US AI Hardware Export Restrictions and Impact on India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
Days before demitting office, the Joe Biden administration has released an expansive regulatory framework on the export of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware such as graphics processing units (GPUs), which could have far-reaching consequences for India’s AI ambitions.
Three-Tier Framework for AI Hardware Export Restrictions
- Tier 1: Closest US Allies
- Countries: Australia, Belgium, Canada, South Korea, UK, etc.
- No restrictions on computing power deployment.
- Minimal security requirements.
- Impact: Free access to AI technology for these nations.
- Tier 2: Majority of Countries (Including India)
- Countries: India, Brazil, South Africa, etc.
- Restrictions: Limited to importing approximately 50,000 advanced AI chips (around $1 billion) through 2027.
- Potential to Double Cap: If countries sign agreements to uphold strict security standards.
- Impact on India:
- Short-Term: Likely to fulfill current demand for 10,000 GPUs for the IndiaAI Mission.
- Long-Term: Challenges in scaling AI infrastructure, with possible delays in large AI data centers and difficulty acquiring large-scale GPUs.
- Tier 3: Countries of Concern (Restricted Nations)
- Countries: Russia, China, North Korea, Iran, etc.
- No Access to US AI Technology: Nearly total prohibition of AI tech exports.
Special Provisions for India and China
- General Validated End User (GVEU) status for India and China:
- India: Authorisation for civilian and military use, excluding nuclear applications.
- China: Only civilian use permitted under similar conditions.
Why the US Imposed These Restrictions?
- National Security: Prevent adversaries (China, Iran, Russia) from acquiring advanced AI technologies.
- US Technological Leadership: To protect US AI leadership and prevent loss of competitive edge.
- Trusted Ecosystem: Build secure and trusted AI environments for allied nations.
Impact on India
- Short-Term:
- IndiaAI Mission: Current procurement of 10,000 GPUs unlikely to be affected.
- Subsidized GPUs: Available for startups, academia, and researchers.
- Long-Term Concerns:
- Licensing Uncertainties: Possible delays in large-scale AI deployments and AI data centers.
- Impact on Large Firms: Companies like Reliance and Yotta may face challenges scaling up AI compute infrastructure.
- National AI Mission Challenges: Difficulty in acquiring enough GPUs for large-scale AI projects beyond 2027.
- Strategic Leverage: US could use AI export restrictions to negotiate trade deals or tariff adjustments.
Nvidia’s Criticism of the AI Diffusion Rules
- Overreach and Bureaucratic: Nvidia criticized the 200+ page regulatory framework as excessive, secretive, and bureaucratic.
- Harming US Competitiveness: Claims that the rules would hinder US innovation and global leadership, weakening the competitiveness of the US semiconductor and software industries.
- Contrast with Trump’s Approach: Praises the earlier Trump administration for fostering AI growth through industry competition without compromising national security.
Enforcement of the Rules
- Regulatory Control: Managed by the US Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) under the Department of Commerce.
- Technology Access: Ensures AI chips and models do not reach adversaries or nations posing security risks.
Potential Impact on India’s AI Strategy
- AI Hardware Infrastructure: Challenges in large-scale AI hardware deployment.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Potential delays or downsizing of AI data centers could affect India’s competitiveness in AI technology.
- Strategic Partnerships: India may need to secure General National Validated End User authorizations to ensure uninterrupted access to advanced chips.
- AI Market Growth: India’s AI market projected to grow to $17 billion by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 25%-35%.
Iran's Capital Relocation

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Iran has announced plans to relocate its capital from Tehran to the Makran coastal region due to economic and environmental concerns.
Reasons Behind Relocation
- Overcrowding and Resource Constraints: Tehran, the capital for over 200 years since the Qajar dynasty (1794-1925), faces overpopulation, air pollution, water scarcity, and energy shortages.
- Strategic Importance of Makran: Located in Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Makran’s proximity to the Gulf of Oman enhances its potential for economic development.
- Economic and Maritime Significance: Home to key ports like Chabahar, Makran is vital for Iran’s petroleum reserves and coastal trade.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The development of Makran as an international trade hub could strengthen Iran’s economic ties with Central Asia and the Indian Ocean region.
About Makran
- Geographical Overview: A semi-desert coastal plateau shared by Pakistan and Iran, bordered by the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman.
- Key Ports and Trade Routes: Gwadar (Pakistan) and Chabahar (Iran) serve as critical gateways to the Strait of Hormuz, a global oil supply route.
Alexander’s Invasion and Makran’s Historical Significance
Background of Alexander’s Invasion (327–325 BCE)
- Entry into India: Alexander, King of Macedonia (336-323 BCE), entered India via the Khyber Pass after conquering Kabul.
- Key Battles:
- Battle of Hydaspes (Jhelum): Faced and defeated King Porus, later reinstating him as an ally.
- Retreat at Hyphasis (Beas River): His army, exhausted and wary of the Nanda Empire’s strength, refused to march further east.
The Gedrosian Desert March
- Extreme Hardships: While retreating through the Makran Desert, Alexander lost a third of his army to dehydration, starvation, and exhaustion.
- Comparison with Cyrus the Great: Unlike Cyrus II, who failed to cross the desert, Alexander’s army endured the harsh terrain, albeit with heavy casualties.
Impact of Alexander’s Invasion on India
- Cultural and Trade Exchanges: Facilitated early Indo-Greek interactions and opened key trade routes linking South Asia and Europe.
- Greek Settlements: Established cities like Alexandria (Kabul) and Boukephala (Jhelum), influencing local governance and trade.
- Mauryan Expansion: Weakened regional rulers enabled Chandragupta Maurya to establish the Mauryan Empire.
- Influence on Art and Culture: Indo-Greek fusion led to the Gandhara School of Art, integrating Greek and Indian artistic traditions.
Indonesia Becomes 10th Member of BRICS
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
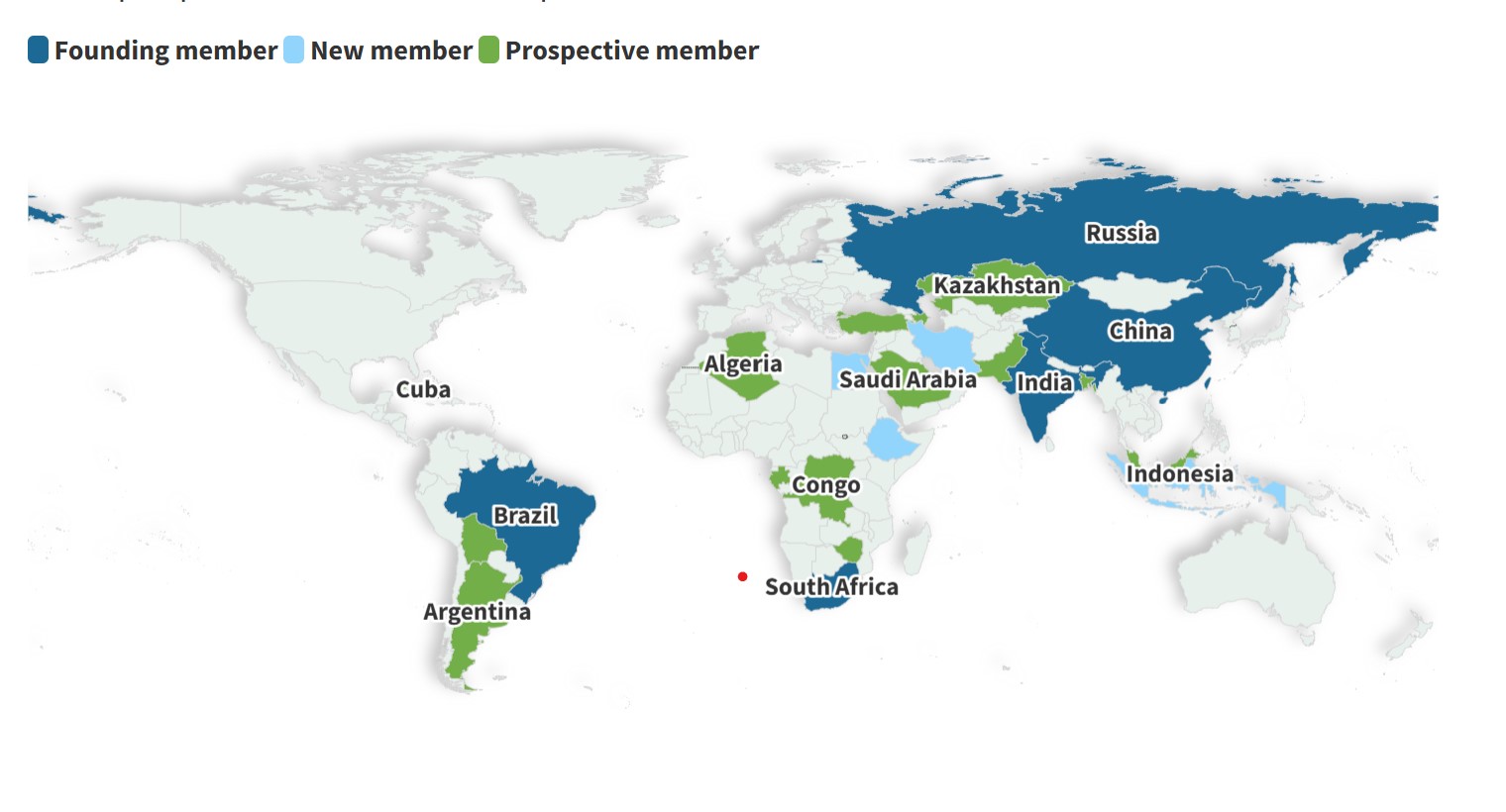
In January 2025, Indonesia officially joined the BRICS group as its 10th member, signaling the expansion of this influential coalition of emerging economies. The addition of Indonesia, a Southeast Asian powerhouse, strengthens BRICS' global position and highlights the group's evolving dynamics.
BRICS Overview:
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) is an informal intergovernmental group that fosters cooperation among major emerging economies. Initially coined as BRIC by economist Jim O'Neill in 2001, the group became BRICS in 2010 with the inclusion of South Africa. The bloc has grown steadily, with Indonesia now joining as its 10th member.
Recent Expansion:
- In 2023, invitations were extended to Saudi Arabia, Iran, UAE, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Argentina.
- By 2024, Iran, Egypt, Ethiopia, and UAE had joined as permanent members.
- Indonesia's membership was finalized in 2025, following its presidential elections and government formation.
Key Objectives of BRICS:
- Economic Growth: Promote trade, investment, and infrastructure development.
- Global Governance Reform: Advocate for equitable representation in global institutions like the UN and IMF.
- Cultural Exchange: Strengthen people-to-people connections and cultural ties.
- South-South Cooperation: Foster collaboration among developing nations.
BRICS Structure and Mechanisms:
- New Development Bank (NDB): Established in 2014, the NDB finances sustainable development projects in BRICS countries.
- Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA): A $100 billion safety net for financial crises.
- BRICS Academic Forum: Encourages academic collaboration across member states.
Global Influence and Economic Impact:
- Global Share: BRICS+ represents over 45% of the world’s population and 35% of global GDP (PPP-based).
- Strategic Position: The group acts as a counterbalance to the G7, challenging Western-dominated global financial systems.
- Financial Independence: BRICS aims to reduce dependence on the US dollar by facilitating local currency transactions and exploring a common currency.
- Technology Collaboration: Member countries, such as India and China, collaborate on digital payments and renewable energy technologies.
Indonesia’s Entry into BRICS:
Indonesia, the world’s fourth-most populous nation, strengthens BRICS’ representation in Southeast Asia. The country brings a robust economy and extensive trade networks, boosting the group's negotiating power. Indonesia’s membership was approved during the 2023 BRICS Summit and finalized in January 2025.
- Strategic Importance for Indonesia: The membership aligns with Indonesia's goals to enhance global cooperation, particularly with the Global South. It also reflects Indonesia's growing influence in international trade and geopolitics.
BRICS Challenges:
- Diverse Interests: Differences in economic priorities, such as India's ties with the US and Russia-China’s geopolitical rivalry, complicate consensus-building.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Disputes like the China-India border issue and Russia’s sanctions limit BRICS' ability to present a unified stance.
- Economic Sanctions and Internal Challenges: Countries like Russia face Western sanctions, while domestic issues in Brazil and South Africa divert attention from regional collaboration.
Significance of BRICS’ Expansion:
The expansion of BRICS marks a pivotal shift in global power dynamics, with a focus on South-South cooperation and equitable global governance. Indonesia’s membership further solidifies the group’s influence in Southeast Asia and adds to its efforts to challenge the dominance of Western-led financial institutions.
- Local Currency Use: The group promotes the use of local currencies for trade to reduce reliance on the US dollar.
- Global South Advocacy: BRICS champions the cause of developing nations, ensuring that emerging economies have a voice in global governance.
Recent and Upcoming BRICS Summits:
- 16th BRICS Summit (2024): Held in Kazan, Russia, with a focus on strengthening local currencies and promoting non-dollar transactions.
- 17th BRICS Summit (2025): Scheduled for July 2025 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, under the theme "Global South," with an emphasis on payment gateways to facilitate intra-BRICS trade.
Emergency Declared in Trinidad and Tobago
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
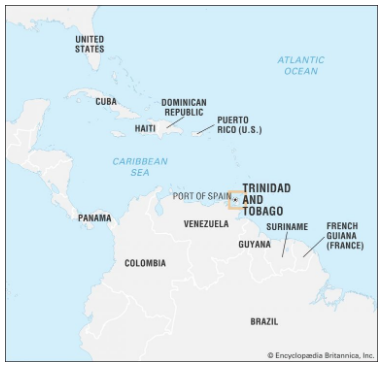
- Trinidad and Tobago declared a state of emergency, in response to a surge in gang violence, which raised the annual death toll to the highest since 2013.
Trinidad and Tobago:
- Location: An island nation in the southern Caribbean, near Venezuela and Guyana.
- Capital: Port of Spain.
- Population: Approximately 1.5 million.
- Ethnic Composition: African (36.3%), Indian (35.4%), Mixed (22.8%), and others.
- Religions: Christianity (64%), Hinduism (18%), Islam (5%), and others.
- Independence: Gained from the UK on August 31, 1962, and became a republic in 1976.
- Member of: Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.
- Major Rivers: Ortoire and Caroni.
- Geography:
- Total Land Area: 5,128 sq. km (Trinidad: 4,768 sq. km, Tobago: 300 sq. km).
- Climate: Tropical, with dry and rainy seasons.
- Highest Point: Mount Aripo.
- Natural Resource: Pitch Lake, the world’s largest asphalt reservoir.
- Mountain Range: Northern Range, part of the Andes extension.
Economic and Cultural Significance
- Exports: Major exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and petrochemicals.
- Culture: Known for Carnival, Calypso music, Soca, and the Steelpan (the only musical instrument invented in the 20th century).
- Infrastructure:
- Ports: Port of Spain, Point Lisas, Scarborough.
- Airports: Piarco International Airport (Trinidad) and A.N.R. Robinson International Airport (Tobago).
Engagement with India
- Trinidad and Tobago became the first Caribbean country to adopt India’s UPI platform.
- Both countries granted each other Most Favored Nation (MFN) status in 1997.
- Bilateral trade reached USD 368.96 million in FY 2023-24.
- The Indian diaspora constitutes about 42% of the population.
Past Emergency Declarations:
- 2014: State of emergency declared in response to gang violence.
- 2021: Emergency declared for Covid-19 restrictions.
- 2011: Limited state of emergency for drug-related crimes.
India-Malaysia Cooperation in Critical Minerals and Rare Earth Elements

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
- On January 7, 2025, during the inaugural India-Malaysia Security Dialogue in New Delhi, both countries agreed to enhance cooperation in critical minerals and rare earth elements (REEs).
- The meeting was co-chaired by India's National Security Adviser, Ajit Doval, and Malaysia’s Director General of the National Security Council, Raja Dato Nushirwan Bin Zainal Abidin.
- The agreement follows the upgrade of bilateral relations to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership during Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim’s visit to India in August 2024.
- The dialogue also focused on other security aspects such as counter-terrorism, cyber security, and maritime security.
Importance of Critical Minerals and REEs:
-
- Critical Minerals: These are essential for a variety of industries like IT, energy, and defense. They are integral to manufacturing electric vehicle batteries, solar cells, and advanced electronics.
-
- Rare Earth Elements (REEs): Used in high-tech applications such as wind turbines, electric vehicle engines, and high-powered magnets. While their extraction is not rare, it is technically difficult due to their complex nature.
Strategic Relevance:
-
- Global Demand: The global demand for critical minerals is rising, and both countries see it as a strategic necessity to ensure a stable supply of these materials.
- Malaysia's Resources: Malaysia possesses significant deposits of non-rare radioactive earth ores, including essential REEs like Neodymium (Nd), Dysprosium (Dy), and Praseodymium (Pr). These elements are crucial in today’s technological innovations.
- India’s Dependence on Imports: India, which currently imports a substantial portion of its critical minerals, aims to diversify its supply chain by collaborating with Malaysia.
Sustainability and Ecological Accountability:
-
- Both countries recognize the environmental challenges of mining these critical resources. Malaysia aims to adopt responsible mining practices that minimize ecological harm.
- India seeks to ensure a supply chain that aligns with sustainable development goals, balancing economic needs with environmental responsibilities.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience:
-
- Diversification of Supply Chain: This partnership aims to reduce India’s dependency on a limited number of countries for critical minerals, enhancing resilience against global supply chain disruptions.
- Collaboration in Extraction and Processing: Both nations are exploring joint ventures in the exploration, extraction, and processing of critical minerals to boost their technological and economic standing globally.
Future Prospects:
-
- The institutionalization of this dialogue through annual meetings is expected to strengthen bilateral cooperation in the critical minerals sector.
- Increased cooperation is likely to enhance economic growth for both countries, aligning them strategically in the global minerals market as demand for these resources continues to soar.
Broader Security Cooperation:
-
- Beyond critical minerals, the India-Malaysia Security Dialogue explored enhanced collaboration in areas like counter-terrorism, cyber security, maritime security, and defense industries.
- This broadening of security cooperation complements the strategic minerals partnership, further solidifying the bilateral ties between the two nations.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Donald Trump threatened to take back the Panama Canal, calling the transfer treaty “foolish”.
Why Trump Called the Panama Canal Transfer 'Foolish'?
- Transit Fees:
- Trump expressed frustration over high transit fees imposed by the Panama Canal Authority (ACP) on U.S. vessels.
- In 2023, due to droughts affecting Lakes Gatun and Alhajuela (which are crucial for canal operations), the ACP reduced crossing slots by 36%, leading to an increase in transit fees for ships.
- Chinese Presence:
- Trump is also concerned about the growing Chinese influence in the Panama Canal region.
- In 2017, Panama became the first Latin American country to sign a Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) agreement with China, increasing Chinese investments.
- Hutchison Ports PPC, a subsidiary of a Hong Kong-based company, operates ports near the canal, raising concerns over China's influence on logistical operations and potential surveillance capabilities.
The Torrijos-Carter Treaties and Canal Transfer:
- Panama Canal Treaty (1977):
- The treaty transferred control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by December 31, 1999.
- The U.S. would no longer control the canal, and Panama would assume full responsibility for its operation and defense.
- Permanent Neutrality Treaty (1977):
- Declared the canal to be neutral and open to vessels of all nations.
- U.S. Right to Defense: The U.S. retained the right to defend the neutrality of the canal and had priority passage in case of military emergencies.
Panama’s Response to Trump’s Criticisms:
- Defense of Transit Rates:
- President José Raúl Mulino rejected Trump’s claims, defending the transit fees as being in line with international standards and based on a transparent procedure.
- Sovereignty:
- Mulino emphasized Panama’s sovereignty over the canal, asserting that Panama’s control over the canal was non-negotiable. He categorically denied the presence of Chinese soldiers in the canal, stating that there would never be any.
China’s Response:
- China's Position:
- China's Foreign Ministry responded by emphasizing that the Panama Canal is a neutral passageway, a vital infrastructure for Panama and the global trade system.
- China affirmed its respect for Panama's sovereignty and denied any military presence in the canal area.
Implications and Future:
- Diplomatic Tensions:
- The issue of transit fees and foreign influence, particularly China's presence in the region, is likely to remain a point of diplomatic negotiation.
- Panama is expected to assert its sovereignty and seek international support to prevent any external interference in the canal’s operations.
- U.S. Influence:
- The U.S. might attempt to renegotiate terms related to the Panama Canal's operations, especially concerning transit fees and military rights, although Panama remains firm on maintaining control.
Torrijos-Carter Treaties:
- Significance:
- Panama Canal Treaty and Permanent Neutrality Treaty marked a major shift in U.S.-Latin America relations, ending U.S. control and restoring Panamanian sovereignty.
- The treaties also ensured the neutrality of the canal while maintaining U.S. military access in emergencies.
- Impact:
- The treaties were a symbol of Panama’s regained sovereignty and played a key role in stabilizing relations between the U.S. and Panama, as well as resolving tensions over control of the canal.
Quad 20th Anniversary
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Quad Foreign Ministers reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, and peaceful Indo-Pacific. Marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation, originally formed to respond to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.
Key Highlights:
- What is the Quad?
- A strategic forum of the US, Japan, India, and Australia aimed at regional security and economic cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Founded on shared principles of democracy, human rights, rule of law, and countering China's influence.
- Origins:
- Quad traces its origins to the 2004 Tsunami relief efforts.
- Formed formally in 2007, but Australia withdrew in 2008 due to regional tensions. It rejoined in 2017 following strengthened US-Australia ties.
- Commitment to Regional Security:
- Focus on countering China’s assertive behavior in the Indo-Pacific.
- Ensuring maritime security, countering illegal fishing, promoting infrastructure, and advancing economic cooperation.
- Key Initiatives:
- IPMDA: Real-time monitoring of maritime activities.
- MAITRI: Capacity-building for maritime security.
- Quad Fellowship: Funds graduate-level STEM education in member countries.
- Open RAN: Promoting secure 5G infrastructure.
- Cancer Moonshot: Focus on cervical cancer prevention.
- Military and Naval Cooperation:
- Malabar Exercises: Joint naval drills between India, Japan, the US, and Australia.
- ASEAN and Regional Cooperation:
- Emphasis on ASEAN's central role in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Support for the Pacific Islands Forum and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
- Future Developments:
- India to host the next Quad Summit in 2025.
- Continued focus on sustainable regional development, scientific collaboration, and disaster relief efforts.
- Significance of the Quad for India:
- Strategic Importance:
- Provides a platform to counter China's assertive policies, especially in the South China Sea and the "String of Pearls" strategy.
- Aligns with India’s Act East Policy, enhancing ties with East and Southeast Asia.
- Maritime Security: Ensures freedom of navigation and counters illegal activities like piracy and illegal fishing in India’s maritime domain.
- Economic Opportunities:
- Strengthens cooperation on infrastructure projects and trade initiatives, such as the Blue Dot Network.
- Post-COVID, Quad may aid India in attracting manufacturing units shifting from China.
- Scientific and People-to-People Collaboration: Supports STEM education and enhances soft power diplomacy through academic and cultural exchanges.
H-1B Visa
- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
In the weeks leading up to his return as US President, Donald Trump’s supporters are embroiled in a public dispute over skilled immigration and H-1B visas.
What is the H-1B Visa Program?
- Purpose and Overview:
- The H-1B visa is a non-immigrant visa allowing U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialized occupations like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and IT, which require at least a bachelor’s degree.
- Introduced in 1990 to help U.S. employers fill positions when there’s a shortage of qualified domestic workers.
- It allows workers to stay in the U.S. for a maximum of six years, with the option to apply for permanent residence (Green Card) or leave for 12 months before reapplying.
- Annual Cap and Exemptions:
- 65,000 new visas are issued annually, with an additional 20,000 for those with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. university.
- Certain petitions, such as for continuing employment or positions in higher education or nonprofit research, are exempt from the cap.
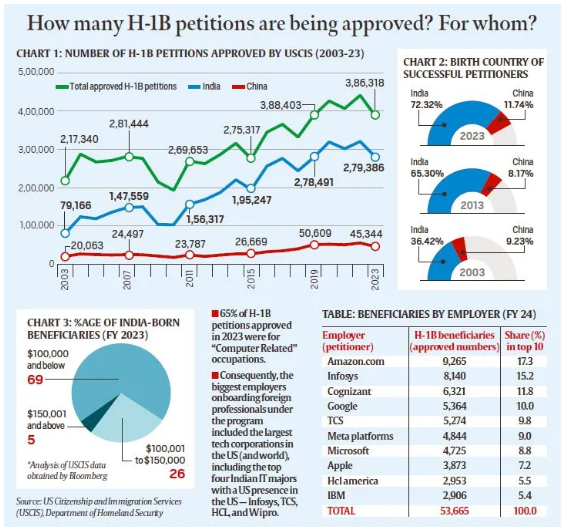
- Dominance of Indian Beneficiaries:
- Indians are the largest beneficiaries, accounting for over 70% of H-1B visa approvals annually since 2015, with China coming second at around 12-13%.
The Current Controversy
- Trigger for Debate:
- The controversy was sparked by Sriram Krishnan, a Chennai-born tech entrepreneur appointed as Donald Trump’s top AI adviser. His post on X (formerly Twitter) in November 2024, advocating for unlocking skilled immigration, led to backlash within Trump’s anti-immigration base.
- The Political Divide:
- Trump’s supporters, particularly from the MAGA (Make America Great Again) faction, voiced opposition to the H-1B visa program, arguing it undermines American workers and wages.
- This prompted pushback from pro-H-1B advocates like Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, who argue that the program is crucial for addressing the U.S.'s STEM talent shortages.
- Economic and Political Context:
- Immigration is a polarizing issue in the U.S., with a focus on low-skilled labor migration and its alleged effects on wages and job opportunities for American workers.
- Trump’s stance against low-skilled immigration echoes similar critiques about H-1B workers being employed at lower salaries in tech companies, which some claim depresses wages and reduces job opportunities for U.S. workers.
Criticisms of the H-1B Program
- Abuse of the System:
- Critics argue that companies exploit the H-1B program by hiring foreign workers, especially from India, at lower wages than American employees, particularly in tech industries.
- Elon Musk suggests that the program is “broken” and needs reform, proposing raising the minimum salary for H-1B workers to make it more expensive to hire overseas talent.
- Salary Disparities:
- Data from USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) shows that 70% of H-1B petitions for Indian professionals in 2023 were for salaries below $100,000, while the median salary for U.S. IT professionals was $104,420.
- Impact on American Jobs:
- Critics argue that companies prefer to hire foreign workers at lower wages to save costs, despite the availability of qualified U.S. talent, thus taking away opportunities for American workers.
Support for the H-1B Program
- Filling the STEM Gap:
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- India and China lead the world in STEM graduates, with 2.55 million and 3.57 million, respectively, compared to the U.S. with 820,000.
- Proponents, including Musk and Ramaswamy, argue that the H-1B visa is essential for filling the STEM skills gap in the U.S., given the global dominance of India and China in STEM fields.
- Economic Benefits:
- The H-1B program helps U.S. companies access top global talent, boosting innovation and economic growth, especially in high-tech industries.
- Tech companies argue that without access to skilled foreign workers, they would struggle to fill critical positions in the technology sector.
China approves construction of World’s Largest Hydropower Dam on the Brahmaputra River

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
China approved the construction of the world's largest dam, stated to be the planet's biggest infra project, on the Brahmaputra river in Tibet close to the Indian border, raising concerns in India and Bangladesh.
Key highlights:
Overview of the Project:
- Location: Lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River (Tibetan name for Brahmaputra), where the river makes a U-turn in the Himalayan region before flowing into Arunachal Pradesh, India.
- Purpose:
- To support China’s carbon neutrality goals.
- To boost industrial growth and create jobs in Tibet.
- Expected to generate 300 billion kWh of electricity annually, over three times the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam in central China.
Significance:
- Scale: The dam is poised to be the world’s largest hydropower project, surpassing the Three Gorges Dam, and becoming the biggest infrastructure project globally, with an estimated cost of USD 137 billion.
- Engineering Challenges: The site is located in a seismic zone on the Tibetan plateau, prone to earthquakes, making construction and operational stability a major engineering challenge.
Concerns:
- Environmental Impact:
- Potential disruption to the local ecosystem and biodiversity.
- Risk of altering the river’s flow and course, which could impact agriculture and water resources downstream, particularly in India and Bangladesh.
- Geopolitical Risks:
- Water control: India and Bangladesh are concerned about China’s ability to control the water flow, with fears of China manipulating the flow to release excess water during conflicts, causing potential flooding in border areas.
- The project could also disrupt the hydrological cycle, affecting the region’s water availability, especially in Assam and Bangladesh.
Background:
- The Brahmaputra River is a trans-boundary river, flowing through China, India, and Bangladesh. Known by different names in these countries, it plays a vital role in the livelihoods of millions of people.
- China has already initiated hydropower generation on the upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo, with plans for additional projects upstream.
India-China Cooperation:
- China and India have an Expert Level Mechanism (ELM) in place since 2006 to manage trans-boundary river issues, under which China shares hydrological data with India, especially during the flood season.
- India is also constructing its own hydropower projects on the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh.
Potential Outcomes:
- Energy Generation: The dam could significantly contribute to China’s energy needs, providing a substantial amount of renewable energy.
- Regional Tensions: The dam’s construction may escalate tensions between China, India, and Bangladesh due to the control over water resources and environmental impact concerns.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
In mid-2024, India surpassed China as the largest importer of Russian oil. This milestone has been accompanied by the operationalization of a new maritime route, the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC), which connects Chennai in India to Vladivostok in Russia. The new sea route is significantly reducing both shipping times and costs, facilitating smoother commodity trade between the two countries, particularly crude oil shipments.
The Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
The EMC, covering a distance of about 5,600 nautical miles, has reduced the shipping time between India and Russia’s Far East by up to 16 days. The Chennai-Vladivostok route now takes just 24 days, compared to over 40 days using the traditional St. Petersburg-Mumbai route. This reduction in transit time makes it a highly efficient route for transporting goods such as crude oil, coal, LNG, fertilizers, and other commodities. Additionally, this new corridor supports India’s maritime sector and aligns with the country’s broader vision for maritime growth and regional strategic engagement.
Key Features of the EMC:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: The route cuts shipping time and distance, reducing costs associated with longer transit periods. For example, a ship traveling between Vladivostok and Chennai now takes only about 12 days at cruising speed, compared to the traditional route's 40+ days.
- Strategic Importance: Vladivostok is Russia’s largest Pacific port, and the corridor strengthens India's strategic presence in the region. This maritime route bypasses traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal, offering faster, more direct access to key markets.
- Diversification of Trade: Besides crude oil, the EMC facilitates the transportation of coal, LNG, fertilizers, and metals, diversifying India's trade portfolio with Russia. It also helps maintain supply chains for essential goods.
- Boosting India’s Maritime Sector: The corridor supports India’s Maritime Vision 2030, which aims to enhance the efficiency and reach of India's maritime trade, a sector responsible for over 70% of the country’s trade value.
Economic and Strategic Impact:
- The new Eastern Maritime Corridor is particularly significant for India’s energy needs. As the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, India imports over 85% of its crude oil demand. The growing imports of Russian crude, especially the Urals grade, are crucial for securing India’s energy future. Additionally, Russia’s competitive pricing on crude, coupled with the savings on shipping costs through the EMC, makes Russian oil even more attractive.
- Beyond the economic benefits, the EMC also supports India’s broader strategic goals, including strengthening ties with Russia, a key partner in defense, nuclear cooperation, and regional geopolitics. The closer maritime links also help counterbalance China's growing dominance in the Pacific region, aligning with India's Act Far East Policy and enhancing trade and diplomatic engagement with East Asia and Russia.
Other Key Maritime Corridors Relevant to India:
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC): A 7,200 km multimodal route linking the Indian Ocean with Russia, offering alternative trade routes to Europe and Central Asia.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A recent project announced at the G20 Summit, which connects India, the Middle East, and Europe via rail, road, and maritime links, fostering greater regional integration.
- Northern Sea Route (NSR): A 5,600 km Arctic route offering shorter transit times between the Barents and Kara Seas and the Bering Strait, gaining importance due to growing imports of Russian energy resources.
In conclusion, the Eastern Maritime Corridor is reshaping India-Russia trade dynamics, boosting economic ties and strategic cooperation between the two nations. By facilitating faster and cheaper transportation, the EMC is not only beneficial for trade in crude oil but also for a range of other commodities, positioning India as a key player in the evolving global trade network.
Exercise Agni Warrior

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Agni Warrior (XAW-2024), a joint military drill between the Indian Army and the Singapore Armed Forces (SAF), concluded successfully at the Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra. The exercise focused on enhancing mutual understanding and interoperability between the two nations’ artillery units.
Key Facts:
- Participating Nations: India and Singapore
- Location: Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra
- Participants:
- 182 personnel from the Singapore Artillery
- 114 personnel from the Indian Army's Regiment of Artillery
- Objective: To maximize mutual understanding of drills and procedures for joint operations under the UN Charter, particularly in firepower planning and execution, utilizing advanced artillery technologies.
- Historical Context: The exercise began in 2004 under a bilateral agreement between India and Singapore and has evolved over the years, now marking 20 years of cooperation.
Purpose and Highlights:
The exercise aimed to reinforce the long-standing defense relationship between India and Singapore, focusing on:
- Joint Firepower Planning and Execution: Both forces demonstrated the use of New Generation Artillery Equipment, enhancing their firepower coordination.
- Enhancing Interoperability: The exercise emphasized seamless coordination between the two armies to operate as a multinational force under the UN Charter, addressing global security challenges.
- Knowledge Sharing: Personnel from both armies exchanged expertise on advanced artillery tactics, fostering a deeper understanding of each other's military capabilities.
- Technological Integration: Both sides integrated cutting-edge technologies, allowing the exchange of best practices in the use of artillery systems.
Key Objectives of XAW-2024:
- Enhanced Interoperability: To ensure smooth coordination in joint operations, fostering the ability to respond to regional security threats.
- Firepower and Coordination Techniques: Sharing expertise on artillery planning, coordination, and execution.
- Advanced Equipment Use: Testing and demonstrating modern artillery systems in joint operations, ensuring both forces are prepared for contemporary warfare.
Structure and Execution:
The exercise was structured to include pre-exercise training, field operations, and a post-exercise evaluation:
- Pre-Exercise: Both armies engaged in interactive sessions to familiarize themselves with each other's artillery tactics and advanced systems.
- Field Operations: Simulated combat scenarios tested joint firepower execution, emphasizing real-time problem-solving and decision-making under pressure.
- Post-Exercise Review: A thorough analysis identified areas for improving joint operations and coordination.
Strategic Significance:
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Agni Warrior reinforces the defense partnership, facilitating joint operations that support regional security.
- Regional Stability: The exercise underscores the commitment of both nations to peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Capacity Building: Both Indian and Singaporean forces gained exposure to sophisticated firepower planning and gained operational readiness for future deployments.
Desert Knight Air Combat Exercise

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
India, France and UAE recently kicked off a major air combat exercise called “Desert Knight” over the Arabian Sea, strengthening trilateral defence cooperation and enhancing military interoperability amid the ongoing geopolitical churn.
Key Highlights:
- What It Is: A trilateral air combat exercise aimed at improving military interoperability and enhancing combat readiness among the participating nations.
- Nations Involved: India, France, and the UAE.
- Location: Conducted over the Arabian Sea, approximately 350-400 km southwest of Karachi.
- Aim of the Exercise:
- To strengthen trilateral defence cooperation among the three nations.
- To enhance combat skills and military interoperability of the air forces involved.
- Details of the Exercise:
- Duration: The exercise lasts for three days.
- The exercise involves large force engagement and intensive combat maneuvers in a realistic operational environment.
- Aircraft Involved:
- India: Deployed Sukhoi-30MKIs, Jaguars, IL-78 mid-air refuellers, and AEW&C (Airborne Early Warning and Control) aircraft from bases like Jamnagar.
- France: Deployed Rafale jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
- UAE: Deployed F-16 jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
Strategic Significance:
- The exercise is part of India’s efforts to build military interoperability with nations in the Persian Gulf region and strengthen defence ties with France and the UAE.
- Enhances combat readiness and strengthens cooperation against both traditional and non-traditional threats.
- Reflects the geopolitical shift and growing military cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, especially in the context of China’s expansionist activities.
- Trilateral Framework: India, France, and the UAE launched a trilateral framework in 2022, focusing on areas like defence, technology, energy, and environment.
- Previous Exercises: In addition to Desert Knight, the countries also conducted their first trilateral maritime exercise in June 2023 to enhance cooperation in maritime security.
Broader Defence Relations:
- India-France: Long-standing strategic partnership with regular joint exercises like Shakti (army), Varuna (navy), and Garuda (air force).
- India-UAE: The defence relationship has grown significantly in recent years, with regular professional exchanges, combat exercises, and staff talks. India participates in the Desert Flag exercise at Al Dhafra airbase annually.
Switzerland Suspends MFN Clause in Tax Treaty with India

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
Switzerland scraps MFN status to India, dividend income to face higher tax
Key Highlights:
- Reason for Suspension:
- The suspension follows a 2023 Supreme Court ruling in India, which clarified that the MFN clause in tax treaties is not automatically triggered when a country joins the OECD if the tax treaty with that country was signed before its OECD membership.
- The Court ruled that the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) cannot be enforced unless it is notified under the Income-Tax Act, 1961.
- Details of the Suspension:
- Starting January 1, 2025, Switzerland will suspend the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) clause in its DTAA with India.
- The MFN clause was part of the India-Switzerland DTAA signed in 1994.
Impact of the Suspension:
- Higher Tax Liabilities for Indian Companies: Withholding tax on dividends from Switzerland will increase from 5% to 10% for Indian companies.
- Effects on Swiss Investments in India: Swiss companies will continue to face a 10% withholding tax on dividends from India, as per the India-Switzerland DTAA.
- Potential Re-evaluation of MFN Clauses by Other Countries: Other countries may reconsider how the MFN clause is applied in their tax treaties with India, following this development.
- No Change for Other Benefits: Other DTAA benefits and investments related to the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) will remain unaffected.
Most Favoured Nation (MFN) Clause Overview:
- Definition: The MFN principle ensures that favorable trading terms given by one WTO member country to another are extended to all other WTO members, promoting non-discrimination.
- Purpose: To ensure equal treatment among trading nations by preventing discrimination, and to promote fair trade and equitable market access.
- Key Features:
- Equal treatment in tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers.
- Members must extend the best terms to all other WTO members.
- Origin: The MFN principle was established after World War II as a cornerstone of the multilateral trading system under the WTO.
- Exceptions:
- Bilateral or regional trade agreements.
- Special access granted to developing countries.
- Non-WTO members (e.g., Iran, North Korea) are not bound by MFN rules.
- Removal of MFN:
- There is no formal procedure under the WTO to suspend MFN status.
- Countries are not obligated to notify the WTO when suspending or removing MFN treatment.
Recent Development:
- From January 1, 2025, Indian companies will face higher withholding tax (10%) on income sourced from Switzerland, as a result of the MFN clause suspension.
China Plus OneStrategy

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India had ‘limited success’ in capturing ‘China Plus One’ opportunity.
Limited Success in ‘China Plus One’ Strategy:
- India has had limited success in attracting multinational companies looking to diversify their supply chains under the ‘China Plus One’ strategy, aimed at reducing dependence on China.
- Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Malaysia have been more successful in benefiting from this shift due to factors like lower labor costs, simplified tax laws, and proactive Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Geopolitical Context - US-China Trade Conflict:
- The fresh US-China trade conflict involves tit-for-tat restrictions, with the US imposing export controls on Chinese high-tech goods and China retaliating by banning key materials.
- India's Position: As a "connecting economy" not directly aligned with the US or China, India stands to benefit from trade diversions arising from this conflict.
Opportunities for India Amid Trade Diversion:
- NITI Aayog CEO BVR Subrahmanyam highlighted opportunities arising from trade diversion, particularly due to US trade policies under President-elect Donald Trump, which could potentially create an economic boom for India.
- India has opportunities to capture a larger share of the global trade, especially in sectors where it currently holds a small market share (less than 1% of world trade in many areas).
Trade Policy Challenges:
- Steel Import Duty Proposal: NITI Aayog Vice Chairperson cautioned against imposing high duties on steel imports, arguing that it could reduce India’s competitiveness and lead to negative consequences for domestic industries reliant on steel.
- The global steel market has been affected by oversupply from China, with India’s iron and steel exports experiencing a sharp decline in Q1 FY25 due to weak domestic demand.
Impact of US Tariffs:
- A general 10% tariff on all imports by the US would not have a major negative impact on India.
- However, a 60% tariff on China could open significant opportunities for India, especially in sectors where it competes directly with China. There might be short-term shocks but long-term benefits.
Ongoing Trade Fragmentation:
- The report noted that trade fragmentation is driven by strict export controls on Chinese goods, implemented by the US to curb China’s growth, particularly in high-tech sectors.
Sectoral Competitiveness:
- While China remains India's key competitor across most export sectors, countries like Brazil, Indonesia, and South Africa generally lag behind India.
- Malaysia and Thailand outperform India in select sectors such as electrical machinery.
Challenges in the EU Market - Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- Iron and steel industry facehigh exposure under the CBAM for EU exports, with tariffs potentially rising by 20-35% due to carbon emissions-related regulations.
- Indian firms could experience higher compliance costs due to the requirement for detailed emissions reporting, impacting competitiveness in the European market.
India and Slovenia Announce Five-Year Collaboration Plan
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
India and Slovenia have announced a five-year scientific collaboration plan (2024-2029) to deepen ties in research and technology. The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) was finalized during a meeting between Dr. Jitendra Singh (Indian Minister for Science and Technology) and Dr. Igor Papi? (Slovenian Minister for Higher Education, Science, and Innovation) on December 5, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Joint Research Focus: The collaboration will focus on hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, AI, renewable energy, and smart cities.
- Over 20 Successful Projects: More than 20 joint initiatives in sectors like health, AI, and energy have already been implemented.
- Future Areas of Collaboration: New research projects will be launched, further strengthening academic exchanges and scientific networks between the countries.
- Hydrogen Technologies: Both ministers emphasized hydrogen's role in global energy sustainability, marking it as a critical area for future research.
- Historical Partnership: This builds on a partnership dating back to a 1995 agreement, with initiatives like the Joint Working Group on Scientific and Technological Cooperation.
What is the Programme of Cooperation (PoC)?
- The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) is a formal agreement between two countries designed to enhance collaboration in specific sectors, such as science, technology, and innovation.
- In the case of India and Slovenia, the PoC for the period 2024–2029 aims to promote joint research efforts, academic exchanges, and partnerships in emerging fields like hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, and other transformative areas.
- The PoC serves as a structured framework for long-term cooperation, enabling both nations to develop networks among scientists and researchers while addressing global challenges through collaborative innovation.
Donald Trump's Threat on BRICS and US Dollar

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
- US President-elect Donald Trump threatens BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) with 100% import tariffs if they create a new currency or support an alternative to the US dollar as the global reserve currency.
- Trump emphasizes that attempts to undermine the US dollar’s dominance will face economic retaliation, asserting the US economy won’t tolerate such moves.
Background
- Weaponization of the Dollar: The US has increasingly used its financial influence to impose sanctions (e.g., Russia, Iran) and cut off countries from systems like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication).
- Concerns: Countries are concerned about their vulnerability to US monetary policies, which can have global impacts (e.g., rising US interest rates causing economic instability in other countries).
Efforts to Reduce Dependence on the US Dollar
- BRICS Countries’ Initiatives:
- Russian President Putin criticizes the weaponization of the dollar.
- Brazil's President Lula advocates for a new BRICS currency to increase payment options and reduce vulnerabilities.
- India's Steps:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows invoicing and payments in Indian rupees for international trade (since 2022), particularly with Russia.
- Prime Minister Modi supports increasing financial integration and cross-border trade in local currencies within BRICS.
- External Affairs Minister Jaishankar emphasizes the importance of mutual trade settlements in national currencies.
- China-Russia Trade: Over 90% of trade between Russia and China is settled in rubles and yuan due to their more balanced trade relations.
Internationalization of the Indian Rupee
- RBI's Role:
- In July 2022, RBI allowed export/import settlements in rupees, starting with Russia in December 2022.
- More than 19 countries, including the UK and UAE, have agreed to settle trade in rupees.
- Challenges:
- The Indian rupee currently accounts for only 1.6% of global forex turnover.
- India’s trade imbalance with Russia limits the effective use of rupee reserves.
- Indian banks are cautious due to the risk of US sanctions.
Global Trends in Currency Diversification
- Multipolarity in Finance: Emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil are advocating for a more decentralized financial system, moving away from US dominance.
- Declining Dollar Share: The US dollar’s share of global reserves is gradually decreasing, with non-traditional currencies like the Chinese yuan gaining ground.
Risks of Moving Away from the US Dollar
- Chinese Dominance: Concerns about increasing Chinese economic influence, especially within BRICS, as China pushes for more use of the yuan in trade.
- Liquidity and Volatility Issues: Alternatives to the dollar may face challenges like lower liquidity and increased exchange rate volatility.
- Implementation Challenges: Countries, especially those with trade imbalances, find it difficult to adopt local currencies for international trade.
Potential Impact of 100% US Tariff on BRICS Imports
- Global Trade Dynamics: A blanket tariff would likely encourage deeper intra-BRICS trade and accelerate the move towards de-dollarization.
- Impact on the US: Higher import costs for American consumers and potential trade diversification to third countries could hurt the US economy without revitalizing domestic manufacturing.
- Retaliation: BRICS countries might retaliate with tariffs on US goods, escalating trade tensions.
India’s Strategic Approach
- Diplomatic Engagement: India should clarify to the US that diversifying trade mechanisms is not anti-American but seeks financial stability and multipolarity.
- Leadership Role in BRICS: India should support financial reforms within BRICS that align with its interests while maintaining strong ties with the US.
- Promotion of Digital Currency: India should accelerate its Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and strengthen international platforms like UPI to enhance its global financial presence.
India-Cambodia Joint Military Exercise CINBAX

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The first edition of CINBAX (Counter-Terrorism Counter-Bio-Terrorism and Intelligence Operations Exercise) was launched on December 1, 2024, at the Foreign Training Node, Pune.
Key Details:
- Participants: 20 personnel from each side – the Indian Army and the Cambodian Army – focusing on enhancing cooperation for UN peacekeeping operations.
- Objective:
- Enhancing Trust and Interoperability: CINBAX aims to foster mutual trust, build camaraderie, and improve operational efficiency between the two armies in conducting peacekeeping operations under UN guidelines.
- Focus Areas: Joint Counter-Terrorism (CT) operations, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), cyber warfare, logistics, casualty management, and disaster relief operations.
- Phases of the Exercise:
- Phase I: Orientation for Counter-Terrorism operations in the context of UN peacekeeping missions.
- Phase II: Conduct of tabletop exercises to simulate and plan response scenarios.
- Phase III: Finalization of plans and review of lessons learned, focusing on operational strategies and tactical decision-making.
- Key Topics Covered:
- Discussions on setting up a Joint Training Task Force for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance.
- Exploring cyber warfare, hybrid warfare, and unconventional tactics.
- Strategies for managing logistics, casualties, and coordination during Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- Promotion of Indigenous Defence Equipment:
- The exercise will showcase Indian-made weapons and defence equipment, supporting India’s commitment to Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance in defence production).
- Objective: To highlight India's advanced military technology and indigenous defence capabilities.
- Significance for India-Cambodia Relations:
- The exercise strengthens military ties between India and Cambodia, contributing to improved cooperation in regional peacekeeping efforts.
- CINBAX marks a significant milestone in India-Cambodiadefence collaboration and sets the stage for future joint operations.
India-Cambodia Bilateral Relations
- Historical Context:
- India and Cambodia share strong religious, cultural, and linguistic ties, with Hindu rituals influencing Cambodian culture and Sanskrit and Khmer sharing common words.
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1952, even before Cambodia's independence from France.
- Key Developments:
- 1954: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru visited Cambodia, initiating strong diplomatic ties, particularly during the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Post-1970s: India played a pivotal role in Cambodia's recovery from the Khmer Rouge regime. India was the first democratic country to recognize the Heng Samrin regime in 1981 and contributed to Cambodia's political reconciliation.
- 1980s: India facilitated dialogue for the Paris Peace Accord and contributed to the success of UNTAC elections in 1993.
- Strategic and Economic Cooperation:
- Defence: Enhanced cooperation in defence capacity building, military training, and infrastructure development.
- Trade: India exports pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, automobiles, and leather products to Cambodia. In return, Cambodia exports organic chemicals, apparel, and footwear to India.
- Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC): Established in 2000, MGC includes Cambodia and aims to enhance cooperation in sectors like trade, education, tourism, and cultural exchanges.
- Recent Collaboration:
- India has extended financial assistance for infrastructure projects in Cambodia, especially in restoring and conserving cultural heritage sites like Angkor Wat.
- MoUs signed in bilateral cooperation, cultural exchanges, and development projects highlight the growing India-Cambodia strategic partnership.
U.N. Peacebuilding Commission

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
India has been re-elected to the United Nations Peacebuilding Commission (PBC) for the term 2025–2026, continuing its strong commitment to global peace and stability.
UN Peacebuilding Commission (PBC)
It is an advisory body established by the UN General Assembly and UN Security Council in 2005. It is tasked with supporting peace efforts in conflict-affected countries by advising and recommending strategies for post-conflict recovery and long-term peacebuilding.
Composition of PBC:
- The PBC is composed of 31 member states, elected from the General Assembly, Security Council, and Economic and Social Council.
- It includes key financial and troop-contributing countries, which play a central role in shaping global peacebuilding initiatives.
Key Mandates of the PBC
- Coordination of Resources and Strategies:The Commission brings together all relevant actors to propose integrated strategies for post-conflict recovery and peacebuilding.
- Reconstruction and Development:It focuses on rebuilding conflict-affected countries through institution-building and supporting sustainable development efforts.
- Improving Coordination:The PBC ensures better coordination within and outside the UN, develops best practices, and secures predictable financing for early recovery initiatives.
- Sustaining Peace:The Commission promotes sustained international attention to peacebuilding efforts and offers political support to countries emerging from conflict, with their consent.
- Integrated Approach:The PBC advocates for an integrated approach that links security, development, and human rights as interrelated and mutually reinforcing.
- Bridging Role:It serves as a platform to connect UN bodies, Member States, national authorities, civil society, and other stakeholders, sharing good practices in peacebuilding.
India’s Contributions to UN Peacebuilding and Peacekeeping
India has been at the forefront of UN peacebuilding initiatives due to its long-standing commitment to international peace and stability.
- Largest Contributor of Personnel:India is one of the largest contributors of uniformed personnel to UN Peacekeeping. Currently, around 6,000 Indian military and police personnel are deployed across multiple missions in Abyei, Central African Republic, Cyprus, Democratic Republic of Congo, Lebanon, Middle East, Somalia, South Sudan, and Western Sahara.
- Sacrifices in Service:India holds the tragic distinction of having lost over 180 peacekeepers, the highest number from any troop-contributing nation. These sacrifices reflect India's enduring commitment to global peace.
- Financial Support:India contributes to the Peacebuilding Fund, the primary financial instrument for conflict prevention and peacebuilding, which supports countries transitioning from conflict to peace.
- Championing South-South Cooperation:India has actively promoted South-South cooperation, a model for post-conflict recovery that emphasizes shared learning and capacity-building among developing nations.
- Women in UN Peacekeeping:India has led efforts for gender parity in UN peacekeeping. In 2007, India became the first country to deploy an all-women contingent to a UN peacekeeping mission. It has since deployed Female Engagement Teams (FETs) and Female Formed Police Units (FFPUs) in Lebanon and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Training and Capacity Building:India has invested in capacity development for both the UN and host nations. The Centre for UN Peacekeeping (CUNPK) in New Delhi, established by the Indian Army, trains over 12,000 troops annually in peacekeeping operations. India also deploys Mobile Training Teams to share best practices with other countries.
India’s Pledges at the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial (2023)
At the UN Peacekeeping Ministerial held in Accra, Ghana (December 2023), India made significant pledges:
- To contribute an Infantry Battalion Group, along with various sub-groups and pre-deployment training courses, for the next two years.
- India’s ongoing commitment to strengthening peacekeeping efforts and supporting the UN’s peacebuilding agenda was reaffirmed.
6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee Meeting
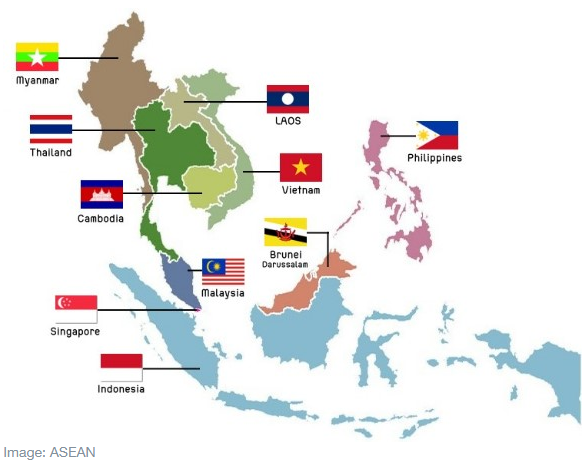
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The 6th ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) Joint Committee and related meetings for discussions on the review of the AITIGA were held recently in Vanijya Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Key Negotiation Areas
- 8 Sub-Committees under the AITIGA Joint Committee discussed:
- Market access, rules of origin, SPS measures, standards and technical regulations.
- Customs procedures, economic and technical cooperation, trade remedies, and legal and institutional provisions.
- 5 Sub-Committees met physically during this round of negotiations.
Progress in Discussions
- Textual Discussions: Sub-Committees made progress in discussions on various provisions.
- Tariff Negotiations: Initial steps towards initiating tariff negotiations were covered.
High-Level Meetings Leading to AITIGA Review
- 21st ASEAN-India Economic Ministers Meeting: Held in September 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
- 21st ASEAN-India Summit: Held in October 2024 in Vientiane, Laos.
Both meetings urged the Joint Committee to expedite negotiations and aim for the conclusion of the review in 2025.
Bilateral Meetings
- ASEAN delegates held separate bilateral meetings with Thailand and Indonesia to discuss bilateral trade issues.
- Indian and ASEAN Chief Negotiators met to align on the ongoing issues and future steps.
India's Review Demands
- Request for Review: India sought a review of AITIGA (implemented in 2010), citing disproportionate trade benefits favoring ASEAN countries.
- India’s Objectives:
- Enhanced Market Access: India pushed for ASEAN countries, especially Vietnam, to commit to greater market-opening for Indian goods.
- Stricter Rules of Origin (ROO): India requested more stringent ROO provisions to prevent Chinese goods from entering India via ASEAN countries at preferential rates.
Trade Relationship and Economic Impact
- Bilateral Trade:
- Total trade with ASEAN reached USD 121 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Trade during April-October 2024 was USD 73 billion, marking a 5.2% growth.
- Trade Deficit: India’s trade deficit with ASEAN widened from USD 4.98 billion in FY 2010-11 to USD 38.4 billion in 2023-24.
- ASEAN accounts for 11% of India’s global trade.
Future Outlook
- The next meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee is scheduled for February 2025 in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The review process aims to further enhance sustainable trade between India and ASEAN countries.
11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus)

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
The 11th ADMM-Plus held in Vientiane, Laos saw Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh engage in discussions with his counterparts from the United States, Japan, and the Philippines.
Focus: The talks centered on strengthening defence partnerships, regional security, and enhancing cooperation among Indo-Pacific nations.
ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- Platform for Dialogue: The ADMM-Plus is a key platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners—Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- Establishment: The inaugural ADMM-Plus was held in HàN?i, Vietnam on 12 October 2010.
- Annual Meetings: Since 2017, the ADMM-Plus has met annually to enhance dialogue and cooperation amidst an increasingly complex regional security environment.
Objectives:
- Capacity Building: To aid ASEAN members in addressing shared security challenges.
- Promote Trust and Transparency: Enhance mutual trust and confidence between ASEAN and partner nations.
- Regional Peace and Stability: Focus on cooperation in defence and security to counter transnational security challenges.
- ASEAN Security Community: Contribute to realizing the ASEAN Security Community, as per the Bali Concord II, aiming for peace, stability, democracy, and prosperity in the region.
- Vientiane Action Programme: Facilitate ASEAN's efforts towards a peaceful, secure, and prosperous ASEAN with outward-looking relations with Dialogue Partners.
Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Daniel Barenboim (Classical Pianist and Conductor) and Ali Abu Awwad (Palestinian Peace Activist) were jointly awarded the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development for 2023.
- Daniel Barenboim was recognized for fostering peace through musical and cultural dialogue initiatives.
- Ali Abu Awwad was honored for his advocacy of peace through dialogue via his organization Roots, which he founded after serving time in Israeli prison.
Significance of the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- The award is given to individuals or organizations who have made outstanding contributions to international peace, disarmament, and development.
- It includes a monetary award of ?25 lakh and a citation.
About the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize:
- Established: 1986 by the Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust in memory of former Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
- Objective: To honor sustained efforts towards international peace, the development of humanity, and the promotion of disarmament.
- Past recipients: Includes prominent figures and organizations such as Mikhail Gorbachev, UNICEF, Jimmy Carter, Angela Merkel, ISRO, and Sir David Attenborough.
2022 Awardees:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize for 2022 was awarded to the Indian Medical Association and the Trained Nurses Association of India, in recognition of their contribution as COVID-19 warriors.
Key Takeaways:
- The Indira Gandhi Peace Prize is regarded as one of the most prestigious awards for promoting peace, disarmament, and development worldwide.
- Daniel Barenboim's musical initiatives and Ali Abu Awwad's work through dialogue exemplify efforts to bridge divides and promote peaceful resolutions to conflict.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
PM Modi receives Nigeria’s second-highest national award.
Key Events and Achievements
- Award Conferred:
- Award Name: Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger (GCON).
- Significance: Nigeria’s second-highest national award, conferred on Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Historical Context: Modi becomes the second foreign dignitary to receive this award, after Queen Elizabeth in 1969.
Strategic and Developmental Ties Between India and Nigeria
- First Visit in 17 Years: Modi’s visit is the first by an Indian PM to Nigeria in 17 years, underscoring the significance of strengthening bilateral ties.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Over 200 Indian companies have invested around $27 billion in Nigeria across key sectors, making India a major economic partner.
- India has provided $100 million in development assistance through concessional loans and is actively involved in capacity-building training programs in Nigeria.
- MoUs Signed:
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Cultural Exchange.
- Customs Cooperation.
- Survey Cooperation.
- Three Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed in the fields of:
- Relief Aid: Modi announced the dispatch of 20 tonnes of relief supplies to help Nigeria recover from the devastating floods that affected the country last month.
Diplomatic Discussions and Initiatives
- Strategic Partnership: Modi described the India-Nigeria partnership as one with immense potential in sectors like defence, energy, technology, trade, health, and education.
- Indian Expatriate Community: Modi acknowledged the 60,000-strong Indian diaspora in Nigeria, recognizing their role as a pillar of bilateral ties.
- Support for Africa:
- Modi highlighted India’s support for the African Union’s membership in the G20, an outcome of the India-hosted G20 summit in 2023.
- Nigeria’s Role: He noted Nigeria’s positive influence on Africa and its importance as a key partner in India’s Africa engagement.
Broader Implications for International Relations
- India-Nigeria Security Cooperation:
- The National Security Advisors (NSA) of India and Nigeria held in-depth discussions on counter-terrorism, extremism, and cybersecurity challenges.
- India and Nigeria are committed to jointly addressing global threats such as arms smuggling and international crime.
- India's Role as a Development Partner:
- India’s growing role as a development partner for African nations is becoming increasingly important, exemplified by Nigeria’s close ties with India.
- Global Diplomacy and Soft Power:
- Modi’s award and visit reflect India’s growing influence in Africa and its emphasis on fostering ties with resource-rich and strategically located nations like Nigeria.
- The Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger is also a reflection of the soft power India is wielding globally.
Key Facts about Nigeria:
- Location: Nigeria is located in West Africa, bordering Niger, Chad, Cameroon, and Benin, with access to the Atlantic Ocean.
- Significance:
- Known as the “Giant of Africa” due to its large population and economic power.
- It has the largest economy in Africa, largely driven by its oil reserves.
Nepal-Bangladesh Power Transfer via India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
Nepal starts exporting energy to Bangladesh with Indian grid support.
Significance of the Power Transfer:
- Energy Cooperation:
- A major step in regional energy cooperation among Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Strengthens sub-regional connectivity in the power sector.
- Nepal’s Hydropower Potential:
- Nepal, a Himalayan nation, possesses untapped hydropower resources, and this agreement opens the door for future cross-border electricity cooperation.
- Nepal’s energy exports are a green energy initiative, supporting sustainable industrial growth in Bangladesh and regional prosperity.
- Electricity Crisis in Bangladesh:
- Bangladesh is facing an ongoing electricity shortage, worsened by the suspension of power supply from Adani’s Godda plant and the maintenance of the Payra thermal unit.
- The addition of 40 MW of Nepalese hydroelectric power aims to alleviate the energy shortfall in Bangladesh.
Tripartite Power Sales Agreement:
- Agreement Details:
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN) (India)
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) (Nepal)
- Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) (Bangladesh).
- Power Export: Nepal has started exporting 40 MW of electricity, which marks a significant milestone in trilateral power cooperation.
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
Key Entities Involved:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN):
- A wholly owned subsidiary of NTPC Ltd. (National Thermal Power Corporation), created to facilitate power trading.
- NVVN is diversifying into renewables, e-mobility, and green fuel solutions.
- NTPC Ltd.:
- A Maharatna PSU under India’s Ministry of Power, established to develop power resources in India.
- Involved in large-scale power generation and clean energy initiatives
Unified Complex Radio Antenna
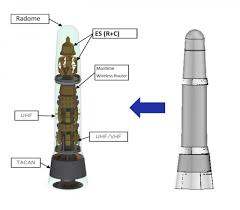
- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- India and Japan recently signed a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) to co-develop the UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) mast for deployment on Indian Navy ships. This pact marks a significant milestone as it is India's first military technology transfer agreement with Japan.
- The deal follows a 2015 agreement on the transfer of defense equipment and technology, further strengthening defense ties between the two countries.
- The UNICORN mast is a cutting-edge communication and radar system designed to enhance the stealth characteristics of naval vessels. This agreement is seen as an important step towards deepening India-Japan defense cooperation.
What is UNICORN?
The UNICORN mast is an advanced, integrated antenna system that combines several communication and radar components into a single conical structure or radome (a radar-absorbing dome). It is designed to reduce the radar cross-section (RCS) of ships, improving their stealth capabilities.
Key features of the UNICORN mast include:
- Integration of multiple antennas: It consolidates various antennas used for tactical data links, communications, and navigation systems (e.g., TACAN - Tactical Air Navigation System).
- Stealth enhancement: By reducing the number of exposed components and consolidating them into a single radome, the mast significantly lowers the ship’s radar signature, making it harder to detect.
- Improved performance: The mast design minimizes mutual interference between antennas, enhances maintainability, and increases lightning resistance.
- Space efficiency: It saves valuable below-deck space and reduces ship-building time by integrating multiple systems into one mast.
The UNICORN system is currently deployed on Mogami-class frigates of the Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force.
India-Japan Defense Cooperation
- 2015 Defense Technology Transfer Agreement: This pact established a framework for defense cooperation between India and Japan, paving the way for joint projects like the UNICORN mast.
- Bilateral Military Exercises:
- Veer Guardian 2023: A bilateral exercise conducted between the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF) and the Indian Air Force (IAF), which deepened defense interoperability between the two nations.
- Tarang Shakti 2024: The first multilateral air exercise hosted by the Indian Air Force, with Japanese fighter aircraft participating.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands Development: Japan has also provided financial aid for infrastructure development in India’s strategically located Andaman and Nicobar Islands, contributing to enhancing India’s maritime security in the region.
Bali Jatra Cuttack Utsav 2024
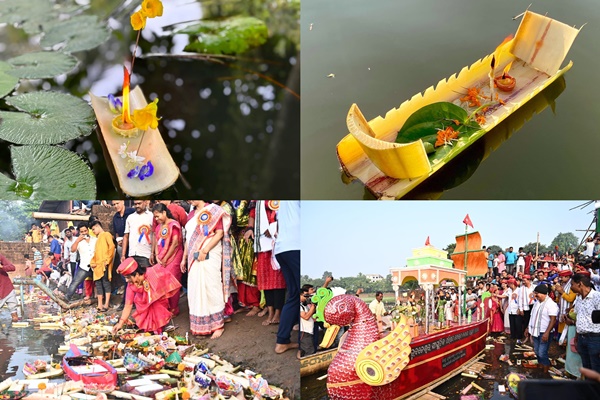

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bali Jatra 2024 is being held from November 15 to November 22 in Cuttack, Odisha.
- The festival celebrates Odisha’s ancient maritime history and its cultural and trade links with Southeast Asia.
- The event has gained international attention due to the participation of diplomats and cultural troupes from ASEAN, BIMSTEC, and Pacific Island countries.
Historical and Cultural Significance:
- Bali Jatra ("Voyage to Bali") commemorates the 2,000-year-old maritime trade routes between ancient Kalinga (modern-day Odisha) and Southeast Asia, including regions like Bali, Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Burma (Myanmar), and Sri Lanka.
- The festival honors the skills of Kalinga sailors who contributed to the prosperity of the region through trade, including commodities like pepper, cinnamon, cardamom, silk, camphor, gold, and jewelry.
- It highlights Odisha’s maritime legacy and the cultural exchanges between India and Southeast Asia, particularly the cultural influence of Odia merchants on Bali.
Commercial and Economic Aspects:
- Bali Jatra is Asia’s largest open-air trade fair, featuring over 2,500 stalls selling a variety of products including artisanal crafts, household items, and food.
- The event is a major commercial activity with business transactions estimated to exceed ?100 crore over the course of the festival.
- The festival provides an opportunity for both local and national traders to exhibit products at competitive prices.
Cultural Performances and International Participation:
- The festival includes daily cultural performances showcasing Odissi dance, Chhau dance, Bihu, Mahari, Gotipua, Sambalpuri, and Santali folk dances.
- This year, cultural troupes from countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Sri Lanka have participated, enhancing the international profile of the festival.
- Diplomats, including Ambassadors, High Commissioners, and Heads of Mission from 14 countries attended the inaugural ceremony.
Historical Background of Bali Jatra:
- The festival is linked to Kartika Purnima, the full moon night of the month of Kartika, marking the annual migration of traders from Odisha to Southeast Asia.
- Traders used boats called Boitas to travel to distant lands, which is now symbolically represented in the festival.
- The event’s cultural significance extends to the recognition of Odisha’s historic maritime routes, with ports like Tamralipti, Manikpatna, Chelitalo, Palur, and Pithunda playing key roles in global trade from as early as the 4th century BC.
Kalinga's Maritime Influence:
- The Kalinga Empire (present-day Odisha) had significant influence over the Bay of Bengal, referred to as the Kalinga Sea.
- Kalinga’s dominance in maritime trade is reflected in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, where the King of Kalinga is called "Lord of the Sea."
- Kalinga's Boitas (ships) were instrumental in connecting India with the Southeast Asian archipelago, including Bali.
Cultural Linkages with Bali:
- Odisha's trade with Bali influenced the culture, religion, and architecture of the region.
- Balinese Hinduism today still reflects Indian influences, with worship of Hindu deities like Shiva, Vishnu, Brahma, and Ganesha.
- The MasakapankeTukad festival in Bali, similar to Bali Jatra in Odisha, is a tribute to the maritime ancestors of Bali and commemorates the long-standing cultural ties.
Recognition and Milestones:
- Bali Jatra 2022 achieved a Guinness World Record for creating the largest collection of origami sculptures.
- The festival has evolved from a traditional trade fair to an international cultural event that highlights Odisha’s historical role in global trade and cultural exchanges.
Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES)
- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
Australia has come up with a new scheme that allows talented young people from India to work in the country for some time.
What is the MATES Scheme?
- Full Name: Mobility Arrangement for Talented Early-professionals Scheme (MATES).
- Objective: To provide Indian university graduates and early-career professionals with an opportunity to live and work in Australia for up to two years.
- Establishment: The scheme is part of the Migration and Mobility Partnership Arrangement (MMPA) between Australia and India, signed on May 23, 2023.
- Launch Date: MATES will open for applicants in December 2024.
Eligibility Criteria
- Age: Applicants must be 30 years or younger at the time of application.
- Educational Qualifications: Must have graduated within the last two years from an eligible institution with a Bachelor’s degree or higher in one of the following fields:
- Renewable Energy
- Mining
- Engineering
- Information Communications Technology (ICT)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Financial Technology (FinTech)
- Agricultural Technology (AgriTech)
- English Proficiency: A minimum score of 6 overall in IELTS (or equivalent), with at least 5 in each module.
- Institutional Criteria: Graduates must be from the top 100 Indian universities as per the NIRF Ranking 2024 (e.g., Panjab University, Chandigarh University, Thapar Institute of Engineering, Lovely Professional University).
- Previous Participation: Applicants must not have previously participated in the MATES scheme.
Key Features of the MATES Scheme
- No Employer Sponsorship Required: Applicants are not required to have sponsorship from an Australian employer.
- Visa Duration: The visa allows a stay of up to 2 years in Australia, with multiple entries permitted.
- Dependents: Visa holders can bring dependents (spouse and children). Dependents will have work rights in Australia but will not count towards the annual cap.
- Visa Application Process:
- The visa will be granted through a ballot system (random selection).
- Application Fee: AUD 25.
- Shortlisted candidates will proceed to further formalities.
Program Features
- Targeted Sectors: MATES focuses on key sectors such as renewable energy, mining, engineering, ICT, AI, FinTech, and AgriTech, aligning with Australia’s demand for skilled professionals in these areas.
- Pilot Program: Initially, the scheme will offer 3,000 places per year for primary applicants.
- Work Flexibility: While the visa does not require applicants to work in their nominated field, it is designed to help young professionals expand their skills and network in Australia’s key industries.
Additional Benefits
- Career Development: Participants will gain international work experience, expanding their professional network and skills.
- Cultural Exchange: The scheme also promotes cultural exchange between India and Australia, fostering stronger bilateral relations.
- Pathway for Future Opportunities: Participants may apply for further temporary or permanent residence in Australia, provided they meet the eligibility requirements.
Impact and Significance
- Bilateral Cooperation: The MMPA, under which MATES is established, enhances migration and mobility between India and Australia while addressing concerns related to illegal migration.
- Youth Empowerment: The scheme offers young professionals a platform to develop their careers internationally, particularly in sectors of global relevance like AI, FinTech, and renewable energy.
- Skill Development: MATES aims to bridge skill gaps in Australia by attracting Indian professionals to key sectors where expertise is in high demand.
- Global Talent Mobility: This scheme supports the global mobility of young talent and strengthens the India-Australia economic and educational partnership.
AUSTRAHIND 2024

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd edition of Exercise AUSTRAHIND started on 8th November 2024 at the Foreign Training Node in Pune, Maharashtra. The exercise will run until 21st November 2024.
Participating Forces:
- Indian Contingent: 140 personnel, primarily from the DOGRA Regiment and Indian Air Force (14 personnel).
- Australian Contingent: 120 personnel from the 13th Light Horse Regiment of the 10th Brigade of the 2nd Division.
Purpose of the Exercise:
- Enhance Military Cooperation between India and Australia.
- Promote Interoperability in conducting joint sub-conventional operations in semi-urban and semi-desert terrain.
- Focus on operations under Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
Key Objectives:
- Joint Tactical Drills and Planning to improve coordination between the forces.
- Training in counter-terrorism operations, special heli-borne operations, and drone countermeasures.
Phases of the Exercise:
Combat Conditioning and Tactical Training Phase:
- Includes drills such as terrorist response, territory capture, and Raid and Search & Destroy Missions.
- Establishment of Joint Operations Centre and securing critical infrastructure like helipads.
- Training on drone operations and counter-drone measures.
Validation Phase: Practical application and testing of skills learned in the previous phase.
Significance:
Best Practices Sharing: Both sides will exchange tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting effective tactical operations.
Camaraderie Building: The exercise will foster a strong bond between soldiers from both countries.
Background: AUSTRAHIND is an annual exercise held alternately in India and Australia. The last edition took place in Australia in December 2023.
21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) Meeting

- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 21st India-US Military Cooperation Group (MCG) meeting was held from November 5 to 6, 2024, at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- The meeting focused on strengthening defence ties between India and the US, covering a wide range of topics aimed at improving military cooperation.
Key Areas of Discussion
- Capacity Building: The meeting discussed initiatives for enhancing defence capacity through training exchanges, joint exercises, and sharing best practices.
- Defence Industrial Cooperation: Both countries explored opportunities for collaborative defence industrial ventures and technology sharing.
- Joint Exercises: The advancement of joint military exercises was highlighted to boost readiness against both conventional and hybrid threats.
- Strategic Objectives: The meeting aimed to enhance interoperability between the two countries' armed forces, enabling more effective joint operations.
Commitment to Strengthen Indo-US Defence Ties
- Strategic Partnership: Both nations reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening the Indo-US defence partnership, recognizing the shared challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Focus on Regional Security: The discussions underscored the importance of ensuring regional security and global stability in the face of emerging threats.
The Role of the MCG
- Purpose: The MCG forum serves as a key platform for enhancing strategic and operational defence collaboration between India and the US.
- Long-term Goals: The MCG aims to build mutual defence capabilities, counter emerging threats, and ensure the security of both nations and the wider region.
India-Algeria Strengthen Defence Ties

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) of India recently visited Algeria, culminating in the signing of a significant Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on defence cooperation.
- Objective: The MoU aims to strengthen the strategic and military ties between India and Algeria.
Recent Developments in India-Algeria Relations
- Important Visit: The CDS’s visit coincided with Algeria’s 70th anniversary of its revolution, celebrated on November 1st, with military parades and ceremonies highlighting Algeria’s historical and political legacy.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India re-established its defence wing in Algeria, and Algeria reciprocated by considering the establishment of its defence wing in India.
- India emphasized its role as a “Vishwa Bandhu” (global partner) and offered to share defence expertise and experiences with Algeria.
- Strategic Discussion: The MoU aims to enhance mutual understanding, laying the foundation for long-term defence collaboration across multiple sectors, including manufacturing under India’s 'Make in India' and 'Make for the World' initiatives.
- Global Peace Support: CDS reiterated India’s commitment to peaceful conflict resolution and expressed support for Algeria’s defence interests.
Significant Areas of India-Algeria Relationship
- Diplomatic Relations:
- India and Algeria established diplomatic ties in July 1962, the same year Algeria gained independence from French colonial rule.
- India supported Algeria's liberation movement and both countries have maintained close ties as part of the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Trade peaked at USD 2.9 billion in 2018 but dropped to USD 1.5 billion by 2021 due to COVID-19 and Algeria’s import restrictions.
- Trade rebounded in 2022, increasing by 24% to USD 2.1 billion.
- Exports from India (2023-24): Rice, pharmaceuticals, granite.
- Imports from Algeria: Petroleum oils, LNG, calcium phosphates.
- Bilateral Agreements:
- 2015 MoU: Between All India Radio (AIR) and Algerian National Radio for cooperation in broadcasting.
- 2018 Space Cooperation Agreement: Focuses on satellite technology for applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Visa Waiver Agreement (2021): Diplomatic and official passport holders are exempt from visa requirements.
- Cultural Engagement:
- International Day of Yoga (2024): Celebrated in Algeria at the Jardin d’Essai du Hamma, attracting over 300 participants.
- Space Cooperation:
- The 2018 India-Algeria Space Cooperation Agreement focuses on joint space science, technology, and applications.
- India has launched four Algerian satellites (2016), and the 2022 Joint Committee Meeting expanded satellite capacity building efforts.
- Algeria’s space agency has engaged with ISRO on satellite applications like crop forecasting and disaster management.
- Indian Community in Algeria:
- Approximately 3,800 Indians live in Algeria, working in various sectors, including technical and semi-skilled roles.
- The community includes 13 Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), 10 Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and 15 Indian students.
Minuteman III ICBM

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
The U.S. Army is scheduled to test launch a Minuteman III ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile) after the closure of voting on Election Day.
Missile Features
- Speed: Hypersonic, capable of reaching speeds up to 15,000 mph (Mach 23).
- Range: 13,000 km.
- Payload: Currently carries one nuclear warhead (as per arms control agreements with Russia), but originally designed for multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRVs).
- Launch Time: Extremely fast, enabling near-instant global retaliation capabilities.
- Testing Reliability: Nearly 100% success rate in tests, with backup airborne launch controllers to ensure continuity of the retaliatory strike capability.
- Length: 18.2 meters.
- Diameter: 1.85 meters.
- Launch Weight: 34,467 kg.
- Type: Three-stage, solid-fuel missile.
Strategic Significance
- Land-Based Nuclear Deterrent: The Minuteman III is a key component of the U.S. nuclear triad, which includes land-based missiles, submarine-launched missiles (SLBMs), and strategic bombers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The Sentinel weapon system (modernized Minuteman III) is viewed as the most cost-effective option for maintaining the land-based leg of U.S. nuclear deterrence until the planned Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD) system replaces it in 2029.
- Global Reach: The missile can strike any target worldwide within minutes, demonstrating U.S. nuclear reach and power projection.
Tumaini Festival

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Tumaini Festival is held annually in the Dzaleka Refugee Camp in Malawi, one of the world’s few music festivals hosted within a refugee camp. It brings together refugees and locals for cultural exchange, showcasing music, art, and crafts.
- Dates: The festival runs from Thursday to Saturday each year, typically in November.
- Founded: In 2014 by Congolese poet Menes La Plume.
Festival Highlights:
- The festival features performances from a diverse range of artists, including refugees and local Malawians, as well as artists from South Africa, Zimbabwe, and beyond.
- In 2024, performances included Jetu, a 72-year-old singer, and Vankson Boy V, a Congolese refugee, alongside other acts like Maveriq Mavo from South Africa.
- The festival aims to:
- Celebrate cultural exchange and community solidarity between refugees and locals.
- Humanize the refugee experience by allowing refugees and locals to share common experiences and celebrate cultural diversity.
- Challenge stereotypes by showing refugees as people with the same aspirations, talents, and desires as locals.
Significance of Dzaleka Refugee Camp:
- Location: Situated near Lilongwe, Malawi, Dzaleka was originally a prison before becoming a refugee camp in 1994.
- Capacity: Initially designed for 10,000 refugees, the camp now hosts over 60,000 individuals from countries like Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- Role: Dzaleka has evolved into a hub for humanitarian aid, cultural exchange, and empowerment of its residents.
Hwasong-19

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- North Korea recently announced the successful test-firing of its latest intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), the ‘Hwasong-19’.
- Claims by North Korea: The missile was described as ‘the world’s strongest strategic missile’ and a ‘perfected weapon system’ by North Korean state media.
Key Features of the Hwasong-19:
- Solid-Fuel Propulsion: The Hwasong-19 reportedly uses solid-fuel propulsion, which enables quicker launches and greater secrecy. This contrasts with liquid-fuel missiles, which take longer to prepare and are more visible.
- Enhanced Performance: The missile is said to have improved altitude and flight duration compared to previous North Korean ICBMs, marking significant progress in missile technology.
- Size: The Hwasong-19 is estimated to be 28 meters long (92 feet), which is notably larger than many other ICBMs, including those from the U.S. and Russia, which are typically under 20 meters (66 feet).
Strategic Implications:
- Reach and Targeting: The Hwasong-19 is believed to have a range of over 13,000 kilometers, which is sufficient to target the U.S. mainland, signaling a significant advancement in North Korea’s missile capabilities.
- Nuclear Capability: While specific details on the missile’s payload remain undisclosed, the Hwasong-19 could potentially be equipped with a nuclear warhead, enhancing North Korea's strategic deterrence.
Impact on Regional and Global Security:
- US-North Korea Tensions: The launch occurred against the backdrop of ongoing U.S.-North Korea tensions, particularly over North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs. The missile could potentially alter the regional security dynamics, especially in East Asia.
What is an ICBM?
- ICBM Definition: An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a long-range missile capable of carrying nuclear warheads (or other payloads) across continents.
- Range and Speed: ICBMs typically have a minimum range of 5,500 km (3,400 miles), with some capable of reaching up to 16,000 km or more, making them far faster and more capable than other ballistic missiles.
- Launch Mechanism: ICBMs are launched from land or submarine platforms, traveling through space before re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere and targeting distant objectives.
- Comparison with India's Agni-V: India’s Agni-V ICBM, which has a range of over 5,000 km, is often compared to North Korea’s missile systems.
Asset Recovery Interagency Network–Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP)

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
- India, represented by the Directorate of Enforcement (ED), has joined the Steering Committee of the Asset Recovery Interagency Network-Asia Pacific (ARIN-AP).
- Leadership Role: India will assume the presidency of ARIN-AP and host the Annual General Meeting (AGM) in 2026, providing a platform for global cooperation in asset recovery and tackling economic crimes.
ARIN-AP Overview:
- Establishment: ARIN-AP is a multi-agency network formed to address the proceeds of crime across the Asia-Pacific region.
- Network Goals: Its mission is to facilitate cross-border collaboration in the areas of asset tracing, freezing, and confiscation.
- Membership: ARIN-AP includes 28 member jurisdictions and 9 observers, and operates as a key component of the Global CARIN Network (Camden Asset Recovery Inter-Agency Network).
- Functioning: ARIN-AP operates through a network of contact points that enable intelligence exchange among member agencies, promoting effective communication and coordination for asset recovery.
Significance of ARIN-AP's Work:
- Combating Economic Crimes: ARIN-AP enhances the efforts of law enforcement agencies in tracing and recovering assets linked to criminal activities, including both movable and immovable assets.
- Informal Exchange of Intelligence: The network allows for the informal exchange of intelligence between agencies, which often accelerates the identification and recovery of proceeds of crime. This can later lead to formal actions through bilateral or multilateral agreements.
- Global Impact: With over 100 jurisdictions in the broader CARIN Network, ARIN-AP plays a key role in global efforts to combat fugitive economic offenders and illicit financial flows.
India’s Contribution and Alignment with G-20 Priorities:
- India’s Leadership: India’s presidency in ARIN-AP will enhance its leadership in asset recovery, facilitating closer cooperation with regional and international law enforcement agencies.
- G-20 Alignment: This role aligns with India’s priorities under the G-20 framework, particularly focusing on the Nine-Point Agenda aimed at tackling fugitive economic offenders and improving asset recovery mechanisms.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Brazilhas opted not to join China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), becoming the second BRICS country after India to reject the multi-billion-dollar infrastructure project.
- Brazil prefers to explore alternative ways to collaborate with Chinese investors without signing a formal treaty, aiming to avoid the perceived risks of the BRI.
BRICS and India’s Role:
- Brazil’s decision follows India’s long-standing opposition to the BRI, particularly due to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passing through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which India views as a violation of its sovereignty.
- India has consistently argued that BRI projects should adhere to international norms, good governance, and transparency, emphasizing that such initiatives should be financially sustainable and not lead to debt traps.
Brazil’s Broader Economic Strategy:
- Brazil aims to balance its relationship with China, which is a major economic partner, but without being bound by the BRI. This decision reflects broader concerns within Brazil about the long-term financial sustainability of BRI projects, especially after witnessing debt crises in other countries like Sri Lanka.
Global Context and the BRI's Impact:
- The BRI, launched by China in 2013, spans several infrastructure sectors and has expanded globally, but it has faced criticism for its potential to trap smaller nations in unsustainable debt.
- India and Brazil’s resistance to the BRI highlights growing skepticism among emerging economies about the long-term implications of joining China's flagship project.
United Nations Day 2024

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
United Nations Day is celebrated each year on October 24 to mark the anniversary of the UN Charter's entry into force, aiming to raise awareness about the goals and achievements of the international body.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Celebrates the anniversary of the UN Charter coming into effect on October 24, 1945, after World War II.
- Goal: Raise awareness about the UN’s objectives and accomplishments.
UN Charter Overview
- Signing & Implementation:
- Signed on June 26, 1945, in San Francisco.
- Came into effect on October 24, 1945.
- India ratified the UN Charter on October 30, 1945.
- Predecessor: The League of Nations, created in 1919 after WWI, aimed at promoting international cooperation and peace.
- Content:
- Foundational document of the UN, binding all member states.
- Establishes principles of international relations, including equality of nations and the prohibition of force between countries.
- Amended three times: 1963, 1965, and 1973.
UN's Core Objectives
- Peace and Security: Maintaining global peace and preventing conflicts.
- Humanitarian Aid: Providing assistance to those in need.
- Human Rights: Protecting and promoting human rights globally.
- International Law: Upholding the rule of law on the global stage.
Main Organs of the UN
- General Assembly (UNGA):
- Comprises all 193 Member States, each with one vote.
- Main policy-making body, addressing international issues covered by the UN Charter.
- Security Council (UNSC):
- Consists of 15 members (5 permanent, 10 elected for two-year terms).
- Permanent members: China, France, Russia, UK, USA.
- India has been elected to the UNSC eight times.
- Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC):
- Composed of 54 members elected by the General Assembly.
- Coordinates policy and addresses economic, social, and environmental issues.
- Trusteeship Council:
- Established to oversee trust territories transitioning to independence.
- International Court of Justice (ICJ):
- The only international court resolving disputes between UN member states.
- Handles contentious cases and provides advisory opinions.
- Secretariat:
- Led by the Secretary-General, appointed by the General Assembly based on Security Council recommendations.
- Acts as the chief administrative body of the UN.
Note: Most UN organs, including the UNGA, UNSC, ECOSOC, Trusteeship Council, and Secretariat, are based in New York, while the ICJ is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
Nobel Peace Prize 2024

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nobel Peace Prize has been awarded to Nihon Hidankyo, an organisation of survivors of the Hiroshima-Nagasaki bombings. In doing so, the Nobel Committee has highlighted the power of their testimonies and the need for disarmament.
Key Points about Nihon Hidankyo and the Hibakusha Movement
- Nihon Hidankyo:
- Established on August 10, 1956, as the nation-wide organization for survivors of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki bombings.
- Focuses on the welfare of Hibakusha (A-bomb survivors), promoting nuclear disarmament, and advocating for compensation for victims.
- Works to share the stories and experiences of Hibakusha, both within Japan and globally.
- Hibakusha (Bomb-affected People):
- Survivors of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
- Played a pivotal role in the global nuclear disarmament movement.
- Their testimonies have helped create the "nuclear taboo," ensuring nuclear weapons have not been used since 1945.
Role of Hibakusha in Nuclear Disarmament
- Global Impact:
- The bombings ignited a global movement for nuclear disarmament.
- Hibakusha's advocacy has highlighted the human cost of nuclear weapons, shaping international policy and promoting the nuclear taboo.
- Nihon Hidankyo’s Advocacy:
- The organization has been instrumental in documenting the effects of nuclear weapons and advocating for their abolition.
- Testimonies from Hibakusha have been key in raising awareness about the catastrophic humanitarian consequences of nuclear warfare.
Nobel Committee's Recognition and Current Nuclear Challenges
- Recognition of Hibakusha's Work:
- The Nobel Committee awarded the Peace Prize to Nihon Hidankyo for its role in promoting nuclear disarmament and for contributing to the nuclear taboo.
- The nuclear taboo is under increasing pressure as new countries seek nuclear weapons and existing powers modernize their arsenals.
- Current Nuclear Landscape:
- The US and Russia continue to maintain large nuclear stockpiles, with the US planning to spend over $1 trillion on upgrading its nuclear capabilities by the 2040s.
- New Threats: Geopolitical tensions, including regional conflicts, raise concerns about the resurgence of nuclear arms races.
Previous Nobel Peace Prizes for Disarmament
- Past Laureates:
- 1974: Former Japanese Prime Minister Eisaku Sato awarded for Japan's commitment to non-nuclear weapons policy.
- 2017: International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN) awarded for its efforts to draw attention to the humanitarian consequences of nuclear weapons and push for a nuclear ban treaty.
- Link with Alfred Nobel’s Vision:
- Alfred Nobel, the founder of the Peace Prize, made his fortune with the invention of dynamite and sought to use his wealth to promote peace, especially through disarmament.
India-Pakistan Kartarpur Corridor Agreement Renewal
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- India and Pakistan have extended the Sri Kartarpur Sahib Corridor Agreement for another five years (until 2029).
- Purpose: The extension ensures uninterrupted operation of the corridor, allowing Indian pilgrims to visit Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan.
- Significance: The extension reflects continued cooperation between India and Pakistan, with potential implications for improving bilateral relations.
Background of Kartarpur Corridor:
- Inception: The agreement was first signed on October 24, 2019, to allow visa-free access for Indian pilgrims to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur near Narowal in Pakistan.
- Pilgrimage Details:
- Eligibility: Indian nationals and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) cardholders can visit the gurdwara on a daily basis.
- Return on Same Day: Pilgrims must return on the same day.
- No Religious Restrictions: Pilgrims of any faith can use the corridor.
- Capacity: Up to 5,000 pilgrims per day can visit the gurdwara.
- Historical Importance: The corridor facilitates the Sikh community's access to a key religious site, located just 4.7 km from the India-Pakistan border.
- Service Charge Dispute:
- Pakistan's Service Fee: Pakistan continues to charge a $20 service fee (approx. ?1,680) per pilgrim, which India has consistently urged Pakistan to waive.
- Pakistan’s Justification: Pakistan maintains the fee to cover the $17 million spent on refurbishing the gurdwara and developing infrastructure for the corridor.
- Geopolitical Context and Timing:
- Recent Developments: The agreement renewal follows External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s visit to Pakistan to attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Council of Heads of Government meeting.
- Improved Bilateral Relations: Jaishankar’s visit marked the first visit by an Indian foreign minister to Pakistan in nearly nine years, signaling potential thaw in relations, despite the lack of formal bilateral dialogue.
- Strategic and Religious Importance:
- Religious Diplomacy: The Kartarpur Corridor is viewed as a confidence-building measure and a symbol of religious diplomacy, particularly for the Sikh community.
- Historical Legacy: The corridor links Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Pakistan to Gurdwara Dera Baba Nanak in India, facilitating access to a site of immense religious significance for Sikhs.
- Implications for India-Pakistan Relations:
- No Formal Bilateral Talks: Despite the successful renewal of the agreement, formal talks between India and Pakistan remain suspended, particularly after India’s revocation of Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir in 2019, which led to a diplomatic freeze.
- Pakistan's Diplomatic Stance: Pakistan had recalled its high commissioner from India in August 2019, and tensions have remained high since then.
- Potential for Future Engagement:
- Diplomatic Channels Opened: The renewal of the Kartarpur agreement and Jaishankar’s visit suggest that diplomatic channels are still open, and there may be scope for further engagement if both sides take steps to address outstanding issues.
IAEA’s 2024 Climate Change and Nuclear Power Report

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
- The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
- The new report was launched last week on the margins of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in Brazil.
Key Highlights:
- Nuclear Power's Role in Climate Change Mitigation:
- Nuclear energy is gaining global interest as nations seek to enhance energy security and decarbonize economies.
- To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, nuclear power is projected to play a pivotal role, with a projected capacity increase of 2.5 times the current level by mid-century in the IAEA's high case scenario.
- Investment Needs for Nuclear Expansion:
- Annual investment required to meet the IAEA's high case scenario (2050 nuclear capacity) is USD 125 billion, a significant increase from USD 50 billion annually from 2017-2023.
- If the aspirational goal to triple nuclear capacity (as pledged by over 20 countries at COP28) is to be met, USD 150 billion annually would be necessary.
- Challenges in Financing: Upfront capital for nuclear power plants is expensive, posing challenges, especially in market-driven economies and developing countries.
- Private Sector and Multilateral Support:
- The private sector will need to play a larger role in financing nuclear projects.
- The IAEA is engaging with multilateral development banks to improve financing options for developing countries to invest in nuclear energy.
- Private finance initiatives: In September 2024, 14 major financial institutions signaled readiness to help fund nuclear newbuild projects.
- Nuclear Financing at Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM):
- The IAEA report was launched during the 15th CEM in Brazil, a high-level forum for advancing clean energy technologies.
- Key stakeholders from Brazil, the IAEA, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the U.S. discussed strategies for securing nuclear power financing, especially in the context of COP29 (2024) where clean energy financing will be a key focus.
- Nuclear Energy in the EU’s Sustainable Financing:
- The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities now includes nuclear power, facilitating the issuance of green bonds for nuclear projects in Finland and France (2023).
- EDF received €4 billion in green bonds and around €7 billion in green loans (2022-2024).
- Investment in Nuclear Power:
- To meet global climate goals, nuclear power capacity must increase by 1.8 times by 2035.
- Effective financing mechanisms are crucial to scale up nuclear power and develop the workforce and supply chains needed for the energy transition.
- Policy Reform and International Partnerships:
- The report advocates for policy reforms and international partnerships to bridge the financing gap and accelerate nuclear power deployment, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies.
- Focus on technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which could play a role in the energy transition.
- Key Areas to Support Nuclear Growth:
- Robust regulatory frameworks and new delivery models are essential to unlock investments.
- Development of skilled labor and effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the expansion of nuclear energy.
- Energy System Modelling and Planning:
- The IAEA’s energy system modelling tools assist countries like Brazil in planning nuclear power projects, including cost analyses for electricity generation and financing strategies.
Role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- Mandate: The IAEA is the leading international body for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear energy and technologies.
- Functions:
- Nuclear safeguards: Ensuring nuclear activities remain peaceful and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- Assisting member states with technical support, knowledge sharing, and strengthening nuclear safety and security.
- The IAEA also supports capacity-building and emergency response in case of nuclear or radiological incidents.
- Structure:
- The IAEA General Conference is made up of all 178 member states, meeting annually to approve budgets and policies.
- The Board of Governors (35 members) meets several times a year to oversee the agency's activities and appointments.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
- The IAEA is part of the United Nations family, reporting to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.
