Sovereign Artificial Intelligence

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been remarkable in recent years. In 2018, a 340-million-parameter AI model was considered large, whereas models like ChatGPT now have 1.8 trillion parameters.
- As part of its ambition to make the digital economy worth USD 1 trillion by 2028, India is focusing on AI sovereignty and investing in semiconductors and AI technologies to achieve this goal.
What is Sovereign AI?
Definition
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s ability to develop, control, and deploy AI using its own resources, including infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This involves not just developing AI models but also creating infrastructure and nurturing homegrown talent to lead AI advancements within the country.
Key Aspects of Sovereign AI
- National Control: Ensures AI technologies align with a country's laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Emphasizes control of data within the country’s borders, protecting privacy, security, and national interests.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is transforming industries, markets, and governance, with AI-powered tools assisting professionals and governments.
- Ethical Considerations: Countries define security protocols and ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI technologies.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign technologies, encouraging domestic development in AI to achieve strategic independence.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is crucial for industrial innovation. Without it, nations risk falling behind in the global economy.
Growth and Importance of AI
Evolution of AI Models
- In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered a significant achievement.
- Today, ChatGPT uses 1.8 trillion parameters, and Google’s Gemini uses 1.5 trillion parameters. In comparison, China’s DeepSeek has a model with 240 billion parameters.
- Parameters are the internal variables of AI models, adjusted during training to improve their performance and accuracy.
Strategic Applications
- Sovereign AI plays a pivotal role in critical sectors such as:
- Defense
- Healthcare
- Transportation
- Governance
- It helps redefine industries, boost innovation, and streamline operations across various sectors.
India’s Position in Sovereign AI
AI Infrastructure Development
- Tata Group and Reliance are building AI infrastructure in India, including the development of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- India has allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project under the IndiaAI Mission, which includes creating an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips.
Government Initiatives
- The IndiaAI Mission is designed to boost India’s AI capabilities by building infrastructure, fostering talent, and supporting innovation within the country.
Global AI Compact
- A Global AI Compact has been proposed to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
- The compact advocates for sharing AI resources globally while promoting cooperation and addressing challenges associated with AI governance.
Dr. V. Narayanan Takes Over as ISRO Chairman
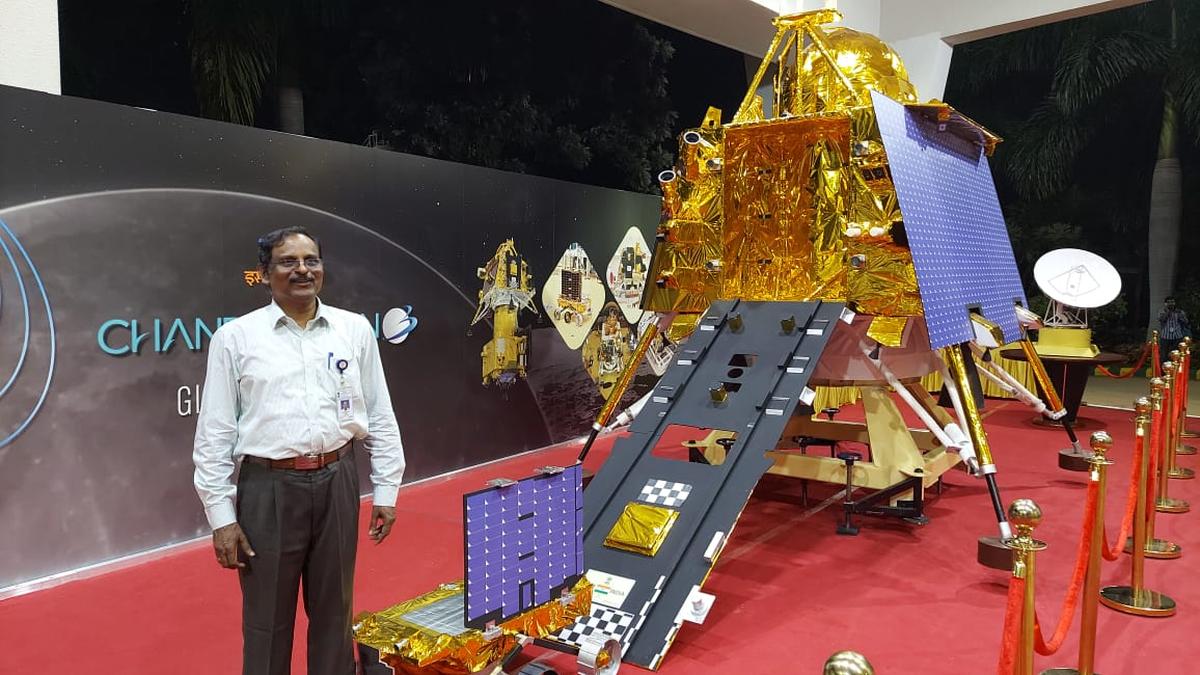

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
Dr. V. Narayanan has been appointed as the new Chairman of ISRO and Secretary of the Department of Space (DoS), effective from January 14, 2025, succeeding Dr. S. Somanath.
Background and Career of Dr. V. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan, currently the Director of Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, has been a key figure in ISRO since joining in 1984. With a focus on cryogenic propulsion, he has played an instrumental role in developing critical technologies for ISRO's launch vehicles. Notably, his work has contributed to India becoming the sixth country globally capable of building and operationalizing cryogenic engines.
Dr. Narayanan’s career highlights include:
- Cryogenic Technology: Leading the development of cryogenic engines for LVM3 (India's heaviest launch vehicle) and PSLV, which are central to missions like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan.
- Chandrayaan-2 & Chandrayaan-3: As part of ISRO’s missions to the moon, his contributions were pivotal in rectifying the propulsion system issues post-Chandrayaan-2's hard landing, leading to the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 in August 2023.
- Gaganyaan Mission: Overseeing the development of the propulsion systems for crew and service modules, critical for India’s ambitious human spaceflight program.
Dr. S. Somanath's Legacy:
Dr. S. Somanath, who served as ISRO Chairman and DoS Secretary spearheaded multiple landmark missions, including:
- Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and INSAT missions.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Re-usable Launch Vehicle (RLV-LEX), and Gaganyaan abort missions.
- National Space Policy 2023 and fostering partnerships between ISRO and private ventures.
Dr. Somanath’s tenure significantly elevated India’s space capabilities, with Chandrayaan-3 marking a historic milestone in India’s lunar exploration.
Dr. Narayanan’s Role in Upcoming ISRO Missions:
As ISRO Chairman, Dr. Narayanan will oversee several ambitious space missions, including:
- NVS-02: The launch of India's navigation satellite as part of the IRNSS constellation.
- Unmanned Gaganyaan Mission: Leading the uncrewed G-1 flight, a precursor to India's first human spaceflight.
- Indo-US NISAR Satellite: A significant collaborative launch with NASA for earth observation.
Additionally, high-profile projects such as Chandrayaan-4, India’s own space station, and future missions to Mars and Venus are in the pipeline, although not all may occur during his tenure.
Vision for ISRO Under Dr. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan aims to expand India’s presence in space, targeting increased global market share, particularly in the space economy, which currently holds 2% of the global space sector. His leadership will focus on:
- Increasing Satellite Capacity: Expanding India’s satellite fleet, which currently stands at 53, to meet growing demands for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Private Sector Involvement: Leveraging space sector reforms and collaborating with private players to drive innovation and meet burgeoning satellite needs.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening ties with other space agencies, as ISRO continues to build respect on the global stage.
Upcoming Space Missions and ISRO's Agenda for 2025:
Under Dr. Narayanan's leadership, ISRO has a packed agenda for 2025:
- GSLV Mk-II/IRNSS-1K Mission
- Gaganyaan G-1 Mission (uncrewed flight)
- Chandrayaan-4, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, and Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) preparations.
Dr. Narayanan’s vision aligns with India's broader goals of becoming a dominant player in the global space economy, aspiring to increase its space market share from 2% to 10%.
Year of Artificial Intelligence

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has declared 2025 as the "Year of Artificial Intelligence" (AI), aiming to empower over 14,000 AICTE-approved colleges and benefit 40 million students. This initiative aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision to make India a global leader in AI and technology.
Key Objectives and Features of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- Positioning India as a Global AI Leader:
- Empowering students with AI skills to drive innovation and lead in the emerging AI-driven economy.
- Preparing India’s workforce for the technological advancements of the future.
- Core Elements of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- AI Affirmation Pledge: Institutions will adopt and display an AI Affirmation Pledge, focusing on innovation, ethics, and education in AI.
- Comprehensive AI Integration:
- Introducing interdisciplinary AI courses and research programs.
- Setting up AI labs in collaboration with industries to meet global standards.
- Promoting ethical AI practices with societal benefits in focus.
- AI Awareness Campaign:
- “AI for All: The Future Begins Here” campaign includes workshops, hackathons, and guest lectures.
- Formation of student-driven AI chapters to foster innovation and research.
- Faculty Development & Industry Partnerships:
- Workshops and certification programs for faculty to improve AI teaching.
- Collaboration with companies like Adobe, CISCO, and IBM for student exposure through internships and mentorships.
- Recognition of Excellence: Institutions excelling in AI integration will be recognized, serving as role models for others.
- Action Plan for Institutions:
- All institutions are required to submit AI Implementation Plans by December 31, 2024. These plans will be evaluated by the AICTE Approval Bureau and exemplary submissions will be highlighted as benchmarks.
- Shaping India as a Global AI Leader:
- AICTE aims to revolutionize India’s education system and enhance its position in the global AI race, focusing on building a self-reliant workforce.
Additional Context on AICTE and its Role:
- AICTE Overview:
- A statutory body and national-level council under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body for technical education in India.
Government Initiatives to Support AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI-driven tools launched to enhance consumer protection, such as the National Consumer Helpline, e-MAAP Portal, and Jago Grahak Jago mobile application.
- New guidelines for regulating deceptive marketing in e-commerce to ensure consumer confidence in the digital market.
- Tools like the e-Daakhil Portal for online complaint filing.
Impact:
- This initiative will have a far-reaching impact, involving more than 14,000 institutions and 40 million students nationwide, preparing them for leadership roles in AI and technology, and helping India secure its future in the global AI-driven economy.
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
Connectivity Technologies:
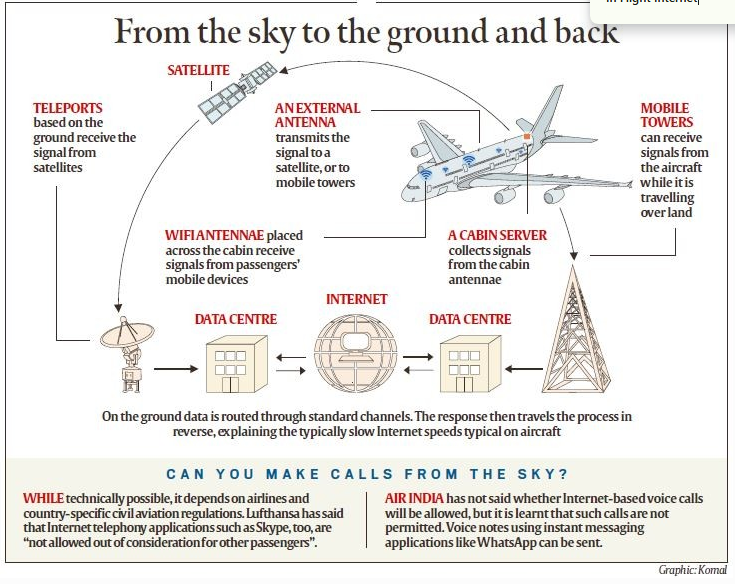
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
How the Shock Syringe Works:
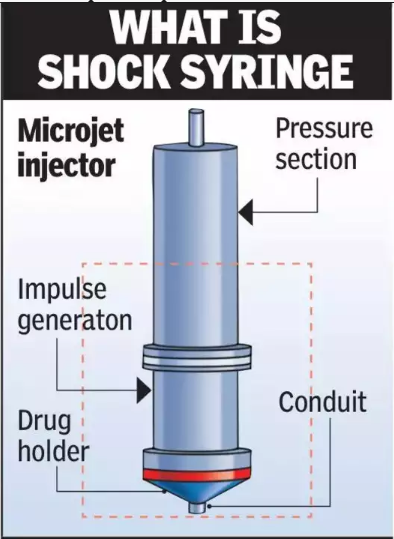
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
Parker Solar Probe’s Closest-Ever Approach to the Sun

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA scientists announced that the Parker Solar Probe survived the closest-ever approach to the Sun. The craft was operating normally after it passed just 6.1 million km from the solar surface.
About the Parker Solar Probe:
- Launched: August 12, 2018, as part of NASA’s Living With a Star program.
- Named After: Eugene Newman Parker, a solar astrophysicist, marking the first NASA mission named after a living researcher.
- Mission Objectives:
- To study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind, investigating why the corona is hotter than the Sun’s surface.
- To explore the origins of solar winds and high-energy particles that impact space weather.
- To understand the structure and dynamics of plasma and magnetic fields around the Sun.
- To examine the mechanisms behind the acceleration and transportation of energetic particles.
Technological Feats:
- Heat Shield: Equipped with a 4.5-inch carbon-composite shield that withstands temperatures up to 1,377°C (2,500°F) while keeping the instruments cool at about 29.4°C (85°F).
- Speed: Travels at a speed of 692,000 km/h (430,000 mph), making it the fastest human-made object.
- Venus Flybys: Uses gravitational assists from Venus to gradually reduce its orbit and get closer to the Sun.
Historic Milestone:
- Closest Approach: On December 24, 2024, Parker Solar Probe reached a historic distance of 6.1 million km from the Sun's surface, the closest any human-made object has ever been.
- Comparison: If the Earth and Sun were 1 meter apart, Parker Solar Probe would be just 4 cm from the Sun.
- Temperature: At its closest, it endured temperatures up to 1,377°C.
Significance of the Mission:
- Scientific Contributions:
- Solar Wind: Helps scientists understand the origins of solar winds, which affect space weather and Earth’s technological systems.
- Corona Heating: Investigates why the Sun's corona is much hotter than its surface (a long-standing astrophysical mystery).
- Space Weather: Provides critical data for predicting space weather events that can impact satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth.
- Practical Implications:
- Improves understanding of space weather, potentially aiding in the protection of Earth’s infrastructure from solar storms.
- Technological and Engineering Marvel:
- Demonstrates advanced spacecraft technology that can withstand extreme conditions close to the Sun.
Recent Developments:
- Data Collection: As the probe passed through the Sun’s outer atmosphere (the corona), it collected valuable data expected to answer fundamental questions about solar behavior.
- Communication: Despite the extreme proximity to the Sun, the probe sent back a signal on December 26, confirming its status.
Key Dates:
- Launch: August 12, 2018.
- Closest Approach: December 24, 2024.
- Data Expected: Detailed telemetry data on January 1, 2025.
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has offered fresh insights into the timing and duration of the Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a).
What is OAE 1a?
- Definition: A period during the Cretaceous Period (~119.5 million years ago) when Earth's oceans became oxygen-depleted (anoxic), causing significant disruption in marine ecosystems.
- Cause: Triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released large amounts of CO?, leading to global warming and depletion of oxygen in oceans. This caused the formation of anoxic marine basins.
- Impact: The depletion of oxygen led to the extinction of marine species, especially plankton, and the formation of black shales (organic carbon-rich layers).
Anoxic Marine Basins:
- Characteristics: These are bodies of water with extremely low or absent oxygen, allowing certain microbes and fungi to thrive, while most aerobic organisms perish.
- Significance: Anoxic basins contribute to carbon sequestration by slowing down the decay of organic material, helping in the reduction of atmospheric CO? levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin, and Orca Basin.
Recent Study Findings (Published in Science Advances):
- Timing: OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted for about 1.1 million years, with a long recovery period for ocean ecosystems.
- Methodology: The study used isotopic analysis of volcanic tuffs from Japan's Hokkaido Island to pinpoint the timing of the event.
- Volcanic Eruptions: The study confirmed that volcanic eruptions, particularly from the Ontong Java Nui complex, released CO?, triggering oceanic oxygen depletion.
- Relevance to Modern Climate Change: The study draws parallels between past volcanic CO? emissions and current human-induced warming, warning that rapid modern warming could cause similar disruptions in marine ecosystems and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction.
Holocene Extinction:
- Definition: The ongoing Sixth Mass Extinction, primarily driven by human activities like overexploitation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
- Impact: Current extinction rates are 1,000-10,000 times higher than natural rates, with severe consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Key Mass Extinction Events:
- Permian Extinction (~250 million years ago): Linked to volcanic activity, global warming, and ocean anoxia, leading to the extinction of over 95% of species.
- Cretaceous Extinction (66 million years ago): Caused by an asteroid impact, exacerbated by volcanic eruptions, leading to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- Holocene Extinction: Caused by human activities, with long-term implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Mitigate Extinction:
- Climate Action: Limiting global warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The 30X30 Initiative, aiming to conserve 30% of lands and oceans globally by 2030.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable resource management to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
GenCast AI
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Google’s GenCast AI is an advanced weather forecasting model developed by DeepMind that uses machine learning techniques to provide more accurate and longer-term weather predictions compared to traditional forecasting methods.
How GenCast Works:
- Training on Reanalysis Data:
- GenCast is trained on 40 years of reanalysis data (from 1979 to 2019). This data combines historical weather observations with modern weather forecasts, providing a comprehensive picture of past weather and climate conditions.
- Ensemble Forecasting with AI:
- Unlike traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models, which run simulations based on physical laws and initial conditions, GenCast uses an ensemble forecasting approach where multiple predictions are generated by an AI model, not an NWP model.
- It produces a range of possible weather scenarios, each with different starting conditions, to reflect the uncertainty in weather forecasts.
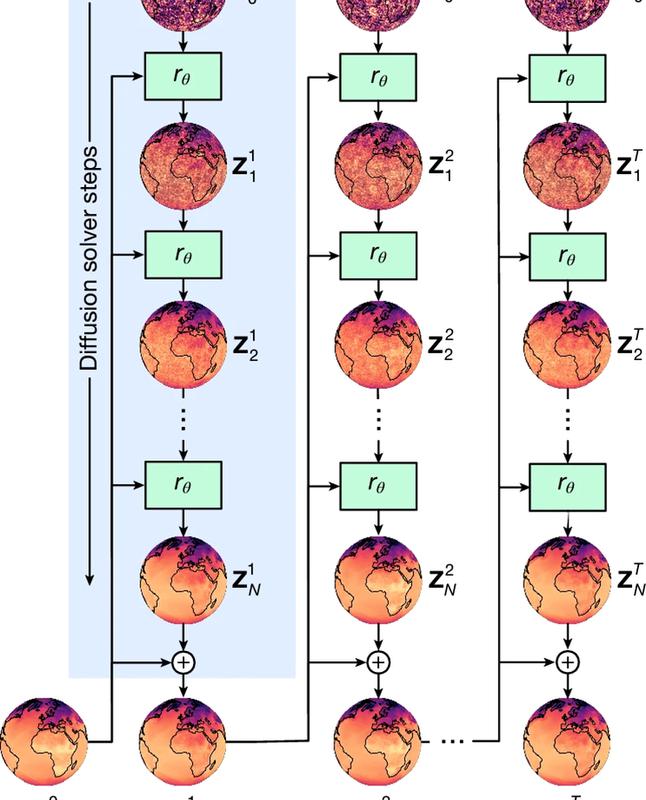
- Neural Network and Diffusion Model:
- GenCast uses a neural network architecture with 41,162 nodes and 240,000 edges that process weather data. Each node accepts data, manipulates it, and passes it to another node, helping to refine and improve predictions.
- It uses a diffusion model, a type of AI model commonly used in generative AI. The model takes noisy input data, processes it through 30 refinement steps, and gradually produces a clearer forecast (de-noising the data).
- The result is a probabilistic forecast, such as "there's a 25% chance of rain in Chennai on December 25," rather than a deterministic forecast, which would provide exact quantities like "5 mm of rain."
- Faster Processing:
- The entire forecast process is incredibly efficient. GenCast can generate 50 ensemble forecasts at once with a spatial resolution of 0.25° x 0.25° (latitude-longitude) and temporal resolution of 12 hours.
- Using Google's TPU v5 units, it can produce these forecasts in just 8 minutes—far faster than traditional supercomputers, which can take several hours to run NWP simulations.
Key Features of GenCast:
- Better Performance on Extreme Weather: GenCast has shown superior accuracy in predicting extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones, compared to traditional NWP models like those from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
- Probabilistic Forecasting: GenCast produces probabilistic forecasts, offering predictions like the likelihood of rain rather than precise measures, which helps with better preparation, especially for extreme weather events.
- Long-Term Forecasting: GenCast can generate forecasts for up to 15 days, which is longer than most traditional models, and is particularly useful for anticipating events like wind power generation and tropical cyclone tracking.
- Efficiency: GenCast's speed and resource efficiency set it apart from traditional NWP models, reducing forecast times dramatically.
Comparison with Traditional Weather Models:
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP): Traditional NWP models rely on solving complex physical equations to simulate the atmosphere and provide deterministic forecasts. These models require significant computational power and are typically limited to weather predictions for about a week.
- GenCast's Probabilistic Forecasts: In contrast, GenCast offers probabilistic predictions, making it better suited for providing early warnings about extreme weather, with better lead times for disaster preparation.
Future Developments:
While GenCast is impressive, Google acknowledges the importance of traditional NWP models for both supplying initial conditions and providing the foundational data needed to train AI models like GenCast. Ongoing collaboration with weather agencies is crucial to enhancing AI-based methods for weather prediction.
Overall, GenCast represents a significant leap forward in the use of AI for weather forecasting, with potential for greater accuracy, efficiency, and longer-term predictions compared to current methods.
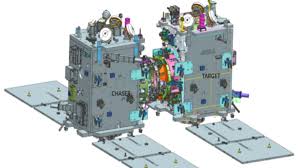
Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) Mission
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission, a key milestone in India’s space capabilities. The mission will deploy two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into a 740 km orbit using the PSLV-C60 rocket. SpaDeX aims to demonstrate the technology for satellite docking, a critical component for future space missions such as lunar exploration and the development of India's own space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
Key Objectives of SpaDeX Mission:
- Primary Objective: To demonstrate the rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft (SDX01 and SDX02) autonomously.
- Secondary Objectives: Include testing electric power transfer between the docked spacecraft, composite spacecraft control, and post-docking payload operations.
The mission will see the two spacecraft gradually approach each other, performing a series of maneuvers, starting at a 20 km distance and closing to millimeter-scale distances before docking. Once docked, they will execute secondary tasks, such as scientific payload operations, using advanced technologies including high-resolution cameras, multi-spectral payloads, and radiation monitors.
Technological Innovations:
- Docking Mechanism: An indigenous, motor-driven, low-impact, androgynous docking system with capture, extension/retraction, and rigidization mechanisms. Both spacecraft are equipped with identical docking systems to simplify operations.
- Advanced Sensors: The spacecraft will use a Laser Range Finder (LRF), Proximity & Docking Sensors (PDS), and Rendezvous Sensors for precise distance measurement and to guide the docking process.
- Inter-Satellite Communication: The spacecraft will employ autonomous inter-satellite links (ISL) for real-time communication and data sharing.
- RODP Processor: This system, based on GNSS, ensures accurate position and velocity determination for the spacecraft during the docking procedure.
Significance of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Technological Milestone: SpaDeX positions India as the fourth country, after the US, Russia, and China, to develop space docking technology.
- Space Exploration: The successful demonstration will facilitate future space exploration, including Chandrayaan-4 and interplanetary missions.
- Modular Space Infrastructure: Space docking is essential for building multi-modular space stations, which allows the construction of large structures in space and enhances flexibility for future missions.
- Satellite Servicing: Docking enables satellite servicing, including repairs, refueling, and upgrades, which increases the operational lifespan of satellites.
SpaDeX Mission for India’s Space Station:
The SpaDeX mission is a crucial step towards India’s plans for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). This will be India’s first modular space station, designed to conduct advanced scientific research, including in life sciences and medicine. BAS is expected to begin operations by 2035, and the development of docking technology is pivotal for its assembly and operation.
Mission Launch Details:
The PSLV-C60 rocket is set to launch the SpaDeX mission from Sriharikota. The mission is a demonstration of India's growing space capabilities and its indigenous technologies, including the Bharatiya Docking System (BDS).
Challenges and Technological Requirements:
The docking process requires extremely precise maneuvering, as the two spacecraft will be traveling at speeds of 28,800 km/h and must reduce their relative velocity to just 0.036 km/h before docking. This level of precision is crucial for future missions involving spacecraft servicing, crew transfers, and the construction of space infrastructure like BAS.
In addition to the docking demonstration, SpaDeX will carry 24 academic and startup payloads aboard the PSLV’s fourth stage, POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4), offering a valuable platform for microgravity research.
Future Prospects:
The success of SpaDeX will pave the way for more complex missions, such as India’s lunar and Mars exploration programs, the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and international collaborations in satellite servicing and space infrastructure.
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)

- 22 Dec 2024
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav inaugurated two groundbreaking facilities at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun: the Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification and the Next Generation DNA Sequencing (NGS) Facility. These facilities are designed to enhance India’s capabilities in wildlife conservation and support the growth of traditional crafts like Pashmina weaving.
Key Highlights
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)
The NGS facility is a cutting-edge research tool that enables the high-throughput analysis of entire genomes. This technology is pivotal in studying wildlife genetics and biodiversity by decoding millions of DNA sequences at once.
Applications in Wildlife Conservation:
- Genetic Diversity and Health: NGS helps assess the genetic diversity of species and their population health.
- Evolutionary Relationships: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history and unique adaptations of species.
- Disease Surveillance: The technology supports studying pathogen-host interactions and monitoring diseases affecting wildlife.
- Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade: NGS can help detect illegal wildlife trade and the movement of endangered species.
- Impact of Climate Change: It is crucial for studying how climate change affects genetic diversity and species survival.
This facility positions WII as a leading hub for molecular research, enabling more precise conservation efforts and studies on endangered species like tigers, elephants, and riverine dolphins.
Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification
Launched under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model between WII and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), the Pashmina Certification Centre (PCC) has been significantly upgraded. The facility now includes a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) for advanced wool testing and certification.
Key Features of the Upgraded Facility:
- Fiber Analysis: The SEM-EDS technology ensures accurate identification and certification of Pashmina fibers, free from any prohibited materials.
- Unique ID and E-certificates: Each certified product is tagged with a unique ID and e-certificate, enhancing traceability and authenticity.
- Global Trade Facilitation: The certification process eliminates delays at exit points, ensuring smoother international trade for certified Pashmina products.
The PCC has already certified over 15,000 Pashmina shawls and plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of artisans and weavers in Jammu & Kashmir. By ensuring the authenticity of Pashmina, the facility also helps combat the illegal trade of Shahtoosh wool, which is harmful to the Tibetan antelope (Chiru).
Significance for Artisans and Conservation:
- Support for Artisans: The upgraded facility helps increase the credibility of Pashmina products in global markets, benefiting local artisans and weavers.
- Conservation Impact: By certifying genuine Pashmina products, the initiative indirectly contributes to the conservation of the Tibetan antelope by reducing illegal poaching and trade.
- Sustainability: The PCC is a self-sustaining model that not only supports conservation but also generates revenue and creates job opportunities.
Overview of the Genome India Project
The Genome India Project is a gene mapping initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology, aiming to create a comprehensive database of genetic variations across the Indian population. The project focuses on understanding genetic diversity and its implications for health, agriculture, and biodiversity conservation in India.
Goals:
- Comprehensive Gene Mapping: The project seeks to map the genetic variations found within India’s diverse population, enabling better healthcare and disease management.
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Insights from the project will also aid in wildlife conservation by understanding the genetic health of endangered species and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
This initiative is aligned with India’s broader goals of using advanced technologies to address modern conservation challenges and foster a sustainable future.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
Hyperloop Technology
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s first hyperloop test track (410 meters) completed by Indian Railways, IIT-Madras’Avishkar Hyperloop team and TuTr (incubated startup) at IIT-M discovery campus, Thaiyur in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
India’s First Hyperloop Test Track:
- Location: IIT Madras’ Discovery Campus, Chennai.
- Collaboration: Indian Railways, IIT-Madras' Avishkar Hyperloop team, and TuTr Hyperloop (startup).
- Track Length: 410 meters.
- Test Speed: Initial successful test at 100 km/h; plans for 600 km/h in the next phase.
- Passenger Capacity: 40–100 passengers per pod, depending on design.
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Concept: A high-speed transport system using pods in low-pressure vacuum tubes, designed to achieve speeds similar to aircraft (up to 1,100 km/h).
- Working:
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Pods float on magnets, eliminating friction.
- Vacuum Tubes: Reduces air resistance for high-speed travel.
- Propulsion: Linear induction motors propel pods.
- Energy: Solar-powered, designed for zero emissions.
India’s Hyperloop Projects:
- Current Status:
- Successful testing of a 410-meter test track at IIT Madras.
- Ongoing feasibility studies for routes like Chennai Airport–Parandur, Mumbai–Pune, and Amritsar–Chandigarh.
- Phase 1 & 2: First phase involves a 11.5-kilometer track; future expansion to 100 km.
- Mumbai–Pune Corridor: Planned as India’s first full-scale Hyperloop system, aiming to reduce travel time from 3–4 hours to 25 minutes.
Benefits of Hyperloop:
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to 1,100 km/h (operational speed around 360 km/h).
- Efficiency: Reduces travel time, energy-efficient with reduced air resistance and friction.
- Sustainability: Powered by renewable energy (e.g., solar power), offering zero emissions.
- Point-to-Point Travel: No intermediate stops, making it more time-efficient.
Challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Expensive to build the vacuum tubes, stations, and supporting systems.
- Land Acquisition: Difficulty in acquiring land, especially in densely populated areas.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of a specific regulatory framework for such advanced transport systems.
- Technological Barriers: Complex engineering challenges, including development of maglev systems and vacuum seals.
Global Context:
- Origin: Concept proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
- Worldwide Adoption: Hyperloop is being explored globally, with projects in the U.S., UAE, and Europe.
GG Tau A System

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
GG Tau A System: Located about 489 light-years from Earth, this system is a triple-star setup that is between 1 to 5 million years old. This makes it an ideal system for studying the early stages of planetary formation.
Findings from the Discovery:
- Protoplanetary Disk: The system features a protoplanetary disk made of gas and dust, where new planets are forming. Researchers from NISER (National Institute of Science Education and Research), Odisha detected emissions from key molecules in the disk.
- Chemical Molecules: The molecules are frozen on tiny dust particles in the coldest regions of the disk (temperatures between 12 K and 16 K). These frozen molecules could serve as the building blocks for new planets.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Triple-Star Configuration: GG Tau A’s triple-star system is rare, and it has complex gravitational interactions among the three stars. This complicates how the gas and dust disk behaves and provides unique insights into planetary formation in multi-star systems.
- Study of Planet Formation: Traditionally, planets form around single stars or in binary systems. However, multi-star systems like GG Tau A present challenges for planet formation. Studying this system helps scientists understand how planets can form in more complex environments.
- Cold Conditions for Planet Formation: The study found that icy conditions in the disk are essential for the accumulation of materials that form planets. These low temperatures (below the freezing point of carbon monoxide) allow dust and gas particles to clump together, creating the foundation for exoplanets.
Broader Implications:
- Exoplanet Diversity: This research enhances our understanding of how planets form in different types of star systems, contributing to the study of exoplanets and their potential diversity across the universe.
- Astrophysics and Planetary Science: This discovery plays a crucial role in improving our knowledge of the early stages of planet formation, especially in complicated star systems like triple-star setups, which are rare but can provide valuable insights into how planetary systems evolve under unique conditions.
Research Tools:
- The team used advanced radio telescopes located in the Atacama Desert (Chile) to observe the emissions from the disk, highlighting the role of cutting-edge technology in space exploration and astronomical research.
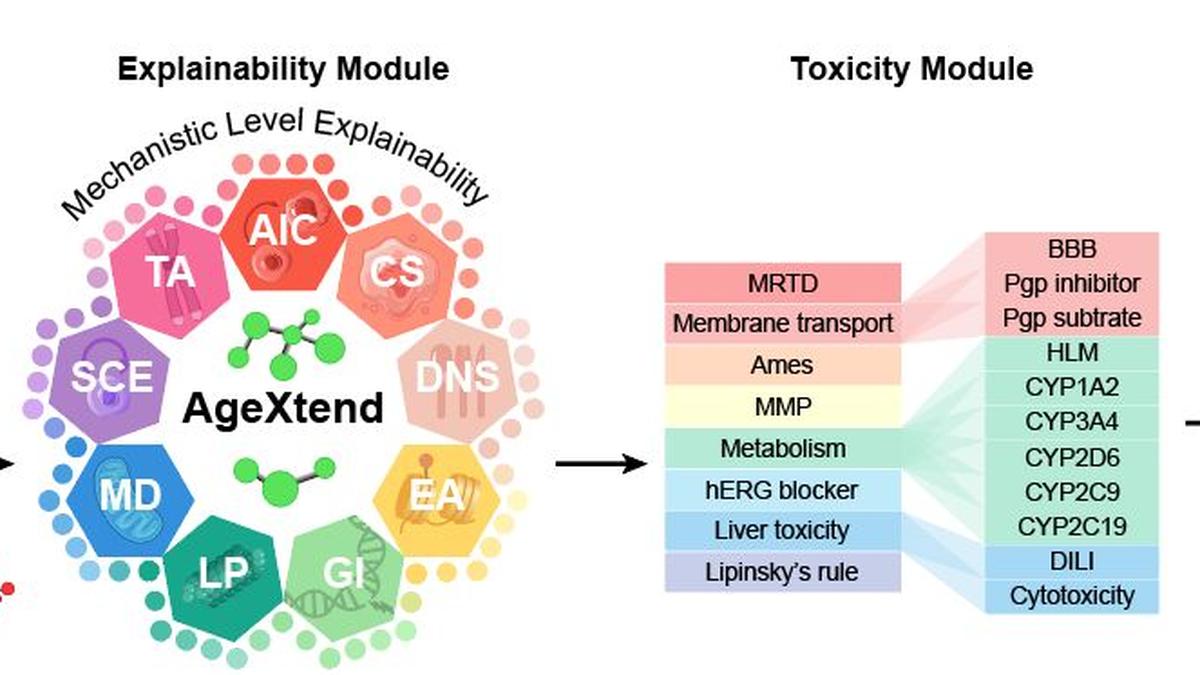
AgeXtend
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- AgeXtend is developed by researchers at Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology – Delhi (IIIT-Delhi) to rapidly identify age-defying compounds, known as geroprotectors, to promote healthy aging.
Key Features of AgeXtend:
- What is AgeXtend?
- An AI-based platform designed to discover compounds with geroprotective (anti-aging) properties.
- Objective: To accelerate the identification of molecules promoting longevity by reducing the time and effort compared to conventional research methods.
- Development: Developed by researchers from the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Delhi.
- Working Mechanism:
- Scans over 1.1 billion compounds to predict, analyze, and validate molecules with anti-aging potential.
- Utilizes machine learning to determine efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action.
- Experimental validation conducted using yeast, worms (C. elegans), and human cell models.
- Significance:
- The largest study on longevity, including compounds from commercial drugs, FDA-approved drugs, Ayurvedic, and Chinese medicine.
- Provides a scientific rationale for identifying geroprotective compounds, aiding targeted research.
- Open-source code and data promote collaboration and allow commercial exploration.
Platform Capabilities:
- AI Analysis:
- Uses bioactivity data from existing geroprotectors to predict new compounds with similar properties.
- Evaluates geroprotective potential, toxicity, and identifies target proteins and mechanisms of action for accuracy and safety.
- Unique Feature: Explains why a compound is considered geroprotective, revealing underlying mechanisms.
- Example Validation: Successfully identified benefits of metformin and taurine without prior knowledge, confirming the platform’s predictive power.
- Study Scale: The study involved scanning over 1.1 billion molecules, making it the largest study on longevity to date.
Open-Source and Commercial Use:
- Availability:
- The code and data are available as open-source for researchers and students. Commercial access is available for a fee.
- A Python package for AgeXtend is available via pip on pypi.org.
- Further Collaboration: The researchers have reached out to pharma companies to further investigate promising compounds.
- Exploring Natural Compounds: AgeXtend also explores natural compounds from the human microbiome, investigating their role in controlling cell aging.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
Heat Shock Protein 70
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
JNU scientists make big discovery that could change malaria, Covid-19 treatment.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Institution: Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), Special Centre for Molecular Medicine.
- Key Discovery: Identification of human protein Hsp70 as a critical factor in the spread of malaria and COVID-19.
- Research Collaboration: Involvement of Indian and Russian researchers.
- Outcome: Development of a small molecule inhibitor of Hsp70 that could act as a broad-spectrum treatment for multiple infections.
About Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70):
- Definition: Hsp70 is a type of molecular chaperone protein.
- Function:
- Helps other proteins fold into their proper shapes.
- Prevents protein misfolding.
- Regulates protein synthesis and protects proteins from stress.
- Elevates during cellular stress to shield cells from damage.
- Role in Cellular Processes:
- Prevents protein aggregation and assists in protein transport across membranes.
- Plays a critical role in protein homeostasis and cell survival during stress conditions.
Hsp70's Role in Disease Spread:
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Interaction:
- Hsp70 interacts with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and human ACE2 receptors.
- Facilitates viral entry into human cells by stabilizing this interaction during fever (when Hsp70 levels rise).
- Malaria:Pathogens like malaria parasites rely on the host's machinery for survival, including Hsp70.
Research Findings and Implications:
- Published in: International Journal for Biological Macromolecules.
- Inhibition of Hsp70:
- Targeting Hsp70 can disrupt viral replication.
- In lab tests, Hsp70 inhibitor (PES-Cl) blocked SARS-CoV-2 replication at low doses.
- Potential for Broad-Spectrum Treatment:
- Hsp70 could be a target for treating multiple infections, not limited to COVID-19 or malaria.
- Prevention of Drug Resistance:
- Host-targeting antivirals are less prone to resistance as the virus cannot mutate the host protein (Hsp70).
- This approach could be especially beneficial for combating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (e.g., Omicron).
Host-Targeting Approach vs. Traditional Drugs:
- Host-Targeting: Targets the host cell machinery (e.g., Hsp70) rather than the virus itself.
- Reduces the likelihood of viral mutation-induced resistance.
- Traditional Drugs: Target the virus directly, which can lead to resistance, especially with rapidly mutating viruses.
Global Health and Pandemic Preparedness:
- Universal Tool for Infectious Diseases: The discovery could serve as a universal tool for managing infections during health emergencies.
- Collaboration and Importance: Highlights the significance of international collaboration in addressing global health challenges (e.g., Dr. Pramod Garg of AIIMS, Ph.D. scholar Prerna Joshi).
- Future Implications:Preparation for future pandemics, as the world must remain vigilant even post-COVID-19.
SheSTEM 2024

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), under the NITI Aayog and the Office of Science & Innovation, at the Embassy of Sweden, in partnership with Nordic collaborators - Innovation Norway, Innovation Centre Denmark, and Business Finland, announced the successful conclusion of SheSTEM 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To inspire youth, especially women, to explore careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and promote innovative solutions for sustainability.
- Theme: Focus on Battery Technology and Energy Storage Systems (BEST), part of the India-Nordic BEST project, aimed at fostering sustainability through advanced energy solutions.
Key Features of the Challenge:
- Target Audience: Students from grades 6–12 across India.
- Participation: Over 1,000 submissions showcasing innovative energy storage solutions.
- Format: Students presented prototypes or concepts via a 2-minute video format.
- Focus Areas: Sustainability, energy storage, and innovative solutions to global challenges.
Significance of SheSTEM 2024:
- Youth Empowerment: Provides a platform for young innovators to showcase their ideas and contribute to global sustainability.
- Global Impact: Encourages collaboration between India and Nordic countries in academia, business, and government to explore energy storage and sustainable technologies.
- Women in STEM: Highlights the importance of gender inclusivity in STEM fields, particularly in sustainability and technology.
Key Facts about AIM (Atal Innovation Mission):
- Established: 2016 by NITI Aayog to foster innovation and entrepreneurship across India.
- Core Functions:
- Promote Entrepreneurship: Financial support, mentorship, and nurturing innovative startups.
- Promote Innovation: Creating platforms for idea generation and collaboration.
- Key Programs: Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centres, Atal New India Challenges, and Mentor India.
- Monitoring: Systematic monitoring of initiatives using real-time MIS systems and dashboards.
Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
Mission Shukrayaan
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
ISRO received approval for its first Venus mission, Shukrayaan. The probe will undertake a detailed investigation of Venus, including its surface, atmosphere and geological structure.
Shukrayaan Mission (Venus Orbiter Mission):
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for 2028.
- Objective: Investigate Venus to gather data on its surface, atmosphere, and geological structure.
- Scientific Focus: Study weather patterns, geological activities, and atmospheric composition (e.g., carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds).
- Instrumentation: Equipped with synthetic aperture radar, infrared, and ultraviolet imaging devices to study Venus’s ionosphere.
- Significance: Offers global coverage of Venus, addressing gaps in previous missions' spatial coverage.
- Cost: Estimated at Rs 1,236 crore.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO plans to use the LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) rocket to launch the mission into an elliptical parking orbit (170 km x 36,000 km).
- Mission Data Processing: Data will be archived and disseminated through the Indian Space Science Data Center (ISSDC).
Chandrayaan 4 Mission:
- Collaborative Effort: Joint mission between India (ISRO) and Japan.
- Launch Objective: Land on the moon's south pole, with a focus on the region at 90°S (compared to previous missions at 69.3°S).
- Mission Details:
- Includes a rover weighing 350 kg (12 times heavier than previous rover).
- The rover will be equipped with advanced scientific tools for lunar exploration.
- Government Approval: Awaiting approval, with a target execution date of 2030.
Gaganyaan Mission (Human Spaceflight Program):
- Timeline: Unmanned flight in 2026, followed by a manned mission.
- Indian Space Station: Construction approved; to be completed by 2035, comprising five modules.
- Purpose: To serve as a transit facility for deep space exploration, including future lunar missions.
Mars Exploration Plans:
- Future Missions: Plans to send satellites to Mars and attempt a landing on the Martian surface.
- Significance: Demonstrates India’s growing ambitions in interplanetary exploration.
INSAT-4 Series of Satellites:
- Goal: Launch of new meteorological and oceanographic sensors to improve weather forecasts and disaster management.
- Technological Advancements: Need for India to catch up with global advancements in space-based sensors.
International Collaboration in Space:
- Chandrayaan 4: A collaboration between ISRO and Japan to explore the moon’s south pole, showcasing India's growing international cooperation in space exploration.
Strategic Importance of Shukrayaan:
- Contribution to Science: The mission’s global dataset will provide unique insights into Venus, enhancing the understanding of planetary atmospheres and geological processes.
- Potential for Discoveries: Research on Venus’s ionosphere and possible volcanic activity.
Proba-3 mission

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will launch the European Space Agency’s Proba-3 mission on its PSLV rocket to study the solar corona, the outermost and hottest part of the Sun’s atmosphere, from Sriharikota on December 4.
Key Highlights:
- Mission Objective:The mission will study the Sun’s outermost and hottest atmosphere, the solar corona. The mission will also demonstrate the first-ever precision formation flying with two satellites working in tandem.
- Satellite Formation:Proba-3 consists of two satellites that will fly together, maintaining a fixed formation to study the Sun's corona.
What is Proba-3?
- Proba-3 is a solar mission developed by ESA, with an estimated cost of 200 million euros. The mission involves launching two satellites that will separate after launch, but fly in precise formation. The satellites will create a solar coronagraph, which blocks the Sun’s bright light to observe the solar corona, the Sun’s outermost atmosphere.
- Orbit: Proba-3 will orbit in a highly elliptical path (600 x 60,530 km) with an orbital period of 19.7 hours.
- Mission Duration: The expected mission life is two years.
What will Proba-3 Study?
The Sun's corona is extremely hot (up to 2 million degrees Fahrenheit), making it difficult to observe with conventional instruments. However, studying the corona is essential because it generates space weather phenomena such as solar storms and solar winds, which can impact satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
Proba-3 will use three main instruments for its mission:
- ASPIICS (Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun):This coronagraph will observe the Sun’s outer and inner corona, similar to how the corona is visible during a solar eclipse. It features a 1.4-meter occulting disk to block the Sun’s light and facilitate close-up observations.
- DARA (Digital Absolute Radiometer):This instrument will measure the Sun’s total energy output (total solar irradiance).
- 3DEES (3D Energetic Electron Spectrometer):It will study electron fluxes as they pass through Earth's radiation belts, providing valuable data on space weather.
Why is Proba-3 Unique?
- Proba-3 is designed to mimic a natural solar eclipse, allowing continuous study of the Sun’s corona. Typically, solar scientists observe the corona for only about 10 minutes during an eclipse, occurring around 1.5 times a year. Proba-3 will provide up to six hours of data per day, equivalent to 50 eclipse events annually.
- The two satellites will maintain a precise formation, with one acting as an occulting spacecraft to cast a shadow, while the other (the coronagraph) stays in the shadow and observes the Sun’s corona. They will be positioned 150 meters apart, maintaining their formation autonomously.
- This artificial eclipse will enable scientists to study the corona and its less-understood features more effectively.
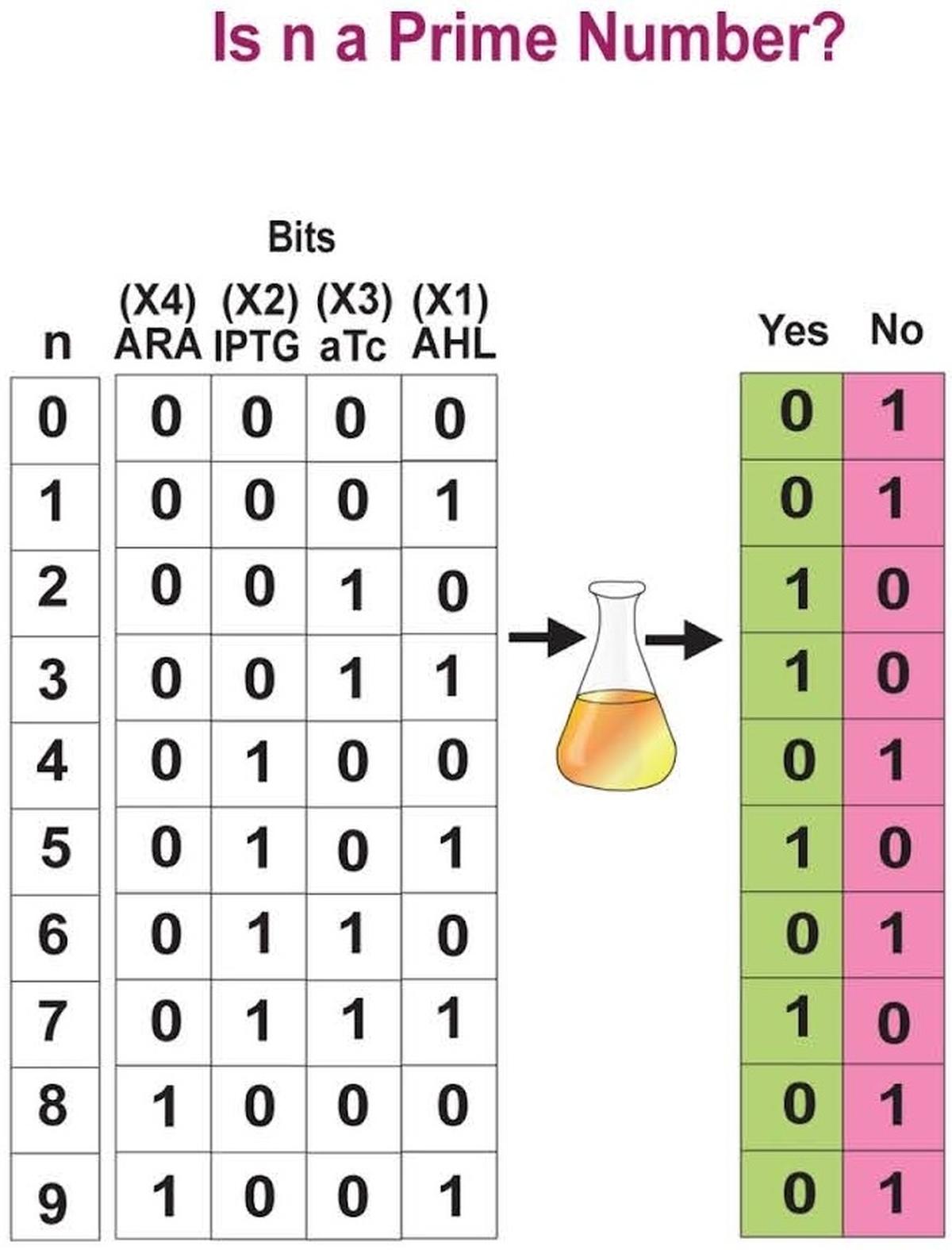
Breakthrough in Bacterial Computing
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists at the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics in Kolkatahave successfully engineered bacteria capable of solving mathematical problems, marking a major step forward in the field of synthetic biology and biocomputing. These engineered bacteria can function like artificial neural networks, performing tasks that were traditionally reserved for humans or conventional computers.
Key Highlights:
- Bacterial Computers:
- The research team introduced genetic circuits into bacteria, turning them into computational units capable of tasks like determining whether a number is prime or identifying vowels in an alphabet.
- These bacterial "computers" mimic artificial neural networks (ANNs), where each type of engineered bacterium (called a "bactoneuron") behaves like a node in a network, processing inputs to generate outputs.
- How it Works:
- The bacteria's genetic circuits are activated by chemical inducers, which represent binary 0s and 1s (the fundamental language of computing). The presence or absence of certain chemicals determines whether a bacterium expresses a specific fluorescent protein, representing the binary states.
- For example, when asked if a number between 0-9 is prime, the bacteria can express green fluorescent proteins (1) for "yes" or red fluorescent proteins (0) for "no", providing binary outputs that solve the problem.
- Complex Tasks:
- The team advanced to more complex tasks, such as asking the bacterial computers whether adding a number (like 2 + 3) results in a prime number or if a number's square can be expressed as the sum of factorials.
- In an even more complex test, the bacteria solved an optimization problem—calculating the maximum number of pieces a pie could be cut into with a given number of straight cuts. The bacteria’s fluorescent output represented binary numbers that were converted to decimal for the correct solution.
- Technical Details:
- The researchers used Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, engineered with transcriptional genetic circuits, which recognize specific DNA sequences and trigger the expression of proteins based on the presence of chemical inducers.
- The system is similar to how ANNs work in traditional computing, where nodes (bactoneurons) take inputs, apply weights, and produce outputs based on activation functions.
- Implications and Future Prospects:
- Synthetic Biology & Biomanufacturing: This breakthrough could revolutionize industries such as pharmaceuticals and biomanufacturing by enabling biocomputers that perform specific tasks in a biological environment, potentially reducing reliance on silicon-based computers.
- Medical Applications: The ability of engineered bacteria to process data could lead to biocomputers capable of diagnosing diseases (such as cancer) at an early stage and even administering localized treatments.
- Understanding Intelligence: Bagh and his team hope to explore the biochemical nature of intelligence, pondering how intelligence could emerge from simple, single-celled organisms.
- Groundbreaking Research:
- The research, published in Nature Chemical Biology, has drawn significant attention in the synthetic biology community. Centre for Synthetic Biology highlighting the potential of bacteria programmed to solve complex problems.
This innovative work paves the way for future developments in biocomputing, where living organisms, instead of silicon chips, could be used to perform sophisticated calculations, offering new ways to think about computing, intelligence, and even the future of technology in medicine.
Chagas Disease
- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
A recent study by Texas A&M University has uncovered a concerning new risk for dogs in Texas related to Chagas disease—the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi), which causes the disease, can survive in dead kissing bugs (Triatominae). This discovery was published in the Journal of Medical Entomology in October 2024 and has raised alarms about how dead insects, which might be found in insecticide-treated dog kennels, could still pose a transmission risk for dogs.
Key Findings:
- Chagas Disease is primarily spread by kissing bugs, which carry T. cruzi in their gut. Dogs can contract the parasite by ingesting the bug's feces, especially when they lick their bite wounds.
- The study shows that even dead kissing bugs, which are often discarded in kennels, can still carry viable T. cruzi. This is particularly worrying in areas where insecticides are used to control the insects but dead bugs remain accessible to dogs.
- Researchers collected live and dead triatomines from six Texas kennels between June and October 2022, using both genetic testing and culture methods to assess whether the bugs were carrying live T. cruzi.
- 28% of the collected bugs tested positive for T. cruzi.
- A dead kissing bug (Paratriatomalecticularia) was found to still harbor live T. cruzi cultures, demonstrating that the parasite can survive even after the insect has died.
Transmission and Risks:
- Kissing bugs typically feed on the blood of animals like dogs, rodents, and raccoons, defecating near the bite site. If the dog licks the contaminated area, they can ingest the parasite-laden feces and become infected.
- The new discovery suggests that dead kissing bugs may pose a secondary transmission route for T. cruzi. Dogs that ingest these dead bugs, either in insecticide-treated areas or natural environments, could still contract the parasite.
- Researchers noted that dead bugs with intact gut contents showed a higher rate of infection than desiccated ones, which suggests that the condition of the bug after death impacts how long the parasite survives.
Implications for Management:
- The findings challenge current insecticide-based control methods. While insecticides kill the bugs, dead insects could still serve as a source of infection, necessitating new approaches for managing Chagas disease transmission in dog kennels.
- The study underscores the importance of regularly removing dead insects in kennels and reconsidering control strategies beyond just using insecticides.
About Chagas Disease:
- Chagas disease is caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite, commonly found in the feces of kissing bugs. It can cause long-term heart and digestive issues if left untreated.
- The disease is common in parts of South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it has been increasingly reported in the southern United States.
- Treatment focuses on killing the parasite in the acute phase, but once it progresses to the chronic phase, treatment is aimed at managing symptoms.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research:
- The Texas A&M team plans to explore how long T. cruzi survives in dead triatomines and whether insecticides affect the parasite’s ability to persist. They are also looking into developing integrated pest management strategies for environments with high kissing bug activity.
- The study also forms part of a broader "One Health" approach, recognizing that both human and animal health are interconnected, and research on Chagas disease in animals can help inform public health strategies.
The science of plant communication

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
More than any organism, plants understand the significance of communication the best.
Communication Through Chemical Warning (Volatile Organic Compounds - VOCs):
- Plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when threatened, such as during herbivore grazing.
- VOCs act as distress signals, alerting neighboring plants to potential dangers.
- Neighboring plants respond by producing defensive compounds or toxins to deter herbivores.
- VOCs can travel through air and soil, enabling distant plants to prepare for threats, thereby enhancing survival across larger areas.
Wood Wide Web (Symbiotic Relationship with Mycorrhizal Fungi):
- Plants form a network with mycorrhizal fungi, connecting their roots in a symbiotic bond.
- This "Wood Wide Web" allows plants to communicate by sending chemical signals through their roots when under stress (e.g., pest attacks or drought).
- Fungi extend the root system and help share nutrients between plants, especially in times of distress.
- The network facilitates collective resilience and survival by ensuring nutrient sharing among plants.
Cooperative Behavior: Sharing Resources for Survival:
- Plants in close proximity, especially in dense forests, often share resources like water, nutrients, and light.
- When a plant detects a neighboring plant in distress, it prioritizes resource allocation to support its growth.
- This cooperative behavior promotes ecosystem stability and the overall health of forests.
- The mutual support system shows how cooperation enhances the survival of individual plants and the broader ecosystem.
Significance of Plant Communication in Ecosystem Health:
- Plants communicate through chemical signals, underground fungal networks, and cooperative behaviors.
- These interactions foster resilience, ensuring the survival of both individual plants and entire ecosystems.
- The silent communication among plants contributes to a dynamic, cooperative environment that thrives on mutual support.
India’s First AI Data Bank

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Science and Technologyrecently launched India’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) data bank that is aimed at propelling innovation and boosting the country’s national securityat the 7th Edition of the ASSOCHAM AI Leadership Meet 2024.
-
- The event theme: “AI for India: Advancing India’s AI Development – Innovation, Ethics, and Governance”.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Propel innovation and enhance national security.
- Provide access to diverse, high-quality datasets for creating scalable and inclusive AI solutions.
- Key Features of the AI Data Bank:
- Target Audience: Researchers, startups, and developers.
- Data Types: Satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- Purpose:
- To enhance national security through real-time analytics.
- Enable predictive analytics for disaster management and cybersecurity.
Strategic Importance of AI in India:
- National Security: AI to strengthen national security by providing real-time analytics from satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- AI for Development:
- AI’s role in reshaping sectors like governance, business, healthcare, education, and space exploration.
- AI as a tool for economic growth, addressing climate change, improving public service delivery, and ensuring national security.
- Ethics and Governance:
- Ensuring responsible AI use with optimal handling.
- Addressing algorithmic bias and data privacy through robust governance frameworks.
- Commitment to transparent and fair AI systems that empower people rather than replace them.
- AI in Disaster Management and Cybersecurity:
- Aligning with India’s goals to use AI for predictive analytics in disaster management.
- Enhancing cybersecurity through AI technologies.
Government’s Vision on AI:
- Empowering Citizens: AI must bridge divides and ensure equitable access to its benefits.
- AI as Backbone for Future Development: India’s focus on making AI an integral part of its future economic and technological growth.
Green World Awards 2024

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Coal India Limited (CIL) under the aegis of the Ministry of Coal, has been conferred with the esteemed Green World Environment Award in the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) category along with the distinguished tile of Green World Ambassador.
Key Highlights:
- Reason for the Award:
- The award was granted to CIL for its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna, a CSR initiative aimed at providing permanent curative treatment for Thalassemia through Bone Marrow Transplants (BMT).
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to ?10 lakh for BMT and has helped over 600 Thalassemia patients across India.
- Background of the Award:
- The Green Organization, an independent, non-political, non-profit environmental group, conferred the award.
- The organization has been recognizing and promoting environmental best practices and CSR initiatives globally since its establishment in 1994.
- CIL’s Role in CSR:
- CIL has been a pioneer in CSR, with its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna being the first of its kind among public sector undertakings in India.
- The initiative partners with 17 prominent hospitals across India to provide stem cell transplants for Thalassemia patients.
- CIL’s Contribution to India's Energy Sector:
- CIL is responsible for producing over 80% of India's coal and contributes to 70% of the total coal-based power generation in the country.
- CIL accounts for 55% of India’s total power generation and meets 40% of the primary commercial energy requirements.
- Environmental Initiatives by CIL:
- CIL has adopted various measures to improve environmental sustainability, including:
- Expanding green cover over mined areas.
- Creating eco-parks and tourism spots.
- Providing mine water for domestic and agricultural use to surrounding villages.
- About Coal India Limited (CIL):
- Established: November 1975.
- Headquarters: Kolkata.
- Status: A Maharatna company and the largest coal-producing company in the world.
- Subsidiaries: CIL has seven producing subsidiaries and is a major corporate employer in India.
- About the Green Organization:
- Founded: 1994.
- Nature: Independent, non-political, non-profit organization.
- Objective: To recognize, reward, and promote environmental and CSR best practices worldwide.
- Initiatives: The Green World Awards are part of global efforts to encourage sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
- Significance of the Award:
- The Green World Environment Award highlights CIL’s commitment to social responsibility and environmental sustainability while maintaining its core role as an energy provider.
- The recognition underscores CIL’s leadership in integrating CSR initiatives with corporate operations to contribute to national development.
India’s First Indigenous Antibiotic

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Nafithromycin is India's first indigenously developed antibiotic aimed at combating drug-resistant pneumonia, developed with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The drug is being marketed under the trade name "Miqnaf" by Wockhardt.
Significance in Combating Drug Resistance:
- Nafithromycin addresses Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP), a serious disease caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
- Pneumonia is responsible for over 2 million deaths globally annually, with India facing 23% of the global burden.
- The drug is 10 times more effective than current treatments like azithromycin, requiring only three doses for effective treatment, offering a safer and faster solution.
Biotechnology Sector and Public-Private Collaboration:
- BIRAC, under the Department of Biotechnology, supported the research and development of Nafithromycin.
- This achievement underscores the public-private collaboration between the government and pharmaceutical industry, demonstrating India’s capacity to develop indigenous solutions for global health challenges.
Global Health Implications:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a growing global health crisis that prolongs illnesses and raises healthcare costs.
- The new antibiotic offers a vital solution to multi-drug-resistant pathogens, contributing significantly to global health.
- India’s leadership in addressing AMR positions the country as a major player in biotechnology innovation.
Importance for Vulnerable Populations:
- Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (e.g., diabetes, cancer patients), are particularly affected by drug-resistant pneumonia.
- Nafithromycin offers a much-needed therapeutic option for these groups.
Impact of AMR Awareness:
- The launch coincides with World AMR Awareness Week, emphasizing the urgency of tackling antimicrobial resistance.
- Public awareness, fostered by the COVID-19 pandemic, has increased the focus on biotechnology and its potential to address global health challenges.
Future Prospects:
- Nafithromycin is awaiting final approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for manufacturing and public use.
- The launch is expected to lead to future breakthroughs in antibiotic development and contribute significantly to improving public health.
Sickle Cell Eradication
- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- On the occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Diwason 15th November 2024, Hon’ble Governor of Madhya Pradesh, and Chief Minister unveiled a commemorative postage stamp dedicated to "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" at PG College, Dhar.
- Significance:Focuses on India’s commitment to eradicate Sickle Cell Anemia by 2047, especially in tribal communities.
Sickle Cell Anemia Overview
- What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Genetic blood disorder leading to abnormal hemoglobin.
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, blocking blood flow and causing pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- Symptoms:
- Chronic anemia causing fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
- Painful episodes (sickle cell crisis) resulting in intense pain in bones, chest, and limbs.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: Relieve anemia and reduce pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of painful episodes.
- Gene Therapy: Includes bone marrow or stem cell transplants and methods like CRISPR for treatment.
Challenges of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India
- Tribal Population Impact:
- India has the world’s largest tribal population (~67.8 million, 8.6% of total population as per 2011 Census).
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is identified as one of the top 10 health issues for tribal communities.
- Challenges:
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal regions.
- Lack of awareness about genetic counseling and preventive care.
- High treatment costs (e.g., CRISPR therapy costs USD 2-3 million).
- Bone marrow donor availability is a challenge.
Government Initiatives for SCD Management
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023):
- Objective: Eliminate SCD as a public health issue by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Mass screening to identify at-risk individuals.
- Genetic Counseling: Educating families on genetic nature of SCD.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Partnership with organizations like Sankalp India.
- Newborn Screening: AIIMS Bhopal provides early detection.
- Technology: A mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking data.
- Progress:Over 3.37 crore people screened, with 3.22 crore confirmed negative.
- Target Groups:Focus on children, adolescents, youth, and adults for screening, counseling, and care.
- National Health Mission (NHM) (2013):
- Emphasizes disease prevention and management, particularly for hereditary conditions like sickle cell.
- Facilitates medications like hydroxyurea for treatment.
- National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research (2017):Regulates stem cell therapies and allows Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy (2019):Guidelines for gene therapies for inherited disorders, including CRISPR treatment for SCD.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:Addresses screening and management challenges of SCD in the state.
Global Awareness and Observances
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day:
- Observed on 19th June annually, with the 2024 theme: "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally".
- Aimed at raising awareness about SCD struggles, improving patient care, and finding a cure.
Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR)

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has launched the Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR) program to significantly boost research and innovation across Indian universities, especially those with limited research infrastructure. The program is designed to bring about a transformative change in India's academic research ecosystem, aligning with the broader goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Details:
- Launch Date: November 2024
- Ministry/Department: Department of Science and Technology (DST)
- Objective:
- To elevate research capabilities in universities that have limited resources by pairing them with well-established, top-tier institutions.
- To foster collaborations that can help these emerging universities enhance their research quality, drive innovation, and make significant, globally competitive research contributions.
- Operational Model: Hub-and-Spoke Framework
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- The top 25 institutions in the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF).
- Institutions of National Importance ranked in the top 50 NIRF.
- Spoke Institutions: These are emerging universities or institutions with limited research infrastructure. These will include:
- Central and State Public Universities ranked within the top 200 NIRF Overall.
- Top 100 NIRF University/State Public Universities.
- Select NITs and IIITs.
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- Funding:
- The program has a budget allocation of up to ?100 crore per PAIR network.
- Distribution of Funds:
- 30% for the Hub institution.
- 70% for the Spoke institutions.
- Private Institutions serving as hubs will need to contribute 25% of their allocated budget.
- Mentorship & Research Focus:
- Hubs will provide mentorship to spoke institutions, guiding them in various aspects of research such as access to resources, advanced infrastructure, and best practices.
- The collaboration is expected to enhance research capabilities, foster innovation, and encourage the development of collaborative networks across institutions.
- Regional Diversity & Inclusion:
- The program ensures regional diversity, with at least one spoke institution located outside the hub's state.
- It also allows the inclusion of one promising university from Category III institutions that may not meet the eligibility criteria but show potential for growth in research.
- Phase-wise Rollout:
- The first phase will focus on institutions ranked within the top 25 NIRF and Institutions of National Importance.
- Future phases will expand the scope, allowing more universities and institutions to participate.
- Goals Aligned with NEP 2020:
- Fostering Research Excellence: By partnering top institutions with emerging ones, PAIR seeks to improve the quality of research in India’s higher education sector.
- Promoting Regional Diversity: Ensuring a geographically diverse set of institutions participate in the research ecosystem.
- Strengthening Innovation: Helping universities in less-researched areas to compete on an international level, particularly in cutting-edge and impactful research.
- Program Implementation:
- Prospective Program Directors from eligible Hub institutions are invited to apply online for the program at ANRF PAIR Application Portal.
About ANRF:
- ANRF was established under the ANRF Act 2023 as an apex body to provide strategic direction for scientific research in India.
- With the formation of ANRF, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), previously established under an act of Parliament in 2008, has been subsumed into ANRF.
Sudden Resurgence of H5N1 in Cambodia

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Cambodia saw a resurgence of H5N1 avian influenza cases after over 10 years of no human infections.
- From February 2023 to August 2024, 16 human cases were reported, with 3 deaths caused by the A/H5 clade 2.3.2.1c virus.
- Notably, 14 of these cases were caused by a novel reassortant virus, involving a mixture of clade 2.3.2.1c and clade 2.3.4.4b gene segments.
Key Points:
- Reassortment of the Virus:
- The reassortment between clades 2.3.2.1c (Southeast Asia) and 2.3.4.4b (global spread) has created a new strain.
- This reassortant virus is responsible for the second wave of infections in humans, starting in October 2023.
- Zoonotic Transmission:
- Investigations confirmed that direct contact with sick poultry or bird droppings was the primary source of human infections.
- There have been no reported cases of human-to-human transmission.
- The novel reassortant virus appears to have replaced the 2.3.2.1c strain in Cambodian poultry.
- Geographic Spread and Spillovers:
- Clade 2.3.2.1c was first reported in Cambodian poultry in March 2014. It continued to circulate in both poultry and wild birds.
- Clade 2.3.4.4b viruses began circulating in Cambodian live bird markets by 2021, co-existing with clade 2.3.2.1c.
- There were two key spillovers to humans:
- The first spillover in February 2023, associated with clade 2.3.2.1c, involved two related individuals, with one death.
- The second spillover, beginning in October 2023, involved the novel reassortant virus.
- Genetic Analysis and Mutation Concerns:
- Genetic sequencing showed significant changes in the hemagglutinin (HA) gene of viruses from human cases, indicating a shift from older local strains to newer sublineages.
- The PB2 627K mutation in the novel reassortant is concerning, as it is linked to increased mammalian adaptation and the potential for airborne transmission, particularly in mammals like ferrets.
- This mutation raises concerns about the virus’s ability to adapt to humans or other mammals.
- Environmental and Epidemiological Factors:
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- High-density poultry farming.
- Wild bird migration.
- Cross-border poultry trade in Southeast Asia.
- These factors heighten the risk of zoonotic transmission, emphasizing the need for continued vigilance in the region.
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- Surveillance and Response:
- One Health investigations linked human cases to infected poultry, highlighting the importance of rapid response through whole genome sequencing.
- The ongoing surveillance is critical, as the novel reassortant strain has already replaced clade 2.3.2.1c in Cambodian poultry.
- Public Health Recommendations:
- There is an urgent need to strengthen sustained surveillance of avian influenza in both poultry and wild birds, particularly in Southeast Asia.
- Public health strategies should focus on:
- Reducing human exposure to infected poultry.
- Promoting safe poultry handling practices.
- Encouraging early healthcare-seeking behavior in individuals with potential symptoms.
3rd Indian Space Conclave
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd Indian Space Conclave, held in New Delhi, was a significant event for India's growing role in global space exploration and strategic partnerships.
- Organized by the Indian Space Association (ISPA), the conclave brought together key stakeholders from the government, industry, academia, and space agencies to discuss India’s space ambitions and the transformative role of space technologies.
Key Highlights:
Satcom as a Transformative Force for Digital India
- Emphasis on Satellite Communication (Satcom) is more than a mere tool—it's a transformative force driving Digital India by connecting every household, village, and remote area of the country.
- Satcom has a wide array of applications that extend across essential sectors such as telecommunications, disaster management, healthcare, education, and agriculture, particularly in underserved regions.
Indo-EU Space Collaboration
- The event also showcased India’s growing space partnerships, particularly with the European Union (EU). The EU Ambassador recognized India as a dynamic space power and highlighted shared goals in Earth observation, space security, and human spaceflight.
- Proposed joint initiatives include training programs, collaborative research, and satellite missions, such as the Proba-3 satellite launch by ISRO, focusing on observing the Sun.
- India’s trustworthiness as a partner in space was underscored by its role in the successful launch of the Proba-1 and Proba-2 missions for the EU, with Proba-3 marking India’s third contribution to EU space exploration.
Space Startups and Innovation
- The rise of space-focused startups in India, spurred by the 2020 space sector reforms, was another key highlight. India now has over 300 space startups, contributing to both economic growth and innovation in the space industry.
- These reforms have helped curb brain drain, with many talented Indian professionals returning from global agencies like NASA to join the expanding Indian space ecosystem.
India’s Long-Term Space Goals
- The Indian space program has ambitious long-term goals, including:
- Gaganyaan, India’s human spaceflight mission.
- A crewed lunar landing by 2040.
- The establishment of an Indian space station by 2035.
- Plans for space tourism by 2040.
- These initiatives demonstrate India’s commitment to becoming a global leader in space exploration and technological innovation.
Space Sector Reforms (2020)
- The Space Sector Reforms 2020 were designed to increase the participation of private players in India’s space activities. The creation of agencies like the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) and the strengthening of New Space India Limited (NSIL) have been pivotal in boosting India’s global space market share.
- IN-SPACe serves as an autonomous body fostering industry, academia, and startups, while NSIL handles commercial activities and promotes high-tech space-related ventures.
India's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission
- ISRO's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission was inaugurated in Leh, Ladakh. This mission simulates the conditions of space habitats, specifically focusing on Mars and Moon environments.
- Ladakh's unique climate—high altitude, low oxygen levels, and extreme temperature fluctuations—makes it an ideal location for testing life support systems, space habitat technologies, and sustainable resource utilization.
Key Aspects of the Analog Mission:
- Life support systems like hydroponics (space farming) and standalone solar power systems to support sustainable food production and renewable energy in space habitats.
- Circadian lighting to simulate daylight cycles, maintaining astronaut health and well-being.
- The mission’s goal is to understand the psychological and operational challenges of living in isolation and extreme conditions, preparing India for future interplanetary exploration.
AntarikshaAbhyas 2024

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- ‘AntarikshaAbhyas – 2024’ is a three-day space exercise held from November 11-13, 2024, hosted by the Defence Space Agency (DSA), Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff.
- The exercise is the first of its kind and focuses on war-gaming the growing threats to space-based assets and services.
Objective of the Exercise:
- Enhance understanding of space-based assets and their operational dependencies.
- Identify vulnerabilities in military operations in case of denial or disruption of space services.
- Integrate India's space capabilities in military operations to secure national strategic objectives.
Participants:
- Defence Space Agency (DSA) and its allied units.
- Personnel from the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Specialist agencies under Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff, including:
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCA)
- Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA)
- Strategic Forces Command (SFC)
- Representatives from ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and DRDO (Defence Research & Development Organisation).
Focus Areas:
- Space-based asset and service operational dependency.
- Securing national interests in space through technological innovation and development.
- Assessing space service vulnerabilities and impacts on military operations.
Zhurong Rover
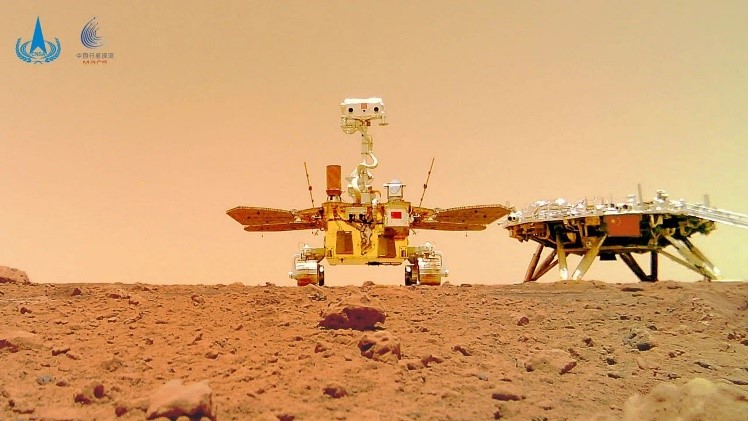

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
Chinese rover helps find evidence of ancient Martian shoreline.
Mission Overview:
- Rover: Zhurong, part of China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration program.
- Mission Launch: Zhurong landed in 2021 in the Utopia Planitia region of Mars' northern hemisphere.
- Key Discovery: Evidence of an ancient ocean on Mars, suggesting a habitable past for the planet.
Key Findings:
- Geological Features Indicating a Coastline:
- Data from Zhurong and orbiting spacecraft (Tianwen-1 Orbiter, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) revealed geological features such as troughs, sediment channels, and mud volcano formations, suggesting the existence of a Martian coastline.
- Features indicate both shallow and deeper marine environments, supporting the idea of a past ocean.
- Age of the Ocean:
- The ocean likely existed around 3.68 billion years ago, with its surface potentially frozen in a geologically short period.
- The ocean is thought to have disappeared by 3.42 billion years ago.
Evolutionary Scenario of Mars:
- At the time of the ocean, Mars might have already begun transitioning away from a habitable planet, losing much of its atmosphere and becoming cold and dry.
- The ocean may have formed after Mars' climate began to change, suggesting that it was once more hospitable, possibly capable of supporting microbial life.
Implications for Life on Mars:
- The presence of water, a key ingredient for life, raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in its early history.
- When Mars had a thick, warm atmosphere, conditions might have been favorable for life, as microbial life would have been more likely to exist.
Significance of Zhurong's Contribution:
- Zhurong exceeded its original mission duration of three months, operating until May 2022, helping provide key data to understand Mars' ancient water history.
- The discovery adds to ongoing efforts to study the disappearance of water on Mars and its implications for the planet's habitability.
Future Exploration:
- Other studies, including seismic data from NASA’s InSight lander, suggest that liquid water might still exist deep beneath the Martian surface, hinting at the possibility of finding water in the planet's subsurface in the future.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
PyPIM platform
- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Israeli researchers from the Israel Institute of Technology have developed the PyPIM platform, which allows computers to process data directly in memory, eliminating the need for a central processing unit (CPU). This breakthrough aims to address key challenges in modern computing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and processing efficiency.
Key Features of the PyPIM Platform:
- Integration with Python and PIM Technology:
- The PyPIM platform merges Python programming with digital processing-in-memory (PIM) technology, facilitating in-memory computing where computations occur directly within memory instead of transferring data to and from the CPU.
- Functionality and Innovations:
- Direct In-Memory Computations: PyPIM uses specialized instructions that enable computations to take place directly in memory, reducing the need for data movement between the CPU and memory.
- Developer-Friendly: It allows developers to use familiar languages like Python to write software for in-memory computing systems.
- Solving the "Memory Wall" Issue:
- The platform addresses the memory wall problem, where the speed of the CPU and memory exceeds the data transfer rates, creating bottlenecks that lead to inefficiencies.
- By performing calculations directly in memory, PyPIM reduces time and energy spent on data transfer, optimizing performance.
- Performance Improvements:
- Energy and Time Efficiency: By minimizing energy-intensive data transfers, PyPIM leads to significant energy and time savings.
- Simulation Tools: The platform includes tools that allow developers to simulate potential performance improvements from in-memory processing.
- Real-World Benefits:
- Faster Processing: Tasks performed using PyPIM have demonstrated faster processing speeds, with minimal code changes, particularly in mathematical and algorithmic tasks.
- The platform delivers a significant performance boost in areas like data analysis and algorithmic operations.
The PyPIM platform marks a pivotal advancement in computing architecture, providing a more energy-efficient and faster alternative to traditional CPU-dependent systems by reducing reliance on external memory processing and cutting down on data transfer delays.
RNA Editing

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Wave Life Sciences became the first biotechnology company to treat a genetic condition by editing RNA at the clinical level.
- What is RNA Editing?
- Definition: RNA editing is the modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) after it’s synthesized from DNA but before it is translated into proteins.
- Process: mRNA consists of exons (coding regions) and introns (non-coding regions). Exons code for proteins, while introns are removed before protein synthesis.
- Types of RNA Modifications:
- Addition: Insertion of a nucleotide.
- Deletion: Removal of a nucleotide.
- Substitution: Replacement of one nucleotide with another.
- Mechanism of RNA Editing:
- Involves Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA (ADAR) enzymes.
- ADAR enzymes modify adenosine to inosine, which is recognized as guanosine, allowing mRNA to be corrected.
- Guide RNA (gRNA) directs ADAR enzymes to the specific mRNA region for editing.
- Clinical Use of RNA Editing:
- Wave Life Sciences used RNA editing to treat α-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a genetic disorder.
- Other potential applications include treating diseases such as Huntington’s disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, and neurological disorders.
- Challenges in RNA Editing:
- Temporary Effects: RNA editing provides temporary changes, requiring repeated treatments for sustained effects.
- Delivery Issues: Current delivery methods, like lipid nanoparticles and adeno-associated virus vectors, have limitations in carrying large molecules.
- Specificity: ADARs may cause unintended changes in non-target regions of mRNA, leading to potential side effects.
- Comparison: RNA Editing vs. DNA Editing:
- Safety: RNA editing causes temporary changes and presents fewer risks than DNA editing, which makes permanent alterations to the genome.
- Immune Response: RNA editing uses enzymes naturally found in the body (ADAR), which reduces the risk of immune reactions, unlike DNA editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 that can trigger immune responses.
- Significance of RNA:
- Structure: RNA is a nucleic acid, similar to DNA but typically single-stranded. It consists of a backbone of ribose sugars and phosphate groups, with bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- Types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Regulatory RNAs: Regulate gene expression.
- α-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD):
- A genetic disorder where the protein α-1 antitrypsin accumulates in the liver, damaging both the liver and lungs.
- Treatments include weekly intravenous therapy or, in severe cases, liver transplants.
- RNA editing offers a potential new treatment approach.
- Global Impact:
- RNA editing is still in its early stages but shows promise for treating a wide range of genetic and chronic conditions.
- Ongoing research and clinical trials suggest RNA editing could become a key part of future gene-editing therapies.
Spraying Diamond Dust to cool the Earth

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- A new study in Geophysical Research Letters suggests that diamond dust could be more effective than any other material in reflecting solar radiation.
- Objective: The goal is to reduce global temperatures by 1.6°C by spraying approximately 5 million tonnes of diamonds annually into the atmosphere.
Background of Geoengineering Solutions:
- Geoengineering refers to large-scale interventions aimed at altering Earth's natural climate system to counteract global warming.
- One proposed solution involves spraying diamond dust in the Earth's upper atmosphere to cool the planet.
- This approach is part of Solar Radiation Management (SRM), which seeks to reflect sunlight away from Earth, thereby reducing global temperatures.
- Previous Materials Considered: Sulphur, calcium, aluminium, silicon, and other compounds have been studied to perform a similar function.
Context of Geoengineering and Climate Crisis:
- Inadequate Progress: Current efforts to mitigate global warming, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, have been insufficient. Global temperatures have continued to rise, and targets like the Paris Agreement's 1.5°C are increasingly out of reach.
- Rising Global Temperatures:
- 2023: Global temperatures were approximately 1.45°C higher than pre-industrial levels.
- Projected Challenge: To meet the Paris goal, global emissions must be reduced by at least 43% by 2030. However, current actions will likely result in only a 2% reduction by 2030.
Geoengineering Technologies:
- Geoengineering Methods:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM): Reflects sunlight to cool Earth.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): Involves capturing and storing CO?.
- SRM Techniques:
- SRM draws inspiration from natural events like volcanic eruptions, where large amounts of sulphur dioxide form particles that reflect sunlight.
- Mount Pinatubo (1991): One of the largest eruptions, which temporarily reduced global temperatures by 0.5°C due to the sulphur dioxide released.
Diamond Dust vs Other Materials:
- Study Comparison: Diamonds were found to be the most effective material compared to other compounds (sulphur, calcium, etc.) for reflecting solar radiation.
- Quantity Needed: To achieve a cooling of 1.6°C, 5 million tonnes of diamonds would need to be dispersed into the upper atmosphere each year.
Broader Geoengineering Context:
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- CCS is already in practice, where CO? emissions from industries are captured and stored underground to reduce atmospheric carbon.
- However, CCS faces high costs and scalability issues, and safe storage sites for CO? are limited.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): A more advanced method where CO? is directly removed from ambient air, but it faces even greater challenges in terms of infrastructure and cost.
Proba-3 Mission

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
Europe's Proba-3 mission to arrive in India for launch aboard PSLV-XL by ISRO
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The Proba-3 mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), aims to observe the Sun’s corona by creating an artificial solar eclipse. This will allow continuous observation of the Sun’s faint outer atmosphere, which is typically only visible during a natural solar eclipse.
- Key Features:
- Artificial Solar Eclipse: The two spacecraft will fly in formation to maintain a shadow between them, enabling the uninterrupted observation of the solar corona.
- Formation Flying: The satellites must maintain a precise formation with an accuracy of one millimetre, equivalent to the thickness of a fingernail.
Mission Details
- Launch Date: Scheduled for December 4, 2024.
- Launch Location: Satish Dhawan Space Centre near Chennai, India.
- Launch Vehicle: The PSLV-XL rocket developed by ISRO will be used for the launch.
- Spacecraft Mass: The combined mass of the two spacecraft is 550 kg.
- Orbit: The spacecraft will be placed in a highly elliptical orbit with a maximum altitude of 60,000 km to facilitate the precise formation flying.
- This high altitude minimizes Earth’s gravitational pull and reduces the amount of propellant required to maintain their positions during the mission.
Mission Significance
- Solar Observation: The primary objective is to observe the Sun’s corona, which has been challenging to study due to its faintness. The artificial eclipse will allow continuous data collection on solar activity.
- Formation Flying: This technology will allow the two satellites to maintain autonomous flight with millimetre-level precision, which is a significant advancement in satellite formation control.
- Six-Hour Observation Windows: Each formation flying session will last for up to six hours, during which the satellites will observe the Sun's corona.
Technological and Scientific Contributions
- ASPIICS Instrument: The ASPIICS (AStronomical PIcture Camera for the Intense Corona of the Sun) will be the mission's primary instrument, developed by the Royal Observatory of Belgium. It will provide crucial data on solar activity and space weather.
- International Collaboration: The mission is a collaborative effort involving 14 ESA member states and various organizations across Europe.
- Mission Control: The mission will be managed from the ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Belgium, with significant pre-launch training and preparations already underway.
ISRO's Role and Historical Context
- Launch by ISRO: The Proba-3 mission will be ISRO’s first launch for ESA since 2001, marking an important milestone in India-Europe space cooperation.
- PSLV-XL Rocket: ISRO’s PSLV-XL rocket is known for its reliability and capability in deploying satellites into precise orbits. It is well-suited to carry the 550 kg Proba-3 duo into a highly elliptical orbit for the mission.
LignoSat
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
The world's first wooden satellite, LignoSat, is set to launch from the Kennedy Space Center aboard a SpaceX rocket. This pioneering satellite is a collaborative effort between Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry Co., marking a significant step towards exploring more sustainable materials in space exploration.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:The primary goal of LignoSat is to test the viability of using wood in space technology, with a focus on the eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness of using renewable materials in satellite construction. The satellite will be tested aboard the International Space Station (ISS) to assess its durability, strength, and ability to withstand extreme space conditions.
- Material:The satellite is crafted from magnolia wood, chosen for its durability and adaptability. Magnolia was selected for its strength, making it a suitable candidate to endure the harsh conditions of space travel and the intense environmental factors faced in space exploration.
- Mission Details:Once launched, LignoSat will be sent to the ISS, where it will be released from the Japanese Experiment Module (Kibo). Researchers will collect data on the satellite’s performance, examining its ability to handle the challenges of space, including temperature fluctuations and physical strain.
- Environmental Benefits:One of the key advantages of wooden satellites is their environmental impact. Traditional metal satellites, when re-entering the Earth's atmosphere, can generate metal particles that contribute to air pollution. In contrast, wooden satellites like LignoSat are designed to be eco-friendly during reentry. Wood is a natural material that burns up more cleanly during reentry, reducing the potential for harmful atmospheric pollution.
First Science Result from India's Aditya-L1 Mission

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Aditya-L1 mission, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on September 2, 2023, is India's first dedicated scientific mission to study the Sun.
- Primary Payload: The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), developed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAp), Bengaluru, is the spacecraft's main instrument.
Key Highlights:
- First Science Outcome:The first scientific result from the mission, involving VELC, has been released. It successfully estimated the onset time of a coronal mass ejection (CME) that occurred on July 16, 2023.
- CMEs are massive solar eruptions that can disrupt electronics in satellites and communications on Earth.
- Key Findings:
- VELC's Role: The VELC payload was crucial in observing the CME close to the solar surface, providing a detailed understanding of its onset.
- CMEs are typically observed in visible light after they have traveled far from the Sun. However, VELC’s unique spectroscopic observations allowed scientists to study the CME much closer to the Sun's surface.
- Publication:The results will be published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
- Future Significance:
- As the Sun approaches the maximum phase of its current solar cycle (No. 25), CMEs are expected to become more frequent. Continuous monitoring with VELC will provide valuable data for understanding these events.
- Monitoring the thermodynamic properties of CMEs near the Sun is essential to understand their source regions and behavior.
- Mission Details:
- The spacecraft is in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- Mission Lifetime: 5 years.
Centre for Science and Environment

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Centre for Science and Environment release a report on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for Plastic Packaging
Key Findings:
- EPR Guidelines (2022) were a step towards enforcing the "polluter pays" principle, but the system faces significant issues in its implementation and registration processes.
- Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) report, released on October 29, 2024, highlights gaps in the EPR system for plastic packaging and suggests corrective actions.
EPR Guidelines Overview:
- Issued by: Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Objective: Hold producers, importers, brand owners (PIBOs), and plastic waste processors (PWPs) responsible for managing plastic packaging waste.
- Key Requirements:
- PIBOs must register on a centralized portal and set targets for collection, recycling, and reuse of plastic packaging.
- Registration involves compliance with targets on end-of-life recycling and recycled content usage.
Problems Identified in the Current EPR System:
- Low Registration and Enrollment:
- 41,577 registrations on the EPR portal, but a significant discrepancy in the type of stakeholders registered.
- 83% of registered entities are importers, 11% are producers, and only 6% are brand owners.
- Producers contribute 65% of the plastic packaging in the market but have low registration.
- Absence of Key Polluters:
- Manufacturers of virgin plastics are notably absent from the portal, despite being required to register.
- Fraudulent Practices:
- 700,000 fake certificates were generated by plastic recyclers, far exceeding the actual certificate generation capacity.
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) found that such fraudulent activities are undermining the integrity of the system.
- For example, end-of-life co-processing units (e.g., cement plants) claimed to have processed 335.4 million tonnes per annum of plastic waste, while their actual capacity is just 11.4 million tonnes per annum.
- Underreporting and Mismanagement:
- Despite 23.9 million tonnes of plastic packaging being introduced into the market, the CPCB’s estimation of plastic waste generation (4.1 MT annually) is underestimated.
- Lack of Stakeholder Representation:
- Urban local bodies and informal waste collectors—key contributors to plastic waste management—are not included in the EPR framework, which limits their incentives and support.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Incorporate the Informal Sector:
- Recognize informal waste collectors and waste management agencies in the EPR framework to improve traceability and ensure better waste management.
- Eliminate Fraudulent Practices:
- Strict actions need to be taken against fraudulent recyclers and fake certificate issuers to restore credibility to the EPR system.
- Establish Fair Pricing for EPR Certificates:
- Undertake baseline cost studies to determine the true costs of plastic waste management, ensuring fair pricing for recycling certificates and preventing undervaluation.
- Standardize Packaging:
- Focus on product standardization to ensure that packaging materials are uniform and easily recyclable.
- Strengthen Monitoring:
- Improve oversight on the registration process and ensure that all polluters (producers, importers, brand owners) comply with the system’s guidelines.
EPR and Plastic Waste Management: Context and Importance
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy approach where the responsibility of managing the entire lifecycle of plastic products (from production to disposal) lies with the producer.
- It is an essential part of India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules (2016), which mandate the recycling and proper disposal of plastic packaging waste.
Key Elements of EPR:
- Producer Accountability: Producers are responsible for the take-back, recycling, and final disposal of plastic packaging.
- Waste Minimization: Encourages reducing waste at the source by promoting sustainable packaging designs.
- Lifecycle Approach: Considers the entire lifecycle of the product, focusing on sustainability from production to disposal.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Ensures that the cost of waste management is borne by those responsible for generating the waste.
Discovery of the First "Black Hole Triple" System

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have discovered a "black hole triple" system, which is a rare configuration in space involving one black hole and two stars.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Location: The system is located 8,000 light years away from Earth, in the constellation Cygnus.
- Key Features:
- A black hole at the center, currently consuming a star that is spiraling very close to it.
- A second, more distant star that orbits the black hole every 70,000 years, and another star that orbits it every 6.5 days.
What is a Black Hole Triple System?
- Black Hole and Two Stars: Unlike typical binary systems (comprising a black hole and one other object), this system contains a black hole surrounded by two stars, one nearby and one far away.
- V404 Cygni: The central black hole in the system is the V404 Cygni, one of the oldest known black holes, roughly 9 times the mass of the Sun.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Questions on Black Hole Formation: The discovery raises new questions about how black holes are formed. Traditionally, black holes are thought to form after the explosion of a massive star (supernova), but this system does not follow that model.
- New Formation Theory: Researchers suggest the black hole may have formed via a "direct collapse" process, where a star collapses into a black hole without undergoing a supernova explosion. This is referred to as a "failed supernova".
- In a failed supernova, the star's collapse happens too quickly for the explosive outer layers to be ejected, leading to the formation of a black hole without the typical violent explosion.
Implications for Other Binary Systems:
- The black hole’s gradual consumption of one of its stars may imply that some binary black hole systems could have originally been triple systems, with one star eventually being consumed by the black hole.
Research and Collaboration:
- Study: The discovery was made by researchers at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- Published in: The findings were published in Nature in October 2024.
Additional Context:
- Distance: The system is about 8,000 light years away, which is vast but still observable with advanced telescopes.
- Mystery of the "Failed Supernova": The concept of a failed supernova offers new insights into the life cycle of massive stars and their transformation into black holes.
ISRO's Analogue Space Mission in Ladakh

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
In a significant leap for the country’s space exploration aspirations, India has embarked on its first analogue space mission in Leh, a landmark step that will attempt to simulate life in an interplanetary habitat to tackle the challenges of a base station beyond Earth.
Mission Overview:
- Objective: To simulate living conditions in an interplanetary habitat, addressing challenges astronauts may face during deep-space missions (e.g., Moon, Mars).
- Goal: Study long-term isolation, habitat design, resource management, and psychological effects on astronauts.
- Partners: ISRO’s Human Spaceflight Centre, AAKA Space Studio, University of Ladakh, IIT Bombay, Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council.
Rationale for Ladakh:
- Geological Similarities: Ladakh’s terrain mirrors Martian and lunar surfaces, making it ideal for testing space technologies.
- Climate: Cold, dry, high-altitude conditions simulate the extreme environments of space.
- Focus Areas: Testing habitat construction, microbial studies, and survival strategies for long-duration space travel.
What are Analogue Space Missions?
- Definition: Simulated space missions on Earth designed to replicate the conditions of space exploration.
- Purpose:
- Test technologies (e.g., life support, habitat design, in-situ resource utilization).
- Study human behavior, psychological impacts of isolation, and operational readiness for extended space travel.
- Relevance: Crucial for preparing astronauts for missions to the Moon, Mars, or asteroids.
Significance of Analogue Missions:
- Technological Testing: Analogue missions help in evaluating systems for habitat design, life support, and health monitoring.
- Human Factors: They provide insights into crew health, teamwork under pressure, and performance during isolation.
- Psychological Studies: Address the impact of confinement, isolation, and communication delays on astronauts.
- Training: Participants (analogue astronauts) are trained for real-world space missions by conducting scientific experiments and managing emergencies.
Global Examples of Analogue Missions:
- NASA’s NEEMO: An underwater mission simulating microgravity conditions to train astronauts for space tasks.
- SIRIUS Program (UAE): Focuses on the psychological impacts of long-duration space isolation, featuring international collaborations.
- Arctic Mars Analogue Svalbard Expedition (AMASE): Uses the extreme Arctic environment of Svalbard to test Mars exploration technologies and procedures.
Relation to India’s Space Aspirations:
- Gaganyaan Mission: ISRO’s human spaceflight mission aiming to send Indian astronauts into space.
- Interplanetary Exploration: The analogue mission supports India’s broader goal of advancing human space exploration and technology development for Mars and beyond.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
What is LiDAR?
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
Anti-Counterfeiting Ink developed using Luminescent Nanomaterials

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- A novel anti-counterfeiting ink has been developed using luminescent nanomaterials, which significantly enhances security in currency, certificates, medicines, and branded goods.
- The ink utilizes the luminescent properties of rare earth ions and bismuth, enabling excitation-dependent luminescence under different light sources, providing a robust solution to combat counterfeiting.
Key Features:
- Multi-Wavelength Luminescence:
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Vibrant blue under 365 nm UV light
- Pink under 395 nm UV light
- Orange-red under 980 nm near-infrared (NIR) light
- These varying color emissions make it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, as traditional covert tags are visible only under UV light and can be easily duplicated.
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Enhanced Durability:
- The ink remains effective under a wide range of conditions, including varying light, temperature, and humidity, ensuring long-term usability without degradation.
- Simple Application Method:
- The luminescent nanomaterials are synthesized through a co-precipitation method at 120°C.
- The resulting nanomaterials are then mixed into commercially available PVC ink using sonication, allowing for easy dispersion of nanoparticles.
- The ink is applied using screen printing to create patterns and texts that exhibit distinct color changes under different lighting conditions.
- Security Features:
- The ink combines rare earth ions with bismuth emissions, boosting its encryption and decryption capabilities. This creates a high level of security for applications on high-value items.
Applications:
- Currency and Certificates: Enhances the authenticity of financial instruments and official documents.
- Branded Goods: Protects products from counterfeiting and fraud.
- Medicines: Helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, preventing the distribution of fake medicines.
Benefits:
- Verification: Both consumers and manufacturers can easily verify the authenticity of products, providing an accessible solution to counterfeiting.
- Practical Solution: The ink offers a practical, reliable, and non-invasive method for detecting counterfeit products, addressing a global challenge in various industries.
ISRO’s First Electric Propulsion-Led Spacecraft (TDS-1)

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India's first home-grown electric propulsion satellite to be launched in Dec.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of TDS-1:
- Purpose: To demonstrate electric propulsion technology for satellite steering, using solar-powered ionized gas.
- Goal: Reduce reliance on chemical fuel, making satellites lighter and more efficient.
- Key Benefits of Electric Propulsion:
- Weight Reduction: The technology can significantly cut down satellite mass. For example, a satellite weighing 4 tonnes could be reduced to around 2 tonnes.
- Fuel Efficiency: By using electric propulsion, the need for chemical fuel is minimized, allowing for a more efficient journey to geostationary orbit.
- Technology Details:
- Fuel Used: Gases like Argon are ionized using solar power to create propulsion.
- Process: The ionized gas is expelled at high speeds to generate thrust, pushing the satellite towards its desired orbit.
- Historical Context:
- The technology was first used in GSAT-9 (South Asia Satellite) in 2017 but with imported Russian components.
- TDS-1 marks the first fully indigenous development of electric propulsion technology by ISRO, highlighting India’s increasing space autonomy.
- Significance for India’s Space Program:
- Self-Reliance: TDS-1 reflects ISRO’s growing capacity to develop advanced space technologies domestically.
- Future Prospects: This breakthrough is expected to lead to more efficient satellite designs, enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global space industry.
New Space Missions and Developments

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The Space Commission also approved a joint moon mission with Japan called the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission. For LUPEX, ISRO is developing a different moon lander than the one it used for Chandrayaan-3
New Space Missions and Developments
- Chandrayaan-4 (Moon Mission):
- Type: Sample-return mission.
- Launch: Expected by 2027.
- Cost: ?2,104 crore.
- Objective: Sample collection of moon soil and rock to return to Earth.
- Mission Details: Two LVM-3 launch vehicles will launch components that will dock in Earth orbit before heading to the moon. The samples will be sent back using a bespoke canister.
- Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX):
- Collaboration: Joint mission with Japan.
- Objective: Exploration of lunar poles with a new lander design, intended for potential crewed missions in future.
- Venus Orbiter Mission:
- Launch Window: March 2028.
- Cost: ?1,236 crore.
- Objective: Study Venus' surface and atmosphere to understand planetary evolution in the Solar System.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV):
- Development Budget: ?8,240 crore for first three development flights.
- Objective: A new launcher developed with private sector collaboration for future space missions.
Cabinet Approvals for Space Initiatives
- Human Spaceflight Programme (Gaganyaan):
- Four new missions under Gaganyaan, including an uncrewed Gaganyaan flight.
- Focus on developing technologies for India’s first space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), planned by 2028.
- Space-Based Surveillance (SBS) Missions:
- Phase 3: Approval for building 21 ISRO satellites, with 31 additional satellites by private companies.
- Total Cost: ?26,968 crore.
- Development of a Third Launch Pad:
- To support the NGLV and additional space missions at Sriharikota.
Upcoming Satellite Missions
- NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar):
- Launch: Early 2025 on a GSAT launch vehicle.
- Purpose: Earth observation using advanced radar technology.
- Issue: Protective coating added due to high temperatures during testing.
- Proba-3 (European Space Agency):
- Launch: November 29, 2024, aboard PSLV-XL.
- Objective: Study the Sun’s corona using two satellites in formation, mimicking an eclipse to capture unique solar data.
Private Sector Involvement
- Manastu Space & Dhruva Space:
- Collaboration: Testing green propulsion technology for the LEAP-3 mission.
- Technology: Hydrogen-peroxide-based green propulsion system.
- Launch: LEAP-3 mission in 2025.
- Bellatrix Aerospace:
- Project: Prototype satellite for ultra-low earth orbit at 200 km altitude.
- Ananth Technologies:
- Achievement: First private company to assemble, integrate, and test Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx) satellites for ISRO.
Space Science and Research Updates
- Chandrayaan-3:
- Findings: The crater where Chandrayaan-3 landed is older than the South Pole-Aitken Basin (4.2-4.3 billion years old).
- Data Source: Optical High-Resolution Camera (Chandrayaan-2) and Pragyaan rover (Chandrayaan-3).
- Astrosat (India’s First Space Observatory):
- Mission Life: Expected to last two more years (originally planned for 5 years).
- Significance: Contributed to over 400 published papers based on multi-wavelength space observatory data.
ISRO-DBT Agreement for Biotechnology Experiments in Space

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have signed an agreement to conduct biotechnology experiments on the upcoming Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
- Timeline for BAS:
- The BAS is expected to be operational from 2028-2035, with the initial module launches slated for 2028 and full expansion by 2035.
- It will be located at an altitude of 400 km above Earth and will support 15–20-day missions in space.
Focus Areas of Research
- Health Impact:
- Weightlessness & Muscle Health: Studying the effects of zero-gravity on muscle loss during space missions.
- Radiation Effects: Investigating how space radiation impacts astronaut health over long durations.
- Bio-Manufacturing:
- Algae Studies: Exploring algae for potential use in nutrient-rich, long-lasting food sources and biofuel production.
- Food Preservation: Identifying algae varieties that can help preserve food for longer periods in space.
- Integration with Gaganyaan Mission:
- Experiments may also be conducted during uncrewed test flights for the Gaganyaan mission (India’s first crewed mission to space, scheduled for 2025-2026).
BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy
- Objective: The BioE3 policy aims to boost bio-manufacturing in India, which is projected to contribute $300 billion to the Indian economy by 2030.
- Key Focus Areas:
- High-Value Bio-Based Products: Promotes the development of bio-based chemicals, biopolymers, enzymes, and smart proteins.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture & Carbon Capture: Aims to strengthen agricultural practices to withstand climate change and promote carbon capture technologies.
- Healthcare & Nutrition: Focuses on advancements in biotherapeutics, functional foods, and regenerative medicine.
- Marine & Space Biotechnology: Encourages research in space and marine biotechnology for new applications.
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship: Supports R&D-driven entrepreneurship through the establishment of bio-manufacturing hubs, bio-AI centers, and biofoundries.
- Employment Growth: Aims to create skilled jobs in the growing bioeconomy, promoting green growth and sustainable industries.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) Overview
- Structure: The station will consist of:
- Command Module
- Habitat Module
- Propulsion Systems
- Docking Ports
- Objective: To support long-term research in space life sciences and bio-manufacturing, with a focus on human health, food sustainability, and biotechnology innovations.
Center for Generative AI, Srijan

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
IndiaAI and Meta have announced the establishment of the Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur, along with the launch of the “YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building” in collaboration with the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), for the advancement of open source artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur:
- Focus on Generative AI (GenAI) research and innovation.
- Meta’s support for ethical and responsible development of AI technologies.
- Aim to empower researchers, students, and practitioners with the tools for responsible AI deployment.
- Focus Areas: Open science, AI policy advisory, and indigenous AI application development.
- YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building:
- Target: Empower 100,000 students and young developers (ages 18-30) with AI skills.
- Core Focus: Leveraging open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) for real-world solutions.
- Skills Development: Generative AI, open-source tools, and sector-specific AI applications (healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, mobility, and financial inclusion).
- Partnership: Collaboration with AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education).
Strategic Goals and Outcomes
- Research and Innovation:
- Strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through groundbreaking research and collaborations.
- Focus on open-source AI and indigenous AI solutions for national challenges.
- Empower India to lead in AI through ethical and responsible AI deployment.
- AI Talent Development:
- Bridge the AI talent gap by training young developers in open-source AI technologies.
- Develop AI solutions for critical sectors like healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, and financial inclusion.
- Program Components:
- GenAI Resource Hub with courses, case studies, and open datasets.
- Unleash LLM Hackathons for students to propose AI solutions for real-world challenges.
- Support for AI startups through an Innovation Accelerator.
Sectoral Focus and Impact
- Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and healthcare delivery.
- Education: AI tools for enhancing learning outcomes and personalized education.
- Agriculture: AI solutions for precision farming, pest control, and crop management.
- Smart Cities: AI in urban planning, traffic management, and public services.
- Mobility: AI applications in transportation, logistics, and urban mobility.
- Financial Inclusion: AI in fintech, digital payments, and financial services for underserved populations.
Additional Programs and Opportunities
- AICTE Collaboration: Mobilizing technical institutions across India to build AI capabilities.
- Master Training Activation Workshops: To introduce foundational AI concepts to students.
- Mentorship and Grants: Top AI solutions from hackathons will receive mentoring, seed grants, and market support.
- Student Startups: AI Innovation Accelerator will incubate 10 student-led AI startups experimenting with open-source models.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
Introduction to Innovative Cancer Detection Technique
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
- Scientists have developed an ultrasound-based technique for detecting cancer, aiming to replace traditional biopsies, which are invasive and painful.
- Promising Alternative: The method uses high-energy ultrasound to release biomarkers (RNA, DNA, and proteins) from cancerous tissue into the bloodstream, allowing for early cancer detection with minimal discomfort.
- Presented at Acoustical Society Conference: The technique was discussed at the joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and Canadian Acoustical Association in May 2024.
Traditional Cancer Detection vs. New Ultrasound Approach
- Current Gold Standard - Biopsy: Traditionally, cancer is diagnosed using biopsies, where a tissue sample is extracted using a needle from suspected cancerous areas. Although effective, biopsies are invasive, painful, and carry some risks.
- Ultrasound as a Non-Invasive Alternative: The new method involves using high-frequency ultrasound waves to break off cancerous tissue into droplets, which are then released into the bloodstream. The biomarkers in the droplets can be analyzed for cancerous mutations.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: This ultrasound-based technique increases the levels of genetic and vesicle biomarkers in blood samples by over 100 times, enabling the detection of cancers and specific mutations that are otherwise undetectable in blood.
Key Findings of the Research
- Single Cancer Cell Detection: The technique allows for the detection of a single cancer cell in blood samples. It works by passing ultrasound waves through isolated blood samples, which break apart circulating cancer cells, releasing biomarkers into the blood.
- Cost-Effective: Traditional methods for detecting circulating cancer cells are costly (e.g., the ‘CellSearch’ test costs $10,000). In contrast, this ultrasound method can detect cancer with a much lower cost, around $100 (?8,400).
- Potential for Early Diagnosis: The research shows promise for detecting cancer at an early stage, even before symptoms appear, using blood samples.
Challenges and Next Steps
- Need for Large-Scale Clinical Trials: While the technique shows potential, large cohort studies involving diverse patient groups across different geographies and ethnicities are needed to validate the approach.
- Long-Term Study for Effectiveness: Further research is required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the technique across various cancer types and to determine the ideal biomarker thresholds for early detection.
- Regulatory Approval and Commercialization: If the clinical trials yield positive results, the method could be commercially available in approximately five years, following regulatory approval.
Understanding Cancer and Its Types
- Cancer Definition: Cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body.
- Types of Cancer:
- Carcinoma: Cancer originating in epithelial cells (e.g., breast, lung, prostate cancer).
- Sarcoma: Affects connective tissues like bones and muscles.
- Leukemia: Affects blood-forming tissues, leading to abnormal white blood cell production.
- Lymphoma: Begins in immune cells, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Melanoma: Cancer of pigment-producing skin cells.
- Key Differences Between Normal and Cancer Cells:
- Cancer cells grow uncontrollably and evade immune detection.
- Cancerous cells accumulate chromosomal abnormalities, unlike normal cells, which follow regulated growth patterns.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)
- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The tiny nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) has played an outsized role in scientific discovery, contributing to four Nobel Prizes over the years.
Key Discoveries from C. elegans Research
- C. elegans and Cellular Processes:
- The worm has helped scientists understand programmed cell death (apoptosis), a vital process in development and disease. This work contributed to the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, addressing how cells are instructed to kill themselves and how this process goes awry in conditions like AIDS, strokes, and degenerative diseases.
- Gene Silencing and RNA Interference:
- In 2006, a Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of gene silencing via RNA interference (RNAi), a process first explored using C. elegans. This discovery led to the development of a new class of RNA-based drugs.
- Cellular Imaging Techniques:
- In 2008, C. elegans contributed to breakthroughs in cellular imaging, as its use helped invent cellular “lanterns” that allowed scientists to visualize the inner workings of cells, earning a Chemistry Nobel.
- Gary Ruvkun’s 2024 Nobel:
- Gary Ruvkun’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024 was the fourth in a series of Nobel recognitions stemming from C. elegans research, reinforcing its role in fundamental biological discoveries.
Key Facts About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans):
- Size: 1 millimeter long.
- Life Cycle: Completes in 3-5 days.
- Cell Count: 959 cells.
- Genome: First multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced in 1998.
- Sexual Reproduction: Hermaphroditic (self-fertilizing) and male.
- Scientific Role: Used to study genetics, developmental biology, neuroscience, and cell biology.
- Nobel Prize Contributions: Four Nobel Prizes, including those in Physiology, Medicine, and Chemistry, for advancements in cell death, gene silencing, and imaging.
Plunging Region of a Black Hole

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, astronomers have observed the area right at the edge of a black hole where matter stops orbiting and plunges straight in at near-light speed.
What is the Plunging Region of a Black Hole?
- The plunging region of a black hole is an area where matter ceases to orbit the celestial object and instead falls directly into its incalculable depths.
- This phenomenon was initially predicted by Albert Einstein's groundbreaking theory of general relativity, which continues to shape our understanding of the cosmos.
- As matter approaches a black hole, it is torn apart and forms a rotating ring known as an accretion disc.
- According to general relativity, there exists an inner boundary within this disc, beyond which nothing can maintain its orbit around the black hole.
- Instead, the material is drawn towards the black hole at nearly the speed of light, marking the beginning of the plunging region.
- This region, situated just outside the event horizon, represents the point of no return for matter falling into a black hole.
- Despite the challenges posed by studying these enigmatic structures, researchers believe that investigating plunging regions could unveil new insights into the formation and evolution of black holes.
- Additionally, these studies may offer valuable information about the fundamental properties of space-time, potentially transforming our understanding of the universe and its most mysterious inhabitants.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a celestial phenomenon that arises from the remnants of a massive star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel and undergone gravitational collapse.
- It is characterized by an unfathomably dense core, known as a singularity, which is enveloped by a boundary called the event horizon.
- The event horizon serves as a point of no return; any matter or light that crosses this boundary is irrevocably drawn towards the singularity, making it impossible to escape the immense gravitational pull.
Black holes are classified into three categories based on their size and formation process:
- Stellar-mass black holes: These form when a massive star collapses at the end of its life cycle. They typically have masses ranging from approximately five to several dozen times that of our Sun.
- Supermassive black holes: Found at the centre of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, these colossal structures boast masses that can reach billions of times the mass of the Sun.
- Intermediate-mass black holes: With masses between those of stellar mass and supermassive black holes, these entities are thought to form through the merger of smaller black holes or the collapse of dense clusters of stars.
- Due to their extreme nature, black holes have been the subject of extensive research and fascination in the scientific community.
- The study of these enigmatic structures continues to yield invaluable insights into the fundamental principles governing our universe.
A first in 100 years, the Indian Science Congress was postponed amid a tussle between organisers, Govt (Indian Express)

- 04 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Science Congress, the largest gathering of scientists and students of science in the country and a permanent annual fixture in the calendar of the participant group for more than a century has been postponed.
Postponement of the Indian Science Congress:
- Unprecedented Interruption: The postponement of the Indian Science Congress holds unprecedented significance.
- Since its inception in 1914, the Congress has been an annual event, except for the years immediately following the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic (2021 and 2022).
- Tradition and Prime Ministerial Engagement: A cornerstone of scientific tradition, the Indian Science Congress is inaugurated by the Prime Minister, making it a fixture on the PM's calendar.
- Typically, it stands as the Prime Minister's first public engagement of the new year.
Why has the Science Congress Been Postponed This Year?
- This year's postponement stems from a protracted dispute between the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), the organizing body, and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) within the Union Ministry of Science and Technology.
- The DST, a key funding entity, withdrew support in September 2023, citing financial irregularities.
- The ISCA refuted the allegations and contested the DST's directive prohibiting government funds for Science Congress-related expenses, leading to an impasse that has resulted in the postponement.
- A legal challenge to the DST's decision is currently pending.
What is the Indian Science Congress (ISC)?
- The Indian Science Congress (ISC) is a unique event in the country that serves as a platform for scientific communities to interact with students and the general public on science-related matters.
- Organized by the Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA), an independent body supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) in the central government, the Science Congress is an annual five-day event from January 3 to 7, considered a permanent fixture on the Prime Minister’s calendar.
- The inaugural session of the Indian Science Congress took place in 1914 at the premises of the Asiatic Society, Calcutta.
- In recent years, the Indian Science Congress (ISC) has faced criticism due to issues such as a lack of substantial discussions, the promotion of pseudoscience, and outlandish claims by certain speakers.
- This has led to concerns among prominent scientists, with some advocating for the discontinuation of the event or, at the very least, the withdrawal of government support.
- While the government provides an annual grant for organizing the Science Congress, it does not play a direct role in its organization.
Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV) (DST Gov)

- 06 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
The study by ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute (ICAR-IVRI), Izatnagar, Bareilly has found the exact status of EEHV and its subtypes circulating among the Asian elephant population in India.
What is Elephant Endotheliotropic Herpesvirus (EEHV)?
- Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus (EEHV) is responsible for one of the most devastating viral infectious diseases in elephants worldwide, especially young Asian elephants.
- EEHV is a double-stranded DNA virus that is classified in the family Herpesviridae.
- The mortality rate is very high (70-85%) and death occurs within a short period (2-4 days).
- In India, the incidence of EEHV-HD was first reported in 1997.
- 9 of 15 potential cases were confirmed from Southern India in wild free-ranging calves in Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu forest reserves, and Madras Zoo.
- Transmission of the disease: EEHV is mostly spread through mucosal secretions which include:
- Saliva, Breast milk, Nasal secretions, Trunk to trunk contacts etc
- The disease can only affect elephants and is not infectious to humans or other animals.
- Symptoms: Some elephants show symptoms such as reduced appetite, nasal discharge and swollen glands.
- Treatment: Treatment involves a combination of strategies such as antiviral therapy, aggressive fluid therapy to counter haemorrhaging, immuno-stimulant drugs like selenium and Vitamins C and E, as well as antipyretics and analgesics to manage fever.
- It's important to note that there is no definitive cure for herpesviruses in animals or humans since these viruses typically enter a latent state.
India International Science Festival (PIB)

- 16 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The 9th edition of the India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023 will be held at Faridabad, Haryana from January 17th-20th, 2024.
About the India International Science Festival (IISF):
- The India International Science Festival (IISF) is an annual science festival organized by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Earth Science, and Vijnana Bharati in India.
- The festival aims to promote science and technology in India and to showcase the latest advancements in these fields.
- The IISF has been held every year since 2007.
- The festival typically lasts for four days and features a variety of events, including exhibitions, seminars, workshops, and competitions.
- The exhibitions feature displays of scientific and technological innovations from India and around the world.
- The seminars and workshops provide opportunities for scientists and technologists to share their knowledge with the public.
- The competitions encourage students to participate in science and technology.
- The IISF is a major event in the Indian scientific community and has been praised for its role in promoting science education and public awareness of science.
- The festival has also been successful in attracting international participation, with scientists and technologists from around the world attending the event.
- The 2022 IISF was held in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, from January 21 to 24.
India International Science Festival (IISF) 2023:
- It will be held at the Campus of Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) and Regional Centre for Biotechnology (RCB) of the Department of Biotechnology in Faridabad.
- Theme: 'Science and Technology Public Outreach in Amrit Kaal'.
- IISF 2023 will have a total of 17 themes to showcase scientific achievements, offering diverse benefits to participants and the general public.
Euclid Mission (NASA)

- 07 Nov 2023
Why in the News?
The Euclid mission, which will investigate the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, released its first five science images recently.
About Euclid Mission:
- Euclid is a European mission, built and operated by European Space Agency (ESA), with contributions from NASA.
- Euclid is designed to give important new insights into the "dark side" of the universe -- namely dark matter and dark energy, both thought to be key components of our cosmos.
- It was launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, (USA) on 1 July 2023 and the launch vehicle used was ‘SpaceX Falcon 9’.
- The mission derives its name from Euclid of Alexandria, an ancient Greek mathematician from around 300 BC, who laid the foundations of geometry.
- Euclid Mission Objective: The primary goal of the Euclid mission is to create a three-dimensional map of the universe, with time as the third dimension.
- This will be achieved by observing billions of galaxies, extending up to 10 billion light-years away, and covering over a third of the celestial sphere.
- Euclid will explore how the Universe has expanded and how structure has formed over cosmic history, revealing more about the role of gravity and the nature of dark energy and dark matter.
- The Euclid Consortium – consisting of more than 2,000 scientists from 300 institutes in 13 European countries, the U.S., Canada, and Japan – is responsible for providing the scientific instruments and scientific data analysis.
- NASA provided the detectors of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer, NISP.
- Euclid is a medium-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme.
