Nine Years of Startup India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 16, 2025, India marks nine years of Startup India, a transformative journey that began in 2016. Designated as National Startup Day, this occasion celebrates the nation’s strides in fostering a robust and inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Current Status (as of Jan 2025)
Over 1.59 lakh startups recognized by DPIIT, making India the 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally.
- More than 100 unicorns (startups valued over $1 billion).
- Key hubs: Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Delhi-NCR; growing contribution from smaller cities.
Key Sectors
- Major sectors: Fintech, Edtech, Health-tech, E-commerce.
- Notable companies: Zomato, Nykaa, Ola exemplify India's shift from job seekers to job creators.
Key Milestones (2016–2025)
- Startups grew from around 500 in 2016 to 1.59 lakh in 2025.
- 73,151 startups with at least one-woman director as of 2024, showcasing rise in women entrepreneurship.
- Over 16.6 lakh jobs created by DPIIT-recognized startups by 2024.
Core Features of Startup India
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplified compliance, self-certification, and single-window clearances.
- Tax Benefits: Three-year tax exemptions for eligible startups.
- Funding Support: ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) supports early-stage funding.
- Sector-Specific Policies: Policies focusing on sectors like biotechnology, agriculture, and renewable energy.
Industry-wise Jobs Created
- IT Services: 2.04 lakh jobs.
- Healthcare & Lifesciences: 1.47 lakh jobs.
- Professional & Commercial Services: 94,000 jobs.
- Total direct jobs created: 16.6 lakh (as of Oct 2024).
Flagship Schemes
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
Other Key Initiatives
- Capacity Building & Handholding: Workshops for regional ecosystems, especially in non-metro cities.
- Outreach & Awareness: Initiatives to facilitate funding, incubation, and mentorship opportunities.
- Ecosystem Development: National-level events like Startup Mahakumbh to bring together key stakeholders.
- International Linkages: India’s G20 Presidency institutionalized Startup20 to enhance global collaborations.
BHASKAR Platform (Launched in Sept 2024)
- Objective: Centralize and streamline interactions within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Key Features:
- Networking: Connects startups, investors, mentors, and government bodies.
- Resources: Provides quick access to essential tools and knowledge for scaling startups.
- Global Outreach: Promotes India as a global innovation hub.
Startup Mahakumbh
- 2024 Edition: Hosted 1,300 exhibitors, 48,000 visitors, and 392 speakers, including unicorn founders and policymakers.
- 2025 Edition (3-5 April, New Delhi): Theme - “Startup India @ 2047 – Unfolding the Bharat Story.”
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry Shri Piyush Goyal launches Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform:
- Objective: Strengthen India's cleantech value chains, especially in solar, wind, hydrogen, and battery storage sectors.
- Platform Features:
- Aims to promote collaboration, co-innovation, and knowledge-sharing among Indian firms.
- Focus on scaling up manufacturing, sharing ideas, technologies, and resources.
- Acts as a financing platform for the cleantech sector.
- Designed to position India as a global leader in sustainability and cleantech innovation.
India's Clean Energy Commitment:
- Target: 500 GW of clean energy capacity by 2030.
- India has been a front-runner in fulfilling its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and UNFCCC.
- Early Achievement: India achieved its 2022 renewable energy target of 200 GW, 8 years ahead of schedule.
- Largest Interconnected Grid: India boasts the world’s largest interconnected power grid, enhancing its renewable energy distribution capacity.
- Gujarat is a pioneer in solar power adoption in India.
Union Minister Shri Piyush Goyal's Views:
- On Product-Linked Incentives (PLIs):
- PLIs and subsidies are seen as short-term aids; long-term growth of the clean energy sector depends on it becoming self-sustaining.
- Urged Indian firms to innovate and scale up manufacturing within the country.
- On Clean Energy and Sustainability:
- Stressed the importance of innovation and collaboration to achieve sustainability goals.
- India aims to attract international investors by creating a compelling business case for cleantech investments.
- 3S Approach (Speed, Scale, and Skill): Key to implementing India's renewable energy program, emphasizing rapid deployment, large-scale adoption, and skill development in the sector.
Bharat Climate Forum 2025:
- Event Objective: A platform for policymakers, industry leaders, and stakeholders to discuss climate action, clean energy, and India’s role in global climate goals.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Aligning India’s clean energy initiatives with global climate goals (UNFCCC, Paris Agreement).
- Emphasizing India’s early achievements in clean energy adoption.
- Promoting sustainable development and clean energy solutions.
India's Performance in Renewable Energy:
- India’s progress has been commendable in meeting its climate targets and setting up clean energy capacity ahead of schedule.
- The government’s initiatives, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, have made solar power affordable and scalable through transparency in auctions, competitive bidding, and speed in project implementation.
Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
GEAPP and ISA Sign $100 Million Agreement for Solar Projects

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) signed a Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF) agreement with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to mobilize $100 million for funding high-impact solar energy projects. This collaboration is part of a wider effort to accelerate India's clean energy transition, bridge financing gaps, and enhance the country's energy systems. Along with this agreement, two other key initiatives were announced:
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition)
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge)
These programs aim to address energy transition challenges by fostering scalable, cost-efficient solutions, digitalizing utilities, and supporting innovations for sustainable energy.
Key Features:
- Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF):
- The MDTF aims to raise and deploy $100 million to finance impactful solar energy projects, with ISA driving the strategic direction.
- GEAPP’s Project Management Unit will provide governance, fundraising, and technical expertise to ensure project success.
- The collaboration emphasizes the importance of solar energy in achieving India's clean energy goals.
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition):
- Focuses on transforming grid systems by digitalizing grid assets and integrating them with smart sensors.
- Real-time data will help reduce transmission losses and facilitate Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) deployment, assisting in the integration of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) into the grid.
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge):
- A platform for identifying and scaling innovative solutions to accelerate the clean energy transition, especially within India's growing startup ecosystem.
- Focuses on supporting investable opportunities for energy transition solutions, building on the earlier success of ENTICE 1.0.
Global Impact of GEAPP:
GEAPP, launched with an initial commitment of $464 million, has already funded 130 projects across 40 countries. These projects have impacted over 50 million people, helping reduce 43 million tons of CO2 emissions. The collaboration with ISA is expected to deepen GEAPP's efforts in mobilizing capital to foster clean energy access and tackle climate change.
India’s Clean Energy Transition:
India has already extended electricity access to over 800 million people, but about 2.5% of households still remain unelectrified. Distributed renewable energy, especially solar energy, will play a pivotal role in reaching these underserved populations. India aims for 47 GW of battery energy storage systems by 2032, which will support grid stability and energy access.
Additional Initiatives and Impact:
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
- GEAPP has also supported India’s first commercial standalone BESS project, which will provide 24/7 power to over 12,000 low-income customers.
- The project is set to lower electricity tariffs by 55%, benefiting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Strategic Alliances:
- The partnership with ISA and the strategic initiatives like DUET and ENTICE 2.0 aim to further India’s climate and energy goals, bringing renewable energy solutions to underserved regions, and supporting the country's energy security.
Role of GEAPP and ISA:
- GEAPP works to mobilize financing, provide technical expertise, and ensure effective implementation of renewable energy projects globally.
- ISA focuses on solar energy solutions, and with this agreement, it seeks to enhance the solar energy capacity in its member countries, aligning with climate targets.
About GEAPP:
GEAPP is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, philanthropy, technology partners, and financial institutions. Its goal is to transition developing economies to clean energy while enhancing economic growth. It aims to:
- Reduce 4 gigatons of carbon emissions.
- Provide clean energy access to 1 billion people.
- Create 150 million new jobs globally.
India’s First Organic Fisheries Cluster

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Union Minister, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh inaugurated and laid the foundation for 50 key projects worth Rs. 50 crores under Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) covering all North East Region States Except Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
Key Highlights:
- Initiative: India’s first Organic Fisheries Cluster, launched under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY). The cluster focuses on sustainable aquaculture, promoting the production of antibiotic, chemical, and pesticide-free organic fish.
- Target Markets: Eco-conscious domestic and global markets.
Sikkim's Role as India’s First Organic State:
- Sikkim's Organic Commitment: Sikkim is the first Indian state to embrace 100% organic farming, covering 75,000 hectares of land.
- Vision: The Organic Fisheries Cluster aligns with Sikkim’s broader goal of promoting organic, sustainable agricultural practices.
Objective of Organic Fisheries Cluster:
- To prevent pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems by using ecologically healthy practices.
- Promotes sustainable fish farming methods, reducing environmental damage.
- Focus on species like amur carp and other carp varieties, aligning with the state’s success in organic farming.
Support from NABARD:
- The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) will provide financial and technical assistance.
- Key support includes:
- Infrastructure development.
- Formation of Fisheries-based Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs).
- Capacity building of local fishers and farmers.
PMMSY: A Comprehensive Fisheries Development Scheme:
- Investment: ?20,050 crore under PMMSY.
- Objective: To revolutionize India’s fisheries sector by promoting sustainable growth, enhancing fish production, and improving infrastructure.
- Implementation Period: FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- Key Goals:
- Boosting fish production and exports.
- Enhancing welfare of fishers and farmers.
- Promoting cluster-based development for better efficiency and competitiveness.
Cluster-Based Approach in Fisheries:
- Objective: To bring together geographically connected enterprises to enhance economies of scale.
- Impact: This approach improves financial viability, strengthens the fisheries value chain, and creates new business and livelihood opportunities.
- Types of Clusters: Includes Pearl, Seaweed, Ornamental Fisheries, Cold Water Fisheries, Organic Fisheries, and more.
Fisheries Focus in the North Eastern Region (NER):
- Fisheries Potential: The North Eastern Region (NER) has abundant freshwater resources and is a biodiversity hotspot.
- Growth: Inland fish production in the NER surged from 4.03 lakh tonnes (2014-15) to 6.41 lakh tonnes (2023-24), marking an impressive 5% annual growth.
- Investment in NER: Over ?2,114 crore invested through schemes like Blue Revolution and PMMSY.
- Key Projects:
- 50 projects worth ?50 crore to boost the region’s fisheries infrastructure, generating over 4,500 jobs.
- Projects include hatcheries, cold storage units, aquaculture parks, and fish kiosks.
India’s Global Fisheries Standing:
- India is the second-largest fish producer in the world, contributing 8% to global fish production.
- Top Rankings:
- Second in aquaculture production.
- Leading in shrimp production and exports.
- Third in capture fisheries.
Government Commitments and Schemes:
- Total Investment: Since 2015, the government has committed ?38,572 crore to fisheries development through key schemes like:
- Blue Revolution.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF).
- PMMSY.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY).
- These initiatives aim to promote sustainable growth, create jobs, and enhance infrastructure in the fisheries sector.
Economic, Environmental, and Social Benefits:
- Economic Impact:
- Higher incomes for fishers and farmers through better production and export.
- Employment generation through infrastructure development.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced pollution and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
- Social Impact: Empowerment of local communities, fostering sustainable livelihoods.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
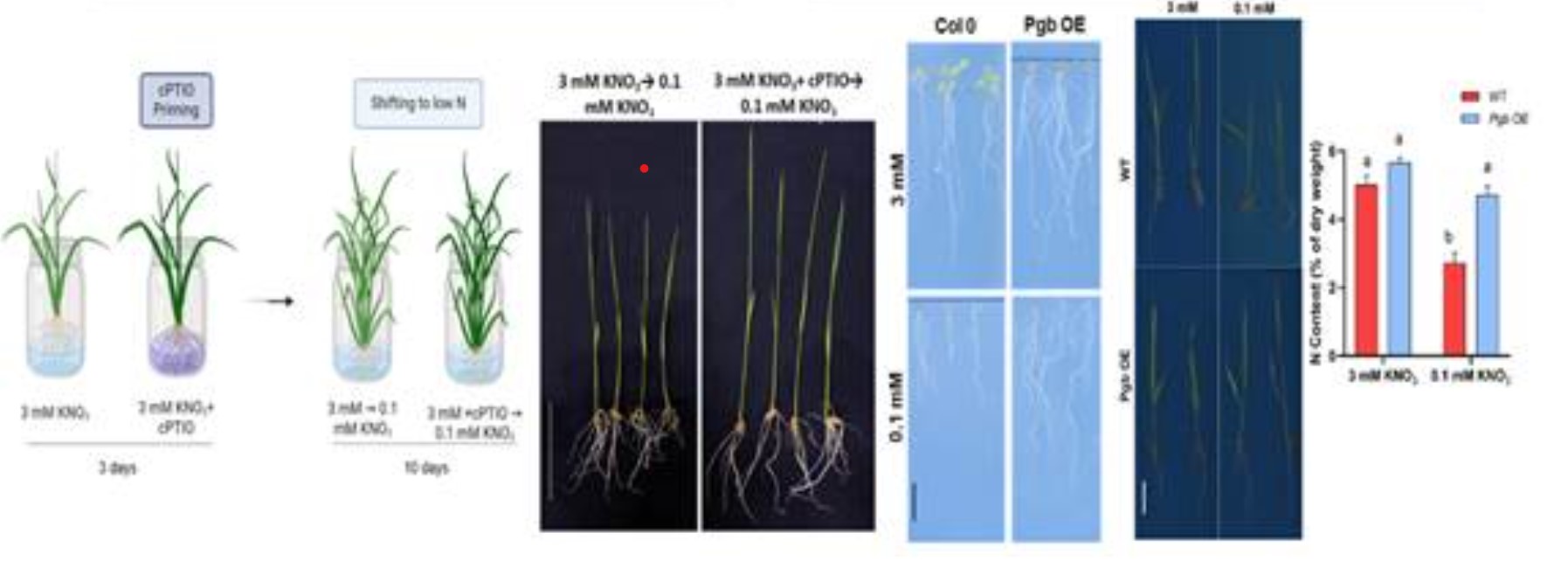
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
Study Methodology:
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
Anji Khad Bridge

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Overview:
- The Anji Khad Bridge is India's first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Jammu and Kashmir’s Reasi district.
- It is a key part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project aimed at enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Kashmir and the rest of India.
- The bridge crosses the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab River, and is expected to transform regional transport, boost tourism, and promote economic growth.
Key Features:
- Dimensions:
- Total length: 725.5 meters.
- Main Pylon Height: 193 meters from the foundation, standing 331 meters above the riverbed.
- The bridge is designed for train speeds of up to 100 km/h and can withstand wind speeds of up to 213 km/h.
- Structure and Design:
- Asymmetrical cable-stayed design supported by 96 cables with varying lengths (82 to 295 meters).
- The structure includes:
- A 120-meter approach viaduct on the Reasi side.
- A 38-meter approach bridge on the Katra side.
- A 473.25-meter cable-stayed portion crossing the valley.
- A 94.25-meter central embankment linking the main bridge to the approach viaduct.
- Construction Techniques:
- Used advanced construction techniques such as DOKA Jump Form Shuttering, Pump Concreting, and Tower Crane Technique to enhance safety and reduce construction time by 30%.
- A 40-ton tower crane imported from Spain was employed for operations at great heights.
- The project utilized site-specific investigations by IIT Roorkee and IIT Delhi due to the region’s complex geological and seismic conditions.
- Engineering Challenges:
- The bridge had to be constructed in the difficult Himalayan terrain, with fragile geological features such as faults and thrusts.
- Seismic activity in the region required additional precautions in the design and construction process.
- Safety and Monitoring:
- Equipped with an integrated monitoring system that includes multiple sensors to ensure the structural health of the bridge during operation.
Importance and Impact:
- Connectivity: The bridge will significantly improve connectivity between Katra and Reasi, ensuring faster rail travel and linking the Kashmir Valley with the rest of India.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Expected to boost tourism and economic development by improving access to the region, attracting visitors, and facilitating smoother transportation of goods and services.
- Sustainability: The bridge's design ensures it remains safe under extreme weather conditions, offering long-term reliability for the Indian Railways network.
Collaboration and International Expertise:
- The design and supervision were handled by ITALFERR (Italy), with proof-checking conducted by COWI (UK).
- The project combines Indian engineering codes with Eurocodes, adhering to international standards for structural integrity.
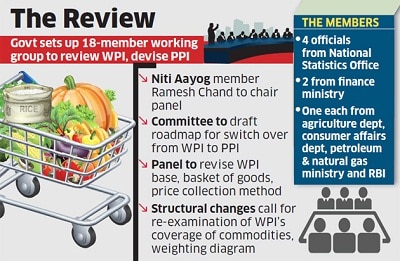
Ramesh Chand Panel
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India has formed an 18-member panel, headed by Ramesh Chand, a member of NITI Aayog, to revise the base year of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to 2022-23 from the current base year of 2011-12. The panel will also work on a roadmap for transitioning from WPI to the Producer Price Index (PPI).
Key Highlights:
Role and Mandates of the Panel:
- Revised Commodity Basket: The panel will recommend a new commodity basket for both WPI and PPI, reflecting structural changes in the economy.
- Review of Price Collection System: The panel will evaluate the current system for price collection and propose improvements.
- Computational Methodology: It will determine the computational methodology for both WPI and PPI to ensure accuracy in tracking price changes.
- The panel has been tasked with submitting its final report to the Office of the Economic Adviser at the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIT) within 18 months.
Understanding WPI vs. PPI:
- WPI (Wholesale Price Index) tracks the price of goods at the wholesale stage (i.e., goods sold in bulk to businesses), and excludes the service sector.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- Does not consider consumer-facing prices.
- Excludes services (about 55% of GDP).
- Can have double-counting bias due to multiple transactions before the final sale.
- Does not account for indirect taxes and may include export/import prices.
- Use: WPI helps in tracking bulk price movements between businesses, but doesn't fully represent consumer price inflation.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- PPI (Producer Price Index) tracks prices at various stages of production, considering both goods and services, and measures the average change in prices received by domestic producers.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
- Excludes indirect taxes (making it more accurate for price movement tracking).
- Includes services, unlike WPI, giving a broader view of price trends across the economy.
- More aligned with international standards (System of National Accounts).
- Reflects prices before consumer consumption, providing a business-oriented perspective of price trends.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
Why the Transition to PPI?
- The PPI is already used by major economies like the US, China, Germany, and Japan as it provides a more comprehensive measure of inflation from a producer’s perspective.
- It is expected to be a better indicator of inflationary trends in the overall economy, including both goods and services.
Challenges and Roadmap:
- The switch to PPI is complex, and the panel will need to ensure that the transition does not disrupt the current data collection and reporting systems. Both WPI and PPI will run concurrently until PPI stabilizes.
Business Ready (B-READY) Report 2024

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The B-READY report, launched by the World Bank in 2024, replaces the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index.
- Focus: It evaluates the global business environment to foster inclusive private sector growth, assessing 10 core topics covering a firm's lifecycle, such as business entry, taxation, labor, and international trade.
India’s Potential Challenges
- Business Entry: India faces multiple steps and incomplete digital integration, making it slower compared to benchmarks like Singapore, which achieves one-day registration at minimal cost.
- Labor Regulations: While India has introduced four labor codes, the implementation remains slow and inconsistent, affecting labor flexibility and compliance.
- International Trade: India struggles with customs delays, inconsistent enforcement, and high logistics costs, unlike countries like Germany and Singapore, which promote trade efficiently.
- Business Location: Regulatory delays and inconsistent approvals hinder the establishment of business facilities, affecting investment decisions.
- Public Services Gap: While regulations may be strong, there is often a gap in the provision of public services that support their effective implementation, leading to inefficiencies.
Key Strengths for India
- India is expected to score well in the areas of Quality of Regulations, Effectiveness of Public Services, and Operational Efficiency.
- The country shows promise in promoting digital adoption and aligning with global environmental sustainability practices, though gender-sensitive regulations need more emphasis.
Significance
- The B-READY report serves as an essential benchmark for assessing India's business environment, offering insights into regulatory reforms and operational efficiency.
- Key policy implications for India include the need to:
- Streamline business operations by digitizing registration and regulatory approval processes.
- Improve logistics and trade efficiency by reducing customs delays.
- Address labor market inefficiencies through better implementation of labor codes.
- Invest in public services and promote digital transformation for better compliance and operational ease.
- Focus on sustainability and inclusivity, ensuring gender-sensitive policies and fostering green business practices.
Global Findings from the B-READY Report
- Economies with strong regulatory frameworks and digital tools (e.g., Rwanda, Georgia) show that even countries with varying income levels can achieve high scores.
- High-income countries like Estonia and Singapore still have room for improvement, especially in areas like taxation and dispute resolution.
Comparison of B-READY with Ease of Doing Business (EoDB)
- Scope: B-READY is broader, covering a firm’s lifecycle and social benefits, while EoDB focused mainly on regulatory burdens.
- Indicators: B-READY uses 1,200 indicators from expert consultations and firm-level surveys, offering more comprehensive insights compared to the EoDB's limited metrics.
- Focus on Public Services: Unlike EoDB, which provided limited attention to public services, B-READY explicitly evaluates public service efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Policy Recommendations
- Streamline Business Operations: Inspired by countries like Singapore, India should simplify business registration and reduce delays in customs and regulatory approvals.
- Strengthen Public Services: Focus on improving tax portals, utility access, and dispute resolution systems through digital tools.
- Promote Sustainability: Encourage environmentally sustainable business practices and adopt gender-sensitive regulations to ensure inclusive growth.
- Peer Learning and Global Collaboration: Encourage India to learn from best practices in countries like Singapore and Estonia for effective reforms.
- Tailored Reforms: India must design policies addressing unique local challenges while adhering to global standards.
Lighthouse Tourism in India

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
Lighthouse tourism in India is rapidly emerging as an exciting and profitable segment of the country's travel and tourism industry. India's coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers, is home to 204 lighthouses, many of which are being transformed into vibrant tourist destinations, celebrating both India's rich maritime history and its natural beauty.
Key Highlights:
- Historical and Scenic Appeal: Lighthouses in India are often located in breathtaking coastal or island locations, offering panoramic sea views and access to surrounding natural beauty. Some of these structures are centuries old and are situated near significant cultural landmarks or UNESCO World Heritage Sites, adding cultural depth to the visitor experience.
- Economic Growth: As part of the broader Maritime India Vision (MIV) 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, the Government of India is keen to transform these historic lighthouses into hubs of economic activity. By developing infrastructure, creating new tourism-related jobs, and fostering local entrepreneurship, lighthouse tourism aims to benefit coastal communities and boost India's tourism economy. As of 2023-24, 75 lighthouses across 10 states have been equipped with modern amenities, attracting 16 lakh visitors—a 400% increase from previous years.
- Government Initiatives:
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- The 1st Indian Lighthouse Festival, “Bharatiya Prakash Stambh Utsav”, was inaugurated on 23rd September, 2023 by the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal and Goa Chief Minister, Shri Pramod Sawant at the historic Fort Aguada in Goa.
- The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held in Odisha. Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, was also joined by Odisha Chief Minister, Mohan Charan Majhi. Shri Sonowal dedicated two new lighthouses at Chaumuck (Balasore) and Dhamra (Bhadrak) and emphasized empowering coastal communities to preserve and promote lighthouses as part of India’s rich maritime heritage.
- Sagarmala Programme: This government initiative integrates infrastructure development with sustainable practices, ensuring that the growth of lighthouse tourism benefits local communities while preserving the environment.
- Tourism Infrastructure: The government has invested ?60 crore in enhancing these sites, providing facilities like museums, parks, amphitheaters, and more to enrich the visitor experience.
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- Sustainable Development: The Indian government places a strong emphasis on eco-friendly tourism. This includes integrating lighthouses into broader coastal circuits and launching digital awareness campaigns to attract domestic and international tourists.
- Community Empowerment and Employment: Lighthouse tourism has already created direct and indirect employment, from hospitality to transportation, local handicrafts, and artisan work, with more than 500 jobs being generated. Local communities are being trained to offer skills in hospitality and tourism services.
Future Plans:
- Skill Development: Programs are being introduced to equip local people with the necessary skills to cater to the tourism industry.
- Sustainable Practices: Eco-friendly practices will continue to be emphasized to protect coastal ecosystems.
- Integration with Coastal Circuits: Lighthouses will become key points of interest in broader coastal tourism itineraries, further enhancing their appeal to tourists.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
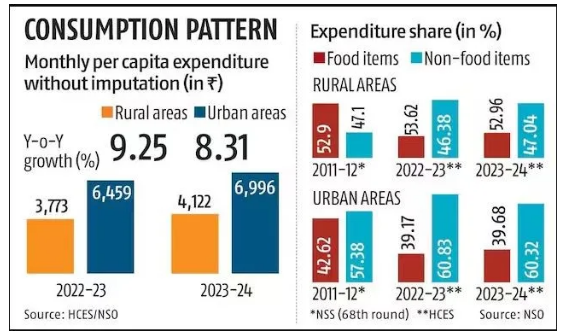
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
Operation Green Scheme

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The government’s flagship Operation Greens scheme, designed to stabilise crop prices and benefit farmers, has spent just 34 per cent of its allocated budget for 2024-25, according to a parliamentary report, even as onion farmers in Maharashtra reel from massive losses and potato shortages grip eastern states.
Key Highlights:
Overview:
- Launched: November 2018 under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana.
- Objective: Stabilize prices and improve farmers' income by enhancing the production and marketing of perishable crops, initially focusing on Tomato, Onion, and Potato (TOP).
- Expanded Scope (2021): Includes 22 perishable crops like mango, banana, ginger, apple, and shrimp.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI).
- Funding: Managed by the National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED).
Key Aims:
- Reduce price volatility in agricultural markets.
- Minimize post-harvest losses.
- Strengthen farm-to-market linkages.
- Enhance farmers’ earnings by stabilizing market prices.
- Promote value addition and food processing.
Scheme Components:
- Short-term Interventions:
- Subsidies on transportation (50%) and storage (50%) to protect farmers from distress sales.
- Price stabilization during periods of surplus or shortage.
- Long-term Interventions:
- Development of farm-gate infrastructure like cold storage and processing facilities.
- Strengthening production clusters and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Building efficient agri-logistics systems.
- Promoting food processing and value addition capacities.
Key Features:
- 50% subsidy on transportation and storage costs for eligible crops.
- Projects eligible for 50% subsidy (up to ?50 crore per project), and for FPOs, a 70% subsidy.
- Demand-driven funding based on applications, with no fixed crop or state-wise allocation.
Key Findings from Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) Report (2024):
- Underutilisation of Budget: Only 34% (?59.44 crore) of the allocated ?173.40 crore for 2024-25 spent by October 2024, leaving 65.73% unspent.
- Slow Implementation: Out of 10 targeted projects, only 3 were completed by October 2024.
- Limited Impact on Price Stabilization:
- Onion prices fell by nearly 50% in Maharashtra, despite the scheme's intent to stabilize prices.
- Potato shortages in states like Odisha and Jharkhand due to weather-induced production dips in West Bengal.
- Inconsistent Policies: Export bans and fluctuating export duties caused frustration among onion farmers, undermining the scheme’s effectiveness in ensuring fair prices.
Impact on Farmers:
- Price Stabilization: Despite the scheme’s aims, price fluctuations continue to affect farmers, especially in Maharashtra with the onion price crash.
- Post-Harvest Losses: The scheme aims to reduce wastage by building infrastructure like cold storage, but challenges remain in implementation.
- Market Linkages: Attempts to connect farmers and FPOs with retail markets have not yet yielded significant results.
Operational Challenges:
- The scheme faces challenges in fulfilling its dual mandate of ensuring fair prices for farmers while keeping consumer prices affordable.
- The slow utilization of funds and incomplete infrastructure projects raise concerns about the effectiveness of the program.
- Inconsistent policy decisions, like the export ban and imposition of export duties, have contributed to farmer discontent.
Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya Committee

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has set up an eight-member committee to create a framework for the responsible and ethical use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the financial sector.
- The committee is chaired by Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya, Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at IIT Bombay.
Key Highlights:
Committee's Objective:
- The primary goal is to develop a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI (FREE-AI) in the financial sector.
- It will guide the ethical adoption of AI in financial services to enhance operational efficiency, decision-making, and risk management.
Scope of the Committee's Work:
- Assess the current global and domestic adoption of AI in financial services.
- Identify potential risks and challenges associated with the integration of AI in the sector.
- Recommend a framework for evaluating, mitigating, and monitoring AI-related risks.
- Propose compliance requirements for various financial entities (e.g., banks, NBFCs, fintech firms).
- Suggest a governance framework for ethical AI usage.
Key Benefits of AI in Financial Services:
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, process large datasets, and enhance accuracy (e.g., loan application processing).
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive analytics in AI help forecast market trends, aiding in better financial decision-making (e.g., algorithmic trading).
- Customer Relationship Management: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer interaction, offering 24/7 support.
- Improved Risk Management: AI enables proactive fraud detection, improving security and preventing financial losses.
Concerns Associated with AI in Finance:
- Embedded Bias: AI models can replicate biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes and financial exclusion.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI poses risks to personal data security, with potential violations of privacy regulations.
- Operational Challenges: AI systems may exhibit inconsistent responses, leading to challenges in trust and effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased use of AI can heighten vulnerability to cyber-attacks and exploitation.
RBI's Role & Governance:
- The RBI aims to ensure that AI adoption in the financial sector is ethical, transparent, and aligned with global best practices.
- The committee's recommendations will influence policies to prevent misuse and safeguard consumer interests.
Rupee and Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The real effective exchange rate (REER) index of the rupee touched a record 108.14 in November, strengthening by 4.5 per cent during this calendar year, according to the latest Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data.
Key Highlights:
- Record REER Index:
- The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the rupee reached an all-time high of 108.14 in November 2024.
- This marks a 4.5% appreciation in REER during the calendar year 2024, according to RBI data.
- What is REER?
- REER is a weighted average of a country’s currency value against the currencies of its major trading partners, adjusted for inflation differentials.
- It considers 40 currencies accounting for about 88% of India's trade.
- REER Calculation:
- Nominal Exchange Rates: The exchange rate between the rupee and each partner's currency.
- Inflation Differentials: Adjusts for inflation differences between India and its trading partners.
- Trade Weights: Based on the trade share with each partner.
- Recent Trends in REER:
- In 2023, REER dropped from 105.32 in January to 99.03 in April.
- It has since been on an appreciating trend, reaching 107.20 in October and 108.14 in November 2024.
- Dollar Strengthening Impact:
- Despite the rupee weakening against the US dollar (from 83.67 to 85.19 between September and December 2024), it has appreciated against the euro, British pound, and Japanese yen.
- The dollar's strengthening was fueled by global economic factors, including inflation expectations in the US and high bond yields, which led to capital outflows from other countries, including India.
- Impact on Exports and Imports:
- Overvaluation: A REER above 100 signals overvaluation, which can harm export competitiveness (exports become costlier) while making imports cheaper.
- Undervaluation: A REER below 100 indicates a currency is undervalued, boosting exports but increasing the cost of imports.
- India's Inflation and REER:
- India's higher inflation relative to trading partners is a key factor behind the rupee’s rising REER, despite its depreciation against major currencies.
- This suggests the rupee is overvalued, which could explain why the RBI may allow the rupee to depreciate further against the dollar.
- Global Context:
- The strengthening of the US dollar, influenced by factors such as tariff policies under the Trump administration and tighter US monetary policies, plays a significant role in the depreciation of the rupee against the dollar.
- This dynamic affects India's trade balance, with potential consequences for export growth.
- Implications for India’s Economy:
- Overvalued currency (as indicated by REER above 100) can lead to a trade deficit, as imports become cheaper and exports less competitive.
- A weaker rupee, particularly against the dollar, could boost Indian exports but raise the cost of imports.
Strengthening Fisheries Extension Services

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
India possesses diverse fisheries resources that provide livelihood opportunities to approximately three crore fishers and fish farmers. The country has witnessed an 83% increase in the national fish production since 2013-14, that stands at a record 175 lakh tons in 2022-23.
Importance of Fisheries Extension Services:
- Livelihood Support: Fisheries provide livelihoods to over 3 crore fishers and fish farmers in India. The sector's growth is crucial for enhancing sustainable practices and ensuring long-term productivity.
- Growth in Fish Production: India’s fish production has seen an 83% increase since 2013-14, reaching 175 lakh tons in 2022-23, with 75% of production coming from inland fisheries. India is the second-largest fish and aquaculture producer globally.
- Role of Extension Services: Extension services bridge the gap between scientific advancements and fishers, offering guidance on:
- Species lifecycle management
- Water quality management
- Disease control
- Sustainable rearing technologies and business models.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Fisheries Extension:
- Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs):
- Launched under PMMSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana) in 2020, MSKs are one-stop centers providing comprehensive extension services.
- Support to Fish Farmers: MSKs offer:
- Disease testing, water, and soil analysis.
- Training on sustainable aquaculture practices.
- Technology infusion in seed/feed management.
- Focus on Inclusivity: Government assistance (up to 60%) is available for women and marginalized communities to set up MSKs.
- Examples:
- Thrissur, Kerala: Equipped with labs for water and microbial analysis.
- Maharashtra (Nasik and Sangli): Capacity-building efforts on seed/feed inputs.
- Collaborations: MSKs mobilize start-ups, cooperatives, and Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs) to share best practices, including regenerative and conservation management in the face of climate change.
- Sagar Mitras:
- Role: Deployed in coastal states and union territories, Sagar Mitras act as a vital interface between the government and marine fishers.
- Functions:
- Collection and dissemination of daily marine catch data, price fluctuations, and market insights.
- Dissemination of important information: weather forecasts, fishing zones, local regulations, and hygienic fish handling.
- Provide support on disaster preparedness and natural calamities.
Enhancing Extension Services through Digital Platforms:
- AquaBazaar: A virtual learning platform initiated by the National Fisheries Development Board to provide expert guidance on:
- Seed production and breeding of commercially important fish species.
- Practical demonstrations to improve fishers' knowledge.
- Digital Outreach: Expanding such platforms will improve access to resources for fishers, especially in rural and remote areas.
Institutional Convergence and Capacity Building:
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Fisheries extension services should be integrated with the over 700 Krishi Vigyan Kendras and state-level agricultural extension services for effective outreach.
- Formalizing the Sector: The World Bank-assisted project aims to create work-based digital identities for fishers and fish farmers, enhancing their access to extension services, training, and awareness programs.
Challenges in Fisheries Extension Services:
- Fragmented Initiatives: Multiple government schemes and programs lack institutional convergence, leading to inefficiencies in reaching the grassroots level.
- Digital Divide: Many rural and coastal areas face challenges in terms of digital literacy and internet connectivity, limiting the effectiveness of online platforms.
- Impact of Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns and resource depletion due to overfishing demand adaptive strategies and the promotion of climate-resilient practices.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
- Institutional Convergence: Combining existing extension machinery like Krishi Vigyan Kendras with fisheries extension services to leverage established networks and knowledge.
- Expand Digital Outreach: Platforms like AquaBazaar should be expanded to ensure wider access to expert knowledge, training, and best practices.
- Private Sector Collaboration: Encouraging public-private partnerships can enhance technology dissemination, capacity building, and resource mobilization in the fisheries sector.
- Focus on Sustainability: Developing climate-resilient and sustainable fisheries practices will be essential to address challenges posed by environmental changes and overfishing.
Private Aviation and Emissions

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Private aviation is releasing more than its ‘fair share’ of emissions.
Key Highlights:
- Aviation Sector's Global Emissions:
- The aviation sector contributed 2% of global CO2 emissions in 2022, around 800 Mt CO2 (International Energy Agency).
- If considered as a nation, aviation would rank among the top 10 emitters worldwide.
- Emissions from aviation have grown faster than other sectors like rail, road, or shipping in recent decades.
- Private Aviation and Its Impact:
- Private jets emit 5 to 14 times more CO2 per passenger than commercial flights and 50 times more than trains.
- Emissions from private aviation increased by 46% between 2019 and 2023.
- Each private flight contributes 3.6 tonnes of CO2 on average, intensifying global warming.
- Private aviation is responsible for significant nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and the creation of vapor trails, which further amplify environmental damage.
Trends in Private Aviation Growth:
- Global Trends:
- The number of private jets increased from 25,993 in December 2023 to 26,454 in February 2024.
- In the U.S., 69% of private aviation activity is concentrated.
- 8,500 more jets are expected to be delivered in the next 10 years globally.
- Private Aviation in India:
- 112 private planes were registered in India as of March 2024, placing it among the top 20 countries for private aircraft ownership.
- India's private aviation sector is expanding, driven by the growing billionaire and millionaire population.
- Private aircraft ownership in India stands at 1 per 1 lakh population, which is low compared to countries like Malta (46.51 per lakh) and the U.S. (5.45 per lakh).
Emission Reduction Efforts and Solutions:
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs):
- SAFs are bio-based or waste-derived fuels that can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuels.
- Airlines like SpiceJet (2018) and AirAsia (2023) have tested SAFs, but large-scale adoption is hindered by high costs and limited production.
- India aims to leverage its ethanol production chain, with potential to meet 15-20% of aviation fuel demand by 2050 if only surplus sugar is used.
- Hydrogen and Electric Aviation:
- Hydrogen offers a higher energy density than kerosene and emits only water vapor, making it a clean fuel alternative. However, hydrogen faces challenges with storage, infrastructure, and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric propulsion offers zero emissions but is currently limited by battery weight, energy density, and charging infrastructure.
India’s Policy and Initiatives:
- Government Initiatives:
- UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) aims to enhance rural connectivity.
- NABH (Nextgen Airports for Bharat Nirman) seeks to increase airport capacity by five times.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- Indian airlines have tested SAFs, such as a 25% jatropha oil blend by SpiceJet in 2018.
- Ethanol for aviation fuel: India plans to use surplus sugar for ethanol, potentially fulfilling 15-20% of aviation fuel needs by 2050.
- Challenges to Decarbonisation:
- SAFs are costly and limited in availability.
- Hydrogen requires extensive infrastructure and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric solutions are currently unsuitable for long-haul flights due to energy limitations.
National Farmers' Day

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
National Farmers' Day, also known as Kisan Diwas, is celebrated annually on December 23rd to honor the vital contributions of Indian farmers and commemorate the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, India's fifth Prime Minister. A passionate advocate for rural development and farmers' welfare, Charan Singh's policies laid the foundation for several reforms aimed at uplifting the agrarian economy. His contributions continue to inspire government initiatives that prioritize the welfare of farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural growth and ensuring food security for the nation.
The Legacy of Chaudhary Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh was born on December 23, 1902, in Noorpur, Uttar Pradesh. His deep understanding of rural issues and commitment to improving farmers’ lives earned him the title of "Kisan Leader". Throughout his political career, he championed reforms such as the Debt Redemption Bill (1939), which alleviated the financial burdens of farmers, and the Land Holding Act (1960), which promoted fair distribution of agricultural land. He also advocated for Minimum Support Price (MSP), and his policies laid the groundwork for NABARD and other farmer-centric institutions.
Significance of Kisan Diwas
Kisan Diwas highlights the importance of agriculture in India’s economy and employment, with farmers constituting nearly 50% of the workforce. The day emphasizes the need for policies that address farmers' challenges such as climate change, financial constraints, and technological adoption. It also serves as a reminder of the necessity to empower farmers through innovative solutions, financial security, and sustainable farming practices.
Key Government Initiatives for Farmer Welfare
The Indian government has launched several schemes to address the challenges faced by farmers and support their socio-economic upliftment:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to mitigate financial risks due to crop loss.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY): A pension scheme for farmers to ensure long-term social security.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient fertilizer use and soil health by providing farmers with personalized soil health reports.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): These entities help farmers collectively access markets, reduce costs, and improve bargaining power.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Provides affordable credit to farmers, especially for agriculture-related activities.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Helps farmers access timely credit for agricultural purposes at concessional rates.
Significant Budget Allocations and New Schemes
The government has drastically increased its budget allocation to the agriculture sector. From Rs. 21,933.50 crore in 2013-14, the budget has risen to Rs. 1,22,528.77 crore for 2024-25, underlining the government's commitment to farmer welfare and sustainable agricultural development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme: This initiative, aimed at empowering Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs), supports the use of drones for agricultural purposes, including fertilizer and pesticide application, with 80% financial assistance.
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP): Enhances the quality and productivity of horticulture crops by ensuring disease-free planting material.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to modernize farming with digital infrastructure, including crop estimation surveys and e-agriculture platforms.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Encourages chemical-free, sustainable farming practices.
Farmers' Role in Nation-Building
India’s agricultural sector not only sustains the livelihoods of millions but also contributes significantly to the country's GDP. In FY 2023-24, agriculture contributed 17.7% to the Gross Value Added (GVA). With over 54% of the country's land dedicated to agriculture, farmers are critical to food security and rural development.
In 2023-24, India achieved a record foodgrain production of 332.2 million tonnes, illustrating the resilience of Indian farmers in ensuring food availability despite challenges like climate change.
SAMARTH UDYOG BHARAT 4.0 INITIATIVE

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative, launched by the Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI), aims to enhance the competitiveness of the Indian capital goods sector by promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. This initiative is part of the Scheme for Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
Key Features of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
- Establishment of Smart Manufacturing Hubs: Under this initiative, four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres have been set up across India:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab, Pune
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing, IIT Delhi
- I-4.0 India @ IISc, Bengaluru
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell, CMTI, Bengaluru
- Cluster Industry 4.0 Experience Centres: In addition to the above centres, 10 cluster Industry 4.0 experience centres have been approved. These will be established under a Hub and Spoke model, managed by the C4i4 Lab in Pune, and spread across India.
- Key Achievements:
- Model Factories: Development of an Industry 4.0 enabled Model Factory at C4i4, Pune, and a smart production-based factory at CMTI Bengaluru.
- Industry 4.0 Solutions: More than 50 use-cases for Industry 4.0 solutions were compiled to support implementation.
- Maturity Assessment Tool: Creation of the Industry 4.0 Maturity Model (I4MM), specifically designed to assess the readiness of Indian manufacturing companies for Industry 4.0.
- Online Assessment Tool: Launch of a free online assessment tool by C4i4 Lab, Pune, to help MSMEs evaluate their maturity in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Training and Awareness:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular awareness seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events are organized to educate industries about Industry 4.0.
- Workforce Training: The SAMARTH Centres have trained over 5000 professionals on smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Consultancy Services: The centres offer consultancy in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics, along with incubation support for start-ups and MSMEs.
- Impact on MSMEs:
- Digital Maturity Assessments: Over 100 digital maturity assessments have been completed for the auto industry, and more than 500 improvement initiatives have been identified.
- Training and Capacity Building: Over 500 digital champions have been trained on Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Focus on MSMEs: While no direct financial assistance is provided to industries, including MSMEs, under this initiative, the SAMARTH Centres play a key role in helping them adopt Industry 4.0 technologies and build their capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative seeks to increase the global competitiveness of India's capital goods and manufacturing sectors.
- It leverages Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, automation, data analytics, and AI to modernize manufacturing processes.
- The initiative involves setting up 4 major Smart Manufacturing Hubs and 10 regional experience centres across the country to facilitate awareness, training, and adoption of Industry 4.0 among manufacturers, especially MSMEs.
- While it does not provide financial aid, it helps industries improve their digital maturity, trains workforce, and guides them through consultancy and workshops.
New Undersea Cables to Boost India’s Digital Connectivity

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
India is expanding its digital infrastructure with the launch of two major undersea cable systems aimed at enhancing its Internet connectivity with Asia and Europe. The India Asia Xpress (IAX) and India Europe Xpress (IEX) are set to provide additional data links between India and these regions, supporting the growing demand for data usage. This also marks India’s increasing involvement in submarine cable resilience and security discussions.
Key Points:
- New Cable Systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
- Total Length: Both cables, together spanning over 15,000 kilometers, will expand India’s undersea cable network.
- Ownership and Investment:
- Both cable systems are owned by Reliance Jio, with a strategic investment from China Mobile.
- Geopolitical Impact:
- These expansions are a response to growing Internet traffic, as well as India's rising geopolitical ambitions. They help bolster India’s defense strategy, improving cable resilience against disruptions from cyberattacks or physical damages.
- India’s active role in maritime cable network security is being closely watched, especially in key regions like the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea.
- Past Cable Disruptions:
- In March, three cables connecting India to West Asia and Europe were disrupted, impacting Internet traffic. However, India’s alternate routing systems and data centers ensured services remained operational, highlighting the country’s resilience.
- International Role:
- India’s role in submarine cable resilience is growing. Telecom Secretary Neeraj Mittal is part of the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Impact on India’s Connectivity:
- Bangladesh's Role:
- Plans to sell bandwidth from Bangladesh to Northeast India were recently put on hold. However, this does not significantly impact India as Northeast India already benefits from substantial fiber-optic connectivity through Power Grid Corporation of India’s transmission lines.
About Underwater Cables:
- What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber-optic cables laid under the ocean to transmit data across vast distances at high speeds.
- New Cable Systems:
- IAX: Connects India to Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia).
- IEX: Connects India to Europe (France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Djibouti).
- How They Work:
- Fiber-optic technology uses laser beams through thin glass fibers to transmit data.
- The cables are protected by multiple layers of insulation, plastic, and steel wires and are buried near shores or laid directly on the ocean floor in deep sea regions.
- Cable Features:
- Data Capacity: New cables can carry up to 224 Tbps (Terabits per second).
- Durability: Designed to avoid damage from fault zones, fishing areas, or anchors.
- Speed: Faster and more cost-efficient than satellite communications for large-scale data transfer.
Why Undersea Cables Over Satellites?
- Higher Capacity: Submarine cables handle far more data than satellites.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable for high-volume data transfers.
- Reliability: Cables provide more stable connections, especially for large-scale data, compared to satellites.
Kisan Kavach

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Scientists develop ‘kisan kavach’ to shield farmers from pesticide sprays.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The Kisan Kavach is designed to shield farm labourers from harmful pesticide exposure. Pesticides, often neurotoxins, can be detrimental to health, causing symptoms like dizziness, headaches, vomiting, and even death with high exposure.
- Development:
- Developed by Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem), Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Launched by Union Minister of State for Science and Technology.
- Fabric Technology:
- The suit uses oxime fabric, which chemically breaks down common pesticides on contact, preventing them from penetrating the skin.
- Mechanism: The fabric works through nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis, deactivating pesticides upon contact and preventing pesticide-induced toxicity and lethality.
- Components of the Kit:
- Consists of a trouser, pullover, and face-cover.
- Washable and reusable: The suit retains its protective properties even after 150 washes, in a wide temperature range, and under UV light exposure.
- Affordability:
- Priced at ?4,000 per kit, with efforts underway to reduce costs through increased production.
- Field Testing and Efficacy:
- Animal studies: Rodent tests showed that animals exposed to pesticides and covered with ordinary cotton cloth died within four days, while those with the activated fabric remained safe.
- Human trials are still pending.
- Health Implications:
- Pesticides are linked to chronic health issues, including cancer, as per studies by the National Institute of Nutrition (Indian Council of Medical Research).
- Global Context:
- In 2020, India used 61,000 tonnes of pesticides, despite producing much more (2,58,130 tonnes in 2022-2023).
- Pesticide-related health issues are a major concern, with 60% of India’s adult workforce engaged in agriculture.
- Impact:
- The suit aims to protect farm labourers from pesticide exposure and promote sustainable agriculture.
- It could help reduce health complications and improve working conditions for farmers, who often lack proper protective gear.
- Future Plans:
- Awareness campaigns will be conducted to inform farmers about this protective technology.
- Efforts are underway to make the kit more affordable as demand increases.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF), launched by Union Minister Pralhad Joshi aims to support farmers by facilitating post-harvest finance using electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to minimize distress selling and ensure financial security for farmers, particularly small and marginalized ones.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Total Corpus: ?1,000 crore for post-harvest finance.
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?75 lakh.
- Non-agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled and cooperative banks.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- Small and marginal farmers/Women/SC/ST/PwD: 85% for loans up to ?3 lakh, and 80% for loans between ?3 lakh to ?75 lakh.
- Other borrowers: 75% coverage for loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Risks Covered: Both credit risk and warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Fees: 0.4% per annum for farmers, and 1% per annum for non-farmers.
Objectives:
- Minimize distress selling: By providing easy access to loans post-harvest, the scheme helps farmers avoid selling produce at low prices due to cash crunches.
- Instill confidence in banks: The scheme provides a guarantee cover to lenders, encouraging them to offer loans against e-NWRs.
- Encourage warehouse registration: The scheme emphasizes the need for more warehouses, particularly those closer to farmland, to improve accessibility for farmers.
About e-NWRs:
- e-NWRs are digital versions of traditional warehouse receipts that enable farmers to pledge stored commodities as collateral for loans.
- These receipts are governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007, and since 2017, e-NWRs have been mandated for use in transactions related to agricultural produce stored in WDRA-accredited warehouses.
Expected Impact:
- This scheme is expected to boost post-harvest lending, with a target of increasing lending to ?5.5 lakh crore in the next decade.
- It will improve farmers’ income, reduce dependence on informal credit sources, and foster better financial inclusion.
- Additionally, it will create a more reliable supply chain for agricultural produce, enhancing food security.
Future Targets:
- Increase the number of registered warehouses under the WDRA to 40,000 in the next 1–2 years.
- Use platforms like e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi to streamline the lending process and avoid repeated visits to banks.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan agreement to enhance horticulture crop productivity by improving plant health management. This initiative is part of India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to provide farmers with access to certified disease-free planting materials to improve yields, quality, and resilience, particularly against climate change impacts.
Key Highlights of the Loan Agreement
- Objective: Improve access to certified, disease-free planting materials for horticulture crops.
- Implementation: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Focus: The initiative will enhance farmers’ productivity, resilience to climate change, and pest/disease management through the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP).
About the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
The Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme aims to tackle critical challenges in horticulture by ensuring farmers have access to high-quality, virus-free planting materials. The program is designed to:
- Enhance crop yields and quality.
- Promote climate-resilient varieties to help farmers adapt to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Safeguard the environment by controlling plant diseases and pests proactively.
Key Components of the CPP
- Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): Establishment of nine world-class CPCs across India, equipped with advanced diagnostic labs and tissue culture facilities to maintain disease-free foundation planting materials.
- Certification Framework: A robust certification system will be introduced to ensure accountability in planting material production, including accreditation for private nurseries.
- Climate Resilience: Focus on developing and disseminating climate-resilient plant varieties, addressing the growing concerns over extreme weather events and changing pest behavior due to climate change.
Significance of the Loan Agreement
- Climate Adaptation: The project will help farmers mitigate the effects of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns and altered pest/disease behaviors.
- Economic Impact: The initiative aligns with India's vision of self-reliance in horticulture (Atmanirbhar Bharat), boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Long-term Benefits: Improved farm productivity, sustainability, and economic well-being for farmers, especially in the face of climate change.
Global Horticulture Significance
- India’s Position: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, contributing 33% to the agricultural GDP.
- Land Coverage: Horticulture occupies 18% of India’s agricultural land, yet its production surpasses that of food grains.
Implementation and Impact
- Implementation Period: The project will be executed from 2024 to 2030, with 50% financial assistance from ADB.
- Institutional Strengthening: The initiative will bolster India’s ability to manage plant health, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques and capacity-building for horticulture professionals.
'Jalvahak' Scheme for Inland Waterways Promotion

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
Govt Unveils ‘Jalvahak’ To Boost Inland Waterways, Cargo Movement Incentivised on NW1, NW2 & NW16
Key Highlights:
- Launch of 'Jalvahak' Scheme:
- Launched by: Union Minister for Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, on December 15, 2024.
- Objective: The scheme aims to promote the use of inland waterways for long-haul cargo transportation, reduce logistics costs, and alleviate congestion in road and rail networks.
- Targeted Waterways:
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- NW 1: River Ganga
- NW 2: River Brahmaputra
- NW 16: River Barak
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- Incentives:
- The scheme offers up to 35% reimbursement on operating expenses for cargo transported over 300 km via these waterways, particularly using the Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route (IBPR).
- Encouraging Private Operators: The scheme also incentivizes the hiring of vessels owned by private operators to promote competition and efficiency.
- Scheduled Cargo Service:
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Kolkata - Patna - Varanasi - Patna - Kolkata (for NW 1)
- Kolkata - Pandu (Guwahati) (for NW 2 via IBPR)
- Transit Times: Predefined and fixed for efficiency:
- Kolkata to Patna: 7 days
- Patna to Varanasi: 5 days
- Kolkata to Varanasi: 14 days
- Kolkata to Pandu: 18 days
- Pandu to Kolkata: 15 days
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Economic and Environmental Impact:
- Cargo Shift Target: The initiative aims to shift 800 million tonne-kilometres of cargo by 2027.
- Growth Projections:
- 200 million tonnes of cargo by 2030.
- 500 million tonnes by 2047, supporting the Blue Economy and Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- The move to waterways aims to reduce the pressure on India's roads and rail systems, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective logistics system.
- Strategic Goals:
- Modal Shift: The scheme seeks to achieve a shift of 800 million tonne-kilometres by 2027 with an investment of ?95.4 crores.
- Sustainability: Inland waterways are considered an environmentally friendly, efficient, and low-cost transportation mode, with a focus on sustainability.
- Logistics Optimization: This initiative is expected to help optimize supply chains for major shipping companies, freight forwarders, and trade bodies involved in bulk and containerized cargo.
- Implementation Agencies:
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI): The main body responsible for the development and regulation of inland waterways.
- Inland & Coastal Shipping Limited (ICSL): A subsidiary of the Shipping Corporation of India, responsible for the operation of vessels.
- Broader Impact:
- Economic Growth: The scheme is expected to foster economic growth by improving logistics efficiency.
- Decongestion: The initiative aims to decongest the road and rail transport systems, facilitating smoother movement of cargo.
- Regional Connectivity: Enhances connectivity, particularly in eastern India, benefiting areas along the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Barak rivers.
- About the National Waterways:
- India has 14,500 km of navigable inland waterways, which include rivers, canals, and backwaters. These waterways are significantly under-utilized compared to other countries.
- The National Waterways Act, 2016 declared 111 waterways (including both existing and newly identified ones) for navigation.
- The Jalvahak scheme is part of India's broader strategy to unlock the potential of its inland waterways, offering an efficient, economical, and environmentally sustainable alternative for cargo transport.
India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Journey Hits $1 Trillion Milestone
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
India has reached a historic milestone, surpassing $1 trillion in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows since April 2000. This achievement highlights India’s growing status as a major global investment hub and is further validated by a 26% increase in FDI inflows, which reached $42.1 billion during the first half of FY 2024-25.
Key Highlights of India’s FDI Growth:
- $1 Trillion Milestone: India has attracted a total of $1 trillion in FDI from April 2000 to September 2024. This figure includes equity, reinvested earnings, and other capital inflows.
- 26% Growth in FDI: FDI inflows surged by 26% in the first half of FY 2024-25, totaling $42.1 billion.
- Top Investors: Major investors include Mauritius (25%), Singapore (24%), and the United States (10%). These countries benefit from favorable tax treaties with India, boosting investment.
- Dominant Sectors: FDI has flowed into sectors like services, manufacturing, technology, and telecommunications, with significant investments also in pharmaceuticals, automobile, and construction development.
Factors Behind India’s FDI Success:
- Policy Reforms: India’s liberalized FDI policies, such as allowing 100% FDI in most sectors under the automatic route, have attracted foreign capital. Key reforms like abolishing angel tax and reducing corporate tax rates in the Income Tax Act of 2024 have also enhanced investor confidence.
- Business Environment: India’s rise in global competitiveness is evident in its improvement in rankings. It moved from 43rd to 40th in the World Competitiveness Index 2024 and climbed to 40th in the Global Innovation Index 2023, up from 81st in 2015.
- Investor Confidence: The government’s efforts, including initiatives like "Make in India", Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sector-specific incentives, have fostered a conducive environment for investment.
- Global Investment Standing: India has been the third-largest recipient of greenfield projects globally and saw a 64% increase in international project finance deals.
Contribution of Mauritius and Singapore:
- Mauritius and Singapore lead as the primary sources of FDI into India. Their favorable tax treaties with India make them attractive gateways for foreign investments. Mauritius accounted for 25%, and Singapore for 24% of the total FDI inflows.
Key Sectors Attracting FDI:
- Services Sector: Significant growth in services, especially financial services, has attracted substantial foreign investments.
- Manufacturing and Technology: These sectors have benefited from policies like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, which encourage foreign investments in high-tech manufacturing.
- Telecommunications and Pharmaceuticals: India’s growing digital ecosystem and strong pharmaceutical industry continue to attract international investments.
Importance of FDI for India:
- Infrastructure Development: FDI plays a crucial role in financing infrastructure projects, helping meet the country’s significant infrastructure needs.
- Balance of Payments: FDI helps bridge India’s current account deficit, ensuring stable foreign exchange reserves.
- Technology Transfer and Employment: Foreign investments bring advanced technology and create jobs, boosting productivity across sectors.
- Currency Stability: FDI supports the Indian Rupee in global markets by injecting foreign capital.
Challenges:
Despite the positive trends, India faces challenges such as geopolitical tensions, regulatory issues, global economic uncertainty, and infrastructure bottlenecks that can affect investor sentiment and capital inflows.
Way Ahead:
- Focus on Infrastructure: Continued investment in infrastructure development, including public-private partnerships (PPPs), will be crucial for sustained economic growth.
- Workforce Skilling: Collaborative efforts to upskill the workforce will ensure that India can meet the evolving demands of industries.
- Research and Development: Strengthening R&D and innovation will enhance India’s productivity and global competitiveness.
Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India announced the appointment of Sanjay Malhotra as the 26th Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). He replaces Shaktikanta Das, whose six-year tenure ends on December 10, 2024.
Background of Sanjay Malhotra:
- Education & Early Career: Sanjay Malhotra is a 1990-batch IAS officer from the Rajasthan cadre. He holds a degree in Computer Science Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur and a Master’s in Public Policy from Princeton University.
- Professional Experience: Malhotra has over 33 years of experience in various sectors including power, finance, taxation, information technology, and mines. He is currently serving as the Revenue Secretary in the Ministry of Finance, a position he has held since October 2022. Prior to this, he was Secretary of the Department of Financial Services.
- Monetary Policy and Challenges: As RBI Governor, Malhotra will inherit the responsibility of steering India's monetary policy, especially as inflation has been a persistent issue and economic growth has slowed. His first monetary policy review is expected in February 2025.
About the Appointment Process:
RBI Governors are appointed by the Government of India, and the appointment process involves the Financial Sector Regulatory Appointment Search Committee, which includes the Cabinet Secretary, the current RBI Governor, the Financial Services Secretary, and two independent members. The committee prepares a list of eligible candidates, interviews them, and the final decision is made by the Cabinet Committee on Appointments, chaired by the Prime Minister.
RBI Governors Eligibility Criteria
- The RBI Act, 1934 does not mention any specific qualification for the governor. People with different educational backgrounds were selected to head the institution. However, the governor traditionally is either a civil services personnel or an economist.
- Candidates should have prior experience in areas such as:
- Working with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or World Bank.
- Serving as Chairman or General Manager of a bank.
- Holding significant positions in reputable financial or banking organizations.
- Working in the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India.
- The candidate must be an Indian citizen aged 35 years or older.
- The candidate cannot be a member of Parliament, State Legislature, or hold any other office for profit
Key Responsibilities of the RBI Governor:
- Monetary Policy: The RBI Governor chairs the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), which is responsible for setting benchmark interest rates and managing inflation.
- Regulation of Financial Institutions: The Governor oversees the regulation of banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions.
- Currency Management: The Governor ensures the proper issuance of currency and the withdrawal of unfit notes.
- Crisis Management and Policy Execution: The Governor is pivotal in managing financial crises and ensuring the execution of policies related to foreign exchange and financial inclusion.
RBI's Stance on De-dollarisation and Risk Diversification

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
- Governor Shaktikanta Das clarified that India is not pursuing "de-dollarisation," but rather aiming to diversify risk in trade. Measures like local currency trade agreements and Vostro accounts are intended to reduce reliance on the US dollar without eliminating it entirely.
- Objective: The goal is to de-risk India's trade, not to fully replace the dollar, especially amidst rising geopolitical tensions.
Key Highlights:
Vostro Accounts and Local Currency Trade:
- Vostro Accounts: These accounts, held by foreign banks in Indian rupees, facilitate transactions in local currencies, helping mitigate the risks of dollar dependency.
- International Currency Trade: By promoting trade in local currencies, the RBI seeks to reduce exposure to fluctuations in the dollar's value. However, these efforts have faced challenges due to India’s limited international presence in goods and services trade.
Gold Purchases by Central Banks:
- Surge in Gold Purchases: Global central banks, including the RBI, have significantly increased gold holdings. India added 27 tonnes in October 2024 alone, the largest increase among central banks.
- Motivations for Gold: The surge in gold buying reflects growing concerns about geopolitical risks, including the Ukraine war, and the potential for secondary sanctions. Gold is seen as a safe haven asset that diversifies reserves away from the US dollar.
Decline in Dollar Dominance:
- Global Shift: The share of the US dollar in global reserves has been gradually declining, partly due to the rise of the Chinese yuan. Central banks are increasingly turning to gold and alternative currencies as part of a diversification strategy.
- Impact on Emerging Markets: Countries like India are particularly motivated to reduce reliance on the dollar due to geopolitical tensions and economic vulnerabilities linked to the dollar’s dominance.
India’s Domestic Currency Trade Initiatives:
- Trade with Russia and UAE: India is actively exploring trade in domestic currencies with countries like Russia and the UAE to reduce dependence on the dollar. However, these efforts have faced slow uptake due to India’s trade deficit with most countries except the US.
- Challenges in Adoption: Despite efforts to internationalize the rupee, high transaction costs and lack of sufficient demand for rupee-based trade are significant barriers.
BRICS and Shared Currency Discussions:
- Geopolitical Complexity: BRICS nations, due to their geographical and economic diversity, have discussed the possibility of a shared currency, but no consensus has been reached.
- Reluctance Toward Yuan: India has resisted using the Chinese yuan for transactions, particularly for Russian oil imports, despite the yuan’s growing acceptance. This reflects India’s desire to maintain economic sovereignty and avoid over-reliance on a single currency.
Regional Implications of Dollar Volatility:
- Neighbourhood Impact: Countries like Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan have experienced significant financial distress due to declining dollar reserves and surging oil prices, exacerbated by the Ukraine war.
- India’s Resilience: India’s strong dollar reserves have helped it maintain economic stability, but the country remains cautious of dollar volatility, particularly as oil prices rise.
Conclusion:
- Strategic Balance: India’s approach reflects a strategic balance of mitigating risks while ensuring global trade stability. The RBI’s emphasis on gold accumulation and pushing for rupee-based trade demonstrates a desire to reduce exposure to the dollar, but challenges like trade deficits and high transaction costs still hinder the full realization of these goals.
- Economic Sovereignty: Through these measures, India seeks to safeguard its economic sovereignty and financial stability in an increasingly unpredictable global economy.
RBI Cuts CRR, Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently made significant monetary policy decisions that could have a broad impact on the economy.
Key Highlights:
Cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- CRR Reduction: The RBI has reduced the CRR by 50 basis points (bps), from 4.5% to 4%.
- Impact on Banks: This move will free up ?1.16 lakh crore in liquidity, which banks can use to lend, boosting the credit flow in the economy.
- Objective: The CRR cut is aimed at easing the liquidity stress in the financial system, which has been tightening due to RBI's foreign exchange interventions.
- Bank Benefits: Banks will benefit as they don’t earn interest on the CRR, and the extra liquidity may help them reduce deposit rates. Additionally, it may encourage banks to pass on benefits to borrowers, particularly in terms of lending rates.
Repo Rate Kept Unchanged at 6.5%
- Decision: The MPC decided to keep the key policy rate, the Repo rate, unchanged at 6.5%, continuing its stance for the 11th consecutive meeting.
- Reasons for Keeping Repo Rate Steady:
- Persistent inflation, particularly food prices, is a key concern. Despite strong growth in sectors like rural consumption, inflation remains high and continues to affect disposable income.
- RBI Governor emphasized that durable price stability is essential for strong, sustained economic growth.
Impact on Borrowers
- Borrowing Costs: With the Repo rate unchanged, external benchmark lending rates (EBLR) linked to the Repo rate will not rise, providing relief to borrowers by keeping Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) stable.
- Deposit Rates: However, the CRR cut may lead to a marginal reduction in deposit rates due to increased liquidity in the system.
Economic Growth Forecast Adjusted
- Reduced GDP Growth Estimate: The RBI has downgraded the GDP growth forecast for FY25 to 6.6%, down from the earlier estimate of 7.2%. This revision comes after the economy showed signs of slowdown in the second quarter of FY25.
- Growth Outlook: Despite the downgrade, the RBI remains cautiously optimistic about recovery driven by festive demand and rural consumption. Governor Das indicated that the slowdown had likely bottomed out and the economy is set to recover in the coming quarters.
Inflation Forecast Raised
- Inflation Outlook: The inflation estimate for FY25 has been revised upward to 4.8%, compared to the earlier forecast of 4.5%. This is largely due to rising food prices, which surged to a 14-month high of 6.21% in October.
- Inflationary Pressures: The MPC noted that inflation has remained above the RBI’s target of 4%, primarily driven by food inflation. As inflation impacts consumption, the RBI aims to balance growth support with inflation management.
Monetary Policy Stance
- Neutral Stance Retained: The RBI has maintained a ‘neutral’ stance, meaning it is neither tightening nor easing monetary policy drastically, focusing instead on bringing inflation closer to its target of 4%.
- Inflation Control: While the RBI is aware of the economic slowdown, it continues to prioritize inflation control to ensure price stability and support sustainable growth.
Global and Domestic Economic Context
- Global Factors: The RBI has also been cautious about global developments, including capital outflows and the impact of U.S. monetary policy on the Indian economy. A rate cut could have further weakened the rupee by narrowing the interest rate differential with the U.S.
- Domestic Concerns: Domestically, the economy faces challenges such as weak manufacturing growth and high inflation. The GDP growth in Q2 FY25 dropped to 5.4%, a seven-quarter low, highlighting concerns over demand and inflationary pressures.
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, the world’s largest domestic rooftop solar initiative, is transforming India’s energy landscape with a bold vision to supply solar power to one crore households by March 2027.
Key Details:
Targeted Installations:
- 10 lakh installations by March 2025.
- 1 crore installations by March 2027.
Subsidy and Financing:
- Offers up to 40% subsidy for rooftop solar installations based on household electricity consumption.
- Collateral-free loans available for up to 3 kW solar systems at a 7% interest rate.
Key Benefits:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana offers several significant benefits to participating households:
- Free Electricity for Households: The scheme provides households with free electricity through the installation of subsidized rooftop solar panels, significantly reducing their energy costs.
- Reduced Electricity Costs for the Government: By promoting the widespread use of solar power, the scheme is expected to save the government an estimated ?75,000 crore annually in electricity costs.
- Increased Use of Renewable Energy: The scheme encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix in India.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: The transition to solar energy under this scheme will help lower carbon emissions, supporting India's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Eligibility Criteria:
1. The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
2. Must own a house with a roof that is suitable for installing solar panels.
3. The household must have a valid electricity connection.
4. The household must not have availed of any other subsidy for solar panels.
Impact
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana is expected to have far-reaching outcomes, both for individual households and the nation as a whole:
- Household Savings and Income Generation: Households will benefit from significant savings on their electricity bills. Additionally, they will have the opportunity to earn extra income by selling surplus power generated by their rooftop solar systems to DISCOMs. For instance, a 3-kW system can generate over 300 units per month on average, providing a reliable source of energy and potential revenue.
- Expansion of Solar Capacity: The scheme is projected to add 30 GW of solar capacity through rooftop installations in the residential sector, significantly contributing to India's renewable energy goals.
- Environmental Benefits: Over the 25-year lifetime of these rooftop systems, it is estimated that the scheme will generate 1000 BUs of electricity while reducing CO2 emissions by 720 million tonnes, making a substantial positive impact on the environment.
- Job Creation: The scheme is also expected to create approximately 17 lakh direct jobs across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, supply chain, sales, installation, operations and maintenance (O&M), and other services, thereby boosting employment and economic growth in the country.
Model Solar Village
- Under the "Model Solar Village" component of the scheme, the focus is on establishing one Model Solar Village per district throughout India.
- This initiative aims to promote solar energy adoption and empower village communities to achieve energy self-reliance.
- An allocation of ?800 crore has been designated for this component, with ?1 crore provided to each selected Model Solar Village.
- To qualify as a candidate village, it must be a revenue village with a population of over 5,000 (or 2,000 in special category states). Villages are selected through a competitive process, evaluated on their overall distributed renewable energy (RE) capacity six months after being identified by the District Level Committee (DLC).
- The village in each district with the highest RE capacity will receive a central financial assistance grant of ?1 crore.
- The State/UT Renewable Energy Development Agency, under the supervision of the DLC, will oversee the implementation, ensuring these model villages successfully transition to solar energy and set a benchmark for others across the country.
RangeenMachli App
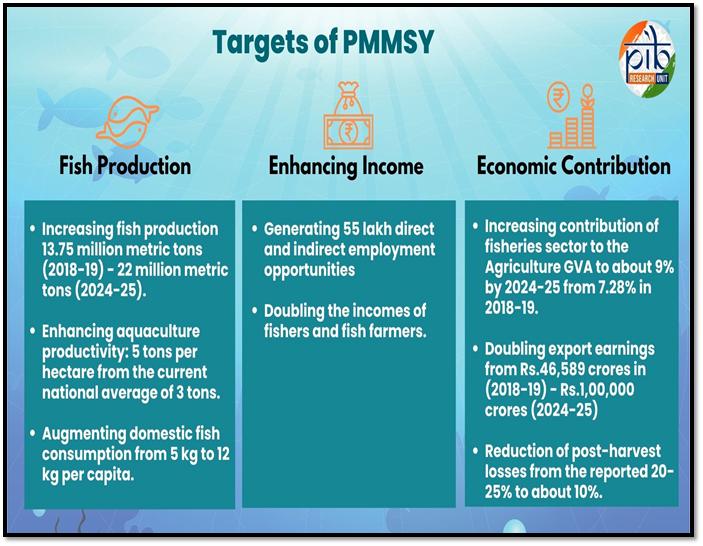
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The app was developed by the ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA) with support from the Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India.
Key Highlights:
- Target Audience: The app caters to hobbyists, farmers, and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Multilingual Support: The app offers content in eight Indian languages, making it accessible to a broad and diverse audience.
- Main Objectives:
- Provide information on popular ornamental fish species and their care.
- Promote local aquarium businesses through dynamic directories.
- Enhance knowledge of ornamental aquaculture techniques for fish farmers and shop owners.
- Serve as an educational tool for newcomers and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Salient Features:
- Multilingual Content: Ensures broader reach and user accessibility.
- Comprehensive Fish Information: Offers detailed guidance on fish care, breeding, and maintenance.
- Find Aquarium Shops Tool: A directory updated by shop owners, helping users find reliable local aquarium shops and promoting local businesses.
- Educational Modules:
- Basics of Aquarium Care: Covers key aspects like aquarium types, filtration, lighting, feeding, and maintenance.
- Ornamental Aquaculture: Focuses on breeding and rearing ornamental fish, particularly for farmers.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Promoting Local Businesses: The app encourages economic growth by increasing visibility for local aquarium shops and creating opportunities for business owners.
- Authenticity and Reliability: Users can access verified information, reducing the reliance on unverified sources and promoting healthier aquariums.
- Sustainability and Growth: The app’s features are designed to foster sustainability and growth in the ornamental fish trade by providing reliable information and empowering users.
Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Objective: Aimed at transforming the fisheries sector, improving fish production, productivity, quality, technology, infrastructure, and management, while strengthening the value chain and promoting the welfare of fishers.
- Launch: The scheme was launched in 2020 with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores for a 5-year period (2020-21 to 2024-25).
- Focus Areas:
- Inland fisheries and aquaculture.
- Fisheries management and regulatory framework.
- Infrastructure and post-harvest management.
- Doubling fishers' and fish farmers' incomes.
- Components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS): Fully funded by the central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS): Partially funded by the central government and implemented by states.
- Sub-Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri MatsyaKisanSamridhiSah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY): Launched under PMMSY to formalize the fisheries sector and support micro and small enterprises with over Rs. 6,000 crore investment (FY 2023-24 to 2026-27).
- Beneficiaries: Includes fishers, farmers, fish vendors, fisheries cooperatives, SC/STs, women, differently-abled persons, state and central entities, and private firms.
Fisheries Sector Contribution:
- Supports around 30 million people.
- India is the 3rd largest fish producer globally, with a fish production of 175.45 lakh tons in FY 2022-23.
- Contributes 1.09% to the Gross Value Added (GVA) of India and 6.72% to agricultural GVA.
Related Schemes:
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Launched with a fund of Rs. 7,522.48 crore.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Extended to fishers and farmers from FY 2018-19.
- Sustainable fisheries development.
- Doubling income and job creation in the sector.
- Boosting exports and agricultural GVA.
- Social and economic security for fishers.
Trade Watch Quarterly
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
NITI Aayog released its first quarterly report, Trade Watch Quarterly (TWQ), on December 4, 2024, focusing on India's trade developments during Q1 FY2024 (April-June).
Overview:
- Purpose: The publication aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of India’s trade performance, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Target: To leverage insights for evidence-based policy interventions and foster informed decision-making, contributing to sustainable growth in India’s trade.
Trade Performance Highlights (Q1 FY24):
- Total Trade: $576 billion (5.45% YoY growth).
- Merchandise Exports: Growth was restrained due to declines in iron & steel, and pearls.
- Imports: Driven by high-value goods, including aircraft, spacecraft, mineral fuels, and vegetable oils.
- Services Exports: Displayed a surplus, particularly in IT services.
- Growth in Services Exports: A positive trend, rising by 10.09% YoY, particularly in IT services and business solutions.
Key Challenges for India’s Trade:
- Limited Success in China-Plus-One Strategy:Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia have gained more from this strategy, benefitting from cheaper labor, simplified tax laws, and lower tariffs.
- CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism):Starting in 2026, CBAM will impose carbon taxes on imports like cement, steel, and fertilizers. India’s iron and steel industry could face significant risks due to this.
- Declining Share in Labor-Intensive Sectors:India’s global market share in labor-intensive sectors (e.g., textiles, leather) has declined despite a strong workforce.
- Geopolitical Instability (West Asia):
- Oil price hikes could increase India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) and fuel inflation.
- Declining agricultural exports to markets like Iran further add to the challenges.
Strategic Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges:
- Infrastructure Modernization:
- Expansion of digital platforms like Trade Connect e-Platform to streamline processes and support exporters.
- Strengthening logistics via the National Logistics Policy.
- Export Incentives:Continuation of schemes like RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) to maintain export competitiveness.
- Technological Integration:Leveraging digital trade to tap into high-growth sectors and foster innovation in trade.
- Strengthening FTAs (Free Trade Agreements):Focus on negotiating strategic FTAs with global partners (e.g., the UK and the EU) to reduce trade barriers and enhance global market access.
Geopolitical and Environmental Risks:
- U.S.-China Trade Tensions:Offers opportunities for India to diversify its supply chains, but also poses challenges in terms of overdependence on certain countries.
- Impact of CBAM:Risk to carbon-intensive Indian exports like steel and aluminium, which will face tariffs starting in 2026.
Sectoral Performance:
- Growing Sectors:
- IT Services: India’s market share of IT services reached 10.2%, continuing to be a strong contributor.
- Pharmaceuticals, Electrical Machinery, and Mineral Fuels: Significant contributors to export growth.
- Declining Sectors:Labor-Intensive Goods: Declines in global market share for textiles, pearls, and leather.
Pathway to $2 Trillion Exports by 2030:
- India's Export Aspirations:To achieve the target of $2 trillion in exports by 2030, India must address structural inefficiencies, diversify exports, and reduce trade barriers.
- Vision 2047:Aligning with India’s broader vision to become a developed nation, the report stresses the importance of strengthening trade, technology, and infrastructure to realize these ambitions.
- Trade's Role in Economic Growth:
- Trade is vital to India’s economic trajectory, contributing significantly to GDP growth.
- Through evidence-based policymaking, infrastructure modernization, and strategic global partnerships, India can achieve sustained growth in trade, leading to the realization of a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
International Debt Report 2024
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently released, World Bank’s "International Debt Report 2024" highlights a worsening debt crisis for developing nations, with 2023 marking the highest debt servicing levels in two decades, driven by rising interest rates and economic challenges.
Key Highlights:
Rising Debt Levels:
- Total external debt of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) reached $8.8 trillion by the end of 2023, an 8% increase since 2020.
- For IDA-eligible countries (those receiving concessional loans from the World Bank), external debt rose by 18%, reaching $1.1 trillion.
Debt Servicing Costs:
- Developing nations paid a record $1.4 trillion in debt servicing costs (principal and interest) in 2023.
- Interest payments surged by 33%, totaling $406 billion, putting immense pressure on national budgets, especially in critical sectors like health, education, and environmental sustainability.
Interest Rate Increases:
- Interest rates on loans from official creditors doubled to 4% in 2023.
- Rates from private creditors rose to 6%, the highest in 15 years, exacerbating the financial burden on developing countries.
Impact on IDA-Eligible Countries:
- IDA countries faced severe financial strain, paying $96.2 billion in debt servicing, including $34.6 billion in record-high interest costs (four times higher than a decade ago).
- On average, 6% of their export earnings were allocated to debt payments, with some countries dedicating up to 38%.
Role of Creditors:
- Private creditors reduced lending, leading to more debt-servicing payments than new loans.
- In contrast, multilateral lenders like the World Bank provided additional support, with the World Bank contributing $28.1 billion.
- Multilateral institutions have emerged as crucial support systems, becoming "lenders of last resort" for poor economies.
Debt Data Transparency:
- Efforts to improve debt transparency led to nearly 70% of IDA-eligible economies publishing accessible public-debt data in 2023, a 20-point increase since 2020.
- Accurate debt data can reduce corruption and promote sustainable investment.
Global Financial Reforms:
- There is a growing call for global financial reforms to address the systemic challenges of developing nations facing rising debt burdens.
- Proposed measures include increased concessional financing, improved restructuring mechanisms, and the establishment of a Global Debt Authority for better debt management.
Impact on Climate and Development Goals:
- Debt servicing has become a larger financial burden than climate initiatives in many countries, with developing nations spending more on debt servicing than climate goals (2.4% of GDP vs. 2.1% for climate investments).
- To meet climate commitments under the Paris Agreement, climate investments would need to rise to 6.9% of GDP by 2030.
Debt Relief Initiatives:
- Programs like the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative and the Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI) provide debt relief to the world’s poorest nations, helping them meet Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- For instance, Somalia saved $4.5 billion in debt service after completing the HIPC program in December 2023.
Global Sovereign Debt Roundtable (GSDR):
- The GSDR brings together debtor nations and creditors (both official and private) to improve debt sustainability and address restructuring challenges.
- Co-chaired by the IMF, World Bank, and G20, the forum aims to find coordinated solutions for sovereign debt issues.
KisanPehchaan Patra
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government is actively promoting the creation of digital identities for farmers through the KisanPehchaan Patra (Farmer ID). The initiative is an essential part of the Digital Agriculture Mission under the AgriStack initiative.
Key Details:
Objective:
- The main goal is to provide digital IDs linked to Aadhaar for farmers, capturing comprehensive agricultural data including land records, crop information, and ownership details.
- These digital identities are designed to enhance farmers' access to government schemes and digital agriculture services.
Farmer ID Creation Timeline:
- The government plans to create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers in phases:
- 6 crore farmers in FY 2024-25.
- 3 crore farmers in FY 2025-26.
- 2 crore farmers in FY 2026-27.
AgriStack Initiative:
- The AgriStack initiative aims to build a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for the agriculture sector, which includes:
- Farmers' Registry.
- Geo-referenced village maps.
- Crop Sown Registry.
Implementation Strategy:
- Camp-mode approach: States have been instructed to organize field-level camps to ensure faster and inclusive registration of farmers.
- Financial Incentives:
- States will receive ?15,000 per camp for organizing these camps.
- Additionally, ?10 per Farmer ID issued.
- Funding is provided through the Pradhan Mantri KisanSamman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme.
Benefits of Digital Farmer ID:
- Targeted Delivery of Benefits: Ensures subsidies and benefits reach legitimate farmers and eliminates duplication.
- Precision Agriculture: Supports data-driven policies for better crop planning, insurance, and market linkages.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates easy access to credit, loans, and crop insurance, empowering farmers financially.
- Better Monitoring: Helps in tracking the actual implementation of schemes and ensures that only eligible farmers benefit.
Progress in States:
- Advanced States: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh have made significant progress in issuing digital Farmer IDs.
- Testing Phase: States like Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha are still in the field-testing phase.
- Special Assistance Scheme: The Finance Ministry allocated ?5,000 crore in August 2024 to assist states in creating the Farmers' Registry, with funds available until March 2025.
Linkage with Land Records and Crop Data:
- The Farmer ID integrates with state land records and crop data, creating a dynamic and accurate database known as the Farmer’s Registry.
- This data helps in the development of better agricultural policies and decision-making.
Digital Agriculture Mission:
- The government approved a substantial outlay of ?2,817 crore for the Digital Agriculture Mission, which is intended to modernize agricultural practices and build robust digital infrastructure.
- The mission also includes the launch of the Digital Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), which will help in crop estimation and better resource allocation.
National Policy on Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India is working on a national policy to enhance female labour force participation (FLFP), focusing on creating a supportive care economy structure.
- The policy is being developed by an inter-ministerial team involving the Ministries of Skill Development, Labour, Rural Development, and Women and Child Development.
- Goal: To reduce barriers for women, especially related to caregiving responsibilities, and increase their participation in the workforce.
Key Focus Areas:
- Care Economy: Involves both paid and unpaid caregiving services, such as childcare, eldercare, domestic work, and health services.
- The policy aims to formalize care work, addressing its undervaluation and encouraging women's workforce participation.
- Proposes a core skilling package for caregivers, particularly for childcare in rural and informal sectors.
- Childcare Facilities: Targeting women working under schemes like MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme).
Current Challenges:
- Post-marriage employment drop: Women face a significant decline in workforce participation after marriage, often due to caregiving roles.
- In India, 53% of women are outside the labour force, mostly due to unpaid domestic work, unlike only 1.1% of men.
- The gender divide in caregiving is stark: Women spend over 5 hours daily on unpaid domestic work (81% of females), compared to 12.4% of males.
Key Initiatives:
- Palna Scheme: Provides daycare through Anganwadi-cum-Crèche facilities for working parents, benefiting children aged 6 months to 6 years. 1,000 crèches are operational.
- Women’s Employment Data:
- In rural India, 36.6% of women participate in the workforce, compared to 23.8% in urban areas.
- Post-marriage, female employment drops by 12 percentage points, even without children.
- Improving Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP): Key to India's growth, as matching women’s workforce participation with men could boost GDP by 27% (IMF).
Barriers to Women’s Workforce Inclusion:
- Unpaid Care Work: Women's disproportionate share of household duties limits paid employment opportunities.
- Cultural Norms: Gender expectations restrict women’s access to employment, especially in rural areas.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to education for girls restricts skill development, lowering job prospects.
- Health & Safety Issues: Health challenges and safety concerns at workplaces hinder women's workforce participation.
- Lack of Supportive Policies: Absence of parental leave and flexible work arrangements for women, especially in the informal sector.
Government Initiatives for Women’s Employment:
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao: Promotes girl child education and empowerment.
- National Education Policy (NEP): Ensures gender equity in education.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks and mandates crèche facilities in large establishments.
- Labour Codes (2019-2020): Codifies labor laws to provide a framework for improving women’s workplace safety and employment opportunities.
Global Examples & Inspiration:
- Japan’s Womenomics: Aimed at increasing female participation, Japan's womenomics reforms have grown women’s labour force participation from 64.9% to 75.2% (2013-2023).
- Flexible Work Models: Countries like Netherlands encourage part-time and remote work, offering flexibility to manage work-life balance.
- Sweden’s Investment in ECCE: Investing 1% of GDP in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) has significantly reduced women’s workforce exclusion.
Way Forward:
- National Women’s Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA): Promotes gender-balanced work environments and childcare facilities at work sites.
- Flexible Work Options: Encouraging remote work, parental leave, and childcare support will empower more women to balance caregiving and employment.
- Investment in the Care Economy: To reduce the care burden on women, substantial investment in ECCE and related sectors is essential to increase women’s participation and economic independence.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
SASCI Scheme for Tourism Development
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Centre clears scheme for development of 40 tourist destinations across 23 States at a cost of ?3,295 crore.
Key Details:
- Focus Areas: The scheme encourages the development of lesser-known destinations such as Bateshwar (Uttar Pradesh), Ponda (Goa), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh), and Porbandar (Gujarat) to reduce overcrowding at popular sites.
- Implementation Timeline: Projects must be completed within two years, with funding released in stages until March 2026.
- Key Features:
- Long-term interest-free loans for 50 years.
- States responsible for project execution and maintenance, often through public-private partnerships (PPP).
- The Ministry of Tourism will monitor progress, and 66% of the funds have already been released.
- Emphasis on sustainability and boosting local economies by creating jobs through tourism.
- States must provide land at no cost and ensure proper infrastructure like safety, connectivity, and utilities.
Selection Criteria for Projects:
- Consultation Process: Detailed regional consultations led to the selection of 40 projects from 87 proposals received by the Ministry of Tourism. West Bengal was the only state not submitting proposals.
- Evaluation Criteria: Projects were evaluated based on:
- Connectivity, tourism potential, and ecosystem.
- Financial viability and sustainability.
- Impact on local economy and job creation.
- Funding Pattern:
- A maximum of ?100 crore for each project, with higher funding considered for exceptional projects.
- Total funding capped at ?250 crore per state, allocated on a first-come, first-served basis.
Importance of the Scheme:
- Economic Growth & Employment: Projects are designed to stimulate local economies, create employment, and promote sustainable tourism.
- Global Branding: The scheme aims to brand and market tourist destinations on a global scale.
- Tourism Infrastructure Growth: It aims to improve the entire tourism value chain, including transportation, accommodation, activities, and services.
Tourism Sector Overview:
- Current Status:
- India ranks 39th among 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) increased by 47.9% in 2023, with 9.52 million tourists.
- Tourism contributed 5% to India’s GDP in 2022-23 and created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs.
- India earned ?2.3 lakh crore in foreign exchange in 2023 through tourism.
- Projected revenue from tourism to exceed $59 billion by 2028.
- Initiatives for Promotion:
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: To develop theme-based circuits.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2020): Promotes domestic tourism.
- PRASHAD & HRIDAY Schemes: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage city development.
MGNREGA Job Card Deletions Issue:
- Context: A significant surge in deletions of job cards under MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) raised concerns over transparency and workers’ rights.
- Reasons for Deletion:
- Permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and refusal to work.
- Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) implementation led to deletions for non-linked cards.
- Implications:
- Violation of workers’ legal right to employment, especially when deletions were made without due process.
- The "Not willing to work" designation undermines livelihood opportunities, especially in high unemployment rural areas.
- Recommendations for Reform:
- Strengthening verification processes and ensuring deletions follow due procedure.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas to review and approve deletions.
- Regular audits and better grievance redressal mechanisms.
Other Government Initiatives in Tourism:
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD): For holistic and sustainable development of pilgrimage tourism.
- Incredible India & E-Visa Initiatives: To attract more foreign tourists.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN): Enhances air connectivity to remote tourist destinations.
- National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): Preserves and rejuvenates heritage sites.
13th National Seed Congress (NSC)

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 13th National Seed Congress (NSC), organized by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, concluded with significant discussions and outcomes focused on advancing India's seed sector.
- The theme for this year's congress, held in Varanasi, was "Innovating for a Sustainable Seed Ecosystem."
Key Highlights:
- Focus Areas:
- Seed Technologies and Biofortification: Emphasis on high-nutrition seeds like iron and zinc-enriched rice and Vitamin A-rich crops to combat malnutrition.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Promoting practices like Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) and the development of stress-tolerant seed varieties to withstand climate change.
- Challenges in India’s Seed Ecosystem:
- Seed Replacement Rate (SRR): SRR in India is around 15-20%, with 100% for hybrid seeds, pointing to the need for higher adoption of certified seeds.
- Monoculture and Seed Market Monopoly: Issues like over-reliance on Bt cotton and domination by multinational companies (e.g., Bayer) in seed markets.
- Government Initiatives:
- National Seed Corporation (NSC): Produces foundation and certified seeds for over 600 varieties.
- Seed Village Programme (Beej Gram Yojana): Focus on improving the quality of farm-saved seeds.
- National Seed Reserve: Ensures seed availability during climatic disruptions.
- Policy Discussions:
- Proposed Seeds Bill: A new bill to regulate seed quality and promote sustainable practices.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations to improve seed production, accessibility, and quality.
- Outcomes:
- Biofortified Seeds: Increased development and distribution of nutrient-rich seeds.
- Climate-Resilient Seed Systems: Enhanced focus on developing crops that can withstand climate challenges.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations in seed technology and policy reform.
Global Wage Report 2024-25

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
A new report from the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000. Despite this positive trend, significant wage differentials persist worldwide.
Global Wage Inequality Trends:
- Wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000.
- Average Annual Decrease in Wage Inequality:
- Ranges from 0.5 to 1.7% globally, depending on the measure used.
- More significant reductions have been observed in low-income countries, where the decrease has ranged from 3.2 to 9.6% over the past two decades.
- Wealthier Countries: Wage inequality has decreased at a slower pace:
- Upper-middle-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 1.3%.
- High-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 0.7%.
Global Real Wage Growth:
- Global real wages grew by 1.8% in 2023, with projections reaching 2.7% growth in 2024 (highest increase in over 15 years).
- This marks a recovery from the negative global wage growth of -0.9% in 2022 due to high inflation rates.
Regional Wage Growth:
- Emerging Economies: Saw stronger wage growth than advanced economies.
- Emerging G20 economies: 1.8% growth in 2022 and 6.0% growth in 2023.
- Advanced Economies: Faced real wage declines.
- G20 advanced economies: Declined by -2.8% in 2022 and -0.5% in 2023.
- Fastest Wage Growth: Observed in regions like Asia-Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Wage Inequality Persistence:
- Income Distribution: The lowest-paid 10% of workers earn just 0.5% of the global wage bill, while the highest-paid 10% earn nearly 38%.
- Wage Inequality in Low-Income Countries: Particularly high, with nearly 22% of wage workers classified as low-paid.
- Women and Informal Economy Workers: More likely to be among the lowest-paid workers, underscoring the need for targeted actions to close wage and employment gaps.
Non-Wage Workers:
- Globally, one in every three workers is a non-wage worker.
- In low- and middle-income countries, many workers are self-employed in the informal economy, which skews overall income inequality measures.
- Income inequality in these regions is higher when including self-employed workers, especially those in informal employment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Targeted Policies: To reduce wage inequality, countries need stronger wage policies and structural support for equitable growth.
- Focus Areas:
- Promote productivity and decent work.
- Formalization of the informal economy to help reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth: The ILO emphasizes that national strategies should aim for inclusive economic growth to achieve fair wages and reduce wage gaps.
Key ILO recommendations include:
- Setting wages through social dialogue: wages should be set and adjusted through collective bargaining or agreed minimum wage systems involving governments, workers and employers.
- Taking an informed approach: wage-setting should take into account both the needs of workers and their families and economic factors.
- Promoting equality, and equal opportunity of treatment and outcomes: wage policies should support gender equality, equity and non-discrimination.
- Using strong data: decisions should be based on reliable data and statistics.
- Addressing root causes of low pay: national policies should reflect each country’s specific context and address the causes of low pay such as informality, low productivity and the under-valuing of jobs in sectors such as the care economy.
India's Gig Economy
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The gig economy market is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17 per cent to reach a gross volume of $455 billion by 2024, according to a white paper by the Forum for Progressive Gig Workers.
Key Sectors Supported by Gig Workers:
- E-commerce: Gig workers play a crucial role in driving growth in the e-commerce sector.
- Transportation and Delivery Services: These sectors are heavily dependent on gig workers for their operations and services.
Impact on Employment:
- Job Creation: The gig economy has the potential to create a significant number of jobs, especially in tier 2 and 3 cities, which are emerging as new growth hubs.
- Alternate Revenue Streams: Gig work provides diverse income opportunities for workers, especially for women, offering them a flexible mode of earning.
Contribution to GDP:
- The gig economy’s contribution is expected to add 1.25% to India’s GDP over time, highlighting its growing economic importance.
Technological Integration and Future Prospects:
- AI and Digital Innovation: Future growth is expected to be driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, and digital innovation, fostering sustainable and inclusive job opportunities.
Social and Economic Benefits:
- Women's Workforce Participation: The gig economy provides women with more earning opportunities and helps integrate them into the workforce.
- Welfare Initiatives: Platforms supporting gig workers are increasingly focusing on welfare initiatives, improving the overall working conditions in the sector.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Challenges: The evolving dynamics between large companies and gig workers pose challenges in terms of worker rights and fair compensation.
- Opportunities: The growth of the gig economy presents opportunities for companies to innovate and create inclusive work environments, especially for underserved communities.
Future Developments:
- Formal Report: The Forum for Progressive Gig Workers plans to collaborate with global organizations to release a formal report with deeper insights and actionable recommendations for the future of gig work
BioE3 Policy

- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The BioE3 Policy outlines guidelines and principles for enabling mechanisms for ‘Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing’ in the country across diverse sectors.
Key Highlights:
Primary Objective:
- Set a framework for the adoption of advanced technologies and innovative research to promote biomanufacturing in India.
- Focus on enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and quality in biomanufacturing.
Alignment with National Goals:
- Supports India’s vision of Green Growth (Union Budget 2023-24) and Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), promoting sustainability.
- Aligns with India’s goal of achieving a Net-Zero carbon economy.
- Supports the Biomanufacturing and Biofoundry initiative announced in the Interim Budget 2024-25.
Key Objectives:
- Revolutionize biomanufacturing for better product quality and environmental sustainability.
- Accelerate the development and commercialization of bio-based, high-value products.
- Foster high-performance biomanufacturing across diverse sectors.
Achievements of Indian Bioeconomy (2014-2023):
- Contribution to GDP: Bioeconomy contributes 4.25% to India’s GDP of $3.55 trillion (as of Dec 2023).
- Growth of Bioeconomy: From $10 billion in 2014 to $151 billion in 2023, surpassing 2025 target.
- Increase in Biotech Startups: From 50 startups in 2014 to 8,531 startups in 2023.
Implementation Strategy:
- Establish BioEnablers including Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs, Biofoundries, and Biomanufacturing Hubs across India.
- Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs will support research and innovation using data-driven approaches and AI to develop technologies for bio-based products.
- Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs will provide infrastructure to scale up bio-based technology for commercial applications.
Focus on Human Resource Development:
- Bio-Enablers will offer training and internships to build a skilled workforce with interdisciplinary and technical skills required for biomanufacturing.
Sectoral Focus Areas:
- Based on consultations, six thematic sectors of national importance have been identified for implementation:
- Bio-based chemicals and enzymes
- Functional foods and smart proteins
- Precision biotherapeutics
- Climate-resilient agriculture
- Carbon capture and utilization
- Futuristic marine and space research
- Sectoral Expert Committees are addressing challenges and gaps identified for each of these sectors.
Government Support:
- The DBT-BIRAC (Department of Biotechnology and Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council) has called for proposals to establish Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs in academia and industry.
- These hubs will support innovation and commercialization of biomanufacturing technologies.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the launching of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) as a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare.
Key Highlights
Objective & Focus:
- Launch of NMNF by the Union Cabinet to promote chemical-free farming in India.
- Aim to improve soil health, reduce input costs, and produce nutritious food.
- Support the shift to natural farming (NF), emphasizing local knowledge and agro-ecological principles.
Financial Allocation:
- Total Outlay: ?2481 crore (Government of India share ?1584 crore, State share ?897 crore) until FY 2025-26.
Key Features of NMNF:
- Coverage: Targeting 15,000 clusters in Gram Panchayats, covering 7.5 lakh hectares and impacting 1 crore farmers.
- Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs): 10,000 BRCs to supply ready-to-use natural farming inputs.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and Agricultural Universities (AUs): Establishment of 2,000 model demonstration farms for hands-on training in natural farming techniques.
- Farmer Training: 18.75 lakh farmers to be trained in NF practices such as preparation of organic inputs like Jeevamrit and Beejamrit.
- Krishi Sakhis/CRPs: Deployment of 30,000 workers for farmer mobilization and awareness.
Implementation Strategy:
- Farmer Certification System: Providing easy, simple certification for marketing natural farming produce with dedicated branding.
- Monitoring: Real-time, geo-tagged monitoring of implementation through an online portal.
- Convergence with other government schemes and organizations for market linkages and support.
Natural Farming Practices:
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): Promote sustainable farming by using local livestock and diverse crop systems.
- Benefits: Reduce dependence on external inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, rejuvenate soil quality, and increase resilience to climate risks (e.g., drought, floods).
- Encourage biodiversity, and improve soil carbon content and water-use efficiency.
Targeted Areas and Farmer Support:
- Focus on areas where NF practices are already being followed or where farmer producer organizations (FPOs) or self-help groups (SHGs) are active.
- Training through model demonstration farms will focus on practical, location-specific NF techniques tailored to regional agro-ecologies.
Impact on Agriculture and Environment:
- Environmental Impact: Encourages sustainable farming by reducing chemical exposure, improving soil health, and promoting climate resilience.
- Farmer Well-being: By reducing input costs and promoting nutritious food, it aims to improve farmer incomes and family health.
- Contributing to the long-term health of the environment, ensuring a healthy Mother Earth for future generations.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Soil Nutrient Compromise: Concerns that some crops, like rice, might require chemical fertilizers (e.g., NPK) for optimal growth, which may not be sufficiently replaced by organic manure alone.
- The shift to natural farming requires significant awareness and training to ensure sustainable and productive yields.
Institutional Framework:
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is the implementing body.
- Collaboration with KVKs, AUs, and farmer organizations ensures grassroots level support and knowledge dissemination.
Riyadh Design Law Treaty (DLT)

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- India reaffirms its commitment to inclusive growth and strengthening its intellectual property (IP) ecosystem.The signing of the treaty comes after nearly two decades of negotiations.
Key Highlights:
Purpose of the DLT:
- Aims to harmonize industrial design protection frameworks across multiple jurisdictions.
- Improves efficiency and accessibility of design registration processes.
Key Features of the DLT:
- Grace Period: A 12-month grace period after the first disclosure of the design, ensuring its validity for registration.
- Flexibility for Applicants: Provides relief measures such as relaxed deadlines, reinstatement of lost rights, and flexibility in adding priority claims.
- Simplified Processes: Includes simplified procedures for design renewals, assignment, and license recording.
- E-Filing Systems: Promotes the adoption of electronic filing systems and exchange of priority documents.
Benefits of DLT:
- Empowering SMEs and Startups: Helps small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups protect designs globally, enhancing competitiveness and market growth.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Standardizes procedures, making the design protection process less complex, more predictable, and affordable.
- Support for Developing Countries: Offers technical assistance for implementation in developing and least-developed countries.
Significance for India:
- India’s rich heritage of design and craftsmanship underscores the importance of design protection for sustainable economic growth.
- Design registrations in India have surged, with a 120% increase in domestic filings over the last two years.
Supporting Programs:
- The treaty’s provisions align with India’s initiatives like Startup India and the Startups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) Scheme to boost the protection and commercialization of designs for Indian innovators.
Broader Impact:
- DLT aims to integrate design protection with traditional knowledge and cultural expressions, further enhancing protection for India’s diverse creative sectors.
About WIPO:
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, is a specialized UN agency established in 1967, promoting IP rights globally.
- India is a member of WIPO, which has 193 member countries.
Overview of Intellectual Property (IP):
- IP includes creations like inventions, industrial designs, literary and artistic works, symbols, and more, which are used in commerce.
- IP rights protect creators, allowing them to benefit from their work when commercially exploited.
National Gopal Ratna Award 2024
- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) declared the winners of the National Gopal Ratna Awards(NGRA); one of the highest National Awards in the field of livestock and dairy sector for the year 2024.
About the National Gopal Ratna Awards (NGRA):
- Purpose:Recognize and encourage individuals, AI technicians, dairy cooperatives, and farmer organizations in the livestock and dairy sector.
- Categories:
- Best Dairy Farmer (Indigenous Cattle/Buffalo Breeds)
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT)
- Best Dairy Cooperative/Milk Producer Company (MPC)/Dairy Farmer Producer Organization
- Addition (2024):Special awards for North Eastern Region (NER) to promote dairy development in the area, with winners in all three categories.
- and Prizes:
- Rs. 5 lakhs for 1st rank, Rs. 3 lakhs for 2nd rank, Rs. 2 lakhs for 3rd rank, and Rs. 2 lakhs for Special NER Award in the categories of Best Dairy Farmer and Best Dairy Cooperative/FPO/MPCs.
- For Best AIT, winners will receive a Certificate of Merit and a memento.
- Process:Winners selected from 2,574 applications via an online portal (https://awards.gov.in).
- The livestock sector is crucial for India's economy, contributing significantly to agriculture and providing livelihood, especially for small and marginal farmers, women, and landless laborers.
- Indigenous breeds have immense genetic potential, but their population and performance have been declining. To address this, the Rashtriya Gokul Mission was launched under the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development in 2014 to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
National Milk Day
- It is celebrated annually on November 26 in India to honor the significant contributions of milk and the dairy industry to the country's development.
- The day commemorates the birth anniversary of Dr VergheseKurien, the "Father of the White Revolution" in India, who played a pivotal role in transforming India into the largest producer of milk globally.
- National Milk Day was first celebrated on November 26, 2014, after the Indian Dairy Association (IDA), along with various dairy institutions across the country.
Nepal-Bangladesh Power Transfer via India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
Nepal starts exporting energy to Bangladesh with Indian grid support.
Significance of the Power Transfer:
- Energy Cooperation:
- A major step in regional energy cooperation among Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Strengthens sub-regional connectivity in the power sector.
- Nepal’s Hydropower Potential:
- Nepal, a Himalayan nation, possesses untapped hydropower resources, and this agreement opens the door for future cross-border electricity cooperation.
- Nepal’s energy exports are a green energy initiative, supporting sustainable industrial growth in Bangladesh and regional prosperity.
- Electricity Crisis in Bangladesh:
- Bangladesh is facing an ongoing electricity shortage, worsened by the suspension of power supply from Adani’s Godda plant and the maintenance of the Payra thermal unit.
- The addition of 40 MW of Nepalese hydroelectric power aims to alleviate the energy shortfall in Bangladesh.
Tripartite Power Sales Agreement:
- Agreement Details:
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN) (India)
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) (Nepal)
- Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) (Bangladesh).
- Power Export: Nepal has started exporting 40 MW of electricity, which marks a significant milestone in trilateral power cooperation.
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
Key Entities Involved:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN):
- A wholly owned subsidiary of NTPC Ltd. (National Thermal Power Corporation), created to facilitate power trading.
- NVVN is diversifying into renewables, e-mobility, and green fuel solutions.
- NTPC Ltd.:
- A Maharatna PSU under India’s Ministry of Power, established to develop power resources in India.
- Involved in large-scale power generation and clean energy initiatives
WIPO 2024 Report

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
India continues to make significant strides in intellectual property filings, ranking among the top 10 countries for patents, trademarks, and industrial designs.
India’s Performance in Global Intellectual Property (IP) Filings:
- Overall Growth: India continues to make significant strides in intellectual property filings, ranking among the top 10 countries for patents, trademarks, and industrial designs.
- Patent Applications: India recorded a +15.7% growth in patent applications in 2023, marking its fifth consecutive year of double-digit growth, placing it among the top contributors to global patent filings.
- Trademark Filings: India ranks 4th globally in trademark filings, reflecting the country’s growing focus on brand protection.
- Industrial Designs: India saw a 36.4% surge in industrial design applications, emphasizing creativity and design innovation.
India’s Global Patent Ranking:
- Global Rank: India ranks 6th globally for patent applications with 64,480 filings in 2023.
- Resident Filings: For the first time, over half (55.2%) of India’s patent applications were filed by residents, highlighting growing domestic innovation.
- Patent Grants: A 149.4% increase in granted patents in 2023 underscores the efficiency of India’s patent office and the rising quality of applications.
Key Metrics and Trends in Patents:
- Patent-to-GDP Ratio: India’s patent-to-GDP ratio grew from 144 in 2013 to 381 in 2023, signaling a knowledge-driven economy.
- Sectoral Diversity: India’s patent filings span diverse sectors, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, IT, and renewable energy, showcasing the broad scope of innovation.
Surge in Industrial Design Applications:
- Growth Rate: A 36.4% increase in industrial design filings in 2023, reflecting a shift towards value-added industries focused on product design and functionality.
- Leading Sectors: Key sectors driving design filings include textiles, accessories, tools, machines, and health & cosmetics.
- Manufacturing Transformation: This growth signals India’s transition from basic manufacturing to a more design-driven, innovation-focused ecosystem.
Trademark Filings:
- Global Rank: India ranks 4th globally in trademark filings with a 6.1% increase over the previous year.
- Resident Filings: Nearly 90% of trademark filings in India were made by domestic entities, highlighting a strong focus on brand protection.
- Active Trademarks: India now has over 3.2 million active trademarks, the second-largest in the world, reflecting a competitive and dynamic domestic marketplace.
Sectoral Trends in Trademarks:
- Leading Sectors: Health (21.9%), agriculture (15.3%), and clothing (12.8%) were the top sectors for trademark filings, underscoring India’s leadership in pharmaceuticals, food production, and fashion.
- Global Expansion: The rise in trademark filings also mirrors the increasing global demand for Indian products and services.
India’s Contribution to Global IP Growth:
- Global Trend: In 2023, a record 3.55 million patent applications were filed worldwide, with India contributing significantly to this surge, particularly in emerging markets.
- Local Innovation Focus: India’s rising resident filings in patents and trademarks point to a shift towards local innovation, with more Indian businesses and startups protecting their intellectual property.
Government Initiatives Fueling IP Growth:
- National IPR Policy: Launched in 2016, this policy fosters innovation, improves IP awareness, and supports domestic IP development.
- Key Measures: Modernization of IP offices, improvements in procedural requirements, and IP education initiatives.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: Government campaigns like Atmanirbhar Bharat have supported local innovation and made Indian businesses more IP-conscious.
- Startup India & Atal Innovation Mission: These initiatives have further strengthened India’s innovation ecosystem by promoting entrepreneurship, research, and technological advancement.
- Startup India: Over 1,49,000 recognized startups as of September 2024.
- Atal Innovation Mission: More than 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs in schools and 3,500+ startups incubated across India.
Assam’s Semiconductor Plant
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
A Semiconductor Plant has been set up in Morigaon, Assam, projected for completion by mid-2025.
Overview of the Morigaon Semiconductor Plant:
- Location: Morigaon, Assam.
- Investor: Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test Pvt Ltd (TSAT).
- Investment: ?27,000 crore.
- Production Capacity: Expected to produce 48 million semiconductor chips daily.
- Technology: Utilizes advanced packaging technologies such as flip chip and Integrated System in Package (ISIP).
- Sectors Served: Automotive, electric vehicles, telecommunications, consumer electronics.
- Completion: Projected to be completed by mid-2025.
- Job Creation: Expected to generate 15,000 direct jobs and 11,000-13,000 indirect jobs.
- Market Reach: Will serve both domestic and international markets, enhancing India's position in the global semiconductor supply chain.
India's Semiconductor Industry and Market Growth:
- Market Size (2023): Estimated at $38 billion.
- Projected Growth: Expected to grow to $109 billion by 2030.
- Government Initiatives: Several initiatives have been launched to promote domestic semiconductor manufacturing, including the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) and the Semicon India Program.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM):
- Objective: To build a self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem in India.
- Launched: 2021 with a financial outlay of ?76,000 crore.
- Scope: Covers semiconductor fabs, packaging, display manufacturing, Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Testing (OSAT), sensors, and other critical components.
- Support Schemes: Includes Modified Schemes for setting up Semiconductor and Display Fabs, as well as support for Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, and Sensors.
Key Projects in Semiconductor Industry:
- Morigaon Facility: Part of the broader government-backed initiative to enhance semiconductor production in India.
- Other Facilities: New semiconductor units by Tata Electronics (Dholera, Gujarat), CG Power (Sanand, Gujarat), and KaynesSemicon Pvt Ltd (Sanand, Gujarat).
- Modernization: The Semi-Conductor Laboratory in Mohali is being modernized, alongside initiatives like the Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors (SPECS) and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
Strategic Importance of Semiconductors:
- Role in Modern Electronics: Semiconductors are critical for a wide range of devices like computers, smartphones, solar cells, LEDs, and integrated circuits.
- Global Dependence: The global semiconductor market has significant reliance on suppliers like Taiwan (44%), China (28%), and South Korea (12%).
- Global Shortage: The 2021 chip shortage highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains, prompting efforts by countries to boost domestic semiconductor production.
Government Support for Semiconductor Manufacturing:
- Financial Incentives: The government offers fiscal support for setting up semiconductor manufacturing plants:
- 50% of project cost support under the Semiconductor Fab Scheme and the Display Fab Scheme.
- Support for Compound Semiconductors and Chips to Startup (C2S) initiatives.
- Training 85,000 engineers through the C2S Programme in collaboration with academic institutions, R&D organizations, and MSMEs.
Europe’s Digital Euro

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The digital euro, a central bank digital currency (CBDC) being developed by the European Central Bank (ECB), aims to revolutionize Europe’s digital payment landscape. However, while the ECB has marketed it as a convenient, free, anonymous, and reliable alternative to existing cashless options like credit cards and mobile payment apps, the true purpose of the digital euro goes beyond these simplified claims.
Key Aspects of the Digital Euro
- Direct Issuance by the ECB: Unlike traditional digital payments that rely on intermediaries like banks or payment service providers, the digital euro is issued directly by the European Central Bank. This allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for third-party banks or payment gateways. It can be used for offline transactions, which is a major technical innovation that sets it apart from other digital currencies.
- A Digital Version of Cash: The digital euro is essentially a digital version of legal tender (cash), providing an alternative to cash in a world increasingly dominated by digital payments. Its key feature is direct payment between users, bypassing the traditional banking system. It aims to offer the same advantages as cash, such as anonymity, but with the convenience of digital transactions.
- Cost Reduction and Micro-Payments: The digital euro promises to lower transaction costs, especially for micro-payments that are currently prohibitively expensive using conventional bank transfers or digital services like PayPal. This cost efficiency is intended to enable new business models by lowering the friction in digital transactions, thus encouraging innovation in commerce.
The ECB’s Claims vs. the Real Motivation
While the ECB portrays the digital euro as a means to make payments easier, faster, and more secure, there is an underlying political and economic agenda that goes beyond improving consumer convenience.
- Sovereignty and Competition: One of the main drivers behind the digital euro is Europe’s desire to assert its digital sovereignty. The ECB positions the digital euro as a tool to strengthen the euro’s competitiveness against non-European payment providers, particularly those from the United States like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. The EU is concerned that foreign companies may dominate the digital payment landscape, thereby reducing Europe's ability to control its own financial systems.
- This is a defensive measure to protect European financial interests. By creating a state-backed alternative to privately controlled digital payment systems, the EU aims to ensure that Europe does not become reliant on foreign corporations for essential services.
- Not About Citizens’ Convenience Alone: While the ECB frames the digital euro as a user-friendly solution for consumers, the real concern is about the control over digital currency. The digital euro offers a more centralized alternative compared to the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The ECB aims to harness the power of the state in regulating and controlling digital transactions, thus consolidating private property and ensuring the smooth functioning of Europe’s monetary policies.
- A Tool for Strengthening the Euro: The digital euro is also seen as part of Europe’s broader ambition to establish the euro as a dominant global currency. As the first fully-regulated digital currency issued by a central bank, it could position the euro to compete against other digital currencies, including the digital yuan or the U.S. dollar. The EU sees the digital euro as a way to expand its geopolitical influence by promoting its own currency as a global standard for digital payments.
Global Maritime Conference
- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
In a bid to enhance India’s clout in the global merchant shipping sector, the government recently hosted a two-day global maritime conference – Sagarmanthan: The Great Oceans Dialogue.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of the Conference:
- To enhance India's maritime influence and position India as a key player in the global maritime sector, especially in merchant shipping and maritime trade.
- To showcase India's ambitions in expanding its role in global maritime trade, governance, and collaboration.
- India's Maritime Ambitions:
- Despite being the most populous nation and one of the largest global economies, India’s maritime clout has been relatively lower than expected.
- The dialogue aims to shift global attention towards India's growing role and contributions to maritime trade and shipping.
- India's Maritime Growth:
- India contributed to 16% of global maritime growth in 2023 and is on track to become the third-largest global economy within three years.
- As India’s economic and geopolitical influence expands, maritime governance will become increasingly significant, necessitating deeper international collaborations in commerce, connectivity, and trade.
- Focus Areas of the Dialogue:
- Global Maritime Trade: India's expanding role in international shipping, trade routes, and maritime security.
- International Collaborations: Promoting deeper engagement in maritime governance and policy-making ecosystems.
- Human Well-being: Highlighting the role of maritime trade in supporting human welfare, particularly in the context of sustainable development and climate change.
- Significance for India:
- The conference serves as a platform to discuss India’s aspirations, policies, and presence in global maritime affairs.
- It is an opportunity to strengthen maritime relations and address issues of global relevance such as trade routes, shipping governance, and environmental sustainability
Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) retained the State Bank of India, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
Overview of D-SIBs
- Definition: D-SIBs are banks that are 'Too Big to Fail' (TBTF) and their failure could significantly disrupt essential banking services, affecting the economy.
- RBI Classification: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has designated SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as D-SIBs.
- Bucketing System: These banks are classified into different buckets based on their systemic importance.
Importance of D-SIBs
- Systemic Importance: Banks are considered systemically important due to their:
- Size
- Cross-jurisdictional activities
- Complexity
- Interconnectedness with the economy
- Impact of Failure: Failure of a D-SIB could cause significant disruption in the banking system and economy, impacting services like payments, loans, etc.
Why D-SIBs are Created
- Risk of Disruption: The failure of a large bank can disrupt essential services and lead to a broader economic crisis.
- TBTF Perception: These banks are often perceived as Too Big to Fail, leading to an expectation of government support during crises. This creates moral hazard, encouraging riskier behavior.
Assessment and Selection of D-SIBs
- Two-Step Process:
- Step 1: Selection of banks based on their size, complexity, and interconnectedness. Only banks with systemic importance are assessed (e.g., banks with assets > 2% of GDP).
- Step 2: Calculation of systemic importance score based on a range of indicators. Banks above a certain threshold are classified as D-SIBs.
- Indicators: Size (measured by Basel III Leverage Ratio Exposure Measure), interconnectedness, substitutability, and complexity are key factors.
Bucket Allocation and Capital Requirements
- D-SIBs are assigned to five buckets based on their systemic importance score:
- Bucket 1: Lowest capital surcharge (e.g., ICICI Bank).
- Bucket 5: Highest capital surcharge.
- Additional Capital Requirements:
- SBI: Additional 0.80% CET1 (Common Equity Tier 1) on Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs).
- HDFC Bank: Additional 0.40% CET1.
- ICICI Bank: Additional 0.20% CET1.
- The higher the bucket, the higher the capital surcharge.
Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs)
- Global List: Identified by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) based on data from the previous year.
- 2023 G-SIB List includes banks like JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, HSBC, etc.
- Capital Requirement for G-SIBs in India: Foreign G-SIBs with branch presence in India must meet additional CET1 requirements, proportional to their operations in India.
Key Terms
- Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs): These are used to calculate the minimum capital a bank must hold. It accounts for the risk level of a bank’s assets.
- Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1): The highest quality of capital a bank can hold, primarily made up of common stock, to absorb losses in times of distress.
Sea Ranching Initiative off Vizhinjam Coast

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- The State Fisheries Department in Kerala launched a sea ranching project by releasing 20,000 pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fingerlings off the Vizhinjam coast as part of the artificial reef project.
- Coordinates: The fingerlings were released near artificial reef modules placed 1.5 nautical miles off the coast.
- Follow-up to Artificial Reef Project: The release of fingerlings is a follow-up to the artificial reef project aimed at replenishing marine fishery resources and promoting sustainable fishing practices.
Project Details
- Fingerling Release: The first batch of 20,000 pompano was released as part of the broader initiative to release 10 lakh fingerlings (pompano and cobia) at 10 locations along the Thiruvananthapuram coast.
- Location and Quantity: At each location, 1 lakh fingerlings will be released, where artificial reefs have already been deployed under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Reef Design: Artificial reefs consist of 150 reef modules (triangular, flower, and pipe-shaped) created at 42 locations off 33 fishing villages in the Thiruvananthapuram district.
Objective and Benefits
- Marine Resource Replenishment: The primary aim is to replenish marine fishery resources in the region by enhancing biodiversity through the introduction of fingerlings.
- Sustainable Fishing: The project aims to promote sustainable fishing practices by supporting fish populations and ensuring long-term fishery health.
- Attraction of Fish Species: The artificial reefs have already attracted a variety of fish species, including tuna, trevally, and mackerel, enhancing the fishing ecosystem.
Implementation and Funding
- Scheme: The project is being implemented under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), which focuses on sustainable fisheries development.
- Central Approval: The National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB) approved the ?3 crore funding for the initial phase in Thiruvananthapuram.
- Proposed Expansions:
- Phase II: A proposal for extending the artificial reef project to 96 villages in the districts of Kollam, Alappuzha, Ernakulam, and Thrissur with an estimated cost of ?29.76 crore.
- Phase III: A similar proposal for 96 villages in the northern districts of Malappuram, Kozhikode, Kannur, and Kasaragod with an estimated cost of ?25.82 crore.
Mission and Fingerlings Details
- Fingerlings:
- Pompano (Trachinotus blochii) and Cobia (Rachycentron canadum) fingerlings were reared at the Ayiramthengu fish farm.
- Each fingerling weighs between 8 to 10 grams.
- The release aims to stock marine areas with species that will contribute to biodiversity and fisheries sustainability.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
- Launched: PMMSY is a Centrally funded scheme under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
- Goal: The scheme focuses on sustainable fisheries development to enhance fisheries production, boost aquaculture, and promote responsible fishing practices.
- Funding: The scheme involves both Central and State Government funding for projects related to fisheries management, infrastructure development, and resource conservation.
Mission Fingerling
- Launched: 2017 by the Union Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.
- Objective: To achieve the Blue Revolution by holistically developing and managing fisheries in India.
- Production Target: The mission aimed to increase fisheries production from 10.79 MMT (2014-15) to 15 MMT by 2020-21.
OECD Report on Indian Agricultural Policies

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- In 2023, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) revealed that Indian farmers faced the highest implicit taxation globally, amounting to USD 120 billion.
- Implicit Taxation: This taxation arises from government policies like export bans, duties, and price controls, aimed at lowering food prices for consumers but reducing the income of farmers.
- Export Restrictions: Key commodities affected include rice, sugar, onions, and de-oiled rice bran.
Impact on Indian Farmers
- Market Price Support (MPS):
- Negative MPS: In 2023, Indian agricultural policies resulted in a negative MPS of USD 110 billion.
- Farmers received lower prices than international market rates due to export bans and trade restrictions, impacting their income.
- Budgetary Support: Despite government subsidies and the Minimum Support Price (MSP) worth USD 10 billion, negative MPS outweighed positive support, leading to an overall loss for farmers.
- Farmer’s Share in Global Negative Support:
- India’s share of global negative price support in 2023 was 62.5%, a significant increase from 61% in 2000-02.
Global Agricultural Policy Trends
- Global Support: Total support for agriculture across 54 countries averaged USD 842 billion annually (2021-2023). However, there was a decline in support in 2022-23 from the pandemic-era peak.
- Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) and climate change are exacerbating global agricultural production and trade.
- Export Restrictions in various countries are distorting international agricultural markets.
- Farmer Protests across countries reflect the economic and social struggles of the farming community.
- Sustainability Issues: Global agricultural productivity growth is slowing, posing challenges to feeding a growing population sustainably.
India's Agricultural Policies
- Export Bans and Restrictions: These policies are intended to control domestic prices but undermine farmers’ income by lowering market prices for key agricultural products.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): MSP is meant to protect farmers, but is often set below international market rates, leading to a negative price effect.
- Regulatory Constraints: Policies like the Essential Commodities Act (1955) and APMC Act (2003), though aimed at ensuring food security, often lead to price suppression for farmers.
- Price Depressing Policies: India's agricultural policies result in lower farm-gate prices due to price controls, government-set procurement prices, and lack of market access.
Negative Market Price Support (MPS)
- Historical Trends:
- From 2014-2016, India’s Producer Support Estimate (PSE) was -6.2%, driven mainly by negative MPS (-13.1%).
- The PSE measures the annual value of transfers to farmers, both from consumers and the government.
- Inefficiencies:
- Infrastructure Gaps: Poor infrastructure and high transaction costs lower the prices farmers receive.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Short-term subsidies for inputs (fertilizers, irrigation) don’t address long-term agricultural challenges like climate change and market access.
Government Support Programs
- Subsidies and Schemes:
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) for organic farming.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) to promote agricultural development.
- Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP) for modernizing agricultural practices.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- The government has introduced initiatives like AgriStack and Mission Organic Value Chain Development in the North East to enhance sustainable agricultural practices and reduce the negative impacts on farmers.
Global Context and Recommendations
- Environmental Public Goods Payments (EPGP): Only 0.3% of total producer support is dedicated to environmental sustainability, despite the growing need for climate-resilient agriculture.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: The OECD advocates for governments to tie producer support to sustainable farming practices, including the use of metrics like Total Factor Productivity (TFP) and Agri-Environmental Indicators (AEIs).
- TFP measures agricultural efficiency, while AEIs assess the environmental impacts of farming.
OECD Overview
- OECD Function: Founded in 1961, the OECD is an international organization of 38 countries that promotes prosperity, equality, and well-being through economic reports, data, and policy analysis.
- India’s Role: India has been an OECD Key Partner since 2007, engaging with the OECD on various policy issues, though it is not a member.
RBI's New Framework for Reclassification of FPI to FDI
- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) directed foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) to obtain necessary approvals from the government and concurrence from the investee companies when their equity holdings go beyond the prescribed limits and they reclassify the holdings as foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Approval Requirement:
- FPIs (Foreign Portfolio Investors) must obtain necessary government approvals when reclassifying their foreign portfolio investments (FPIs) into Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- Approvals are mandatory, including those related to investments from countries sharing a land border with India.
- Investment Limits:
- According to FEMA (NDI) Rules, 2019, an FPI’s investment in an Indian company should not exceed 10% of the total paid-up equity capital (on a fully diluted basis).
- If the FPI exceeds this limit, it has 5 trading days from the settlement of trades to either divest or reclassify the excess holdings as FDI.
- Restrictions on Reclassification:
- Reclassification to FDI is not allowed in sectors where FDI is prohibited.
- FPIs must ensure compliance with FDI norms, such as entry routes, sectoral caps, investment limits, pricing guidelines, and other related conditions.
- Concurrence from Investee Companies:
- The FPI must obtain the concurrence of the investee company for reclassifying the investment into FDI.
- This ensures that the company adheres to conditions related to prohibited sectors, sectoral caps, and government approvals.
- Reclassification Procedure:
- The FPI must clearly state its intent to reclassify the investment to FDI and provide the necessary approvals and concurrence to its custodian.
- The custodian is responsible for freezing the FPI's purchase transactions in the investee company’s equity instruments until the reclassification is complete.
- Regulatory Adherence:
- The reclassification must follow the relevant provisions for FDI, including compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) and FDI guidelines.
Nano-Coating Technology for Fertilizer Efficiency

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A mechanically stable, biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating material can enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers by tuning them for slow release, thereby limiting their interaction with the rhizosphere soil, water and microbes.
Development of Slow-Release Fertilizers:
- A biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating has been developed to enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers.
- The nanocoating allows for slow release of nutrients, thus limiting excessive interaction with soil, water, and microbes, and optimizing fertilizer usage.
Coating Composition:
- The coating is made from nanoclay-reinforced binary carbohydrates, primarily chitosan (a biopolymer from chitin) and lignin (a plant-based polymer).
- These materials are low-cost, naturally derived, and eco-friendly, ensuring sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of fertilizer use.
Technological Innovation:
- The coating process involves using a drum rotor method to uniformly coat fertilizers, improving their efficiency.
- The tuning of hydrophobicity in the nanocoating alters the release kinetics of fertilizers, ensuring that nutrients are released in accordance with the crop’s nutrient uptake needs.
Sustainability and Biodegradability:
- The nanocoating is biodegradable, which ensures that it does not harm the environment post-application, unlike conventional chemical fertilizers that may lead to soil degradation and water pollution.
- Life cycle assessment confirms the product's long-term sustainability compared to traditional fertilizers.
Enhanced Crop Productivity:
- The slow-release coating enables a reduced fertilizer dose, while maintaining or even increasing crop yields, particularly for staple crops like rice and wheat.
- This technology facilitates higher agricultural output with fewer inputs, contributing to food security.
Industrial Viability:
- The mechanical stability of the coated fertilizers ensures they can withstand transportation and handling, making them suitable for large-scale industrial application.
- The rotary drum system used for coating ensures uniform application and superior mechanical performance, ensuring that the fertilizers are not damaged during the supply chain process.
Economic Benefits:
- The use of slow-release fertilizers can reduce overall fertilizer costs for farmers while enhancing yields, leading to improved socio-economic conditions for farmers.
- The technology holds potential for economic growth by boosting agricultural productivity and reducing the financial burden on farmers for chemical fertilizer inputs.
Global Relevance:
- The research is significant in the context of global sustainable development goals, aiming to reduce the over-reliance on conventional chemical fertilizers that contribute to soil degradation, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Research Collaboration:
- This breakthrough was achieved by scientists from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, in collaboration with the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science: Nano, highlighting its scientific validation.
State of Food and Agriculture 2024Report
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- India's annual hidden costs from agrifood systems total $1.3 trillion, the third-largest globally, after China ($1.8 trillion) and the US ($1.4 trillion).
- These costs are mainly driven by unhealthy dietary patterns leading to non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
Major Contributors to Hidden Costs:
- Unhealthy Diets: Over 73% of India’s hidden costs stem from unhealthy dietary habits, including:
- Excessive consumption of processed foods and additives ($128 billion).
- Low intake of plant-based foods, fruits, and beneficial fatty acids ($846 billion).
- These dietary risks contribute to a significant health burden, increasing the prevalence of NCDs and reducing labor productivity.
Global Context:
- Global hidden costs of agrifood systems amount to $12 trillion annually.
- 70% of these costs (~$8.1 trillion) arise from unhealthy dietary patterns, which include high intakes of sugar, salt, and processed foods, contributing to diseases and economic losses.
Health Impacts:
- The report identifies 13 dietary risk factors that contribute to NCDs, including insufficient intake of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and excessive sodium, with varying effects across different agrifood systems.
Environmental and Social Costs:
- Environmental Costs: High costs from unsustainable agricultural practices, including greenhouse gas emissions and nitrogen runoff. In some agrifood systems, environmental costs can reach up to 20% of GDP.
- Social Costs: High poverty rates among agrifood workers and undernourishment in systems like protracted crises and traditional agrifood systems contribute significantly to the hidden costs.
India’s Agrifood System Profile:
- India’s agrifood system faces significant challenges related to low wages, poor productivity, and poverty among agrifood workers, driven by distributional failures.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Issues like droughts, floods, and soil degradation threaten food security and agricultural sustainability in India.
Recommendations for Transformative Change:
- True Cost Accounting: Implementing this method can help better capture hidden costs and enable more informed decision-making for a sustainable agrifood system.
- Healthier Diets: Policies to make nutritious food more affordable and accessible to reduce health-related hidden costs.
- Sustainability Incentives: Encouraging practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, harmful land-use changes, and biodiversity loss, using labelling, certification, and industry standards.
- Consumer Empowerment: Providing accessible information about the environmental, social, and health impacts of food choices, ensuring even vulnerable households benefit from healthier options.
India’s Path Forward:
- India has several ongoing initiatives for sustainable agriculture, including:
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- Eat Right Initiative.
- Digital Agriculture Mission (DAM).
- However, challenges like climate change, soil degradation, and low productivity among smallholder farmers hinder progress toward sustainable food systems.
Key Focus Areas for India’s Agrifood Systems:
- Support for Smallholder Farmers: Enhancing access to technology, markets, and financial services for marginalized farmers.
- Sustainable Practices: Adoption of water-efficient practices, soil health restoration, and environmentally friendly farming methods.
- Collaboration with International Agencies: Cooperation with FAO, WFP, and others to strengthen agricultural reforms and support smallholder farmers.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) Initiative

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- India is in talks with Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Maldives, and Singapore to establish cross-border electricity transmission lines.
- This is part of the ambitious OSOWOG initiative to create a global renewable energy grid.
Key Points:
- Proposed by the Prime Minister of India at the 2018 International Solar Alliance (ISA) Assembly.
- Aims to create a transnational electricity grid that delivers power worldwide.
- Led by India and the UK, in collaboration with ISA and the World Bank Group.
Vision of OSOWOG:
- Connect regional grids through a common infrastructure for the transfer of renewable energy, focusing on solar power.
- Harness solar and other renewable energy from regions where the sun is shining and efficiently transmit it to areas of need.
- Aim to provide power to 140 countries using clean and efficient solar energy.
Phases of OSOWOG:
- Phase 1:
- Connect the Indian grid with grids in the Middle East, South Asia, and South-East Asia.
- Share solar and other renewable energy resources.
- Phase 2:
- Expand the interconnected grid to include renewable resources from Africa.
- Phase 3:
- Achieve a global interconnection aiming for 2,600 GW by 2050.
- Integrate as many countries as possible into a single renewable energy grid.
Global Collaboration:
- Involves national governments, international organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts.
- Focus on accelerating infrastructure development for a clean energy-powered world.
India's Green Leap

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
India's journey toward a sustainable energy future has gained significant momentum with a series of policy reforms designed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and accelerate the shift to clean energy. The recent Asia-Pacific Climate Report from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) highlights India's remarkable progress in reforming its fossil fuel subsidy system and its efforts to foster renewable energy, positioning the country as a leader in the region's green transformation.
Key Highlights from the Report:
India's Fossil Fuel Subsidy Reform
- India has successfully reduced fossil fuel subsidies by 85%, from a peak of $25 billion in 2013 to just $3.5 billion by 2023.
- The reform strategy is built on a "remove, target, and shift" approach, which involved phasing out subsidies on petrol and diesel from 2010 to 2014, followed by incremental tax hikes on these fuels through 2017.
- These fiscal changes created space for funding renewable energy projects, such as solar parks, electric vehicle initiatives, and infrastructure improvements.
Role of Taxation in Supporting Clean Energy
- Between 2010 and 2017, India introduced a cess on coal production and imports, which contributed significantly to funding clean energy projects. Approximately 30% of the cess was directed to the National Clean Energy and Environment Fund.
- This funding supported major renewable energy initiatives, including the National Solar Mission and Green Energy Corridor project, helping reduce the cost of utility-scale solar energy and expand off-grid renewable energy solutions.
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017 altered the financial landscape, redirecting the cess funds to GST compensation rather than directly to clean energy.
Government Schemes and Initiatives
- India is advancing its clean energy agenda through several key government schemes:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Aimed at establishing India as a leader in green hydrogen production.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme: Focused on promoting solar energy among farmers, allowing them to produce renewable power.
- PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana: A program designed to provide solar energy access to rural communities, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
A Strategic Shift: From Subsidies to Clean Energy
- India’s subsidy reforms are an important part of its strategy to transition from a reliance on fossil fuels to a focus on renewable energy investments.
- These changes reflect India’s long-term goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070, as outlined in its climate action plans.
Global Significance of India’s Efforts
- The reduction in fossil fuel subsidies and the surge in clean energy investment serve as a model for other nations seeking to balance economic development with climate action.
- India’s approach demonstrates that policy reforms and innovative financing mechanisms can be used to accelerate the transition to a cleaner, greener economy while creating job opportunities and fostering economic growth.
NAMO DRONE DIDI

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare has released the Operational Guidelines of Central Sector Scheme “NAMO DRONE DIDI”
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Empower women through Self-Help Groups (SHGs) by providing drones for agricultural rental services.
- Aim to support 14,500 SHGs from 2024 to 2026.
Scheme Overview:
- Type: Central Sector Scheme, under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM).
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Target: Women SHGs for providing drone services in agriculture (e.g., nutrient and pesticide spraying).
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance:
- 80% subsidy (up to ?8 lakh) for SHGs to purchase drones.
- Loans for the remaining 20% via the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with 3% interest subvention.
- Drone Package:
- Includes drones, spray assemblies, batteries, cameras, chargers, and measurement tools.
- Additional batteries and propellers allow up to 20 acres of coverage per day.
- Training Program:
- One SHG member will be selected for 15 days of mandatory training.
- Focus on drone operation and agricultural tasks (nutrient and pesticide spraying).
- Implementation & Oversight:
- Central Governance: Empowered Committee comprising secretaries from key ministries (Agriculture, Rural Development, Fertilizers, Civil Aviation, and Women and Child Development).
- State Level: Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs) will implement the scheme in coordination with state departments and SHG federations.
- Monitoring: IT-based Management Information System (MIS) through the Drone Portal for real-time tracking and fund disbursement.
- Financial Flexibility:
- SHGs can access loans through other Ministry of Rural Development schemes if needed.
Implementation Details:
- Governance: Central level oversight by the Empowered Committee and state-level execution by Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Ownership: Drones procured by LFCs will be owned by SHGs or their Cluster Level Federations (CLFs).
- Monitoring: The scheme will be tracked and managed through the Drone Portal, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has decided to introduce four new components under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), aimed at promoting modern farming techniques:Hydroponics, Aquaponics, Vertical Farming&Precision Agriculture
Key Features of MIDH:
- MIDH is a Central Sponsored Scheme (CSS) aimed at the integrated development of various horticulture crops, including:
- Fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa, and bamboo.
- The scheme focuses on pre-production, production, post-harvest management, processing, and marketing activities.
Revision of Operational Guidelines and Cost Norms:
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare is revising the MIDH operational guidelines and cost norms, which were last updated in April 2014.
- The revised guidelines are expected to be released within one month.
- Cost norms are likely to increase by 20% compared to the existing rates, addressing concerns from various states about outdated guidelines.
Reason for Revision:
- Several states, including Odisha, have raised concerns over the old rates under MIDH. For example, Odisha’s Agriculture Minister highlighted that the state was still using 10-year-old rates.
- The Union Cabinet had already approved the rationalization of all CSS operating under the Ministry into two umbrella schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (PM-RKVY)
- Krishonnati Yojana (KY)
Growth in India's Horticulture Sector:
- India’s horticulture production has significantly increased in recent years:
- Total production reached 334.60 million metric tonnes in 2020-21, up from 240.53 million metric tonnes in 2010-11.
- India is now the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, surpassing food grain production.
- MIDH Annual Budget:The annual allocation for MIDH in the current financial year (2024-25) is ?2,000 crore.
21st Livestock Census

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
The Livestock Census is a crucial tool for understanding the current status of India’s livestock sector and its contribution to the economy and society.
What is the Livestock Census?
- The Livestock Census is a nationwide survey conducted every five years to assess the number, species, breed, age, sex, and ownership status of domesticated animals and poultry, including stray animals.
- Purpose: It helps in collecting comprehensive data about the livestock population and their role in the economy and society.
- First Census: The first livestock census was conducted in 1919, and this is the 21st edition.
- Next Census: The 21st Livestock Census will be conducted between October 2024 and February 2025 by approximately 87,000 enumerators across 30 crore households in India.
Animals Covered in the Census
- The census will account for 16 species of animals, including:
- Cattle, Buffalo, Mithun, Yak, Sheep, Goat, Pig, Camel, Horse, Ponies, Mule, Donkey
- Dog, Rabbit, Elephant
- Poultry: Fowl, Chicken, Duck, Turkey, Geese, Quail, Ostrich, and Emu
- The census will also collect data on 219 indigenous breeds of these species recognized by the ICAR-National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR).
Objectives of the Livestock Census
- Economic Contribution: The livestock sector contributes approximately:
- 30% of the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the agricultural sector
- 4.7% of India's overall GVA
- It plays a crucial role in rural employment, particularly in poultry and animal husbandry.
- Policy Formulation and Planning:
- The data from the census is critical for formulating and implementing policies related to livestock, ensuring sustainable growth in the sector.
- It helps in monitoring and estimating GVA from livestock.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Provides vital data for tracking the progress towards Goal 2 of SDGs (Zero Hunger) and Target 2.5, which focuses on maintaining genetic diversity in livestock, particularly addressing local breeds at risk of extinction (Indicator 2.5.2).
- Sectoral Monitoring:
- The census helps in monitoring the performance and health of India’s livestock sector, which is vital for ensuring food security, rural livelihoods, and economic growth.
Key Features of the 21st Livestock Census
- Digitization:
- Like the 2019 Census, this year’s census will be fully digitized, with data collected via a mobile application.
- Digital Monitoring: A dashboard will monitor progress at various levels, and the latitude and longitude of the data collection locations will be recorded.
- A software-based livestock census report will be generated to streamline analysis.
- New Data Points:
- For the first time, data on pastoral animals and pastoralists will be collected, focusing on their socio-economic status and livestock holdings.
- Granular Data: The census will gather information on:
- Proportions of households that rely on livestock for major income.
- Gender-based data on stray cattle.
- Extended Scope:
- In addition to animal population statistics, the census will also focus on the socio-economic contributions of the livestock sector, gender inclusion, and employment.
Significance of the Livestock Census
- A Comprehensive Livestock Profile:
- Provides a holistic view of livestock population and the interlinkages between animal husbandry, agriculture, and rural economies.
- Assists in the management and preservation of indigenous animal breeds.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Helps policymakers, researchers, and development organizations in formulating strategies for sectoral growth, genetic diversity preservation, and livelihood enhancement for rural communities.
- Monitoring Livestock Health:
- The census helps in tracking the health and sustainability of India’s livestock population, which is essential for ensuring food security and preventing animal diseases.
Findings of the 2019 Livestock Census
- Total Livestock Population: 535.78 million
- Cattle: 192.9 million
- Goats: 148.88 million
- Buffaloes: 109.85 million
- Sheep: 74.26 million
- Pigs: 9.06 million
- Other species contributed a small fraction to the total livestock population (0.23%).
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Financial Services Secretary stated that Microfinance institutions (MFIs) have played a crucial role in fostering financial inclusion but they should refrain from any reckless lending.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) and Financial Inclusion:
- MFIs provide small loans and financial services to low-income and marginalized groups, particularly those without access to formal banking services.
- Goal: To promote financial inclusion and empower marginalized communities, especially women, by enabling them to become self-sufficient and improve their socio-economic status.
- In India, over 168 MFIs serve around 3 crore clients across 29 states and 563 districts.
- The sector has grown significantly and is crucial for empowering Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) to access credit and other financial services.
Concerns over Reckless Lending:
- The Financial Services Secretary, emphasized that MFIs should avoid reckless lending practices that could harm both borrowers and the sector.
- Poor underwriting and irresponsible lending could lead to unsustainable debt, especially for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) with limited financial literacy.
- Key Advice: Lending practices must be responsible, careful, and should aim to empower borrowers, not exploit their limited understanding.
Government Programs Supporting MFIs:
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme: Over 77 lakh SHGs with a total loan outstanding of ?2.6 lakh crore, benefiting around 10 crore households.
- Lakhpati Didi Yojana: Aimed at empowering women, this scheme helps transform SHG members into women entrepreneurs.
Challenges Facing Microfinance Institutions:
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Many MFIs face scrutiny for high interest rates and non-compliance with borrower assessments. The RBI has urged MFIs to reassess lending practices.
- Over-Indebtedness: Many borrowers take loans from multiple MFIs, leading to unsustainable debt. As of March 2024, over 12% of borrowers had multiple loans, risking defaults.
- Low Financial Literacy: A significant challenge is low financial literacy among borrowers, which increases the risk of defaults and harms the reputation of MFIs.
RBI Guidelines on Microfinance (2022):
- Collateral-Free Loans: For households with income up to ?3 lakh, loans should be collateral-free.
- Repayment Cap: Monthly loan repayments should not exceed 50% of the borrower’s monthly income.
- Flexibility in Repayment: MFIs must offer flexible repayment options and ensure proper income assessment.
- Interest Rate Cap: The RBI has implemented guidelines to limit excessive interest rates charged by MFIs.
Government Schemes for Microfinance:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Provides financial assistance to non-corporate, non-farm small/micro enterprises.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Promotes rural livelihoods through the formation and capacity building of Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Antyodaya Yojana: Focuses on the empowerment of rural poor through skill development and income generation.
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE): Provides guarantee cover to micro and small enterprises.
Way Forward for Microfinance Sector:
- Responsible Lending: MFIs must prioritize affordable lending practices, ensuring borrower’s repayment capacity is carefully assessed to avoid over-indebtedness.
- Enhancing Financial Literacy: MFIs should focus on financial education for borrowers, enabling them to make informed choices.
- Adherence to Regulatory Guidelines: MFIs should comply strictly with RBI regulations, including interest rate caps and borrower income assessments, to enhance sector transparency and trust.
- Malegam Committee Recommendations: Implementing suggestions like capping interest rates, tracking multiple loans, and improving transparency to prevent over-indebtedness.
- Diversifying Funding Sources: To reduce vulnerability to economic downturns, MFIs should work on diversifying their funding sources, reducing dependence on external capital.
Environmental Ship Index (ESI)
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Mormugao Port Authority (MPA) has been globally recognized as an incentive provider on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) platform, acknowledged by the International Association of Ports and Harbours (IAPH).
- Mormugao is India's first port to implement Green Ship Incentives through the ESI, contributing to global efforts to reduce maritime air emissions.
‘Harit Shrey’ Scheme:
- Launched in October 2023, the ‘Harit Shrey’ scheme provides discounts on port fees based on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) scores of commercial vessels.
- Ships with higher ESI scores (indicating better environmental performance) are rewarded with incentives to encourage eco-friendly practices in shipping.
ESI and Global Efforts for Emission Reduction:
- The Environmental Ship Index (ESI) is a global system to evaluate and reward ships based on their environmental performance, particularly their emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxides (SOx).
- The 2023 IMO greenhouse gas strategy aims to reduce the carbon intensity of international shipping by at least 40% by 2030.
Incentives and Benefits:
- The Harit Shrey scheme has already benefitted several vessels, promoting greenhouse gas emission reductions and contributing to sustainable maritime operations.
- The scheme aligns with global sustainability goals, particularly in reducing the carbon footprint of shipping operations.
Sustainability Recognition:
- The Mormugao Port Authority has submitted the Harit Shrey scheme for consideration in the IAPH Sustainability Awards under the World Port Sustainability Programme (WPSP), reflecting its commitment to environmental sustainability.
The Environmental Ship Index (ESI):
- ESI is a system that evaluates and rewards ships for better environmental performance than the standards set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- Ships are assessed based on their emissions of NOx and SOx, with greenhouse gas reporting also included in the evaluation.
Main Features of ESI:
- Port-Centric: Developed as a port-to-port system, where ports can offer incentives based on the ESI score.
- Voluntary Participation: Shipowners participate voluntarily to demonstrate their vessels' environmental performance.
- Automated Calculation: The ESI score is automatically calculated and updated.
- Incentives: Ships with higher ESI scores may receive benefits such as reduced port fees and priority berthing.
IMF's World Economic Outlook (WEO)
- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has maintained India’s GDP growth forecast at 7% for FY2024, marking a moderation from 8.2% in 2023.
- FY2025 Projection: Growth is expected to slow further to 6.5% in FY2025.
- India’s growth is expected to be stronger than most other large economies, yet the downward revision reflects challenges in the global economy and moderation in domestic economic momentum.
Global Economic Growth Projections:
- Global Growth (2024-2025): Global growth is projected at 3.2% in 2024 and 2025, which is stable but modest. This growth rate is largely unchanged from previous IMF forecasts.
- Long-Term Outlook: The IMF's long-term projection for global growth is 3.1%, which is considered subpar compared to pre-pandemic growth rates, signaling a potential era of low growth.
Key Risks and Uncertainties:
- The IMF highlights several downside risks to global growth, including:
-
- Monetary tightening: Central banks' high-interest rate policies to combat inflation could have long-term negative effects on economic growth and financial stability.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, could disrupt global supply chains and trade, exacerbating inflation and slowing growth.
- China’s Economic Slowdown: China, the world’s second-largest economy, is facing a slower growth trajectory, especially in its real estate sector, which is dragging down its overall growth.
- Structural Challenges: The aging population and weak productivity are long-term growth inhibitors in many advanced economies, adding uncertainty to future growth prospects.
-
- Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
- 2023: Global inflation is expected to reach 6.7%.
- 2024: It is forecast to fall to 5.8%, with advanced economies expected to return to inflation targets sooner than emerging markets.
- 2025: A further decline to 4.3%.
- The primary driver of disinflation is not interest rate hikes but the unwinding of pandemic-related shocks, supply chain improvements, and the gradual return of labor supply.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks are likely to ease policies once inflation nears target levels, but risks of further commodity price spikes or geopolitical tensions could delay this.
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
US and Europe Growth:
- Emerging Markets and Developing Economies:
- Growth Outlook: The IMF forecasts growth in emerging markets and developing economies at 4.2% for 2024 and 2025, with a slight moderation to 3.9% by 2026.
- Emerging Asia: Growth in emerging Asia (led by India and China) is expected to slow, from 5.7% in 2023 to 5% in 2025.
- India’s Relative Strength: India’s growth continues to outperform many emerging economies, though the slowdown from 8.2% in 2023 to 7% in 2024 reflects global economic headwinds.
- Income Inequality Risks:
- The IMF warns that low growth over an extended period (4+ years) could exacerbate income inequality within countries, as sluggish growth affects job creation and wage growth.
- Countries with slow economic recovery are likely to see a widening gap between rich and poor, undermining social cohesion and stability.
Cyberfraud Losses and Economic Impact

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- ?1.2 lakh crore is the projected financial loss due to cyber frauds in India over the next year (2024), according to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Union Home Ministry.
- This could amount to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Mule Accounts:
- Mule accounts are a significant contributor to cyber frauds. These accounts are used to facilitate money laundering and illegal transactions.
- On average, around 4,000 mule accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- Mule accounts typically facilitate the transfer of funds out of India, often through cryptocurrency transactions.
- Sources of Cyber Scams:
- A majority of frauds are linked to Chinese entities or China-based operations, with about half of the cybercrime complaints originating from China.
- Other major hubs for cyber frauds include Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, which house call-centre-like scam compounds.
- Azerbaijan has also been identified as a new hotspot for such scams.
- International Dimension:
- Fraudulent withdrawals have been reported from ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia using mule accounts.
- The international nature of these scams often involves routing stolen funds through various countries, using methods like cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Cybercrime and Terror Financing:
- Cyber scams have potential ramifications beyond financial losses; they can be used for terror financing and money laundering.
- Cryptocurrency is a common medium for laundering money, with an example cited of ?5.5 crore laundered through 350 transactions in a short span.
- ATM Hotspots and Fraudulent Withdrawals:
- 18 ATM hotspots have been identified across India where fraudulent withdrawals occur.
- Fraudsters exploit these locations to withdraw money, often using mule bank accounts and cross-border ATM networks.
- Government Response:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is working to combat these frauds by convening meetings with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The objective is to curb the operation of mule accounts and strengthen the banking system to prevent such frauds.
- Banks are being urged to flag unusually high-value transactions or accounts with low balances that are engaging in suspicious activity.
- Fraudulent Calls and Scam Compounds:
- Indian fraudsters, in collaboration with international scam rings, use Indian mobile phone numbers to deceive citizens.
- Countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, and Azerbaijan have been identified as hubs for investment scams involving fraudulent calls.
- Helpline and Cyber Fraud Reporting System:
- The Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (part of I4C) and the 1930 helpline provide mechanisms to report financial frauds.
- ?11,269 crore in financial frauds was reported during the first half of 2024 via these channels.
- The system also involves cooperation with over 200 financial intermediaries, including banks and wallets.
IMF retains India’s growth projection at 7% for FY25
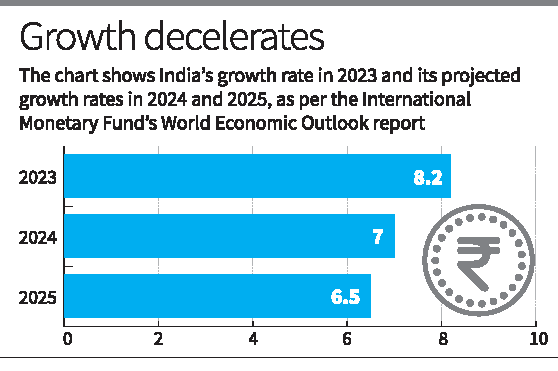
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised India's GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 7%, up by 20 basis points from its previous estimate of 6.8%.
- India’s Growth Projections:
- Current Fiscal Year (FY2024-25): India’s GDP growth is projected at 7%, unchanged from June 2024 estimates.
- Next Fiscal Year (FY2025-26): Growth expected at 6.5%.
- Growth Decline from FY2023 (8.2%): The slowdown is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand post-pandemic and the economy returning to its potential.
- Global Economic Growth:
- World Output: Projected global growth at 3.2% in both 2024 and 2025.
- Advanced Economies: U.S. GDP growth revised upward to 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
- Emerging Markets & Developing Economies: Growth revised upwards, largely due to stronger economic activity in Asia, with China and India being key contributors.
- Global Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Inflation Decline: Global inflation has decreased from its peak of 9.4% in Q3 2022 to 3.5% projected by end-2025.
- Inflation Outlook: Despite reductions in inflation, price pressures persist in some regions.
- Monetary Policy Tightening: IMF acknowledges challenges due to tight monetary conditions in several economies and their potential impacts on labor markets.
- Global Risks and Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating conflicts in West Asia (e.g., Lebanon) have increased geopolitical risks, potentially affecting commodity markets.
- Protectionism: Growing protectionist policies worldwide are a risk to global trade and economic stability.
- Sovereign Debt Stress: Debt burdens in several countries could become a source of instability.
- Weak Chinese Economy: Slower-than-expected recovery in China remains a significant concern for global economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Risks: Prolonged tight monetary policies in some countries could impact labor markets and economic recovery.
- IMF’s Policy Recommendations for Medium-Term Growth:
- Monetary Policy Neutrality: Countries should adopt a neutral monetary policy stance to balance growth and inflation control.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustment: Build fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy to ensure stability.
- Structural Reforms: Implement structural reforms to boost productivity and cope with challenges like aging populations, the climate transition, and the need for youth employment.
- India’s Economic Outlook - Key Drivers:
- Rural Consumption Growth: The upward revision of India's FY2024-25 GDP forecast to 7% is driven by improved consumption, especially in rural areas.
- Upward Revisions for 2023: The increased growth forecast also reflects positive carryover effects from India's 8.2% growth in 2023.
- Emerging Asia's Growth: The growth outlook for emerging Asia is supported by India and China, though long-term growth prospects for China are weaker (projected to slow to 3.3% by 2029).
- Global Economic Outlook:
- World Growth Projections: Global growth is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025.
- Diverging Growth Rates: Growth across economies is converging as output gaps close, particularly in advanced economies (e.g., U.S. labor market cooling, euro area recovery).
