International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (DownToEarth)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Experts from The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) called for ‘bold action’ and ‘urgent finance’ to prevent collapse of nature in High Mountain Asia on February 5, 2024, in the Nepalese capital of Kathmandu.
About the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD):
- The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) is an intergovernmental knowledge and learning center dedicated to serving the communities of the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region.
- Established and inaugurated on December 5, 1983, its mission is to generate and share knowledge that informs regional policy and action, attracting investments to facilitate the transition to greener, more inclusive, and climate-resilient development.
Membership and Governance:
- ICIMOD's member countries include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Its highest governing body is the Board of Governors, composed of representatives from each member country and independent members nominated by the ICIMOD Support Group based on their professional expertise and experience.
Functions and Objectives:
- The center serves the HKH region by generating and sharing information and knowledge to address critical mountain-related challenges.
- It bridges scientific research with policy formulation and practical on-the-ground implementation.
- Furthermore, ICIMOD provides a regional platform for experts, planners, policymakers, and practitioners to exchange ideas and perspectives, facilitating sustainable mountain development.
- Headquarters of ICIMOD is in Kathmandu, Nepal.
Key Facts about the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) Region:
- The Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region spans 3,500 km across eight countries, from Afghanistan in the west to Myanmar in the east.
- It serves as the source of ten major Asian river systems, including the Amu Darya, Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, and others.
- The HKH region plays a vital role in providing water, ecosystem services, and livelihoods to the people living within its boundaries.
Restoring Lake Victoria: CSE, Tanzanian authorities hold multi-nation stakeholder consultation (DownToEarth)
- 23 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
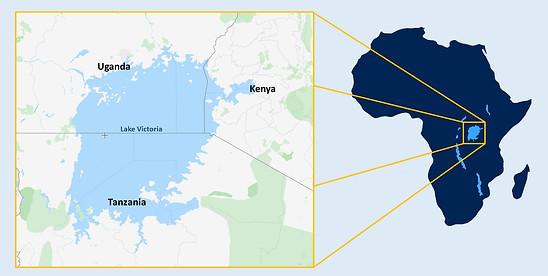
Lake Victoria, the largest freshwater lake in Africa and the world’s second-largest faces numerous environmental challenges that demand collective efforts for restoration and conservation.
About Lake Victoria:
Geography:
- Located in East Africa and bordered by Tanzania, Uganda, and Kenya.
- Africa's largest lake by area (approximately 59,947 km²) and the world's second-largest freshwater lake after Lake Superior.
- Lies in a shallow depression within the East African Rift Valley.
- The average depth of 40 meters, maximum depth of 80-81 meters.
Hydrology:
- The main source of water is rainfall, supplemented by rivers like the Kagera.
- The only outlet is the Victoria Nile, which flows into the White Nile and ultimately the Nile River.
- Plays a crucial role in the water supply and livelihoods of millions of people in East Africa.
Ecology:
- Supports a diverse ecosystem with over 200 fish species, including the Nile perch and Nile tilapia.
- Important habitat for birds, reptiles, and amphibians.
- Facing challenges like pollution, overfishing, and invasive species.
History and Culture:
- Named after Queen Victoria by British explorer John Hanning Speke in 1858.
- Has been a vital source of transportation, trade, and food for centuries.
- Plays a significant role in the cultural traditions and folklore of the surrounding communities.
An ancient system that could bring water to dry areas (DownToEarth)
- 18 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Some of Africa’s dry areas face serious water shortages due to minimal rainfall. An ancient system of drawing water from aquifers, the “qanat system”, could help.
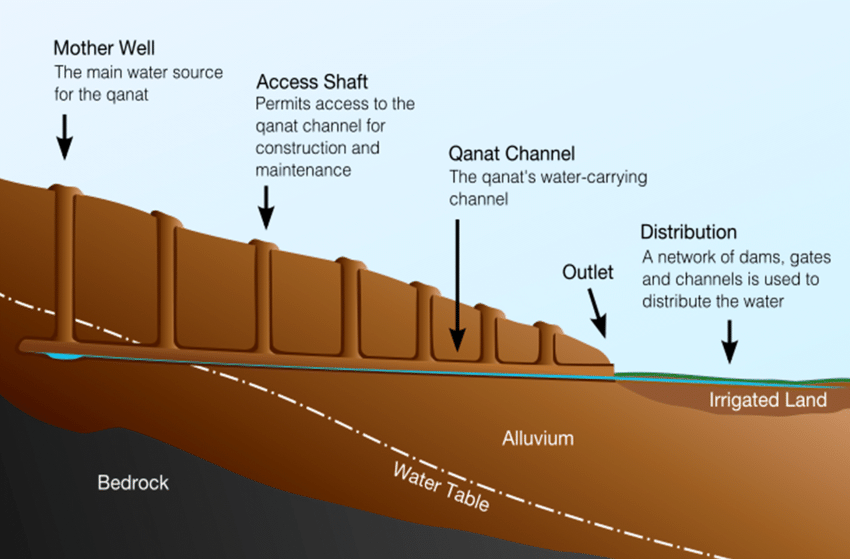
What is the Qanat system?
- The qanats have been used for centuries in arid and semi-arid parts of North Africa, the Middle East and Asia, where water supplies are limited.
- It’s known by a variety of names, “foggara” in North Africa, “falaj” in Oman and “qarez” in parts of Asia.
- It’s thought to have been developed in Persia in the first millennium BC.
- As the Islamic Empire spread across the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, north Africa and parts of Europe from 661 to 750 CE, so did knowledge about qanats.
- Today, some of the region’s qanat systems, like those in Iran, are protected under heritage status.
- Some of these qanats, although declining in number, are still used.
- They are largely protected for historical and cultural reasons.
How does the qanat system work?
- There are bodies of water underground known as aquifers, some of which can be found at the tops of valleys or near mountains.
- A qanat system taps these aquifers and, using underground tunnels, moves the water, using gravity, over many kilometres.
- The tunnel then exits at a lower-lying area.
- When the water exits the tunnel, farmers can use it to irrigate their crops.
- People can also access the water along the stretch of the tunnel using wells.
- It’s a system that’s managed by everyone and its benefits are shared.
- Everybody has a vested interest and a role to play and community bonds can be strengthened.
Advantages of qanat systems:
- Efficient use of water: Qanats allow for the extraction and transport of groundwater from deep underground sources to the surface.
- This allows for a more efficient use of water resources, as the water is extracted and transported to the surface for irrigation and other purposes.
- Sustainable water supply: Qanats can provide a reliable and sustainable source of water for communities, even in arid regions where surface water is scarce.
- Cool and humid air supply: The cool and humid air that flows through the qanat can be used to provide a natural air conditioning system for buildings, as well as to irrigate crops and orchards.
- Low maintenance: Qanats require minimal maintenance once they are constructed, making them a cost-effective and long-lasting water supply solution.
- Disaster resilience: Qanats are resilient to natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods, as they are located underground and protected from damage.
The first-ever IUCN assessment of the Himalayan Wolf is out. And it is grim (DownToEarth)

- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Himalayan Wolf is a prominent lupine predator found across the Himalayas the taxonomic status which was a puzzle till late, has been assessed for the first time in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List.
Key Findings:
- Population Decline: The IUCN assessment highlights a persistent reduction in the habitat area, extent, and quality of Himalayan wolves.
- The estimated total population ranges from 2,275 to 3,792 mature individuals, with 227 to 378 in India.
Primary Threats:
- Depredation Conflict: Arising from habitat modification, encroachment, and depletion of wild prey populations.
- Hybridization with Dogs: Particularly in Ladakh and Spiti, where feral dog populations are on the rise.
- Illegal Hunting: Driven by trade in fur and body parts, including paws, tongues, and heads.
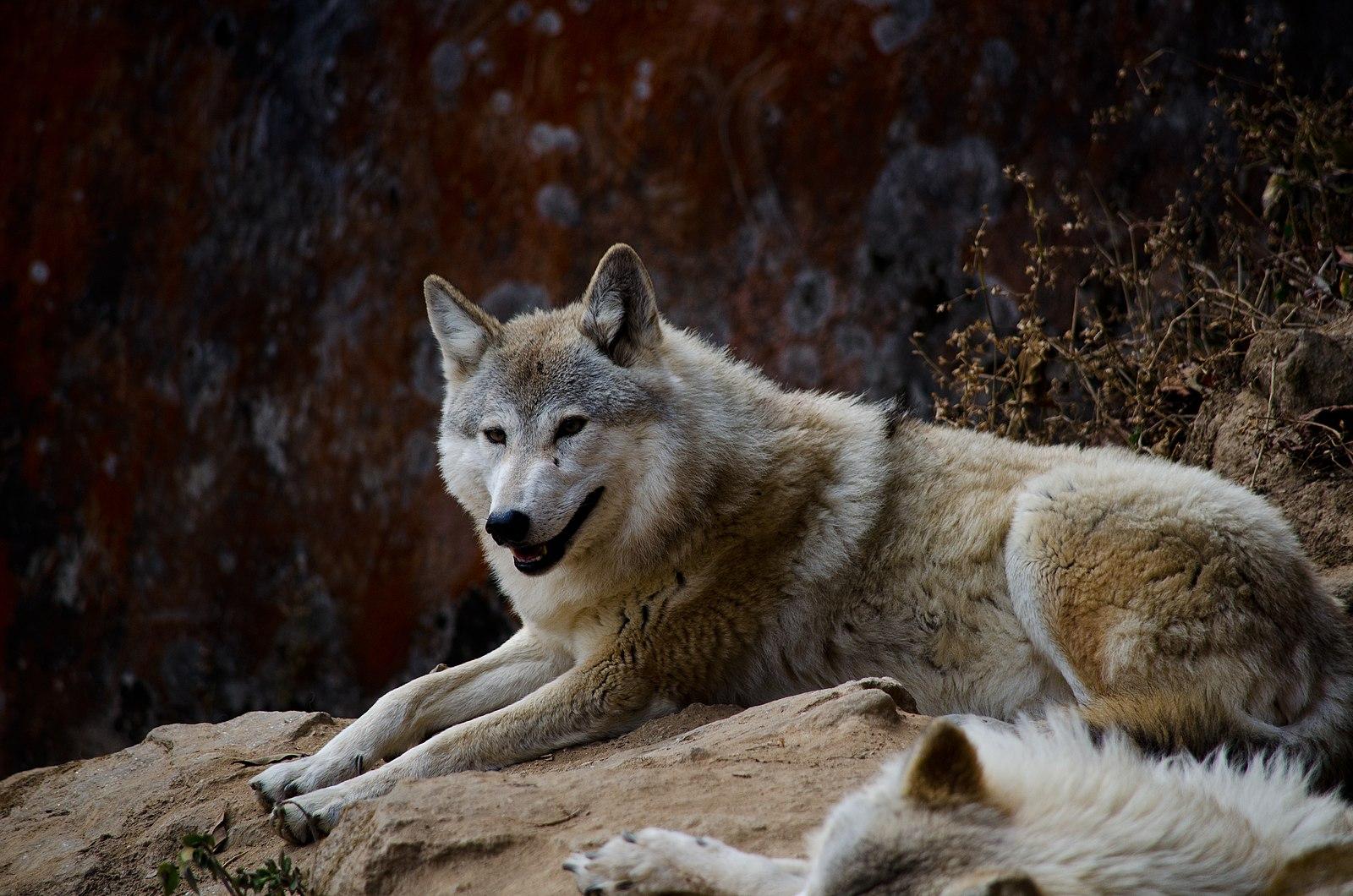
About the Himalayan Wolf (Canis lupus chanco):
- It is also called Tibetan wolves, which live at more than 4,000 metres altitudes.
- Habitat: It is found in the Himalayas (Nepal and India) and the Tibetan Plateau.
- Exhibits genetic adaptations to cope with hypoxic conditions.
- Characteristics: Adorned with thick fur, displaying brown colouration on the back and tail, complemented by paler yellows on the face, limbs, and underside.
- Larger than Indian and European wolves.
- Shows a preference for wild prey over domestic options.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN’s Red List: Categorized as Vulnerable.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Listed under Schedule I.
- CITES: Included in Appendix I.
Recommended Actions for the Conservation of Himalayan Wolves:
- Ensure the preservation and restoration of robust wild prey populations and their natural habitats.
- Foster collaborative transboundary initiatives to safeguard and conserve the species across its range of countries.
- Integrate the Himalayan Wolf into comprehensive conservation programs for enhanced protection and sustainable management.
Horticulture boost: Litchi cultivation has expanded to 19 Indian states, according to officials (DownToEarth)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
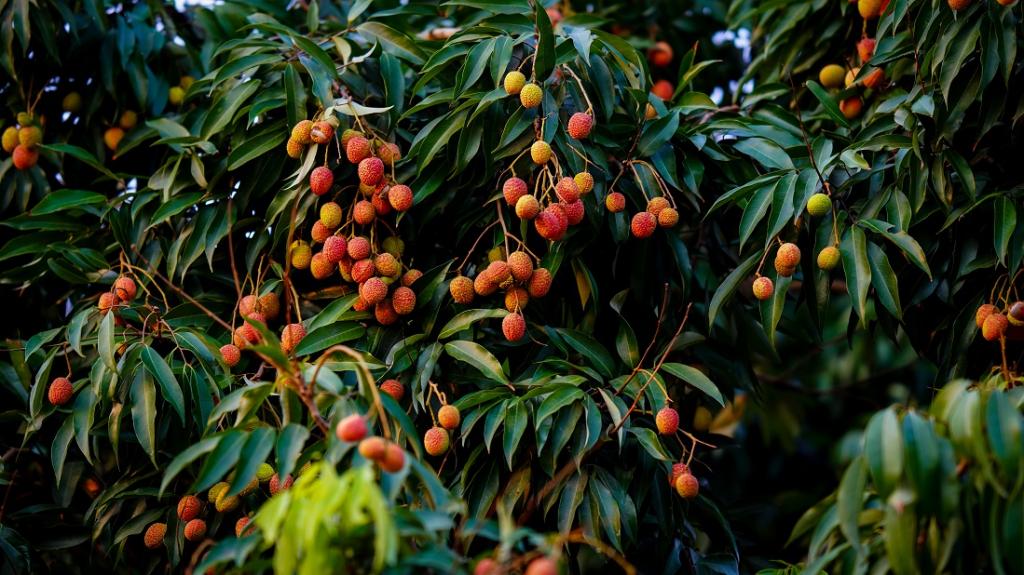
Litchi which is synonymous with India's hot summers, is now under cultivation in 19 Indian states, extending beyond its traditional confinement to Muzaffarpur in Bihar.
About Litchi Cultivation:
- Litchi, a delicious and succulent fruit of superior quality, belongs to the Sapindaceae family from a botanical perspective.
- Its translucent and flavorful aril, or edible flesh, is widely enjoyed as a table fruit in India.
- Agro-climatic Requirements: Litchi is a sub-tropical fruit that thrives optimally in moist sub-tropical climates.
- Ideally cultivated at low elevations, it can be grown up to an altitude of 800 meters.
- The crop flourishes in deep, well-drained loamy soil rich in organic matter, with an ideal pH range of 5.0 to 7.0.
- Temperature: The crop's temperature tolerance ranges from avoiding extremes, not exceeding 40.5 degrees Celsius in summer and staying above freezing point in winter.
- Rainfall: Prolonged rainfall, especially during flowering, can be detrimental as it interferes with pollination.
- Young trees necessitate protection from frost and hot winds until firmly established, although some temperature variation is necessary for proper fruiting.
- Frost during winter and intense summer heat are limiting factors for successful cultivation.
- Traditionally, commercial cultivation in India was confined to the northern foothills of the Himalayas from Tripura to Jammu & Kashmir, and the plains of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- However, due to increasing demand and the crop's viability, commercial cultivation has expanded to various states such as Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, etc.
- India ranks second in the world in production of Litchi production after China.
- Other significant producers include Thailand, Australia, South Africa, Madagascar, and the US.
- Statewise, Bihar tops in Litchi production followed by West Bengal (12 % of the total) and Jharkhand (10 %).
About National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL):
- The National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL) serves as the leading national institute dedicated to research and development in the field of litchi.
- It plays a pivotal role in providing national leadership, serving as a repository for comprehensive information on litchi production, processing, value addition, and extending consultancy services to end-users.
Bihar’s Only Ramsar Site 'Kanwar Lake' Drying Up (DownToEarth)

- 13 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Bihar’s only wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention lies neglected and is on the brink of drying up, even as the state is pitching other waterbodies for classification.
About Kanwar Lake:
- Kanwar Taal, known as Kabar Taal or Kabartal Wetland, is an oxbow lake in Begusarai district, Bihar, India.
- It is the largest freshwater oxbow lake in Asia, covering an area of 67.5 km².
- The lake was established as a bird sanctuary in 1987 and is now a designated Ramsar site since 2020.
- Covering the majority of the Indo-Gangetic plains in northern Bihar, this lake was declared a Ramsar site in 2020, making it the first wetland in Bihar to be included in the Ramsar convention.
- Kanwar Taal is a significant wetland in Bihar and is an essential stopover for migratory waterbirds along the Central Asian Flyway.
- The lake provides vital flood absorption during the monsoon season and supports agriculture during the dry season.
- It also houses five critically endangered species and over 50 fish species.
- Biodiversity: Kanwar Taal is rich in biodiversity.
- It is home to a wide range of plant and animal species.
- It supports 165 plant species and 394 animal species, including 221 species of birds.
- These bird species include both resident and migratory birds, with the lake serving as an important stopover point for migratory waterbirds travelling along the Central Asian Flyway.
- Flood Absorption: The wetland plays a crucial role in flood absorption during the monsoon season.
- It helps in reducing the impact of floods in the region by absorbing excess water, which is important for flood control and the protection of nearby areas.
- Agricultural Support: During the dry season, Kanwar Taal supports agriculture in the surrounding areas.
- The water from the lake is used for irrigation, benefiting local farmers and contributing to the region's agricultural productivity.
- Endangered Species: The wetland is home to five critically endangered species, highlighting its significance in conserving rare and threatened wildlife.
- Additionally, it hosts over 50 fish species, contributing to the aquatic biodiversity of the region.
What are Oxbow Lakes?
- Oxbow lakes are crescent-like water bodies formed due to erosion and deposition in meanders of rivers.
- Meanders are loops or curved structures formed in the course of a river due to friction or tectonic activity.
- The speed of water flow in the outer section of this meander is more than the inner part causing its neck to become narrower over time.
- Eventually, the size of this loop increases making it harder for the river to flow through it so it opts for a straight path.
- Finally, the ends of this meandered loop are separated by deposition of sediments or silt separating the river and a horseshoe-like structure called oxbow lake.
Microalgae are Adapting to Warming Climate (DownToEarth)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
A recent study finds microalgae are firing up a light-responsive protein to use sunlight for growth.
What is the Microalgae?
- Microalgae are microscopic algae prevalent in freshwater and marine environments, consisting of unicellular species that can exist independently or in chains and groups.
- Comprising unicellular algal varieties such as green algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates, these organisms exhibit sizes ranging from a few micrometres to several hundred micrometres.
- Their colour, determined by predominant pigments, categorizes them into groups like green, red, or brown.
- Unlike higher plants, microalgae lack roots, stems, or leaves, and they predominantly engage in photosynthesis, fueled by photosynthetic pigments.
- Heterotrophic microalgae, lacking these pigments, rely on other organisms for sustenance.
Significance:
- Microalgae play a foundational role in the aquatic food chain, offering vital nutrients for zooplankton, small fish, and various aquatic organisms.
- They serve as a primary food source for filter-feeding organisms.
- Moreover, photosynthetic microalgae contribute significantly to global carbon and oxygen cycles, absorbing carbon dioxide and generating oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Approximately half of atmospheric oxygen is produced by these organisms.
- Microalgae can also establish symbiotic relationships, as seen in their association with corals (zooxanthellae), providing nutrients through photosynthesis.
- Certain microalgae, like Nostoc, Anabaena, and Oscillatoria, exhibit nitrogen-fixing capabilities.
- Additionally, microalgae are rich in nutrients and can be consumed by humans. Notable examples like Spirulina and Chlorella are often utilized as dietary supplements.
What are Macroalgae?
- Macroalgae, commonly known as seaweeds, are marine plants engaging in photosynthesis but reproducing without flowers.
- Visible to the naked eye, in contrast to microalgae, they typically grow attached to the seabed or reef substrate.
- These macroscopic algae play crucial roles in reef ecosystems, providing both food and habitat for a diverse array of species while contributing significantly to nutrient dynamics.
Centre Notifies Green Credit Programme and Ecomark Scheme (DownToEarth)

- 14 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change on October 13, 2023, notified the ‘green credit’ programme, a first-of-a-kind market-based instrument designed to incentivise individuals, industries and local bodies for their voluntary environmental actions across diverse sectors.
About Green Credit Programme (GCP):
- Green Credit Program (GCP ) is an innovative market-based mechanism designed to incentivize voluntary environmental actions across diverse sectors, by various stakeholders like individuals, communities, private sector industries, and companies.
- The GCP's governance framework is supported by an inter-ministerial Steering Committee and The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) serves as the GCP Administrator, responsible for program implementation, management, monitoring, and operation.
- In its initial phase, the GCP focuses on two key activities: water conservation and afforestation.
- A user-friendly digital platform will streamline the processes for registration of projects, verification, and issuance of Green Credits.
- The Green Credit Registry and trading platform, being developed by ICFRE along with experts, would facilitate the registration and thereafter, the buying and selling of Green Credits.
- To obtain Green Credits, individuals and entities must register their activities through the central government's dedicated app/website www.moefcc-gcp.in.
- The Administrator will verify the activity through a designated agency, with self-verification for small projects.
- Once verification is complete, the Administrator will grant a Green Credit certificate which will be tradable on the Green Credit platform.
What is the Ecomark Scheme?
- The Ecomark Scheme provides accreditation and labelling for household and consumer products that meet specific environmental criteria while maintaining quality standards as per Indian norms.
- Products accredited under the Ecomark Scheme will adhere to specific environmental criteria, ensuring minimal environmental impact.
- It will build consumer awareness of environmental issues and encourage eco-conscious choices.
- It will also motivate manufacturers to shift towards environmentally friendly production. The scheme seeks to ensure accurate labelling and prevent misleading information about products.
- The Central Pollution Control Board administers the Ecomark Scheme in partnership with the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), which is the national body for standards and certification.
Both initiatives mark significant steps in promoting sustainable living, and environmental conservation, and, through individual and collective choice, embody eco-friendly practices in India. They align with global sustainability goals and reflect the government's commitment to conservation and protection of the environment.
Migratory Birds Arrive in Odisha’s Chilika Before Winter (DownToEarth)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Migratory birds have started their annual journey to Chilika Lake—India’s largest waterbird habitat in Odisha — ahead of winter this year.
About Chilika Lake:
- Chilika Lake is the largest brackish water lake and a shallow lagoon with estuarine character spread across the districts of Puri, Khurda and Ganjam in the state of Odisha in eastern India.
- It is considered to be the largest lagoon in India and is counted amongst the largest lagoons in the world.
- It is the largest wintering ground for migratory waterfowl found anywhere on the Indian sub-continent.
- It is one of the hotspots of biodiversity in the country, and some rare, vulnerable and endangered species listed in the IUCN Red List of threatened Animals inhabit the Lake area for at least part of their life cycle.
- On account of its rich bio-diversity, Chilika Lake was designated as a "Ramsar Site", i.e. a wetland of International Importance.
- The Nalaban Island within the lake is notified as a Bird Sanctuary under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- The National Wetlands, Mangroves and Coral Reefs Committee of the Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India, have also identified the lake as a priority site for conservation and management.
- The Lake is a highly productive ecosystem, with rich fishery resources.
- The rich fishing grounds sustain the livelihood of more than 0.2 million fisherfolk who live in and around the lake.
- It has a great heritage value and maritime trade to the far east countries used to take place from here.
- It is the largest winter ground of migratory birds in the Indian sub-continent and home to more than 150 highly threatened Irrawaddy dolphins, which is the largest lagoonal population globally.
- It supports some of the largest congregation of migratory birds from large parts of Asia, particularly during the winters that arrive from as far as the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea, remote parts of Russia, Kirghiz steppes of Mongolia, Central and South East Asia, Ladakh and the Himalayas to feed and breed in its fertile waters.
“FLip” mutations of SARS-COV-2 may be evading immunity and leading to a surge in COVID cases, suggest researchers (DownToEarth)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The omicron subvariant JN.1. is likely to soon become the dominant lineage of the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide, according to researchers at the University of Tokyo. The subvariant has a mutation in its spike protein, L455S, also called a “FLip” mutation.
Context:
- The mutations denoted as L455S and L455F are termed "FLip" mutations due to their role in interchanging the positions of amino acids F and L within the spike protein.
- These mutations enhance the virus's transmissibility.
- The substitution associated with these mutations reduces the receptor binding capacity of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a protein present in epithelial cells across various body parts, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys.
- ACE2 serves as a crucial entry point for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, binding through its spike-like protein on the virus's surface.
- The FLip mutations, specifically L455F and F456L, are characterized by the swapping of positions between two amino acids, F and L, within the spike protein.
What is Flip Mutation?
- A flip mutation, also known as bit flip mutation, is a genetic operator used in evolutionary algorithms, particularly genetic algorithms (GAs).
- It works by randomly flipping the values of individual genes (bits) within a chromosome, introducing small changes to the genetic makeup of an individual.
- Imagine a chromosome as a string of 0s and 1s, representing the genetic code for a specific trait or characteristic.
- A flip mutation randomly selects one or more of these bits and changes their values.
- For example, a 0 might be flipped to a 1, or vice versa.
- The following image depicts flip mutation:
How does it work:?
- Individual selection: An individual is selected from the population.
- Gene selection: One or more genes (bits) within the individual's chromosome are randomly chosen.
- Bit flipping: The value of each selected gene is flipped. This means that a 0 is changed to a 1, and vice versa.
Mythimna Separata (DownToEarth)

- 24 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Persistent high temperatures over an extended period might be responsible for the severe infestation of the Mythimna separata pest in Assam, causing damage to paddy crops in at least 15 districts.
About Mythimna Separata:
- This is a common long-distance migratory insect and a significant pest for various grain crops.
- Distribution: Mythimna separata is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, including China, Japan, Southeast Asia, India, and eastern Australia.
- It has also been introduced to New Zealand and some Pacific islands.
- In India, it was initially identified as a sporadic pest in Tamil Nadu in 1937 and later in Kerala and Odisha in 1957.
- Known by various names such as the ear-head-cutting caterpillar, rice ear-cutting caterpillar, or armyworm, this pest feeds on leaves and has the capability to cut off panicles from the base of a crop plant.
- Its feeding habits often leave the field resembling it has been grazed by cattle.
- During an outbreak, the pest multiplies rapidly and moves in swarms from one field to another, similar to an army, causing harm to crops.
- The pest population tends to increase under favorable conditions, particularly when there is a rise in temperatures coupled with dryness.
State of the Cryosphere Report 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
As per the 2023 State of the Cryosphere report, the anticipated disappearance of almost all tropical glaciers, a significant majority of mid-latitude glaciers, and polar regions is expected, even if global efforts successfully limit the rise in temperatures to 2 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels.
About the State of the Cryosphere Report 2023:
- The State of the Cryosphere Report annually assesses the condition of Earth's snow and ice regions, and has been reviewed and endorsed by over 60 leading cryosphere scientists.
- This report is published by The International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI.)
- The cryosphere is a term for the regions of our globe that are covered in ice and snow – either seasonally or year-round.
- The Report describes how a combination of melting polar ice sheets, vanishing glaciers, and thawing permafrost will have rapid, irreversible, and disastrous impacts worldwide.
Key findings in the report on the impact of 2°C of warming include:
- Ice sheets: nearly all of Greenland, much of West Antarctica, and even vulnerable portions of East Antarctica will be triggered to very long-term, inexorable sea-level rise.
- Glaciers: extensive, irreversible ice loss from the world’s glaciers in many major river basins, with some disappearing entirely.
- As glaciers melt, risks of catastrophic events such as landslides, sudden ice shears, and glacial lake outburst floods increase.
- Sea ice: extensive sea ice loss at both poles, with severe feedback to global weather and climate.
- By 2°C, the Arctic Ocean will be sea ice-free in summer every year, potentially for several months.
- Permafrost: extensive permafrost thaw and resulting greenhouse gas emissions will cause temperatures to continue to rise, even once human emissions reach zero.
- At 2°C, annual total permafrost emissions (both CO2 and methane) would total the size of the entire European Union’s emissions from 2019.
- Polar ocean acidification: year-round, permanent corrosive ocean acidification conditions in many regions of Earth’s polar and near-polar seas.
- Shell-building animals and commercial fisheries that rely on them in the food chain may not survive.
About International Cryosphere Climate Initiative (ICCI):
- It was formed in 2009 following COP-15 in Copenhagen
- ICCI is a network of senior policy experts and researchers working with governments and organizations to create, shape, and implement initiatives designed to preserve as much of the Earth’s cryosphere as possible.
- ICCI programs target the unique climate dynamics at work in the cryosphere, while at the same time lending increased urgency to global climate efforts aimed at CO2 and other greenhouse gases by communicating the unexpected rapidity and global implications of cryosphere warming.
What is ‘noma’, the latest addition to WHO’s list of neglected tropical diseases (DownToEarth)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) on December 15, 2023, added one of the world’s most under-recognised health challenges, noma, to its official list of neglected tropical diseases (NTD).
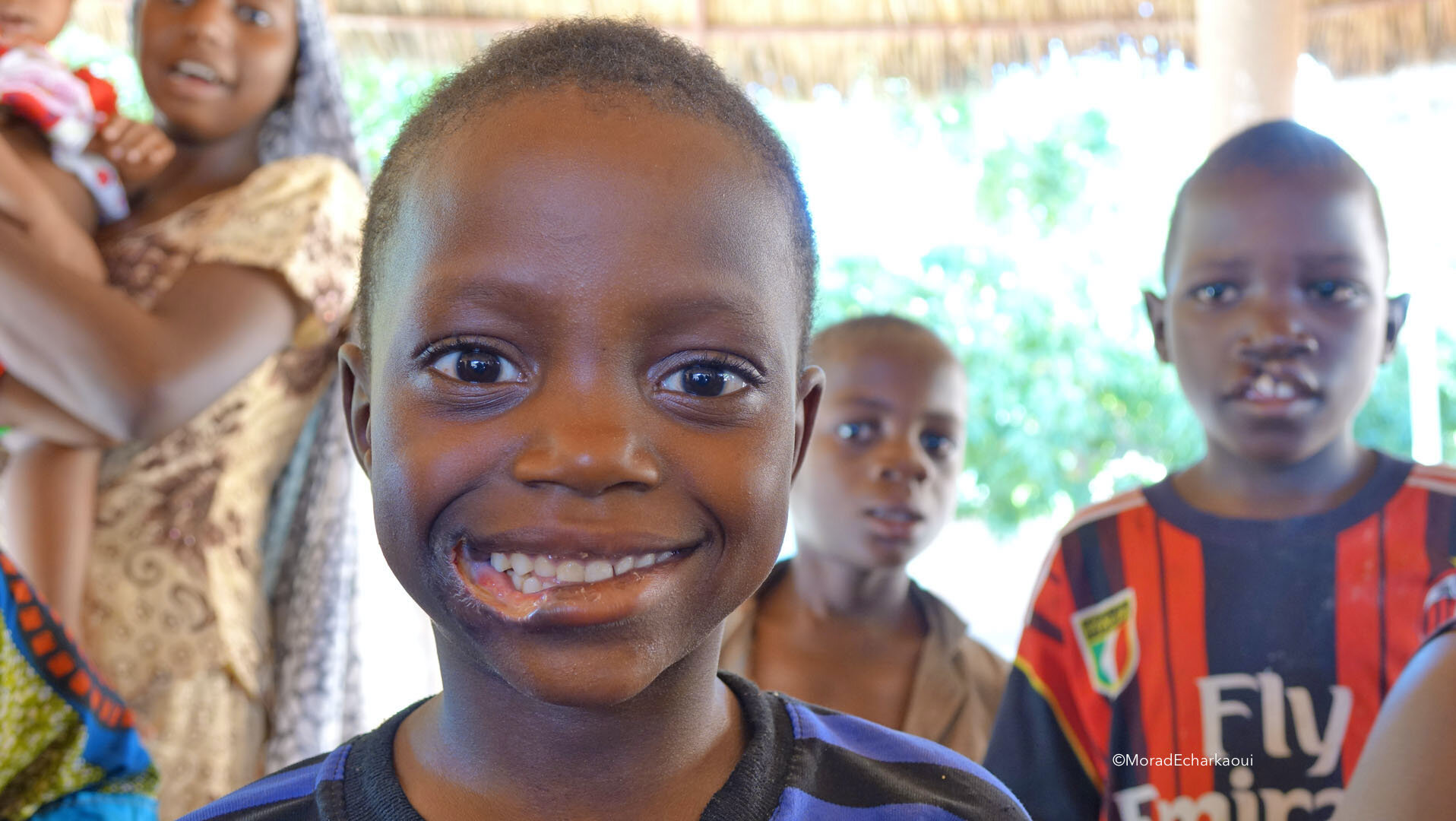
About the Noma disease:
- Noma is a severe gangrenous disease of the mouth and face with a mortality rate of approximately 90 per cent.
- It is also known as cancrum oris or gangrenous stomatitis and is often associated with extreme poverty, malnutrition and poor access to sanitation and oral hygiene.
- The name of the disease comes from the Greek word “nom?”, meaning “to devour”, as noma eats away facial tissue and bones if not treated early.
- Noma mainly affects children aged 2-6 years old and is found most commonly among those living in poor communities.
- The illness’s ‘hidden’ or neglected nature is most likely due to the fact that it affects the world’s most marginalised children.
- Noma is associated with a number of risk factors, including poor oral hygiene, malnutrition, weakened immune systems, infections, and extreme poverty.
- While the disease is not contagious, it prefers to attack when the body’s defences are weak.
- The NTD often starts as an ulcer on the mucous membrane lining, commonly after a bout of measles or other diseases, stated another 2003 study.
- “It quickly develops into a massive necrosis, moving from the inside outward, often involving major portions of the face.
- Treatment: “Early treatment with antibiotics, rehydration, correction of electrolytic imbalances, and administering nutritional supplements will halt the disease.
- The patients who survive face many consequences, like significant facial disfigurement, spasms of the jaw muscles, oral incontinence and speech problems.
- The disease is also called the ‘face of poverty’, as effective drugs like sulfonamides and penicillin and adequate surgical treatment for the effects remain inaccessible for many due to extreme poverty.
- “The recognition of noma as an NTD aims to amplify global awareness, catalyse research, stimulate funding, and boost efforts to control the disease through multisectoral and multi-pronged approaches.
Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
According to a new report, global climate finance is on the rise, yet it is not increasing at a scale and pace sufficient to address the climate crisis effectively.
About Global Landscape of Climate Finance 2023:
- The Global Landscape of Climate Finance is an annual report published by the Climate Policy Initiative (CPI).
- It provides the most comprehensive overview of global climate-related primary investment, covering both public and private finance.
- The report tracks climate finance flows across a range of sectors, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, transport, climate adaptation, and mitigation.
- This report concludes by calling for governments and investors to increase their support for climate finance, particularly for adaptation finance.
- It also recommends that more data be collected on climate finance flows to better understand where the gaps are and how to address them.
- It is an important tool for tracking global progress on climate finance and identifying areas where further investment is needed.
- It is an essential resource for policymakers, investors, and other stakeholders who are working to finance the transition to a low-carbon and climate-resilient economy.
- Key findings from the 2023 edition of the Global Landscape of Climate Finance report:
- Global climate finance reached an estimated USD 1.3 trillion on an annual average in 2021/2022, up from USD 653 billion in 2019/2020.
- The majority of climate finance is still directed towards mitigation activities, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency.
- There was a significant increase in climate finance for adaptation activities in 2021/2022.
- The growth in global climate finance was concentrated in a handful of geographies, with China, the US, Europe, Brazil, Japan, and India receiving 90% of increased funds.
- Private finance accounted for 60% of global climate finance in 2021/2022, up from 52% in 2019/2020.
Adaptation Gap Report 2023 (DownToEarth)

- 04 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Adaptation Gap Report states that funding for adaptation measures in developing nations has been declining and is insufficient of what is required.
About the Adaptation Gap Report:
- The Adaptation Gap Report (AGR) is an annual United Nation Enviroment Programme (UNEP) flagship publication.
- The report's primary objective is to inform the negotiators of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Member States, and the broader UNFCCC constituency, about the status and trends within climate adaptation at global and regional levels.
- AGR offers science-based recommendations to policymakers and decision-makers to enhance climate adaptation efforts in key climate-sensitive sectors.
- Since 2014, UNEP has been producing these assessments to support effective adaptation responses aligned with the UNFCCC's temperature and adaptation goals.
- The "adaptation gap" refers to the difference between actual adaptation efforts and the goals set by society, influenced by factors like climate change impacts, available resources, and competing priorities.
Key Findings of the Report:
- Adaptation costs are expected to rise significantly by 2050, especially in high-warming scenarios.
- The financial needs for adaptation are 10-18 times higher than the current international public adaptation fund flows.
- Urgent action is required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance adaptation efforts to protect vulnerable populations worldwide.
- In 2021, funding from developed countries to support adaptation projects in developing countries decreased by 15% compared to previous years.
- The report suggests seven strategies to bridge the adaptation gap, including increasing international financial support and mobilizing domestic resources.
- It also calls for a reform of the global financial system to facilitate easier access to climate-related funding from multilateral agencies such as the World Bank or the IMF.
Great Nicobar Island Project (DownToEarth)
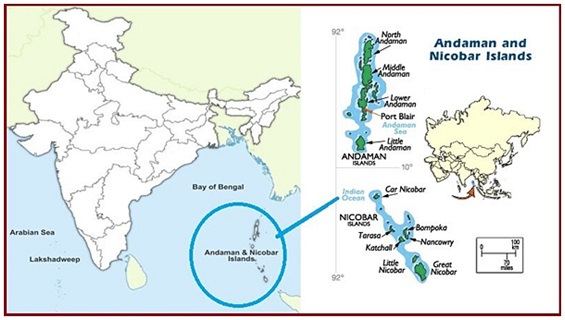
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change's statement in the Rajya Sabha, approximately 964,000 trees are expected to be cut down for the implementation of the Great Nicobar Island Project.
About Great Nicobar Island Project:
- Ministry:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Implementing Agency:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- The project is a massive undertaking with a budget of ?72,000 crore and is spearheaded by NITI Aayog, known as NITI Aayog's Project for Great Nicobar Island.
- Objective:
- The primary goal of the project is to achieve holistic development for the Great Nicobar Island (GNI).
- The project's vision is to transform the Great Nicobar Island, situated in the Bay of Bengal, into a modern, sustainable, and self-sufficient territory, thus facilitating the comprehensive development of Great Nicobar.
The plan comprises four key components:
- A transshipment port at Galathea Bay with an investment of ?35,000 crore.
- Development of a dual-use military-civil international airport.
- Establishment of a power plant.
- Creation of a township to support the overall project.
CHD1L gene (DownToEarth)
- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A new study indicates that some individuals of African descent have a CHD1L gene variant that may be involved in controlling the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
What is the CHD1L gene?
- The CHD1L gene encodes proteins that aid in repairing DNA damage within the body.
- A specific variant of the CHD1L gene is found predominantly in the African population and has been associated with a decreased viral load (amount of HIV in the blood) of HIV-1, the most common and severe type of HIV compared to HIV-2.
- Through the analysis of DNA from nearly 4,000 people of African descent living with HIV-1, researchers identified the presence of a gene variant of CHD1L located on chromosome 1.
- Individuals carrying this particular gene variant exhibited a low viral load, reducing their risk of transmitting the virus and slowing the progression of their own HIV-related illness.
- The study suggests that between 4% and 13% of people with African origins could be carrying this specific CHD1L gene variant.
Iberian wolf (DownToEarth)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
As per the regional government, the Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus) has been declared extinct in the historical region of Andalusia, located in the southernmost part of Iberia, since the year 2020.
About the Iberian Wolf:
- The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the Grey wolf, distinguished by its prolonged isolation from other wolf populations for over a century.
- With the largest wolf population in Western Europe, this magnificent species is native to the Iberian Peninsula, encompassing Spain and Portugal.
- Thriving in diverse habitats, Iberian wolves inhabit forests, inland wetlands, shrublands, grasslands, pastures, and mountainous areas.
- These wolves lead a social lifestyle, living, hunting, and traveling in small packs.
- Each pack includes the alpha male and female, along with their young and older offspring.
- The alphas serve as the pack leaders, responsible for establishing territory, selecting den sites, tracking down, and hunting prey.
- Primarily carnivorous, the Iberian wolf's diet comprises various animal species.
- With regard to conservation, the Iberian wolf holds the status of "Vulnerable" according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
SC pulls up Bhopal municipal corporation for flouting Solid Waste Management Rules (DownToEarth)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
There is non-compliance with the provision of the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 by the Bhopal Municipal Corporation, the Supreme Court observed December 1, 2023 after going through the affidavit filed by the corporation.
What is About Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)?
- The Supreme Court of India, in 2001, mandated the creation of the Compensatory Afforestation Fund and the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
- Initially, an ad-hoc CAMPA was established in 2006 to manage the Compensatory Afforestation Fund.
- (CAMPA) are meant to promote afforestation and regeneration activities as a way of compensating for forest land diverted to non-forest uses.
- National CAMPA Advisory Council has been established as per orders of The Hon’ble Supreme Court with the following mandate:
- Lay down broad guidelines for State CAMPA.
- Facilitate scientific, technological and other assistance that may be required by State CAMPA.
- Make recommendations to State CAMPA based on a review of their plans and programmes.
- Provide a mechanism to State CAMPA to resolve issues of an inter-state or Centre-State character.
CAMPA Act:
- To address the loss of forest area and ensure sustainability, the Government of India introduced the CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority) Act.
- This legislation establishes the National Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of India and a State Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of each state.
- These funds receive payments for compensatory afforestation, net present value of forests (NPV), and other project-specific payments.
- The National Fund gets 10% of these funds, while the State Funds receive the remaining 90%.
- As per the Act, companies diverting forest land must provide alternative land for compensatory afforestation.
- For afforestation purposes, companies are required to pay for planting new trees in the alternative land provided to the state.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (DownToEarth)

- 03 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
As per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development's Review of Maritime Transport 2023, international shipping witnessed a notable increase of 20 percent in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2023 compared to the previous decade.
Key Highlights from the Review:
- The shipping industry plays a pivotal role, accounting for over 80 percent of global trade volume, yet contributes nearly three percent of total global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Containerized trade, after a 3.7 percent decline in 2022, is projected to grow by 1.2 percent in 2023 and is expected to further expand by three percent from 2024 to 2028.
- Oil and gas trade exhibited robust growth in 2022, with tanker freight rates experiencing a significant resurgence driven by geopolitical developments.
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- UNCTAD serves as the United Nations' primary institution addressing trade and development matters.
- Established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly, it functions as a permanent intergovernmental body.
- UNCTAD's mission is to promote equitable and effective access to the benefits of a globalized economy for developing countries.
- It offers economic and trade analysis, fosters consensus-building, and provides technical assistance to assist developing nations in leveraging trade, investment, finance, and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, UNCTAD publishes influential reports, including the Trade and Development Report, the World Investment Report, and The Least Developed Countries Report.
