National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan urges states to accelerate efforts under the National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to enhance domestic production of edible oils and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Facts Regarding the NMEO-OP Scheme:
About the Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance domestic production of crude palm oil (CPO) and reduce India's dependence on edible oil imports.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Focuses on expanding oil palm cultivation in India.
Key Targets:
- Area Expansion: Aim to cover an additional 6.5 lakh hectares by 2025-26, reaching a total of 10 lakh hectares.
- Production Increase: CPO production is targeted to rise from 0.27 lakh tonnes (2019-20) to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26, and further to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
- Per-Capita Consumption: Maintain a consumption level of 19 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
Focus Regions:
- Special Focus: North-Eastern States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands for oil palm cultivation and CPO production.
Key Features:
- Viability Price (VP) Mechanism: Aims to protect farmers from market volatility by providing price assurance. Payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Increased Assistance:
- Assistance for planting material increased from Rs 12,000/ha to Rs 29,000/ha.
- Special assistance of Rs 250 per plant for rejuvenating old gardens.
- Regional Support:
- For North-East and Andaman, an additional 2% of the CPO price is borne by the government to ensure fair payments to farmers.
- Special provisions for half-moon terrace cultivation, bio-fencing, and land clearance for integrated farming.
Oil Palm Cultivation:
- Origin: Native to the tropical rainforests of West Africa, oil palm is a new crop in India with high oil-yielding potential.
- Oil Yield: Oil palm produces five times the yield of traditional oilseeds per hectare.
- Types of Oil Produced:
- Palm Oil: Extracted from the mesocarp (fruit's fleshy part), containing 45-55% oil.
- Palm Kernel Oil: Derived from the kernel, used in lauric oils.
- Major States for Cultivation: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of total production).
- Other Key States: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland.
India's Oil Palm Potential:
- Cultivated Area: India currently has 3.70 lakh hectares under oil palm cultivation.
- Total Potential Area: Around 28 lakh hectares.
- Imports: India is the world's largest palm oil importer, with imports of 9.2 million tonnes in 2023-24, accounting for 60% of total edible oil imports. The country primarily imports from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Kisan Kavach
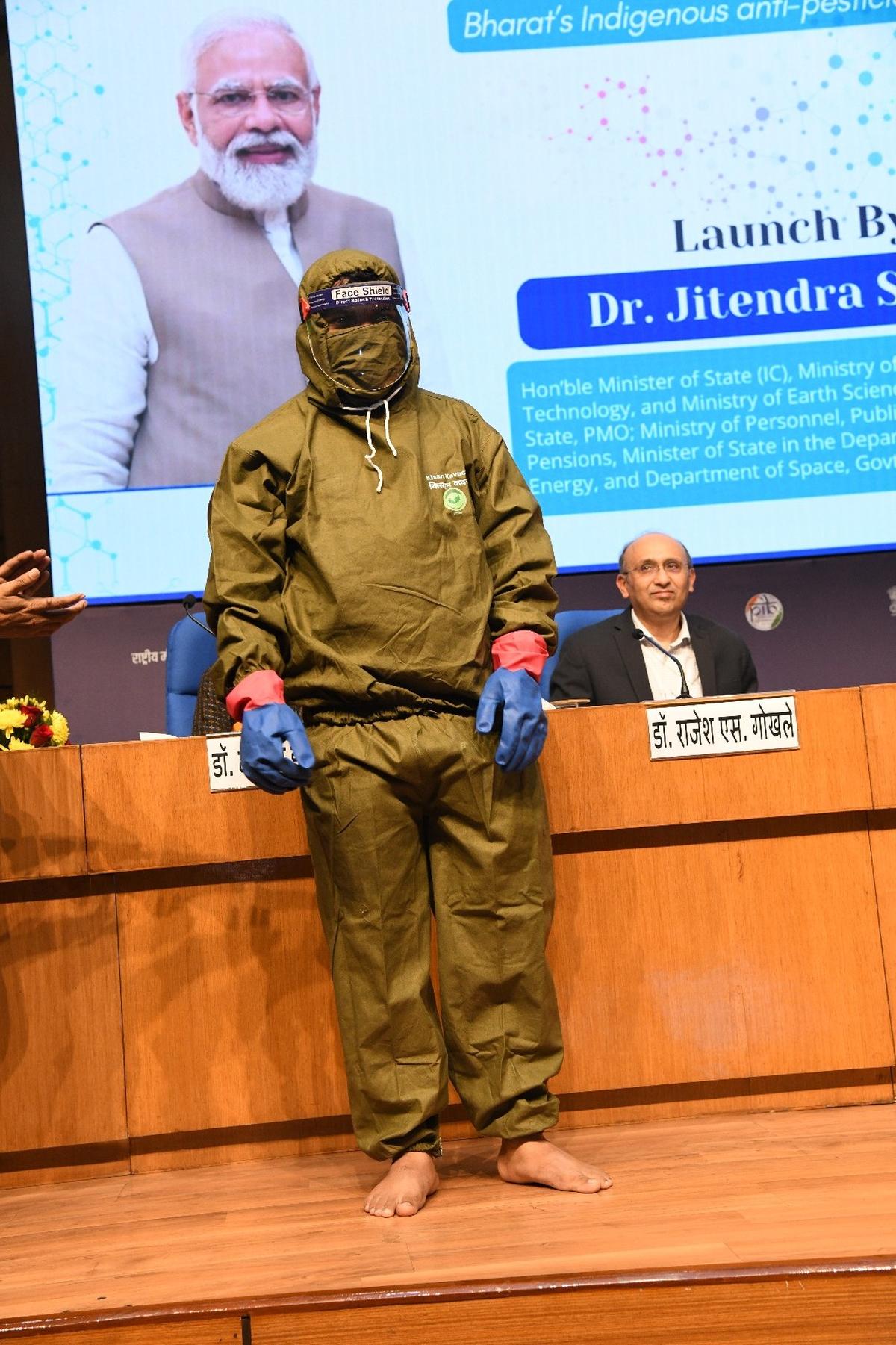

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Scientists develop ‘kisan kavach’ to shield farmers from pesticide sprays.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The Kisan Kavach is designed to shield farm labourers from harmful pesticide exposure. Pesticides, often neurotoxins, can be detrimental to health, causing symptoms like dizziness, headaches, vomiting, and even death with high exposure.
- Development:
- Developed by Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem), Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Launched by Union Minister of State for Science and Technology.
- Fabric Technology:
- The suit uses oxime fabric, which chemically breaks down common pesticides on contact, preventing them from penetrating the skin.
- Mechanism: The fabric works through nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis, deactivating pesticides upon contact and preventing pesticide-induced toxicity and lethality.
- Components of the Kit:
- Consists of a trouser, pullover, and face-cover.
- Washable and reusable: The suit retains its protective properties even after 150 washes, in a wide temperature range, and under UV light exposure.
- Affordability:
- Priced at ?4,000 per kit, with efforts underway to reduce costs through increased production.
- Field Testing and Efficacy:
- Animal studies: Rodent tests showed that animals exposed to pesticides and covered with ordinary cotton cloth died within four days, while those with the activated fabric remained safe.
- Human trials are still pending.
- Health Implications:
- Pesticides are linked to chronic health issues, including cancer, as per studies by the National Institute of Nutrition (Indian Council of Medical Research).
- Global Context:
- In 2020, India used 61,000 tonnes of pesticides, despite producing much more (2,58,130 tonnes in 2022-2023).
- Pesticide-related health issues are a major concern, with 60% of India’s adult workforce engaged in agriculture.
- Impact:
- The suit aims to protect farm labourers from pesticide exposure and promote sustainable agriculture.
- It could help reduce health complications and improve working conditions for farmers, who often lack proper protective gear.
- Future Plans:
- Awareness campaigns will be conducted to inform farmers about this protective technology.
- Efforts are underway to make the kit more affordable as demand increases.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF), launched by Union Minister Pralhad Joshi aims to support farmers by facilitating post-harvest finance using electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to minimize distress selling and ensure financial security for farmers, particularly small and marginalized ones.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Total Corpus: ?1,000 crore for post-harvest finance.
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?75 lakh.
- Non-agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled and cooperative banks.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- Small and marginal farmers/Women/SC/ST/PwD: 85% for loans up to ?3 lakh, and 80% for loans between ?3 lakh to ?75 lakh.
- Other borrowers: 75% coverage for loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Risks Covered: Both credit risk and warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Fees: 0.4% per annum for farmers, and 1% per annum for non-farmers.
Objectives:
- Minimize distress selling: By providing easy access to loans post-harvest, the scheme helps farmers avoid selling produce at low prices due to cash crunches.
- Instill confidence in banks: The scheme provides a guarantee cover to lenders, encouraging them to offer loans against e-NWRs.
- Encourage warehouse registration: The scheme emphasizes the need for more warehouses, particularly those closer to farmland, to improve accessibility for farmers.
About e-NWRs:
- e-NWRs are digital versions of traditional warehouse receipts that enable farmers to pledge stored commodities as collateral for loans.
- These receipts are governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007, and since 2017, e-NWRs have been mandated for use in transactions related to agricultural produce stored in WDRA-accredited warehouses.
Expected Impact:
- This scheme is expected to boost post-harvest lending, with a target of increasing lending to ?5.5 lakh crore in the next decade.
- It will improve farmers’ income, reduce dependence on informal credit sources, and foster better financial inclusion.
- Additionally, it will create a more reliable supply chain for agricultural produce, enhancing food security.
Future Targets:
- Increase the number of registered warehouses under the WDRA to 40,000 in the next 1–2 years.
- Use platforms like e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi to streamline the lending process and avoid repeated visits to banks.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan agreement to enhance horticulture crop productivity by improving plant health management. This initiative is part of India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to provide farmers with access to certified disease-free planting materials to improve yields, quality, and resilience, particularly against climate change impacts.
Key Highlights of the Loan Agreement
- Objective: Improve access to certified, disease-free planting materials for horticulture crops.
- Implementation: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Focus: The initiative will enhance farmers’ productivity, resilience to climate change, and pest/disease management through the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP).
About the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
The Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme aims to tackle critical challenges in horticulture by ensuring farmers have access to high-quality, virus-free planting materials. The program is designed to:
- Enhance crop yields and quality.
- Promote climate-resilient varieties to help farmers adapt to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Safeguard the environment by controlling plant diseases and pests proactively.
Key Components of the CPP
- Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): Establishment of nine world-class CPCs across India, equipped with advanced diagnostic labs and tissue culture facilities to maintain disease-free foundation planting materials.
- Certification Framework: A robust certification system will be introduced to ensure accountability in planting material production, including accreditation for private nurseries.
- Climate Resilience: Focus on developing and disseminating climate-resilient plant varieties, addressing the growing concerns over extreme weather events and changing pest behavior due to climate change.
Significance of the Loan Agreement
- Climate Adaptation: The project will help farmers mitigate the effects of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns and altered pest/disease behaviors.
- Economic Impact: The initiative aligns with India's vision of self-reliance in horticulture (Atmanirbhar Bharat), boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Long-term Benefits: Improved farm productivity, sustainability, and economic well-being for farmers, especially in the face of climate change.
Global Horticulture Significance
- India’s Position: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, contributing 33% to the agricultural GDP.
- Land Coverage: Horticulture occupies 18% of India’s agricultural land, yet its production surpasses that of food grains.
Implementation and Impact
- Implementation Period: The project will be executed from 2024 to 2030, with 50% financial assistance from ADB.
- Institutional Strengthening: The initiative will bolster India’s ability to manage plant health, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques and capacity-building for horticulture professionals.
KisanPehchaan Patra
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government is actively promoting the creation of digital identities for farmers through the KisanPehchaan Patra (Farmer ID). The initiative is an essential part of the Digital Agriculture Mission under the AgriStack initiative.
Key Details:
Objective:
- The main goal is to provide digital IDs linked to Aadhaar for farmers, capturing comprehensive agricultural data including land records, crop information, and ownership details.
- These digital identities are designed to enhance farmers' access to government schemes and digital agriculture services.
Farmer ID Creation Timeline:
- The government plans to create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers in phases:
- 6 crore farmers in FY 2024-25.
- 3 crore farmers in FY 2025-26.
- 2 crore farmers in FY 2026-27.
AgriStack Initiative:
- The AgriStack initiative aims to build a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for the agriculture sector, which includes:
- Farmers' Registry.
- Geo-referenced village maps.
- Crop Sown Registry.
Implementation Strategy:
- Camp-mode approach: States have been instructed to organize field-level camps to ensure faster and inclusive registration of farmers.
- Financial Incentives:
- States will receive ?15,000 per camp for organizing these camps.
- Additionally, ?10 per Farmer ID issued.
- Funding is provided through the Pradhan Mantri KisanSamman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme.
Benefits of Digital Farmer ID:
- Targeted Delivery of Benefits: Ensures subsidies and benefits reach legitimate farmers and eliminates duplication.
- Precision Agriculture: Supports data-driven policies for better crop planning, insurance, and market linkages.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates easy access to credit, loans, and crop insurance, empowering farmers financially.
- Better Monitoring: Helps in tracking the actual implementation of schemes and ensures that only eligible farmers benefit.
Progress in States:
- Advanced States: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh have made significant progress in issuing digital Farmer IDs.
- Testing Phase: States like Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha are still in the field-testing phase.
- Special Assistance Scheme: The Finance Ministry allocated ?5,000 crore in August 2024 to assist states in creating the Farmers' Registry, with funds available until March 2025.
Linkage with Land Records and Crop Data:
- The Farmer ID integrates with state land records and crop data, creating a dynamic and accurate database known as the Farmer’s Registry.
- This data helps in the development of better agricultural policies and decision-making.
Digital Agriculture Mission:
- The government approved a substantial outlay of ?2,817 crore for the Digital Agriculture Mission, which is intended to modernize agricultural practices and build robust digital infrastructure.
- The mission also includes the launch of the Digital Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), which will help in crop estimation and better resource allocation.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
13th National Seed Congress (NSC)

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 13th National Seed Congress (NSC), organized by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, concluded with significant discussions and outcomes focused on advancing India's seed sector.
- The theme for this year's congress, held in Varanasi, was "Innovating for a Sustainable Seed Ecosystem."
Key Highlights:
- Focus Areas:
- Seed Technologies and Biofortification: Emphasis on high-nutrition seeds like iron and zinc-enriched rice and Vitamin A-rich crops to combat malnutrition.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Promoting practices like Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) and the development of stress-tolerant seed varieties to withstand climate change.
- Challenges in India’s Seed Ecosystem:
- Seed Replacement Rate (SRR): SRR in India is around 15-20%, with 100% for hybrid seeds, pointing to the need for higher adoption of certified seeds.
- Monoculture and Seed Market Monopoly: Issues like over-reliance on Bt cotton and domination by multinational companies (e.g., Bayer) in seed markets.
- Government Initiatives:
- National Seed Corporation (NSC): Produces foundation and certified seeds for over 600 varieties.
- Seed Village Programme (Beej Gram Yojana): Focus on improving the quality of farm-saved seeds.
- National Seed Reserve: Ensures seed availability during climatic disruptions.
- Policy Discussions:
- Proposed Seeds Bill: A new bill to regulate seed quality and promote sustainable practices.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations to improve seed production, accessibility, and quality.
- Outcomes:
- Biofortified Seeds: Increased development and distribution of nutrient-rich seeds.
- Climate-Resilient Seed Systems: Enhanced focus on developing crops that can withstand climate challenges.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations in seed technology and policy reform.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the launching of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) as a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare.
Key Highlights
Objective & Focus:
- Launch of NMNF by the Union Cabinet to promote chemical-free farming in India.
- Aim to improve soil health, reduce input costs, and produce nutritious food.
- Support the shift to natural farming (NF), emphasizing local knowledge and agro-ecological principles.
Financial Allocation:
- Total Outlay: ?2481 crore (Government of India share ?1584 crore, State share ?897 crore) until FY 2025-26.
Key Features of NMNF:
- Coverage: Targeting 15,000 clusters in Gram Panchayats, covering 7.5 lakh hectares and impacting 1 crore farmers.
- Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs): 10,000 BRCs to supply ready-to-use natural farming inputs.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and Agricultural Universities (AUs): Establishment of 2,000 model demonstration farms for hands-on training in natural farming techniques.
- Farmer Training: 18.75 lakh farmers to be trained in NF practices such as preparation of organic inputs like Jeevamrit and Beejamrit.
- Krishi Sakhis/CRPs: Deployment of 30,000 workers for farmer mobilization and awareness.
Implementation Strategy:
- Farmer Certification System: Providing easy, simple certification for marketing natural farming produce with dedicated branding.
- Monitoring: Real-time, geo-tagged monitoring of implementation through an online portal.
- Convergence with other government schemes and organizations for market linkages and support.
Natural Farming Practices:
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): Promote sustainable farming by using local livestock and diverse crop systems.
- Benefits: Reduce dependence on external inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, rejuvenate soil quality, and increase resilience to climate risks (e.g., drought, floods).
- Encourage biodiversity, and improve soil carbon content and water-use efficiency.
Targeted Areas and Farmer Support:
- Focus on areas where NF practices are already being followed or where farmer producer organizations (FPOs) or self-help groups (SHGs) are active.
- Training through model demonstration farms will focus on practical, location-specific NF techniques tailored to regional agro-ecologies.
Impact on Agriculture and Environment:
- Environmental Impact: Encourages sustainable farming by reducing chemical exposure, improving soil health, and promoting climate resilience.
- Farmer Well-being: By reducing input costs and promoting nutritious food, it aims to improve farmer incomes and family health.
- Contributing to the long-term health of the environment, ensuring a healthy Mother Earth for future generations.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Soil Nutrient Compromise: Concerns that some crops, like rice, might require chemical fertilizers (e.g., NPK) for optimal growth, which may not be sufficiently replaced by organic manure alone.
- The shift to natural farming requires significant awareness and training to ensure sustainable and productive yields.
Institutional Framework:
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is the implementing body.
- Collaboration with KVKs, AUs, and farmer organizations ensures grassroots level support and knowledge dissemination.
Global Soil Conference 2024
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
- Global Soil Conference (GSC) 2024 held in New Delhi.
- Focused on soil health's importance for food security, climate change mitigation, and ecosystem services.
What is the Global Soil Conference 2024?
- Organizers: Indian Society of Soil Science (ISSS) in collaboration with the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS).
- Objective: Address sustainable soil/resource management challenges and foster global dialogue.
- Theme: "Caring Soils Beyond Food Security: Climate Change Mitigation & Ecosystem Services."
Key Highlights of GSC 2024:
- Soil Health Issues:
- Soil degradation threatens productivity and global food security.
- 30% of India's soil is compromised by erosion, salinity, pollution, and organic carbon loss.
- Soil erosion is linked to SDG 15 (Sustainable Development Goal 15), aiming to protect terrestrial ecosystems.
- SDG 15:
- Goals: Promote sustainable land use, combat desertification, halt land degradation, protect biodiversity.
Concerns Regarding Soil Health in India:
- Soil Degradation:One-third of India's land faces degradation due to poor farming practices.
- Soil Erosion & Fertility Loss:
- India loses 15.35 tonnes of soil/hectare annually.
- Results in crop losses, economic damage, and environmental issues like floods and droughts.
- Soil Salinity:Reduces water infiltration, nutrient uptake, and aeration, making land infertile.
- Low Organic Content:
- Organic carbon in Indian soil is 0.54%, which hampers fertility.
- Over 70% of soils are affected by acidity or alkalinity, disrupting nutrient cycles.
- Desertification:Reduces soil fertility, increases erosion, and worsens food insecurity.
- Diversion of Fertile Land:Fertile agricultural land is diverted for non-agricultural purposes.
India's Initiatives for Soil Conservation:
- Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme:Provides farmers with soil nutrient information.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana:Focuses on efficient water use.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming & Natural Farming Mission:Promotes sustainable farming practices to protect soil health.
OECD Report on Indian Agricultural Policies

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- In 2023, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) revealed that Indian farmers faced the highest implicit taxation globally, amounting to USD 120 billion.
- Implicit Taxation: This taxation arises from government policies like export bans, duties, and price controls, aimed at lowering food prices for consumers but reducing the income of farmers.
- Export Restrictions: Key commodities affected include rice, sugar, onions, and de-oiled rice bran.
Impact on Indian Farmers
- Market Price Support (MPS):
- Negative MPS: In 2023, Indian agricultural policies resulted in a negative MPS of USD 110 billion.
- Farmers received lower prices than international market rates due to export bans and trade restrictions, impacting their income.
- Budgetary Support: Despite government subsidies and the Minimum Support Price (MSP) worth USD 10 billion, negative MPS outweighed positive support, leading to an overall loss for farmers.
- Farmer’s Share in Global Negative Support:
- India’s share of global negative price support in 2023 was 62.5%, a significant increase from 61% in 2000-02.
Global Agricultural Policy Trends
- Global Support: Total support for agriculture across 54 countries averaged USD 842 billion annually (2021-2023). However, there was a decline in support in 2022-23 from the pandemic-era peak.
- Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) and climate change are exacerbating global agricultural production and trade.
- Export Restrictions in various countries are distorting international agricultural markets.
- Farmer Protests across countries reflect the economic and social struggles of the farming community.
- Sustainability Issues: Global agricultural productivity growth is slowing, posing challenges to feeding a growing population sustainably.
India's Agricultural Policies
- Export Bans and Restrictions: These policies are intended to control domestic prices but undermine farmers’ income by lowering market prices for key agricultural products.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): MSP is meant to protect farmers, but is often set below international market rates, leading to a negative price effect.
- Regulatory Constraints: Policies like the Essential Commodities Act (1955) and APMC Act (2003), though aimed at ensuring food security, often lead to price suppression for farmers.
- Price Depressing Policies: India's agricultural policies result in lower farm-gate prices due to price controls, government-set procurement prices, and lack of market access.
Negative Market Price Support (MPS)
- Historical Trends:
- From 2014-2016, India’s Producer Support Estimate (PSE) was -6.2%, driven mainly by negative MPS (-13.1%).
- The PSE measures the annual value of transfers to farmers, both from consumers and the government.
- Inefficiencies:
- Infrastructure Gaps: Poor infrastructure and high transaction costs lower the prices farmers receive.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Short-term subsidies for inputs (fertilizers, irrigation) don’t address long-term agricultural challenges like climate change and market access.
Government Support Programs
- Subsidies and Schemes:
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) for organic farming.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) to promote agricultural development.
- Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP) for modernizing agricultural practices.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- The government has introduced initiatives like AgriStack and Mission Organic Value Chain Development in the North East to enhance sustainable agricultural practices and reduce the negative impacts on farmers.
Global Context and Recommendations
- Environmental Public Goods Payments (EPGP): Only 0.3% of total producer support is dedicated to environmental sustainability, despite the growing need for climate-resilient agriculture.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: The OECD advocates for governments to tie producer support to sustainable farming practices, including the use of metrics like Total Factor Productivity (TFP) and Agri-Environmental Indicators (AEIs).
- TFP measures agricultural efficiency, while AEIs assess the environmental impacts of farming.
OECD Overview
- OECD Function: Founded in 1961, the OECD is an international organization of 38 countries that promotes prosperity, equality, and well-being through economic reports, data, and policy analysis.
- India’s Role: India has been an OECD Key Partner since 2007, engaging with the OECD on various policy issues, though it is not a member.
Nano-Coating Technology for Fertilizer Efficiency

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A mechanically stable, biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating material can enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers by tuning them for slow release, thereby limiting their interaction with the rhizosphere soil, water and microbes.
Development of Slow-Release Fertilizers:
- A biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating has been developed to enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers.
- The nanocoating allows for slow release of nutrients, thus limiting excessive interaction with soil, water, and microbes, and optimizing fertilizer usage.
Coating Composition:
- The coating is made from nanoclay-reinforced binary carbohydrates, primarily chitosan (a biopolymer from chitin) and lignin (a plant-based polymer).
- These materials are low-cost, naturally derived, and eco-friendly, ensuring sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of fertilizer use.
Technological Innovation:
- The coating process involves using a drum rotor method to uniformly coat fertilizers, improving their efficiency.
- The tuning of hydrophobicity in the nanocoating alters the release kinetics of fertilizers, ensuring that nutrients are released in accordance with the crop’s nutrient uptake needs.
Sustainability and Biodegradability:
- The nanocoating is biodegradable, which ensures that it does not harm the environment post-application, unlike conventional chemical fertilizers that may lead to soil degradation and water pollution.
- Life cycle assessment confirms the product's long-term sustainability compared to traditional fertilizers.
Enhanced Crop Productivity:
- The slow-release coating enables a reduced fertilizer dose, while maintaining or even increasing crop yields, particularly for staple crops like rice and wheat.
- This technology facilitates higher agricultural output with fewer inputs, contributing to food security.
Industrial Viability:
- The mechanical stability of the coated fertilizers ensures they can withstand transportation and handling, making them suitable for large-scale industrial application.
- The rotary drum system used for coating ensures uniform application and superior mechanical performance, ensuring that the fertilizers are not damaged during the supply chain process.
Economic Benefits:
- The use of slow-release fertilizers can reduce overall fertilizer costs for farmers while enhancing yields, leading to improved socio-economic conditions for farmers.
- The technology holds potential for economic growth by boosting agricultural productivity and reducing the financial burden on farmers for chemical fertilizer inputs.
Global Relevance:
- The research is significant in the context of global sustainable development goals, aiming to reduce the over-reliance on conventional chemical fertilizers that contribute to soil degradation, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Research Collaboration:
- This breakthrough was achieved by scientists from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, in collaboration with the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science: Nano, highlighting its scientific validation.
State of Food and Agriculture 2024Report
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- India's annual hidden costs from agrifood systems total $1.3 trillion, the third-largest globally, after China ($1.8 trillion) and the US ($1.4 trillion).
- These costs are mainly driven by unhealthy dietary patterns leading to non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
Major Contributors to Hidden Costs:
- Unhealthy Diets: Over 73% of India’s hidden costs stem from unhealthy dietary habits, including:
- Excessive consumption of processed foods and additives ($128 billion).
- Low intake of plant-based foods, fruits, and beneficial fatty acids ($846 billion).
- These dietary risks contribute to a significant health burden, increasing the prevalence of NCDs and reducing labor productivity.
Global Context:
- Global hidden costs of agrifood systems amount to $12 trillion annually.
- 70% of these costs (~$8.1 trillion) arise from unhealthy dietary patterns, which include high intakes of sugar, salt, and processed foods, contributing to diseases and economic losses.
Health Impacts:
- The report identifies 13 dietary risk factors that contribute to NCDs, including insufficient intake of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and excessive sodium, with varying effects across different agrifood systems.
Environmental and Social Costs:
- Environmental Costs: High costs from unsustainable agricultural practices, including greenhouse gas emissions and nitrogen runoff. In some agrifood systems, environmental costs can reach up to 20% of GDP.
- Social Costs: High poverty rates among agrifood workers and undernourishment in systems like protracted crises and traditional agrifood systems contribute significantly to the hidden costs.
India’s Agrifood System Profile:
- India’s agrifood system faces significant challenges related to low wages, poor productivity, and poverty among agrifood workers, driven by distributional failures.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Issues like droughts, floods, and soil degradation threaten food security and agricultural sustainability in India.
Recommendations for Transformative Change:
- True Cost Accounting: Implementing this method can help better capture hidden costs and enable more informed decision-making for a sustainable agrifood system.
- Healthier Diets: Policies to make nutritious food more affordable and accessible to reduce health-related hidden costs.
- Sustainability Incentives: Encouraging practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, harmful land-use changes, and biodiversity loss, using labelling, certification, and industry standards.
- Consumer Empowerment: Providing accessible information about the environmental, social, and health impacts of food choices, ensuring even vulnerable households benefit from healthier options.
India’s Path Forward:
- India has several ongoing initiatives for sustainable agriculture, including:
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- Eat Right Initiative.
- Digital Agriculture Mission (DAM).
- However, challenges like climate change, soil degradation, and low productivity among smallholder farmers hinder progress toward sustainable food systems.
Key Focus Areas for India’s Agrifood Systems:
- Support for Smallholder Farmers: Enhancing access to technology, markets, and financial services for marginalized farmers.
- Sustainable Practices: Adoption of water-efficient practices, soil health restoration, and environmentally friendly farming methods.
- Collaboration with International Agencies: Cooperation with FAO, WFP, and others to strengthen agricultural reforms and support smallholder farmers.
NAMO DRONE DIDI

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare has released the Operational Guidelines of Central Sector Scheme “NAMO DRONE DIDI”
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Empower women through Self-Help Groups (SHGs) by providing drones for agricultural rental services.
- Aim to support 14,500 SHGs from 2024 to 2026.
Scheme Overview:
- Type: Central Sector Scheme, under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM).
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Target: Women SHGs for providing drone services in agriculture (e.g., nutrient and pesticide spraying).
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance:
- 80% subsidy (up to ?8 lakh) for SHGs to purchase drones.
- Loans for the remaining 20% via the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with 3% interest subvention.
- Drone Package:
- Includes drones, spray assemblies, batteries, cameras, chargers, and measurement tools.
- Additional batteries and propellers allow up to 20 acres of coverage per day.
- Training Program:
- One SHG member will be selected for 15 days of mandatory training.
- Focus on drone operation and agricultural tasks (nutrient and pesticide spraying).
- Implementation & Oversight:
- Central Governance: Empowered Committee comprising secretaries from key ministries (Agriculture, Rural Development, Fertilizers, Civil Aviation, and Women and Child Development).
- State Level: Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs) will implement the scheme in coordination with state departments and SHG federations.
- Monitoring: IT-based Management Information System (MIS) through the Drone Portal for real-time tracking and fund disbursement.
- Financial Flexibility:
- SHGs can access loans through other Ministry of Rural Development schemes if needed.
Implementation Details:
- Governance: Central level oversight by the Empowered Committee and state-level execution by Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Ownership: Drones procured by LFCs will be owned by SHGs or their Cluster Level Federations (CLFs).
- Monitoring: The scheme will be tracked and managed through the Drone Portal, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has decided to introduce four new components under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), aimed at promoting modern farming techniques:Hydroponics, Aquaponics, Vertical Farming&Precision Agriculture
Key Features of MIDH:
- MIDH is a Central Sponsored Scheme (CSS) aimed at the integrated development of various horticulture crops, including:
- Fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa, and bamboo.
- The scheme focuses on pre-production, production, post-harvest management, processing, and marketing activities.
Revision of Operational Guidelines and Cost Norms:
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare is revising the MIDH operational guidelines and cost norms, which were last updated in April 2014.
- The revised guidelines are expected to be released within one month.
- Cost norms are likely to increase by 20% compared to the existing rates, addressing concerns from various states about outdated guidelines.
Reason for Revision:
- Several states, including Odisha, have raised concerns over the old rates under MIDH. For example, Odisha’s Agriculture Minister highlighted that the state was still using 10-year-old rates.
- The Union Cabinet had already approved the rationalization of all CSS operating under the Ministry into two umbrella schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (PM-RKVY)
- Krishonnati Yojana (KY)
Growth in India's Horticulture Sector:
- India’s horticulture production has significantly increased in recent years:
- Total production reached 334.60 million metric tonnes in 2020-21, up from 240.53 million metric tonnes in 2010-11.
- India is now the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, surpassing food grain production.
- MIDH Annual Budget:The annual allocation for MIDH in the current financial year (2024-25) is ?2,000 crore.
National Workshop on SATHI Portal

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Department of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare (DA&FW) organised a National Workshop on the SATHI (Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory) Portal in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Purpose & Focus
- SATHI Portal: Focuses on Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory to enhance seed certification, improve seed traceability, and streamline the seed supply chain.
- Primary Objective: Ensure availability of high-quality seeds to farmers through a transparent and efficient seed management system.
Key Features of the SATHI Portal
- Seed Certification: Aims to streamline seed certification processes across states for faster and more accurate seed certifications.
- Seed Traceability: Enhances transparency and traceability of seeds to ensure quality and authenticity.
- Inventory Management: The portal facilitates seed inventory management, helping farmers and stakeholders access reliable and transparent seed information.
- Technological Integration: Developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), the portal incorporates technology-driven solutions to minimize transactional time for registrations, approvals, and certifications.
Phase-II Rollout
- Focus on seed inventory management, with the objective of offering farmers reliable access to certified seed varieties.
- It aims to integrate state-specific seed processes into the national framework for greater standardization and efficiency.
Workshops & Technical Sessions
- NIC and ICAR Presentations: Covered the core components of the SATHI Portal, including:
- Seed Law Enforcement
- DNA Fingerprinting for ensuring seed authenticity.
- Seed Laboratory Processes to uphold quality control.
- Review of Phase-I: Discussions on achievements of Phase-I, focusing on improvements in seed certification processes across states.
- State Experiences: 10 state representatives shared insights on their experiences with the portal, discussing both benefits and challenges in the implementation phase.
Role of NIC & Technology
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) is the technology partner behind the SATHI Portal, which is designed to enhance the efficiency of seed certification and inventory management.
- The portal contributes to larger digital initiatives like the Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP), which aim to support agricultural development through technology.
