162 cases of Covid sub-variant JN.1 detected in India; highest from Kerala, Gujarat: INSACOG (Live Mint)
- 30 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
India reported a total of 109 JN.1 COVID variant cases in the country as of December 26, Health Ministry sources recently said.
What is Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG)?
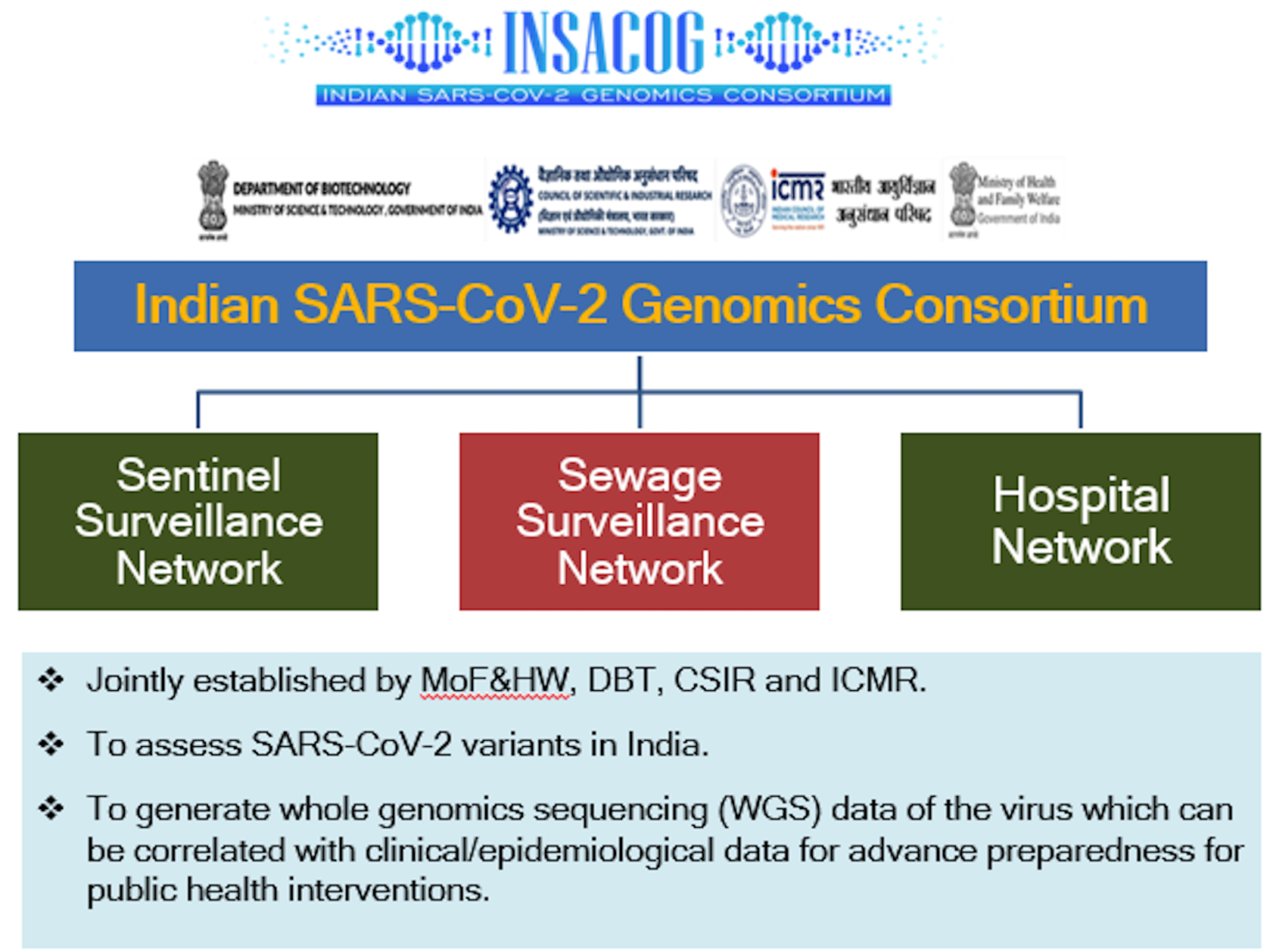
- Established in December 2020, INSACOG is a collaborative initiative involving the Union Ministry of Health, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Council for Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- The consortium's primary mission is to expand whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus responsible for Covid-19, across India.
- This initiative aims to comprehend the virus's spread and evolution.
- INSACOG initially engaged 10 national research laboratories of the central government and has grown into a network of 38 labs, including private labs, following a hub-and-spoke model.
- The consortium's Genome Sequencing Laboratories guide new laboratories, working in tandem to monitor genomic variations through sentinel sequencing facilitated by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) under the Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP) of the central government.
- Beyond sequencing efforts, INSACOG endeavors to establish a systematic correlation between genome sequencing and clinical outcomes.
- It is actively building a nationwide hospital network to investigate clinical correlations in mild versus severe cases of Covid-19.
- Additionally, the consortium is conducting a longitudinal study to comprehend long-term post-Covid complications and changes in immunity.
- Looking ahead, INSACOG is exploring sewage surveillance as an early detection tool and assessing the spread of variants in hotspot localities.
