Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
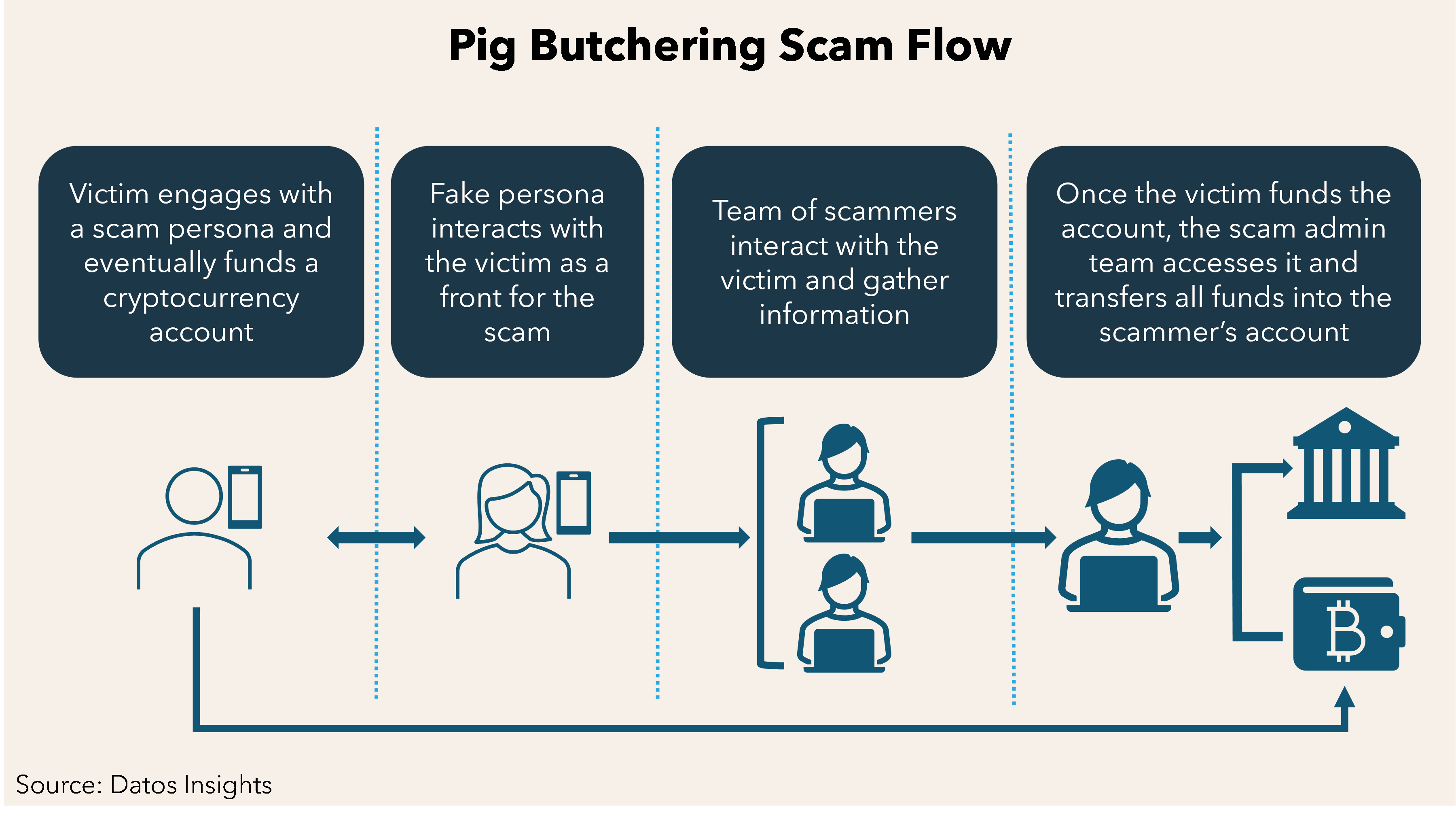
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
Under the Sal Tree Theatre Festival

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
“Under the Sal Tree” Theatre Festival, held annually in Rampur, Assam, promotes eco-friendly and sustainable practices in theatre while showcasing rich cultural diversity.
Overview:
- Location: Rampur village, Goalpara district, Assam
- Organizer: Badungduppa Kalakendra, a social and cultural organization
- Founded: 1998 by Sukracharjya Rabha
- Festival Focus: Eco-friendly theatre practices, cultural diversity, and sustainability
Key Features
- Unique Setting: Open-air festival under Sal trees, with no artificial lighting or electric sound systems.
- Sustainability:
- No use of plastic.
- Carbon-neutral, with eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, straw, and cane.
- Performances in natural daylight, avoiding electric lights.
- International Participation: Theatre groups from countries like Poland, South Korea, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, North Korea, Bolivia, and Holland have performed.
- Cultural Celebration: Highlights indigenous art forms, languages, and traditions, e.g., Rabha and Bodo plays.
Festival Activities
- Performances:
- Includes plays like “Dadan Raja” (Rabha language play), “Kindhan Charithiram” (Tamil), and “Kisan Raj” (Hindi).
- Focus on themes such as societal change and resilience of farmers.
- Workshops & Community Projects: For performing artists, promoting artistic innovation and social impact.
- Anniversary Celebrations:
- 25th anniversary celebrated with special events and book releases, e.g., “Resonance: Echoing the Spirit of Badungduppa” and “Sukracharjya Rabha on the Back Stage”.
Impact & Legacy
- Theatre Movement: Celebrates art amidst nature, breaking geographical barriers despite the remote location.
- Founder’s Vision: Sukracharjya Rabha believed in the synergy between art and nature, aiming to bring social change through theatre.
- Local Involvement:
- 20 resident artists contribute to the festival’s success.
- Festival has become a major cultural attraction in Assam, drawing thousands of theatre enthusiasts.
Financial Action Task Force (Deccan Herald)
- 02 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India has suggested to all G20 nations to actively cooperate to deal comprehensively and efficiently with fugitive economic offenders as part of the action against them and recovery of the assets.
Facts About:
- The FATF is an international organization made up of governments that focuses on creating policies and standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Objective: Its main goal is to establish global standards and encourage the development of policies at both national and international levels to prevent money laundering and the financing of terrorism.
- The FATF provides recommendations to combat financial crimes, assesses its member countries' policies and procedures, and strives to promote the adoption of anti-money laundering regulations worldwide.
- Formation: The FATF was established in 1989 during the G7 Summit in Paris with the initial aim of addressing money laundering. In 2001, its scope expanded to include combating terrorism financing.
- Headquarters: Its headquarters are located in Paris, France.
- Membership: The FATF comprises 39 member countries, including the United States, India, China, Saudi Arabia, Britain, Germany, France, and the European Union.
- India became a member in 2010.
- As part of its efforts, the FATF maintains two lists: the blacklist and the greylist.
Black List:
- The blacklist contains countries referred to as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs). These are countries known for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering activities.
- The FATF regularly updates this list, adding or removing countries as needed.
Grey List:
- The grey list includes countries considered to be safe havens for supporting terrorism funding and money laundering. Placement on this list serves as a warning that a country may eventually be placed on the blacklist.
- Currently, three countries on the FATF blacklist are North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar.
Consequences of Being on the FATF Blacklist:
- Countries on the FATF blacklist do not receive financial aid from organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank (ADB), and the European Union (EU).
- Additionally, they face various international economic and financial restrictions and sanctions.
