6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee Meeting
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The 6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee and related meetings for discussions on the review of the AITIGA were held recently in Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Key Negotiation Areas
- 8 Sub-Committees under the AITIGA Joint Committee discussed:
- Market access, rules of origin, SPS measures, standards and technical regulations.
- Customs procedures, economic and technical cooperation, trade remedies, and legal and institutional provisions.
- 5 Sub-Committees met physically during this round of negotiations.
Progress in Discussions
- Textual Discussions: Sub-Committees made progress in discussions on various provisions.
- Tariff Negotiations: Initial steps towards initiating tariff negotiations were covered.
High-Level Meetings Leading to AITIGA Review
- 21st ASEAN-India Economic Ministers Meeting: Held in September 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
- 21st ASEAN-India Summit: Held in October 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
Both meetings urged the Joint Committee to expedite negotiations and aim for the conclusion of the review in 2025.
Bilateral Meetings
- ASEAN delegates held separate bilateral meetings with Thailand and Indonesia to discuss bilateral trade issues.
- Indian and ASEAN Chief Negotiators met to align on the ongoing issues and future steps.
India's Review Demands
- Request for Review: India sought a review of AITIGA (implemented in 2010), citing disproportionate trade benefits favoring ASEAN countries.
- India’s Objectives:
- Enhanced Market Access: India pushed for ASEAN countries, especially Vietnam, to commit to greater market-opening for Indian goods.
- Stricter Rules of Origin (ROO): India requested more stringent ROO provisions to prevent Chinese goods from entering India via ASEAN countries at preferential rates.
Trade Relationship and Economic Impact
- Bilateral Trade:
- Total trade with ASEAN reached USD 121 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Trade during April-October 2024 was USD 73 billion, marking a 5.2% growth.
- Trade Deficit: India’s trade deficit with ASEAN widened from USD 4.98 billion in FY 2010-11 to USD 38.4 billion in 2023-24.
- ASEAN accounts for 11% of India’s global trade.
Future Outlook
- The next meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee is scheduled for February 2025 in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The review process aims to further enhance sustainable trade between India and ASEAN countries.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA)

- 13 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The 4th joint committee meeting for the review of AITIGA (ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement) was held in Putrajaya, Malaysia recently.
About ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009.
- The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- In 2019-20, trade between India and ASEAN was worth US$86 billion.
- Though this represented a decline from US$97 billion in 2018-19 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, it was an increase from US$81.3 billion in the 2017-18 financial year.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products and it does not apply to trade in services.
- ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
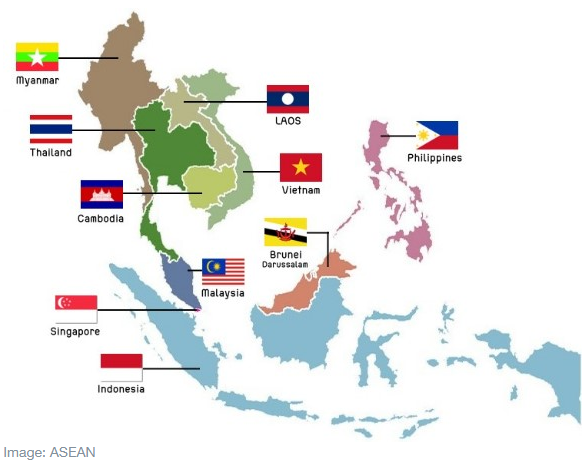
About the Association of the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
- The Association of the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a geopolitical and economic organization established to accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development among its ten (10) member states.
- It also aims to promote peace and stability in the region, active collaboration and mutual assistance on matters of common interest, Southeast Asian studies, and maintain close and beneficial cooperation with other regional and international organizations.
- It was established on 8 August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration by the founding members of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Brunei Darussalam then joined in 1984, Viet Nam in 1995, Lao PDR and Myanmar in 1997, and Cambodia in 1999, making up the current 10 Member States of ASEAN.
- The ASEAN Secretariat was set up in February 1976 and is based in Jakarta, Indonesia.
