Coal Ministry Hosts Industry Interaction on Coal Gasification (ET)
- 16 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Ministry of Coal has announced it will host an Industry Interaction on February 16, 2024, in Hyderabad to discuss the development of coal and lignite gasification projects across India.
What is Coal Gasification?
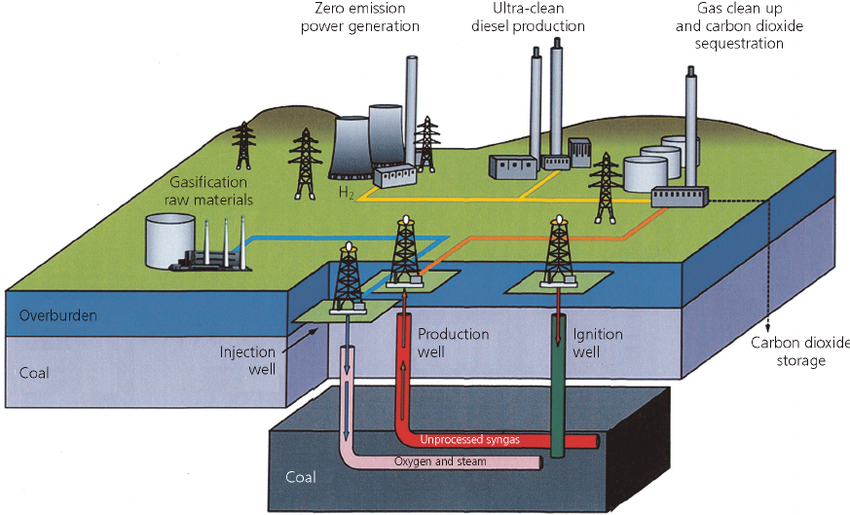
- Coal gasification is a process where coal undergoes partial oxidation with air, oxygen, steam, or carbon dioxide to produce a fuel gas.
- This gas serves as an alternative to piped natural gas or methane for energy generation.
- Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) is a technique involving the conversion of coal into gas within the seam, extracted through wells.
- Production of Syngas: This process yields Syngas, a mixture primarily comprising methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas finds applications in producing fertilisers, fuels, solvents, and synthetic materials.
- Significance: In manufacturing, steel companies traditionally rely on costly imported coking coal. Syngas derived from coal gasification offers a cost-effective alternative.
- It is utilized in electricity generation, chemical feedstock production, and hydrogen-based applications like ammonia production and fueling a hydrogen economy.
Advantages of Coal Gasification:
- Coal gasification offers a solution to local pollution issues.
- It is deemed environmentally cleaner than direct coal combustion.
- Decreasing dependence on imported natural gas, methanol, ammonia, and other vital commodities, enhances energy security.
- This technology has the potential to mitigate environmental impacts by curbing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable approaches, aligning with India's global objectives for a more environmentally sustainable future.
Concerns Associated with Coal Gasification Plants?
- The main disadvantage of coal gasification is that it is an expensive process.
- The process can produce a number of harmful emissions, including carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and mercury.
- The process produces a lot of ash, which can pollute the environment.
- The process uses a lot of water, which can lead to water shortages in areas where it is used.
Centre approves incentive of Rs 8,500 crore for coal gasification projects (Indian Express)

- 25 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to achieve the target of coal gasification of 100 million tonnes (MT) of coal by 2023 in India, the government recently approved Rs 8,500 crore incentives.
What is Coal Gasification?
- Coal gasification is a thermo-chemical procedure wherein the pressure and heat of the gasifier disintegrate coal into its chemical components.
- The resulting "syngas" are mostly carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen, with some other gaseous substances thrown in for good measure.
- Coal gasification is an in-situ method wherein oxygen is infused into the seam together with water and ignited at high temperatures, causing coal to partly oxidised into hydrogen, CO, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and hydrogen sulphide (H2S).
- Ex-situ reactors are designed to simulate the gasification process above the ground's surface.
- Sulphur in coal is transformed to H2S and trace volumes of carbonyl sulphide during the gasification process (COS).
- Acid gas removal technology can easily and cost-effectively discard these sulphur compounds.
- There is no scrubber sludge produced by coal gasification plants, which necessitates careful and expensive disposal.
- The majority of the wash water is reprocessed, and residual wastewater from gasification plants can be treated effectively.
- As a result, coal gasification is regarded as a cleaner coal technology when compared to coal combustion.
- Furthermore, coal could be used to generate a range of products using clean coal innovations such as hydrogen, methanol, and fertilisers via coal gasification.
- Carbon fibres and plastic composites made from coal power plant ash/residue.
How can it be used?
- Syngas, according to proponents of coal gasification, can be used to generate power, in energy-efficient fuel cell technology, or as chemical "building components" for industrial applications.
- The hydrogen can also be extracted and used to power a hydrogen economy.
- Coal gas can also be transformed into a transportation fuel to be used in automobiles as a replacement for gasoline, but it is less efficient than the current output and combustion of petroleum-based gasoline.
- Coal gasification is said to be more efficient than traditional coal burning since it can use the gases two times: the coal gases are first purified of contaminants before being fired inside a turbine to produce energy.
- The gas turbine exhaust heat can be then collected and used to produce steam for a steam turbine generator.
- This is known as a combined process, and according to DOE, a coal gasification processing facility using this dual method can possibly attain an efficiency of 50% or higher, compared to the customary coal power plant, which is typically just above 30%.
Significance of Coal Gasification:
- India announced environmental targets as its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) under the Paris Agreement in 2016.
- In order to meet these objectives, coal gasification aids in the decrease of emission levels and the advancement of non-fossil fuel-based energy resources.
- The syngas produced by coal gasification can be used to generate urea and a variety of products such as methanol, Dimethyl ether (DME), and olefins, allowing India to minimise imports and become self-sufficient.
- Syngas CO and H2 are essential reducing agents for steel production and are regarded as an environmentally friendly technique of steel production because they reduce the import of furnace oil.
- India has ambitious plans to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) domestically rather than importing them from China.
- As a result, the potential of Syngas requirement for making APIs, as well as methanol as a solvent, is being investigated.
- The synthesis gas can be used in an Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) system to generate electricity in an efficient and environmentally friendly manner.
Initiatives taken by India:
- The Ministry of Coal, through Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan, has taken the initiative, National Coal Gasification Mission, that is to utilise coal through coal gasification, with the goal of achieving 100 MT coal gasification by 2030.
- It has also been recommended that all coal companies assign a nodal officer and formulate a plan for gasifying at least 10 per cent of their coal production.
- SHAKTI policy was implemented in coal gasification projects to minimise operating costs by allocating long-term coal linkages through auction.
