thought to be a key to explaining the universe.
Black Swan Event

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Army Chief Gen Manoj Pande on Monday called upon the force to be always prepared for 'black swan' events and "expect the unexpected" even as he identified technology as the new area for strategic competition among nations.
What is the Black Swan Event?
- A black swan is a rare, unpredictable event that comes as a surprise and has a significant impact on society or the world.
- These events are said to have three distinguishing characteristics:
- They are extremely rare and outside the realm of regular expectations
- They have a severe impact after they hit; and
- They seem probable in hindsight when plausible explanations appear.
When did the Term Originate?
- The black swan theory was put forward by author and investor Nassim Nicholas Taleb in 2001 and later popularised in his 2007 book – The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable.
- In his book, Taleb does not try to lay out a method to predict such events but instead stresses building “robustness” in systems and strategies to deal with black swan occurrences and withstand their impact.
- The term itself is linked to the discovery of black swans.
- Europeans believed all swans to be white until 1697 when a Dutch explorer spotted the first black swan in Australia.
- The metaphor ‘black swan event’ is derived from this unprecedented spotting from the 17th century, and how it upended the West’s understanding of swans.
Implications of Black Swan Events:
- Black Swan events are characterized by their extreme rarity, severe impact, and widespread implications across various sectors.
- These unanticipated occurrences can trigger substantial disruptions, unveiling vulnerabilities in systems once thought resilient and prompting reassessments of risk management practices.
- Disruption: Black Swan events have the potential to disrupt economies, industries, and societies on a global scale.
- Their unforeseen nature can cause sudden shifts in financial markets, business operations, and everyday life, leaving lasting effects on the overall landscape.
- Uncertainty: The inability to predict Black Swan events using traditional methods injects considerable uncertainty into decision-making and planning for individuals, organizations, and governments.
- Navigating through such unpredictable circumstances can pose significant challenges for all affected parties.
- Vulnerability: These rare events can expose vulnerabilities in systems that were previously thought to be impervious or resilient.
- By doing so, Black Swan events emphasize the importance of preparedness and encourage the development of more robust risk management practices.
- Reassessment of Risk: In the aftermath of a Black Swan event, there is often a renewed focus on identifying and mitigating previously overlooked risks.
- This heightened awareness can lead to changes in investment strategies, regulatory policies, and overall risk management practices.
- Regulatory and Policy Responses: Governments and regulatory bodies may implement new regulations or policies in response to Black Swan events.
- These measures are designed to prevent or mitigate the impact of similar occurrences in the future, ultimately shaping the economic and social landscape.
- Behavioral and Attitude Changes: Black Swan events can significantly alter behaviors and attitudes as individuals and organizations adapt to the new reality.
- These shifts may include changes in consumer behavior, investment strategies, and approaches to risk management.
Examples of Black Swan Events:
- The Dot-com Bubble: In 2000, the valuation of many internet-based companies plummeted after a period of rapid growth.
- The 9/11 Terrorist Attacks: The events of September 11, 2001, had far-reaching consequences on global security, politics, and economies.
- The 2008 Financial Crisis: A series of shocks to Wall Street due to the unraveling of subprime lending practices caused significant economic turmoil.
- Brexit: The unexpected decision of the United Kingdom to leave the European Union in June 2016 caught many by surprise and caused the British pound to plummet against the US dollar.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: The ongoing global health crisis continues to significantly affect economies and markets worldwide.
- These instances illustrate the profound and widespread implications of Black Swan events, underscoring the importance of adaptability and resilience in an ever-changing global landscape.
TSAT-1A Satellite

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
SpaceX successfully launched and deployed the TSAT-1A satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in partnership with Satellogic Inc.
About TSAT-1A Satellite:
- TSAT-1A is a groundbreaking optical sub-meter resolution Earth observation satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in collaboration with Latin American company Satellogic Inc.
- This collaboration began in late 2023, culminating in TSAT-1A's assembly at TASL's Assembly, Integration, and Testing (AIT) plant in Karnataka, India.
- Launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United States, via SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket, TSAT-1A has since garnered attention for its advanced capabilities and strategic significance.
Key Features of TSAT-1A:
- Sub-meter resolution imagery: TSAT-1A's primary strength lies in its ability to capture high-resolution military-grade imagery of Earth's surface, providing precision of less than one meter per pixel.
- Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging: This technology enables TSAT-1A to gather data across a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, offering a detailed and nuanced understanding of land, water, and other natural resources.
- Enhanced performance: TSAT-1A offers improved collection capacity, a wider dynamic range, and low-latency data delivery, ensuring efficient and reliable intelligence gathering.
Strategic Applications and Implications:
- Designed for use by Indian defense forces, TSAT-1A is set to play a pivotal role in discreet information gathering, with the potential for data-sharing among friendly nations.
- By enhancing defense forces' preparedness, response capabilities, and strategic decision-making, TSAT-1A represents a significant milestone in India's space industry and a potential game-changer in the realm of defense and security.
About SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket:
- The Falcon 9 is a partially reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX.
- Known for its reliable and safe transportation capabilities, Falcon 9 is primarily used to launch payloads and crew into Earth orbit.
- Since its first launch in 2010, Falcon 9 has made significant strides in the aerospace industry, becoming the first commercial rocket to launch humans to orbit in 2020 and maintaining a strong safety record with only one flight failure to date.
SUVIDHA Portal

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Election Commission said that over 73 thousand applications had been received on the Suvidha Portal in just 20 days since the announcement of General Elections 2024.
About SUVIDHA Portal:
- The Suvidha portal is a technological solution developed by the Election Commission of India (ECI) to ensure a level playing field upholding the democratic principles of free, fair, and transparent elections.
- Suvidha's robust track record showcases its ability to streamline requests for permissions and facilities during election campaigns, catering to diverse needs such as rallies, canvassing, and temporary party offices.
- The Suvidha portal offers both online and offline submission options, ensuring inclusivity and equal opportunity for all stakeholders.
- Permission requests can be processed efficiently through a robust IT platform managed by nodal officers from various state departments.
- The portal's user-friendly design allows political parties and candidates to submit requests from anywhere, at any time.
- To enhance transparency and convenience, Suvidha also provides a companion app for real-time tracking of application statuses.
- Available on both iOS and Android platforms, the app ensures a seamless user experience.
- Moreover, the Suvidha portal promotes accountability by offering features such as real-time tracking, status updates, timestamped submissions, and SMS communication.
- Data collected on the Suvidha platform serves as a valuable resource for scrutinizing election expenditures, thereby promoting greater integrity in the electoral process.
- With Suvidha, the Election Commission of India demonstrates its commitment to facilitating a fair, efficient, and transparent electoral environment, granting equal access to all political parties and candidates seeking permissions and clearances during election campaigns.
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In its manifesto for the Lok Sabha election, the primary opposition party pledged to cease the weaponization of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) if entrusted with power.
About the Prevention of Money Laundering Act:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) constitutes the cornerstone of India's legal framework aimed at combating money laundering, with its enactment and enforcement starting from July 1, 2005.
- Enacted by India's Parliament under Article 253, which authorizes legislation for implementing international conventions, the Act has three primary objectives:
- Prevention and control of money laundering
- Confiscation of proceeds derived from laundering, and
- Addressing related issues within India.
- The Act empowers the Director of the Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND) and the Director (Enforcement) with exclusive and concurrent powers to enforce its provisions.
- Subsequent amendments were made in 2009 and 2012 through the Prevention of Money Laundering (Amendment) Acts.
What is Money Laundering?
- Money laundering is defined as the process through which an illegal fund, such as black money, is obtained from illegal activities and disguised as legal money, eventually portrayed as white money.
- The money laundered is passed on through various channels or phases of conversions and transfers to make it legal and eventually reach a legally acceptable institution, like a bank.
Brief History of the PMLA:
- In response to the emergence of global terrorism in the 1990s and the subsequent imperative to curb illicit financial flows, international efforts intensified, culminating in the establishment of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) in 1989 to coordinate anti-money laundering endeavors worldwide.
Legislative Response:
- Against this backdrop, India, as a member of FATF, was prompted to enact domestic legislation to combat money laundering following the United Nations General Assembly's political declaration in 1998 urging member states to implement national anti-money laundering measures.
Enactment Process:
- The initial iteration of the Prevention of Money-Laundering Bill in 1998 was introduced by the NDA government, aiming to address various aspects such as the prevention of money laundering, confiscation of illicit proceeds, and establishment of coordinating agencies.
- However, concerns regarding potential misuse of the proposed law led to bipartisan opposition, prompting referral to the Department-related Standing Committee on Finance.
- Despite deliberations and amendments, the bill was eventually passed by Parliament in 2002, with enforcement commencing in 2005 following the formulation of accompanying rules under the subsequent UPA government.
Significant Amendments in the PMLA:
- Over the years, the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) has undergone various revisions, but it was the amendments introduced in 2009 and 2012 that notably empowered the Enforcement Directorate (ED) to take coercive measures against politicians.
- In 2009, amendments expanded the PMLA's scope to include 'Criminal conspiracy' under Section 120B of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), enabling the ED to intervene in cases alleging conspiracy, even if the primary offense isn't listed in the PMLA.
- For instance, this broadening facilitated the ED's pursuit of cases like the land-grabbing accusations against a former Jharkhand CM, currently incarcerated in Ranchi.
- Furthermore, the 2009 amendments granted the ED international jurisdiction for tracking laundered money, enhancing its global reach.
- In 2012, the PMLA was amended to elevate the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 (PC Act) to Part A of the statute's schedule from Part B.
- This move imposed stricter bail conditions on corruption suspects, requiring courts to ascertain substantial evidence of guilt if bail opposition arises from the public prosecutor.
- Part A of the schedule encompassed various serious offenses, including acts like waging war against the nation, drug trafficking, and violations of the PC Act, among others.
Supreme Court's Verdicts on the Constitutionality of PMLA:
- In the case of Vijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors vs Union of India (2022), a three-judge Bench of the Supreme Court upheld the constitutional validity of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), which faced challenges in over 200 individual petitions.
- One of the primary challenges was regarding the creation of an alternative criminal law system by the PMLA, as the Enforcement Directorate (ED) operates outside the ambit of the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC).
- Not being classified as 'police', the ED is not bound by CrPC provisions for searches, seizures, arrests, and property attachments.
- The judgment affirmed the ED's expansive powers, including the admissibility of statements made to it in court.
- In Nikesh Tarachand Shah v Union of India (2017), the PMLA, akin to the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), imposed stringent bail conditions, requiring accused individuals to prove the absence of a "prima facie" case against them and their commitment to refraining from future offenses.
- The Supreme Court initially struck down these provisions as unconstitutional.
- However, Parliament reintroduced them through an amendment to the PMLA via the Finance Act, of 2018, which the Supreme Court upheld in 2021.
- While certain aspects of the 2021 ruling, such as the ED's non-obligation to disclose the ECIR (similar to an FIR in criminal cases), are currently under review, the ruling stands as the prevailing law of the land.
South Korea’s ‘Artificial Sun’ KSTAR Reaches 100 Million Degrees Celsius
- 03 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
South Korean scientists have set a new world record for the length of time they sustained temperatures of 100 million degrees Celsius.
Key Highlights:
- The Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) fusion reactor reached temperatures of 100 million Celsius for 48 seconds.
- Scientists hope to harness this unlimited energy.
- It is also significant that the KSTAR maintained the high confinement mode (H-mode) for over 100 seconds.
- H-mode is a stable plasma state.
- The earlier record of achieving this temperature was for 30 seconds which took place in 2021.
- The scientists at the Korea Institute of Fusion Energy (KFE) said they managed to extend the time by tweaking the process.
- They also used tungsten instead of carbon in the 'diverters', which extract heat and impurities produced by the fusion reaction.
- The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor in southern France has the world's biggest tokamak and what the scientists in South Korea achieve will help French scientists.
What is an Artificial Sun?
- An artificial sun typically refers to a device or facility designed to replicate some aspects of the nuclear fusion processes that occur naturally in stars like the Sun.
- These facilities aim to generate and sustain controlled nuclear fusion reactions, usually through the use of high temperatures, pressures, and magnetic fields.
- Scientists generally use a donut-shaped reactor called a tokamak in which hydrogen variants are heated to extraordinarily high temperatures to create a plasma.
- High temperatures and high-density plasmas are vital for the future of nuclear fusion reactors.
- This is called artificial Sun because it replicates the reaction of fusion taking place there and unleashes a massive amount of heat energy.
- The goal is to harness fusion energy as a potential future source of clean and abundant energy for various applications, including electricity generation.
What is Nuclear Fusion?
- Fusion is the reaction that makes the sun and other stars shine.
- It involves fusing hydrogen and other light elements to release massive power that experts in the field hope to harness for unlimited, zero-carbon electricity.
- In this reaction, two atoms of hydrogen or helium come together and fuse to unleash huge amounts of energy.
Leap Second

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Glaciers are melting so fast that we may need to delay adding that 'negative leap second' to keep clocks aligned with Earth's rotation.
What Is a Leap Second?
- Leap seconds serve as a tool to synchronize global timekeeping with the Earth's gradually slowing rotation due to factors such as the melting and refreezing of ice caps.
- Introduced in the early 1970s, leap seconds are added periodically to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to align it with the Earth's actual rotation time.
- UTC is derived from the combined output of over 300 highly precise Atomic clocks worldwide, which offer accuracy within 1 second over millions of years.
- In contrast, Astronomical Time (UT1) corresponds to the Earth's rotation and determines day length.
- The primary reason for leap second additions is the irregularity of Earth's rotation, influenced by various factors like the moon's gravitational forces, causing ocean tides.
- This creates a gradual desynchronization between UTC and UT1. When the discrepancy between UTC and UT1 nears 0.9 seconds, a leap second is added to UTC, ensuring global timekeeping remains aligned with the Earth's rotation.
- Since its introduction, 27 leap seconds have been added to UTC, typically on June 30 or December 31.
- The leap second system continues to serve as an essential mechanism for maintaining synchronization between atomic timekeeping and the Earth's rotation.
What is Negative Leap Second?
- A negative leap second is a proposed time adjustment involving the subtraction of one second from our clocks to synchronize them with Earth's rotation.
- Unlike positive leap seconds, which are added to account for slower rotation, a negative leap second would address the Earth spinning faster than usual.
- So far, no negative leap second has been implemented since Earth's rotation has generally been slow in recent decades.
- However, as Earth's rotation has recently accelerated, timekeepers are considering using negative leap seconds for the first time.
- The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) closely monitors the Earth's rotation and determines when to add or subtract leap seconds.
- A decision to implement a negative leap second would serve as a corrective measure, ensuring our timekeeping systems remain aligned with the planet's rotation.
- While negative leap seconds have yet to be utilized, they offer a potential solution to the challenge posed by variations in Earth's rotational speed, ensuring the ongoing synchronization of our timekeeping methods with the planet's natural rhythms.
Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT)

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Congress has hailed as an “important first step” the Supreme Court’s notice to the Election Commission and the Centre on a plea seeking a complete count of VVPAT slips and said the matter should be decided before the Lok Sabha polls commence.
What is the Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT)?
- The Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail, or VVPAT system, was first introduced in 2014 for the first time during the 2014 Lok Sabha Elections.
- The ECI conducted pilot tests of VVPAT systems in a few constituencies in 2011, and after successful trials, VVPAT was gradually deployed across all polling stations in subsequent elections.
- It is connected to Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) and enables voters to confirm that their votes were cast as intended.
- The concept of VVPAT was to enhance the credibility and transparency of EVMs.
What are VVPAT Slips?
- VVPAT slips are an integral part of the EVMs used in elections.
- It provides a physical paper trail for voters to verify that their vote has been correctly recorded by the EVM.
- It ensures transparency and accountability in the electoral process by allowing voters to verify their vote before casting it finally.
- The VVPAT produces a paper slip that permits the voter to confirm the accuracy of their vote on the EVM.
- This slip displays the name and symbol of the party chosen by the voter.
- Additionally, the machine features a transparent window through which the voter can observe the printed slip.
- Subsequently, the slip is securely deposited into a sealed compartment within the machine.
- However, in the event of a dispute, this sealed box can be opened for further examination.
Controversies Surrounding VVPAT:
- Despite its intended purpose of enhancing transparency, VVPAT has been subject to several controversies over the years.
- Some critics have raised concerns about the reliability of VVPAT systems, citing instances of malfunctioning printers, paper jams, and discrepancies between electronic and paper records.
- The Opposition parties within the INDIA bloc have been advocating for the full counting of VVPATs, to bolster public trust in the EVMs, which itself has been subjected to intense scrutiny recently.
- Their concern has mostly stemmed from allegations of delay in the printing and displaying of VVPAT slips for every vote, which they claim can significantly increase the time required for vote counting.
Supreme Court’s intervention in VVPATs:
- In April 2019, the SC asked the poll panel to increase the number of EVMs that undergo VVPAT physical verification from one to five per assembly segment in a parliamentary constituency.
- In the month of May the same year, the Supreme Court dismissed a writ petition seeking 100 percent counting of VVPAT in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections.
- Earlier in the same month, the Supreme Court had also dismissed the review petition filed by opposition parties to increase verification of VVPAT-EVM to 50 percent.
Fukushima Water Issue

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Japan announced that its experts have engaged in discussions with their Chinese counterparts to address Beijing's concerns regarding the release of treated radioactive wastewater from the damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the sea.
What is the Fukushima Water Issue?
- In 2021, the Japanese government unveiled plans to gradually discharge over one million tonnes of contaminated water from the Fukushima nuclear plant into the ocean over the next three decades.
- The contaminated water is a residual product of the devastating 2011 earthquake and tsunami that incapacitated the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant, resulting in the release of radioactive materials.
- After more than ten years of storing this wastewater, Japan asserts that they are facing storage space limitations and contends that the treated water is now safe for release.
Concerns Surrounding the Fukushima Water Discharge:
- Tritium and Carbon-14: The water from Fukushima undergoes filtration via the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), effectively reducing most radioactive contaminants to acceptable safety levels, except tritium and carbon-14.
- While both emit low levels of radiation, consumption in large quantities could potentially pose risks.
- Insufficient Research: Scientists emphasize the need for further investigation into the potential impact of the water discharge on the ocean bed and marine ecosystems.
- The Pacific Islands Forum regional group has labeled the proposed plan as "another significant nuclear contamination disaster," citing ongoing challenges faced by its member nations due to past US nuclear testing.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF):
- The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories of Oceania, including the formation of a trade bloc and regional peacekeeping operations.
- It was founded in 1971 as the South Pacific Forum (SPF), and changed its name in 1999 to "Pacific Islands Forum", to be more inclusive of the Forum's Oceania-spanning membership of both north and south Pacific island countries, including Australia.
- It is a United Nations General Assembly observer.
- The PIF secretariat is located in Suva, the capital of Fiji.
Nuclear Incidents:
- A nuclear and radiation incident denotes an occurrence that has resulted in significant repercussions for individuals, the environment, or the facility involved.
- These may entail fatal consequences for individuals, substantial releases of radioactivity into the environment, or reactor core meltdowns.
- Globally, there have been a total of 99 incidents at nuclear power plants.
- Fifty-seven of these incidents have transpired since the Chornobyl disaster, with the United States accounting for 57% of all nuclear-related incidents.
- Noteworthy nuclear power plant mishaps encompass:
- Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011)
- Chernobyl disaster (1986)
- Three Mile Island accident (1979), and
- The SL-1 accident (1961).
Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Eight years after Parliament passed the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs is in the process of reviewing the functioning of the Act, including by holding regular meetings with homebuyers and setting up a data collection unit within the Ministry.
What Is Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 (RERA)?
- The Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 is an act of the Parliament of India that strives to protect home buyers and helps escalate the investment made in the real estate industry.
- It was established under this Act to regulate the real estate sector.
- Additionally, it acts as the adjudicating body for faster dispute resolution related to the real estate industry.
The Primary Objectives of the Act:
- Ensuring Transparency: Promoting transparency in the real estate sector regarding the sale of flats, apartments, plots, buildings, or any real estate project.
- Establishing Dispute Resolution: Setting up an adjudicating mechanism to swiftly resolve disputes.
- Protecting Buyer Interests: Safeguarding the interests of buyers/allottees in the real estate domain.
- Building Trust: Fostering trust between buyers and promoters by leveraging regulatory authority.
- Furthermore, the Act mandates that Real Estate Regulatory Authorities establish and maintain a web portal containing pertinent details of all registered real estate projects for public access.
Reasons for RERA Implementation:
- The introduction of RERA was necessitated by challenges faced by the Indian real estate sector since 2012, including factors such as unemployment, recession, low rental yield, inventory pile-up, and ambiguous tax and arbitration frameworks.
Projects Covered by RERA:
- RERA covers commercial and residential projects, including plotted developments, that exceed 500 square meters or comprise more than 8 units.
- Additionally, projects lacking a Completion Certificate prior to the Act's commencement are subject to its provisions.
Benefits of RERA Implementation:
- Standardization: RERA ensures uniformity in the real estate sector concerning aspects like carpet areas and common areas, thereby preventing malpractices such as alterations in layout, area, agreements, and specifications.
- It also mandates disclosure of details regarding brokers, architects, and contractors.
- Timely Delivery: Developers are obligated to adhere to scheduled delivery timelines for office spaces or homes.
- Failure to comply may result in stringent penalties or imprisonment for the developer.
- Regulatory Compliance: RERA mandates obtaining clearance from government departments before the sale of any residential or commercial property.
- Financial Transparency: Developers are required to maintain separate bank accounts for each project, enhancing financial transparency and accountability.
- Warranty Protection: Buyers are empowered to report any structural defects in the building to the developer within one year of possession, with the developer obligated to rectify them free of charge.
Challenges Associated with RERA:
- Limited Scope: The regulations of RERA do not extend to ongoing projects or those stalled due to clearance issues, potentially leaving certain projects outside its jurisdiction.
- Approval Delays: Delays in approval and clearance from government agencies may impede the timely completion and delivery of real estate projects, affecting both developers and buyers.
- Exemption for Small Developers: Small-scale developers overseeing projects smaller than 500 square meters are exempt from RERA's provisions, and registration with the regulatory authority is not compulsory for them.
- Project Launch Delays: Projects cannot be launched without necessary clearances, which may result in delays in the commencement of new projects.
International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT)
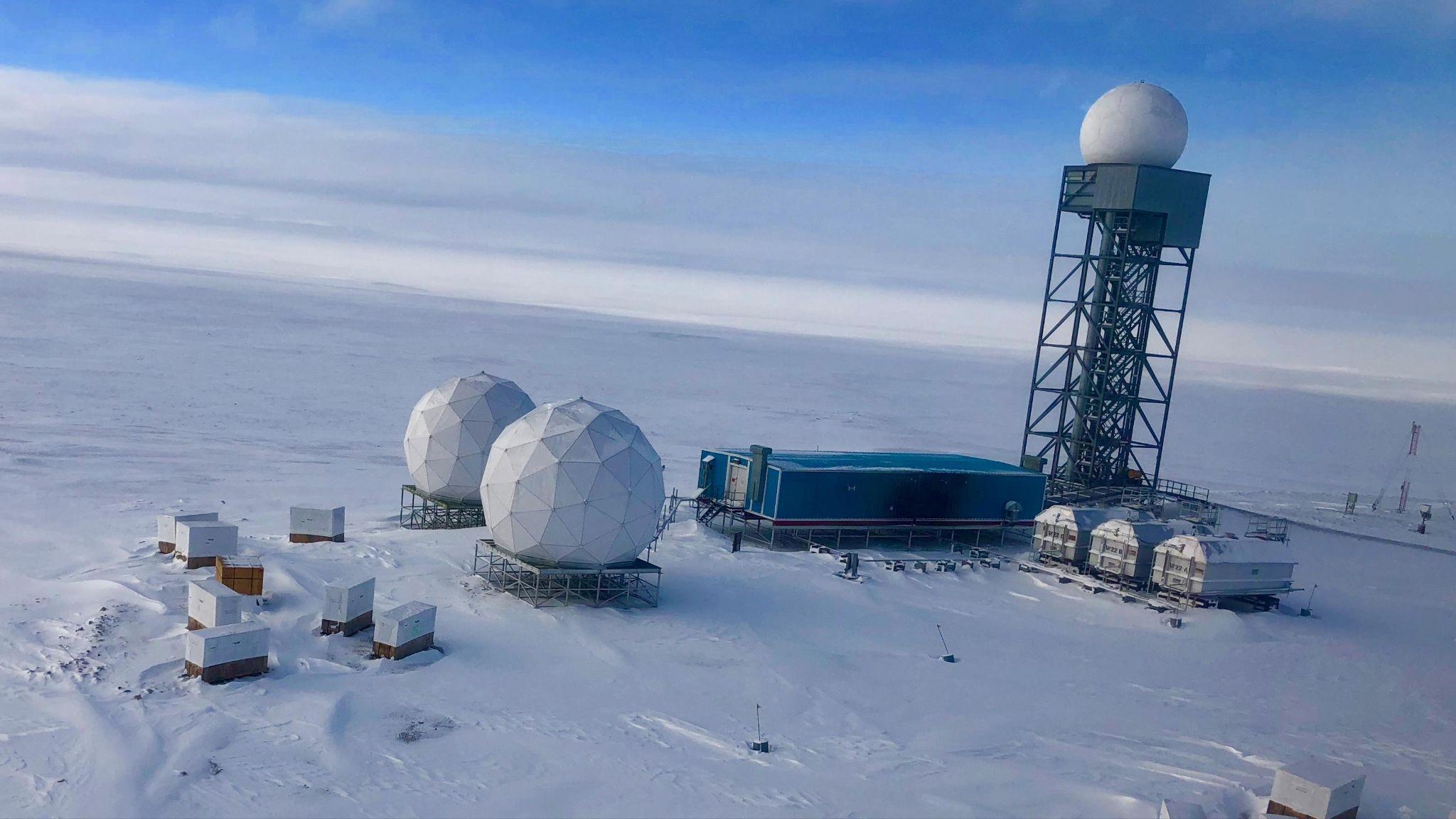

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent development, Arctic research stations under INTERACT reported a significant loss of over 1,000 billion tonnes of ice over the past four decades.
About the International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT):
- The International Network for Terrestrial Research and Monitoring in the Arctic (INTERACT) is an infrastructure project under the auspices of SCANNET.
- INTERACT specifically seeks to build capacity for research and monitoring in the European Arctic and beyond and is offering access to numerous research stations through the Transnational Access program.
- It aims to build capacity for identifying, understanding, predicting, and responding to diverse environmental changes throughout the wide environmental and land-use envelopes of the Arctic.
- The project, which is funded by the EU, has the main objective of building capacity for identifying, understanding, predicting, and responding to diverse environmental changes throughout the wide environmental and land-use envelopes of the Arctic.
- INTERACT is a multidisciplinary initiative; collectively, its stations host thousands of scientists worldwide who collaborate on projects spanning glaciology, permafrost studies, climate research, ecology, biodiversity, and biogeochemical cycling.
About the Scandinavian Network for Coordinated Observation of the Atmosphere and Terrestrial Environment (SCANNET):
- SCANNET is a circum-Arctic network of currently 77 terrestrial field bases in northern Europe, Russia, the US, Canada, Greenland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, and Scotland as well as stations in northern alpine areas.
- The primary aim of SCANNET is to facilitate coordinated observations and research activities focused on the atmosphere and terrestrial environment in the Arctic region.
- These observations cover a wide range of scientific disciplines, including meteorology, climatology, ecology, geology, and environmental science.
- By leveraging the diverse geographical locations of its field bases, SCANNET enables scientists to study various environmental phenomena, such as changes in weather patterns, shifts in ecosystems, permafrost dynamics, and the impact of climate change on Arctic landscapes.
- Moreover, SCANNET serves as a platform for collaboration and information sharing among researchers from different institutions and countries.
- It fosters partnerships and promotes the exchange of data, methodologies, and best practices, thereby enhancing our understanding of Arctic processes and their global implications.
CoViNet
- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a global network of laboratories to identify and monitor potentially novel coronaviruses that could emerge shortly.
What is CoViNet?
- The Coronavirus Network (CoViNet) is a global collaboration of laboratories with expertise in human, animal, and environmental coronavirus surveillance.
- This network aims to identify and monitor potential new coronaviruses that could emerge and impact public health worldwide.
- To enhance pandemic preparedness, CoViNet will expand its scope to include animal health and environmental surveillance, as well as timely risk assessments.
- This will allow the World Health Organization (WHO) to develop more informed policies and protective measures against future viral outbreaks.
- CoViNet will also play a pivotal role in building and supporting laboratory capacities in low- and middle-income countries to monitor MERS-CoV and other emerging coronaviruses of public health importance.
- By fostering knowledge exchange and capacity building, CoViNet aims to strengthen the global response to coronavirus threats.
- Furthermore, data generated through CoViNet's efforts will guide the work of the WHO's Technical Advisory Groups on Viral Evolution (TAG-VE) and Vaccine Composition (TAG-CO-VAC). These groups rely on cutting-edge research and surveillance data to inform public health policies and vaccination strategies.
- With 36 laboratories from 21 countries across all six WHO regions, CoViNet currently encompasses a wide range of expertise and resources.
- Three Indian institutions, namely, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology in Pune, and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, proudly represent the country in this global network dedicated to coronavirus surveillance and preparedness.
About the World Health Organization (WHO):
- The World Health Organization (WHO) stands as a paramount global health authority, dedicated to promoting health, preventing diseases, and improving healthcare systems worldwide.
- Established in 1948, WHO operates as a specialized agency of the United Nations, with its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It collaborates with governments, international organizations, and civil society to address pressing health challenges and provide guidance and support to countries in need.
- WHO's mandate encompasses a wide array of health-related issues, including infectious diseases, non-communicable diseases, mental health, maternal and child health, and environmental health.
- Through research, policy development, and technical assistance, WHO plays a vital role in shaping health policies, setting standards, and coordinating responses to health emergencies such as pandemics and natural disasters.
- With a mission to ensure the highest attainable level of health for all people, WHO continues to lead efforts in global health governance, advocacy, and capacity-building, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable world.
T+0 Settlement Cycle

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The BSE and NSE introduced trading in the T+0 rolling settlement cycle in the equity segment on an optional basis today.
What is Trade Settlement?
- Trade settlement encompasses the bilateral process of transferring funds and securities on the designated settlement date.
- It signifies the completion of a trade transaction when the purchased securities of a listed company are successfully delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the agreed-upon payment.
- The evolution of the trade settlement cycle in India has seen notable adjustments over time.
- Initially shortened by SEBI to T+3 from T+5 in 2002 and further to T+2 in 2003, the current cycle in the Indian stock market stands at T+1.
- This migration to the T+1 cycle took effect in January 2023, positioning India as the second country globally, after China, to implement the T+1 settlement cycle for top-listed securities.
What is the T+0 Trading Settlement Cycle?
- In December last year, the capital markets regulator SEBI proposed to introduce a facility for clearing and settlement of funds and securities on T+0 (same day) on an optional basis, in addition to the existing T+1 settlement cycle.
- The regulator has also proposed to introduce optional instant settlement at a later stage.
- Under the T+0 trade cycle, the settlement of trades will happen on the same day after the closure of the T+0 market.
- If investors sell a share, they will get the money credited to their account the same day, and the buyer will also get the shares in their demat account on the very day of the transaction.
What are the Benefits of T+0 Trade Settlement?
- A shortened settlement cycle will bring cost and time efficiency, transparency in charges to investors, and strengthen risk management at clearing corporations and the overall securities market ecosystem.
- The T+0 trade cycle is expected to provide flexibility in terms of faster pay-out of the funds against the securities to the sellers and faster pay-out of securities against the funds to the buyers.
- It will allow better control over funds and securities by the investors.
- For the securities market ecosystem, a shorter settlement cycle will further free up capital in the securities market, thereby enhancing the overall market efficiency.
- It will enhance the overall risk management of Clearing Corporations (CCs) as the trades are backed by upfront funds and securities.
Who can Participate in the T+0 Settlement Cycle?
- All investors are eligible to participate in the segment for the T+0 trade settlement cycle if they are able to meet the timelines, process, and risk requirements as prescribed by the Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs).
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
Carlsberg Ridge & Afanasy-Nikitin Seamount
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian delegates have been visiting the International Seabed Authority (ISA), Jamaica to strengthen efforts to explore two deep sea regions in the Indian Ocean for mining, according to reports this week.
What is the Carlsberg Ridge?
- The Carlsberg Ridge is the northern section of the Central Indian Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary between the African Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate, traversing the western regions of the Indian Ocean.
- The ridge of which the Carlsberg Ridge is a part extends northward from a triple point junction near the island of Rodrigues (the Rodrigues Triple Point) to a junction with the Owen Fracture Zone.
- The ridge started its northwards propagation in the late Maastrichtian and reached the incipient Arabian Sea in the Eocene.
- Then it continued to accrete basalt but did not propagate for nearly 30 million years ago.
- Then, in the early Miocene, it started to propagate westwards towards the Afar hot spot, opening the Gulf of Aden.
- The Carlsberg Ridge is seismically active, with a major earthquake being recorded by the U.S. Geological Survey at 7.6 on the moment magnitude scale in July 2003.
- The ridge was discovered by the Danish research vessel Dana during the Carlsberg Foundation's Oceanographic Expedition around the world (1928–1930), better known as the 2nd Dana Expedition, and named after the Carlsberg Foundation, which funded the entire expedition and subsequent analysis and publication of results.
About the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (ANS) Seabed:
- The ANS is a major structural feature in the Indian Ocean, rising up above the sea bed but below the surface, and forming a seamount.
- It is 400 km long and 150 km wide, and is located in the Central Indian Basin — southeast of Sri Lanka, right below the equator, to the west of Singapore.
- It was formed about 80 million years ago, while dinosaurs still roamed the Earth.
- The Seamount is named after Afanasy Nikitin, a 15th-century Russian merchant who was one of the first to document his travels to India.
- A black monolith is also erected in his honor at Revdanda, about 100 km away from Mumbai, where he is thought to have first set foot in the country.
- The ANS seamount is about 3,000 km from India’s coast and is rich in cobalt, copper, manganese, and nickel.
What are Seamounts?
- Seamounts are submarine mountains originating from volcanic eruptions beneath the ocean's surface, serving as critical habitats for diverse marine ecosystems.
- Similar to terrestrial volcanoes, seamounts can exhibit varying states of activity, including active, dormant, or extinct stages.
- They typically form near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates separate, allowing magma to ascend and solidify on the seabed.
- Notably, seamounts also emerge near intraplate hotspots and oceanic island chains, such as island arcs, characterized by volcanic and seismic activity.
- These underwater formations hold significant scientific value, offering insights into mantle composition, plate tectonics, and oceanic circulation dynamics.
- Moreover, seamounts play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and marine life proliferation, fostering localized upwelling of nutrient-rich waters that support diverse biological communities.
Magnetofossils
- 27 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In the depths of the Bay of Bengal, scientists have discovered a 50,000-year-old sediment — a giant magnetofossil and one of the youngest to be found yet.
What are Magnetofossils?
- Magnetofossils represent the fossilized remnants of magnetic particles originated by magnetotactic bacteria, also referred to as magnetobacteria, encapsulated within the geological archives.
About Magnetotactic Bacteria:
- Magnetotactic bacteria, predominantly prokaryotic microorganisms, possess the unique ability to align themselves in alignment with Earth's magnetic field.
- These organisms were traditionally believed to utilize the Earth's magnetic field as a navigational aid to locate environments with optimal oxygen levels.
- Comprising distinctively structured particles abundant in iron, these bacteria harbor small sacs that function akin to a compass.
- Magnetotactic bacteria synthesize minute crystals composed of iron-rich minerals such as magnetite or greigite, facilitating their navigation amidst fluctuations in oxygen concentrations within their aquatic habitats.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Sediment Composition: The sediment core, measuring three meters in length and extracted from the southwestern Bay of Bengal, primarily comprised "pale green silty clays."
- Foraminifera Abundance: Researchers observed abundant benthic and planktic foraminifera, which are single-celled organisms characterized by shells found near the seabed and freely floating in water.
- Oxygen Concentration: At depths ranging from approximately 1,000 to 1,500 meters, the Bay of Bengal exhibited notably low oxygen levels.
- Analysis of the sediment sample confirmed fluctuations in monsoon activity, as evidenced by the presence of magnetic mineral particles from distinct geological periods.
- Role of Rivers: Rivers such as the Godavari, Mahanadi, Ganga-Brahmaputra, Cauvery, and Penner, which discharge into the Bay of Bengal, played a pivotal role in magnetofossil formation.
- Nutrient Supply: The nutrient-rich sediment transported by these rivers supplied reactive iron, which, combined with organic carbon in the suboxic conditions of the Bay of Bengal, created a conducive environment for magnetotactic bacteria growth.
- Impact of Oceanographic Processes: Factors such as freshwater discharge from rivers and oceanographic phenomena like eddy formation influenced the oxygen content in these waters, distinguishing them from other low-oxygen zones.
- Persistence of Suboxic Conditions: The presence of magnetofossils indicated the prolonged persistence of suboxic conditions in the Bay of Bengal, fostering an environment conducive to the proliferation of magnetotactic bacteria.
Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP)

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kerala's shift towards an alternative approach for the implementation of smart electricity meters, sidelining the Central government's Rs 3 lakh crore project, poses a challenge to the Union Government's initiative of replacing 250 million traditional meters with smart meters in all households by March 2025.
About the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP):
- The Indian government has initiated the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) to revolutionize the country's energy sector through the implementation of smart meters.
- By replacing 25 crore conventional meters, the SMNP aims to enhance the operational efficiency and revenue management of distribution companies (DISCOMs).
- Under the leadership of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), a joint venture of four National Public Sector Enterprises, the scheme is set to make waves in the energy sector.
- EESL, comprised of NTPC Limited, PFC, REC, and POWERGRID, operates under the Ministry of Power and is committed to undertaking the necessary capital and operational expenditures with zero upfront investment from states and utilities.
- The Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) model facilitates the recovery of smart meter costs via the monetization of energy savings resulting from improved billing accuracy, reduced meter reading costs, and increased efficiency.
- In accordance with guidelines set forth by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), the strategic deployment of these smart meters adheres to industry standards.
Smart meters offer a multitude of advantages:
-
- Consumers can monitor their electricity usage and make informed decisions to reduce their bills.
- Utilities benefit from enhanced operational efficiency, enabling better power demand management.
- Web-based Monitoring: The interconnected smart meter network can mitigate utilities' commercial losses, enhance revenue generation, and propel power sector reforms.
- The Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) paves the way for a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape in India, revolutionizing the way utilities operate and consumers engage with their electricity usage.
What are Smart Meters?
- A smart meter serves as an advanced tool for recording electricity consumption and voltage levels, offering a significant upgrade over traditional metering systems.
- While conventional meters simply measure power usage, smart meters take it a step further by transmitting real-time data to utility providers at intervals of 15 minutes or hourly.
- Smart meters truly live up to their name by utilizing internet connectivity to facilitate two-way communication.
- On one hand, they empower consumers with up-to-date information on energy usage patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions and manage consumption more efficiently.
- On the other hand, utility providers gain valuable insights for monitoring purposes and ensuring accurate billing.
- In essence, smart meters pave the way for improved energy management, increased transparency, and enhanced efficiency, catering to the evolving needs of both consumers and utility providers in today's digital era.
Netravati River

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The principal bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) in New Delhi has initiated action on the Netravati Waterfront Promenade Development Project in Mangaluru.
About the Netravati River:
- The Netravati River, also known as Netravathi Nadi, originates from the Bangrabalige valley, Yelaneeru Ghat in Kudremukh, Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka, India.
- It passes through the revered pilgrimage site Dharmasthala, earning recognition as one of India's sacred rivers.
- Converging with the Kumaradhara River at Uppinangadi, it eventually flows into the Arabian Sea, south of Mangalore city, serving as the primary water source for Bantwal and Mangalore.
- The Netravati railway bridge, a prominent structure, acts as the gateway to Mangalore.
- Historically known as the Bantwal River, it was documented as unfordable during the South-West Monsoon in the 1855 Gazetteer of Southern India.
- The river's navigability by small country craft and its influence on local geography and transport, including the naming of the Netravati Express train, underscores its significance in the region's history.
- Instances of flooding, notably in 1928 and 1974, have shaped the lives of residents, prompting relocations and resilience
About the National Green Tribunal:
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) was established under the National Green Tribunal Act of 2010.
- While its principal seat is located in New Delhi, it also holds sessions in Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata, and Chennai.
- The NGT is entrusted with the responsibility of adjudicating applications or appeals, ensuring their final disposition within six months of filing.
Composition:
- The tribunal comprises a Chairperson, Judicial Members, and Expert Members, each serving a non-renewable term of five years.
- The appointment of the Chairperson is made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India (CJI).
- A Selection Committee, constituted by the Central Government, is responsible for appointing both Judicial and Expert Members.
- The tribunal can accommodate a minimum of 10 and a maximum of 20 full-time Judicial and Expert Members.
Powers & Jurisdiction:
- Established to efficiently handle cases concerning environmental protection and conservation of natural resources, including forests.
- It possesses appellate jurisdiction akin to a court.
- While not bound by the procedural formalities outlined in the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, the NGT operates based on the principles of natural justice.
Pusa Basmati Rice

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Even as basmati rice exports from the country are poised to scale a new high, scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) have red-flagged the “illegal” cultivation of its blockbuster varieties in Pakistan.
Unauthorized Cultivation and Export of Pusa Basmati Rice Varieties in Pakistan:
- Despite being officially registered and protected Indian varieties, several IARI-bred Basmati rice varieties, such as Pusa Basmati 1121, Pusa Basmati-6, and Pusa Basmati 1509, are being illegally cultivated and marketed in Pakistan.
- Recent YouTube videos even feature newer IARI varieties like Pusa Basmati-1847, PB-1885, and PB-1886, released in late 2021.
- Pakistan's unauthorized Basmati exports have been substantial, with 7.58 lt ($694.55 million) in 2021-22 and 5.95 lt ($650.42 million) in 2022-23 (July-June).
- This growth is partly due to the depreciation of the Pakistani rupee, allowing the country to offer lower export prices than India.
- The proliferation of these protected varieties in Pakistan can be attributed to the ease of seed multiplication.
- With just a small quantity of seeds, large-scale cultivation can be established within two years of the variety's release in India.
- This unauthorized cultivation not only undermines India's intellectual property rights but also impacts the competitiveness of India's Basmati rice exports in the global market.
What is the Basmati Crop Improvement Program?
- The Basmati Crop Improvement Program focuses on refining the unique qualities of Basmati rice, such as its distinct grain characteristics, cooking properties, and pleasing aroma.
- IARI has played a crucial role in the genetic enhancement, leading to the development of high-yielding, semi-dwarf, and photo-insensitive Basmati varieties like Pusa Basmati 1.
- These improvements have significantly reduced the crop duration from 160 to 120 days and increased productivity from 2.5 to 6-8 tons per hectare.
- As a result, these advanced Basmati varieties account for approximately 90% of India's projected $5.5 billion exports in 2023-24.
- This achievement contributes to substantial foreign exchange earnings and economic growth for the country.
Key Features of IARI-Developed Basmati Rice Varieties:
- IARI has cultivated various Basmati rice varieties with distinct characteristics, including:
- Pusa Basmati 1121: Known as the world's longest Basmati rice, it matures in 145 days with an average yield of 45 q/ha.
- Pusa Basmati 1509: Derived from Pusa 1121 x Pusa 1301, this variety addresses Pusa Basmati 1121's weaknesses, matures in 115 days, and yields 5 tons/ha.
- Improved Pusa Basmati 1 (Pusa 1460): This variety, the first product of molecular breeding in Indian rice, is an enhanced Pusa Basmati 1 with bacterial leaf blight resistance.
- Pusa Basmati 6 (Pusa 1401): Offering superior grain quality, this variety improves upon Pusa 1121's yielding ability, agronomy, and cooking quality.
- Pusa RH10: The world's first superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid, it was released in 2001 for commercial cultivation in specific irrigated ecosystems.
Registration and Cultivation Areas of Pusa Basmati Rice in India:
- All Pusa Basmati rice varieties are officially recognized under the Seeds Act 1966 and can be cultivated within the designated Geographical Indication (GI) area of Basmati rice in India, encompassing seven northern states.
- These varieties are further registered under the Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers' Rights Act 2001, which permits only Indian farmers to sow, save, re-sow, exchange, or share the seeds of protected/registered varieties.
State of Global Climate Report 2023

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with a host of observations by climate agencies in the preceding three months, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has officially confirmed 2023 to be the hottest year on record.
About the State of Global Climate Report 2023:
- Published annually by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the State of Global Climate Report provides a detailed analysis of the Earth's climate system.
- Contributors to the report include various UN organizations, National Meteorological and Hydrological Services, Global Data and Analysis Centers, Regional Climate Centres, the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), and more.
Highlights of the 2023 Report:
- Record-Breaking Global Temperatures: 2023 was the hottest year on record, with a global average near-surface temperature of 1.45°Celsius (±0.12°C) above the pre-industrial baseline.
- The past ten years were also the warmest decade recorded.
- Extensive Marine Heatwaves: Nearly one-third of the global ocean experienced a marine heatwave on an average day in 2023.
- Over 90% of the ocean had faced heatwave conditions at some point during the year, negatively impacting ecosystems and food systems.
- Unprecedented Glacier Ice Loss: Preliminary data reveals the largest loss of ice since 1950 for the global set of reference glaciers, driven by extreme melt in western North America and Europe.
- Surge in Renewable Energy Capacity: Renewable capacity additions in 2023 increased by almost 50% from 2022, totaling 510 gigawatts (GW) and marking the highest rate in the past two decades.
- These findings emphasize the pressing need to address climate change through effective international cooperation, policymaking, and sustainable practices.
About the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO):
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that fosters international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Founded in 1950, WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization established in 1873 to facilitate the exchange of weather data and research.
- Today, WMO comprises 193 member countries and territories and promotes the free exchange of meteorological and hydrological data, information, and research.
- By collaborating with various partners, WMO contributes to environmental protection, climate change mitigation, and sustainable development efforts worldwide.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
FSSAI Launches Comprehensive Lab Network for Pathogen Testing

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
With food poisoning and diarrhea becoming a common occurrence, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is working towards creating a network of 34 microbiology labs across the country that will be equipped to test food products for 10 pathogens, including E coli, salmonella, and listeria.
About the Initiative:
- To address the growing concern of microbial contamination in food products, a network of 34 advanced microbiology laboratories has been established across the country.
- These state-of-the-art facilities are specifically designed to test and monitor a wide range of food products for the presence of harmful pathogens, including E. coli, salmonella, and listeria, among others.
- The nationwide initiative aims to strengthen the existing food safety framework by enhancing the early detection and prevention of foodborne illnesses.
- By analyzing food samples collected during routine surveillance, the labs will play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and quality of consumable goods.
- With a focus on safeguarding public health and well-being, this collaborative effort will contribute significantly to the overall improvement of food security and foster greater confidence in the food industry.
- As the network continues to expand and evolve, it will undoubtedly become an essential asset in the ongoing battle against foodborne pathogens and contamination.
Need for the Initiative:
- India has witnessed a surge in food poisoning and diarrhea cases in recent years, emphasizing the critical need for improved food safety measures.
- According to data from the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), over 1,100 outbreaks of acute diarrhoeal disease and around 550 incidents of food poisoning occurred within the last four years.
- These troubling statistics underscore the urgency to address this pressing public health issue.
- State food safety laboratories, responsible for ensuring the safety of consumable products, currently lack the necessary resources and infrastructure to effectively identify and mitigate the presence of dangerous pathogens.
- The complexities of maintaining live reference samples, the high costs of reagents, and the requisite expertise of microbiologists pose significant challenges in maintaining optimal food safety standards.
- Consequently, the establishment of a comprehensive microbiology lab network becomes crucial in effectively addressing the growing threat of foodborne illnesses.
- By enhancing testing capabilities and promoting early detection, this initiative will ultimately contribute to a safer food supply, improved public health outcomes, and increased consumer confidence in the food industry.
About the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI):
- As an autonomous body under India's Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the FSSAI was established in 2006 under the Food Safety and Standards Act.
- This act serves as a consolidating statute focusing on food safety and regulation in India.
- The FSSAI's mission is to set global standards for food, encourage adherence to these standards, promote good manufacturing and hygiene practices, and enable citizens' access to safe and nutritious food.
Key functions include:
-
- Protecting public health by regulating and supervising food safety.
- Setting standards and guidelines for food articles.
- Issuing licenses, registrations, and accreditations for food businesses.
- Controlling food imports to prevent harmful ingredients.
- Accrediting food testing laboratories nationwide.
- Overseeing food certification in India, including accreditation of certification systems and food safety management systems for food businesses.
- Through these efforts, the FSSAI plays a vital role in maintaining high food safety standards and safeguarding the well-being of India's citizens.
Predictive AI: Its Applications and Advantages

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Predictive AI is revolutionizing data analysis, decision-making, and industry leadership, offering businesses unprecedented insights and strategic advantages.
What is Predictive Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Predictive artificial intelligence (AI) utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and forecast future events, distinguishing it from traditional AI focused solely on retrospective analysis.
- This cutting-edge technology employs advanced algorithms and machine learning models to sift through extensive datasets, identifying subtle patterns and trends.
- Unlike conventional approaches, Predictive AI doesn't just analyze data; it transforms it into actionable insights, enabling organizations to:
- Anticipate future outcomes,
- Predict market shifts, and
- Make strategic decisions with unprecedented foresight.
- By continuously learning from past data and adapting to changing trends, Predictive AI becomes an invaluable tool, guiding businesses through uncertain landscapes.
How Predictive AI Work?
- Leveraging Big Data: Predictive AI relies on access to extensive datasets, often referred to as "big data," as larger datasets typically lead to more accurate analyses.
- Utilizing Machine Learning (ML): As a subset of AI, ML involves training computer programs to analyze data autonomously, without human intervention.
- In the realm of predictive AI, ML algorithms are applied to vast datasets to extract valuable insights.
- Autonomous Processing: Predictive AI models are capable of autonomously processing massive datasets, eliminating the need for human oversight.
- Pattern Recognition: Through ML techniques, predictive AI learns to recognize patterns within datasets, associating specific data points or occurrences with potential future events.
- By examining numerous factors, predictive AI can identify intricate patterns indicative of recurring events, enabling organizations to anticipate future outcomes effectively.
Difference Between Predictive AI and Generative AI:
- Predictive AI and generative AI both employ machine learning techniques and leverage extensive datasets to generate their outputs.
- However, while predictive AI utilizes machine learning to forecast future outcomes, generative AI employs machine learning to produce original content.
- For instance, a predictive AI model may inform fishermen about impending storms, whereas a generative AI model may craft a fictional narrative depicting various scenarios involving weather and fishing expeditions.
- While both types of AI rely on statistical analysis to discern patterns, their objectives, machine learning methodologies, and applications differ significantly.
Various Applications of Predictive AI:
- Assessing the Impact of Natural Disasters: With the recent eruption of a volcano in Iceland, the potential repercussions on air travel echo concerns from a similar event in 2010, which disrupted flights across Europe.
- Predictive AI leverages data analysis to identify patterns and anticipate the impact of such extreme weather events on air travel. Platforms like Yandex offer interactive maps for real-time monitoring of ash clouds post-eruption.
- Enhancing Oil and Gas Exploration: In the realm of oil and gas exploration, companies possess extensive historical geological data that can inform predictive AI systems.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- For instance, Saudi Aramco utilizes its meta-brain generative AI to optimize drilling plans, analyze geological data, and forecast drilling outcomes accurately.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- Inventory and Supply chain management: Predictive AI aids in inventory and supply chain management by identifying peak consumer demand periods, facilitating proactive stock adjustments, and optimizing resource allocation to address fluctuations in road congestion and meet increased user demands.
- Marketing campaigns: Just as predictive AI can anticipate user or customer behavior, it can help prognosticate what kinds of content or products prospective customers may be interested in.
- Advancing Medical Research: Predictive AI plays a pivotal role in drug discovery, a cornerstone of contemporary medical research.
- Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly collaborating to leverage predictive AI models for analyzing vast datasets and identifying potential drug candidates. Initiatives like the 'MELLODDY Project', supported by the EU Innovative
- Medicines Initiative and multiple pharmaceutical firms, exemplify this collaborative effort in pooling data and leveraging predictive AI for drug discovery.
'ETHANOL 100' hits the road at 183 Indian Oil stations in five states

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a strategic advance towards cleaner fuel alternatives, India commenced the sale of ETHANOL 100 across 183 Indian Oil outlets in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, New Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
What is ETHANOL 100 Fuel?
- ETHANOL 100 fuel represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, offering a high-octane rating ranging from 100 to 105.
- This elevated octane level is particularly advantageous for high-performance engines, delivering improved efficiency and power output while simultaneously reducing environmental impact.
- One of the key features of ETHANOL 100 is its remarkable versatility, making it suitable for a diverse range of vehicles, including flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) designed to accommodate various fuel types such as gasoline, ethanol, or any blend thereof.
- This adaptability ensures that ETHANOL 100 can seamlessly integrate into existing automotive fleets without requiring extensive modifications or infrastructure upgrades.
- The composition of ETHANOL 100 consists of approximately 93 to 93.5 percent ethanol blended with 5 percent petrol and 1.5 percent co-solvent acting as a binder.
- This well-balanced formulation not only enhances fuel performance but also contributes to its practicality as a mainstream fuel option.
- In addition to its performance benefits, ETHANOL 100 stands out as a cleaner and greener alternative to traditional gasoline.
- By emitting lower levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and particulate matter, ETHANOL 100 plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and improving air quality in our communities.
- With the right infrastructure and support mechanisms in place, ETHANOL 100 has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry by offering a sustainable and eco-friendly fuel solution that aligns with the global efforts to combat environmental degradation and promote sustainable development.
What are Flex-fuel Vehicles?
- Flex-fuel vehicles are engineered to operate on a diverse range of fuels, offering consumers the flexibility to choose between petrol, ethanol, or methanol at the point of refueling.
- Equipped with an internal combustion engine (ICE), these vehicles can seamlessly switch between different fuel types, providing versatility and convenience to drivers.
- While possessing similarities to conventional petrol-only cars, flex-fuel vehicles undergo minor modifications to accommodate the use of alternative fuels, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across various fuel options.
Honoring, the Architect of Mumbai (Bombay)

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Maharashtra cabinet recently decided to ask the Ministry of Railways to rename Mumbai Central Station after Nana Jagannath Shankarseth.
Who was Nana Jagannath Shankarseth?
- Nana Jagannath Shankarseth was a social reformer, educationist, and philanthropist and often described as the “architect” of Mumbai (then Bombay).
- He made extremely valuable contributions in terms of both ideas and money to multiple sectors, to lay a strong foundation for the city.
- Shankarseth was greatly inspired by the legendary merchant and philanthropist Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy.
- As a social reformer and community leader, Shankarseth earned the goodwill of both Indians and the British.
- He became the first Indian to be nominated to the Legislative Council of Bombay.
Shankarseth’s Most Significant Contributions:
- Education: Shankarseth was deeply committed to the growth and spread of education in Bombay, and donated land owned by his family for educational institutions.
- Like many social reformers of his age, he believed that Indians could progress through education.
- He also worked for the education of girls and women.
- Shankarseth founded the Native School of Bombay, which was renamed first as the Bombay Native Institution, and then as the Board of Education.
- Finally, this institution evolved into the prestigious Elphinstone College.
- Museum, Temples: Shankarseth was among the wealthy donors who helped promote Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum in Byculla, which was designed by a famous London-based architect.
- The Bhawani Shankar Temple near Nana Chowk was Shankarseth’s tribute to his late mother Bhawanibai Murkute.
- He also built a Ram temple.
- Railways: The first train in India ran between Boribunder and Thane on April 16, 1853.
- The 34-km project was undertaken by the Great Indian Peninsular Railway Company.
- The committee that gave the project impetus included Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy and Nana Shankarseth.
Methane emissions from fossil fuels remain high despite progress, US tops list of emitters: IEA

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As per the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Global Methane Tracker 2024, methane emissions from fuel consumption in 2023 approached record levels, nearing their highest point in history.
About the Global Methane Tracker:
- The Global Methane Tracker is an annual publication issued by the International Energy Agency (IEA), presenting the latest data on methane emissions primarily from the energy sector. It integrates recent scientific research, measurement campaigns, and satellite data.
Key Highlights from the Global Methane Tracker 2024:
- Methane emissions from fuel usage in 2023 approached record levels, reaching approximately 120 million tonnes (Mt), marking a slight increase from the previous year.
- Bioenergy, derived from plant and animal waste, contributed an additional 10 million tons of emissions.
- Out of the total methane emissions, around 80 million tons originated from ten countries, with the United States and Russia leading in emissions from oil and gas operations, and China leading in emissions from coal operations.
- Despite indications of declining emissions in certain regions, the overall methane emissions remain alarmingly high, posing a significant challenge to achieving global climate objectives.
- To align with the Paris Agreement goal of limiting warming to 1.5°C, there is a critical need to reduce methane emissions from fossil fuels by 75 percent by 2030.
- Achieving this target would require an estimated investment of approximately $170 billion, representing less than 5 percent of the revenue generated by the fossil fuel industry in 2023.
About the International Energy Agency (IEA):
- The International Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Paris, established in 1974.
- Its primary mandate is to ensure stability in the international oil supply, a response to the oil crisis of 1973, which led to temporary disruptions in the global oil supply chain.
- Operational Framework: The IEA functions within the broader scope of the Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership: As of 2022, the IEA comprises 31 member nations, with India joining as an associate member in 2017.
- Key Requirement: Member countries are obligated to maintain reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net oil imports.
- These reserves must be readily accessible by the government to address potential disruptions in the global oil supply chain, even if the reserves are not owned directly by the government.
NITI Aayog launches 'vocal for local' initiative to promote grassroots-level entrepreneurship

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog on Wednesday launched the 'Vocal for Local' initiative under its Aspirational Blocks Programme to bolster local economies and foster grassroots-level entrepreneurship, an official statement said.
What is the ‘Vocal for Local’ Initiative?
- The 'Vocal for Local' initiative, led by NITI Aayog through its Aspirational Blocks Programme, aims to foster self-reliance and sustainable development.
- Under this initiative, products from 500 aspirational blocks have been curated and unified under the Aakanksha brand.
- Aakanksha is an overarching brand, with potential extensions into various sub-brands to tap into global markets.
- A dedicated section has been established on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal under the Aakanksha brand to promote these products.
- Additionally, partners in the initiative offer support in areas such as e-commerce facilitation, establishing market linkages, financial and digital literacy, documentation and certification, and skill enhancement.
About Aspirational Blocks Programme:
- Inspired by the Aspirational District Programme launched in 2018, the Aspirational Blocks Programme extends its reach to 112 districts nationwide.
- This new initiative targets the enhancement of underperforming blocks across various development indicators.
- It aims to foster comprehensive growth in regions requiring additional support.
- Initially encompassing 500 districts across 31 States and Union Territories, the programme focuses on blocks in six key states: Uttar Pradesh (68 blocks), Bihar (61), Madhya Pradesh (42), Jharkhand (34), Odisha (29), and West Bengal (29).
What is the Government e-Marketplace (GeM)?
- Established in 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) serves as an online platform for public procurement.
- GeM acts as a centralized portal, streamlining the procurement process for common-use Goods & Services required by various Government Departments, Organizations, and PSUs.
- Purchases made through GeM by Government users are mandated by the Ministry of Finance under the General Financial Rules, 2017.
- GeM is operated by GeM SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle), a 100% Government-owned, non-profit company operating under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Govt's new code bars unethical marketing of drugs by pharma firms

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has notified a new legal code to curb the unethical marketing of drugs and banning medical representatives from using “inducement” to access healthcare professionals
About the Uniform Code of Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (UCPMP) 2024:
- The UCPMP 2024 has been implemented to regulate unethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, with a focus on promoting transparency and ethical conduct.
- The updated guidelines encompass various aspects, including drug endorsement, promotion, ethical behavior for medical representatives, and the maintenance of professional relationships with healthcare professionals.
Key provisions of the UCPMP 2024 include:
- Prohibiting the offering of gifts and travel facilities to healthcare professionals or their family members by pharmaceutical companies.
- Mandating that medical representatives should not use any form of inducement or subterfuge to gain interviews with healthcare professionals, nor should they provide payment for access under any guise.
- Holding pharmaceutical companies responsible for the actions of their medical representatives.
- Banning the supply of free drug samples to individuals who are not qualified to prescribe such products.
- Requiring each pharmaceutical company to maintain detailed records of free samples provided to healthcare practitioners, with the total value of distributed samples not exceeding two percent of the company's domestic sales per year.
- Compulsory constitution of an Ethics Committee for Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (ECPMP) by all pharmaceutical associations, along with the establishment of a dedicated UCPMP portal on their websites for implementation and monitoring purposes.
- Detailed guidelines on how drugs should be promoted in textual and audio-visual marketing materials, ensuring that information is balanced, up-to-date, verifiable, and non-misleading.
- Restrictions on making unverified claims and comparisons about a drug's usefulness, as well as using terms like "safe" and "new" without proper qualification.
- Assigning responsibility for adherence to the UCPMP 2024 to the Chief Executive Officers of pharmaceutical companies.
- Outlining penalties for violating the code and establishing a clear process for handling complaints, ensuring accountability and effective oversight.
- The UCPMP 2024 serves as a comprehensive framework for promoting ethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, aiming to protect the interests of patients, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders while fostering an environment of transparency and integrity.
Every village to have agricultural credit societies by 2027

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah Friday said that the Centre has decided to ensure formation of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027.
Context:
- Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah recently announced the Centre's commitment to establishing Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027, introducing 20 new activities to enhance their profitability.
- Emphasizing the significance of computerization in PACS, Shah highlighted its role in fostering development opportunities.
- He also inaugurated the National Cooperative Database and unveiled the 'National Cooperative Database 2023: A Report' to bridge existing gaps through comprehensive analysis.
- The database initiative progressed through three phases, including mapping approximately 2.64 lakh societies across agriculture, dairy, and fisheries sectors in the first phase.
- Subsequent phases involved data collection from various federations, banks, and mapping of the remaining 8 lakh primary cooperative societies in other sectors.
- The unveiling revealed over 8 lakh registered societies in the country, connecting more than 30 crore citizens.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)?
- PACS are grassroots cooperative credit societies, constituting the final tier in a three-tier cooperative credit system led by State Cooperative Banks (SCBs) at the state level.
- SCBs channel credit to District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) operating at the district level, which collaborate with PACS, directly serving farmers.
- PACS operate as cooperative entities, with individual farmers as members and elected office-bearers from within the community. Villages may host multiple PACS.
- These societies extend short-term and medium-term agricultural loans to farmers for various farming activities.
Number of PACS in India:
- Established since 1904, India currently boasts over 1,00,000 PACS nationwide, engaging a significant member base exceeding 13 crore farmers.
- However, operational PACS stand at only 63,000, indicating the need for enhanced functionality and outreach.
Why are PACS Appealing?
- PACS offer crucial last-mile connectivity, ensuring farmers have access to capital at the onset of agricultural activities.
- They streamline credit extension processes, providing farmers with timely financial support with minimal paperwork, unlike traditional banks known for cumbersome procedures.
- PACS simplify paperwork and administrative tasks, offering farmers collective strength and assistance from PACS office-bearers.
- Unlike individual interactions required with commercial banks, PACS enable farmers to navigate loan processes collectively, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Challenges Faced by PACS:
- Political influences often overshadow financial prudence within PACS, impacting loan recovery.
- Various committees have highlighted systemic issues within the cooperative system, including low member participation, lack of professionalism, inadequate governance, bureaucratic hurdles, and a workforce with aging and disengaged employees.
Trees in Corbett fell prey to greedy nexus, says Supreme Court

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Wednesday condemned the illegal felling of over 6,000 trees to construct buildings, ostensibly for “eco-tourism” at the Jim Corbett National Park in Uttarakhand, as a “classic case” of nexus between politicians and officials working to ransack the environment for short-term commercial ends.
News Summary:
- In 2023, a series of applications brought attention to the creation of alleged illegal buildings and encroachment on water bodies, prompting court intervention.
- Petitioners highlighted violations of environmental norms and encroachment into core wildlife habitats.
- Evidence presented during proceedings revealed unauthorized constructions within the national park, including concrete and iron enclosures purportedly intended for a 'safari' experience.
- Moreover, it was disclosed that over 6,000 trees had been felled in the national park under the pretext of safari development.
Supreme Court’s Observations:
- The Court has raised concerns regarding the necessity of developing facilities within natural forest environments, particularly in areas designated for the protection of endangered species like tigers.
- Directing the Government to establish a committee, the Supreme Court seeks recommendations on whether tiger safaris should be permitted in buffer or fringe areas and what guidelines should govern their establishment if allowed.
- Additionally, the Court has strongly criticized the illegal constructions and extensive tree felling in Uttarakhand's Corbett National Park.
What are the Core and Buffer Areas in Tiger Reserves?
- As per the Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act of 2006, a Tiger Reserve comprises core or critical habitat and a buffer zone surrounding it.
- Core areas hold the legal status of a National Park or a Sanctuary.
- Buffer zones consist of a mix of forest and non-forest land, managed as a multiple-use area.
- The buffer area acts as a protective barrier, absorbing the impact of poaching pressure on tiger and other wildlife populations.
About Jim Corbett National Park:
- Location: Situated in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand, Jim Corbett National Park is renowned for its rich biodiversity.
Key Facts:
- Established in 1935, it is India’s oldest national park.
- Initially named Hailey National Park after its founder Sir Malcolm Hailey, it was renamed Corbett National Park in 1956 to honor Jim Corbett's contributions to wildlife preservation in India.
- Corbett National Park boasts the highest population of tigers in India, highlighting its importance for tiger conservation efforts.
- Flora: Dominated by Sal, Semal, Kharpat, Sissoo, Khair, Dhak, Khingan, Bakli, Bel, Ber, Bamboo, Khingam, Jamun, Kanju, Rohini, and Pula trees.
- Sal, Khair, and Sissoo are prominently featured throughout the park.
- Fauna: Home to diverse wildlife including Tiger, Leopard, Elephant, Chital Deer, Sambar Deer, Hogg Deer, Barking Deer, Wild Boar, Langur, Wild pig, Rhesus Monkey, Jackal, Rabbit, Yellow Throated Martin, and Otters.
- Various reptiles such as Crocodile, Gharial, King Cobra, Common Krait, Cobra, Russell's Viper, Rock Python, and Monitor Lizard inhabit the park.
- The Kosi River feeds the eastern periphery of Corbett National Park.
- The Ramganga River (West) and its tributaries Sonanadi, Palain, and Mandal serve as significant hydrological resources for the park.
Google-backed satellite to track global oil industry methane emissions
- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
MethaneSAT — a satellite which will track and measure methane emissions at a global scale — was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California recently.
What is MethaneSAT?
- MethaneSAT will orbit the Earth 15 times a day, monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- It will create a large amount of data, which will tell “how much methane is coming from where, who’s responsible, and are those emissions going up or down over time”.
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be made public for free in near real-time.
- This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Institutions involved in the development:
- The entity behind MethaneSAT is the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) — a US-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
- To develop the satellite, EDF partnered with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency.
Features of MethaneSAT:
- Historically, tracking the source of methane emissions and measuring them has been quite challenging.
- ?While some satellites can provide high-resolution data, they can only scan specific, pre-targeted sites.
- Others can examine larger areas and detect large emitting events, but cannot scan “smaller sources that account for the majority of emissions in many, if not most, regions,” the EDF statement added.
- Due to this discrepancy, according to an International Energy Agency (IEA) report, global methane emissions are about 70 per cent higher than levels reported by national governments.
- MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Equipped with a high-resolution infrared sensor and a spectrometer, the satellite will fill critical data gaps.
- It can track differences in methane concentrations as small as three parts per billion in the atmosphere, which enables it to pick up smaller emissions sources than the previous satellites.
- MethaneSAT also has a wide-camera view — of about 200 km by 200 km — allowing it to identify larger emitters so-called “super emitters”.
Significance of MethaneSAT:
- Advancing the Goals of the Global Methane Pledge 2021: The Global Methane Pledge, signed by over 150 countries in 2021, aims to reduce collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- During the previous year's COP, over 50 companies pledged to significantly reduce methane emissions and routine flaring.
- MethaneSAT will play a crucial role in helping these entities achieve their targets.
- Enhancing Transparency: The satellite will usher in a new era of transparency by providing publicly available data accessible to anyone worldwide.
- This data will enable monitoring of methane commitments made by governments and corporations, promoting accountability and transparency in emission reduction efforts."
Why Do We Need to Track and Measure Methane Emission?
- Methane is an invisible but strong greenhouse gas, and the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide, responsible for 30 percent of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme, over a period of 20 years, methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
- The gas also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone — a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the Earth’s surface.
- According to a 2022 report, exposure to ground-level ozone could be contributing to one million premature deaths every year.
- Therefore, it is crucial to cut methane emissions and the main culprit, fossil fuel operations, which account for about 40 percent of all human-caused methane emissions.
- The objective of MethaneSAT is to help achieve this goal.
Several OPEC+ nations extend oil cuts to boost prices

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Moscow, Riyadh, and several other OPEC+ members announced extensions to oil production cuts first announced in 2023 as part of an agreement among oil producers to boost prices following economic uncertainty.
What is the OPEC+ Oil Alliance?
- OPEC+ is a coalition of oil-exporting nations that convenes regularly to determine the quantity of crude oil to offer on the global market.
- Origin: This alliance was established in late 2016 to formalize a framework for collaboration between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing nations on a consistent and sustainable basis.
- The primary objective of these nations is to collaborate on regulating crude oil production to stabilize the oil market.
- OPEC+ collectively controls approximately 40% of global oil supplies and holds over 80% of proven oil reserves.
- At its core, OPEC+ consists of OPEC member states, predominantly comprising nations from the Middle East and Africa.
- Membership: It includes OPEC member states along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC):
- OPEC, short for the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent intergovernmental organization comprised of oil-exporting nations.
Mission:
- To coordinate and harmonize the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- To ensure the stability of oil prices in global oil markets, aiming to eliminate detrimental and unnecessary fluctuations.
- Formation: Founded in 1960 by the five original members - Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Presently, it consists of 13 member countries, which include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Headquarters: Located in Vienna, Austria.
. First-of-its-kind Micro Turbojet Engine made in India

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A micro turbojet engine designed and developed indigenously by Hyderabad-based firm Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools with the support of the IIT Hyderabad has been unveiled.
Key Highlights of the Micro Turbojet Engine “INDRA RV25: 240N”:
- It is an indigenous micro turbojet engine made in India.
- Its primary focus is on serving unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones.
- Beyond UAVs, the engine exhibits versatile applications in air taxis, jetpacks, auxiliary power units, range extenders, and potential use in power generation for the future.
- Indigenous design and development: Engineered entirely in India by the Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools (RVMT) team of skilled engineers & supported by IIT, Hyderabad.
- A great demonstration of the potential of Industry-Academia partnership
- Self-reliance and autonomy: By reducing reliance on imported technologies, components, and expertise, the Micro Turbojet Engine contributes to India’s goal of achieving self-sufficiency in critical sectors, bolstering national security and economic resilience
- Empowering local manufacturing: The launch of the indigenous Micro Turbojet Engine not only drives technological innovation but also stimulates the growth of the domestic aerospace and defense manufacturing ecosystem, creating jobs and fostering economic growth.
What Is a Turbojet Engine and How Does It Work?
- Turbojet engines are jet engines that, like other jet engines, generate propulsion by discharging or expelling heated air.
- They feature a combustion chamber in which they burn fuel and air.
- As they burn this mixture, turbojet engines will discharge heated air.
- It can find turbojet engines in commercial airplanes, civilian airplanes, and military aircraft.
How Turbojet Engines Work?
- The process begins by drawing air through an intake.
- Turbojet engines feature an air intake, which is typically located near the front of the engine.
- Air will flow into this intake, at which point it will be redirected to the engine’s interior.
- After entering the engine, the air will become compressed.
- Turbojet engines feature a set of rotating blades. Known as compressors, these rotating blades are designed to compress the air.
- The next step in the process is combustion which involves the burning of fuel and air.
- Turbojet engines will inject fuel into the same combustion chamber where the compressed air is located.
- A spark will then ignite the mixture of fuel and compressed air, thereby generating hot, high-pressure exhaust gas.
- The exhaust gas generated by the combustion is expelled out the rear of the turbojet engine.
- This rearward expulsion allows for forward propulsion.
- As the exhaust gas is discharged out the rear of the turbojet engine, the airplane will be propelled forward.
PM Modi Inaugurates 'Sudarshan Setu', India's Longest Cable-Stayed Bridge

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently inaugurated the Sudarshan Setu, a four-lane cable-stayed bridge connecting Okha to Beyt Dwarka island in Gujarat.
About the Sudarshan Setu:
- 'Sudarshan Setu' is the country's longest cable-stayed bridge 2.32 km on the Arabian Sea connecting Beyt Dwarka island to mainland Okha in Gujarat's Devbhumi Dwarka district.
- It boasts a unique design, featuring a footpath adorned with verses from the Bhagavad Gita and images of Lord Krishna on both sides.
- It also has solar panels installed on the upper portions of the footpath, generating one megawatt of electricity.
- The 2.32 km bridge, including 900 metres of a central double-span cable-stayed portion and a 2.45 km long approach road, has been constructed at a cost of Rs 979 crore.
About Beyt Dwarka:
- Bet/Beyt (pronounced ‘Bait’ Dwarka also known as Shankhodara, is an island located near the shores of Okha which is situated around 30 km from Dwarka, in the Gulf of Kutch.
- It said that Lord Krishna resided here while Dwarka was his constitutional seat.
History:
- Bet Dwarka derived its name from the word ‘bet’ which translates to ‘gift’ and is believed that Lord Krishna received it from his friend Sudama.
- In the ancient epic, Mahabharata, Bet Dwarka is known by the name of ‘Antardvipa’ to which people of the Yadava clan needed to travel by boat.
- Explorations and excavations carried out under the sea have revealed the presence of settlements whose age can be traced back to the era of the Harappan civilisation and that of the Mauryan rule.
- In the later years, the region was under the administration of the Gaekwad clan of the state of Baroda.
- During the revolt of 1857, Vaghers attacked the region and captured it, but had to concede defeat in two years and return the region back to the Gaekwads.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
Cabinet approves Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for the period 2021-26

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of “Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)” with a total outlay of Rs. 4,100 crore for a period of 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
About the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP):
- The FMBAP Scheme is being implemented throughout the country for effective flood management, erosion control and anti-sea erosion and to help in maintaining peace along the border.
- The scheme benefits towns, villages, industrial establishments, communication links, agricultural fields, infrastructure etc. from floods and erosion in the country.
- The catchment area treatment works will help in the reduction of sediment load into rivers.
- The Scheme aims at the completion of the ongoing projects already approved under FMP.
The Scheme has two components:
- Under the Flood Management Programme (FMP) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 2940 crore, central assistance will be provided to State Governments for taking up critical works related to flood control, anti-erosion, drainage development and anti-sea erosion, etc.
- The pattern of funding to be followed is 90% (Centre): 10% (State) for Special Category States (8 North-Eastern States and Hilly States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and UT of Jammu & Kashmir) and 60% (Centre):40% (State) for General/ Non-Special Category States.
- Under the River Management and Border Areas (RMBA) component of FMBAP with an outlay of Rs. 1160 crore, flood control and anti-erosion work on common border rivers with neighbouring countries including hydrological observations and flood forecasting, and investigation & pre-construction activities of joint water resources projects (with neighbouring countries) on common border rivers will be taken up with 100% central assistance.
- The Scheme has the provision of incentivizing the States which implement flood plain zoning, recognized as an effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Importance:
- While the primary duty of flood management lies with the State Governments, the Union Government actively promotes and advocates for the adoption of modern technology and innovative approaches.
- Additionally, projects executed under the RMBA component serve to safeguard critical installations of security agencies and border outposts situated along border rivers from the perils of floods and erosion.
- Furthermore, the scheme includes provisions for incentivizing states that implement flood plain zoning, a recognized and effective non-structural measure for flood management.
Will the ‘Paruveta Festival’ celebrated in Andhra’s Ahobilam get UNESCO recognition?

- 22 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
INTACH is striving to obtain UNESCO recognition for the yearly 'Paruveta' festival, emphasising its cultural significance.
About the Paruveta Festival:
- Paruveta Festival, also known as the 'mock hunting festival', is a celebrated tradition at the Sri Narasimha Swamy temple in Ahobilam, Andhra Pradesh.
- It stands out as a symbol of communal harmony, where devotees from various religious backgrounds, including Muslims, come together to offer prayers.
Origin and Significance:
- According to folklore, the festival commemorates Lord Vishnu's incarnation as Narasimha, who married Chenchulakshmi, a tribal girl, symbolising unity across different communities.
- The festival's rituals, typically observed during Vijayadashami or Sankranti, extend for a 'mandala' period of forty days in Ahobilam.
Activities and Customs:
- During the festival, the temple deity is carried to the 32 Chenchu tribal villages surrounding Ahobilam for forty days.
- The journey begins with a symbolic act where tribals shoot arrows at the deity's palanquin, signifying protection and reverence.
- Chenchus participated by undertaking 'Narasimha Deeksha', wearing yellow robes and Tulasi Mala, while observing celibacy.
- The temple staff reside in these villages throughout the festival, showcasing the tradition of a casteless society with no traces of untouchability.
Key Points about Chenchu Tribes:
- Geographic Distribution: Chenchu tribes primarily inhabit the hills of southern India, particularly in Andhra Pradesh.
- Additionally, Chenchu communities can be found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Orissa.
- Language and Communication: Their native language, known as Chenchu, belongs to the Dravidian language family.
- While many Chenchu individuals speak Telugu, their traditional language holds cultural significance.
- Livelihood and Occupation: Historically, Chenchu people pursued a nomadic lifestyle, relying on food gathering.
- However, due to factors such as agricultural expansion, many have transitioned to working as farmers or forest labourers.
- Housing and Settlements: Chenchu dwellings are typically hive-shaped structures constructed from wattle thatch, composed of interwoven poles, twigs, reeds, or branches.
- These houses reflect their traditional architectural style and are adapted to their environment.
- Social Structure: Chenchu society is organised into clans, which are extended family units, as well as local groups and individual families.
- They adhere to exogamous marriage practices, prohibiting unions within the same clan.
- Additionally, Chenchu kinship is patrilineal, tracing descent through male lineage.
Gold Hunt by Villagers Reveals Ancient Harappan Settlement in Gujarat

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The newly discovered Harappan settlement at Lodrani village in the Kutch region of Gujarat has sparked widespread interest in the fascinating remains of this ancient civilisation, making it an important site for archaeological exploration and research.
Features of Harappan site Morodharo:
- Morodharo is a fortified settlement of the Harappan era, with the fortification measuring 102 m to the west and 58 m north to the south.
- The thickness of the wall is 3.3 m on average.
- Morodhara has a 10x10 m platform on the southwest side and a well on the northeast side.
- Burial cairns have been found at Morodharo.
- A cairn is an intentionally constructed mound of stones, typically created for marking a location or serving as a burial mound.
- Harappan pottery with perforated jar sherds, reserved slipware and terracotta cakes have also been unearthed.
- All these items have a striking resemblance to those found in Dholavira.
About Harappan Civilization:
- The Harappan civilization, also known as the Indus Valley civilization was South Asia's first urban civilization, flourishing concurrently with Mesopotamia and Egypt.
- It encompassed the most extensive territory, covering approximately 800,000 square kilometres, compared to its contemporaries.
- Prominent cities during the Harappan period included Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro in present-day Pakistan, along with Dholavira, Lothal, and Surkotada in Gujarat, India, among others.
- Urban planning in Harappan cities followed a meticulous grid layout, with streets intersecting at right angles, dividing the cities into neat rectangular blocks.
- The streets and alleys were deliberately designed for efficient movement, accommodating carts and pedestrians, often featuring covered drains alongside.
- For defence and security, the cities were enclosed by sturdy walls made of mud bricks, shielding against intruders and natural calamities.
- Each city was structured into an elevated citadel and a lower town, with the former housing monumental structures like granaries and administrative buildings.
- Residential areas comprised multi-story brick houses clustered around courtyards, some equipped with private wells and well-ventilated bathrooms.
- A sophisticated drainage system ensured efficient waste disposal, with individual house drains connected to street-level drainage networks.
- Granaries and storage facilities were strategically positioned to manage surplus agricultural yields, reflecting advanced urban planning and resource management.
BSNL floats Rs 65,000 crore tender for phase-III BharatNet project

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
BSNL, the state-owned telecommunications company, has initiated a tender process amounting to approximately Rs 65,000 crore for the implementation of the phase-III BharatNet project.
What is the BharatNet Phase III Project?
- The BharatNet phase-III project adopts a three-level architecture:
- Internet leased line bandwidth
- Middle-mile connectivity, and
- Last-mile connectivity
- It aims to involve village-level entrepreneurs or Udyamis in providing last-mile connectivity to households on a revenue-sharing basis.
- BSNL aims to provide 15 million home fibre connections over five years using the BharatNet Udyami model.
About BharatNet Project:
- The BharatNet Project is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world.
- It aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats across India in a phased manner.
- Its core objective is to ensure equitable access to broadband services for all telecom service providers, fostering the deployment of services like e-health, e-education, and e-governance in rural and remote areas.
- Initiated in 2011 and executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in 2012, the project operates in three phases.
- Phase I launched in 2011, focused on creating the National Optical Fibre Network, leveraging existing infrastructure and laying additional fibre to bridge connectivity gaps up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Phase II, approved in 2017, builds upon Phase I’s experiences, aligning with the Digital India vision.
- It adopts a flexible approach, integrating various media such as Optical Fibre Cable (OFC), Radio, and satellite to connect Gram Panchayats, utilizing models like State-led, Private Sector, and CPSU Models for implementation.
- Phase III, spanning from 2019 to 2023, aims to establish a robust, future-ready network with district-to-block fibre connectivity, featuring ring topology for redundancy.
- This comprehensive approach ensures the creation of a resilient and inclusive telecom infrastructure, facilitating socio-economic development in rural India.
ISRO’s ‘Naughty Boy’ Rocket Launches INSAT-3DS (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) recently launched its weather satellite INSAT-3DS board spacecraft Geosynchronous Launch Vehicle (GSLV) F14, nicknamed the ‘naughty boy’ for its spotty record.
What is the GSLV-F14?
- The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), standing at a height of 51.7 metres, is a three-stage launch vehicle with a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes.
- First stage: Its first stage (GS1) features a solid propellant (S139) motor with 139 tons of propellant and four earth-storable propellant stages (L40) strapons, each carrying 40 tons of liquid propellant.
- Second Stage: The second stage (GS2) also utilises an earth-storable propellant system with a 40-ton propellant load.
- Third Stage: The third stage (GS3) is equipped with a cryogenic system containing 15 tons of propellant, consisting of liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
- GSLV-F14 serves as a versatile launch vehicle, capable of deploying various types of spacecraft for communication, navigation, earth resource surveys, and other specialised missions.
GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission Overview and Key Goals:
- INSAT-3DS Satellite marks a significant advancement in the Third Generation of Meteorological Satellite series from Geostationary Orbit, with substantial contributions from Indian industries.
- Fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), the mission aims to enhance meteorological services, complementing the existing capabilities of INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR satellites.
Key Objectives:
- Earth Observation and Oceanic Monitoring: Utilise various spectral channels to monitor Earth's surface, conduct oceanic observations, and assess environmental conditions critical for meteorology.
- Atmospheric Parameter Profiling: Provide vertical profiles of essential meteorological parameters within the atmosphere, enhancing our understanding of atmospheric dynamics.
- Data Collection and Dissemination: Facilitate the collection and dissemination of data from Data Collection Platforms (DCPs), ensuring timely access to crucial meteorological information.
- Satellite Aided Search and Rescue (SAR) Services: Enable Satellite Aided Search and Rescue services, enhancing emergency response capabilities through advanced satellite technology.
Significance of the GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS Mission:
- The launch of INSAT-3DS holds a lot of significance for India's space agency as it is equipped to provide extremely accurate weather forecast information by studying the surface of the ocean, also being helpful in disaster prevention.
- The GSLV has encountered challenges in the past, with four out of 15 launches facing setbacks, contrasting with the higher success rates of ISRO's PSLV and LVM-3.
- The success of this mission is critical, especially considering the upcoming launch of the Earth observation satellite, NISAR, later this year, a collaborative effort between NASA and ISRO.
- INSAT-3DS, with a mission lifespan of 10 years, will assume the roles of INSAT-3D (2013) and INSAT-3DR (2016), which have reached the end of their operational lives.
- This mission will enhance meteorological forecasting capabilities, enabling better prediction of extreme weather events like thunderstorms, providing visibility assessments for aviation, and facilitating research on forest fires, smoke, snow cover, and climate dynamics.
RBI Put Restraints on a Certain Card Network (Indian Express)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has ordered a certain card network to stop “unauthorised payments” made using business cards.
What is a Card Network?
- Card networks connect banks, merchants, and customers (card users) to one another so that transactions can be carried out smoothly and securely.
- Card networks are operating in the background every time a customer uses her card to make a payment.
- There are five authorised card networks in India:
- Visa
- Mastercard
- RuPay
- Diners Club, and
- American Express
Reasons Behind the RBI Order:
- Payments to Non-Card-Accepting Entities: The network facilitated card payments from corporations for commercial transactions, transferring the funds to non-card-accepting recipients via IMPS, RTGS, or NEFT without proper authorization, violating the Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act, 2007.
- Non-Adherence to KYC Requirements: Additionally, the RBI expressed concerns regarding non-compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) norms in these transactions.
What are the RBI’s Concerns?
- Under Section 4 of the PSS Act, such a payment system requires authorisation, which had not been obtained in this case.
- There were two other concerns as well.
- First, the intermediary in such an arrangement pooled a large amount of funds into an account that was not a designated account under the PSS Act.
- Second, transactions processed under this arrangement did not comply with the ‘originator and beneficiary information’ requirements, as stipulated under the ‘Master Direction on KYC’ issued by the RBI.
- Steps taken by the RBI: The RBI has instructed the card network to suspend all such arrangements until further notice.
- However, regular usage of business credit cards remains unaffected.
India initiates Anti-Dumping Probe into Solar Glass Imports from China and Vietnam (TOI)

- 17 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India has launched an anti-dumping investigation into the import of solar glass from China and Vietnam following a complaint from domestic players.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- Anti-dumping duty is a tariff levied on imports from foreign countries when their prices are lower than the fair market value of similar goods in the domestic market.
- It's implemented by governments to counteract the practice of "dumping," where foreign goods are sold at unfairly low prices in the domestic market, posing a threat to local businesses.
- The primary objective of anti-dumping duty is to safeguard domestic industries from unfair competition and restore fair trade practices.
- This measure is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to address instances where dumping causes genuine harm to domestic industries.
- To impose anti-dumping duties, governments must provide evidence of dumping, quantify its extent in terms of costs, and demonstrate the resulting injury or threat to domestic markets.
- While aimed at protecting local industries, anti-dumping duties can sometimes lead to increased prices for consumers within the country.
About Countervailing Duty (CVD):
- Countervailing duty (CVD) is a type of tariff imposed by a government to offset the adverse effects of import subsidies on domestic producers.
- It serves as an import tax applied by the importing country on subsidised products from abroad.
- CVD is imposed to address situations where foreign governments provide subsidies to their producers, lowering the cost of their goods and potentially disrupting fair competition.
- To prevent the influx of subsidised products into their markets, importing countries levy CVD, effectively neutralising the price advantage enjoyed by these imports.
- The imposition of CVD is permitted by the World Trade Organization (WTO) to help maintain fair trade practices among its member countries.
Difference Between Anti-dumping Duty and Countervailing Duty:
- Anti-dumping duty is enacted to safeguard domestic markets from the harmful effects of low-priced foreign goods, while CVD targets products benefiting from government subsidies, resulting in artificially low prices.
- The amount of Anti-dumping duty is determined by the margin of dumping, whereas CVD is calculated based on the subsidy value granted to foreign goods.
Coal Ministry Hosts Industry Interaction on Coal Gasification (ET)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Coal has announced it will host an Industry Interaction on February 16, 2024, in Hyderabad to discuss the development of coal and lignite gasification projects across India.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a process where coal undergoes partial oxidation with air, oxygen, steam, or carbon dioxide to produce a fuel gas.
- This gas serves as an alternative to piped natural gas or methane for energy generation.
- Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) is a technique involving the conversion of coal into gas within the seam, extracted through wells.
- Production of Syngas: This process yields Syngas, a mixture primarily comprising methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas finds applications in producing fertilisers, fuels, solvents, and synthetic materials.
- Significance: In manufacturing, steel companies traditionally rely on costly imported coking coal. Syngas derived from coal gasification offers a cost-effective alternative.
- It is utilized in electricity generation, chemical feedstock production, and hydrogen-based applications like ammonia production and fueling a hydrogen economy.
Advantages of Coal Gasification:
- Coal gasification offers a solution to local pollution issues.
- It is deemed environmentally cleaner than direct coal combustion.
- Decreasing dependence on imported natural gas, methanol, ammonia, and other vital commodities, enhances energy security.
- This technology has the potential to mitigate environmental impacts by curbing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable approaches, aligning with India's global objectives for a more environmentally sustainable future.
Concerns Associated with Coal Gasification Plants?
- The main disadvantage of coal gasification is that it is an expensive process.
- The process can produce a number of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and mercury.
- The process produces a lot of ash, which can pollute the environment.
- The process uses a lot of water, which can lead to water shortages in areas where it is used.
8th Century Kotravai Sculpture from Pallava Period Discovered (Indian Express)

- 15 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, archaeologists discovered an eighth-century Kotravai sculpture, an artefact that dates back to the Pallava period, near Ulundurpet, Tamil Nadu.
About the Kotravai Sculpture:
- Kotravai sculpture is made in a slab stone of five-feet height and four-feet width.
- The idol is depicted with eight hands, indicating its origin in the eighth century during the Pallava period.
- The sculpture depicts various elements such as chakkara, sword, bell, and abhaya mudra in the right hands.
- Conch, bow, shield, and Uru Mudhra are shown in the left side hands along with bangles in all hands.
- The presence of trishul (soolam) and lion (simmam) on the right side of head, and blackbuck (kavarimann) on the left side.
- Kotravai is portrayed standing on the head of a buffalo, with two guards on each side.
About the Pallava Dynasty:
- The Pallava Dynasty, a prominent power in South India, thrived from the 3rd to the 9th centuries.
- Their dominion encompassed the northern regions of Tamil Nadu, portions of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana, with Kanchipuram serving as their capital.
- The Pallavas were known for their patronage of Buddhism, Jainism, and Brahminical faith, as well as their support for music, painting, and literature.
- Origins: Initially vassals of the Andhra Satavahanas, the Pallavas gained autonomy following the latter's decline in Amaravati.
- Gradually expanding southward, they established their capital in Kanchipuram during the 4th century CE.
- Under the reigns of Mahendravarman I (571 - 630 CE) and Narasimhavarman I (630 - 668 CE), the Pallava realm experienced significant growth in wealth and power.
- According to the accounts of Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang, Bodhidharma, the founder of the Chan (Zen) school of Buddhism in China, was purportedly a prince of the Pallava empire.
- The Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang visited Kanchipuram, the capital of Pallavas, during the reign of Narasimha Varman I and lauded their benevolent governance.
Architectural Contributions of the Pallavas:
- The Pallava Dynasty is renowned for its patronage of Dravidian architecture, particularly temple construction.
- They played a pivotal role in the evolution from rock-cut architecture to stone temples.
- Their most celebrated architectural achievements can be found in Mahabalipuram, which flourished as a significant hub of art, architecture, and literature during Pallava rule.
- Narasimhavarman II commissioned notable structures such as the Kailasanatha Temple in Kanchipuram and the Shore Temple.
- Among these temples, Kailasanatha and Vaikuntaperumal stand out for their architectural excellence.
- The Vaikuntaperumal shrine, erected in the 8th century AD, is renowned for its intricate sculptures depicting Pallava history.
- Religion: The Pallavas embraced Shaivism, a predominant local religion, thereby aligning themselves with Dravidian cultural traditions.
Military Engagements and Decline of the Pallava Dynasty:
- Throughout their reign, the Pallavas engaged in persistent conflicts with both the Chalukya Dynasty to the north and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola and Pandyas to the south.
- The Pallavas faced ongoing battles with the Chalukyas of Badami and ultimately succumbed to the supremacy of the Chola kings in the 8th century CE.
- The ascent of the Rashtrakutas marked the decline of the Pallava Dynasty.
- In 897 AD, Vijayalaya, the Chola King, decisively defeated Aparajitavarman, the last Pallava King, thereby sealing the fate of the Pallava Dynasty.
India's retail inflation moderates to 5.10 per cent in January (The Hindu)

- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's retail inflation has eased to 5.10% on an annual basis, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation.
What is Retail Inflation or CPI-based Inflation?
- Retail inflation, also known as Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation tracks the change in retail prices of goods and services which households purchase for their daily consumption.
- CPI is released by The National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- To measure inflation, we estimate how much CPI has increased in terms of percentage change over the same period the previous year.
- If prices have fallen, it is known as deflation (negative inflation).
- The Central Bank (RBI) pays very close attention to this figure in its role of maintaining price stability in the economy.
- The CPI monitors retail prices at a certain level for a particular commodity; and price movement of goods and services at rural, urban and all-India levels.
- The change in the price index over a period of time is referred to as CPI-based inflation or retail inflation.
- Generally, CPI is used as a macroeconomic indicator of inflation, as a tool by the central bank and government for inflation targeting and for inspecting price stability, and as a deflator in the national accounts.
- CPI also helps understand the real value of salaries, wages, and pensions, the purchasing power of the nation’s currency, and regulating rates.
- CPI, one of the most important statistics to ascertain economic health, is generally based on the weighted average of the prices of commodities.
- It basically gives an idea of the cost of the standard of living.
- CPI specifically identifies periods of deflation or inflation for consumers in their day-to-day living expenses.
- If there is inflation (when goods and services cost more) the CPI will rise over a period of time.
- If the CPI drops, that means there is deflation or a steady reduction in the prices of goods and services.
How is CPI calculated (CPI formula)?
- To calculate CPI, multiply 100 by the fraction of the cost price of the current period and the base period.
- CPI formula: (Price of the basket in current period / Price of the basket in base period) x 100
Regulating India's Online Gaming Industry (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will act as a regulator for the online gaming sector rather than an industry-led self-regulatory organization (SRO).
What are Online Games?
- Online games refer to games that are played over some form of computer network, most often the Internet.
- Online games can range from simple text-based games to games incorporating complex graphics and virtual worlds populated by many players simultaneously.
Types of Online Gaming:
- e-Sports: Originally played offline or on gaming consoles, e-Sports now thrive in the online realm, featuring structured competitions among professional players or teams.
- Fantasy Sports: These games involve assembling virtual teams composed of real-life athletes from different sports teams.
- Points are earned based on the actual performance of these athletes, as seen in platforms like Dream11.
- Online Casual Games: These diversions can be skill-based, where success relies on mental or physical prowess, or chance-based, where outcomes are determined by random events, like dice rolls.
How Big is India's Online Gaming Industry?
- The online gaming sector in India is primarily nurtured by a burgeoning startup ecosystem, boasting a robust 27% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
- Projections suggest that the integration of AI and online gaming could contribute up to $300 billion to India's GDP by 2026-27.
- India leads the global charts in terms of the percentage of new paying users (NPUs) in gaming, soaring from 40% in 2020 to an anticipated 50% in 2021.
- Transactional gaming revenue witnessed a notable 26% surge in India, with the number of paying players escalating from 80 million in 2020 to 95 million in 2021, as per a FICCI report.
Challenges Confronting India's Online Gaming Sector:
- Regulatory Void: The absence of a regulatory framework poses challenges in implementing essential measures such as grievance redressal, player protection, data security, and curbing deceptive advertisements.
- Illegal Offshore Markets: Illicit offshore gambling and betting platforms pose threats to financial integrity and national security, with estimated annual tax losses to India amounting to $45 billion.
- Interstate Quandary: Varied state regulations on online gaming create inconsistencies, compounded by the Internet's borderless nature, making enforcement difficult.
- Societal Implications: The surge in online gaming raises concerns about addiction, mental health, financial fraud, and privacy breaches, warranting a comprehensive approach to address these issues.
The Problem of Self-Regulatory Bodies Under the IT Rules:
- The implementation of the IT (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 represented a significant stride in regulatory oversight.
- According to these rules, online real-money gaming platforms must obtain approval from a regulatory authority, while those not involving real money are exempt from such requirements.
- In April 2023, the government issued online gaming regulations and provided a three-month window for the industry to propose Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs).
- However, the proposals submitted were predominantly influenced by gaming companies and their industry associations, raising concerns about their ability to function as impartial regulatory bodies.
PM-SVANidhi Boosted the Annual Income of Street Vendors (Indian Express)

- 12 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A study that evaluated the impact of the PM SVANidhi, a small working capital loan scheme for street vendors, has found that the first tranche of `10,000 led to an additional annual income of `23,460 for each beneficiary.
News Summary:
- Commissioned by the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the study was conducted by the Centre for Analytical Finance at the Indian School of Business (ISB) from January to June 2023.
- Although the report's findings will inform the Ministry's assessment of the PM SVANidhi scheme, it is not expected to be publicly released.
Key Findings of the Report:
- 94% of beneficiaries who received the initial Rs 10,000 loan reported using it for business investments, rising to 98% for those who received a second loan.
- The first loan contributed to an average additional monthly income of Rs 1,955, totalling Rs 23,460 over the one-year loan period.
- Approximately 13.9% of disbursed loans were categorized as non-performing assets (NPAs), indicating no payments for three months or more.
- Beneficiaries demonstrated a lower debt-to-income (DTI) ratio compared to typical small businesses, indicating high creditworthiness.
- Despite the PM SVANidhi program, there was limited improvement in street vendors accessing formal credit from other sources, with only 9% having loans from financial institutions.
What is PM SVANidhi?
- The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) stands as a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, launched on June 1, 2020.
- Its core aim is to extend accessible credit to street vendors, enabling them to revive their businesses and achieve self-reliance.
- The scheme is specifically tailored to empower street vendors, including hawkers, rehri walas, thelewala, and those operating in urban and peri-urban areas.
- PM SVANidhi facilitates eligible street vendors to obtain working capital loans devoid of collateral requirements.
- These loans, with a maximum cap of Rs. 10,000 and a one-year tenure, are intended to support vendors in procuring essential items, securing raw materials, and meeting their operational expenses.
- Furthermore, the scheme offers a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, promoting timely repayments and fostering financial discipline.
How Does PM SVANidhi Work?
- The PM SVANidhi scheme operates through a streamlined and accessible application process designed to maximize participation and outreach among street vendors.
- Vendors can apply for the scheme via a dedicated online portal or through Common Service Centers (CSCs) established nationwide.
- Once the application is submitted, it undergoes a brief verification process conducted by relevant authorities.
- Upon successful verification, the loan amount is directly transferred to the vendor's bank account.
- Vendors can then utilize the funds to revive their businesses, purchase inventory, and cover operational expenses.
Key Features and Benefits of PM SVANidhi:
- Affordable Credit: PM SVANidhi offers accessible working capital loans of up to Rs. 10,000 to street vendors, facilitating credit access without the need for collateral.
- Interest Subsidy: The scheme provides a 7% interest subsidy to vendors who repay their loans promptly, incentivizing timely repayments and easing financial burdens.
- Digital Empowerment: PM SVANidhi promotes digital transactions and payments among street vendors, fostering adaptation to evolving business practices and enhancing financial literacy.
- Enhanced Livelihood: By availing of PM SVANidhi benefits, street vendors can improve their livelihoods, expand their businesses, and generate sustainable income for themselves and their families.
- Access to Social Security Schemes: Street vendors enrolled in PM SVANidhi are eligible for various social security schemes, including Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) and Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), providing financial coverage and protection during unforeseen events.
Conclusion
The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) scheme stands as a beacon of hope for street vendors throughout India. By offering accessible credit, digital empowerment, and access to social security schemes, PM SVANidhi is propelling the advancement and prosperity of street vendors, empowering them to establish sustainable livelihoods. This groundbreaking initiative, with its manifold advantages and inspiring success stories, underscores the Government of India's dedication to fostering an inclusive and self-sufficient economy.
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of RBI (The Hindu)

- 10 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has prudently opted to persist with its objective of ‘ensuring that inflation progressively aligns to the target’ by keeping benchmark interest rates unchanged, and sticking with its stance of ‘withdrawal of accommodation’.
About the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC):
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), chaired by its Governor.
- The RBI shall organise at least four meetings of the Monetary Policy Committee in a year.
- Established under Section 45ZB of the RBI Act, 1934, the government forms this six-member committee.
Composition of MPC:
- Comprising six members, three are from the RBI, while the remaining members are appointed by the Government of India.
- Members include the RBI Governor (Chairperson), the RBI Deputy Governor responsible for monetary policy, one official nominated by the RBI Board, and three members proposed by the Government of India (chaired by the Cabinet Secretary).
- MPC members serve a single four-year term and are not eligible for reappointment.
Functions:
- The primary responsibility of the MPC is to determine the benchmark policy interest rate (repo rate) to manage inflation within the prescribed target level.
- The current mandate of the committee is to maintain annual consumer price index (CPI) inflation at 4% within a band of +/- 2% until March 31, 2026.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY) (PIB)

- 09 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY), a sub-scheme under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana.
About Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana:
- Implemented as a Central Sector Sub-scheme within the broader framework of the PMMSY, this initiative aims to bolster the fisheries sector.
- Funding: With an estimated outlay of Rs. 6,000 crore, the scheme comprises 50% public finance, including contributions from the World Bank and the AFD, and the remaining 50% anticipated investment from beneficiaries and the private sector.
- Duration: Operational for four years from FY 2023-24 to FY 2026-27, spanning all States and Union Territories.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Fishers, Fish (Aquaculture) Farmers, Fish workers, Fish Vendors or such other persons directly engaged in the fisheries value chain.
- Micro and Small enterprises in the form of Proprietary Firms, Partnership Firms and Companies registered in India, Societies, Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), Cooperatives, Federations, Village Level Organizations like Self Help Groups (SHGs), Fish Farmers Producer Organizations (FFPOs) and Startups engaged in fisheries and aquaculture value chains.
- FFPOs also include Farmer's Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Any other beneficiaries that may be included by the Department of Fisheries, Gol as targeted beneficiaries.
Aims and objectives of PM-MKSSY:
- Gradual Formalization of the unorganized fisheries sector through self-registration of fishers, fish farmers and supportive workers under a National Fisheries Sector Digital Platform including the creation of work-based digital identities of fish workers for improved service delivery.
- Facilitating access to institutional financing fisheries sector micro and small enterprises.
- Providing a one-time incentive to beneficiaries for purchasing aquaculture insurance.
- incentivising fisheries and aquaculture microenterprises through performance grants for improving fisheries sector value-chain efficiencies including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
- Incentivising micro and small enterprises through performance grants for the adoption and expansion of fish and fishery product safety and quality assurance systems including the creation and maintenance of jobs.
Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative (India Today)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) recently introduced a scheme named 'Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad' (SSPCA).
About the Support to Students for Participating in Competitions Abroad (SSPCA) Initiative:
- The SSPCA Initiative, spearheaded by the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), aims to enhance the global competitiveness of Indian students in technical education.
- Crafted to provide financial backing to students aspiring to excel in international scientific events, the initiative offers a comprehensive support system.
Financial Assistance and Mentorship:
- Under the SSPCA scheme, individual students or student teams can avail themselves of travel grants to engage in international competitions.
- This assistance encompasses financial aid, mentorship, logistical support, and networking opportunities, empowering students to effectively represent India on the global stage.
- Financial aid extended by the AICTE scheme amounts to up to Rs 2 lakh per student, covering various expenses such as international and domestic travel, registration fees, visa applications, accommodation, airport taxes, travel insurance, and equipment costs associated with the competition.
Eligibility:
- Eligibility for the SSPCA initiative extends to students enrolled in diploma, B.E./B. Tech, integrated M. Tech, and M./M. Tech programs in AICTE-approved institutions.
- Each team of students is entitled to financial support under the scheme once during the course of their study.
About the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE):
- Established as the statutory body and national-level council for technical education in India, the AICTE has played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of technical education in the country.
- Founded in 1945 as an advisory body, it gained statutory status through an Act of Parliament in 1987.
Functions:
- The AICTE is responsible for granting approval for the establishment of new technical institutions, the introduction of new courses, and variations in intake capacity.
- It sets and upholds norms and standards for technical institutions to ensure quality development.
- Additionally, the AICTE promotes technical education through various schemes aimed at fostering innovation, faculty development, research and development, and inclusivity for women, the handicapped, and marginalized sections of society.
- Technical institutions under the AICTE's purview encompass a wide array of programs, including post-graduate, undergraduate, and diploma courses across multiple disciplines.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, the AICTE continues to be at the forefront of advancing technical education and innovation in India.
Lok Sabha passes Finance Bill (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Lower House of Parliament recently passed the Finance Bill moved by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
Context:
- The Lok Sabha passed the Finance Bill, 2024 by voice vote recently.
- Also, the House passed the Appropriation Bill, granting authorization for government expenditures for four months in the upcoming fiscal year.
- The Appropriation Bill is a significant legislative measure that empowers the government to utilize public funds allocated in the annual budget.
- It serves to uphold accountability and transparency by necessitating parliamentary approval for expenditures and prevents unauthorized withdrawals from the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Furthermore, the lower house sanctioned the Rs 1.8 lakh crore budget for the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
What is a Finance Bill?
- The Finance Bill, classified as a Money Bill under Article 110 of the Constitution, is an annual presentation in the Lok Sabha following the Union Budget announcement.
- It encapsulates the government's fiscal proposals concerning taxation, expenditure, and other financial affairs.
- Through this bill, the government submits its proposals for imposing new taxes, altering the existing tax framework, or extending the current tax structure beyond the approved period to Parliament.
- Accompanied by a Memorandum elucidating its provisions, the Finance Bill is exclusively introduced in the Lok Sabha, though amendments can be recommended by the Rajya Sabha.
- Approval from both houses of Parliament is requisite for the bill to become law, with a mandate for passage within 75 days of its introduction.
- While all Money Bills fall under the category of Financial Bills, not all Financial Bills qualify as Money Bills.
- For instance, a Finance Bill solely focusing on tax proposals is classified as a Money Bill.
- Conversely, a Bill addressing taxation or expenditure alongside other subjects is categorized as a Financial Bill.
- Thus, if a Bill entails government expenditure along with other matters, it is designated as a financial bill.
Highlights of the 2024 Finance Bill:
- Stability in Income Tax: With the impending general elections in April-May 2024, the bill prioritizes continuity by retaining the current tax framework for the fiscal year 2024-2025.
- Targeted Relief Measures: Incorporates slight tax concessions tailored to particular sectors or taxpayer groups.
- Promotion of Economic Expansion: Encompasses provisions aimed at fostering infrastructure enhancement, investment stimulation, and streamlining business operations.
- Fiscal Discipline: Pursues fiscal consolidation objectives through proposed strategies to manage expenditures or enhance revenue generation.
Extending the Retirement Age of Supreme Court and High Court Judges (Indian Express)

- 08 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has told a parliamentary panel that extending the retirement age of Supreme Court and High Court judges based on their performance may not be practical.
Key Insights from the Report on Judicial Processes and Reform:
- On August 07, 2023, the Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, and Law and Justice, chaired by Mr. Sushil Kumar Modi, presented its findings.
- Among its significant findings and recommendations, the Committee emphasized the necessity of raising the retirement age for judges.
- They highlighted the importance of aligning this age with advancements in medical sciences and increased life expectancy.
- At present, Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) judges retire at 65 and 62 years, respectively.
- The Committee proposes amending relevant Articles (124 and 217) of the Constitution to extend these retirement ages.
- The retirement age of the High Court Judges was increased from 60 to 62 years, after the 15th constitutional Amendment according to section 4 of the Constitutional Act 1963.
- Furthermore, the Committee suggests implementing a system of appraisal by the SC Collegium to assess judges' performance and health conditions, as well as the quality and quantity of judgments delivered, before extending their tenure.
Debate Regarding the Retirement Age for Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) Judges:
- Retiring SC judges have frequently reflected on their time in office, often feeling that their tenure didn't allow them sufficient opportunity to make meaningful contributions to the judiciary.
- In 2022, former Chief Justice of India (CJI) N.V. Ramana engaged in a dialogue with Justice Stephen Breyer of the US Supreme Court, who chose to retire at age 83 after serving for 27 years.
- Expressing his views, CJI Ramana, who was scheduled to retire after 8.5 years on the SC bench, remarked that 65 seemed 'too early an age for retirement.'
- Despite this, CJI Ramana's tenure surpassed that of most other SC judges.
- Among the current 32 Judges of the SC, only CJI Chandrachud, and Justices J.B. Pardiwala, K.V. Viswanathan, and Dipankar Datta are expected to exceed the 8-year mark.
- These judges represent a minority who surpass the average tenure of sitting SC judges, which stands at 5.4 years.
Why is the Government Resistant to Elevating the Retirement Age for SC and HC Judges?
- The government asserts that raising the retirement age for Supreme Court (SC) and High Court (HC) judges might lead to potential issues of favouritism.
- They argue that such a move would grant excessive authority to the SC Collegium, potentially diminishing parliamentary oversight in evaluating judges for tenure extensions.
- Additionally, the government expresses concerns that this change could subject judges to external pressures, compromising their ability to maintain impartiality.
- Moreover, they highlight the strain it would place on the already limited human resources within the Judiciary and the Executive involved in the appointment process.
Additional Insights from the Report on Judicial Processes and Reform:
- Establishment of Regional SC Benches: The Committee highlighted the challenge faced by litigants from distant regions due to the centralized nature of the Supreme Court in Delhi.
- They proposed leveraging Article 130 to create regional benches in four or five locations.
- These regional benches would handle appellate matters, while constitutional issues would remain under Delhi's jurisdiction.
- Enhancing Social Diversity in Judicial Appointments: Recognizing a diversity deficit in the higher judiciary, the Committee pointed out the low representation of marginalized communities.
- They noted that since 2018, only a small percentage of High Court judges belonged to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- To address this, the Committee recommended that the Supreme Court and High Court Collegiums prioritize the nomination of women and candidates from marginalized communities, including minorities.
- Implementation of Mandatory Asset Declaration: While constitutional functionaries and government servants are obligated to declare their assets annually, judges are exempt from this requirement.
- The Committee urged the central government to enact legislation mandating higher judiciary judges to disclose their assets and liabilities each year to the appropriate authority.
- Revision of Vacation Practices in SC and HCs: The Committee observed that simultaneous vacations for the entire court contribute to case backlog and inconvenience for litigants.
- They proposed a staggered vacation system, wherein judges take leave at different times throughout the year, to mitigate this issue.
- Publication of Annual Reports by HCs: Presently, only a few High Courts publish annual reports, unlike the Supreme Court, which regularly issues its report.
- The Committee recommended that the Department of Justice collaborate with the Supreme Court to ensure that all High Courts prepare and publish their annual reports, promoting transparency and accountability in judicial operations.
Hydrothermal System Beneath the Waters of Lake Rotorua in New Zealand's North Island (India Today)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
In a big revelation, scientists have unveiled a hidden hydrothermal system beneath the waters of Lake Rotorua, a site steeped in Maori legend and situated atop a dormant volcanic crater on New Zealand's North Island.
What are Hydrothermal Systems?
- Hydrothermal systems manifest in regions with intense heat, occurring both on continents near convergent plate boundaries and on the ocean floor in proximity to mid-ocean ridges.
- Three essential components—fluids, heat, and permeable rock structures—are crucial for their formation.
- Formation Dynamics:
- These systems are frequently situated near mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates diverge, leading to the creation of new seafloor.
- Operational Mechanism:
- Hydrothermal systems initiate as seawater infiltrates fractures in the oceanic crust, gaining heat from the Earth's interior as it descends.
- Interacting with the oceanic crust, the seawater, reaching temperatures of 350-400 degrees Celsius, undergoes chemical modifications, extracting elements from the rocks.
- Despite the extreme pressure at ocean depths preventing boiling, this process generates hydrothermal fluid—a mixture of gasses and dissolved elements, including metals.
- Return to the Seafloor:
- The superheated fluid is ejected back to the seafloor and rapidly cools upon contact with near-freezing ocean bottom waters.
- Chimney-Like Deposits:
- Chemicals dissolved in the fluid precipitate at the vent, creating chimney-like deposits.
- These formations support unique deep-sea chemosynthetic communities—organisms relying on chemicals, not photosynthesis, to sustain their metabolism.
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)

- 05 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
The Uttarakhand Cabinet on Sunday approved the final draft of the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) without any changes, a day before the state Assembly convenes for a special session to take up the Bill.
What is Uniform Civil Code (UCC)?
- A Uniform Civil Code signifies a unified legal framework for the entire country, applicable across all religious communities concerning personal matters like marriage, divorce, inheritance, and adoption.
- The objective is to replace the current fragmented personal laws that govern interpersonal relationships within different religious communities.
Constitutional Framework:
- Article 44 of the Constitution mandates the State to strive for a Uniform Civil Code applicable to all citizens.
- Positioned in Part-IV as a Directive Principle, Article 44, while not justiciable, serves as a fundamental governance guideline.
- These principles, outlined in Article 37, provide overarching ideas for the State to consider in policy formulation and law enactment.
Current Landscape of Personal Laws:
- In the Concurrent list of the Constitution, matters such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance fall under both Parliament and state legislature jurisdictions.
- Hindu personal laws have been codified into four parts since 1956, while Muslim laws, not codified per se, draw from religious texts.
- Christians, Zoroastrians, and Jews are governed by their own personal laws. Goa stands as an exception, following the Portuguese Civil Code.
Need for Uniform Civil Code:
- A UCC aims to establish equal status for all citizens, addressing the inconsistency and lack of uniformity in personal laws across different religions.
- This inconsistency, conflicting with Article 14's Equality before the Law guarantee, often results in gender disparities.
Challenges and Criticisms:
- While advocating equality, the UCC concept raises concerns about potential clashes with the Right to Freedom of Religion (Article 25).
- Critics argue that separate personal laws uphold the right to practice one's religion, particularly crucial for minorities.
- Striking a balance, the Law Commission's 2018 report suggests preserving diversity in personal laws while ensuring alignment with fundamental rights.
The Way Forward:
- Encouraging a progressive mindset through education, awareness, and sensitization is vital for understanding the spirit of the UCC.
- Simultaneously, discriminatory personal laws should be amended or abolished.
- The Law Commission recommends codifying different personal laws to derive universal principles prioritizing equity, rather than imposing a blanket Uniform Civil Code
: Law Commission of India (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 22nd Law Commission of India led by Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi has recommended that the offense of criminal defamation should be retained in the new criminal laws.
About the Law Commission of India:
- The Law Commission of India is a non-statutory body, constituted by the Government of India from time to time.
- The commission's function is to research and advise the government on legal reform, and is composed of legal experts, and headed by a retired judge.
- The commission is established for a fixed tenure and works as an advisory body to the Ministry of Law and Justice.
- The first Law Commission was established during colonial rule in India by the East India Company under the Charter Act of 1833 and was presided over by Lord Macaulay.
- After that, three more commissions were established in British India.
- The first Law Commission of independent India was established in 1955 for a three-year term.
- Since then, twenty-one more commissions have been established.
- The 22nd Law Commission has been notified with effect from 21st February 2020 for a term of 3 years.
- Cabinet approves the extension of the term of the 22nd Law Commission of India up to 31st August 2024.
- Justice Rituraj Awasthi (Former Chief Justice of the Karnataka HC) was appointed as the chairperson of the current 22nd Law Commission.
- The last chairman of the 21st Law Commission was retired Supreme Court judge Justice B.S. Chauhan.
The Responsibilities of the Law Commission:
- Identification of laws which are no longer relevant and recommending the repeal of obsolete and unnecessary enactments;
- Suggesting enactment of new legislations as may be necessary to implement the Directive Principles and to attain the objectives set out in the Preamble of the Constitution;
- Considering and conveying to the Government its views on any subject relating to law and judicial administration that may be specifically referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Considering the requests for providing research to any foreign countries as may be referred to it by the Government through the Ministry of Law & Justice (Department of Legal Affairs);
- Preparing and submitting to the Central Government, from time to time, reports on all issues, matters, studies and research undertaken by it and recommending such reports for effective measures to be taken by the Union or any State; and
- Performing such other functions as may be assigned to it by the Central Government from time to time.
Govt To Sell Bharat Rice At Rs 29/Kg in Retail Market (Indian Express)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government will launch retail sales of Bharat Rice at ?29 per kg from next week to provide relief to consumers. It has also directed traders to disclose rice stock to control prices.
Context:
- The recent announcement by the Union government regarding the retail sale of rice at Rs 29 per kg through three cooperatives has garnered attention in the news.
- This initiative, known as 'Bharat Rice,' seeks to address the upward trend in rice prices.
- Over the past year, retail prices have surged by 14.5%, while wholesale prices have seen a 15.5% increase.
- This move aims to mitigate the impact of rising rice prices on consumers and ensure the affordability and accessibility of this staple food item.
Recent Developments:
- In response to escalating domestic rice prices and to ensure food security within the country, the Union government implemented measures in 2023.
- These included a ban on the export of white (non-basmati) rice and the imposition of a 20% export duty on par-boiled rice.
- The decision to restrict rice exports was driven by the need to stabilize domestic prices and guarantee an ample food supply for the nation.
- Experts predict that these restrictions are likely to remain in place until the upcoming general election scheduled for April-May 2024.
- Challenges in rice production during the 2023-24 kharif season, exacerbated by dry weather conditions attributed to El Nino, have further complicated the supply situation.
- Despite these trade limitations, local rice prices have remained firm, prompting government warnings to retailers.
Government Intervention:
- Union Food Secretary Sanjeev Chopra highlighted a 14.51% increase in retail rice prices over the past year.
- In response to rising rice prices, the government has mandated traders, wholesalers, retailers, and processors to report their rice and paddy stocks every Friday to manage food inflation and curb speculative activities.
- To counter inflationary pressures, the government has initiated the retail sale of 'Bharat Rice' to the general populace.
- Initially, 5 lakh tonnes of rice will be allocated for retail sale under this brand through agencies like NAFED, NCCF, and Kendriya Bhandar, priced at ?29 per kilogram in 5 kg and 10 kg bags.
- Furthermore, the Food Corporation of India (FCI) has ample stocks of good-quality rice available for sale to traders and wholesalers under the open market sales scheme at a reserve price of ?29 per kilogram.
Status of India’s Rice Exports:
- India holds the position of the world's largest rice exporter, accounting for 45% of the global rice market share.
- During April-May 2023, overall rice exports witnessed a notable increase of 21.1% compared to the previous fiscal year.
- Basmati rice exports in May 2023 alone surged by 10.86% compared to May 2022, reflecting a sustained upward trend.
- The export of non-Basmati rice has been steadily rising over the past three years, with Basmati rice exports in 2022-2023 surpassing the previous year's figures.
- Recent data provided by the government indicates a 15% increase in total rice exports (excluding broken rice) by August 17 compared to the corresponding period in the previous year.
- Regional Dynamics: Thailand anticipates a nearly 25% decrease in rice production for the 2023-2024 season, while Myanmar has halted raw rice exports.
- Similarly, rice availability is expected to be limited in Iraq and Iran.
- India annually exports more than 4 million tons of basmati - a premium long-grain variety famed for its aroma - to Iran, Iraq, Yemen, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and the United States, among others.
Three New Major Railway Corridors Announced Under PM GatiShakti in the Interim Budget 2024-25 (PIB)

- 03 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Interim Budget for 2024-25 announcement for implementation of three Economic Railway Corridors identified under the PM GatiShakti for enabling multi-modal connectivity.
Context:
- The Interim Budget for 2024-25 has laid the groundwork for implementing three major Economic Railway Corridors under the PM GatiShakti initiative.
- This will enable multi-modal connectivity, including:
- Energy, mineral, and cement corridors
- Port connectivity corridors and
- High-traffic density corridors
Significance of the Three Corridors:
- Logistics Efficiency Boost: These Corridors serve as catalysts for enhancing logistics efficiency, thereby cutting down on the costs associated with rail transportation.
- By streamlining rail movements, they pave the way for smoother and more cost-effective logistics operations.
- Alleviating Rail Congestion: One of their primary roles is to alleviate congestion on heavily trafficked rail routes.
- By diverting some of the traffic to these designated Corridors, the strain on high-density rail networks is relieved, ensuring smoother and more reliable transportation across the board.
- Promoting Modal Shift: The Corridors play a pivotal role in encouraging a modal shift from road to rail and coastal shipping.
- By providing efficient rail connections and integrating coastal shipping options, they offer viable alternatives to traditional road transport, thereby reducing congestion on highways and minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Sustainability: A key benefit of these Corridors is the reduction of the carbon footprint associated with logistics operations.
- By promoting more environmentally friendly modes of transportation such as rail and coastal shipping, they contribute to mitigating the environmental impact of freight movement, fostering sustainability in logistics practices.
About PM GatiShakti National Master Plan:
- The government of India initiated the Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti National Master Plan to transform the nation's infrastructure.
- PM Modi launched the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP) on 13th October 2021, on the 75th Independence Day to provide multimodal connectivity infrastructure to various economic zones.
- The scheme is expected to smooth out the execution of projects across the nation and foster coordination between different ministries engaged with these projects.
Advantages of PM Gati Shakti:
- It lays out a centralised portal to unite the infrastructural initiatives of 16 central ministries and departments.
- Facilitates these ministries, gives a centralised transportation and logistics grid for smoother data flow and sped up project clearance.
- Large-scale infrastructure projects like UDAAN, expansion of the railway network, Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, and Bharat Net will be executed by the Gati Shakti master plan.
- The Gati Shakti master plan aims to create employment potential for a large number of individuals.
- The plan's three primary targets are smooth multimodal connectivity, enhanced prioritisation and optimal usage of resources to create capacities on time, and resolution of issues like standardisation, disjointed planning and clearances.
- The Gati Shakti mission aims to create world-class infrastructure in the country and foster logistical synergy across various modes of movement.
- The general objective of the drive is to increase competitiveness and economic development in India.
Expansion of Nano DAP (Indian Express)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, presenting the interim budget on (February 1), announced the expansion of the application of Nano DAP on various crops in all agro-climatic zones.
What is DAP?
- Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a fertilizer containing phosphorus and nitrogen, crucial nutrients for plant growth.
- Its chemical formula is (NH?)?HPO?. DAP is widely utilized in agriculture to offer plants a quick and easily accessible nutrient source.
- It ranks as the second most utilized fertilizer in India, following urea. Notably, DAP is rich in phosphorus (P), which plays a vital role in promoting root establishment and development.
- Application of DAP is typically done just before or at the time of sowing to ensure optimal plant growth and development.
What is Nano DAP?
- Nano DAP is an innovative liquid fertilizer formulation comprising nanoparticles of Diammonium Phosphate (DAP).
- Serving as a rich source of nitrogen and phosphorus, the two primary nutrients crucial for crop growth, Nano DAP offers unique advantages.
- Its small particle size, measuring less than 100 nm, coupled with a high surface area, facilitates easy absorption by plant leaves.
- This novel nano-formulation contributes to enhanced crop growth and yield, decreased environmental impact, and improved profitability for farmers.
Why Nano DAP?
- In addition to being more efficient than conventional DAP, Nano DAP has a few other benefits.
- First, it is more pocket-friendly than its conventional counterpart.
- A 500 ml bottle of Nano DAP, equivalent to a 50-kg bag of conventional DAP, is priced at only Rs 600 (compared to Rs 1,350 for the bag).
- Since the government provides significant subsidies on DAP, the adoption of a more inexpensive fertiliser will likely be a significant relief to the government’s subsidy burden.
- Second, for farmers, Nano DAP is also significantly more convenient.
- Simply put, 500 ml bottles are easier to transport, store, and use than 50kg bags.
- The fertiliser is sprayed on crops, with 250-500 ml of DAP, dissolved in water, required per spray, per acre.
- Most importantly, however, India currently imports significant quantities of fertiliser to meet domestic demand.
- The adoption of domestically-produced Nano DAP — produced in Kalol, Gujarat — is set to significantly reduce this import burden.
- This revolutionary step will not only take Indian agriculture forward in foodgrain production but it will also make India self-reliant in fertiliser production.
- The adoption of Nano DAP will help in achieving self-sufficiency in fertilisers and greatly benefit our farmers.
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (PIB)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the continuation of the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) to be implemented under the Infrastructure Development Fund (IDF) with an outlay of Rs.29,610.25 crore for another three years up to 2025-26.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund:
- This initiative operates as a Central Sector Scheme aimed at incentivizing investments from various entities, including individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSMEs, Farmer’s Producers Organizations (FPOs), and Section 8 companies.
- These investments are directed towards establishing infrastructure for:
- Dairy processing and value addition
- Meat processing and value addition
- Animal feed plants
Objectives:
- Facilitating the expansion of milk and meat processing capacity and diversification of products, thereby granting unorganized rural milk and meat producers greater access to organized markets.
- Enhancing price realization for producers and ensuring the availability of quality milk and meat products for domestic consumers.
- Promoting exports and elevating the sector's contribution to export revenue.
- Providing quality concentrated animal feed to cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry, ensuring balanced rations at affordable prices.
- The Government of India offers a 3% interest subvention for a period of 8 years, including a two-year moratorium, for loans covering up to 90% of the investment.
- These loans are accessible from scheduled banks, the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC), NABARD, and NDDB.
- Notably, government entities and cooperatives are excluded from availing benefits under this scheme.
What is Animal Husbandry?
- Animal husbandry encompasses the controlled cultivation, management, and production of domestic animals, with a focus on enhancing desirable qualities through breeding.
- It serves as a vital branch of agriculture dedicated to animals raised for various purposes such as meat, fibre, milk, and other products.
- This involves day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the overall management of livestock.
- In India, animal husbandry plays a crucial role in the livelihoods of many farmers, offering significant self-employment opportunities, particularly for landless labourers, small and marginal farmers, and women.
- The sector contributes to providing affordable and nutritious food to millions of Indians through the production of meat, eggs, milk, and other essential items.
- Additionally, it serves as a valuable source of raw materials such as hides, skins, bones, blood, and fat.
- Animals are often regarded as the best insurance against natural calamities like drought, famine, and other adversities, providing a degree of stability to farmers in unpredictable conditions.
Digital Detox for Responsible Gaming (TOI)

- 02 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Karnataka government recently said it would launch a 'Digital Detox' initiative in collaboration with the All India Game Developers Forum (AIGDF), with special emphasis on gaming and social media.
What is Digital Detox?
- A digital detox entails voluntarily refraining from using digital devices like smartphones, computers, and social media platforms for a defined period.
- This period can range from a few hours to as long as a week or even a month.
- Research indicates that approximately 25% of smartphone owners aged 18 to 44 cannot recall the last time they were separated from their phones.
Benefits:
- Overcoming Technology Addiction: Studies reveal that around 61% of individuals acknowledge their addiction to the internet and digital screens.
- A digital detox aids in combating this addiction.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Disconnecting from technology can alleviate stress and anxiety, thereby fostering improved mental health and overall well-being.
- Increased Productivity and Creativity: Taking a break from continuous digital engagement bolsters focus and concentration, leading to heightened productivity and creativity.
- Improved Sleep: Excessive screen time has been linked to poor sleep quality. A digital detox helps in promoting better sleep by reducing exposure to blue light and stimulating content.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Reducing online time allows for more face-to-face interactions, nurturing better communication skills and social connections.
Challenges:
- Feelings of Disconnection: Detox participants may feel disconnected from friends and family members.
- Fear of Missing Out: Participants may experience FOMO (fear of missing out) or anxiety about missing important information.
- Boredom or Restlessness: Detoxes may lead to feelings of boredom or restlessness.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Some individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety or boredom.
Way forward:
- Start Small: Initiate the detox with shorter periods and gradually extend the duration.
- Inform Others: Notify friends and family about the detox to avoid misinterpretations.
- Engage in Healthy Activities: Utilize detox time for activities like reading, spending time outdoors, or exercising.
- Minimize Notifications: Turn off device notifications and store them out of sight.
- Reward Progress: Offer yourself incentives for achieving detox goals.
Conclusion
Digital dependence can contribute to mental health issues, shorter attention spans, and strained interpersonal relationships. While technology offers convenience and connectivity, excessive screen time exacts a toll. A digital detox presents an opportunity to enhance mental and physical well-being, as well as nurture healthier relationships. With proper planning and commitment, a successful and fulfilling detox experience is achievable.
5 Wetlands Added to The Global List of Wetlands of International Importance under Ramsar Convention (TOI)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of World Wetlands Day, five more wetlands in India got the tag of international importance under the Ramsar Convention, making it the fourth largest country in terms of the number of sites on the list.
About the New Ramsar sites:
- The five newly added Indian sites in the list are Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu, and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve and Aghanashini Estuary in Karnataka.
- In India, Tamil Nadu continues to have the maximum number of Ramsar sites (16) followed by Uttar Pradesh (10).
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu): Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary is one of the largest inland wetlands of Tamil Nadu and is a significant source of groundwater recharge for the area.
- Water from the wetland is utilized by the villagers for cultivating crops such as paddy, sugar cane, cotton, corn, and split red gram.
- Karaivetti has one of the largest congregations of waterbirds in the State of Tamil Nadu.
- The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu): The Longwood Shola Reserve Forest derives its name from the Tamil word, "Solai", which means ‘tropical rainforest’.
- The ‘Sholas’ are found in the upper reaches of the Nilgiris, Anamalais, Palni hills, Kalakadu, Mundanthurai and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
- These forested wetlands serve as habitats for the globally endangered Black-chinned Nilgiri Laughing thrush (Strophocincla cachinnans), Nilgiri Blue Robin (Myiomela major), and vulnerable Nilgiri Wood-pigeon (Columba elphinstonii).
- As many as 14 out of 26 endemic bird species of the Western Ghats are found in these wetlands.
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve (Karnataka): Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve is a human made Village Irrigation Tank built centuries back and is spread over an area of 98.76ha.
- It is an ecologically important wetland, rich in biodiversity, comprising over 210 species of plants, mammal species, reptiles, birds etc.
- It supports more than 1% of the biogeographic population of Painted Stork and Black-headed Ibis.
- Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka): Aghanashini Estuary is formed at the confluence of the Aghanashini River with the Arabian Sea.
- The brackish water of the Estuary provides diverse ecosystem services including flood and erosion risk mitigation, biodiversity conservation and livelihood support.
- The wetland also provides livelihoods to families by supporting fishing, agriculture, collection of edible bivalves and crabs, shrimp aquaculture, traditional fish farming in the estuarine rice fields (locally known as Gazni rice fields), bivalve shell collection and salt production.
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve (??Karnataka): Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, is a human-made wetland with an area of nearly 50 hectares which was constructed to store rainwater for irrigation purposes.
- The wetland harbors two vulnerable species, namely the Common pochard and River tern and four near-threatened species, namely the Oriental Darter Black-headed Ibis Woolly-necked Stork and Painted Stork.
- It is also one of the largest wintering grounds for the Bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in Southern India.
- The wetland is a designated Important Bird Area (IBA) and is also listed as a priority area for conservation in India.
What is the Ramsar Convention?
- The Ramsar Convention was signed on 2nd February 1971 to preserve the ecological character of their wetlands of international importance.
- It is named after Ramsar, the Iranian city where the treaty was signed in 1971, and places chosen for conservation under it are given the tag ‘Ramsar site’.
- The World Wetlands Day, celebrated on 2 February to raise global awareness about the importance of wetlands for human prosperity and a healthy planet.
Framework for Voluntary Carbon Market in Agriculture Sector (Down To Earth)

- 30 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The central government recently launched a framework to promote voluntary carbon markets in the agriculture sector.
What are Carbon Markets?
- Carbon markets are trading systems in which carbon credits are sold and bought.
- Companies or individuals can use carbon markets to compensate for their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing carbon credits from entities that remove or reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- One tradable carbon credit equals one tonne of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas reduced, sequestered or avoided.
- When a credit is used to reduce, sequester, or avoid emissions, it becomes an offset and is no longer tradable.
Why are Carbon Markets Important?
- Scientists warn that 2°C of warming will be exceeded during the 21st century unless we achieve deep reductions in GHG emissions now.
- Effective action will require concerted and sufficient investment, knowing also that the costs of inaction will be far higher.
- The latest IPCC report finds all countries are falling way short, with financial flows three to six times lower than levels needed by 2030 – and even starker differences in some regions of the world.
- Many countries are turning to carbon markets as a key component in driving and financing the necessary transformation to tackle the climate crisis.
How Many Types of Carbon Markets Are There?
- There are broadly two types of carbon markets: compliance and voluntary.
- Compliance markets are created as a result of any national, regional and/or international policy or regulatory requirement.
- Voluntary carbon markets (VCM)– national and international – refer to the issuance, buying and selling of carbon credits, on a voluntary basis.
- The current supply of voluntary carbon credits comes mostly from private entities that develop carbon projects, or governments that develop programs certified by carbon standards that generate emission reductions and/or removals.
Importance of Establishing a VCM Framework in the Agricultural Sector:
- Emission Concerns: Agriculture in India contributes approximately 15% of the nation's greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the urgent need for mitigation strategies.
- Vulnerability: With around 50% of cultivated land being rainfed and more than 80% of farmers categorized as small or marginal, the sector is highly susceptible to the impacts of climate change.
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (2010): This initiative focuses on promoting adaptation measures such as agroforestry, micro irrigation, and soil health management, which not only reduce emissions but also offer opportunities for carbon sequestration.
- Additional Income Opportunities: Through the implementation of these practices, farmers can potentially generate additional income streams.
World's First 'Black Tiger Safari', to be Established in Odisha (TOI)

- 29 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Odisha is gearing up to provide an unparalleled experience to visitors through its upcoming black tiger safari, offering a rare glimpse into the lives of these majestic creatures in their natural habitat.
What are Black Tigers or Melanistic Tigers?
- Black tigers, also known as melanistic tigers, are a unique phenomenon resulting from a genetic condition called melanism.
- Melanism causes an increased production of melanin, a pigment responsible for hair, eye, and skin colouration, resulting in black or nearly black skin, feathers, or hair in animals.
- In Simlipal Tiger Reserve, many royal Bengal tigers belong to a distinct lineage characterized by higher-than-normal levels of melanin.
- These tigers exhibit black and yellow interspersed stripes on their coats, though they are not entirely black.
- Therefore, they are more accurately described as pseudo-melanistic.
- As per the 2022 All-India Tiger Estimation, 16 tigers were recorded in Similipal Tiger Reserve, out of which 10 were melanistic.
- However, ongoing tiger surveys conducted by the state government suggest that the actual number of royal Bengal tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve may be higher than reported by the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Factors Contributing to (Pseudo) Melanism:
- Research conducted by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) in Bengaluru indicates that a single mutation in the gene Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) is responsible for the enlargement or spreading of black stripes into the yellow background of black tigers.
- Genetic analyses and computer simulations suggest that Similipal's black tigers may have originated from a very small founding population of tigers and are likely inbred.
- Additionally, the isolation of tigers in Similipal Tiger Reserve leads to breeding within the population, further contributing to the prevalence of melanism among these tigers.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal, which derives its name from the ‘Simul’ (Silk Cotton) tree, is a national park and a Tiger Reserve situated in the northern part of Orissa’s Mayurbhanj district.
- It spans an expansive area of 2,750 square kilometres (1,060 square miles), bordering Jharkhand and West Bengal.
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is a key component of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which encompasses three protected areas:
- Similipal Tiger Reserve
- Hadagarh Wildlife Sanctuary, and
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary
- Biodiversity: Similipal is renowned for its rich biodiversity, boasting a diverse array of wildlife including the majestic Bengal tiger, the iconic Asian elephant, the formidable gaur, and the elusive chausingha.
- Recognized as a UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves site since 2009, it stands as Asia's second-largest biosphere reserve, following the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat.
- Notably, Similipal Tiger Reserve holds the distinction of being the sole natural habitat in India for melanistic royal Bengal tigers, adding to its ecological significance.
Interim Budget 2024: Exporters seek higher allocation for MAI scheme (Business Standard)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the interim Budget 2024, exporters have urged the government to allocate funds worth $3.88 billion for the Market Access Initiative (MAI) scheme to promote Indian exports and help them hit the ambitious $2 trillion target by 2030.
What is the Market Access Initiatives (MAI) Scheme?
- The Market Access Initiative (MAI) Scheme is an Export Promotion Scheme envisaged to act as a catalyst to promote India’s exports on a sustained basis.
- The scheme is formulated on a focus product-focus country approach to evolve specific markets and specific products through market studies/surveys.
- Assistance would be provided to Export Promotion Organizations/Trade Promotion Organizations/National Level Institutions/ Research Institutions/Universities/Laboratories, Exporters etc., for enhancement of exports through accessing new markets or through increasing the share in the existing markets.
- Under the Scheme, the level of assistance for each eligible activity has been fixed.
- The following activities will be eligible for financial assistance under the Scheme:
- Marketing Projects Abroad
- Capacity Building
- Support for Statutory Compliances
- Studies
- Project Development
- Developing Foreign Trade Facilitation Web Portal
- To support Cottage and handicraft units
How does the MAI Scheme work?
- The scheme’s primary goal is to facilitate export growth by enabling entities to enter new markets or enhance their presence in existing markets.
- To accomplish this, the scheme provides predetermined levels of assistance for each eligible activity.
- By directing attention to key products and specific markets, the MAI Scheme serves as a catalyst for driving India’s export expansion in a sustainable and strategic manner.
Who is eligible to receive assistance under the MAI Scheme?
- Various entities are eligible to receive financial assistance under the MAI Scheme, including:
- Export promotion organizations
- Trade promotion organizations
- National level institutions
- Research institutions
- Universities
- Laboratories
- Individual exporters
- Start-ups
Who administers the MAI Scheme?
- The MAI Scheme is administered by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, through the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
India overtakes Hong Kong as the world’s fourth-largest stock market by market capitalisation (Live Mint)

- 24 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India’s stock market has overtaken Hong Kong’s to rank as the fourth-biggest equity market globally for the first time.
News Summary:
- As of January 22, 2024, data compiled by Bloomberg indicates that the combined value of shares listed on Indian exchanges has reached USD 4.33 trillion, surpassing Hong Kong's USD 4.29 trillion.
- The top three global stock markets are currently the United States, China, and Japan.
What is Stock Market?
- A stock market is a platform where individual and institutional investors trade various securities, including stocks, bonds, Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), and derivatives.
- Stock markets are categorized into two types:
- Primary Market: Involves the initial offering of new shares, bonds, etc.
- Secondary Market: Encompasses the trading of existing securities like equities and bonds.
- Examples include stock exchanges such as the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Importance of Stock Market:
- For Businesses: Facilitates access to capital, risk diversification, and supports business expansion.
- For Investors: Offers better returns compared to traditional savings instruments, provides tax benefits, and contributes to capital growth.
- For Society: Drives social impact through instruments like Social Impact Bonds, encourages sustainable investment via Green bonds and promotes responsible financial practices.
- For Economy: Mobilizes idle savings, fosters entrepreneurship through venture capital funds, and plays a vital role in economic development.
Challenges in Indian Stock Markets:
- High Volatility: Market fluctuations can be significant, posing challenges for investors.
- Limited Issuer and Investor Base: Constraints on both issuers and investors can adversely impact liquidity.
- Sub-optimal Corporate Debt Market: Dominance of government bonds hampers the growth of the corporate debt market.
- Other Issues: Various factors, such as regulatory complexities and market inefficiencies, can affect the optimal functioning of Indian stock markets.
How is the Stock Market Regulated in India?
- The stock market in India is regulated by various bodies, with the primary regulatory authority being the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- SEBI is a statutory regulatory body established in 1992 to protect the interests of investors and promote the development of the securities market in India.
- It operates under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
- Also, while SEBI is the primary regulatory authority for the Indian stock market, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supports its efforts by ensuring overall financial stability, implementing monetary policies, and regulating aspects related to banking and foreign investments.
- Additionally, these bodies contribute to the nation's economic progress by facilitating capital formation.
First meeting of Social Audit Advisory Body reviews social justice schemes (ET)

- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The first meeting of the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) was held last week at the conference hall, Dr Ambedkar International Centre, New Delhi.
What is the Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB)?
- Social Audit Advisory Body (SAAB) is a first-of-its-kind advisory body in India.
- It is set up under the National Institute of Social Defence (NISD), which functions under the Department of Social Justice & Empowerment (DoSJE), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It will guide the Ministry as it institutionalizes social audits for each of its programs.
- It will support the Social Justice Cell of the Social Audit Unit members in developing their abilities.
What is a Social Audit:?
- A social audit is a procedure that involves looking over and evaluating a plan or program.
- People actively participate in the process, which involves comparing government data with actual ground realities.
- Important tenets of SA include:
- Protection of citizens (Suraksha)
- Participation (Bhagidari), and
- Information access (Jaankari).
Implementation of Social Audit:
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), among other hallmark programs, now include the provision of Social Audit (SA) with the efforts of the Union Government.
- In order to guarantee SA through specialized Social Audit Units at the state level, DoSJE developed the National Resource Cell for Social Audit (NRCSA).
- The first state to put a social audit statute into effect was Meghalaya.
Significance: Promote transparency and accountability,
-
- strengthen institutions at the grassroots level etc.
Challenges: Lack of awareness among stakeholders, apathetic attitude of implementing agency etc.
Steps for SocialAudit:
- Orientation and Sensitization:: Conducted by the implementing agency.
- Presentation: Creating a social audit team.
- Verification: Verifying information with beneficiaries, inmates, stakeholders, and institution staff.
- Validation: Presenting the initial report for validation.
- Presentation and Action: Sharing findings at the district level with all stakeholders present.
Davos meeting 2024: 5 key takeaways (Indian Express)

- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
This year’s edition of the World Economic Forum (WEF) annual meeting was held from January 15 to January 19.
Key Highlights from Davos Meeting 2024:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The focal point of discussion at this year's World Economic Forum (WEF) meeting was Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Conversations delved into its transformative potential for human welfare, addressing concerns such as the necessity for regulation, apprehensions about job losses, risks associated with impersonation and misinformation, and the potential exacerbation of inequalities.
- Despite acknowledging these challenges, participants generally agreed that the positive aspects of AI outweigh the negatives, with no substantial threat to human intelligence.
- War and Uncertainty: The summit underscored the risks emanating from a delicate geopolitical landscape, ongoing conflicts in the Middle East and Europe, threats to global supply chains, and uncertainties surrounding food security.
- Notably, the head of the Palestine Investment Fund estimated a requirement of at least $15 billion solely for the reconstruction of houses in Gaza.
- However, Arab states asserted their reluctance to fund reconstruction without a guarantee of lasting peace.
- Climate: The imperative for businesses to adapt to climate change and nations to collaborate despite differences in combating it emerged as another key theme.
- Discussions emphasized the necessity for developed countries to assist in financing climate action in developing nations to prevent a widening inequality that could result in winners and losers.
- China's Economy: Against the backdrop of a slowing economy, China sought increased investment from the West, which has experienced some cooling.
- With a GDP growth of 5.2% in 2023, still below pre-pandemic levels, China grappled with efforts by the United States to isolate it, particularly evident in the semiconductor trade standoff.
- India-Specific Observations: McKinsey and Company's assessment of Davos 2024 highlighted India's rapid transformation as one of the fastest-growing large economies globally.
- The summit marked the launch of the Global Good Alliance for Gender Equity and Equality, endorsed by the WEF and the Government of India.
- Originating from the G20 Leaders' Declaration, the alliance aims to bring together global best practices, knowledge sharing, and investments in women's health, education, and enterprise.
- Supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the alliance will be hosted by the CII Centre for Women Leadership, with the World Economic Forum as a 'Network Partner' and Invest India as an 'Institutional Partner.'
About the World Economic Forum:
- The World Economic Forum is the International Organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It was established in 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab.
- It is a not-for-profit foundation and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- The Forum strives in all its efforts to demonstrate entrepreneurship in the global public interest while upholding the highest standards of governance.
Reports released by WEF:
-
- Global Gender Gap Index
- Global Risks Report
- Fostering Effective Energy Transition Report
- Global Cyber Security Outlook
- Global Competitiveness Report
- Travel and Tourism Development Index
About Davos Meet:
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) organizes a meeting annually at the end of January in Davos, a mountain resort in Graubünden, in the eastern Alps region of Switzerland.
- The Annual Meeting, also known as the Davos Agenda, has the objective of orienting global leaders on the imperatives of the year ahead.
- This year's theme for the Annual Meeting in Davos is 'From Lab to Life: Science in Action'.
Govt cuts windfall tax on petroleum crude to Rs 1,700 per tonne (The Hindu)

- 16 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has cut the windfall tax on domestically-produced crude oil to ?1,700 per tonne from ?2,300 per tonne with effect from January 16.
What is Windfall Tax?
- A Windfall Tax is imposed by governments on specific industries that experience exceptionally high profits due to economic conditions surpassing the norm.
- The term "windfall" denotes an unforeseen surge in profits, leading to the imposition of the windfall tax on the excess gains.
- Imposition Criteria: Governments impose the Windfall Tax when there is a sudden and substantial increase in an industry's revenue.
- Notably, this increase must be unrelated to the company's intentional actions, such as business strategies or expansions, but instead linked to external events beyond its control.
- A Windfall Tax is typically triggered by external occurrences, such as the unexpected surge in profits observed in the oil and gas industries amid the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Tax Rates: Governments tax these windfall gains at rates higher than the standard tax rates applicable to regular profits.
- Target Industries: Commonly, industries such as oil, gas, and mining become targets for windfall gains tax.
Objectives:
- Redistribution of Gains: To redistribute unexpected profits, especially when high prices benefit producers at the expense of consumers.
- Funding Social Welfare Schemes: Utilizing the windfall tax revenue to support social welfare initiatives.
- Supplementary Revenue Source: Acting as an additional revenue stream for the government.
- Addressing Trade Deficit: Providing a means for the government to mitigate the widening trade deficit in the country.
When Did India Introduce Windfall Tax?
- To address the shortage of energy products on the domestic market, the Indian government added a special additional excise duty on the export of gasoline and diesel, known as the Windfall Tax, on July 1st, 2022.
Why are Countries Levying Windfall Taxes Now?
- Since the past few years, gasoline prices, crude oil, gas, and coal have significantly increased.
- COVID-19 and the conflict between Ukraine and Russia made this increase even more pronounced.
- Because of this, energy companies profited handsomely at the expense of consumers, who now pay much higher prices for their energy use.
- The UN Secretary-General, therefore, encouraged nations to impose windfall taxes on those companies that have greatly benefited from the rise in the price of fossil fuels.
- As a result, many countries, including the UK, Germany, and others, besides India, are considering imposing Windfall Taxes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a windfall tax is a tax that a government may impose or an additional tax that may be imposed on a business when it generates a sizable unanticipated profit, particularly if the company has benefited from favourable economic conditions.
Companies in specific economic sectors, such as the oil and gas industry, that profit from circumstances like commodity shortages that significantly drive up the cost of their goods at the expense of consumers may be subject to windfall taxes.
Science Ministry team visits Hawaii to take stock of international telescope project (The Hindu)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a signal of renewed enthusiasm for a global scientific project, an official delegation from the Department of Science and Technology visited Mauna Kea, an inactive volcano on the island of Hawai’i in the United States, to discuss “challenges” to the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) project.
About Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) Project:
- The name "Thirty Metre" denotes the telescope's substantial 30-meter mirror diameter, composed of 492 glass segments seamlessly integrated.
- It is an international collaboration involving institutions such as CalTech, the Universities of California, Canada, Japan, China, and India, facilitated by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE).
- Significance: Upon completion, it will surpass the world's largest existing visible-light telescope in width by threefold.
- A larger mirror enables greater light collection, enhancing the telescope's capability to observe distant, faint objects.
- It is projected to be over 200 times more sensitive than current telescopes and possess 12 times the resolving power of the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Application: The TMT's primary purpose includes the study of exoplanets, specifically exploring whether their atmospheres contain water vapour or methane, potential indicators of extraterrestrial life.
- Opposition against Construction: The proposed site, Mauna Kea in Hawaii, is contested due to its sacred significance to native Hawaiians, who perceive such projects as desecrating the mountain.
Contribution of India:
- India expects to be a major contributor to the project and will provide:
- Hardware (segment support assemblies, actuators, edge sensors, segment polishing, and segment coating)
- Instrumentation (first light instruments), and
- Software (observatory software and telescope control systems) worth $200 million.
- Of the 492 precisely polished mirrors that the telescope needs, India will contribute 83.
- The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAP) is leading the consortium of Indian institutions that are involved with the TMT project.
Article 30 Not Intended To Ghettoise Minorities, Minority Institution Can Include Others In Administration: Supreme Court In AMU Case Hearing (Indian Express)

- 12 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a recent observation, the Supreme Court, headed by Chief Justice of India D Y Chandrachud, highlighted that the right granted to religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer their educational institutions under Article 30(1) of the constitution was not intended to "ghettoise" them.
What is Article 30 of the Indian Constitution?
- Article 30 of the Indian Constitution states the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions.
- It says: “All minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.”
When was Article 30 adopted?
- Article 30 was adopted on December 8, 1948.
Features of Article 30 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 30 of the Indian constitution consists of provisions that safeguard various rights of the minority community in the country keeping in mind the principle of equality as well.
- Article 30(1) says that all minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- Article 30(1A) deals with the fixation of the amount for the acquisition of property of any educational institution established by minority groups.
- Article 30(2) states that the government should not discriminate against any educational institution on the ground that it is under the management of a minority, whether based on religion or language while giving aid.
The debate around Article 30:
- On December 8, 1948, the Constituent Assembly debated the need for imparting primary education in one's mother tongue.
- One of the members of the Assembly moved an amendment to restrict the scope of this article to linguistic minorities.
- He argued that a secular state should not recognise minorities based on religion.
- Another member of the Assembly proposed to guarantee linguistic minorities the fundamental right to receive primary education in their language and script.
- He was concerned about the status of minority languages, even in regions which had a significant minority population.
- The Constituent Assembly rejected the proposals.
What is Article 29 of the Indian Constitution?
- Both Article 29 and Article 30 guarantee certain rights to minorities.
- Article 29 protects the interests of minorities by making a provision that any citizen/section of citizens having a distinct language, script or culture has the right to conserve the same.
- Article 29 mandates that no discrimination would be done on the grounds of religion, race, caste, language or any of them.
Concept of Minority in the Indian Constitution:
Religious minorities:
- While Article 30 and Article 29 of the Constitution do not specify 'minorities' in India, it is classified into religious minorities and linguistic minorities.
Religious Minorities in India:
- The basic ground for a community to be nominated as a religious minority is the numerical strength of the community.
- For example, in India, Hindus are the majority community.
- As India is a multi-religious country, it becomes important for the government to conserve and protect the religious minorities of the country.
- Section 2, clause (c) of the National Commission of Minorities Act, declares six communities as minority communities. They are:
- Muslims
- Christians
- Buddhists
- Sikhs
- Jains and
- Zoroastrians (Parsis)
Linguistic Minorities:
- A class or group of people whose mother language or mother tongue is different from that of the majority groups is known as the linguistic minority.
- The Constitution of India protects the interests of these linguistic minorities.
World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 Report (The Hindu)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The global unemployment rate is set to increase in 2024 while growing social inequalities remain a concern, according to the International Labour Organisation’s (ILO) World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 report released in Vienna recently.
Key Findings:
- Employment Trends: Joblessness and the jobs gap have both decreased below pre-pandemic levels, but global unemployment is expected to rise in 2024.
- The macroeconomic environment witnessed a significant deterioration in 2023.
- Global Economic Challenges: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and persistent inflation led to frequent and aggressive actions by central banks.
- Monetary authorities in both advanced and emerging economies implemented the fastest interest rate increases since the 1980s, with widespread global repercussions.
- Economic Slowdown in Key Economies: China, Türkiye, and Brazil experienced notable slowdowns, adversely affecting global industrial activity, investment, and trade.
- Despite the economic slowdown, global growth in 2023 surpassed expectations, and labour markets displayed unexpected resilience.
- Unemployment Dynamics: The global unemployment rate in 2023 improved modestly to 5.1% compared to 2022.
- Labour market participation rates largely recovered from pandemic lows, but concerns arise about structural imbalances persisting.
- Wage Trends: Real wages declined in most G20 countries as increases failed to keep pace with inflation.
- Workers living in extreme poverty (earning less than US$2.15 per day per person in PPP terms) increased by about one million globally in 2023.
- Positive real wage growth was observed in China, the Russian Federation, Mexico, India, and Türkiye.
Recommendations As per the Report:
- Inclusive Labor Policies: Policymakers in rapidly ageing countries should focus on supporting the participation of groups with weak labour market attachment, including youth, women, and older workers.
- Investment and Skills Strategies: Investment and skills policies should aim to enhance productivity, and potential growth, and promote a more productive utilization of technological progress.
- Sectoral Improvements: Motivating workers who leave due to low pay and challenging working conditions can be achieved by improving conditions in sectors and occupations with these challenges.
- International Workforce Matching: Facilitating the matching of internationally mobile workers to suitable jobs could alleviate some of the shortages in the labour market.
- Long-Term Engagement: Recognizing that structural challenges in labour market adjustment are unlikely to vanish in the short term, it is crucial for governments and social partners to engage in ongoing efforts to address these challenges.
International Labour Organization (ILO)
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) stands as the United Nations agency dedicated to the world of work.
- Mission: The core mission of the ILO is to promote social and economic justice by establishing and advancing international labour standards.
- Motto: At the heart of the ILO's mission is the pursuit of Decent Work for all, encapsulating the commitment to fostering conditions that are fair and dignified.
- Headquarters: Situated in Geneva, Switzerland, the ILO operates from its global headquarters.
- Parent Organization: Functioning under the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations, the ILO is a vital component of the UN system.
- Additionally, it is a member of the United Nations Development Group (UNDP), collaborating with other UN organizations to achieve Sustainable Development Goals.
- Historical Background: Established in 1919 under the Treaty of Versailles, following the conclusion of World War I, the ILO was conceived with the conviction that enduring and universal peace could only be realized through a foundation of social justice.
- In 1946, it transitioned into a specialized agency within the newly formed United Nations.
- Membership: The ILO boasts a diverse membership, with 187 member states, encompassing 186 out of the 193 UN member states along with the Cook Islands.
- Organizational Structure: Distinguishing itself as the only tripartite U.N. agency, the ILO brings together representatives from governments, employers, and workers of its 187-member states, fostering collaborative efforts in shaping global labour standards and policies.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) (Indian Express)

- 11 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India has flagged concerns relating to sensitive and confidential trade data of its exporters getting compromised while complying with the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
What Is Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
- CBAM is a policy tool introduced by the European Union (EU) to reduce carbon emissions by imposing a carbon tax on imported products, ensuring that they are subject to the same carbon costs as products produced within the EU.
- It is part of the EU's "Fit for 55 in 2030 package" to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
- The aim of CBAM is to prevent carbon-intensive imports from undermining the EU's climate objectives and to encourage the adoption of cleaner production practices around the world.
- To implement CBAM, importers will need to declare the quantity of goods imported and their greenhouse gas emissions on an annual basis.
- They will need to surrender a corresponding number of CBAM certificates to offset these emissions, and the price of these certificates will be based on the weekly average auction price of EU Emission Trading System (ETS) allowances in Euro/tonne of CO2 emitted.
- It encourages non-EU countries to adopt stricter environmental regulations, reduce global carbon emissions, and prevent carbon leakage by discouraging companies from moving to countries with weaker environmental regulations.
- Additionally, the revenue generated from CBAM will be used to support EU climate policies, which can serve as an example for other countries to promote green energy.
Impact of CBAM on India:
- The EU's carbon border adjustment mechanism will have a negative impact on India's exports of metals such as iron, steel, and aluminium products.
- The mechanism will subject these exports to extra scrutiny and impose carbon levies ranging from 19.8% to 52.7%, which could threaten India's major exports to the EU.
- From 1st January 2026, the EU will start collecting the carbon tax on each consignment of steel, aluminium, cement, fertilizer, hydrogen and electricity, which could further harm India's exports to the EU.
- The high carbon intensity of Indian products, due to coal being the dominant energy source, is a concern for the country as it may result in higher carbon tariffs from the EU.
- India's use of coal is much higher than the EU and the global average, with coal-fired power accounting for almost 75% of India's energy consumption.
- This makes direct and indirect emissions from industries like iron, steel and aluminium a significant worry for India.
- The lack of a domestic carbon pricing scheme in India poses a risk to its export competitiveness, particularly for sectors such as refined petroleum products, organic chemicals, pharma medicaments, and textiles, which are among the top 20 goods imported by the EU from India.
- Countries with a carbon pricing system may have a competitive advantage as they may pay less carbon tax or receive exemptions.
- This risk could expand to other sectors in the future.
What can be done?
- India can take a multi-pronged approach to mitigate the impact of the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) on its exports.
- One of the ways is to implement a Decarbonization Principle, which refers to reducing or eliminating greenhouse gas emissions from human activities such as transportation, power generation, manufacturing, and agriculture.
- The government could complement its existing schemes such as the National Steel Policy and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme with a Decarbonization Principle.
- This would encourage industries to focus on carbon efficiency, making their products more competitive in a carbon-conscious world.
- Another way is to negotiate with the EU to recognize its energy taxes as equivalent to a carbon price.
- India could also negotiate with the EU to transfer clean technologies and financing mechanisms to aid in making India's production sector more carbon efficient.
- One way to finance this is to propose that a portion of the EU's CBAM revenue could be set aside to support India's climate commitments.
- Additionally, India could begin preparing for the new system by establishing a Carbon Trading System, as China and Russia do.
- India can encourage sustainable and eco-friendly production by providing incentives, which will enable the country to stay competitive in a more carbon-conscious future while achieving its 2070 Net Zero Targets. This will help India pursue its developmental goals and economic aspirations without any compromise.
How AI can help detect cancer and why India’s biggest cancer treatment hospital is utilising it (Indian Express)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Given the escalating cases of cancer, the shortage of specialists poses a significant challenge in curbing fatalities. To address this gap, Mumbai’s Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), the biggest cancer hospital in India, is turning to artificial intelligence (AI).
Context:
- With the rising cancer cases, a notable challenge is the shortage of specialists, impacting efforts to reduce fatalities.
- To tackle this issue, Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH) in Mumbai, India, the country's largest cancer hospital, is embracing artificial intelligence.
- The hospital is leveraging deep learning to establish a Bio-Imaging Bank for cancer, employing AI to develop a tailored algorithm specific to cancer diagnosis.
What is the Role of AI in Cancer Detection and Treatment?
- Early Detection through Identification of Tissue Changes and Potential Malignancies: AI analyzes radiological and pathological images, learning from extensive datasets to recognize unique features associated with various cancers.
- This technology facilitates early detection by identifying tissue changes and potential malignancies.
- Predictive Models for Tumor Survival and Treatment Guidance: Comprehensive imaging generates longitudinal patient data, aiding in understanding behavior, treatment response, disease recurrence, and overall survival.
- AI and machine learning protocols utilize this data to develop predictive models for tumor survival and guide treatment aggressiveness.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Chemotherapy: The creation of a tumor image bank allows for the development of algorithms for different tumors, assessing treatment responses directly from images and avoiding unnecessary chemotherapy for predicted non-responders.
- Maintaining Diagnostic Quality while Decreasing Radiation Exposure: Tata Memorial Hospital has added data from 60,000 patients to the biobank over the past year.
- Using this data, AI successfully reduces radiation by enhancing images with AI algorithms, ensuring a significant decrease in radiation exposure to children without compromising diagnostic quality.
- Potential to Reduce Cancer Fatalities in the Future:
- AI is poised to play a transformative role in cancer treatment, particularly in mitigating fatalities in rural India.
- Its potential lies in tailoring treatment approaches based on diverse patient profiles, optimizing therapy outcomes.
- AI swiftly detects cancer, eliminating the need for extensive tests and enabling even general practitioners to diagnose complex cancers.
- This technology is set to significantly enhance precision in cancer solutions.
What is Bio-Imaging Bank?
- The overarching objective is to establish a robust repository incorporating radiology and pathology images intricately linked with clinical information, outcome data, treatment specifics, and additional metadata.
- This strategic design aims at facilitating the training, validation, and rigorous testing of AI algorithms.
- Functioning: In conjunction with creating the database, the project involves training and testing multiple AI algorithms using the accumulated data.
- It is tailored to address medically relevant tasks, including screening for lymph node metastases, nucleus segmentation and classification, biomarker prediction, and therapy response prediction.
- Institutions Involved: The multi-institutional project receives funding from the Department of Biotechnology and collaborates with IIT-Bombay, RGCIRC-New Delhi, AIIMS-New Delhi, and PGIMER-Chandigarh.
From red ant chutney to black rice, the 7 Odisha products that have bagged GI tags (Indian Express)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Seven products from Odisha, ranging from the Similipal Kai chutney made with red weaver ants to the embroidered Kapdaganda shawl, have bagged the coveted Geographical Indication (GI) tag in recognition of their exclusivity to the state.
What is Geographical Indication (GI) Tag?
- Geographical Indications of goods refer to the place of origin of a product.
- Such tags are accorded as they convey an assurance of quality and distinctiveness, attributable to the fact of its origin in a specific geographical locality, region or country.
- In India, the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, awards GIs.
- A GI registration is given to an area, not a trader, but once a product gets the registration, traders dealing in the product can apply to sell it with the GI logo.
- Authorised traders are each assigned a unique GI number.
- If any unauthorised trader tries selling the product under that name, they can be prosecuted under The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999.
- A marker of authentic products, the GI tags also help protect the interests of the local growers and artisans by preventing duplicity of the products and sale from unauthorised traders.
- Consumers, through the tags, can know which goods are certified.
The Seven Products and Their Distinctiveness:
- Kapdaganda shawl: Woven and embroidered by the women of the Dongria Kondh tribe, a particularly vulnerable tribal group (PVTG) in the Niyamgiri hills in Odisha’s Rayagada and Kalahandi districts, the shawl reflects the rich tribal heritage of the Dongria Kondhs.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Green symbolises the mountains and hills, and yellow stands for peace and happiness.
- Red stands as the symbol of blood.
- The motifs in the shawls are mostly lines and triangles, believed to be a reflection of the importance of mountains for the community.
- The shawl is worn by both men and women and the Dongrias gift it to their family members as a token of love and affection.
- It is embroidered on an off-white coarse cloth with red, yellow and green coloured threads, with each colour holding significance.
- Lanjia Saura Painting: The painting is also known as Idital. The artworks are famous for their beauty, aesthetics, ritualistic association and iconography.
- The art form belongs to the Lanjia Saura community, a PVTG largely residing in the Rayagada district.
- These paintings are in the form of exterior murals painted on the mud walls of homes.
- White paintings figure over a crimson-maroon background.
- It is believed that the Lanjia Sauras paint their walls with Idital artworks to show gratitude to their deities and forefathers, and also for the well-being of their community.
- Reflecting the love and affection of the primitive tribes for nature, they feature subjects like tribal humans, trees, animals, birds, the Sun and the Moon.
- Koraput Kala Jeera Rice: The black-coloured rice variety, also known as the ‘Prince of Rice’, is famous for its aroma, taste, texture and nutritional value.
- Tribal farmers of the Koraput region have preserved the rice variety for around 1,000 years.
- As the rice grains resemble cumin seeds, it is also called Kala Jeera. Consumption of the rice variety helps in increasing haemoglobin levels and improves metabolism in the body.
- The farmers and producers of Koraput Kala Jeera rice have followed the traditional knowledge and practices in cultivation.
- Similipal Kai chutney: The chutney made with red weaver ants is a traditional delicacy of the tribals in Odisha’s Mayurbhanj district.
- The ants are found in the forests of Mayurbhanj, including in the Similipal forests – Asia’s second-largest biosphere.
- Rich in medicinal and nutritional value, the chutney is believed to be a good source of nutrients like protein, calcium, zinc, vitamin B-12, iron, magnesium, potassium, etc.
- The tribals prepare the Kai chutney by grinding the ants manually on a Sil Batta or the grinding stone.
- Mayurbhanj’s tribals also earn their livelihood by selling the red ants and the chutney made from the ants.
- They believe that its consumption helps boost immunity and prevents diseases.
- Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal: Nayagarh Kanteimundi Brinjal is known for its prickly thorns on the stems and the whole plant.
- The green and round fruits contain more seeds as compared to other genotypes.
- It is famous for its unique taste and relatively short quick cooking time. The plants are resistant to major insects and can be grown with minimal pesticide.
- It is being widely cultivated in Nayagarh district of the state.
- Odisha Khajuri Guda: Odisha’s “Khajuri Guda” or jaggery is a natural sweetener extracted from date palm trees and has its origin in the Gajapati district.
- Traditionally, the jaggery is prepared in a trapezoidal form called ‘Patali Gur’ and is organic by nature.
- It is dark brown and has a unique taste.
- Dhenkanal Magji: Dhenkanal Magji is a type of sweet made from cheese from buffalo milk, with distinct characteristics in terms of appearance, taste, flavour, shape, and size.
- It also has unique nutritional values that distinguish it from other cheese-based sweets.
- The sweet is prepared by draining moisture from the cheese and then frying it, finally forming balls from the mixture.
iDEX innovators to exhibit futuristic technologies at Vibrant Gujarat summit (ET)

- 08 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The Ministry of Defence on Sunday said that Innovations for Defence Excellence-Defence Innovation Organization (iDEX-DIO) will participate in the 10th edition of the Vibrant Gujarat Summit from January 10 to 12 in Gandhinagar.
About iDEX:
- iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence), the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Defence, Govt of India launched by Prime Minister Modi in 2018.
- The objective of the scheme is to cultivate an innovation ecosystem in the Defence and Aerospace sector by collaborating with startups, innovators, MSMEs, incubators, and academia.
- iDEX offers grants and support for R&D with significant potential for future adoption in Indian defense and aerospace.
- It is currently engaged with around 400+ Startups and MSMEs, till now procurement of 31 items worth over Rs 2000 Cr. has been cleared.
- Recognized as a game-changer in the defense ecosystem, iDEX has received the PM Award for Innovation in the defense sector.
What is the Vibrant Gujarat Summit?
- The Government of Gujarat organizes the Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit, also known as Vibrant Gujarat, a biennial global business event held in the state of Gujarat, India.
- It attracts business leaders, investors, corporations, thought leaders, and policymakers, serving as a platform to understand and explore business opportunities in Gujarat.
- Launched in 2003 and now held every two years, the summit aims to promote Gujarat as an attractive investment destination, fostering partnerships and collaborations across various sectors.
- Industry associations, both nationally and internationally, support the summit, making it one of Gujarat's crucial economic forums.
- The event creates a platform for business leaders, policymakers, and investors to explore opportunities for investment, collaboration, and partnership in sectors such as energy, manufacturing, infrastructure, information technology, agriculture, healthcare, and more.
- It facilitates discussions, negotiations, and agreements in these key sectors.
- The Tenth edition of Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit is being held from 10 to 12 January 2024 in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
- Its theme is 'Gateway to the Future'.
- This Tenth Edition of the Summit will celebrate “20 Years of Vibrant Gujarat as the Summit of Success”.
- There are 34 Partner countries and 16 Partner organizations for this year’s Summit.
- Further, the Ministry of Development of North-Eastern Region will utilize the Vibrant Gujarat platform to showcase investment opportunities in the North-Eastern regions.
High-frequency waves detected in the Martian Upper Atmosphere could help understand plasma processes over Mars (PIB)
- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
Recently, scientists have detected the existence of high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian Upper Atmosphere with novel narrowband and broadband features that can help to understand plasma processes in the Martian plasma environment.
What are Plasma Waves?
- Plasma waves, commonly observed in Earth's magnetosphere, denote short-time scale fluctuations in electric and magnetic fields.
- These waves play a crucial role in energizing and transporting charged particles within Earth's magnetosphere.
- Specific plasma waves, like electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves, serve as a safeguard, cleansing Earth's radiation belt, known to pose threats to satellites.
- Researchers, intrigued by this phenomenon, seek to understand the presence of diverse plasma waves around planets without intrinsic magnetic fields, such as Mars.
Key Observations:
- Scientists utilized high-resolution electric field data from NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution Mission (MAVEN) spacecraft to examine high-frequency plasma waves in the Martian environment.
- These waves manifest as either parallel-propagating electron oscillations (Langmuir waves) or perpendicular-propagating electron oscillations (upper-hybrid type waves) in Mars' magneto sheath region.
- Two distinct wave modes, below and above the electron plasma frequency, were observed in the Martian magnetosphere.
- Broadband and narrowband waves exhibited identifiable features in the frequency domain, with broadband waves displaying periodic patchy structures at intervals of 8–14 milliseconds.
Significance:
- The presence of these waves offers a valuable tool to investigate how electrons gain or dissipate energy within the Martian plasma environment.
Cabinet clears PRITHVI initiative for ease of research in earth sciences (Indian Express)

- 06 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
The government Friday approved an initiative that will give it the flexibility to pursue research and use funds allocated to five different sub-schemes related to earth sciences over a five-year period.
About the PRITHVI Scheme:
- The PRITHVI Scheme is an initiative by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) designed to deepen our understanding of the Earth and its essential indicators.
- With a substantial allocation of Rs 4,797 crore spanning 2021-26, this comprehensive initiative aims to significantly advance research, modeling, and service delivery in critical domains like weather, climate, oceans, and polar regions.
- The scheme amalgamates five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere and Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems and Services (ACROSS)
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART)
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER)
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE)
- Research, Education, Training, and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Collectively, these programs strive to deepen our comprehension of Earth's vital signs and translate scientific knowledge into practical services for the benefit of society, the environment, and the economy.
Objectives:
- A primary aim of PRITHVI is to enhance and sustain long-term observations across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth.
- This facilitates the recording and monitoring of vital signs and changes within the Earth System.
- The scheme places emphasis on developing predictive models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards while advancing our understanding of climate change science.
- Exploring polar regions and high seas is a significant aspect, targeting the discovery of new phenomena and resources.
- The scheme underscores the development of technology for exploring and sustainably harnessing oceanic resources for societal applications.
Implementation:
- Various components of the PRITHVI scheme are interdependent, executed in an integrated manner through the collective efforts of the institutes under the MoES.
Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change submits proposals for Wetland City Accreditation under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands for cities of Indore, Bhopal and Udaipur (The New Indian Express)

- 05 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News
MoEF&CC has submitted three nominations from India for Wetland City Accreditation (WCA) of Indore (Madhya Pradesh), Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh) & Udaipur (Rajasthan) under the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
What is Wetland City Accreditation (WCA)?
- Recognizing the importance of wetlands in urban and peri-urban environments and to take appropriate measures to conserve and protect these wetlands, the Ramsar Convention during COP12 held in the year 2015 approved a voluntary Wetland City Accreditation system under Resolution XII.10.
- It recognizes cities which have taken exceptional steps to safeguard their urban wetlands.
- The Wetland City Accreditation scheme aims to further promote the conservation and wise use of urban and peri-urban wetlands, as well as sustainable socio-economic benefits for local populations.
- Additionally, the Accreditation seeks to encourage cities that are close to and dependent on wetlands.
- Primarily Wetlands of International Importance, but also wetlands with other conservation category status, to develop and strengthen a positive relationship with these valuable ecosystems.
- To be formally accredited, a candidate for the Wetland City Accreditation should satisfy the standards used to implement each of the six international criteria mentioned Operational Guidance for WCA of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands.
- This voluntary scheme provides an opportunity for cities that value their natural or human-made wetlands to gain international recognition and positive branding opportunities for their efforts in demonstrating strong positive relationships with wetlands.
- The ongoing Amrit Dharohar initiative of the MoEF&CC announced as part of this year’s budget also aims to achieve similar goals by promoting unique conservation values of Ramsar Sites.
- In this context, WCA will not only generate public awareness about conservation of urban and peri-urban wetlands but will also help in implementation of Amrit Dharohar across the country.
The Three Nominated Cities Include:
- Indore: Founded by Holkars, Indore is the cleanest city in India and the recipient of India’s Smart City Award 2023 for its best sanitation, water and urban environment.
- Sirpur Lake, a Ramsar Site in the city, has been recognised as an important site for water bird congregation and is being developed as a Bird Sanctuary.
- A strong network of more than 200 wetland mitras is engaged in bird conservation and sensitising local community to protect Sarus Crane.
- Bhopal: One of the cleanest cities in India that has proposed conservation zones around the wetlands in its draft City Development Plan 2031.
- Bhoj Wetland, Ramsar Site is the city’s lifeline, equipped with the world-class wetlands interpretation centre, Jal Tarang.
- Additionally, the Bhopal Municipal Corporation has a dedicated Lake Conservation Cell.
- A network of more than 300 wetland mitras is engaged in wetland management and conservation of Sarus Crane.
- Udaipur: Located in Rajasthan, the city is surrounded by five major wetlands, namely, Pichola, Fateh Sagar, Rang Sagar, Swaroop Sagar, and Doodh Talai.
These wetlands are an integral part of the city’s culture and identity, help maintain the city’s microclimate, and provide a buffer from extreme events.
India to use SpaceX rocket to launch communications satellite (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is gearing up for the launch of its communication satellite GSAT-20, weighing 4,700kg, an initiative marking India's entry into a new era of satellite technology.
Context:
- The commercial arm of ISRO, NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) will launch GSAT-20 (renamed as GSAT-N2), on-board SpaceX’s Falcon-9 during the second quarter of 2024.
- ISRO's current flagship rocket, the LVM3, holds a maximum carrying capacity of four tons.
- Falling short by 700kg for the GSAT-20.
- This satellite will cater to cellular backhaul service needs particularly to remote and unconnected regions.
What is GSAT 20 Satellite?
- GSAT-20 is an Indian geostationary Ka-band high-throughput communications satellite.
- GSAT 20 is built on the I-3K unified modular bus with electric-only propulsion.
- It will be India's first satellite to rely entirely on electric propulsion, which can be five to six times more efficient than chemical-based propulsion.
- It features a Ka × Ka high-throughput communications payload with 70 Gbps throughput utilizing 32 spot beams with each 2 polarisations providing broadband services across the Indian region.
- The satellite was initially set for a 2020 launch on a GSLV Mk.3 (2) rocket but got moved up to 2019 on an Ariane-5ECA+.
- In 2021, the plan returned to a GSLV Mk.3 (2) launch.
- In early 2024, a contract with SpaceX was signed for a Falcon-9 v1.2 (Block 5) launch.
What is SpaceX’s Falcon-9 Rocket?
- Falcon 9 is a reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX “for the reliable and safe transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond".
- It is the world’s first orbital-class reusable rocket.
- Reusability allows SpaceX to re-fly the most expensive parts of the rocket, which in turn drives down the cost of space access," it added.
- Till now, it has undertaken 285 launches, 243 landings, and 217 re-flights.
Namibian cheetah Aasha gives birth to 3 cubs in Kuno; ‘indicator that animals are acclimatising’ (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a Namibian cheetah named Aasha has given birth to three cubs at Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
About Kuno National Park (KNP):
- Location: Situated in the Sheopur district of Madhya Pradesh, Kuno National Park is nestled near the Vindhyan Hills.
- The park is aptly named after the Kuno River, a significant tributary of the Chambal River that traverses its expanse.
- Originally designated as a wildlife sanctuary, Kuno National Park attained the status of a national park in 2018.
- This transformation aligns with its pivotal role in the 'Action Plan for Introduction of Cheetah in India.'
- Vegetation and Flora: Kuno predominantly features a grassland landscape, punctuated by occasional rocky outcrops.
- The flora encompasses a diverse mix, including dominant species such as Kardhai, Salai, and Khair trees.
- The park boasts a rich composition with 123 tree species, 71 shrub species, 32 exotic and climbing species, and 34 bamboo and grass species.
- Fauna: The protected region of Kuno National Park shelters an array of wildlife, including the jungle cat, Indian leopard, sloth bear, Indian wolf, striped hyena, golden jackal, Bengal fox, and dhole.
- The park also delights bird enthusiasts with a habitat supporting over 120 bird species.
What is Project Cheetah?
- The Wildlife Trust of India started talks in 2009 to bring the cheetah back to India.
- Over five years, 50 cheetahs will be imported from African nations and placed in various national parks as part of the "Action Plan for Reintroduction of Cheetahs in India."
- Prime Site Selection - Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP): Among the surveyed sites in central Indian states, Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP) in Madhya Pradesh emerged as the most suitable location.
- This acclaim is attributed to its conducive habitat and ample prey base.
- KNP is deemed capable of supporting 21 Cheetahs, uniquely standing as a wildlife site where villages have been entirely relocated from within the park.
- Moreover, Kuno offers the prospect of harmoniously accommodating four of India's prominent big cats - tiger, lion, leopard, and Cheetah.
- Additional Recommended Sites: The project identifies other potential sites, including Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh), Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary - Bhainsrorgarh Wildlife Sanctuary complex (Madhya Pradesh), Shahgarh bulge in Jaisalmer (Rajasthan), and Mukundara Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan).
- Implementation Progress: As a significant stride in the project's realization, 20 Cheetahs, comprising 8 from Namibia and 12 from South Africa, were introduced to Kuno Palpur National Park last year.
- This marks a historic initiative to establish a free-ranging Cheetah population in India, reviving their presence after a 70-year absence.
Another eye in the sky, on the ground: India is now part of the world’s largest radio telescope project (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian government’s recent approval to join the SKA project, accompanied by a financial commitment of Rs 1,250 crore, marks the initial step towards this ratification.
What is the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO)?
- SKAO is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to radio astronomy and is headquartered in the UK.
- At the moment, organisations from ten countries are a part of the SKAO.
- These include Australia, Canada, China, India, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, the Netherlands and the UK.
What is significant about the SKA telescope?
- The telescope, proposed to be the largest radio telescope in the world, will be located in Africa and Australia whose operation, maintenance and construction will be overseen by SKAO.
- The completion is expected to take nearly a decade at a cost of over £1.8 billion.
- Some of the questions that scientists hope to address using this telescope include:
- Beginning of the universe
- How and when the first stars were born
- The life cycle of a galaxy
- Exploring the possibility of detecting technologically-active civilisations elsewhere in our galaxy and
- Understanding where gravitational waves come from.
- As per NASA, the telescope will accomplish its scientific goals by measuring neutral hydrogen over cosmic time, accurately timing the signals from pulsars in the Milky Way, and detecting millions of galaxies out to high redshifts.
- Significantly, the development of SKA will use the results of various surveys undertaken using another powerful telescope called the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), which is developed and operated by the country’s science agency CSIRO.
- This telescope, which has been fully operational since February 2019 mapped over three million galaxies in a record 300 hours during its first all-sky survey.
- ASKAP surveys are designed to map the structure and evolution of the Universe, which it does by observing galaxies and the hydrogen gas that they contain.
What are radio telescopes?
- Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can detect invisible gas and, therefore, they can reveal areas of space that may be obscured by cosmic dust.
- Significantly, since the first radio signals were detected by physicist Karl Jansky in the 1930s, astronomers have used radio telescopes to detect radio waves emitted by different objects in the universe and explore them.
- According to NASA, the field of radio astronomy evolved after World War II and became one of the most important tools for making astronomical observations.
- The Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico, which was the second-largest single-dish radio telescope in the world, collapsed in December 2020.
- The telescope was built in 1963 and because of its powerful radar, scientists employed it to observe planets, asteroids and the ionosphere, making several discoveries over the decades, including finding prebiotic molecules in distant galaxies, the first exoplanets, and the first millisecond pulsar.
162 cases of Covid sub-variant JN.1 detected in India; highest from Kerala, Gujarat: INSACOG (Live Mint)
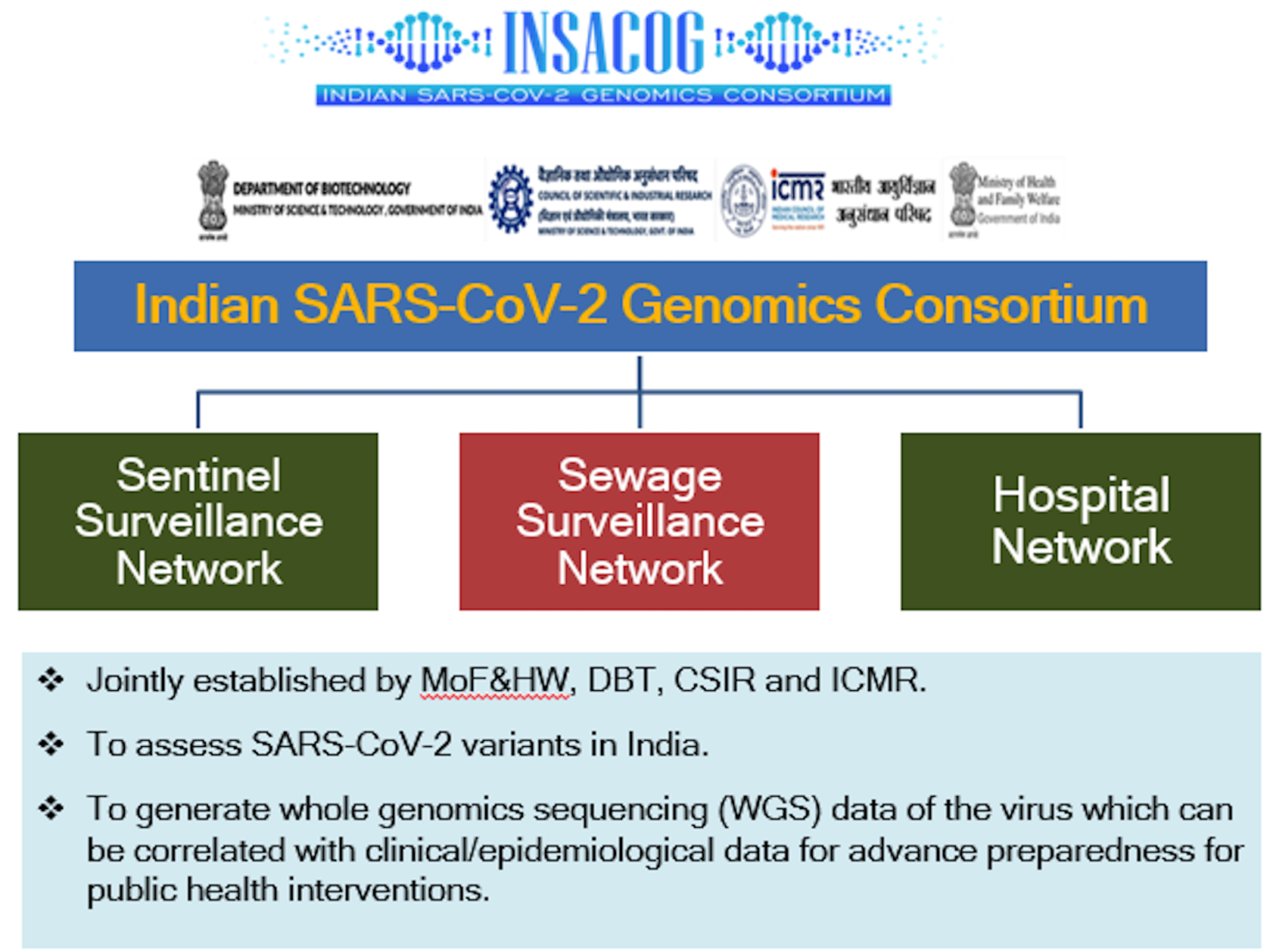
- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India reported a total of 109 JN.1 COVID variant cases in the country as of December 26, Health Ministry sources recently said.
What is Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG)?
- Established in December 2020, INSACOG is a collaborative initiative involving the Union Ministry of Health, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Council for Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- The consortium's primary mission is to expand whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus responsible for Covid-19, across India.
- This initiative aims to comprehend the virus's spread and evolution.
- INSACOG initially engaged 10 national research laboratories of the central government and has grown into a network of 38 labs, including private labs, following a hub-and-spoke model.
- The consortium's Genome Sequencing Laboratories guide new laboratories, working in tandem to monitor genomic variations through sentinel sequencing facilitated by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) under the Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP) of the central government.
- Beyond sequencing efforts, INSACOG endeavors to establish a systematic correlation between genome sequencing and clinical outcomes.
- It is actively building a nationwide hospital network to investigate clinical correlations in mild versus severe cases of Covid-19.
- Additionally, the consortium is conducting a longitudinal study to comprehend long-term post-Covid complications and changes in immunity.
- Looking ahead, INSACOG is exploring sewage surveillance as an early detection tool and assessing the spread of variants in hotspot localities.
MEA’s Flagship ‘Know India Programme’ for youth diaspora completes 20 years (MEA GOI)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The flagship programme of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) for the youth diaspora, the ‘Know India Programme’, has completed 20 years.
About the Know India Programme (KIP):
- The Know India Programme is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of External Affairs designed to enhance awareness about India, its cultural heritage, and art, and to familiarize participants with various aspects of contemporary India and their ancestral homeland.
- This program is open to Persons of Indian Origin (21-35 years) (excluding non-resident Indians) from all over the world, with a preference for youth from Girmitiya countries, such as those from Mauritius, Fiji, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad & Tobago, South Africa, and Jamaica.
- The program has been in existence since its inception in 2003.
Features of Know India Programme (KIP):
- It is a 21 days’ programme (excluding international travel) during which the participant will visit Delhi, Agra and a select state in India alongwith visits to places of historical, cultural, and religious significance.
- KIP participants will also have a 2-day orientation programme in New Delhi.
- Participants will meet opinion makers, leaders, and officials to get an overview of India’s economy, society and ongoing growth and development story.
- Participants are provided local hospitality e.g. boarding and Internal transportation in India, return air tickets from their country of residence to India provided participants bear 10% of the cost of total air fare.
- Gratis visa shall be granted to participants by the Indian Missions/Posts abroad.
- Some of the key elements of the Programme include:
- Visits to places of historical and cultural importance;
- Familiarisation with Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical forms of Music and Dance;
- Visit to institutions of democracy and governance like Parliament of India, Election Commission of India, Rashtrapati Bhawan;
- Interaction with leading educational institutions;
- Exposure to flagship economic and development schemes like Digital India, StartUp India, and Make in India; and
- visits to industrial sites, public and private firms to highlight India’s strength in Manufacturing & Service sector.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Minimum qualification required for participating in KIP is graduation from a recognized University /Institute or enrolled for graduation and the ability to speak in English.
- The applicant should not have visited India through any previous Programme of Government of India.
- Those who have not visited India before will be given preference.
- Applicant must provide documentary evidence to prove Indian origin or an undertaking about Indian origin which must be countersigned by the Indian Embassy/High Commission/Consul General.
States Returning to OPS Pose Significant Financial Burden: RBI (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the RBI released a report saying, the return to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) by a few states would put a huge burden on their finances, restricting them from undertaking capital expenditure to drive the growth.
What is the Old Pension Scheme (OPS)?
- The Old Pension Scheme (OPS), popularly OPS, is for state and central government employees who have completed 10 or more years of service.
- The appeal of the Old Pension Scheme lies in its commitment to provide a guaranteed or 'defined' benefit to retirees, classifying it as a 'Defined Benefit Scheme.'
- It provides government employees with pensions based on their final salary, amounting to 50% of the last drawn salary.
- For instance, if a government employee's final monthly salary upon retirement was Rs 10,000, they would receive a guaranteed pension of Rs 5,000.
- Similar to government employees' salaries, pension payouts increased with government-declared dearness allowance (DA) hikes.
- The Central government discontinued OPS in 2003.
What were the issues with the OPS?
- The primary concern was the unfunded nature of the pension liability, lacking a dedicated corpus that could grow over time to meet payment needs.
- The annual Government of India budget allocated funds for pensions without a clear strategy for sustaining future payments.
- The 'pay-as-you-go' approach raised inter-generational equity concerns, burdening the present generation with the escalating load of pension responsibilities.
- Recently, the RBI expressed alarm over some states, including Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Punjab, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan, reverting to the OPS, citing it as a significant fiscal challenge.
- The RBI warned that by deferring current expenses to the future, states risk accumulating unfunded pension liabilities in the years to come.
What is the New Pension Scheme (NPS)?
- Introduced by the Central government in 2004 as an alternative to OPS, NPS is accessible to employees across public, private, and unorganized sectors, excluding those in the armed forces.
- This pension initiative encourages individuals to invest in a pension account regularly during their employment.
- Upon retirement, subscribers can withdraw a specific percentage of the accumulated corpus.
- The remaining amount is disbursed as a monthly pension post-retirement.
- Regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA).
How does NPS differ from OPS?
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS) ensures a fixed and guaranteed pension amount.
- In contrast, the National Pension Scheme (NPS) is an investment-cum-pension scheme, exposing returns to market volatility.
- NPS contributions are defined, but benefits are contingent on market performance.
Protein from Budgett’s frog can block enzymes of disease-causing pathogens (The Hindu)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science’s (IISc.) molecular biophysics unit in a study have identified that peptides (short protein) produced from Budgett’s frog can combat enzymes of disease-causing pathogens.
Key Research Findings:
- The research focused on peptides, or short proteins, derived from amphibian skin, a subject of prolonged study due to their capacity to counter adverse environmental conditions, including harmful pathogens.
- A peptide secreted by frogs demonstrated inhibitory effects on two crucial enzymes, namely subtilisin Carlsberg and proteinase K, which are produced by pathogens.
- These enzymes play a crucial role in fostering infections by breaking down specific protective proteins within the infected individual.
- The studied peptide exhibited its inhibitory action through a slow-tight binding pathway, proving to be as effective as SSI, a well-established subtilisin inhibitor.
- The researchers illustrated the formation of a Michaelis complex—an intact, noncovalent complex with the inhibitor—during the process.
About Budgett’s frog:
- Budgett’s frogs exhibit high intelligence and a notably assertive nature.
- When alarmed, they employ a defensive strategy by inflating themselves, standing on short legs, and, if necessary, lunging at potential threats with an open, imposing mouth accompanied by a distinctive shriek.
- During the dry season, these frogs take refuge in burrows they construct at the bottoms of water pools.
- Within these burrows, they shed multiple layers of skin to create a waterproof cocoon, ensuring their moisture retention.
- Equipped with exceptional night vision and a keen sensitivity to movement, Budgett’s frogs showcase effective hunting skills.
- Habitat/Range: Found in proximity to permanent or seasonal bodies of water, Budgett’s frogs inhabit regions across Paraguay, Argentina, and Bolivia.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Classified as Least Concern.
Royal Bengal Tiger spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary (PTI)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a Royal Bengal Tiger was spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim at an altitude of 3,640 metres.
Context
- Royal Bengal Tiger has been sighted in the Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim roaming at an altitude of 3,640 meters.
- The Royal Bengal Tiger was captured by trap cameras of a team of the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) which is conducting a study in the sanctuary in collaboration with the Sikkim Forest Department.
- It was under a larger project called "Conservation and Use of Five Wetlands in three Himalayan States to Secure Habitats of Birds Migrating within the Central Asian Flyway (CAF)."
- This project was sanctioned under the National Mission on Himalayan Studies (NMHS), and aims to protect and conserve wetland sites in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Sikkim.
About Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary is located at the tri-junction of Sikkim, Bengal and Bhutan and is spread over 128 square kilometres.
- The sanctuary is strategically located in the East Sikkim district, connecting the forests of Bhutan and the Neora Valley National Park in West Bengal.
- It is the largest wildlife sanctuary in Sikkim.
- Vegetation: The Sanctuary has typical alpine-temperate-subtropical vegetation with high-altitude lakes around Jelep La.
- Flora: Rhododendron, Silver Fir, Juniper forest and associated ground flora, moss-filled oak forests with dense bamboo thickets etc.
- Fauna: It is home to various species, including red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan musk deer, Himalayan goral, and Himalayan black bears.
Sub-Neptune Planets (The Hindu)
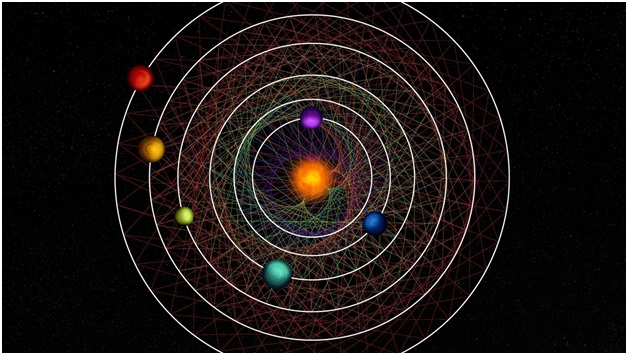
- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently astronomers have discovered an uncommon star system located just 100 light-years away from us, with six planets huddled immensely close to their host star.
What about sub-Neptunes?
- Sub-Neptunes are generally any planet that has a smaller radius than Neptune, although some could still be more massive.
- There are no sub-Neptunes in our solar system even though they are now known to be more common around other stars than Neptune-sized worlds.
- They might be rocky planets with thick atmospheres of hydrogen and helium gas, planets made of rock and ice bearing warm and water-rich atmospheres.
- These sub-Neptune planets were Initially detected in 2020 by NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and are about two to three times as big as Earth.
What are the findings?
- The newly discovered sub-Neptunes range from 1.9 to 2.9 times Earth's diameter.
- All appear to possess a large atmosphere.
- They and their star are located around 100 light-years from Earth.
- A light year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
- The system has six planets, all about the same size and they've barely changed since its formation up to 12 billion years ago.
- Their star, called HD110067, is visible in Earth's night sky in the northern constellation Coma Berenices.
- These undisturbed conditions make it ideal for learning how these worlds formed and whether they host life.
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) (PIB)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) has recently praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
About Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):
- The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body created by WHO and FAO of the United Nations with 188 member countries.
- It is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular session once a year alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO with all work subject to approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organizations.
- The Commission works in the six UN official languages.
- India has been a member of this commission since 1964.
- The 46th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was held from 27 November to 2 December (2023) in Rome, Italy.
- In the current session, India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millet, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet, and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
Exercise Milan (The Hindu)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Navy To Conduct One Of Its Largest Naval Exercises — MILAN — Next February; More Than Fifty Countries Expected To Participate
About Exercise Milan:
- Exercise Milan is a biennial multilateral naval exercise that began in 1995, and has since significantly expanded in scope and scale to become the largest exercise held by India.
- Initially involving only Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, it has evolved significantly in terms of participants and exercise complexity.
- Aligned with India's 'Look East Policy' initially, Milan expanded under the 'Act East Policy' and Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative, welcoming Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs).
- The mid-planning conference for Milan-24 occurred in October.
- The last edition of Milan, which is held off Visakhapatnam, saw participation from over 40 countries showcasing its substantial growth in scale and international engagement.
- The next edition of Exercise MILAN is scheduled to be held in February 2024 and is expected to see the participation of over 50 countries.
- It reflects the significant expansion of the Navy’s engagements as well as its capacity to assist countries in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) as the first responder and Preferred Security Partner.
World AIDS Day 2023 (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the World AIDS Day 2023, observed each year on December 1, the World Health Organisation emphasised recognising and remembering the contribution of communities in controlling HIV-AIDS.
About World AIDS Day 2023:
- World AIDS Day which is observed every year on December 1 is a global movement to unite people in the fight against HIV and AIDS.
- Since 1988, when the World Health Organisation (WHO) recognised the day, communities have stood together on World AIDS Day to show strength and solidarity against HIV stigma and to remember lives lost.
- It is an opportunity to reflect on the progress made to date and raise awareness about the challenges that remain to achieve the goals of ending AIDS by 2030.
- The theme of World AIDS Day 2023 is– “Let Communities Lead"
What is HIV/AIDS?
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, compromising the body's ability to fight off infections and diseases.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the advanced stage of HIV infection, characterized by severe immune system damage.
- Transmission: HIV spreads through unprotected sexual contact, sharing contaminated needles, and from an infected mother to her child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Treatment: Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) is the primary treatment for HIV/AIDS, managing the virus and supporting the immune system.
- Lifelong adherence is essential, ensuring viral suppression.
- Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is vital, and global challenges such as stigma and healthcare access persist in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
Siena Galaxy Atlas (SGA) (Space)

- 19 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Astronomers have recently crafted a stunning atlas comprising 400,000 galaxies situated in the cosmic vicinity of the Milky Way, aptly named the Siena Galaxy Atlas.
About the Siena Galaxy Atlas:
- It is a digital atlas designed to help learn more about our universe by highlighting a number of well-known galaxies.
- It was produced using information gathered from three astronomical surveys conducted at Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) and Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) between 2014 and 2017. These surveys collectively are referred to as the DESI Legacy Surveys.
Distinguishing Features:
- Setting itself apart from previous atlases, the Siena Galaxy Atlas relies on state-of-the-art digital images captured by advanced technology.
- Unlike its predecessors, which utilized outdated equipment and photographic plates, this atlas leverages highly sensitive instruments to produce the most precise and accurate data available.
- Notably, it marks the first cosmic atlas to showcase the light profiles of galaxies—a curve illustrating the variation in brightness from the galaxy's brightest point to its dimmest.
Significance:
- The introduction of the Siena Galaxy Atlas carries immense importance in astronomical exploration for several reasons:
- By relying on digital images captured with advanced instruments, the atlas ensures a level of precision and detail that surpasses previous methods, enhancing the overall quality of data.
- Light Profiles of Galaxies: A pioneering feature, the inclusion of light profiles in the atlas provides a unique perspective, allowing astronomers to glean valuable insights into the structure and characteristics of galaxies.
- Pattern Recognition: Cosmic atlases, such as the Siena Galaxy Atlas, play a pivotal role in aiding astronomers in identifying patterns.
- This capability is particularly valuable in categorizing phenomena like transient events, such as stars that exhibit sudden flares and then disappear.
- The atlas facilitates the identification of celestial objects worthy of more detailed follow-up studies, enabling astronomers to delve deeper into specific areas of interest.
- From unravelling the mysteries surrounding the birth and evolution of galaxies to investigating the distribution of dark matter and the propagation of gravitational waves through space, the Siena Galaxy Atlas serves as a versatile tool for astronomers in their cosmic pursuits.
Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” Portal Launched (PIB)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Development of the North-East Region virtually launched the “MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard” and “Poorvottar Sampark Setu” portal at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi recently.
About Poorvottar Sampark Setu Portal:
- The Poorvottar Sampark Setu portal is a robust tool designed to streamline and improve the monitoring of Union Ministers' fortnightly visits to the North Eastern Region (NER)
Key features include:
- Insightful Dashboard: The portal offers a comprehensive dashboard presenting valuable insights and graphical information on state-wise/district-wise visits to NER by Union Ministers, serving as a centralized resource for stakeholders.
- Curated Minister List: It generates a curated list of Ministers eligible for nomination for visits to NER in the upcoming months, facilitating efficient planning.
- Online Tour Reporting: After their visit, Ministers can conveniently submit tour reports and recommendations online, streamlining the reporting process.
- Recommendation Analysis: MDoNER (Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region) can analyze and forward the received recommendations to respective line Ministries, Departments, and State Governments for prompt action.
- Summary Report Generation: The portal offers a one-click summary report generation feature, simplifying the overview of visits for effective decision-making.
What is the MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard?
- The MDoNER Data Analytics Dashboard is a comprehensive platform integrating data from 112 schemes across 55 Departments and Ministries.
Its key benefits include:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Empowers stakeholders with data-driven insights for informed decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines operations, ensuring a seamless and efficient workflow.
- Centralized Monitoring: Provides a centralized hub for monitoring diverse schemes and initiatives.
- Policy-Level Decision Tool: Functions as a valuable tool for crafting policies based on robust data analysis.
- Information Integration: Integrates information seamlessly, fostering coherence and accessibility.
- Focused Monitoring: Keeps a vigilant eye on NER Aspirational districts, North East border districts, and the most backward districts in NER for targeted interventions.
Is Halley’s Comet returning? (India Today)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The celestial calendar for 2023 is set to offer a spectacular show as the Orionid meteor shower is expected to rain down its greatest number of meteors on the mornings of October 21 and 22.
About the Orionid Meteor Shower:
- An annual celestial spectacle illuminating the night sky every October, the Orionid meteor shower is a captivating phenomenon with a fascinating origin.
- This cosmic event transpires as Earth traverses the remnants of debris left by Halley's Comet, officially designated as 1P/Halley.
- Halley's Comet, on a roughly 76-year orbit around the sun, sheds dust particles from its nucleus during each passage through the inner solar system.
- This process creates a distinctive trail of debris along its path.
- In late October each year, Earth intersects this celestial trail, giving rise to the mesmerizing display known as the Orionid meteor shower.
- Measuring about five by nine miles in size, Halley's Comet undergoes a remarkable transformation, losing between three to ten feet of material with each journey through the inner solar system.
- The resulting debris becomes the source of the Orionid meteors.
- This celestial event offers a visual treat for observers in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres, particularly during the post-midnight hours.
- It provides an opportunity to witness the graceful streaks of light as the meteors traverse the night sky.
What are Meteors?
- Meteors, often referred to as "shooting stars," are a captivating manifestation of meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at high speed and subsequently burning up.
- Meteor showers, occurring annually or at regular intervals, are linked to the Earth passing through the dusty debris trail left behind by a comet.
- In the case of the Orionid meteor shower, the meteors are named after the constellation Orion, close to where these luminous streaks appear in the sky.
- This annual celestial event not only captivates observers with its dazzling display but also serves as a reminder of the dynamic interactions between Earth and the celestial bodies that grace our cosmic neighbourhood.
Is Pegasus spyware targeting journalists in India? (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amnesty International and Washington Post recently announced that it has found the presence of Pegasus spyware, sold only to governments, on two Indian journalists’ phones.
What is Pegasus Spyware, and How Does it Infiltrate Devices?
- Pegasus is a sophisticated form of malware, covertly designed to gather information without the user's knowledge.
- Developer: Developed by the Israeli security firm NSO Group.
- Objectives: Pegasus serves three primary purposes:
- Collecting historical data on a device discreetly.
- Continuously monitoring user activities and gathering personal information.
- Transmitting the collected data to third parties.
Infiltration Mechanisms:
- Pegasus utilizes "zero-click exploits," exploiting vulnerabilities in popular apps like iMessage and WhatsApp.
- Notably, zero-click exploits require no user interaction, differentiating them from typical cyberattacks.
- Network injection attacks are another method employed by Pegasus, where unsecured websites are used to infiltrate devices within milliseconds of the user's visit.
What is a Zero-click exploit?
- A zero-click exploit involves the installation of malicious software on a device without the device owner's consent.
- Notably, it does not require any action from the device owner to initiate or complete the installation.
Specific Exploit in the Recent Case with Indian Journalists:
- The particular exploit reportedly used in the incidents is known as BLASTPAST (previously identified as BLASTPASS), unfolding in two phases.
- Initial Phase: The attack aims to establish a connection with Apple HomeKit, a platform enabling users to control various smart devices on their network.
- The primary objective of this phase might be to assess how the device could be vulnerable to exploitation or to maintain visibility for potential future attacks.
- Second Phase: Malicious content is sent through the iMessage app to the target device.
- This stage is pivotal as it delivers the complete spyware payload, enabling extensive surveillance and data collection.
Chennai's Pallikaranai Wetlands Welcoming Migratory Bird Flocks (The Hindu)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
With over 150 garganeys, and several other species, including waders and raptors, flocking the Pallikaranai marshland, the curtain for the migratory season has been raised.
About Pallikaranai Marshland:
- Location: Pallikaranai marshland is a freshwater and partly saline wetland, located approximately 20 kilometres south of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- The eastern border of the marsh is flanked by the Buckingham Canal.
- Rich Ecosystem: The diverse ecosystem of Pallikaranai supports an impressive array of wildlife, including 115 bird species, 10 mammals, 21 reptiles, 10 amphibians, 46 fish, nine molluscs, five crustaceans, and seven butterfly species.
- Notable Species: Among the diverse wildlife are noteworthy species such as the Russell’s viper (Daboia siamensis), glossy ibis (Plegadis falcinellus), grey-headed lapwings (Vanellus cinereus), and Pheasant-tailed jacana (Hydrophasianus chirurgus).
- Biodiversity Significance: Beyond its biodiversity, the marshland serves a crucial role in flood prevention for Chennai, absorbing water during wet periods and releasing it during dry spells.
- Environmental Threats: Despite its ecological importance, the site faces threats from invasive non-native species, household sewage, urban wastewater, and periodic droughts.
- Ramsar Designation: Acknowledging its ecological significance, Pallikaranai marshland holds the status of being one of India's Ramsar sites, recognized for its importance in wetland conservation on an international scale.
India, Sri Lanka Launch Ferry Service Across Palk Strait (The Hindu)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
An international, high-speed passenger ferry service between Nagapattinam on the eastern coast of Tamil Nadu and Kankesanthurai in the northern province of Sri Lanka, has resumed as of Saturday, October 14, 2023, after a gap of nearly four decades.
About the Palk Strait:
- Palk Strait, situated between the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the island nation of Sri Lanka, derives its name from Robert Palk, the governor of Madras Presidency (1755-1763) during the British Raj.
- Bounded by Pamban Island (India), Adam's (Rama's) Bridge, the Gulf of Mannar, and Mannar Island (Sri Lanka) to the south, the strait serves as a crucial link connecting the Bay of Bengal in the northeast with the Gulf of Mannar in the southwest.
- The southwestern segment of the strait is referred to as Palk Bay.
- Spanning 40 to 85 miles (64 to 137 km) in width, 85 miles in length, and with a depth of less than 330 feet (100 meters), it features the inflow of several rivers, including Tamil Nadu's Vaigai River.
- The port of Jaffna, serving as the commercial hub for northern Sri Lanka, is situated along this significant waterway.
Facts About Adam's Bridge:
- Adam's Bridge, also recognized as Rama's Bridge or Rama Setu, constitutes a series of limestone shoals situated between Pamban Island (Rameswaram Island) off the south-eastern coast of Tamil Nadu, India, and Mannar Island off the north-western coast of Sri Lanka.
- Geological evidence supports the idea that this bridge once formed a land connection between India and Sri Lanka.
- Extending over 50 km, it delineates the separation between the Gulf of Mannar to the southwest and the Palk Strait to the northeast.
- Featuring dry sandbanks and shallow waters ranging from 1 to 10 meters in depth, hindering navigation, scientists posit that Ram Setu is a natural formation resulting from tectonic movements and the entrapment of sand in corals.
- Significantly, this structure holds cultural significance in Hindu and Muslim mythology.
- Hindus believe it to be the bridge constructed by Lord Ram and his army for their journey to Lanka to confront Ravan.
- According to Islamic legend, Adam traversed this bridge to reach Adam’s Peak in Sri Lanka, where he purportedly stood on one foot in repentance for 1,000 years.
A new non-invasive formaldehyde sensor can detect adulterated fish at room temperature (DST GOI)
- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A new low-cost sensor made of metal oxide nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide composite can detect formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature in a non-invasive way. The sensor shows long-term stability with a low detection limit.
Context:
- A sensor designed for the detection of formalin in fish has been developed by the Nanomaterials and Nanoelectronics Laboratory at Guwahati University, Assam.
- The formalin sensor utilizes a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide, synthesized through a process involving the wet chemical approach for Graphene Oxide (GO) and the hydrothermal route followed by calcination for the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Testing of the sensor has been conducted both at the laboratory scale and on fish procured from the fish markets in the Guwahati region, specifically targeting potential adulteration.
- This groundbreaking research has received support from DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence) and has been documented in the journal ACS Appl. Nano Mater.
- Research Support: The research behind this innovative sensor is backed by DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence).
About Non-Invasive Formaldehyde Sensor:
- This non-invasive formaldehyde sensor incorporates a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide (rGO-SnO2) as its key materials.
- While reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has been widely utilized for detecting various toxic gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), tin oxide (SnO2) has demonstrated notable efficacy in formaldehyde detection, both in its pristine form and when combined with different compounds, including graphene.
- This combination is favoured for its heightened stability and sensitivity to low concentrations of formaldehyde.
- Synthesis Process: The fabrication process involves a wet chemical approach for the production of graphene oxide (GO), followed by the hydrothermal route and subsequent calcination to synthesize the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Comparison with Existing Sensors: Unlike commercial formalin sensors for fish, which are primarily electrochemical-based or colorimetric-based and often invasive, this novel sensor, made from metal oxide nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide, offers a cost-effective and non-invasive method for detecting formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature.
- Challenges with Existing Sensors: Traditional electrochemical sensors, though widely used, tend to be expensive, and colourimetric sensors, while more cost-effective, share the invasive nature of their electrochemical counterparts. Both face challenges related to low-level and selective detection.
- Significance of the New Sensor: The development of gas sensors based on 2D materials, such as graphene, opens up new possibilities for the effective detection of toxic vapours at room temperature.
- These sensors hold promise for accurately detecting formalin emanating from adulterated food products.
What is Formaldehyde?
- Formaldehyde (CH?O) is an odorless, colorless gas with high toxicity and flammability under standard room temperature conditions.
- Primary Applications:
- Production of fertilizers, paper, plywood, and certain resins.
- Utilized as a food preservative.
- Found in glues, resins, dyes, textiles, disinfectants, building materials, automotive components, embalming processes, and laboratory settings.
- Incorporated into household items like antiseptics, medications, and cosmetics.
- Potential Health Effects:
- Exposure to formaldehyde may result in irritation of the skin, throat, lungs, and eyes. Additionally, formaldehyde is recognized as a carcinogenic substance.
AstroSat detects millisecond X-ray bursts from high magnetic field neutron stars (DD News)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s first multi-wavelength space-based observatory, AstroSat, has detected intense sub-second X-ray bursts emanating from a neutron star with an ultrahigh magnetic field, known as a magnetar.
What is X-ray Bursts?
- X-ray bursts manifest in low-mass X-ray binary systems featuring a neutron star and a low-mass main sequence star orbiting each other.
- The occurrence of these bursts is intricately linked to the gravitational dynamics of the neutron star and its companion.
- In this system, the proximity and intense gravitational forces of the neutron star cause the companion star to exceed its Roche-lobe, leading to the formation of an accretion disk around the neutron star.
- This disk becomes a repository for hydrogen drawn from the overflowing companion star.
- As hydrogen accumulates on the neutron star's surface, the extreme temperatures and pressures prevailing there catalyze its transformation into helium.
- This ongoing process results in the formation of a thin surface layer of helium.
- When this helium layer reaches a critical mass, a sudden explosive ignition occurs, elevating the entire neutron star's surface temperature to several tens of millions of degrees and releasing a burst of X-rays.
- Following the outburst, the binary system returns temporarily to a quiescent state, allowing the neutron star to reaccumulate the helium surface layer gradually.
- This cyclic process leads to the recurrence of X-ray bursts, typically unfolding at regular intervals separated by several hours or days.
About Indias’ AstroSat:
- AstroSat stands as India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory, pioneering a mission focused on the simultaneous study of celestial sources across X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands.
- Launched with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, AstroSat took flight aboard the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota on September 28, 2015.
- It entered a 650 km orbit, inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The Mission Operations Complex (MOX) at ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru oversees the satellite throughout its mission life.
- With a minimum useful life of around 5 years, AstroSat is dedicated to achieving the following scientific objectives:
- Understanding high-energy processes in binary star systems housing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimating magnetic fields associated with neutron stars.
- Investigating star birth regions and high-energy processes in star systems beyond our galaxy.
- Detecting new, briefly bright X-ray sources in the celestial sphere.
- Conducting a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
‘Dunki’ and immigration: How the first modern passports came to be (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The recently released Shah Rukh Khan’s movie ‘Dunki’ is said to be based on the ‘donkey route’ or ‘donkey flight’ that lakhs of Indians take to reach countries like the US, the UK or some other European countries.
What is a Donkey Journey?
- Dunki is the Punjabi idiom that means to "hop from place to place", according to the Migration Policy Institute (MPI).
- It is a colloquial term for "donkey flights" or the "donkey flights method", which is a dangerous illegal immigration technique involving crossing a country's borders through a backdoor route via multiple stops in other countries.
How does the donkey flight method or dunki work?
- The desire for a higher quality of life has given rise to an industry driven by "agents" who charge exorbitant fees to help smuggle people to the country of their choice.
- Some agents may even run legitimate businesses while offering this dangerous option.
- The agents can offer various services, from fake papers to help through otherwise legal migration processes to smuggling people through ship containers.
Which countries are most targeted using the Dunki method?
- While donkey flight can be used to enter any country, the US, Canada, and the UK are some of the most popular destinations undertaken by Indian immigrants.
- According to a report, between February 2019 and March 2023, as many as 149,000 Indians were detained for attempting to enter the US illegally.
- Of this, most of those detained were from Gujarat and Punjab.
Risks involved in the dunki method:
- Dunki comes with tremendous risks, including the risk of capture, imprisonment, and deportation.
- When facilitated by an agent, the system is highly exploitative.
- Many sell off their assets, including ancestral land, to pay these agents.
- Agents may also withhold people's passports or other important documents to extort more money and assets.
- Moreover, smuggled migrants are also more vulnerable to becoming victims of other crimes during the smuggling process.
- The terrains of the places through which immigrants may have to travel pose a range of risks, including harsh weather conditions, rugged terrains, and access to basic resources like food and water.
- It must be noted that migrant smuggling is not the same as human trafficking.
- However, these crimes may sometimes interlink, adding another layer of risk for those engaging in illegal immigration.
About Passports:
- Rooted in history, passports trace back to mentions in the Hebrew Bible and structured systems in nations like France and the UK.
- The evolution into modern passports was catalyzed by the British Nationality and Status of Aliens Act in 1914, introducing features such as photographs and distinctive characteristics.
- The League of Nations' 1920 conference sought to standardize passport regulations, contributing to the establishment of a common British system.
- During the 1920s, the United States linked immigration laws to passports, imposing limitations on inflows.
- Despite initial reservations, passports have persisted as an integral element of contemporary citizenship.
- Indian Passports: The initiation of issuing Indian passports dates back to the First World War (1914-1918) through the Defence of India Act, as mandated by the British government for travel.
NSG Takes on Invasive Vilayati Kikar/Prosopis Juliflora (Indian Express)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The National Security Guard (NSG) is actively combating the encroachment of the invasive plant species known as vilayati kikar at its Manesar campus, situated near the Delhi-Ajmer highway.
What is Prosopis Juliflora?
- Prosopis juliflora, a shrub or small tree belonging to the Fabaceae family and classified as a type of mesquite, is indigenous to Mexico, South America, and the Caribbean.
- Introduced to Delhi by the British in the 1920s during the construction of the national capital, this species is locally known by various names in India, including Bellary jaali, seemai karuvelam, seemai jaali, gando baval, and vilayati kikar.
- Known for its high ecological adaptability, Prosopis juliflora can thrive in diverse soil types, ranging from sand dunes to clay, and from saline to alkaline soils.
- It exhibits a wide altitude range, growing below 200 to above 1500 meters above sea level, with a mean annual rainfall varying from 50 to 1500 mm.
- However, despite its adaptability, it is recognized as an invasive plant with a propensity for vigorous growth, enabling it to outcompete indigenous plant species.
Impacts on the Environment: This invasive species pose significant environmental challenges:
- Prosopis juliflora absorbs more than four litres of water to produce one kilogram of biomass.
- The plant generates less oxygen and more carbon dioxide, making it less conducive to supporting bird habitats.
- It has the potential to contaminate groundwater, posing risks to the overall quality of this vital resource.
- The species contributes to land erosion by displacing grasslands that serve as habitats for native plants and animals.
- The invasive nature of Prosopis juliflora raises concerns about its ecological impact and necessitates efforts to manage and control its spread in affected regions.
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Says Unemployment Rate Declined (The Hindu)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) has reported that the unemployment rate in the country has shown a decrease between April and June 2023.
Key Observations of the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Improved Work Metrics: Both the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) and Worker-Population Ratio (WPR) showed positive trends in the recent period.
- Urban Employment Trends: In urban areas, LFPR increased from 47.5% (April-June 2022) to 48.8% (April-June 2023) for individuals aged 15 and above.
- The WPR in urban areas rose from 43.9% (April-June 2022) to 45.5% in the corresponding months this year.
- Gender-specific Changes:
- Male LFPR increased from 68.3% to 69.2%.
- Female LFPR showed notable growth from 18.9% to 21.1% during the observed period.
What is the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Conducted by the National Sample Survey (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Launched in April 2017 by the National Statistical Office (NSO) to provide more frequent labour force data.
Objectives:
- Estimate key employment and unemployment indicators every three months for urban areas.
- Annually estimate indicators for both 'Usual Status' and 'Current Weekly Status' in rural and urban areas.
- Key Indicators:
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): Percentage of individuals in the population who are part of the labour force (working, seeking, or available for work).
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): Percentage of employed persons in the population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR): Percentage of unemployed persons among those in the labour force.
- Current Weekly Status (CWS): Activity status determined based on the activities in the last 7 days before the survey.
India to Hold Satellite Spectrum Auctioning (The Hindu BusinessLine)

- 10 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Elon Musk vs Mukesh Ambani battle on whether to auction or allocate satellite spectrum has attracted intervention from the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
What is Satellite Spectrum?
- The satellite spectrum is like a special section of radio waves reserved for satellites when they're up in space.
- It's part of the larger family of radio waves that we use for things like Wi-Fi, TV, and radio.
- This spectrum serves as a vital resource for countries, facilitating satellite broadcasting, communication, and weather services.
Key Points:
- Limited Resource: The satellite spectrum is finite, allocated for activities like satellite broadcasting and communication.
- It plays a crucial role in facilitating services provided by communication satellites and weather satellites.
- Frequency Bands: The spectrum is categorized into different frequency bands, chosen based on diverse applications.
- The frequency assigned during a satellite's construction remains unchanged post-launch.
- Impact on Data Transfer: The frequency of a signal dictates the speed of data transfer.
- Higher frequencies enable faster data transmission, but they also entail shorter wavelengths, leading to signal attenuation over distances and increased interference risks.
- Frequency Range: Satellites typically transmit in the frequency range of 1.5 to 51.5 gigahertz.
- High-speed broadband operations often use the higher end of this spectrum.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Founded in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, later becoming a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Functions:
- Allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordinates and sets technical standards for telecommunication/ICT.
- Strives to enhance ICT access in underserved communities globally.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership: Comprises 193 countries and nearly 800 private sector entities and academic institutions.
- India's Association with ITU: India has actively participated in the ITU since 1869, maintaining a consistent presence on the ITU Council since 1952.
Reliance General gets ?923cr GST notices from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) (TOI)

- 09 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Reliance General Insurance Company (RGIC), a subsidiary of the Anil Ambani-led Reliance Capital, has received multiple show-cause notices worth Rs 922.58 crore from the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI).
About Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI):
- Formerly known as the Directorate General of Central Excise Intelligence (DGCEI), the Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) stands as a premier intelligence organization operating under the Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs, within the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- Its primary focus is on collecting, collating, and disseminating intelligence pertaining to Goods and Services Tax (GST) evasion and duties related to Central Excise and Service Tax on a pan-India basis.
- Evolution: Originally designated as the Directorate General of Anti-Evasion (DGAE), it was established in 1979 as an independent wing under the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, New Delhi.
- Became a full-fledged Directorate in 1983, headed by a Director.
- In 1988, attained the status of Directorate General under a Director General.
- Currently comprises 04 offices of the Director General (East, West, North, and South), 26 Zonal Units, and 40 Regional Units.
Key Responsibilities:
- Intelligence Gathering: Collects information from various sources, including GST returns, financial statements, and other documents, to identify potential GST law violations.
- Investigation: Empowered to conduct investigations into suspected cases of GST evasion or non-compliance, involving summoning individuals, examining records, and executing searches and seizures.
- Enforcement: Enforces provisions of the GST law, taking legal action against offenders, imposing penalties, and recovering taxes or duties owed.
- Additional Functions: Collaborates with agencies like the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) and State GST authorities for effective GST law implementation.
- Plays a crucial role in raising awareness about GST compliance and educating taxpayers on their legal obligations.
- Provides technical and legal assistance to field officers and other government entities involved in GST administration.
NGT Investigates Removal of Invasive Mussels in Ennore-Pulicat Wetland (The Hindu)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Southern Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has asked the Fisheries Department and the Tamil Nadu State Wetland Authority to file a detailed report on the removal of invasive mussel species from the Ennore-Pulicat wetland.
What is Mytella strigata?
- Mytella strigata is a moderately large mussel known for its symmetrical shell, commonly found in the middle intertidal and subtidal waters of estuaries and coastal areas.
- These mussels attach to surfaces using byssus threads.
- Appearance: Individual mussels display diverse external colours such as black, dark bluish, brown, grey, orange, and occasionally green.
- The species exhibits various shell patterns, including zigzags, spots, or concentric bands.
- Habitat and Distribution: Found in dense clusters on hard substrates and in epibenthic habitats, Mytella strigata is prevalent along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of tropical South and Central America.
- It has also expanded its presence to regions like Taiwan, the Philippines, Singapore, the Gulf of Thailand, the west coast of India, and the southeastern United States.
- Threats: These mussels pose a threat as they spread across river bottoms, forming carpets that hinder prawns from grazing or burying themselves in the sediment.
About Pulicat Lake:
- Pulicat is an extensive brackish-to-saline lagoon with marshes and a brackish swamp on the north.
- This is the second-largest saltwater lagoon in India and a Ramsar site (internationally recognized wetland under the Ramsar Convention).
- Only 16% of the lagoon is in Tamil Nadu; the rest is in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is fed by the Araani River at the southern tip and the Kalangi River from the northwest.
- Buckingham Canal, a navigation channel, passes through the lagoon.
- On the eastern boundary of this lagoon is Shriharikota Island, which separates the lagoon from the Bay of Bengal.
- The lagoon is shallow with large areas of mudflats and sandflats.
Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission (HT)

- 07 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Dr Aroh Barjatya, an Indian-origin scientist is set to lead the multi-institution NASA rocket mission on October 14.
About Atmospheric Perturbations around the Eclipse Path (APEP) mission:
- The APEP mission entails the launch of three rockets, each equipped with scientific instruments, to explore changes in the upper atmosphere during a solar eclipse, particularly during the critical phase of sudden light reduction.
- Mission Objective: To investigate alterations in the ionosphere induced by the abrupt decrease in sunlight during an eclipse, leading to the generation of waves in this atmospheric layer.
- Measurements will encompass changes in electric and magnetic fields, as well as variations in density and temperature.
- Launch Details: The launch site is the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, with a specific focus on studying the ionosphere's response during an eclipse.
- Potential Impact on Communications: NASA notes projections indicating a temperature and density reduction in the ionosphere during the eclipse, potentially causing disruptive wave disturbances that could affect GPS and satellite communications.
- Process: Rockets will be strategically positioned just beyond the path of annularity, where the Moon directly aligns with the Sun.
- Each rocket will deploy four compact scientific instruments designed to capture data on electric and magnetic fields, density, and temperature changes.
- NASA's primary objective is to achieve unprecedented simultaneous measurements from multiple ionospheric locations during a solar eclipse.
- Rationale for Rocket Selection: Sounding rockets were chosen for their precision in pinpointing and measuring specific regions of space.
- Their ability to investigate lower altitudes, inaccessible to satellites, makes them ideal for this mission.
- Sounding rockets offer precise data recording as they ascend and descend during suborbital flights, covering altitudes ranging from 45 to 200 miles (70 to 325 kilometres) above Earth's surface along their flight path.
Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) (The Hindu)

- 30 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently gave its approval for the three-year extension of fast-track courts that are specifically used to handle sexual offense cases.
About Fast Track Special Court (FTSC):
- The Fast Track Special Court (FTSC) initiative started in August 2019 as a centrally sponsored scheme to handle cases related to rape and the POCSO Act.
- Originally planned for one year, it got extended to March 2023, and now it's extended further until March 2026 with a financial allocation of Rs. 1952.23 crore from the Nirbhaya Fund.
- These specialized courts, totaling 761, including 414 exclusive POCSO Courts, operate across all States and Union Territories.
- The Department of Justice, Ministry of Law & Justice, oversees their implementation.
- The primary aim is to expedite justice, offering quick relief to victims and reinforcing the nation's commitment to ending sexual and gender-based violence.
- The expected outcomes of this scheme are significant.
- They include a substantial reduction in pending cases related to Rape & POCSO Act, providing swift access to justice for victims through improved facilities and expedited trials, and reducing the burden on the judicial system by managing the number of cases effectively.
Parthenon Sculptures (Indian Express)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A diplomatic row sparked between Greece and the UK recently after British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak canceled a meeting with his Greek counterpart Kyriakos Mitsotakis over the status of the Parthenon Sculptures housed at the British Museum.
What are the Parthenon Sculptures?
- The Parthenon Sculptures at the British Museum are more than 30 ancient stone sculptures from Greece that are more than 2,000 years old.
- Most of them originally adorned the walls and grounds of the Parthenon temple on the rocky Acropolis hill in Athens.
- Completed in 432 BC, the temple is dedicated to the goddess Athena and is seen as the crowning glory of Athens’ Golden Age.
- While one notable sculpture, which is 75 meters long, depicts a procession for the birthday of Athena, others show gods, heroes, or mythical creatures.
How did the sculptures reach Britain?
- They were removed from the Parthenon in the early 19th century by Thomas Bruce, the 7th Earl of Elgin and then-British ambassador to the Ottoman Empire.
- The marbles were taken to Britain and purchased by the British Museum in 1816.
Comet P12/Pons-Brooks (The Hindu)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Astronomers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have used the Himalayan Chandra Telescope (HCT) in Hanle, Ladakh, to photograph the Comet P12/Pons-Brooks.
About Comet P12/Pons-Brooks:
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is a Halley-type periodic comet that was first discovered by Jean-Louis Pons on July 12, 1812.
- It is nicknamed the 'Devil Comet' or likened to the 'Millennium Falcon' for its distinctive appearance.
- It has an orbital period of about 71.3 years.
- During its closest approach to the Sun or perihelion, the comet comes within about 0.78 astronomical units (AU) of the Sun, while at its furthest point, or aphelion, it is located at a distance of about 17.2 AU.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is also known for being the probable parent body causing the κ-Draconids meteor shower.
- It will make its return in 2024 and it is expected to reach its maximum brightness (potentially visible to the naked eye) during the month of April.
- With its closest approach occurring just a few days before a total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, it presents a unique opportunity for skywatchers to potentially view the comet during the eclipse.
- However, since the comet's brightness can be unpredictable, there is no guarantee it will be visible.
- Comet 12P/Pons-Brooks is currently in the constellation of Lyra Constellation.
ISRO's AstroSat (PTI)

- 28 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
India's AstroSat space telescope has achieved a significant milestone by detecting more than 600 Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB), each marking the death of a massive star or merging of neutron stars.
About ISRO’s AstroSat:
- AstroSat is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- One of the unique features of the AstroSat mission is that it enables the simultaneous multi-wavelength observations of various astronomical objects with a single satellite.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched by the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The minimum useful life of the AstroSat mission is expected to be 5 years.
- It carried a total of five scientific payloads, enabling imaging and studying the temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra-galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- The scientific objectives of AstroSat’s mission are:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
- At present, all the payloads are operational and are observing the cosmic sources.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) (Indian Express)

- 27 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
SEBI on Saturday decided to bring entities facilitating fractional investment in real estate under a regulatory framework, whereby they will be required to operate as Small and Medium Real Estate Investment Trusts.
About Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
- A Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) is a company that owns and typically operates income-generating real estate or related assets.
- It pools funds from investors, directing them into various commercial real estate ventures, including office buildings, shopping malls, apartments, hotels, resorts, self-storage facilities, warehouses, and mortgages or loans.
- In contrast to conventional real estate firms, REITs don't develop properties for resale; rather, they acquire and develop properties primarily for inclusion in their investment portfolio.
- REITs offer individual investors an opportunity to share in the income generated by commercial real estate without the need to directly purchase such properties.
- Typically specializing in specific real estate sectors, REITs may focus on diversified or specialty portfolios, encompassing various property types like office and retail spaces.
- Most REITs are publicly traded on stock exchanges, similar to stocks, providing high liquidity compared to physical real estate investments.
- This stock-like nature allows investors to buy or sell REIT shares on the exchange at any time.
Coming soon, a ‘Cafeteria’ for oil spill-hit birds at Ennore Creek (The Hindu)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Experts from the Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) and the Besant Memorial Animal Dispensary (BMAD) are planning to establish feeding stations for birds at the creek, where contamination due to an oil spill from industries in Manali has brought down the bird population drastically.
About Ennore Creek:
- Ennore Creek, situated in Thiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu, is a backwater channel branching off from the Kosathalaiyar River.
- It merges with the Bay of Bengal at Mugathwara Kuppam, while its northern channel links to Pulicat Lake, the country's second-largest brackish water lake.
- For generations, this creek has been a lifeline for communities in the neighbouring villages, designated as CRZ IV (Water Body) in the coastal zone management plan by the Tamil Nadu State Coastal Zone Management Authority.
- Its significance is heightened for local fisherfolk, alongside the Buckingham Canal and the broader Pulicat water system.
- The Ennore Creek has historically fostered a robust aquatic ecosystem renowned for its biodiversity.
- This ecologically sensitive area once boasted extensive mangrove swamps, contributing not only to sustainable fish resources but also playing a crucial role in flood mitigation during periods of heavy rainfall, high tides, and cyclones.
About the Wildlife Trust of India:
- Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) is an Indian Non-profit Organisation (NGO) committed to nature conservation.
- Motto: In Service of Nature
- It was formed in November 1998, in response to the rapidly deteriorating condition of the country's wildlife.
- Its mission is to:
- Conserve wildlife and its habitat and
- Work for the welfare of individual wild animals, in partnership with communities and governments.
- WTI has earned recognition for accomplishing significant conservation milestones, including the recovery of populations for critically endangered species, successful species translocation, and the mitigation of human-animal conflicts.
Deepfakes (TOI)

- 25 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The government has warned top social media and internet companies that their platforms may be temporarily suspended and even be ordered blocked in case they are unable to tackle the menace of deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- The term "deepfake" combines the concepts of deep learning with the fabrication of content.
- Deepfakes involve the creation of synthetic images and audio using machine-learning algorithms, intending to disseminate misleading content by replacing a real person's appearance, voice, or both with artificially generated likenesses or voices.
- These manipulated creations can either depict nonexistent individuals or simulate real people engaging in actions or utterances they never did.
- Originating in 2017, the word "deepfake" emerged when a Reddit user named "deepfakes" shared explicit videos featuring celebrities.
- The process of crafting deepfakes utilizes machine learning models employing neural networks to manipulate visual and auditory elements.
- To generate a convincing deepfake video, creators train the neural network on extensive real footage of the targeted person, facilitating a realistic understanding of their appearance from various angles and lighting conditions.
- This trained network is then combined with computer graphics to overlay the person onto a different actor.
- Regrettably, this technology is increasingly exploited for malicious purposes, including scams, celebrity impersonation, election interference, social engineering, disinformation attacks, identity theft, and financial fraud.
- The distinguishing factor of deepfakes lies in their challenging detection due to their sophisticated nature.
Black-spotted Croaker, or the Ghol Fish (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The black-spotted croaker, or the ghol fish — considered a fisherman’s lottery — was declared the state fish of Gujarat on Tuesday.
About Ghol Fish:
- The Ghol fish is a rare and valuable marine species known for its richness in essential nutrients such as iodine, omega-3, DHA, EPA, iron, taurine, magnesium, fluoride, and selenium.
- Habitat: Typically found in the Indo-Pacific region, stretching from the Persian Gulf to the Pacific Ocean, the Ghol fish thrives in the marine areas of Gujarat and Maharashtra in India, exhibiting a distinctive golden-brown color.
- Size and Price: With a length of around one-and-a-half meters, the Ghol fish's price increases with its size, reaching up to Rs 5 lakh per unit length.
- Referred to as 'Sea Gold,' the Ghol fish earns this moniker due to a pouch in its stomach with potent medicinal properties, making it highly valued in the overseas market.
- Health Benefits:
- Eye Health: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins, the Ghol fish contributes to maintaining eyesight.
- Anti-Ageing: The collagen content in the fish helps prevent wrinkles, preserving skin elasticity.
- Cognitive Development: The omega-3 content supports the growth of brain cells, enhancing the IQ of infants if consumed regularly.
- Muscle Toning: The fish is known for its muscle-toning properties.
- Economic Value: In high demand for both its meat and air bladder (sold separately), the Ghol fish serves various purposes, from culinary use to making beer and wine, with its air bladder finding applications in pharmaceuticals.
Psyche Mission (Indian Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A NASA experiment on the Psyche spacecraft has beamed back a near-infrared laser that contains test data from almost 16 million kilometers away.
About the Psyche Mission:
- Psyche is a NASA mission to study a metal-rich asteroid ‘Psyche’, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- The mission launched on October 13, 2023, from Kennedy Space Center and will arrive at Psyche in August 2029.
- The spacecraft will orbit the asteroid for about two years, studying its geology, composition, and magnetic field.
- Scientists believe that Psyche may be the exposed core of an early planet that never fully formed.
- If so, studying Psyche could provide important insights into the formation of our solar system.
- It is also the first in a series of NASA science missions to be the primary payload launched on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
- The goals of the Psyche mission are to:
- Understand the composition and structure of a metallic asteroid.
- Determine how Psyche formed and evolved.
- Learn more about the formation of planetary cores.
- The Psyche spacecraft is a solar-powered spacecraft that uses Hall effect thrusters for propulsion.
- The spacecraft also carries a suite of scientific instruments, including:
- A magnetometer to measure Psyche's magnetic field.
- A spectrometer to measure the composition of Psyche's surface.
- A gamma-ray spectrometer to measure the abundance of elements on Psyche's surface.
Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (Financial Express)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister announced the launch of two India-led initiatives: the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository and a Social Impact Fund aimed at promoting the development of Social Impact Fund to advance Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in the Global South during the Virtual G20 Leaders’ Summit on 22nd November 2023.
About the Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository:
- It was developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It is an extensive resource center that combines knowledge and insights from G20 members and visiting countries.
- Its primary objective is to fill the knowledge gap in the decision-making processes and methodologies necessary for designing, constructing, deploying, and governing Digital Public Infrastructures (DPIs).
- The GDPIR presents information in a standardized format from countries and organizations that have successfully implemented DPIs on a large scale.
- This includes elements such as maturity scales, source codes (where available), and governance frameworks.
- Currently, the GDPIR showcases 54 DPIs from 16 countries.
- The DPIs from India featured in the GDPIR include
- Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), eSanjeevani, Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), DigiLocker, Umang, Co-WIN, Government e-marketplace, API Setu, Diksha, E-Hospital and Poshan Tracker etc.
What about the Social Impact Fund?
- The fund will financially support countries developing DPIs, providing “upstream technical and non-technical assistance”.
- The platform allows other governments, international organisations, and philanthropies to contribute to the fund too.
- India has pledged an initial commitment of $25 million (USD) to the fund.
Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) (Financial Express)

- 23 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
The AIM and NITI Aayog have recently introduced a new accelerator known as Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) aimed at providing support to startups in the circular economy sector in both Australia and India.
About Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE):
- RISE, a collaborative initiative between Australia’s national science agency (CSIRO), and Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), the Government of India’s flagship initiative for fostering innovation and entrepreneurship, is a dedicated accelerator.
- This program is designed to support startups and small to mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) in India and Australia focusing on circular economy technologies and solutions.
Key Highlights:
- Focus Themes: The RISE Accelerator targets startups in India and Australia engaged in circular economy technologies, specifically in:
- Climate Smart Agriculture
- Clean Energy
- Circular Economy and Waste Management, and
- Climate Smart Mobility.
- Nine-Month Program: Over the course of nine months, the RISE Accelerator aims to assist startups in navigating early steps in a new region, establishing connections with the right partners, customers, and talent, and building credibility to succeed in international markets.
- First Round Focus: In its initial round, the accelerator concentrates on supporting startups and SMEs involved in technologies and solutions related to waste and the circular economy.
- Financial Support: Participating startups have the opportunity to receive up to INR 40,00,000 in non-equity grants.
- Future Rounds: Subsequent rounds of the accelerator will shift focus to climate-smart agriculture, clean energy, and climate-smart mobility.
Tantalum (Indian Express)

- 22 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
A team of researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Ropar has found the presence of tantalum, a rare metal, in the Sutlej river sand in Punjab.
What is Tantalum?
- Tantalum is a rare metal with the atomic number 73.
- Tantalum was first discovered by Anders Gustaf Ekenberg, a Swedish chemist, in 1802.
- It has been named after a Greek mythological figure Tantalus.
Properties:
- It’s grey, heavy, very hard, and one of the most corrosion-resistant metals in use today.
- It possesses high corrosion resistance because when exposed to air, it forms an oxide layer that is extremely difficult to remove, even when it interacts with strong and hot acid environments.
- When pure, tantalum is ductile, meaning it can be stretched, pulled, or drawn into a thin wire or thread without breaking.
- Moreover, it “is almost completely immune to chemical attack at temperatures below 150°C, and is attacked only by hydrofluoric acid, acidic solutions containing the fluoride ion, and free sulphur trioxide.
- Notably, tantalum also has an extremely high melting point, exceeded only by tungsten and rhenium.
Applications:
- Tantalum is most prominently used in the electronic sector.
- The capacitors made from tantalum are capable of storing more electricity in smaller sizes without much leakage than any other type of capacitor.
- This makes them ideal for use in portable electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and digital cameras.
- As tantalum has a high melting point, it is frequently used as a substitute for platinum, which is more expensive.
- The rare metal is also used to make components for chemical plants, nuclear power plants, aeroplanes, and missiles.
- Tantalum does not react with bodily fluids and is used to make surgical equipment and implants, like artificial joints.
SAT quashes Sebi's order against Kishore Biyani, and others (Live Mint)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) on Wednesday quashed regulator Sebi's order banning Future Retail chairperson Kishore Biyani and some other promoters from the securities market for one year in an insider trading case.
About the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT):
- Established as a statutory and autonomous entity under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Act, 1992, the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) serves as a crucial forum for adjudicating appeals against decisions made by SEBI or its adjudicating officers.
Key Functions:
- Appeals Jurisdiction: Primarily tasked with hearing appeals against orders issued by SEBI or its adjudicating officers under the SEBI Act.
- Extended Jurisdiction: Additionally, SAT entertains appeals concerning orders from the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) related to cases filed before them.
Composition:
- Presiding Officer: A retired or sitting Supreme Court judge, Chief Justice of a High Court, or a High Court judge with at least seven years of service.
- Judicial Member: High Court judge with a minimum of five years of service.
- Technical Member: Individual with expertise and a minimum of 15 years of experience in the financial sector, including securities market, pension funds, commodity derivatives, or insurance.
- This member can be a senior official in the Central or State Government or a person of proven ability and integrity.
Appointment and Tenure:
- Appointments made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India or its nominee.
- Presiding Officer and members serve a term of five years, eligible for reappointment for an additional term of up to five years.
- No member shall hold office after reaching the age of 70.
Powers and Authority:
- They are empowered with the same powers as a civil court under the code of civil procedure when adjudicating suits.
- Appeals to SAT can be made by any person aggrieved by SEBI or adjudicating officer orders, excluding those made with the consent of all parties.
Appeals Process:
- Appeals against SAT decisions can be filed in the Supreme Court, limited to questions of law.
- No appeal is permissible against orders made with the consent of all parties.
- The SAT, with its specific mandate and composition, plays a pivotal role in ensuring fairness and justice in the regulatory framework of the securities market in India.
What is Insider Trading?
- Insider trading is the act of buying or selling securities of a publicly traded company based on material information not yet disclosed to the public.
- Material information encompasses any data that could significantly influence an investor's decision to buy or sell the security.
- For instance, Consider a scenario where a government employee, possessing knowledge about an upcoming regulation that would favour a sugar-exporting company, takes advantage of this information by purchasing the company's shares before the regulation becomes public knowledge.
Dwarf Planet Eris (The Hindu)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, scientists have discovered the inside structure of the enigmatic dwarf planet Eris.
About Dwarf Planet Eris:
- This new dwarf planet is the largest object found in orbit around the sun since the discovery of Neptune and its moon Triton in 1846.
- It was discovered on Jan. 5, 2005, and It is larger than Pluto, discovered in 1930.
- Like Pluto, the new dwarf planet is a member of the Kuiper belt, a swarm of icy bodies beyond Neptune in orbit around the sun.
- Eris is named for the ancient Greek goddess of discord and strife.
- The surface of Eris is extremely cold, so it seems unlikely that life could exist there.
- With a radius of about 1,163 kilometers, Eris is about 1/5 the radius of Earth.
- Eris, like Pluto, is a little smaller than Earth's Moon.
- Eris takes 557 Earth years to make one trip around the Sun.
- As Eris orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 25.9 hours, making its day length similar to ours.
- Moons: Eris has a very small moon called Dysnomia.
- Dysnomia has a nearly circular orbit lasting about 16 days.
- Eris most likely has a rocky surface similar to Pluto.
- Atmosphere: The dwarf planet is often so far from the Sun that its atmosphere collapses and freezes, falling to the surface as snow.
- As it gets closest to the Sun in its faraway orbit, the atmosphere thaws.
Wasp-107b (TOI)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
In its latest discovery, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has discovered a planet "Wasp-107b" where specks of sand fall as rain.
What is “Wasp-107b”?
- WASP-107b is a warm exoplanet with Neptune’s mass and Jupiter’s radius.
- This makes it ‘fluffy’ compared to the giant gas planets in our Solar System.
- This unusual size-to-mass ratio has given astronomers a unique opportunity to probe its atmosphere roughly 50 times deeper than more dense planets like Jupiter.
- This gas giant, often referred to as a "super-Neptune," holds several remarkable characteristics that set it apart from other known exoplanets.
Key Characteristics of WASP-107b:
- Size and Mass: WASP-107b is roughly the size of Jupiter, but with only about 12% of Jupiter's mass.
- This makes it one of the least dense exoplanets ever discovered.
- Orbit and Proximity: WASP-107b orbits its host star, WASP-107, very closely, completing an orbit in just 5.7 days.
- It is located about 200 light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo.
- Sand Rain: WASP-107b exhibits a unique water cycle similar to Earth's, but with a peculiar twist: instead of water droplets, the planet experiences sand rain.
- These sand grains, composed of silicates, rise from lower atmospheric levels and condense into clouds before falling back down.
- Atmosphere: WASP-107b possesses a puffy atmosphere, likely due to its low density.
- In 2018, scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope detected helium in its atmosphere, marking the first detection of this element in an exoplanet's atmosphere.
- Potential for Atmospheric Characterization: WASP-107b's large size and proximity to its star make it a promising target for future atmospheric characterization studies.
- Scientists hope to glean more insights into the composition and dynamics of its atmosphere.
One Station One Product’ scheme (New Indian Express)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian Railway has established more than a thousand outlets in railway stations across the nation under its ‘One Station One Product’ (OSOP) initiative which aimed at providing a platform for skilled artisans to sell their indigenous products.
About One Station One Product’ (OSOP):
- The OSOP scheme is a unique initiative by the Indian Railways and aims to provide livelihood opportunities through skill development to local artisans, potters, weavers, and craftsmen.
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- The scheme, designed by the National Institute of Design, Ahmedabad, provides distinctive outlets that give high visibility to indigenous products, benefiting local craftsmen.
- Railways allot the outlets at its stations through a tendering process.
- The scheme’s outreach measures include advertising, social media, public announcements, press notifications, and personal visits to artisans.
- The products at these outlets range from artifacts and handicrafts to textiles and traditional appliances, indigenous to the region, and are crafted by local artisans or tribals.
- They also include locally made or grown food products in processed or semi-processed forms.
- It provides uniquely designed sale outlets for locals to sell indigenous products, and is now operational at 1,037 stations nationwide.
GPS Anklets (Indian Express)

- 14 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
For the first time in India, a prisoner in J&K has been given bail on the condition that his movements are monitored constantly.
About GPS Anklets/Tracker:
- The GPS tracker is a compact wearable gadget secured around the ankle, offering real-time location details.
- It is designed to be tamper-proof, triggering an alarm if any attempt is made to interfere with it.
- Removal by the wearer or any unauthorized individual without causing damage is virtually impossible.
- This versatile tracker can be attached to either the ankle or the arm, presenting as GPS anklets or GPS bracelets.
- While commonplace for bail conditions in countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Malaysia, this marks the inaugural use of GPS trackers for this purpose in India.
What is GPS?
- GPS, or the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system with a global reach.
- It functions through a network of satellites orbiting Earth, transmitting signals to GPS receivers.
- This technology has revolutionized navigation, offering precise location and time information for diverse applications, from driving to hiking.
- Originally developed for military purposes, GPS is now widely used in civilian life, integrated into smartphones for location-based services and emergency response.
- Its applications extend to real-time tracking of vehicles and assets, contributing to enhanced security and efficient management.
- Ongoing advancements ensure that GPS remains a crucial tool in modern navigation.
Exercise ‘CORPAT’ And ‘Bongosagar’ (NewsOnAir)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Exercise CORPAT and BONGOSAGAR between the Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy were conducted in the Northern Bay of Bengal from 07 - 09 Nov 2023.
About Exercise CORPAT and Bongosagar:
- The 4th edition of the Bilateral Exercise between the Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy, BONGOSAGAR-23, and the 5th edition of Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT) by the two navies were held at Visakhapatnam.
- Ships and aircraft from both navies undertook joint patrolling along the International Maritime Boundary Line and maritime exercises to enhance interoperability.
- Indian Navy Ships Kuthar, Kiltan, and Maritime Patrol Aircraft (MPA) Dornier participated in the exercise.
- The ships undertook communication drills, surface gun-shoots, tactical maneuvers, and other exercises.
- INS Kuthar is an indigenously built guided-missile Corvette, whereas INS Kiltan is an indigenously built anti-submarine Corvette.
- Both ships are part of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet based at Visakhapatnam, which functions under the operational command of the FOCINC ENC.
- CORPAT-23 also included the maiden Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief drills held between the two navies.
- The bilateral exercises and coordinated patrols have strengthened mutual understanding and cooperation between the two navies.
India-OPEC Energy Dialogue (PIB)

- 13 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 6th High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue took place on 9 November 2023, at the OPEC Secretariat in Vienna, Austria
Highlights of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue 2023:
- The 6th High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue took place on November 9th, in Vienna, Austria.
- The Meeting was co-chaired by HE Haitham Al Ghais, Secretary General of OPEC, and Hardeep Singh Puri, Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas and Minister of Housing and Urban Affairs of India.
- Discussions revolved around ensuring availability, affordability, and sustainability in energy markets, emphasizing India's crucial role in global economic growth and energy demand.
- The 6th High-Level Meeting concluded with both parties underscoring the importance of fostering enhanced cooperation between India and OPEC moving forward.
- It was agreed to hold the next High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue during the course of 2024 in India.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries(OPEC):
- OPEC, or the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent international organization comprising oil-exporting nations.
- Its core mission is to coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- This coordination aims to stabilize oil prices in global markets, working towards eliminating harmful and unnecessary price fluctuations.
- It was established in 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela, OPEC has since expanded to include 13 members.
- Member countries are Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela.
- With the addition of another 11 allied major oil-producing countries including Russia, the grouping is known as OPEC+.
- The organization's headquarters is located in Vienna, Austria.
Phreatomagmatic Eruptions (TOI)

- 11 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently a new island emerged near Japan's Ogasawara island chain after an undersea volcano erupted.
What is Phreatomagmatic Eruption?
- A phreatomagmatic eruption is a volcanic eruption caused by the interaction of magma and water.
- They differ exclusively from magmatic and phreatic eruptions.
- Unlike phreatic eruptions, the products of phreatomagmatic eruptions contain juvenile (magmatic) debris.
- Large explosive eruptions typically contain magmatic and phreatomagmatic components.
- Phreatomagmatic ash is formed by the same mechanism over a wide range of basic and acidic compositions.
- A blocky and uniform crust with low vesicle content is formed.
- Deposits from phreatomagmatic eruptions are thought to be better classified and finer-grained than those from magmatic eruptions.
- This is the result of higher fragmentation of phreatomagmatic eruptions.
About Ogasawara Islands:
- The Ogasawara Islands are a group of more than 30 small subtropical islands in the North-Western Pacific Ocean roughly 1,000 km south of the main Japanese Archipelago.
- It is also known as the Bonin Islands.
- It is one of the famous UNESCO World Heritage sites of Japan.
First Prehistoric Pictorial Cave Art Found in Madagascar Offers Clues Regarding Ancient Connections Between Borneo, Egypt (The Hindu)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, distinctive prehistoric rock art depictions were unearthed within the Andriamamelo Cave in western Madagascar.
Key Discoveries:
- Within this cave's truly pictorial art, human-like and animal-like figures depicting scenes from nature have been revealed.
- The remarkable findings unveiled surprising cultural connections, with some scenes directly linking to Egyptian religious motifs from the Ptolemaic period (300-30 BCE).
- Additionally, symbols and inscriptions on the cave walls indicated connections to the Ethiopian and Afro-Arab regions.
- Furthermore, the prevalent symbology and motifs echoed a cave art style from Borneo dating back two millennia.
- Notably, depictions within the cave may include three extinct animals of Madagascar — a giant sloth lemur, an elephant bird, and a giant tortoise.
- The potential connection to Egypt is suggested by eight significant images, including representations of a falcon (Horus), the bird-headed god Thoth, the ostrich goddess Ma`at, and two human-animal figures resembling Anubis, the ancient Egyptian god typically portrayed with a canine head.
About Andriamamelo Cave:
- The Andriamamelo Cave is situated in western Madagascar, nestled within the karstified limestone of the Paysage Harmonieux Protege de Beanka.
- This cave is a component of a vast karst region that encompasses the UNESCO World Heritage site, Parc National de Bemaraha, to the south, and the less-explored Antsingimavo karst area to the north.
INDUS-X Initiative (Financial Express)

- 09 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
On the eve of the India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, the inaugural INDUS-X Investors Meet was held in New Delhi.
What is the INDUS X Initiative?
- The INDUS-X initiative, also known as the India-U.S. Defense Acceleration Ecosystem, was launched in June 2023 during the State Visit of the Prime Minister of India to the United States.
- Its primary objective is to expand the strategic technology partnership and defense industrial cooperation between the governments, businesses, and academic institutions of India and the United States.
- INDUS-X is envisioned as a defense innovation bridge, encompassing Joint Challenges, a Joint Innovation Fund, academia engagement, industry-startup connections, private sector investment in defense projects, mentorship by experts, and niche technology projects, among other initiatives.
- This collaborative effort holds the promise of ushering in a new era of defense innovation and cooperation between India and the United States.
About INDUS X Investors Meet:
- The first-ever INDUS-X Investors Event brought all the stakeholders including Startups, Investors, Incubators, and Industry from both sides under one roof to discuss the collaborative agendas and opportunities thereon.
- The event also had focused panel discussions with a select audience of 50 thought leaders, including start-ups, investors, government officials, and business leaders from the defence industry.
- The panel discussed ‘Investment Opportunities in the Defence Sector’, elaborating upon establishing a sustainable commercial foundation for defence collaboration and co-production.
- The INDUS-X Educational Series (Gurukul) was also launched during the event.
- The Gurukul initiative is aimed at helping innovators and startups to navigate the defence eco-system of the US and India.
Scientists find hydrogen cyanide, a key molecule for life formation, in Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus (Sci News)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, planetary scientists have detected several compounds of strong importance to the habitability of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, including hydrogen cyanide, acetylene, propylene and ethane, using data from NASA’s Cassini mission.
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest icy moon of Saturn. It has a white, streaky surface made of water ice.
- Beneath this frozen crust lies a warmer, salty ocean that covers the whole moon.
- This circular moon is just about 500 km wide, with a surface temperature of -200°C.
- But its interiors host several sources of energy and heat.
- Enceladus is tugged and pulled in all directions by Saturn’s gravity and the gravity of other more massive moons, thus creating heat in its interior.
- Its rocky core may also be undergoing radioactive decay and chemical reactions that generate heat.
- Moreover, it is also an active source of water volcanism, where giant plumes of water, ice, dust, and gases are ejected into space like volcanic explosions.
- The material from the plumes replenishes one of the rings of Saturn as well, as the icy particles that make up the rings slowly drift inwards and get pulled into Saturn.
- The presence of a global saltwater ocean with nutrients and a heat source suggests a suitable aquatic environment for life.
- However, no life has been found on Enceladus or anywhere else beyond Earth.
About Hydrogen cyanide:
- Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N.
- It presents itself as a colourless or pale-blue liquid or gas, characterized by a bitter, almond-like fragrance.
- Alternatively referred to as hydrocyanic acid or HCN, this substance has the potential to disrupt the body's oxygen utilization, posing risks to the brain, heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
- While Hydrogen cyanide boasts excellent solvent properties for numerous salts, its utilization as a solvent is limited due to its inherent toxicity.
- In various industrial settings, it finds application in tasks such as fumigation, electroplating, mining, chemical synthesis, and the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides.
World Local Production Forum (WLPF) (PIB)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian delegation led by Shri Bhagwant Khuba, Union Minister of State for Chemicals and Fertilizers participated in the Second World Local Production Forum (WLPF) held in Hague, Netherlands.
About the World Local Production Forum (WLPF):
- The World Local Production Forum (WLPF) is an initiative by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The inaugural WLPF took place virtually in 2021.
- Main Objective: The core aim of this forum is to enhance access to essential medicines and other health technologies.
- Role and Function: The WLPF serves as a regular platform for Member States and the global community to collaboratively develop strategies, mobilize collective efforts, and establish partnerships.
- These actions are directed towards promoting sustainable local production, ensuring timely and equitable access to high-quality health products.
- Secretariat: The Local Production and Assistance (LPA) Unit at the WLPF is responsible for overseeing the forum's activities.
- Second WLPF Goals: The second WLPF has several key objectives:
- To create a global platform for discussions addressing the primary challenges related to local production and technology transfer.
- To explore opportunities and mechanisms for overcoming obstacles in this regard.
- To champion sustainable local production capabilities that lead to improved access to safe, effective, and high-quality health products and technologies.
ENCORE (NewsOnAIR)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Election Commission of India (ECI) has developed in-house software named ‘ENCORE’ designed for efficient candidate and election management.
About ‘ENCORE’:
- The Election Commission of India has designed in-house software for complete Candidate and election management through ‘ENCORE’ which stands for Enabling Communications on Real-time Environment.
- This provides a seamless facility for Returning Officers to process candidate nomination, affidavit, Voter turnout, counting, results and data management.
- The ENCORE counting application is an end-to-end application for returning officers to digitize the votes polled, tabulate the round-wise data and then take out various statutory reports of counting.
- An additional application, the ENCORE Scrutiny Application, allows Returning Officers to scrutinize online nominations submitted by candidates.
- This process involves verifying and marking the status of nominations as Accepted, Rejected, or Withdrawn, facilitating the creation of the final list of contesting candidates and symbol assignment.
- The ECI offers an online portal for candidate nomination and affidavit submission.
- Candidates can create accounts, complete nomination forms, submit security deposits, and plan their visits to the Returning Officer through this portal.
- The Candidate Affidavit portal is designed to display information about a candidate's financial assets and liabilities, offering transparency in candidates' financial disclosures.
- The ENCORE Nodal App serves as a platform for various government departments, including fire, education, police, environment, and CPWD, to issue 'no objection' certificates.
- These certificates are required before granting permission for political parties or candidates to hold rallies, road shows, and meetings, ensuring that all necessary clearances are obtained before public events.
Bletchley Declaration 2023 (Indian Express)

- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The United Kingdom hosted a major Artificial Intelligence (AI) meeting, bringing together political leaders and technological professionals to explore the potential benefits and risks of this fast-evolving technology.
About the Bletchley Declaration:
- The Bletchley Declaration provides a comprehensive overview of the worldwide perspective on the potential benefits and risks associated with artificial intelligence (AI).
- It underlines the necessity of aligning AI systems with human intentions and encourages a deeper exploration of AI's full capabilities.
- Furthermore, the document acknowledges the potential for significant harm caused by AI, whether intentional or unintentional, including the possibility of catastrophic consequences.
- The Bletchley Declaration places great emphasis on safeguarding human rights, promoting transparency, ensuring explainability, upholding fairness, ensuring accountability, establishing regulation, prioritizing safety, incorporating human oversight, adhering to ethical standards, addressing bias issues, safeguarding privacy, and protecting data.
- This document is a reflection of the intricate negotiations between nations with differing interests and legal systems, encompassing countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, the European Union, and China.
- The Bletchley Declaration highlights the crucial role of civil society in addressing AI safety concerns, despite some criticism from civil society groups that felt excluded from the summit.
- It also places a significant responsibility on companies engaged in the development of cutting-edge AI systems, emphasizing the need to ensure their safety through rigorous testing, evaluation, and the implementation of appropriate measures.
Food versus Fuel: What’s happening with Centre’s ethanol blending scheme (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After banning sugar exports, the Centre has taken the next step towards augmenting domestic availability – restricting the diversion of the sweetener for ethanol production.
What is the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme?
- The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) programme was launched in January 2003.
- The programme sought to promote the use of alternative and environment-friendly fuels and to reduce import dependency for energy requirements.
- Effective from April 1, 2019, across the nation (excluding UTs of Andaman Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands), Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) sell petrol blended with up to 10% ethanol.
- The average ethanol blending in petrol has surged from 1.6% in 2013-14 to 11.8% in 2022-23.
- India targets a 20% ethanol blending ratio by 2025, revised from the initial 2030 deadline per the NITI Aayog's roadmap.
- Benefits of the EBP Programme:
- Reducing India’s import bill.
- Mitigating environmental pollution.
- Augmenting farm income.
- Offering a biofuel option with minimal additional investment for manufacturers.
- Challenges for 20% Ethanol Blending:
- Engine modifications are required to process petrol blended with 20% ethanol.
- Ethanol combustion yields no CO2, yet it doesn't address nitrous oxide emissions.
- Concerns about inefficient land use in ethanol production and the substantial water demand for cultivating crops.
- Food security considerations due to uncertainties about future agricultural output.
Why is the Restriction on Sweetener Diversion for Ethanol Production Imposed?
- Sugar Supply Concerns: Closing the 2022-23 sugar year with stocks slightly exceeding 57 lakh tonnes (lt), the lowest since 2016-17 (39.4 lt), raises apprehensions.
- The stock level falls significantly below the peak of 143.3 lt in 2018-19.
- Uncertainties surround the sugar production for the ongoing 2023-24 year, with Maharashtra and Karnataka anticipating substantial declines due to insufficient rainfall and low reservoir water levels in key cane-growing regions.
- Key Implication of the Decision: The recent decision, coupled with the ban on sugar shipments since May 2023, underscores a clear priority.
- Governments emphasize domestic supply over exports, favouring consumers over producers and prioritizing food over fuel.
Strategies to Boost Ethanol Production without Compromising Food Security:
- Diversification of Feedstocks: The government's ethanol policy, marked by favourable pricing and the incorporation of alternative feedstocks such as 2G ethanol sources, has been instrumental.
- The historical dependence on sugarcane-based feedstocks, which constituted 100% of ethanol sources (reduced to 76% in 2022-23), is no longer the sole reliance of the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program.
About Ethanol:
- Ethanol, an anhydrous ethyl alcohol having the chemical formula of C2H5OH, can be produced from sugarcane, maize, wheat, etc which have high starch content.
- In India, ethanol is mainly produced from sugarcane molasses by fermentation process.
- Ethanol can be mixed with gasoline to form different blends.
- As the ethanol molecule contains oxygen, it allows the engine to more completely combust the fuel, resulting in fewer emissions and thereby reducing the occurrence of environmental pollution.
- Since ethanol is produced from plants that harness the power of the sun, ethanol is also considered a renewable fuel.
Calling for caution, PM flags need for ethics, democratic values in AI (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document on the proper use of AI, the guardrails for the technology, and how it can be democratised.
Context:
- India is currently hosting the 4th Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi, scheduled from December 12-14, 2023.
- The first three GPAI summits were held in Montreal, Paris and Tokyo, respectively.
- Prime Minister Modi emphasized the dual nature of AI, portraying it as a significant development tool for the 21st century but also highlighting potential risks.
- He called for a global framework to ensure responsible AI use and urged caution in deployment.
- Addressing concerns like deepfakes, cybersecurity, and cyber-terrorism, he proposed an audit mechanism categorizing AI tools based on their capabilities.
- PM Modi is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document outlining proper AI use, technology guardrails, and democratization.
- Recognizing AI's role in economic growth, he announced India's upcoming AI mission, focusing on AI computing power for startups and innovators, with applications in agriculture, health, and education.
- The mission aims to extend AI skills to Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- PM Modi stressed ethical AI use as a guiding principle and suggested the inclusion of development and deployment protocols for high-risk AI systems in the global framework.
- He underscored AI's potential for connecting people and envisioned its ethical use in promoting economic growth, equality, and social justice.
About the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit:
- The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit is a three-day event starting December 12, which will see representatives from 28 member countries and the European Union.
- India is the Lead Chair for the alliance in 2024.
- The founding members of the GPAI: are Australia, Canada, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, Slovenia, the UK, the US, and the EU.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the summit on December 12.
- The objective of this summit is to bridge the gap between theory and practice on AI by supporting cutting-edge research and applied activities on AI-related priorities.
- It will feature a number of seminars covering a wide range of subjects, including AI and global health, education and skill development, AI and data governance, and machine learning workshops.
- More than 150 speakers from various nations will be present at the summit, including more than fifty GPAI experts.
- Moreover, leading global AI innovators such as Intel, Google, Meta, Microsoft, etc will be taking part in these events.
- Additionally, start-ups and students who win under the YUVA AI programme will present their AI models and solutions.
Missiles from rebel territory in Yemen miss a ship near key Bab el-Mandeb Strait, US official says (TOI)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Two missiles fired by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
Context:
- Two missiles fired from territory held by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the key Bab el-Mandeb Strait on Wednesday.
- An American warship also shot down a suspected Houthi drone flying in its direction during the incident.
- The ship was carrying Indian-manufactured jet fuel and was heading for either Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
- It was coming from Mangalore in southern India and had an armed security crew on board.
- The Houthis have carried out a series of attacks on vessels in the Red Sea and launched drones and missiles targeting Israel.
About Bab el-Mandeb Strait:
- The Bab-el-Mandeb is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa.
- It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait is a chokepoint between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East and is a strategic link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is one of the world's most important routes for global seaborne commodity shipments, particularly crude oil and fuel.
- The Perim Island divides the strait into two channels, of which the eastern is known as the Bab Iskender (Alexander's Strait), while the western is known as Dact-el-Mayun.
What is the Horn of Africa?
- The Horn of Africa, the world's fourth-largest peninsula, is located in Northeast Africa, extending eastwards from the African mainland and bordered by the Red Sea, Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean.
- Positioned equidistantly from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer, it encompasses diverse landscapes, including the Ethiopian Plateau, Ogaden desert, and Eritrean and Somalian coasts.
- The Horn of Africa includes the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- This region has experienced historical complexities, including imperialism, neo-colonialism, the Cold War, ethnic tensions, intra-African conflicts, poverty, disease, and famine.
In a monthly report, the IEA projected that India's oil product demand growth would slow to 2.5% next year from 4.1% in 2023. (ET)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA) said recently that the "explosive growth" in Indian oil product consumption may be coming to an end.
About International Energy Agency:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an autonomous intergovernmental organization founded in 1974 in Paris, France.
- Its primary focus revolves around energy policies, emphasizing economic development, energy security, and environmental protection, collectively known as the '3 E’s of IEA.'
- The IEA Clean Coal Centre is dedicated to providing independent information and analysis on making coal a cleaner energy source in line with UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Originating in response to the oil crisis of 1973-1974, the IEA's mandate has evolved to include tracking global energy trends, advocating sound energy policies, and fostering international energy technology cooperation.
- Mission: The IEA's mission is to ensure reliable, affordable, and clean energy for its member countries and beyond.
- Focus Areas: Key focus areas include energy security, economic development, environmental awareness, and global engagement.
- The IEA collaborates closely with non-member countries, particularly major producers and consumers, to find solutions to shared energy and environmental concerns.
- IEA’s Membership: The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
- It also includes eight association countries. Four countries are seeking accession to full membership, Chile, Colombia, Israel and Lithuania.
- A candidate country to the IEA must be a member country of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership Criteria:
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- These reserves, accessible to the government even if not directly owned, should be readily deployable to address disruptions in the global oil supply.
- Demand Restraint Program: Candidates are required to implement a demand restraint program aimed at reducing national oil consumption by up to 10%.
- Emergency Response Capability: Member countries must have legislation and organizational frameworks in place to operate Coordinated Emergency Response Measures (CERM) on a national basis.
- Transparent Reporting: Legislation and measures should be established to ensure that all oil companies under the jurisdiction of the candidate country promptly report information upon request.
- Collective Action Capability: Measures must be in place to guarantee the country's capability to contribute its share in collective actions initiated by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- India joined this organization in 2017 as an Associate member.
- However, in 2021, the International Energy Agency (IEA) invited India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, to become its full-time member.
- Major reports published by the IEA include the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report, World Energy Statistics, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, and the India Energy Outlook Report.
State Food Safety Index (SFSI) (Indian Express)

- 02 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) published the State Food Safety Index in which 15 out of 20 states recorded lower 2023 scores compared to 2019.
About the State Food Safety Index:
- Since 2019, FSSAI has released the State Food Safety Index (SFSI) each year on June 7 on the occasion of World Food Safety Day.
- SFSI scores are given out of a total of 100 points that are calculated based on five parameters with different weightages:
- Human Resources and Institutional Data
- Compliance
- Food Testing Infrastructure
- Training and Capacity Building
- Consumer Empowerment.
- In the 2023 index, a new parameter called ‘Improvement in SFSI Rank’ was added, which assesses improvement in each state’s rank from the year before.
- The primary goal of this index is to ensure that citizens have access to safe and nutritious food.
- This index is a dynamic and comprehensive system that offers an objective way to assess food safety across all states and UTs.
- States and UTs are categorized into three groups: large states, small states, and UTs, for evaluation and comparison.
Key findings from the report:
- 19 out of 20 large states — including Maharashtra, Bihar, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh — recorded a drop in their 2023 scores from 2019.
- The most substantial drop was observed in the 'Food Testing Infrastructure' category, with states like Maharashtra, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh receiving lower scores in this aspect.
- Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Jharkhand also had reduced scores in the 'Compliance' category.
- In the 2023 index, the 'Human Resources and Institutional Data' category was given the third-highest importance, accounting for 18% of the evaluation (it was 20% in previous years).
- The only category that showed notable improvement was 'Training and Capacity Building,' which was given the least importance, 8%, in the 2023 index (compared to 10% in previous years).
Samudrayaan (IndiaToday)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
India's ambitious Samudrayaan project, aimed at exploring the deep ocean and its resources, is set to send three personnel to a depth of 6000 meters in a submersible vehicle.
About Samudrayaan Project:
- India's inaugural manned mission to delve into the depths of the ocean for exploration.
- Its primary objectives include studying deep ocean resources and conducting biodiversity assessments.
- The mission is designed to ensure minimal disturbance to the ecosystem, focusing solely on exploration.
- Part of the comprehensive Deep Ocean Mission aligned with the Central Government's Blue Economy policy.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) leads the implementation of this ambitious, multi-institutional endeavor.
What is the Blue Economy?
- Blue economy refers to the sustainable use of marine resources for exploration, economic growth, improved livelihoods, and transport while preserving the health of marine and coastal ecosystems.
- In India, the blue economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including shipping, tourism, fisheries, and offshore oil and gas exploration.
Here to enhance partnership between EFTA, India: Norway's trade minister (Business Standard)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Norway's Minister of Trade and Industry Jan Christian Vestre has said his India visit aims to enhance collaboration between European free trade partners and India and improve framework conditions for job creation, value creation, and investments.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1960 by the Stockholm Convention.
- Its core objective is to foster free trade and economic integration among its member countries, both within Europe and on a global scale.
- Member Countries: EFTA comprises four member countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland.
- These nations are characterized by open, competitive economies, demonstrating a shared commitment to progressively liberalize trade both within multinational forums and through individual free trade agreements.
- Customs Distinction: Unlike the European Union (EU), EFTA operates differently as it is not a customs union.
- This key distinction allows each EFTA State the autonomy to establish its own customs tariffs and formulate foreign trade measures independently concerning non-EFTA States.
- Association Responsibilities:
- EFTA manages various aspects crucial to its objectives, including:
- Facilitating free trade among EFTA countries.
- Overseeing EFTA's engagement in the European Economic Area (EEA), encompassing the European Union and three EFTA countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, excluding Switzerland).
- Managing EFTA's extensive network of free trade agreements globally.
- Free Trade Agreement Network: EFTA member countries boast one of the largest networks of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) globally.
- This comprehensive network spans over 60 countries and territories, incorporating the European Union among others.
EFTA plays a pivotal role in promoting economic collaboration, free trade, and global engagement, distinguishing itself from the EU through its approach to customs and foreign trade measures.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between two or more nations aimed at lowering barriers to imports and exports among them.
- In a free trade scenario, goods and services can move across international borders with minimal government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or restrictions hindering their exchange.
- The principle of free trade stands in contrast to trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs come in various forms, including Preferential Trade Agreements, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements, and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPA).
India is expected to withstand global shocks as its current account deficit improves due to falling crude oil prices. (ET)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After two years of battling inflation and growth pangs, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was in for a pleasant surprise when the economic growth trumped its expectations to hit 7.2 per cent in the last month.
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has unveiled its most recent monetary policy report, projecting a robust economic recovery for the country in the current fiscal year.
- Anticipating a significant upswing, the central bank foresees the gross domestic product (GDP) to expand by 7 percent in 2021-22, a notable rebound from the 7.3 percent contraction witnessed in the preceding year.
- However, the RBI issues a cautionary note about the challenges posed by inflation, which has consistently exceeded the target range of 2-6 percent over several months.
- The report attributes inflationary pressures to supply-side disruptions, escalating commodity prices, increased fuel taxes, and demand-related factors.
- The RBI anticipates inflation to remain elevated in the short term before gradually moderating in the latter half of the year.
- The RBI's stance mirrors a delicate equilibrium, emphasizing the intricate balance between fostering economic growth and managing inflation, often characterized as the Goldilocks Effect.
- This effect alludes to a scenario where the economy is neither excessively overheated nor excessively sluggish but rather poised for optimal growth with minimal inflationary pressures.
What is the Goldilocks Effect?
- The Goldilocks Effect, also known as the Goldilocks Principle, posits that individuals have a predisposition to seek an amount that is 'just right' for their specific needs or preferences.
- This concept, derived from the children's story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears, reflects a preference for options that are neither too extreme nor too moderate, falling within an optimal and desirable range.
- This principle finds application across various fields and disciplines, encompassing psychology, hard sciences, economics, marketing, and engineering, each incorporating its unique interpretation of the principle.
- Goldilocks Pricing: One notable application of the Goldilocks Effect is in Goldilocks Pricing, a psychological pricing strategy grounded in concepts such as product differentiation, comparative pricing, and bracketing.
- Product differentiation involves distinguishing certain products from others, a crucial step for businesses looking to leverage the Goldilocks Effect.
- This differentiation is then coupled with comparative pricing, where businesses simultaneously offer multiple versions of a product with varying quality levels attached to corresponding price points.
- The strategy hinges on providing three options: one priced too high for most, one priced too low for most, and one priced just right.
- When executed effectively, this approach enables businesses to appeal to diverse segments of the market, capturing premium buyers, standard consumers, and discount seekers.
Amit Shah to chair 26th meeting of Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar on Sunday (Business Standard)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah will chair the 26th meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar's capital on Sunday, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) said on Saturday.
What are Zonal Councils?
- The conceptualization of Zonal Councils can be attributed to the visionary initiative of India's first Prime Minister, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru, in 1956.
- These councils are statutory bodies established by an Act of Parliament, namely the States Reorganisation Act of 1956.
- The act delineated the country into five zones (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern), assigning a Zonal Council to each.
Present Composition of Zonal Councils:
- Northern Zonal Council: Includes Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, National Capital Territory of Delhi, and Union Territory of Chandigarh.
- Central Zonal Council: Encompasses Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Eastern Zonal Council: Comprises Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, and West Bengal.
- Western Zonal Council: Involves Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
- Southern Zonal Council: Consists of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Exclusion and Special Council: The North Eastern States (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Nagaland) are not part of Zonal Councils.
- Instead, their unique challenges are addressed by the North Eastern Council, established under the North Eastern Council Act of 1972.
- Sikkim was included in the North Eastern Council in 2002.
Organizational Structure:
- Chairman: The Union Home Minister serves as the Chairman for each Zonal Council.
- Vice Chairman: Chief Ministers of the states in each zone act as Vice-Chairman, rotating annually.
- Members: Chief Minister and two nominated Ministers from each state, along with two members from Union Territories in the zone.
- Advisers: Planning Commission nominees, Chief Secretaries, and another officer/Development Commissioner from each state in the zone.
Objectives:
- The primary objectives of Zonal Councils include promoting national integration and curbing acute State consciousness, regionalism, linguism, and particularistic tendencies.
- Additionally, they aim to facilitate cooperation, idea exchange, and a climate of collaboration among states for the successful execution of development projects.
Functions:
- Zonal Councils function as advisory bodies, empowered to discuss common interests between the Union and represented states.
- They can recommend courses of action to the Central Government and individual state governments.
- Specific areas of discussion may include economic and social planning, border disputes, linguistic minorities, inter-state transport, and matters arising from the reorganization of states under the States Reorganisation Act.
Navy plans to get undersea chariots, made in India, for special operations (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is planning to acquire indigenously made swimmer delivery vehicles — also known as underwater chariots and midget submarines — as part of efforts to modernise and strengthen the capabilities of its Marine Commandos (MARCOS) for special undersea operations.
News Summary:
- In a strategic move, the Indian Navy set to deploy domestically manufactured undersea chariots for specialized operations.
- These innovative vessels, designed to accommodate a crew of at least six, will be equipped with cutting-edge lithium-ion batteries for enhanced performance.
- The significant size of these undersea chariots opens up new possibilities, allowing divers to transport larger cylinders.
- This advancement translates to extended underwater missions, thereby amplifying operational capabilities in shallow waters.
- Moreover, the spacious design of these chariots facilitates the carriage of extra weaponry, providing the Navy with increased flexibility for diverse and complex operations.
- This development signifies a noteworthy stride in bolstering the Navy's underwater capabilities through indigenous technological advancements.
What are Chariots?
- Nearly all modern navies in the world use chariots, which are extremely specialized platforms.
- These self-propelled vehicles can be deployed from ships or submarines, tailored to their size and designated roles.
- Notably, during World War II, manned human torpedoes were commonly referred to as chariots.
- Functionality: Chariots prove invaluable for naval operations in shallow waters, offering a spectrum of missions.
- These include shallow-water surveillance, targeted assaults on adversary coastal installations, and even engagements with ships in harbours.
- Particularly advantageous is their ability to grant marine commandos access to areas close to adversary harbours—locations that submarines, constrained by shallow waters, may find challenging to reach.
- Furthermore, these chariots facilitate the efficient transportation of weapons and equipment to operational zones.
- Utilization in India: While detailed information on the swimmer delivery vehicles employed by the Indian Navy is not widely available, some sources suggest the utilization of Italian-made chariots for several years.
- Around 2012, recognizing the strategic importance of these platforms, the Ministry of Defence entrusted Hindustan Shipyard Limited with the construction of two such submarines, underscoring India's commitment to enhancing its maritime capabilities.
What are Marine Commandos (MARCOS)?
- The Marine Commandos, known by the acronym MARCOS and formally recognized as the Marine Commando Force (MCF), stand as the specialized forces within the Indian Navy entrusted with the execution of special operations.
- Established in February 1987, MARCOS possesses versatile capabilities to operate effectively across diverse environments, encompassing sea, air, and land.
- Over time, the force has accumulated valuable experience, earning an esteemed international reputation for its high level of professionalism.
- MARCOS routinely engage in specialized maritime operations in regions such as Jammu and Kashmir, navigating the Jhelum River and Wular Lake with precision and expertise.
PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Schemer (Indian Express)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry has recently announced a fresh target for its PM SVANidhi scheme, focusing on empowering street vendors.
About PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme:
- Launched on June 01, 2020, by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the PM SVANidhi Scheme aims to assist street vendors affected by the Covid-19 lockdown in reviving their livelihoods.
- As a micro-credit initiative, it provides street vendors with a collateral-free loan of Rs. 10,000 at a low-interest rate (below 12%) for one year, facilitating their financial recovery.
- Originally scheduled until March 2022, the scheme has now been extended till December 2024 with a focus on expanding the affordable loan corpus, encouraging digital transactions, and promoting holistic socio-economic development for street vendors and their families.
- Eligibility for the loan requires street vendors who were vending on or before March 24, 2020, and hold a certificate of vending issued by the Town Vending Committees (comprising local authorities and vendors) after conducting a survey.
- The scheme offers several benefits, including an interest subsidy of 7% per annum on timely loan repayment, no penalty on early repayment, cash back incentives up to Rs. 100 per month to promote digital transactions, and the possibility of credit limit escalation for prompt loan repayment.
- The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) serves as the implementation agency for the scheme, ensuring efficient delivery and monitoring of financial support to street vendors across the country.
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) (Indian Express)
- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Telangana High Court's division bench recently conveyed its discontentment over the absence of specific information regarding measures taken to manage the outbreak of Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) in cattle.
What is Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD):
- Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a highly infectious viral disease that affects cattle, ranging from acute to chronic in nature.
- It is caused by the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV), belonging to the genus Capripoxvirus within the poxviridae family (related to smallpox and monkeypox viruses), but it is not zoonotic, meaning it does not spread to humans.
- Symptoms of LSD include the enlargement of lymph nodes, resulting in lumps on the cattle's skin, primarily appearing on the head, neck, limbs, udder, genitalia, and perineum.
- The cutaneous nodules, usually 2–5 cm in diameter, may develop into ulcers and scabs over time.
- Other signs of infection include high fever, reduced milk yield, nasal and ocular discharge, salivation, loss of appetite, depression, damaged hides, emaciation, infertility, and abortions.
- Transmission occurs through blood-feeding insects such as certain flies, mosquitoes, and ticks, as well as the movement of affected animals and contaminated equipment.
- Direct animal-to-animal transmission can also occur in some cases.
- While no direct antiviral treatment is available for LSD, supportive care is provided to infected animals, including the use of antibiotics, painkillers, and wound care sprays to alleviate symptoms.
- Vaccines are used to control disease transmission, as there is no specific cure.
- LSD is economically significant as it can lead to temporary reductions in milk production, temporary or permanent sterility in bulls, hide damage, and, in some instances, fatalities among the affected cattle population.
Worldcoin Project (The Hindu)

- 31 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent announcement, the CEO of OpenAI officially reintroduced his Worldcoin project, which had previously taken a backseat to the widespread popularity of ChatGPT.
What is Worldcoin Project?
- The Worldcoin Project aims to establish a digital network that enables everyone to participate and claim some form of stake in the digital economy.
- The project operates on a straightforward model:
- Individuals can prove their uniqueness as humans by allowing their eyes to be scanned, and in return, they receive a cryptocurrency reward and an identification called a "World ID."
- Worldcoin relies on a device called "Orb," which is used by volunteers known as "Orb operators."
- These operators scan a person's iris pattern to collect their biometric data and facilitate the issuance of a World ID through the World app.
- Participants who have been scanned can use the World app to receive the Worldcoin cryptocurrency at regular intervals or engage in transactions using their World ID wherever applicable.
- This process, known as "proof of personhood," ensures that individuals cannot register multiple times to gain more crypto rewards.
Rare ‘Ureilite’ Meteorite (Weather Channel)

- 27 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, a team of scientists from Allahabad University and the University of Bern, Switzerland, made an intriguing discovery. They unveiled that the Dhala crater was formed by the impact of an exceedingly uncommon and ancient meteorite called Ureilite.
Key Facts About Ureilite:
- Ureilite is an extraordinary type of meteorite, characterized by its rarity, making up only a minuscule portion of the meteorites found on Earth.
- The name "Ureilite" originates from the location of its first discovery, the Novo Urei village in Russia.
- Composition:
- Ureilites are primarily composed of silicate rock, with olivine and pyroxene being the dominant minerals.
- They also contain a smaller fraction of carbon, which can be in the form of either diamond or graphite, along with metal sulphides and a few fine-grained silicates.
- Elongated cavities are commonly found, typically oriented in the same direction.
- Lack of Chondrules:
- Unlike many other stony meteorites, ureilites do not contain chondrules, which are small, spherical grains that formed in the early solar system.
- Primitive Nature:
- Ureilites are regarded as primitive meteorites because their composition closely resembles the material from which the solar system originated.
- Their unique characteristics offer valuable insights into the early stages of our cosmic environment.
About Dhala Crater:
- Dhala Crater holds significance as India's oldest and largest impact crater, with an estimated formation age of approximately 2500 million years.
- Named after the village Dhala, it remains an eroded remnant of the original impact structure.
- Situated in the Shivpuri district of Madhya Pradesh, the crater boasts an impressive size, spanning a massive 11 km in diameter, making it the largest impact crater in Asia.
INDIAai (ET)

- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
In a recent development, INDIAai and Meta India entered into a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to create a collaborative framework for cooperation and partnership in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) and emerging technologies.
About INDIAai:
- INDIAai, the National artificial intelligence Portal of India, was launched on 28th May 2020 as a comprehensive platform.
- It serves as a knowledge portal, research organization, and ecosystem-building initiative.
- Its primary aim is to foster unity and encourage collaborations within India's AI ecosystem by bringing together various entities.
- This joint initiative is supported by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), and NASSCOM.
- NeGD, established in 2009 under the Digital India Corporation (a not-for-profit company set up by MeitY), plays a crucial role in this venture.
- NASSCOM, a prominent not-for-profit industry association, serves as the apex body for India's IT and IT-enabled products and services sector.
- INDIAai functions as the central knowledge hub for artificial intelligence and related fields, catering to aspiring entrepreneurs, students, professionals, academics, and all other stakeholders in the domain.
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science: It involves the development of intelligent machines that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence.
- Machine Learning and Algorithms: AI systems utilize machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of data, learn from it, and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
- Applications in various fields: AI finds applications in diverse domains, including natural language processing, image recognition, robotics, healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles, among others. Its goal is to mimic human cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, reasoning, and decision-making.
Hike in US Federal Reserve Interest and Impact on Indian Economy (Live Mint)
- 26 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
The US Federal Reserve is expected to raise benchmark rates by 25 bps to the 5.25-5.50 percent range on Wednesday. Investors will be watching for cues on inflation and rate hike trajectory.
About US Federal Reserve:
- The US Federal Reserve, also known as the Fed, serves as the central banking system of the United States, offering a secure, adaptable, and steady monetary and financial framework.
- It operates through 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks, each responsible for a designated U.S. geographic area.
- The Fed's primary functions encompass conducting national monetary policy, overseeing and regulating banks, ensuring financial stability, and delivering banking services.
Impacts of US Federal Reserve Interest Hike:
- The US Fed's Significance: As the world's most powerful central bank, the decisions taken by the US Federal Reserve regarding interest rates have significant implications worldwide. These decisions influence both developed and emerging economies across the globe.
- Global Effects: Changes in US interest rates have a ripple effect that extends beyond the nation's borders. The adjustments impact various economies worldwide, leading to shifts in investment patterns and financial flows.
- Appeal of American Assets: When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, American assets become more attractive to investors seeking higher returns. Consequently, there is a possibility of capital outflows from emerging and riskier markets to the US.
- Impact on Capital-Intensive Sectors: Sectors heavily reliant on Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs) are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of a US interest rate hike. The increased cost of borrowing may affect their growth prospects.
- Global Liquidity Tightening: Higher US interest rates can lead to a tightening of global liquidity. Foreign investors may face challenges in obtaining affordable funds, which could have implications for their investment decisions and overall economic activities.
Potential Impacts on the Indian Economy:
- Interest Rate Differential: Following a rate hike by the US Federal Reserve, the gap between interest rates in the US and India narrows, adversely affecting currency trade and financial flows.
- Foreign Investor Response: With higher returns available in the US due to increased interest rates and attractive Dollar and US Treasury yields, foreign investors may be inclined to withdraw investments from the Indian market, leading to capital outflows.
- Currency and RBI Response: The relative strengthening of the US currency (Dollar) makes the Indian rupee weaker, prompting the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to consider a rate hike domestically.
- RBI's Action to Curb Outflows: To mitigate the outflows of funds from Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) and safeguard the rupee's stability, the RBI may find it necessary to increase interest rates within India.
- Forex Reserve Management: In the event of a significant decline in the rupee's value, the RBI might be compelled to sell some of its Dollar reserves to support the domestic currency. This action, however, depletes the country's foreign exchange reserves.
NanoPtA (The Hindu)
- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science's Materials Research Centre (MRC) have recently created a novel enzyme mimic known as NanoPtA.
About NanoPtA:
- The research team at the Materials Research Centre (MRC), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), has created a unique platinum-based nanozyme called NanoPtA.
- This nanozyme can be turned into a powder for use in industries.
- When NanoPtA encounters wastewater, the molecule's benzene rings and long alkyl chains engage in multiple non-covalent interactions.
- Individual NanoPtA molecules link together to form tape-like structures that emit light, which is the source of its oxidizing capability.
- In the presence of sunlight, this nanozyme can break down pollutants in wastewater, reducing its toxicity.
- Remarkably, the nanozyme can rapidly degrade even small amounts of common contaminants like phenols and dyes (micromolar levels) within ten minutes when exposed to sunlight.
- The researchers also observed that the NanoPtA complex remained stable for up to 75 days at room temperature.
Applications:
- Besides wastewater treatment, this nanozyme could find applications in healthcare and serve as a valuable diagnostic tool for neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.
Yak Churpi (TOI)

- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Arunachal Pradesh, a northeastern state, achieved a noteworthy milestone as the distinctive and culturally important yak milk product known as 'Yak Churpi' has received the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About 'Yak Churpi':
- Yak Churpi is a special dairy product crafted from the milk of the indigenous Arunachali yak breed.
- It's produced by Brokpas, tribal yak herders who migrate with their yaks to higher altitudes (above 10,000 ft) during summers and return to mid-altitude mountainous areas in winters.
- These exceptional yaks are primarily found in the West Kameng and Tawang districts of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Churpi is a naturally fermented dairy item with a high protein content.
- It plays a vital role in the diets of tribal communities living in the cold, mountainous regions of the state.
- It's often used as a vegetable substitute and is a common ingredient in vegetable and meat dishes, frequently enjoyed with rice.
- The GI tag for Yak Churpi has significant benefits, including the conservation of yaks and the improvement of the socio-economic status of yak herders.
- Arunachali yaks are unique in terms of their body characteristics, size, strain, and weight, making them the only registered yak breed in India.
Bojjannakonda (The Hindu)

- 05 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, the Central government allocated 7.30 crore rupees to undertake landscaping and develop tourist amenities at the Bojjannakonda site.
About Bojjannakonda:
- Bojjannakonda is situated in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- It was excavated by Alexander Rim in 1906.
- Originally known as ‘Buddhuni konda’ (meaning hill of the Buddha), it eventually came to be known as ‘Bojjannakonda’ over time.
- Approximately 2,000 years ago, Buddhist monks used this hill for their practices.
- During excavations, various artifacts were unearthed, including a gold coin from the Samudra Gupta period, copper coins from the Chalukya king Kubja Vishnu Vardhan, coins from the Andhra Satavahanas, and pottery.
- Bojjannakonda is unique as it reflects features of all three phases of Buddhism: Hinayana, Mahayana, and Vajrayana.
- Notable discoveries at the site include a figure of ‘Kalabhairava’ with the head of Lord Ganesha adorned with conch shells and the statue of a Buddhist monk named ‘Harati.’
- There is a large double-storeyed cave on the hill with a rectangular doorway flanked by 'dwarapalakas' on both sides.
- At its center stands a rock-cut stupa on a square platform.
- The northern side of the hill features a series of rock-cut caves and monolithic structures on rock platforms.
- The upper cave has a rectangular doorway, with Buddha figures on either side.
- The prominent attractions for tourists at Bojjannakonda are the imposing figures of the Buddha seated in a meditative posture and the stupa.
- At the hill's summit, there are structural buildings and a vihara (monastery), which are now in ruins.
- To the west of Bojjannakonda lies another hillock called Lingalakonda or Lingalametta, where several monolithic and structural stupas can be found.
- Interestingly, the structures on Lingalametta served as inspiration for the Buddhist temple at Barabodur in Java.
- Similarities between the caves at Bojjannakonda and those in Takshasila suggest Buddhist influences, although the word ‘Sangrama’ was used in Takshasila but not in Andhra Pradesh.
Basohli Pashmina is Recognized with GI Tag (HT)

- 04 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Basohli Pashmina, a traditional craft with over a century of history from the Kathua district in Jammu and Kashmir, has been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Basohli Pashmina:
- Basohli Pashmina is renowned for its exceptional softness, fineness, lightweight quality, insulation, and durability.
- Pashmina products include shawls, mufflers, blankets, and baskets.
- Pashmina is a premium variety of cashmere, obtained from the fine undercoat of the Changthangi mountain goats.
- These goats are found on the Changthang Plateau in Tibet and parts of Ladakh.
- The Changpa people, who are nomads living on the Changthang plateau of Tibet, are traditional producers of pashmina wool.
Sanwariya Seth Temple (PIB)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Prime Minister recently visited and paid his respects at the Sanwariya Seth Temple located in Chittorgarh, Rajasthan.
About Sanwariya Seth Temple:
- Sanwariya Seth Temple is a Hindu place of worship dedicated to Lord Krishna, particularly in his cherished child form known as “Sanwariya Seth” or “Shyam Seth."
- Location: Situated in the village of Mandaphia, Chittorgarh district, Rajasthan.
- Historical Origin: The temple dates back to its construction in the year 1840 A.D.
- Architectural Marvel:
- The temple embodies the quintessential Rajasthan architectural style, renowned for its intricate carvings, distinctive domes, and vivid color palette.
- The primary temple structure is crafted from pristine white marble.
- Elaborate carvings grace the walls, pillars, and ceilings, illustrating scenes from Hindu mythology and an array of motifs.
- Multiple ornate domes adorn the temple, enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
- The temple boasts a prominent spire, or 'shikhar,' which soars above the central sanctum.
- Sanctum Sanctorum: Inside the temple's innermost chamber rests a black stone idol of Lord Krishna.
- Welcoming Spaces: The temple offers expansive, pillared halls that serve as communal gathering areas for devotees and visitors alike.
Sela Tunnel Project (Times of India)
- 02 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The officials from BRO (Border Roads Organization) recently announced that they have almost finished about 96 percent of the work on the strategically important Sela Tunnel. It's expected to be officially opened by the end of this year.
About Sela Tunnel Project:
- Location: Situated in the West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- When it's finished, the Sela tunnel will be the world's longest two-lane tunnel, located at an altitude above 13,000 feet.
- Its purpose is to provide year-round connectivity between Guwahati in Assam and Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh.
- This tunnel is being constructed underneath the Sela Pass as part of NH-13, a segment of the Trans-Arunachal Highway system.
- The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is responsible for its construction under Project Vartak, which began on April 1, 2019.
- Project Details:
- Tunnel 1: This tunnel is 980 meters long and has a single tube.
- Tunnel 2: A two-lane tunnel that spans 1555 meters, equipped with an emergency escape tunnel.
- Roads: The road leading to Tunnel 1 is 7100 meters long, the road connecting the two tunnels is 1340 meters long, and the road leading to Tunnel 2 is 340 meters in length.
CARBON NANOFLORETS (The Hindu)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Carbon nanoflorets made by IIT Bombay researchers can convert incident sunlight to heat with 87% efficiency.
Facts About:
Carbon nanoflorets (NCFs) are a newly discovered type of carbon nanostructure that resembles tiny marigold flowers.
- They are made up of a network of carbon nanotubes arranged in a conical microcavity structure. NCFs have a number of unusual properties, including:
Broadband absorption: NCFs can absorb sunlight at all wavelengths, from ultraviolet to infrared.
- This is because their conical microcavity structure traps light for a longer period of time, allowing it to be absorbed by the carbon nanotubes.
- They are also extremely black, absorbing more than 95% of sunlight across a broad spectrum of wavelengths.
High light-heat conversion efficiency: NCFs can convert sunlight to heat with an efficiency of up to 87%.
- This is much higher than the efficiency of other solar-thermal materials, such as photovoltaic cells.
Low thermal conductivity: NCFs have a very low thermal conductivity, which means that they can efficiently convert sunlight to heat without losing much of the energy to conduction.
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) reported that NCFs could convert incident sunlight to heat with an efficiency of 87%.
- This is significantly higher than the efficiency of other solar thermal materials, such as black carbon.
- It effectively absorbs over 97 per cent of sunlight's ultraviolet, visible, and infrared components, converting them into thermal energy.
- The resulting heat can be efficiently transferred to either air or water for practical applications.
- Research reveals that NCFs can raise the temperature of the surrounding air from room temperature to 60 degrees Celsius, providing smoke-free space-heating solutions.
NASA-ISRO SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR (NISAR) (TOI)
- 29 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The 'NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar' (NISAR) is set to enable the investigation of how changes in Earth's forest and wetland ecosystems affect the worldwide carbon cycle and exert an influence on climate change.
Facts About:
- NASA and ISRO collaborated to develop the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observatory known as NISAR.
It's about the size of an SUV and weighs 2,800 kilograms.
- It is a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite, having both L-band and S-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instruments.
- The first satellite mission to measure variations in the surface of our planet will be NISAR, which will use two distinct radar frequencies (L-band and S-band).
No matter the weather, SAR can gather data day or night and penetrate clouds to gather information.
- NASA has contributed GPS, an L-band radar, a payload data subsystem, and a high-capacity solid-state recorder for data storage.
ISRO on the other hand supplied the S-band radar, as well as the GSLV launch system and spacecraft.
- Additionally, it has a sizable 39-foot stationary antenna reflector with an upward-facing feed on the instrument structure that will be used to focus "the radar signals emitted and received."
The reflector is constructed of gold-plated wire mesh.
- The mission's objectives are to measure the dynamic surfaces, ice masses, and changing ecosystems of Earth in order to gather data on groundwater, biomass, natural hazards, and sea level rise.
- NISAR is going to perform global 12-day regular observations of Earth's land and ice-covered surfaces during ascending and descending passes.
SATELLITE INTERNET TECHNOLOGY (Indian Express)
- 28 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
Reliance Jio recently declared that it had effectively tested the first gigabit internet service in India, based on satellite technology.
Facts About:
- Satellite Internet operates in a way similar to satellite TV.
- It begins with an internet service provider launching satellites into space to orbit the Earth.
These satellites, placed in low- or high-Earth orbit, transmit a signal.
- A receiver dish, positioned in your home or business, captures this signal.
It should have an unobstructed view of the sky.
- You connect a modem to this dish to convert the received signal into usable internet connectivity.
- High-speed satellite internet is typically delivered through constellations of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- LEO satellites orbit the planet at altitudes ranging from 250 to 2,000 kilometers.
- Communication between these satellites and Earth occurs using radio waves.
Advantages of Satellite Internet:
- Satellite Internet is ideal for users residing in rural or remote areas, far from urban centers or cable/phone offices.
- It relies on a satellite dish for two-way communication and doesn't require telephone cables or lines.
- When compared to other internet options, satellite internet experiences fewer or minimal network outages.
ANCIENT LANDSCAPE UNEARTHED BENEATH ANTARCTIC ICE SHEET (Space.com)
- 26 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A new study finds that beneath East Antarctica's undulating ice sheet lies an ancient, river-carved landscape that provides a perfect snapshot of the region before glaciers covered the continent.
Facts About:
- In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have unveiled an ancient, hidden world beneath the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, offering a correction to the traditional perception of a frozen wasteland.
This revelation reshapes our understanding of Antarctica's history and environmental conditions.
- This newly discovered landscape, believed to have been shaped by rivers over 14 million years ago, predates the initial formation of the East Antarctic ice around 34 million years ago.
- This ancient terrain comprises valleys and ridges that are strikingly reminiscent of the glacially-altered landscape in North Wales, UK, signifying the long-term temperature stability of the ice sheet in the studied region.
- The recent discovery builds upon the team's prior work, which revealed concealed mountain ranges, canyons, and lakes beneath the Antarctic ice.
The researchers suggest that additional undiscovered ancient landscapes may remain hidden under the East Antarctic Ice Sheet.
- This discovery underscores the significance of ongoing exploration and research in this largely uncharted territory, emphasizing that there is much more to uncover beneath the ice.
- This revelation prompts a re-evaluation of the conventional perception of Antarctica, demonstrating that it has a rich geological history dating back millions of years.
TRIBAL COOPERATIVE MARKETING DEVELOPMENT FEDERATION (TRIFED) (PTI)
- 23 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Union Tribal Affairs Ministry on Saturday declared "null and void" the suspension of the managing director of TRIFED.
Facts About:
The Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation (TRIFED) is a national-level organization operating under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Its primary focus is on the development and marketing of tribal handicrafts and natural products.
Established in 1987, it became registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 1984 (now the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002).
TRIFED's main objectives include enhancing the capabilities of tribal communities, promoting their products, and creating marketing opportunities to ensure better prices for tribal products, ultimately improving their income sustainably.
Some of its key goals are:
- Enhancing the socio-economic welfare of tribal communities.
- Facilitating and providing services to improve production within tribal communities.
- Offering training to enhance artistic skills using modern technology, making tribal products more competitive in the global market.
- Promoting tribal art and crafts to provide a stable livelihood.
- Identifying target groups, monitoring activities, and providing input to the Ministry.
Under retail marketing, TRIFED is responsible for marketing of tribal products under the brand name "TRIBES INDIA."
It promotes and establishes a sustainable market through retail outlets, exhibitions like Aadishilp, Aadichitra, and OCTAVE, international fairs, and e-marketing.
The Government of India has also entrusted TRIFED with the implementation of the Minimum Support Price Scheme for Minor Forest Produce.
Headquarter: New Delhi
It continues to operate a system of Regional Offices throughout India and a collection of TRIBES INDIA Retail Outlets.
e-Cabinet System (Indian Express)
- 29 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Tripura inaugurated an e-cabinet system in Agartala, aimed at advancing digital infrastructure and enhancing the digitization of government services and information.
Facts About:
- The e-Cabinet system is a robust software portal designed for State Governments to facilitate electronic and online Cabinet meetings.
- It has been developed by the National Information Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY).
- Tripura is now the fourth state, and the second in the Northeast region, to implement the e-cabinet system, following in the footsteps of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Key Features:
- Enhances the utilization of technology in meetings and reduces paper consumption.
- Streamlines workflow activities for meetings, covering pre-meeting, during the meeting, and post-meeting phases.
- Offers a user-friendly interface designed for smart tablets, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Incorporates a secure push and pull mechanism to safeguard sensitive Cabinet matters.
- Establishes an institutional memory and knowledge repository, facilitating quick searches and retrieval of information.
- For virtual meetings, eCabinet seamlessly integrates with the Bharat VC solution of NIC.
Benefits and Impact of eCabinet:
- Substantial savings in paper, fuel, and manpower resources.
- Real-time data updates.
- Enhanced information accessibility, promoting coordinated actions.
- Improved decision-making processes and swift retrieval of meeting decisions and action taken.
- Enables virtual participation of Ministers in Cabinet proceedings.
Emerging Markets Bond Index (Down to Earth)
- 26 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Bhopal (IISER Bhopal) pinpointed a particular circular RNA (circRNA) named 'ciTRAN.' This circRNA plays a vital role in the replication of the HIV-1 virus, which causes AIDS, inside the human body.
Facts About:
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a molecule found in living cells that carries genetic instructions and aids in protein production.
- Most RNAs have a linear, open-end structure, but circular RNA, known as 'circRNA,' forms a closed loop.
- CircRNA plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and is essential for various biological processes.
- Its involvement in the replication of HIV-1 was not well understood for a long time.
- Identifying circular RNA can be challenging because it is typically present in lower amounts, making it harder to detect in its natural form.
- During viral infections, the abundance of viral genetic material can make it difficult to isolate less common components like circular RNA.
Emerging Markets Bond Index (Indian Express)
- 25 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
JP Morgan Chase & Co will add Indian government bonds to its emerging markets bond index starting in June 2024.
Facts About:
- This index serves as a benchmark for measuring how well international government and corporate bonds from emerging market countries perform.
These countries must meet specific liquidity and structural requirements.
- Emerging market bonds are debt instruments issued by developing nations.
They usually offer higher yields compared to bonds from developed countries.
- A total of 23 Indian Government Bonds (IGBs) with a combined notional value of $330 billion are eligible for inclusion.
They are all categorized as "fully accessible" for non-residents.
- Advantages of this inclusion:
This development is expected to lead to higher demand for the Indian rupee, potentially protecting it from depreciation.
Lower borrowing costs could support important infrastructure projects.
Increased liquidity may result in more efficient trading conditions.
- India's local bonds will become part of JP Morgan's Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) index.
- They are expected to make up a maximum of 10 percent of the GBI-EM Global Diversified Index (GBI-EM GD).
International Organisation of Legal Metrology (OIML) (Indian Express)
- 16 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Secretary of the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs announced that India has achieved the status of being an OIML certificate-issuing authority.
Facts About:
- OIML, short for the International Organisation of Legal Metrology, was established in 1955 as an international body.
- Its primary role is to develop model regulations, standards, and related documents that are used by legal metrology authorities and industry worldwide.
- OIML plays a vital part in aligning national laws and regulations concerning the accuracy of measuring instruments such as clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analyzers, radar speed measuring devices, ship tanks at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India joined the OIML in 1956 and simultaneously signed the metric convention.
- Headquartered in Paris, France.
Interbank Call Money Market (ET)
- 11 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The RBI is considering launching a pilot program for a central bank digital currency (CBDC) specifically designed for interbank borrowing or the call money market.
Facts About:
- The Interbank Call Money Market is a short-term financial market where big institutions borrow and lend money to each other at interbank rates, which are the interest rates banks charge when they borrow from one another.
- The loans in this market are very short, typically lasting only a week or less.
- These loans are often used by banks to meet their reserve requirements.
- It's not just banks that use this market; other participants can include financial institutions, mutual funds, large corporations, and insurance companies.
Competition Commission of India (CCI) (TOI)
- 08 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Competition Commission of India has recently unveiled preliminary rules for overseeing mergers and acquisitions involving significant India-based operations, particularly those in the technology sector, thereby extending the authority of the antitrust regulator.
Facts About:
- CCI is a government-established statutory body founded in March 2009 under the Competition Act, 2002.
- The primary objective of CCI is to foster fair competition in the economy, ensuring a level playing field for producers and promoting market dynamics that benefit consumers.
- The Commission's key focus areas include eradicating practices detrimental to competition, fostering and maintaining competitive environments, safeguarding consumer interests, and upholding the freedom of trade in India's markets.
Mandate: CCI enforces the provisions of The Competition Act, 2002, which:
- Prohibits anti-competitive agreements and the abuse of dominant positions by enterprises.
- Regulates mergers and acquisitions (M&A) that could potentially harm competition within India. Hence, deals exceeding certain thresholds require clearance from CCI.
- Monitors the activities of large enterprises to ensure they do not misuse their 'dominant position' by controlling supply, setting high purchase prices, or engaging in unethical practices that may harm emerging businesses.
Composition: CCI functions as a quasi-judicial body, consisting of one chairperson and six additional members, all appointed by the Central Government.
Headquarters: The Commission is headquartered in New Delhi.
One-hour Trade Settlement (Indian Express)
- 07 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which previously stated its intention to introduce real-time settlement of trades in July, is now considering implementing one-hour settlement of trades as the initial step.
Facts About:
In a one-hour settlement, when an investor sells a share, the money will be deposited into their account within an hour, and the buyer will have the shares in their demat account within an hour.
Trade settlement is a process that involves the transfer of funds and securities on the settlement date.
- It's considered complete when the purchased securities from a listed company are delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the money.
- Previously, trade settlements followed the T+1 cycle, meaning they occurred within one day or 24 hours of the actual transactions.
This changed in January 2023 when India shifted to the T+1 settlement cycle, making it the second country globally, after China, to adopt this cycle for top-listed securities.
Umiam Lake (ET)
- 04 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Meghalaya government has just started using advanced AI-powered robots to ensure that Umiam Lake, a popular tourist destination, remains clean and free from pollution.
Facts About:
Umiam Lake, also known as Barapani Lake, is located 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) north of Shillong, the capital of Meghalaya.
- This beautiful lake is surrounded by the lush green hills of East Khasi and covers an expansive 10 square kilometers.
The history of Umiam Lake dates back to 1965 when a dam was built to generate hydroelectric power as part of the Umiam Umtru Hydroelectric Power Project, marking the lake's inception.
The primary source of water for the lake is the confluence of two streams, Umkhrah and Umshvrpi, which merge to form the Wah Ro-ro stream in the northwest of the town.
- This stream then joins the River Umiam, ensuring a steady flow of water into the lake.
The catchment area for the lake and dam extends over 220 square kilometers, encompassing not only Shillong but also its neighboring regions.
- Umiam Lake has gained popularity as a hub for water sports and adventure activities, making it a favorite destination for thrill-seekers and nature enthusiasts alike.
Seethakali folk art (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 20-member group is going to perform Seethakali folk art, outside Kerala for the first time as to revive one of the fading dance forms of Kerala.
Facts About:
- In the early times, Seethakali was performed as part of the harvest festival Onam.
- From Atham star till the 28th day after Onam, the performers who belong to the subaltern communities go from one house to another performing this art.
Key Features of Seethakali:
- Folk Dance Drama: Seethakali is a traditional folk dance drama that was once performed during the festival days in erstwhile Desinganad (Kollam, Kerala), primarily during the Onam festivities.
- Dalit Artists: The performance was carried out by Dalit artists belonging to the Veda and Pulaya communities, focusing on presenting episodes from the Ramayana from Sita’s perspective.
- Vanayatra to Andardhanam: Seethakali portrays the journey from “vanayatra” (exile to the forest) to “andardhanam” (descend into the earth) of Sita, featuring a blend of songs, storytelling, and fast movements.
- Instruments: The dance drama is accompanied by instruments such as ganjira, manikatta, chiratta, and kaimani.
- Narrative through Songs: Seethakali’s story is conveyed through songs, with 28 collected over three years, featuring a folk style influenced by Vallappaattu, Kuthirappaattu, and Rakshasappattu.
- Oral Tradition: Seethakali songs were orally transmitted from one generation to the next, which led to a pause in the tradition.
- Basic Movements: The dance involves basic steps, striving to preserve the original essence of the art form.
- Character Ensemble: The performance includes key characters such as Sita, Ram, Lakshman, Ravan, and Hanuman.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/artistes-breathe-a-new-life-into-seethakali-folk-art/article67234768.ece
Insurance Surety Bonds (PIB)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)is advocating for the adoption of surety bond insurance products for highway projects
Facts About:
These bonds can be defined in their simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act.
These are instruments where insurance companies act as ‘Surety’ and provide the financial guarantee that the contractor will fulfil its obligation as per the agreed terms.
Surety is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement.
The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal: The party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety: The insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee: The party who requires and often receives the benefit of the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organisation.
What are the advantages?
- It will act as a security arrangement for infrastructure projects and will insulate the contractor as well as the principal.
- The product will cater to the requirements of a diversified group of contractors, many of whom are operating in today’s increasingly volatile environment.
- The product gives the principal a contract of guarantee that contractual terms and other business deals will be concluded in accordance with the mutually agreed terms.
- In case the contractor doesn’t fulfil the contractual terms, the Principal can raise a claim on the surety bond and recover the losses they have incurred.
- Unlike a bank guarantee, the Surety Bond Insurance does not require large collateral from the contractor, thus freeing up significant funds for the contractor, which they can utilise for the growth of the business.
- The product will also help in reducing the contractors’ debts to a large extent, thus addressing their financial worries.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1951715
20th ASEAN India Economic Ministers’ Meeting (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India participated in the 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting.
Facts About:
- The 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ meeting was held in Semarang, Indonesia.
- The Economic Ministers or their representatives from all the 10 ASEAN countries viz. Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam participated in the meeting.
- The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste also joined the Meeting as an observer.
- The Ministers reviewed the bilateral trade and investment relations between India and ASEAN and underscored their commitment to strengthen and enhance the economic partnership between India and ASEAN to ensure that the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership delivers meaningful benefits for both sides, particularly in the post-pandemic era.
- The Ministers also interacted with the ASEAN-India Business Council (AIBC).
- The main agenda of this year’s meeting was the timely review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) which was signed in 2009.
- India and ASEAN registered a bilateral trade of USD 131.5 billion in 2022-23. The trade with ASEAN accounted for 11.3% of India’s global trade in 2022-23.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- AITIGA is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009. The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products and not services trade.
ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
Along with the ASEAN-India Investment Agreement, the three agreements collectively form the ASEAN-India Free Trade Area.
- Under the Agreement, ASEAN and India have committed to progressively eliminating duties on 76.4 percent of goods and to liberalize tariffs on over 90 percent of goods.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1950902#:~:text=Shri%20Rajesh%20Agrawal%2C%20Additional%20Secretary,%2C%20Minister%20of%20Trade%2C%20Indonesia.
Vegetated Canopies (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In a recent development in Spain, tensioned sail-like vegetated awnings or canopies known as “Greenshades” have been strategically installed on the facades of buildings.
Facts About:
- Vegetated canopies are innovative structures designed to reintroduce greenery into urban landscapes.
- Inspired by the natural canopies found in forests and diverse plant ecosystems, these canopies play a crucial role in mitigating the urban heat island effect and enhancing the overall environmental quality of urban areas.
- This installation approach not only adds an aesthetic dimension to the urban architecture but also serves as a practical solution for reintroducing green elements in areas where traditional planting is challenging.
Emulating Nature’s Canopies:
- Mimicking the canopy formations observed in forest ecosystems, these vegetated awnings recreate a semblance of natural green cover.
- By doing so, they provide shade, reduce direct sunlight exposure, and create a more pleasant atmosphere in commercial streets and public spaces.
- This is particularly valuable in areas where the presence of trees and vegetation is limited.
Hydroponic Growth System:
- The vegetation integrated within these awnings grows using a hydroponic growth system.
- This method utilises a water supply point to provide the plants with the necessary moisture and nutrients. Additionally, a water outlet is incorporated into the design to facilitate efficient drainage.
- This innovative approach ensures that the greenery thrives even in non-traditional planting environments.
BENEFITS OF VEGETATED CANOPIES
Cooling Effects via Evapotranspiration
- Singular Green’s innovative canopy design efficiently reduces temperatures in both immediate areas and beneath the awnings.
- Achieved through evapotranspiration, where plants transfer water to the atmosphere, this cooling process enhances comfort.
Air Quality Improvement through Plant Selection
- Carefully chosen plants possess a special ability to absorb gases, including pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide.
- This contributes to better urban air quality and healthier living conditions.
Noise Reduction with Sound Wave Absorption
- Vegetated canopies excel at absorbing sound waves, minimising noise pollution and creating a more serene urban environment.
- Incorporating sound-absorbing substrates enhances the auditory experience.
Oxygen Generation and Gas Filtration
- Surprisingly, a single square metre of these canopies produces a year’s worth of oxygen for an individual.
- Moreover, they serve as natural filters, removing harmful gases from the air and thus improving overall air quality.
Efficient Water and Lighting Integration
- Beyond their green benefits, these canopies facilitate centralised water and lighting installations.
- Integrated lights equipped with motion sensors respond to real-time needs, promoting energy-efficient urban infrastructure.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
- Introducing these canopies into urban spaces fosters biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse wildlife.
- This initiative aligns with the vision of sustainable, nature-friendly cities, nurturing a harmonious urban ecosystem.
In the face of climate change-induced challenges, our response must be proactive, multifaceted, and holistic. The success of vegetated canopies as a means to combat extreme heat waves demonstrates that nature-inspired solutions have the power to transform urban environments into havens of sustainability, resilience, and well-being. By embracing such strategies and embarking on a collective journey, we can build cities that thrive in harmony with the planet.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/vegetated-canopies-green-spaces-urban-spain-8893918/
Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket (Economic Times)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Chennai-based start-up AgniKul Cosmos, has commenced the process of integrating its cutting-edge Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket at its private Launchpad in Sriharikota.
Facts About:
- The integration process was initiated on Independence Day on August 15, 2023.
- A successful launch would make AgniKul the second Indian space tech start-up to send its launch vehicle into space after Skyroot Aerospace.
- AgniKul: Established in 2017, by aerospace engineers Srinath Ravichandran and Moin SPM, along with IIT-Madras faculty member Prof. Sathyanarayan R Chakravarthy.
About Agnibaan SOrTeD (SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator):-
Type: single-stage launch vehicle.
Powered by: AgniKul’s patented Agnilet engine.
- Agnilet engine: It is the world’s sole single-piece 3D-printed engine.
- It is a single-piece, 6 kilonewton (kN) semi-cryogenic engine.
- Initial trial: early 2021.
- Verified at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in Thiruvananthapuram.
- 3D printing: uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items.
Payloads: up to 100 kg.
Altitude: 700 km
- It can carry payloads in five different configurations. (LVM3-M2 rocket)
Stages: It is a customizable launch vehicle that could be launched in one or two stages.
Unique feature: unlike traditional sounding rockets that launch from guide rails, it will lift off vertically and follow a predetermined trajectory to perform a precisely orchestrated set of maneuvers during flight.
The rocket’s first stage could have up to seven Agnilet engines, depending on the mission, which are powered by Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene.
The rocket is also designed for launch from more than 10 different launch ports.
To ensure its compatibility with multiple launch ports, AgniKul has built a launch pedestal named ‘Dhanush’.
- It will support the rocket’s mobility across all its configurations.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/science/chennai-based-agnikul-prepares-for-maiden-sub-orbital-flight-of-agnibaan-rocket/articleshow/102805834.cms?from=mdr
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) (LiveMint)

- 25 Jul 2023
Why in the News?
Taking advantage of the substantial number of written-off loans held by lenders and the government's recovery endeavors, ARCs are seizing the opportunity to acquire these loans.
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs):
- The Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC) functions as a distinct financial institution that acquires Non Performing Assets (NPAs) from banks and financial institutions, facilitating the process of cleansing their balance sheets.
- This enables banks to focus on their core banking activities. Instead of expending time and effort pursuing defaulters, banks can opt to sell the troubled assets to ARCs at a mutually agreed-upon value.
Legal Basis:
- The establishment of ARCs in India is supported by the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- The SARFAESI Act streamlines the reconstruction of bad assets, avoiding the need for court intervention.
- Subsequently, numerous ARCs were established and registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which holds regulatory authority over these institutions.
Capital Needs for ARCs:
- Following the 2016 amendment to the SARFAESI Act, ARCs were mandated to possess a minimum Net Owned Fund of Rs. 2 crores. However, in 2017, the RBI increased this threshold to Rs. 100 crores.
- ARCs must maintain a Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) equivalent to 15% of their risk-weighted assets.
