Purulia Observatory

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
New observatory at remote Purulia district West Bengal is expected to contribute significantly to Astrophysics.
Key Highlights:
Location and Significance:
- Established by: S.N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
- Location: The observatory is situated at Panchet Hill, in the Garpanchakot area of Purulia district, West Bengal, at an elevation of 600 meters above ground level.
- Longitude Gap: Positioned at a longitude of approximately 86° E, this observatory fills a critical longitudinal gap in global astronomical observation networks. There are very few observatories along this longitude, making it strategically important for observing transient astronomical phenomena that last from minutes to hours.
- Global Impact: This location will allow for unique contributions to global astrophysical research, especially in observing transient events, which require observatories spread across all global longitudes.
Technological and Educational Role:
- The observatory is equipped with a 14-inch telescope for scientific observations.
- It will serve as a training ground for students and researchers, helping them to handle telescopes, record astronomical data, and engage in research.
- The observatory aims to foster national and international collaborations in astronomical research, furthering India’s contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Ecosystem Development:
- MOU with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University: The observatory will be run jointly with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University, sharing resources and responsibilities. The collaboration promises to bring scientific and educational advancements to Purulia, a district traditionally considered backward.
- The establishment of the observatory is expected to boost the local ecosystem, creating a space for scientific engagement and inspiring students in the region.
Research and Contributions:
- The research team, from the Department of Astrophysics at SNBCBS, contributed to the conceptualization, site characterization, and installation of the telescope.
- Their efforts ensure the observatory will be capable of high-quality scientific observations, especially with regard to weather parameters and astronomical seeing conditions.
Future Prospects:
- Scientists emphasized that the observatory will significantly contribute to the global body of knowledge in observational astronomy.
- Also highlighted the potential of the observatory to create a scientific ecosystem in the region.
- The observatory will also serve as a source of inspiration for students in Purulia and provide a much-needed boost to local education in the fields of science and astrophysics.
Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
One Nation One Subscription (ONOS)

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Cabinet approves One Nation One Subscription (ONOS) Scheme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: It is a new initiative to provide unified access to international scholarly research articles and journals for all government-managed higher education institutions and research institutions in India.
- Scheme Overview:ONOS aims to make nearly 13,000 scholarly journals accessible to over 1.8 crore students, faculty, researchers, and scientists in more than 6,300 institutions across India. These journals will cover all academic disciplines, promoting both core and interdisciplinary research, including in tier 2 and tier 3 cities.
- Digital Platform:The scheme will be implemented through a fully digital process, coordinated by the Information and Library Network (INFLIBNET), an autonomous center under the University Grants Commission (UGC). The platform will provide easy access to the journals and facilitate a streamlined subscription process.
- Investment and Coverage:A total of ?6,000 crore has been allocated for ONOS for three years (2025-2027). The scheme will cover major international publishers such as Elsevier, Springer, Wiley, and Oxford University Press. It will enable institutions to access 13,000 journals from 30 global publishers.
Benefits of the Scheme:
- Access to Top-Quality Research:ONOS will provide wide access to top-tier scholarly journals, benefiting institutions, researchers, and students across various fields. It will significantly improve the research environment in the country, especially for institutions that previously lacked the resources to access high-impact journals.
- Fostering Research and Development:The initiative aligns with India's vision of becoming an Atmanirbhar and Viksit Bharat by 2047, supporting the government's goals under the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF). It will help foster a culture of research and innovation in Indian institutions.
- Inclusivity:The scheme will particularly benefit institutions in smaller towns and rural areas, helping bridge the knowledge gap between urban and rural academic institutions.
- Simplified Access:The scheme eliminates the need for separate subscriptions to individual journals by different institutions, streamlining access to high-quality content through a single platform.
Implementation Details:
- Platform and Process:The ONOS platform will allow institutions to access journals through a unified portal, providing easy and coordinated access. The Department of Higher Education (DHE)will be responsible for conducting awareness campaigns about the initiative, ensuring widespread utilization among students and faculty.
- Review Mechanism:The ANRF will monitor and periodically review the usage of ONOS and track the contributions of Indian authors in the journals, ensuring that the initiative continues to support India’s research landscape.
- Operational Date:The ONOS platform is set to become operational on January 1, 2025, providing comprehensive access to research materials for government-managed higher education and research institutions.
The One Nation One Subscription scheme is a major step towards enhancing India's position in the global research ecosystem. It will provide unparalleled access to scholarly resources, supporting research excellence and innovation across the country.
Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) retained the State Bank of India, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
Overview of D-SIBs
- Definition: D-SIBs are banks that are 'Too Big to Fail' (TBTF) and their failure could significantly disrupt essential banking services, affecting the economy.
- RBI Classification: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has designated SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as D-SIBs.
- Bucketing System: These banks are classified into different buckets based on their systemic importance.
Importance of D-SIBs
- Systemic Importance: Banks are considered systemically important due to their:
- Size
- Cross-jurisdictional activities
- Complexity
- Interconnectedness with the economy
- Impact of Failure: Failure of a D-SIB could cause significant disruption in the banking system and economy, impacting services like payments, loans, etc.
Why D-SIBs are Created
- Risk of Disruption: The failure of a large bank can disrupt essential services and lead to a broader economic crisis.
- TBTF Perception: These banks are often perceived as Too Big to Fail, leading to an expectation of government support during crises. This creates moral hazard, encouraging riskier behavior.
Assessment and Selection of D-SIBs
- Two-Step Process:
- Step 1: Selection of banks based on their size, complexity, and interconnectedness. Only banks with systemic importance are assessed (e.g., banks with assets > 2% of GDP).
- Step 2: Calculation of systemic importance score based on a range of indicators. Banks above a certain threshold are classified as D-SIBs.
- Indicators: Size (measured by Basel III Leverage Ratio Exposure Measure), interconnectedness, substitutability, and complexity are key factors.
Bucket Allocation and Capital Requirements
- D-SIBs are assigned to five buckets based on their systemic importance score:
- Bucket 1: Lowest capital surcharge (e.g., ICICI Bank).
- Bucket 5: Highest capital surcharge.
- Additional Capital Requirements:
- SBI: Additional 0.80% CET1 (Common Equity Tier 1) on Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs).
- HDFC Bank: Additional 0.40% CET1.
- ICICI Bank: Additional 0.20% CET1.
- The higher the bucket, the higher the capital surcharge.
Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs)
- Global List: Identified by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) based on data from the previous year.
- 2023 G-SIB List includes banks like JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, HSBC, etc.
- Capital Requirement for G-SIBs in India: Foreign G-SIBs with branch presence in India must meet additional CET1 requirements, proportional to their operations in India.
Key Terms
- Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs): These are used to calculate the minimum capital a bank must hold. It accounts for the risk level of a bank’s assets.
- Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1): The highest quality of capital a bank can hold, primarily made up of common stock, to absorb losses in times of distress.
National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) 2024-2030

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The updated NBSAP was released by India at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Overview of the NBSAP (2024-30):
- Title:Updated National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plan: A Roadmap for Conservation of India’s Biodiversity.
- Objective: To provide a comprehensive roadmap for biodiversity conservation, aligning with global frameworks like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Features of the Updated NBSAP:
- Alignment with Global Frameworks:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) adopted in 2022 aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- India’s updated NBSAP aligns with KMGBF’s goals, focusing on biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource use, and ensuring fair benefit-sharing.
- 23 National Biodiversity Targets:
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Reducing threats to biodiversity
- Ensuring sustainable use of biodiversity
- Enhancing tools for biodiversity implementation
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Key Domains of Focus:
- Area-based conservation: Protecting ecosystems and habitats.
- Ecosystem resilience: Enhancing the ability of ecosystems to withstand environmental stressors.
- Recovery and conservation of threatened species.
- Conservation of agrobiodiversity: Ensuring the sustainability of agricultural biodiversity.
- Sustainable management of biodiversity.
- Enabling tools and solutions: Including financial and technical support for implementation.
- Financial Plan and Expenditure:
- Biodiversity Expenditure Review (BER) estimated an average annual expenditure of Rs 32,20,713 crore (FY 2017-2022) for biodiversity conservation.
- Future funding requirements (FY 2024-2030) estimated at Rs 81,664.88 crore annually at the central government level.
- Biodiversity Finance Plan suggests financing solutions, including public finance, corporate social responsibility (CSR), Ecological Fiscal Transfer (EFT), and Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) mechanisms.
- Capacity Building:
- The NBSAP stresses the need for capacity building across various levels—national, state, and local.
- Focus on skills acquisition for biodiversity management and enhancing knowledge to implement conservation strategies.
Implementation Framework:
- Multi-Level Governance:
- At the national level, the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) will oversee implementation with involvement from 22 other ministries.
- State-level: Involves State Biodiversity Boards and Union Territory Biodiversity Councils.
- Local level: Community-driven efforts through Biodiversity Management Committees.
- BIOFIN and Resource Mobilization:
- India is recognized as a leading country in the implementation of the Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN).
- Encouragement for private entrepreneurs, businesses, and international donors to invest in biodiversity through innovative financial instruments like:
- Green Bonds
- Green Funds
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES)
- Incentives for Financial Solutions:
- India aims to explore funding from corporate social responsibility (CSR), ecological fiscal transfers, and access and benefit sharing mechanisms to meet the financial needs for biodiversity conservation.
Challenges and Strategies:
- Challenges India Faces:
- Habitat fragmentation
- Pollution
- Illegal wildlife trade
- Adverse effects of climate change
- Strategic Responses:
- The updated NBSAP provides strategies to address these challenges, ensuring comprehensive conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
MACE Observatory

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
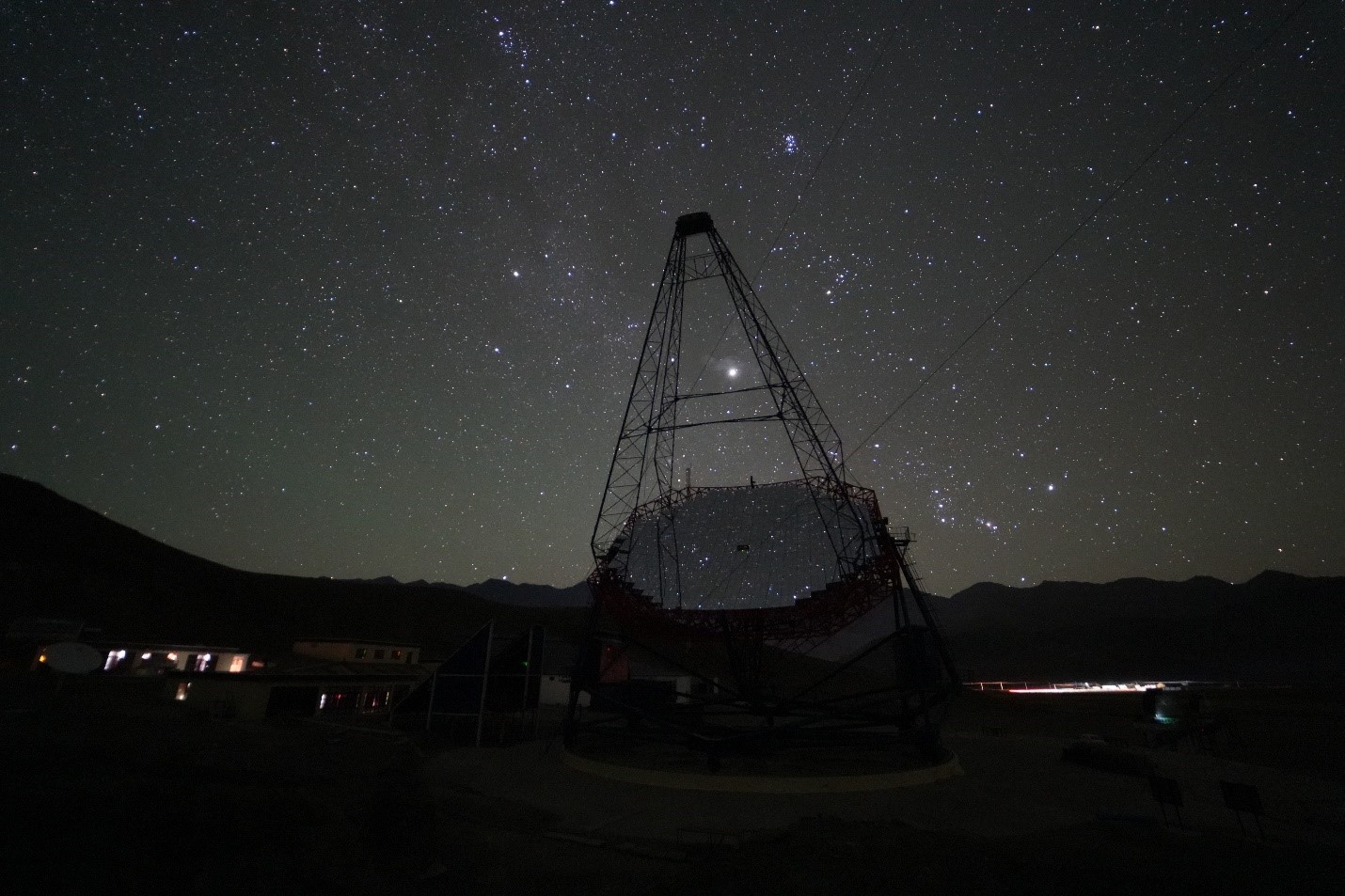
The MACE Observatory was recently inaugurated by the Secretary of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission in Hanle, Ladakh.
About MACE Observatory
- Name: Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Experiment (MACE) Observatory.
- Significance:
- Largest imaging Cherenkov telescope in Asia.
- Highest imaging Cherenkov observatory in the world.
- Location: Situated at approximately 4,300 meters altitude in Hanle, Ladakh.
- Indigenous Development:
- Built by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- Supported by the Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL), Hyderabad, and other Indian industry partners.
Scientific Contributions
- Research Focus:
- Enhances understanding in astrophysics, fundamental physics, and particle acceleration mechanisms.
- Observes high-energy gamma rays to investigate cosmic phenomena like supernovae, black holes, and gamma-ray bursts.
- Global Impact:
- Aims to foster international collaborations in space research.
- Strengthens India’s position in the global scientific community.
Socio-Economic Role
- Local Impact: Contributes to the socio-economic development of Ladakh, promoting scientific awareness and opportunities.
Understanding Cherenkov Radiation
- Definition: A blue glow emitted when charged particles (e.g., electrons and protons) travel faster than light in a specific medium.
- Historical Note: Named after Pavel Cherenkov, who, along with Ilya Frank and Igor Tamm, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958 for his work in demonstrating and explaining this phenomenon.
IBSA (INDIA, BRAZIL, SOUTH AFRICA) GROUPING

- 28 Sep 2024
In News:
In a significant move for global security, the Foreign Ministers of the IBSA (India, Brazil, South Africa) grouping issued a strong declaration against terrorism during the 79th UN General Assembly in New York. This declaration condemned terrorism in all its forms and reaffirmed the collective responsibility of the international community to eliminate terrorist safe havens worldwide.
Key Points from the IBSA Declaration:
- Universal Threat: The ministers stressed that terrorism is a threat that transcends borders, cultures, and governments.
- Rule of Law: They emphasized that counter-terrorism efforts must adhere to international law, particularly the UN Charter and human rights laws, ensuring civil liberties are respected.
- International Framework: A call was made for establishing a comprehensive international counter-terrorism framework, with the United Nations at its core, to coordinate global efforts against terrorism.
- Cross-Border Security: The declaration highlighted the need for stringent actions against the movement of terrorists and the financing of terrorist networks, condemning groups like Al-Qaeda, ISIS/Daesh, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT), and Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM).
- Comprehensive Convention: A renewed commitment to accelerate the adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism at the UN was emphasized, aiming to create a unified legal framework for combating terrorism.
Mundra Port

- 28 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
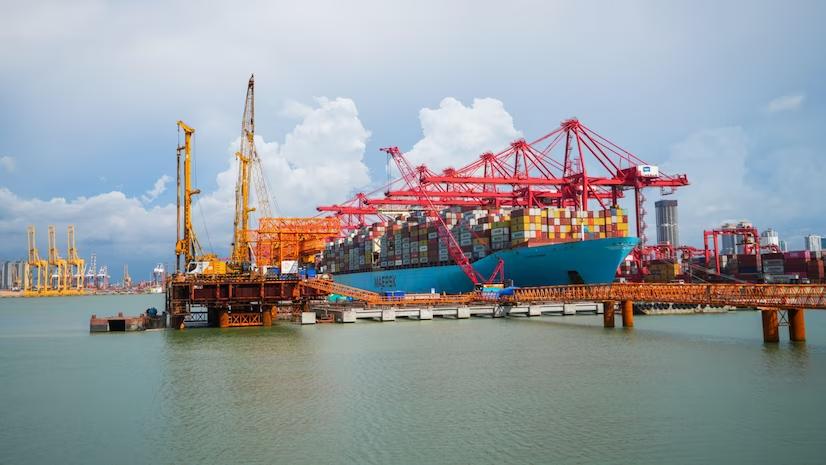
Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Ltd (APSEZ) on Sunday said its flagship Mundra Port has created yet another record by welcoming the largest container ship to call at an Indian port.
About Mundra Port:
- Mundra Port is the largest private and container port in India.
- It is situated on the northern shores of the Gulf of Kutch, near Mundra in the Kutch district of Gujarat.
- It is a deep-draft, all-weather port and a designated special economic zone (SEZ).
- Mundra Port handles 33% of India's container traffic and is a critical hub for the nation's trade.
Ownership and Operations:
- Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (APSEZ), India's largest commercial port operator, oversees nearly one-fourth of the country's cargo movement.
Handling Capacity:
- Capacity: The port has a capacity of 260 million metric tons (MMT) and handled over 155 MMT in the fiscal year 2022-23, which represents nearly 11% of India’s maritime cargo.
- Facilities: Equipped with 26 berths and two single-point moorings, Mundra Port can accommodate a diverse range of vessels and cargo types, including containers, dry bulk, break bulk, liquid cargo, and automobiles.
- Coal Terminal: It hosts the country's largest coal import terminal, ensuring rapid cargo processing with minimal turnaround time.
- Connectivity: The port's rail network connects seamlessly with the national rail system, facilitating cargo transportation to any location in India.
What is MSC Anna?
- MSC Anna is the largest container ship ever to dock at an Indian port.
- Size: The vessel measures 399.98 meters in length, approximately the length of four football fields, making it one of the largest container ships globally.
- Capacity: MSC Anna can carry up to 19,200 TEUs (20-foot equivalent units).
With an arrival draft of 16.3 meters, it can only be accommodated at Adani Ports' Mundra Port, as no other port in India has the capability to berth such a deep-draft vessel.
Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)

- 14 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Technical experts from across the world are gathered at the United Nations headquarters in Kenya in preparation for the 16th Conference of Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (COP16).
About the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty that has the main objective of developing national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity.
- It is a multilateral treaty established in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (also known as the Earth Summit) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- Signed by 150 government leaders, the Convention on Biological Diversity is dedicated to promoting sustainable development.
- Conceived as a practical tool for translating the principles of Agenda 21 into reality, the Convention recognizes that biological diversity is about more than plants, animals and microorganisms and their ecosystems – it is about people and our need for food security, medicines, fresh air and water, shelter, and a clean and healthy environment in which to live.
The CBD has so far produced two important international agreements:
- The Cartagena Protocol on biosafety entered into force in 2003, seeks to protect the environment from the potential risks of Genetically Modified (GM) organisms.
- The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety to the Convention on Biological Diversity is an international treaty governing the movements of living modified organisms (LMOs) resulting from modern biotechnology from one country to another.
- It aims to ensure the safe handling, transport, and use of living-modified organisms (LMOs) that may have adverse effects on biological diversity, taking into account human health, especially focusing on transboundary movements.
- The protocol was adopted in January 2000 in Cartagena, Colombia, and entered into force on September 11, 2003.
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources entered into force in 2014, aims at sharing the benefits arising from the utilisation of genetic resources in a fair and equitable way.
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization is a supplementary agreement to the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- It provides a legal framework for the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources, with a particular focus on ensuring that benefits are shared with the countries and communities that provide those resources.
- The protocol aims to promote the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity while also respecting the rights of indigenous and local communities over their traditional knowledge and genetic resources.
- It was adopted in Nagoya, Japan, in 2010 and entered into force in 2014.
- The Conference has also implemented many positive decisions that have contributed to the promotion of environmental integrity and the rights of Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities.
- In 2010, the conference in Nagoya adopted a Strategic Plan for Biodiversity, including the Aichi Biodiversity Targets for the 2011-2020 period.
- The convention provides a framework for member countries to develop national strategies and action plans for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity.
- As of now, 196 countries have ratified the convention, making it a widely accepted and crucial international agreement for addressing global environmental issues.
‘Hanooman’ GenAI Platform

- 11 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Homegrown generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) platform Hanooman went live in 98 global languages, including 12 Indian languages recently.
What is the ‘Hanooman’ Platform?
- Hanooman is India's Gen AI platform, launched in 98 languages including 12 Indian languages such as Hindi, Marathi, Gujarati, Bengali, Kannada, Odia, Punjabi, Assamese, Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, and Sindhi.
- Abu Dhabi-based AI investment firm 3AI Holding Limited and SML India have built this indigenous platform.
- Named after the revered Hindu deity Hanuman, known for his unparalleled strength, wisdom, and devotion, Hanooman embodies the core principles of intelligence, agility, and resilience.
- The development of Hanooman was driven by a vision to create an AI platform that combines human-like intelligence with advanced machine-learning capabilities to tackle complex problems and drive innovation across diverse domains.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Hanooman boasts advanced NLU capabilities that enable it to understand and interpret human language with remarkable accuracy.
- Whether it's processing text, speech, or multimedia content, Hanooman can analyze and extract meaningful insights to facilitate intelligent decision-making.
- Contextual Awareness: Hanooman is equipped with contextual awareness technology that allows it to understand the context of a given situation and adapt its responses accordingly.
- This enables Hanooman to provide personalized recommendations, anticipate user needs, and deliver tailored experiences across various applications and interfaces.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Leveraging state-of-the-art deep learning algorithms and neural networks, Hanooman is capable of learning from vast amounts of data and continuously improving its performance over time.
- This enables Hanooman to tackle complex problems, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency.
- Multi-Modal Learning: Hanooman supports multi-modal learning, allowing it to process and integrate information from multiple sources, including text, images, and audio.
- This enables Hanooman to understand and analyze complex data sets more comprehensively, leading to more informed decision-making and actionable insights.
Applications and Uses:
- Healthcare: Hanooman can be used to analyze medical imaging data, diagnose diseases, and develop personalized treatment plans based on individual patient profiles.
- Finance: It can analyze market trends, predict financial risks, and optimize investment strategies to maximize returns and minimize losses.
- Manufacturing: It can optimize production processes, detect anomalies in manufacturing equipment, and improve quality control measures to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Retail: It can analyze customer data, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize inventory management to drive sales and increase customer satisfaction.
AlphaFold 3

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google Deepmind has unveiled the third major version of its “AlphaFold” artificial intelligence model, designed to help scientists design drugs and target diseases more effectively.
About AlphaFold 3:
- AlphaFold 3 is a major advancement in artificial intelligence created by Google's DeepMind in collaboration with Isomorphic Labs.
- It's essentially a powerful tool that can predict the structures and interactions of various biological molecules such as:
- Predict structures of biomolecules: Unlike previous versions that focused on proteins, AlphaFold 3 can predict the 3D structure of a wide range of molecules, including DNA, RNA, and even small molecules like drugs (ligands).
- This is a significant leap in understanding how these molecules function.
- Model molecular interactions: AlphaFold 3 goes beyond just structure prediction.
- It can also model how these molecules interact with each other, providing valuable insights into cellular processes and disease mechanisms.
The potential applications of AlphaFold 3 are vast. It has the potential to revolutionize fields like:
- Drug discovery: By understanding how drugs interact with their targets, researchers can design more effective medications.
- Genomics research: AlphaFold 3 can help scientists understand the function of genes and how mutations can lead to disease.
- Materials science: By modelling the interactions between molecules, scientists can design new materials with specific properties.
- AlphaFold 3 is a significant breakthrough and is freely available for non-commercial use through AlphaFold Server.
- This makes this powerful tool accessible to researchers around the world, potentially accelerating scientific advancements.
Shaksgam Valley
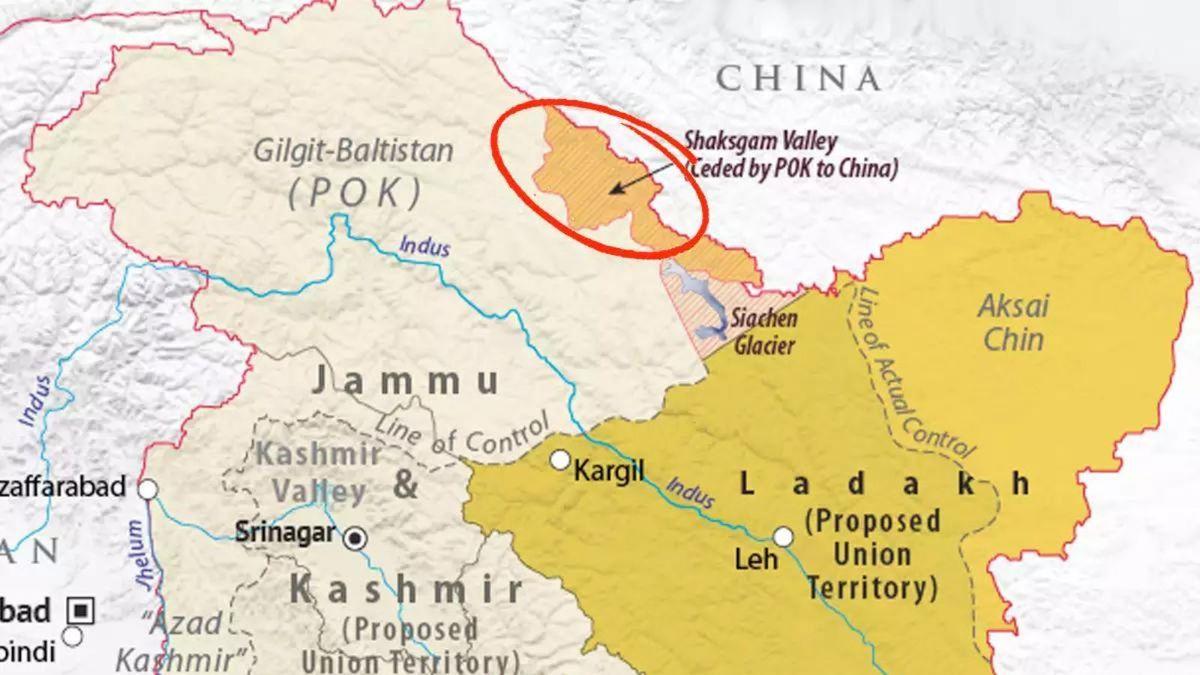
- 03 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently said it has lodged a strong protest with China for carrying out construction activities in the Shaksgam Valley in an "illegal" attempt to alter the situation on the ground.
Context:
- Recently, the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) said that the Shaksgam Valley is a part of the territory of India amid reports of China building infrastructure in the valley.
- The Shaksgam Valley strategically located region that is now part of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- MEA spokesperson Randhir Jaiswal recently said that India "never accepted the so-called China-Pakistan Boundary Agreement of 1963 through which Pakistan unlawfully attempted to cede the area to China".
- Lodging a strong protest with China for carrying out construction activities, India called it an "illegal" attempt to alter the situation on the ground.
Where is the Shaksgam Valley Located?
- The Shaksgam Valley, or the Trans Karakoram Tract, is part of the Hunza-Gilgit Region of PoK.
- It is bordered by the Xinjiang Province of the People's Republic of China to the north.
- The northern areas of PoK are to its west and south.
- And the Siachen Glacier region to the east.
How did Pakistan cede Shaksgam valley to China?
- In 1963, Pakistan ceded the Shaksgam Valley to China when it signed a border agreement with Beijing to settle their border disputes.
- But, Article 6 of the 1963 agreement clearly stated that “the two Parties have agreed that after the settlement of the Kashmir dispute between Pakistan and India, the sovereign authority concerned will reopen negotiations with the Government of the People's Republic of China, on the boundary as described in Article 2 of the present Agreement, to sign a formal Boundary Treaty to replace the present agreement.”
- The agreement laid the basis for the construction of the Karakoram Highway, which was jointly built by Chinese and Pakistani engineers during the 1970s.
What is the History of Shaksgam Valley?
- When the British asked the Mir of Hunza, a vassal of the Maharaja of Kashmir, to give up his rights to the Taghdumbash Pamirs and the Raskam valley in 1936, the Shaksgam valley to the south-west had remained in his possession.
- This remained the traditional frontier of British India until independence and was inherited by India following Jammu & Kashmir's accession in 1947.
- And, this was the border that Pakistan compromised in its 1963 agreement with China.
- Pakistan established diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China in 1951.
- Back then, Pakistan was viewed as a member of the non-Soviet block due to its membership in two anti-communist military pacts -- SEATO and CENTO -- led by the United States.
- China was on the opposite side.
- After Chinese troops invaded Tibet in 1950, Pakistan even offered transit facilities to US aircraft so they could supply equipment to Tibetan rebels.
- Chinese troops began to cross the border in eastern Hunza after the Partition of India.
- This started in 1953 and in 1959 they took some livestock out of the area.
- This prompted a furious response from Pakistan, which was determined to protect its borders.
- The then President of Pakistan, Ayub Khan, however, saw an opportunity to appease the Chinese in the late 1950s as India-China relations were rapidly deteriorating.
- Subsequently, Beijing developed closer ties with Islamabad after the India-China War of 1962.
- China went on to support Pakistan diplomatically during the 1965 India-Pakistan war.
- Amid these developments, Pakistan chose to downgrade historical claims made by the Mir of Hunza and signed over the Shaksgam Valley to China in 1963.
What was the Consequence?
- In granting China's claim to a border along the Karakoram Range, Pakistan compromised India's traditional frontier along the KunLun Range to the northwest of the Karakoram Pass.
- It also allowed China to extend a claim eastward along the Karakoram in Ladakh.
- This enabled China to claim all of Aksai-Chin.
Nutrient-based Subsidy

- 01 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Capping consumption of urea and DAP to correct worsening plant nutrient imbalance is likely to be on the priority list of the government post the Lok Sabha polls.
What is Meant by the Term "Balanced Fertilization"?
- Fertilisers are basically food for crops, containing nutrients necessary for plant growth and grain yields.
- Balanced fertilisation means supplying these primary (N, phosphorus-P, and potassium-K), secondary (sulphur-S, calcium, magnesium), and micro (iron, zinc, copper, manganese, boron, molybdenum) nutrients in the right proportion, based on soil type and the crop’s own requirement at different growth stages.
What is a Nutrient-based Subsidy?
- Nutrient-based subsidy (NBS) is a system started in 2010 to help farmers use the right amount of nutrients in fertilizers.
- Instead of giving a subsidy for each type of fertilizer, the government decided to give subsidies based on nutrients like Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), and Sulfur (S) in the fertilizers.
- The idea was to encourage farmers to use fertilizers with a balanced mix of nutrients, instead of just focusing on certain types like urea, DAP, and MOP.
- These balanced fertilizers contain a mix of N, P, K, S, and other nutrients in the right amounts.
- At first, this plan seemed to work. Between 2010 and 2012, farmers started using more balanced fertilizers and less of the ones with just one or two nutrients.
- But there was a problem: urea, which is heavily used by farmers, was not included in this plan.
- Since the government controlled the price of urea and only went up a little bit after the NBS was introduced, farmers kept using it more and more.
- This means that even though the NBS helped with other fertilizers, it didn't do much to reduce the use of urea.
Challenges:
- The challenges arise from recent changes in fertilizer pricing and consumption patterns.
- Earlier, companies set prices for non-urea fertilizers, with the government providing subsidies based on their nutrient content.
- However, in the past few years, even non-urea fertilizers have come under price control, especially since January 2024, possibly due to upcoming elections.
- This shift has led to imbalances in nutrient usage.
- For example, the current price of DAP is lower than certain NPKS complex fertilizers, even though it contains less nitrogen and phosphorus.
- As a result, farmers tend to overuse DAP, similar to urea. On the other hand, the price of MOP does not incentivize its use, leading to its reduced incorporation into fertilizers, despite its importance for crop immunity and nitrogen uptake.
- To address these issues, it's crucial to establish a proper price hierarchy among non-urea fertilizers.
- DAP should be priced highest, followed by complexes, with MOP priced the lowest. Additionally, DAP usage should be limited to rice and wheat, while other crops can fulfil their phosphorus needs through complexes and SSP.
- Improving the acceptability of SSP, despite its lower price, can be achieved by marketing it in granular form, which is less prone to adulteration and ensures a slower release of phosphorus without drift during application.
National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG)

- 29 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
A central government delegation is on a three-day visit to Bangladesh beginning Sunday to further boost bilateral ties on governance matters, according to an official statement.
About the National Centre for Good Governance:
- The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) was set up in 2014 by the Government of India as an apex–level autonomous institution under the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- The Centre traces its origin to the National Institute of Administrative Research (NIAR), which was set up in 1995 by the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), the Government of India's topmost training institute for civil services.
- NIAR was subsequently rechristened and subsumed into NCGG.
- NCGG deals with a gamut of governance issues from local, state to national levels, across all sectors.
- The Centre is mandated to work in the areas of governance, policy reforms, capacity building, and training of civil servants and technocrats of India and other developing countries.
- It also works as a think tank.
- Since its inception, the Centre has been extensively working in areas such as primary and elementary education, decentralized planning at district and block levels, capacity building of Panchayat Raj Institutions (PRIs), participatory models of learning and action, rural development, cooperatives, and public sector management, etc.
- In addition, it focuses on issues related to good governance, social accountability, water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH), among other sectors.
- The Centre encapsulates the essence of good governance and weighs on the importance of the rule of law, bringing in transparency, working to promote public participation in governance, service delivery, and reforms, as well as in developing accountable institutions, access to information, etc.
International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI)

- 25 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Countries must build “resilient infrastructure” against natural disasters that are becoming more frequent and severe, said Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently.
About the Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI):
- The Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) is a global partnership comprising national governments, UN agencies and programs, multilateral development banks, private sector entities, and academic institutions.
- Established during the United Nations Climate Action Summit in 2019 in New York, CDRI is dedicated to addressing the challenges associated with building resilience in infrastructure systems and development processes.
Objectives:
- CDRI aims to enhance the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks, thereby promoting sustainable development.
- It seeks to expedite the development and retrofitting of resilient infrastructure to meet the imperatives of the Sustainable Development Goals, including universal access to basic services and fostering prosperity and decent work.
- Serving as an inclusive multi-stakeholder platform, CDRI is led and managed by national governments. It facilitates the exchange of knowledge on various aspects of infrastructure resilience.
- CDRI brings together diverse stakeholders to create mechanisms assisting countries in upgrading their capacities, systems, standards, regulations, and practices related to infrastructure development, tailored to their risk contexts and economic needs.
Membership:
- Since its inception, 39 countries, 7 international organizations, and 2 private sector organizations joined as members.
- International organizations include:
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- World Bank Group
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)
- European Union
- European Investment Bank, and
- The Private Sector Alliance for Disaster-Resilient Societies (ARISE)
- The CDRI is the second major coalition launched by India outside of the UN, the first being the International Solar Alliance.
Secretariat:
- CDRI's secretariat is based in New Delhi, India.
Project Nimbus

- 23 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Google's employees staged protests against the company's collaboration with the Israeli government on "Project Nimbus", a $1.2 billion cloud computing initiative.
What is Project Nimbus?
- Google’s Project Nimbus is a $1.2 billion cloud computing initiative with the Israeli government.
- The project aims to provide public cloud services to address challenges within various sectors in Israel, including healthcare, transportation, and education in Israel.
- However, the project has sparked controversy leading to protests and layoffs within the company.
- Project Nimbus involves Google establishing a secure instance of Google Cloud on Israeli soil.
- This would allow the Israeli government to perform large-scale data analysis, AI training, database hosting, and other forms of powerful computing using Google’s technology.
- The project is a joint contract between Google and Amazon signed in 2021.
- As part of the agreement, Google Cloud will work with the public sector on the formulation of best practices for cloud migration, integration, and optimization of cloud services.
- According to the official announcement in the year 2021, Google Cloud will also provide training to the country’s technical government employees and senior leaders to enhance digital skills.
What is the Controversy Surrounding Project Nimbus?
- Despite the potential benefits, Project Nimbus has sparked controversy due to concerns about the potential misuse of AI and other technologies.
- Employees fear that the technology developed under Project Nimbus could be used in harmful ways.
- There have been reports suggesting that Israel is using AI to eliminate its targets.
- Israeli outlets +972 Magazine and Local Call claimed that two AI systems, "Lavender" and "Where's Daddy?" were used to identify 37,000 Hamas operatives.
- However, there's no official confirmation regarding any connection between Project Nimbus and these AI systems.
- The use of AI also causes concern as it is still a relatively new technology on the battlefield and is yet to be regulated by governments across the globe.
Google Response to the Accusations Regarding Project Nimbus?
- Google clarified that the project is intended for use by Israeli government ministries in areas such as finance, healthcare, transportation, and education, emphasizing that it is not aimed at handling highly sensitive or classified military operations related to weaponry or intelligence services.
National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)

- 11 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
iBUS, a digital infrastructure solutions company, said recently it has raised $200 million from the government-backed National Investment and Infrastructure Fund Limited (NIIF).
What is the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF)?
- The National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF) stands as a pioneering fund manager dedicated to investing in India's infrastructure and related sectors.
- Established in 2015, NIIF marks India's inaugural sovereign wealth fund (SWF), embodying a collaborative investment platform for both international and domestic investors.
Key Aspects of NIIF:
- Investment Mandate: NIIF operates with a mandate to deploy equity capital into domestic infrastructure projects, spanning greenfield, brownfield, and stalled ventures.
- Its investment horizon extends across diverse asset classes, including infrastructure, private equity, and other sectors, all aimed at delivering attractive risk-adjusted returns.
- Ownership and Independence: With 49% ownership by the Indian government, NIIF boasts over $4.9 billion in assets under management, solidifying its status as the nation's largest infrastructure fund.
- Despite its close ties with the government, NIIF maintains autonomy in its investment decisions, ensuring a professional and impartial approach to its operations.
- Professional Management: The fund is predominantly owned by institutional investors and managed by a proficient team with expertise in both investments and infrastructure.
- This professional oversight ensures the strategic deployment of capital and efficient management of investments.
- Regulatory Compliance: NIIF operates within the regulatory framework as an Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) registered with the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- It actively raises capital from a spectrum of domestic and international institutional investors, further bolstering its financial resources.
NIIF manages capital through four distinct funds:
- NIIF Master Fund: Focused on infrastructural projects such as roads, ports, airports, and power, it stands as India's largest infrastructure fund.
- NIIF Private Markets Fund: Invests in infrastructure and associated sectors through third-party managed funds.
- NIIF Strategic Opportunities Fund: Devoted to developing large-scale businesses and greenfield projects deemed strategically significant for the nation.
- India-Japan Fund: NIIF's bilateral initiative aimed at environmental preservation in India, with contributions from both the Indian government and the Japan Bank for International Cooperation.
- NIIF catalyzes fostering sustainable infrastructure development in India while facilitating fruitful collaborations between Indian and international stakeholders, exemplifying a robust model for investment-driven growth.
CDP-SURAKSHA

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has come up with a new platform to disburse subsidies to horticulture farmers under the Cluster Development Programme (CDP) — the Centre’s initiative to promote horticulture crops.
What is the CDP-SURAKSHA?
- The CDP-SURAKSHA is essentially a digital platform.
- SURAKSHA stands for “System for Unified Resource Allocation, Knowledge, and Secure Horticulture Assistance.”
- The platform will allow an instant disbursal of subsidies to farmers in their bank accounts by utilizing the e-RUPI voucher from the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- The CDP-SURAKSHA has features such as database integration with PM-KISAN, cloud-based server space from NIC, UIDAI validation, eRUPI integration, local government directory (LGD), content management system, geotagging, and geo-fencing.
How does the CDP-SURAKSHA work?
- The platform allows access to farmers, vendors, implementing agencies (IA), cluster development agencies (CDAs), and officials of the National Horticulture Board (NHB).
- A farmer can log in using their mobile number and place an order for planting materials such as seeds, seedlings, and plants based on their requirement.
- Once the demand has been raised by the farmer, the system will ask them to contribute their share of the cost of planting material.
- The subsidy amount paid by the government will appear on the screen automatically.
- After the farmer pays their contribution, an e-RUPI voucher will be generated.
- This voucher will then be received by a vendor, who will provide the required planting material to the farmer.
- Once the ordered planting material is delivered to the farmer, they have to verify the delivery through geo-tagged photos and videos of their field.
- It is only after the verification that the IA will release the money to the vendor for the e-RUPI voucher.
- The vendor will be required to upload an invoice for the payment on the portal.
- The IA will collect all the documents and share them with the CDA for subsidy release, then only the subsidy will be released to the IA.
- However, the farmer, who raised the demand for the plant material using the platform, can avail of the subsidy at the first stage only.
What is e-RUPI?
- The CDP-SURAKSHA platform uses e-RUPI vouchers from the NPCI.
- The voucher is a one-time payment mechanism that can be redeemed without a card, digital payments app, or internet banking access, at the merchants accepting e-RUPI.
- According to the NPCI, the e-RUPI can be shared with the beneficiaries for a specific purpose or activity by organizations or government via SMS or QR code.
What is the Cluster Development Program (CDP)?
- The CDP is a component of the central sector scheme of NHB.
- It is aimed at leveraging “the geographical specialization of horticulture clusters and promoting integrated and market-led development of pre-production, production, post-harvest, logistics, branding, and marketing activities.”
- So far, 55 horticulture clusters have been identified, out of which 12 have been selected for the pilot.
- These clusters are in different stages of development.
- Four more clusters:
- A floriculture cluster in West Bengal
- Coconut clusters in Kerala and Tamil Nadu, and
- White onion clusters in Gujarat
- Each cluster will have an implementing agency and a cluster development agency (CDA).
- According to the government, about 9 lakh hectares of area will be covered through all 55 clusters, covering 10 lakh farmers.
- It is estimated that the initiative will attract private investment of Rs 8,250 crore, in addition to the government’s assistance, which is fixed according to the size of the cluster, up to Rs 25 crore for mini cluster (size up to 5,000 ha), up to Rs 50 crore for medium clusters (5,000 to 15,000), and up to Rs 100 crore for mega clusters (more than 15,000 ha).
TSAT-1A Satellite

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
SpaceX successfully launched and deployed the TSAT-1A satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in partnership with Satellogic Inc.
About TSAT-1A Satellite:
- TSAT-1A is a groundbreaking optical sub-meter resolution Earth observation satellite developed by Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) in collaboration with Latin American company Satellogic Inc.
- This collaboration began in late 2023, culminating in TSAT-1A's assembly at TASL's Assembly, Integration, and Testing (AIT) plant in Karnataka, India.
- Launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United States, via SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket, TSAT-1A has since garnered attention for its advanced capabilities and strategic significance.
Key Features of TSAT-1A:
- Sub-meter resolution imagery: TSAT-1A's primary strength lies in its ability to capture high-resolution military-grade imagery of Earth's surface, providing precision of less than one meter per pixel.
- Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging: This technology enables TSAT-1A to gather data across a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, offering a detailed and nuanced understanding of land, water, and other natural resources.
- Enhanced performance: TSAT-1A offers improved collection capacity, a wider dynamic range, and low-latency data delivery, ensuring efficient and reliable intelligence gathering.
Strategic Applications and Implications:
- Designed for use by Indian defense forces, TSAT-1A is set to play a pivotal role in discreet information gathering, with the potential for data-sharing among friendly nations.
- By enhancing defense forces' preparedness, response capabilities, and strategic decision-making, TSAT-1A represents a significant milestone in India's space industry and a potential game-changer in the realm of defense and security.
About SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket:
- The Falcon 9 is a partially reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX.
- Known for its reliable and safe transportation capabilities, Falcon 9 is primarily used to launch payloads and crew into Earth orbit.
- Since its first launch in 2010, Falcon 9 has made significant strides in the aerospace industry, becoming the first commercial rocket to launch humans to orbit in 2020 and maintaining a strong safety record with only one flight failure to date.
Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS)

- 08 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Consumer confidence for the year ahead has improved further on the back of higher optimism, which resulted in the Future Expectations Index (FEI) rising by 2.1 points to 125.2, the highest level since mid-2019, according to a Reserve Bank of India survey conducted in March 2024.
What is the Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS)?
- The Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS) is a comprehensive assessment conducted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to gauge consumer perceptions of the current economic landscape.
- Administered across various cities, the CCS measures consumer confidence based on key indicators such as economic conditions, employment prospects, price levels, income, and spending patterns.
- The survey collects valuable insights into consumer sentiments by posing a series of questions about both present and future economic scenarios.
- These responses offer a glimpse into consumers' perceptions of the prevailing financial environment, shedding light on economic trends, opportunities, and potential challenges.
- As a vital tool for policymakers, the Consumer Confidence Survey contributes to shaping effective strategies aimed at fostering sustainable economic growth and improving overall financial stability.
Highlights of the Survey:
- The survey revealed optimistic consumer sentiments across all parameters, reflecting a positive outlook on the current and future economic landscape.
- Key indicators, such as the Current Situation Index (CSI) and Future Expectations Index (FEI), showcased significant improvements, reaching their highest levels since mid-2019.
- Current Situation Index (CSI): Measuring overall consumer perception of the present economic situation, the CSI experienced a notable increase of 3.4 points compared to the previous survey, currently standing at 98.5.
- Future Expectations Index (FEI): Evaluating consumer sentiment for the next 12 months, the FEI witnessed a substantial surge, reaching its highest point since mid-2019 and indicating a positive outlook for the upcoming year.
- The CSI and FEI are calculated based on net responses concerning the economic situation, income, spending, employment, and price levels, comparing the current period with one year ago and the anticipated changes in the year ahead, respectively.
- Households’ Inflation Expectation Survey: There was a slight increase in the proportion of households anticipating an overall rise in prices and inflation within the next three months and one year, as observed across general prices and most product categories when compared to the previous survey round.
- Additionally, the survey results revealed noteworthy enhancements in households' perceptions regarding the general economic situation and employment prospects, signaling a sense of optimism for both the current period and the years ahead.
India Abstains from UNHRC Resolution on Gaza Ceasefire

- 06 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
India recently abstained on a resolution at the Human Rights Council that called on Israel for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza.
India's Voting Pattern on Israel-Palestine Issues at the UNHRC:
- India's stance on the Israel-Palestine conflict has been reflected in its voting behavior at the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC).
- While India has voted in favor of resolutions criticizing Israel for human rights violations, occupation of the Syrian Golan, and affirming Palestinian self-determination, it has also abstained from certain resolutions.
- In a significant development, India abstained from a resolution calling for an immediate ceasefire in Gaza and an arms embargo on Israel.
- This decision followed instances of violence, including the killing of aid workers and airstrikes.
- India's abstention is believed to be in line with its previous votes on resolutions involving "accountability."
- India's approach indicates its belief that both parties should be held accountable for their actions.
- As a result, it refrains from supporting resolutions that single out one side for condemnation.
- By taking a balanced stance, India aims to promote peace and stability in the region while advocating for the rights of all parties involved.
About the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC):
- The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is an inter-governmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2006.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, the council serves as a key platform for addressing human rights issues globally.
- The High Commissioner for Human Rights serves as the principal human rights official within the UN system.
- The council convenes three times annually to address human rights violations worldwide.
Membership:
- Comprising 47 member states, the council is responsible for promoting and safeguarding human rights across the globe.
- Member states are elected individually via secret ballot by a majority vote of the General Assembly.
- The election of members occurs within geographical groups to ensure equitable representation.
Tenure:
- Council members serve for a term of three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after two consecutive terms.
The UNHRC's primary functions include:
- Promoting universal respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms.
- Addressing violations of human rights, including gross and systematic violations.
- Developing international human rights law and making recommendations to the UN General Assembly.
- Conducting investigations into alleged human rights abuses through special rapporteurs and working groups.
- Reviewing the human rights records of all UN member states through the Universal Periodic Review process.
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KOSO)

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since ancient times, seafarers, mathematicians, astronomers, and physicists have all diligently studied and tracked the Sun and its phenomena, with the establishment of the Madras Observatory by the British East India Company in 1792 marking a pioneering effort in this region.
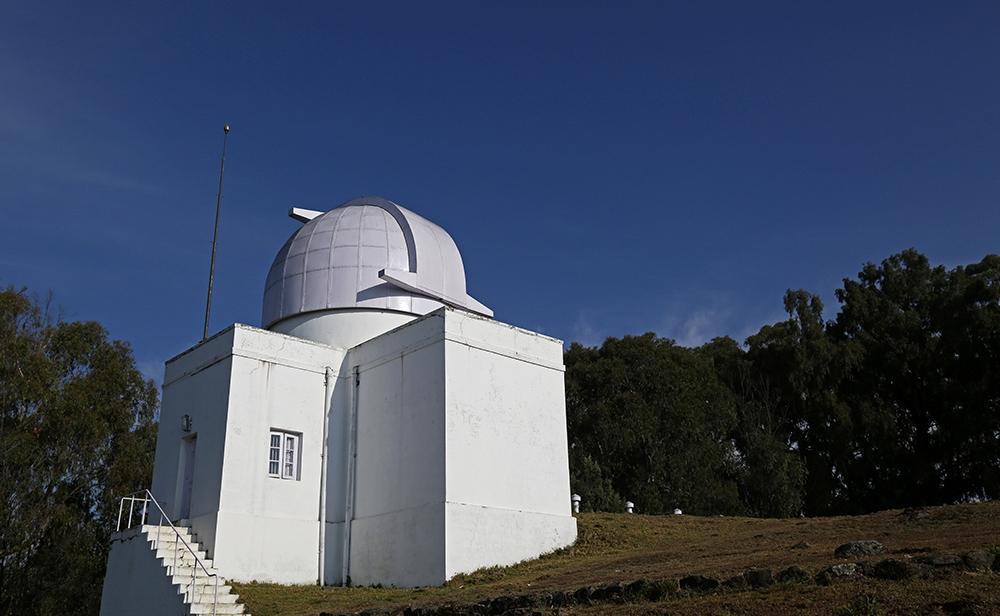
About Kodaikanal Solar Observatory:
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory is a solar observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru.
- It is on the southern tip of the Palani Hills 4 kilometers from Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu).
- The Government of India separated Astrophysics from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in April 1971.
- From solar data recorded on basic photographic plates or films, the 125-year-old KoSO boasts a mammoth digital repository containing 1.48 lakh digitized solar images of 10 terabytes.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots) and thousands of other images of the Sun recorded every day since the start of the 20th century.
- KoSO is the only observatory offering high-resolution digitized images for such a long period (with coverage of more than 75 percent).
- Today, it houses a spectrum of advanced instruments like the H-alpha telescope to perform full disc imaging, a White light Active Region Monitor (WARM) with calcium and sodium filters to make full disc simultaneous observations of the photosphere and chromosphere layers of the Sun, a solar tunnel telescope and more.
Links to the Great Drought:
- Scanty rainfall over south India during the winter monsoon of 1875 triggered one of the worst droughts the country had experienced till then.
- Multiple failed crops over the famine-stricken peninsular India killed 12.2 to 29.3 million people across the Madras and Mysore Provinces during 1875-1877.
- India, along with China, Egypt, Morocco, Ethiopia, southern Africa, Brazil, Columbia, and Venezuela, suffered concurrent multi-year droughts during 1876-1878, later named the Great Drought, and an associated global famine that killed nearly 50 million.
- The drought was thought to be due to multiple reasons:
- Solar activity
- Cool Pacific Ocean conditions followed by a record-breaking El Nino (1877-1878)
- Strong Indian Ocean Dipole and
- Warm North Atlantic Ocean conditions.
Solar Physics Observatory in Palani Hills:
- Established in response to the British Raj's acknowledgment of solar activity's link to India's weather patterns, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory, also known as the Indian Solar Observatory, was founded to conduct systematic studies on solar phenomena and their correlation with Indian meteorology.
- Located in Kodaikanal, selected for its favorable atmospheric conditions after careful consideration by Charles Michie Smith (a Professor of Physics at the Madras Christian College), the observatory was officially sanctioned by the Government of India in August 1893 and inaugurated by Lord Wenlock (the then Governor of Madras) in 1895.
- Commencing systematic observations in 1901, it merged with the Madras Observatory, enriching its instrumentation.
- Notable discoveries ensued, including the identification of the Evershed Effect.
- Over time, the observatory expanded its research domains to encompass cosmic rays, radio astronomy, and ionospheric physics, among others, solidifying its status as a pioneering institution in the field of astrophysics.
- Notably, it initiated solar radio observations in 1952, marking a significant milestone in Indian solar research.
- Despite the closure of contemporaneous observatories, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory has endured, continuing to contribute to our understanding of the Sun and its effects on Earth's climate and space weather.
Why Study the Sun?
- Being the primary source of energy, life on Earth is supported by the Sun.
- Any change on the solar surface or its periphery could significantly affect the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Powerful solar storms and solar flares can be potentially harmful to Earth’s satellite-based operations, power grids, and navigational networks.
- The KoSO (Kodaikanal Solar Observatory), which has been imaging the Sun for over a century now, has a rich repository of data.
- This is extremely useful not only to reconstruct the Sun’s historic past but also to link its behavioral changes to better understand and predict its future and its impact on life on Earth and Space weather.
T+0 Settlement Cycle

- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The BSE and NSE introduced trading in the T+0 rolling settlement cycle in the equity segment on an optional basis today.
What is Trade Settlement?
- Trade settlement encompasses the bilateral process of transferring funds and securities on the designated settlement date.
- It signifies the completion of a trade transaction when the purchased securities of a listed company are successfully delivered to the buyer, and the seller receives the agreed-upon payment.
- The evolution of the trade settlement cycle in India has seen notable adjustments over time.
- Initially shortened by SEBI to T+3 from T+5 in 2002 and further to T+2 in 2003, the current cycle in the Indian stock market stands at T+1.
- This migration to the T+1 cycle took effect in January 2023, positioning India as the second country globally, after China, to implement the T+1 settlement cycle for top-listed securities.
What is the T+0 Trading Settlement Cycle?
- In December last year, the capital markets regulator SEBI proposed to introduce a facility for clearing and settlement of funds and securities on T+0 (same day) on an optional basis, in addition to the existing T+1 settlement cycle.
- The regulator has also proposed to introduce optional instant settlement at a later stage.
- Under the T+0 trade cycle, the settlement of trades will happen on the same day after the closure of the T+0 market.
- If investors sell a share, they will get the money credited to their account the same day, and the buyer will also get the shares in their demat account on the very day of the transaction.
What are the Benefits of T+0 Trade Settlement?
- A shortened settlement cycle will bring cost and time efficiency, transparency in charges to investors, and strengthen risk management at clearing corporations and the overall securities market ecosystem.
- The T+0 trade cycle is expected to provide flexibility in terms of faster pay-out of the funds against the securities to the sellers and faster pay-out of securities against the funds to the buyers.
- It will allow better control over funds and securities by the investors.
- For the securities market ecosystem, a shorter settlement cycle will further free up capital in the securities market, thereby enhancing the overall market efficiency.
- It will enhance the overall risk management of Clearing Corporations (CCs) as the trades are backed by upfront funds and securities.
Who can Participate in the T+0 Settlement Cycle?
- All investors are eligible to participate in the segment for the T+0 trade settlement cycle if they are able to meet the timelines, process, and risk requirements as prescribed by the Market Infrastructure Institutions (MIIs).
Reverse Flipping
- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Payments major Pine Labs and quick commerce firm Zepto are among the startups looking to relocate their headquarters from foreign shores to India, to capitalize on the country's burgeoning tech landscape.
What is Reverse Flipping?
- Reverse flipping is a growing trend where overseas startups relocate their domicile to India and list on Indian stock exchanges.
- The primary motivation behind this shift is the potential for a higher valuation and more certain exit opportunities in India's thriving economic landscape.
Several factors contribute to the rise of reverse flipping:
- Access to a large, expanding economy: India's significant market size and sustained economic growth offer foreign startups attractive prospects for business expansion and success.
- Abundant venture capital: India's substantial venture capital resources provide a strong financial foundation for startups, fueling innovation and growth.
- Favorable tax policies: The country's tax regulations encourage foreign startups to establish operations in India, helping them maximize profits and minimize costs.
- Enhanced intellectual property protection: India's robust IP protection framework fosters innovation and creativity, safeguarding the unique ideas and technologies of startups.
- Skilled, youthful workforce: The availability of a talented, young, and educated population provides startups with a valuable human resource pool to drive growth and success.
- Supportive government policies: The Indian government actively promotes entrepreneurship and innovation through various initiatives and policies, creating a conducive environment for startups.
- The Economic Survey 2022-23 acknowledged the importance of reverse flipping and suggested measures to expedite the process, including simplifying tax vacation procedures, ESOP taxation, capital movement, and reducing tax layers.
- These efforts aim to further enhance India's appeal as a destination for foreign startups and foster economic growth.
What is Flipping?
- Flipping refers to the process by which an Indian company becomes a 100% subsidiary of a foreign entity after moving its headquarters overseas, involving a transfer of intellectual property (IP) and other assets.
- This transforms an Indian startup into a fully-owned subsidiary of a foreign entity, with founders and investors maintaining their ownership through the new overseas structure by exchanging their shares.
The process of flipping poses several concerns for India:
- The brain drain of entrepreneurial talent: As Indian startups move their operations overseas, India experiences a loss of innovative and entrepreneurial talent, which could otherwise contribute to the country's economic growth and development.
- Value creation in foreign jurisdictions: Flipping redirects potential value creation to foreign countries, depriving India of the economic benefits that could result from successful startups and innovations.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: When companies relocate and transfer their intellectual property overseas, India loses valuable IP assets, undermining the country's competitive advantage and innovation potential.
- Reduced tax revenue: Flipping also contributes to decreased tax revenue for India as companies shift their operations and profits to other jurisdictions, which may have more favorable tax policies.
New sensor can detect 'forever chemicals' in drinking water

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A team of chemists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has designed a breakthrough method for the detection of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
What are Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)?
- Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a class of man-made chemicals that have been in use since the 1940s.
- Due to their unique properties, such as high chemical stability and resistance to heat, grease, and water, PFAS have been widely used in various industrial and commercial applications.
- They are commonly found in products such as stain- and water-resistant fabrics, cleaning products, paints, and fire-fighting foams.
- PFAS are often referred to as "forever chemicals" because they do not break down naturally in the environment.
- This is due to the strong carbon-fluorine bond that characterizes these compounds, making them highly persistent and resistant to degradation.
- The widespread use of PFAS has resulted in increasing levels of environmental contamination, with PFAS being detected in air, water, and soil samples worldwide.
- Exposure to these chemicals has been linked to a range of health risks, including decreased fertility, developmental effects in children, interference with body hormones, increased cholesterol levels, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Due to their persistent nature and potential health risks, there is growing concern about the widespread use of PFAS and the need for improved regulation and remediation strategies to manage their environmental and health impacts.
- Environmental Persistence: Due to their strong carbon-fluorine bonds, PFAS do not break down easily in the environment.
- They can accumulate in soil, water, and living organisms, posing a long-term risk to ecosystems and human health.
- Bioaccumulation: PFAS can accumulate in living organisms, including humans, through the food chain.
- Even small amounts of PFAS in the environment can build up to harmful levels in animals and humans over time.
- Regulatory Action: Due to the potential health and environmental risks associated with PFAS, many countries are taking regulatory action to restrict their use and manage their environmental impacts.
- This includes banning certain PFAS-containing products, setting drinking water standards, and requiring the clean-up of contaminated sites.
BSNL floats Rs 65,000 crore tender for phase-III BharatNet project

- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
BSNL, the state-owned telecommunications company, has initiated a tender process amounting to approximately Rs 65,000 crore for the implementation of the phase-III BharatNet project.
What is the BharatNet Phase III Project?
- The BharatNet phase-III project adopts a three-level architecture:
- Internet leased line bandwidth
- Middle-mile connectivity, and
- Last-mile connectivity
- It aims to involve village-level entrepreneurs or Udyamis in providing last-mile connectivity to households on a revenue-sharing basis.
- BSNL aims to provide 15 million home fibre connections over five years using the BharatNet Udyami model.
About BharatNet Project:
- The BharatNet Project is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world.
- It aimed at providing broadband connectivity to all Gram Panchayats across India in a phased manner.
- Its core objective is to ensure equitable access to broadband services for all telecom service providers, fostering the deployment of services like e-health, e-education, and e-governance in rural and remote areas.
- Initiated in 2011 and executed by Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in 2012, the project operates in three phases.
- Phase I launched in 2011, focused on creating the National Optical Fibre Network, leveraging existing infrastructure and laying additional fibre to bridge connectivity gaps up to the Gram Panchayat level.
- Phase II, approved in 2017, builds upon Phase I’s experiences, aligning with the Digital India vision.
- It adopts a flexible approach, integrating various media such as Optical Fibre Cable (OFC), Radio, and satellite to connect Gram Panchayats, utilizing models like State-led, Private Sector, and CPSU Models for implementation.
- Phase III, spanning from 2019 to 2023, aims to establish a robust, future-ready network with district-to-block fibre connectivity, featuring ring topology for redundancy.
- This comprehensive approach ensures the creation of a resilient and inclusive telecom infrastructure, facilitating socio-economic development in rural India.
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 (Indian Express)

- 06 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Centre on Monday introduced a Bill that would enable it to prescribe the norms for nominating chairpersons of State Pollution Control Boards, exempt certain industrial units from restrictions, and decriminalize “minor offenses” related to water pollution.
News Summary:
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024 has been introduced in the Rajya Sabha.
- It is applicable to Himachal Pradesh and Rajasthan, with the potential to extend to other states through resolutions under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- The Bill empowers the Centre to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions and issue guidelines related to industry establishment.
About Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Amendment Bill, 2024:
- Enacted in 1974, the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act aimed to prevent and control water pollution, establishing penal provisions for non-compliance.
Rationale for the Amendment:
- The Amendment Bill underscores the importance of democratic governance, emphasizing trust in people and institutions. It addresses the outdated regulations leading to a trust deficit.
Key Amendments Proposed:
- The Amendment Bill seeks to modernize the existing penal provisions, replacing imprisonment with fines for minor violations. This move aligns with the principles of Ease of Living and Ease of Doing Business.
Major Features of the Amendment Bill:
- The Bill proposes several key changes, including:
- Prescribing the process for nominating the chairman of the State Pollution Control Board by the Central Government.
- Granting the Central government authority to exempt certain industrial plants from restrictions on new outlets and discharges.
- Issuing guidelines on matters related to the establishment of industries by the Central government.
- Decriminalizing minor offenses and substituting them with monetary penalties.
- Specifying the adjudication process for penalties by officers of appropriate rank.
- Outlining penalties for non-compliance with regulations regarding new outlets, discharges, and sewage.
- Allocation of penalty amounts to the Environmental Protection Fund established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
RBI Action Against Paytm Payments Bank (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently barred Paytm Payments Bank from offering all its core services — including accounts and wallets — from March, effectively crippling the company’s business.
News Summary
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has directed Paytm Payment Bank to halt accepting money in any customer account, including wallets and prepaid instruments like FASTags, from March 1.
- This action comes due to ongoing non-compliance and significant supervisory concerns highlighted by the RBI.
What Does the RBI Directive Include?
- Barred Services: Paytm Payment Bank is prohibited from offering most of its essential services.
- Account Closure: Paytm cannot accept deposits or top-ups after February 29, and nodal accounts of its parent company, One97 Communications, and Paytm Payments Services, must be terminated by February 29.
- Transaction Settlement: All pending transactions and nodal accounts initiated by February 29 must be settled by March 15.
- Customer Withdrawals: Customers are permitted to freely withdraw or use the money from their Paytm accounts, including savings and current accounts, prepaid instruments, FASTags, etc., within their available balance.
Reasons Behind the Action:
- Ongoing Scrutiny: Paytm Payment Bank has been under RBI scrutiny since 2018.
- Compliance Concerns: While specifics were not disclosed, it's believed the action stems from RBI's concerns about KYC compliance and IT-related issues.
- Data Security: RBI is cautious about safeguarding depositors' money and protecting data.
- Concerns arose when Paytm Payment Bank and its parent company lacked sufficient barriers to prevent unauthorized access to data by China-based entities with indirect stakes in the parent company.
What is a Payments Bank?
- Payment banks function similarly to traditional banks but on a smaller scale and without engaging in credit risk.
- Established based on recommendations from the Nachiket Mor Committee, their primary objective is to promote financial inclusion by providing banking and financial services to underserved areas, including migrant workers, low-income households, and small entrepreneurs.
Legal Framework and Features:
- Registered as public limited companies under the Companies Act 2013 and licensed under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act 1949, payments banks operate under various regulations such as the Banking Regulation Act 1949, RBI Act 1934, and Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999.
Key features include:
- Differentiation: Payments banks are distinct from universal banks and operate on a smaller scale.
- Capital Requirement: The minimum paid-up equity capital for payment banks is set at 100 crores, with promoters required to contribute at least 40% during the first five years of operation.
- Permissible Activities: Payments banks can accept deposits up to Rs. 2,00,000, invest in government securities to meet statutory liquidity requirements and provide various banking services such as remittance, mobile payments, ATM/debit cards, and net banking.
- Additionally, they can serve as banking correspondents for other banks.
- Limitations: Payments banks are restricted from issuing loans and credit cards, accepting time deposits or NRI deposits, and establishing subsidiaries for non-banking financial activities.
CBSE Proposes New Plan For Class 10 & 12 (Indian Express)

- 01 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
CBSE is reported to have proposed significant changes to the academic framework for secondary and higher secondary education, including a shift from studying two languages to three in Class 10, with the requirement that at least two must be native Indian languages.
Key Highlights of the Proposal:
Proposed Changes for Class 10:
- Transition from studying two languages to three, with a stipulation that at least two must be native Indian languages.
- Potential requirement for students to pass in 10 subjects, contrasting with the current mandate of five.
Proposed Changes for Class 12:
- Shift to studying two languages instead of one, with the condition that at least one must be a native Indian language.
- Introduction of a necessity to clear examinations in six subjects for high school graduation, up from the existing requirement of five.
The objective behind the Proposed Changes:
- These modifications are part of CBSE's broader initiative to implement a national credit framework in school education, addressing the absence of a formalized credit system in the standard curriculum.
Academic Year and National Learning Hours:
- According to the CBSE plan, an academic year will comprise 1200 notional learning hours, equivalent to earning 40 credits.
- Notional learning denotes the specified time required for an average student to achieve set outcomes.
- This encompasses both academic learning at school and non-academic or experiential learning outside of it.
Storage of Earned Credits:
- The scheme of studies has been adjusted to outline teaching hours and credits earned for each subject.
- These earned credits will be digitally stored in the Academic Bank of Credits, accessible through a linked Digilocker account.
What is the National Credit Framework (NCrF)?
- The draft NCrF was introduced by the Union Ministry of Education (MoE) in 2022, based on recommendations from an inter-ministerial committee.
- It serves as a guideline for schools, colleges, and universities to adopt the credit system, marking the inclusion of the entire school education system under its purview.
- Previously, only the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) followed a credit system, but the NCrF extended its coverage to include skill and vocational education.
Proposed Benefits of NCrF for Various Stakeholders:
- Students:
- Facilitates multidisciplinary education with flexible curricula.
- Eliminates distinctions between different streams like arts, science, social sciences, and commerce.
- Rewards students with credits for academic, skill, and experiential learning.
- Expands core learning to encompass both foundational and cognitive aspects.
- Institutions:
- Fosters collaboration between institutions.
- Simplifies and standardizes credit mechanisms.
- Emphasizes research and innovation.
- Utilizes institutional infrastructure efficiently.
- Government:
- Expected to increase student enrollment rates.
- Complements India's demographic dividend, aiming to become the Skill Capital of the World.
- Industry:
- Enables students to acquire NSQF-approved foundational skills from the industry, enhancing employability.
- Allows for quick educational upgradation and up-skilling through micro-credentials.
Significance of NCrF:
- Aligns with the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 by integrating academic and vocational domains for flexibility and mobility.
- Facilitates re-entry into the education system for students who have dropped out.
- Promotes Recognition of Prior Learning, acknowledging skills acquired informally through various means.
SC directs UOI to frame a policy to phase out heavy-duty diesel vehicles & replace them with BS VI (The New Indian Express)
- 13 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court has directed the Centre to frame a policy within six months to replace heavy-duty diesel vehicles and replace them with BS VI vehicles, observing that the right to clean air is not the entitlement of people living in Delhi alone.
What are BS-VI Norms?
- Bharat stage (BS) emission standards are laid down by the government to regulate the output of air pollutants from internal combustion engines and spark-ignition engine equipment, including motor vehicles.
- The central government has mandated that vehicle makers must manufacture, sell and register only BS-VI (BS6) vehicles from April 1, 2020.
- The first emission norms were introduced in India in 1991 for petrol and in 1992 for diesel vehicles.
- Following this, the catalytic converter became mandatory for petrol vehicles and unleaded petrol was introduced in the market.
What is the Difference Between BS4 and BS6?
- Both BS-IV and BS-VI are unit emission norms that set the maximum permissible levels for pollutants that an automotive or a two-wheeler exhaust can emit.
- Compared to the BS4, BS6 emission standards are stricter
- Whereas makers use this variation to update their vehicles with new options and safety standards, the biggest modification comes in the permissible emission norms.
What area unit BSI, BSII, BSIII, BSIV, and BSVI emission norms?
- The abbreviation BS refers to ‘Bharat Stage’.
- It is prefixed to the iteration of the actual emission norms.
- The primary rules with the soubriquet Asian nation 2000 were introduced in the year 2000, with the second and third iterations being introduced in 2001 and 2005 with the soubriquet BSII (BS2) and BSIII (BS3), respectively.
- The fourth iteration, BSIV, was introduced in 2017 and therefore the delay between the introduction of BS3 and BS4 resulted in fast-tracking the BSVI or BS6 emission norms rather than BSV (BS5) norms.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- Carmakers were not prepared for this transition and in a subsequent judgment, the implementation of Euro II was deferred.
- On 29 April 1999, the Supreme Court of India ruled that all vehicles in the country had to meet Euro I or India 2000 norms by June 1, 1999, and Euro II would be mandatory in the National Capital Region (NCR) from April 2000.
- In 2002, the government accepted the report submitted by the Mashelkar committee, which proposed a road map for the rollout of Euro-based emission norms in India.
- It also recommended a phased implementation of future norms, with regulations being implemented in major cities first and extended to the rest of the country after a few years.
- Based on the recommendations of the committee, the National Auto Fuel policy was announced officially in 2003.
- The road map for the implementation of the BS norms was laid out in 2010.
- The policy also created guidelines for auto fuels, reduction of pollution from older vehicles and R&D for air quality data creation and health administration.
- The standards and the timeline for implementation are set by the Central Pollution Control Board under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Since October 2010, Bharat Stage (BS) III norms have been enforced across the country.
- BS-IV emission norms were put in place in 13 major cities from April 2010, and the entire country from April 2017.
- In 2016, the government announced that the country would skip the BS-V norms altogether and adopt BS-VI norms by 2020.
Namibian cheetah Aasha gives birth to 3 cubs in Kuno; ‘indicator that animals are acclimatising’ (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a Namibian cheetah named Aasha has given birth to three cubs at Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
About Kuno National Park (KNP):
- Location: Situated in the Sheopur district of Madhya Pradesh, Kuno National Park is nestled near the Vindhyan Hills.
- The park is aptly named after the Kuno River, a significant tributary of the Chambal River that traverses its expanse.
- Originally designated as a wildlife sanctuary, Kuno National Park attained the status of a national park in 2018.
- This transformation aligns with its pivotal role in the 'Action Plan for Introduction of Cheetah in India.'
- Vegetation and Flora: Kuno predominantly features a grassland landscape, punctuated by occasional rocky outcrops.
- The flora encompasses a diverse mix, including dominant species such as Kardhai, Salai, and Khair trees.
- The park boasts a rich composition with 123 tree species, 71 shrub species, 32 exotic and climbing species, and 34 bamboo and grass species.
- Fauna: The protected region of Kuno National Park shelters an array of wildlife, including the jungle cat, Indian leopard, sloth bear, Indian wolf, striped hyena, golden jackal, Bengal fox, and dhole.
- The park also delights bird enthusiasts with a habitat supporting over 120 bird species.
What is Project Cheetah?
- The Wildlife Trust of India started talks in 2009 to bring the cheetah back to India.
- Over five years, 50 cheetahs will be imported from African nations and placed in various national parks as part of the "Action Plan for Reintroduction of Cheetahs in India."
- Prime Site Selection - Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP): Among the surveyed sites in central Indian states, Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP) in Madhya Pradesh emerged as the most suitable location.
- This acclaim is attributed to its conducive habitat and ample prey base.
- KNP is deemed capable of supporting 21 Cheetahs, uniquely standing as a wildlife site where villages have been entirely relocated from within the park.
- Moreover, Kuno offers the prospect of harmoniously accommodating four of India's prominent big cats - tiger, lion, leopard, and Cheetah.
- Additional Recommended Sites: The project identifies other potential sites, including Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh), Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary - Bhainsrorgarh Wildlife Sanctuary complex (Madhya Pradesh), Shahgarh bulge in Jaisalmer (Rajasthan), and Mukundara Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan).
- Implementation Progress: As a significant stride in the project's realization, 20 Cheetahs, comprising 8 from Namibia and 12 from South Africa, were introduced to Kuno Palpur National Park last year.
- This marks a historic initiative to establish a free-ranging Cheetah population in India, reviving their presence after a 70-year absence.
Another eye in the sky, on the ground: India is now part of the world’s largest radio telescope project (Indian Express)

- 03 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian government’s recent approval to join the SKA project, accompanied by a financial commitment of Rs 1,250 crore, marks the initial step towards this ratification.
What is the Square Kilometre Array Observatory (SKAO)?
- SKAO is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to radio astronomy and is headquartered in the UK.
- At the moment, organisations from ten countries are a part of the SKAO.
- These include Australia, Canada, China, India, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, the Netherlands and the UK.
What is significant about the SKA telescope?
- The telescope, proposed to be the largest radio telescope in the world, will be located in Africa and Australia whose operation, maintenance and construction will be overseen by SKAO.
- The completion is expected to take nearly a decade at a cost of over £1.8 billion.
- Some of the questions that scientists hope to address using this telescope include:
- Beginning of the universe
- How and when the first stars were born
- The life cycle of a galaxy
- Exploring the possibility of detecting technologically-active civilisations elsewhere in our galaxy and
- Understanding where gravitational waves come from.
- As per NASA, the telescope will accomplish its scientific goals by measuring neutral hydrogen over cosmic time, accurately timing the signals from pulsars in the Milky Way, and detecting millions of galaxies out to high redshifts.
- Significantly, the development of SKA will use the results of various surveys undertaken using another powerful telescope called the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP), which is developed and operated by the country’s science agency CSIRO.
- This telescope, which has been fully operational since February 2019 mapped over three million galaxies in a record 300 hours during its first all-sky survey.
- ASKAP surveys are designed to map the structure and evolution of the Universe, which it does by observing galaxies and the hydrogen gas that they contain.
What are radio telescopes?
- Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can detect invisible gas and, therefore, they can reveal areas of space that may be obscured by cosmic dust.
- Significantly, since the first radio signals were detected by physicist Karl Jansky in the 1930s, astronomers have used radio telescopes to detect radio waves emitted by different objects in the universe and explore them.
- According to NASA, the field of radio astronomy evolved after World War II and became one of the most important tools for making astronomical observations.
- The Arecibo telescope in Puerto Rico, which was the second-largest single-dish radio telescope in the world, collapsed in December 2020.
- The telescope was built in 1963 and because of its powerful radar, scientists employed it to observe planets, asteroids and the ionosphere, making several discoveries over the decades, including finding prebiotic molecules in distant galaxies, the first exoplanets, and the first millisecond pulsar.
Article 356 of the Indian Constitution (The Hindu)

- 12 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The Supreme Court recently held that the declaration of State emergency under Article 356 and the subsequent actions of the President should have a “reasonable nexus”.
What is Article 356 of the Indian Constitution?
Article 356 of the Constitution of India is based on Section 93 of the Government of India Act, 1935. According to Article 356, the President's Rule can be imposed on any state of India on the grounds of the failure of the constitutional machinery.
There are two types:
- If the President receives a report from the state's Governor or otherwise is convinced or satisfied that the state's situation is such that the state government cannot carry on the governance according to the provisions of the Constitution.
- Article 365: As per this Article, President's Rule can be imposed if any state fails to comply with all directions given by the Union on matters it is empowered to.
In simple words, President's Rule is when the state government is suspended and the central government directly administers the state through the office of the governor (centrally appointed. It is also called State Emergency or Constitutional Emergency.
President's Rule:
- Parliamentary approval is necessary for the imposition of the President's Rule on any state.
- The proclamation of President's Rule should be approved in both Houses of Parliament within two months of its issue.
- The approval is through a simple majority.
- The President's Rule is initially for a period of six months.
- Later, it can be extended for a period of three years with parliamentary approval, every six months.
- The 44th Amendment to the Constitution (1978) brought in some constraints on the imposition of the President's Rule beyond a period of one year. It says that the President's Rule cannot be extended beyond one year unless:
- There is a national emergency in India.
- The Election Commission of India certifies that it is necessary to continue the President's Rule in the state because of difficulties in conducting assembly elections in the state.
What happens after the President's Rule is imposed?
- The governor carries on with the administration of the state on behalf of the President. He or she takes the help of the state's Chief Secretary and other advisors/administrators whom he or she can appoint.
- The President has the power to declare that the state legislature's powers will be exercised by the Parliament.
- The state legislative assembly would be either suspended or dissolved by the President.
- When the Parliament is not in session, the President can promulgate ordinances with respect to the state's administration.
When is the President's Rule imposed?
- President's Rule is typically imposed when any of the following circumstances occur:
- The state legislature is unable to elect a leader as the Chief Minister within the time prescribed by the state's governor.
- Breakdown of a coalition in the state government, resulting in the Chief Minister having minority support in the legislature, and the CM is unable to prove a majority within the time prescribed by the governor.
- A vote of no confidence in the legislative assembly leads to a loss of majority.
- Postponement of elections due to unavoidable reasons such as a natural disaster, epidemic, or war.
Revocation of President's Rule:
- President's Rule can be revoked anytime after such a proclamation has been made by a subsequent proclamation by the President.
- A proclamation of revocation does not require approval by the Parliament.
- This occurs when the leader of a political party produces letters indicating majority support for him in the assembly and stakes his claim to form the state government.
Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TOI)

- 15 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A dominant tiger named Bajrang said to have sired at least 50 cubs during his lifetime, recently died in a territorial fight with another powerful tiger, Chhota Matka, in the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR).
About Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve is the oldest and largest National Park in the Chandrapur district of Maharashtra.
- It is one of India's 47 project tiger reserves existing in India.
- The total area of the tiger reserve is 1,727 Sq.km, which includes the Tadoba National Park, created in the year 1955.
- The Andhari Wildlife Sanctuary was formed in the year 1986 and was amalgamated with the park in 1995 to establish the present Tadoba Andheri Tiger Reserve.
- The word 'Tadoba' is derived from the name of God "Tadoba" or "Taru," which is praised by local tribal people of this region, and "Andhari" is derived from the name of the Andhari river that flows in this area.
- Tadoba is presently home to more than 115 tigers, which is one of the highest in India.
- The vegetation of Tadoba forest is of Southern tropical dry deciduous type and is spread on around 626 sq. km.
- Teak is the prominent tree species in the forest.
- The Tadoba Tiger Reserve is rich in flora and fauna
- Flora: Some of the famous and widely seen flora of this park include Teak, Ain, Bija, Bamboo, Black Plum, and many others.
- Fauna: Tigers, Indian leopards, Sloth bears, Gaur, Nilgai, Striped Hyena, Spotted Deer, Barking Deer, Marsh Crocodile, etc.
Hydroclimate Extremes (PIB)
- 03 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
A recent study conducted at Banaras Hindu University explored the impact of global warming on hydroclimate extremes in the Indian River Basins (IRBs).
About Hydroclimate Extremes:
- Hydroclimatic extremes are severe events with significant impacts on both human societies and ecosystems.
- These events encompass phenomena such as floods, droughts, heat waves, and heavy rainstorms.
Key Findings:
- The research utilized highly detailed simulated precipitation data derived from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project-6 (CMIP6) experiments.
- The study's results suggest an anticipated rise in the frequency of extreme rainfall in the Western Ghats and Northeast River basins.
- Additionally, heavy rainfall intensity is predicted to increase in the Upper Ganga and Indus basins.
- The research sheds light on an agricultural drought in the lower Ganga basin, attributed to a reduction in average rainfall.
Importance:
- This study underscores the importance of policymakers creating strategies to address both excess and shortage of water resources.
- It anticipates a 4% to 10% rise in intense rainfall in the western regions of Indian river basins, along with noteworthy shifts in precipitation patterns in specific areas.
- These alterations in hydroclimate extremes could greatly impact agriculture, public health, and socio-economic conditions.
- Furthermore, the research identifies critical areas prone to urban flooding in densely populated cities, emphasizing the need for policymakers to devise tailored climate adaptation and mitigation plans.
- These should encompass policies related to water management and emergency services to mitigate the risks posed by extreme events in these basins.
THE SUBSURFACE WATER ICE MAPPING (SWIM) PROJECT (TOI)
- 30 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project, funded by NASA, has released its fourth map pinpointing potential subsurface water ice locations on Mars.
Facts About:
The Subsurface Water Ice Mapping (SWIM) project goal is to find the best locations to access water ice buried beneath the Mars' surface.
Recently, they released their fourth set of maps, which are the most detailed and accurate maps so far since the project began in 2017.
This project is led by the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
- They gather data from various NASA missions like the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), the 2001 Mars Odyssey, and the now-inactive Mars Global Surveyor.
To create these maps, SWIM utilized two high-resolution cameras on the MRO.
- They used Context Camera data to make better maps of the Northern Hemisphere.
- For the first time, they used HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) data to get the closest, most detailed view of the ice's edge near the equator.
The SWIM project was done in two phases.
- The first phase, finished in 2019, focused on the northern hemisphere, and
- The second phase, completed in 2020, included the southern hemisphere.
One exciting thing about the new map is that it shows 'polygon terrain,' where the ice beneath the surface causes the ground to crack into polygonal shapes.
- This suggests there's more ice hidden below.
WHITE PHOSPHOROUS BOMBS (Indian Express)
- 21 Oct 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent reports, Israeli forces have been using white phosphorous against the civilian population of Gaza.
Facts About:
It is a waxy solid that is colorless, white, or yellow.
Occurrence:
- It does not occur naturally. Phosphate rocks are used to make it.
- It is a highly flammable substance that reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere.
- As little as 10 to 15 degrees above room temperature can cause it to catch fire.
Every country has strict regulations regarding its manufacturing and handling due to its combustible nature.
Applications:
- It is primarily used in the military, but it may also be used as a component in fertilizers, food additives, and cleaning compounds.
- It was originally used in pesticides and fireworks, but many countries have banned its use in a variety of industries.
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), an intergovernmental organization and the implementing body for the Chemical Weapons Convention, has not included White Phosphorus in any of the three Chemical Weapons Schedules.
