Human Papillomavirus (HPV)

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, and the focus on this month underscores the critical importance of preventing cervical cancer, a disease responsible for significant mortality among women in India. At the heart of this prevention is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which is recognized as the most effective measure to prevent cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers. Despite its potential, the HPV vaccine remains out of reach for many due to its high cost and the need for greater awareness.
HPV and its Impact in India
HPV is responsible for 99.7% of cervical cancers worldwide, making it one of the primary causes of cancer in women. In India, cervical cancer is the third most common cancer among women, accounting for about 6-29% of all cancers in women. As of GLOBOCAN 2020, India alone has 20% of the global burden of cervical cancer, with over 123,000 cases and a 9.1% mortality rate.
Additionally, HPV can lead to several other cancers, including anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, and throat cancers, making its vaccination vital for overall cancer prevention.
The HPV Vaccine: A Game-Changer
The HPV vaccine is the most effective tool to prevent infections caused by the virus and reduce the incidence of associated cancers. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies that neutralize the virus before it can cause damage. There are different types of vaccines authorized in India, including:
- Gardasil (protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18)
- Cervarix (a bivalent vaccine targeting HPV 16 and 18)
- Cervavac (India's first HPV vaccine, developed by the Serum Institute of India)
The vaccine is recommended for both males and females between 9 and 26 years, with a special focus on children aged 12 to 13 years, as the vaccine is most effective when administered before exposure to the virus. It’s also suitable for people who are immunocompromised or HIV-infected.
Challenges to HPV Vaccination in India
Despite the obvious benefits, the uptake of the HPV vaccine in India faces several barriers:
- High Costs: The price of the vaccine remains prohibitively high. For example:
- Gardasil 9 costs ?10,850 per dose.
- Gardasil 4 is priced between ?2,000 to ?4,000 per dose.
- Cervavac, the Indian-made vaccine, costs around ?2,000 per dose, which is more affordable but still out of reach for many.
- Awareness and Cultural Perceptions: There is a lack of awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer. Cultural factors, particularly around reproductive health, can also create reluctance to vaccinate, especially in rural or conservative areas.
- Limited Access: Currently, the vaccine is available through private practitioners and is not part of the National Immunisation Programme (NIP), limiting access to the broader population.
The Way Forward: National Immunisation and Awareness Campaigns
The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI) has recommended that the HPV vaccine be included in India’s National Immunisation Programme (NIP). This would enable broader access and affordability, especially for girls aged 9–14 years and ensure that a routine vaccination schedule is implemented at the age of 9 years. Some states like Punjab and Sikkim have already taken steps to introduce the vaccine in their state-level immunization programs.
Additionally, a nationwide HPV vaccination campaign could raise awareness about the vaccine and its benefits, helping to overcome the challenges of cost, safety concerns, and cultural perceptions. Regular cervical cancer screenings (such as Pap smears and HPV tests) should also be encouraged to identify precancerous changes early.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Odisha has become the 34th state to implement the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY). The National Health Authority (NHA) of the Union Ministry of Health signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Department of Health and Family Welfare, Government of Odisha to onboard the state under the scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The scheme will be implemented alongside the existing Gopabandhu Jan Arogya Yojana in Odisha.
- It provides health coverage of Rs. 5 lakh per family per annum, with an additional Rs. 5 lakh for women members.
- Approximately 1.03 crore families will be covered under the scheme.
- Shri JP Nadda, Union Health Minister, emphasized that the scheme is the world’s largest and fastest-growing health coverage initiative.
- Shri Mohan Charan Majhi, Chief Minister of Odisha, highlighted that people will now have access to cashless treatment in over 29,000 empaneled hospitals.
About Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY:
- Launched in 2018 under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoH&FW).
- Targets 12 crore families (~55 crore beneficiaries).
- Provides cashless hospital coverage for secondary and tertiary care.
- Fully funded by the government, with cost-sharing between the Centre and states.
- Covers nearly 2,000 medical procedures, including major surgeries.
Since its inception, over 8.19 crore hospital admissions have been recorded, with ?1.13 lakh crore spent on healthcare for marginalized sections.
AnemiaPhone
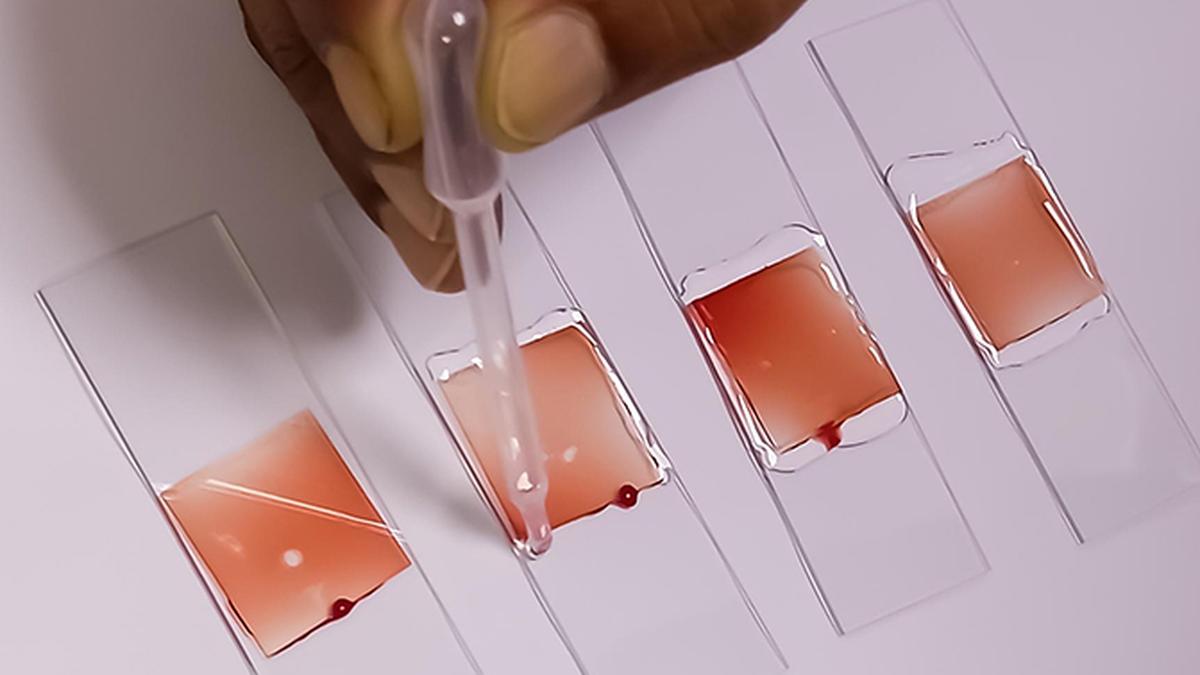

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
AnemiaPhone, a technology developed by Cornell University researchers to accurately, quickly, and cheaply, assess iron deficiency, has been transferred to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for integration into its programmes for anaemia, women’s health, and maternal and child health throughout the country.
Key Highlights:
- Technology Features:
- Portable, Rapid, and Affordable: AnemiaPhone is designed to detect iron deficiency efficiently at low cost.
- Requires a fingerstick (small blood sample).
- Results are available within minutes.
- Wireless: Data uploaded to a clinical database via mobile, tablet, or computer.
- Can be used by healthcare workers to assess iron deficiency on the spot and take action (guidance, triage, referral).
- Working Mechanism:
- A drop of blood is placed on a test strip.
- The reader processes the sample.
- Data is uploaded for immediate diagnosis and action.
- Test results assist in on-the-spot intervention by healthcare workers.
Anaemia and Iron Deficiency:
- Prevalence in India:
- Iron deficiency is a leading cause of anaemia.
- 50%-70% of pregnant women in India suffer from anaemia.
- 59% of women and 47% of children (6-59 months) in India suffer from anaemia (NFHS data).
- Consequences of Anaemia:
- Fatigue, dizziness, organ failure, complications in childbirth, and in severe cases, death.
- Contributes to higher maternal and child mortality rates in India.
- Impact on Health in India:
- India has one of the highest rates of anaemia in the world.
- Iron deficiency is a significant contributor to maternal deaths.
ICMR's Role and Integration into National Programs:
- ICMR and AnemiaPhone:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has integrated AnemiaPhone into its Anaemia Mukt Bharat (Anaemia-Free India) program.
- The program focuses on eliminating anaemia by 2025 through screening, diagnosis, and treatment in women and children, especially in remote areas.
- Transfer of Technology:
- In November 2024, Cornell University transferred the technology to ICMR for free.
- This collaboration aims to improve health outcomes by sharing innovative health technologies.
Advantages of AnemiaPhone:
- Cost-Effective and Portable:
- Low-cost compared to traditional lab tests.
- Portable and can be used in remote and underserved areas.
- Quick Diagnosis: Results are processed in minutes, allowing healthcare workers to act without delay.
- No Need for Expensive Labs:
- Can be used at primary health centers or in door-to-door health surveys.
- Facilitates healthcare in rural or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Wireless and Easy to Use: The device is user-friendly and does not require extensive training.
Impact on Healthcare System:
- Improvement in Accessibility:
- Helps reduce the need for people to travel long distances for diagnosis, especially in rural areas.
- Ensures early diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency and anaemia.
- Enhancing Maternal and Child Health: AnemiaPhone will contribute to reducing maternal and child mortality rates linked to anaemia.
Technology Testing and Development:
- Testing in India:
- AnemiaPhone has been tested in India and has shown accurate results in diagnosing iron deficiency.
- Single-use test strips help ensure accuracy and prevent contamination.
Global Health Context:
- Global Prevalence of Anaemia: More than 2 billion people worldwide suffer from anaemia, particularly pregnant women and young children.
- WHO’s Role: The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies anaemia as a major global health issue.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
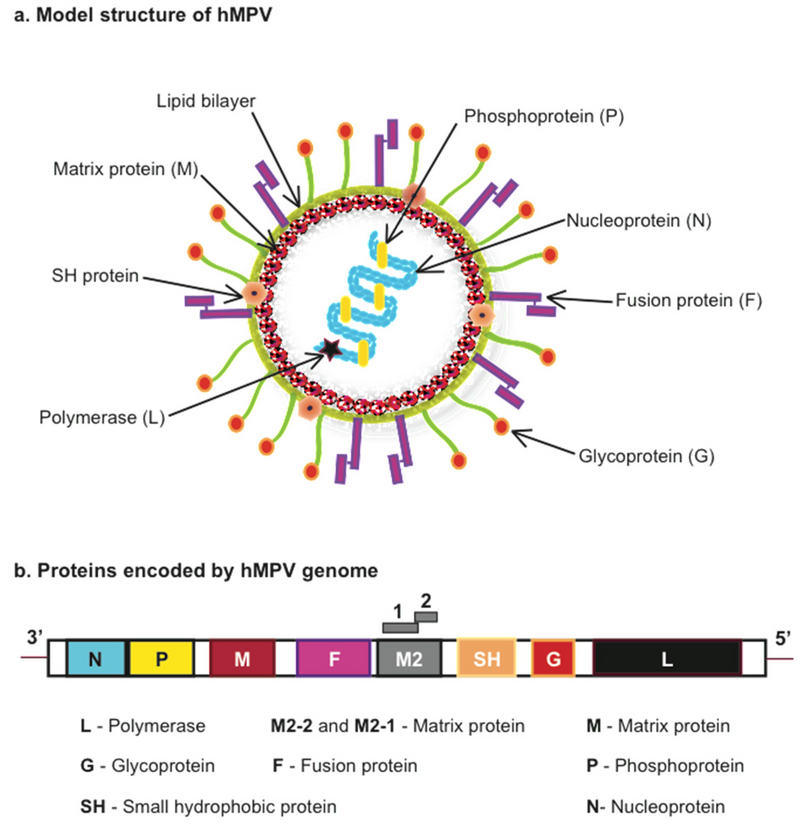
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
Five years after the COVID pandemic, China is experiencing a surge in HMPV cases, particularly in children under 14 years of age
Key Highlights:
- What is HMPV?
- A respiratory virus from the Pneumoviridae family, discovered in 2001.
- Causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, similar to the common cold or flu.
- Origin and Discovery:
- Identified in the Netherlands in 2001 through genomic sequencing of respiratory samples.
- Risk Groups:
- Children under 5 years, especially infants.
- Elderly individuals (65+).
- Immunocompromised persons and those with chronic respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma).
- Symptoms:
- Common: Cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat.
- Severe: Wheezing, shortness of breath, potentially leading to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Incubation Period: 3-6 days.
- Transmission:
- Spread via droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact (e.g., handshakes, hugs).
- Contaminated surfaces, touching face after contact.
- Treatment:
- No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine available.
- Symptom management: hydration, rest, OTC medications for fever and congestion.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization (oxygen therapy, IV fluids).
- Diagnosis:
- NAATs (Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests): Detect viral genetic material.
- Antigen-based immunoassays: For severe cases or outbreaks.
- Complications:
- Can lead to bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, or COPD flare-ups.
- Risk of ear infections (otitis media) in some cases.
- Prevention:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Physical Distancing: Avoid close contact, wear masks in crowded settings.
- Caution for Vulnerable Groups: Extra care for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Global Situation:
- China: Experiencing a rise in HMPV cases, particularly among children under 14 years.
- India: No reported cases yet, but monitoring the situation closely.
Key Facts:
- HMPV is a winter virus commonly seen in colder months (winter and early spring).
- Estimated 10%-12% of respiratory illnesses in children are caused by HMPV.
- The virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, alongside respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles, and mumps.
No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV; antibiotics are ineffective.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
African Swine Fever

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
African Swine Fever has been reported at two pig farms in Koottickal and Vazhoor grama panchayats in Kottayam district.
Action Taken:
- Culling of Pigs: All pigs in the affected farms and within a 1 km radius will be culled and disposed of according to Central Government guidelines.
- Infected Zone: A 1 km radius around the affected farms has been declared an infected zone.
- Surveillance Zone: A 10 km radius around the infected area has been designated a surveillance zone.
About African Swine Fever (ASF)
- African swine fever (ASF) is a highly contagious and hemorrhagic viral disease of domestic and wild pigs. It is a notifiable disease and its outbreak should be immediately reported to the higher authorities.
- ASF causes destructive effect on piggery due to high morbidity and mortality (up to 90-100 %). In India it was first confirmed in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in February-March 2020.
- Currently, there is no effective vaccine available against ASF, so prevention by adopting strict biosecurity measures is the only way to prevent ASF.
CLINICAL SIGNS
- High fever (106-1080 F), lethargy and loss of appetite
- Increased respiration rate
- Blue-purple discoloration of skin of ears, abdomen and rear legs
- Discharge from the eyes and nose; bloody froth from the nose/mouth
- Constipation or bloody diarrhea
- Abortion
- Death of pigs in 6-15 days
Diagnosis: Confirmatory diagnosis in gov. laboratories
Indian Scientists Develop Novel Gene Therapy for Haemophilia
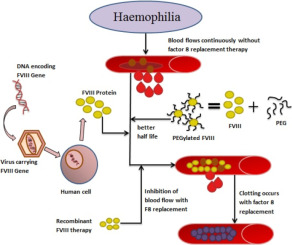
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian scientists have developed a successful gene therapy treatment for severe haemophilia A, a rare inherited blood disorder causing spontaneous, potentially fatal bleeding episodes.
Key Highlights:
Trial Success:
- The trial, conducted at Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore, involved five patients from Tamil Nadu.
- Results: None of the five patients reported bleeding episodes for over a year after receiving the treatment. The follow-up period averaged 14 months.
- This marks a significant improvement, as haemophilia patients typically experience frequent bleeding episodes requiring regular treatment.
Gene Therapy as a One-Time Solution:
- Traditional treatments involve frequent injections of clotting factors to prevent bleeding.
- The new gene therapy offers a one-time solution, teaching the body to produce enough clotting factor to prevent hemorrhages.
Haemophilia A - Overview:
- Caused by the absence of Factor VIII, a critical blood-clotting protein.
- Hemophilia A primarily affects males (since it's an X-linked disorder), though some females with two defective X chromosomes can also develop the condition.
- Symptoms include prolonged bleeding from minor injuries or internal bleeding in joints and muscles.
Current Treatment Challenges:
- Haemophilia treatments can be expensive and require lifelong care, costing up to ?2.54 crore over a 10-year period.
- The therapy requires repeated infusions of clotting factors or synthetic alternatives, which can be burdensome.
Gene Therapy Details:
- The gene therapy used in this trial involves fusing stem cells with the gene for Factor VIII using a lentivirus vector (safer than other vectors like adenovirus).
- This therapy eliminates the need for repeated Factor VIII infusions, providing a more cost-effective and sustainable solution.
Global Context:
- India has one of the world’s largest haemophilia populations, with an estimated 40,000 to 100,000 patients.
- The success of this gene therapy in India could lead to localized production, reducing treatment costs and increasing accessibility to gene therapy in resource-constrained settings.
Comparison with Roctavian:
- Roctavian, the only FDA-approved gene therapy for haemophilia A, also uses gene delivery to produce Factor VIII, but requires immunosuppressive therapy and is not approved for children.
- In contrast, the Vellore trial's lentivirus-based approach is considered safer, especially for children, with the potential for broader application.
World Malaria Report 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The World Malaria Report 2024 released by the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights significant progress in malaria control, particularly in India, but underscores the continued burden of malaria in Southeast Asia, where India accounts for half of all malaria cases.
About Malaria:
- Cause: Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, primarily P. falciparum and P. vivax, transmitted through bites from infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Transmission: Non-contagious; transmitted via mosquito bites.
- Symptoms: Fever, chills, and headaches appear 10–15 days after the mosquito bite. In some individuals, the symptoms may be mild.
- Prevention: Includes vector control strategies like insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor spraying. Malaria is treatable with early diagnosis and prompt medication.
India’s Malaria Status:
- Progress:
- India has made significant strides in reducing malaria, with cases decreasing from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023, a reduction of 82.4%.
- Similarly, malaria-related deaths dropped by 82.9%, from 35,000 in 2000 to 6,000 in 2023.
- Exit from High-Burden-High-Impact (HBHI) Group:
- India exited this group in 2024, signaling its success in reducing malaria burden.
- Cases dropped by 69% (from 6.4 million in 2017 to 2 million in 2023), and deaths fell by 68% (from 11,100 to 3,500 in the same period).
Key Strategies Behind India's Success:
- Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapy (ACT): Used to treat malaria effectively.
- Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLIN): Widely deployed to control mosquito populations.
- Targeted Interventions: Focused on forested and tribal areas where malaria transmission is higher, particularly in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, and the North-East.
- Effective Monitoring: Ensures proper implementation of strategies and interventions.
WHO's Global Malaria Report 2024 Highlights:
- Global Burden: In 2023, there were 263 million malaria cases globally and 597,000 deaths. The African region remains the hardest hit, accounting for 95% of malaria deaths.
- Progress Since 2000: Malaria incidence and deaths have significantly decreased. The global number of malaria cases and deaths dropped substantially, with over 2.2 billion cases and 12.7 million deaths averted.
- Malaria-Free Countries: As of November 2024, 44 countries and one territory, including Egypt, have been certified malaria-free.
- Emerging Threats: Drug resistance (especially to Artemisinin) and insecticide resistance are growing concerns, affecting control efforts.
India and Southeast Asia:
- India contributes nearly half of the malaria cases in Southeast Asia, while Indonesia accounts for about one-third. Despite progress, India and Indonesia together accounted for 88% of malaria deaths in the region.
- South-East Asia Progress: The region reduced malaria cases by 82.4% from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023. Timor-Leste and Bhutan reported zero indigenous malaria cases in 2023.
Global Recommendations:
- WHO stresses the need for continued investment, innovative strategies, and targeted actions, especially in high-burden areas like Africa, to sustain progress and tackle remaining challenges, such as drug resistance, insecticide resistance, and new vector species like Anopheles stephensi, which thrives in urban areas.
Ayush Visa

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Recently, the government introduced a separate category of Ayush Visa for foreigners seeking treatment under the Ayush systems of medicine (Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy).
- The Ayush Visa is available in four sub-categories:
- Ayush Visa: For foreigners visiting India for therapeutic care and wellness treatment in accredited hospitals/wellness centers.
- Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients seeking Ayush treatment.
- e-Ayush Visa: An electronic version of the Ayush Visa for convenience.
- e-Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients on an e-Ayush Visa.
- Visa Statistics (as of December 4, 2024):
- 123 regular Ayush visas have been issued.
- 221 e-Ayush visas issued.
- 17 e-Ayush attendant visas issued.
- Advantage Healthcare India Portal:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the Advantage Healthcare India portal, an official platform for Medical Value Travel (MVT).
- The portal facilitates information for international patients seeking medical treatment and wellness services in India.
- The website for accessing the portal is www.healinindia.gov.in.
- Government's Objectives: The government aims to sensitize stakeholders involved in MVT, including Ayush facility providers, to ensure smooth services for international patients.
Kawasaki Disease
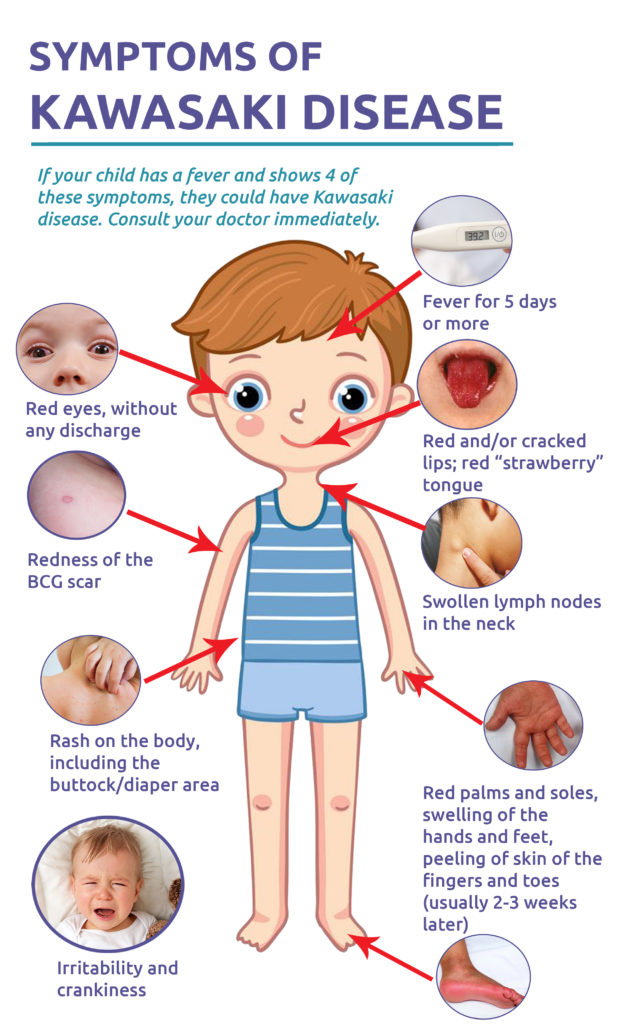
- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Comedian Munawar Faruqui recently opened up about a tough time in his life when his young son was diagnosed with Kawasaki disease.
What is Kawasaki Disease?
- Kawasaki disease is a rare condition that primarily affects children under the age of five.
- It causes inflammation in the blood vessels, including those that supply blood to the heart.
- With early treatment, most children recover without long-term health issues.
Possible Causes:
- The exact cause of Kawasaki disease is not well understood.
- Experts believe it may be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including certain infections.
Symptoms: Kawasaki disease symptoms typically appear in two phases and may last for several weeks. Common symptoms include:
- High fever lasting more than five days.
- Red eyes without discharge.
- A rash on the body, particularly in the chest and groin area.
- Swollen hands and feet, sometimes accompanied by redness.
- Red, cracked lips and a swollen, red tongue.
- Swollen lymph nodes, particularly on one side of the neck.
Detection & Treatment:
- There’s no test that can directly detect Kawasaki disease. But healthcare providers can do tests that support a diagnosis of Kawasaki disease or rule out other possible illnesses.
- Treatment for Kawasaki disease includes:Immune globulin (IVIG), or human blood proteins you receive by IV. About 10% of children may not respond to the first dose of IVIG and will need a second dose or other medications.
International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Day of Persons with Disabilities (IDPD), observed annually on December 3, celebrates the resilience, contributions, and leadership of persons with disabilities (PwDs) worldwide.
- Theme: “Amplifying the leadership of persons with disabilities for an inclusive and sustainable future”
History
- Proclamation: Established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1992 to promote the rights and well-being of persons with disabilities (PwDs).
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD): Adopted in 2006, further advanced the rights and well-being of PwDs and supports the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Initiatives
Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities
- In order to give focused attention to policy issues and meaningful thrust to the activities aimed at the welfare and empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), a separate Department of Disability Affairs was carved out of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment on May 12, 2012.
- The Department was renamed the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities on December 8, 2014.
- The Department acts as a nodal agency for matters pertaining to disability and persons with disabilities, including effecting closer coordination among different stakeholders: related Central Ministries, State/UT Governments, NGOs, etc., in matters pertaining to disability.
Accessible India Campaign
- The Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan), launched on December 3, 2015 aims to achieve universal accessibility for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) across India.
- The key focus areas include improving Built Environment Accessibility in public spaces, enhancing Transportation Accessibility for independent mobility, creating an accessible Information and Communication ecosystem, and expanding Sign Language Access through interpreter training and better media support.
Deendayal Divyangjan Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS)
- DDRS is a central sector scheme to provide grant-in-aid to non-governmental organizations (NGOs) for projects relating to the rehabilitation of persons with disabilities aimed at enabling persons with disabilities to reach and maintain their optimal, physical, sensory, intellectual, psychiatric, or socio-functional levels.
District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC)
- The District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC) aims to address the needs of persons with disabilities through a multifaceted approach.
- Its objectives include early identification and intervention, raising awareness, and assessing the need for assistive devices along with their provision and fitment, arrangement of loans for self-employment and more. Additionally, it acts as an outreach center for services provided by National Institutes and works to promote a barrier-free environment for individuals with disabilities.
Assistance to Persons with Disabilities for Purchase/Fitting of Aids/ Appliances (ADIP) Scheme.
- The main objective of the Scheme is to provide grants-in-aid to the various implementing agencies (National Institutes/Composite Regional Centers/Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India.
Schemes For Implementation Of Rights of Persons With Disabilities Act 2016 (SIPDA)
- The Scheme for Implementation of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (SIPDA) is a comprehensive "Central Sector Scheme" that encompasses 10 sub-schemes following its revision during the Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) meeting on 11th August 2021.
- This revised scheme, approved by the Hon'ble Finance Minister, is designed to operate from 2021–22 to 2025–26.
Divya Kala Mela
- The Divya Kala Mela is a national-level fair dedicated to Divyangjan and represents a significant milestone in India’s journey toward inclusivity and empowerment of the Divyangjan, or differently-abled individuals.
PM-DAKSH
- PM-DAKSH (Pradhan Mantri DakshtaAurKushaltaSampannHitgrahi) Yojana is a one-stop destination for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), skill training organizations, and employers across India to be a part of the National Action Plan for Skill Development of Persons with Disabilities implemented by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD). Under this portal, there are two modules:
- Divyangjan Kaushal Vikas: Skill training is conducted for PwDs through the portal across the country.
- Divyangjan Rozgar Setu: The platform aims to act as a bridge between PwDs and employers having jobs for PwDs. The platform provides geo-tagged based information on employment/earning opportunities within private companies as well as PwDs across India.
World AIDS Day 2024
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
World AIDS Day is observed annually on December 1 since 1988 to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS and demonstrate solidarity with affected individuals. It commemorates lives lost to AIDS and highlights progress and ongoing challenges in prevention, treatment, and care.
Key Highlights:
- 2024 Theme: "Take the Rights Path: My Health, My Right!"
- Focuses on healthcare access, human rights, and addressing systemic inequalities in HIV prevention and treatment services.
- Aims to empower individuals to manage their health and reduce stigma.
- Advocates for inclusivity and global cooperation to eradicate AIDS.
Global and National Perspective on HIV/AIDS
- Global Progress:
- According to UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2023, significant strides have been made globally in reducing new HIV infections and improving treatment access.
- India has been acknowledged for its robust legal framework and financial investments in HIV control.
- India's HIV Statistics:
- Over 2.5 million people live with HIV in India.
- Annual new infections: 66,400, a 44% reduction since 2010.
- HIV prevalence among adults is 0.2%.
- Free lifelong treatment is provided to over 16 lakh people at 725 ART centers (as of 2023).
India’s Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Response
- Early Initiatives:
- India’s response to HIV/AIDS began in 1985 with sero-surveillance and blood safety measures.
- The National AIDS and STD Control Programme (NACP) was launched in 1992, evolving into one of the world’s largest HIV/AIDS control programs.
- Evolution of NACP:
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focused on awareness and blood safety.
- Phase II (1999-2007): Introduced direct interventions in prevention, detection, and treatment.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Expanded decentralized management at the district level.
- Phase IV (2012-2017): Increased funding and sustainability of interventions.
- Phase IV Extended (2017-2021): Passage of the HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017; introduction of the ‘Test and Treat’ policy; and response to the COVID-19 pandemic with IT innovations.
- NACP Phase V (2021-2026):
- Central Sector Scheme with an outlay of Rs. 15,471.94 crore.
- Goals: Reduce new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2025-26 from 2010 levels.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis, reduce stigma, and ensure universal access to STI/RTI services for vulnerable populations.
- Key strategies include community-centered approaches, technology integration, gender-sensitive responses, and public-private sector partnerships.
Key Objectives of NACP Phase V
- Prevention & Control:
- Ensure 95% of high-risk individuals access prevention services.
- Achieve the 95-95-95 targets: 95% of HIV-positive individuals know their status, are on treatment, and achieve viral suppression.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis.
- Reduce stigma and discrimination to less than 10%.
- STI/RTI Prevention:
- Universal access to high-quality services for at-risk populations.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
Access to Medicine Index Report 2024

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
- Recently, Access to Medicine Index Report 2024 was released by the Access to Medicine Foundation. The report evaluates 20 leading pharmaceutical companies on their efforts to expand access to medicines in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).The biennial report has been published since 2008.
- Key Highlights:
- Key Areas of Evaluation
- Governance of Access: Companies’ leadership in addressing access issues.
- Research & Development (R&D): Focus on innovations for diseases prevalent in LMICs.
- Product Delivery: Efforts to ensure medicines and vaccines are accessible.
- Findings from the 2024 Report
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Many pharmaceutical companies are adopting ‘inclusive business models,’ but outcomes are mixed, with transparent reporting still lacking.
- 61% of products lack specific access strategies for low-income countries.
- Exclusion from Clinical Trials:Only 43% of clinical trials take place in LMICs, despite these countries representing 80% of the global population.
- Limited Technology Transfers & Local Availability:
- Technology transfers and voluntary licensing are concentrated in countries like Brazil, China, and India.
- Sub-Saharan Africa (excluding South Africa) remains largely overlooked.
- Decline in R&D for Priority Diseases:
- Pharmaceutical companies are moving away from diseases like malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases, which disproportionately affect LMICs.
- Gaps in Access for Low-Income Countries:
- Key Issues in Accessing Medicines in LMICs
- Economic Barriers:
- High costs of essential medicines, including patented drugs, limit access for patients in LMICs with low purchasing power.
- Out-of-pocket expenditures lead to catastrophic financial consequences for families.
- Infrastructure Challenges:
- Poor transportation and cold chain infrastructure hamper the efficient distribution of medicines, especially in rural areas.
- Disruptions in supply chains (e.g., during pandemics) exacerbate medicine shortages.
- Regulatory Issues:Weak enforcement of regulatory frameworks results in the proliferation of substandard and counterfeit medicines, compromising treatment efficacy.
- Workforce Limitations:
- A shortage of trained healthcare professionals restricts appropriate prescription and management of medicines.
- Cultural beliefs and low health literacy further complicate adherence to treatments.
- Economic Barriers:
- Challenges Specific to LMICs
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- LMICs face both infectious diseases and non-communicable diseases (NCDs), putting strain on fragile healthcare systems.
- 17 million people die from NCDs before age 70 annually, with 86% of these deaths occurring in LMICs.
- Need for Local Manufacturing:
- Strengthening local pharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution networks is crucial to ensure a reliable supply of essential medicines and reduce dependence on imports.
- Dual Burden of Diseases:
- Recommendations for Improving Access
- Companies should scale up efforts to bridge the health equity gap and use innovative approaches and local partnerships to improve access.
- Focus on increasing transparency in access reporting and addressing the lack of strategies for low-income countries.
- Pharmaceutical companies should refocus on diseases prevalent in LMICs, such as malaria and tuberculosis, and ensure that their R&D addresses the needs of these regions.
- Key Areas of Evaluation
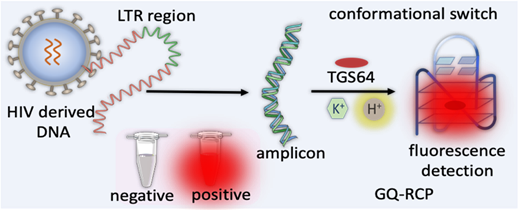
GQ-RCP Platform
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have developed a technology for targeted better detection of HIV-genome derived G-Quadruplex (GQ).
Key Features of the GQ-RCP Platform
- Technology: GQ Topology-Targeted Reliable Conformational Polymorphism (GQ-RCP) platform developed by Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR).
- Detection Mechanism: Uses a fluorometric test to detect HIV-derived GQ DNA through reverse transcription and amplification.
- Advantage: Increases diagnostic reliability by reducing false positives associated with non-specific DNA probes.
- Process: pH-mediated transition of double-stranded DNA into GQ conformation for targeted detection.
- Flexibility: Initially designed for SARS-CoV-2, now adapted for HIV diagnosis.
About HIV
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) attacks the immune system, specifically CD4 cells, weakening the body's ability to fight infections.
- Transmission: Spread through bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- AIDS: Without treatment, HIV progresses to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), where the immune system becomes severely damaged.
- Management: No cure; managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which controls viral replication.
Current HIV Situation in India
- Prevalence: As of 2021, ~2.4 million people living with HIV in India, with a 0.22% adult prevalence rate.
- Demographic Distribution: High prevalence among female sex workers (2.61%) and injecting drug users (5.91%). Women represent 39% of HIV-positive population.
- High-Prevalence States: Northeastern states have the highest prevalence (e.g., Mizoram - 2.70%) and southern states (e.g., Andhra Pradesh - 0.67%).
Government Initiatives on HIV
- National AIDS Control Program (NACP): Launched in 1992, aims for prevention, treatment, and care.
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focus on awareness, blood safety, and surveillance.
- Phase II (1999-2006): Expanded interventions for high-risk populations.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Increased targeted interventions and civil society involvement.
- Phase IV (2012-2021): Focused on integration of HIV services into public health systems.
- Phase V (2021-2026): Aim to reduce new infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2026.
- Legislative Framework: The HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Act (2017) ensures the rights of people living with HIV and access to treatment without discrimination.
- International Support: India receives support from UNAIDS, WHO, the World Bank, and foundations like Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
India’s First Indigenous Antibiotic

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Nafithromycin is India's first indigenously developed antibiotic aimed at combating drug-resistant pneumonia, developed with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The drug is being marketed under the trade name "Miqnaf" by Wockhardt.
Significance in Combating Drug Resistance:
- Nafithromycin addresses Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP), a serious disease caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
- Pneumonia is responsible for over 2 million deaths globally annually, with India facing 23% of the global burden.
- The drug is 10 times more effective than current treatments like azithromycin, requiring only three doses for effective treatment, offering a safer and faster solution.
Biotechnology Sector and Public-Private Collaboration:
- BIRAC, under the Department of Biotechnology, supported the research and development of Nafithromycin.
- This achievement underscores the public-private collaboration between the government and pharmaceutical industry, demonstrating India’s capacity to develop indigenous solutions for global health challenges.
Global Health Implications:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a growing global health crisis that prolongs illnesses and raises healthcare costs.
- The new antibiotic offers a vital solution to multi-drug-resistant pathogens, contributing significantly to global health.
- India’s leadership in addressing AMR positions the country as a major player in biotechnology innovation.
Importance for Vulnerable Populations:
- Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (e.g., diabetes, cancer patients), are particularly affected by drug-resistant pneumonia.
- Nafithromycin offers a much-needed therapeutic option for these groups.
Impact of AMR Awareness:
- The launch coincides with World AMR Awareness Week, emphasizing the urgency of tackling antimicrobial resistance.
- Public awareness, fostered by the COVID-19 pandemic, has increased the focus on biotechnology and its potential to address global health challenges.
Future Prospects:
- Nafithromycin is awaiting final approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for manufacturing and public use.
- The launch is expected to lead to future breakthroughs in antibiotic development and contribute significantly to improving public health.
India’s Polio Eradication Journey

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
India's achievement of becoming polio-free in 2014 stands as one of the most remarkable successes in global public health. This milestone, which was celebrated worldwide, represents decades of consistent efforts, collaboration, and innovative strategies, culminating in the elimination of wild poliovirus in the country.
Key Milestones in Polio Eradication
- Pulse Polio Programme Launch (1995):
- The Pulse Polio Immunization Programme was a game-changer, initiating large-scale vaccination campaigns across India, with the first nationwide campaign held on 2nd October 1994 (Gandhi Jayanti) in Delhi.
- The campaign used the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) and reached over 1 million children.
- The slogan "Do BoondZindagi Ki" (Two drops of life) became synonymous with India’s polio eradication efforts.
- Routine Immunization and System Strengthening:
- The Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), which launched in 1985, made polio one of the first diseases targeted for elimination. UIP is now one of the world’s largest immunization programs, aiming to provide vaccines against 12 preventable diseases, including polio.
- Cold chain management was improved through systems like the National Cold Chain Training Centre (NCCTE) and Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN), ensuring proper storage and distribution of vaccines.
- Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) Introduction (2015):
- As part of the Global Polio Endgame Strategy, India introduced the Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV) in 2015 to provide enhanced protection, particularly against type 2 poliovirus.
- This move followed the global transition from trivalent OPV to bivalent OPV (which excludes the type 2 strain) and helped ensure continued protection against all forms of polio.
- Surveillance Systems:
- India implemented Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) Surveillance to track unexplained paralysis in children, a symptom of polio.
- Environmental Surveillance, involving monitoring sewage water for poliovirus strains, played a critical role in identifying potential outbreaks and residual poliovirus transmission.
- Political Will & Community Engagement:
- Strong political commitment from both central and state governments ensured sustained resources and focus on the program.
- Community participation was also vital, with health workers and volunteers working to ensure vaccination coverage in the most remote areas.
The Final Leap: Certification and Maintenance
- 2011 marked the last case of wild poliovirus in Howrah, West Bengal, and India ramped up its surveillance and response efforts to ensure no further cases.
- India achieved polio-free certification from the World Health Organization (WHO) on 27th March 2014, after meeting strict criteria, including three years without wild poliovirus transmission and robust surveillance systems.
Post-Certification Efforts: Keeping Polio at Bay
Even after achieving polio-free status, India remains vigilant to maintain this achievement:
- Annual National Immunization Days (NID) and Sub-National Immunization Days (SNID) are held regularly to boost immunity levels and ensure no child is missed.
- Continuous surveillance and vaccination at international borders help prevent the risk of re-importation of the virus.
- Mission Indradhanush (MI), launched in 2014, aims to increase immunization coverage to 90%, focusing on hard-to-reach areas and improving vaccine coverage.
Ongoing Commitment to Immunization
India’s immunization programs continue to evolve:
- New vaccines like Rotavirus, Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV), and Measles-Rubella (MR) are being added to protect against other vaccine-preventable diseases.
- Mission Indradhanush’s intensified phase has played a crucial role in improving vaccination rates, particularly in underserved areas.
High-Altitude Sickness

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
In September, a trekker from Idukki, Kerala, died in Uttarakhand while attempting to scale Garur Peak due to respiratory failure. Every year, numerous tourists like this succumb to the effects of high-altitude sickness in the pristine but challenging inner Himalayas. These regions present hidden dangers due to their extreme altitudes, where thinner air and reduced oxygen can lead to potentially fatal conditions.
What is High-Altitude Sickness?
- Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) occurs when the body struggles to acclimatize to high altitudes, typically above 8,000 feet (2,400 meters), where oxygen levels are lower.
- As altitude increases, oxygen levels decrease, leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen). Early symptoms include:Headache, Nausea, Fatigue&Shortness of breath
- If untreated, AMS can develop into:
- High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE): Fluid accumulation in the lungs, leading to severe breathing problems.
- High-altitude cerebral edema (HACE): Fluid in the brain causing confusion, hallucinations, or coma.
- Both conditions are life-threatening and require immediate descent to lower altitudes.
Infrastructural Issues
- Many Himalayan regions lack adequate healthcare facilities beyond major towns like Shimla.
- Leh is an exception, with specialized facilities for high-altitude ailments, but most areas lack preventive health measures.
- Implementing health screenings at entry points to high-altitude zones (like Kinnaur or Lahaul-Spiti) could significantly improve prevention and response to AMS.
Mandatory Registration System for Tourists
- Tourist Registration: A system where tourists must register before entering remote mountain areas would allow authorities to monitor movements and provide timely medical assistance.
- Benefits:
- Quick emergency responses by having data on tourists' locations.
- Research support: Tracking demographic patterns and risk factors to better understand how altitude impacts different populations.
Early Intervention for High-Altitude Sickness
- Gradual Ascent: To allow the body to acclimatize, gradual ascent is crucial. Every 3-4 days, take a rest day and avoid increasing sleeping altitude by more than 500 meters/day.
- Medications: Doctors recommend:
- Acetazolamide to promote better oxygenation.
- Dexamethasone for reducing inflammation in severe cases.
- For those with a history of HAPE, Nifedipine may be used preventively.
- However, no medication guarantees immunity from AMS. Travelers with pre-existing conditions should consult a doctor before traveling.
Treatment Strategies
- Descent: The best treatment for AMS is to descend to lower altitudes (300-1,000 meters), where symptoms improve rapidly.
- Additional Measures: If available, supplemental oxygen or a portable hyperbaric chamber can help in emergencies.
- Medications like acetazolamide and dexamethasone can provide short-term relief but are not substitutes for descent.
Policy Recommendations
- Medical Infrastructure: Establish state-of-the-art medical facilities in high-altitude regions of the Himalayas.
- Research: Set up research centers to study high-altitude illnesses.
- Air-ambulance Services: Equip states with air-ambulance services for rapid medical evacuation in emergencies.
- Health and Safety Information: Provide accessible information on government websites and at check-in points to educate tourists on preventing and managing AMS.
Preventive Measures Before Scaling the Himalayas
- Acclimatization: Gradual ascent is essential for preventing AMS.
- Health Checks: Get a medical check-up to assess risk factors before travel.
- Medications: Consult a doctor for potential preventive medications.
- Hydration and Rest: Stay hydrated and take ample rest during the ascent.
- Monitor Symptoms: Be aware of early symptoms like headaches or nausea and stop ascending if they occur.
By addressing these measures, the risks associated with high-altitude sickness can be mitigated, improving safety for tourists and trekkers in the Himalayas.
Sickle Cell Eradication
- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- On the occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Diwason 15th November 2024, Hon’ble Governor of Madhya Pradesh, and Chief Minister unveiled a commemorative postage stamp dedicated to "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" at PG College, Dhar.
- Significance:Focuses on India’s commitment to eradicate Sickle Cell Anemia by 2047, especially in tribal communities.
Sickle Cell Anemia Overview
- What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Genetic blood disorder leading to abnormal hemoglobin.
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, blocking blood flow and causing pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- Symptoms:
- Chronic anemia causing fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
- Painful episodes (sickle cell crisis) resulting in intense pain in bones, chest, and limbs.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: Relieve anemia and reduce pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of painful episodes.
- Gene Therapy: Includes bone marrow or stem cell transplants and methods like CRISPR for treatment.
Challenges of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India
- Tribal Population Impact:
- India has the world’s largest tribal population (~67.8 million, 8.6% of total population as per 2011 Census).
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is identified as one of the top 10 health issues for tribal communities.
- Challenges:
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal regions.
- Lack of awareness about genetic counseling and preventive care.
- High treatment costs (e.g., CRISPR therapy costs USD 2-3 million).
- Bone marrow donor availability is a challenge.
Government Initiatives for SCD Management
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023):
- Objective: Eliminate SCD as a public health issue by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Mass screening to identify at-risk individuals.
- Genetic Counseling: Educating families on genetic nature of SCD.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Partnership with organizations like Sankalp India.
- Newborn Screening: AIIMS Bhopal provides early detection.
- Technology: A mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking data.
- Progress:Over 3.37 crore people screened, with 3.22 crore confirmed negative.
- Target Groups:Focus on children, adolescents, youth, and adults for screening, counseling, and care.
- National Health Mission (NHM) (2013):
- Emphasizes disease prevention and management, particularly for hereditary conditions like sickle cell.
- Facilitates medications like hydroxyurea for treatment.
- National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research (2017):Regulates stem cell therapies and allows Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy (2019):Guidelines for gene therapies for inherited disorders, including CRISPR treatment for SCD.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:Addresses screening and management challenges of SCD in the state.
Global Awareness and Observances
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day:
- Observed on 19th June annually, with the 2024 theme: "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally".
- Aimed at raising awareness about SCD struggles, improving patient care, and finding a cure.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP-IV)

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
As Delhi’s AQI worsened, the Commission for Air Quality Management issued the order to activate Stage-IV of the Graded Response Action Plan.
Restrictions Under GRAP-IV in Delhi-NCR
- Truck Movement:
- Banned except for essential goods and trucks using clean fuels (LNG, CNG, BS-VI diesel, or electric).
- Non-essential light commercial vehicles registered outside Delhi are also banned unless they are CNG or BS-VI diesel or electric vehicles (EVs).
- Delhi-registered BS-IV or older diesel vehicles (medium and heavy goods vehicles) are banned, except for those in essential services.
- Construction Activities:Suspension of all construction work, including public projects like highways, roads, flyovers, power lines, pipelines, etc.
- Schools and Work:
- Online classes for students of Classes 6 to 9 and Class 11.
- Work from home (WFH) recommendations for 50% office capacity in NCR.
- Central government employees may also be asked to work from home.
- Offline classes for Classes 10 and 12 continue, but schools for other classes must shift to online mode.
- Other Measures:
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
- Closure of colleges.
- Odd-even vehicle scheme.
- Restrictions on non-essential commercial activities.
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
About GRAP (Graded Response Action Plan)
- Purpose: A plan to reduce air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region based on AQI levels.
- Approved By: Supreme Court in 2016 (M.C. Mehta v. Union of India).
- Notified by MoEFCC: 2017.
- Implementation Authority: CAQM (Commission for Air Quality Management).
Stages of GRAP
GRAP is an incremental system, with measures activated as air quality deteriorates:
- Stage 1: Poor AQI (201-300) – Basic pollution control measures.
- Stage 2: Very Poor AQI (301-400) – Enhanced measures.
- Stage 3: Severe AQI (401-450) – Stricter actions like shutting down industries.
- Stage 4: Severe Plus AQI (Above 450) – Most stringent restrictions, as activated on November 18, 2024.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Introduced: 2014, by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Categories:
- Good: 0-50
- Satisfactory: 51-100
- Moderately Polluted: 101-200
- Poor: 201-300
- Very Poor: 301-400
- Severe: 401-450
- Severe Plus: 451 and above (current status in Delhi).
- Pollutants Considered: PM10, PM2.5, NO?, SO?, CO, O?, NH?, and Pb.
- Measurement: 24-hour average values for PMs, and 8-hour averages for CO and O?.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- Established: Under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) Act, 2021.
- Mandate: To coordinate, research, and manage air quality issues in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- Composition: Includes government officials, technical experts, and NGO representatives.
- Jurisdiction: Covers Delhi and parts of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
World Diabetes Day 2024
- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- World Diabetes Day is observed on November 14th each year to raise awareness about diabetes, its prevention, and management.
- It was created by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Significance: Commemorates the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting, who co-discovered insulin in 1922 alongside Charles Best.
- Theme (2024): "Access to Diabetes Care: Empowering Better Health for All".
History:
- Established in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and World Health Organization (WHO).
- Recognized as a global observance by the UN in 2006.
- Activities: Awareness campaigns, health check-ups, educational seminars, and lighting of Blue Circle Monuments worldwide as a symbol of unity in the fight against diabetes.
Global Diabetes Data (2022):
- Total Diabetic Adults: 828 million globally.
- India's Share: 212 million (approximately 25% of global cases).
- Other Countries:
-
- China: 148 million.
- USA: 42 million.
- Pakistan: 36 million.
- Indonesia: 25 million.
- Brazil: 22 million.
Risk Factors for Diabetes:
- Global Factors: Obesity and poor diets are key contributors.
- India-Specific Factors: Dietary habits, lack of exercise, and socio-economic disparities contribute significantly to the high prevalence.
Untreated Cases:
- Global untreated cases (2022): 445 million (59% of diabetics globally).
- India untreated cases (2022): 133 million (64 million men, 69 million women).
- Complications: Untreated diabetes leads to severe health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and premature death.
Types of Diabetes:
- Diabetes Mellitus: The most common type of diabetes, characterized by issues with insulin production or its efficient use.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
- Autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
- Primarily affects children and young adults.
- Type 2 Diabetes (T2D):
- Insulin resistance combined with reduced insulin production.
- Often linked to lifestyle factors like obesity and physical inactivity.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- Occurs in pregnant women, leading to high blood sugar.
- Typically resolves after childbirth.
- Diabetes Insipidus:
- Imbalance of water regulation due to inadequate secretion or response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
- Leads to excessive urination and dehydration.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D):
Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Frequent urination.
- Excessive thirst and hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Blurred vision.
- Fatigue.
- Slow-healing wounds.
Role of Insulin in Managing Diabetes:
- Function of Insulin: A hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood glucose levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells.
- In Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin injections or pumps are essential for survival.
- In Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin or oral medications may be prescribed alongside lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise.
Government Initiatives in India:
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS): Focuses on awareness, early diagnosis, and management of diabetes.
- National Health Policy (2017): Aims to reduce premature deaths from non-communicable diseases by 25% by 2025.
- Ayushman Bharat – Health and Wellness Centres: Provides free screenings and consultations for diabetes and other non-communicable diseases.
- Eat Right Movement: Promotes healthier dietary habits to combat obesity and reduce diabetes risks.
- School Health Programs: Aims to educate children on healthy lifestyles to prevent the early onset of Type 2 diabetes.
India’s Vision of ‘Adaptive Defence’

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Shri Rajnath Singh introduced the concept of ‘Adaptive Defence’ at the inaugural Delhi Defence Dialogue (DDD).
- Adaptive Defence aims to prepare India's military for the rapidly changing landscape of modern warfare, with evolving threats and technologies shaping global security.
Key Aspects of Adaptive Defence:
- Strategic Approach:
- Adaptive Defence is an evolving strategy where military and defence systems continuously adjust to emerging threats, focusing on proactive preparedness rather than reactive responses.
- It is based on anticipating future threats, fostering flexibility, resilience, and agility in both strategic and tactical responses.
- Core Elements:
- Situational Awareness: The ability to understand and respond to dynamic, often unpredictable environments.
- Flexibility & Agility: At both the strategic and tactical levels to ensure swift and effective responses.
- Resilience: The capacity to recover and adapt quickly to unforeseen circumstances.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Emphasis on adopting cutting-edge technologies like AI, drones, and cybersecurity to stay ahead of adversaries.
The Changing Nature of Warfare:
- Grey Zone & Hybrid Warfare:
- Modern conflicts now often occur in the grey zone and involve hybrid warfare, blending traditional and non-traditional threats like cyber-attacks, terrorism, and psychological warfare.
- These new threats demand continuous adaptation in strategies, doctrines, and military operations.
- Technological Transformation:
- Drones and swarm technologies are reshaping warfare. India aspires to become a global hub for drones, leveraging these technologies for both economic and military growth.
- The increasing significance of Artificial Intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, and quantum technologies in defence highlights the need for international collaboration in research and innovation.
- Psychological Warfare:
- The rise of information overload and psychological warfare challenges traditional defence paradigms. Manipulation of information to influence public opinion and disrupt decision-making processes is now a key threat.
Government Initiatives for Adaptive Defence:
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Establishment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and initiatives to enhance jointness among the three armed services (Army, Navy, Air Force) to create a unified strategic force.
- Reform of training curricula and emphasis on integrated operations to ensure readiness for new-age warfare.
- Focus on Self-Reliance:
- Strengthening the indigenous defence sector through initiatives like Make in India and the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign.
- Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) in defence and promoting defence exports, with India currently exporting to over 100 nations.
- Drone Hub Vision:
- India aims to become the world’s drone hub, supporting R&D and fostering innovation to develop reliable certification mechanisms and enhance Indian intellectual property in the drone sector.
- Programs like iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) and ADITI are rewarding innovation and driving India's defence sector towards greater self-sufficiency.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Focus on cybersecurity, AI, and quantum technologies to develop solutions that address both national and global security challenges.
- India is also working on Theaterisation, integrating the three services into a unified force structure for enhanced coordination and joint operations.
- Defence Acquisition and Export:
- Introduction of the Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020, establishment of Defence Industrial Corridors in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, and a Positive Indigenisation List to boost self-reliance.
- India is actively increasing defence exports, aiming for Rs 50,000 crore worth of exports by 2029, with key export destinations including the USA, France, and Armenia.
Strategic Vision for the Future:
- Collaborative Approach:
- Given the interconnectedness of global security, the defence minister emphasized the importance of a collaborative approach in dealing with transnational threats.
- Cross-border issues, cyberspace threats, and the potential of quantum and nanotechnologies demand the sharing of knowledge and strategies across borders.
- Joint Military Vision:
- Jointness in defence strategy should go beyond national borders and should involve international cooperation in response to global security challenges.
- The need for interconnected solutions in the face of transnational threats underscores the importance of multilateral cooperation.
Sudden Resurgence of H5N1 in Cambodia

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Cambodia saw a resurgence of H5N1 avian influenza cases after over 10 years of no human infections.
- From February 2023 to August 2024, 16 human cases were reported, with 3 deaths caused by the A/H5 clade 2.3.2.1c virus.
- Notably, 14 of these cases were caused by a novel reassortant virus, involving a mixture of clade 2.3.2.1c and clade 2.3.4.4b gene segments.
Key Points:
- Reassortment of the Virus:
- The reassortment between clades 2.3.2.1c (Southeast Asia) and 2.3.4.4b (global spread) has created a new strain.
- This reassortant virus is responsible for the second wave of infections in humans, starting in October 2023.
- Zoonotic Transmission:
- Investigations confirmed that direct contact with sick poultry or bird droppings was the primary source of human infections.
- There have been no reported cases of human-to-human transmission.
- The novel reassortant virus appears to have replaced the 2.3.2.1c strain in Cambodian poultry.
- Geographic Spread and Spillovers:
- Clade 2.3.2.1c was first reported in Cambodian poultry in March 2014. It continued to circulate in both poultry and wild birds.
- Clade 2.3.4.4b viruses began circulating in Cambodian live bird markets by 2021, co-existing with clade 2.3.2.1c.
- There were two key spillovers to humans:
- The first spillover in February 2023, associated with clade 2.3.2.1c, involved two related individuals, with one death.
- The second spillover, beginning in October 2023, involved the novel reassortant virus.
- Genetic Analysis and Mutation Concerns:
- Genetic sequencing showed significant changes in the hemagglutinin (HA) gene of viruses from human cases, indicating a shift from older local strains to newer sublineages.
- The PB2 627K mutation in the novel reassortant is concerning, as it is linked to increased mammalian adaptation and the potential for airborne transmission, particularly in mammals like ferrets.
- This mutation raises concerns about the virus’s ability to adapt to humans or other mammals.
- Environmental and Epidemiological Factors:
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- High-density poultry farming.
- Wild bird migration.
- Cross-border poultry trade in Southeast Asia.
- These factors heighten the risk of zoonotic transmission, emphasizing the need for continued vigilance in the region.
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- Surveillance and Response:
- One Health investigations linked human cases to infected poultry, highlighting the importance of rapid response through whole genome sequencing.
- The ongoing surveillance is critical, as the novel reassortant strain has already replaced clade 2.3.2.1c in Cambodian poultry.
- Public Health Recommendations:
- There is an urgent need to strengthen sustained surveillance of avian influenza in both poultry and wild birds, particularly in Southeast Asia.
- Public health strategies should focus on:
- Reducing human exposure to infected poultry.
- Promoting safe poultry handling practices.
- Encouraging early healthcare-seeking behavior in individuals with potential symptoms.
First in the World Challenge
- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
ICMR announces ‘First in the World Challenge’ to encourage scientists to find innovative ideas to tackle health issues.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Encourage bold, out-of-the-box ideas for solving difficult health problems.
- Aim to foster novel and groundbreaking biomedical innovations (vaccines, drugs, diagnostics, interventions, etc.).
- Target projects that are “first of their kind” and have never been tried or tested globally.
- Key Features of the Initiative:
- Focus on Groundbreaking Innovations:
- Emphasis on high-risk, high-reward ideas with potential for significant global health impact.
- Excludes proposals aiming for incremental knowledge or process innovation.
- Scope of Research:
- Breakthroughs in biomedical and health technologies such as:
- Vaccines
- Drugs/Therapeutics
- Diagnostics
- Interventions
- Breakthroughs in biomedical and health technologies such as:
- Focus on Groundbreaking Innovations:
- Funding & Support:
- Provides funding for projects at various stages, from proof-of-concept to prototype development and final product.
- Support for projects that have the potential to lead to “first-of-its-kind” biomedical innovations.
- Application Process:
- Open to individual researchers or teams (from single or multiple institutions).
- Teams must designate a Principal Investigator responsible for the project’s technical, administrative, and financial aspects.
- Selection Criteria:
- A selection committee will be formed with:
- Experts, innovators, policymakers, and distinguished scientists with an outstanding research record.
- Proposals evaluated based on originality, impact potential, and innovation.
- A selection committee will be formed with:
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- History:Founded in 1911 as the Indian Research Fund Association (IRFA), renamed ICMR in 1949.
- Role & Mandate:
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- Formulates, coordinates, and promotes biomedical research in India.
- Focus on improving public health and addressing national health challenges.
- Vision:“Translating Research into Action for Improving the Health of the Population.”
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
Ayurveda Day 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
Celebrated on 29th October 2024, marking the 9th Ayurveda Day, with the theme “Ayurveda Innovations for Global Health”.
- Global Participation: Over 150 countries participating, reflecting Ayurveda's growing global influence.
- Venue: Major events held at the All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA), New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Ayurveda and its Global Outreach
- Ancient System: Ayurveda is one of the oldest healthcare systems, focusing on holistic well-being, rooted in Vedic traditions, and dating back over 5,000 years.
- Global Recognition: Recognized in 24 countries and Ayurveda products exported to over 100 countries.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts through forums like BRICS, SCO, BIMSTEC, and WHO to integrate Ayurveda into global health policies.
Role of Dhanvantri in Ayurveda Day
- Dhanvantari Jayanti: Ayurveda Day coincides with Dhanteras, marking the birth anniversary of Lord Dhanvantri, considered the divine physician.
- Cultural & Religious Significance: Worshiped for promoting health and longevity, Dhanvantri symbolizes the healing powers of Ayurveda.
Innovations and Relevance of Ayurveda
- Research and Innovation: The theme emphasizes scientific advancements in Ayurveda to address global health challenges such as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), mental health, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and geriatric care.
- Startup Ecosystem: Focus on fostering innovation through Ayurveda startups, particularly in the North Eastern states and across India.
Ayurveda’s Role in Addressing Global Health Issues
- Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs): Ayurveda offers preventive and holistic treatment for diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions.
- Mental Health: Ayurveda promotes balance in the mind, body, and spirit, with methods addressing stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Emphasizing traditional medicinal plants and natural remedies to combat resistance to antibiotics.
- Geriatric Health: Ayurveda's role in managing aging and enhancing quality of life through rejuvenation therapies.
Focus Areas for Ayurveda Innovation
- Women’s Health: Developing Ayurvedic solutions tailored for women's health issues, including reproductive health and hormonal balance.
- Workplace Wellness: Integrating Ayurveda in workplace settings to improve mental and physical health.
- School Wellness Programs: Promoting Ayurvedic practices in schools to boost immunity and overall health of children.
- Food Innovation: Modernizing Ayurvedic dietary concepts, focusing on nutritional balance and preventive health.
Government Initiatives and Digital Transformation
- Ayush Digital Platforms: Initiatives like Ayush Grid, Ayurgyan Scheme, Ayush Research Portal, and Namaste Portal are enhancing accessibility to Ayurvedic knowledge.
- WHO Integration: Ayurveda's inclusion in the WHO ICD-11 Traditional Medicine Module facilitates global standardization and recognition.
- I Support Ayurveda Campaign: A public awareness campaign aiming to garner over 250 million votes in support of Ayurveda.
Ayurvedic Education and Research
- Research Centers: Government-supported centers like the Research Centre for Innovation in Ayurveda Biology and WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre advancing Ayurveda's global integration.
- Academic Contributions: Institutes like National Institute of Ayurveda, Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda, and North Eastern Institute of Ayurveda and Homeopathy are leading innovation and education in Ayurveda.
Ayurveda and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Ayurveda contributes significantly to public health, with a focus on preventive care and holistic health.
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC): Ayurveda supports affordable, accessible healthcare solutions, complementing the global health agenda.
'Act4Dyslexia' Campaign

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- On October 27, 2024, prominent landmarks such as Rashtrapati Bhawan, Parliament House, India Gate, and the North and South Blocks in Delhi were illuminated in red to raise awareness for Dyslexia and other learning disabilities.
- Similar illuminations took place in major cities like Patna, Ranchi, Jaipur, Kohima, Shimla, and Mumbai, highlighting the importance of dyslexia awareness.
Key Highlights:
- Collaboration for Awareness:
- The campaign is organized in collaboration with UNESCO Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Education for Peace and Sustainable Development (MGIEP) and the ChangeInkk Foundation.
- Its goal is to remove stigma and foster understanding of dyslexia and other learning disabilities, which affect 20% of India’s population—around 35 million students.
- Flagging off the ‘Walk4Dyslexia’:
- The ‘Walk4Dyslexia’ event, aimed at promoting collective action for dyslexia awareness, was flagged off by Shri Rajesh Aggarwal, Secretary of the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), along with Mr. Shombi Sharp, UN Resident Coordinator in India.
- The walk was organized by ChangeInkk Foundation, UNESCO MGIEP, Orkids Foundation, and Soch Foundation.
- Growth of the Campaign:
- The Act4Dyslexia campaign saw a significant expansion in 2024, with over 1,600 walks held across the country, from state capitals to villages, engaging over 4 lakh participants.
- The campaign mobilized 2 billion steps in support of dyslexia awareness, with 150+ organizations joining forces.
- Focus on Equal Rights and Opportunities:
- Dyslexia and other specific learning disabilities (SLDs) were officially recognized under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016. This law mandates equal educational and employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities.
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 further emphasizes inclusive education, calling for early identification, teacher capacity building, and necessary support and accommodations.
- Understanding Dyslexia:
- Dyslexia is often misunderstood as a sign of being a "slow learner", but people with dyslexia often excel in areas like logical reasoning, problem-solving, and innovation.
- Notably, 40% of self-made millionaires have dyslexia, and historical figures like Albert Einstein were also dyslexic.
- Global Impact:
- The campaign aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aiming to unlock the untapped potential of individuals with learning disabilities, thereby contributing to societal development at a global level.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
E. coli Outbreak Linked to McDonald's Burgers

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- An E. coli outbreak has been linked to McDonald's burgers in the United States. The infection has affected at least 10 states.
E. coli in India:
- Prevalence: E. coli infections are common in India, especially during the summer and rainy seasons, when there is an increase in gastrointestinal infections.
- Transmission: E. coli spreads mainly through contaminated food and water.
- National statistics: Over 500 outbreaks of diarrhoeal diseases were reported in India in 2023. E. coli is one of the most common pathogens causing gastrointestinal infections in India.
- ICMR data: According to the latest report from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), E. coli was found in 23.19% of patient samples from tertiary care hospitals across India.
- FSSAI's Role: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is establishing a network of 34 microbiology labs to test food for pathogens like E. coli, salmonella, and listeria.
Symptoms of E. coli Infection:
- Common symptoms include:
- High fever (over 102°F)
- Persistent diarrhoea, sometimes bloody
- Vomiting
- Dehydration due to fluid loss
- Severe cases may lead to acute kidney injury.
Treatment of E. coli Infections:
- E. coli is treated with antibiotics, but medical consultation is necessary before taking any medication.
- Antimicrobial resistance is a growing concern, as E. coli's susceptibility to antibiotics, including carbapenem, has declined from 81.4% in 2017 to 62.7% in 2023.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Consult a doctor if:
- Diarrhoea lasts more than a couple of days.
- Frequent visits to the toilet (every half hour to an hour).
- Bloody diarrhoea.
- Vomiting frequently or inability to retain fluids.
Food Safety Measures:
- The FSSAI is working to improve food safety by implementing better testing protocols for microbial contamination in food products across India.
WHO Approves First Mpox Diagnostic Test for Emergency Use

- 21 Oct 2024
In News:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has listed the Alinity m MPXV Assay under its Emergency Use Listing (EUL) procedure.
- The test, developed by Abbott Molecular Inc., will help expand diagnostic capacity in countries experiencing Mpox outbreaks, particularly in Africa.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis:
- Early diagnosis enables timely treatment and virus control.
- It is critical for improving Mpox surveillance, especially in areas with high transmission.
Current Mpox Situation
- Global Context:
- Over 30,000 suspected cases reported in Africa in 2024.
- India has reported 30 cases since the WHO declared Mpox a global health emergency in August 2024.
- Testing Capacity:
- Limited testing capacity and delays in confirming cases have been a significant barrier to controlling the spread, especially in Africa.
- In India, 35 laboratories are currently equipped to test suspected Mpox cases.
Mpox Diagnostic Test Details
- Alinity m MPXV Assay:
- A real-time PCR test that detects monkeypox virus (MPXV) DNA from skin lesion swabs.
- Used by trained clinical laboratory personnel proficient in PCR techniques.
- Helps confirm suspected Mpox cases from pustular or vesicular rash samples.
- WHO's Role:
- The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) procedure accelerates the availability of life-saving products during public health emergencies.
- WHO aims to increase access to quality-assured diagnostics in regions most affected by Mpox.
About Mpox
- What is Mpox?
- Zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus, part of the Orthopoxvirus genus (family Poxviridae).
- Closely related to smallpox, but generally less severe in humans.
- Transmission:
- Spread via physical contact with infected lesions, body fluids, or contaminated materials.
- Can also spread through animal bites, or activities like hunting, skinning, or eating infected animals.
- Two Clades:
- Clade I: Predominantly in Central and East Africa.
- Clade II: More common in West Africa; linked to the 2022 outbreak.
- Symptoms:
- Rashes, blisters, fever, sore throat, headache, muscle aches, back pain, swollen lymph nodes.
- Lesions typically scab over as they heal.
- Most people experience mild symptoms, but children, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals are at greater risk.
Treatment and Prevention
- No Specific Cure:
- Supportive care (e.g., pain relief, hydration) is recommended.
- In some cases, antivirals like tecovirimat (developed for smallpox) may be used under exceptional circumstances.
- Vaccination:
- Three smallpox vaccines are recommended for at-risk individuals: MVA-BN, LC16, and OrthopoxVac.
- Mass vaccination is not recommended by WHO.
Kala-azar Disease
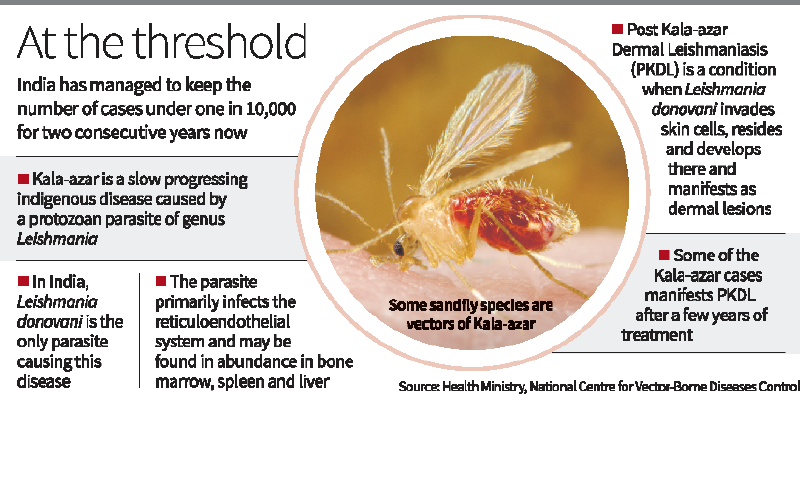
- 20 Oct 2024
In News:
India to seek WHO certification for eliminating disease.
Overview of Kala-Azar (Visceral Leishmaniasis)
- Cause: Kala-azar is caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani, transmitted by the bite of infected female sandflies (Phlebotomus argentipes in India).
- Symptoms: Includes irregular fevers, weight loss, swelling of the spleen and liver, severe anaemia. If untreated, it is fatal in over 95% of cases.
- Affected Areas: Historically, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and parts of Uttar Pradesh report the highest number of cases, with Bihar alone accounting for over 70% of India's cases.
India's Achievement in Kala-Azar Control
- Current Status:
- India has managed to maintain Kala-azar case numbers below 1 per 10,000 population for two consecutive years.
- This meets the WHO's criteria for elimination certification.
- 2023 and 2024 Statistics:
- 2023: 595 cases and 4 deaths.
- 2024 (so far): 339 cases and 1 death.
WHO Certification for Elimination
- WHO's Target: The World Health Organization aims to eliminate Kala-azar as a public health problem by 2030.
- Elimination Criteria: A country can be certified when:
- Local transmission is interrupted for a specified period.
- There is a system in place to prevent re-emergence of the disease.
- Global Context: Bangladesh is the first country to have eliminated Kala-azar, receiving WHO certification in October 2024, after reporting fewer than 1 case per 10,000 people for three consecutive years.
India's Kala-Azar Elimination Strategies
- National Health Policy (2002): Initially set the target to eliminate Kala-azar by 2010, revised multiple times, and is now aiming for 2030.
- Key Strategies:
- Active Case Detection: Identification and treatment of all cases.
- Vector Control: Targeting sandfly breeding grounds through insecticides and environmental management.
- Community Awareness: Educating the public on disease prevention and early diagnosis.
- Improved Surveillance: Ensuring rapid diagnosis and treatment access, including the use of the rK39 diagnostic kit.
- Integrated Vector Management: Combining insecticide spraying with environmental changes to reduce sandfly populations.
Challenges and Areas of Focus
- Root Causes: Persistent issues like poverty, inadequate sanitation, and malnutrition contribute to the spread of Kala-azar, particularly in rural, impoverished areas.
- Long-term Solutions:
- Strengthen vector control and improve sanitation.
- Address socio-economic factors like poverty and displacement.
- Invest in research for vaccines and new treatments.
Public Health Impact and the Way Forward
- Elimination Milestone: If India continues to reduce cases, it will join Bangladesh in eliminating Kala-azar as a public health threat.
- Sustaining Gains:
- Surveillance and quick response to new cases remain critical.
- Expand access to rapid diagnostic tools and effective anti-parasitic treatments.
- Focus on inter-sectoral convergence, integrating efforts from various government sectors, including health, sanitation, and housing.
Jipmer Launches ‘Tele-MANAS’ Mental Health Helpline

- 14 Oct 2024
In News:
- Jipmer (Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) has launched the "Tele-MANAS" (Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States) helpline, a toll-free service (14416) aimed at providing mental health support.
- This initiative is part of the National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP), launched by the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Purpose and Need:
- With an estimated 1 in 10 people in India suffering from mental illness, and about 1% experiencing severe conditions, the service addresses significant gaps in mental health access, particularly in rural and remote areas.
- The helpline aims to provide immediate support for issues such as anxiety, depression, and emotional distress.
Training and Operations:
- Jipmer will train qualified counsellors who will subsequently train additional counsellors to expand the reach of the service.
- Counselors will be available 24/7, including holidays, to ensure continuous support.
Support Structure:
- Trained counselors will serve as the first point of contact for individuals seeking help, providing responses, suggestions, and necessary referrals to advanced mental health facilities.
- Jipmer will supervise the program, ensuring regular retraining and maintaining service quality.
Integration with National Programs:
- The initiative is coordinated by the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), which acts as the National Apex Centre for the NTMHP.
- It includes a comprehensive information library on mental health and guidance for managing early signs of stress and emotional challenges.
Impact on Mental Health Services:
- The program aims to enhance the overall quality of mental health services across states and union territories in India, making them more accessible to a larger population.
- Emphasizes the importance of mental health as a public health priority.
Trachoma

- 09 Oct 2024
In News:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has now recognised that India has successfully eliminated trachoma, a bacterial infection that affects the eyes, as a public health problem.
WHO Declaration:
- India has eliminated Trachoma as a public health problem (2024).
- Third country in the South-East Asia Region to achieve this milestone.
Trachoma Overview:
- Bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis.
- Contagious; spreads through contact with infected secretions.
- Can lead to irreversible blindness if untreated.
- Considered a neglected tropical disease.
Global Impact:
- WHO estimates 150 million affected worldwide; 6 million at risk of blindness.
- Most prevalent in underprivileged communities with poor living conditions.
Historical Context in India:
- Leading cause of blindness in the 1950s-60s.
- National Trachoma Control Program launched in 1963.
- Control efforts integrated into the National Program for Control of Blindness (NPCB).
Statistics:
- Blindness due to Trachoma was 5% in 1971; now reduced to less than 1%.
- Implementation of the WHO SAFE strategy (Surgery, Antibiotics, Facial hygiene, Environmental cleanliness).
Milestones:
- India declared free from infective Trachoma in 2017.
- Continued surveillance for cases from 2019 to 2024.
National Trachomatous Trichiasis (TT) Survey:
- Conducted in 200 endemic districts (2021-2024) under NPCBVI.
- Mandated by WHO to confirm elimination status.
44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses

- 08 Oct 2024
In News:
India Participates in 44th Session of Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses
Key Contributions:
- Nutrient Reference Values:
- Advocated for reference values for ages 6 to 36 months.
- Suggested combining NRV-R values by averaging those for 6-12 months and 12-36 months.
- This proposal was accepted by the committee.
- Probiotic Guidelines:
- Emphasized the need to update FAO/WHO probiotic guidelines, which are two decades old.
- Highlighted the lack of international harmonization in probiotic regulations affecting global trade.
- Committee agreed to revisit guidelines and requested FAO and WHO to conduct a literature review on probiotics.
- Discussion on Sweetness Assessment:
- Disagreed with the EU’s sensory testing proposal for carbohydrate sources in Follow-up Formula, citing lack of scientific validation.
- Supported by USA, Canada, and others; this led to the committee discontinuing the topic for now.
- Noted that ISO 5495 or other methods could be used in the absence of harmonized methods.
- Delegation:
- Included representatives from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Advocated for various food safety, consumer health, and trade-related issues.
- Outcome:
- India’s suggestions were officially incorporated into the final report, significantly influencing global food safety and nutrition standards.
- Additional Announcements:
- FAO/WHO plans for a Joint Statement on Healthy Diet Principles.
- Updates on reviewing benefits and risks of Alternative Animal Source Foods (A-ASFs).
- FAO introduced a new “Food and Diet” domain on its FAOSTAT database.
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India

- 03 Sep 2024
Overview
India’s mental healthcare landscape is evolving, with increasing awareness and decreasing stigma around mental health issues. However, access to mental healthcare remains a significant challenge due to a shortage of professionals. Here are the key points:
Current State of Mental Healthcare in India
- Rising Demand: Shifts in societal attitudes have led to more individuals seeking mental health support. Awareness and willingness to access treatment have notably increased.
- Professional Shortage: Despite the rising demand, there are only 0.75 psychiatrists per one lakh population, far below the World Health Organization’s recommendation of three per lakh. As of the latest data, India has about 9,000 psychiatrists, while an estimated 36,000 are needed to meet the standard.
- Slow Workforce Growth: Approximately 1,000 psychiatrists enter the workforce annually, but with attrition and unemployment, it could take around 27 years to reach the WHO target without intervention.
- Comparative Analysis: India has one of the lowest psychiatrist-to-population ratios among BRICS nations, trailing only Ethiopia. However, it performs better than many South Asian countries.
Limitations of Current Data
- Outdated Survey: The data largely relies on the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) conducted between 2015 and 2016, which is based on a limited sample size of around 40,000 people across 12 states.
- Narrow Focus: The NMHS primarily addressed specific mental illnesses and overlooked milder conditions, emotional issues, and vulnerable populations like prisoners and the homeless.
- Need for Updated Research: A second NMHS is scheduled for release next year, which may provide more comprehensive data and insights.
Improvements in Awareness and Attitudes
- Positive Attitudinal Shift: A study by the LiveLoveLaugh Foundation found significant improvements in how Indians perceive mental health. For instance, the percentage of people believing that individuals with mental illnesses can handle responsibilities rose from 32% in 2018 to 65% in 2021.
- Willingness to Seek Help: Over 90% of respondents in 2021 indicated they would seek treatment for themselves or support others in doing so, a substantial increase from 54% in 2018.
- Increased Awareness: Awareness of mental health issues has grown, with 96% of respondents in 2021 recognizing mental health compared to 87% in 2018.
Conclusion
While India is making strides in reducing stigma and increasing awareness around mental health, the critical shortage of mental health professionals poses a significant barrier to accessing timely care. Addressing this issue requires targeted policy interventions and incentives to boost the supply of mental health professionals and improve the overall infrastructure for mental healthcare in the country.
India’s Commitment to Social Determinants of Health at UNGA
- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
- Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, represented India at the G20 Joint Finance-Health Task Force meeting during the 79th UN General Assembly.
- Focus: The session emphasized the importance of investing in health and addressing social determinants of health (SDH) through initiatives like debt-for-health swaps.
Key Highlights:
- Role of SDH: Underscored how social determinants such as housing, sanitation, water access, and income security are crucial for health investment priorities.
- Flagship Programs: India’s notable initiatives include:
- Ayushman Bharat: The world’s largest health insurance scheme.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Aiming for a cleaner India.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: Ensuring water access for all.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Promoting housing for all.
- Impact of PM-JAY: Highlighted improvements in access to healthcare and outcomes, especially for non-communicable diseases.
Data and Policymaking
- Importance of Data: Stressed the need for enhanced data availability and standardization on SDH indicators to support effective policymaking.
- Unified Approach: Called for G20 nations to collaborate on data collection and analysis for better health systems globally.
Exploring Debt-for-Health Swaps
- Potential Mechanism: Discussed debt-for-health swaps as a means to relieve financial pressure while promoting health equity.
- Next Steps: Emphasized the need for stakeholder engagement and pilot programs to ensure effective implementation.
Conclusion
- Global Leadership: India reaffirmed its commitment to health equity through evidence-based policies and partnerships.
- Shared Vision: Advocated for a unified effort towards achieving “Health for All,” highlighting the significance of investments in social determinants of health.
About Social determinants of health (SDOH)
- SDOH are non-medical factors that affect a person's health, well-being, and quality of life. They include the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age.
- SDOH also include the broader systems that shape everyday life, such as economic policies, social norms, and political systems.
- Some examples of SDOH include:
- Safe housing, transportation, and neighborhoods
- Racism, discrimination, and violence
- Education, job opportunities, and income
- Access to nutritious foods and physical activity opportunities
- Polluted air and water
- Language and literacy skills
JORDAN
- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
Jordan has made history by becoming the first country in the world to be officially verified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as having eliminated leprosy. This achievement marks a significant advancement in global public health efforts.
Key Highlights:
- WHO Recognition: WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus praised Jordan for this milestone, emphasizing the importance of stopping transmission and alleviating the suffering and stigma associated with leprosy.
- Historic Achievement: This success is not just about disease elimination but also about combating stigma and socio-economic harm.
- No Local Cases: Jordan has not reported any locally transmitted cases of leprosy for over two decades, demonstrating its effective public health strategies and strong political commitment.
- Independent Verification: WHO commissioned an independent team to conduct a thorough assessment, leading to the official recognition of leprosy elimination.
- Ongoing Vigilance: While celebrating this success, both the WHO and the Jordanian Ministry of Health emphasize the need for robust surveillance systems to detect and manage any future cases, including those from abroad.
Additional Context:
Leprosy, or Hansen's disease, is a chronic infectious condition caused by Mycobacterium leprae, primarily affecting the skin and nerves. Although it remains a neglected tropical disease, with over 200,000 new cases reported annually across more than 120 countries, Jordan's success showcases the potential for eradication through dedicated efforts.
This milestone serves as a beacon of hope, illustrating that with strong commitment, collaboration, and strategic planning, even longstanding public health challenges can be addressed effectively.
Poshan Tracker Initiative
- 05 Sep 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Women and Child Development recently earned the National Award for e-Governance 2024 (Gold) for its Poshan Tracker initiative, which has made significant strides in enhancing child health and nutrition.
About the Poshan Tracker Initiative
The Poshan Tracker initiative focuses on identifying and addressing growth-related issues in children aged 0-6 years. By using real-time monitoring and WHO growth charts, the program ensures that children receive optimal nutrition.
Key components of the initiative include:
- Role of Anganwadi Workers (AWWs): These workers are essential in assessing children's health and implementing necessary interventions when deviations from expected growth are observed.
- Technology Integration: The program employs advanced ICT tools and Growth Measuring Devices (GMD) at Anganwadi Centers (AWCs) to enable precise data collection and regular monitoring.
- Impact: Real-time growth monitoring through the Poshan Tracker has substantially improved child health outcomes in India, benefiting millions of children under the Mission Poshan 2.0 initiative.
Key Features of the Poshan Tracker App
- Comprehensive Overview: The app offers a complete view of Anganwadi Centre activities, including service deliveries and beneficiary management for pregnant women, lactating mothers, and children under six.
- Digitization and Automation: It replaces physical registers used by workers with digital records, thereby enhancing the quality and efficiency of their work.
- Smartphone Provision: Anganwadi workers have been provided with smartphones through the Government e-Market (GeM) to streamline service delivery.
- Technical Support: Each state has a designated nodal person to provide technical assistance and resolve issues related to the Poshan Tracker application.
- Service Accessibility: Migrant workers who registered in their original state can access services at the nearest Anganwadi in their current location.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024

- 06 Sep 2024
In News:
Union Minister of State for Women and Child Development, launched the Rashtriya Poshan Maah 2024 in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh on 1st September,2024.
Key Highlights:
- As part of the 7th Rashtriya POSHAN Maah, awareness programs are being organized at various levels.
- Under the ICDS (Integrated Child Development Services) Project, complementary feeding activities were conducted at Anganwadi Centres (AWC) Paduck Bagicha, South Andaman.
- Also, at AWC, Champin Nancowrie, Nicobar district (Andaman & Nicobar) under the ICDS Tribal initiative, local food items and nutrition sources were displayed.
- These efforts aim to further the Prime Minister's vision of a ‘Suposhit Bharat’ by conducting diverse large-scale activities, harnessing the potential of Gram Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies.
Rashtriya Poshan Maah:
- The programme is annually celebrated in the month of September, with a different theme each year, primarily focusing on addressing malnutrition by ensuring convergence of various nutrition-related schemes and programmes.
- The objective of the Poshan Maah is to ensure community mobilisation and bolster people’s participation for addressing malnutrition amongst young children, and women and to ensure health and nutrition for everyone.
Poshan Abhiyaan:
- POSHAN Abhiyan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme For Holistic Nourishment) focuses on advancing nutritional outcomes for children under six years, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- To cultivate widespread awareness about nutrition at each stage of life, it is celebrated annually as Poshan Maah (1st—30th September) and Poshan Pakhwada (fortnight of March).
- POSHAN Abhiyan (National Nutrition Month) aims to strengthen efforts to end hunger and malnutrition.
- It focuses to improving the nutritional outcomes among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers by focusing on prenatal care, diet, and optimal breastfeeding.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development plans month-long activities under Poshan Maah, focusing on issues such as the hygiene and sanitation, anaemia prevention, maternal and infant health, among others.
- There are outreach programmes, identification drives, camps, and fairs with a special focus on pregnant and lactating women, children below six years, and adolescent girls in order to realise the vision of ‘Swasth Bharat’.
Health Ministry approves new treatment regimen for multidrug-resistant TB
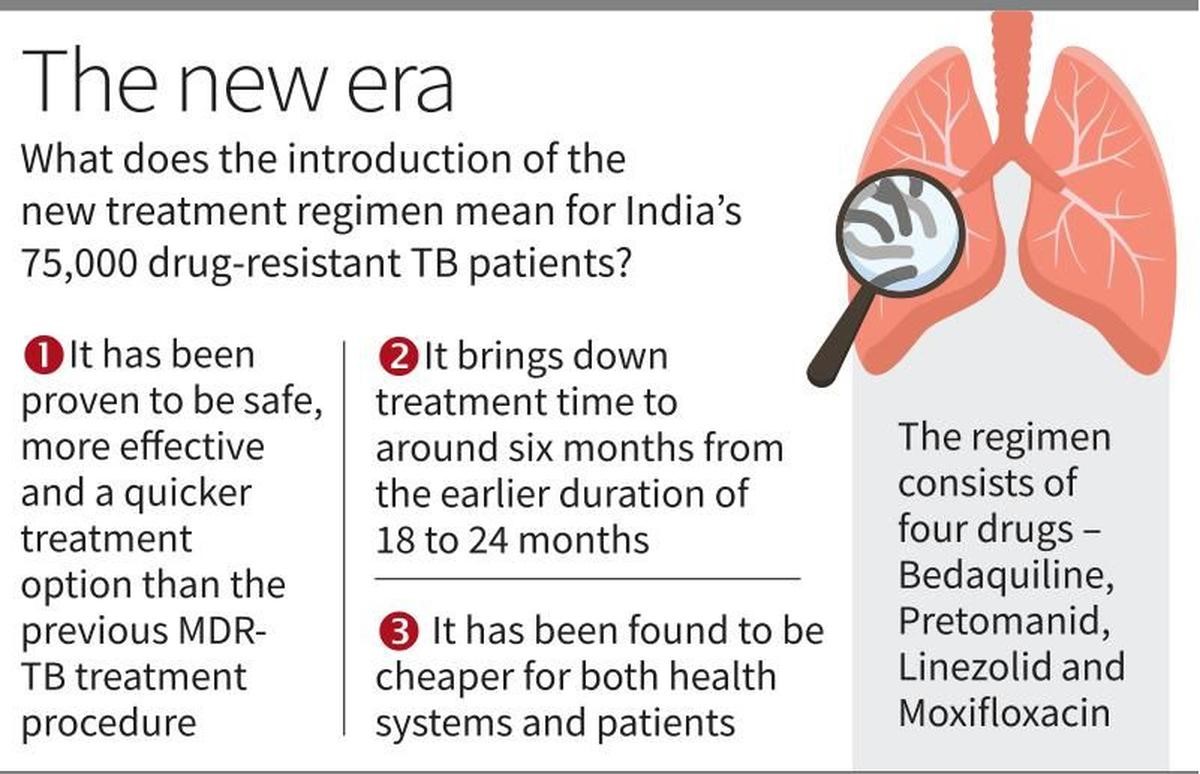
- 08 Sep 2024
The recent approval of the BPaLM regimen by India's Union Health Ministry marks a significant advancement in the fight against multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). This new treatment combines four drugs—Bedaquiline, Pretomanid, Linezolid, and Moxifloxacin—and offers several benefits over traditional treatments.
Key Points:
- Enhanced Effectiveness: The BPaLM regimen has demonstrated a higher efficacy in treating MDR-TB compared to previous methods.
- Shorter Treatment Duration: Unlike traditional treatments, which can take up to 20 months and often come with severe side effects, the BPaLM regimen shortens the treatment period to just six months.
- Improved Safety: The new regimen is noted for its safety profile, potentially reducing the risk of adverse effects compared to older treatments.
- Cost Savings: By shortening the treatment duration and improving outcomes, the BPaLM regimen is expected to lower overall treatment costs.
- Integration into National TB Elimination Programme: This regimen will be incorporated into India’s National TB Elimination Programme, aligning with the country’s ambitious goal to eliminate TB by 2025, which is five years ahead of the global target.
- Infrastructure and Testing Facilities: India boasts a comprehensive TB laboratory network, including 7,767 rapid molecular testing facilities and 87 culture and drug susceptibility testing laboratories, which will support the implementation of the new regimen.
This development represents a significant step forward in TB care and aligns with broader global efforts to combat drug-resistant TB more effectively.
World Health Assembly 2024

- 25 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Assembly will convene from May 27 to June 1 to discuss amendments to the International Health Regulations, aimed at improving the ability of countries to respond to public health emergencies and prepare a potential new pandemic agreement.
What is the World Health Assembly?
- The World Health Assembly is the decision-making body of the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations (UN) agency dedicated to promoting the global population's health and access to the highest levels of healthcare provision.
- Its main functions are to determine WHO's policies, elect the Organization's Director-General, supervise financial policies, and review and approve the proposed WHO budget.
- Delegates from WHO member states come together at an annual assembly held at the UN headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, to focus on a specific healthcare agenda created by the organization's Executive Board.
- The Executive Board comprises 34 technically qualified members, each elected for a three-year term.
- They meet every year in January to agree on the agenda and any resolutions that will be put before the World Health Assembly for consideration.
- Now in its 76th session, the theme for this year’s event is “Health For All: 75 Years of Improving Public Health”.
What does the Assembly do?
- Delegates at the annual World Health Assembly discuss the Executive Board's policy agenda for the coming year and decide which health goals and strategies will guide the WHO's public health work.
- Other functions include voting to appoint the organization's Director-General to serve a five-year term.
- Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus holds the post currently, having been re-elected in 2022 to serve a second term as head of the world's leading public health agency.
Why is it important?
- Since its inauguration, the Assembly has presided over WHO policies that have helped eradicate deadly diseases like smallpox and the poliovirus and helped foster international collaborations to develop and distribute vaccines for diseases like malaria and COVID-19.
About International Health Regulations (IHR):
- First adopted by the World Health Assembly (WHA) in 1969, the IHR was last revised in 2005. These regulations aim to maximize collective efforts in managing public health events while minimizing disruptions to travel and trade.
- The IHR has 196 State Parties, including all 194 WHO Member States, plus Liechtenstein and the Holy See.
- The IHR provide a comprehensive legal framework that outlines countries' rights and obligations in managing public health events and emergencies with the potential to cross borders.
- The regulations introduce crucial safeguards to protect the rights of travellers and others, covering the treatment of personal data, informed consent, and non-discrimination in the application of health measures.
- Legally Binding Instrument: As an instrument of international law, the IHR is legally binding on 196 countries.
Widal Blood Test

- 09 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Widal test's tendency to produce inaccurate results is clouding the understanding of India's typhoid burden, leading to increased costs, and exacerbating antimicrobial resistance risks.
What is the Widal Blood Test?
- A Widal test is a serological diagnostic test for typhoid fever.
- It helps evaluate the level of antibodies produced by the body in response to the Salmonella bacterial infection that causes typhoid fever in patients.
- Widal blood test is also known as a typhoid blood test report, as it is widely used for diagnosing typhoid fever.
- The symptoms of typhoid fever may be similar to those of other diseases, which can make the diagnosis of typhoid difficult without proper testing.
- Typhoid fever is a severe illness caused by a bacterium called Salmonella Typhi.
- This bacterium affects the gastrointestinal system and causes a range of symptoms such as high fever, diarrhoea or constipation, headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, weight loss, and red spots.
- The bacteria usually enter the body through contaminated food or water.
- Typhoid requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications such as severe intestinal perforation or bleeding.
- The Widal blood test is a quick and easy serological test that can help confirm or rule out whether a fever is due to a typhoid infection.
- Typically, typhoid symptoms appear within 6 to 30 days of exposure to the bacterial infection.
- The Widal test is designed to detect antibodies against O (somatic) and H (flagellar) antigens that cause the infection and typhoid fever.
- Infection through these antigens produces specific antibodies in response.
- The Widal blood test analyses the interaction between these two antigens and the antibodies produced in the patient's body through a blood sample.
- Detecting the presence of these antibodies in the Widal blood test indicates a bacterial infection.
- However, it has several limitations and has been phased out in many countries due to its potential for inaccuracy.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) advises against relying heavily on the Widal Test because various factors can influence its results.
- For example, a single positive result does not definitively confirm an active typhoid infection and a negative result does not necessarily rule it out.
- Additionally, obtaining an accurate diagnosis requires testing at least two serum samples taken 7-14 days apart, which can be time-consuming and often impractical.
- In areas with a continuous high burden of typhoid, baseline antibody levels may already be elevated, complicating the interpretation of results without knowing the appropriate cut-off values.
- Furthermore, cross-reactivity with antibodies produced against other infections or vaccinations can lead to false positives.
- Prior antibiotic therapy can also impact antibody levels, resulting in false negatives.
- Despite its accessibility and historical significance, the Widal Test's limitations emphasize the need for more accurate and reliable diagnostic methods for typhoid fever.
West Nile Fever

- 08 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Kerala health department has issued an alert after cases of West Nile fever were reported in Malappuram, Kozhikode and Thrissur districts.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily by mosquitoes, caused by the West Nile virus (WNV).
- The virus is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America, and West Asia.
- Most people infected with the West Nile virus don’t experience any symptoms.
- About 20% of people who become infected with WNV will develop West Nile fever.
- However, for some, particularly the elderly or those with weakened immune systems, symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, fatigue etc.
- Transmission occurs when mosquitoes become infected after feeding on infected birds, and then bite humans.
Why is it named West Nile Fever?
- West Nile Virus was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), It was identified in birds in the Nile Delta region in 1953,
Symptoms:
- West Nile Fever can manifest with a range of symptoms, although the majority of individuals infected with the West Nile virus (WNV) remain asymptomatic.
- For those who do exhibit symptoms, they typically appear within 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
- Common symptoms include fever, headache, body aches, and fatigue, which are similar to those of the flu.
- Additionally, individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and swollen lymph glands.
- Skin rash and swollen joints are also reported in some cases.
- In more severe instances, West Nile Fever can lead to neurological complications.
- These may include meningitis (inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Signs of neurological involvement may include severe headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, seizures, paralysis, and coma.
Treatment:
- While there is no specific treatment for West Nile Fever, supportive care such as pain management, fluids, and rest can help alleviate symptoms and aid recovery.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, especially for those experiencing neurological symptoms, as these can be life-threatening.
BFI Biome Virtual Network Program

- 22 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) has joined the Blockchain for Impact (BFI) Biome Virtual Network Program to accelerate transformative healthcare solutions through biomedical innovation.
About BFI Biome Virtual Network Program:
- The BFI-Biome Virtual Network Program is a pioneering initiative uniting incubators and research institutes under a single umbrella.
- This fosters collaborations among the stakeholders in the translational pipeline, the process of transforming research discoveries into real-world applications.
- Through this program, BFI will allocate over 200,000 USD over the course of three years, leveraging C-CAMP’s expertise to develop essential programs for healthcare-based startups.
- C-CAMP being an organization to foster deep science research and innovation for societal impact, the goals and mandates of both partners naturally align and complement each other.
- The partnership is expected to blur disciplinary boundaries in approaching biotech R&D, promote cross-integration of expertise and infrastructure, and provide multidisciplinary insights into need identification, problem-solving, and solution implementation.
What is C-CAMP?
- Centre for Cellular And Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) is an initiative of the Dept of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, with a mandate to be an enabler of cutting edge Life Science Research and Innovation.
- C-CAMP is also a member of the Bangalore Life Sciences Cluster (BLiSC).
- It facilitates Bioscience Research and Entrepreneurship by providing Research, Development, Training, and Services in state-of-the-art Technology Platforms.
- As a part of C-CAMP's mandate of promoting entrepreneurship and innovation, C-CAMP has created and fostered an entrepreneur-friendly culture in and around the Academic/Research environment through its involvement in Seed Funding Schemes for Startups, Entrepreneur Mentorship program, and Bio-Incubation facility.
- It has established State-Of-The-Art Platform Technologies which are essential requirements for success and leadership in the field of Life Sciences.
- C-CAMP allows Investigators to use Techniques as tools and not be limited by Technological barriers while pursuing challenging scientific questions.
myCGHS App

- 04 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the government has launched the 'myCGHS' app for iOS to provide Central Government Health Scheme beneficiaries access to electronic health records, information, and resources.
About myCGHS app:
- The Union Health Ministry launched the myCGHS app for iOS (Apple Users) to provide easy access for the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) beneficiaries to their Electronic Health Records, information, and other resources.
- The myCGHS iOS app is developed by the technical teams of the National Informatics Centre (NIC) Himachal Pradesh and the NIC Health Team.
- It is a convenient mobile application offering features aimed at enhancing information and accessibility for CGHS beneficiaries.
- The app is said to offer a range of services including:
- Online appointment booking and cancellation
- Downloading CGHS card and index card
- Accessing lab reports from CGHS labs
- Checking medicine history
- Monitoring medical reimbursement claim status
- Accessing referral details
- Locating nearby wellness centers
- Staying updated with news and highlights, and
- Finding nearby impaneled hospitals, labs, and dental units.
- Additionally, users can access the contact details of wellness centers and offices conveniently.
- To ensure data security, the app also features security measures such as two-factor authentication and mPIN function to be able to access the app once they are logged in.
- Users on the Apple ecosystem can find the app on the App Store and download it free of charge.
- The myCGHS app has been available for Android users since February 2022.
Key Highlights of the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS):
- CGHS provides healthcare services to registered employees and pensioners of the Central Government of India.
- Enrolled members receive reimbursement and cashless healthcare facilities through this scheme.
- It encompasses healthcare services from various systems of medicine including Allopathy, Homeopathy, Ayurveda, and Unani.
- CGHS beneficiaries have the flexibility to undergo treatment at any impaneled private hospital of their preference.
CoViNet
- 29 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a global network of laboratories to identify and monitor potentially novel coronaviruses that could emerge shortly.
What is CoViNet?
- The Coronavirus Network (CoViNet) is a global collaboration of laboratories with expertise in human, animal, and environmental coronavirus surveillance.
- This network aims to identify and monitor potential new coronaviruses that could emerge and impact public health worldwide.
- To enhance pandemic preparedness, CoViNet will expand its scope to include animal health and environmental surveillance, as well as timely risk assessments.
- This will allow the World Health Organization (WHO) to develop more informed policies and protective measures against future viral outbreaks.
- CoViNet will also play a pivotal role in building and supporting laboratory capacities in low- and middle-income countries to monitor MERS-CoV and other emerging coronaviruses of public health importance.
- By fostering knowledge exchange and capacity building, CoViNet aims to strengthen the global response to coronavirus threats.
- Furthermore, data generated through CoViNet's efforts will guide the work of the WHO's Technical Advisory Groups on Viral Evolution (TAG-VE) and Vaccine Composition (TAG-CO-VAC). These groups rely on cutting-edge research and surveillance data to inform public health policies and vaccination strategies.
- With 36 laboratories from 21 countries across all six WHO regions, CoViNet currently encompasses a wide range of expertise and resources.
- Three Indian institutions, namely, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Virology in Pune, and the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute, proudly represent the country in this global network dedicated to coronavirus surveillance and preparedness.
About the World Health Organization (WHO):
- The World Health Organization (WHO) stands as a paramount global health authority, dedicated to promoting health, preventing diseases, and improving healthcare systems worldwide.
- Established in 1948, WHO operates as a specialized agency of the United Nations, with its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It collaborates with governments, international organizations, and civil society to address pressing health challenges and provide guidance and support to countries in need.
- WHO's mandate encompasses a wide array of health-related issues, including infectious diseases, non-communicable diseases, mental health, maternal and child health, and environmental health.
- Through research, policy development, and technical assistance, WHO plays a vital role in shaping health policies, setting standards, and coordinating responses to health emergencies such as pandemics and natural disasters.
- With a mission to ensure the highest attainable level of health for all people, WHO continues to lead efforts in global health governance, advocacy, and capacity-building, striving for a healthier, safer, and more equitable world.
Hepatitis B
- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Public knowledge and awareness about Hepatitis B, a deadly disease that can cause end-stage liver cirrhosis and liver cancer, is dismal in India, according to a new study conducted by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi.
What is Hepatitis B?
- It is a severe liver infection that can lead to liver damage, cancer, and death.
- The virus spreads through contact with an infected person's blood or bodily fluids.
- One can get hepatitis B through sexual contact, sharing needles or other drug-injection equipment, or from mother to child during childbirth.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is a severe viral infection of the liver that can cause inflammation and scarring.
- Symptoms include fatigue, fever, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice.
Causes of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- HBV is found in the blood and body fluids of an infected person. It can spread through contact with fluids, such as:
- Blood, through needle sharing or accidental needle sticks
- Contact with body fluids, such as saliva, etc.
- Sexual contact with someone who has HBV
- From a mother to a child through childbirth
- Hepatitis B can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as:
- Sharing personal items like toothbrushes or razors with someone who has HBV
- Getting a tattoo or body piercing with contaminated equipment
Types of Hepatitis B:
- There are three main types of hepatitis B: acute, chronic, and carriers.
- Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after exposure to the virus. It is the most common type of hepatitis B in children.
- Chronic hepatitis B is a long-term illness that can lead to serious health problems, including liver failure and liver cancer.
- Carriers of hepatitis B have the virus in their blood but do not show any symptoms.
Treatment for Hepatitis B
- Several medications can help treat hepatitis B.
- These include antiviral drugs, which can help reduce the amount of virus in the body, and immunomodulators, which can help boost the immune system to better fight the virus.
- If the liver is damaged, one may also need medication to help protect it from further damage.
- HBIG (Hepatitis B Immuno Globulin) is one of the best ways to treat hepatitis B.
- Adults who have been exposed to hepatitis should get HBIG and vaccination as soon as possible, preferably within 24 hours but not later than 14 days after the exposure.
Prevention of Hepatitis B:
- The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated.
- The vaccine is given as a series of shots.
- The first shot is usually given at birth; the rest at 1–2 months old, 6–18 months old, and 4–6 years old.
- If one was not vaccinated as a child, they can receive the vaccines as an adult.
WHO launches digital health platform agreed upon in India’s G20 presidency

- 21 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Achieving one of the three priority areas agreed upon during India’s G20 presidency in 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) recently launched the Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) virtually, a platform for sharing knowledge and digital products among countries.
About Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH):
- The Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) is a network managed by the World Health Organization (WHO), dedicated to enhancing and coordinating efforts for country-led digital health transformation through collaborative partnerships and knowledge sharing.
- It was launched by the WHO and the Government of India during the G20 Health Ministerial Meeting in Gandhinagar.
- Functioning as a platform for inter-country knowledge exchange and digital product dissemination, GIDH strives to achieve several key objectives through collective action:
- Assess and prioritise countries' requirements for sustainable digital health transformation.
- Enhance the alignment of digital health resources and address unfunded priorities at the country level.
- Facilitate the accelerated attainment of the strategic objectives outlined in the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025.
- Promote capacity building and synergize efforts to support local development, maintenance, and adaptation of digital health technologies to evolving needs.
- Comprising four primary components, GIDH operates as a network of networks:
- Country Needs Tracker: Tracks and prioritises country-specific digital health requirements.
- Country Resource Portal: Provides a comprehensive map of available digital health resources within each country.
- Transformation Toolbox: Shares quality-assured digital tools to support country-led digital health initiatives.
- Knowledge Exchange: Facilitates the exchange of insights and best practices among member countries.
- GIDH extends support to countries in three fundamental ways:
- By attentively addressing their needs
- By fostering resource alignment to prevent fragmentation, and
- By offering access to quality-assured digital products.
- Membership in GIDH is open to all institutions actively involved in the digital health domain.
What is Digital Health?
- Digital health denotes the utilisation of technology, encompassing mobile devices, software applications, and various digital tools, to enhance health outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery.
- Essentially, it represents an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of technology and healthcare, integrating a diverse array of concepts and innovations.
- This encompasses a broad spectrum of technologies and services, spanning telemedicine, electronic health records, wearable devices, health information exchange, and more.
- Examples of notable digital health initiatives include India’s CoWIN platform and UNICEF's RapidPro and FamilyConnect programs.
- RapidPro, UNICEF’s real-time information platform, serves as a foundational component in its digital health portfolio.
- FamilyConnect, another UNICEF initiative, delivers targeted, lifecycle-based messages via SMS to various recipients, including pregnant women, new mothers, and heads of households.
India Initiatives on Digital Health:
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM): Designed to establish a comprehensive national digital health ecosystem featuring unique health IDs, electronic health records (EHRs), and a platform for health data exchange.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): Aims to develop a digital infrastructure for the Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM), incorporating health registries, electronic claim processing, and telemedicine services.
- E-Sanjeevani Telemedicine Platform: Enables virtual consultations between healthcare providers and patients nationwide, enhancing access to medical care.
- Jan Arogya Setu App and CoWIN Platform: Offers access to healthcare services, facilitates appointment scheduling, and disseminates COVID-19-related information.
- Digital Aarogya Mitra (DAM): Implements a community health worker program utilising technology for data collection and community-based health interventions.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Guinea (WHO)
- 18 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that Guinea's Health Ministry has officially notified them of a diphtheria outbreak.
What is Diphtheria?
- Diphtheria, an extremely contagious and infectious disease, instigates severe inflammation in the nose, throat, and trachea (windpipe).
- This ailment is caused by strains of bacteria known as Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which produce a potent toxin responsible for the onset of illness.
Causes:
- The bacterial infection spreads through various means, including respiratory droplets emitted during coughing or sneezing.
- Transmission can also occur through contact with infected open sores or ulcers. The bacteria's toxin is the primary culprit behind the illness.
Symptoms:
- Manifesting 2-5 days post-infection, symptoms of diphtheria encompass a thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, a sore throat, hoarseness, swollen glands in the neck, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, fever, chills, and fatigue.
- If the toxin enters the bloodstream, it can lead to damage to the heart, nerves, and kidneys.
Infection and Spread:
- Diphtheria bacteria thrive on person-to-person transmission, emphasizing respiratory droplets as a common mode of contagion.
- Skin infections are possible but seldom result in severe disease.
Treatment:
- Combatting diphtheria involves a dual-pronged approach:
- Antitoxin (Anti-diphtheritic Serum): This neutralizes bacterial toxins and is specifically employed for respiratory system infections. The antitoxin acts on toxins that haven't bound with cells and tissues.
- Antibiotics (Erythromycin or Penicillin): These medications eradicate the bacteria, preventing further spread. Antibiotics are effective against both the respiratory system and skin infections caused by diphtheria.
Union Health Minister Launches MedTech Mitra Platform to Empower Medical Technology Innovators (NewsOnAir)

- 26 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Union Health Minister Dr Mansukh Mandaviya has launched MedTech Mitra - a strategic initiative to empower MedTech innovators and advance healthcare solutions.
What is the MedTech Mitra Portal?
- The MedTech Mitra portal is an online platform designed to support medtech innovators by assisting in clinical evaluation, regulatory facilitation, and the adoption of new products in the medical technology sector.
- This collaborative initiative is overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), operating under the direction/guidance of NITI Aayog’s Atal Innovation Mission.
Significance:
- In conjunction with recent policies and incentive schemes, such as the medical devices policy and the production-linked incentive scheme, the MedTech Mitra platform aims to catalyze growth in the medical devices sector and promote domestic manufacturing.
- These initiatives seek to foster the indigenous development of affordable and high-quality MedTech devices and diagnostics, thereby significantly reducing the sector's reliance on imports.
- The platform is envisioned to streamline the innovation process and facilitate research and development for emerging start-ups, ensuring a smoother journey from concept to product.
- By offering comprehensive guidance, including support for animal and clinical trials, the platform aims to bridge gaps for startups and promote ease of innovation.
- The MedTech Mitra portal is poised to foster collaborations between engineers, scientists, and clinicians, addressing a previously existing gap in partnerships within the sector.
About the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) serves as the apex institution in India responsible for formulating, coordinating, and advancing biomedical research.
- With a primary mandate to conduct, coordinate, and implement medical research for societal benefit, ICMR is dedicated to translating medical innovations into tangible products and processes, subsequently integrating them into the public health system.
- Financial support for ICMR is provided by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) (NewsOnAir)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Health Authority (NHA) has recently declared the extension of its Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) until the 31st of December 2023.
About Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS):
- Launched in December 2022, the DHIS became effective from 1st January 2023.
- The scheme is implemented by the National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Its primary objectives include giving a further impetus to digital health transactions across the country through the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
Salient Features of DHIS:
- The scheme offers incentives of up to four crore rupees, determined by the number of digital health records created and linked to patients' Ayushman Bharat Health Account numbers.
- Incentives are extended to hospitals, diagnostic labs, and providers of digital health solutions, including Hospital/Health Management Information Systems (HMIS) and Laboratory Management Information Systems (LMIS).
- Health facilities (hospitals and diagnostic labs) registered with the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission's Health Facility Registry (HFR) and meeting the specified eligibility criteria can avail of the incentives.
Benefits of DHIS:
- Incentives for Digitization: Healthcare facilities and Digital Solution Companies participating in the scheme can earn incentives to cover expenses related to digitization.
- Enhanced Efficiency in Healthcare Delivery: DHIS streamlines the healthcare process, eliminating hassles in registration, appointment scheduling, consultations, IPD admission, discharge, and more.
- Robust Digital Health Ecosystem: The scheme contributes to the development of a strong digital health ecosystem, encompassing various levels of healthcare facilities.
- Improved Quality of Care: DHIS facilitates evidence-based, accessible, and high-quality healthcare services, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
NanoPtA (The Hindu)
- 06 Oct 2023
Why in the News?
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science's Materials Research Centre (MRC) have recently created a novel enzyme mimic known as NanoPtA.
About NanoPtA:
- The research team at the Materials Research Centre (MRC), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), has created a unique platinum-based nanozyme called NanoPtA.
- This nanozyme can be turned into a powder for use in industries.
- When NanoPtA encounters wastewater, the molecule's benzene rings and long alkyl chains engage in multiple non-covalent interactions.
- Individual NanoPtA molecules link together to form tape-like structures that emit light, which is the source of its oxidizing capability.
- In the presence of sunlight, this nanozyme can break down pollutants in wastewater, reducing its toxicity.
- Remarkably, the nanozyme can rapidly degrade even small amounts of common contaminants like phenols and dyes (micromolar levels) within ten minutes when exposed to sunlight.
- The researchers also observed that the NanoPtA complex remained stable for up to 75 days at room temperature.
Applications:
- Besides wastewater treatment, this nanozyme could find applications in healthcare and serve as a valuable diagnostic tool for neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.
