Horticulture boost: Litchi cultivation has expanded to 19 Indian states, according to officials (DownToEarth)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Litchi which is synonymous with India's hot summers, is now under cultivation in 19 Indian states, extending beyond its traditional confinement to Muzaffarpur in Bihar.
About Litchi Cultivation:
- Litchi, a delicious and succulent fruit of superior quality, belongs to the Sapindaceae family from a botanical perspective.
- Its translucent and flavorful aril, or edible flesh, is widely enjoyed as a table fruit in India.
- Agro-climatic Requirements: Litchi is a sub-tropical fruit that thrives optimally in moist sub-tropical climates.
- Ideally cultivated at low elevations, it can be grown up to an altitude of 800 meters.
- The crop flourishes in deep, well-drained loamy soil rich in organic matter, with an ideal pH range of 5.0 to 7.0.
- Temperature: The crop's temperature tolerance ranges from avoiding extremes, not exceeding 40.5 degrees Celsius in summer and staying above freezing point in winter.
- Rainfall: Prolonged rainfall, especially during flowering, can be detrimental as it interferes with pollination.
- Young trees necessitate protection from frost and hot winds until firmly established, although some temperature variation is necessary for proper fruiting.
- Frost during winter and intense summer heat are limiting factors for successful cultivation.
- Traditionally, commercial cultivation in India was confined to the northern foothills of the Himalayas from Tripura to Jammu & Kashmir, and the plains of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- However, due to increasing demand and the crop's viability, commercial cultivation has expanded to various states such as Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, etc.
- India ranks second in the world in production of Litchi production after China.
- Other significant producers include Thailand, Australia, South Africa, Madagascar, and the US.
- Statewise, Bihar tops in Litchi production followed by West Bengal (12 % of the total) and Jharkhand (10 %).
About National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL):
- The National Research Centre on Litchi (NRCL) serves as the leading national institute dedicated to research and development in the field of litchi.
- It plays a pivotal role in providing national leadership, serving as a repository for comprehensive information on litchi production, processing, value addition, and extending consultancy services to end-users.
MEA’s Flagship ‘Know India Programme’ for youth diaspora completes 20 years (MEA GOI)

- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The flagship programme of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) for the youth diaspora, the ‘Know India Programme’, has completed 20 years.
About the Know India Programme (KIP):
- The Know India Programme is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of External Affairs designed to enhance awareness about India, its cultural heritage, and art, and to familiarize participants with various aspects of contemporary India and their ancestral homeland.
- This program is open to Persons of Indian Origin (21-35 years) (excluding non-resident Indians) from all over the world, with a preference for youth from Girmitiya countries, such as those from Mauritius, Fiji, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad & Tobago, South Africa, and Jamaica.
- The program has been in existence since its inception in 2003.
Features of Know India Programme (KIP):
- It is a 21 days’ programme (excluding international travel) during which the participant will visit Delhi, Agra and a select state in India alongwith visits to places of historical, cultural, and religious significance.
- KIP participants will also have a 2-day orientation programme in New Delhi.
- Participants will meet opinion makers, leaders, and officials to get an overview of India’s economy, society and ongoing growth and development story.
- Participants are provided local hospitality e.g. boarding and Internal transportation in India, return air tickets from their country of residence to India provided participants bear 10% of the cost of total air fare.
- Gratis visa shall be granted to participants by the Indian Missions/Posts abroad.
- Some of the key elements of the Programme include:
- Visits to places of historical and cultural importance;
- Familiarisation with Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical forms of Music and Dance;
- Visit to institutions of democracy and governance like Parliament of India, Election Commission of India, Rashtrapati Bhawan;
- Interaction with leading educational institutions;
- Exposure to flagship economic and development schemes like Digital India, StartUp India, and Make in India; and
- visits to industrial sites, public and private firms to highlight India’s strength in Manufacturing & Service sector.
Eligibility Criteria:
- Minimum qualification required for participating in KIP is graduation from a recognized University /Institute or enrolled for graduation and the ability to speak in English.
- The applicant should not have visited India through any previous Programme of Government of India.
- Those who have not visited India before will be given preference.
- Applicant must provide documentary evidence to prove Indian origin or an undertaking about Indian origin which must be countersigned by the Indian Embassy/High Commission/Consul General.
States Returning to OPS Pose Significant Financial Burden: RBI (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the RBI released a report saying, the return to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS) by a few states would put a huge burden on their finances, restricting them from undertaking capital expenditure to drive the growth.
What is the Old Pension Scheme (OPS)?
- The Old Pension Scheme (OPS), popularly OPS, is for state and central government employees who have completed 10 or more years of service.
- The appeal of the Old Pension Scheme lies in its commitment to provide a guaranteed or 'defined' benefit to retirees, classifying it as a 'Defined Benefit Scheme.'
- It provides government employees with pensions based on their final salary, amounting to 50% of the last drawn salary.
- For instance, if a government employee's final monthly salary upon retirement was Rs 10,000, they would receive a guaranteed pension of Rs 5,000.
- Similar to government employees' salaries, pension payouts increased with government-declared dearness allowance (DA) hikes.
- The Central government discontinued OPS in 2003.
What were the issues with the OPS?
- The primary concern was the unfunded nature of the pension liability, lacking a dedicated corpus that could grow over time to meet payment needs.
- The annual Government of India budget allocated funds for pensions without a clear strategy for sustaining future payments.
- The 'pay-as-you-go' approach raised inter-generational equity concerns, burdening the present generation with the escalating load of pension responsibilities.
- Recently, the RBI expressed alarm over some states, including Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Punjab, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan, reverting to the OPS, citing it as a significant fiscal challenge.
- The RBI warned that by deferring current expenses to the future, states risk accumulating unfunded pension liabilities in the years to come.
What is the New Pension Scheme (NPS)?
- Introduced by the Central government in 2004 as an alternative to OPS, NPS is accessible to employees across public, private, and unorganized sectors, excluding those in the armed forces.
- This pension initiative encourages individuals to invest in a pension account regularly during their employment.
- Upon retirement, subscribers can withdraw a specific percentage of the accumulated corpus.
- The remaining amount is disbursed as a monthly pension post-retirement.
- Regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA).
How does NPS differ from OPS?
- Old Pension Scheme (OPS) ensures a fixed and guaranteed pension amount.
- In contrast, the National Pension Scheme (NPS) is an investment-cum-pension scheme, exposing returns to market volatility.
- NPS contributions are defined, but benefits are contingent on market performance.
Why Rural India Needs Women Drone Pilots? (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The NAMO Drone Didi Scheme provides new work opportunities to women and makes them the backbone of the rural economy.
What is the NAMO Drone Didi Scheme?
- The Prime Minister has recently approved the Central Sector Scheme (NAMO Drone Didi Scheme) for providing Drones to the Women Self Help Groups (SHGs), with an outlay of Rs. 1261 Crore.
- The scheme aims to provide drones to 15,000 selected Women SHGs during the period 2023-24 to 2025-2026 for providing rental services to farmers for agriculture purposes.
- The scheme seeks to empower women Self Help Groups (SHGs) and bring new technologies through drone services in the agriculture sector.
The highlights of this scheme are as follows:
- Departments involved: The scheme converges the resources and efforts of the Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (DA&FW); Department of Rural Development (DoRD); Department of Fertilizers (DoF); Women SHGs and Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Identification of SHGs: The women SHGs would be identified from the total 89 lakh SHGs formed under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana.
- Financial Assistance:
- Central Financial Assistance covering 80% of drone costs up to a maximum of Rs. 8 Lakh will be provided.
- The remaining amount can be raised through the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with a provision of interest subvention @ 3% on the AIF loan.
- Training:
- One of the members of SHGs will be trained in drone piloting skills and agriculture purposes of nutrient and pesticide application.
- Another member will be trained as a drone technician.
- This will allow them to not just operate the drone but also repair and maintain it.
- Nano Fertilizers: The scheme also promotes the use of Nano Fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP through drone services.
- Opportunities for Start-ups: The scheme not only empowers women but also opens avenues for dynamic start-ups in the field of drone aeronautics, tapping into significant untapped potential in this emerging sector.
Significance of the NAMO Drone Didi Scheme:
- Empowering Rural Women: Fosters technological empowerment of rural women, positioning them as the backbone of the rural economy.
- Places drone technology in the hands of women pilots from Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Modernizing Agricultural Practices: Addresses the imperative to modernize agricultural practices.
- Aims to elevate agricultural productivity through cutting-edge technology, contributing to a new agricultural revolution.
- Job Opportunities in Drone Aeronautics: Creates opportunities in the emerging field of drone aeronautics with substantial untapped potential.
- Opens avenues for rural women as pilots, mechanics, and spare-part dealers.
- Efficient Fertigation System Development: Facilitates the development of an efficient fertigation system.
- Introduces innovative liquid fertilizers like Nano Urea and Nano DAP with foliar application.
- Time-Efficient Spraying System: Automation of the spraying system through agri-drones ensures a time-saving and efficient application system.
- Equitable Agrarian Family Culture: Contributes to making the agrarian family culture more equitable and robust.
Article 356 of the Indian Constitution (The Hindu)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently held that the declaration of State emergency under Article 356 and the subsequent actions of the President should have a “reasonable nexus”.
What is Article 356 of the Indian Constitution?
Article 356 of the Constitution of India is based on Section 93 of the Government of India Act, 1935. According to Article 356, the President's Rule can be imposed on any state of India on the grounds of the failure of the constitutional machinery.
There are two types:
- If the President receives a report from the state's Governor or otherwise is convinced or satisfied that the state's situation is such that the state government cannot carry on the governance according to the provisions of the Constitution.
- Article 365: As per this Article, President's Rule can be imposed if any state fails to comply with all directions given by the Union on matters it is empowered to.
In simple words, President's Rule is when the state government is suspended and the central government directly administers the state through the office of the governor (centrally appointed. It is also called State Emergency or Constitutional Emergency.
President's Rule:
- Parliamentary approval is necessary for the imposition of the President's Rule on any state.
- The proclamation of President's Rule should be approved in both Houses of Parliament within two months of its issue.
- The approval is through a simple majority.
- The President's Rule is initially for a period of six months.
- Later, it can be extended for a period of three years with parliamentary approval, every six months.
- The 44th Amendment to the Constitution (1978) brought in some constraints on the imposition of the President's Rule beyond a period of one year. It says that the President's Rule cannot be extended beyond one year unless:
- There is a national emergency in India.
- The Election Commission of India certifies that it is necessary to continue the President's Rule in the state because of difficulties in conducting assembly elections in the state.
What happens after the President's Rule is imposed?
- The governor carries on with the administration of the state on behalf of the President. He or she takes the help of the state's Chief Secretary and other advisors/administrators whom he or she can appoint.
- The President has the power to declare that the state legislature's powers will be exercised by the Parliament.
- The state legislative assembly would be either suspended or dissolved by the President.
- When the Parliament is not in session, the President can promulgate ordinances with respect to the state's administration.
When is the President's Rule imposed?
- President's Rule is typically imposed when any of the following circumstances occur:
- The state legislature is unable to elect a leader as the Chief Minister within the time prescribed by the state's governor.
- Breakdown of a coalition in the state government, resulting in the Chief Minister having minority support in the legislature, and the CM is unable to prove a majority within the time prescribed by the governor.
- A vote of no confidence in the legislative assembly leads to a loss of majority.
- Postponement of elections due to unavoidable reasons such as a natural disaster, epidemic, or war.
Revocation of President's Rule:
- President's Rule can be revoked anytime after such a proclamation has been made by a subsequent proclamation by the President.
- A proclamation of revocation does not require approval by the Parliament.
- This occurs when the leader of a political party produces letters indicating majority support for him in the assembly and stakes his claim to form the state government.
How do web browsers work? (The Hindu)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Web browsers are our digital passports to the vast universe of the internet. Their simplicity is deceptive: beneath their user-friendly interfaces lies a world of intricate processes that transform clicks into the web pages we interact with every day.
What are web browsers?
- Fundamentally, the browser is an application that people use to send and receive messages via the internet.
- In other words, the browser is a program that runs on our device, with its purpose being to fetch information in different formats from the internet and show it on the device.
- It also does the reverse, receiving your input (say, a click), translating it to code, and transmitting it to some other machine across the internet.
- In the year 1990, the English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee introduced the concept of the World Wide Web also named ‘WorldWideWeb’.
What Constitutes a Web Browser?
Web browsers today comprise numerous essential components, each representing a sophisticated technology. Additionally, they depend on various supporting technologies and adhere to established standards governing the functioning of the Internet.
- Request and Response: When we enter a website's URL, the browser sends a request to a server, asking for the specific web page.
- The server processes the request and sends back a response containing the information needed to construct the page.
- This response, akin to a digital blueprint, travels back to our browser.
- Deconstructing the Response: The server's response comprises various files encoded in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- HTML outlines the webpage structure, CSS adds style and aesthetics, while JavaScript brings interactivity, making the page dynamic and engaging.
- Rendering: The browser deciphers HTML, applies CSS for styling, and executes JavaScript for interactivity, rapidly assembling the final webpage.
- Rendering engines are crucial technology enabling quick and cohesive visual presentation.
- Managing Data: Browsers use cookies for retaining site preferences and cache for storing frequently accessed files.
- Cookies act like post-it notes, preserving login status and preferences, while the cache accelerates page loading by retrieving stored files instead of downloading them again.
- Security: Browsers prioritize security by employing encryption protocols like HTTPS for data exchange.
- They create secure 'tunnels' to shield information during transmission. Warning systems alert users about potential threats, enhancing overall online safety.
As technology advances, web browsers are on a trajectory of continuous evolution. They are integrating state-of-the-art technologies such as WebAssembly, facilitating near-native performance within the browser. The future holds promises of support for virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences, offering immersive online interactions. Privacy features are also being fortified, empowering users with enhanced control over their digital presence.
Oil Producers Water Down Provision on Fossil Fuel Phase-out (Indian Express)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After four days of deadlock, a new draft agreement text emerged at the COP28 climate meeting that severely watered down earlier provisions on fossil fuel elimination but singled out coal for a rapid phase-down, which could be problematic for India.
Context:
- The 28th Conference of the Parties (COP 28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is underway in the United Arab Emirates from November 30 to December 12, 2023.
- During the climate meeting on December 10, negotiators took an initial step toward enhancing action on adapting to climate change.
- A draft text outlining potential "global goals" on adaptation was introduced for the first time, serving as a starting point for further negotiations.
- Negotiators are actively discussing various topics, including the contentious issue of fossil fuel phase-out, in informal sessions to find common ground.
- The draft document is titled 'Global Goal on Adaptation' (GGA) and aims to establish a shared global objective for adaptation, similar to the global goal of limiting temperature rise below the 1.5 degrees Celsius threshold for mitigation.
- This initiative addresses a longstanding demand from developing countries, emphasizing the need for increased focus and resource mobilisation for adaptation efforts.
- Notably, the draft removes the term 'phasing out' of fossil fuels but includes stronger language against coal, urging a "rapid phase-down of unabated coal," a point that may face objections from major consumers like India, Indonesia, and China, all developing countries heavily reliant on coal power.
Responses to the Draft Text 'Global Goal on Adaptation':
- The European Union (EU) and certain small island states promptly dismissed the draft agreement text.
- The EU climate commissioner criticized the overall insufficiency of the text, deeming it inadequate in addressing the climate change challenge.
- Primary dissatisfaction arose from the weakening of a provision related to the use of fossil fuels.
- The draft initially urged countries to "reduce both consumption and production of fossil fuels, in a just, orderly, and equitable manner."
- Notably, fossil fuels, responsible for nearly 80 percent of greenhouse gas emissions, have never been explicitly mentioned in prior COP decisions.
- While previous decisions emphasized the need to cut emissions, they avoided specifying actions for emission reduction.
- COP28 marked the first formal discussion of a fossil fuel phase-out but attempts to incorporate a robust provision faced resistance from oil-producing nations like Saudi Arabia and Russia.
- India, while not offering an immediate reaction to the draft agreement, has consistently asserted that singling out coal for accelerated reduction is discriminatory.
Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI (YUVAi) (NewsOnAir)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
YUVAi Student Finalists to showcase their AI-enabled social impact projects at the GPAI summit.
About Youth for Unnati and Vikas with AI (YUVAi) Initiative:
- YUVAi is aimed at fostering a deeper understanding of AI, to equip school students from classes 8th to 12th across the nation with AI skills, and to empower them to become human-centric designers and users of AI.
- In addition, the program offers an applied learning experience for students to understand and identify how AI technology can tackle critical problems and lead to the inclusive development of the nation.
- It is a collaborative initiative of the National e-Governance Division (NeGD), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India and Intel India.
- The objectives of YUVAi are to :
- Foster a deeper understanding of AI-tech and social skills
- Enable youth to develop AI-enabled solutions as a sign of achievement
- Empower youth to become human-centric designers and users of AI
- The program will be conducted in three phases.
- In the initial phase, teachers will be selected to identify students from their respective schools and share their details with the organizing team.
- Next, online orientation sessions will be conducted for registered students around core AI concepts by experts to facilitate understanding of the ideation process.
- Finally, students will be encouraged to submit ideas (individually or in teams of 2) through a 120-second video explaining a proposed AI-enabled solution for any one of the eight core themes- agriculture, healthcare, education, environment and clean energy, transportation, rural development, smart cities and law and justice.
- Shortlisted students will attend online deep dive AI training in the second phase.
- A 3-day face-to-face boot camp will be organized to provide adequate mentorship and guidance by YUVAi coaches.
- After the mentorship camps, students will use this newly gained knowledge to develop AI-enabled innovations/projects on any of the eight core themes and submit final entries.
- Finally, the most innovative AI-based solutions will be announced and invited to a national showcase and felicitation ceremony.
- Rewards: Upon a successful idea submission, students will be awarded a Certificate of Appreciation.
Protein from Budgett’s frog can block enzymes of disease-causing pathogens (The Hindu)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science’s (IISc.) molecular biophysics unit in a study have identified that peptides (short protein) produced from Budgett’s frog can combat enzymes of disease-causing pathogens.
Key Research Findings:
- The research focused on peptides, or short proteins, derived from amphibian skin, a subject of prolonged study due to their capacity to counter adverse environmental conditions, including harmful pathogens.
- A peptide secreted by frogs demonstrated inhibitory effects on two crucial enzymes, namely subtilisin Carlsberg and proteinase K, which are produced by pathogens.
- These enzymes play a crucial role in fostering infections by breaking down specific protective proteins within the infected individual.
- The studied peptide exhibited its inhibitory action through a slow-tight binding pathway, proving to be as effective as SSI, a well-established subtilisin inhibitor.
- The researchers illustrated the formation of a Michaelis complex—an intact, noncovalent complex with the inhibitor—during the process.
About Budgett’s frog:
- Budgett’s frogs exhibit high intelligence and a notably assertive nature.
- When alarmed, they employ a defensive strategy by inflating themselves, standing on short legs, and, if necessary, lunging at potential threats with an open, imposing mouth accompanied by a distinctive shriek.
- During the dry season, these frogs take refuge in burrows they construct at the bottoms of water pools.
- Within these burrows, they shed multiple layers of skin to create a waterproof cocoon, ensuring their moisture retention.
- Equipped with exceptional night vision and a keen sensitivity to movement, Budgett’s frogs showcase effective hunting skills.
- Habitat/Range: Found in proximity to permanent or seasonal bodies of water, Budgett’s frogs inhabit regions across Paraguay, Argentina, and Bolivia.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Classified as Least Concern.
Royal Bengal Tiger spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary (PTI)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a Royal Bengal Tiger was spotted in Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim at an altitude of 3,640 metres.
Context
- Royal Bengal Tiger has been sighted in the Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary in Sikkim roaming at an altitude of 3,640 meters.
- The Royal Bengal Tiger was captured by trap cameras of a team of the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) which is conducting a study in the sanctuary in collaboration with the Sikkim Forest Department.
- It was under a larger project called "Conservation and Use of Five Wetlands in three Himalayan States to Secure Habitats of Birds Migrating within the Central Asian Flyway (CAF)."
- This project was sanctioned under the National Mission on Himalayan Studies (NMHS), and aims to protect and conserve wetland sites in Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Sikkim.
About Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Pangalokha Wildlife Sanctuary is located at the tri-junction of Sikkim, Bengal and Bhutan and is spread over 128 square kilometres.
- The sanctuary is strategically located in the East Sikkim district, connecting the forests of Bhutan and the Neora Valley National Park in West Bengal.
- It is the largest wildlife sanctuary in Sikkim.
- Vegetation: The Sanctuary has typical alpine-temperate-subtropical vegetation with high-altitude lakes around Jelep La.
- Flora: Rhododendron, Silver Fir, Juniper forest and associated ground flora, moss-filled oak forests with dense bamboo thickets etc.
- Fauna: It is home to various species, including red pandas, snow leopards, Himalayan musk deer, Himalayan goral, and Himalayan black bears.
EU’s Landmark Deal on Artificial Intelligence Regulation (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently European Union policymakers agreed on a provisional deal on landmark rules governing the use of artificial intelligence (AI).
On December 8, EU member states and lawmakers reached a consensus on the formulation of "historic" rules governing artificial intelligence models like ChatGPT, concluding prolonged negotiations.
However, these rules are slated to come into effect no earlier than 2025, allowing room for technological advancements in the interim.
Key Highlights:
- The inception of the Artificial Intelligence Act dates back to 2021, aiming to instil transparency, trust, and accountability in AI practices.
- Its overarching goal is to establish a framework to address risks to safety, health, fundamental rights, and democratic values within the EU.
- Featuring a two-tier approach, the Act imposes transparency requirements on all general-purpose AI models, with more stringent measures for the more powerful ones.
- The Act proposes the creation of an EU-wide database cataloguing high-risk AI systems, with provisions for the inclusion of future technologies meeting high-risk criteria.
- The legislation seeks a delicate balance between fostering AI adoption and preventing or mitigating harms associated with specific applications of the technology.
Global Perspectives on Artificial Intelligence Governance:
- The dynamic evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) development has prompted diverse global perspectives on the regulation of these technologies.
- In May 2023, members of the European Parliament reached a preliminary agreement on a revised draft of the European Union's ambitious Artificial Intelligence Act.
- This Act envisions the creation of an EU-wide database for high-risk AI systems and outlines criteria for the inclusion of future technologies that meet these high-risk parameters.
- In contrast, the United States currently lacks comprehensive AI regulations and has adopted a relatively hands-off approach.
- On the opposite end of the spectrum, China has, in the past year, introduced some of the world's initial nationally binding regulations specifically targeting certain types of algorithms and AI.
- It has implemented a law to govern recommendation algorithms, with a particular focus on how these algorithms disseminate information.
India’s Position on Artificial Intelligence:
- Initially, the Union Minister for Electronics and Information Technology stated that the government was not contemplating any legislation to oversee the development of AI in India.
- However, in the lead-up to the G20 summit in September 2023, the Indian government hinted at the potential regulation of AI.
- Officials indicated that the forthcoming Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2022 would extend to AI developers engaged in creating and facilitating AI technologies.
- Given the substantial data collection and utilization by AI developers to train their algorithms and enhance AI solutions, they may be classified as data fiduciaries and held accountable for the responsible use of personal data.
- Prime Minister Modi recently expressed India's aspiration to "take a giant leap in AI to empower its citizens and actively contribute to its evolution."
- India is gearing up to host the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi from December 12-14.
- As a co-founder of GPAI, India, along with 28 member countries and the EU, is committed to guiding the responsible development and utilization of AI.
India's Ambitious Initiative to Expand Renewable Energy Capacity (Indian Express)

- 11 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has proposed an exemption for green hydrogen developers from adhering to its list of authorised manufacturers to enable them to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China.
What Does The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) Propose?
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is exploring the option of granting an exemption to green hydrogen developers from its list of authorized manufacturers.
- This proposed exemption would enable these developers to import solar PV modules and wind turbine models from China, aiming to enhance the competitiveness of green hydrogen exports.
- It's noteworthy that Chinese manufacturers are presently absent from MNRE's Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) and Revised List of Models and Manufacturers (RLLM).
The MNRE’s Proposal Background:
- After the 2020 Galwan Valley skirmishes, the Indian government issued directives to restrict the involvement of Chinese vendors in public procurement.
- Recently, the Indian procurement portal GeM announced the removal of hundreds of Chinese vendors over the past three years.
- At a time when energy companies are intensifying efforts to mass-produce green hydrogen, essential for which are renewable energy equipment and electrolysers, the government has sidelined Chinese manufacturers.
- This aligns with the MNRE's policy to enhance domestic manufacturing of renewable energy equipment.
- While central PSUs may face restrictions on importing electrolysis machinery from China, others continue to do so.
- In FY23, India witnessed a 40% increase, in importing machines and apparatus for electroplating, electrolysis, and electrophoresis, worth $45.61 million, compared to the preceding fiscal year.
What is the Significance of the MNRE’s Proposal?
- ??The proposal to import solar PV modules from China carries significance in bolstering the supply chain and enhancing the global competitiveness of Indian green hydrogen exports.
- Central PSUs such as Indian Oil Corporation Ltd and NTPC Ltd, both actively involved in green hydrogen projects, would benefit by sourcing equipment from Chinese manufacturers.
- This move is poised to strengthen India's position in the global green hydrogen market, aligning with the objectives outlined in the National Green Hydrogen Mission and facilitating the achievement of set targets.
Painkiller Meftal could cause DRESS syndrome (Financial Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) has recently issued a drug safety alert for doctors and patients about the use of the commonly used painkiller mefenamic acid, popularly sold under the brand name Meftal.
Context:
- The Pharma standard body, Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (IPC) in its preliminary analysis of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) from the PvPI database revealed that Meftal can lead to Drug Reactions with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome.
- According to doctors, this syndrome causes a diverse array of clinical symptoms, anywhere from 2 to 8 weeks after initiating the offending drug.
What is DRESS syndrome?
- DRESS syndrome (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms) is an adverse reaction term that is currently used to describe a hypersensitivity reaction.
- Experts classify DRESS syndrome as a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- It is a serious drug reaction affecting the skin and other organs, with a mortality rate of up to 10%.
- It manifests when the immune system excessively responds to specific medications, leading to a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
- This reaction can manifest with various symptoms across the body, including fever, abnormalities in blood, and inflammation of organs.
What are the symptoms of DRESS syndrome?
- Patients diagnosed with DRESS syndrome typically present with a rash, fever, and eosinophilia but can have a variety of symptoms including liver, lung, or kidney involvement.
- “DRESS syndrome should be suspected if a diffuse rash erupts and is accompanied by fever, facial edema, and enlarged lymph two to six weeks after starting a new high-risk medication.
How to treat DRESS Syndrome?
- The most important step to treat DRESS Syndrome is to stop the medication involved in the reaction, and sometimes, no further treatment is needed.
- Topical steroids can be given to treat the rash and in certain cases, further treatment is needed to protect the organs from damage, such as with steroids, which can be given either intravenously or orally.
- “Treatment with steroids can be needed for weeks or even months, and lab work is monitored carefully during this time.
- The average time to recovery is six to nine weeks.
Odisha Invokes ESMA to Ban Strikes by Health Department Staffs (The Hindu)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Odisha Government invoked the Orissa Essential Services (Maintenance) Act (ESMA) prohibiting strikes by paramedical staff, including nurses, pharmacists, technicians, Class III and IV employees, to ensure that medical services are not disrupted.
About Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA):
The Indian Parliament enacted ESMA in 1968 to ensure the continuous provision of critical services crucial to people's daily lives. This legislation prohibits employees in essential services from striking, regardless of bandhs or curfews.
- Designated Essential Services: Public conservation, sanitation, water supply, hospitals, national defense, petroleum, coal, electricity, steel, fertilizer production, and banking-related services fall under the ambit of essential services.
- Communication, transportation, and government initiatives for food grain acquisition and distribution are also covered.
- State-Specific Application: State governments, individually or collaboratively, can enforce ESMA within their territories, each having its own version with slightly varied provisions.
- This allows states to address disruptions that impact specific regions.
- Central Government Activation: In the case of a nationwide disruption, especially in sectors like railways, the central government may invoke ESMA.
- Consequences for Striking Employees: Employees engaging in illegal strikes under ESMA can face disciplinary action, including dismissal. Legal consequences may involve arrests without a warrant, with imprisonment for up to one year, fines, or both for those participating or instigating the strike.
UN Secretary-General Invokes Article 99 on Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza (The Hindu)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amid Israel’s ongoing military attacks on the Gaza Strip, particularly in its southern region, United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter in a bid to establish a ceasefire.
Context:
- The United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has decided to invoke Article 99 of the UN Charter as the death toll in Israeli bombardments on Gaza crosses 16,000.
- He also urged the UN Security Council to act on the humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
- The development comes as Israel increased the intensity of its operations, especially in the areas of southern Gaza with Israel's defence leadership claiming that “half of Hamas’ battalion commanders" are killed.
What is Article 99 of the UN Charter?
- The Secretary-General may bring to the attention of the Security Council any matter which in his opinion may threaten the maintenance of international peace and security.”
- It is seen as a discretionary power.
- The responsibility it confers upon the Secretary-General will require the exercise of the highest qualities of political judgment, tact and integrity” according to a 1945 report of the Preparatory Commission of the United Nations.
- According to the UN, the President of the Security Council is under the obligation to call a meeting of the Council if the Secretary-General brings to the attention of the Council any matter under Article 99.
When has Article 99 Been Activated in the Past?
- 1960: Following the Congo Crisis, Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld invoked Article 99 to address the aftermath of Belgium's withdrawal and the ensuing internal conflict.
- 1971: Amid the Bangladesh Liberation War, Secretary-General U Thant activated Article 99 to draw attention to the humanitarian crisis, urging international intervention.
- 1979: In response to the Iranian Revolution and hostage crisis, Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim triggered Article 99 to underscore the seriousness of the situation and the necessity for a peaceful resolution.
- 1989: Confronted with the ongoing Lebanese Civil War and hostage abductions, Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar invoked Article 99 to emphasize the requirement for international support and engagement.
‘Garba Of Gujarat’ Declared as Intangible Cultural Heritage by UNESCO (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Garba, the folk art of Gujarat, receives the intangible cultural heritage of humanity (ICH) tag from Unesco.
Context:
- 'Garba of Gujarat' has been inscribed in the Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) of Humanity by UNESCO.
- The decision was taken at the 18th session of the UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Committee for Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage held in the Republic of Botswana.
- Garba of Gujarat is the 15th ICH element from India to join this list.
- This inscription underscores Garba’s pivotal role as a unifying force that fosters social and gender inclusivity.
About Garba Dance:
- Garba is a ritualistic and devotional dance deeply rooted in the traditions of Gujarat, India.
- This vibrant dance is a central part of the nine-day Navratri festival, dedicated to the worship of feminine energy or Shakti.
- The cultural richness of Garba vividly expresses the divine feminine through its performances and visuals.
- Taking place in various settings, from homes and temple courtyards to public spaces, streets, and open grounds, Garba transforms into a widespread, inclusive community celebration.
- Beyond its religious significance, Garba serves as a social equalizer, breaking down barriers related to socio-economic status, gender, and sect divisions.
- This inclusive dance form fosters community unity, bringing together diverse and marginalized groups and reinforcing social bonds.
- Notably, Garba holds the distinction of being the 15th cultural element from India to be recognized by UNESCO.
What is Intangible Cultural Heritage?
- Cultural heritage extends beyond physical structures and object collections.
- It encompasses traditions and living expressions transmitted from our forebears to descendants.
- This includes oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, and the knowledge associated with nature, the universe, as well as the skills involved in traditional craftsmanship.
Chandrayaan-3 Propulsion Module Retraces Steps to Earth Orbit (Indian Express)

- 07 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have brought the Propulsion Module (PM) of the Chandrayaan-3 mission , which initially brought the Vikram lander to within 100 km of the Moon's surface before detaching and executing a historic controlled descent on August 23, back into Earth orbit.
What is a Propulsion Module in Chandrayaan-3?
- The Propulsion Module is a rectangular component of the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft, equipped with solar panels for power.
- Its primary purpose was to transport the Lander module to the lunar polar circular orbit and facilitate its separation.
- Following separation, the SHAPE payload within the Propulsion Module was activated.
- Initially intended for a three-month operation during the mission, the ISRO announced on December 4th that the Chandrayaan-3's Propulsion Module had been manoeuvred out of lunar orbit.
- Placed high above Earth for an additional mission, the module is currently sustained by residual fuel.
- This bonus mission will showcase technologies crucial for future lunar sample retrieval, according to ISRO.
- As of now, the ISRO has not disclosed its plans for the spacecraft once it depletes its fuel.
Importance of Propulsion Module's Return to Earth's Orbit:
- ISRO highlighted the key achievements resulting from the return manoeuvres conducted on the Propulsion Module (PM) in connection to upcoming missions:
- Planning and executing the trajectory and manoeuvres for the return journey from the Moon to Earth.
- Developing a software module for planning such manoeuvres, along with its initial validation.
- Planning and executing a gravity-assisted flyby around a planet or celestial body.
- Preventing uncontrolled crashing of the PM onto the Moon's surface at the end of its life, aligning with the requirement of avoiding debris creation.
What is Chandrayaan-3 Mission?
Mystery of megamouth shark solved after one washes up in Philippines (Business Insider)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently a dead 18-foot megamouth shark that washed up on the beach in the Philippines was pregnant, confirming for the first time that these mysterious creatures give birth to live young.
About Megamouth Shark:
- Researchers have found Megamouth sharks to be particularly elusive.
- Since their discovery in 1976, there have been fewer than 300 sightings of these deep-sea sharks.
- Uncovering fewer than 150 specimens, scientists have identified them as the smallest of three species of filtering sharks.
- Their scientific name is Megachasma pelagios.
- Similar to their relatives, the basking sharks, Megamouth sharks feed on krill suspended in seawater, utilizing their oversized mouths to sieve their food.
- Although most sightings have occurred near the Philippines and Taiwan, these sharks have been observed around the world.
- These sharks are found in deep, warm oceanic water and inhabit the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans.
- Characterized by their substantial size, Megamouth Sharks can reach weights of up to 2700 pounds (1215 kg) and lengths ranging from 425 to 515 cm. Females are generally larger than males.
- Easily recognizable by their large, soft head and anteriorly positioned mouth, their colouration varies from grey to bluish-black above and pale grey below.
- They possess small, hooked teeth along both top and bottom jaws.
- As filter feeders, they swim with their mouths continuously wide open, filtering their preferred planktonic prey.
- The inside of their mouths is equipped with light-producing organs that may attract pelagic crustaceans and other potential prey.
- On the conservation front, the Megamouth Shark is listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List.
Closest-ever Sun photo captured by Solar Orbiter (India Today)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The European Space Agency's Solar Orbiter has captured the most detailed image of the Sun's full disc and outer atmosphere, the corona, to date.
What is the Solar Orbiter?
- Solar Orbiter is a Sun-observing satellite, equipped with 10 state-of-the-art science instruments, that aims to provide unprecedented insights into the workings of the Sun.
- It intends to conduct an in-depth study of both the Sun and the inner heliosphere, exploring the uncharted regions closest to our Solar System.
- A collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, it represents the most intricate scientific laboratory ever dispatched to study the Sun.
- Distinguished by its capability to capture images of the Sun from a closer vantage point than any preceding spacecraft, it also marks the first exploration of the Sun's previously uncharted polar regions.
- Launched on February 10, 2020, the mission unveiled its initial images in June of the same year.
- Following gravitational assist manoeuvres at Earth and Venus, it commenced full science operations in December 2021.
- Solar Orbiter actively orbits the Sun in an elliptical trajectory, with its closest point, the perihelion, located approximately 25 million miles (40 million kilometres) from the Sun—closer than the orbit of Mercury.
- In terms of instrumentation, it actively carries six remote-sensing instruments for observing the Sun and the solar corona, along with four in-situ instruments for measuring the solar wind, energetic particles, and electromagnetic fields.
- The mission actively aims to continue its scientific operations until at least 2027.
Panchayat Development Index (PIB)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of State for Panchayati Raj recently informed Lok Sabha about the Panchayat Development Index.
About the Panchayat Development Index:
- The Panchayat Development Index serves as a comprehensive and versatile metric designed to actively evaluate the holistic advancement, efficacy, and ongoing progress of panchayats.
- This index actively considers a spectrum of socio-economic indicators and parameters, offering an actively nuanced understanding of the well-being and developmental status of local communities within the panchayat's jurisdiction.
- Objectives: The primary objective is to actively play a pivotal role in assessing performance and progress towards actively achieving Sustainable Development Goals at the grassroots level.
- An active component of this initiative is the Local Indicators Framework, which encompasses nine key themes for actively localising Sustainable Development Goals.
- These themes actively encompass creating poverty-free and thriving livelihoods, ensuring health and actively child-friendly environments, actively promoting water sufficiency, actively fostering clean and green spaces, actively developing self-sufficient infrastructure, actively establishing socially just and secure communities, actively promoting good governance, and actively creating women-friendly villages.
How Ranking Works?
- Ranks within the index are actively assigned based on scores, actively categorising panchayats into four grades.
- Those actively scoring below 40 percent are actively classified as Grade D,
- 40-60 percent as Grade C,
- 60-75 percent as Grade B
- 75-90 percent as Category A
- and those actively surpassing 90 percent are actively designated as A+.
- Significance of this Index: The significance of this index lies in its ability to actively offer valuable insights into areas requiring attention and improvement within rural areas under panchayat jurisdiction.
- It actively aids in identifying disparities, gauging the achievement of development goals, and actively crafting targeted policies and interventions to elevate the overall well-being and quality of life in rural communities.
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) (DST Gov)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The study by ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute (ICAR-IVRI), Izatnagar, Bareilly has found the exact status of EEHV and its subtypes circulating among the Asian elephant population in India.
What is Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV)?
- Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus (EEHV) is responsible for one of the most devastating viral infectious diseases in elephants worldwide, especially young Asian elephants.
- EEHV is a double-stranded DNA virus that is classified in the family Herpesviridae.
- The mortality rate is very high (70-85%) and death occurs within a short period (2-4 days).
- In India, the incidence of EEHV-HD was first reported in 1997.
- 9 of 15 potential cases were confirmed from Southern India in wild free-ranging calves in Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu forest reserves, and Madras Zoo.
- Transmission of the disease: EEHV is mostly spread through mucosal secretions which include:
- Saliva, Breast milk, Nasal secretions, Trunk to trunk contacts etc
- The disease can only affect elephants and is not infectious to humans or other animals.
- Symptoms: Some elephants show symptoms such as reduced appetite, nasal discharge and swollen glands.
- Treatment: Treatment involves a combination of strategies such as antiviral therapy, aggressive fluid therapy to counter haemorrhaging, immuno-stimulant drugs like selenium and Vitamins C and E, as well as antipyretics and analgesics to manage fever.
- It's important to note that there is no definitive cure for herpesviruses in animals or humans since these viruses typically enter a latent state.
Scientists uncover seismic clues in Kopili Fault zone, advancing earthquake preparedness (PIB)
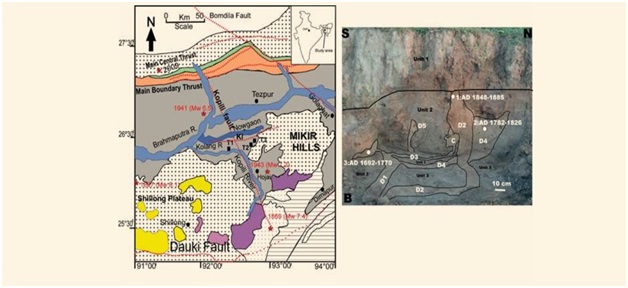
- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, scientists at the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have detected seismogenic liquefaction characteristics within the dynamically active Kopili Fault (KF) zone.
About Kopili Fault Zone:
- The Kopili Fault extends from the western part of Manipur up to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- It covers a distance of about 400 km and is closer to the Himalayan Frontal Thrust.
- The Kopili fault bisects the Meghalaya Plateau and isolates the Mishmi block from the main part of the plateau.
- The Kopili fault is almost passing through the Kopili River.
- The river Kopili rises in the North Cachar Hills District in Borail Range at an altitude of 1525 meters.
- From a field study, it is observed that the Kopili Fault region is moving in the northeast direction at an average velocity of 28.397N mm/yr and 40.227E mm/yr.
- This region is characterized by heightened seismic activity, classified within the most critical Seismic Hazard Zone V.
- The geological dynamics are attributed to collisional tectonics, where the Indian Plate subducts beneath the Eurasian Plate.
- The fault itself is a transpressional fracture, producing dextral strike-slip earthquakes in the lower crust.
- The Kopili fault zone, a tectonic depression filled by the alluvium of the Kopili River and its tributaries, has experienced numerous seismic events, notable among them being the 1869 earthquake (magnitude 7.8) and the 1943 earthquake (magnitude 7.3).
Iyothee Thass Pandithar (The Hindu)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin on Friday unveiled a statue of late anti-caste activist Iyothee Thass Pandithar installed at the Gandhi Mandapam campus at Guindy in Chennai.
About Iyothee Thass Pandithar:
- Iyothee Thass Pandithar was an important anti-caste activist and practiced Siddha medicine.
- He was born on 20 May 1845 in Madras presidency.
- In the 1870s, Thass brought together the Todas and other tribes of the Nilgiri Hills for the freedom movement.
- In 1876, he started the Advaidananda Sabha and, with Rev. John Rathina, launched a magazine called Dravida Pandian.
- In 1891, he founded the "Dravida Mahajana Sabha'' with Rettamalai Srinivasan.
- Also, he established the Sakya Buddhist Society in Madras, which had branches all over South India.
- This society, also known as the Indian Buddhist Association, was formed in 1898.
- To organize and oversee the society's activities, he began a weekly magazine, Tamizhan, in 1907.
INS Trinkat (Indian Express)
- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Navy has appointed the first woman commanding officer in a naval ship in line with the Navy’s philosophy of “all roles-all ranks” to deploying women in the service, Navy Chief Admiral R Hari Kumar said on Friday.
About INS Trinkat:
- INS Trinkat is a patrol vessel crafted by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers in Kolkata, West Bengal, and serves the Indian Navy.
- The role of the INS Trinkat is for anti-poaching operations, counter-insurgency operations, and Search and Rescue Operations in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep Islands, and India's Exclusive Economic Zone.
- It is capable of detecting and destroying fast-moving surface craft.
- It can also carry out policing anti-smuggling and fisheries protection operations.
- These patrol vessels are aptly named after Trinkat Island, one of the 24 islands constituting the Nicobar Islands chain situated in the northeast Indian Ocean, between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea.
About Group Captain Shaliza Dhami:
- Group Captain Shaliza Dhami, is an esteemed officer in the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- She holds the distinction of being the first woman officer in the IAF to secure a permanent commission and the pioneer woman to attain the role of a Flight Commander.
- Adding to her achievements, she became the first woman IAF officer selected for a front-line combat unit.
- Shaliza Dhami is an officer who is a qualified navigation instructor and has been involved in training observers inducted into the Navy.
- She is also learned to be the first woman officer who served as an observer in the Navy’s Tupolev Tu-142 maritime patrol aircraft.
- It's noteworthy that she is poised to make history once again by assuming command of a ship, marking a significant milestone in her career.
Sub-Neptune Planets (The Hindu)
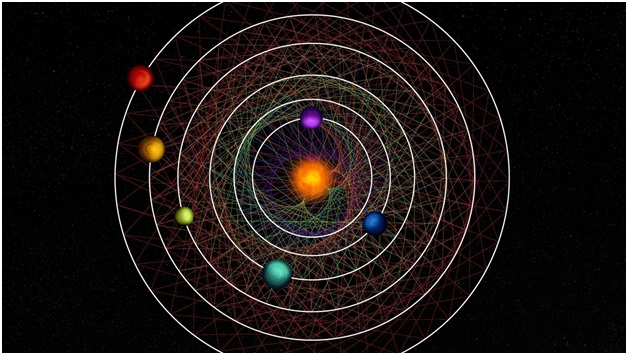
- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently astronomers have discovered an uncommon star system located just 100 light-years away from us, with six planets huddled immensely close to their host star.
What about sub-Neptunes?
- Sub-Neptunes are generally any planet that has a smaller radius than Neptune, although some could still be more massive.
- There are no sub-Neptunes in our solar system even though they are now known to be more common around other stars than Neptune-sized worlds.
- They might be rocky planets with thick atmospheres of hydrogen and helium gas, planets made of rock and ice bearing warm and water-rich atmospheres.
- These sub-Neptune planets were Initially detected in 2020 by NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and are about two to three times as big as Earth.
What are the findings?
- The newly discovered sub-Neptunes range from 1.9 to 2.9 times Earth's diameter.
- All appear to possess a large atmosphere.
- They and their star are located around 100 light-years from Earth.
- A light year is the distance light travels in a year, 5.9 trillion miles (9.5 trillion km).
- The system has six planets, all about the same size and they've barely changed since its formation up to 12 billion years ago.
- Their star, called HD110067, is visible in Earth's night sky in the northern constellation Coma Berenices.
- These undisturbed conditions make it ideal for learning how these worlds formed and whether they host life.
Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL) (The Hindu)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Bank of England (BoE) on Friday signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) concerning cooperation and exchange of information in relation to the Clearing Corporation of India Ltd (CCIL).
About Clearing Corporation of India Limited (CCIL):
- The Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) was set up in April 2001 to provide guaranteed clearing and settlement functions for transactions in Money, G-Secs, Foreign Exchange, and Derivative markets.
- Objective: The prime objective has been to improve efficiency in the transaction settlement process, insulate the financial system from shocks emanating from operations-related issues, and undertake other related activities that would help to broaden and deepen the money, debt, and forex markets in the country.
- Promoters of CCIL: State Bank of India, IDBI Bank Ltd, ICICI Bank Ltd, Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), Bank of Baroda, and HDFC Bank Ltd.
- The company was incorporated with an authorised equity share capital of Rs. 50 crores.
- CCIL’s adherence to the stringent principles governing its operations as a Financial Market Infrastructure (FMI) has resulted in its recognition as a Qualified Central Counterparty (QCCP) by the Reserve Bank of India in 2014.
- CCIL is also the trade repository for all OTC transactions in the Forex, Interest Rate, and Credit derivative transactions.
- Through its fully owned subsidiary, Clearcorp Dealing Systems Limited (CDSL), CCIL has introduced various platforms for the electronic execution of deals in various market segments.
- Further, CDSL has developed, implemented, and manages the NDS-OM, the RBI-owned anonymous electronic trading system for dealing in G-Secs and also for reporting OTC deals, as well as the NDS-CALL platform, which facilitates electronic dealing in the Call, Notice & Term Money market.
Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) (PIB)

- 02 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) has recently praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
About Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC):
- The Codex Alimentarious Commission (CAC) is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body created by WHO and FAO of the United Nations with 188 member countries.
- It is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular session once a year alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO with all work subject to approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organizations.
- The Commission works in the six UN official languages.
- India has been a member of this commission since 1964.
- The 46th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) was held from 27 November to 2 December (2023) in Rome, Italy.
- In the current session, India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millet, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet, and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
Exercise Milan (The Hindu)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Indian Navy To Conduct One Of Its Largest Naval Exercises — MILAN — Next February; More Than Fifty Countries Expected To Participate
About Exercise Milan:
- Exercise Milan is a biennial multilateral naval exercise that began in 1995, and has since significantly expanded in scope and scale to become the largest exercise held by India.
- Initially involving only Indonesia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, it has evolved significantly in terms of participants and exercise complexity.
- Aligned with India's 'Look East Policy' initially, Milan expanded under the 'Act East Policy' and Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) initiative, welcoming Friendly Foreign Countries (FFCs).
- The mid-planning conference for Milan-24 occurred in October.
- The last edition of Milan, which is held off Visakhapatnam, saw participation from over 40 countries showcasing its substantial growth in scale and international engagement.
- The next edition of Exercise MILAN is scheduled to be held in February 2024 and is expected to see the participation of over 50 countries.
- It reflects the significant expansion of the Navy’s engagements as well as its capacity to assist countries in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) as the first responder and Preferred Security Partner.
Sindhudurg Fort (Financial Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is gearing up to showcase its operational prowess in a significant ‘Operational Demonstration’ scheduled for December 4, 2023, at Sindhudurg Fort in Maharashtra.
About Sindhudurg Fort:
- Sindhudurg Fort is a historically significant stronghold situated on an islet in the Arabian Sea, just off the coast of Maharashtra in western India.
- Positioned on Kurte Island near Malvan town in Sindhudurg District within the Konkan region of Maharashtra, this formidable fortress was commissioned and constructed under the reign of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj of the Maratha Empire in 1664.
- The primary objective behind its construction was to counteract the escalating influence of foreign colonizers, including English, Dutch, French, and Portuguese merchants, and to curb the rise of the Siddis of Janjira.
- The Bakhar (a form of historical narrative written in Marathi prose) written by Chitragupta aptly mentions this fort as the most invaluable asset to Shivaji Maharaj.
Key Features:
- The fort spans 48 acres and boasts fortified walls that are 29 feet high and 12 feet thick, extending for a distance of two miles.
- Guarding these walls are 52 bastions equipped with embrasures for cannons.
- Access to the fort is through the Dilli Darwaja, the main gate, uniquely designed to blend seamlessly with the walls and visible only from close quarters.
- The fort is surrounded by several smaller forts, including Padmagad, Rajkot, and Sarjekot.
- An intriguing feature within the fort is a slab bearing the handprint and footprint of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Additionally, a small temple dedicated to the Maratha King is situated within the fort's bounds
Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Delhi High Court has criticized the forest department's proposal to hold a walkathon and cyclathon in a wildlife sanctuary, calling it a "haphazard exercise."
About Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary covers 32.71 sq. km on the Southern Delhi Ridge of the Aravalli hill range, bordering Delhi and Haryana.
- It's in Southern Delhi and parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts in Haryana.
- It's a part of the Sariska-Delhi Wildlife Corridor, linking Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan to Delhi Ridge.
- The sanctuary gets its name from the contiguous Asola village near Tughlaqabad in the Delhi NCR.
- Vegetation: The vegetation is classified as Northern Tropical Thorn Forests, known for thorny appendages and special leaves.
- The climate has extreme summer heat and significant winter cold due to its inland position.
- Flora: The main exotic plant is Prosopis juliflora, and the primary native plant is Diospyros montana.
- Fauna: The sanctuary is home to various animals like Golden Jackals, striped hyenas, Indian Crested Porcupines, Civets, Jungle Cats, Snakes, Monitor Lizards, and Mongoose.
- This sanctuary plays a crucial role in connecting wildlife across different areas.
World AIDS Day 2023 (Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the World AIDS Day 2023, observed each year on December 1, the World Health Organisation emphasised recognising and remembering the contribution of communities in controlling HIV-AIDS.
About World AIDS Day 2023:
- World AIDS Day which is observed every year on December 1 is a global movement to unite people in the fight against HIV and AIDS.
- Since 1988, when the World Health Organisation (WHO) recognised the day, communities have stood together on World AIDS Day to show strength and solidarity against HIV stigma and to remember lives lost.
- It is an opportunity to reflect on the progress made to date and raise awareness about the challenges that remain to achieve the goals of ending AIDS by 2030.
- The theme of World AIDS Day 2023 is– “Let Communities Lead"
What is HIV/AIDS?
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, compromising the body's ability to fight off infections and diseases.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is the advanced stage of HIV infection, characterized by severe immune system damage.
- Transmission: HIV spreads through unprotected sexual contact, sharing contaminated needles, and from an infected mother to her child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Treatment: Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) is the primary treatment for HIV/AIDS, managing the virus and supporting the immune system.
- Lifelong adherence is essential, ensuring viral suppression.
- Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is vital, and global challenges such as stigma and healthcare access persist in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant Safety) System (New Indian Express)

- 01 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
"In a first", through cutting-edge indigenous technology, the Indian Railways has successfully developed a system, preliminarily called as ‘Gajraj Suraksha (Elephant safety) system’ to prevent elephant–train collisions in the forest areas.
About Gajraj Suraksha:
- Gajraj Suraksha uses an AI-based algorithm and a network of sensitive optical fiber cables to detect elephants approaching railway tracks, aiming to address elephant fatalities resulting from train accidents.
- How this will work?
- The system functions by sensing pressure waves generated by elephant movements along the tracks.
- As elephants move, the optical fibers detect vibrations from their footsteps, triggering signals within the fiber network.
- This enables the system to identify elephants up to 200 meters ahead of their arrival on the track.
- The Optical Fibre Cable (OFC)-based Intrusion Detection System sends alarms to station masters upon detecting movement along the tracks.
- The network is designed to accurately track elephant movement, allowing prompt communication to nearby station masters.
- This ensures timely information to locomotive drivers, facilitating the slowing down or stopping of trains to prevent potential collisions with elephants.
- The Indian Railway plans to introduce this system in West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, Assam, Kerala, certain parts of Chhattisgarh, and Tamil Nadu.
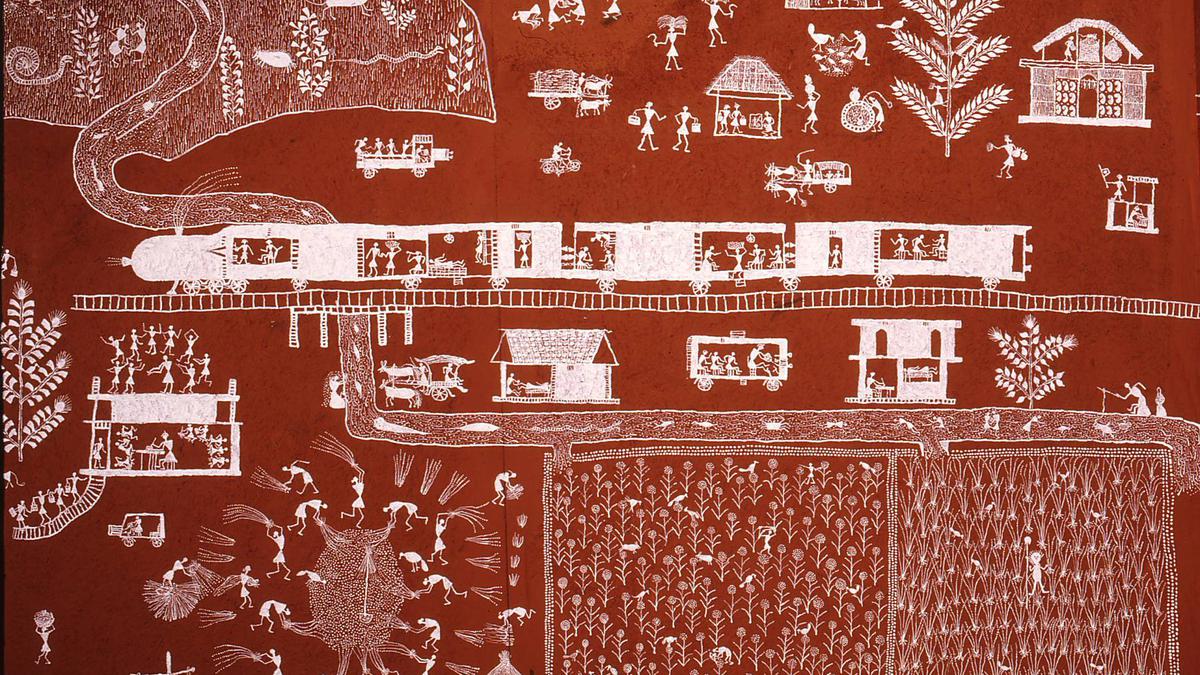
Life through geometry in Warli (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Warli Whisperers, an exhibition by the Inherited Arts Forum, traces the artistic journey of the celebrated Mashe family from Maharashtra.
About the Warli Art:
- Origin: Warli art is a tribal form originating from the North Sahyadri region of Maharashtra, with roots dating back to the 10th century AD.
- However, it gained recognition for its unique style in the early 1970s.
- Practitioners: Traditionally, Warli art was practiced by Suvasinis, the women of the Warli tribe, who adorned the Lagn Chowk or wedding square with their artistic expressions.
- Characteristics: Warli artists draw inspiration from nature, depicting scenes of farming, food gathering, village life, and elements from the natural world.
- These paintings are mainly dominated by basic geometric shapes like circles, triangles and squares.
- These geometric shapes stand as a symbol of natural elements in our environment.
- For example, the circles represent the sun and moon, the triangles represent the mountains and the squares are considered as the central motifs of the painting.
- Techniques and Materials: The paintings showcase triangles, circles, and lines in stark white against a mud brown background, narrating stories of village life, customs, and traditions.
- Modified bamboo sticks serve as paintbrushes, and the colours are derived from nature, such as brown and orange from henna, indigo from dye, red from bricks, and white from thick rice paste.
- Warli art serves as a vibrant portrayal of the everyday and social occurrences within the Warli tribe of Maharashtra, serving as a means to adorn the walls of village houses.
- Concerns: It was not recognised as an art form even though it was in practice for centuries.
Warli Tribe
- The Warli tribe, categorized as indigenous Adivasis, inhabit both the mountainous and coastal regions near the Maharashtra-Gujarat border.
- Their communication is conducted through an unwritten Varli language, classified within the southern zone of Indo-Aryan languages.
SC Collegium recommends names for Chief Justices of five High Courts (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court Collegium headed by Chief Justice of India D.Y. Chandrachud has recommended the appointment of Chief Justices to five High Courts.
What is the Collegium System?
- It is a system under which appointments and transfers of judges are done in the Supreme Court and High Courts.
- It is not rooted in the Constitution, iInstead, it has evolved through judgments of the Supreme Court.
- The Supreme Court Collegium, headed by the Chief Justice of India, consists of the court's four other most senior judges.
- Similarly, the High Court Collegium is chaired by its Chief Justice, along with the four other most senior judges of that specific high court.
Appointment of Judges: Constitutional Framework
- Constitutional Provision: Under Article 217, the President holds the authority to appoint judges of a high court.
- The appointment of the Chief Justice involves consultation with the Chief Justice of India and the respective state's governor.
- Similarly, consultation with the Chief Justice of the concerned high court is essential for appointing other judges.
- In cases where a high court serves multiple states, the President consults with the governors of all relevant states.
- No Minimum Age Requirement: The Constitution does not specify a minimum age for the appointment of high court judges.
- Qualifications of Judges: To qualify for a high court judge, an individual must:
- Be a citizen of India.
- Have held a judicial office within India's territory for ten years; or
- Have been an advocate of a high court (or successive high courts) for ten years.
Supreme Court Judgements:
- Second Judges Case (1993): The Supreme Court decreed that the appointment of a high court judge must align with the Chief Justice of India's opinion.
- Third Judges Case (1998): The Supreme Court emphasized that for the appointment of high court judges, the Chief Justice of India should consult a collegium comprising the two most senior judges of the Supreme Court.
- The consultation process involves more than the Chief Justice of India's individual opinion.
Is Pegasus spyware targeting journalists in India? (The Hindu)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amnesty International and Washington Post recently announced that it has found the presence of Pegasus spyware, sold only to governments, on two Indian journalists’ phones.
What is Pegasus Spyware, and How Does it Infiltrate Devices?
- Pegasus is a sophisticated form of malware, covertly designed to gather information without the user's knowledge.
- Developer: Developed by the Israeli security firm NSO Group.
- Objectives: Pegasus serves three primary purposes:
- Collecting historical data on a device discreetly.
- Continuously monitoring user activities and gathering personal information.
- Transmitting the collected data to third parties.
Infiltration Mechanisms:
- Pegasus utilizes "zero-click exploits," exploiting vulnerabilities in popular apps like iMessage and WhatsApp.
- Notably, zero-click exploits require no user interaction, differentiating them from typical cyberattacks.
- Network injection attacks are another method employed by Pegasus, where unsecured websites are used to infiltrate devices within milliseconds of the user's visit.
What is a Zero-click exploit?
- A zero-click exploit involves the installation of malicious software on a device without the device owner's consent.
- Notably, it does not require any action from the device owner to initiate or complete the installation.
Specific Exploit in the Recent Case with Indian Journalists:
- The particular exploit reportedly used in the incidents is known as BLASTPAST (previously identified as BLASTPASS), unfolding in two phases.
- Initial Phase: The attack aims to establish a connection with Apple HomeKit, a platform enabling users to control various smart devices on their network.
- The primary objective of this phase might be to assess how the device could be vulnerable to exploitation or to maintain visibility for potential future attacks.
- Second Phase: Malicious content is sent through the iMessage app to the target device.
- This stage is pivotal as it delivers the complete spyware payload, enabling extensive surveillance and data collection.
Mines Ministry unveils draft rules for offshore minerals auction (The Hindu Business Line)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s Mines Ministry has proposed a new set of rules for the auction of offshore mineral blocks. It is also in the process of identifying such mineral blocks, including those in exclusive economic zones beyond territorial waters.
Context:
- To implement the amended Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act), the ministry has unveiled two draft rules:
- Offshore Areas Mineral Auction Rules: These rules delineate provisions governing the auctioning of production leases.
- Offshore Areas Existence of Mineral Resources Rules: These rules set forth norms for the exploration of minerals and deposits in offshore areas.
Offshore Areas Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 2002 (OAMDR Act):
- The OAMDR Act governs the development and regulation of mineral resources in India's territorial waters, continental shelf, exclusive economic zones, and other maritime zones.
About Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
- The Bill proposes amendments to the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, governing mining activities in India's maritime zones.
Key highlights include:
- Empowering the government to reserve offshore areas without operating rights.
- Granting the administering authority the discretion to issue composite licenses or production leases to the government or a government company.
- Eliminating the provision for renewing production leases and setting a fixed fifty-year period, aligning with the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Mandating the grant of production leases to the private sector through competitive bidding.
- Allowing non-competitive bidding for operating rights in mineral-bearing areas reserved by the central government for government entities or corporations.
- Restricting the grant of exploration licenses or production leases for atomic minerals to government or government corporations.
- Introducing a four-year timeline for the commencement of production and dispatch after executing a composite license or production lease, with a two-year timeline (extendable by one year) for re-commencement after discontinuation.
- Authorizing the central government to establish rules for mineral conservation, systematic development, and environmental protection in offshore areas, preventing or controlling pollution from exploration or production operations.
India's Maritime Zone Mineral Resources:
- India's maritime zone hosts diverse mineral resources, including lime mud off the Gujarat and Maharashtra coasts within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Additionally, the region boasts construction-grade sand along the Kerala coast and heavy mineral placers in the inner-shelf and mid-shelf regions off Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra.
- Phosphorite is found in the Eastern and Western continental margins, while the Andaman Sea and Lakshadweep Sea house Polymetallic Ferromanganese (Fe-Mn) nodules and crusts.
Govt issues PMLA notice to Binance, 8 other offshore crypto firms, asks IT Min to block URLs (Indian Express)

- 29 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India's Financial Intelligence Unit has issued show cause notices to nine offshore crypto-currency operators, including Binance, for not complying with the anti-money laundering PML Act.
About the Financial Intelligence Unit India:
- Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND) was set by the Government of India in November 2004 as the central national agency responsible for receiving, processing, analyzing and disseminating information relating to suspect financial transactions.
- FIU-IND is also responsible for coordinating and strengthening efforts of national and international intelligence, investigation and enforcement agencies in pursuing the global efforts against money laundering and financing of terrorism.
- It is an independent body reporting directly to the Economic Intelligence Council (EIC) headed by the Finance Minister.
Key Functions of FIU-IND:
- Information Collection: Act as the central hub for receiving various reports, including Cash Transaction Reports (CTRs), Non-Profit Organisation Transaction Reports (NTRs), Cross Border Wire Transfer Reports (CBWTRs), Reports on the Purchase or Sale of Immovable Property (IPRs), and Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) from diverse reporting entities.
- Information Analysis: Analyze the received information to unveil transaction patterns indicative of potential money laundering and associated criminal activities.
- Information Sharing: Collaborate by sharing intelligence with national intelligence/law enforcement agencies, national regulatory authorities, and foreign Financial Intelligence Units, fostering a collective effort against financial crimes.
- Central Repository: Establish and maintain a national database by consolidating reports received from reporting entities.
- Coordination: Strengthen the collection and sharing of financial intelligence through efficient national, regional, and global networks to combat money laundering and related crimes.
- Research and Analysis: Conduct ongoing monitoring and identification of strategic areas related to money laundering trends, typologies, and developments.
What are Virtual Digital Assets?
- As per the Income Tax Act, a 'virtual digital asset' is described as any information, code, number, or token (excluding Indian currency or foreign currency) generated through cryptographic means and blockchain technologies.
- These assets can be electronically transferred, stored, or traded.
- The definition explicitly covers non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or tokens of a similar nature, regardless of nomenclature.
A New Discovery: Unveiling an Underwater Mountain Range in the Southern Ocean (India Today)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have discovered an ancient underwater mountain range hidden within the world's strongest ocean current, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
Context:
- During a recent research expedition, scientists discovered a previously unknown mountain range deep beneath the Southern Ocean’s surface.
- Using state-of-the-art sonar technology, researchers were able to map out the underwater landscape with astonishing accuracy, revealing a vast range of peaks, ridges, and valleys.
- This newfound mountain range spans hundreds of miles and is estimated to be millions of years old.
- Geological Significance: This discovery holds immense importance for our understanding of the Earth’s geological history.
- The underwater mountain range provides key evidence of plate tectonics and the movement of Earth’s crust, as well as the formation of new landmasses.
- By studying the composition and structure of these underwater formations, scientists will be able to gain insights into the geological processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
- Moreover, the discovery raises intriguing questions about the relationship between underwater mountains and the surface landscapes they may be connected to.
- Researchers are eager to investigate whether similar mountain ranges exist on land and whether they share a common origin.
- Implications for Climate and Ecosystems: The newfound underwater mountain range also has significant implications for climate and marine ecosystems.
- These underwater peaks can act as barriers, influencing ocean currents and affecting nutrient distribution.
- Understanding the impact of these formations on ocean dynamics is crucial for predicting climate patterns and better managing marine resources.
- Additionally, these underwater mountains create a unique habitat for a diverse range of marine species.
- The ridges and valleys provide sheltered zones where marine life can thrive, with the potential for new species discoveries.
- Protecting these habitats will be critical in preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
About the Southern Ocean:
- The Southern Ocean, also referred to as the Antarctic Ocean is one of the Earth's five major ocean basins.
- Its formation traces back approximately 34 million years when Antarctica and South America underwent a gradual separation, resulting in the creation of the Drake Passage.
- This passage, situated between the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and South America, delineates the Southern Ocean from the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, encompassing their tributary seas surrounding Antarctica below the 60° S latitude.
- Physiography: The ocean floor structure features a continental shelf, typically less than 160 miles (about 260 km) wide, expanding to a maximum width exceeding 1,600 miles (2,600 km) near the Weddell and Ross seas.
- Renowned for its robust winds, intense storms, marked seasonal variations, and frigid temperatures, the Southern Ocean is predominantly influenced by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC).
- This current, the longest, strongest, and deepest-reaching on Earth, follows a clockwise circulation around the continent, surpassing all others in the volume of water it transports globally.
- Biodiversity: The Southern Ocean sustains diverse flora and fauna, with a majority of marine life relying on the nutrient-rich phytoplankton found in the Antarctic Convergence.
- Notable species include whales, penguins, orcas, and seals, contributing to the region's rich biodiversity.
A new non-invasive formaldehyde sensor can detect adulterated fish at room temperature (DST GOI)
- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A new low-cost sensor made of metal oxide nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide composite can detect formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature in a non-invasive way. The sensor shows long-term stability with a low detection limit.
Context:
- A sensor designed for the detection of formalin in fish has been developed by the Nanomaterials and Nanoelectronics Laboratory at Guwahati University, Assam.
- The formalin sensor utilizes a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide, synthesized through a process involving the wet chemical approach for Graphene Oxide (GO) and the hydrothermal route followed by calcination for the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Testing of the sensor has been conducted both at the laboratory scale and on fish procured from the fish markets in the Guwahati region, specifically targeting potential adulteration.
- This groundbreaking research has received support from DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence) and has been documented in the journal ACS Appl. Nano Mater.
- Research Support: The research behind this innovative sensor is backed by DST-PURSE (Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence).
About Non-Invasive Formaldehyde Sensor:
- This non-invasive formaldehyde sensor incorporates a composite of tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide (rGO-SnO2) as its key materials.
- While reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has been widely utilized for detecting various toxic gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), tin oxide (SnO2) has demonstrated notable efficacy in formaldehyde detection, both in its pristine form and when combined with different compounds, including graphene.
- This combination is favoured for its heightened stability and sensitivity to low concentrations of formaldehyde.
- Synthesis Process: The fabrication process involves a wet chemical approach for the production of graphene oxide (GO), followed by the hydrothermal route and subsequent calcination to synthesize the tin oxide-reduced graphene oxide composite (rGO-SnO2).
- Comparison with Existing Sensors: Unlike commercial formalin sensors for fish, which are primarily electrochemical-based or colorimetric-based and often invasive, this novel sensor, made from metal oxide nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide, offers a cost-effective and non-invasive method for detecting formalin adulteration in fishes at room temperature.
- Challenges with Existing Sensors: Traditional electrochemical sensors, though widely used, tend to be expensive, and colourimetric sensors, while more cost-effective, share the invasive nature of their electrochemical counterparts. Both face challenges related to low-level and selective detection.
- Significance of the New Sensor: The development of gas sensors based on 2D materials, such as graphene, opens up new possibilities for the effective detection of toxic vapours at room temperature.
- These sensors hold promise for accurately detecting formalin emanating from adulterated food products.
What is Formaldehyde?
- Formaldehyde (CH?O) is an odorless, colorless gas with high toxicity and flammability under standard room temperature conditions.
- Primary Applications:
- Production of fertilizers, paper, plywood, and certain resins.
- Utilized as a food preservative.
- Found in glues, resins, dyes, textiles, disinfectants, building materials, automotive components, embalming processes, and laboratory settings.
- Incorporated into household items like antiseptics, medications, and cosmetics.
- Potential Health Effects:
- Exposure to formaldehyde may result in irritation of the skin, throat, lungs, and eyes. Additionally, formaldehyde is recognized as a carcinogenic substance.
For Huntington’s disease clues, scientists are looking in fruit flies (The Hindu)
- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists at the University of Szeged in Hungary have made significant progress in advancing our understanding of Huntington's disease through the study of fruit flies.
What is Huntington’s Disease?
- Huntington’s disease (HD) is a brain disorder that is passed down in families from generation to generation.
- It is caused by an error in the DNA instructions that build our body and keep it running.
- DNA is made up of thousands of genes, and people with HD have a small defect in a gene called huntingtin.
- Over time, this error causes damage to the brain and causes symptoms of Huntington’s disease.
- Huntington’s disease causes a person’s physical, mental and emotional abilities to deteriorate, usually during their prime at work, and there is currently no cure.
- Most people start developing symptoms in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50, but HD can also occur in children and young adults.
- Huntington’s disease is known as a family disease because each child of a parent with HD has a 50/50 chance of inheriting the defective gene.
Huntington’s Disease Symptoms:
- Symptoms of Huntington’s disease can vary greatly from person to person but typically include:
- Personality changes, mood swings and depression
- Forgetfulness and impaired judgment
- Unsteady gait and involuntary movements (chorea)
- Slurred speech, difficulty swallowing and significant weight loss.
- Symptoms typically worsen over the course of 10 to 25 years, affecting the ability to reason, walk, and speak.
- The person with HD or their friends and family may notice difficulty planning, remembering, and concentrating on the task.
- They can develop mood swings such as depression, anxiety, irritability, and anger.
- Most people with Huntington’s disease become “fidgety” and develop facial and limb movements known as chorea, which they cannot control.
- The symptoms of Huntington’s disease are sometimes described as ALS, Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s all at the same time.
Huntington’s Disease Treatment:
- No treatment can stop or reverse the progression of Huntington’s disease.
- Antipsychotic medications can relieve chorea and help control hallucinations, delusions, and violent outbursts.
- Huntington’s disease causes disability that gets worse over time.
How the PM JANMAN scheme can help Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (Indian Express)

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN), aimed at providing PVTG households and habitations with basic facilities such as safe housing, clean drinking water and sanitation, improved access to education, health and nutrition, road and telecom connectivity, and sustainable livelihood opportunities.
What is the PM-JANMAN Scheme?
- PM-JANMAN is a government initiative aimed at integrating tribal communities into the mainstream of development.
- The scheme, comprising both Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes, will be executed collaboratively by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, State governments, and Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG) communities.
Key Features:
- Implementation Scope: The scheme focuses on 11 critical interventions managed by 9 line Ministries, ensuring the effective execution of existing schemes within villages inhabited by PVTGs.
- Sectoral Coverage: PM-JANMAN spans various sectors, encompassing initiatives such as ensuring safe housing through the PM-AWAS Scheme, access to clean drinking water, improved healthcare, education, nutrition, road and telecommunications connectivity, and the promotion of sustainable livelihoods.
- Special Initiatives: The plan includes specific initiatives such as the establishment of Van Dhan Vikas Kendras to facilitate the trade of forest produce, deployment of off-grid solar power systems for 1 lakh households, and installation of solar street lights.
- Objectives: PM-JANMAN aims to enhance the quality of life and overall well-being of PVTGs by addressing the various forms of discrimination and exclusion they face.
- Additionally, it recognizes and values the unique and significant contributions of PVTGs to both national and global development.
How Does PM-JANMAN Differ?
- Distinctive Identification and Recognition: Criticism has arisen over outdated criteria for identifying Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- The presence of repetitive names and discrepancies in recognition across states has led to confusion and exclusion.
- Addressing these concerns, PM-JANMAN introduces a Human Development Index for PVTGs, aiming to enhance proper identification and tailored development planning based on updated and comprehensive data.
- Participatory Bottom-Up Approach: In a departure from the 'one-size-fits-all' approach, PM-JANMAN adopts customised strategies that respect the unique needs and priorities of PVTGs.
- Emphasizing a participatory bottom-up approach, the scheme actively involves PVTGs in decision-making processes, particularly regarding land rights, social inclusion, and cultural preservation.
- Livelihood Promotion: PM-JANMAN focuses on sustainable livelihoods for PVTGs by providing skills training, essential resources such as land and credit, and implementing the Forest Rights Act (FRA) to secure land titles, particularly under Section 3(1)(e) for primitive tribal groups and pre-agricultural communities.
- The scheme encourages the preservation of cultural heritage through the promotion of traditional technologies and skill enhancement via industry partnerships.
- Health, Nutrition, and Education: To address the unique challenges faced by PVTGs, PM-JANMAN incorporates Mobile Medical Health Units for healthcare outreach in remote areas.
- The scheme also emphasizes cultural sensitivity in education by integrating PVTG culture and language into the curriculum, providing transportation, and training teachers about PVTG cultural contexts.
- Infrastructure Development: Recognizing that PVTG habitations may not meet standard criteria for existing schemes, PM-JANMAN relaxes guidelines for infrastructure schemes like Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, and Jal Jeevan Mission.
- This ensures improved access to housing, water, sanitation, electricity, and connectivity for PVTGs.
What are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)?
- PVTGs represent the most vulnerable segments within tribal communities, facing heightened challenges in various aspects of development.
- Due to their distinct vulnerabilities, more developed and assertive tribal groups often receive a significant portion of tribal development funds, necessitating a focused allocation of resources for the advancement of PVTGs.
- The designation of PVTGs dates back to 1975 when, based on the recommendations of the Dhebar Commission, the Government of India identified 52 tribal groups with unique vulnerabilities.
- Presently, there are 75 PVTGs among the 705 Scheduled Tribes in India.
- Geographically, PVTGs are distributed across 18 states and one Union Territory, as per the 2011 census, with Odisha having the highest number, exceeding 2.5 lakh individuals.
- Distinctive Characteristics of PVTGs:
- Stagnant or declining trends.
- Primarily pre-agricultural practices.
- Exceptionally low educational attainment.
- Predominantly subsistence level, indicating a reliance on basic, self-sustaining economic activities.
How Japan’s moon-landing attempt in January will affect Chandrayaan 4 (The Hindu)
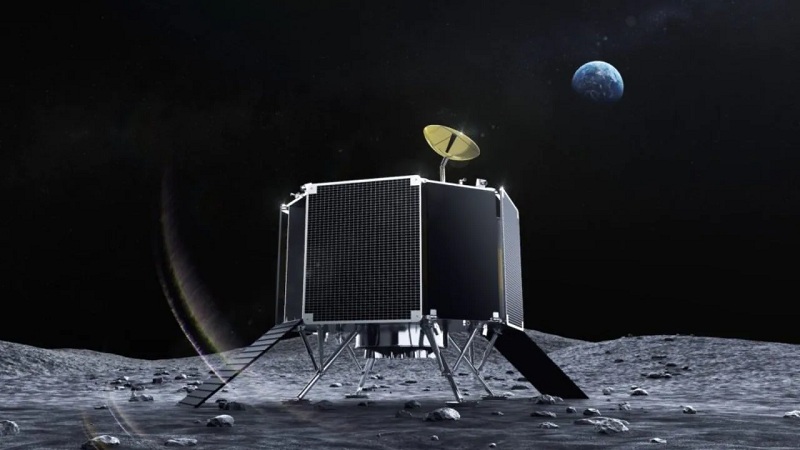

- 28 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the “Moon Sniper” lander developed by Japan’s space agency successfully entered lunar orbit.
About the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) Mission:
- The Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) is a spacecraft crafted and launched by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) on September 7, 2023, from the Tanegashima spaceport.
- Remarkably lightweight at 590 kg, SLIM embarked on its mission alongside XRISM, a cutting-edge X-ray space telescope, on an H-2A rocket.
- Upon launch, SLIM assumed an elliptical orbit around the moon within a span of approximately three minutes.
- Notably, the apogee (farthest point) of this orbit extends to 4,000 km, while the perigee (closest point) hovers at 600 km above the lunar surface.
Objectives of SLIM on the Lunar Surface:
- Before its lunar descent, SLIM is programmed to release two compact rovers known as Lunar Excursion Vehicle (LEV) 1 and 2.
- Working in tandem with SLIM, LEV-1, and LEV-2 are tasked with conducting a comprehensive study of the lunar surface near the designated landing area.
- Their mission encompasses the collection of temperature and radiation readings, as well as endeavours to investigate the moon's mantle.
- This collaborative effort by SLIM and its rovers aims to enhance our understanding of lunar conditions and contribute valuable insights to lunar exploration.
What is the XRISM Mission:
- The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) is a collaborative effort between the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with valuable contributions from the European Space Agency (ESA).
- Mission Objective: XRISM is designed to observe X-rays emanating from deep space, aiming to precisely identify their wavelengths with an unprecedented level of accuracy.
- The mission employs cutting-edge spectroscopy techniques to measure changes in the brightness of celestial objects across various wavelengths.
- Technological Advancements: Leveraging state-of-the-art spectroscopy, XRISM can detect X-rays within a broad energy spectrum ranging from 400 to 12,000 electron volts.
- To provide a perspective, the energy of visible light typically falls within the 2 to 3 electron volts range.
- This expanded energy range enables astrophysicists to gain novel insights into some of the universe's most dynamic regions, vast structures, and entities characterized by formidable gravitational forces.
India, Russia ink pacts on the construction of future power units of the Kudankulam nuclear plant (The Hindu)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a major boost to their time-tested partnership, India and Russia recently signed some "very important" agreements related to the construction of the future power-generating units of the Kudankulam nuclear power plant.
About the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project:
- The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project is India's largest nuclear power plant situated in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu.
- It is being developed by the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) in collaboration with Russia's Rosatom State Atomic Energy Corporation.
- The construction began in March 2002.
- Since February 2016, the first power unit of the Kudankulam NPP has been steadily operating at its design capacity of 1,000 MW.
- The plant is expected to start operating at full capacity in 2027.
- Water-Water Energy Reactor: The Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project employs VVER (Water-Water Energy Reactor) technology, a pressurized water reactor design developed in the former Soviet Union, known for its safety and reliability.
- Power Generation Capacity: The current power generation capacity is 2×1,000 MWe VVER, expected to significantly increase with the construction of four additional reactors, estimated at ?89,470 crore.
- All units are subject to International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) safety analysis, except the Kalpakkam nuclear plant, reserved for strategic use under the India-US Nuclear Agreement.
What is the 3-Stage Nuclear Programme of India?
- India's nuclear program is structured into three stages, strategically designed to harness the extensive Thorium deposits within the country, constituting approximately 25% of the world's total reserves.
- This focus on Thorium is crucial as India possesses limited Uranium reserves, accounting for about 2% of the global uranium reserves.
- 1st Stage: The initial stage employs Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors that operate on natural uranium, consisting of 99.3% U-238 and 0.7% U-235.
- The fissile U-235 triggers a chain reaction, while the non-fissile U-238 transforms into Pu-239 as a byproduct (spent fuel).
- This Pu-239 is subsequently utilized in the Fast Breeder Reactors in the 2nd stage.
- 2nd Stage: Fast Breeder Reactors primarily rely on Plutonium, utilizing a combination of Plutonium-239 from the 1st stage and the abundant U-238 found on Earth to generate additional Plutonium inside the reactor.
- As U-238 does not initiate a chain reaction, the reactors are termed Breeder reactors.
- To maximize the chances of neutron interaction with U-238, these reactors, known as Fast Breeder Reactors, omit a moderator to slow down neutrons.
- Once Plutonium-239 is fully consumed, Thorium is introduced to convert it into U-233, to be used in the 3rd stage.
- 3rd Stage: Thermal Breeder Reactors utilize U-233 produced in the 2nd stage, incorporating thorium-232.
- Notably, Thorium is non-radioactive and non-fissile. Since these reactors also generate U-233 from Thorium-232, they are classified as breeder reactors.
- India's significant reserves of thorium, particularly in the form of monazite sand, emphasize the critical role of the 3rd stage in India's nuclear energy portfolio.
PM Narendra Modi calls upon religious leaders and social organizations to launch a mass movement against drugs (NewsOnAir)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Veer Bal Diwas in New Delhi, PM Narendra Modi calls upon religious leaders and social organizations to launch a mass movement against drug menace.
Drug Menace in India:
- Alcohol, cannabis, opium, and heroin constitute the primary drugs abused in India.
- Approximately 13% of substance abusers in the country are under 20 years old.
- Adolescence is identified as a critical-risk period for the initiation of substance use.
- Children impacted by substance abuse fall under the category of children in need of care and protection as per the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015.
- In various regions, including Punjab, Assam, Mizoram, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Bihar, Delhi, etc., drug abuse prevalence is notably high.
- Key causes of drug abuse include factors such as poverty, peer pressure, illiteracy, low self-esteem, and genetic predisposition.
Challenges in Combating the Drug Menace:
- India, strategically located between the Death Triangle (Thailand, Myanmar, and Laos) and Death Crescent (Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Iran), is a prominent hub for drug trafficking, particularly in major opium production regions globally.
- Porous borders exacerbate the problem, and technological advancements, such as the utilization of the dark net and cryptocurrency for drug trafficking, further complicate law enforcement efforts.
- Criminalizing drug abuse contributes to social stigma for addicts, deterring them from seeking essential medical assistance.
- There is a notable absence of comprehensive studies assessing the societal impact of drug abuse, hindering the formulation of informed strategies.
Efforts to Combat the Drug Menace:
- The Narcotics Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act of 1985 outlines measures for identification, treatment, and rehabilitation.
- The Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan targets 272 highly vulnerable districts with a focus on community outreach.
- The Seizure Information Management System (SIMS) portal facilitates the management of cases involving substantial drug seizures.
- The National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) spanning 2018-2025 adopts a comprehensive, multi-pronged strategy.
- Furthermore, adherence to international conventions, including the Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961) and the Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971), reinforces India's commitment to addressing the global issue of drug abuse.
Atomic watchdog report says Iran is increasing production of highly enriched uranium (Indian Express)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Iran has increased the rate at which it is producing near weapons-grade uranium in recent weeks, reversing a previous slowdown that started in the middle of this year, the International Atomic Energy Agency said in a report.
What is Uranium Enrichment?
- Natural uranium is comprised of two isotopes, with approximately 99% being U-238 and only about 0.7% being U-235.
- U-235 is a fissile material capable of sustaining a chain reaction within a nuclear reactor.
- The enrichment process involves increasing the proportion of U-235 through isotope separation, effectively isolating U-238 from U-235.
- For the production of nuclear weapons, enrichment is necessary up to 90% or more, referred to as weapons-grade uranium.
- Low-enriched uranium, typically containing a 3-5% concentration of U-235, is suitable for generating fuel for commercial nuclear power plants.
- In contrast, highly enriched uranium, boasting a purity of 20% or more, finds application in research reactors.
Key Facts About Uranium:
- Discovered in 1789 by the German chemist Martin Klaproth, Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element found in the periodic table, characterized by its atomic number 92.
- This element holds the distinction of having the highest atomic weight among all naturally occurring elements.
- Naturally present in low concentrations in soil, rock, and water, uranium is commercially extracted from minerals like uraninite.
- The mining of uranium ore can be undertaken through open pits or underground excavations, followed by crushing and processing at a mill to isolate the valuable uranium.
- An alternative method involves the direct dissolution of uranium from ore deposits in the ground, known as in-situ leaching, with the extracted uranium then pumped to the surface.
About the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- The International Atomic Energy Agency is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons.
- Established as an autonomous entity through its international treaty, the IAEA Statute, the organization, nonetheless, reports to both the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- Headquartered in Vienna, Austria, the IAEA collaborates with its Member States and various global partners to advance the safe and peaceful utilization of nuclear technologies.
- It employs nuclear safeguards, encompassing monitoring, inspection, information analysis, and other measures, to ensure the peaceful nature of nuclear activities and to detect and deter any potential diversion towards weapons-related purposes.
- The IAEA plays a crucial role in implementing comprehensive safeguards agreements mandated by the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), acting as a frontline defense against nuclear weapons proliferation.
- Additionally, the agency facilitates the exchange of scientific and technical information among its Member States.
- A key function of the IAEA is to bolster national, regional, and international capabilities to respond effectively to nuclear and radiological incidents, thereby minimizing their impact.
Zombie deer disease: Why are scientists concerned over its transmission to humans? (TOI)
- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Researchers in the US have warned that Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) spreading among wildlife across North America, could also spread to humans.
What is Zombie Deer Disease??
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Zombie deer disease or chronic wasting disease is a prion disease that affects deer, elk, reindeer, sika deer and moose.
- Prion diseases affect both humans and animals and are distinguished by long incubation periods.
- In the case of chronic wasting disease or the zombie deer disease, "it may take over a year before an infected animal develops symptoms.
- History of the Disease?: The zombie deer disease was first discovered in Colorado (USA) in 1967.
- Until now, reports of humans getting affected have not come to the fore.
- However, the findings of several studies suggest that it can easily jump to human beings.
Why are health experts and scientists worried about a possible transmission??
- Experts are giving examples of the mad cow disease or the Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE).
- “The BSE outbreak in Britain provided an example of how, overnight, things can get crazy when a spillover event happens from livestock to people.
Symptoms of the Disease:
- The common signs of the disease are drastic weight loss (wasting), stumbling, and other neurologic symptoms.
- Other symptoms seen in animals infected with this disease are listlessness, drooling, excessive thirst or urination, drooping ears, and lack of fear of people.
It is difficult to eradicate this disease??
- The chronic wasting disease is extremely difficult to eradicate from the environment once the infection has started.
- It can persist for years in dirt or on surfaces, and it is resistant to disinfectants, formaldehyde, radiation, and incineration at 600C (1,100F).
- Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) is fatal to animals, and there are no treatments or vaccines.
Prevention?:
- To avoid the spread of the disease, humans should avoid shoot, handling, or eating meat from deer and elk that look sick or are acting strangely or are found dead.
- Individuals should wear latex or rubber gloves when dressing the animal or handling the meat.
Speed up measures for a new dam at Mullaperiyar, Kerala tells Central Water Commission (The Hindu)

- 27 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently the State government of kerala has urged the Centre to speed up measures for building a new dam at Mullaperiyar in the Idukki district at a meeting with the Central Water Commission.
About the Central Water Commission (CWC):
- The Central Water Commission (CWC) is a leading technical organization in India dedicated to water resources management.
- Currently operating as an attached office of the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India, it plays a pivotal role in overseeing various aspects of water resource management nationwide.
Key Functions:
- Initiation and Coordination: The Commission is responsible for initiating, coordinating, and advancing schemes in collaboration with concerned State Governments.
- These schemes focus on controlling, conserving, and utilizing water resources for Flood Control, Irrigation, Navigation, Drinking Water Supply, and Water Power Development.
- Investigation and Execution: The CWC undertakes the investigation, construction, and execution of water resource schemes as deemed necessary.
- Leadership and Structure: The Commission is led by a Chairman, holding the status of Ex-Officio Secretary to the Government of India.
- The organizational structure includes three wings:
- Designs and Research (D&R) Wing
- River Management (RM) Wing
- Water Planning and Projects (WP&P) Wing
- Each wing is overseen by a full-time member with the status of Ex-Officio Additional Secretary to the Government of India.
- Headquarters: The headquarters of the Central Water Commission is located in New Delhi.
Key Facts About Mullaperiyar Dam:
- The Mullaperiyar Dam is a masonry gravity dam, situated on the Periyar River in Thekkady, Idukki district of Kerala.
- Situated at an elevation of 881 meters above sea level, it graces the Cardamom Hills within the Western Ghats.
- The dam is strategically located at the convergence of the Mullayar and Periyar rivers.
- Its construction, led by the British Corps of Royal Engineers under Pennycuick, commenced in 1887 and concluded in 1895.
- Utilizing limestone and "Surkhi" (a blend of burnt brick powder, sugar, and calcium oxide), the dam serves the purpose of redirecting west-flowing River Periyar waters to the rain shadow regions of Theni, Madurai, Sivaganga, and Ramanathapuram districts in Tamil Nadu.
- The Periyar National Park is located around the dam's reservoir.
- Despite its location in Kerala, the dam is operated and maintained by Tamil Nadu under a 999-year lease agreement established during British rule.
Good Governance Day: Govt launches 3 new features on iGOT Mission Karmayogi platform (TOI)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of Good Governance Day, Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh launched the Extended Version of Mission Karmayogi by introducing three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform that include My iGOT, Blended Programs and Curated Programs..
About Mission Karmayogi:
- Mission Karmayogi, the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), is geared towards equipping Civil Servants with enhanced creativity, constructiveness, and innovation, utilising transparency and technology to prepare them for future challenges.
- This innovative program serves as a cornerstone for the country's civil servants, emphasizing a balanced approach between 'on-site learning' and traditional 'off-site learning.'
- Approved by the Government on September 2, 2020, Mission Karmayogi encompasses six key pillars:
- Policy Framework
- Institutional Framework
- Competency Framework
- Digital Learning Framework (iGOT-Karmayogi)
- The electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS), and
- The Monitoring and Evaluation Framework.
- Encompassing all civil servants, including contractual employees, across various ministries, departments, organizations, and agencies of the Union Government, the program introduces three new features on the iGOT Karmayogi platform:
- My iGOT: Delivers targeted training courses on the home page of individual officers, directly addressing their unique capacity-building needs identified in the Capacity-Building Plan for their Ministries/Departments.
- Blended Programs: Facilitates equitable access to training methodologies across all levels by integrating traditional offline (in-person) classroom courses with online learning components.
- This approach enables officers and faculty to benefit from both the flexibility of online courses and the invaluable interactions of face-to-face classroom sessions.
- Curated Programs: Designed to cater to diverse learning needs of Ministries/Departments and Training Institutions, offering a custom approach to address the specific requirements of different segments within the civil services.
Six armed poachers, timber mafia held by forest officials at Similipal National Park (New Indian Express)
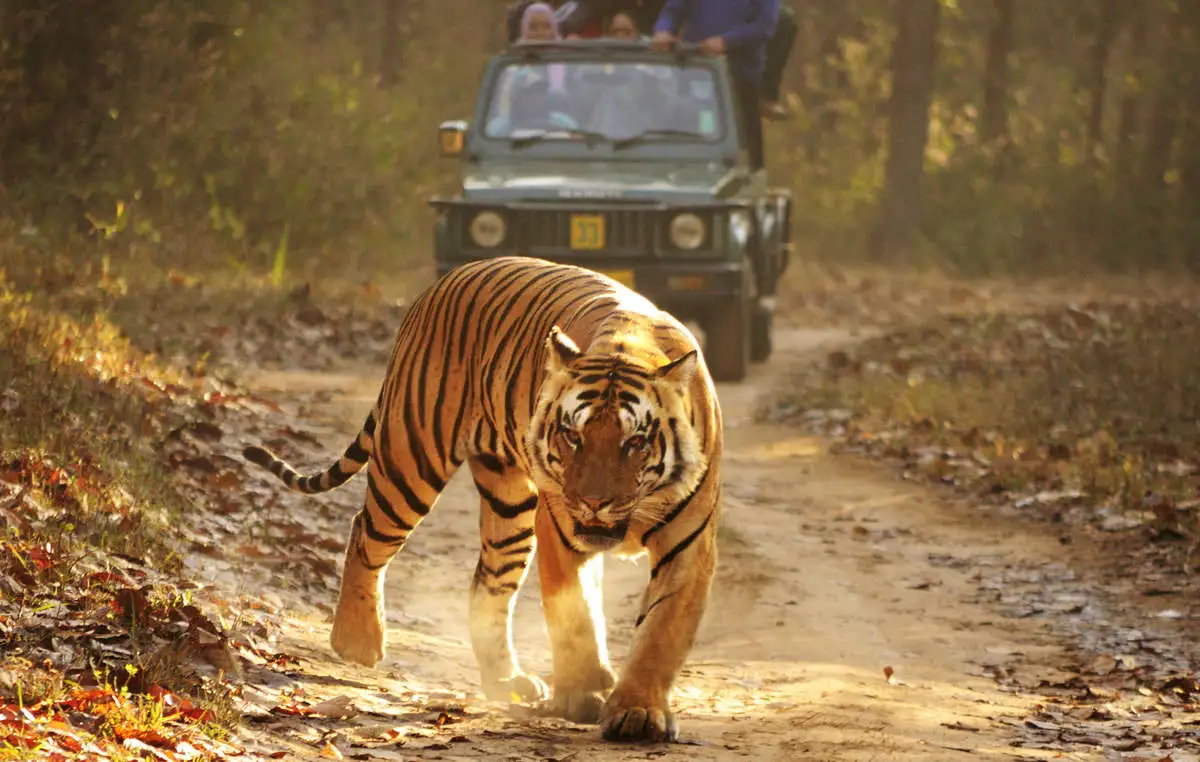

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In a significant breakthrough, forest officials at Similipal National Park apprehended four armed poachers and two members of the timber mafia in separate locations on Saturday night.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Similipal Tiger Reserve is located within the Mayurbhanj District, in the Northernmost part of Odisha.
- Declared a 'Tiger Reserve' in 1956, STR became a part of the national conservation initiative 'Project Tiger' in 1973.
- Recognized by UNESCO in 2009, STR, along with a transitional area covering 2250 sq. km, was included in the World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- Terrain: Surrounded by high plateaus and hills, STR boasts the twin peaks of Khairiburu and Meghashini, reaching 1515m above mean sea level.
- The undulating and hilly terrain features open grasslands and wooded areas, with the inclined plateau rising abruptly from the low coastal plains.
- Hydrography: The region is crisscrossed with perennial water sources, contributing to rivers like Budhabalanga, Salandi, and various tributaries of the Baitarani River.
- Vegetation: STR encompasses a diverse mix of forest types and habitats, with Northern tropical moist deciduous dominating alongside semi-evergreen patches.
- Notably, it hosts the world's only landscape with melanistic tigers.
- Tribes: The vicinity of STR is inhabited by various tribes, including Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia, and Sahara.
- Flora: Home to an impressive 1078 plant species, including 94 orchid species, STR is characterized by the dominance of Sal trees.
- Fauna: The reserve is home to a variety of wildlife, including leopard, gaur, elephant, langur, barking and spotted deer, sloth bear, mongoose, flying squirrel, porcupine, turtle, monitor lizard, python, sambar, pangolin, and more.
What is the Special Tiger Protection Force (STPF)?
- Realizing the importance of ‘tiger protection’ in biodiversity conservation, the Finance Minister announced policy initiatives in February 2008, for constituting the ‘Special Tiger Protection Force’ (STPF).
- Based on the one-time grant of Rs. 50 crore was provided to the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) for raising, arming and deploying a Special Tiger Protection Force, the proposal for the said force has been approved by the competent authority for 13 tiger reserves.
- The STPF has been made operational in the States of Karnataka (Bandipur), Maharashtra (Pench, Tadoba-Andhari, Nawegaon-Nagzira, Melghat), Rajasthan (Ranthambhore), Odisha (Similipal) and Assam (Kaziranga), out of 13 initially selected tiger reserves, with 60% central assistance under the ongoing Centrally Sponsored Scheme of Project Tiger (CSS-PT).
Union Health Minister Launches MedTech Mitra Platform to Empower Medical Technology Innovators (NewsOnAir)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Health Minister Dr Mansukh Mandaviya has launched MedTech Mitra - a strategic initiative to empower MedTech innovators and advance healthcare solutions.
What is the MedTech Mitra Portal?
- The MedTech Mitra portal is an online platform designed to support medtech innovators by assisting in clinical evaluation, regulatory facilitation, and the adoption of new products in the medical technology sector.
- This collaborative initiative is overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), operating under the direction/guidance of NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission.
Significance:
- In conjunction with recent policies and incentive schemes, such as the medical devices policy and the production-linked incentive scheme, the MedTech Mitra platform aims to catalyze growth in the medical devices sector and promote domestic manufacturing.
- These initiatives seek to foster the indigenous development of affordable and high-quality MedTech devices and diagnostics, thereby significantly reducing the sector's reliance on imports.
- The platform is envisioned to streamline the innovation process and facilitate research and development for emerging start-ups, ensuring a smoother journey from concept to product.
- By offering comprehensive guidance, including support for animal and clinical trials, the platform aims to bridge gaps for startups and promote ease of innovation.
- The MedTech Mitra portal is poised to foster collaborations between engineers, scientists, and clinicians, addressing a previously existing gap in partnerships within the sector.
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) serves as the apex institution in India responsible for formulating, coordinating, and advancing biomedical research.
- With a primary mandate to conduct, coordinate, and implement medical research for societal benefit, ICMR is dedicated to translating medical innovations into tangible products and processes, subsequently integrating them into the public health system.
- Financial support for ICMR is provided by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
AstroSat detects millisecond X-ray bursts from high magnetic field neutron stars (DD News)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India’s first multi-wavelength space-based observatory, AstroSat, has detected intense sub-second X-ray bursts emanating from a neutron star with an ultrahigh magnetic field, known as a magnetar.
What is X-ray Bursts?
- X-ray bursts manifest in low-mass X-ray binary systems featuring a neutron star and a low-mass main sequence star orbiting each other.
- The occurrence of these bursts is intricately linked to the gravitational dynamics of the neutron star and its companion.
- In this system, the proximity and intense gravitational forces of the neutron star cause the companion star to exceed its Roche-lobe, leading to the formation of an accretion disk around the neutron star.
- This disk becomes a repository for hydrogen drawn from the overflowing companion star.
- As hydrogen accumulates on the neutron star's surface, the extreme temperatures and pressures prevailing there catalyze its transformation into helium.
- This ongoing process results in the formation of a thin surface layer of helium.
- When this helium layer reaches a critical mass, a sudden explosive ignition occurs, elevating the entire neutron star's surface temperature to several tens of millions of degrees and releasing a burst of X-rays.
- Following the outburst, the binary system returns temporarily to a quiescent state, allowing the neutron star to reaccumulate the helium surface layer gradually.
- This cyclic process leads to the recurrence of X-ray bursts, typically unfolding at regular intervals separated by several hours or days.
About Indias’ AstroSat:
- AstroSat stands as India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory, pioneering a mission focused on the simultaneous study of celestial sources across X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands.
- Launched with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, AstroSat took flight aboard the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota on September 28, 2015.
- It entered a 650 km orbit, inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The Mission Operations Complex (MOX) at ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru oversees the satellite throughout its mission life.
- With a minimum useful life of around 5 years, AstroSat is dedicated to achieving the following scientific objectives:
- Understanding high-energy processes in binary star systems housing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimating magnetic fields associated with neutron stars.
- Investigating star birth regions and high-energy processes in star systems beyond our galaxy.
- Detecting new, briefly bright X-ray sources in the celestial sphere.
- Conducting a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
India shedding mentality of slavery, says PM Modi (The Hindu)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Speaking at a "Veer Bal Diwas" event to commemorate the martyrdom of two sons of Guru Gobind Singh, PM Modi said their sacrifices are not only being remembered in India but also globally through programmes in other countries as well
About Veer Bal Diwas:
- Veer Bal Diwas is observed annually on December 26th to commemorate the valour and sacrifice of the four sons of Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh guru.
- The four sons, named Zorawar Singh, Fateh Singh, Jai Singh, and Kulwant Singh, played a significant role in resisting the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb and his army.
- Zorawar Singh and Fateh Singh were captured by the Mughals at the ages of six and nine, respectively, after defending the fort of Anandpur Sahib from a siege.
- Subsequently, they were taken to Sirhind, where, steadfast in their faith, they refused to convert to Islam and were sentenced to a tragic death by being bricked alive in 1705.
- Jai Singh and Kulwant Singh, also captured at Anandpur Sahib, managed to escape from Sirhind with the assistance of loyal followers.
- They later joined their father in his final battle at Sirhind, where Guru Gobind Singh was wounded by a musket shot.
- The unwavering courage and sacrifice of Guru Gobind Singh's sons became a symbol of inspiration for generations of Sikhs, reflecting their dedication to the cause of Sikhism.
About Guru Gobind Singh:
- Guru Gobind Singh, the last of the ten Sikh Gurus, was born on December 22, 1666, in Patna, Bihar.
- His birth anniversary is observed according to the Nanakshahi calendar.
- Assuming the role of Sikh Guru at the tender age of nine after the passing of his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, he served until his assassination in 1708.
Contributions:
- Religious: Guru Gobind Singh made profound contributions to the Sikh religion, introducing practices such as wearing a turban to cover hair.
- He laid the foundation for the Khalsa (1699), embodying the Five 'K's: kesh (uncut hair), kanga (wooden comb), kara (iron or steel bracelet), kirpan (dagger), and kachera (short breeches).
- These articles of faith became integral to the identity of a Khalsa.
- Establishing various rules for Khalsa warriors, including abstaining from tobacco, alcohol, and halal meat, Guru Gobind Singh emphasized their duty to protect innocent people from persecution.
- Guru Gobind Singh designated Guru Granth Sahib as the spiritual guide for both the Khalsas and Sikhs.
- Martial: Engaging in the battle of Muktsar in 1705, Guru Gobind Singh fiercely opposed the Mughals.
- The Battle of Anandpur in 1704 resulted in the tragic loss of the Guru's mother and two minor sons, who were executed. His eldest son also fell in battle.
- Literary: Guru Gobind Singh's legacy includes compositions like Jaap Sahib, Benti Chaupai, and Amrit Savaiye.
- Notably, he wrote the Zafarnama, a letter addressed to the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb, showcasing his literary prowess and resilience.
‘Dunki’ and immigration: How the first modern passports came to be (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The recently released Shah Rukh Khan’s movie ‘Dunki’ is said to be based on the ‘donkey route’ or ‘donkey flight’ that lakhs of Indians take to reach countries like the US, the UK or some other European countries.
What is a Donkey Journey?
- Dunki is the Punjabi idiom that means to "hop from place to place", according to the Migration Policy Institute (MPI).
- It is a colloquial term for "donkey flights" or the "donkey flights method", which is a dangerous illegal immigration technique involving crossing a country's borders through a backdoor route via multiple stops in other countries.
How does the donkey flight method or dunki work?
- The desire for a higher quality of life has given rise to an industry driven by "agents" who charge exorbitant fees to help smuggle people to the country of their choice.
- Some agents may even run legitimate businesses while offering this dangerous option.
- The agents can offer various services, from fake papers to help through otherwise legal migration processes to smuggling people through ship containers.
Which countries are most targeted using the Dunki method?
- While donkey flight can be used to enter any country, the US, Canada, and the UK are some of the most popular destinations undertaken by Indian immigrants.
- According to a report, between February 2019 and March 2023, as many as 149,000 Indians were detained for attempting to enter the US illegally.
- Of this, most of those detained were from Gujarat and Punjab.
Risks involved in the dunki method:
- Dunki comes with tremendous risks, including the risk of capture, imprisonment, and deportation.
- When facilitated by an agent, the system is highly exploitative.
- Many sell off their assets, including ancestral land, to pay these agents.
- Agents may also withhold people's passports or other important documents to extort more money and assets.
- Moreover, smuggled migrants are also more vulnerable to becoming victims of other crimes during the smuggling process.
- The terrains of the places through which immigrants may have to travel pose a range of risks, including harsh weather conditions, rugged terrains, and access to basic resources like food and water.
- It must be noted that migrant smuggling is not the same as human trafficking.
- However, these crimes may sometimes interlink, adding another layer of risk for those engaging in illegal immigration.
About Passports:
- Rooted in history, passports trace back to mentions in the Hebrew Bible and structured systems in nations like France and the UK.
- The evolution into modern passports was catalyzed by the British Nationality and Status of Aliens Act in 1914, introducing features such as photographs and distinctive characteristics.
- The League of Nations' 1920 conference sought to standardize passport regulations, contributing to the establishment of a common British system.
- During the 1920s, the United States linked immigration laws to passports, imposing limitations on inflows.
- Despite initial reservations, passports have persisted as an integral element of contemporary citizenship.
- Indian Passports: The initiation of issuing Indian passports dates back to the First World War (1914-1918) through the Defence of India Act, as mandated by the British government for travel.
Assam-Meghalaya panels for boundary dispute to submit reports by December 31 (The Hindu)
- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The regional committees on the boundary dispute between Assam and Meghalaya have been asked to submit their reports by December 31, a Meghalaya government official said on Friday, December 22.
What is the Assam-Meghalaya Border Dispute?
- The Assam and Meghalaya have a longstanding dispute in 12 stretches of their 884-km shared border.
- The areas include Upper Tarabari, Gazang Reserve Forest, Hahim, Langpih, Borduar, Boklapara, Nongwah, Matamur, Khanapara-Pilangkata, Deshdemoreah Block I and Block II, Khanduli, and Retacherra.
Historical Context:
- During British rule, undivided Assam encompassed present-day Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, and Mizoram.
- Meghalaya was delineated in 1972, following the Assam Reorganisation (Meghalaya) Act of 1969, but differing interpretations of the border emerged.
- In 2011, Meghalaya identified 12 disputed areas, covering approximately 2,700 sq km.
Key Point of Contention:
- A focal point of discord is Langpih in West Garo Hills, bordering Kamrup district in Assam.
- Post-Independence, Langpih transitioned from Kamrup district to Garo Hills and Meghalaya.
- Assam contends it's part of the Mikir Hills, while Meghalaya questions the inclusion of Blocks I and II of the Mikir Hills (now Karbi Anglong) in Assam.
Efforts to Resolve Dispute:
- In 1985, an official committee, led by former Chief Justice of India Y V Chandrachud, was formed but didn't yield a resolution.
- Both states identified six out of 12 disputed areas for resolution, resulting in a Memorandum of Understanding in March 2022.
- The second round of discussions for the remaining areas commenced in November 2022.
Potential Solutions:
- Utilizing satellite mapping for precise border demarcation.
- Leveraging constitutional provisions like Article 263 for the Inter-state Council to advise on disputes and coordinate policies.
- Reviving Zonal Councils to address common concerns among states in each zone, including border disputes and economic planning.
- Embracing the spirit of cooperative federalism to strengthen India's unity in diversity.
IIT Guwahati researchers devise mathematical model to help prevent riverbank erosion (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A team of researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Guwahati has developed a new award-winning mathematical model to help prevent erosion of rivers like Brahmaputra.
What is BRAHMA-2D?
- BRAHMA-2D (Braided River Aid: Hydro-Morphological Analyzer) is a sophisticated mathematical model designed for assessing the flow dynamics of expansive braided rivers such as the Brahmaputra.
- Functioning as a quasi-3D river flow model, BRAHMA-2D offers insights into water velocity at various depths within the river and the circulation patterns around structures like spurs, crucial for preventing river bank erosion.
- Developed through collaboration between researchers at IIT Guwahati and the Brahmaputra Board under the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti, this innovative model plays a pivotal role in the design of sustainable hydraulic structures.
- Engineers can leverage BRAHMA-2D to create effective structures like spurs, river bends, and other protective measures to combat river bank erosion.
- The model's successful validation on the Brahmaputra River near Majuli Island in Assam, a region prone to river bank erosion, underscores its practical applicability.
- BRAHMA-2D integrates a two-dimensional water movement model with entropy theory, focusing on disorder or randomness.
- Notably, it identifies a unique dip phenomenon near spurs, where water flows underneath intensifies—a phenomenon absent at points away from these structures.
- Beyond erosion prevention, BRAHMA-2D extends its utility to environmental studies by assessing the habitat suitability of aquatic species, particularly endangered ones.
- This assessment is based on factors such as required depth and flow velocity, showcasing the model's versatility in addressing multifaceted challenges in river ecosystems.
About Brahmaputra River:
- Originating as Siang or Dihang from the Chemayungdung glacier in the Kailash range near Mansarovar Lake, the Brahmaputra enters India to the west of Sadiya town in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Tributaries: Dibang, Lohit, Siang, Burhi Dihing, Tista, and Dhansari contribute to its flow.
- This perennial river exhibits distinctive features influenced by its geography and prevailing climatic conditions.
- Experiencing biannual flooding, the first occurs from the melting Himalayan snow in summer, and the second is a consequence of monsoon flows.
- Climate change has amplified the frequency and intensity of these floods, posing a threat to populations and food security in the lower riparian states of India and Bangladesh.
- Known for its dynamism, the Brahmaputra undergoes frequent changes in course, driven by landslides and geological activities.
Three heritage projects in Punjab and Haryana bag UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards 2023 (Business Standard)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The resilient urban revitalisation of Rambagh Gate and Ramparts in Punjab, and heritage conservation projects related to Haryana's Church of Epiphany and Delhi's Bikaner House won Unescoawards on Thursday.
About Rambagh Gate & Ramparts:
- A three-story architectural marvel, the Rambagh Gate underwent meticulous restoration employing traditional building techniques.
- Locally sourced materials, including Nanak Shahi bricks set in lime mortar, were integral to the restoration process.
About Pipal Haveli, Gurdaspur:
- Pipal Haveli in Gurdaspur stands as a testament to ecological and traditional building methods, incorporating locally sourced materials and embracing vernacular architectural language.
- Notably, it actively promotes women's empowerment through initiatives like the BaRi Collective, offering programs that enhance women's livelihoods through environmentally conscious craft practices.
What is the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation?
- UNESCO aims to promote private sector engagement and foster collaborations between the public and private sectors to preserve the cultural heritage of the Asia-Pacific region for the benefit of present and future generations.
- Since the year 2000, the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation have been acknowledging the accomplishments of private sector entities and public-private initiatives in effectively conserving or restoring structures, places, and properties of significant heritage value in the region.
- Noteworthy, among the recognized sites, five are located in China, six in India, and one in Nepal.
- Highlights of Award-Winning Sites in India:
- Rambagh Gate in Amritsar: Received the prestigious "Award of Excellence," the highest recognition across all categories.
- Pipal Haveli in Punjab: Honored for its sustainable development as a heritage rural homestay.
- Karnikara Mandapam at Kunnamangalam Bhagawati Temple in Kerala: Earned the esteemed "Award of Distinction."
- Epiphany in Haryana, David Sassoon Library and Reading Room in Mumbai, and Bikaner House in New Delhi: Recognized with the "Award of Merit" for their outstanding contributions to cultural heritage conservation.
CISF to take over security of Parliament complex after Lok Sabha breach | What's the plan (Indian Express)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Union Home Ministry has approved the deployment of the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) in the Parliament complex, according to a government order.
News Summary:
- Following the security breach on December 13, the Union Home Ministry has given the green light for CISF deployment in the Parliament complex.
- Collaborating with Parliament Security Services, CISF will oversee access control for both the new and old Parliament buildings.
What are the Current Security Arrangements in Parliament?
- The Delhi Police currently handles access control, including frisking and baggage scanning.
- In response to the recent incident, eight Delhi Police security personnel responsible for these duties were suspended.
- In the event of armed intervention, the Parliament Duty Group (PDG), an armed unit of the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), is deployed.
- The overall responsibility for security lies with the Parliament Security Service under the Lok Sabha Speaker.
About Central Industrial Security Force (CISF):
- Established under the Central Industrial Security Force Act, 1968, CISF is a key Central Armed Police Force (CAPF).
- Initially formed in 1969 with three battalions, it has evolved into a versatile organization boasting a current strength of 1,63,590 personnel.
- Operating under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Home Affairs, CISF's headquarters is situated in New Delhi.
Key Operations:
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: Safeguarding 353 establishments nationwide, including Atomic Power Plants, Space Installations, Defence Production Units, Mines, Oil Fields, and Refineries.
- Fire Protection: Maintaining a dedicated Fire Wing catering to 104 establishments for fire safety services.
- VIP Security: Mandated to provide security to VIP protectees categorized as Z+, Z, Y, and X across the country.
- Airport Security: Entrusted with the specialized task of airport security since 2000, following the hijacking of Indian Airlines Flight IC-814 to Kandahar.
- Private Sector Security: Authorized by an amendment to the CISF Act, the force offers security services, on a payment basis, to vital private and joint venture industrial entities contributing to the nation's security and economy.
- Examples include Infosys campuses, Patanjali Food and Herbal Park, and the Reliance refinery.
- Overseas Deployment: Contributing contingents to the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH).
- CISF stands out as the only Central Armed Police Force with a daily public interface, playing a crucial role in securing airports, the Delhi Metro, and iconic monuments.
Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar linking the Mediterranean and the Atlantic for shipping (The Hindu)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Iran has threatened to close the Strait of Gibraltar and the Mediterranean Sea unless Israel stops bombing Gaza.
About the Strait of Gibraltar:
- The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow water passage that serves as a crucial link connecting Europe and Africa, facilitating the connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Historical Significance: Prior to the inauguration of the Suez Canal in 1869, the Strait of Gibraltar held exclusive prominence as the sole gateway to the Mediterranean Sea.
- Geographical Borders: Positioned between Spain and the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar in the north, and Morocco and the Spanish exclave of Ceuta in the south, the strait spans approximately 58 km and reaches a width of about 13 km at its narrowest point.
- Depth and Geological Formation: With depths ranging from 300 to 900 meters, the strait constitutes a significant divide between the elevated plateau of Spain and the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa.
- Geological studies indicate that the strait originated from the northward movement of the African Plate towards the European Plate.
- High Maritime Activity: Recognized as one of the world's busiest waterways, the Strait of Gibraltar witnesses the daily transit of around 300 ships, equivalent to approximately one ship every 5 minutes.
- The Moroccan port of Tanger-Med, situated near Tangier, is a prominent port along the strait.
- Pillars of Heracles: Marking the eastern extremity of the strait, the area between the Rock of Gibraltar in the north and Mount Hacho or Jebel Moussa in the south spans approximately 23 km.
- These two land features referred to as the Pillars of Heracles, hold historical and geographical significance.
About the Mediterranean Sea:
- The Mediterranean Sea, an intercontinental body of water, is flanked by Europe to the north, Asia to the east, and Africa to the south.
- In the western expanse, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the narrow Strait of Gibraltar.
- To the extreme northeast, it links to the Black Sea via the Dardanelles Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Bosporus Strait.
- In the southeast, the Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Red Sea through the Suez Canal.
- Historical Significance: Recognized as the cradle of Western civilization, the Mediterranean Sea has played a pivotal role in the development of ancient cultures.
- Notable civilizations, including the Phoenicians, Ancient Greece, and the Roman Empire, flourished along its shores.
- Countries and Territories Along the Coast: A total of 22 countries, along with one territory (Gibraltar, a British Overseas Territory), have coastlines along the Mediterranean Sea.
- European nations with Mediterranean coastlines include Spain, France, Italy, Malta, Monaco, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, and Greece.
- Countries from the West Asian (Middle Eastern) region bordering the Mediterranean Sea include Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine (Gaza Strip), and the divided island of Cyprus.
- Additionally, five North African nations, namely Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Egypt, have coastlines along the Mediterranean.
PM to release ‘Collected Works of Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya’ on 25th December (PIB)

- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
On the occasion of the 162nd birth anniversary of Mahamana Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi will release the first series of 11 volumes of ‘Collected Works of Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya’, on 25th December, 2023.
About Pandit Madan Mohan Malaviya:
- Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya, born on December 25, 1861, in Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, made significant contributions to India's education system and actively participated in the Indian Independence movement.
- Acknowledged as a venerable soul, Mahatma Gandhi bestowed upon him the title of 'Mahamana,' considering him an elder brother.
- In 2014, posthumously, Pandit Malviya was honoured with the Bharat Ratna, the highest civilian award in the country.
- In tribute to his legacy, the Indian Railways launched the Varanasi-New Delhi Mahamana Express in 2016.
Significant Contributions:
- Banaras Hindu University: In 1916, Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya played a pivotal role in the Indian independence struggle against British rule and established the Banaras Hindu University (BHU).
- Serving as the Vice-Chancellor at BHU from 1919 to 1938 showcased his dedication to education and leadership.
- Hindu Mahasabha: A founding member of the Hindu Mahasabha in 1906, Malaviya demonstrated his early leadership in this organization.
- As a social reformer and accomplished legislator, he contributed significantly during his 11-year tenure (1909–20) as a member of the Imperial Legislative Council.
- Scout and Guide Movement: Pandit Malviya was instrumental in establishing the Scout and Guide movement in India, showcasing his commitment to youth development and character building.
- 'Satyamev Jayate': Renowned for coining the famous slogan 'Satyamev Jayate,' Pandit Malviya proclaimed it during the 1918 Indian National Congress session when he served as the President.
- President of INC: Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya's leadership extended to the Indian National Congress, where he held the position of President for four sessions (1909, 1913, 1919, and 1932).
- His active role in the Civil Disobedience and Non-cooperation movements, led by Mahatma Gandhi, underscored his commitment to India's struggle for independence.
- Media Role: From 1924 to 1946, Pandit Malviya served as the Chairman of Hindustan Times and also founded several Hindi and English newspapers, including The Leader, Hindustan Dainik, and Maryada.
- Advocacy for Education and Social Causes: Malaviya championed free and compulsory primary education, opposed the system of indentured labour in the British Empire, and advocated for the nationalization of railways, reflecting his dedication to societal progress and reform.
“FLip” mutations of SARS-COV-2 may be evading immunity and leading to a surge in COVID cases, suggest researchers (DownToEarth)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The omicron subvariant JN.1. is likely to soon become the dominant lineage of the SARS-CoV-2 virus worldwide, according to researchers at the University of Tokyo. The subvariant has a mutation in its spike protein, L455S, also called a “FLip” mutation.
Context:
- The mutations denoted as L455S and L455F are termed "FLip" mutations due to their role in interchanging the positions of amino acids F and L within the spike protein.
- These mutations enhance the virus's transmissibility.
- The substitution associated with these mutations reduces the receptor binding capacity of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a protein present in epithelial cells across various body parts, including the lungs, heart, and kidneys.
- ACE2 serves as a crucial entry point for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, binding through its spike-like protein on the virus's surface.
- The FLip mutations, specifically L455F and F456L, are characterized by the swapping of positions between two amino acids, F and L, within the spike protein.
What is Flip Mutation?
- A flip mutation, also known as bit flip mutation, is a genetic operator used in evolutionary algorithms, particularly genetic algorithms (GAs).
- It works by randomly flipping the values of individual genes (bits) within a chromosome, introducing small changes to the genetic makeup of an individual.
- Imagine a chromosome as a string of 0s and 1s, representing the genetic code for a specific trait or characteristic.
- A flip mutation randomly selects one or more of these bits and changes their values.
- For example, a 0 might be flipped to a 1, or vice versa.
- The following image depicts flip mutation:
How does it work:?
- Individual selection: An individual is selected from the population.
- Gene selection: One or more genes (bits) within the individual's chromosome are randomly chosen.
- Bit flipping: The value of each selected gene is flipped. This means that a 0 is changed to a 1, and vice versa.
Odisha Government has declared Leprosy as a 'Reportable Disease' in the State (New Indian Express)
- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Odisha government on Friday declared leprosy a reportable disease in the state and asked hospitals and persons dealing with diagnosis and treatment, institutions imparting medical education and providing diagnostic services to report all cases to the respective district health authorities.
What is Leprosy?
- Leprosy, often referred to as Hansen's disease, is a persistent infectious illness brought on by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae.
- The skin, eyes, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract, and peripheral nerves are the main areas affected by this condition.
- If left untreated, the condition has the potential to produce gradual and irreversible impairments.
- Prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, leprosy qualifies as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) found in over 120 countries.
- Its occurrence spans all age groups, encompassing early childhood to advanced age.
- Transmission of Disease: Transmission of leprosy transpires through droplets from the nose and mouth, necessitating prolonged, close contact with an untreated individual.
- Contrary to misconceptions, casual interactions such as handshakes, hugs, shared meals, or proximity do not facilitate transmission.
- Symptoms: Symptoms usually manifest 3 to 5 years post-exposure to the leprosy-causing bacteria.
- Red patches on the skin.
- Skin Lesion
- Numbness in arms, hands, and legs.
- Ulcers on the soles of feet.
- Muscle Weakness and excessive weight loss.
- Nerve damage can result in loss of sensation in limbs and potential mucous membrane complications like a stuffy nose or nosebleeds.
- Treatment: Leprosy is curable through Multi-Drug Therapy (MDT), with early intervention crucial in preventing disability.
- Importantly, the commencement of treatment not only aids in recovery but also halts the transmission of the disease.
About the National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP):
- The National Leprosy Eradication Programme is a centrally sponsored Health Scheme under the National Health Mission of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India.
- The Programme is headed by the Deputy Director of Health Services (Leprosy ) under the administrative control of the Directorate General Health Services, Govt. of India.
- While the NLEP strategies and plans are formulated centrally, the programme is implemented by the States/UTs.
- The major concern of the Programme is to detect cases of leprosy at an early stage and provide complete treatment, free of cost, in order to prevent the occurrence of Grade II Disability (G2D) in affected persons.
- India has achieved the elimination of leprosy as a public health problem as per WHO criteria of less than 1 case per 10,000 population at the National level in 2005.
- However, there are few districts within States where leprosy is still endemic.
Sports Ministry requests IOA to constitute an ad-hoc committee to manage WFI affairs (Indian Express)

- 25 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After suspending the newly elected Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) body on Sunday, the Sports Ministry have requested the Indian Olympic Association to constitute an ad-hoc committee to manage and control the affairs of the federation.
News Summary:
- Three days after the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) elected a new governing council to run the sport in India, the Union Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports directed the body to suspend all activities.
- It issued a letter to the Indian Olympic Association (IOA) to create an ad-hoc committee to manage and control the affairs of the WFI.
About the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI):
- Established in 1958 and headquartered in New Delhi, the Wrestling Federation of India (WFI) serves as the governing body for wrestling.
- Mission: WFI plays a pivotal role in nurturing and promoting wrestling talent for prestigious events such as the Olympics, Asian Games, National Wrestling Championships, and World Wrestling Championships.
- Affiliation: As an integral part of the Indian Olympic Association (IOA), WFI operates in accordance with the rules and regulations set forth by both the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and United World Wrestling (UWW).
- The UWW, recognized as the international governing body for wrestling, holds responsibilities ranging from overseeing wrestling competitions at the World Championships to ensuring adherence to standards at the Olympic level.
- WFI's Contract System for Wrestlers: In a groundbreaking move in 2018, WFI introduced an innovative contract system designed to support wrestlers.
- This system categorizes wrestlers into four grades:
- Grade A, providing financial assistance of 30 lakh rupees.
- Grade B offers a financial support package of 20 lakh rupees.
- Grade C, extending support amounting to 10 lakh rupees.
- Grade D provides a support package of 5 lakh rupees.
- To ensure relevance and fairness, the contracts undergo a thorough review on an annual basis, reflecting WFI's commitment to the ongoing development and support of wrestling talent.
About Indian Olympic Association (IOA):
- The Indian Olympic Association acts as the governing body overseeing the Olympic Movement and the Commonwealth Games within India.
- It holds affiliation with prominent international bodies, including the International Olympic Committee (IOC), Commonwealth Games Federation (CGF), Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), and Association of National Olympic Committees (ANOC).
- In fulfilling its role, the IOA manages key aspects of sports governance and prioritizes the welfare of athletes across the nation.
- Responsibilities: As a recognized entity by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, the IOA undertakes the crucial responsibility of coordinating the representation of athletes and teams in major international multi-sport events such as the Olympic Games, Commonwealth Games, Asian Games, and others sanctioned by the IOC, CGF, OCA, and ANOC.
- Historical Perspective: Established in 1927 with Sir Dorabji Tata serving as the Founding President and Dr. A.G. Noehren as the Secretary-General, the IOA operates as a Non-Profit Organization under the Societies Registration Act of 1860.
- This history underscores its enduring commitment to the promotion of sports.
- Governance Structure: Currently governed by a 32-member Executive Council, the IOA is led by a President.
- Elections for the Executive Council occur once every four years, emphasizing democratic and periodic leadership changes within the organization.
Ministry of Textiles launches “Paat-Mitro” application to facilitate jute farmers (PIB)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
To provide important information about MSP and agronomy to jute farmers, the Ministry of Textiles launched “Paat-Mitro” - a mobile application, developed by The Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) during the ‘Jute Symposium’.
What is Paat Mitro?
- Paat Mitro is a mobile application crafted by the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) with the primary aim of furnishing vital information on Minimum Support Prices (MSP) and agronomy to jute farmers.
Key Features:
- The application is accessible in six languages, ensuring inclusivity.
- All functionalities within the app are provided to users free of charge.
- Paat Mitro offers a comprehensive range of information, encompassing the latest agronomic practices, MSP details, Jute Gradation Parameters, farmer-centric schemes like ‘Jute-ICARE,’ weather forecasts, locations of JCI’s Purchase Centres, and Procurement Policies.
- Farmers can conveniently track the payment status for the raw jute they sell to JCI under the MSP Operation.
- The app integrates advanced technology features such as a Chatbot, facilitating farmers in resolving queries effectively.
Key Information about the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI):
- Established in 1971 under the aegis of the Government of India, the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) serves as the official agency dedicated to ensuring minimum support prices (MSP) for jute cultivators.
- JCI functions as the executing body for several Government of India initiatives aimed at enhancing the jute crop and the welfare of jute growers.
- It operates under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Textiles.
- The geographical reach of JCI spans seven states renowned for jute cultivation in India, including West Bengal, Bihar, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, Orissa, and Andhra Pradesh.
- With an authorized and paid-up capital of Rs. 5 crore, JCI plays a pivotal role in implementing the government's policy decisions, obligatorily purchasing any quantity of jute offered by growers at support rates without quantitative limitations.
- Incurred losses during policy implementation by JCI are subject to reimbursement by the Government of India.
Rating agencies too subjective, loaded against India, need reform: CEA (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Credit rating agencies need to reform their sovereign rating process to correctly reflect the default risk of developing economies, saving billions in funding costs, the government’s chief economic adviser, V Anantha Nageswaran, said recently.
What is a Sovereign Credit Rating?
- A Sovereign Credit Rating serves as an assessment of a government's ability to meet its debt obligations, with a lower rating reflecting higher credit risk.
- Rating agencies typically consider multiple factors such as growth rate, inflation, government debt, short-term external debt as a percentage of GDP, and political stability.
- A positive credit rating not only boosts credibility but also indicates a history of timely loan repayments, aiding banks and investors in evaluating loan applications and determining appropriate interest rates.
- The global credit rating industry is dominated by three major agencies: Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch.
- Despite India's ascent from the 12th to the 5th largest economy globally in 2023, with the second-highest growth rate among comparable economies, its credit ratings from S&P and Fitch stand at BBB, while Moody's rates it at Baa3—indicating the lowest investment-grade level.
Concerns Regarding Credit Rating Methodology:
- A quantitative examination revealed that more than 50% of credit ratings rely on qualitative components.
- Institutional Quality, predominantly gauged through the World Bank’s Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGIs), emerges as the primary factor influencing the credit rating of a developing economy.
- This poses a challenge as these metrics are often non-transparent, perception-driven, and derived from a limited group of experts, making them inadequate in representing the sovereign's willingness to meet its financial obligations.
- The non-trivial impact of these indicators on ratings implies that developing economies must exhibit progress along subjective indicators to secure a credit rating upgrade.
CEA's Suggestions for Credit Rating Reform:
- The Chief Economic Advisor (CEA) proposed a shift towards primarily considering a country's historical debt repayment record as a key determinant of its 'willingness to pay,' in contrast to relying on potentially suboptimal qualitative information.
- Embracing such a model would significantly enhance the credibility of Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs).
- The use of qualitative information and judgment should only be a last resort when genuine, verifiable data options are unavailable.
- If governance indicators are to be employed, they should be grounded in clear, well-defined, and measurable principles, steering away from subjective assessments by CRAs.
- CRAs possess a comprehensive database of global best practices, influencing their judgments.
- Sharing this knowledge with the countries they assess would empower sovereigns to take targeted actions to enhance their creditworthiness.
Coming soon, a ‘Cafeteria’ for oil spill-hit birds at Ennore Creek (The Hindu)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Experts from the Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) and the Besant Memorial Animal Dispensary (BMAD) are planning to establish feeding stations for birds at the creek, where contamination due to an oil spill from industries in Manali has brought down the bird population drastically.
About Ennore Creek:
- Ennore Creek, situated in Thiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu, is a backwater channel branching off from the Kosathalaiyar River.
- It merges with the Bay of Bengal at Mugathwara Kuppam, while its northern channel links to Pulicat Lake, the country's second-largest brackish water lake.
- For generations, this creek has been a lifeline for communities in the neighbouring villages, designated as CRZ IV (Water Body) in the coastal zone management plan by the Tamil Nadu State Coastal Zone Management Authority.
- Its significance is heightened for local fisherfolk, alongside the Buckingham Canal and the broader Pulicat water system.
- The Ennore Creek has historically fostered a robust aquatic ecosystem renowned for its biodiversity.
- This ecologically sensitive area once boasted extensive mangrove swamps, contributing not only to sustainable fish resources but also playing a crucial role in flood mitigation during periods of heavy rainfall, high tides, and cyclones.
About the Wildlife Trust of India:
- Wildlife Trust of India (WTI) is an Indian Non-profit Organisation (NGO) committed to nature conservation.
- Motto: In Service of Nature
- It was formed in November 1998, in response to the rapidly deteriorating condition of the country's wildlife.
- Its mission is to:
- Conserve wildlife and its habitat and
- Work for the welfare of individual wild animals, in partnership with communities and governments.
- WTI has earned recognition for accomplishing significant conservation milestones, including the recovery of populations for critically endangered species, successful species translocation, and the mitigation of human-animal conflicts.
How an AI tool can make weather forecasts more accurate and help tackle climate change (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
At the recent COP28, NASA and IBM announced that an Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool called watsonx.ai would be available on the open-source AI platform Hugging Space.
What is watsonx.ai?
- Watsonx.ai is a collaborative Artificial Intelligence tool developed by IBM and NASA.
- Its primary function is to enable users to monitor Earth from space, assessing past environmental changes and offering predictions about future occurrences.
- User-Friendly Interface: The tool is designed for simplicity, requiring users to select a location and a date.
- Watsonx.ai then highlights changes in floodwater, reforestation efforts, and other pertinent factors.
Functionality:
- Watsonx.ai is built on a foundation model trained on a diverse set of uncategorized data, allowing it to extrapolate information from one context to another.
- NASA provides datasets in the form of satellite images, and IBM developed the foundation model to interpret these visual inputs.
- The model's training involves comprehending visual sequences over time by reconstructing images with blank areas. This process enhances its ability to understand the connections between photos.
- Adjustments were made to the model for specific tasks such as segmenting and categorizing photos.
Additional Components:
- Watsonx.data: A specialized data store optimized for governed data and AI workloads.
- It facilitates the scaling of AI workloads by leveraging the entire data landscape.
- Watsonx.governance: An end-to-end toolkit encompassing both data and AI governance. It aids clients in establishing responsible, transparent, and explainable AI workflows.
- The toolkit provides governance capabilities for model management throughout the AI lifecycle.
Why rain and flood woes have hit Tamil Nadu hard in December (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Tamil Nadu has battled heavy rainfall throughout December. At the beginning of the month, parts of Chennai and its neighbourhood experienced massive flooding because of Cyclone Michaung.
News Summary:
- Tamil Nadu has experienced significant rainfall, recording 450mm since October 1.
- Among the 38 districts, only 14 have reported deficient rainfall until December 20.
Seasonal Rainfall Norms:
- December rainfall is typical for Tamil Nadu, with the northeast monsoon being crucial for the region.
- Nearly 48% of the annual rainfall (443.3mm) in Tamil Nadu occurs from October to December, impacting rabi cultivation.
Recent Rainfall Patterns in Southern Tamil Nadu:
- Three districts in southern Tamil Nadu witnessed 'exceptionally' heavy rainfall from December 17 to 19.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported a 100% or more surplus during this period compared to the previous week (December 6-13, 2023).
Factors Contributing to Record Rainfall:
- Vigorous northeast monsoon over Tamil Nadu and Kerala, particularly in the southern regions.
- Development of a cyclonic circulation in the southwest Bay of Bengal on December 16, enhancing northeast monsoon winds.
- The persistence of this system over southern Tamil Nadu on December 18 and 19, led to heavy cloud convection and hefty rainfall.
IMD's Forecast:
- The cyclonic circulation has moved away from the Indian landmass, currently positioned over the southeast Arabian Sea.
- No significant rainfall is expected in Tamil Nadu, but the IMD predicts light to moderate intensity rainfall (up to 64mm in 24 hours) in certain areas of southern Tamil Nadu.
What is Northeast Monsoon?
- The northeast monsoon stands as a significant and permanent element within the Indian subcontinent's climate system.
- Its nomenclature originates from the prevailing direction of the monsoon winds—blowing from the northeast to the southwest.
- In their trajectory, these winds accumulate moisture from the Bay of Bengal, subsequently depositing it over southern states such as Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, south Telangana, and Karnataka.
- This monsoon is alternatively known as the winter monsoon, retreating monsoon, or reverse monsoon.
- Period: The northeast monsoon maintains activity throughout the three-month span from October to December.
- Causes and Influences: One of the primary instigators of the northeast monsoon is the southward shift of the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ).
- The ITCZ, a dynamic belt near the Equator, marks the convergence of trade winds from the northern and southern hemispheres.
- The southward displacement of the ITCZ, coupled with the warming of the Indian Ocean, induces a reversal in the lower-atmosphere moisture-laden winds' direction—from southwest to northeast—thereby triggering the Northeast Monsoon (NEM).
Government bans anti-cold drug combination for kids aged under four (Indian Express)
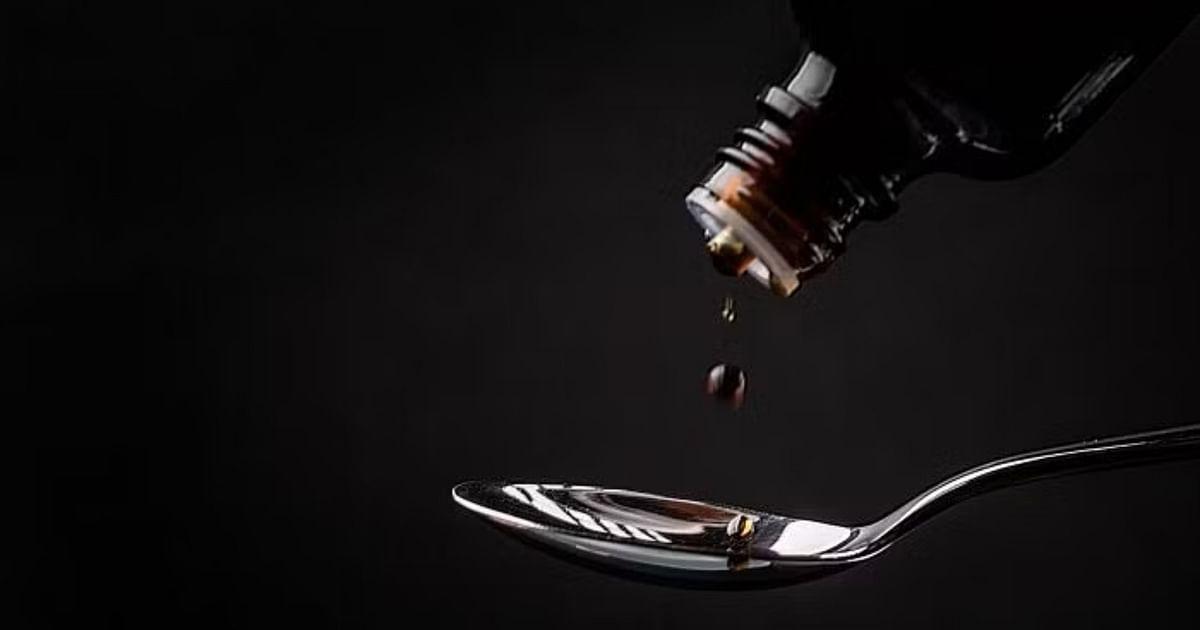

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has prohibited the use of anti-cold fixed drug combinations in children below four years of age.
What are Fixed Dose Combination (FDC) Drugs?
- Fixed-dose combination (FDC) drugs, also referred to as combination products, embody a formulation containing two or more active drugs within a single dosage form.
- The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) defines a combination product as a composition involving a drug and a device, a biological product and a device, or a combination of a drug, device, and biological product.
- While the conventional approach favours formulating drugs as single compounds, the acceptance of fixed-ratio combination products hinges on two key criteria:
- Dosage Requirements: Each ingredient in the combination must meet the dosage criteria tailored to a specific population group.
- Proven Advantages: The combination should demonstrate a clear advantage over administering individual compounds separately in terms of therapeutic effect, safety, or compliance.
- FDCs have witnessed significant popularity in the Indian pharmaceutical market, experiencing notable growth in recent years.
About the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO):
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) serves as the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) in India, overseeing the medical devices industry per the Drugs & Cosmetics Rules.
- Positioned under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, it is led by the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) with its headquarters situated in New Delhi.
- Operationalizing under the provisions of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is entrusted with several crucial responsibilities, including the approval of new drugs, the facilitation of clinical trials, the establishment of standards for drugs, ensuring control over the quality of imported drugs, and coordination of activities among State Drug Control Organizations.
- One of its significant roles lies in collaboration with state regulators for granting licenses related to specialized categories of critical drugs.
- These encompass vital medical components such as blood and blood products, I.V. fluids, vaccines, and sera.
- The CDSCO plays a pivotal role in upholding standards, ensuring quality, and fostering coordination across the regulatory landscape for the benefit of public health in India.
Why the UK banned Air France, Lufthansa, and Etihad ads over ‘greenwashing’ claims (Indian Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Earlier in December, the United Kingdom’s ad regulator banned advertisements from Air France, Lufthansa, and Etihad for allegedly misleading consumers regarding the environmental impact of air travel.
What is Greenwashing?
- Greenwashing is the deceptive practice of creating a false impression or providing misleading information about the environmental sustainability of a company's products.
- It involves making unverified claims to lead consumers to believe that a company's products are more environmentally friendly or have a more positive impact on the environment than is accurate.
- Furthermore, greenwashing can occur when a company highlights the sustainable aspects of a product to divert attention from its involvement in environmentally harmful practices.
- Companies may employ greenwashing tactics by using vague claims that lack substantiated data or scientific validation.
- For instance, a car vendor might assert that a vehicle is eco-friendly due to increased fuel efficiency, conveniently overlooking or downplaying the broader environmental impact of vehicle manufacturing processes.
What are the Concerns With Greenwashing?
The practice of greenwashing raises apprehensions on several fronts:
- Authenticity of Climate Goals: There is a risk of undermining the authenticity of climate goals when misleading or exaggerated information about environmental initiatives is presented.
- Unwarranted Recognition and Benefits: Entities involved in greenwashing may receive undeserved recognition or benefits, potentially rewarding irresponsible behaviour and discouraging genuine sustainability efforts.
- Market Distortion: Greenwashing can distort markets by creating an uneven playing field.
- Entities engaging in deceptive practices might gain an unfair advantage over those genuinely adhering to stringent environmental standards.
- Lack of Comprehensive Regulations: The absence of comprehensive regulations and standards for environmental claims allows greenwashing to persist without adequate scrutiny, contributing to a lack of transparency.
- Challenges to Carbon Credit Systems: The practice of greenwashing introduces challenges to the integrity of carbon credit systems.
- This is particularly evident in informal markets, where the expansion of credit sources and certification by unofficial entities raise concerns about transparency and reliability.
- It's crucial to note that in the context of carbon credits, one credit represents the removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide or equivalent greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
- The concept of carbon credits was introduced by the Kyoto Protocol, providing rewards to countries or firms surpassing emission reduction mandates.
Global Initiatives Addressing Greenwashing:
- During the 27th Conference of Parties (COP27), the United Nations Secretary-General declared a zero-tolerance stance against greenwashing.
- Private corporations were urged to rectify their practices to align with genuine environmental efforts.
- In a landmark move in October 2023, the European Union approved the world's first green bond standards.
- These standards, under the "European Green Bond" label, mandate transparency and direct 85% of funds towards sustainable activities within the EU.
- The legislation aims to support the EU's transition to climate neutrality.
Laws in India:
- In India, greenwashing is classified as an unfair trade practice under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- This legislation prohibits deceptive claims and outlines penalties and remedies for consumers adversely affected by such misleading practices.
- In February 2023, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) issued guidelines for issuers of green debt securities.
- These guidelines are designed to ensure transparency, prevent greenwashing, protect investors, and regulate the development of the securities market.
- The Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI), a voluntary self-regulatory organization, plays a crucial role in monitoring advertising practices.
- It holds jurisdiction over allegations of greenwashing, ensuring that ads are not only legal but also honest and fair.
- The ASCI's regulatory efforts aim to safeguard consumer interests and promote fair competition within the Indian advertising landscape.
Bhoomi Rashi Portal is revolutionizing land acquisition for Highway projects – Here’s how (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari revealed in a recent statement to the Rajya Sabha that the Bhoomi Rashi portal is instrumental in expediting the development of highway infrastructure in India.
About the Bhoomi Rashi Portal:
- The acquisition of land was done manually before the year 2018. The data files were moved physically, leading to some limitations. This included delays in issuing notices, errors in land details, etc.
- To overcome the issues, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways came up with a system.
- It is known as “Bhoomi Rashi”.
- The portal came into force on 1st April 2018
- The system is digital and automates the whole land acquisition (LA) process.
- It made and still makes the LA process more transparent and error-free.
- The portal processes the notices at every stage on a real-time basis.
Key Objectives:
- Acceleration of Land Acquisition: The primary goal is to facilitate a quicker and more efficient land acquisition process for National Highways.
- Centralized Processing: Acting as a singular online platform, it consolidates the processing of land acquisition notifications, contributing to the swift development of highway infrastructure projects.
- Transparency and Accountability: Ensures transparency and accountability throughout the land acquisition process.
- Direct Benefit Transfer: Facilitates the electronic transfer of benefits directly to the accounts of the beneficiaries involved in the land acquisition.
Salient Features:
- Bilingual application with Hindi and English for easy usability
- Preparation of interface for adding basic details of the project, including land acquisition sanction details
- Preparation of interface for Land Acquisition locations. villages
- Preparation of Interface for Competent Authority for Land Acquisition (CALA) details. CALA is a revenue functionary of the State Government appointed for each NH Project.
- Interface for generating land acquisition notification
- Interface for land Details
- Interface for generation of notification: organisational email IDS for all those involved in the process flow to ensure smooth e-office management
- Interface for Objections and processing
- Interface for compensation determination and finalisation
- Interface for land owners and affected parties
- Interface for reports generation
The portal is seamlessly integrated with the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) of the Ministry of Finance, ensuring real-time deposit of compensation into the accounts of affected/interested individuals.
What is Land Acquisition?
- Land acquisition is the governmental process, whether at the state or union level, through which private land is procured for infrastructure development, urbanization, or industrialization.
- In exchange, the government provides appropriate compensation to the landowner based on market value and assumes responsibility for the rehabilitation and resettlement of those affected by the land acquisition.
SAT quashes Sebi's order against Kishore Biyani, and others (Live Mint)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) on Wednesday quashed regulator Sebi's order banning Future Retail chairperson Kishore Biyani and some other promoters from the securities market for one year in an insider trading case.
About the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT):
- Established as a statutory and autonomous entity under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Act, 1992, the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) serves as a crucial forum for adjudicating appeals against decisions made by SEBI or its adjudicating officers.
Key Functions:
- Appeals Jurisdiction: Primarily tasked with hearing appeals against orders issued by SEBI or its adjudicating officers under the SEBI Act.
- Extended Jurisdiction: Additionally, SAT entertains appeals concerning orders from the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) related to cases filed before them.
Composition:
- Presiding Officer: A retired or sitting Supreme Court judge, Chief Justice of a High Court, or a High Court judge with at least seven years of service.
- Judicial Member: High Court judge with a minimum of five years of service.
- Technical Member: Individual with expertise and a minimum of 15 years of experience in the financial sector, including securities market, pension funds, commodity derivatives, or insurance.
- This member can be a senior official in the Central or State Government or a person of proven ability and integrity.
Appointment and Tenure:
- Appointments made by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India or its nominee.
- Presiding Officer and members serve a term of five years, eligible for reappointment for an additional term of up to five years.
- No member shall hold office after reaching the age of 70.
Powers and Authority:
- They are empowered with the same powers as a civil court under the code of civil procedure when adjudicating suits.
- Appeals to SAT can be made by any person aggrieved by SEBI or adjudicating officer orders, excluding those made with the consent of all parties.
Appeals Process:
- Appeals against SAT decisions can be filed in the Supreme Court, limited to questions of law.
- No appeal is permissible against orders made with the consent of all parties.
- The SAT, with its specific mandate and composition, plays a pivotal role in ensuring fairness and justice in the regulatory framework of the securities market in India.
What is Insider Trading?
- Insider trading is the act of buying or selling securities of a publicly traded company based on material information not yet disclosed to the public.
- Material information encompasses any data that could significantly influence an investor's decision to buy or sell the security.
- For instance, Consider a scenario where a government employee, possessing knowledge about an upcoming regulation that would favour a sugar-exporting company, takes advantage of this information by purchasing the company's shares before the regulation becomes public knowledge.
MSME Ministry launches 3 sub-schemes under RAMP programme; makes ZED scheme free for women (Financial Express)

- 21 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
MSME Minister Narayan Rane recently launched three sub-schemes under the ministry’s existing RAMP ((Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity) programme.
About the RAMP Programme:
- The Raising & Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) program, supported by the World Bank and inaugurated in 2022, is dedicated to enhancing the performance of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) across India.
Program Objectives:
- Market and Credit Access: Facilitate improved access to markets and credit for MSMEs.
- Institutional Strengthening: Enhance institutional and governance structures at both central and state levels.
- Center-State Collaborations: Foster improved linkages and partnerships between central and state entities.
- Delayed Payment Issues: Address challenges related to delayed payments within the MSME sector.
- Greening of MSMEs: Promote sustainable practices and the adoption of green technologies within MSMEs.
- The National MSME Council has been set up by the Ministry to work as an administrative and functional body of the RAMP Programme.
Sub Schemes under RAMP:
- MSME GIFT Scheme: Aims to support MSMEs in adopting green technology through interest subvention and credit guarantee assistance.
- MSE SPICE Scheme: Focuses on promoting circular economy projects, with credit subsidy mechanisms, aligning with the MSME sector's goal of achieving zero emissions by 2070.
- MSE ODR Scheme: A pioneering initiative leveraging modern IT tools and Artificial Intelligence to address delayed payment incidents for Micro and Small Enterprises.
- Implementing Agencies for Sub Schemes:
- MSME GIFT and MSME SPICE Schemes: Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- MSE ODR Scheme: National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI)
- These sub-schemes, under the RAMP umbrella, signify a comprehensive effort to fortify and propel the growth of MSMEs, incorporating technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Cops lose Rs 12 crore in chit fund scheme, probe on (TOI)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Around 70 persons belonging to AP special police have lost nearly Rs 12 crore in a chit fund scheme in Mangalagiri, said the police. Mangalagiri police registered a case and launched an public sector investigation.
What are Chit Funds?
- Chit funds, also known as Kuri and Chitty, serve as versatile financial instruments encompassing both borrowing and saving components.
- In this financial arrangement, a group of individuals collectively contributes a fixed sum at regular intervals, with the understanding that one member will receive the total pooled amount during each interval.
- This process repeats until every member has received their share.
- Typically managed by a chit-fund company, this financial instrument operates by having a group of contributors make regular contributions toward the chit value for a duration equivalent to the total number of subscribers.
- The recipient of the pooled money is determined through an auction or lucky draw, employing a reverse auction system where the individual willing to accept the lowest amount is chosen.
- The sum forfeited by the winning bidder is distributed among other bidders, deducting a foreman's charges and commission.
- The share each bidder receives is termed a dividend. Interestingly, a winning bidder can continue to invest in subsequent intervals, even after claiming their sum.
Types of Chit Funds:
Chit funds can be categorized into three types:
- Chit Funds Run by State Governments:
- Managed and regulated by state governments.
- Public sector undertakings (PSUs) also fall under this category.
- These funds are considered safe, with limited chances of loss. Business processes are transparent and well-regulated.
- Private Registered Chit Funds:
- Registered under the Chit Funds Act of 1982.
- Typically initiated by well-established financial institutions or business entities.
- While participation in these funds may not be as secure as state-run or public-sector funds, the calculated risk is manageable due to their association with reputable private-sector entities.
- Unregistered Chit Funds:
- These chit-funds lack legal recognition, and participation involves a higher risk.
- Commonly found throughout India, they are often formed by a close-knit group of associates.
- Participation in unregistered chit funds is discouraged due to the potential for disputes, which rely heavily on the integrity and honesty of the members involved.
What is Saradha Chit Fund Scam?
- The Saradha scam, also known as the Saradha Group financial scandal, was a major financial scam that surfaced in 2013.
The Saradha scheme:
- The scheme, run by Saradha Group (an umbrella company with 200 private players), was launched in the early 2000s by businessman Sudipto Sen.
- Aimed at small investors, the scheme became popular in a very short time as it promised high returns.
- The money was collected through a wide network of agents, who were paid commissions of over 25 per cent.
- The Saradha Group raised about Rs 2,500 crore in a few years time.
- The company used varied marketing means to build its brand.
- Apart from popular marketing techniques like celebrity endorsements, the company used to sponsor cultural events such as Durga Puja and invest in popular football clubs to attract more investors.
- The scheme soon expanded to Odisha, Assam, and Tripura, and the number of investors reached close to 1.7 million.
US launches Red Sea force as ships reroute to avoid attacks (The Hindu)
- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin on Tuesday announced the creation of a multinational operation to safeguard commerce in the Red Sea following a series of missile and drone attacks by Yemen's Iran-aligned Houthis.
Context:
- The U.S. Defense Secretary recently revealed the establishment of a multinational operation to protect commerce in the Red Sea.
- This decision comes in response to a string of missile and drone attacks by Yemen's Iran-aligned Houthis.
- The gravity of these attacks has prompted several shipping companies to instruct their vessels to remain stationary and avoid entering the Bab el-Mandeb Strait until the security concerns are addressed.
About the Red Sea:
- The Red Sea is a narrow waterway extending southeastward from Suez, Egypt, to the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
- The Bab-el-Mandeb Strait links the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden, providing a connection between the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Sea.
- Essentially, it is a narrow inland sea positioned between the Arabian Peninsula and Africa.
- The Red Sea acts as a boundary, separating the coastlines of Egypt, Sudan, and Eritrea from those of Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
- The Gulf of Aqaba, an extension to the northeast, stretches into southern Israel and southwestern Jordan.
- Significance: The Red Sea boasts some of the planet's hottest and saltiest seawater.
- It stands as one of the most heavily traversed water routes globally, facilitating maritime traffic between Europe and Asia.
- Relevance for India:
- Potential disruptions along this route could lead to a significant surge, up to 25-30%, in freight rates for Indian shipments bound for Europe and Africa.
- For India, the Red Sea trade route serves as the most direct path for ships traveling from Asia to Europe.
- India heavily depends on the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait for crucial aspects such as crude oil, LNG imports, and trade with regions in West Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- This passage is critical, accounting for 30% of global container traffic.
Who are the Houthi Rebels?
- The Houthis are a Shiite Muslim sect with roots that date back centuries in Yemen.
- Members of the religion are a minority in Yemen, which is predominantly Sunni Muslim, but they are a significant one, numbering in the hundreds of thousands and making up as much as a third of the overall population.
- Named after the Houthi tribe, they adhere to Zaydi Shia beliefs within Islam, emphasizing the lineage of Prophet Muhammad's family as the political leaders of the state.
- Also recognized as Ansar Allah, translating to "Supporters of God."
- Involvement in Yemen's Civil War: A major faction in Yemen's nearly decade-long civil war, starting in 2014 when Houthi insurgents seized control of Yemen's capital, Sanaa.
- By early 2015, Saudi Arabia, supported by other Gulf states and the U.S., conducted airstrikes against the Houthis, who have backing from Iran.
- Although a ceasefire was signed in 2022, it lapsed after six months, with the parties involved not returning to full-scale conflict.
- Houthi Attacks on Red Sea Ships:
- Iran-backed Houthi rebels from Yemen have targeted ships in the Red Sea in response to Israel's military actions in Gaza.
- The Houthis, supporting Hamas, declared on November 19 their intent to attack vessels they believe are traveling to and from Israel.
Full-blown late blight attack damages potato crops in Punjab (Indian Express)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Days after the experts from Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) had cautioned farmers against the late blight disease attack on potato crop, the worst fears of the potato farmers have come true.
About Late Blight Disease:
- Late Blight disease is attributed to the fungus Phytophthora infestans and stands as a significant threat to potato crops, potentially causing rapid failures if appropriate control measures are not implemented.
- Common in humid regions with specific temperature conditions, this disease manifests with initial symptoms of small, light to dark green, circular to irregular water-soaked spots.
- In cool, moist weather, these spots rapidly expand into large, dark brown or black lesions, often exhibiting a greasy appearance.
- A pale green to yellow border typically surrounds these lesions.
- The spread of Late Blight is facilitated by infected tubers and soil, acting as a primary source of infection.
- Infected tubers play a crucial role in the disease's persistence from one crop to another. Airborne infection occurs through sporangia.
- Effective control measures involve the prompt destruction of infected crop residue in the field to prevent the disease from spreading to nearby areas.
Diseases Caused by Bacteria on Potato Crops:
- Ring Rot
- Brown Rot
Diseases Caused by Fungi on Potato Crops:
- Late Blight
Diseases Caused by Virus on Potato Crops:
- Leaf Roll
- Mosaic
First Prehistoric Pictorial Cave Art Found in Madagascar Offers Clues Regarding Ancient Connections Between Borneo, Egypt (The Hindu)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, distinctive prehistoric rock art depictions were unearthed within the Andriamamelo Cave in western Madagascar.
Key Discoveries:
- Within this cave's truly pictorial art, human-like and animal-like figures depicting scenes from nature have been revealed.
- The remarkable findings unveiled surprising cultural connections, with some scenes directly linking to Egyptian religious motifs from the Ptolemaic period (300-30 BCE).
- Additionally, symbols and inscriptions on the cave walls indicated connections to the Ethiopian and Afro-Arab regions.
- Furthermore, the prevalent symbology and motifs echoed a cave art style from Borneo dating back two millennia.
- Notably, depictions within the cave may include three extinct animals of Madagascar — a giant sloth lemur, an elephant bird, and a giant tortoise.
- The potential connection to Egypt is suggested by eight significant images, including representations of a falcon (Horus), the bird-headed god Thoth, the ostrich goddess Ma`at, and two human-animal figures resembling Anubis, the ancient Egyptian god typically portrayed with a canine head.
About Andriamamelo Cave:
- The Andriamamelo Cave is situated in western Madagascar, nestled within the karstified limestone of the Paysage Harmonieux Protege de Beanka.
- This cave is a component of a vast karst region that encompasses the UNESCO World Heritage site, Parc National de Bemaraha, to the south, and the less-explored Antsingimavo karst area to the north.
Goa Liberation Day: Why India waited for 14 years after independence to move troops to Goa (Indian Express)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Goa Liberation Day is commemorated annually on December 19. In 2023, we observe the 62nd anniversary of the liberation of Goa.
Key Highlights:
- This day commemorates the liberation of Goa in 1961 by the Indian armed forces, ending 450 years of Portuguese rule.
- Portuguese colonization in India began in 1510, but by the late 19th century, their colonies were limited to Goa, Daman, Diu, Dadra, Nagar Haveli, and Anjediva Island.
- After India's independence in 1947, attempts to persuade Portugal to cede their territories were unsuccessful.
- The Goa liberation movement gained momentum from small-scale revolts, peaking between 1940 and 1960.
- In 1961, diplomatic efforts failed and Operation Vijay was executed, leading to the annexation of Daman, Diu, and Goa to the Indian mainland on December 19.
About Operation Vijay:
- Operation Vijay, a 36-hour military initiative initiated on December 18, 1961, and concluded on December 19, 1961, aimed at liberating the Portuguese territories of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
- This marked a significant milestone as possibly the first tri-service operation by the Indian armed forces.
- The Indian Air Force executed bombings on the Portuguese airbase at Dabolim, complementing the army's advancement from the north and east into Goa.
- Simultaneously, the Indian Navy played a crucial role in preventing hostile actions by Portuguese warships, securing access to Mormugao harbor, and establishing control over the Anjadip Island off the coast of Karwar.
- By the evening of December 19, 1961, Portuguese Governor General Vassalo De Silva signed the surrender document as the Indian armed forces, led by the army with support from the air force and navy, had effectively outnumbered and outgunned the Portuguese forces.
Granting Statehood to Goa after Liberation:
- Following its liberation, Goa came under the administration of the Indian government, becoming a constituent of the Indian Union as the Union Territory of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
- However, in 1967, a plebiscite was conducted to decide on the potential merger of the state with Maharashtra.
- The majority of Goans voted against the merger, leading to the continuation of its status as a Union Territory.
- This arrangement persisted until 1987 when Goa was accorded statehood, emerging as the 25th state of India.
- Meanwhile, Daman and Diu retained their status as a Union Territory.
'World's Largest Meditation Centre': PM Modi inaugurates Swarved Mahamandir in Varanasi (ET)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the world’s largest meditation centre, Swarved Mahamandir, in Varanasi on December 18.
About the Swarved Mahamandir:
- The Swarved Mahamandir stands as the world's largest meditation centre, accommodating 20,000 individuals in collective contemplation.
- Situated in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, this spiritual haven aspires to cast a luminous spiritual aura, enveloping the globe in a state of tranquil attentiveness.
- Named after the Swarved, a profound spiritual text penned by Sadguru Shri Sadafal Deoji Maharaj, the visionary behind Vihangam Yoga and an enduring yogi, the temple serves as a bastion for disseminating Swarveda teachings.
- Emphasizing Brahma Vidya, a profound body of knowledge, it guides spiritual seekers toward sustaining an unwavering equilibrium of peace and happiness.
- Architecturally, the Mahamandir is an imposing seven-floor superstructure, adorned with a captivating design featuring 125-petal lotus domes.
- Crafted from teakwood, the intricate carvings embellishing the ceiling and doors add to its allure.
- Pink sandstone envelops the temple walls, complemented by an enchanting garden featuring medicinal herbs.
- Imprinted on the Mahamandir's walls are verses from the Swarveda, serving as an enduring testament to the spiritual wisdom that resonates within its sacred confines.
What is Vihangam Yoga?
- Vihangam Yoga, an indigenous form of Yoga and meditation, was established by Sadguru Sadafal Deo Ji Maharaj in 1924.
- The nomenclature of this practice is derived from two foundational words: "Vihag," signifying bird, and "Yog," denoting union.
- The name encapsulates the profound concept of a bird ascending from the terrestrial realm, soaring high and unbounded in the sky.
- This symbolism mirrors the ultimate aim of Vihangam Yoga – the liberation of the soul from attachments to the material world, allowing it to recognize and embrace its innate, unshackled essence.
- Only through this liberation can an individual's consciousness seamlessly merge with the universal consciousness, often referred to as the Supreme Being, leading to a state of enduring tranquillity and bliss.
Telecommunications Bill, 2023: The changes it seeks in the telecom sector, why some have raised concerns (Indian Express)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Telecommunications Bill, 2023, was introduced in the Lok Sabha on Monday. The bill allows the government to take over, manage or suspend telecommunication services or a network over national security.
Key Features of the Telecommunications Bill, 2023
- Repeal of Existing Laws: The bill annuls the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, the Indian Wireless Telegraphy Act, 1933, and the Telegraph Wires (Unlawful Possession) Act, 1950, while introducing amendments to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Act, 1997.
- Authorization for Telecom Activities: Central government approval is mandatory for telecommunication services, network establishment, operation, maintenance, expansion, or possession of radio equipment.
- Existing licenses remain valid for their granted period or five years if unspecified.
- Spectrum Assignment: Spectrum allocation, except for specific purposes, will be through auction.
- Exceptions include national security, disaster management, and services by state-owned entities.
- Interception and Search Powers: Messages may be intercepted, monitored, or blocked for public safety, emergencies, or specified grounds like state security and prevention of offences.
- Government's Extraordinary Powers: The government can take temporary possession of telecom infrastructure during public emergencies, with the authority to suspend telecom services.
- Authorized officers may search for unauthorized equipment.
- Standards Specification Authority: The central government can prescribe standards for telecom equipment, infrastructure, networks, and services.
- Right of Way for Telecom Infrastructure: Facility providers can seek a right of way over public or private property for telecom infrastructure on a non-discriminatory basis.
- User Protection Measures: The government may implement measures to protect users, including consent for specific messages, creation of Do Not Disturb registers, and a mechanism for reporting malware.
- TRAI Appointments and Experience Requirements: Amendments allow individuals with at least 30 years of professional experience to serve as TRAI chairperson and those with at least 25 years of membership.
- Digital Bharat Nidhi: The Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) is renamed Digital Bharat Nidhi, allowing its use for research and development (R&D).
- Adjudication Process: An adjudicating officer, of the rank of joint secretary and above, will handle inquiries and orders against civil offences.
- Appeals can be made to the Designated Appeals Committee and further to TDSAT.
- Offences and Penalties: The Bill outlines criminal and civil offences, imposing penalties and imprisonment for unauthorized telecom services, network access, and equipment possession.
- Civil penalties apply for breaches of authorization terms.
What are the Reasons behind the introduction of the Telecommunications Bill, of 2023?
- The telecommunications sector plays a pivotal role in fostering economic and social progress, serving as the conduit for digital services.
- Given its significance, the security of our nation relies substantially on the robustness of telecommunication networks.
- Hence, there is an imperative to establish a legal and regulatory structure that prioritizes the security and resilience of telecommunication networks, fostering a digitally inclusive trajectory for growth.
- The dynamic evolution of telecommunication, its patterns of use, and underlying technologies in recent years underscores the necessity for legislation that aligns with the evolving needs of our society.
Mines Ministry to Launch National Geoscience Data Repository Portal To Foster Innovation in Exploration (PIB)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Ministry of Mines is to launch the National Geoscience Data Repository (NGDR) Portal on 19th December 2023 in a ceremony in New Delhi.
What is the National Geoscience Data Repository Portal?
- This extensive online platform facilitates the retrieval, exchange, and examination of geospatial information nationwide.
- Spearheaded by the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and the Bhaskaracharya Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), the NGDR initiative marks a notable advancement in democratizing crucial geoscience data.
- It empowers stakeholders in various industries and academia by providing unparalleled access to invaluable resources.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) originated in 1851 with the primary objective of identifying coal deposits for the Railways.
- Since its inception, GSI has transformed into a repository of geo-scientific information, achieving international recognition for its contributions.
- The organization is dedicated to creating and updating national geoscientific data, conducting mineral resource assessments, and providing impartial geological expertise crucial for policy decisions, commercial ventures, and socio-economic needs.
- GSI focuses on comprehensive documentation of geological processes, employing state-of-the-art techniques in geological, geophysical, and geochemical surveys.
- As an attached office of the Ministry of Mines, GSI operates from its headquarters in Kolkata, with six regional offices in Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong, and Kolkata, along with state unit offices across India.
About BISAG (N):
- Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) operates as an Autonomous Scientific Society registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, falling under the MeitY, Government of India.
- Its multifaceted mission encompasses technology development and management, research and development, fostering national and international collaboration, capacity building, and facilitating technology transfer and entrepreneurship development in the realm of geospatial technology.
- BISAG-N has played a pivotal role in implementing GIS and geospatial technologies for major ministries and nearly all states, integrating diverse technological domains such as geo-spatial science, information science systems, and mathematics science systems.
- The institute operates as a state agency under the Department of Science and Technology, Government of Gujarat, situated in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
mRNA, easy to customise, is the next frontier for personalised medicine (The Hindu)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The therapeutic use of messenger RNA (mRNA) has fueled great hope to combat a wide range of incurable diseases.
What is mRNA?
- mRNA, or messenger RNA, represents a type of nucleic acid responsible for conveying genetic instructions.
- Within cells, mRNA serves as a messenger, transporting codes from the DNA located in the nucleus to the sites of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm, where ribosomes are situated.
- The genetic information in DNA undergoes transcription, or copying, into mRNA before proteins can be synthesized.
- Each mRNA molecule encodes information for a specific protein, with every sequence of three nitrogen-containing bases dictating the inclusion of a particular amino acid in the protein.
Advantages of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Scalability: The production of mRNA in the laboratory is highly scalable, as the method for generating mRNA remains consistent across different types.
- This contrasts with traditional drugs, where each compound has distinct chemistry, requiring varied manufacturing methods.
- Patient-Centric: mRNA, being naturally degradable by cells when no longer needed, allows for flexible dosage adjustments to cater to changing patient requirements.
- Broad Therapeutic Potential: mRNA-based medicine holds promise for addressing a wide range of diseases rooted in cellular errors, such as the production of incorrect proteins, mutant protein versions, or insufficient normal protein levels.
- By delivering corrected mRNA to affected cells, scientists aim to facilitate the production of the correct proteins.
Prospects of mRNA-Based Medicine:
- Diverse Treatment Applications: The future of mRNA-based medicine extends to addressing conditions like heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and bone loss, among others.
- Enhanced Wound Healing: mRNA drugs exhibit the potential to stimulate the formation of new blood vessels.
- This capability is particularly beneficial for diabetic patients with compromised blood circulation, reducing the risk of amputation.
- Treatment for Rare Conditions: mRNA-based medicine holds promise in treating rare disorders like propionic acidaemia, characterized by insufficient levels of liver proteins crucial for preventing the accumulation of toxic by-products in the body, especially in children.
Way Forward
- The capacity to tailor and manufacture mRNA easily enhances its prospects as a potent and personalized therapy, offering the potential for reduced side effects and widespread applicability.
- Despite these advancements, mRNA-based therapeutics are in the early stages of development, facing challenges such as the short lifespan of mRNA in cells and limited protein production duration.
- Addressing these hurdles is crucial to optimizing mRNA effectiveness and minimizing the quantity of mRNA needed.
MoEFCC has launched the Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme to promote sustainable forest management and agroforestry practices across the country (Indian Express)

- 19 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Amid rising international concerns about deforestation and illicit trade in timber, the government has launched its own “national” forest certification scheme to validate entities that adhere to sustainable practices in the management of forests and their products.
About the Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme (IFWCS):
- The Indian Forest & Wood Certification Scheme (IFWCS) serves as the national forest certification initiative, focusing on fostering sustainable forest management and the sustainable utilization of Trees outside Forests (TOF) across India.
- Voluntary Participation: The scheme provides a voluntary third-party certification mechanism to encourage agroforestry practices within the country.
- Alternatives to Foreign Certifications: IFWCS presents an indigenous alternative to foreign certification agencies that have been prevalent in the Indian market for the past two decades.
- Applicability: The certification applies nationwide, covering both forest areas and TOF plantations on government, private, agroforestry, and other lands.
- It encompasses both timber and non-timber forest produce (NTFP).
- Necessity: With major export markets like Europe and the United States imposing stricter rules on forest product imports due to deforestation concerns related to climate change, IFWCS can provide market incentives for entities practising responsible forest management.
- Significance: The scheme aims to enhance trust, transparency, and international acceptability of Indian forest-based products.
- It is especially beneficial for state forest departments, individual farmers, or Farmer Producer Organizations engaged in agroforestry.
- Compliance and Legal Status: While the certification may gain recognition from various regulatory authorities, it does not serve as legal advice on compliance with specific laws, regulations, or requirements.
- Foundation: Forest Management certification relies on the Indian Forest Management Standard, a crucial component of the National Working Plan Code 2023, introduced this year.
- The Indian Forest and Wood Certification Council, acting as a multi-stakeholder advisory body, will supervise the scheme.
- The council comprises members from esteemed institutions like the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education, Forest Survey of India, and the Indian Institute of Forest Management, along with representatives from relevant ministries.
- Implementation: The Indian Institute of Forest Management in Bhopal will serve as the scheme's operating agency.
- Certification bodies conducting independent audits will be accredited by the National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies under the Quality Council of India.
Management of Forests in India:
- The administration of forests in India aligns with individual working plans specific to each forest area.
- Recently, these plans have undergone revisions incorporating the newly formulated Indian Forest Management Standards.
- Comprising 8 criteria, 69 indicators, and 254 verifiers, these standards are obligatory for implementation across all forest divisions nationwide.
- While forest divisions are not compelled to obtain certification, adhering to these standards renders them eligible.
- The decision to pursue certification is contingent upon specific requirements and considerations.
India's Akash missile engages four targets at once at 25km, a global first (ET)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India demonstrated the capability of the Akash missile system to engage four aerial targets simultaneously at a range of 25 kilometres, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) said on Sunday.
Context:
- During the recent Exercise Astrashakti 2023, a solitary unit of the Akash weapon system demonstrated its capability by effectively engaging and eliminating four unmanned targets simultaneously.
- This showcase positions India as the pioneer, being the first country to showcase the proficiency of engaging multiple targets at considerable distances concurrently through command guidance from a single firing unit.
About the Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System:
- The Akash Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Defence System is a Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (SRSAM) designed to safeguard vulnerable areas and points from airborne threats.
- Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), it boasts several notable features:
- Versatility: Capable of simultaneously engaging multiple targets and effectively neutralizing manoeuvring threats, including unmanned aerial vehicles, fighter aircraft, cruise missiles, and helicopter-launched missiles.
- Electronic Counter-Counter Measures (ECCM): Equipped with built-in ECCM features, enhancing its resilience against electronic countermeasures.
- Flexible Deployment: The entire system is configured for launch from both static and mobile platforms such as battle tanks and wheeled trucks, ensuring adaptable deployment options.
- Transportability: Road and rail transportable, with swift mobilization and deployment capabilities, facilitating rapid response scenarios.
- Range: Capable of engaging aerial targets at a distance of approximately 25 km.
- Altitude of Operation: Ranging from 100 meters up to 20 km.
- Weight: 710 kg.
- Guidance System: Command Guidance.
- Automation: Fully automatic with a quick response time from target detection to neutralization.
- Open-System Architecture: Designed with an open-system architecture, ensuring adaptability to current and future air defence environments.
What is ‘noma’, the latest addition to WHO’s list of neglected tropical diseases (DownToEarth)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) on December 15, 2023, added one of the world’s most under-recognised health challenges, noma, to its official list of neglected tropical diseases (NTD).
About the Noma disease:
- Noma is a severe gangrenous disease of the mouth and face with a mortality rate of approximately 90 per cent.
- It is also known as cancrum oris or gangrenous stomatitis and is often associated with extreme poverty, malnutrition and poor access to sanitation and oral hygiene.
- The name of the disease comes from the Greek word “nom?”, meaning “to devour”, as noma eats away facial tissue and bones if not treated early.
- Noma mainly affects children aged 2-6 years old and is found most commonly among those living in poor communities.
- The illness’s ‘hidden’ or neglected nature is most likely due to the fact that it affects the world’s most marginalised children.
- Noma is associated with a number of risk factors, including poor oral hygiene, malnutrition, weakened immune systems, infections, and extreme poverty.
- While the disease is not contagious, it prefers to attack when the body’s defences are weak.
- The NTD often starts as an ulcer on the mucous membrane lining, commonly after a bout of measles or other diseases, stated another 2003 study.
- “It quickly develops into a massive necrosis, moving from the inside outward, often involving major portions of the face.
- Treatment: “Early treatment with antibiotics, rehydration, correction of electrolytic imbalances, and administering nutritional supplements will halt the disease.
- The patients who survive face many consequences, like significant facial disfigurement, spasms of the jaw muscles, oral incontinence and speech problems.
- The disease is also called the ‘face of poverty’, as effective drugs like sulfonamides and penicillin and adequate surgical treatment for the effects remain inaccessible for many due to extreme poverty.
- “The recognition of noma as an NTD aims to amplify global awareness, catalyse research, stimulate funding, and boost efforts to control the disease through multisectoral and multi-pronged approaches.
Surat Diamond Bourse to create 150,000 jobs! Modi is confident ‘world’s largest office building’ will be a boon for artisans and businessmen (Financial Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the inauguration ceremony of the Surat diamond bourse in Gujarat, Prime Minister Narendra Modi revealed plans for the creation of 150,000 new jobs, emphasising the bourse’s role as a “one-stop shop” for artisans and businessmen.
About Surat Diamond Bourse:
- Established in February 2015 by the former Chief Minister of Gujarat, Smt. Anandiben Patel, the Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is a prominent diamond trade centre situated in DREAM (Diamond Research and Mercantile) city, Surat, Gujarat.
- Recognized as the "diamond city" due to its diamond industry, which processes 85 to 90% of the world's rough diamonds, the SDB stands as the world's largest diamond trading hub, spanning an expansive floor space of 660,000 square meters and surpassing The Pentagon as the largest office building globally.
- Themed around the 'panch tatva,' symbolizing the five elements of nature – air, water, fire, earth, and sky, the SDB is designed with thematic landscaping.
- As a global centre for both rough and polished diamond and jewellery trading, it unifies various facets of the diamond industry, including cutting, polishing, and trading activities, within its vast expanse.
- The Bourse features a state-of-the-art 'Customs Clearance House' for Import-Export, a Jewelry mall for retail jewellery business, and facilities for International Banking and Safe Vaults.
Importance of the SDB Project:
- The Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) is set to accommodate a diverse range of diamond-related enterprises, encompassing the sale of both rough and polished diamonds, diamond manufacturing machinery, diamond planning software, diamond certificate firms, lab-grown diamonds, and more.
- Anticipated to be a major contributor to employment, the SDB is poised to generate substantial job opportunities.
- With an expected direct employment impact on over 1.5 lakh individuals across various roles within the diamond industry, it aims to bolster economic activity and livelihoods.
- Acknowledging its commitment to environmental responsibility, the complex has earned pre-certification as a green building by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC).
- This recognition is a testament to the SDB's implementation of eco-friendly and sustainable practices in its operations.
What is DREAM City?
- DREAM City, short for Diamond Research and Mercantile City, is an emerging business district located in Surat.
- Encompassing 810 hectares (2,000 acres) of land near Khajod, it follows the model of the Gujarat International Finance Tec (GIFT) City and Dholera Smart City near Ahmedabad.
- Envisioned as a comprehensive urban development, DREAM City is slated to feature office spaces, residential areas, and associated amenities.
- The project is under the purview of a special-purpose vehicle established by the Government of Gujarat.
- With an anticipated opening in 2030, DREAM City is poised to become Gujarat's third smart city, aligning with the state's commitment to fostering modern and sustainable urban environments.
Scientists find hydrogen cyanide, a key molecule for life formation, in Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus (Sci News)
- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, planetary scientists have detected several compounds of strong importance to the habitability of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, including hydrogen cyanide, acetylene, propylene and ethane, using data from NASA’s Cassini mission.
What is Enceladus?
- Enceladus is the sixth-largest icy moon of Saturn. It has a white, streaky surface made of water ice.
- Beneath this frozen crust lies a warmer, salty ocean that covers the whole moon.
- This circular moon is just about 500 km wide, with a surface temperature of -200°C.
- But its interiors host several sources of energy and heat.
- Enceladus is tugged and pulled in all directions by Saturn’s gravity and the gravity of other more massive moons, thus creating heat in its interior.
- Its rocky core may also be undergoing radioactive decay and chemical reactions that generate heat.
- Moreover, it is also an active source of water volcanism, where giant plumes of water, ice, dust, and gases are ejected into space like volcanic explosions.
- The material from the plumes replenishes one of the rings of Saturn as well, as the icy particles that make up the rings slowly drift inwards and get pulled into Saturn.
- The presence of a global saltwater ocean with nutrients and a heat source suggests a suitable aquatic environment for life.
- However, no life has been found on Enceladus or anywhere else beyond Earth.
About Hydrogen cyanide:
- Hydrogen cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structural formula H−C≡N.
- It presents itself as a colourless or pale-blue liquid or gas, characterized by a bitter, almond-like fragrance.
- Alternatively referred to as hydrocyanic acid or HCN, this substance has the potential to disrupt the body's oxygen utilization, posing risks to the brain, heart, blood vessels, and lungs.
- While Hydrogen cyanide boasts excellent solvent properties for numerous salts, its utilization as a solvent is limited due to its inherent toxicity.
- In various industrial settings, it finds application in tasks such as fumigation, electroplating, mining, chemical synthesis, and the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, plastics, dyes, and pesticides.
How Indian states fare on logistics: What the Centre’s latest survey says (Indian Express)

- 18 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) perception survey, released by the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry, flags some challenges in logistics and states performance on a regional basis.
Key highlights of the Report:
- Only five states namely Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Telangana continue to make up 70 per cent of exports. Over the years this has caused a widening gap in income and job generation between the landlocked states and coastal states.
- Performance of Landlocked States: Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh have received low perception scores on these counts while user satisfaction in Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab improved.
- Notably, Jharkhand saw below-average scores across all indicators, encompassing infrastructure, services, and operating and regulatory categories.
- Performance of North-East Group: In Manipur, user satisfaction levels for the state are generally lower than the average of the North-East Group for all indicators across pillars.
- The data indicated relatively high stress in the ‘easy of entry’ category.
- While Assam performed better than average on most counts, the user performance assessment was also below the average of North-East Group in the case of Meghalaya.
- Odisha, West Bengal Lag Among Coastal States: Indian coastal states including Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal account for 75 per cent of total exports from the country and have fared well in logistics historically.
- Gujarat accounts for 33% followed by Maharashtra with 16% and Tamil Nadu with 9% share.
- However, the survey showed that Goa, Odisha and West Bengal continue to perform below the average among coastal states.
- In the case of Odisha, the survey said that there has been an improvement in the overall perception of the state’s logistics ecosystem since 2019 but despite this, the indicator averages for this year have remained below the Coastal Group average.
What is Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS)?
- Initiated in 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry, LEADS draws inspiration from the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
- Unlike the LPI, which relies solely on perception-based surveys, LEADS incorporates both perception and objectivity, thereby enhancing the robustness and comprehensiveness of its evaluation.
- LEADS focuses on three pivotal pillars:
- Logistics Infrastructure
- Logistics Services, and
- Operating and Regulatory Environment.
- The recently released 5th edition, LEADS 2023, illuminates the evolving performance of states and union territories across these pillars.
- It provides valuable insights into the enhancement of logistics performance at the State/UT level, emphasizing an augmented stakeholder perception and the impact of various reforms.
- This report not only signals a positive transformation in the performance of states but also empowers State/UT Governments with region-specific insights, facilitating informed decision-making and comprehensive growth.
Importance of the LEADS Initiative:
- The LEADS report serves as a catalyst in fostering healthy competition among States/UTs, driving improvements in logistics performance.
- Notably, 23 States/UTs have aligned their State Logistics Policies with the National Logistics Policy, while 16 have accorded industry status to logistics, collectively contributing to the elevation of India's global positioning in the logistics ecosystem.
- This initiative significantly enhances the overall competitiveness of India's logistics sector, as evidenced by the country's ascent by six places to the 38th position in the 2023 Logistics Performance Index.
- Integral to this success are digital reforms like PM GatiShakti, Logistics Data Bank, Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP), and GST, which have propelled India's improved global ranking.
- Developed collaboratively and through a consultative approach, the LEADS report introduces objectivity in assessing both infrastructure development and process-related reforms.
Saint Lucia’s Tax Inspectors without Borders (TIWB) programme launched in partnership with India (ET)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India will help Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and sharing best practices under the ‘Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) programme’.
Key Highlights:
- India has been chosen as the Partner Administration and will provide Tax Experts for this programme.
- This programme is expected to be of 12-18 months’ duration in which India, in collaboration with the TIWB Secretariat and support of the UNDP Country Office, Barbados and the Eastern Caribbean, aims to aid Saint Lucia in strengthening its tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills to its tax administration, and through sharing of best practices.
- The focus of the programme will be on the effective use of automatic exchange of information under the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) framework.
What is Tax Inspectors without Borders programme?
- Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) is a joint initiative of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- It is designed to support developing countries to build tax audit capacity.
- TIWB facilitates well-targeted, specialised tax audit assistance in developing countries around the world.
- Under TIWB, tax audit experts work alongside local officials of developing country tax administrations on tax audit and tax audit-related issues.
- TIWB aims to transfer technical know-how and skills to developing countries’ tax auditors, as well as share general audit practices.
- The host administrations of developing countries are the lead partners in TIWB programmes, clearly specifying their needs and scope of work.
- A dedicated central unit (TIWB Secretariat) jointly managed by OECD and UNDP operates as a clearing house to match the demand for auditing assistance with appropriate expertise.
- TIWB is a capacity-building programme.
State Bank of India (SBI) has raised its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) by up to 10 basis points for selected tenures (Financial Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
State Bank of India (SBI) on Friday hiked its marginal cost of funds-based lending rate (MCLR) on various tenures by 5-10 basis points (bps), a move that could make consumer loans, such as auto or home loans, more expensive for borrowers.
What is the Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate (MCLR)?
- The MCLR, or Marginal Cost of Funds Based Lending Rate, represents the minimum lending rate below which a bank is not authorized to lend.
- This mechanism aims to facilitate the calculation of the minimum interest rate applicable to various types of loans offered by banks.
- Introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on April 1, 2016, the MCLR methodology serves to improve the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission and enhance transparency in the interest rate-setting process, replacing the earlier base rate structure established in July 2010.
- Calculation of MCLR: MCLR is internally determined by the bank, considering the remaining period for the loan repayment. This rate is closely tied to actual deposit rates and is calculated based on four key components:
- The marginal cost of funds
- Negative carry-on account of the cash reserve ratio
- Operating costs
- Tenor premium
- Under the MCLR framework, banks have the flexibility to offer loans at fixed or floating interest rates across all categories.
- The actual lending rates for various loan categories and tenors are determined by adding the components of spread to the MCLR.
- Consequently, the bank is restricted from lending at a rate lower than the MCLR for a specific maturity concerning all loans linked to that benchmark.
- Banks review and publish MCLRs for different maturities on a monthly basis.
- Certain loan rates, such as those for fixed-rate loans with tenors exceeding three years and special loan schemes offered by the government, remain unaffected by MCLR fluctuations.
Difference Between MCLR and Base Rate:
MCLR stands as a more evolved iteration of the base rate, presenting several distinctions between the two:
- Origin and Regulation: The base rate is the RBI-set minimum interest rate, and financial institutions cannot lend below this rate.
- MCLR, on the other hand, is an internal benchmarking system used by financial institutions, allowing them to set lending rates based on a predetermined spread.
- Cost Calculation: The base rate relies on the average cost of funds.
- MCLR is rooted in the marginal or incremental cost of money, providing a more dynamic reflection of the current cost scenario.
- Impact of RBI's Repo Rate: The base rate remains unaffected by changes in the RBI's repo rate.
- MCLR, however, is directly influenced by revisions in the repo rate, adjusting accordingly.
- Consideration Factors: The base rate typically considers the minimum rate of return or profit margin.
- In contrast, when determining the MCLR, factors such as the tenor premium are taken into account, resulting in a more nuanced rate-setting process.
‘Sacrifice forever etched in our hearts’: PM Modi, leaders across parties pay tributes on Vijay Diwas (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Leaders across the political lines paid tributes to the soldiers who fought in the 1971 war, on the occasion of 52nd Vijay Diwas on Saturday.
About Vijay Diwas:
- Vijay Diwas, observed on December 16 annually, is a commemoration honouring the triumph of the Indian armed forces over Pakistan in the 1971 war and paying tribute to the soldiers who made the ultimate sacrifice for their country.
- This day is also recognized in Bangladesh as 'Bijoy Dibos' or Victory Day, symbolizing the nation's formal independence from Pakistan.
Historical Background:
- The roots of the 1971 war lay in the genocide perpetrated by the oppressive Pakistani military regime, led by General Yahya Khan, against the people of East Pakistan.
- The conflict emerged following the victory of the Sheikh Mujibur Rahman-led Awami League in the 1970 elections.
- Post-elections, the Pakistani military used force to manipulate the results, resulting in a mass exodus from East Pakistan.
- India intervened during this critical period, with then-Prime Minister Indira Gandhi offering refuge to those fleeing from the other side of the border.
- Tensions escalated on December 3, 1971, when Pakistan initiated air strikes on 11 Indian airbases.
- In response, Indira Gandhi instructed India's Army Chief, General Sam Manekshaw, to launch a full-scale war against Pakistan.
- India supported Bangladesh nationalist groups and executed 'Operation Trident,' led by the Indian Navy, to target Karachi Port.
- After a 13-day battle, India achieved a decisive victory on December 16, 1971, leading to the establishment of Bangladesh from the former East Pakistan.
- On this momentous day, General Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi of Pakistan signed the Instrument of Surrender, capitulating with 93,000 Pakistani soldiers before the Indian Army and the Mukti Bahini of Bangladesh, marking the most substantial military surrender post-World War II.
How the hottest summer ever affected the Arctic: 5 things you need to know (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Rising temperatures in the Arctic have led to unprecedented wildfires that forced communities to evacuate, a decline in sea ice extent, devastating floods, food insecurity, and a rise in sea level.
Highlights from the Arctic Report Card 2023:
- The period from October 2022 to September 2023 ranked as the sixth-warmest year in the Arctic since the initiation of record-keeping in 1900.
- Notably, this timeframe aligns with the Arctic monitoring year, spanning from October to September to cover the region's cold season.
- This marks the 14th consecutive year wherein Arctic temperatures surpassed the average recorded between 1991 and 2020.
- The elevated temperatures observed in the northern polar region had significant consequences, including unprecedented wildfires necessitating community evacuations, a reduction in sea ice coverage, severe floods, concerns about food security, and an elevation in sea levels.
The most severe consequences of the soaring temperatures in the Arctic:
- Thawing of Subsea permafrost: Subsea permafrost is essentially frozen soil beneath the seabed that contains organic matter.
- While it has been gradually thawing for thousands of years, warmer ocean temperatures are accelerating this process.
- When subsea permafrost thaws, the organic matter it contains decays and releases methane and carbon dioxide – greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming and worsen ocean acidification.
- Food insecurity: Due to the impact of climate change on freshwater bodies and marine ecosystems, Western Alaska recorded another year of extremely low numbers of Chinook and chum salmon. The size of adult salmon has also decreased.
- It led to fishery closures, worsened user conflicts, and had profound cultural and food security impacts in Indigenous communities that have been tied to salmon for millennia.
- Interestingly, while the population of Chinook and chum salmon declined, sockeye salmon increased in Western Alaska.
- According to scientists, the diverging impacts are affecting Indigenous communities that depend on the salmon for food, and challenging fishery managers as the different species respond in unique ways to the warming climate.
- Raging wildfires: Canada with 40% of its land mass is considered Arctic and Northern was among the worst affected regions when it comes to wildfires.
- Canada witnessed its worst wildfire season on record with fires burning more than 10 million acres in the Northwest Territories.
- This happened as high temperatures dried up vegetation and soil, coupled with below-average rainfall, creating perfect conditions for wildfires.
- Canada witnessed its worst wildfire season on record with fires burning more than 10 million acres in the Northwest Territories.
- Severe flooding: Rising temperatures have led to dramatic thinning of the Mendenhall Glacier, located in Alaska, over the past 20 years.
- As a result, over the years, the meltaway water has annually caused floods in the region.
- One such disaster took place in August 2023, when a glacial lake on a tributary of the Mendenhall Glacier burst through its ice dam.
- It caused unprecedented flooding and severe property damage” in Alaska’s Juneau.
- Greenland ice sheet melting: The highest point on Greenland’s ice sheet experienced melting for only the fifth time in the 34-year record.
- Not only this, the ice sheet continued to lose mass despite above-average winter snow accumulation.
- Between August 2022 and September 2023, it lost roughly 350 trillion pounds of mass.
- Notably, Greenland’s ice sheet melting is the second-largest contributor to sea-level rise.
India joins the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for flying wing technology in tailless configuration (Indian Express)

- 16 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully carried out a flight trial of the Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator, an indigenous high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) from the Aeronautical Test Range, Chitradurga in Karnataka.
About the Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator:
- The Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator is a domestically developed high-speed flying-wing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) crafted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)’s Aeronautical Development Establishment.
- Its inaugural flight took place in July 2022, marking significant progress in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems, real-time integration, hardware-in-loop simulation, and an advanced Ground Control Station.
- The project team successfully optimized avionic systems, integration processes, and flight operations, culminating in the seventh and final flight in the ultimate configuration.
- Constructed with a complex arrowhead wing platform, the UAV prototype utilizes a lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- A noteworthy feature is the autonomous landing capability, eliminating the need for ground radars, infrastructure, or a pilot.
- This unique capability demonstration allows take-off and landing from any runway with surveyed coordinates.
- This technology demonstrator has been developed for India's secretive stealth combat drone called Ghatak.
- The successful flight in a tailless configuration has propelled India into the prestigious group of nations that have perfected the controls for the Flying wing configuration
Indian Joins Elite Club:
- With this flight in the tailless configuration, India has joined the elite club of countries to have mastered the controls for the flying wing technology.
- These flight tests led to achievements in the development of robust aerodynamic and control systems; integrated real-time and hardware-in-loop simulation, and a state-of-the-art Ground Control Station, informed the DRDO.
Aatmanirbharta
- The DRDO team had optimised the avionic systems, integration and flight operations towards the successful seventh flight in the final configuration.
- The aircraft prototype, with a complex arrowhead wing platform, is designed and manufactured with lightweight carbon prepreg composite material developed indigenously.
- Also, the composite structure, impregnated with fibre interrogators for health monitoring, is a showcase of ‘Aatmanirbharta’ in aerospace technology.
Global Stocktake should account for failures of developed nations: BASIC nations at COP28 (The Hindu)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The BASIC grouping, comprising Brazil, South Africa, India and China, has pushed during annual climate talks here that the Global Stocktake should also account for the failures of the developed nations.
About Global Stocktake:
- The global stocktake serves as a mechanism for nations and stakeholders to collectively assess their progress in achieving the objectives outlined in the Paris Climate Change Agreement, highlighting areas of success and areas needing improvement.
- In essence, it is akin to taking inventory on a global scale.
- Essentially, the global stocktake involves a comprehensive examination of everything related to the world's status regarding climate action and support.
- It entails identifying gaps and collaboratively strategizing to steer a more effective course towards accelerating climate action.
- This evaluation occurs every five years, with the inaugural stocktake scheduled to conclude at COP28.
- Background: In 2015, during COP21 in Paris, it became obligatory for all countries to establish emissions reduction targets and adapt to climate change impacts, known as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- The agreement mandated that countries evaluate their progress, starting in 2023 and subsequently every five years.
- Initial Assessment: The UN released a technical report on the first Global Stocktake in September 2023.
- According to this report, while the global community demonstrated some progress, it fell short of the necessary scale.
- The report emphasizes the need to expedite implementation, adopting an all-of-society approach to enhance ambition across all aspects, aligning with the goals of the Paris Agreement and addressing the climate crisis.
- The report acknowledges existing progress but underscores the urgency for more concerted efforts.
- Recognizing well-known gaps, the technical findings also spotlight opportunities and creative solutions, addressing both current challenges and those emerging.
- Additionally, the report notes that the average global temperature has risen by nearly 1.2 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times.
INCOIS wave rider buoy washes ashore in Gopalpur (New Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A wave rider buoy, equipped belonging to the Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), with GPS and various weather-related instruments, was found ashore at the Gopalpur Military Station in Ganjam district on Saturday.
About Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS):
- INCOIS is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is a unit of the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO), New Delhi.
- It is located in Hyderabad & was established in 1999.
- The ESSO operates as an executive arm of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) for its policies and programmes.
- It is mandated to provide the best possible ocean information and advisory services to society, industry, government agencies and the scientific community through sustained ocean observations and constant improvement through systematic and focused research.
What is the Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO)?
- Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO) is a virtual organisation set up by the Ministry of Earth Sciences GOI in 2007 and it is the executive arm of MoES.
- It has three major branches of earth sciences viz.,
- Ocean Science & Technology
- Atmospheric Science & Technology
- Geosciences and Technology.
- The overall vision of the ESSO is to excel in knowledge and technology enterprise for the earth system science realm towards the socio-economic benefit of the Indian sub-continent and in the Indian Ocean region.
- The ESSO contributes to the areas of Weather (General) and Weather advisories specific to agriculture, aviation, shipping, sports, etc. Monsoon, Disasters (cyclones, earthquakes, tsunamis, sea level rise), Living and non-living resources (fishery advisory, poly-metallic nodules, gas hydrates, freshwater etc), Coastal and Marine Ecosystems and Climate Change, Underwater Technology.
Scientists Create Tiny Robots Called 'Anthrobots' From Human Cells (India Times)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Scientists have created 'Anthrobots' , tiny living robots from human cells and the robots are able to move around in a lab dish and one day may be helpful in healing wounds or damaged tissue.
What is an Anthrobots?
- Anthrobots are self-assembling biological robots made from human tracheal cells, capable of movement and encouraging neuron growth.
- They can be created from adult human cells without genetic modifications, making them a potential patient-specific therapeutic tool.
- Anthrobots represent a significant advancement in regenerative medicine, potentially aiding in treating a variety of diseases and injuries.
- The multicellular robots, ranging in size from the width of a human hair to the point of a sharpened pencil, were made to self-assemble and shown to have a remarkable healing effect on other cells.
- The discovery is a starting point for the researchers’ vision to use patient-derived biobots as new therapeutic tools for regeneration, healing, and treatment of disease.
What are Tracheal cells?
- Tracheal cells come from the lining of the bronchi and trachea, forming the network of tubes that transport air to the lungs.
- These cells, a type of epithelial cell, are crucial for producing lubricating mucus to maintain the functionality of the airways.
- They are responsible for generating not only mucus but also various other compounds, all of which play a vital role in the process of respiration.
Is White Lung Syndrome caused by a new pathogen? Here is what you need to know (Indian Express)
- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
An outbreak of a respiratory illness in northern China and Ohio in the US — the White Lung Syndrome as people are calling it — has sparked speculation online of a new pandemic threat after COVID-19.
About White Lung Syndrome:
- “White lung syndrome” is a term used to describe a severe form of pneumonia characterized by the appearance of white patches on chest X-rays.
- While the term suggests a specific disease, it is actually used to describe a variety of conditions that cause similar symptoms.
- Symptoms: The specific symptoms of white lung syndrome can vary depending on the underlying cause, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Cough, feThere is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- ver, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, loss of appetite and wheezing
- In severe cases, white lung syndrome can lead to respiratory failure, which is a life-threatening condition.
- Causes: There are many different causes of white lung syndrome, including:
- Viral infections: These are the most common cause of white lung syndrome, including viruses like influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and COVID-19.
- Bacterial infections: These are less common than viral infections, but can still cause white lung syndrome.
- Fungal infections: These are rare, but can occur in people with weakened immune systems.
- Inhalation of harmful substances: This can include inhaling dust, fumes, or chemicals.
- Autoimmune diseases: These are diseases in which the body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues.
- Prevention: There is no specific way to prevent white lung syndrome.
- However, there are vaccines available for some of the viruses that can cause white lung syndrome, such as influenza and COVID-19.
- Treatment: The treatment for white lung syndrome depends on the underlying cause.
- In some cases, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed.
- In more severe cases, oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
11 bodies recovered after the volcanic eruption in Indonesia, and 12 climbers are still missing (Indian Express)

- 04 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The bodies of 11 climbers were recovered on Monday a day after a furious eruption of the Mount Marapi volcano as Indonesian rescuers searched for 12 apparently still missing.
About Mount Marapi:
Don't confuse it with Mount Merapi, which is located on Java Island.
- ‘Mount Marapi’ located is a volcanic mountain located in West Sumatra of Indonesia.
- It also known as Marapi or Gunuang Marapi in Minangkabau.
- According to legend, the mountain is the site first settled by the Minangkabau people after their ship landed on the mountain when it was the size of an egg and surrounded by water.
- There are large numbers of upright burial stones in the region which are oriented in the direction of the mountain, indicating its cultural significance.
- A significant eruption occurred in 1979, and in April-May 2018, ashfalls to the southeast were recorded.
About Mount Merapi:
- Mount Merapi is a volcanic mountain on the island of Java in Indonesia and is the most active volcano in Indonesia (out of a total of 30 active volcanoes).
- Although Mount Merapi was discovered by humans in 1754, geologists have estimated that the volcanic mountain is over 400,000 years old.
- The last major eruption of Mount Merapi back in 2010. This eruption took the lives of 347 people, and a further 20,000 locals were forced to evacuate the area.
- The local name for Mount Merapi is Gunung Merapi which can be translated to Fire Mountain or Mountain of Fire.
- Mount Merapi is considered sacred by local people. They believe that a supernatural kingdom exists there.
- Mount Merapi has erupted countless times, which haven't been recorded in modern history.
- However, we do know that Merapi has erupted over 68 since 1548.
- Merapi has now been active for approximately 10,000 years.
PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" launched under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 Crore supports 2 lakh micro food processing enterprises following One District One Product (ODOP) approac

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
As part of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) is implementing a centrally sponsored "PM Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme" for providing financial, technical and business support for setting up / upgradation of micro food processing enterprises in the country.
About PM Formalisation of Micro food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme:
- Launched on 29th June 2020, PMFMPE is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
- It is designed to address the challenges faced by the micro-enterprises and to tap the potential of groups and cooperatives in supporting the upgradation and formalization of these enterprises.
- Aims:
- Enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing industry and promote formalization of the sector; and
- Support Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), and Producers Cooperatives along their entire value chain.
- Objectives: To build the capability of microenterprises to enable:
- Increased access to credit by existing micro food processing entrepreneurs, FPOs, Self Help Groups, and Co-operatives.
- Integration with an organized supply chain by strengthening branding & marketing.
- Support for the transition of existing 2,00,000 enterprises into a formal framework.
- Increased access to common services like common processing facilities, laboratories, storage, packaging, marketing, and incubation services.
- Strengthening of institutions, research, and training in the food processing sector; and
- Increased access for the enterprises, to professional and technical support.
- Outlay:
- The scheme envisages an outlay of ? 10,000 crores over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25.
- The expenditure under the scheme would be shared in a 60:40 ratio between Central and State Governments, in a 90:10 ratio with the North
- In Eastern and the Himalayan States, a 60:40 ratio with UTs with the legislature and 100% by the Center for other UTs.
- Coverage:
- Under the scheme, 2,00,000 micro food processing units will be directly assisted with credit-linked subsidies.
- Adequate supportive common infrastructure and institutional architecture will be supported to accelerate the growth of the sector.
The Supreme Court directed the governments to provide details on “the estimated inflow of illegal migrants into India.. after March 25, 1971”. (Indian Express)
- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court on Thursday asked the Centre and Assam government to provide details on the “estimated inflow of illegal migrants” to Assam and other Northeastern states after March 25, 1971, and the status of border fencing.
News Summary:
- During the hearing of petitions, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court expressed concerns about the perceived 'unlimited influx' of illegal migrants from Bangladesh, impacting demographics and straining resources for Indian citizens.
- The court questioned the application of Section 6A, granting Indian citizenship benefits to illegal migrants, solely in Assam and not in West Bengal, which shares a larger border with Bangladesh.
- The Supreme Court directed the Home Secretary to submit an affidavit by May 11, 2023, detailing the estimated inflow of illegal migrants, steps taken to address illegal immigration, and specifics on border-fencing extent and timelines.
- The government was also instructed to provide information on illegal immigration along the West Bengal border post on March 25, 1971.
Why Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955 is Under Challenge?
- Presently, a Supreme Court bench is reviewing petitions from indigenous Assamese groups challenging Section 6A of the Citizenship Act.
- These groups assert that the special provision serves as a 'beacon' for illegal entrants to settle in Assam, gain Indian citizenship, and subsequently deprive locals of political, and economic rights, jeopardizing Assamese cultural identity.
- The petitioners question the constitutional validity of Section 6A, claiming it is arbitrary, specifically singles out Assam, violates Article 14, and has led to an influx of illegal migrants from Bangladesh.
- They advocate for establishing 1951 as the cutoff date for inclusion in the National Register of Citizens instead of 1971.
- The primary petitioner, Assam Sanmilita Mahasangha (ASM), argues that Section 6A is discriminatory, arbitrary, illegal, and infringes upon the rights of indigenous Assamese people by establishing a different citizenship cutoff date for Assam compared to the rest of India (July 1948).
What are the Arguments of the Central Government?
- The central government refutes the accusation of unfairly burdening the state with the responsibility of handling illegal migrants, contending that different states of India can be classified differently based on historical and geographical factors.
- According to the government, the classification implied in Section 6-A is founded on intelligible differentia.
- Dismissing claims of arbitrariness, the Centre asserts that the guarantee against non-arbitrariness under Article 14 does not mandate universal application for every law, irrespective of dissimilarity or the nature of the individuals it pertains to.
Global River Cities Alliance with 267 river cities including India, USA and Denmark to be launched on December 10, 2023 (PIB)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) on behalf of River Cities Alliance (RCA), has signed a Memorandum of Common Purpose (MoCP) with the Mississippi River Cities and Towns Initiative (MRCTI), representing 124 cities/towns situated along the banks of the Mississippi River, USA.
What is River Cities Alliance (RCA)?
- The River Cities Alliance (RCA) is a joint initiative of the Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation under the Ministry of Jal Shakti (MoJS) & the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), with a vision to connect river cities and focus on sustainable river centric development.
- Beginning with 30 member cities in November 2021, the Alliance has expanded to 109 river cities across India and one international member city from Denmark.
- 30 cities include Dehradun, Rishikesh, Haridwar, Srinagar, Varanasi, Kanpur, Prayagraj, Farrukhabad, Mirzapur, Mathura, Bijnor, Ayodhya, Patna, Bhagalpur, Begusarai, Munger, Sahibganj, Rajmahal, Howrah, Jangipur, Hugli-Chinsurah, Berhampore, Maheshtala, Aurangabad, Chennai, Bhubaneshwar, Hyderabad, Pune, Udaipur and Vijayawada.
- The Alliance is open to all river cities of India. Any river city can join the Alliance at any time.
- Objective: To provide the member cities with a platform to discuss and exchange information on aspects that are vital for sustainable management of urban rivers, sharing best practices and supporting innovation.
- It focuses on three broad themes- Networking, Capacity Building and Technical Support.
- The Secretariat of the Alliance is set up at the National Institute for Urban Affairs (NIUA) Delhi.
About the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG):
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India, established the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) as a registered society to take proactive measures for preventing, controlling, and abating environmental pollution in the Ganga River.
- Its mission includes ensuring a continuous and adequate flow of water to rejuvenate the river.
- Initially serving as the implementation arm of the dissolved National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA), NMCG aims to achieve effective pollution abatement and river rejuvenation through a river basin approach, promoting inter-sectoral coordination and environmentally sustainable development.
- Post the dissolution of NGRBA in 2016, NMCG continues its objectives through the National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection, and Management of River Ganga, also known as the National Ganga Council.
- The mission focuses on maintaining minimum ecological flows in the Ganga to ensure water quality and sustainable development.
- Structure: NMCG follows a two-tier management structure comprising the Governing Council and the Executive Committee, both led by the Director General.
- The Executive Committee holds the authority to approve projects up to Rs. 1000 crores.
- At the state level, State Programme Management Groups (SPMGs) serve as the implementing arms of State Ganga Committees.
- The Director General of NMCG holds the position of Additional Secretary in the Government of India.
Mining for critical minerals: what is the auction process, and why is it important? (Indian Express)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A total of twenty critical mineral blocks are currently open for commercial bidding by private entities. The auction process commenced on November 29, and interested parties have the opportunity to submit bids until January 22 of the following year.
What are Critical Minerals?
- A mineral attains critical status when there is a relatively higher risk of supply shortage and its impact on the economy compared to other raw materials.
- These minerals play a pivotal role in economic development and national security, and their scarcity, concentration in specific geographic locations, or limited extraction/processing options may pose potential vulnerabilities in the supply chain.
- Critical minerals, including lithium, graphite, cobalt, titanium, and rare earth elements, are indispensable for advancements in various sectors such as high-tech electronics, telecommunications, transport, and defense.
- They are integral to strategic value chains, including initiatives for clean technologies (e.g., zero-emission vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels), information and communication technologies (e.g., semiconductors), and advanced manufacturing inputs and materials (e.g., defense applications, permanent magnets, ceramics).
What are the Estimated Reserves of Key Critical Minerals in these Blocks?
- J&K Block: In the J&K block, there is an inferred reserve of 5.9 million tonnes of bauxite, containing over 3,400 tonnes of lithium metal content.
- Additionally, this block boasts more than 70,000 tonnes of titanium metal content.
- Odisha Block: In the Odisha block, the National Institute of Transforming India (NITI) estimates an inferred value of 2.05 million tonnes of nickel ore, equivalent to 3,908 tonnes of nickel metal content.
- Chhattisgarh Block: While the Chhattisgarh block contains lithium and rare earth elements (REEs), no drilling has been conducted to assess total reserves as of yet.
- Other Blocks: Nickel ore reserves have been identified in three blocks, situated in Bihar, Gujarat, and Odisha.
- However, drilling has not been carried out for the Bihar and Gujarat blocks.
How does India presently source these minerals?
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, India imported 2,145 tonnes of lithium carbonate and lithium oxide.
- Lithium carbonate, containing up to 19% lithium, and lithium oxide, typically converted to lithium hydroxide and containing 29% lithium, were part of the imports.
- Additionally, India imported 32,000 tonnes of unwrought nickel and 1.2 million tonnes of copper ore during the same period.
- Notably, India is entirely dependent on imports for its lithium and nickel demand, while for copper, this reliance stands at 93%.
Recent Initiatives by the Indian Government to Boost the Critical Minerals Sector:
- Identification of 30 Critical Minerals: In July 2023, the Indian government released a list of 30 critical minerals, including Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium, and Cadmium.
- Mining Permissions: The government amended a key law, allowing for the mining of three critical minerals – lithium, niobium, and REEs.
- New royalty rates for critical minerals, aligning with global benchmarks, were specified to attract bidders.
- Geological Survey of India's Exploration: The Geological Survey of India initiated 125 projects in the current fiscal to explore critical mineral reserves.
- Notably, it estimated 5.9 million tonnes of lithium ore in the Salal-Haimna areas (Reasi district, J&K).
- In the preceding eight fiscal years, a total of 625 mineral exploration projects were undertaken.
- Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals: The Committee on Identification of Critical Minerals recommended establishing a Centre of Excellence for Critical Minerals to formulate policies and incentives for creating a comprehensive value chain of critical minerals in the country.
- Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL): A joint venture company, Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL), is mandated to identify and acquire overseas mineral assets of a critical and strategic nature, such as lithium and cobalt, to ensure a secure supply.
- Mineral Security Partnership (MSP): India joined the US-led Mineral Security Partnership (MSP), a collaboration of 14 countries aiming to catalyze public and private investment in critical mineral supply chains globally.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (Indian Express)

- 08 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Earlier this year, a South Korean laboratory unveiled a significant advancement that holds promise as a potential solution to the energy crisis.
What is Google DeepMind's Project?
- Google has introduced the Graph Networks for Materials Exploration (GNoME), an AI tool developed by DeepMind.
- Leveraging Artificial Intelligence, GNoME successfully predicted the structures of over 2 million new materials.
- The potential applications span diverse sectors, including renewable energy, battery research, semiconductor design, and enhanced computing efficiency.
How does GNoME operate?
- GNoME functions as an advanced graph neural network model (GNN), where input data takes the form of a graph resembling connections between atoms.
- The model employs 'active learning,' initially training on a small specialized dataset and later incorporating new targets for machine learning with human assistance.
- This adaptability suits the algorithm well for material discovery, as it involves identifying patterns not present in the original dataset.
Operational Mechanism of GNoME:
- GNoME employs two pipelines for discovering stable materials with low energy.
- The structural pipeline generates candidates with structures akin to known crystals, while the compositional pipeline follows a more randomized approach based on chemical formulas.
- Outputs from both pipelines undergo evaluation using established Density Functional Theory calculations, contributing to the GNoME database and guiding subsequent rounds of active learning.
- Consequently, the model has significantly improved its precision rate for predicting material stability, reaching around 80%, up from an initial 50%.
- DeepMind's research, encompassing 380,000 stable predictions, is equivalent to nearly 800 years of knowledge, facilitating further breakthroughs in materials discovery for researchers.
What is the Significance of GNoME?
- This breakthrough in artificial intelligence dramatically expands the inventory of 'stable materials,' multiplying it by tenfold in a single stride.
- These materials encompass inorganic crystals crucial for a spectrum of modern technologies, from computer chips to batteries.
- Stability is paramount for these crystals, as any instability could lead to decomposition.
- While the synthesized and tested processes still lie ahead, DeepMind has shared a curated list of 381,000 crystal structures from the predicted 2.2 million, offering a promising foundation for advancing new technologies.
- In comparison, human experimentation over the last decades has revealed the structures of around 28,000 stable materials, catalogued in the Inorganic Crystal Structures Database, representing a noteworthy advancement in material discovery.
Food versus Fuel: What’s happening with Centre’s ethanol blending scheme (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After banning sugar exports, the Centre has taken the next step towards augmenting domestic availability – restricting the diversion of the sweetener for ethanol production.
What is the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme?
- The Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) programme was launched in January 2003.
- The programme sought to promote the use of alternative and environment-friendly fuels and to reduce import dependency for energy requirements.
- Effective from April 1, 2019, across the nation (excluding UTs of Andaman Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands), Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) sell petrol blended with up to 10% ethanol.
- The average ethanol blending in petrol has surged from 1.6% in 2013-14 to 11.8% in 2022-23.
- India targets a 20% ethanol blending ratio by 2025, revised from the initial 2030 deadline per the NITI Aayog's roadmap.
- Benefits of the EBP Programme:
- Reducing India’s import bill.
- Mitigating environmental pollution.
- Augmenting farm income.
- Offering a biofuel option with minimal additional investment for manufacturers.
- Challenges for 20% Ethanol Blending:
- Engine modifications are required to process petrol blended with 20% ethanol.
- Ethanol combustion yields no CO2, yet it doesn't address nitrous oxide emissions.
- Concerns about inefficient land use in ethanol production and the substantial water demand for cultivating crops.
- Food security considerations due to uncertainties about future agricultural output.
Why is the Restriction on Sweetener Diversion for Ethanol Production Imposed?
- Sugar Supply Concerns: Closing the 2022-23 sugar year with stocks slightly exceeding 57 lakh tonnes (lt), the lowest since 2016-17 (39.4 lt), raises apprehensions.
- The stock level falls significantly below the peak of 143.3 lt in 2018-19.
- Uncertainties surround the sugar production for the ongoing 2023-24 year, with Maharashtra and Karnataka anticipating substantial declines due to insufficient rainfall and low reservoir water levels in key cane-growing regions.
- Key Implication of the Decision: The recent decision, coupled with the ban on sugar shipments since May 2023, underscores a clear priority.
- Governments emphasize domestic supply over exports, favouring consumers over producers and prioritizing food over fuel.
Strategies to Boost Ethanol Production without Compromising Food Security:
- Diversification of Feedstocks: The government's ethanol policy, marked by favourable pricing and the incorporation of alternative feedstocks such as 2G ethanol sources, has been instrumental.
- The historical dependence on sugarcane-based feedstocks, which constituted 100% of ethanol sources (reduced to 76% in 2022-23), is no longer the sole reliance of the Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program.
About Ethanol:
- Ethanol, an anhydrous ethyl alcohol having the chemical formula of C2H5OH, can be produced from sugarcane, maize, wheat, etc which have high starch content.
- In India, ethanol is mainly produced from sugarcane molasses by fermentation process.
- Ethanol can be mixed with gasoline to form different blends.
- As the ethanol molecule contains oxygen, it allows the engine to more completely combust the fuel, resulting in fewer emissions and thereby reducing the occurrence of environmental pollution.
- Since ethanol is produced from plants that harness the power of the sun, ethanol is also considered a renewable fuel.
This explosion in space, will now form a new solar system! James Webb Telescope captures Cassiopeia A in its latest discovery (Business Today)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The James Webb Space Telescope by NASA has recently documented a striking image of a star that underwent a supernova explosion within the Cassiopeia A (Cas A) supernova remnant.
What is Cassiopeia A?
- Cassiopeia A is the aftermath of a colossal star's explosion approximately 340 years ago, standing as the most recently formed remnant of its kind in our galaxy.
- Renowned for its status as a prototypical type of supernova remnant, it has been the subject of extensive exploration by various ground- and space-based observatories.
- Encompassing around 10 light-years, this remnant resides 11,000 light-years away in the Cassiopeia constellation, offering valuable insights into the intricate dynamics of supernovae.
What is Supernova?
A supernova is a powerful and catastrophic stellar explosion that occurs during the final stages of a massive star's life cycle. This extraordinary event releases an immense amount of energy, temporarily outshining entire galaxies and producing luminosities that can briefly outshine an entire galaxy.
What happens during a supernova explosion?
- Massive stars: Supernovas typically occur in massive stars, at least 8 times the mass of our sun.
- These stars burn brightly and fiercely, fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores.
- Nuclear fusion: As the star ages, it runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core.
- The core starts to collapse inwards due to gravity, while the outer layers expand and cool.
- This increased pressure and temperature trigger the nuclear fusion of heavier elements, like carbon and oxygen, releasing immense energy.
- Bounce and shockwave: The core's collapse eventually leads to a sudden rebound, called the core bounce.
- This bounce creates a shockwave that rips through the star's outer layers, ejecting them outwards in a violent explosion.
Types of supernovae: There are two main types of supernovae:
- Core-collapse supernovae: The explosion blows away the star's outer layers, leaving behind a neutron star or, if the mass is even greater, a black hole.
- Type Ia supernovae: These occur in binary systems where a white dwarf, the remnant of a low-mass star, siphons material from its companion star.
- This builds up mass on the white dwarf until it reaches a critical point and undergoes thermonuclear runaway, leading to a massive explosion.
Significance of supernovae: Supernovae play a crucial role in the universe's evolution.
- Enrich the interstellar medium with heavy elements: The ejected material from supernovae is rich in elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, which are essential for the formation of new stars and planets.
- Trigger star formation: The shockwaves from supernovae can compress surrounding gas clouds, triggering the formation of new stars.
- Create black holes and neutron stars: The most massive stars leave behind black holes or neutron stars, incredibly dense objects with fascinating properties.
Calling for caution, PM flags need for ethics, democratic values in AI (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document on the proper use of AI, the guardrails for the technology, and how it can be democratised.
Context:
- India is currently hosting the 4th Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit at Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi, scheduled from December 12-14, 2023.
- The first three GPAI summits were held in Montreal, Paris and Tokyo, respectively.
- Prime Minister Modi emphasized the dual nature of AI, portraying it as a significant development tool for the 21st century but also highlighting potential risks.
- He called for a global framework to ensure responsible AI use and urged caution in deployment.
- Addressing concerns like deepfakes, cybersecurity, and cyber-terrorism, he proposed an audit mechanism categorizing AI tools based on their capabilities.
- PM Modi is negotiating with GPAI member countries for a consensus on a declaration document outlining proper AI use, technology guardrails, and democratization.
- Recognizing AI's role in economic growth, he announced India's upcoming AI mission, focusing on AI computing power for startups and innovators, with applications in agriculture, health, and education.
- The mission aims to extend AI skills to Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- PM Modi stressed ethical AI use as a guiding principle and suggested the inclusion of development and deployment protocols for high-risk AI systems in the global framework.
- He underscored AI's potential for connecting people and envisioned its ethical use in promoting economic growth, equality, and social justice.
About the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit:
- The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit is a three-day event starting December 12, which will see representatives from 28 member countries and the European Union.
- India is the Lead Chair for the alliance in 2024.
- The founding members of the GPAI: are Australia, Canada, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, Slovenia, the UK, the US, and the EU.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the summit on December 12.
- The objective of this summit is to bridge the gap between theory and practice on AI by supporting cutting-edge research and applied activities on AI-related priorities.
- It will feature a number of seminars covering a wide range of subjects, including AI and global health, education and skill development, AI and data governance, and machine learning workshops.
- More than 150 speakers from various nations will be present at the summit, including more than fifty GPAI experts.
- Moreover, leading global AI innovators such as Intel, Google, Meta, Microsoft, etc will be taking part in these events.
- Additionally, start-ups and students who win under the YUVA AI programme will present their AI models and solutions.
Missiles from rebel territory in Yemen miss a ship near key Bab el-Mandeb Strait, US official says (TOI)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Two missiles fired by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
Context:
- Two missiles fired from territory held by Yemen's Houthi rebels missed a commercial tanker near the key Bab el-Mandeb Strait on Wednesday.
- An American warship also shot down a suspected Houthi drone flying in its direction during the incident.
- The ship was carrying Indian-manufactured jet fuel and was heading for either Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
- It was coming from Mangalore in southern India and had an armed security crew on board.
- The Houthis have carried out a series of attacks on vessels in the Red Sea and launched drones and missiles targeting Israel.
About Bab el-Mandeb Strait:
- The Bab-el-Mandeb is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa.
- It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden.
- The Bab el-Mandeb Strait is a chokepoint between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East and is a strategic link between the Mediterranean Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is one of the world's most important routes for global seaborne commodity shipments, particularly crude oil and fuel.
- The Perim Island divides the strait into two channels, of which the eastern is known as the Bab Iskender (Alexander's Strait), while the western is known as Dact-el-Mayun.
What is the Horn of Africa?
- The Horn of Africa, the world's fourth-largest peninsula, is located in Northeast Africa, extending eastwards from the African mainland and bordered by the Red Sea, Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean.
- Positioned equidistantly from the equator and the Tropic of Cancer, it encompasses diverse landscapes, including the Ethiopian Plateau, Ogaden desert, and Eritrean and Somalian coasts.
- The Horn of Africa includes the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- This region has experienced historical complexities, including imperialism, neo-colonialism, the Cold War, ethnic tensions, intra-African conflicts, poverty, disease, and famine.
India’s first Pompe disease patient passes away: What is this rare genetic disorder? (Indian Express)

- 13 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Nidhi Shirol, India’s first Pompe disease patient, passed away last month at the age of 24 years after battling the disease. She spent the last six years in a semi-comatose state.
What is Pompe Disease?
- Pompe disease is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) and is also known as Glycogen Storage Disease Type II.
- This enzyme is crucial for breaking down glycogen into glucose within the lysosomes of cells.
- Its prevalence estimates range from 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 300,000 births and occur across diverse ethnicities and populations.
- The age of onset and severity can vary, leading to a spectrum of clinical presentations.
How does Pompe disease affect an individual?
The severity of the condition and the progression of symptoms may differ among individuals. Some key symptoms are:
- Muscle weakness: Progressive muscle weakness is a primary feature of Pompe disease.
- It affects both skeletal and smooth muscles, leading to difficulties in mobility and daily activities.
- Weakness in the respiratory muscles can result in breathing difficulties, especially during physical exertion or even while lying down.
- Motor skill delay: Children with the disease may experience delays in achieving motor milestones, such as sitting, crawling, and walking.
- The degree of motor skill delay can vary, and some individuals may never attain certain motor milestones.
- Degenerative impact on bones: Prolonged muscle weakness and reduced mobility can have a degenerative impact on bones, leading to joint contractures and skeletal deformities.
- Respiratory complications: The weakening of respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm, can have an impact.
- Patients may experience shortness of breath, respiratory infections, and in severe cases, respiratory failure.
- Cardiac involvement: In some cases, Pompe disease can affect the heart muscles, leading to complications.
- Symptoms such as heart palpitations, fatigue, and chest pain, may manifest.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Pompe disease can cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, characterised by the thickening of the heart muscle walls.
- This can lead to impaired heart functions and cardiovascular symptoms.
- Implications for daily living: Patients may face challenges in performing daily activities independently due to muscle weakness and respiratory limitations.
- Assistive devices such as wheelchairs and respiratory support equipment may become necessary.
How is Pompe disease diagnosed?
- Diagnosing Pompe disease involves a multi-faceted approach.
- Enzyme assays are conducted to measure the activity of acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), the deficient enzyme.
- Genetic testing identifies mutations in the responsible GAA gene.
- Clinical evaluations consider the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
- Enzyme tests, often performed on blood or skin cells, provide crucial insights into GAA deficiency.
- Genetic analysis confirms the presence of specific mutations associated with Pompe Disease.
- The combination of these diagnostic tools enables healthcare professionals to accurately identify and confirm the disease, helping achieve timely intervention and management.
Is Pompe disease curable?
- While there is currently no cure for Pompe disease, treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is a standard treatment, involving the infusion of the missing enzyme to alleviate glycogen buildup.
Data | Sharp rise in Indians illegally crossing U.S. northern border from Canada (The Hindu)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
In the last ten years, the number of unauthorized Indian migrants entering the U.S. has surged significantly, climbing from a mere 1,500 a decade ago to an astonishing 96,917 in 2023, as reported by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
What are the Implications for India Amidst the Surge in Illegal Migrants?
- Bilateral Relations: The surge in illegal migration poses potential challenges to bilateral relations between India and the USA, impacting areas such as trade negotiations, security cooperation, and strategic partnerships.
- Economic Factors: India faces the risk of a brain drain, as skilled individuals seek illegal entry, potentially affecting sectors with a demand for skilled labour and impacting the country's economy.
- The outflow of skilled and educated individuals through illegal migration can have adverse effects on India's economy, leading to a depletion of talent and expertise.
- Labour Market Challenges: The departure of skilled or semi-skilled workers may create labour shortages in specific sectors, affecting India's workforce and economic productivity.
- Policy Repercussions: India may need to institute stringent policies to address the root causes of illegal migration, potentially diverting resources and attention from other developmental priorities.
What are the Causes Behind the Surge in Illegal Indian Migrants to the USA?
- Pull Factors: The USA's reputation for offering improved employment prospects, higher wages, and career advancement acts as a significant attraction for migrants.
- The allure of quality education and prestigious academic institutions in the USA attracts students and families in search of educational opportunities.
- The desire to reunite with family members or relatives already settled in the USA motivates some migrants to seek illegal entry for proximity to loved ones.
- Push Factors: Numerous push factors, including limited job opportunities and economic prospects in India, drive individuals to seek better employment opportunities abroad.
- Social conflicts or a lack of confidence in India's governance structure may prompt some individuals to search for a more stable environment elsewhere.
- Visa Backlogs and Alternative Routes: Smugglers adapt their methods, providing sophisticated services to facilitate illegal entry into America.
- Prolonged visa backlogs prompt individuals to explore alternative, albeit illegal, pathways to enter the USA due to extended waiting times and limited legal entry options.
- Global Migration Trends: The overall increase in global migration post-pandemic contributes to this surge as individuals seek improved opportunities and security in different countries.
- Misinformation: Social media and deceptive travel agencies disseminate misinformation, misleading desperate migrants and encouraging them to embark on perilous journeys guided by multiple facilitators across continents.
- Desperate migrants may undertake complex, multi-leg journeys through various continents and countries, facing numerous risks and challenges along the way.
What can be Done?
Prioritizing economic stability, job creation, and social welfare programs to alleviate distress and offer improved opportunities within India. Initiating diplomatic dialogues to comprehend and address concerns that contribute to migration, fostering collaboration with other nations to safeguard the rights of migrants.
In a monthly report, the IEA projected that India's oil product demand growth would slow to 2.5% next year from 4.1% in 2023. (ET)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA) said recently that the "explosive growth" in Indian oil product consumption may be coming to an end.
About International Energy Agency:
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) is an autonomous intergovernmental organization founded in 1974 in Paris, France.
- Its primary focus revolves around energy policies, emphasizing economic development, energy security, and environmental protection, collectively known as the '3 E’s of IEA.'
- The IEA Clean Coal Centre is dedicated to providing independent information and analysis on making coal a cleaner energy source in line with UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Originating in response to the oil crisis of 1973-1974, the IEA's mandate has evolved to include tracking global energy trends, advocating sound energy policies, and fostering international energy technology cooperation.
- Mission: The IEA's mission is to ensure reliable, affordable, and clean energy for its member countries and beyond.
- Focus Areas: Key focus areas include energy security, economic development, environmental awareness, and global engagement.
- The IEA collaborates closely with non-member countries, particularly major producers and consumers, to find solutions to shared energy and environmental concerns.
- IEA’s Membership: The IEA is made up of 30 member countries.
- It also includes eight association countries. Four countries are seeking accession to full membership, Chile, Colombia, Israel and Lithuania.
- A candidate country to the IEA must be a member country of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Membership Criteria:
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- These reserves, accessible to the government even if not directly owned, should be readily deployable to address disruptions in the global oil supply.
- Demand Restraint Program: Candidates are required to implement a demand restraint program aimed at reducing national oil consumption by up to 10%.
- Emergency Response Capability: Member countries must have legislation and organizational frameworks in place to operate Coordinated Emergency Response Measures (CERM) on a national basis.
- Transparent Reporting: Legislation and measures should be established to ensure that all oil companies under the jurisdiction of the candidate country promptly report information upon request.
- Collective Action Capability: Measures must be in place to guarantee the country's capability to contribute its share in collective actions initiated by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Adequate Reserves: Prospective member countries must maintain crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year's net imports.
- India joined this organization in 2017 as an Associate member.
- However, in 2021, the International Energy Agency (IEA) invited India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, to become its full-time member.
- Major reports published by the IEA include the World Energy Outlook, World Energy Investment Report, World Energy Statistics, World Energy Balances, Energy Technology Perspectives, and the India Energy Outlook Report.
NASA all set to launch of PACE mission to study air quality, key climate factors and more (NASA)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
NASA is ready to enhance our understanding of Earth’s atmosphere with the upcoming Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission, scheduled for launch in early 2024.
What is NASA's PACE Mission?
- The mission will leverage advanced polarimeters to investigate the intricate interactions of light, aerosols, and clouds, enhancing our understanding of their impact on both air quality and climate.
- Beyond aerosol analysis, the PACE mission will delve into the study of ocean colour.
- At its core, the Ocean Colour Instrument (OCI) serves as the primary science instrument for PACE, designed to measure the ocean's colour across a spectrum ranging from ultraviolet to shortwave infrared.
- The mission includes two polarimeters:
- The Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and
- The Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2)
- Working in tandem, these instruments offer complementary spectral and angular sampling, ensuring polarimetric accuracy and extensive spatial coverage.
- This integrated approach aims to deliver enhanced atmospheric correction and a comprehensive dataset on aerosols and clouds, surpassing the capabilities of OCI alone.
- The collaborative payload of OCI, SPEXone, and HARP2 is poised to achieve significant breakthroughs in aerosol-cloud-ocean research.
What are Aerosols and their Effect?
- Aerosols are comprised of liquid or solid particles suspended in a gaseous or liquid medium.
- In the atmosphere, these particles are predominantly found in the lower layers (< 1.5 km) since aerosol sources are terrestrial.
- However, specific aerosols may extend into the stratosphere, particularly those ejected by volcanoes at high altitudes.
- Sources of Aerosols:
- Natural Sources: Generated from breaking waves (sea salt), wind-blown mineral dust from the surface, and volcanic emissions.
- Anthropogenic Aerosols: These include sulphate, nitrate, and carbonaceous aerosols, primarily originating from fossil fuel combustion.
- Effects of Aerosols:
- Impact on Atmospheric Chemistry.
- Reduction of Visibility.
- Significance for Air Quality and Human Health: Aerosols can adversely affect the heart and lungs.
- Role as Nuclei: Serve as nuclei for cloud droplets or ice crystals in ice clouds.
Mumps outbreak: Worrying symptoms to watch out for, preventive tips (India TV)
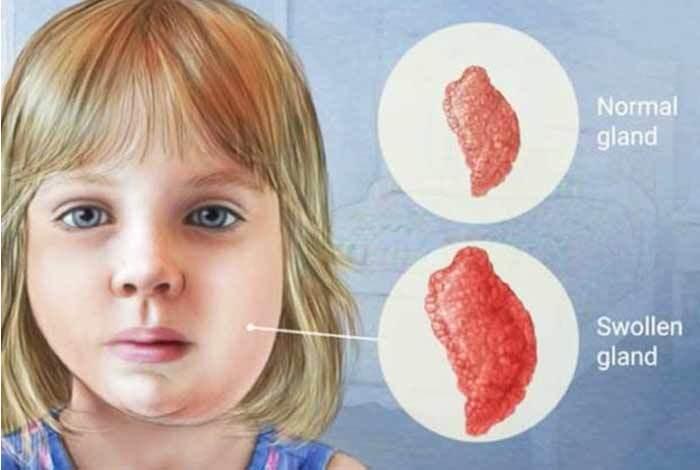
- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
A mumps outbreak has recently been reported in several states across the country, causing concern among public health officials.
What is Mumps Disease?
- Mumps is a contagious disease caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the paramyxovirus family.
- It typically involves painful swelling in the parotid salivary glands, located on the sides of the face below and in front of the ears.
- These swollen glands often give the infected person a characteristic "chipmunk-cheek" appearance.
- Humans are the only known host for the mumps virus, which is spread via direct contact or by airborne droplets from the upper respiratory tract of infected individuals.
- Transmission of mumps: Mumps is spread through contact with the saliva or respiratory droplets of an infected person. This can happen through coughing, sneezing, kissing, sharing utensils, or close contact.
- Symptoms:
- Mumps typically manifest after an incubation period of 2 to 4 weeks, starting with nonspecific symptoms like myalgia, headache, malaise, and low-grade fever.
- Within days, these initial symptoms progress to the swelling of the parotid salivary glands, either unilaterally or bilaterally, with other salivary glands affected in 10% of cases.
- Prevention: The best way to prevent mumps is to get vaccinated with the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine.
- The MMR vaccine is safe and effective for most people.
- Other preventive measures include practising good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick people, and covering your coughs and sneezes.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for mumps. Most people recover on their own within a few weeks.
- Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as with pain relievers and fever reducers.
- In general, mumps is a mild, self-limiting disease that resolves without lasting effects.
- However, complications can arise, including encephalitis or sensorineural deafness.
- Orchitis, a painful inflammation of the testes, occurs in approximately 20% of young adult males who contract mumps.
The Hindu Parliament security breach | 14 Opposition MPs suspended from House amid face-off (LiveMint)

- 15 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Fourteen MPs have been suspended for "unruly conduct" as stormy scenes played out in Parliament in the wake of the massive security breach recently.
Context:
- A total of 14 MPs, 13 from Lok Sabha and one from Rajya Sabha, were suspended from Parliament on Thursday for the remainder of the Winter Session.
- This follows after stormy scenes played out in Parliament on Thursday, December 14, in the wake of the massive security breach a day before.
- Earlier in the day, TMC member Derek O'Brien was suspended from the Rajya Sabha for the remainder of the Winter session for "unruly behaviour" and "misconduct".
Suspension of MPs:
- The Presiding Officer, whether the Speaker of the Lok Sabha or the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, plays a crucial role in maintaining order for the smooth functioning of the House.
- Empowered to uphold proper proceedings, the Speaker/Chairman has the authority to compel a Member to withdraw from the House, ensuring the orderly conduct of parliamentary affairs.
What are the Rules under which the Presiding Officer/Chairman acts?
- In Lok Sabha: Rule 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business empowers presiding officers to direct an MP to withdraw for disorderly conduct.
- The suspended Member must remain absent for the remainder of the day's sitting.
- Rules 374 and 374A are invoked for more persistent disruptions.
- Rule 374 allows the Speaker to name legislators for continued disruptions, leading to a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Rule 374A, added in December 2001, facilitates automatic suspension for five days or the remaining session part.
- In Rajya Sabha: Rule 255 grants the Chairman the authority to immediately direct withdrawal for disorderly conduct.
- Rule 256 enables the Chairman to name members persistently disregarding the Chair's authority or abusing Council rules.
- The House may then pass a motion for suspension not exceeding the session's remainder.
- Unlike Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha cannot suspend members without a formal motion.
Judicial Oversight in MP Suspension Cases:
- While Article 122 of the Indian Constitution shields parliamentary proceedings from judicial review, there are instances of courts intervening in legislative procedures.
- In a case involving the Maharashtra Legislative Assembly's 2021 Monsoon Session, where 12 BJP MLAs were suspended for a year, the Supreme Court stepped in.
The Court ruled that the assembly's resolution had legal limitations and was only applicable for the duration of the Monsoon Session, underscoring the judiciary's role in assessing the legality and effectiveness of legislative actions.
India to launch female robot astronaut 'Vyommitra' ahead of manned mission (IndiaTV News)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Minister of Science & Technology, Dr Jitendra Singh, announced on Wednesday that India is set to launch Vyommitra, a female robot astronaut, into space as part of the ambitious Gaganyaan project.
What is Vyommitra?
- Vyommitra is an AI-enabled female robot.
- It was introduced at the inaugural session of the "Human Spaceflight and Exploration — Present Challenges and Future Trends" event in January 2020.
- The name is a combination of two Sanskrit words: Vyoma (Space) and Mitra (Friend), and it was created for the unmanned Gaganyaan mission.
- Because she lacks legs, she is described as a half-humanoid robot.
- She may, however, bend to the sides and forward.
- The ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU) designed, developed, and integrated the robot.
- At the same time, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), a sister Isro facility based in Thumba, built its fingers.
- This robot is designed to ride aboard a rocket and survive stress and vibrations while in flight.
- With the ability to speak, see, and make facial expressions, it has been created to resemble a human.
- Vyommitra will also acquire a digital twin.
- The twin would be built through collaboration with academic institutions such as the IITs.
- Vyommitra will accompany astronauts on manned missions in addition to the unmanned Gaganyaan mission.
- Vyommitra's mission is to perform specific tasks in order to analyse how astronauts might behave.
- She will mimic every action that astronauts are required to take and respond to them in two languages.
- She will monitor via module parameters, alert, carry out life support procedures, carry out tasks like operating switch panels, and imitate other human actions in space throughout the uncrewed flight.
What is the Gaganyaan mission?
- Named after the Sanskrit word for craft or vehicle to the sky, the Gaganyaan project has been developed at the cost of ?90 billion.
- If it succeeds, India will become only the fourth country to send a human into space after the Soviet Union, the US, and China.
- Under the Gaganyaan Mission, ISRO will be sending three humans to an orbit of 400 km for a 3-day mission and bring them back safely to Earth.
- Launch Vehicle: GSLV Mk III, also called the LVM-3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3,) the three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle, will be used to launch Gaganyaan as it has the necessary payload capability.
- Training Collaboration with Russia: In June 2019, ISRO's Human Space Flight Centre partnered with Russia's Glavkosmos, a government-owned entity, under a contract encompassing comprehensive astronaut training.
- However, four astronauts selected for the Gaganyaan have been undergoing mission-specific training at the Astronaut Training Facility in Bengaluru.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (India Today)
- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has reported a significant anthrax outbreak in Zambia, marking an alarming spread of the disease across nine out of the country's ten provinces.
What is anthrax?
- According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), anthrax is a highly infectious disease that is caused by the gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis.
- Although it affects animals like cows, sheep, and goats, humans can get sick if they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Anthrax is not contagious, which means we can't catch it from another person like the cold or flu.
Symptoms of anthrax:
- The disease manifests in three forms depending on the route of infection: cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and inhalational.
- Cutaneous anthrax, the most common form, presents with itchy bumps that develop into black sores, often accompanied by fever and muscle aches.
- Gastrointestinal anthrax resembles food poisoning initially but can escalate to severe abdominal pain and bloody diarrhoea.
- Inhalational anthrax, the deadliest form, starts with cold-like symptoms before progressing to severe respiratory distress and shock.
How is anthrax diagnosed?
- Anthrax can be diagnosed by identifying Bacillus anthracis in blood, skin lesions, or respiratory secretions through laboratory culture, PCR, or ELISA tests.
- While there is no specific test to determine exposure to anthrax, public health investigations play a crucial role in identifying potential cases.
Treatment for anthrax:
- Treatment for anthrax is available and includes antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, or levofloxacin.
- If diagnosed early, antibiotic treatment can cure most anthrax infections.
- In severe cases, hospitalisation and treatments like continuous fluid drainage and mechanical ventilation may be necessary.
- Vaccines are also available for both livestock and humans, although human vaccines are typically reserved for those at high occupational risk.
How Google DeepMind’s AI breakthrough could revolutionise chip, and battery development (The Hindu)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Road traffic deaths fell by 5% to 1.19 million fatalities annually worldwide between 2010 and 2021, with 108 UN member nations reporting a drop, a report by the World Health Organization (WHO) said. India, however, registered a 15% increase in fatalities.
News Summary:
- The fifth edition of the WHO Global Status Report on Road Safety, released in 2023, serves as a comprehensive assessment of progress in mitigating road traffic deaths.
- This report evaluates advancements made between 2010 and 2021, establishing a foundation for meeting the ambitious target of the United Nations Decade of Action 2021–2030—to cut road traffic fatalities in half by 2030.
- Declared by the United Nations General Assembly in September 2020, the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030 strives to achieve a 50% reduction in road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030.
- Generous support from Bloomberg Philanthropies has played a crucial role in producing this report.
- Since 2007, Bloomberg Philanthropies has committed $500 million to facilitate road safety initiatives in low- and middle-income countries and cities worldwide
Key Insights from the Global Status Report on Road Safety 2023:
- Countries Achieving Over 50% Reduction in Road Traffic Deaths: Ten countries, including Belarus, Brunei Darussalam, Denmark, Japan, Lithuania, Norway, Russian Federation, Trinidad and Tobago, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela, have successfully reduced road traffic deaths by more than 50%.
- Additionally, 35 more countries have made commendable progress, achieving a reduction in road traffic deaths ranging from 30% to 50%.
- Leading Cause of Death for Children and Youth: As of 2019, road traffic crashes have become the primary cause of death for children and youth aged five to 29 years.
- Globally, these crashes rank as the 12th leading cause of death across all age groups.
- 5% Reduction in Road Traffic Fatalities in the Last Decade: Despite a population growth of nearly 14 billion over the last decade, there has been a 5% reduction in the absolute number of road traffic fatalities.
- The road fatality rate has declined from 18 per 1 lakh people in 2010 to 15 per 1 lakh in 2021, marking a 16% decrease in the road traffic death rate since 2010.
- Regional Distribution of Traffic Deaths: The regional breakdown indicates that:
- 28% of global road traffic deaths occurred in the WHO’s South-East Asia Region
- 25% in the Western Pacific Region
- 19% in the African Region
- 12% in the Region of the Americas
- 11% in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, and
- 5% in the European Region.
- The situation in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Nine out of 10 road traffic deaths transpire in low- and middle-income countries, with fatalities in these nations being disproportionately higher (three times) in comparison to the number of vehicles and roads they possess.
- Countries Meeting WHO Best Practices for Risk Factors: Only six countries have legislation aligning with WHO best practices for all risk factors (speeding, drunk driving, and the use of motorcycle helmets, seatbelts, and child restraints).
- Meanwhile, 140 countries, constituting two-thirds of UN Member States, have such laws governing at least one of these risk factors.
- India-Specific Observation: In India, the reported deaths due to road crashes increased from 1,50,785 in 2018 to 1,53,792 in 2021.
- Notably, the number stood at 1.3 lakh in 2010.
Here to enhance partnership between EFTA, India: Norway's trade minister (Business Standard)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Norway's Minister of Trade and Industry Jan Christian Vestre has said his India visit aims to enhance collaboration between European free trade partners and India and improve framework conditions for job creation, value creation, and investments.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1960 by the Stockholm Convention.
- Its core objective is to foster free trade and economic integration among its member countries, both within Europe and on a global scale.
- Member Countries: EFTA comprises four member countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland.
- These nations are characterized by open, competitive economies, demonstrating a shared commitment to progressively liberalize trade both within multinational forums and through individual free trade agreements.
- Customs Distinction: Unlike the European Union (EU), EFTA operates differently as it is not a customs union.
- This key distinction allows each EFTA State the autonomy to establish its own customs tariffs and formulate foreign trade measures independently concerning non-EFTA States.
- Association Responsibilities:
- EFTA manages various aspects crucial to its objectives, including:
- Facilitating free trade among EFTA countries.
- Overseeing EFTA's engagement in the European Economic Area (EEA), encompassing the European Union and three EFTA countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, excluding Switzerland).
- Managing EFTA's extensive network of free trade agreements globally.
- Free Trade Agreement Network: EFTA member countries boast one of the largest networks of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) globally.
- This comprehensive network spans over 60 countries and territories, incorporating the European Union among others.
EFTA plays a pivotal role in promoting economic collaboration, free trade, and global engagement, distinguishing itself from the EU through its approach to customs and foreign trade measures.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between two or more nations aimed at lowering barriers to imports and exports among them.
- In a free trade scenario, goods and services can move across international borders with minimal government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or restrictions hindering their exchange.
- The principle of free trade stands in contrast to trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs come in various forms, including Preferential Trade Agreements, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements, and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPA).
COP28: What was the most important deal short (Indian Express)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
COP28: The annual climate conference this year saw some key resolutions on fossil fuels, methane emissions, and funds to fight global warming, among others. However, many concerns remain.
Context:
- The 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference, also referred to as COP28 took place from November 30 to December 12 at Expo City in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
- While the event yielded significant outcomes, it, akin to its predecessors, fell short of meeting the anticipated expectations.
Key Outcomes of COP28:
- Fossil Fuel Transition Ambiguity: Acknowledging the role of fossil fuels in global warming for the first time, the agreement calls for countries to contribute to transitioning away from fossil fuels to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.
- However, the lack of specific time schedules and targets disappointed some nations that expected a more explicit commitment to a "fossil fuel phase-out."
- Renewable Energy Tripling: The agreement calls on countries to contribute to tripling the global installed capacity of renewable energy and doubling annual improvements in energy efficiency.
- This measure is expected to result in emissions avoidance of approximately 7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent by 2030.
- However, the global nature of this target raises questions about individual country responsibilities.
- Coal Phase-Down Continuation: The agreement reiterates the commitment to the phase-down of coal, following up on the decision made at COP26.
- While there were considerations to impose restrictions on new coal-fired power plants without carbon capture and storage, these were dropped due to resistance from countries like India, China, and South Africa.
- The agreement lacks specifics on measurement criteria or baseline for this phase-down.
- Methane Emission Challenges: Despite the significance of methane as a greenhouse gas, responsible for nearly 25% of emissions and is 80 times more potent than CO2, the agreement avoids setting targets for methane emission cuts in 2030.
- Countries like India are opposed to mandates due to the agricultural sector's major role in methane emissions.
- Operational Loss & Damage Fund: A significant outcome for vulnerable nations, COP28 operationalized the Loss and Damage Fund, established in COP27.
- Commitments, totaling around US$ 800 million, were made during the conference to assist countries recovering from climate-induced disasters.
- Global Goal on Adaptation Establishment: COP28 adopted a global framework for adaptation, addressing a historic imbalance where adaptation efforts received less attention and resources compared to mitigation activities.
- The framework, though established, lacks financial provisions, necessitating further strengthening in subsequent years.
- Adaptation Challenges: While the global adaptation framework is a positive step, there is still work to be done, particularly in defining indicators for measuring progress on each global goal.
- Adaptation efforts historically focused on local initiatives, and the agreement aims to garner more attention and resources for these endeavours on a global scale.
- Climate Action Acceleration Shortcomings: The final agreement falls short of providing sufficient impetus for the acceleration of climate action in the immediate term.
What is the Conference of the Parties (COP)?
- In 1992, Rio Earth Summit, 154 countries joined an international treaty, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, as a framework for international cooperation to combat climate change by limiting average global temperature increases and the resulting climate change, and coping with impacts that were, by then, inevitable.
- The COP is the supreme decision-making body of the Convention.
- All States that are Parties to the Convention are represented at the COP, at which they review the implementation of the Convention and any other legal instruments that the COP adopts and take decisions necessary to promote the effective implementation of the Convention, including institutional and administrative arrangements.
- Currently, there are 198 'parties' or signatories of the Convention.
Green Rising initiative launched at RewirEd summit to empower Youth-Led climate solutions (DD News)

- 09 Dec 2023
What is the Green Rising Initiative?
- The "Green Rising" initiative focuses on engaging youth for impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level, aligning with the global effort to address the severe impacts of climate change.
- This initiative encompasses both the global "Green Rising" initiative and the "Green Rising India Alliance," a collaborative endeavor that brings together UNICEF, Generation Unlimited, and a diverse network of public, private, and youth partners.
- The primary objective is to mobilize millions of young individuals globally, encouraging their active engagement in green initiatives aimed at addressing and adapting to the profound impacts of climate change within their communities.
- In India, this effort is channelled through the YuWaah campaign, which specifically focuses on harnessing the energy and commitment of the youth to drive impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level.
About UNICEF:
UNICEF, or the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, is a specialized agency of the United Nations committed to promoting the well-being and rights of every child globally.
- Foundation and Establishment: Established in 1946 by the United Nations General Assembly, UNICEF was originally designed to provide emergency food and healthcare to children in countries devastated by World War II.
- Over time, UNICEF's scope evolved to include long-term developmental programs, focusing on education, healthcare, nutrition, clean water, sanitation, and protection for children in need.
- UNICEF is governed by an Executive Board consisting of 36 members who are elected to terms of three years by the United Nations Economic and Social Council.
- Universal Presence: UNICEF operates in over 190 countries and territories worldwide, making it one of the most extensive and widely recognized humanitarian organizations globally.
- Child Rights Advocacy: UNICEF is a leading advocate for children's rights, working to ensure that every child has the right to survive, thrive, and reach their full potential, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Emergency Response: In times of crises, including natural disasters, conflicts, and pandemics, UNICEF plays a crucial role in providing immediate and life-saving assistance to affected children and communities.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: UNICEF collaborates with governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), other UN agencies, and the private sector to implement its programs and maximize its impact.
- Funding Mechanism: UNICEF is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from governments, private donors, businesses, and the general public. It relies on these funds to carry out its programs and respond to emergencies.
- Focus on Equality and Inclusion: UNICEF emphasizes the importance of equality and inclusion, working to address disparities and ensure that the most vulnerable children, including those with disabilities or from marginalized communities, are not left behind.
- Global Campaigns: UNICEF spearheads global campaigns to address critical issues affecting children, such as vaccination drives, education initiatives, and efforts to eliminate child labour and violence against children. These campaigns aim to rally public support and create awareness about the challenges faced by children worldwide.
- It was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1965 for the “promotion of brotherhood among the nations”.
- Headquarters: New York City
India is expected to withstand global shocks as its current account deficit improves due to falling crude oil prices. (ET)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
After two years of battling inflation and growth pangs, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was in for a pleasant surprise when the economic growth trumped its expectations to hit 7.2 per cent in the last month.
Context:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has unveiled its most recent monetary policy report, projecting a robust economic recovery for the country in the current fiscal year.
- Anticipating a significant upswing, the central bank foresees the gross domestic product (GDP) to expand by 7 percent in 2021-22, a notable rebound from the 7.3 percent contraction witnessed in the preceding year.
- However, the RBI issues a cautionary note about the challenges posed by inflation, which has consistently exceeded the target range of 2-6 percent over several months.
- The report attributes inflationary pressures to supply-side disruptions, escalating commodity prices, increased fuel taxes, and demand-related factors.
- The RBI anticipates inflation to remain elevated in the short term before gradually moderating in the latter half of the year.
- The RBI's stance mirrors a delicate equilibrium, emphasizing the intricate balance between fostering economic growth and managing inflation, often characterized as the Goldilocks Effect.
- This effect alludes to a scenario where the economy is neither excessively overheated nor excessively sluggish but rather poised for optimal growth with minimal inflationary pressures.
What is the Goldilocks Effect?
- The Goldilocks Effect, also known as the Goldilocks Principle, posits that individuals have a predisposition to seek an amount that is 'just right' for their specific needs or preferences.
- This concept, derived from the children's story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears, reflects a preference for options that are neither too extreme nor too moderate, falling within an optimal and desirable range.
- This principle finds application across various fields and disciplines, encompassing psychology, hard sciences, economics, marketing, and engineering, each incorporating its unique interpretation of the principle.
- Goldilocks Pricing: One notable application of the Goldilocks Effect is in Goldilocks Pricing, a psychological pricing strategy grounded in concepts such as product differentiation, comparative pricing, and bracketing.
- Product differentiation involves distinguishing certain products from others, a crucial step for businesses looking to leverage the Goldilocks Effect.
- This differentiation is then coupled with comparative pricing, where businesses simultaneously offer multiple versions of a product with varying quality levels attached to corresponding price points.
- The strategy hinges on providing three options: one priced too high for most, one priced too low for most, and one priced just right.
- When executed effectively, this approach enables businesses to appeal to diverse segments of the market, capturing premium buyers, standard consumers, and discount seekers.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which is marking its 75th anniversary? (Indian Express)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Seventy-five years ago on Sunday, the UN General Assembly approved the Universal Declaration of Human Rights at a meeting in Paris – laying one of the foundation stones of the international order that emerged following the horrors of World War II.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)?
- On 10 December 1948, during a session in Paris, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously endorsed the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), marking a pivotal moment in shaping the post-World War II international order.
- The UDHR emerged as a response to wartime atrocities and aimed to establish a shared understanding of the fundamental rights and freedoms inherent to all individuals.
- A concise yet impactful document, the declaration comprises a preamble and 30 articles that delineate essential rights and freedoms.
- These 30 articles encompass a comprehensive spectrum of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Emphasizing their universality, these rights are deemed applicable to all individuals, irrespective of nationality, ethnicity, gender, religion, or any other status.
- While not legally binding, the UDHR has functioned as a guiding force inspiring the development of international human rights law.
Key Features:
- Preamble: The preamble elucidates the reasons behind adopting the declaration, underscoring the inherent dignity and the equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family.
- Articles: The UDHR articulates 30 articles outlining a wide array of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights. Examples of these rights include:
- The right to life, liberty, and security of person.
- The right to freedom of religion, expression, and assembly.
- The right to work and education.
- The right to an adequate standard of living.
- The declaration asserts that "all are equal before the law" and emphasizes the entitlement of everyone to "a fair and public hearing by an independent and impartial tribunal."
- It also affirms the right of "everyone to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution.
Achievements of UNDHR:
- The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UNDHR) is acknowledged for its significant impact, having served as the inspiration and foundation for over 70 human rights treaties at both global and regional levels, as noted by the United Nations.
- It played a pivotal role in inspiring movements such as decolonization, the anti-apartheid movement, and various struggles for freedom worldwide, including those related to gender, LGBTIQ+ rights, and opposition against racism.
What is the Current Situation?
- As the 75th anniversary is commemorated, human rights face challenges amid conflicts such as the Israel-Hamas war, Russia's actions in Ukraine, internal strife in Myanmar and Sudan, and numerous other global situations.
- UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has remarked that the Universal Declaration has been frequently misused and abused, exploited for political gain, and often ignored by those who should uphold it.
- Contrastingly, Amnesty International asserts that the declaration serves as living proof that a global vision for human rights is attainable and can be realized.
- Despite instances of neglect or exploitation, the declaration remains relevant, and the world is encouraged to recognize its successes while learning from its failures.
Amit Shah to chair 26th meeting of Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar on Sunday (Business Standard)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah will chair the 26th meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar's capital on Sunday, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) said on Saturday.
What are Zonal Councils?
- The conceptualization of Zonal Councils can be attributed to the visionary initiative of India's first Prime Minister, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru, in 1956.
- These councils are statutory bodies established by an Act of Parliament, namely the States Reorganisation Act of 1956.
- The act delineated the country into five zones (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern), assigning a Zonal Council to each.
Present Composition of Zonal Councils:
- Northern Zonal Council: Includes Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, National Capital Territory of Delhi, and Union Territory of Chandigarh.
- Central Zonal Council: Encompasses Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Eastern Zonal Council: Comprises Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, and West Bengal.
- Western Zonal Council: Involves Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
- Southern Zonal Council: Consists of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Exclusion and Special Council: The North Eastern States (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Nagaland) are not part of Zonal Councils.
- Instead, their unique challenges are addressed by the North Eastern Council, established under the North Eastern Council Act of 1972.
- Sikkim was included in the North Eastern Council in 2002.
Organizational Structure:
- Chairman: The Union Home Minister serves as the Chairman for each Zonal Council.
- Vice Chairman: Chief Ministers of the states in each zone act as Vice-Chairman, rotating annually.
- Members: Chief Minister and two nominated Ministers from each state, along with two members from Union Territories in the zone.
- Advisers: Planning Commission nominees, Chief Secretaries, and another officer/Development Commissioner from each state in the zone.
Objectives:
- The primary objectives of Zonal Councils include promoting national integration and curbing acute State consciousness, regionalism, linguism, and particularistic tendencies.
- Additionally, they aim to facilitate cooperation, idea exchange, and a climate of collaboration among states for the successful execution of development projects.
Functions:
- Zonal Councils function as advisory bodies, empowered to discuss common interests between the Union and represented states.
- They can recommend courses of action to the Central Government and individual state governments.
- Specific areas of discussion may include economic and social planning, border disputes, linguistic minorities, inter-state transport, and matters arising from the reorganization of states under the States Reorganisation Act.
Navy plans to get undersea chariots, made in India, for special operations (Indian Express)
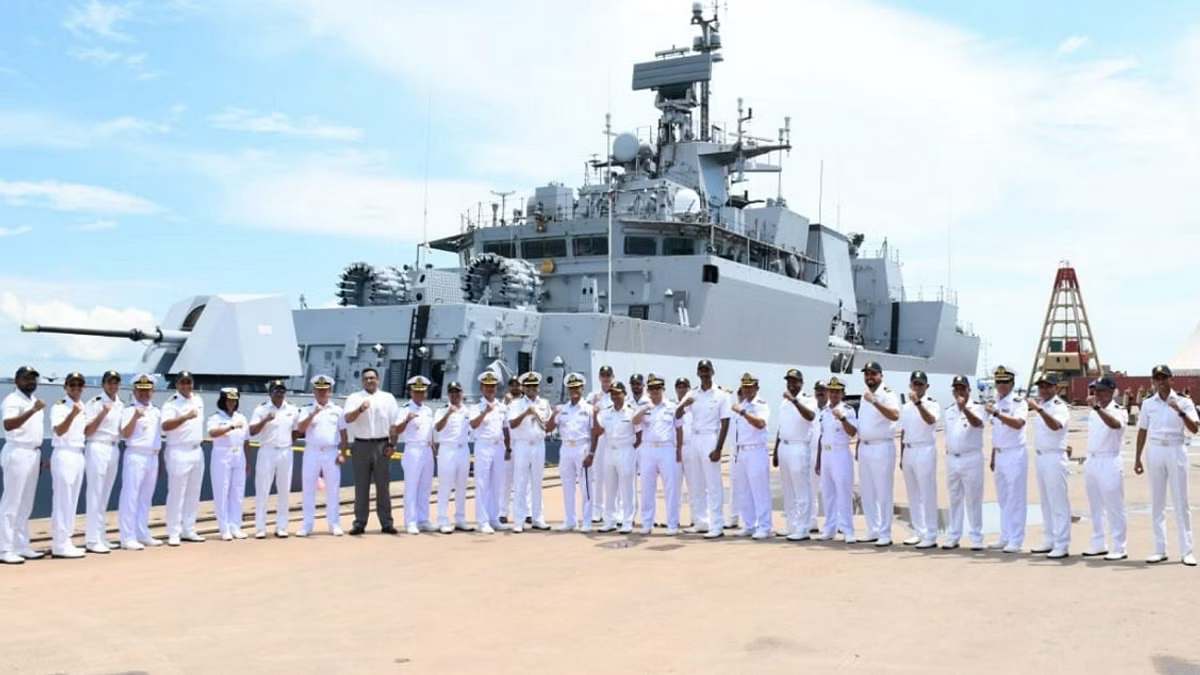

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Navy is planning to acquire indigenously made swimmer delivery vehicles — also known as underwater chariots and midget submarines — as part of efforts to modernise and strengthen the capabilities of its Marine Commandos (MARCOS) for special undersea operations.
News Summary:
- In a strategic move, the Indian Navy set to deploy domestically manufactured undersea chariots for specialized operations.
- These innovative vessels, designed to accommodate a crew of at least six, will be equipped with cutting-edge lithium-ion batteries for enhanced performance.
- The significant size of these undersea chariots opens up new possibilities, allowing divers to transport larger cylinders.
- This advancement translates to extended underwater missions, thereby amplifying operational capabilities in shallow waters.
- Moreover, the spacious design of these chariots facilitates the carriage of extra weaponry, providing the Navy with increased flexibility for diverse and complex operations.
- This development signifies a noteworthy stride in bolstering the Navy's underwater capabilities through indigenous technological advancements.
What are Chariots?
- Nearly all modern navies in the world use chariots, which are extremely specialized platforms.
- These self-propelled vehicles can be deployed from ships or submarines, tailored to their size and designated roles.
- Notably, during World War II, manned human torpedoes were commonly referred to as chariots.
- Functionality: Chariots prove invaluable for naval operations in shallow waters, offering a spectrum of missions.
- These include shallow-water surveillance, targeted assaults on adversary coastal installations, and even engagements with ships in harbours.
- Particularly advantageous is their ability to grant marine commandos access to areas close to adversary harbours—locations that submarines, constrained by shallow waters, may find challenging to reach.
- Furthermore, these chariots facilitate the efficient transportation of weapons and equipment to operational zones.
- Utilization in India: While detailed information on the swimmer delivery vehicles employed by the Indian Navy is not widely available, some sources suggest the utilization of Italian-made chariots for several years.
- Around 2012, recognizing the strategic importance of these platforms, the Ministry of Defence entrusted Hindustan Shipyard Limited with the construction of two such submarines, underscoring India's commitment to enhancing its maritime capabilities.
What are Marine Commandos (MARCOS)?
- The Marine Commandos, known by the acronym MARCOS and formally recognized as the Marine Commando Force (MCF), stand as the specialized forces within the Indian Navy entrusted with the execution of special operations.
- Established in February 1987, MARCOS possesses versatile capabilities to operate effectively across diverse environments, encompassing sea, air, and land.
- Over time, the force has accumulated valuable experience, earning an esteemed international reputation for its high level of professionalism.
- MARCOS routinely engage in specialized maritime operations in regions such as Jammu and Kashmir, navigating the Jhelum River and Wular Lake with precision and expertise.
Lok Sabha passes Advocates (Amendment) Bill to weed out touts from court complexes(The Hindu)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Lok Sabha recently passed a Bill that seeks to regulate the legal profession by targeting “touts”, with Law Minister Arjun Ram Meghwal asserting there should be no role of such persons in courts.
About the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- The Rajya Sabha introduced the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023, in August 2023.
- This bill amends the Advocates Act of 1961, specifically repealing certain sections related to touts under the Legal Practitioners Act of 1879.
- The 1961 Act consolidates laws regarding legal practitioners and establishes Bar Councils and the All-India Bar.
- Having already passed in the Rajya Sabha during the Monsoon Session, the bill aims to regulate the legal profession through a single act with a focus on addressing the issue of touts.
Key Features of the Advocates (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- Touts: High Courts, district judges, sessions judges, district magistrates, and revenue officers are empowered to create and publish lists of touts.
- A tout is defined as a person who either seeks or secures the employment of a legal practitioner in legal matters for payment or frequents specific locations to obtain such employment.
- The Court or judge has the authority to bar any person listed as a tout from the premises of the Court.
- Preparation of Lists: Authorities with the power to create tout lists may instruct subordinate courts to conduct inquiries into individuals suspected or alleged to be touts.
- If proven, the person's name can be included in the list, ensuring due process is followed before inclusion.
- Penalty: Individuals acting as touts while being listed can face imprisonment up to three months, a fine up to Rs 500, or both.
Will India reassess its position on China-backed Asian trade bloc RCEP? (Business Standard)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is keeping a watchful eye on its neighbour countries’ recent deliberations to join the China-backed Asian trade bloc, Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), although the government is yet to “re-evaluate” the position it took four years ago.
What is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)?
- RCEP, or the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, is a proposed agreement involving ASEAN member states and their free trade agreement partners.
- Introduced in 2011, negotiations started in 2012, aiming to finalize the deal by November 2019.
- After the withdrawal of India, there are 15 members of RCEP, which includes 10 ASEAN countries and 5 other countries, namely:
- Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- RCEP's objective is to establish an integrated market, facilitating the availability of products and services across the region.
- The negotiations cover trade, investment, intellectual property, dispute settlement, e-commerce, SMEs, and economic cooperation.
- Initially proposed by Beijing in 2012 to counter the Trans-Pacific Partnership, RCEP became a key tool for China after the U.S. withdrew from the TPP in 2016.
- India chose not to sign the RCEP in 2019 due to concerns about its industries competing with China and potential flooding of Indian markets.
- Despite some sectors anticipating gains, India emphasized the need for a deal favorable to all countries and sectors.
SC pulls up Bhopal municipal corporation for flouting Solid Waste Management Rules (DownToEarth)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
There is non-compliance with the provision of the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 by the Bhopal Municipal Corporation, the Supreme Court observed December 1, 2023 after going through the affidavit filed by the corporation.
What is About Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)?
- The Supreme Court of India, in 2001, mandated the creation of the Compensatory Afforestation Fund and the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA).
- Initially, an ad-hoc CAMPA was established in 2006 to manage the Compensatory Afforestation Fund.
- (CAMPA) are meant to promote afforestation and regeneration activities as a way of compensating for forest land diverted to non-forest uses.
- National CAMPA Advisory Council has been established as per orders of The Hon’ble Supreme Court with the following mandate:
- Lay down broad guidelines for State CAMPA.
- Facilitate scientific, technological and other assistance that may be required by State CAMPA.
- Make recommendations to State CAMPA based on a review of their plans and programmes.
- Provide a mechanism to State CAMPA to resolve issues of an inter-state or Centre-State character.
CAMPA Act:
- To address the loss of forest area and ensure sustainability, the Government of India introduced the CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority) Act.
- This legislation establishes the National Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of India and a State Compensatory Afforestation Fund in the Public Account of each state.
- These funds receive payments for compensatory afforestation, net present value of forests (NPV), and other project-specific payments.
- The National Fund gets 10% of these funds, while the State Funds receive the remaining 90%.
- As per the Act, companies diverting forest land must provide alternative land for compensatory afforestation.
- For afforestation purposes, companies are required to pay for planting new trees in the alternative land provided to the state.
Houthi attacks on vessels in Red Sea sound alarm for global trade (Financial Times)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Shipowners have called for more military protection on maritime routes in the Middle East after attacks by Iran-backed rebels in the Red Sea sparked fears of new disruptions to global trade, including of energy supplies.
Key Facts the about Red Sea:
- The Red Sea is a semi-enclosed inlet of the Indian Ocean situated between Africa and Asia.
- It stands out as one of the warmest seas globally.
- Connecting to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean through the Gulf of Aden and Bab El-Mandeb strait to the south, it is divided by the Sinai Peninsula into the Gulf of Aqaba and the Gulf of Suez in the north.
- The Gulf of Suez is linked to the Mediterranean Sea via the famous Suez Canal.
- The Red Sea is bordered by Yemen and Saudi Arabia to the east, while Egypt is to the north and west, and Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti are to the west.
- Covering an area of about 438,000 km2, it stretches approximately 2,250 km.
- The sea's maximum width is 355 km, and its deepest point, the central Suakin Trough, reaches 3,040 m, with an estimated average depth of 490 m.
- Notable islands in the Red Sea include Tiran Island near the mouth of the Gulf of Aqaba and Shadwan Island at the entrance of the Gulf of Suez.
Meghalaya’s Lakadong turmeric gets GI Tag (Northeast Live)

- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Meghalaya’s Lakadong turmeric has received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag from the Registrar of Geographical Indications in Chennai.
About Lakadong Turmeric:
- Lakadong Turmeric is known as one of the best turmerics in the world and is sourced from a village in Meghalaya’s Jaintia Hills.
- Lakadong, a distinct type of turmeric, is exceptionally abundant in curcumin, with levels ranging from 7-8%, a significant contrast to the typical varieties containing only 2-3% curcumin.
- Curcumin has numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Under the “One District One Product” scheme, Lakadong turmeric gained recognition in the West Jaintia Hills district.
- India produces 78% of the world’s turmeric.
What is One District One Product (ODOP)?
- One District One Product (ODOP) initiative is aimed at fostering balanced regional development across all districts of the country.
- The initiative aims to select, brand, and promote at least One Product from each District (One District - One Product) of the country for enabling holistic socioeconomic growth across all regions.
- The ODOP Initiative has identified a total of 1102 products from 761 districts across the country.
- Under the ODOP initiative, all products have been selected by States/UTs by taking into consideration the existing ecosystem on the ground, products identified under Districts as Export Hubs (DEH), and GI-tagged products.
- The finalized list is communicated to DPIIT by the relevant Department of States/UTs.
- All activities including exhibitions, capacity building, etc. are undertaken at the State/UT and district level, in consultation and coordination with the States/UTs.
