Fast Track Immigration FTI-TTP

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India is launching the Fast Track Immigration Trusted Traveller Program (FTI-TTP) to streamline immigration at seven major airports.
Key Highlights:
- The initiative, inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, aims to enhance the travel experience for Indian nationals and Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) cardholders.
- This comes seven months after the programme was first introduced at Indira Gandhi International (IGI) Airport, New Delhi. The airports included in this initial phase are: Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Cochin and Ahmedabad
Objectives of FTI-TTP
- Provide seamless and secure immigration services.
- Reduce human intervention using automated e-gates.
- Align with the Viksit Bharat@2047 vision for modern infrastructure.
How the Programme Works
The FTI-TTP simplifies immigration with automated e-gates. Travellers must complete a one-time online registration to enroll. The process involves:
- Online Registration: Submit personal details and upload necessary documents via the official portal (https://ftittp.mha.gov.in).
- Biometric Submission: Fingerprints and facial images must be submitted at an airport or Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO).
- Immigration Clearance via E-Gates:
- Passengers scan their boarding passes and passports at e-gates.
- Biometrics are automatically verified.
- Upon authentication, the e-gate opens, granting clearance.
Validity: Registration is valid for five years or until the registered passport expires, whichever comes first.
Who is Eligible?
The first phase of the FTI-TTP is open to:
- Indian nationals.
- OCI cardholders aged between 12 and 70 years.
- Children aged 12-18 can register using their parents’ email/phone number.
- ECR (Emigration Check Required) passport holders are not eligible.
Documents Required for Registration
- Passport-sized photograph (as per Indian passport specifications).
- Scanned copy of passport (front and back pages).
- Proof of current address.
- OCI card details (if applicable).
Key Points to Note
- Registration may take up to a month due to verification by field agencies.
- Applications with incorrect or outdated information may be rejected.
- In case of passport loss or expiry, travellers must reapply and submit fresh biometrics.
- Passports must have at least six months’ validity at the time of applying.
- For support, travellers can reach out via email at india.ftittp-boi@mha.gov.in.
Implementation Phases
The FTI-TTP will be implemented in two phases:
- Phase 1: Covers Indian citizens and OCI cardholders.
- Phase 2: Will extend to foreign travellers.
- The programme will be expanded to 21 major airports across the country.
Comparison with Similar Global Programmes
Several countries have implemented similar fast-track immigration systems:
United States: Global Entry
- Introduced in 2008.
- Offers self-service kiosks for pre-approved travellers.
- Requires background checks and in-person interviews.
United Kingdom: Registered Traveller Service
- Launched in 2015.
- Allows frequent visitors from select countries, including India, to use e-gates.
- Requires visa eligibility or multiple prior visits.
European Union: Smart Borders Initiative
- Implemented in 2016, with full deployment expected by 2024.
- Pre-registers biometric data for faster processing at Schengen Area borders.
Australia: SmartGate
- Started in 2007 for Australian and New Zealand passport holders.
- Uses automated kiosks for identity verification via passport scans and photos.
Saudi Arabia: Smart Travel System
- Launched in 2019.
- Uses automated e-gates for faster immigration clearance.
- Expanding as part of Vision 2030 to improve travel experience, particularly for Hajj pilgrims.
Sovereign Artificial Intelligence

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been remarkable in recent years. In 2018, a 340-million-parameter AI model was considered large, whereas models like ChatGPT now have 1.8 trillion parameters.
- As part of its ambition to make the digital economy worth USD 1 trillion by 2028, India is focusing on AI sovereignty and investing in semiconductors and AI technologies to achieve this goal.
What is Sovereign AI?
Definition
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s ability to develop, control, and deploy AI using its own resources, including infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This involves not just developing AI models but also creating infrastructure and nurturing homegrown talent to lead AI advancements within the country.
Key Aspects of Sovereign AI
- National Control: Ensures AI technologies align with a country's laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Emphasizes control of data within the country’s borders, protecting privacy, security, and national interests.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is transforming industries, markets, and governance, with AI-powered tools assisting professionals and governments.
- Ethical Considerations: Countries define security protocols and ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI technologies.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign technologies, encouraging domestic development in AI to achieve strategic independence.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is crucial for industrial innovation. Without it, nations risk falling behind in the global economy.
Growth and Importance of AI
Evolution of AI Models
- In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered a significant achievement.
- Today, ChatGPT uses 1.8 trillion parameters, and Google’s Gemini uses 1.5 trillion parameters. In comparison, China’s DeepSeek has a model with 240 billion parameters.
- Parameters are the internal variables of AI models, adjusted during training to improve their performance and accuracy.
Strategic Applications
- Sovereign AI plays a pivotal role in critical sectors such as:
- Defense
- Healthcare
- Transportation
- Governance
- It helps redefine industries, boost innovation, and streamline operations across various sectors.
India’s Position in Sovereign AI
AI Infrastructure Development
- Tata Group and Reliance are building AI infrastructure in India, including the development of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- India has allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project under the IndiaAI Mission, which includes creating an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips.
Government Initiatives
- The IndiaAI Mission is designed to boost India’s AI capabilities by building infrastructure, fostering talent, and supporting innovation within the country.
Global AI Compact
- A Global AI Compact has been proposed to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
- The compact advocates for sharing AI resources globally while promoting cooperation and addressing challenges associated with AI governance.
Section 479 of the BNSS 2023

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Centre urges states, UTs to ensure undertrial prisoner relief in jails.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The MHA has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to implement provisions of Section 479 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 to provide relief to undertrial prisoners (UTPs) in jails. This initiative aims to address issues such as long detention and overcrowding in prisons.
Key Provisions of Section 479 of BNSS, 2023
- Purpose: To offer relief to undertrial prisoners by mandating their release on bail or bond under specific conditions.
- Key Provisions:
- Subsection (1):
- Release on Bail: UTPs who have served half the maximum sentence for their offense (except offenses punishable by death or life imprisonment) are eligible for release on bail.
- Release on Bond for First-Time Offenders: First-time offenders, who have served one-third of the maximum sentence, are eligible for release on bond by the court.
- Subsection (3):
- Mandatory Application: It is the responsibility of the prison superintendent to apply to the concerned court for the release of eligible prisoners on bail or bond.
- Subsection (1):
- Superintendent’s Role:
- Prison superintendents are mandated to ensure timely applications for bail or bond are filed for eligible UTPs.
Implementation and Reporting
- MHA’s Advisory:
- On January 1, the MHA issued a letter to the Chief Secretaries, Director Generals, and Inspectors General of prisons in all states and UTs to ensure compliance with the provisions of Section 479 of BNSS.
- States and UTs were instructed to report the status of implementation in a prescribed format starting from January 1, 2025.
- Data to be Reported:
- First-Time UTPs: Number of first-time UTPs who have served one-third of their maximum sentence.
- Court Applications: Number of applications for bail filed by jail superintendents.
- Release on Bail: Number of UTPs released on bond or bail after meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Other UTPs: Number of UTPs who have completed half of their sentence, and the number of applications filed for their release.
- MHA’s Campaign:
- Launched on Constitution Day (November 26), this campaign encouraged states and UTs to identify eligible prisoners and file their bail applications, thus helping to reduce overcrowding in prisons and mitigate long-term detention.
Background and Context
- Why Section 479?
- Section 479 aims to reduce the prolonged detention of undertrials, some of whom may have already served significant portions of their maximum sentences. This will not only alleviate overcrowding in prisons but also expedite justice for prisoners who have spent extended periods in jail awaiting trial.
- Earlier MHA Initiatives:
- Prior to this directive, the MHA had issued an advisory on October 16, 2024, encouraging states and UTs to implement Section 479. A special push was also made during Constitution Day to move applications for the release of eligible prisoners.
- Expected Outcome:
- The measures are expected to significantly ease the challenges of overcrowded jails and provide timely relief to undertrials, especially first-time offenders. By enforcing these provisions, the government seeks to improve the judicial process for UTPs and contribute to a more effective and humane criminal justice system.
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
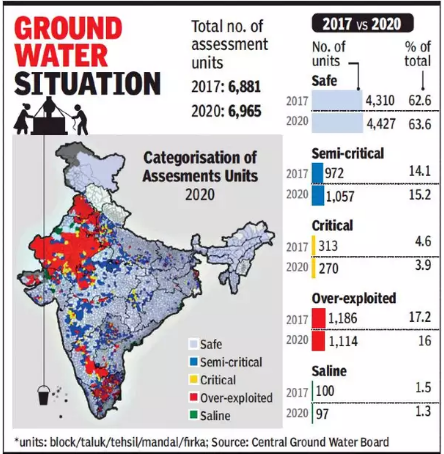
The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) report on groundwater quality reveals alarming levels of contamination in India's groundwater, with a focus on nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and uranium. The report highlights the impact of agricultural practices, poor waste management, and urbanisation on water quality.
Key Highlights:
Nitrate Contamination:
- 440 districts in India report excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, with 20% of samples exceeding the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/L (WHO and BIS standards).
- High-risk regions: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) are the top states with high nitrate levels. Other affected states include Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Causes: Nitrate contamination is mainly due to excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, over-irrigation, and poor management of animal waste. Urbanisation and improper sewage systems exacerbate the problem.
Other Groundwater Contaminants:
- Fluoride contamination: A significant concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic contamination: Elevated arsenic levels found in several states, especially in floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur).
- Uranium contamination: 42% of uranium-contaminated samples are from Rajasthan, and 30% from Punjab. Chronic exposure to uranium leads to kidney damage.
Groundwater Extraction and Availability:
- 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India.
- 73% of groundwater blocks are classified as in the ‘safe’ zone, an improvement from 67.4% in 2022.
Monsoon Impact:
- Nitrate contamination increases post-monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season.
Health Implications:
- High nitrate levels, particularly dangerous for infants, can cause blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia).
- Long-term exposure to contaminants like fluoride and arsenic can lead to fluorosis and increase the risk of cancers and skin lesions.
Sources of Contamination:
- Agricultural practices: Excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and improper irrigation.
- Waste disposal: Leaking septic systems, sewage, and hazardous waste sites contribute to contamination.
- Urbanisation: Increased wastewater and sewage, along with poor waste management, worsen the issue.
Measures to Address Contamination:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) and Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) aim to conserve and manage groundwater resources.
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM) to assess and map aquifer systems.
- Pollution control programs: Under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, and initiatives like sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants to manage wastewater.
- Public awareness: Campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Catch the Rain educate communities on the importance of groundwater conservation.
Key Statistics:
- 56% of districts in India report groundwater nitrate levels exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg/L.
- Monsoon effects: Post-monsoon data shows a significant increase in contamination levels (32.66% vs. 30.77% pre-monsoon).
Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) Mission
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
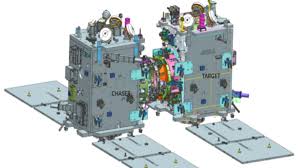
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission, a key milestone in India’s space capabilities. The mission will deploy two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into a 740 km orbit using the PSLV-C60 rocket. SpaDeX aims to demonstrate the technology for satellite docking, a critical component for future space missions such as lunar exploration and the development of India's own space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
Key Objectives of SpaDeX Mission:
- Primary Objective: To demonstrate the rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft (SDX01 and SDX02) autonomously.
- Secondary Objectives: Include testing electric power transfer between the docked spacecraft, composite spacecraft control, and post-docking payload operations.
The mission will see the two spacecraft gradually approach each other, performing a series of maneuvers, starting at a 20 km distance and closing to millimeter-scale distances before docking. Once docked, they will execute secondary tasks, such as scientific payload operations, using advanced technologies including high-resolution cameras, multi-spectral payloads, and radiation monitors.
Technological Innovations:
- Docking Mechanism: An indigenous, motor-driven, low-impact, androgynous docking system with capture, extension/retraction, and rigidization mechanisms. Both spacecraft are equipped with identical docking systems to simplify operations.
- Advanced Sensors: The spacecraft will use a Laser Range Finder (LRF), Proximity & Docking Sensors (PDS), and Rendezvous Sensors for precise distance measurement and to guide the docking process.
- Inter-Satellite Communication: The spacecraft will employ autonomous inter-satellite links (ISL) for real-time communication and data sharing.
- RODP Processor: This system, based on GNSS, ensures accurate position and velocity determination for the spacecraft during the docking procedure.
Significance of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Technological Milestone: SpaDeX positions India as the fourth country, after the US, Russia, and China, to develop space docking technology.
- Space Exploration: The successful demonstration will facilitate future space exploration, including Chandrayaan-4 and interplanetary missions.
- Modular Space Infrastructure: Space docking is essential for building multi-modular space stations, which allows the construction of large structures in space and enhances flexibility for future missions.
- Satellite Servicing: Docking enables satellite servicing, including repairs, refueling, and upgrades, which increases the operational lifespan of satellites.
SpaDeX Mission for India’s Space Station:
The SpaDeX mission is a crucial step towards India’s plans for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). This will be India’s first modular space station, designed to conduct advanced scientific research, including in life sciences and medicine. BAS is expected to begin operations by 2035, and the development of docking technology is pivotal for its assembly and operation.
Mission Launch Details:
The PSLV-C60 rocket is set to launch the SpaDeX mission from Sriharikota. The mission is a demonstration of India's growing space capabilities and its indigenous technologies, including the Bharatiya Docking System (BDS).
Challenges and Technological Requirements:
The docking process requires extremely precise maneuvering, as the two spacecraft will be traveling at speeds of 28,800 km/h and must reduce their relative velocity to just 0.036 km/h before docking. This level of precision is crucial for future missions involving spacecraft servicing, crew transfers, and the construction of space infrastructure like BAS.
In addition to the docking demonstration, SpaDeX will carry 24 academic and startup payloads aboard the PSLV’s fourth stage, POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4), offering a valuable platform for microgravity research.
Future Prospects:
The success of SpaDeX will pave the way for more complex missions, such as India’s lunar and Mars exploration programs, the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and international collaborations in satellite servicing and space infrastructure.
Green fixed deposits

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
Green fixed deposits (FDs) are a type of investment scheme offered by banks and financial companies, aimed at environmentally-conscious investors. They function similarly to traditional fixed deposits, where funds are locked in with a bank for a fixed tenure. The primary distinction between green and regular deposits lies in the allocation of funds. While regular deposits are pooled into a common fund, the funds from green deposits are exclusively allocated to projects that promote environmental sustainability.
Key Features of Green Fixed Deposits:
- Investment Purpose: The funds raised through green FDs are directed towards environmentally beneficial projects, such as renewable energy initiatives (solar and wind power), clean technology, organic farming, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Eligibility: Green deposits are available to various entities, including individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), societies, clubs, non-profit organizations, and sole proprietorships.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on green deposits may or may not differ from regular deposits, depending on the policies set by the lending institution. Some banks and financial institutions, like IndusInd Bank, Federal Bank, DBS Bank India, and HDFC Ltd., offer green deposits, with Bank of Baroda recently launching the BOB Earth Green Term Deposit with an interest rate of up to 7.15% per annum.
- Safety: Like regular fixed deposits, green deposits are insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) under the provisions of the DICGC Act, 1961, ensuring the safety of the investment.
- Overdraft Facility: Banks may offer overdraft facilities against green deposits, providing more flexibility to investors.
- Premature Withdrawal: If the investor chooses to withdraw the deposit before the agreed tenure (after six months), the green FD will be converted into a regular fixed deposit.
- Denomination: Green deposits are denominated in Indian Rupees only.
26 Rafale-Marine Jets

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- Deal for 26 Rafale-M jets nearing completion, with final formalities expected to be completed by January 2025.
- These jets are designed for naval operations and will be deployed on INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- Rafale-M Features: Multi-role, advanced avionics, AESA radar, and armaments like Meteor, MICA, SCALP, EXOCET.
- Three Scorpene Submarines: Additional three Scorpene-class submarines to be procured from France.
- These are part of a repeat order to Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), with five of the earlier six already inducted into service.
Nuclear Capabilities:
- INS Arighaat: Successfully fired a Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), marking a significant milestone for India's nuclear deterrence.
- Indigenous Nuclear Attack Submarine (SSN): India’s first indigenous SSN expected by 2036-37.
Strategic Maritime Engagement:
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR): Active monitoring of maritime activities, especially of China's PLA Navy and Chinese research vessels.
- Pakistan Navy Expansion: Acknowledged Pakistan’s efforts to become a 50-ship Navy, including the acquisition of 8 Chinese submarines. Indian Navy is adapting its plans to address this.
Nuclear Submarine Program (SSBN):
- INS Arihant: Conducted multiple deterrence patrols.
- INS Arighaat: Ongoing trials including the recent K4 SLBM test, with a range of 3,500 km.
Naval Vision 2047:
- Navy Chief released Vision 2047 document, outlining the future direction and growth of the Indian Navy.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements:
- Participation in various bilateral and multilateral exercises, including RIMPAC 2024 (Hawaii) and Russian Federation Navy’s Raising Day (St. Petersburg).
Mission Shukrayaan
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
ISRO received approval for its first Venus mission, Shukrayaan. The probe will undertake a detailed investigation of Venus, including its surface, atmosphere and geological structure.
Shukrayaan Mission (Venus Orbiter Mission):
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for 2028.
- Objective: Investigate Venus to gather data on its surface, atmosphere, and geological structure.
- Scientific Focus: Study weather patterns, geological activities, and atmospheric composition (e.g., carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds).
- Instrumentation: Equipped with synthetic aperture radar, infrared, and ultraviolet imaging devices to study Venus’s ionosphere.
- Significance: Offers global coverage of Venus, addressing gaps in previous missions' spatial coverage.
- Cost: Estimated at Rs 1,236 crore.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO plans to use the LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) rocket to launch the mission into an elliptical parking orbit (170 km x 36,000 km).
- Mission Data Processing: Data will be archived and disseminated through the Indian Space Science Data Center (ISSDC).
Chandrayaan 4 Mission:
- Collaborative Effort: Joint mission between India (ISRO) and Japan.
- Launch Objective: Land on the moon's south pole, with a focus on the region at 90°S (compared to previous missions at 69.3°S).
- Mission Details:
- Includes a rover weighing 350 kg (12 times heavier than previous rover).
- The rover will be equipped with advanced scientific tools for lunar exploration.
- Government Approval: Awaiting approval, with a target execution date of 2030.
Gaganyaan Mission (Human Spaceflight Program):
- Timeline: Unmanned flight in 2026, followed by a manned mission.
- Indian Space Station: Construction approved; to be completed by 2035, comprising five modules.
- Purpose: To serve as a transit facility for deep space exploration, including future lunar missions.
Mars Exploration Plans:
- Future Missions: Plans to send satellites to Mars and attempt a landing on the Martian surface.
- Significance: Demonstrates India’s growing ambitions in interplanetary exploration.
INSAT-4 Series of Satellites:
- Goal: Launch of new meteorological and oceanographic sensors to improve weather forecasts and disaster management.
- Technological Advancements: Need for India to catch up with global advancements in space-based sensors.
International Collaboration in Space:
- Chandrayaan 4: A collaboration between ISRO and Japan to explore the moon’s south pole, showcasing India's growing international cooperation in space exploration.
Strategic Importance of Shukrayaan:
- Contribution to Science: The mission’s global dataset will provide unique insights into Venus, enhancing the understanding of planetary atmospheres and geological processes.
- Potential for Discoveries: Research on Venus’s ionosphere and possible volcanic activity.
India's Gig Economy
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The gig economy market is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17 per cent to reach a gross volume of $455 billion by 2024, according to a white paper by the Forum for Progressive Gig Workers.
Key Sectors Supported by Gig Workers:
- E-commerce: Gig workers play a crucial role in driving growth in the e-commerce sector.
- Transportation and Delivery Services: These sectors are heavily dependent on gig workers for their operations and services.
Impact on Employment:
- Job Creation: The gig economy has the potential to create a significant number of jobs, especially in tier 2 and 3 cities, which are emerging as new growth hubs.
- Alternate Revenue Streams: Gig work provides diverse income opportunities for workers, especially for women, offering them a flexible mode of earning.
Contribution to GDP:
- The gig economy’s contribution is expected to add 1.25% to India’s GDP over time, highlighting its growing economic importance.
Technological Integration and Future Prospects:
- AI and Digital Innovation: Future growth is expected to be driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, and digital innovation, fostering sustainable and inclusive job opportunities.
Social and Economic Benefits:
- Women's Workforce Participation: The gig economy provides women with more earning opportunities and helps integrate them into the workforce.
- Welfare Initiatives: Platforms supporting gig workers are increasingly focusing on welfare initiatives, improving the overall working conditions in the sector.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Challenges: The evolving dynamics between large companies and gig workers pose challenges in terms of worker rights and fair compensation.
- Opportunities: The growth of the gig economy presents opportunities for companies to innovate and create inclusive work environments, especially for underserved communities.
Future Developments:
- Formal Report: The Forum for Progressive Gig Workers plans to collaborate with global organizations to release a formal report with deeper insights and actionable recommendations for the future of gig work
National Education Day 2024

- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
National Education Day is celebrated annually on November 11 to honor the birth anniversary of Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, India's first Education Minister and a prominent freedom fighter, scholar, and educator.
Key Highlights:
- Establishment:
- The observance was instituted by the Ministry of Human Resource Development (now Ministry of Education) in 2008 to recognize Azad’s pivotal contributions to India’s education system and his vision for a progressive, educated society.
- Azad's Contributions to Education:
- Azad played a significant role in shaping India's post-independence educational landscape, establishing critical institutions such as:
- University Grants Commission (UGC)
- All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE)
- Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT), including IIT Kharagpur
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR)
- Promoted scientific research, cultural institutions, and technical education.
- Azad played a significant role in shaping India's post-independence educational landscape, establishing critical institutions such as:
- Significance of National Education Day:
- Reflects India’s commitment to promoting quality and inclusive education.
- Emphasizes the importance of education in empowering individuals and fostering national progress.
- Highlights educational reforms, literacy, and equal access to education as tools for societal transformation and empowerment.
- Theme for 2024:
- Although not officially published yet, the theme is expected to focus on inclusive, high-quality education, underlining the need for educational systems that equip students with skills to thrive in a rapidly evolving world.
- Focus Areas:
- Promoting literacy, equal access to education, and educational reforms.
- Developing critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence in students.
Asia-Pacific Climate Report 2024

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Climate change to put APAC GDP on thin ice with 41% melt by 2100.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Losses Due to Climate Change:
- APAC Region: High-end greenhouse gas emissions could reduce GDP by 17% by 2070 and 41% by 2100.
- India: Projected to experience a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070, with neighboring countries like Bangladesh (30.5%), Vietnam (30.2%), and Indonesia (26.8%) facing even steeper declines.
- Major Drivers of Economic Losses:
- Sea-Level Rise: Up to 300 million people at risk of coastal flooding by 2070. Annual damages could reach $3 trillion by 2070.
- Labour Productivity: The APAC region could lose 4.9% of GDP from reduced labour productivity, with India facing a sharper 11.6% loss.
- Cooling Demand: Rising temperatures could reduce regional GDP by 3.3%, but India's cooling demands could cut its GDP by 5.1%.
- Flooding and Storms: Increased rainfall and storm intensity will exacerbate flooding and landslides, particularly in mountainous regions like the India-China border, where landslides could rise by 30-70% under severe warming.
- Impact on Key Sectors:
- River Flooding: By 2070, annual riverine flooding could cause $1.3 trillion in damages across the APAC, affecting over 110 million people. India could face over $1,100 billion in flood-related damages annually.
- Forest Productivity: Climate change could reduce forest productivity by 10-30% by 2070 across APAC. India could see losses over 25%, making it one of the hardest-hit countries, alongside Vietnam and Southeast Asia.
- Climate Risks and Vulnerabilities:
- Coastal Flooding: Coastal flooding could lead to widespread economic damage, with India expected to suffer significant losses, particularly in coastal areas.
- Ecosystem Threats: Intensified storms, rainfall, and landslides will affect ecosystems, forests, and agriculture across the region.
- Climate Change and Adaptation Needs:
- Investment Requirements: Developing Asia requires $102–431 billion annually for climate adaptation, far exceeding the $34 billion tracked from 2021 to 2022.
- Private Investment: The report highlights the need for greater private climate investment and regulatory reforms to attract capital for adaptation initiatives.
- Renewable Energy: APAC is well-positioned to embrace renewable energy for a net-zero transition, and the use of carbon markets could help achieve climate goals cost-effectively.
- Regional Net-Zero Goals and Progress:
- Net-Zero Targets: 36 out of 44 Asian economies have set net-zero emissions targets, but only 4 have legally committed to these goals. India and China target 2070 and 2060, respectively, while many OECD countries aim for 2050 targets.
- Policy Gaps: Developing Asia needs clearer policies and increased financing to meet climate ambitions. Institutions like ADB are crucial in supporting these efforts.
- Action Plan for the Future:
- Urgent Climate Action: The report stresses the importance of coordinated action to address escalating climate risks.
- Enhanced Adaptation Finance: There is a need to scale up adaptation-focused finance to tackle the growing climate challenges facing the region.
India's Vulnerability and Climate Challenges:
- Labour Impact: India is expected to experience a 11.6% GDP loss due to declining labour productivity, the highest among APAC countries.
- Cooling Demands: A 5.1% reduction in GDP due to increased cooling demand.
- Flood Damage: India’s flood-related losses could surpass $1.1 trillion annually by 2070, with damages to residential and commercial properties.
ISRO's Analogue Space Mission in Ladakh

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
In a significant leap for the country’s space exploration aspirations, India has embarked on its first analogue space mission in Leh, a landmark step that will attempt to simulate life in an interplanetary habitat to tackle the challenges of a base station beyond Earth.
Mission Overview:
- Objective: To simulate living conditions in an interplanetary habitat, addressing challenges astronauts may face during deep-space missions (e.g., Moon, Mars).
- Goal: Study long-term isolation, habitat design, resource management, and psychological effects on astronauts.
- Partners: ISRO’s Human Spaceflight Centre, AAKA Space Studio, University of Ladakh, IIT Bombay, Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council.
Rationale for Ladakh:
- Geological Similarities: Ladakh’s terrain mirrors Martian and lunar surfaces, making it ideal for testing space technologies.
- Climate: Cold, dry, high-altitude conditions simulate the extreme environments of space.
- Focus Areas: Testing habitat construction, microbial studies, and survival strategies for long-duration space travel.
What are Analogue Space Missions?
- Definition: Simulated space missions on Earth designed to replicate the conditions of space exploration.
- Purpose:
- Test technologies (e.g., life support, habitat design, in-situ resource utilization).
- Study human behavior, psychological impacts of isolation, and operational readiness for extended space travel.
- Relevance: Crucial for preparing astronauts for missions to the Moon, Mars, or asteroids.
Significance of Analogue Missions:
- Technological Testing: Analogue missions help in evaluating systems for habitat design, life support, and health monitoring.
- Human Factors: They provide insights into crew health, teamwork under pressure, and performance during isolation.
- Psychological Studies: Address the impact of confinement, isolation, and communication delays on astronauts.
- Training: Participants (analogue astronauts) are trained for real-world space missions by conducting scientific experiments and managing emergencies.
Global Examples of Analogue Missions:
- NASA’s NEEMO: An underwater mission simulating microgravity conditions to train astronauts for space tasks.
- SIRIUS Program (UAE): Focuses on the psychological impacts of long-duration space isolation, featuring international collaborations.
- Arctic Mars Analogue Svalbard Expedition (AMASE): Uses the extreme Arctic environment of Svalbard to test Mars exploration technologies and procedures.
Relation to India’s Space Aspirations:
- Gaganyaan Mission: ISRO’s human spaceflight mission aiming to send Indian astronauts into space.
- Interplanetary Exploration: The analogue mission supports India’s broader goal of advancing human space exploration and technology development for Mars and beyond.
India-Pakistan Kartarpur Corridor Agreement Renewal
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- India and Pakistan have extended the Sri Kartarpur Sahib Corridor Agreement for another five years (until 2029).
- Purpose: The extension ensures uninterrupted operation of the corridor, allowing Indian pilgrims to visit Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan.
- Significance: The extension reflects continued cooperation between India and Pakistan, with potential implications for improving bilateral relations.
Background of Kartarpur Corridor:
- Inception: The agreement was first signed on October 24, 2019, to allow visa-free access for Indian pilgrims to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur near Narowal in Pakistan.
- Pilgrimage Details:
- Eligibility: Indian nationals and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) cardholders can visit the gurdwara on a daily basis.
- Return on Same Day: Pilgrims must return on the same day.
- No Religious Restrictions: Pilgrims of any faith can use the corridor.
- Capacity: Up to 5,000 pilgrims per day can visit the gurdwara.
- Historical Importance: The corridor facilitates the Sikh community's access to a key religious site, located just 4.7 km from the India-Pakistan border.
- Service Charge Dispute:
- Pakistan's Service Fee: Pakistan continues to charge a $20 service fee (approx. ?1,680) per pilgrim, which India has consistently urged Pakistan to waive.
- Pakistan’s Justification: Pakistan maintains the fee to cover the $17 million spent on refurbishing the gurdwara and developing infrastructure for the corridor.
- Geopolitical Context and Timing:
- Recent Developments: The agreement renewal follows External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s visit to Pakistan to attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Council of Heads of Government meeting.
- Improved Bilateral Relations: Jaishankar’s visit marked the first visit by an Indian foreign minister to Pakistan in nearly nine years, signaling potential thaw in relations, despite the lack of formal bilateral dialogue.
- Strategic and Religious Importance:
- Religious Diplomacy: The Kartarpur Corridor is viewed as a confidence-building measure and a symbol of religious diplomacy, particularly for the Sikh community.
- Historical Legacy: The corridor links Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan to Gurdwara Dera Baba Nanak in India, facilitating access to a site of immense religious significance for Sikhs.
- Implications for India-Pakistan Relations:
- No Formal Bilateral Talks: Despite the successful renewal of the agreement, formal talks between India and Pakistan remain suspended, particularly after India’s revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir in 2019, which led to a diplomatic freeze.
- Pakistan's Diplomatic Stance: Pakistan had recalled its high commissioner from India in August 2019, and tensions have remained high since then.
- Potential for Future Engagement:
- Diplomatic Channels Opened: The renewal of the Kartarpur agreement and Jaishankar’s visit suggest that diplomatic channels are still open, and there may be scope for further engagement if both sides take steps to address outstanding issues.
Unexpected Transformation of the Sahara Desert
- 10 Oct 2024
In News:
The Sahara Desert, one of the driest regions globally, is undergoing a surprising transformation due to an extratropical cyclone that impacted northwestern Africa on September 7-8, leading to patches of green across Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya.
Key Details:
- Satellite Observations: NASA's satellite images reveal extensive greenery sprouting in areas typically known for drought conditions, as reported by NASA’s Earth Observatory.
- Flourishing Vegetation: Climate researcher Sylwia Trzaska noted that shrubs and trees are thriving in low-lying regions like riverbeds. Peter de Menocal, president of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, highlighted that plant life can quickly respond to significant rainfall, transforming dunes into vibrant landscapes.
- Historical Context: Research indicates that the Sahara was once a lush environment with lakes and vegetation between 11,000 and 5,000 years ago. Recent heavy rains have replenished normally dry lakes.
- Rainfall Dynamics: The unusual rainfall event is attributed to the northward shift of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which has moved further north than usual, resulting in equatorial-like downpours in the Sahara. Some areas experienced over half a foot of rain, surpassing typical annual precipitation levels.
- Impact of Rain Patterns: While the rains primarily affected less populated regions, severe flooding has resulted in over 1,000 fatalities and impacted around four million people across 14 African nations, according to reports from the World Food Programme and Associated Press.
- Climate Change Factors: Experts suggest that the repositioning of the ITCZ may be connected to record-high ocean temperatures and climate change, potentially altering rainfall patterns across Africa.
- Future Projections: As global ocean temperatures stabilize, de Menocal predicts that the rain belt may revert to a more southerly position, potentially crossing the equator.
- Sahara Desert Facts:
o The Sahara is the world's largest hot desert, spanning approximately 4,800 km in length and 1,800 km in width.
o It covers about 31% of the African continent, extending across 11 North African nations, including Algeria, Egypt, Mali, Morocco, Western Sahara, Tunisia, Chad, Libya, Mauritania, Niger, and Sudan
India’s Tripartite Agreement

- 07 Oct 2024
In News:
Nepal, India, and Bangladesh have signed a tripartite agreement to facilitate cross-border electricity trade, enabling Nepal to export surplus electricity to Bangladesh via India.
Key Details of the Agreement
- Export Period: The agreement allows for electricity exports from June 15 to November 15 each year.
- Initial Export Volume: In the first phase, Nepal will export 40 MW of hydroelectricity to Bangladesh through Indian territory.
- Electricity Rate: The fixed rate per unit of electricity is set at 6.4 cents.
- Projected Revenue: Nepal is expected to earn approximately $9.2 million annually from this trade.
This agreement aims to enhance regional cooperation in energy trade and support sustainable development in the participating countries.
Cruise Bharat Mission

- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
The central government launched the five-year Cruise Bharat Mission, aiming to boost cruise tourism in India to 1 million passengers and create 400,000 jobs by 2029.
Mission Goals
- Passenger Traffic: Increase from 0.5 million to 1 million sea cruise passengers by 2029.
- River Cruise Passengers: Grow from 0.5 million to 1.5 million.
- Job Creation: Generate 400,000 jobs in the cruise sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion:
- International cruise terminals: From 2 to 10.
- River cruise terminals: From 50 to 100.
- Marinas: From 1 to 5.
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1 (2024-2025):
- Conduct studies and master planning.
- Form alliances with neighboring countries.
- Modernize existing cruise terminals and destinations.
- Phase 2 (2025-2027):
- Develop new cruise terminals and marinas.
- Activate high-potential cruise locations.
- Phase 3 (2027-2029):
- Integrate cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Continue developing infrastructure and enhancing cruise experiences.
Strategic Focus Areas
- Sustainable Infrastructure:
- Develop world-class terminals, marinas, and water aerodromes.
- Emphasize digitalization (e.g., facial recognition) and decarbonization (shore power).
- Create a National Cruise Infrastructure Masterplan 2047.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Streamline operations using digital solutions (e.g., e-clearance and e-visa facilities).
- Cruise Promotion & Circuit Integration:
- Focus on international marketing and investment.
- Host events like the "Cruise India Summit."
- Form alliances with neighboring countries (UAE, Maldives, Singapore).
- Regulatory and Financial Policies:
- Establish tailored fiscal and financial policies.
- Launch a National Cruise Tourism Policy.
- Capacity Building & Employment:
- Create a Centre of Excellence for cruise-related economic research.
- Develop National Occupational Standards to enhance youth employment opportunities.
Expected Outcomes
- Tourism Growth: Position India as a global cruise destination.
- Cultural Promotion: Highlight the cultural, historical, and natural heritage of Bharat through cruise circuits.
- Community Benefits: Ensure inclusive growth for local communities and stakeholders in the cruise sector.
The Cruise Bharat Mission is set to redefine India's cruise tourism landscape, focusing on infrastructure development, operational efficiency, and promoting cultural heritage, while ensuring economic growth and job creation for the future.
INDIA-UZBEKISTAN BILATERAL INVESTMENT TREATY (BIT)

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
India and Uzbekistan signed the Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) aimed at boosting the confidence of investors of both the countries.
Key Highlights:
- Investor Protections:
- Assured Protection: The BIT guarantees protection for investors from both countries, aligning with international standards.
- Minimum Standards: It establishes a minimum standard of treatment and non-discrimination for investors.
- Dispute Resolution: An independent arbitration forum will be available for dispute settlement.
- Investment Safeguards:
- Protection from Expropriation: The treaty safeguards investments from unjust expropriation.
- Transparency and Compensation: Provisions are included for transparency and compensation for losses incurred.
- Regulatory Balance: While protecting investors, the treaty maintains a balance with the state's right to regulate, ensuring adequate policy space for both countries.
Economic Context
- Shared Commitment: The BIT reflects the commitment of both nations to foster economic ties and create a resilient investment environment.
- Expected Outcomes: It is anticipated that the treaty will facilitate increased bilateral investments, benefiting businesses and economies in India and Uzbekistan.
- Current Investment Landscape: As of August 2024, Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) from India to Uzbekistan stands at $20 million, with Indian investments notable in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, amusement parks, automobile components, and hospitality.
India and Bilateral Investment Treaties
BITs are reciprocal agreements between two countries designed to promote and protect foreign private investments within each other's territories.
- Key Guarantees Established:
- National Treatment: Foreign investors are treated on par with domestic companies.
- Fair and Equitable Treatment: Investors receive treatment aligned with international law.
- Protection from Expropriation: Limits the ability of a country to seize foreign investments without appropriate compensation.
- Status of BITs in India
- Historical Context:
- Until 2015, India had signed BITs with 83 countries, with 74 currently in force. These agreements were based on the Indian Model BIT established in 1993.
- Revisions and Current Approach: In 2015, India revised its Model BIT text. Since then, India has:
- Signed new BITs/Investment Agreements with four countries.
- Entered negotiations with 37 countries/blocks for new agreements.
- Terminated older BITs with 77 countries, with only six remaining in force.
- Historical Context:
- Key Features of the Revised Model BIT
- Investor Protection:
- Provides robust protection for foreign investors in India and Indian investors abroad.
- Balances investor rights with government obligations.
- Investor Confidence:
- Enhances investor confidence by ensuring non-discriminatory treatment and a level playing field.
- Establishes an independent arbitration forum for dispute resolution.
- Investment Definition:
- Adopts an "enterprise"-based definition of investment to encompass various forms of investment.
- Dispute Settlement Provisions:
- Refined Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) provisions require investors to exhaust local remedies before seeking international arbitration.
- Limits arbitration tribunals to awarding monetary compensation only.
- Regulatory Authority Preservation:
- Excludes government procurement, taxation, subsidies, compulsory licenses, and national security from BIT coverage, ensuring the government retains regulatory authority.
- Investor Protection:
- Strategic Impact
- Preferred FDI Destination: The revised BIT aims to position India as a preferred destination for foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Protection of Outbound FDI: It also focuses on safeguarding outbound investments made by Indian entities.
eShram portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Labour & Employment (MoLE) stated in a latest update that in the short span of three years since its launch, eShram has registered more than 30 crore unorganised workers, showcasing its rapid and widespread adoption among the unorganised workers.
Key Highlights:
- The Government envisages to establishing the eShram portal as a "One-Stop-Solution" for Country’s unorganised workers.
- During Budget speech 2024-25 it has been announced that, A comprehensive integration of eShram portal with other portals will facilitate such One-Stop-Solution.
- This initiative aims to facilitate access of various social security schemes being implemented by different Ministries/ Departments to unorganised workers through the eShram portal.
- As part of the eShram - One Stop Solution project, Ministry of Labour and Employment (MoLE) has been working to integrate major schemes like Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), Pradhan Mantri Street Vendors Atmanirbhar Nidhi (PM-SVANidhi), Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G), Ration Card scheme etc. for the benefit of the unorganised workers.
What is e-Shram and its purpose?
- e-Shram is a comprehensive National Database of Unorganised Workers (NDUW) launched by the Government of India under the Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- Its primary purpose is to facilitate delivery of welfare benefits and social security measures to unorganised sector workers across the country.
- The platform aims to register and provide identity cards to unorganised workers, enabling them to access various government schemes, benefits, and services more efficiently.
Who are unorganised workers?
Any worker who is a home-based worker, self-employed worker or a wage worker working in the unorganised sector and not a member of ESIC or EPFO, is called an unorganised worker.
What is unorganised sector?
Unorganised sector comprises of establishment/ units which are engaged in the production/ sale of goods/ services and employs less than 10 workers. These units are not covered under ESIC & EPFO.
What is UAN?
UAN or Universal Account Number is a 12 digit number uniquely assigned to each unorganised worker after registration on e-Shram portal. UAN is a permanent number i.e., once assigned, it will remain unchanged for any worker.
myCGHS App

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the government has launched the 'myCGHS' app for iOS to provide Central Government Health Scheme beneficiaries access to electronic health records, information, and resources.
About myCGHS app:
- The Union Health Ministry launched the myCGHS app for iOS (Apple Users) to provide easy access for the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) beneficiaries to their Electronic Health Records, information, and other resources.
- The myCGHS iOS app is developed by the technical teams of the National Informatics Centre (NIC) Himachal Pradesh and the NIC Health Team.
- It is a convenient mobile application offering features aimed at enhancing information and accessibility for CGHS beneficiaries.
- The app is said to offer a range of services including:
- Online appointment booking and cancellation
- Downloading CGHS card and index card
- Accessing lab reports from CGHS labs
- Checking medicine history
- Monitoring medical reimbursement claim status
- Accessing referral details
- Locating nearby wellness centers
- Staying updated with news and highlights, and
- Finding nearby impaneled hospitals, labs, and dental units.
- Additionally, users can access the contact details of wellness centers and offices conveniently.
- To ensure data security, the app also features security measures such as two-factor authentication and mPIN function to be able to access the app once they are logged in.
- Users on the Apple ecosystem can find the app on the App Store and download it free of charge.
- The myCGHS app has been available for Android users since February 2022.
Key Highlights of the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS):
- CGHS provides healthcare services to registered employees and pensioners of the Central Government of India.
- Enrolled members receive reimbursement and cashless healthcare facilities through this scheme.
- It encompasses healthcare services from various systems of medicine including Allopathy, Homeopathy, Ayurveda, and Unani.
- CGHS beneficiaries have the flexibility to undergo treatment at any impaneled private hospital of their preference.
International Day of Forests 2024

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On March 21, 2024, people around the world celebrate World Forest Day. It's a day to remind everyone about how important forests are and all the good things they do for us.
About World Forest Day:
- World Forestry Day, also known as International Day of Forests, is celebrated on March 21 each year.
- The day aims to promote the sustainable management, conservation, and development of all types of forests for the benefit of current and future generations.
The theme for International Day of Forests 2024:
- This year's theme, "Forests and Innovation: New Solutions for a Better World" highlights the critical role of innovation and technology in protecting our forests.
- From advanced monitoring systems that track deforestation to sustainable forestry practices, innovation is key to overcoming the challenges threatening our forests.
History of International Day of Forests:
- The United Nations General Assembly announced March 21 to be the International Day of Forests in 2012.
- The day aims to respect and promote the value of a wide range of forests. Countries are encouraged to take part in regional, global, and local drives to set up a scope of forest and tree-related campaigns, like planting campaigns.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the United Nations Forum on Forests are the coordinators of the International Day of Forests.
Importance of International Day of Forests:
- As per the UNGA, "The United Nations Forum on Forests and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), in collaboration with Governments, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests and other relevant organizations in the field are responsible for organizing the events and campaigns related to the World Forestry Day."
- The importance of the International Day of Forests is to spread awareness and give instruction at all levels to guarantee feasible forest management and biodiversity preservation.
The Enduring Significance of Forests:
- Forests are often referred to as the "lungs of the planet" for a reason.
They play a vital role in:
- Combating Climate Change: Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing vast amounts of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
- Protecting Biodiversity: Forests provide habitats for countless species of plants and animals, ensuring the health and balance of ecosystems.
- Providing Clean Air and Water: Forests filter air and water, regulating our climate and providing us with essential resources.
- Supporting Livelihoods: Millions of people around the world depend on forests for food, medicine, and income generation.
Celebrating and Taking Action:
- World Forestry Day is a springboard for action and we can get involved by:
- Support Organizations: Donate to or volunteer with organizations working towards forest conservation and sustainable forestry practices.
- Reduce Consumption: Make conscious choices to reduce consumption of paper and wood products, minimizing environmental footprint.
- Plant a Tree: Plant a tree in our community or support tree-planting initiatives.
- Spread Awareness: Educate ourselves and others about the importance of forests and the threats they face.
- By taking action, big or small, we can all contribute to a future where our forests continue to thrive, ensuring a healthier planet for generations to come.
World Pi Day 2024: International Day Of Mathematics And Worldwide Celebrations

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
About International Day of Mathematics:
- Every year, International Day of Mathematics (IDM) is celebrated on March 14 to spread awareness about its role in solving real-world problems.
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the International Day of Mathematics at the 40th General Conference on November 19, 2019.
- This day also sheds light on Mathematics' importance in different areas like climate change, energy, artificial intelligence, and sustainable development.
- International Day of Mathematics coincides with International Pi Day.
- Pi is one of the most widely known mathematical constants and it is rounded to 3.14, which is why it is observed on March 14.
- IDM is an opportunity to educate students about the role and importance of mathematics in improving quality of life.
- It also empowers women and girls to contribute to achieving sustainable development goals for the 2030 agenda.
History:
- The 205th session of UNESCO’s Executive Council adopted the International Day of Mathematics.
- The 40th session of UNESCO's General Conference adopted March 14 as the International Day of Mathematics, which was the first official celebration with the theme 'Mathematics is Everywhere'.
- It is an opportunity to understand the importance of mathematics in daily life promoting mathematics use for the advancement of society.
Significance:
- International Day of Mathematics is celebrated to promote Mathematics in different fields highlighting the role of mathematics in solving the real-life world and addressing social concerns.
- IDM shows the application of mathematics in different fields of life including science, technology, engineering, and economics.
- IDM promotes mathematics at different levels encouraging educators, policymakers, parents and to stress the importance of mathematics and inspire students to pursue careers in STEM fields.
- STEM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics. It is an opportunity to share research, discoveries, and insights with the general public and demystify the subject to make it more accessible.
- International Day of Mathematics is a global initiative to foster collaboration and exchange ideas across borders, cultures, and disciplines.
- The day aims to promote mathematics and help address global challenges through it.
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024:
The theme for International Day of Mathematics 2024 is 'Playing With Math.'
Govt's new code bars unethical marketing of drugs by pharma firms

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has notified a new legal code to curb the unethical marketing of drugs and banning medical representatives from using “inducement” to access healthcare professionals
About the Uniform Code of Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (UCPMP) 2024:
- The UCPMP 2024 has been implemented to regulate unethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, with a focus on promoting transparency and ethical conduct.
- The updated guidelines encompass various aspects, including drug endorsement, promotion, ethical behavior for medical representatives, and the maintenance of professional relationships with healthcare professionals.
Key provisions of the UCPMP 2024 include:
- Prohibiting the offering of gifts and travel facilities to healthcare professionals or their family members by pharmaceutical companies.
- Mandating that medical representatives should not use any form of inducement or subterfuge to gain interviews with healthcare professionals, nor should they provide payment for access under any guise.
- Holding pharmaceutical companies responsible for the actions of their medical representatives.
- Banning the supply of free drug samples to individuals who are not qualified to prescribe such products.
- Requiring each pharmaceutical company to maintain detailed records of free samples provided to healthcare practitioners, with the total value of distributed samples not exceeding two percent of the company's domestic sales per year.
- Compulsory constitution of an Ethics Committee for Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (ECPMP) by all pharmaceutical associations, along with the establishment of a dedicated UCPMP portal on their websites for implementation and monitoring purposes.
- Detailed guidelines on how drugs should be promoted in textual and audio-visual marketing materials, ensuring that information is balanced, up-to-date, verifiable, and non-misleading.
- Restrictions on making unverified claims and comparisons about a drug's usefulness, as well as using terms like "safe" and "new" without proper qualification.
- Assigning responsibility for adherence to the UCPMP 2024 to the Chief Executive Officers of pharmaceutical companies.
- Outlining penalties for violating the code and establishing a clear process for handling complaints, ensuring accountability and effective oversight.
- The UCPMP 2024 serves as a comprehensive framework for promoting ethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, aiming to protect the interests of patients, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders while fostering an environment of transparency and integrity.
Holistic Progress Card: How NCERT is planning to change student assessment

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The New Education Policy (NEP), established in 2020, proposed redesigning the assessment system of school students in India recently.
About the Holistic Progress Card (HPC):
- It Is Developed by Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development (PARAKH), a standard-setting body under the NCERT.
- The Holistic Progress Card (HPC) marks a significant departure from traditional assessment methods for students in the foundational stage (Classes 1 and 2), preparatory stage (Classes 3 to 5), and middle stage (Classes 6 to 8), aligning with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Features:
- Incorporates feedback from parents, classmates, and self-evaluation by students.
- Aims to provide a comprehensive view of students' academic performance, cognitive abilities, socio-emotional skills, and creativity during class activities.
- Aligns with the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCFSE) to prioritize learner-centric evaluation.
- Emphasizes a shift from numerical grades to a 360-degree evaluation, focusing on students' active engagement in class activities and the demonstration of diverse skills and competencies.
- Enables teachers to identify students' strengths and weaknesses, fostering personalized support and intervention.
- Encourages students to reflect on their progress and set academic and personal goals, fostering self-awareness and accountability.
- Involves parents in the learning process, integrating their insights on homework, classroom engagement, and extracurricular activities.
- Includes peer evaluation, allowing students to assess their classmates' contributions to activities.
Benefits:
- Goes beyond numerical grades, providing descriptive and analytical evaluations that encompass academic achievements and critical skill development.
- Promotes a shift from summative to formative assessment, fostering competency-based evaluation and holistic growth.
Analysis of Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23 Report

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The per capita monthly household expenditure more than doubled in 2022-23 as compared to 2011-12, according to the latest study by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO).
Context:
- As per the 2022-23 report, rising inequality between the top and bottom of the pyramid.
- Urban and rural households register higher expenditure, spending less on food items.
- New methodology and questionnaire used in Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2022-23.
About the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO):
- The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) comes under the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation headed by a Director General.
- It is responsible for the conduct of large-scale sample surveys in diverse fields on an All-India basis.
- Primarily data are collected through nationwide household surveys on various socio-economic subjects, Annual Survey of Industries (ASI), etc.
- Besides these surveys, NSSO collects data on rural and urban prices and plays a significant role in the improvement of crop statistics through supervision of the area enumeration and crop estimation surveys of the State agencies.
- It also maintains a frame of urban area units for use in sample surveys in urban areas.
The NSSO has four Divisions:
- Survey Design and Research Division (SDRD): This Division, located at Kolkata, is responsible for the technical planning of surveys, formulation of concepts and definitions, sampling design, designing of inquiry schedules, drawing up of tabulation plans, and analysis and presentation of survey results.
- Field Operations Division (FOD): The Division, with its headquarters at Delhi/Faridabad, is responsible for the collection of primary data for the surveys undertaken by NSS.
- Data Processing Division (DPD): The Division, with its headquarters at Kolkata is responsible for sample selection, software development, processing, validation and tabulation of the data collected through surveys.
- Survey Coordination Division (SCD): This Division, located in New Delhi, coordinates all the activities of different Divisions of NSS.
- It also brings out the bi-annual journal of NSS, titled “Sarvekshana”, and organizes National Seminars on the results of various Socio-economic surveys undertaken by NSS.
Key Insights From the 2022-23 Survey:
- Evolution of Food Expenditure: Over the past two decades, there has been a notable shift in spending patterns on food in India.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2022-23, both urban and rural households witnessed a gradual decline in the share of expenditure allocated to food.
- This period marks the first instance where food expenditure has dropped to below 50% in rural India and below 40% in urban India.
- Changing Dietary Preferences: The composition of food consumption has also undergone significant changes.
- Cereals and pulses have seen a reduction in their share of overall food consumption expenditure, while spending on milk has surged, surpassing that on cereals and pulses combined.
- In a noteworthy shift, the average Indian now spends more on fruits and vegetables than on food grains.
- Furthermore, expenditure on animal proteins like eggs, fish, and meat has shown a growing trend, indicating a preference for animal-based proteins over plant-based ones.
- Rise in Processed Food Consumption: There has been an observed increase in the share of expenditure allocated to processed foods, beverages, and purchased cooked meals.
- This trend aligns with the Engel Curve hypothesis, suggesting that as incomes rise, households allocate a smaller proportion of their spending to food and tend to prefer superior items over inferior ones.
- Closing Rural-Urban Consumption Gap: Consumption growth in rural areas has outpaced that in urban areas, leading to a narrowing of the rural-urban consumption divide.
- If this trend continues, it could potentially lead to parity in urban and rural incomes and consumption patterns in the future.
- Challenges in Inflation Calculation: The findings of the latest Household Consumption Expenditure (HCE) Survey underscore the need to review the inflation basket.
- The current Consumer Price Index (CPI)-based inflation calculation, established in 2012, may not accurately reflect contemporary consumption patterns.
- For instance, the disparity between the weightage assigned to cereals in the CPI basket and actual expenditure on cereals by rural households highlights the need for recalibration.
- Insights on Poverty Reduction: According to NITI Aayog CEO B V R Subrahmanyam, the latest survey indicates a reduction in poverty to five per cent nationwide.
- Both rural and urban areas are witnessing increased prosperity, as evidenced by rising per capita monthly expenditure.
- Demand for Legal Guarantee to MSP: While there is a demand for a legal guarantee to Minimum Support Price (MSP) for 23 crops, including food grains and sugarcane, the survey data suggests that the growth in the farm sector is being primarily driven by livestock, fisheries, and horticulture crops.
- This poses a pertinent question regarding the promotion of production: should the focus be on crops outside the MSP purview, such as milk, fish, poultry products, fruits, and vegetables, given their growing consumption trends?
India contributes $1 million to fund combating poverty and hunger

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, India has contributed 1 million US Dollars to the Poverty and Hunger Alleviation Fund established by India, Brazil, and South Africa, IBSA.
What is the IBSA Fund?
- Established in 2004 and operational since 2006, the IBSA Fund embodies the collaborative efforts of India, Brazil, and South Africa.
- Contributing one million dollars annually each, the IBSA countries unite in a spirit of partnership to champion Southern-led, demand-driven projects in developing nations.
- With a focus on identifying replicable and scalable initiatives, the fund aims to address pressing development challenges in recipient countries.
- Supported projects align with partner countries' national priorities and international development agendas, including the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The fund's objectives encompass diverse areas such as promoting food security, combating HIV/AIDS, and expanding access to safe drinking water, among others, to advance sustainable development.
- To date, the IBSA Fund has allocated USD 50.6 million, funding 45 projects across 37 countries in the Global South.
- The United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC) fulfils the roles of Fund Manager and Secretariat for the IBSA Fund.
What is IBSA?
- IBSA stands for the India, Brazil, and South Africa Dialogue Forum, a unique platform that unites three major democracies and significant economies from diverse continents, collectively addressing common challenges.
- Formally established as the IBSA Dialogue Forum during a historic meeting of the Foreign Ministers from India, Brazil, and South Africa in Brasilia on June 6, 2003, the forum's inception was marked by the issuance of the Brasilia Declaration.
- To date, five IBSA Leadership Summits have been convened, with the 5th Summit held in Pretoria on October 18, 2011.
- In 2021, India held the chairmanship of IBSA under the theme "Democracy for Demography and Development."
- On March 2, 2023, Brazil assumed the rotating presidency of the India, Brazil, South Africa Dialogue Forum (IBSA), further advancing the forum's collaborative agenda.
BSNL floats Rs 65,000 crore tender for phase-III BharatNet project

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
BSNL, the state-owned telecommunications company, has initiated a tender process amounting to approximately Rs 65,000 crore for the implementation of the phase-III BharatNet project.
What is the BharatNet Phase III Project?
- The BharatNet phase-III project adopts a three-level architecture:
- Internet leased line bandwidth
- Middle-mile connectivity, and
- Last-mile connectivity
- It aims to involve village-level entrepreneurs or Udyamis in providing last-mile connectivity to households on a revenue-sharing basis.
- BSNL aims to provide 15 million home fibre connections over five years using the BharatNet Udyami model.
About BharatNet Project:
- The BharatNet Project is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world.
- It aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats across India in a phased manner.
- Its core objective is to ensure equitable access to broadband services for all telecom service providers, fostering the deployment of services like e-health, e-education, and e-governance in rural and remote areas.
- Initiated in 2011 and executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in 2012, the project operates in three phases.
- Phase I launched in 2011, focused on creating the National Optical Fibre Network, leveraging existing infrastructure and laying additional fibre to bridge connectivity gaps up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Phase II, approved in 2017, builds upon Phase I’s experiences, aligning with the Digital India vision.
- It adopts a flexible approach, integrating various media such as Optical Fibre Cable (OFC), Radio, and satellite to connect Gram Panchayats, utilizing models like State-led, Private Sector, and CPSU Models for implementation.
- Phase III, spanning from 2019 to 2023, aims to establish a robust, future-ready network with district-to-block fibre connectivity, featuring ring topology for redundancy.
- This comprehensive approach ensures the creation of a resilient and inclusive telecom infrastructure, facilitating socio-economic development in rural India.
Employer Rating Survey to Assess Women Participation in Workforce (Business Standard)

- 31 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
To bolster the representation of women in the workforce and advance gender equality, various ministries of the central government issued a series of advisories and surveys on Tuesday, aimed at industries and employers.
About the Survey:
- This survey aims to evaluate the prevalence of women-friendly practices across the nation's workplaces.
- The government is collecting information on several key aspects, including the establishment of internal complaints committees (ICC) for preventing sexual harassment, the provision of childcare facilities, ensuring pay equity, offering flexible or remote work options for women, and providing safe transportation during late hours.
- Additionally, various ministries of the Central government have issued advisories to enhance women's representation in the workforce.
Factors Affecting Low Women Workforce Participation:
- Cultural and Social Norms: Traditional gender roles and societal expectations often discourage women from pursuing full-time employment due to responsibilities for caregiving and homemaking, limiting their participation in the workforce.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to quality education can hinder women from acquiring the necessary skills and qualifications for certain jobs, further reducing their workforce participation.
- Gender Pay Gap: Disparities in wages between men and women discourage women from entering or remaining in the workforce, contributing to lower participation rates.
- Structural Constraints: India's manufacturing and service sectors often have rigid structures that limit employment opportunities, particularly in the informal sector where many women work.
- Security Concerns: Instances of sexual harassment in the workplace create safety concerns for women, acting as a barrier to their participation in the labour force.
Government Initiatives Supporting Women's Empowerment:
- Code on Wages, 2019: Ensures equal pay for equal work without discrimination based on gender, fostering fairness in wage practices across establishments.
- Code on Occupational Safety, Health And Working Conditions (OSH), 2020: Proposes amendments to improve employment conditions for women workers, particularly in above-ground mines, ensuring their safety and well-being.
- Maternity Benefit Act, 2017: Enhances maternity benefits and fosters a healthier work environment for pregnant and nursing women, promoting their well-being and work-life balance.
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh (RMK): A national organization offering microfinance services to empower economically disadvantaged women, supporting their livelihood projects and economic independence.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Focuses on creating sustainable self-employment opportunities for rural women through skill training, capacity building, and financial assistance, enabling them to engage in income-generating activities.
- MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act): Guarantees 100 days of wage employment annually to rural households, actively encouraging women's participation and ensuring equitable employment opportunities.
Way Forward
Continued government initiatives aimed at empowering women in the workforce through skill development and expanded employment opportunities have yielded positive results, as evidenced by the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) released by the Labour Bureau in 2023. This survey indicated a notable increase in women's participation, rising from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37% in 2022-23.
Interim Budget 2024: Exporters seek higher allocation for MAI scheme (Business Standard)

- 27 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the interim Budget 2024, exporters have urged the government to allocate funds worth $3.88 billion for the Market Access Initiative (MAI) scheme to promote Indian exports and help them hit the ambitious $2 trillion target by 2030.
What is the Market Access Initiatives (MAI) Scheme?
- The Market Access Initiative (MAI) Scheme is an Export Promotion Scheme envisaged to act as a catalyst to promote India’s exports on a sustained basis.
- The scheme is formulated on a focus product-focus country approach to evolve specific markets and specific products through market studies/surveys.
- Assistance would be provided to Export Promotion Organizations/Trade Promotion Organizations/National Level Institutions/ Research Institutions/Universities/Laboratories, Exporters etc., for enhancement of exports through accessing new markets or through increasing the share in the existing markets.
- Under the Scheme, the level of assistance for each eligible activity has been fixed.
- The following activities will be eligible for financial assistance under the Scheme:
- Marketing Projects Abroad
- Capacity Building
- Support for Statutory Compliances
- Studies
- Project Development
- Developing Foreign Trade Facilitation Web Portal
- To support Cottage and handicraft units
How does the MAI Scheme work?
- The scheme’s primary goal is to facilitate export growth by enabling entities to enter new markets or enhance their presence in existing markets.
- To accomplish this, the scheme provides predetermined levels of assistance for each eligible activity.
- By directing attention to key products and specific markets, the MAI Scheme serves as a catalyst for driving India’s export expansion in a sustainable and strategic manner.
Who is eligible to receive assistance under the MAI Scheme?
- Various entities are eligible to receive financial assistance under the MAI Scheme, including:
- Export promotion organizations
- Trade promotion organizations
- National level institutions
- Research institutions
- Universities
- Laboratories
- Individual exporters
- Start-ups
Who administers the MAI Scheme?
- The MAI Scheme is administered by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, through the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
India signs an agreement to acquire five lithium mines in Argentina (Business Standard)

- 17 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Indian govt. signed an agreement to acquire five lithium brine blocks for exploration and development in Argentina.
Context:
- The Mines Ministry, operating through KhanijBidesh India Limited (KABIL), has entered into an agreement with Argentina's state-owned CAMYEN for the development of five lithium blocks.
- CAMYEN, officially known as Catamarca Minera Y Energetica Sociedad Del Estado, is headquartered in the Catamarca province of the Latin American nation.
- Key Points: KABIL, a government-owned entity, will initiate the exploration and development activities for five lithium brine blocks—Cortadera-I, Cortadera-VII, Cortadera-VIII, Cateo-2022-01810132, and Cortadera-VI, collectively spanning an area of approximately 15,703 hectares.
- As part of its expansion, KABIL is planning to establish a branch office in Catamarca, Argentina.
- This marks a significant milestone as it represents the first lithium exploration and mining project undertaken by a government company in India.
- Argentina, situated within the global "Lithium Triangle" alongside Chile and Bolivia, collectively possesses more than half of the world's total lithium resources.
Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL):
- It is a Joint Venture Company among National Aluminium Company (NALCO), Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL) and Mineral Exploration Corporation Limited (MECL).
- It has been formed in August 2019.
- KABIL is focusing on identifying and sourcing battery minerals like Lithium and Cobalt.
- KABIL is a joint venture company focused on identifying, acquiring, developing, processing and making commercial use of strategic minerals in overseas locations for supply in India.
Current Statistics About Lithium in India:
- India has recently discovered 5.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves in Jammu & Kashmir and ranks seventh globally.
- The primary lithium reserve in India has been discovered in the Salal-Haimana area of Reasi District in Jammu and Kashmir, with additional smaller reserves identified in Karnataka.
- Presently, India fulfils its entire lithium demand through imports.
- In the fiscal year 2023, there was a notable increase in lithium imports in India, reaching approximately $3 billion (around ?24,900 crore), indicating a 58% growth compared to the figures in FY22.
- More than 95% of India's lithium imports are sourced from China and Hong Kong.
Global Reserves of Lithium:
- Approximately half of the world's lithium resources are concentrated in Latin America, primarily in countries such as Bolivia, Argentina and Chile along with significant deposits in USA, Australia and China.
- Bolivia has the highest identified lithium resources in the world with 20 million tonnes, as per the US Geological Survey data.
- Argentina has the second-largest lithium reserve estimated to be close to 20 million tonnes.
- The United States follows Argentina with 12 million tonnes of lithium reserves.
- Chile ranks fourth globally with 11 million tonnes of lithium reserves.
- Australia occupies the fifth spot with 7.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves, according to the available data.
- China, the largest country in Asia, ranks sixth globally with 6.8 million tonnes of lithium reserve. China, without having the largest lithium reserves, continues to dominate lithium mining and processing in the world.
- Argentina holds a substantial portion, accounting for 20% of the world's total lithium resources, making it the second-largest contributor after Bolivia.
- Argentina is a key participant in the 'Lithium Triangle,' alongside Chile and Bolivia.
- Collectively, these three nations possess over two-thirds of the global lithium resources.
- The Lithium Triangle is a region in the Andes known for its rich lithium reserves.
- Notably, Argentina ranks second globally in terms of lithium resources, third in lithium reserves, and fourth in lithium production.
Importance of the Agreement:
- This agreement holds strategic value as it enables India to enhance its lithium supply, fostering the growth of both countries' lithium mining and downstream sectors.
- It contributes to the diversification of the supply chain for essential materials, aligning with the pursuit of Global Net Zero objectives.
- Given that a significant portion, approximately 54%, of India's lithium imports are currently sourced from China, which dominates 80% of the global supply, this deal helps reduce dependence on a single supplier.
- The initiative aligns with the Mineral Security Partnership (MSP), of which India is an active participant.
Govt extends PLI scheme for the auto sector by a year with 'partial amendments' (Business Standard)

- 02 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Ministry of Heavy Industries announced the extension of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Automobile and Auto Components by one year with "partial amendments".
PLI Scheme for Automobile Sector:
- The Union Cabinet approved the PLI-Auto Scheme in 2021, allocating a budgetary outlay of Rs. 25,938 crore for five years (FY2022-23 to FY2026-27).
- Aimed at enhancing the production of Advanced Automotive Technology (AAT) Products, the PLI-AUTO Scheme is designed to promote extensive localisation for AAT products and facilitate the development of both domestic and global supply chains.
- This scheme primarily targets Zero Emission Vehicles (ZEVs), specifically Battery Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles.
- In a recent amendment, the incentive period was extended to cover five consecutive financial years, commencing from the financial year 2023-24, with disbursement scheduled for the subsequent financial year, 2024-25.
- The amended scheme stipulates that approved applicants can avail benefits for five consecutive financial years, but the eligibility period will not extend beyond the financial year ending on March 31, 2028.
- Additionally, the amendments specify that if an approved company fails to meet the determined threshold for an increase in Determined Sales Value over the initial year's threshold, it will not receive any incentives for that particular year.
What is the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Programme?
- Around 5 years ago, the Indian government aimed to stimulate domestic manufacturing by encouraging more companies to produce goods.
- Recognizing manufacturing as a crucial driver of economic growth with a multiplier effect, wherein each job and investment in manufacturing positively influences other sectors, the government introduced the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme.
- Under the PLI scheme, both foreign and domestic companies engaged in manufacturing receive financial incentives from the government.
- The annual incentive payout is determined as a percentage of the revenue generated by these companies and is applicable for a period of up to five years.
DGCA Implements New Rules for Hang Gliders (Business Standard)

- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Aviation regulator DGCA has issued amended norms for operating powered hang gliders in the country.
About Hang Gliders:
- A hang glider is a distinctive type of aircraft that relies on air currents to remain airborne, setting it apart from conventional aircraft with engines and propellers.
- These aerodynamic marvels depend on wind dynamics for lift rather than propulsion.
- Operational Mechanics: Due to their unpowered nature, hang gliders necessitate launching from elevated points such as hills or mountains.
- Gravity, acting as the primary force, encompasses the weight of both the pilot and the wing.
- This weight generates thrust, propelling the aerofoil through the air.
- The aerofoil's distinctive shape prevents the hang glider from descending rapidly and facilitates lift.
- The aerofoil's design manipulates airflow, compelling the air above the wing to move faster, creating a low-pressure area.
- Simultaneously, the wing's downward and forward motion compresses the air beneath, fostering lift as the aerofoil is drawn into the low-pressure zone.
- Pilots maintain control during flight by manipulating the trapeze and adjusting direction and speed.
- Powered Hang Gliders: In a departure from traditional hang gliders, powered hang gliders integrate features of both hang gliders and powered aircraft.
- Equipped with a small engine, these variants enable pilots to take off and sustain flight without relying on natural elements like thermals or wind conditions, making them accessible to less-experienced aviators.
DGCA Regulations for Powered Hang Gliders:
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) mandates strict regulations governing powered hang gliders:
- Operation Authorization: Individuals must obtain prior authorization from a DGCA-approved examiner or instructor before operating a powered hang glider.
- Examiner Qualifications: Approved examiners must possess a minimum of 50 hours of experience on powered hang gliders, including at least 10 hours on a dual machine.
- Test Flight Criteria: Individuals conducting test flights must meet specific criteria, holding a valid Commercial Pilot Licence (CPL) with at least 25 hours of flying experience on a powered hang glider or authorization with 50 hours of flying experience.
- Transaction Certification: The sale or transfer of a powered hang glider requires a DGCA-issued certificate following a background check conducted by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Lease and Operation Restrictions: Owners or operators are prohibited from leasing, renting, or lending powered hang gliders.
- The use of certain equipment and devices is strictly regulated, with explicit permissions required.
- Safety Protocols: Security measures endorsed by the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) are obligatory at parking and operational locations, ensuring compliance with established guidelines for safe flight operations.
BCCC Cautions Entertainment Channels on Depicting SCs, STs. (Business Standard)

- 17 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Broadcasting Content Complaint Council (BCCC) on Tuesday asked entertainment channels to exercise "extreme caution" while portraying the scheduled castes and scheduled tribes in television programmes to avoid hurting the sentiments of the members of the two communities.
About the Broadcasting Content Complaints Council (BCCC):
- The Indian Broadcasting and Digital Foundation (IBDF) established the BCCC in June 2011 as an independent self-regulatory body.
- Regulatory Role: The primary function of the BCCC is to enforce self-regulatory guidelines for non-news channels, covering general entertainment, kids, and special interest channels.
- Formulation of Guidelines: Guidelines address crucial areas, including national interest, racial and religious harmony, treatment of children, social values, explicit content (sex and nudity), violence, crime, gambling, drugs, smoking, tobacco, alcohol, defamation, harm, and offence.
- Complaint Lodging Process: Any viewer can file a complaint regarding television programs, non-news channels, and digital content of IBDF India members.
- Composition of BCCC:
- The council comprises 13 members, including a chairperson, four non-broadcast members, four representatives from national-level statutory commissions, and four members from the broadcast industry.
- Functioning Mechanism: Upon receiving a valid complaint, the concerned channel is required to present its viewpoint on the contested content within one working week.
- If the BCCC committee finds the channel's response unsatisfactory, it holds the authority to issue directives, mandating modifications or withdrawal of the content.
- Reporting to Authorities: In case of non-compliance with directives, the BCCC promptly submits a detailed report to the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting within 24 hours.
Key Details about the Indian Broadcasting & Digital Foundation (IBDF):
- Founded in 1999, the Indian Broadcasting Foundation initially served as the apex body for broadcasters.
- Recently rebranded as the Indian Broadcasting and Digital Foundation (IBDF) to encompass digital platforms, consolidating oversight over all digital over-the-top streaming firms.
- Representative Role: Recognized as the official spokesperson for the Indian broadcasting industry, IBDF plays a crucial role in articulating industry perspectives.
- IBDF's membership includes a diverse range of channels, covering both news and non-news categories such as General Entertainment Channels (GEC), sports, music, movies, and infotainment.
- Actively involved in providing research-based legislative inputs to the government, IBDF engages in advocacy efforts on various fronts, including fiscal, regulatory, and business issues.
- The organization plays a pivotal role in facilitating the formulation of favourable policies, addressing industry challenges, and advocating for essential changes in the overall system.
Amazon River Hits Lowest Levels in a Century Amid Drought in Brazil (Business Standard)

- 16 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The Amazon River fell to its lowest level in over a century on Monday at the heart of the Brazilian rainforest as a record drought upended the lives of hundreds of thousands of people and damaged the jungle ecosystem.
About the Amazon River:
- The Amazon River holds the distinction of being the world's largest river in terms of both water volume and width.
- Length and Course: Spanning an impressive 6,400 kilometres, it is the second-longest river globally, surpassed only by the Nile.
- Originating high in the Andes Mountains, the river courses its way eastward through vast rainforests and lowlands before reaching its culmination at the northeastern coast of Brazil, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Dynamic Width: During the dry season, the Amazon River exhibits a width ranging from 4 to 5 kilometres, expanding significantly to 50 kilometres in certain areas during the wet season.
- Unparalleled Drainage Area: The Amazon boasts the largest drainage area globally, with its watershed spanning across Brazil, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Bolivia.
- Approximately two-thirds of the Amazon's mainstream and the majority of its basin lie within the borders of Brazil.
- Water Discharge and Global Impact: With a staggering water discharge of 300,000 cubic meters per second into the Atlantic Ocean, the Amazon contributes one-fifth of the total freshwater volume entering the world's oceans.
- This immense water flow plays a pivotal role in regulating global oxygen and carbon cycles.
- Extensive Tributaries: Featuring over 1,100 tributaries, including seventeen exceeding 1,500 kilometres in length, notable contributors include the Rio Negro, the Madeira River, and the Xingu River.
- Environmental Significance: The Amazon Rainforest, constituting approximately half of the Earth's remaining rainforest, stands as the largest repository of biological resources.
- Often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," the Amazon plays a crucial role in maintaining the planet's oxygen and carbon balance.
Three heritage projects in Punjab and Haryana bag UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards 2023 (Business Standard)

- 23 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The resilient urban revitalisation of Rambagh Gate and Ramparts in Punjab, and heritage conservation projects related to Haryana's Church of Epiphany and Delhi's Bikaner House won Unescoawards on Thursday.
About Rambagh Gate & Ramparts:
- A three-story architectural marvel, the Rambagh Gate underwent meticulous restoration employing traditional building techniques.
- Locally sourced materials, including Nanak Shahi bricks set in lime mortar, were integral to the restoration process.
About Pipal Haveli, Gurdaspur:
- Pipal Haveli in Gurdaspur stands as a testament to ecological and traditional building methods, incorporating locally sourced materials and embracing vernacular architectural language.
- Notably, it actively promotes women's empowerment through initiatives like the BaRi Collective, offering programs that enhance women's livelihoods through environmentally conscious craft practices.
What is the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation?
- UNESCO aims to promote private sector engagement and foster collaborations between the public and private sectors to preserve the cultural heritage of the Asia-Pacific region for the benefit of present and future generations.
- Since the year 2000, the UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation have been acknowledging the accomplishments of private sector entities and public-private initiatives in effectively conserving or restoring structures, places, and properties of significant heritage value in the region.
- Noteworthy, among the recognized sites, five are located in China, six in India, and one in Nepal.
- Highlights of Award-Winning Sites in India:
- Rambagh Gate in Amritsar: Received the prestigious "Award of Excellence," the highest recognition across all categories.
- Pipal Haveli in Punjab: Honored for its sustainable development as a heritage rural homestay.
- Karnikara Mandapam at Kunnamangalam Bhagawati Temple in Kerala: Earned the esteemed "Award of Distinction."
- Epiphany in Haryana, David Sassoon Library and Reading Room in Mumbai, and Bikaner House in New Delhi: Recognized with the "Award of Merit" for their outstanding contributions to cultural heritage conservation.
Govt Notifies Changes in PLI Scheme for White Goods (Business Standard)

- 11 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The central government has introduced changes to the rules governing the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for white goods, specifically air conditioners and light-emitting diode lights, with the goal of ‘simplifying the scheme’s operations’ and promoting the ease of doing business, according to an official statement on Wednesday.
What are White Goods?
- Major home appliances, commonly known as white goods, encompass substantial household devices like stoves, refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, tumble dryers, dishwashers, and air conditioners.
- While these durable consumer durables were initially available only in white, contemporary options offer a variety of colours, yet they persistently retain the term "white goods."
- Renowned for their robustness and extended lifespan, white goods are engineered to endure the rigours of daily use.
- Additionally, the term "white goods" may extend to white fabrics, particularly linen or cotton, including items like curtains, towels, or sheets, which historically were crafted from white cloth.
- In the beverage industry, the term "white goods" refers to colourless spirits such as vodka or gin.
What is Brown Goods?
- Brown goods refer to relatively lightweight electronic consumer durables, including computers, digital media players, TVs, and radios.
- In contrast to large household appliances (white goods), brown goods are primarily geared towards entertainment, communication, and convenience.
- Typically featuring electronic components, these devices are designed to deliver audio, video, or data-related services as their primary functions.
What is Grey Goods?
- When a commodity is traded through distribution channels, which are unofficial but legal are known as the grey goods.
- They are goods that are traded in a specific area, where the manufacturer does not intend to sell the product, but with different specifications.
- Grey goods are sold without the knowledge of the original manufacturer.
- They are typically less costly than the ones that are available by the authorised distributor.
- Also, they might be made to pertain to some jurisdiction.
- Example: A factory-unlocked version of the iPhone. It is made to suit US standards but is sold in India for a lesser price than the iPhone made for Indian standards.
- When it comes to such Grey goods, the manufacturer does not provide any warranty for the product.
INS Imphal (Business Standard)

- 29 Nov 2023
Why is it in the News?
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently unveiled the crest of the Indian Navy's stealth-guided missile destroyer Imphal.
About INS Imphal:
- INS Imphal is the third ship in the Visakhapatnam-class stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- INS Imphal is the third of the four Project 15B stealth-guided missile destroyers.
- It's one of the biggest destroyers made in India, measuring 164 meters long and weighing over 7500 tonnes.
- Powered by Combined Gas and Gas (COGAG) propulsion, the ship is capable of achieving speeds in excess of 30 knots (56 km/hour).
- It's equipped to handle various tasks in maritime warfare.
- The ship boasts a high indigenous content of approximately 75 percent that includes BrahMos surface-to-surface missiles, medium-range surface-to-air missiles, anti-submarine indigenous rocket launchers, and 76mm super rapid gun mount.
- "Designed by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau and built by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited, Imphal is a hallmark of indigenous shipbuilding and is amongst the most technologically advanced warships in the world.
- The crest design on the ship represents the Kangla Palace and 'Kangla-Sa.'
- The Kangla Palace is a historical and archaeological site in Manipur, serving as the traditional seat of the past kingdom.
- On the right side of the crest, 'Kangla-Sa' is depicted—a mythical being with a dragon's head and lion's body from Manipur's history, symbolizing the guardian of its people.
- ‘Kangla-Sa' is also the state emblem of Manipur.
- Interestingly, INS Imphal is the first capital warship named after a city in the northeast—Imphal, the capital of Manipur.
Card-on-File Tokenisation (CoFT) (Business Standard)

- 18 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Recently, Visa has highlighted that the primary advantage of tokenization is a decreased risk of data breaches.
What is Card-on-File Tokenisation?
- Tokenisation is a process where the cardholder’s original card number, one which is written on the card and is extensively used for transactions and card identification, is replaced with a surrogate term called ‘token.’
- This process allows enhanced card protection by converting the customers’ card numbers into tokens.
- The exchange of tokens happens between the token requestor and the network, which empowers customers to receive a secure and reliable online payment experience.
- All relationship evidence of such exchange between token and crucial card information is securely saved in a vault that is only accessible to the card networks.
- Resultantly, the customers’ card details will be highly protected from online fraud and hackers.
How Does Card-on-File Tokenisation Work?
- When a customer makes a transaction by using their card at a tokenisation-based-authentication server:
- A credit/debit card is used for transactions at a POS device or an e-commerce website
- The tokenisation system receives and interprets the credit card number
- The tokenisation system goes on to replace the original credit card number with a 16-digit random character token for security
- The tokenisation system then provides the converted 16-digit random token number to the e-commerce marketplace and replaces the user’s credit card number with the same in their system
- For instance, card number (example): 4018 2255 6984 7854 will be replaced with token number: 4325 5214 8574 6658.
- The tokenisation system is an important tool for separating crucial data in ecosystems and databases while also offering enhanced card protection to cardholders.
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) (Business Standard)

- 17 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
Among 1.39 million cyber security cases last year, vulnerable services made up 875,892 of the total incidents tackled by Cert-In
What is CERT-In?
- CERT-In stands for the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team.
- It is a government agency that functions under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It was established in January 2004 with the objective of securing Indian cyberspace.
- It is the national nodal agency for dealing with cyber security threats like hacking and phishing.
- It strengthens the security-related defence of the Indian Internet domain.
- The Information Technology Act of 2000 designated CERT-In to serve as the national agency to perform the following functions in the area of cyber security:
- Prevention of cyber attacks: CERT-In works to prevent cyber attacks by issuing advisories and guidelines to organizations and users.
- It also conducts vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and remediate security weaknesses.
- Incident response: It provides technical assistance to organizations that have been affected by cyber-attacks.
- It helps them to contain and recover from the incident, and to minimize the damage.
- Cyber security awareness: It raises cyber security awareness among the Indian public through various initiatives, such as workshops, seminars, and online resources.
- Coordination with other agencies: CERT-In coordinates with other cyber security agencies in India and around the world to share information and best practices.
- The constituency of CERT-In is the Indian cyber community and Indian cyberspace.
- CERT-In provides services to organisations in the Government, Public, and Private sectors.
- In addition, CERT-In provides services to individuals and home users as well.
- Disclosure of information will be followed in accordance with Indian Constitutional laws.
Here to enhance partnership between EFTA, India: Norway's trade minister (Business Standard)

- 14 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Norway's Minister of Trade and Industry Jan Christian Vestre has said his India visit aims to enhance collaboration between European free trade partners and India and improve framework conditions for job creation, value creation, and investments.
About the European Free Trade Association (EFTA):
- The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is an intergovernmental organization established in 1960 by the Stockholm Convention.
- Its core objective is to foster free trade and economic integration among its member countries, both within Europe and on a global scale.
- Member Countries: EFTA comprises four member countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland.
- These nations are characterized by open, competitive economies, demonstrating a shared commitment to progressively liberalize trade both within multinational forums and through individual free trade agreements.
- Customs Distinction: Unlike the European Union (EU), EFTA operates differently as it is not a customs union.
- This key distinction allows each EFTA State the autonomy to establish its own customs tariffs and formulate foreign trade measures independently concerning non-EFTA States.
- Association Responsibilities:
- EFTA manages various aspects crucial to its objectives, including:
- Facilitating free trade among EFTA countries.
- Overseeing EFTA's engagement in the European Economic Area (EEA), encompassing the European Union and three EFTA countries (Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, excluding Switzerland).
- Managing EFTA's extensive network of free trade agreements globally.
- Free Trade Agreement Network: EFTA member countries boast one of the largest networks of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) globally.
- This comprehensive network spans over 60 countries and territories, incorporating the European Union among others.
EFTA plays a pivotal role in promoting economic collaboration, free trade, and global engagement, distinguishing itself from the EU through its approach to customs and foreign trade measures.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- A Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is an agreement between two or more nations aimed at lowering barriers to imports and exports among them.
- In a free trade scenario, goods and services can move across international borders with minimal government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or restrictions hindering their exchange.
- The principle of free trade stands in contrast to trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs come in various forms, including Preferential Trade Agreements, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements, and Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPA).
Amit Shah to chair 26th meeting of Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar on Sunday (Business Standard)

- 09 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah will chair the 26th meeting of the Eastern Zonal Council in Bihar's capital on Sunday, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) said on Saturday.
What are Zonal Councils?
- The conceptualization of Zonal Councils can be attributed to the visionary initiative of India's first Prime Minister, Pandit Jawahar Lal Nehru, in 1956.
- These councils are statutory bodies established by an Act of Parliament, namely the States Reorganisation Act of 1956.
- The act delineated the country into five zones (Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern), assigning a Zonal Council to each.
Present Composition of Zonal Councils:
- Northern Zonal Council: Includes Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, National Capital Territory of Delhi, and Union Territory of Chandigarh.
- Central Zonal Council: Encompasses Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Eastern Zonal Council: Comprises Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, and West Bengal.
- Western Zonal Council: Involves Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
- Southern Zonal Council: Consists of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Exclusion and Special Council: The North Eastern States (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Nagaland) are not part of Zonal Councils.
- Instead, their unique challenges are addressed by the North Eastern Council, established under the North Eastern Council Act of 1972.
- Sikkim was included in the North Eastern Council in 2002.
Organizational Structure:
- Chairman: The Union Home Minister serves as the Chairman for each Zonal Council.
- Vice Chairman: Chief Ministers of the states in each zone act as Vice-Chairman, rotating annually.
- Members: Chief Minister and two nominated Ministers from each state, along with two members from Union Territories in the zone.
- Advisers: Planning Commission nominees, Chief Secretaries, and another officer/Development Commissioner from each state in the zone.
Objectives:
- The primary objectives of Zonal Councils include promoting national integration and curbing acute State consciousness, regionalism, linguism, and particularistic tendencies.
- Additionally, they aim to facilitate cooperation, idea exchange, and a climate of collaboration among states for the successful execution of development projects.
Functions:
- Zonal Councils function as advisory bodies, empowered to discuss common interests between the Union and represented states.
- They can recommend courses of action to the Central Government and individual state governments.
- Specific areas of discussion may include economic and social planning, border disputes, linguistic minorities, inter-state transport, and matters arising from the reorganization of states under the States Reorganisation Act.
Infrastructure investment trust (InvIT) (Business Standard)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The government is actively developing a proposal to introduce a new Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) dedicated to national highways. This initiative aims to enable domestic retail investors to own units of the trust, expanding opportunities for individual investors to participate in highway infrastructure projects.
What is Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT)?
- An Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) functions as a Collective Investment Scheme, offering a pathway for both individual and institutional investors to directly invest in diverse infrastructure projects.
- Operating akin to mutual funds, InvITs are established as trusts and undergo registration with Sebi (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
- InvITs involve four key parties:
- the Trustee, Sponsor(s), Investment Manager, and Project Manager. The Sebi-certified Trustee assumes the crucial role of overseeing the InvIT's performance. Meanwhile, the Sponsor(s) act as the company's promoters responsible for creating and setting up the InvIT.
- Overall, InvITs present an attractive investment option, as they allow investors to participate in the development of vital infrastructure projects while enjoying the benefits of a collective investment structure similar to mutual funds.
What is NHAI InvIT?
- NHAI InvIT is an infrastructure investment trust proudly sponsored by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) to bolster the government's National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) initiative.
- This Trust has been established by NHAI in accordance with the Indian Trusts Act, of 1882, and adheres to the regulations set forth by SEBI (Security and Exchange Board of India).
- The NHAI InvIT plays a vital role in supporting the nation's infrastructure development by providing a platform for investors to participate in highway projects' growth and monetization.
- Through this innovative investment vehicle, NHAI aims to tap into private and institutional investments to enhance the funding and execution of critical infrastructure projects across the country, ultimately contributing to India's overall economic progress.
Will India reassess its position on China-backed Asian trade bloc RCEP? (Business Standard)
- 05 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India is keeping a watchful eye on its neighbour countries’ recent deliberations to join the China-backed Asian trade bloc, Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), although the government is yet to “re-evaluate” the position it took four years ago.
What is Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)?
- RCEP, or the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, is a proposed agreement involving ASEAN member states and their free trade agreement partners.
- Introduced in 2011, negotiations started in 2012, aiming to finalize the deal by November 2019.
- After the withdrawal of India, there are 15 members of RCEP, which includes 10 ASEAN countries and 5 other countries, namely:
- Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- RCEP's objective is to establish an integrated market, facilitating the availability of products and services across the region.
- The negotiations cover trade, investment, intellectual property, dispute settlement, e-commerce, SMEs, and economic cooperation.
- Initially proposed by Beijing in 2012 to counter the Trans-Pacific Partnership, RCEP became a key tool for China after the U.S. withdrew from the TPP in 2016.
- India chose not to sign the RCEP in 2019 due to concerns about its industries competing with China and potential flooding of Indian markets.
- Despite some sectors anticipating gains, India emphasized the need for a deal favorable to all countries and sectors.
FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE (FATF) (Business Standard)
- 31 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), an inter-governmental body that sets anti-money laundering standards, has removed the offshore tax haven Cayman Islands from its ‘grey list’.
Facts About:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an intergovernmental organization that was founded in 1989 as part of the G7's effort to develop laws to combat money laundering.
- Its directive was extended to cover financing of terrorism in 2001.
- Only a few nations are listed in the grey and black lists that the FATF releases.
- To monitor the country's progress in combating money laundering and terrorism financing, a grey list is established.
- Non-cooperative nations are included on a blacklist in an effort to combat money laundering and financing of terrorism.
About the Cayman Islands:
- The Cayman Islands are situated in the Western Caribbean Sea and are a British Overseas Territory.
- Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman are the three islands that make up the territory; they are situated northwest of Jamaica and south of Cuba.
- Its topography is low-lying, with coral reefs.
- Economy: The islands are a thriving offshore financial hub, with a mixed economic system.
MANAGEMENT & ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND PROFESSIONAL SKILLS COUNCIL (Business Standard)

- 27 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was recently signed by the Management & Entrepreneurship and Professional Skills Council (MEPSC) and Magic Bus India Foundation, a prominent non-profit in the education and skilling sector.
Facts About:
MEPSC is a horizontal Sector Skill Council (SSC) that was established using a unique Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model in 2013 and registered as a Section-8 (Not for Profit Company) under the Companies Act.
The Ministry of Skill Development has been providing guidance to the Council during its operations.
The only organization promoting it is the All India Management Association (AIMA), which is the highest authority for the management profession in India.
MEPSC receives support from the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) and is acknowledged as an awarding body by the National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET), the skills regulator.
Over the next ten years, MEPSC aims to train and certify about 4.75 lakh trainees, create and develop 50 Qualifications Packs (QPs)/National Occupational Standards (NOS), and train over 550 trainers.
It will take the lead on skill development programs in five major areas, including:
- Assessment and training
- Professional skills (including Security)
- Non-Teaching job roles in the education sector
- Entrepreneurship
The MEPSC Board of Directors is made up of several well-known and experienced business leaders, academics, NSDC, AIMA, and Ministry officials.
West Coast Refinery Project (Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
India and Saudi Arabia have recently decided to accelerate the progress of the $50 billion West Coast refinery project.
Facts About:
- The West Coast refinery project, also known as Ratnagiri Refinery and Petrochemicals Ltd. (RRPCL), was initially conceived in 2014.
It is intended to be India's largest greenfield refinery, boasting a massive capacity of 60 million tonnes per annum.
This project is set to become the world's largest integrated refinery and petrochemical facility.
- Location-wise, the project is planned to be situated on India's western coast, specifically in Ratnagiri, Maharashtra.
- Upon completion, the refinery is anticipated to produce approximately 1.2 million barrels of oil daily, in addition to various petroleum products generated by the attached petrochemical facilities.
- Three prominent government-owned enterprises in the Indian oil and gas sector came together to establish a joint venture named RRPCL.
- RRPCL is a joint venture in which India's three national oil companies, namely Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL), Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL), and Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL), hold stakes of 50%, 25%, and 25%, respectively.
- In 2019, Saudi Aramco and the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) also joined the project by acquiring a collective 50 percent stake.
This investment is estimated to be valued at around Rs 3 lakh crore, covering the setup costs.
Overnight Index Swap )Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Indian overnight index swap (OIS) rates have surged to their highest levels in a span of 10 months. This increase has been attributed to offshore payments and the triggering of stop-loss orders.
Facts About:
- An Overnight Index Swap (OIS) is a financial tool that involves exchanging returns from a fixed-rate asset for a predetermined daily overnight reference rate index for an agreed-upon duration.
- The primary goal of OIS is to mitigate interest rate risk, specifically the risk linked to changes in the overnight lending rate.
- An OIS rate is computed daily, and it is based on the average interest rate that institutions with loans tied to the overnight rate have paid for that particular day.
How does an OIS Operate:
- OIS instruments enable financial institutions to exchange the interest rates they are currently paying, all without the need to refinance or alter the terms of their existing loans.
- In a typical overnight index swap arrangement, one financial institution swaps an overnight (floating) interest rate, while the other swaps a fixed short-term interest rate.
- To initiate the swap, both institutions agree to maintain their loan obligations as usual.
- However, at the end of an agreed-upon timeframe, the institution that ends up paying less interest will compensate the other institution for the difference.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC) (Business Standard)
- 14 Sep 2023
What is the News ?
The Indian shipping Minister recently mentioned that India and Russia want to start working on the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC).
Facts About:
- The EMC is like a new sea road that connects the Indian port of Chennai with the Russian port of Vladivostok.
- This new road is expected to make it much faster to move things between Indian and Russian ports in the Far East. It could be up to 40 percent faster, which means instead of taking 40 days, it might only take 24 days.
- Right now, when things are shipped from Mumbai, India, to St. Petersburg, Russia, it's a really long trip of 8,675 nautical miles.
- The EMC, on the other hand, is a shorter route, only about 5,600 nautical miles, which is way quicker than the current path through the Suez Canal.
- So, when the EMC is ready, it will be a faster way to send stuff from India to Far East Russia.
- It's great for India, because it's a quicker and better route to reach places in the Far East like China and Japan.
