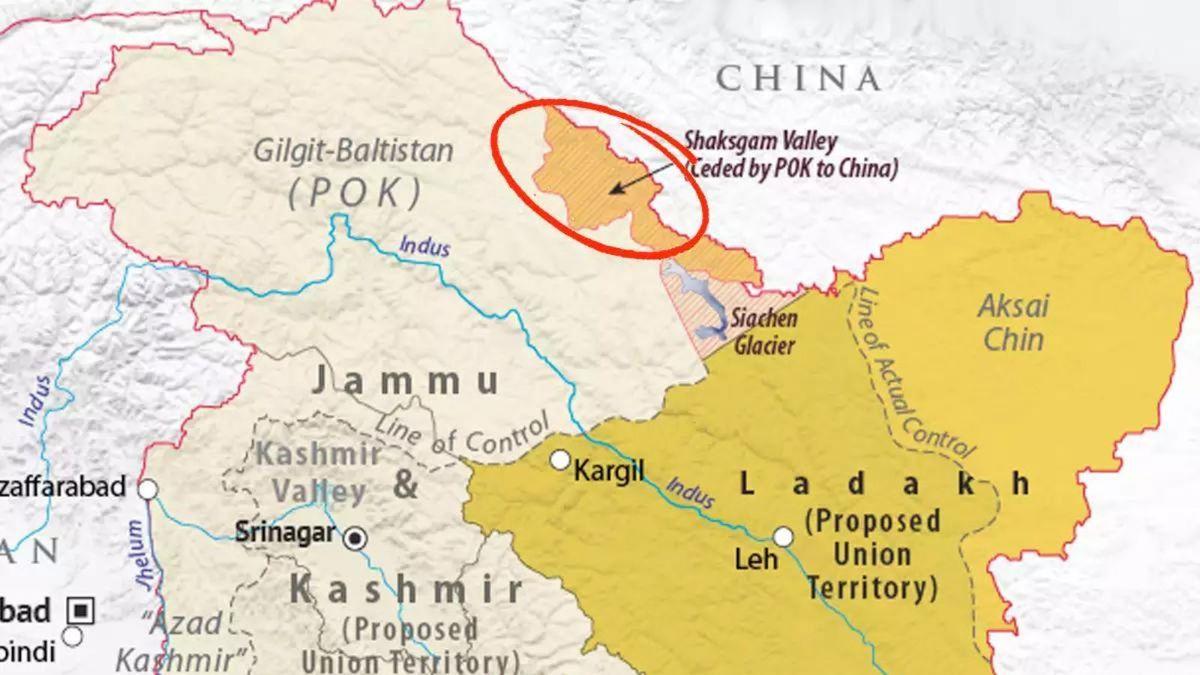
Shaksgam Valley
- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently said it has lodged a strong protest with China for carrying out construction activities in the Shaksgam Valley in an "illegal" attempt to alter the situation on the ground.
Context:
- Recently, the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) said that the Shaksgam Valley is a part of the territory of India amid reports of China building infrastructure in the valley.
- The Shaksgam Valley strategically located region that is now part of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- MEA spokesperson Randhir Jaiswal recently said that India "never accepted the so-called China-Pakistan Boundary Agreement of 1963 through which Pakistan unlawfully attempted to cede the area to China".
- Lodging a strong protest with China for carrying out construction activities, India called it an "illegal" attempt to alter the situation on the ground.
Where is the Shaksgam Valley Located?
- The Shaksgam Valley, or the Trans Karakoram Tract, is part of the Hunza-Gilgit Region of PoK.
- It is bordered by the Xinjiang Province of the People's Republic of China to the north.
- The northern areas of PoK are to its west and south.
- And the Siachen Glacier region to the east.
How did Pakistan cede Shaksgam valley to China?
- In 1963, Pakistan ceded the Shaksgam Valley to China when it signed a border agreement with Beijing to settle their border disputes.
- But, Article 6 of the 1963 agreement clearly stated that “the two Parties have agreed that after the settlement of the Kashmir dispute between Pakistan and India, the sovereign authority concerned will reopen negotiations with the Government of the People's Republic of China, on the boundary as described in Article 2 of the present Agreement, to sign a formal Boundary Treaty to replace the present agreement.”
- The agreement laid the basis for the construction of the Karakoram Highway, which was jointly built by Chinese and Pakistani engineers during the 1970s.
What is the History of Shaksgam Valley?
- When the British asked the Mir of Hunza, a vassal of the Maharaja of Kashmir, to give up his rights to the Taghdumbash Pamirs and the Raskam valley in 1936, the Shaksgam valley to the south-west had remained in his possession.
- This remained the traditional frontier of British India until independence and was inherited by India following Jammu & Kashmir's accession in 1947.
- And, this was the border that Pakistan compromised in its 1963 agreement with China.
- Pakistan established diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China in 1951.
- Back then, Pakistan was viewed as a member of the non-Soviet block due to its membership in two anti-communist military pacts -- SEATO and CENTO -- led by the United States.
- China was on the opposite side.
- After Chinese troops invaded Tibet in 1950, Pakistan even offered transit facilities to US aircraft so they could supply equipment to Tibetan rebels.
- Chinese troops began to cross the border in eastern Hunza after the Partition of India.
- This started in 1953 and in 1959 they took some livestock out of the area.
- This prompted a furious response from Pakistan, which was determined to protect its borders.
- The then President of Pakistan, Ayub Khan, however, saw an opportunity to appease the Chinese in the late 1950s as India-China relations were rapidly deteriorating.
- Subsequently, Beijing developed closer ties with Islamabad after the India-China War of 1962.
- China went on to support Pakistan diplomatically during the 1965 India-Pakistan war.
- Amid these developments, Pakistan chose to downgrade historical claims made by the Mir of Hunza and signed over the Shaksgam Valley to China in 1963.
What was the Consequence?
- In granting China's claim to a border along the Karakoram Range, Pakistan compromised India's traditional frontier along the KunLun Range to the northwest of the Karakoram Pass.
- It also allowed China to extend a claim eastward along the Karakoram in Ladakh.
- This enabled China to claim all of Aksai-Chin.
