Trade Watch Quarterly
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
NITI Aayog released its first quarterly report, Trade Watch Quarterly (TWQ), on December 4, 2024, focusing on India's trade developments during Q1 FY2024 (April-June).
Overview:
- Purpose: The publication aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of India’s trade performance, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Target: To leverage insights for evidence-based policy interventions and foster informed decision-making, contributing to sustainable growth in India’s trade.
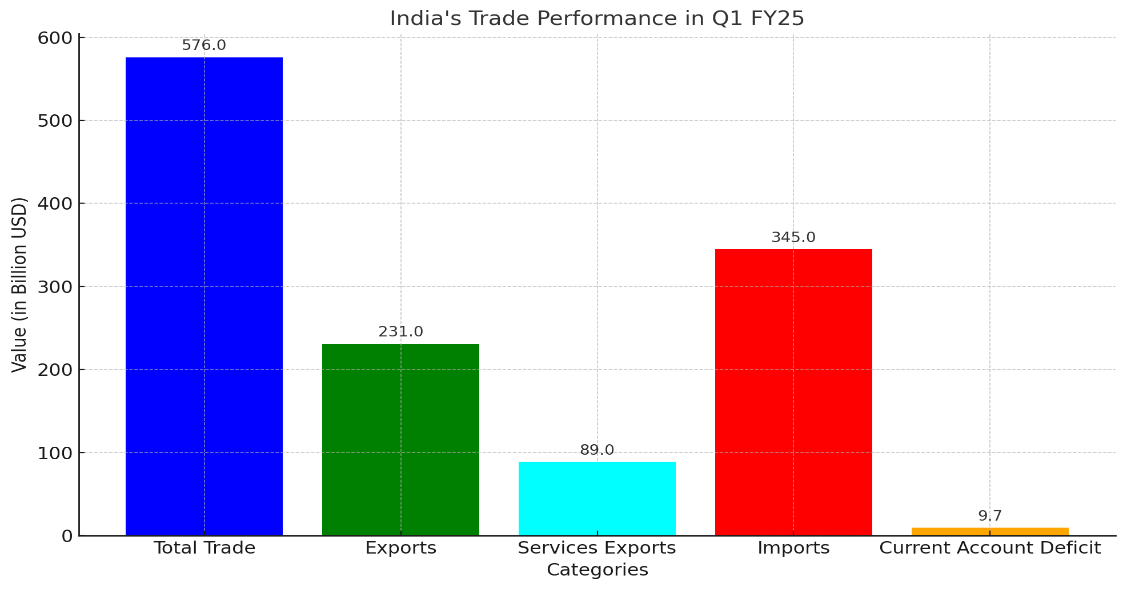
Trade Performance Highlights (Q1 FY24):
- Total Trade: $576 billion (5.45% YoY growth).
- Merchandise Exports: Growth was restrained due to declines in iron & steel, and pearls.
- Imports: Driven by high-value goods, including aircraft, spacecraft, mineral fuels, and vegetable oils.
- Services Exports: Displayed a surplus, particularly in IT services.
- Growth in Services Exports: A positive trend, rising by 10.09% YoY, particularly in IT services and business solutions.
Key Challenges for India’s Trade:
- Limited Success in China-Plus-One Strategy:Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia have gained more from this strategy, benefitting from cheaper labor, simplified tax laws, and lower tariffs.
- CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism):Starting in 2026, CBAM will impose carbon taxes on imports like cement, steel, and fertilizers. India’s iron and steel industry could face significant risks due to this.
- Declining Share in Labor-Intensive Sectors:India’s global market share in labor-intensive sectors (e.g., textiles, leather) has declined despite a strong workforce.
- Geopolitical Instability (West Asia):
- Oil price hikes could increase India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) and fuel inflation.
- Declining agricultural exports to markets like Iran further add to the challenges.
Strategic Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges:
- Infrastructure Modernization:
- Expansion of digital platforms like Trade Connect e-Platform to streamline processes and support exporters.
- Strengthening logistics via the National Logistics Policy.
- Export Incentives:Continuation of schemes like RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) to maintain export competitiveness.
- Technological Integration:Leveraging digital trade to tap into high-growth sectors and foster innovation in trade.
- Strengthening FTAs (Free Trade Agreements):Focus on negotiating strategic FTAs with global partners (e.g., the UK and the EU) to reduce trade barriers and enhance global market access.
Geopolitical and Environmental Risks:
- U.S.-China Trade Tensions:Offers opportunities for India to diversify its supply chains, but also poses challenges in terms of overdependence on certain countries.
- Impact of CBAM:Risk to carbon-intensive Indian exports like steel and aluminium, which will face tariffs starting in 2026.
Sectoral Performance:
- Growing Sectors:
- IT Services: India’s market share of IT services reached 10.2%, continuing to be a strong contributor.
- Pharmaceuticals, Electrical Machinery, and Mineral Fuels: Significant contributors to export growth.
- Declining Sectors:Labor-Intensive Goods: Declines in global market share for textiles, pearls, and leather.
Pathway to $2 Trillion Exports by 2030:
- India's Export Aspirations:To achieve the target of $2 trillion in exports by 2030, India must address structural inefficiencies, diversify exports, and reduce trade barriers.
- Vision 2047:Aligning with India’s broader vision to become a developed nation, the report stresses the importance of strengthening trade, technology, and infrastructure to realize these ambitions.
- Trade's Role in Economic Growth:
- Trade is vital to India’s economic trajectory, contributing significantly to GDP growth.
- Through evidence-based policymaking, infrastructure modernization, and strategic global partnerships, India can achieve sustained growth in trade, leading to the realization of a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
