El Niño and La Nina
- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Last month, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) forecasted above-normal rain in the upcoming monsoon season in India, with “favourable” La Nina conditions expected to set in by August-September.
What are El Niño and La Nina?
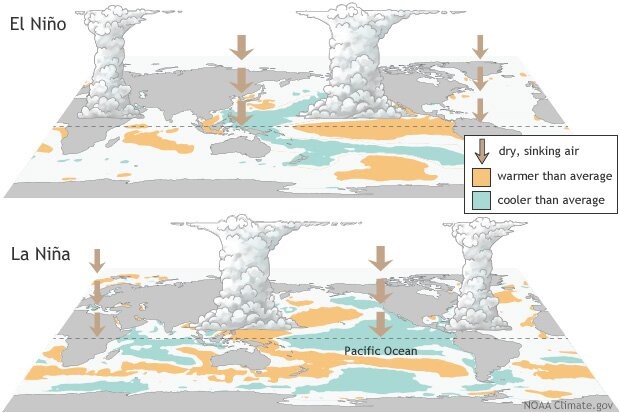
- El Niño (meaning “little boy” in Spanish) and La Nina (meaning “little girl” in Spanish) are climate phenomena that are a result of ocean-atmosphere interactions, which impact the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean which affects global weather.
- The Earth’s east-west rotation causes all winds blowing between 30 degrees to the north and south of the equator to slant in their trajectory.
- As a result, winds in the region flow towards a southwesterly direction in the northern hemisphere and a northwesterly direction in the southern hemisphere which is known as the Coriolis Effect.
- Due to this, winds in this belt (called trade winds) blow westwards on either side of the equator.
- Under normal ocean conditions, these trade winds travel westwards along the equator from South America towards Asia.
- Wind movement over the ocean results in a phenomenon called upwelling, where cold water beneath the ocean surface rises and displaces the warm surface waters.
- At times, the weak trade winds get pushed back towards South America and there is no upwelling.
- Thus, warmer-than-usual sea surface temperatures are recorded along the equatorial Pacific Ocean, and this is known as the emergence of El Niño conditions.
- Conversely, during La Nina, strong trade winds push warm water towards Asia.
- Greater upwelling gives rise to cold and nutrient-rich water towards South America.
- Thus, climatologically, El Niño and La Nina are opposite phases of what is collectively called the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- It also includes a third neutral phase.
- El Niño events are far more frequent than La Nina ones.
- Once every two to seven years, neutral ENSO conditions get interrupted by either El Niño or La Nina.
- Recently, La Nina conditions prevailed between 2020 and 2023.
How could the incoming La Nina impact global weather?
- La Niña, driven by the cooling of ocean waters due to the ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation) cycle, can significantly influence global weather patterns.
- The air circulation loop in the region, affected by these temperature changes, impacts precipitation levels in neighbouring areas and can alter the Indian monsoon.
- Currently, the El Niño event that began in June last year has significantly weakened.
- Neutral ENSO conditions are expected to be established by June.
- Following this, La Niña conditions are anticipated to emerge, with its effects likely becoming apparent from August.
La Nina’s Impact on India:
- With above normal rain forecast, the seasonal rainfall is expected to be 106 per cent of the Long Period Average (LPA), which is 880mm (1971-2020 average).
- Except in east and northeast India, all remaining regions are expected to receive normal or above-seasonal rainfall.
- Heavy rains could result in some regions witnessing riverine and urban flooding, mudslides, landslides and cloudbursts.
- East and northeast India region, during La Nina years, receive below average seasonal rainfall.
- Therefore, there may be a shortfall in water reserves there this year.
- During La Nina years, incidents of thunderstorms generally increase.
- “The east and northern India regions could experience thunderstorms accompanied by lightning.
- With increased farming activities undertaken during the July and August rainy months, which coincides with the season’s enhanced lightning and thunderstorms, there is a high risk of fatalities in these regions.
- In addition to ENSO, there are other parameters that can impact the monsoon.
- However, in a La Nina year, a deficit monsoon over India can be easily ruled out.
La Nina’s Impact on the World:
- Similar to India, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and their neighbouring countries receive good rainfall during a La Nina year.
- This year, Indonesia has already witnessed floods.
- On the other hand, droughts are common in southern regions of North America, where winters become warmer than usual.
- Canada and the northwestern coast of the United States see heavy rainfall and flooding.
- Southern Africa receives higher than usual rainfall, whereas eastern regions of the continent suffer below-average rainfall.
- ENSO has a huge impact on hurricane activity over the Atlantic Ocean.
- During a La Nina year, the hurricane activity here increases.
- For instance, the Atlantic Ocean churned out a record 30 hurricanes during the La Nina year 2021.
Is Climate Change Affecting ENSO?
- Over India, El Niño is known to suppress the southwest monsoon rainfall and drive higher temperatures and intense heat waves, like the present summer season.
- In the past, monsoon seasons during years following an El Niño were 1982-1983 and 1987-1988, with both 1983 and 1988 recording bountiful rainfall.
- At present too, a similar situation could play out.
- The 2020-2023 period witnessed the longest La Nina event of the century.
- Thereafter, ENSO neutral conditions developed, which soon gave way to El Niño by June 2023 which has been weakening since December last year.
- Scientists say that climate change is set to impact the ENSO cycle.
- Many studies suggest that global warming tends to change the mean oceanic conditions over the Pacific Ocean and trigger more El Niño events.
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has also said that climate change is likely to affect the intensity and frequency of extreme weather and climate events linked to El Niño and La Nina.
La Nina impacted air quality in India in the winter of 2022
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new study suggests that monsoon rainfall over India, which is strongly influenced by El Niño and La Niña events—alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean impacting global weather may also affect air quality in the country.
Key Findings of the New Study on the Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- According to the researchers at the National Institute of Advanced Studies (Bengaluru) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (Pune), the strong influence of El Niño and La Niña events on monsoon rainfall over India, driven by the alternating warming and cooling of the eastern Pacific Ocean, with far-reaching effects on global weather patterns.
- Remarkably, this study marks the first time that air quality in Indian cities has been directly linked to a La Niña event, suggesting an indirect connection to climate change, which intensifies the severity of El Niño and La Niña occurrences.
- Traditionally, northern Indian cities, notably Delhi, face elevated concentrations of PM2.5 pollutants from October to January.
- However, the winter of 2022 witnessed a notable deviation from this trend, with northern cities experiencing cleaner air than usual, while western and southern cities like Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Chennai saw worsened air quality.
- Specifically, Delhi observed a 10% reduction in PM2.5 concentrations, contrasted with a 30% increase in Mumbai and a 20% rise in Bengaluru.
- The researchers, investigating this anomaly, identified the potent effects of the La Niña event, notably stronger than typical occurrences, leading to significant changes in wind circulation patterns over India.
- This impact became pronounced in the third year of La Niña, suggesting a cumulative effect that may amplify over time.
- While La Niña events are associated with improved air quality in northern India, the study emphasizes the need for further research to understand the potential impacts of El Niño events, which may produce contrasting effects on air quality across the country.
What are El Niño and La Niña?
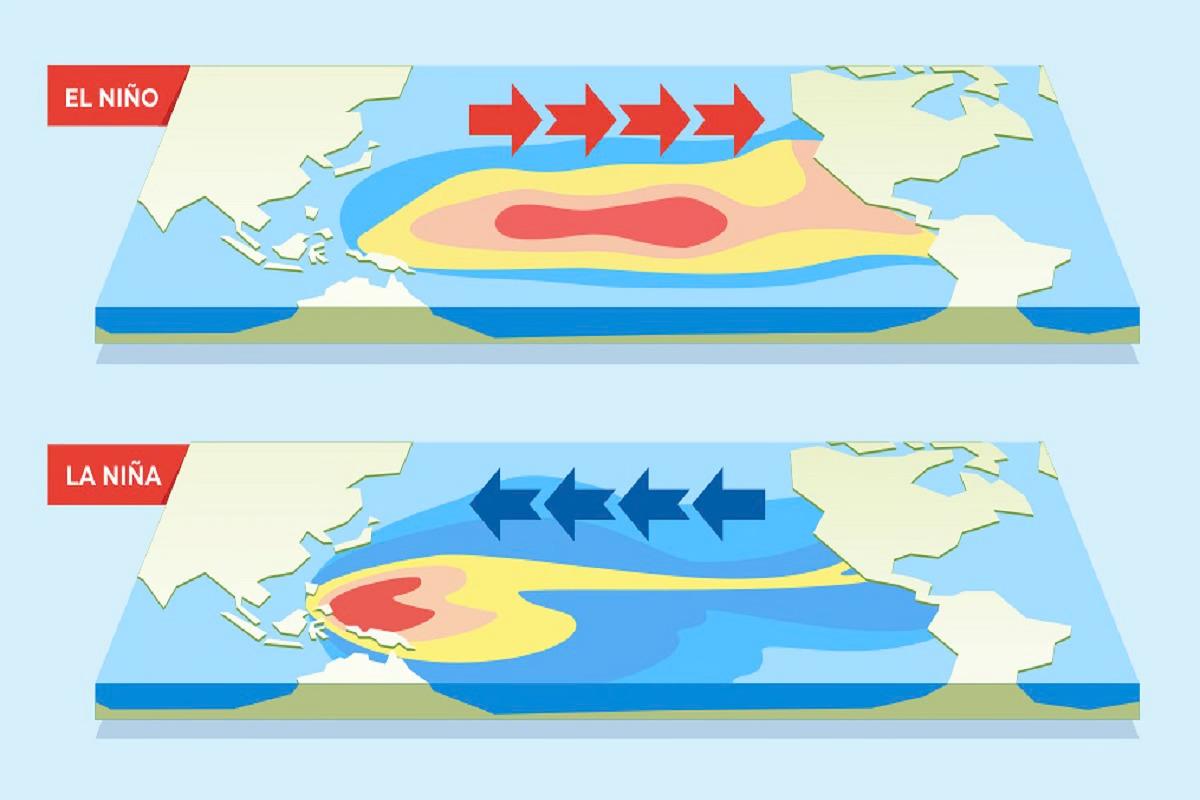
- El Niño refers to a band of warmer water spreading from west to east in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- Similarly, a La Niña occurs when the band of water spreads east to west and is cooler.
- Both phenomena affect the weather worldwide and can have drastic effects on economies that depend on rainfall.
- Together, El Niño and La Niña make up a cyclical process called the El Niño Southern Oscillation.
- An El Niño year creates a global warming crisis in miniature because the warm water spreading across the tropical Pacific releases a large amount of heat into the atmosphere.
- El Niño: El Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, El Niño events often correlate with below-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to drought conditions in some regions, affecting agriculture and water resources.
- El Niño can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing warmer temperatures during El Niño events.
- La Niña: La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
- In India, La Niña events often correlate with above-average rainfall during the monsoon season.
- This can lead to increased precipitation in some regions, potentially causing flooding, while other areas may experience drought conditions.
- La Niña can also influence temperature patterns, with some parts of India experiencing cooler temperatures during La Niña events.
Impact of La Niña on Air Quality in India:
- Altering Wind Patterns: During the winter of 2022, the typical north-westerly winds, carrying agricultural pollutants from Punjab and Haryana towards Delhi and the Gangetic plains, were disrupted.
- Instead, wind circulation shifted to a north-south direction, diverting pollutants away from Delhi.
- Consequently, pollutants bypassed Delhi, travelling over Rajasthan and Gujarat towards southern regions.
- Modifying Local Wind Circulation near Mumbai: In Mumbai, the local wind circulation, which alternates between land-to-sea and sea-to-land flows every few days, experienced prolonged unidirectional winds.
- This sustained wind pattern prevented the dispersal of pollutants from the city, leading to their accumulation within Mumbai's atmosphere throughout the winter of 2022.
- These changes in wind patterns, influenced by La Niña, significantly impacted air quality dynamics in India, highlighting the intricate relationship between climate phenomena and regional atmospheric conditions.
