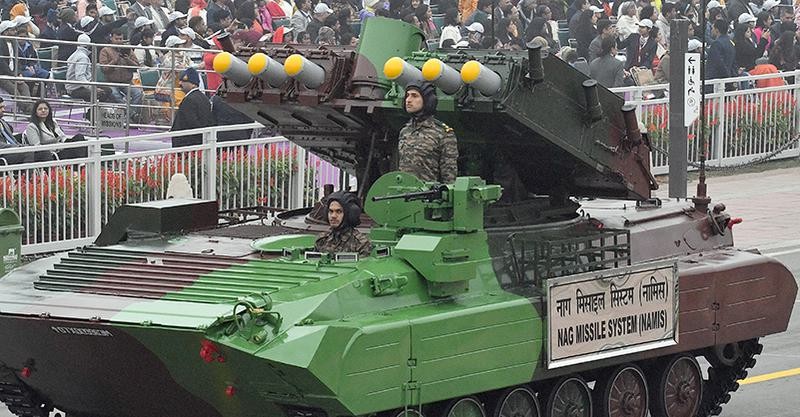
Nag Mark-2

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Madhav Gadgil, an Indian ecologist, received the UN Environment Programme (UNEP)'s Champions of the Earth Award in 2024.
- The Champions of the Earth Award is UNEP’s highest environmental honor, recognizing individuals, organizations, and governments for significant contributions to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Contributions of Madhav Gadgil:
- Work in Western Ghats:
- Gadgil is recognized for his seminal work in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive region in India, which is a global biodiversity hotspot.
- He chaired the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), formed by the Indian government to assess the impacts of population pressure, climate change, and development on the region.
- Recommendations by WGEEP:
- Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA): Recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats range as an ESA.
- The WGEEP suggested dividing the Western Ghats into three Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ) based on environmental sensitivity.
- Development Restrictions: Proposed a ban on activities like mining, quarrying, thermal power plants, and large-scale hydropower projects in the most sensitive zones (ESZ-1).
- Governance Recommendations: Suggested a bottom-to-top governance approach, beginning with Gram Sabhas, and the creation of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority (WGEA) for effective management.
- Impact of Gadgil’s Work:
- His research and recommendations have played a crucial role in shaping environmental policy and public opinion in India.
- The UNESCO World Heritage status for the Western Ghats in 2012 was a significant step in global recognition of the region’s ecological importance.
About the Champions of the Earth Award:
- History & Significance:
- Established in 2005, the award recognizes trailblazers working towards addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- Since its inception, it has honored 122 laureates who have shown outstanding leadership in environmental conservation.
- 2024 Awardees:
- Madhav Gadgil (India) – for his work on the Western Ghats.
- Sonia Guajajara (Brazil) – for advocacy for Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
- Amy Bowers Cordalis (USA) – for her work in Indigenous rights and ecosystem restoration.
- Gabriel Paun (Romania) – for defending Europe’s old growth forests from illegal logging.
- Lu Qi (China) – for contributions to afforestation and combating desertification.
- SEKEM (Egypt) – for advancing sustainable agriculture.
Key Facts about UNEP:
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Established in 1972, UNEP is a leading global authority on environmental issues.
- UNEP aims to address climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution through scientific research, policy support, and public advocacy.
- UNEP is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya and works closely with 193 Member States to tackle the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
Digital Population Clock

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bengaluru's first digital population clock was inaugurated at the Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC) on November 8, 2024.
- The initiative is collaboration between ISEC and the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
Purpose:
- The clock provides real-time population estimates for Karnataka and India.
- It aims to enhance awareness about population dynamics and provide accurate demographic data for research and policy analysis.
Key Features:
- Real-time Updates:
- Karnataka’s population is updated every 1 minute and 10 seconds.
- India’s population updates every 2 seconds.
- Precision:
- The clock operates with satellite connections for real-time, accurate data updates.
- It functions autonomously with integrated components, ensuring continuous and precise tracking.
- Location: The clock is prominently displayed at the entrance of ISEC.
- National Expansion: Similar digital population clocks are being installed in 18 Population Research Centres across India by MoHFW.
Significance:
- Awareness: The clock serves as a visual tool to highlight the rapid pace of population growth and its implications for sustainable development.
- Research and Analysis: The clock is part of a broader effort to improve demographic studies and inform policy-making.
- Census Data Research Workstation:
- ISEC has introduced a new research workstation, supported by MoHFW, for in-depth demographic analysis.
- The facility is equipped with advanced software for studying population trends and supporting academic research.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
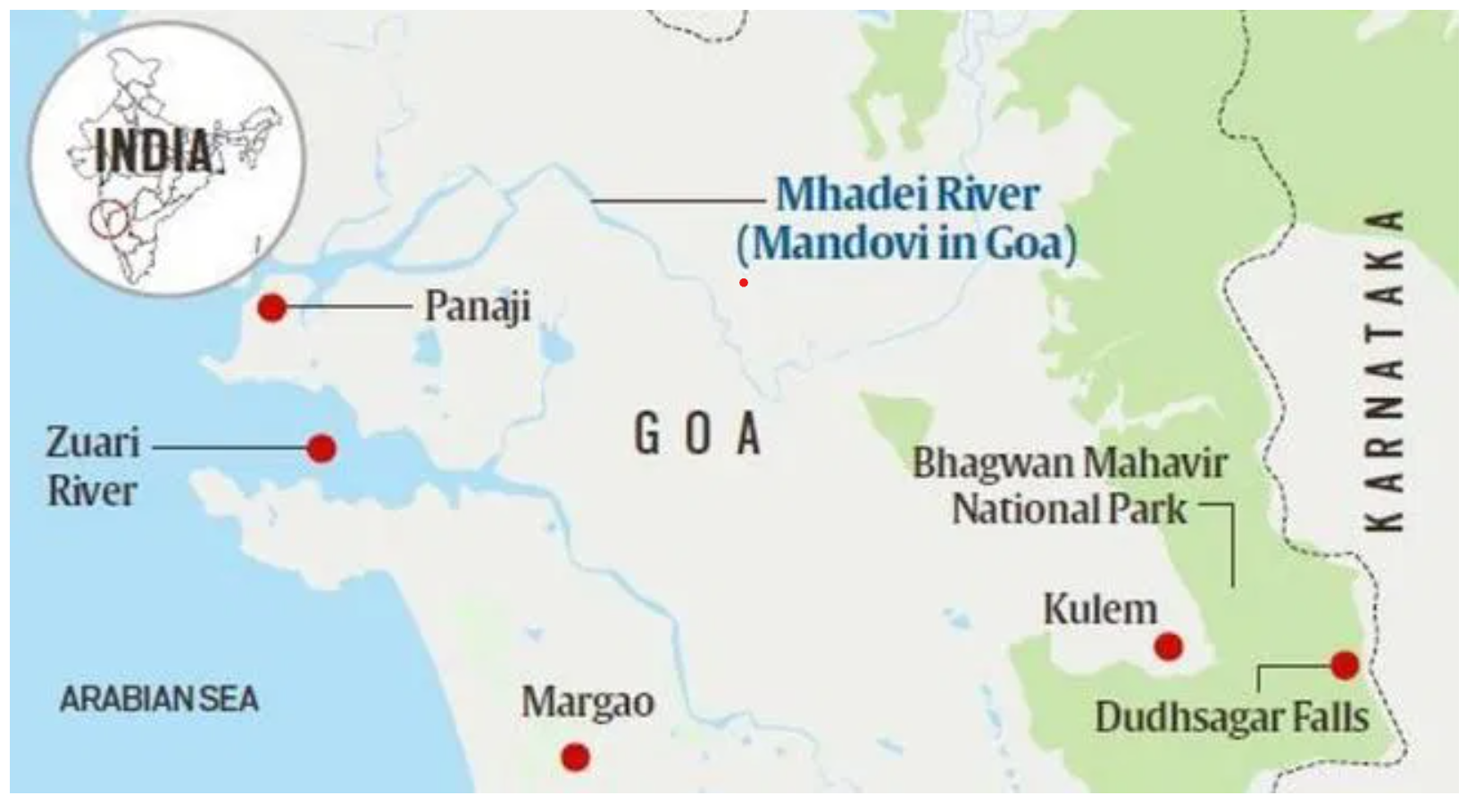
Location and Geography:
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
- 25 Oct 2024
A critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (GIB) chick was successfully born through artificial insemination (AI) at a breeding center in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, marking a crucial step in efforts to save the species.
Endangered Status:
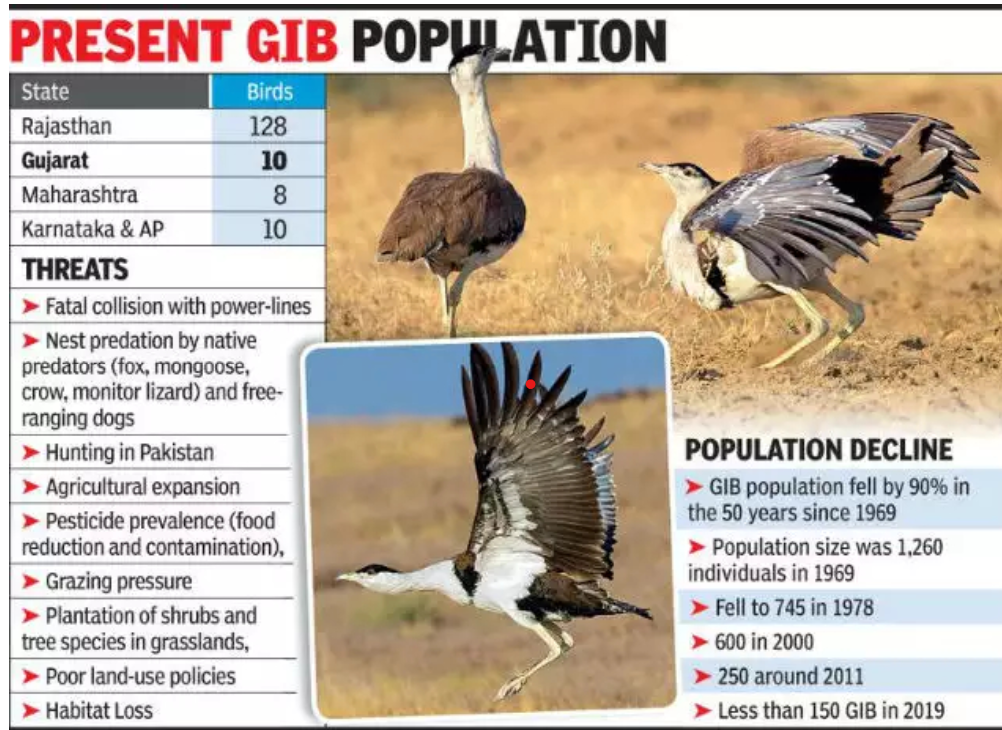
- The Great Indian Bustard is classified as critically endangered with fewer than 150 individuals left in the wild in India.
- About 90% of these birds are found in the desert areas of Rajasthan, with smaller populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Main Threats to the Species:
- Habitat Loss: The primary threat is the loss of habitat, which is often perceived as wasteland and is diverted for infrastructure projects like roads and development.
- Slow Reproductive Rate: The bustard’s low reproductive rate exacerbates its risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts: Bustard Recovery Program
- In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched the Bustard Recovery Program to focus on captive breeding and creating a sustainable environment for the reintroduction of GIBs into the wild.
- A dedicated GIB breeding center was set up at the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, as part of this initiative.
- Protection Status of GIB:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- It is also the state bird of Rajasthan, emphasizing its importance in the region’s biodiversity.
