Future of Jobs Report 2025

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Economic Forum's latest "Future of Jobs Report 2025" has highlighted significant trends and predictions for the global labor market by 2030.
Key Highlights:
Fastest Growing Jobs by 2030
The report identified the following jobs as the fastest-growing by 2030:
- Big Data Specialists
- FinTech Engineers
- AI and Machine Learning Specialists
- Software and Applications Developers
- Security Management Specialists
- Data Warehousing Specialists
- Autonomous and Electric Vehicle Specialists
- UI/UX Designers
- Delivery Drivers
- Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
Job Disruption and Creation
- 22% of jobs globally will be disrupted by 2030 due to automation and technological advancements.
- 170 million new jobs are expected to be created, resulting in a net increase of 78 million jobs.
- Technological shifts, economic uncertainty, and demographic changes are expected to play significant roles in this transformation.
Skills in High Demand
- AI, Big Data, Cybersecurity: Skills related to artificial intelligence and big data are expected to see an 87% rise, while networks and cybersecurity skills are projected to increase by 70%.
- Creative Thinking, Flexibility: Skills like creative thinking, resilience, flexibility, and agility are also expected to see a significant rise, emphasizing the importance of soft skills in a technology-driven world.
Declining Jobs
The report lists the following positions as expected to decline by 2030:
- Postal Service Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Data Entry Clerks
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Telemarketers
- Printing Workers
- Accounting and Bookkeeping Clerks
These roles are being replaced or transformed by automation and AI, which are reshaping traditional job functions.
Technological Advancements
- Digital Access: 60% of employers believe that expanding digital access will be the most transformative trend for businesses.
- AI and Robotics: Employers are investing heavily in AI, robotics, and energy technologies, creating a demand for skilled workers in these sectors.
- Energy Technologies: Jobs related to the green transition, including renewable energy and environmental engineering, will see an uptick as countries strive to meet climate goals.
Key Drivers of Change
- Technological Change: AI, machine learning, and automation will continue to reshape industries.
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions and economic shifts are prompting businesses to transform their models, leading to a greater demand for cybersecurity and security management roles.
- Aging Populations: The growing demand for healthcare services, especially in high-income economies, will result in more jobs in the care economy (e.g., nursing professionals, social workers).
- Green Transition: The global shift toward clean energy and environmental sustainability will create numerous opportunities for jobs in renewable energy and climate change mitigation.
Implications for India
- AI and Robotics Investment: Indian companies are leading the way in investing in AI, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Growth Sectors: India’s rapidly developing tech sector will see a rising demand for AI, machine learning, and big data specialists.
- Disruptions in Traditional Jobs: Roles like postal clerks, cashiers, and data entry clerks in India are also expected to face significant reductions due to automation.
Challenges for Employment in India
- Skill Mismatch: There is a significant skill gap, with many workers lacking expertise in emerging fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science.
- Digital Divide: Urban areas are adapting to new technologies faster than rural areas, which may widen employment disparities.
- Informal Sector: India’s large informal workforce faces challenges in transitioning to technology-driven jobs due to limited access to training and education.
Reskilling and Upskilling
- The WEF report emphasizes that 59% of the global workforce will need reskilling or upskilling by 2030 to remain competitive.
- Workers must adapt to new roles, especially in technology and the green transition, to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
Twigstats

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The tracing of genetic ancestry remains a challenging task due to the statistical similarity among populations across geographical regions. However, recent advances in genetic analysis, particularly the development of the Twigstats tool, are significantly enhancing our ability to reconstruct genetic histories at a very high resolution.
Key Insights from Genetic Research:
- Ancient DNA (aDNA): Prehistoric human ceremonial burials, mass grave mounds, and war graves are rich sources of ancient genetic material, offering key insights into population dynamics. These samples help us understand past migrations, cultural transitions, and the genetic legacy of ancient groups.
- Challenges in Ancestry Tracing:
- Populations often share many genetic similarities, complicating the task of tracing ancestry across regions.
- Ancient DNA samples are typically of lower quality compared to modern samples, limiting the precision of past genetic studies.
- The movement of genes across time and space, through processes like gene flow, adds complexity to the understanding of population ancestry.
Traditional Genetic Techniques:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Used to identify natural genetic variations, SNP analysis has been central to reconstructing genetic histories. However, it is limited by its reliance on high-quality samples and struggles with closely related groups.
- Haplotypes and Genealogical Trees: By analyzing shared DNA segments (haplotypes) and rare variants, researchers gain a more comprehensive understanding of population structure and ancestry, which can reveal shifts in population over time.
The Emergence of Twigstats:
- What is Twigstats?
- Twigstats is an advanced analytical tool that enhances the precision of ancestry analysis through time-stratified ancestry analysis, a method that allows for a more fine-grained look at genetic data.
- It is designed to address the limitations of traditional methods by integrating SNPs, haplotypes, and rare genetic variants, providing a more holistic view of ancestry.
- The tool is powered by statistical languages R and C++, which help researchers better manage and analyze complex genetic data.
- How It Works: Twigstats builds family trees by analyzing shared genetic mutations, identifying recent mutations that offer a clearer understanding of historical periods and events. It helps trace the evolution of populations and offers insights into their migrations, mixing, and cultural shifts.
Key Features and Impact of Twigstats:
- Time-Stratified Ancestry Analysis: Allows researchers to study how populations evolved over time, with a focus on specific historical periods.
- Enhanced Precision: Reduces statistical errors and enhances the precision of individual-level ancestry reconstruction.
- Higher-Resolution Mapping: Provides high-resolution genetic maps of migration patterns and admixture events across centuries.
Applications of Twigstats:
- Historical Case Studies: The tool has been used to study ancient genomes from Europe, particularly the Iron, Roman, and Viking Ages (500 BC to 1000 AD). It revealed the fine-scale genetic history of populations in regions like northern and central Europe, including the movement of Germanic and Scandinavian peoples.
- Viking Age Insights: Researchers were able to trace the early presence of Scandinavian-like ancestry in regions such as Britain and the Baltic before the traditionally believed start of the Viking Age. This suggests earlier interactions and migrations from Scandinavia, which aligns with historical records of Anglo-Saxon and Viking movements.
- Cultural Transitions: The analysis identified shifts in population genetics corresponding to cultural changes, such as the shift from the Corded Ware culture to the Bronze Age and the influence of the Wielbark culture.
Genetic Methods Used in the Study:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs): Commonly used to trace ancestry but requires high-quality samples.
- Haplotypes and Rare Variants: Offer more nuanced insights into population movements by considering combinations of genetic markers inherited together.
- Genealogical Tree Inference: Applied to both ancient and modern genomes, it provides detailed demographic and ancestry information, supporting the reconstruction of high-resolution genetic histories.
Case Study: India’s Genetic History (2009 Study)
- Researchers used SNP analysis to trace the genetic history of India, revealing two major ancestral groups:
- Ancestral North Indians (ANI): Genetically closer to Central Asian, European, and Middle Eastern populations.
- Ancestral South Indians (ASI): A distinct genetic group, showcasing India’s diverse population structure.
Pig-Butchering Scam
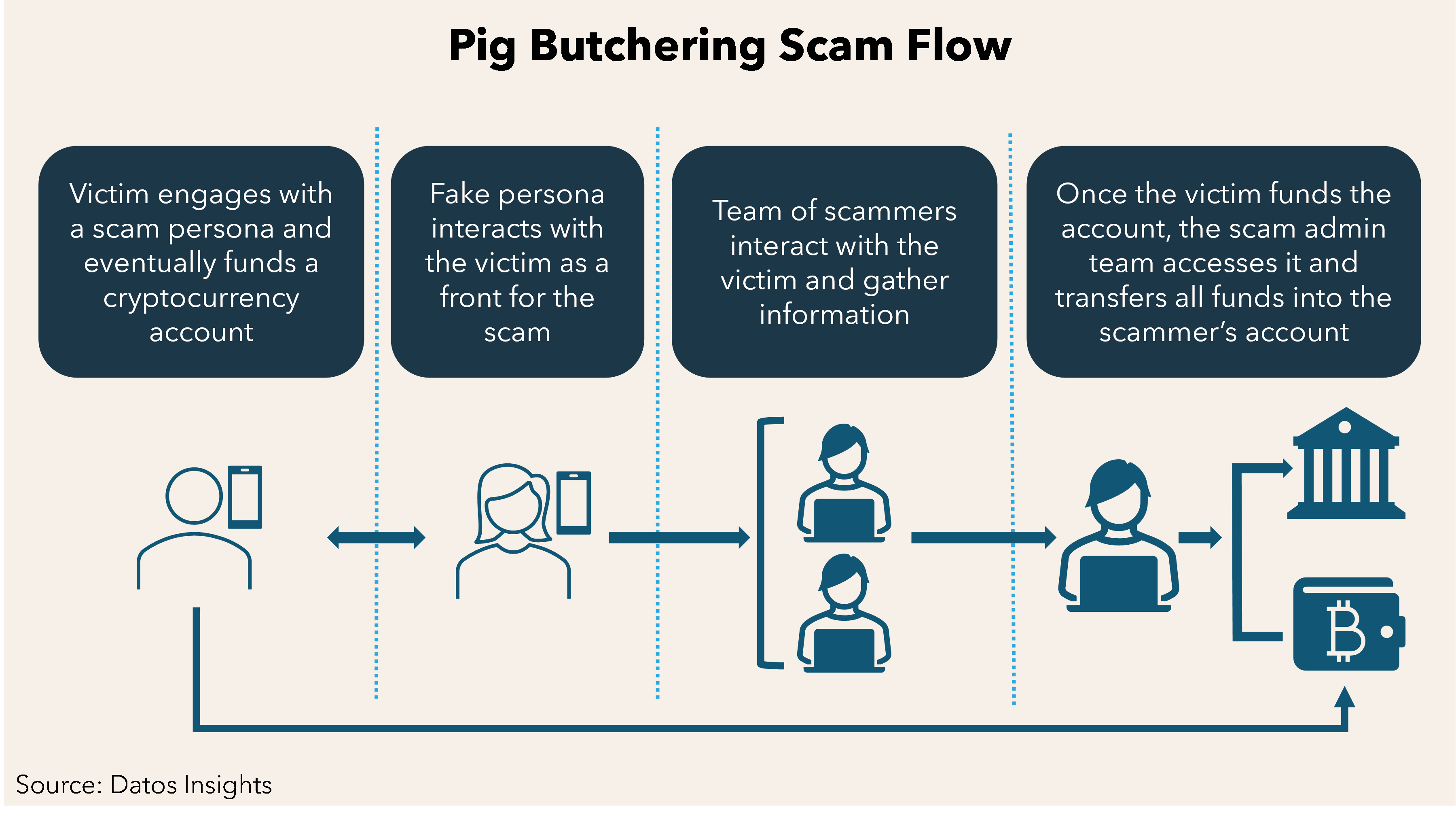
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
Chhattisgarh’s Link between Forest Ecosystem and Green GDP

- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
In a first, the Chhattisgarh state has introduced an innovative plan that connects the ecosystem services of its forests with the Green Gross Domestic Product (Green GDP).
Key Highlights:
Chhattisgarh's Green GDP Initiative:
- First State in India to link forest ecosystem services with Green GDP.
- Forests cover 44% of Chhattisgarh's land area, playing a vital role in climate change mitigation.
- Key forest products (tendu leaves, lac, honey, medicinal plants) contribute significantly to the rural economy.
Green GDP:
- Definition: An adjustment of traditional GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and ecosystem degradation.
- Formula:
- Green GDP = Net Domestic Product (NDP) − (Cost of Resource Depletion + Ecosystem Degradation)
- NDP = GDP − Depreciation of Produced Assets.
Importance of Green GDP:
- Traditional GDP overlooks the environmental cost, treating activities like deforestation as economic gains.
- Green GDP adjusts for sustainability, ensuring long-term economic growth aligns with environmental preservation.
Global Context & Initiatives:
- SEEA (System of Environmental-Economic Accounting): Developed by the UN to track economic-environment relationships.
- WAVES: World Bank initiative integrating natural capital into national economic accounts.
- Bhutan’s GNH: Emphasizes ecological sustainability in development.
Benefits of Green GDP for Chhattisgarh:
- Promotes sustainable development by integrating economic and environmental goals.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forests help absorb CO2, playing a key role in carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supports sustainable use of resources, preserving ecosystems.
- Cultural Integration: Acknowledges forests' cultural and spiritual importance to local tribal communities (e.g., sacred groves).
Key Features of the Initiative:
- Valuing Ecosystem Services: Includes clean air (CO? absorption), water conservation, and biodiversity.
- Eco-tourism Promotion: Developing jungle safaris and national parks, boosting local employment.
- Scientific Assessments: Employing experts to quantify forest contributions to the economy.
Challenges of Green GDP Framework:
- Valuation Complexity: Difficult to assign monetary value to non-market environmental benefits like biodiversity.
- Data Gaps: Lack of comprehensive data on environmental degradation and resource usage.
- Implementation: Requires significant changes in accounting systems and policymaking.
- Forest Definition: Plantations like oil palm may be counted as forests, misleading environmental assessments.
- Political Resistance: States may manipulate data to secure funding, prioritizing plantations over natural forests.
- Local Integration: Difficulties in involving local bodies like Panchayats due to literacy and awareness gaps.
Future of Green GDP:
- Sustainable Resource Use: Encourages responsible consumption and production, aligning with SDG 12.
- Climate Action: Contributes to the reduction of fossil fuel reliance and promotes renewable energy, aligning with SDG 13.
- Green Investments: Stimulates green technologies and industries, fostering sustainable economic growth (SDG 8).
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
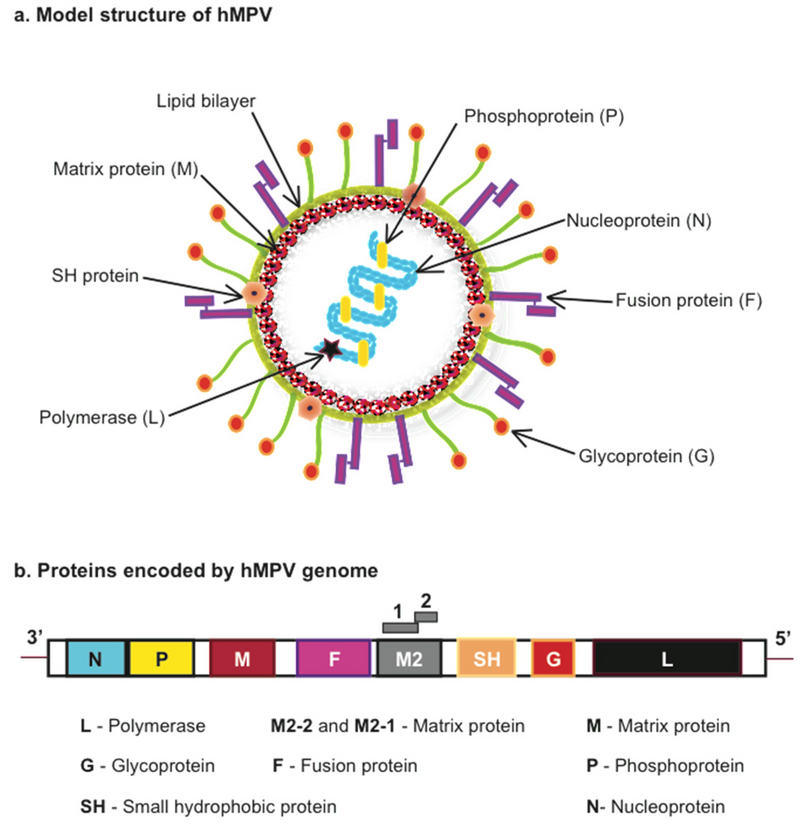
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
Five years after the COVID pandemic, China is experiencing a surge in HMPV cases, particularly in children under 14 years of age
Key Highlights:
- What is HMPV?
- A respiratory virus from the Pneumoviridae family, discovered in 2001.
- Causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, similar to the common cold or flu.
- Origin and Discovery:
- Identified in the Netherlands in 2001 through genomic sequencing of respiratory samples.
- Risk Groups:
- Children under 5 years, especially infants.
- Elderly individuals (65+).
- Immunocompromised persons and those with chronic respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma).
- Symptoms:
- Common: Cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat.
- Severe: Wheezing, shortness of breath, potentially leading to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Incubation Period: 3-6 days.
- Transmission:
- Spread via droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact (e.g., handshakes, hugs).
- Contaminated surfaces, touching face after contact.
- Treatment:
- No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine available.
- Symptom management: hydration, rest, OTC medications for fever and congestion.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization (oxygen therapy, IV fluids).
- Diagnosis:
- NAATs (Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests): Detect viral genetic material.
- Antigen-based immunoassays: For severe cases or outbreaks.
- Complications:
- Can lead to bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, or COPD flare-ups.
- Risk of ear infections (otitis media) in some cases.
- Prevention:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Physical Distancing: Avoid close contact, wear masks in crowded settings.
- Caution for Vulnerable Groups: Extra care for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Global Situation:
- China: Experiencing a rise in HMPV cases, particularly among children under 14 years.
- India: No reported cases yet, but monitoring the situation closely.
Key Facts:
- HMPV is a winter virus commonly seen in colder months (winter and early spring).
- Estimated 10%-12% of respiratory illnesses in children are caused by HMPV.
- The virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, alongside respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles, and mumps.
No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV; antibiotics are ineffective.
Ramesh Chand Panel
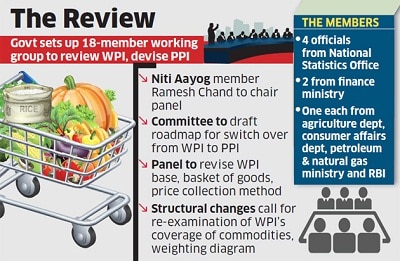
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Government of India has formed an 18-member panel, headed by Ramesh Chand, a member of NITI Aayog, to revise the base year of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) to 2022-23 from the current base year of 2011-12. The panel will also work on a roadmap for transitioning from WPI to the Producer Price Index (PPI).
Key Highlights:
Role and Mandates of the Panel:
- Revised Commodity Basket: The panel will recommend a new commodity basket for both WPI and PPI, reflecting structural changes in the economy.
- Review of Price Collection System: The panel will evaluate the current system for price collection and propose improvements.
- Computational Methodology: It will determine the computational methodology for both WPI and PPI to ensure accuracy in tracking price changes.
- The panel has been tasked with submitting its final report to the Office of the Economic Adviser at the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIT) within 18 months.
Understanding WPI vs. PPI:
- WPI (Wholesale Price Index) tracks the price of goods at the wholesale stage (i.e., goods sold in bulk to businesses), and excludes the service sector.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- Does not consider consumer-facing prices.
- Excludes services (about 55% of GDP).
- Can have double-counting bias due to multiple transactions before the final sale.
- Does not account for indirect taxes and may include export/import prices.
- Use: WPI helps in tracking bulk price movements between businesses, but doesn't fully represent consumer price inflation.
- Key Characteristics of WPI:
- PPI (Producer Price Index) tracks prices at various stages of production, considering both goods and services, and measures the average change in prices received by domestic producers.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
- Excludes indirect taxes (making it more accurate for price movement tracking).
- Includes services, unlike WPI, giving a broader view of price trends across the economy.
- More aligned with international standards (System of National Accounts).
- Reflects prices before consumer consumption, providing a business-oriented perspective of price trends.
- Key Characteristics of PPI:
Why the Transition to PPI?
- The PPI is already used by major economies like the US, China, Germany, and Japan as it provides a more comprehensive measure of inflation from a producer’s perspective.
- It is expected to be a better indicator of inflationary trends in the overall economy, including both goods and services.
Challenges and Roadmap:
- The switch to PPI is complex, and the panel will need to ensure that the transition does not disrupt the current data collection and reporting systems. Both WPI and PPI will run concurrently until PPI stabilizes.
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
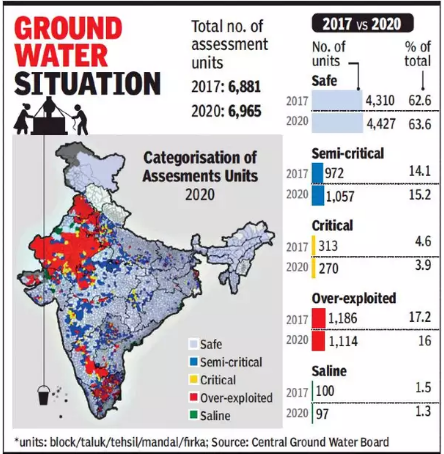
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) report on groundwater quality reveals alarming levels of contamination in India's groundwater, with a focus on nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and uranium. The report highlights the impact of agricultural practices, poor waste management, and urbanisation on water quality.
Key Highlights:
Nitrate Contamination:
- 440 districts in India report excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, with 20% of samples exceeding the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/L (WHO and BIS standards).
- High-risk regions: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) are the top states with high nitrate levels. Other affected states include Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Causes: Nitrate contamination is mainly due to excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, over-irrigation, and poor management of animal waste. Urbanisation and improper sewage systems exacerbate the problem.
Other Groundwater Contaminants:
- Fluoride contamination: A significant concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic contamination: Elevated arsenic levels found in several states, especially in floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur).
- Uranium contamination: 42% of uranium-contaminated samples are from Rajasthan, and 30% from Punjab. Chronic exposure to uranium leads to kidney damage.
Groundwater Extraction and Availability:
- 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India.
- 73% of groundwater blocks are classified as in the ‘safe’ zone, an improvement from 67.4% in 2022.
Monsoon Impact:
- Nitrate contamination increases post-monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season.
Health Implications:
- High nitrate levels, particularly dangerous for infants, can cause blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia).
- Long-term exposure to contaminants like fluoride and arsenic can lead to fluorosis and increase the risk of cancers and skin lesions.
Sources of Contamination:
- Agricultural practices: Excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and improper irrigation.
- Waste disposal: Leaking septic systems, sewage, and hazardous waste sites contribute to contamination.
- Urbanisation: Increased wastewater and sewage, along with poor waste management, worsen the issue.
Measures to Address Contamination:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) and Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) aim to conserve and manage groundwater resources.
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM) to assess and map aquifer systems.
- Pollution control programs: Under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, and initiatives like sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants to manage wastewater.
- Public awareness: Campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Catch the Rain educate communities on the importance of groundwater conservation.
Key Statistics:
- 56% of districts in India report groundwater nitrate levels exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg/L.
- Monsoon effects: Post-monsoon data shows a significant increase in contamination levels (32.66% vs. 30.77% pre-monsoon).
Business Ready (B-READY) Report 2024

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
- The B-READY report, launched by the World Bank in 2024, replaces the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) index.
- Focus: It evaluates the global business environment to foster inclusive private sector growth, assessing 10 core topics covering a firm's lifecycle, such as business entry, taxation, labor, and international trade.
India’s Potential Challenges
- Business Entry: India faces multiple steps and incomplete digital integration, making it slower compared to benchmarks like Singapore, which achieves one-day registration at minimal cost.
- Labor Regulations: While India has introduced four labor codes, the implementation remains slow and inconsistent, affecting labor flexibility and compliance.
- International Trade: India struggles with customs delays, inconsistent enforcement, and high logistics costs, unlike countries like Germany and Singapore, which promote trade efficiently.
- Business Location: Regulatory delays and inconsistent approvals hinder the establishment of business facilities, affecting investment decisions.
- Public Services Gap: While regulations may be strong, there is often a gap in the provision of public services that support their effective implementation, leading to inefficiencies.
Key Strengths for India
- India is expected to score well in the areas of Quality of Regulations, Effectiveness of Public Services, and Operational Efficiency.
- The country shows promise in promoting digital adoption and aligning with global environmental sustainability practices, though gender-sensitive regulations need more emphasis.
Significance
- The B-READY report serves as an essential benchmark for assessing India's business environment, offering insights into regulatory reforms and operational efficiency.
- Key policy implications for India include the need to:
- Streamline business operations by digitizing registration and regulatory approval processes.
- Improve logistics and trade efficiency by reducing customs delays.
- Address labor market inefficiencies through better implementation of labor codes.
- Invest in public services and promote digital transformation for better compliance and operational ease.
- Focus on sustainability and inclusivity, ensuring gender-sensitive policies and fostering green business practices.
Global Findings from the B-READY Report
- Economies with strong regulatory frameworks and digital tools (e.g., Rwanda, Georgia) show that even countries with varying income levels can achieve high scores.
- High-income countries like Estonia and Singapore still have room for improvement, especially in areas like taxation and dispute resolution.
Comparison of B-READY with Ease of Doing Business (EoDB)
- Scope: B-READY is broader, covering a firm’s lifecycle and social benefits, while EoDB focused mainly on regulatory burdens.
- Indicators: B-READY uses 1,200 indicators from expert consultations and firm-level surveys, offering more comprehensive insights compared to the EoDB's limited metrics.
- Focus on Public Services: Unlike EoDB, which provided limited attention to public services, B-READY explicitly evaluates public service efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Policy Recommendations
- Streamline Business Operations: Inspired by countries like Singapore, India should simplify business registration and reduce delays in customs and regulatory approvals.
- Strengthen Public Services: Focus on improving tax portals, utility access, and dispute resolution systems through digital tools.
- Promote Sustainability: Encourage environmentally sustainable business practices and adopt gender-sensitive regulations to ensure inclusive growth.
- Peer Learning and Global Collaboration: Encourage India to learn from best practices in countries like Singapore and Estonia for effective reforms.
- Tailored Reforms: India must design policies addressing unique local challenges while adhering to global standards.
Parker Solar Probe’s Closest-Ever Approach to the Sun

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA scientists announced that the Parker Solar Probe survived the closest-ever approach to the Sun. The craft was operating normally after it passed just 6.1 million km from the solar surface.
About the Parker Solar Probe:
- Launched: August 12, 2018, as part of NASA’s Living With a Star program.
- Named After: Eugene Newman Parker, a solar astrophysicist, marking the first NASA mission named after a living researcher.
- Mission Objectives:
- To study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind, investigating why the corona is hotter than the Sun’s surface.
- To explore the origins of solar winds and high-energy particles that impact space weather.
- To understand the structure and dynamics of plasma and magnetic fields around the Sun.
- To examine the mechanisms behind the acceleration and transportation of energetic particles.
Technological Feats:
- Heat Shield: Equipped with a 4.5-inch carbon-composite shield that withstands temperatures up to 1,377°C (2,500°F) while keeping the instruments cool at about 29.4°C (85°F).
- Speed: Travels at a speed of 692,000 km/h (430,000 mph), making it the fastest human-made object.
- Venus Flybys: Uses gravitational assists from Venus to gradually reduce its orbit and get closer to the Sun.
Historic Milestone:
- Closest Approach: On December 24, 2024, Parker Solar Probe reached a historic distance of 6.1 million km from the Sun's surface, the closest any human-made object has ever been.
- Comparison: If the Earth and Sun were 1 meter apart, Parker Solar Probe would be just 4 cm from the Sun.
- Temperature: At its closest, it endured temperatures up to 1,377°C.
Significance of the Mission:
- Scientific Contributions:
- Solar Wind: Helps scientists understand the origins of solar winds, which affect space weather and Earth’s technological systems.
- Corona Heating: Investigates why the Sun's corona is much hotter than its surface (a long-standing astrophysical mystery).
- Space Weather: Provides critical data for predicting space weather events that can impact satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth.
- Practical Implications:
- Improves understanding of space weather, potentially aiding in the protection of Earth’s infrastructure from solar storms.
- Technological and Engineering Marvel:
- Demonstrates advanced spacecraft technology that can withstand extreme conditions close to the Sun.
Recent Developments:
- Data Collection: As the probe passed through the Sun’s outer atmosphere (the corona), it collected valuable data expected to answer fundamental questions about solar behavior.
- Communication: Despite the extreme proximity to the Sun, the probe sent back a signal on December 26, confirming its status.
Key Dates:
- Launch: August 12, 2018.
- Closest Approach: December 24, 2024.
- Data Expected: Detailed telemetry data on January 1, 2025.
Exercise SURYA KIRAN

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian Army Contingent Departs for 18th Edition of Exercise SURYA KIRAN (India-Nepal Joint Military Exercise).
Key Highlights:
- Event Overview:
- Name: 18th Edition of Battalion-Level Joint Military Exercise SURYA KIRAN.
- Dates: 31st December 2024 to 13th January 2025.
- Location: Saljhandi, Nepal.
- Participants: Indian Army (334 personnel, led by a Battalion from the 11th Gorkha Rifles) and Nepal Army (Srijung Battalion).
- Objective of Exercise:
- Enhance interoperability in jungle warfare, counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrain, and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) under the UN Charter.
- Focus on operational preparedness, aviation training, medical aspects, and environmental conservation.
- Key Features:
- Training Focus: Improving combat skills and coordination to operate together in challenging situations.
- Exchange of Ideas: Soldiers from both nations will share best practices, enhance mutual understanding of operational procedures.
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: Reinforces strong bonds of friendship, cultural linkages, and defense cooperation between India and Nepal.
- Significance:
- Historical Context: Exercise held alternately in India and Nepal since 2011.
- Enhances Combat Readiness: Prepares both armies to address shared security challenges and improve operational capabilities.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Fosters a productive professional environment between India and Nepal.
- Recent Developments:
- The exercise follows visits by General Upendra Dwivedi (Indian Army Chief) to Nepal and General Ashok Raj Sigdel (Nepali Army Chief) to India, strengthening military ties.
- Previous Editions:
- 17th Edition: Conducted in Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand (24th Nov - 7th Dec 2023).
Lighthouse Tourism in India

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
Lighthouse tourism in India is rapidly emerging as an exciting and profitable segment of the country's travel and tourism industry. India's coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers, is home to 204 lighthouses, many of which are being transformed into vibrant tourist destinations, celebrating both India's rich maritime history and its natural beauty.
Key Highlights:
- Historical and Scenic Appeal: Lighthouses in India are often located in breathtaking coastal or island locations, offering panoramic sea views and access to surrounding natural beauty. Some of these structures are centuries old and are situated near significant cultural landmarks or UNESCO World Heritage Sites, adding cultural depth to the visitor experience.
- Economic Growth: As part of the broader Maritime India Vision (MIV) 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, the Government of India is keen to transform these historic lighthouses into hubs of economic activity. By developing infrastructure, creating new tourism-related jobs, and fostering local entrepreneurship, lighthouse tourism aims to benefit coastal communities and boost India's tourism economy. As of 2023-24, 75 lighthouses across 10 states have been equipped with modern amenities, attracting 16 lakh visitors—a 400% increase from previous years.
- Government Initiatives:
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- The 1st Indian Lighthouse Festival, “Bharatiya Prakash Stambh Utsav”, was inaugurated on 23rd September, 2023 by the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal and Goa Chief Minister, Shri Pramod Sawant at the historic Fort Aguada in Goa.
- The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held in Odisha. Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, was also joined by Odisha Chief Minister, Mohan Charan Majhi. Shri Sonowal dedicated two new lighthouses at Chaumuck (Balasore) and Dhamra (Bhadrak) and emphasized empowering coastal communities to preserve and promote lighthouses as part of India’s rich maritime heritage.
- Sagarmala Programme: This government initiative integrates infrastructure development with sustainable practices, ensuring that the growth of lighthouse tourism benefits local communities while preserving the environment.
- Tourism Infrastructure: The government has invested ?60 crore in enhancing these sites, providing facilities like museums, parks, amphitheaters, and more to enrich the visitor experience.
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- Sustainable Development: The Indian government places a strong emphasis on eco-friendly tourism. This includes integrating lighthouses into broader coastal circuits and launching digital awareness campaigns to attract domestic and international tourists.
- Community Empowerment and Employment: Lighthouse tourism has already created direct and indirect employment, from hospitality to transportation, local handicrafts, and artisan work, with more than 500 jobs being generated. Local communities are being trained to offer skills in hospitality and tourism services.
Future Plans:
- Skill Development: Programs are being introduced to equip local people with the necessary skills to cater to the tourism industry.
- Sustainable Practices: Eco-friendly practices will continue to be emphasized to protect coastal ecosystems.
- Integration with Coastal Circuits: Lighthouses will become key points of interest in broader coastal tourism itineraries, further enhancing their appeal to tourists.
Strengthening Fisheries Extension Services

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
India possesses diverse fisheries resources that provide livelihood opportunities to approximately three crore fishers and fish farmers. The country has witnessed an 83% increase in the national fish production since 2013-14, that stands at a record 175 lakh tons in 2022-23.
Importance of Fisheries Extension Services:
- Livelihood Support: Fisheries provide livelihoods to over 3 crore fishers and fish farmers in India. The sector's growth is crucial for enhancing sustainable practices and ensuring long-term productivity.
- Growth in Fish Production: India’s fish production has seen an 83% increase since 2013-14, reaching 175 lakh tons in 2022-23, with 75% of production coming from inland fisheries. India is the second-largest fish and aquaculture producer globally.
- Role of Extension Services: Extension services bridge the gap between scientific advancements and fishers, offering guidance on:
- Species lifecycle management
- Water quality management
- Disease control
- Sustainable rearing technologies and business models.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Fisheries Extension:
- Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs):
- Launched under PMMSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana) in 2020, MSKs are one-stop centers providing comprehensive extension services.
- Support to Fish Farmers: MSKs offer:
- Disease testing, water, and soil analysis.
- Training on sustainable aquaculture practices.
- Technology infusion in seed/feed management.
- Focus on Inclusivity: Government assistance (up to 60%) is available for women and marginalized communities to set up MSKs.
- Examples:
- Thrissur, Kerala: Equipped with labs for water and microbial analysis.
- Maharashtra (Nasik and Sangli): Capacity-building efforts on seed/feed inputs.
- Collaborations: MSKs mobilize start-ups, cooperatives, and Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs) to share best practices, including regenerative and conservation management in the face of climate change.
- Sagar Mitras:
- Role: Deployed in coastal states and union territories, Sagar Mitras act as a vital interface between the government and marine fishers.
- Functions:
- Collection and dissemination of daily marine catch data, price fluctuations, and market insights.
- Dissemination of important information: weather forecasts, fishing zones, local regulations, and hygienic fish handling.
- Provide support on disaster preparedness and natural calamities.
Enhancing Extension Services through Digital Platforms:
- AquaBazaar: A virtual learning platform initiated by the National Fisheries Development Board to provide expert guidance on:
- Seed production and breeding of commercially important fish species.
- Practical demonstrations to improve fishers' knowledge.
- Digital Outreach: Expanding such platforms will improve access to resources for fishers, especially in rural and remote areas.
Institutional Convergence and Capacity Building:
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Fisheries extension services should be integrated with the over 700 Krishi Vigyan Kendras and state-level agricultural extension services for effective outreach.
- Formalizing the Sector: The World Bank-assisted project aims to create work-based digital identities for fishers and fish farmers, enhancing their access to extension services, training, and awareness programs.
Challenges in Fisheries Extension Services:
- Fragmented Initiatives: Multiple government schemes and programs lack institutional convergence, leading to inefficiencies in reaching the grassroots level.
- Digital Divide: Many rural and coastal areas face challenges in terms of digital literacy and internet connectivity, limiting the effectiveness of online platforms.
- Impact of Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns and resource depletion due to overfishing demand adaptive strategies and the promotion of climate-resilient practices.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
- Institutional Convergence: Combining existing extension machinery like Krishi Vigyan Kendras with fisheries extension services to leverage established networks and knowledge.
- Expand Digital Outreach: Platforms like AquaBazaar should be expanded to ensure wider access to expert knowledge, training, and best practices.
- Private Sector Collaboration: Encouraging public-private partnerships can enhance technology dissemination, capacity building, and resource mobilization in the fisheries sector.
- Focus on Sustainability: Developing climate-resilient and sustainable fisheries practices will be essential to address challenges posed by environmental changes and overfishing.
Private Aviation and Emissions

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Private aviation is releasing more than its ‘fair share’ of emissions.
Key Highlights:
- Aviation Sector's Global Emissions:
- The aviation sector contributed 2% of global CO2 emissions in 2022, around 800 Mt CO2 (International Energy Agency).
- If considered as a nation, aviation would rank among the top 10 emitters worldwide.
- Emissions from aviation have grown faster than other sectors like rail, road, or shipping in recent decades.
- Private Aviation and Its Impact:
- Private jets emit 5 to 14 times more CO2 per passenger than commercial flights and 50 times more than trains.
- Emissions from private aviation increased by 46% between 2019 and 2023.
- Each private flight contributes 3.6 tonnes of CO2 on average, intensifying global warming.
- Private aviation is responsible for significant nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and the creation of vapor trails, which further amplify environmental damage.
Trends in Private Aviation Growth:
- Global Trends:
- The number of private jets increased from 25,993 in December 2023 to 26,454 in February 2024.
- In the U.S., 69% of private aviation activity is concentrated.
- 8,500 more jets are expected to be delivered in the next 10 years globally.
- Private Aviation in India:
- 112 private planes were registered in India as of March 2024, placing it among the top 20 countries for private aircraft ownership.
- India's private aviation sector is expanding, driven by the growing billionaire and millionaire population.
- Private aircraft ownership in India stands at 1 per 1 lakh population, which is low compared to countries like Malta (46.51 per lakh) and the U.S. (5.45 per lakh).
Emission Reduction Efforts and Solutions:
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs):
- SAFs are bio-based or waste-derived fuels that can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuels.
- Airlines like SpiceJet (2018) and AirAsia (2023) have tested SAFs, but large-scale adoption is hindered by high costs and limited production.
- India aims to leverage its ethanol production chain, with potential to meet 15-20% of aviation fuel demand by 2050 if only surplus sugar is used.
- Hydrogen and Electric Aviation:
- Hydrogen offers a higher energy density than kerosene and emits only water vapor, making it a clean fuel alternative. However, hydrogen faces challenges with storage, infrastructure, and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric propulsion offers zero emissions but is currently limited by battery weight, energy density, and charging infrastructure.
India’s Policy and Initiatives:
- Government Initiatives:
- UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) aims to enhance rural connectivity.
- NABH (Nextgen Airports for Bharat Nirman) seeks to increase airport capacity by five times.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- Indian airlines have tested SAFs, such as a 25% jatropha oil blend by SpiceJet in 2018.
- Ethanol for aviation fuel: India plans to use surplus sugar for ethanol, potentially fulfilling 15-20% of aviation fuel needs by 2050.
- Challenges to Decarbonisation:
- SAFs are costly and limited in availability.
- Hydrogen requires extensive infrastructure and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric solutions are currently unsuitable for long-haul flights due to energy limitations.
GenCast AI
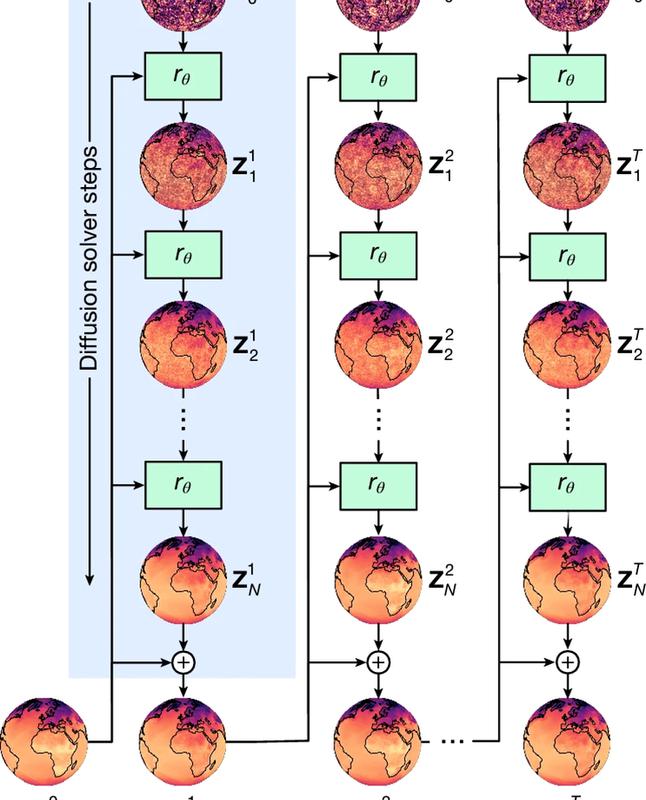
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Google’s GenCast AI is an advanced weather forecasting model developed by DeepMind that uses machine learning techniques to provide more accurate and longer-term weather predictions compared to traditional forecasting methods.
How GenCast Works:
- Training on Reanalysis Data:
- GenCast is trained on 40 years of reanalysis data (from 1979 to 2019). This data combines historical weather observations with modern weather forecasts, providing a comprehensive picture of past weather and climate conditions.
- Ensemble Forecasting with AI:
- Unlike traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models, which run simulations based on physical laws and initial conditions, GenCast uses an ensemble forecasting approach where multiple predictions are generated by an AI model, not an NWP model.
- It produces a range of possible weather scenarios, each with different starting conditions, to reflect the uncertainty in weather forecasts.
- Neural Network and Diffusion Model:
- GenCast uses a neural network architecture with 41,162 nodes and 240,000 edges that process weather data. Each node accepts data, manipulates it, and passes it to another node, helping to refine and improve predictions.
- It uses a diffusion model, a type of AI model commonly used in generative AI. The model takes noisy input data, processes it through 30 refinement steps, and gradually produces a clearer forecast (de-noising the data).
- The result is a probabilistic forecast, such as "there's a 25% chance of rain in Chennai on December 25," rather than a deterministic forecast, which would provide exact quantities like "5 mm of rain."
- Faster Processing:
- The entire forecast process is incredibly efficient. GenCast can generate 50 ensemble forecasts at once with a spatial resolution of 0.25° x 0.25° (latitude-longitude) and temporal resolution of 12 hours.
- Using Google's TPU v5 units, it can produce these forecasts in just 8 minutes—far faster than traditional supercomputers, which can take several hours to run NWP simulations.
Key Features of GenCast:
- Better Performance on Extreme Weather: GenCast has shown superior accuracy in predicting extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones, compared to traditional NWP models like those from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
- Probabilistic Forecasting: GenCast produces probabilistic forecasts, offering predictions like the likelihood of rain rather than precise measures, which helps with better preparation, especially for extreme weather events.
- Long-Term Forecasting: GenCast can generate forecasts for up to 15 days, which is longer than most traditional models, and is particularly useful for anticipating events like wind power generation and tropical cyclone tracking.
- Efficiency: GenCast's speed and resource efficiency set it apart from traditional NWP models, reducing forecast times dramatically.
Comparison with Traditional Weather Models:
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP): Traditional NWP models rely on solving complex physical equations to simulate the atmosphere and provide deterministic forecasts. These models require significant computational power and are typically limited to weather predictions for about a week.
- GenCast's Probabilistic Forecasts: In contrast, GenCast offers probabilistic predictions, making it better suited for providing early warnings about extreme weather, with better lead times for disaster preparation.
Future Developments:
While GenCast is impressive, Google acknowledges the importance of traditional NWP models for both supplying initial conditions and providing the foundational data needed to train AI models like GenCast. Ongoing collaboration with weather agencies is crucial to enhancing AI-based methods for weather prediction.
Overall, GenCast represents a significant leap forward in the use of AI for weather forecasting, with potential for greater accuracy, efficiency, and longer-term predictions compared to current methods.
Specialised Investment Fund (SIF)
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
SEBI has introduced a new asset class called Specialised Investment Fund (SIF), designed to bridge the gap between Mutual Funds (MFs) and Portfolio Management Services (PMS). This new asset class is targeted at informed investors who are willing to take on higher risks.
SIFs offer a blend of the flexibility seen in PMS and the regulatory framework governing MFs, making them suitable for investors seeking more customized and riskier investment strategies.
Key Features of SIF:
- Minimum Investment: The minimum investment threshold for SIFs is Rs. 10 lakh. However, accredited investors (who meet specific eligibility criteria) can invest with lower amounts.
- Expense Structure: SIFs will follow the same expense structure as mutual funds. For equity schemes up to Rs 500 crore in size, the maximum allowable fee is 2.25% of assets under management (AUM), with the cap decreasing as the fund size grows. This ensures transparency and keeps management fees in line with existing mutual fund norms.
- Investment Strategies: SIFs can offer a mix of open-ended, close-ended, and interval investment strategies. Specific details on permissible strategies will be released by SEBI in the future.
- Investment Restrictions:
- For debt instruments, a single issuer's exposure is capped at 20% of the total AUM. However, this can be raised to 25% with approval from the Asset Management Company (AMC)’s trustees and board of directors. Government securities are exempt from this limit.
- For equities, the exposure is capped at 10% of the total AUM, in line with the norms for mutual funds.
- Ownership in Companies: The maximum permissible ownership in any company is raised to 15%, including the MF exposure.
- REITs and InvITs: SIFs can invest a maximum of 20% of their AUM in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs). However, the exposure to a single issuer in these areas is limited to 10%.
- Branding and Marketing: SEBI mandates AMCs to distinguish SIFs clearly from MFs through distinct branding, advertising, and website presence. This helps in creating a clear differentiation between the two products for investors.
- Risk Management and Compliance: AMCs managing SIFs are required to have robust risk management systems, internal control systems, and expertise to handle the investments effectively. Trustees are responsible for ensuring that the AMC complies with all risk management, investor protection, and disclosure norms.
Regulatory Context:
- The regulations on SIFs are similar to those governing mutual funds, including taxation and other compliance requirements.
- SEBI also introduced the Mutual Fund Lite regulations to encourage the growth of passively managed funds, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds. These regulations are designed to reduce compliance burdens and lower the barriers to entry for new players in the mutual fund industry.
Significance of SIFs:
- Targeted Audience: SIFs cater to investors who are knowledgeable and willing to take on riskier investments, thereby filling a gap between traditional MFs (which are more conservative) and PMS (which offer highly customized solutions).
- Higher Flexibility: While SIFs maintain some regulations of MFs, they offer more flexibility in investment choices, allowing AMCs to explore more dynamic strategies.
- Investor Protection: By maintaining the same expense structure as mutual funds and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks, SEBI aims to protect investor interests while allowing for higher returns that come with riskier investments.
Smuggling in India Report 2023-24
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The annual ‘Smuggling in India - Report 2023-24’ report, which highlights DRI’s performance and experience over the last financial year as well as trends in the field of anti-smuggling and commercial fraud, will be released during the celebration.
Major Narcotics Hubs and Routes:
- Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan (The Death Crescent):
- Primary source of heroin trafficked into India.
- Routes via Africa, the Gulf, and India-Pakistan border.
- Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand (The Death Triangle):
- Significant source of synthetic drugs and heroin.
- Drugs often enter India through porous northeastern borders (e.g., Assam, Mizoram).
- Vulnerable regions: Moreh, Churachandpur, Zokhawthar.
- Maritime Routes:
- India’s vast coastline provides opportunities for drug trafficking, often through concealed shipping containers and fishing vessels.
- Air Routes:
- Increased trafficking due to international air traffic.
- Smuggled drugs often concealed in luggage, courier packages, or ingested by mules.
Major Narcotics Trends and Seizures (FY24):
- Cocaine:
- Significant increase in trafficking, particularly from South America and Africa.
- 47 seizures, up from 21 in the previous year.
- Seized quantity: 107 kg.
- Methamphetamine:
- Spiked in northeastern states like Assam and Mizoram.
- Seized quantity in FY24: 136 kg; increased in the first half of FY25 with 123 kg.
- Hydroponic Marijuana:
- Increasing smuggling from the US, Thailand, and other countries.
- Black Cocaine:
- New form of cocaine coated with substances like charcoal or iron oxide to evade detection.
- Contraband Cigarettes:
- Smuggling through sea routes, especially from Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- Seizures increased by 19% in FY25, reaching 3.95 crore sticks.
- Illicit Gold:
- Significant destination for gold smuggling from West Asia (UAE, Saudi Arabia).
- Seized quantity fell slightly (1,319 kg in FY24), with land and air routes being primary methods.
- Wildlife Smuggling:
- Seizures included 53.5 kg of elephant tusks, leopard skins, live pangolins, and more.
Challenges and Issues:
- Porous Borders:
- Smuggling across eastern borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal remains a significant challenge.
- Difficult terrain in these regions aids traffickers.
- Air and Sea Routes:
- Growing use of air and maritime routes due to faster movement of goods.
- Technology and Detection:
- Emergence of “black cocaine” challenges traditional detection methods.
Anti-Smuggling and Drug Control Efforts:
- International Cooperation:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) lead global efforts.
- Paris Pact Initiative targets Afghan opiate trafficking.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) provides legal framework.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) work together for enforcement.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan focus on awareness and rehabilitation.
ABOUT DRI
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is the premier intelligence and enforcement agency on anti-smuggling matters under the aegis of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC), Government of India.
- It came into existence on 4th December 1957.
- With its Headquarters at New Delhi, 12 Zonal Units, 35 Regional Units and 15 Sub-Regional Units, DRI has been carrying out its mandate of preventing and detecting cases of smuggling of narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances, gold, diamonds, precious metals, wildlife products, cigarettes, arms, ammunitions & explosives, counterfeit currency notes, foreign currency, SCOMET Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) items, hazardous & environmentally sensitive materials, antiques etc. and taking punitive action against the organised crime groups engaged therein.
- DRI is also engaged in unearthing commercial frauds and instances of customs duty evasion.
Hyperloop Technology
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s first hyperloop test track (410 meters) completed by Indian Railways, IIT-Madras’Avishkar Hyperloop team and TuTr (incubated startup) at IIT-M discovery campus, Thaiyur in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
India’s First Hyperloop Test Track:
- Location: IIT Madras’ Discovery Campus, Chennai.
- Collaboration: Indian Railways, IIT-Madras' Avishkar Hyperloop team, and TuTr Hyperloop (startup).
- Track Length: 410 meters.
- Test Speed: Initial successful test at 100 km/h; plans for 600 km/h in the next phase.
- Passenger Capacity: 40–100 passengers per pod, depending on design.
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Concept: A high-speed transport system using pods in low-pressure vacuum tubes, designed to achieve speeds similar to aircraft (up to 1,100 km/h).
- Working:
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Pods float on magnets, eliminating friction.
- Vacuum Tubes: Reduces air resistance for high-speed travel.
- Propulsion: Linear induction motors propel pods.
- Energy: Solar-powered, designed for zero emissions.
India’s Hyperloop Projects:
- Current Status:
- Successful testing of a 410-meter test track at IIT Madras.
- Ongoing feasibility studies for routes like Chennai Airport–Parandur, Mumbai–Pune, and Amritsar–Chandigarh.
- Phase 1 & 2: First phase involves a 11.5-kilometer track; future expansion to 100 km.
- Mumbai–Pune Corridor: Planned as India’s first full-scale Hyperloop system, aiming to reduce travel time from 3–4 hours to 25 minutes.
Benefits of Hyperloop:
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to 1,100 km/h (operational speed around 360 km/h).
- Efficiency: Reduces travel time, energy-efficient with reduced air resistance and friction.
- Sustainability: Powered by renewable energy (e.g., solar power), offering zero emissions.
- Point-to-Point Travel: No intermediate stops, making it more time-efficient.
Challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Expensive to build the vacuum tubes, stations, and supporting systems.
- Land Acquisition: Difficulty in acquiring land, especially in densely populated areas.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of a specific regulatory framework for such advanced transport systems.
- Technological Barriers: Complex engineering challenges, including development of maglev systems and vacuum seals.
Global Context:
- Origin: Concept proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
- Worldwide Adoption: Hyperloop is being explored globally, with projects in the U.S., UAE, and Europe.
GG Tau A System

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
GG Tau A System: Located about 489 light-years from Earth, this system is a triple-star setup that is between 1 to 5 million years old. This makes it an ideal system for studying the early stages of planetary formation.
Findings from the Discovery:
- Protoplanetary Disk: The system features a protoplanetary disk made of gas and dust, where new planets are forming. Researchers from NISER (National Institute of Science Education and Research), Odisha detected emissions from key molecules in the disk.
- Chemical Molecules: The molecules are frozen on tiny dust particles in the coldest regions of the disk (temperatures between 12 K and 16 K). These frozen molecules could serve as the building blocks for new planets.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Triple-Star Configuration: GG Tau A’s triple-star system is rare, and it has complex gravitational interactions among the three stars. This complicates how the gas and dust disk behaves and provides unique insights into planetary formation in multi-star systems.
- Study of Planet Formation: Traditionally, planets form around single stars or in binary systems. However, multi-star systems like GG Tau A present challenges for planet formation. Studying this system helps scientists understand how planets can form in more complex environments.
- Cold Conditions for Planet Formation: The study found that icy conditions in the disk are essential for the accumulation of materials that form planets. These low temperatures (below the freezing point of carbon monoxide) allow dust and gas particles to clump together, creating the foundation for exoplanets.
Broader Implications:
- Exoplanet Diversity: This research enhances our understanding of how planets form in different types of star systems, contributing to the study of exoplanets and their potential diversity across the universe.
- Astrophysics and Planetary Science: This discovery plays a crucial role in improving our knowledge of the early stages of planet formation, especially in complicated star systems like triple-star setups, which are rare but can provide valuable insights into how planetary systems evolve under unique conditions.
Research Tools:
- The team used advanced radio telescopes located in the Atacama Desert (Chile) to observe the emissions from the disk, highlighting the role of cutting-edge technology in space exploration and astronomical research.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Madhav Gadgil, an Indian ecologist, received the UN Environment Programme (UNEP)'s Champions of the Earth Award in 2024.
- The Champions of the Earth Award is UNEP’s highest environmental honor, recognizing individuals, organizations, and governments for significant contributions to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Contributions of Madhav Gadgil:
- Work in Western Ghats:
- Gadgil is recognized for his seminal work in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive region in India, which is a global biodiversity hotspot.
- He chaired the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), formed by the Indian government to assess the impacts of population pressure, climate change, and development on the region.
- Recommendations by WGEEP:
- Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA): Recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats range as an ESA.
- The WGEEP suggested dividing the Western Ghats into three Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ) based on environmental sensitivity.
- Development Restrictions: Proposed a ban on activities like mining, quarrying, thermal power plants, and large-scale hydropower projects in the most sensitive zones (ESZ-1).
- Governance Recommendations: Suggested a bottom-to-top governance approach, beginning with Gram Sabhas, and the creation of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority (WGEA) for effective management.
- Impact of Gadgil’s Work:
- His research and recommendations have played a crucial role in shaping environmental policy and public opinion in India.
- The UNESCO World Heritage status for the Western Ghats in 2012 was a significant step in global recognition of the region’s ecological importance.
About the Champions of the Earth Award:
- History & Significance:
- Established in 2005, the award recognizes trailblazers working towards addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- Since its inception, it has honored 122 laureates who have shown outstanding leadership in environmental conservation.
- 2024 Awardees:
- Madhav Gadgil (India) – for his work on the Western Ghats.
- Sonia Guajajara (Brazil) – for advocacy for Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
- Amy Bowers Cordalis (USA) – for her work in Indigenous rights and ecosystem restoration.
- Gabriel Paun (Romania) – for defending Europe’s old growth forests from illegal logging.
- Lu Qi (China) – for contributions to afforestation and combating desertification.
- SEKEM (Egypt) – for advancing sustainable agriculture.
Key Facts about UNEP:
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Established in 1972, UNEP is a leading global authority on environmental issues.
- UNEP aims to address climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution through scientific research, policy support, and public advocacy.
- UNEP is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya and works closely with 193 Member States to tackle the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges.
AgeXtend
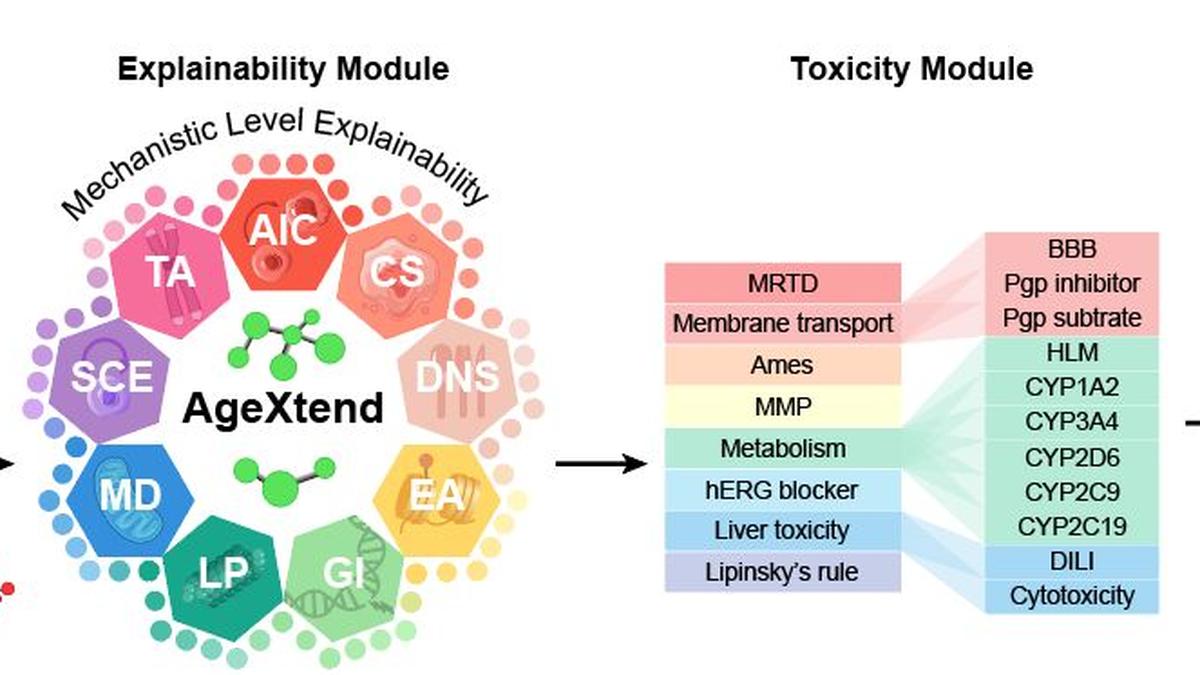
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- AgeXtend is developed by researchers at Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology – Delhi (IIIT-Delhi) to rapidly identify age-defying compounds, known as geroprotectors, to promote healthy aging.
Key Features of AgeXtend:
- What is AgeXtend?
- An AI-based platform designed to discover compounds with geroprotective (anti-aging) properties.
- Objective: To accelerate the identification of molecules promoting longevity by reducing the time and effort compared to conventional research methods.
- Development: Developed by researchers from the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Delhi.
- Working Mechanism:
- Scans over 1.1 billion compounds to predict, analyze, and validate molecules with anti-aging potential.
- Utilizes machine learning to determine efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action.
- Experimental validation conducted using yeast, worms (C. elegans), and human cell models.
- Significance:
- The largest study on longevity, including compounds from commercial drugs, FDA-approved drugs, Ayurvedic, and Chinese medicine.
- Provides a scientific rationale for identifying geroprotective compounds, aiding targeted research.
- Open-source code and data promote collaboration and allow commercial exploration.
Platform Capabilities:
- AI Analysis:
- Uses bioactivity data from existing geroprotectors to predict new compounds with similar properties.
- Evaluates geroprotective potential, toxicity, and identifies target proteins and mechanisms of action for accuracy and safety.
- Unique Feature: Explains why a compound is considered geroprotective, revealing underlying mechanisms.
- Example Validation: Successfully identified benefits of metformin and taurine without prior knowledge, confirming the platform’s predictive power.
- Study Scale: The study involved scanning over 1.1 billion molecules, making it the largest study on longevity to date.
Open-Source and Commercial Use:
- Availability:
- The code and data are available as open-source for researchers and students. Commercial access is available for a fee.
- A Python package for AgeXtend is available via pip on pypi.org.
- Further Collaboration: The researchers have reached out to pharma companies to further investigate promising compounds.
- Exploring Natural Compounds: AgeXtend also explores natural compounds from the human microbiome, investigating their role in controlling cell aging.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
INS Tushil Commissioned into the Indian Navy in Russia

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy officially commissioned INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, at Kaliningrad, Russia. This marks a significant milestone in India-Russia defense cooperation and strengthens India’s maritime capabilities.
About INS Tushil:
- Class & Design: INS Tushil is the seventh ship in the Krivak III class (Project 1135.6) of frigates. It is part of an upgraded series, following the Talwar-class and Teg-class frigates, and was built at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia.
- Development & Contract: The construction was initiated under a 2016 contract between the Indian Government, JSC Rosoboronexport (a Russian defense company), and the Indian Navy. The ship incorporates 26% indigenous technology, highlighting growing cooperation between Indian and Russian industries.
- Key Features:
- Stealth Design: With advanced radar-absorbing features, it is less detectable by enemy radar.
- Weaponry: Equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles, anti-submarine torpedoes, electronic warfare systems, and more.
- Versatility: Designed for blue-water operations, the ship can engage in air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic warfare.
- Helicopter Deck: Supports operations of upgraded Kamov 28 and Kamov 31 helicopters.
- Speed: Capable of exceeding 30 knots.
Significance:
- Enhanced Naval Capabilities: The commissioning of INS Tushil boosts India’s defense strength in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a vital area for global maritime trade and security.
- Maritime Security: INS Tushil is designed to support India’s vision of maintaining stability in the IOR and to act as a deterrent against piracy and other maritime threats.
- Defense Cooperation: This commissioning exemplifies the growing defense ties between India and Russia, underscored by joint development, technology transfer, and shared expertise. The ship reflects a major step in India's self-reliance in defense, in line with the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
- Strategic Role in Global Defense: The ship is a key asset in the Indian Navy's efforts to secure maritime trade routes, enhance regional security, and provide humanitarian assistance in times of need.
Key Events & Facts:
- Construction Timeline: The keel of INS Tushil was laid in 2013, and it launched in 2021. After completing extensive sea and weapon trials in 2024, it was formally commissioned into the Navy.
- Collaborative Effort: The ship is a product of collaborative efforts between Indian and Russian industries, marking a significant achievement in joint defense manufacturing.
Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India announced the appointment of Sanjay Malhotra as the 26th Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). He replaces Shaktikanta Das, whose six-year tenure ends on December 10, 2024.
Background of Sanjay Malhotra:
- Education & Early Career: Sanjay Malhotra is a 1990-batch IAS officer from the Rajasthan cadre. He holds a degree in Computer Science Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur and a Master’s in Public Policy from Princeton University.
- Professional Experience: Malhotra has over 33 years of experience in various sectors including power, finance, taxation, information technology, and mines. He is currently serving as the Revenue Secretary in the Ministry of Finance, a position he has held since October 2022. Prior to this, he was Secretary of the Department of Financial Services.
- Monetary Policy and Challenges: As RBI Governor, Malhotra will inherit the responsibility of steering India's monetary policy, especially as inflation has been a persistent issue and economic growth has slowed. His first monetary policy review is expected in February 2025.
About the Appointment Process:
RBI Governors are appointed by the Government of India, and the appointment process involves the Financial Sector Regulatory Appointment Search Committee, which includes the Cabinet Secretary, the current RBI Governor, the Financial Services Secretary, and two independent members. The committee prepares a list of eligible candidates, interviews them, and the final decision is made by the Cabinet Committee on Appointments, chaired by the Prime Minister.
RBI Governors Eligibility Criteria
- The RBI Act, 1934 does not mention any specific qualification for the governor. People with different educational backgrounds were selected to head the institution. However, the governor traditionally is either a civil services personnel or an economist.
- Candidates should have prior experience in areas such as:
- Working with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or World Bank.
- Serving as Chairman or General Manager of a bank.
- Holding significant positions in reputable financial or banking organizations.
- Working in the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India.
- The candidate must be an Indian citizen aged 35 years or older.
- The candidate cannot be a member of Parliament, State Legislature, or hold any other office for profit
Key Responsibilities of the RBI Governor:
- Monetary Policy: The RBI Governor chairs the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), which is responsible for setting benchmark interest rates and managing inflation.
- Regulation of Financial Institutions: The Governor oversees the regulation of banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions.
- Currency Management: The Governor ensures the proper issuance of currency and the withdrawal of unfit notes.
- Crisis Management and Policy Execution: The Governor is pivotal in managing financial crises and ensuring the execution of policies related to foreign exchange and financial inclusion.
Oilfields Amendment Bill, 2024

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
To encourage domestic production of petroleum and other mineral oils, along with private investment in these sectors to reduce import dependence, the Rajya Sabha passed the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024.
Key Details:
- Objective:
- Encourage domestic petroleum production.
- Reduce import dependence by promoting private investment in the oil sector.
- Key Amendments:
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- The Bill separates petroleum and mineral oil production from mining activities.
- The Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act, 1948, is amended to focus on mineral oils, distinct from the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Expanded Definition of Mineral Oils:
- Includes hydrocarbons in various forms (natural gas, crude oil, petroleum, coal bed methane, and shale gas/oil).
- Excludes coal, lignite, and helium from the definition (falling under the Mines and Minerals Act).
- Petroleum Lease:
- Replaces the term "mining lease" with "petroleum lease."
- Covers activities such as exploration, development, production, and transportation of mineral oils.
- Private Investment:
- Provisions to attract private investment by clarifying rules for petroleum leases.
- Current mining leases remain valid without altering terms to the lessee's disadvantage.
- Decriminalization and Penalties:
- Replaces criminal punishment with financial penalties.
- Fines can go up to Rs. 25 Lakh, with additional penalties for ongoing violations.
- Rule-making Power of Central Government:
- Expands the Centre's authority over petroleum lease regulations, conservation, royalties, mergers, facility sharing, environmental protection, and dispute resolution.
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- Significance of the Bill:
- Energy Access and Security: Ensures energy security by boosting domestic production.
- Attracting Investment: Creates a conducive environment for private sector investment.
- Environmental Safeguards: Provisions to control carbon emissions and promote renewable energy in oilfields.
- Opposition Criticism:
- State Rights on Mining: Concerns raised by opposition parties, particularly the DMK, about the reduction of state control over resource taxation (taxing mineral rights).
- Impact on Federal Balance: States traditionally manage mining rights under the Constitution’s State List (Entry 50). The Bill may shift control to the Union List (Entry 53), creating constitutional concerns.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Opposition figures like P.P. Suneer (CPI) argue for prioritizing public companies like ONGC, fearing privatization may worsen environmental governance.
- Adjudication of Disputes:
- Appeals against penalty decisions will be handled by the Appellate Tribunal, as per the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Broader Significance:
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on fuel imports, fostering energy security and economic stability.
- Regulation: Strengthens the enforcement mechanism for petroleum operations while encouraging private participation.
Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB):
- Formation: Established under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Functions: Regulates refining, transportation, distribution, storage, marketing, and sale of petroleum products and natural gas.
- Role in the Bill: Ensures competitive markets for gas and handles appeals regarding regulatory decisions.
Markhor Spotted in North Kashmir's Baramulla

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, a Markhor, a rare wild goat with spiral-shaped horns, was spotted in Noorkha village of Boniyar in Baramulla district, North Kashmir.The animal was seen near a waterfall in Noorkha, prompting locals to alert the authorities.
Key Highlights:
- The Markhor (Capra falconeri) is a large, wild goat species native to mountainous regions in Central and South Asia, including countries such as Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, and others.
- The species is considered endangered and is listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- The Markhor population in India is concentrated in areas like Shopian, Banihal Pass, Shamsbari, and Kazinag in Jammu and Kashmir.An estimated 300 Markhors live in Kashmir's dense pine and birch forests.
- Threats and Conservation Status:
- The Markhor faces threats due to human activities and natural factors, leading to a decline in its population.
- It is classified as 'Near Threatened' on the IUCN Red List and protected under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act and the Jammu and Kashmir Wildlife Protection Act.
- Significance of the Sighting:The sighting of the Markhor has excited both villagers and wildlife enthusiasts, as these animals are not typically found outside their natural habitats, particularly near human settlements.
Community and Individual Forest Rights in Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR)

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Coimbatore District Collector, granted community and individual forest rights under the Forest Rights Act, 2006, to tribal settlements in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) on December 6, 2024.These rights were handed over to three tribal settlements and 14 families at a function in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
- Community Forest Rights:
- Three tribal settlements in ATR—Nagaroothu I, Nagaroothu II, and Chinnarpathi—were granted community rights.
- These rights allow the settlements to collect forest produce excluding timber, such as mango, amla, honey, tamarind, and grass for making brooms.
- Individual Forest Rights:
- Individual rights were granted to 14 families from the Old Sarkarpathy tribal settlement.
- The families had requested these rights for traditional cultivation practices passed down by their ancestors.
- The individual rights were approved after the recommendation of a sub-divisional committee and scrutiny by a district-level committee.
- About the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- Purpose: The FRA was enacted to address historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities and ensure their livelihood and food security.
- Key Provisions:
- Individual Rights: Self-cultivation, habitation, and in-situ rehabilitation.
- Community Rights: Access to grazing, fishing, water bodies in forests, and protection of traditional knowledge and customary rights.
- Eligibility: Rights can be claimed by any community or individual who has lived in the forest for at least three generations (75 years) before December 13, 2005.
- Critical Wildlife Habitats: The Act mandates that critical wildlife habitats in national parks and sanctuaries remain inviolate for wildlife conservation.
- Authorities Involved in Vesting Forest Rights:
- Gram Sabha: Initiates the process for determining the nature and extent of rights.
- Sub-Divisional Level Committee: Examines resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha.
- District Level Committee: Grants final approval for forest rights.
- Challenges with Forest Rights Implementation:
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- Arbitrary rejection of claims.
- Lack of deadlines for claims processing.
- Unaddressed rights of communities displaced by development projects.
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, at an altitude of 1,400 meters.
- Established as a tiger reserve in 2007, it is surrounded by multiple protected areas like the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Eravikulam National Park.
- Biodiversity in Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Habitats: The reserve contains wet evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, and unique habitats like montane grasslands and marshy grasslands.
- Flora: The reserve is home to around 2,500 species of angiosperms, including species like balsam, orchids, and wild relatives of cultivated crops such as mango, jackfruit, cardamom, and pepper.
- Fauna: It supports various wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, sambars, spotted deer, leopards, jackals, and jungle cats.
Sacred Groves

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Preserving India’s sacred groves can help country achieve its conservation & climate goals.
Sacred Groves in India:
- Sacred groves are forest patches that are culturally and spiritually important for various communities.
- They are known by different names across India: sarnas in Jharkhand, devgudis in Chhattisgarh, and orans in Rajasthan.
- Groves vary in size from small clusters of trees to expansive forests covering several acres.
Threats to Sacred Groves:
- Sacred groves are increasingly under threat due to deforestation, mining, and development activities.
- Many sacred groves are being displaced or degraded, putting biodiversity and cultural practices at risk.
Ecological and Cultural Importance:
- Sacred groves are rich in biodiversity and serve as important carbon sinks, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- They have been maintained by indigenous communities for centuries, creating a deep connection between people and nature.
- Sacred groves also play a crucial role in preserving indigenous spiritual practices and cultural heritage.
Contribution to Climate and Conservation Goals:
- India’s climate commitment of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 requires the protection of forests, including sacred groves.
- Sacred groves, when properly managed, can help in carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation.
- Preserving these groves can support forest conservation and foster coexistence with wildlife, ensuring a balance between development and environmental preservation.
Role of Indigenous Communities:
- Indigenous communities have long used sacred groves to regulate the use of forest resources and ensure environmental sustainability.
- Before modern ecological concepts, sacred groves were seen as natural conservation practices guided by spiritual beliefs.
- This traditional wisdom can be leveraged to enhance conservation efforts in India.
Examples of Successful Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Waghoba Grove in Maharashtra:
- Located in Chinchwadi village, the Taata chi Vanrai grove is dedicated to Waghoba, the tiger deity, and covers eight acres.
- Local communities, including the Thakars, have successfully resisted illegal timber extraction and helped conserve the grove, witnessing the return of wildlife like leopards.
- Worship of Waghoba has played a significant role in preserving forest patches and fostering human-animal coexistence.
- Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Sacred groves around the Tadoba Reserve, dedicated to Waghoba, are important in reducing human-wildlife conflicts by promoting spiritual ties with the forest.
Government and Community Efforts:
- The Jharkhand government introduced the concept of gherabandi (boundary walls) in 2019 to conserve sacred groves.
- In Chhattisgarh, the renovation of sacred groves has been undertaken to protect and restore these areas.
- Despite these efforts, challenges remain in involving local communities and integrating sacred groves into broader conservation policies.
The Role of OECMs in Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Sacred groves are considered part of Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures (OECMs), which are areas conserved for biodiversity outside protected regions.
- OECMs recognize the cultural, spiritual, and socio-economic value of these areas and promote sustainable conservation practices that benefit both biodiversity and local communities.
- Sacred groves play an essential role in achieving long-term biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services.
World’s Oldest Wild Bird Lays Egg at 74 in Hawaii

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Wisdom, the world’s oldest known wild bird, a Laysan albatross, has laid her estimated 60th egg at the age of 74. This remarkable event occurred at the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge in the Pacific Ocean, part of the Hawaiian Archipelago.
Background on Wisdom and Laysan Albatrosses
Wisdom, first banded as an adult in 1956, has been a part of the albatross population in the Pacific for decades. Laysan albatrosses are known for their strong migratory habits and lifelong pair bonding.
The Life Cycle of the Laysan Albatross
The egg incubation process for Laysan albatrosses is shared between both parents and lasts around seven months. Once the chick hatches, it takes five to six months to develop before it is ready to take its first flight over the ocean. These seabirds, which predominantly feed on squid and fish eggs, spend the majority of their lives soaring across the open seas.
Wisdom’s longevity and success in raising up to 30 chicks over her lifetime have been notable achievements. While Laysan albatrosses typically live up to 68 years, Wisdom’s age surpasses this average by several years.
About the Laysan Albatross
The Laysan albatross (Phoebastriaimmutabilis) is a large seabird found across the North Pacific. The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands host nearly the entire population of Laysan albatrosses, with most breeding pairs found on islands like Laysan and Midway Atoll. These birds are known for their long-distance soaring capabilities, with some covering hundreds of miles a day without flapping their wings.
Laysan albatrosses have blackish-brown upper wings and backs, with flashes of white in their primary feathers. They are monogamous, forming lifelong bonds with a single mate. Despite their impressive flying ability and vast range, their population is currently listed as "Near Threatened" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
‘Anna Chakra’ and SCAN Portal

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and New & Renewable Energy, launched ‘Anna Chakra’, the Public Distribution System (PDS) Supply chain optimisation tool and SCAN (Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA) portal a significant step towards modernizing the Public Distribution System and subsidy claim mechanisms of the States.
Anna Chakra: PDS Supply Chain Optimization Tool
- Purpose: A tool developed to enhance the efficiency of PDS logistics across India, optimizing food grain transportation.
- Collaboration: Developed by the Department of Food and Public Distribution, in collaboration with the World Food Programme (WFP) and IIT-Delhi’s Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT).
- Functionality: Uses advanced algorithms to identify optimal transportation routes for food grains.
- Key Features:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Achieves annual savings of Rs 250 crores by reducing fuel consumption, time, and logistics costs.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces transportation-related emissions by cutting transportation distance by 15-50%, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
- Wide Coverage: Impacts 30 states, 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops (FPS), and 6,700 warehouses in the PDS supply chain.
- Technology Integration: Linked with the Freight Operations Information System (FOIS) of Railways and PM Gati Shakti platform, enabling geo-location mapping of FPS and warehouses.
SCAN Portal: Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA
- Objective: To streamline the subsidy claim process under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) 2013, ensuring better utilization of funds.
- Functionality: Provides a unified platform for states to submit food subsidy claims, reducing administrative complexity and delays.
- Key Features:
- Single Window Submission: Simplifies subsidy claim submission for states, enhancing coordination.
- Automated Workflow: End-to-end automation ensures efficiency, transparency, and faster settlements.
- Rule-Based Processing: Claims are scrutinized and approved through a rule-based system, speeding up the approval process.
Public Distribution System (PDS) Overview
- Purpose: Ensures food security by providing subsidized food grains to vulnerable populations under the NFSA, benefitting nearly 80 crore people.
- Management: A joint effort between the Central and State/UT Governments. The Food Corporation of India (FCI) handles procurement and transportation, while state governments manage local distribution.
- Commodities: Primarily wheat, rice, sugar, and kerosene, with some states also distributing pulses and edible oils.
Initiatives to Reform PDS in India
- One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC):
- Goal: To allow portability of ration cards, benefiting migrant workers and seasonal laborers.
- Features: Biometric authentication, digital payments, and enhanced inclusivity.
- SMART-PDS Scheme (2023-2026):
- Objective: To upgrade technology in PDS, including computerized FPS, point-of-sale (POS) machines, and GPS tracking for transparency and fraud reduction.
- Aadhaar and Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- Purpose: Ensures proper beneficiary identification and cash transfers, allowing beneficiaries to purchase grains from the open market.
- Technology and Transparency Enhancements:
- GPS and SMS Monitoring: Ensures the proper delivery of food grains to FPS and provides citizens with updates via SMS.
RBI Cuts CRR, Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently made significant monetary policy decisions that could have a broad impact on the economy.
Key Highlights:
Cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- CRR Reduction: The RBI has reduced the CRR by 50 basis points (bps), from 4.5% to 4%.
- Impact on Banks: This move will free up ?1.16 lakh crore in liquidity, which banks can use to lend, boosting the credit flow in the economy.
- Objective: The CRR cut is aimed at easing the liquidity stress in the financial system, which has been tightening due to RBI's foreign exchange interventions.
- Bank Benefits: Banks will benefit as they don’t earn interest on the CRR, and the extra liquidity may help them reduce deposit rates. Additionally, it may encourage banks to pass on benefits to borrowers, particularly in terms of lending rates.
Repo Rate Kept Unchanged at 6.5%
- Decision: The MPC decided to keep the key policy rate, the Repo rate, unchanged at 6.5%, continuing its stance for the 11th consecutive meeting.
- Reasons for Keeping Repo Rate Steady:
- Persistent inflation, particularly food prices, is a key concern. Despite strong growth in sectors like rural consumption, inflation remains high and continues to affect disposable income.
- RBI Governor emphasized that durable price stability is essential for strong, sustained economic growth.
Impact on Borrowers
- Borrowing Costs: With the Repo rate unchanged, external benchmark lending rates (EBLR) linked to the Repo rate will not rise, providing relief to borrowers by keeping Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) stable.
- Deposit Rates: However, the CRR cut may lead to a marginal reduction in deposit rates due to increased liquidity in the system.
Economic Growth Forecast Adjusted
- Reduced GDP Growth Estimate: The RBI has downgraded the GDP growth forecast for FY25 to 6.6%, down from the earlier estimate of 7.2%. This revision comes after the economy showed signs of slowdown in the second quarter of FY25.
- Growth Outlook: Despite the downgrade, the RBI remains cautiously optimistic about recovery driven by festive demand and rural consumption. Governor Das indicated that the slowdown had likely bottomed out and the economy is set to recover in the coming quarters.
Inflation Forecast Raised
- Inflation Outlook: The inflation estimate for FY25 has been revised upward to 4.8%, compared to the earlier forecast of 4.5%. This is largely due to rising food prices, which surged to a 14-month high of 6.21% in October.
- Inflationary Pressures: The MPC noted that inflation has remained above the RBI’s target of 4%, primarily driven by food inflation. As inflation impacts consumption, the RBI aims to balance growth support with inflation management.
Monetary Policy Stance
- Neutral Stance Retained: The RBI has maintained a ‘neutral’ stance, meaning it is neither tightening nor easing monetary policy drastically, focusing instead on bringing inflation closer to its target of 4%.
- Inflation Control: While the RBI is aware of the economic slowdown, it continues to prioritize inflation control to ensure price stability and support sustainable growth.
Global and Domestic Economic Context
- Global Factors: The RBI has also been cautious about global developments, including capital outflows and the impact of U.S. monetary policy on the Indian economy. A rate cut could have further weakened the rupee by narrowing the interest rate differential with the U.S.
- Domestic Concerns: Domestically, the economy faces challenges such as weak manufacturing growth and high inflation. The GDP growth in Q2 FY25 dropped to 5.4%, a seven-quarter low, highlighting concerns over demand and inflationary pressures.
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, the world’s largest domestic rooftop solar initiative, is transforming India’s energy landscape with a bold vision to supply solar power to one crore households by March 2027.
Key Details:
Targeted Installations:
- 10 lakh installations by March 2025.
- 1 crore installations by March 2027.
Subsidy and Financing:
- Offers up to 40% subsidy for rooftop solar installations based on household electricity consumption.
- Collateral-free loans available for up to 3 kW solar systems at a 7% interest rate.
Key Benefits:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana offers several significant benefits to participating households:
- Free Electricity for Households: The scheme provides households with free electricity through the installation of subsidized rooftop solar panels, significantly reducing their energy costs.
- Reduced Electricity Costs for the Government: By promoting the widespread use of solar power, the scheme is expected to save the government an estimated ?75,000 crore annually in electricity costs.
- Increased Use of Renewable Energy: The scheme encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix in India.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: The transition to solar energy under this scheme will help lower carbon emissions, supporting India's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Eligibility Criteria:
1. The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
2. Must own a house with a roof that is suitable for installing solar panels.
3. The household must have a valid electricity connection.
4. The household must not have availed of any other subsidy for solar panels.
Impact
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana is expected to have far-reaching outcomes, both for individual households and the nation as a whole:
- Household Savings and Income Generation: Households will benefit from significant savings on their electricity bills. Additionally, they will have the opportunity to earn extra income by selling surplus power generated by their rooftop solar systems to DISCOMs. For instance, a 3-kW system can generate over 300 units per month on average, providing a reliable source of energy and potential revenue.
- Expansion of Solar Capacity: The scheme is projected to add 30 GW of solar capacity through rooftop installations in the residential sector, significantly contributing to India's renewable energy goals.
- Environmental Benefits: Over the 25-year lifetime of these rooftop systems, it is estimated that the scheme will generate 1000 BUs of electricity while reducing CO2 emissions by 720 million tonnes, making a substantial positive impact on the environment.
- Job Creation: The scheme is also expected to create approximately 17 lakh direct jobs across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, supply chain, sales, installation, operations and maintenance (O&M), and other services, thereby boosting employment and economic growth in the country.
Model Solar Village
- Under the "Model Solar Village" component of the scheme, the focus is on establishing one Model Solar Village per district throughout India.
- This initiative aims to promote solar energy adoption and empower village communities to achieve energy self-reliance.
- An allocation of ?800 crore has been designated for this component, with ?1 crore provided to each selected Model Solar Village.
- To qualify as a candidate village, it must be a revenue village with a population of over 5,000 (or 2,000 in special category states). Villages are selected through a competitive process, evaluated on their overall distributed renewable energy (RE) capacity six months after being identified by the District Level Committee (DLC).
- The village in each district with the highest RE capacity will receive a central financial assistance grant of ?1 crore.
- The State/UT Renewable Energy Development Agency, under the supervision of the DLC, will oversee the implementation, ensuring these model villages successfully transition to solar energy and set a benchmark for others across the country.
RangeenMachli App
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The app was developed by the ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA) with support from the Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India.
Key Highlights:
- Target Audience: The app caters to hobbyists, farmers, and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Multilingual Support: The app offers content in eight Indian languages, making it accessible to a broad and diverse audience.
- Main Objectives:
- Provide information on popular ornamental fish species and their care.
- Promote local aquarium businesses through dynamic directories.
- Enhance knowledge of ornamental aquaculture techniques for fish farmers and shop owners.
- Serve as an educational tool for newcomers and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Salient Features:
- Multilingual Content: Ensures broader reach and user accessibility.
- Comprehensive Fish Information: Offers detailed guidance on fish care, breeding, and maintenance.
- Find Aquarium Shops Tool: A directory updated by shop owners, helping users find reliable local aquarium shops and promoting local businesses.
- Educational Modules:
- Basics of Aquarium Care: Covers key aspects like aquarium types, filtration, lighting, feeding, and maintenance.
- Ornamental Aquaculture: Focuses on breeding and rearing ornamental fish, particularly for farmers.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Promoting Local Businesses: The app encourages economic growth by increasing visibility for local aquarium shops and creating opportunities for business owners.
- Authenticity and Reliability: Users can access verified information, reducing the reliance on unverified sources and promoting healthier aquariums.
- Sustainability and Growth: The app’s features are designed to foster sustainability and growth in the ornamental fish trade by providing reliable information and empowering users.
Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Objective: Aimed at transforming the fisheries sector, improving fish production, productivity, quality, technology, infrastructure, and management, while strengthening the value chain and promoting the welfare of fishers.
- Launch: The scheme was launched in 2020 with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores for a 5-year period (2020-21 to 2024-25).
- Focus Areas:
- Inland fisheries and aquaculture.
- Fisheries management and regulatory framework.
- Infrastructure and post-harvest management.
- Doubling fishers' and fish farmers' incomes.
- Components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS): Fully funded by the central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS): Partially funded by the central government and implemented by states.
- Sub-Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri MatsyaKisanSamridhiSah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY): Launched under PMMSY to formalize the fisheries sector and support micro and small enterprises with over Rs. 6,000 crore investment (FY 2023-24 to 2026-27).
- Beneficiaries: Includes fishers, farmers, fish vendors, fisheries cooperatives, SC/STs, women, differently-abled persons, state and central entities, and private firms.
Fisheries Sector Contribution:
- Supports around 30 million people.
- India is the 3rd largest fish producer globally, with a fish production of 175.45 lakh tons in FY 2022-23.
- Contributes 1.09% to the Gross Value Added (GVA) of India and 6.72% to agricultural GVA.
Related Schemes:
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Launched with a fund of Rs. 7,522.48 crore.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Extended to fishers and farmers from FY 2018-19.
- Sustainable fisheries development.
- Doubling income and job creation in the sector.
- Boosting exports and agricultural GVA.
- Social and economic security for fishers.
Trade Watch Quarterly
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
NITI Aayog released its first quarterly report, Trade Watch Quarterly (TWQ), on December 4, 2024, focusing on India's trade developments during Q1 FY2024 (April-June).
Overview:
- Purpose: The publication aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of India’s trade performance, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Target: To leverage insights for evidence-based policy interventions and foster informed decision-making, contributing to sustainable growth in India’s trade.
Trade Performance Highlights (Q1 FY24):
- Total Trade: $576 billion (5.45% YoY growth).
- Merchandise Exports: Growth was restrained due to declines in iron & steel, and pearls.
- Imports: Driven by high-value goods, including aircraft, spacecraft, mineral fuels, and vegetable oils.
- Services Exports: Displayed a surplus, particularly in IT services.
- Growth in Services Exports: A positive trend, rising by 10.09% YoY, particularly in IT services and business solutions.
Key Challenges for India’s Trade:
- Limited Success in China-Plus-One Strategy:Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia have gained more from this strategy, benefitting from cheaper labor, simplified tax laws, and lower tariffs.
- CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism):Starting in 2026, CBAM will impose carbon taxes on imports like cement, steel, and fertilizers. India’s iron and steel industry could face significant risks due to this.
- Declining Share in Labor-Intensive Sectors:India’s global market share in labor-intensive sectors (e.g., textiles, leather) has declined despite a strong workforce.
- Geopolitical Instability (West Asia):
- Oil price hikes could increase India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) and fuel inflation.
- Declining agricultural exports to markets like Iran further add to the challenges.
Strategic Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges:
- Infrastructure Modernization:
- Expansion of digital platforms like Trade Connect e-Platform to streamline processes and support exporters.
- Strengthening logistics via the National Logistics Policy.
- Export Incentives:Continuation of schemes like RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) to maintain export competitiveness.
- Technological Integration:Leveraging digital trade to tap into high-growth sectors and foster innovation in trade.
- Strengthening FTAs (Free Trade Agreements):Focus on negotiating strategic FTAs with global partners (e.g., the UK and the EU) to reduce trade barriers and enhance global market access.
Geopolitical and Environmental Risks:
- U.S.-China Trade Tensions:Offers opportunities for India to diversify its supply chains, but also poses challenges in terms of overdependence on certain countries.
- Impact of CBAM:Risk to carbon-intensive Indian exports like steel and aluminium, which will face tariffs starting in 2026.
Sectoral Performance:
- Growing Sectors:
- IT Services: India’s market share of IT services reached 10.2%, continuing to be a strong contributor.
- Pharmaceuticals, Electrical Machinery, and Mineral Fuels: Significant contributors to export growth.
- Declining Sectors:Labor-Intensive Goods: Declines in global market share for textiles, pearls, and leather.
Pathway to $2 Trillion Exports by 2030:
- India's Export Aspirations:To achieve the target of $2 trillion in exports by 2030, India must address structural inefficiencies, diversify exports, and reduce trade barriers.
- Vision 2047:Aligning with India’s broader vision to become a developed nation, the report stresses the importance of strengthening trade, technology, and infrastructure to realize these ambitions.
- Trade's Role in Economic Growth:
- Trade is vital to India’s economic trajectory, contributing significantly to GDP growth.
- Through evidence-based policymaking, infrastructure modernization, and strategic global partnerships, India can achieve sustained growth in trade, leading to the realization of a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
Heat Shock Protein 70
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
JNU scientists make big discovery that could change malaria, Covid-19 treatment.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Institution: Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), Special Centre for Molecular Medicine.
- Key Discovery: Identification of human protein Hsp70 as a critical factor in the spread of malaria and COVID-19.
- Research Collaboration: Involvement of Indian and Russian researchers.
- Outcome: Development of a small molecule inhibitor of Hsp70 that could act as a broad-spectrum treatment for multiple infections.
About Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70):
- Definition: Hsp70 is a type of molecular chaperone protein.
- Function:
- Helps other proteins fold into their proper shapes.
- Prevents protein misfolding.
- Regulates protein synthesis and protects proteins from stress.
- Elevates during cellular stress to shield cells from damage.
- Role in Cellular Processes:
- Prevents protein aggregation and assists in protein transport across membranes.
- Plays a critical role in protein homeostasis and cell survival during stress conditions.
Hsp70's Role in Disease Spread:
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Interaction:
- Hsp70 interacts with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and human ACE2 receptors.
- Facilitates viral entry into human cells by stabilizing this interaction during fever (when Hsp70 levels rise).
- Malaria:Pathogens like malaria parasites rely on the host's machinery for survival, including Hsp70.
Research Findings and Implications:
- Published in: International Journal for Biological Macromolecules.
- Inhibition of Hsp70:
- Targeting Hsp70 can disrupt viral replication.
- In lab tests, Hsp70 inhibitor (PES-Cl) blocked SARS-CoV-2 replication at low doses.
- Potential for Broad-Spectrum Treatment:
- Hsp70 could be a target for treating multiple infections, not limited to COVID-19 or malaria.
- Prevention of Drug Resistance:
- Host-targeting antivirals are less prone to resistance as the virus cannot mutate the host protein (Hsp70).
- This approach could be especially beneficial for combating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (e.g., Omicron).
Host-Targeting Approach vs. Traditional Drugs:
- Host-Targeting: Targets the host cell machinery (e.g., Hsp70) rather than the virus itself.
- Reduces the likelihood of viral mutation-induced resistance.
- Traditional Drugs: Target the virus directly, which can lead to resistance, especially with rapidly mutating viruses.
Global Health and Pandemic Preparedness:
- Universal Tool for Infectious Diseases: The discovery could serve as a universal tool for managing infections during health emergencies.
- Collaboration and Importance: Highlights the significance of international collaboration in addressing global health challenges (e.g., Dr. Pramod Garg of AIIMS, Ph.D. scholar Prerna Joshi).
- Future Implications:Preparation for future pandemics, as the world must remain vigilant even post-COVID-19.
International Debt Report 2024
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently released, World Bank’s "International Debt Report 2024" highlights a worsening debt crisis for developing nations, with 2023 marking the highest debt servicing levels in two decades, driven by rising interest rates and economic challenges.
Key Highlights:
Rising Debt Levels:
- Total external debt of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) reached $8.8 trillion by the end of 2023, an 8% increase since 2020.
- For IDA-eligible countries (those receiving concessional loans from the World Bank), external debt rose by 18%, reaching $1.1 trillion.
Debt Servicing Costs:
- Developing nations paid a record $1.4 trillion in debt servicing costs (principal and interest) in 2023.
- Interest payments surged by 33%, totaling $406 billion, putting immense pressure on national budgets, especially in critical sectors like health, education, and environmental sustainability.
Interest Rate Increases:
- Interest rates on loans from official creditors doubled to 4% in 2023.
- Rates from private creditors rose to 6%, the highest in 15 years, exacerbating the financial burden on developing countries.
Impact on IDA-Eligible Countries:
- IDA countries faced severe financial strain, paying $96.2 billion in debt servicing, including $34.6 billion in record-high interest costs (four times higher than a decade ago).
- On average, 6% of their export earnings were allocated to debt payments, with some countries dedicating up to 38%.
Role of Creditors:
- Private creditors reduced lending, leading to more debt-servicing payments than new loans.
- In contrast, multilateral lenders like the World Bank provided additional support, with the World Bank contributing $28.1 billion.
- Multilateral institutions have emerged as crucial support systems, becoming "lenders of last resort" for poor economies.
Debt Data Transparency:
- Efforts to improve debt transparency led to nearly 70% of IDA-eligible economies publishing accessible public-debt data in 2023, a 20-point increase since 2020.
- Accurate debt data can reduce corruption and promote sustainable investment.
Global Financial Reforms:
- There is a growing call for global financial reforms to address the systemic challenges of developing nations facing rising debt burdens.
- Proposed measures include increased concessional financing, improved restructuring mechanisms, and the establishment of a Global Debt Authority for better debt management.
Impact on Climate and Development Goals:
- Debt servicing has become a larger financial burden than climate initiatives in many countries, with developing nations spending more on debt servicing than climate goals (2.4% of GDP vs. 2.1% for climate investments).
- To meet climate commitments under the Paris Agreement, climate investments would need to rise to 6.9% of GDP by 2030.
Debt Relief Initiatives:
- Programs like the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative and the Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI) provide debt relief to the world’s poorest nations, helping them meet Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- For instance, Somalia saved $4.5 billion in debt service after completing the HIPC program in December 2023.
Global Sovereign Debt Roundtable (GSDR):
- The GSDR brings together debtor nations and creditors (both official and private) to improve debt sustainability and address restructuring challenges.
- Co-chaired by the IMF, World Bank, and G20, the forum aims to find coordinated solutions for sovereign debt issues.
Overview of Global Plastic Treaty Negotiations

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent negotiations for a global treaty aimed at curbing plastic pollution, held in Busan, South Korea, concluded without reaching a legally binding agreement. This marked the fifth round of discussions since the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) initiated the process in March 2022, with the goal of finalizing a treaty by the end of 2024. The failure to adopt a treaty was primarily due to disagreements over production cap goals and the elimination of specific plastic chemicals and products.
Key Points of Dispute
- Production Cap Goals: A coalition of over 100 countries, including many from Africa, Latin America, and the European Union, pushed for clear production cap goals in the treaty. They argued that such measures are essential for effective regulation of plastic pollution.
- Opposition from Oil-Producing Nations: Conversely, a group of “like-minded countries” such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Russia, and Iran opposed these provisions. They contended that regulating production cuts exceeded the original mandate set by UNEA and could lead to trade restrictions disguised as environmental measures. India and China aligned with this coalition, emphasizing their concerns regarding economic impacts.
Draft Treaty Highlights
Despite the failure to finalize an agreement, discussions produced a draft text that included both consensus points and contentious issues:
- Consensus Points:
- Proposals for banning open dumping and burning of plastics.
- Definitions for various plastic types were suggested but lacked clarity on contentious terms like microplastics.
- Contentious Issues:
-
- The draft did not adequately address definitions for microplastics or recycling standards.
- References to single-use plastics were included but faced pushback from certain nations.
India’s Position
India articulated its stance focusing on several key areas:
- Development Rights: Emphasized the need for recognizing varying responsibilities among countries in managing plastic pollution while considering their developmental rights.
- Technical and Financial Support: Advocated for provisions ensuring technical assistance and financial support for developing nations to manage plastic waste effectively.
- Opposition to Production Caps: India opposed any articles that would impose caps on polymer production, arguing that such measures were not directly linked to reducing plastic pollution.
Future Steps
The negotiations will continue with plans to reconvene in 2025. In the meantime, global plastic production is projected to rise significantly, potentially tripling by 2050 if no urgent action is taken. The ongoing dialogue will need to address both environmental concerns and developmental needs to create a balanced approach toward managing plastic pollution globally.
Global Context and Initiatives
The need for a global treaty is underscored by alarming statistics:
- Over 462 million tons of plastic are produced annually, with a significant portion contributing to pollution.
- Microplastics have infiltrated ecosystems worldwide, affecting biodiversity and human health.
Countries like Rwanda and Austria have implemented successful measures to reduce plastic waste, serving as models for global efforts. Initiatives such as the UNDP Plastic Waste Management Program in India aim to enhance waste management practices while addressing environmental impacts.
SheSTEM 2024

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), under the NITI Aayog and the Office of Science & Innovation, at the Embassy of Sweden, in partnership with Nordic collaborators - Innovation Norway, Innovation Centre Denmark, and Business Finland, announced the successful conclusion of SheSTEM 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To inspire youth, especially women, to explore careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and promote innovative solutions for sustainability.
- Theme: Focus on Battery Technology and Energy Storage Systems (BEST), part of the India-Nordic BEST project, aimed at fostering sustainability through advanced energy solutions.
Key Features of the Challenge:
- Target Audience: Students from grades 6–12 across India.
- Participation: Over 1,000 submissions showcasing innovative energy storage solutions.
- Format: Students presented prototypes or concepts via a 2-minute video format.
- Focus Areas: Sustainability, energy storage, and innovative solutions to global challenges.
Significance of SheSTEM 2024:
- Youth Empowerment: Provides a platform for young innovators to showcase their ideas and contribute to global sustainability.
- Global Impact: Encourages collaboration between India and Nordic countries in academia, business, and government to explore energy storage and sustainable technologies.
- Women in STEM: Highlights the importance of gender inclusivity in STEM fields, particularly in sustainability and technology.
Key Facts about AIM (Atal Innovation Mission):
- Established: 2016 by NITI Aayog to foster innovation and entrepreneurship across India.
- Core Functions:
- Promote Entrepreneurship: Financial support, mentorship, and nurturing innovative startups.
- Promote Innovation: Creating platforms for idea generation and collaboration.
- Key Programs: Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centres, Atal New India Challenges, and Mentor India.
- Monitoring: Systematic monitoring of initiatives using real-time MIS systems and dashboards.
ICJ Hearing on Landmark Climate Change Case

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has begun hearings on a landmark climate change case, seeking an advisory opinion on the obligations of countries under international law regarding climate change.
- The case stems from a UN General Assembly (UNGA) resolution initiated by Vanuatu in March 2023, co-sponsored by 132 countries.
Background:
- Vanuatu, a small island nation, faces existential threats from rising sea levels.
- The resolution was passed to clarify climate obligations in light of international laws, including the UNFCCC, Paris Agreement, and other legal instruments like the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas, and the Universal Declaration on Human Rights.
Global Impact of the Case:
- The outcome of the case could influence global climate governance, particularly in the context of climate negotiations.
- It may broaden the legal basis for climate obligations and underscore the legal consequences for non-compliance.
India’s Position:
- India has voiced concerns about the judicial process being the best approach to tackle climate issues, advocating for diplomatic efforts.
- India is scheduled to make its submission on December 5, highlighting its preference for a collaborative, non-top-down approach in climate discussions.
Implications for Developed and Developing Countries:
- The case highlights the historical responsibility of developed countries for climate change due to their higher emissions.
- The ICJ's advisory opinion could reinforce the argument that developed countries' obligations extend beyond the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, incorporating broader international legal frameworks.
Climate Litigation and Precedent:
- The ICJ ruling could set a precedent for climate litigation, potentially influencing over 2,600 ongoing climate lawsuits globally.
- Notable rulings include the European Court of Human Rights, which held Switzerland accountable for failing to meet emissions targets, and India's Supreme Court recognizing the right to be free from adverse climate impacts in 2023.
Record Participation and Importance of the Case:
- The ICJ has received over 90 written submissions, with 97 countries and 12 international organizations participating in the hearings.
- The case is significant for the growing number of climate-related lawsuits and the evolving nature of international climate law.
Future Prospects:
- The ICJ’s advisory opinion, though non-binding, could significantly impact future climate negotiations, particularly in terms of responsibility sharing and climate finance.
- The outcome could also influence calls for compensation for climate damages, especially from vulnerable states like small island nations.
1984 Bhopal disaster

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Forty years after the Bhopal disaster on December 2-3, 1984, several hundred tonnes of toxic waste still remain around the ill-fated Union Carbide plant.
Overview of the incident:
The 1984 Bhopal disaster, one of the world’s worst industrial accidents, was caused by the release of methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas, which was a key component in the production of pesticides at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) plant. However, the toxic legacy of the disaster extends far beyond MIC, with a range of other harmful substances lingering in the environment. These include:
- Methyl Isocyanate (MIC):Primary toxic agent: MIC is a highly toxic, volatile compound. Exposure can cause severe respiratory distress, eye irritation, pulmonary edema, and even death.
- Heavy Metals:The site of the plant is contaminated with various heavy metals, including:
- Mercury: Known to accumulate in the body and affect the nervous system, kidneys, and liver. Even small doses over time can lead to chronic health problems.
- Chromium: Exposure to high levels of chromium, particularly hexavalent chromium, is associated with lung cancer and damage to the respiratory system.
- Lead: A potent neurotoxin, lead can cause developmental delays, memory problems, and damage to the kidneys.
- Nickel: Can cause respiratory and lung cancers when inhaled in significant quantities.
- Copper: High levels of copper exposure can damage the liver and kidneys.
- Organic Compounds:Several organic chemicals were found at the site, including:
- Hexachlorobutadiene: A suspected carcinogen that can cause liver damage, kidney damage, and neurological issues upon exposure.
- Chloroform (Trichloromethane): Known for its effects on the central nervous system, exposure can lead to dizziness, loss of consciousness, and even death at high concentrations. It is also a possible carcinogen.
- Carbon Tetrachloride: A potent liver toxin, exposure can result in liver damage, cancer, and nervous system toxicity.
- Trichlorobenzene: These compounds are volatile and can spread through air and water, accumulating in fatty tissues and causing damage to organs like the liver and kidneys.
- Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs):Some of the contaminants, particularly the organic compounds, are classified as persistent organic pollutants, which do not degrade easily in the environment. These can lead to:
- Cancer: Several of these compounds are carcinogenic.
- Neurological damage: Prolonged exposure can affect both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Reproductive and developmental disorders: Exposure has been linked to adverse effects on fertility and developmental health in humans.
- Environmental and Long-term Health Effects:
- Even decades later, contamination continues to affect the health of people living around the site, with high rates of cancers, birth defects, respiratory diseases, and other health issues. Water sources in the region remain unsafe due to heavy contamination with toxic chemicals. Persistent organic pollutants have been identified in local communities, indicating that the contamination continues to spread.
26 Rafale-Marine Jets

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- Deal for 26 Rafale-M jets nearing completion, with final formalities expected to be completed by January 2025.
- These jets are designed for naval operations and will be deployed on INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- Rafale-M Features: Multi-role, advanced avionics, AESA radar, and armaments like Meteor, MICA, SCALP, EXOCET.
- Three Scorpene Submarines: Additional three Scorpene-class submarines to be procured from France.
- These are part of a repeat order to Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), with five of the earlier six already inducted into service.
Nuclear Capabilities:
- INS Arighaat: Successfully fired a Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), marking a significant milestone for India's nuclear deterrence.
- Indigenous Nuclear Attack Submarine (SSN): India’s first indigenous SSN expected by 2036-37.
Strategic Maritime Engagement:
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR): Active monitoring of maritime activities, especially of China's PLA Navy and Chinese research vessels.
- Pakistan Navy Expansion: Acknowledged Pakistan’s efforts to become a 50-ship Navy, including the acquisition of 8 Chinese submarines. Indian Navy is adapting its plans to address this.
Nuclear Submarine Program (SSBN):
- INS Arihant: Conducted multiple deterrence patrols.
- INS Arighaat: Ongoing trials including the recent K4 SLBM test, with a range of 3,500 km.
Naval Vision 2047:
- Navy Chief released Vision 2047 document, outlining the future direction and growth of the Indian Navy.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements:
- Participation in various bilateral and multilateral exercises, including RIMPAC 2024 (Hawaii) and Russian Federation Navy’s Raising Day (St. Petersburg).
Madhya Pradesh’s 8th Tiger Reserve: Ratapani

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh was officially declared a Tiger Reserve, making it the 8th such reserve in the state. This declaration follows approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Key Details:
- Core Area: 763.8 sq. km
- Buffer Area: 507.6 sq. km
- Total Area: 1,271.4 sq. km
- Ratapani Tiger Reserve is located in the Raisen and Sehore districts, within the Vindhya hills, and is home to approximately 90 tigers.
- It also forms a crucial part of Madhya Pradesh’s tiger habitat and serves as a migration corridor from the Satpura ranges.
Economic and Ecotourism Benefits:
- The designation will boost ecotourism, generating employment and improving livelihoods for local communities.
- Eco-development programs will support residents, providing new opportunities and addressing the balance between conservation and human interests.
Wildlife Conservation and Management:
- The reserve will focus on habitat management, wildlife protection, and community engagement.
- The core area has been recognized as a critical tiger habitat under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Efforts will include strengthening anti-poaching measures, improving surveillance, and enhancing prey base restoration.
Significance for Madhya Pradesh:
- This move places Madhya Pradesh as the "Tiger State of India", with significant conservation focus on the Ratapani and Madhav National Park (also in the process of becoming a tiger reserve).
- Madhya Pradesh now hosts 8 tiger reserves, contributing significantly to the country's overall tiger conservation efforts.
Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)was held in New Delhi, India, hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This annual event brings together meteorologists, earth scientists, and satellite data users to discuss advancements in satellite technology for weather and climate monitoring.
Key Facts:
- Objective:
- Promote Satellite Observations: Highlight the importance of satellite data for meteorology and climatology.
- Advance Remote Sensing Science: Foster advancements in satellite technology and its application in weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
- Encourage Collaboration: Facilitate dialogue between satellite operators and users to enhance the use of satellite data across the Asia-Oceania region.
- Discuss Future Plans: Update on the current status and future plans of international space programs.
- Engage Young Scientists: Encourage the involvement of young researchers in satellite science and meteorology.
- Participants:
- Around 150 participants from various countries, including key international space organizations like WMO, NASA, ESA, JAXA, and other meteorological and space entities.
- The conference will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on satellite data application.
- Significance of the Conference:
- Regional Cooperation: AOMSUC promotes stronger cooperation between countries in the Asia-Oceania region, addressing shared challenges in meteorology and satellite data usage.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances satellite data utilization for more accurate weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and climate monitoring.
- Disaster Risk Management: Strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events, improving disaster preparedness and response.
- Capacity Building: Offers training and workshops for local meteorologists, boosting the capacity of countries to use satellite data effectively for weather forecasting and climate services.
- Data Sharing: Encourages collaboration in satellite data sharing, facilitating better access to meteorological data across national borders.
- History of AOMSUC:The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China in 2010. Since then, the conference has been held annually in various Asia-Oceania locations and has become a leading event for the meteorological community.
KisanPehchaan Patra
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government is actively promoting the creation of digital identities for farmers through the KisanPehchaan Patra (Farmer ID). The initiative is an essential part of the Digital Agriculture Mission under the AgriStack initiative.
Key Details:
Objective:
- The main goal is to provide digital IDs linked to Aadhaar for farmers, capturing comprehensive agricultural data including land records, crop information, and ownership details.
- These digital identities are designed to enhance farmers' access to government schemes and digital agriculture services.
Farmer ID Creation Timeline:
- The government plans to create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers in phases:
- 6 crore farmers in FY 2024-25.
- 3 crore farmers in FY 2025-26.
- 2 crore farmers in FY 2026-27.
AgriStack Initiative:
- The AgriStack initiative aims to build a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for the agriculture sector, which includes:
- Farmers' Registry.
- Geo-referenced village maps.
- Crop Sown Registry.
Implementation Strategy:
- Camp-mode approach: States have been instructed to organize field-level camps to ensure faster and inclusive registration of farmers.
- Financial Incentives:
- States will receive ?15,000 per camp for organizing these camps.
- Additionally, ?10 per Farmer ID issued.
- Funding is provided through the Pradhan Mantri KisanSamman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme.
Benefits of Digital Farmer ID:
- Targeted Delivery of Benefits: Ensures subsidies and benefits reach legitimate farmers and eliminates duplication.
- Precision Agriculture: Supports data-driven policies for better crop planning, insurance, and market linkages.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates easy access to credit, loans, and crop insurance, empowering farmers financially.
- Better Monitoring: Helps in tracking the actual implementation of schemes and ensures that only eligible farmers benefit.
Progress in States:
- Advanced States: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh have made significant progress in issuing digital Farmer IDs.
- Testing Phase: States like Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha are still in the field-testing phase.
- Special Assistance Scheme: The Finance Ministry allocated ?5,000 crore in August 2024 to assist states in creating the Farmers' Registry, with funds available until March 2025.
Linkage with Land Records and Crop Data:
- The Farmer ID integrates with state land records and crop data, creating a dynamic and accurate database known as the Farmer’s Registry.
- This data helps in the development of better agricultural policies and decision-making.
Digital Agriculture Mission:
- The government approved a substantial outlay of ?2,817 crore for the Digital Agriculture Mission, which is intended to modernize agricultural practices and build robust digital infrastructure.
- The mission also includes the launch of the Digital Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), which will help in crop estimation and better resource allocation.
National Policy on Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India is working on a national policy to enhance female labour force participation (FLFP), focusing on creating a supportive care economy structure.
- The policy is being developed by an inter-ministerial team involving the Ministries of Skill Development, Labour, Rural Development, and Women and Child Development.
- Goal: To reduce barriers for women, especially related to caregiving responsibilities, and increase their participation in the workforce.
Key Focus Areas:
- Care Economy: Involves both paid and unpaid caregiving services, such as childcare, eldercare, domestic work, and health services.
- The policy aims to formalize care work, addressing its undervaluation and encouraging women's workforce participation.
- Proposes a core skilling package for caregivers, particularly for childcare in rural and informal sectors.
- Childcare Facilities: Targeting women working under schemes like MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme).
Current Challenges:
- Post-marriage employment drop: Women face a significant decline in workforce participation after marriage, often due to caregiving roles.
- In India, 53% of women are outside the labour force, mostly due to unpaid domestic work, unlike only 1.1% of men.
- The gender divide in caregiving is stark: Women spend over 5 hours daily on unpaid domestic work (81% of females), compared to 12.4% of males.
Key Initiatives:
- Palna Scheme: Provides daycare through Anganwadi-cum-Crèche facilities for working parents, benefiting children aged 6 months to 6 years. 1,000 crèches are operational.
- Women’s Employment Data:
- In rural India, 36.6% of women participate in the workforce, compared to 23.8% in urban areas.
- Post-marriage, female employment drops by 12 percentage points, even without children.
- Improving Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP): Key to India's growth, as matching women’s workforce participation with men could boost GDP by 27% (IMF).
Barriers to Women’s Workforce Inclusion:
- Unpaid Care Work: Women's disproportionate share of household duties limits paid employment opportunities.
- Cultural Norms: Gender expectations restrict women’s access to employment, especially in rural areas.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to education for girls restricts skill development, lowering job prospects.
- Health & Safety Issues: Health challenges and safety concerns at workplaces hinder women's workforce participation.
- Lack of Supportive Policies: Absence of parental leave and flexible work arrangements for women, especially in the informal sector.
Government Initiatives for Women’s Employment:
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao: Promotes girl child education and empowerment.
- National Education Policy (NEP): Ensures gender equity in education.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks and mandates crèche facilities in large establishments.
- Labour Codes (2019-2020): Codifies labor laws to provide a framework for improving women’s workplace safety and employment opportunities.
Global Examples & Inspiration:
- Japan’s Womenomics: Aimed at increasing female participation, Japan's womenomics reforms have grown women’s labour force participation from 64.9% to 75.2% (2013-2023).
- Flexible Work Models: Countries like Netherlands encourage part-time and remote work, offering flexibility to manage work-life balance.
- Sweden’s Investment in ECCE: Investing 1% of GDP in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) has significantly reduced women’s workforce exclusion.
Way Forward:
- National Women’s Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA): Promotes gender-balanced work environments and childcare facilities at work sites.
- Flexible Work Options: Encouraging remote work, parental leave, and childcare support will empower more women to balance caregiving and employment.
- Investment in the Care Economy: To reduce the care burden on women, substantial investment in ECCE and related sectors is essential to increase women’s participation and economic independence.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
SASCI Scheme for Tourism Development
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Centre clears scheme for development of 40 tourist destinations across 23 States at a cost of ?3,295 crore.
Key Details:
- Focus Areas: The scheme encourages the development of lesser-known destinations such as Bateshwar (Uttar Pradesh), Ponda (Goa), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh), and Porbandar (Gujarat) to reduce overcrowding at popular sites.
- Implementation Timeline: Projects must be completed within two years, with funding released in stages until March 2026.
- Key Features:
- Long-term interest-free loans for 50 years.
- States responsible for project execution and maintenance, often through public-private partnerships (PPP).
- The Ministry of Tourism will monitor progress, and 66% of the funds have already been released.
- Emphasis on sustainability and boosting local economies by creating jobs through tourism.
- States must provide land at no cost and ensure proper infrastructure like safety, connectivity, and utilities.
Selection Criteria for Projects:
- Consultation Process: Detailed regional consultations led to the selection of 40 projects from 87 proposals received by the Ministry of Tourism. West Bengal was the only state not submitting proposals.
- Evaluation Criteria: Projects were evaluated based on:
- Connectivity, tourism potential, and ecosystem.
- Financial viability and sustainability.
- Impact on local economy and job creation.
- Funding Pattern:
- A maximum of ?100 crore for each project, with higher funding considered for exceptional projects.
- Total funding capped at ?250 crore per state, allocated on a first-come, first-served basis.
Importance of the Scheme:
- Economic Growth & Employment: Projects are designed to stimulate local economies, create employment, and promote sustainable tourism.
- Global Branding: The scheme aims to brand and market tourist destinations on a global scale.
- Tourism Infrastructure Growth: It aims to improve the entire tourism value chain, including transportation, accommodation, activities, and services.
Tourism Sector Overview:
- Current Status:
- India ranks 39th among 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) increased by 47.9% in 2023, with 9.52 million tourists.
- Tourism contributed 5% to India’s GDP in 2022-23 and created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs.
- India earned ?2.3 lakh crore in foreign exchange in 2023 through tourism.
- Projected revenue from tourism to exceed $59 billion by 2028.
- Initiatives for Promotion:
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: To develop theme-based circuits.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2020): Promotes domestic tourism.
- PRASHAD & HRIDAY Schemes: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage city development.
MGNREGA Job Card Deletions Issue:
- Context: A significant surge in deletions of job cards under MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) raised concerns over transparency and workers’ rights.
- Reasons for Deletion:
- Permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and refusal to work.
- Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) implementation led to deletions for non-linked cards.
- Implications:
- Violation of workers’ legal right to employment, especially when deletions were made without due process.
- The "Not willing to work" designation undermines livelihood opportunities, especially in high unemployment rural areas.
- Recommendations for Reform:
- Strengthening verification processes and ensuring deletions follow due procedure.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas to review and approve deletions.
- Regular audits and better grievance redressal mechanisms.
Other Government Initiatives in Tourism:
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD): For holistic and sustainable development of pilgrimage tourism.
- Incredible India & E-Visa Initiatives: To attract more foreign tourists.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN): Enhances air connectivity to remote tourist destinations.
- National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): Preserves and rejuvenates heritage sites.
13th National Seed Congress (NSC)

- 30 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 13th National Seed Congress (NSC), organized by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare, concluded with significant discussions and outcomes focused on advancing India's seed sector.
- The theme for this year's congress, held in Varanasi, was "Innovating for a Sustainable Seed Ecosystem."
Key Highlights:
- Focus Areas:
- Seed Technologies and Biofortification: Emphasis on high-nutrition seeds like iron and zinc-enriched rice and Vitamin A-rich crops to combat malnutrition.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Promoting practices like Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) and the development of stress-tolerant seed varieties to withstand climate change.
- Challenges in India’s Seed Ecosystem:
- Seed Replacement Rate (SRR): SRR in India is around 15-20%, with 100% for hybrid seeds, pointing to the need for higher adoption of certified seeds.
- Monoculture and Seed Market Monopoly: Issues like over-reliance on Bt cotton and domination by multinational companies (e.g., Bayer) in seed markets.
- Government Initiatives:
- National Seed Corporation (NSC): Produces foundation and certified seeds for over 600 varieties.
- Seed Village Programme (Beej Gram Yojana): Focus on improving the quality of farm-saved seeds.
- National Seed Reserve: Ensures seed availability during climatic disruptions.
- Policy Discussions:
- Proposed Seeds Bill: A new bill to regulate seed quality and promote sustainable practices.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations to improve seed production, accessibility, and quality.
- Outcomes:
- Biofortified Seeds: Increased development and distribution of nutrient-rich seeds.
- Climate-Resilient Seed Systems: Enhanced focus on developing crops that can withstand climate challenges.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Strengthening collaborations in seed technology and policy reform.
Global Wage Report 2024-25

- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
A new report from the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000. Despite this positive trend, significant wage differentials persist worldwide.
Global Wage Inequality Trends:
- Wage inequality has decreased in about two-thirds of all countries since 2000.
- Average Annual Decrease in Wage Inequality:
- Ranges from 0.5 to 1.7% globally, depending on the measure used.
- More significant reductions have been observed in low-income countries, where the decrease has ranged from 3.2 to 9.6% over the past two decades.
- Wealthier Countries: Wage inequality has decreased at a slower pace:
- Upper-middle-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 1.3%.
- High-income countries: annual decrease of 0.3 to 0.7%.
Global Real Wage Growth:
- Global real wages grew by 1.8% in 2023, with projections reaching 2.7% growth in 2024 (highest increase in over 15 years).
- This marks a recovery from the negative global wage growth of -0.9% in 2022 due to high inflation rates.
Regional Wage Growth:
- Emerging Economies: Saw stronger wage growth than advanced economies.
- Emerging G20 economies: 1.8% growth in 2022 and 6.0% growth in 2023.
- Advanced Economies: Faced real wage declines.
- G20 advanced economies: Declined by -2.8% in 2022 and -0.5% in 2023.
- Fastest Wage Growth: Observed in regions like Asia-Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe.
Wage Inequality Persistence:
- Income Distribution: The lowest-paid 10% of workers earn just 0.5% of the global wage bill, while the highest-paid 10% earn nearly 38%.
- Wage Inequality in Low-Income Countries: Particularly high, with nearly 22% of wage workers classified as low-paid.
- Women and Informal Economy Workers: More likely to be among the lowest-paid workers, underscoring the need for targeted actions to close wage and employment gaps.
Non-Wage Workers:
- Globally, one in every three workers is a non-wage worker.
- In low- and middle-income countries, many workers are self-employed in the informal economy, which skews overall income inequality measures.
- Income inequality in these regions is higher when including self-employed workers, especially those in informal employment.
Policy Recommendations:
- Targeted Policies: To reduce wage inequality, countries need stronger wage policies and structural support for equitable growth.
- Focus Areas:
- Promote productivity and decent work.
- Formalization of the informal economy to help reduce income inequality.
- Inclusive Growth: The ILO emphasizes that national strategies should aim for inclusive economic growth to achieve fair wages and reduce wage gaps.
Key ILO recommendations include:
- Setting wages through social dialogue: wages should be set and adjusted through collective bargaining or agreed minimum wage systems involving governments, workers and employers.
- Taking an informed approach: wage-setting should take into account both the needs of workers and their families and economic factors.
- Promoting equality, and equal opportunity of treatment and outcomes: wage policies should support gender equality, equity and non-discrimination.
- Using strong data: decisions should be based on reliable data and statistics.
- Addressing root causes of low pay: national policies should reflect each country’s specific context and address the causes of low pay such as informality, low productivity and the under-valuing of jobs in sectors such as the care economy.
Mission Shukrayaan
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
ISRO received approval for its first Venus mission, Shukrayaan. The probe will undertake a detailed investigation of Venus, including its surface, atmosphere and geological structure.
Shukrayaan Mission (Venus Orbiter Mission):
- Launch Timeline: Scheduled for 2028.
- Objective: Investigate Venus to gather data on its surface, atmosphere, and geological structure.
- Scientific Focus: Study weather patterns, geological activities, and atmospheric composition (e.g., carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds).
- Instrumentation: Equipped with synthetic aperture radar, infrared, and ultraviolet imaging devices to study Venus’s ionosphere.
- Significance: Offers global coverage of Venus, addressing gaps in previous missions' spatial coverage.
- Cost: Estimated at Rs 1,236 crore.
- Launch Vehicle: ISRO plans to use the LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) rocket to launch the mission into an elliptical parking orbit (170 km x 36,000 km).
- Mission Data Processing: Data will be archived and disseminated through the Indian Space Science Data Center (ISSDC).
Chandrayaan 4 Mission:
- Collaborative Effort: Joint mission between India (ISRO) and Japan.
- Launch Objective: Land on the moon's south pole, with a focus on the region at 90°S (compared to previous missions at 69.3°S).
- Mission Details:
- Includes a rover weighing 350 kg (12 times heavier than previous rover).
- The rover will be equipped with advanced scientific tools for lunar exploration.
- Government Approval: Awaiting approval, with a target execution date of 2030.
Gaganyaan Mission (Human Spaceflight Program):
- Timeline: Unmanned flight in 2026, followed by a manned mission.
- Indian Space Station: Construction approved; to be completed by 2035, comprising five modules.
- Purpose: To serve as a transit facility for deep space exploration, including future lunar missions.
Mars Exploration Plans:
- Future Missions: Plans to send satellites to Mars and attempt a landing on the Martian surface.
- Significance: Demonstrates India’s growing ambitions in interplanetary exploration.
INSAT-4 Series of Satellites:
- Goal: Launch of new meteorological and oceanographic sensors to improve weather forecasts and disaster management.
- Technological Advancements: Need for India to catch up with global advancements in space-based sensors.
International Collaboration in Space:
- Chandrayaan 4: A collaboration between ISRO and Japan to explore the moon’s south pole, showcasing India's growing international cooperation in space exploration.
Strategic Importance of Shukrayaan:
- Contribution to Science: The mission’s global dataset will provide unique insights into Venus, enhancing the understanding of planetary atmospheres and geological processes.
- Potential for Discoveries: Research on Venus’s ionosphere and possible volcanic activity.
Eklavya Digital Platform
- 29 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Indian Army launched the “Eklavya” online learning platformnmunder the leadership of General Upendra Dwivedi, Chief of the Army Staff (COAS).
- It is part of the Army’s “Decade of Transformation” initiative and aligns with the theme for 2024, “Year of Technology Absorption.”
Platform Development:
- Developed by the Army Training Command (ATC) and sponsored by the Army War College.
- Created at zero cost in collaboration with the Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N), Gandhinagar.
- Hosted on the Army Data Network with scalable architecture to integrate various training establishments.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple courses from 17Category ‘A’ Training Establishments of the Army.
- Allows student officers to register for several courses simultaneously.
- Aims to decongest physical courses and integrate contemporary, application-focused content.
Categories of Courses:
- Pre-Course Preparatory Capsules: Online study material for physical courses, allowing focus on contemporary topics during offline training.
- Appointment-Specific Courses: Online courses for officers appointed to specialized roles (e.g., information warfare, financial planning, etc.), helping them gain domain-specific expertise before posting.
- Professional Development Suite: Includes courses on strategy, leadership, operational art, finance, emerging technologies, etc., focusing on holistic officer development.
Knowledge Highway:
- A searchable database featuring journals, research papers, and articles to support continuous professional education and development.
Impact:
- Promotes continuous professional military education.
- Enhances the efficiency and specialization of officers, particularly in emerging domains.
- Streamlines training processes and integrates modern technology in the Army’s educational system.
India's Gig Economy
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The gig economy market is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17 per cent to reach a gross volume of $455 billion by 2024, according to a white paper by the Forum for Progressive Gig Workers.
Key Sectors Supported by Gig Workers:
- E-commerce: Gig workers play a crucial role in driving growth in the e-commerce sector.
- Transportation and Delivery Services: These sectors are heavily dependent on gig workers for their operations and services.
Impact on Employment:
- Job Creation: The gig economy has the potential to create a significant number of jobs, especially in tier 2 and 3 cities, which are emerging as new growth hubs.
- Alternate Revenue Streams: Gig work provides diverse income opportunities for workers, especially for women, offering them a flexible mode of earning.
Contribution to GDP:
- The gig economy’s contribution is expected to add 1.25% to India’s GDP over time, highlighting its growing economic importance.
Technological Integration and Future Prospects:
- AI and Digital Innovation: Future growth is expected to be driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), predictive analytics, and digital innovation, fostering sustainable and inclusive job opportunities.
Social and Economic Benefits:
- Women's Workforce Participation: The gig economy provides women with more earning opportunities and helps integrate them into the workforce.
- Welfare Initiatives: Platforms supporting gig workers are increasingly focusing on welfare initiatives, improving the overall working conditions in the sector.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Challenges: The evolving dynamics between large companies and gig workers pose challenges in terms of worker rights and fair compensation.
- Opportunities: The growth of the gig economy presents opportunities for companies to innovate and create inclusive work environments, especially for underserved communities.
Future Developments:
- Formal Report: The Forum for Progressive Gig Workers plans to collaborate with global organizations to release a formal report with deeper insights and actionable recommendations for the future of gig work
Global Matchmaking Platform (GMP)
- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
- GMP was launched at COP29, on Energy Day, by the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and the Climate Club.
- Aimed at accelerating industrial decarbonisation in heavy-emitting industries of emerging and developing economies (EMDEs).
- The platform addresses the annual funding gap of US$125 billion required to achieve net-zero emissions goals.
Key Highlights:
Support Mechanism:
- GMP operates as a support mechanism for the Climate Club, with the secretariat hosted by UNIDO.
- Activities are supported by the interim secretariat of the OECD and the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Key Objectives:
- Match country-specific decarbonisation needs with global technical and financial resources.
- Facilitate the decarbonisation of energy and emissions-intensive industrial sectors, such as steel, cement, chemicals, and aluminium.
- Offer assistance in policy development, technology transfer, and investment facilitation to promote low-carbon industrial practices.
Global Participation:
- Countries like Germany, Chile, Uruguay, Turkey, Bangladesh, and Indonesia are actively involved.
- Non-state actors include UNIDO, World Bank, Climate Investment Funds (CIF), and GIZ, supporting the platform’s initiatives.
Funding Gap:
- Industrial decarbonisation requires an increase in investments from US$15 billion (current) to US$70 billion by 2030, and US$125 billion by 2050, especially for sectors like steel and cement.
Climate Club Work Programme (2025-26):
- The GMP is part of the Climate Club's new work programme for 2025-26, focusing on:
- Advancing ambitious climate change mitigation policies.
- Transforming industries through decarbonisation.
- Boosting international climate cooperation.
Industrial Decarbonisation:
- Decarbonisation refers to reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from industrial activities.
- Key sectors for decarbonisation include petroleum refining, chemical manufacturing, iron and steel, cement production, and the food and beverage sector.
Support for EMDEs:
- The platform focuses on helping emerging and developing economies overcome challenges such as lack of resources, technology, and capacity to adopt cleaner industrial methods.
- Climate finance is crucial to pilot and scale low-carbon technologies in these regions.
Future Role of GMP:
- The GMP will play a critical role in incorporating industrial decarbonisation into countries’ Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) for COP30.
- The platform aims to accelerate progress by connecting developing countries with finance, technology, and expertise to transition to low-emission industries.
BioE3 Policy

- 28 Nov 2024
In News:
The BioE3 Policy outlines guidelines and principles for enabling mechanisms for ‘Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing’ in the country across diverse sectors.
Key Highlights:
Primary Objective:
- Set a framework for the adoption of advanced technologies and innovative research to promote biomanufacturing in India.
- Focus on enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and quality in biomanufacturing.
Alignment with National Goals:
- Supports India’s vision of Green Growth (Union Budget 2023-24) and Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), promoting sustainability.
- Aligns with India’s goal of achieving a Net-Zero carbon economy.
- Supports the Biomanufacturing and Biofoundry initiative announced in the Interim Budget 2024-25.
Key Objectives:
- Revolutionize biomanufacturing for better product quality and environmental sustainability.
- Accelerate the development and commercialization of bio-based, high-value products.
- Foster high-performance biomanufacturing across diverse sectors.
Achievements of Indian Bioeconomy (2014-2023):
- Contribution to GDP: Bioeconomy contributes 4.25% to India’s GDP of $3.55 trillion (as of Dec 2023).
- Growth of Bioeconomy: From $10 billion in 2014 to $151 billion in 2023, surpassing 2025 target.
- Increase in Biotech Startups: From 50 startups in 2014 to 8,531 startups in 2023.
Implementation Strategy:
- Establish BioEnablers including Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs, Biofoundries, and Biomanufacturing Hubs across India.
- Bio-AI Intelligence Hubs will support research and innovation using data-driven approaches and AI to develop technologies for bio-based products.
- Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs will provide infrastructure to scale up bio-based technology for commercial applications.
Focus on Human Resource Development:
- Bio-Enablers will offer training and internships to build a skilled workforce with interdisciplinary and technical skills required for biomanufacturing.
Sectoral Focus Areas:
- Based on consultations, six thematic sectors of national importance have been identified for implementation:
- Bio-based chemicals and enzymes
- Functional foods and smart proteins
- Precision biotherapeutics
- Climate-resilient agriculture
- Carbon capture and utilization
- Futuristic marine and space research
- Sectoral Expert Committees are addressing challenges and gaps identified for each of these sectors.
Government Support:
- The DBT-BIRAC (Department of Biotechnology and Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council) has called for proposals to establish Biofoundries and Biomanufacturing Hubs in academia and industry.
- These hubs will support innovation and commercialization of biomanufacturing technologies.
National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF)
- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the launching of the National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF) as a standalone Centrally Sponsored Scheme under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare.
Key Highlights
Objective & Focus:
- Launch of NMNF by the Union Cabinet to promote chemical-free farming in India.
- Aim to improve soil health, reduce input costs, and produce nutritious food.
- Support the shift to natural farming (NF), emphasizing local knowledge and agro-ecological principles.
Financial Allocation:
- Total Outlay: ?2481 crore (Government of India share ?1584 crore, State share ?897 crore) until FY 2025-26.
Key Features of NMNF:
- Coverage: Targeting 15,000 clusters in Gram Panchayats, covering 7.5 lakh hectares and impacting 1 crore farmers.
- Bio-Input Resource Centres (BRCs): 10,000 BRCs to supply ready-to-use natural farming inputs.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) and Agricultural Universities (AUs): Establishment of 2,000 model demonstration farms for hands-on training in natural farming techniques.
- Farmer Training: 18.75 lakh farmers to be trained in NF practices such as preparation of organic inputs like Jeevamrit and Beejamrit.
- Krishi Sakhis/CRPs: Deployment of 30,000 workers for farmer mobilization and awareness.
Implementation Strategy:
- Farmer Certification System: Providing easy, simple certification for marketing natural farming produce with dedicated branding.
- Monitoring: Real-time, geo-tagged monitoring of implementation through an online portal.
- Convergence with other government schemes and organizations for market linkages and support.
Natural Farming Practices:
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): Promote sustainable farming by using local livestock and diverse crop systems.
- Benefits: Reduce dependence on external inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, rejuvenate soil quality, and increase resilience to climate risks (e.g., drought, floods).
- Encourage biodiversity, and improve soil carbon content and water-use efficiency.
Targeted Areas and Farmer Support:
- Focus on areas where NF practices are already being followed or where farmer producer organizations (FPOs) or self-help groups (SHGs) are active.
- Training through model demonstration farms will focus on practical, location-specific NF techniques tailored to regional agro-ecologies.
Impact on Agriculture and Environment:
- Environmental Impact: Encourages sustainable farming by reducing chemical exposure, improving soil health, and promoting climate resilience.
- Farmer Well-being: By reducing input costs and promoting nutritious food, it aims to improve farmer incomes and family health.
- Contributing to the long-term health of the environment, ensuring a healthy Mother Earth for future generations.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Soil Nutrient Compromise: Concerns that some crops, like rice, might require chemical fertilizers (e.g., NPK) for optimal growth, which may not be sufficiently replaced by organic manure alone.
- The shift to natural farming requires significant awareness and training to ensure sustainable and productive yields.
Institutional Framework:
- Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare is the implementing body.
- Collaboration with KVKs, AUs, and farmer organizations ensures grassroots level support and knowledge dissemination.
Riyadh Design Law Treaty (DLT)

- 27 Nov 2024
In News:
- India reaffirms its commitment to inclusive growth and strengthening its intellectual property (IP) ecosystem.The signing of the treaty comes after nearly two decades of negotiations.
Key Highlights:
Purpose of the DLT:
- Aims to harmonize industrial design protection frameworks across multiple jurisdictions.
- Improves efficiency and accessibility of design registration processes.
Key Features of the DLT:
- Grace Period: A 12-month grace period after the first disclosure of the design, ensuring its validity for registration.
- Flexibility for Applicants: Provides relief measures such as relaxed deadlines, reinstatement of lost rights, and flexibility in adding priority claims.
- Simplified Processes: Includes simplified procedures for design renewals, assignment, and license recording.
- E-Filing Systems: Promotes the adoption of electronic filing systems and exchange of priority documents.
Benefits of DLT:
- Empowering SMEs and Startups: Helps small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups protect designs globally, enhancing competitiveness and market growth.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Standardizes procedures, making the design protection process less complex, more predictable, and affordable.
- Support for Developing Countries: Offers technical assistance for implementation in developing and least-developed countries.
Significance for India:
- India’s rich heritage of design and craftsmanship underscores the importance of design protection for sustainable economic growth.
- Design registrations in India have surged, with a 120% increase in domestic filings over the last two years.
Supporting Programs:
- The treaty’s provisions align with India’s initiatives like Startup India and the Startups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) Scheme to boost the protection and commercialization of designs for Indian innovators.
Broader Impact:
- DLT aims to integrate design protection with traditional knowledge and cultural expressions, further enhancing protection for India’s diverse creative sectors.
About WIPO:
- The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, is a specialized UN agency established in 1967, promoting IP rights globally.
- India is a member of WIPO, which has 193 member countries.
Overview of Intellectual Property (IP):
- IP includes creations like inventions, industrial designs, literary and artistic works, symbols, and more, which are used in commerce.
- IP rights protect creators, allowing them to benefit from their work when commercially exploited.
Proba-3 mission

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will launch the European Space Agency’s Proba-3 mission on its PSLV rocket to study the solar corona, the outermost and hottest part of the Sun’s atmosphere, from Sriharikota on December 4.
Key Highlights:
- Mission Objective:The mission will study the Sun’s outermost and hottest atmosphere, the solar corona. The mission will also demonstrate the first-ever precision formation flying with two satellites working in tandem.
- Satellite Formation:Proba-3 consists of two satellites that will fly together, maintaining a fixed formation to study the Sun's corona.
What is Proba-3?
- Proba-3 is a solar mission developed by ESA, with an estimated cost of 200 million euros. The mission involves launching two satellites that will separate after launch, but fly in precise formation. The satellites will create a solar coronagraph, which blocks the Sun’s bright light to observe the solar corona, the Sun’s outermost atmosphere.
- Orbit: Proba-3 will orbit in a highly elliptical path (600 x 60,530 km) with an orbital period of 19.7 hours.
- Mission Duration: The expected mission life is two years.
What will Proba-3 Study?
The Sun's corona is extremely hot (up to 2 million degrees Fahrenheit), making it difficult to observe with conventional instruments. However, studying the corona is essential because it generates space weather phenomena such as solar storms and solar winds, which can impact satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids on Earth.
Proba-3 will use three main instruments for its mission:
- ASPIICS (Association of Spacecraft for Polarimetric and Imaging Investigation of the Corona of the Sun):This coronagraph will observe the Sun’s outer and inner corona, similar to how the corona is visible during a solar eclipse. It features a 1.4-meter occulting disk to block the Sun’s light and facilitate close-up observations.
- DARA (Digital Absolute Radiometer):This instrument will measure the Sun’s total energy output (total solar irradiance).
- 3DEES (3D Energetic Electron Spectrometer):It will study electron fluxes as they pass through Earth's radiation belts, providing valuable data on space weather.
Why is Proba-3 Unique?
- Proba-3 is designed to mimic a natural solar eclipse, allowing continuous study of the Sun’s corona. Typically, solar scientists observe the corona for only about 10 minutes during an eclipse, occurring around 1.5 times a year. Proba-3 will provide up to six hours of data per day, equivalent to 50 eclipse events annually.
- The two satellites will maintain a precise formation, with one acting as an occulting spacecraft to cast a shadow, while the other (the coronagraph) stays in the shadow and observes the Sun’s corona. They will be positioned 150 meters apart, maintaining their formation autonomously.
- This artificial eclipse will enable scientists to study the corona and its less-understood features more effectively.
National Gopal Ratna Award 2024
- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) declared the winners of the National Gopal Ratna Awards(NGRA); one of the highest National Awards in the field of livestock and dairy sector for the year 2024.
About the National Gopal Ratna Awards (NGRA):
- Purpose:Recognize and encourage individuals, AI technicians, dairy cooperatives, and farmer organizations in the livestock and dairy sector.
- Categories:
- Best Dairy Farmer (Indigenous Cattle/Buffalo Breeds)
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician (AIT)
- Best Dairy Cooperative/Milk Producer Company (MPC)/Dairy Farmer Producer Organization
- Addition (2024):Special awards for North Eastern Region (NER) to promote dairy development in the area, with winners in all three categories.
- and Prizes:
- Rs. 5 lakhs for 1st rank, Rs. 3 lakhs for 2nd rank, Rs. 2 lakhs for 3rd rank, and Rs. 2 lakhs for Special NER Award in the categories of Best Dairy Farmer and Best Dairy Cooperative/FPO/MPCs.
- For Best AIT, winners will receive a Certificate of Merit and a memento.
- Process:Winners selected from 2,574 applications via an online portal (https://awards.gov.in).
- The livestock sector is crucial for India's economy, contributing significantly to agriculture and providing livelihood, especially for small and marginal farmers, women, and landless laborers.
- Indigenous breeds have immense genetic potential, but their population and performance have been declining. To address this, the Rashtriya Gokul Mission was launched under the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development in 2014 to conserve and develop indigenous bovine breeds.
National Milk Day
- It is celebrated annually on November 26 in India to honor the significant contributions of milk and the dairy industry to the country's development.
- The day commemorates the birth anniversary of Dr VergheseKurien, the "Father of the White Revolution" in India, who played a pivotal role in transforming India into the largest producer of milk globally.
- National Milk Day was first celebrated on November 26, 2014, after the Indian Dairy Association (IDA), along with various dairy institutions across the country.
Nayi Chetna 3.0 – PahalBadlaav Ki

- 26 Nov 2024
In News:
Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan launches the third edition of ‘Nayi Chetna – PahalBadlaav Ki’ a month-long national campaign against gender-based violence in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) under the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Led by: DAY-NRLM’s extensive Self-Help Group (SHG) network.
- Aim of the Campaign: Raise awareness and encourage grassroots-level action to combat gender-based violence.
- Campaign Slogan: “EkSaath, EkAwaaz, HinsaKeKhilaaf” (United Voice Against Violence).
- Approach:
- Adopts a "whole-of-government" approach with collaboration from 9 key ministries:
-
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Department of School Education and Literacy
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting
- Department of Justice
- Key Objectives:
- Raise awareness about all forms of gender-based violence.
- Mobilize communities to demand accountability and action.
- Facilitate access to timely intervention and support systems.
- Empower local institutions to take action against violence.
- Goals for Nayi Chetna 3.0:
- Generate widespread awareness about gender-based violence.
- Foster collective action at the grassroots level.
- Drive convergence among government ministries and community stakeholders.
- Create a sustainable and informed movement for gender equality and women’s empowerment.
Narasapur Crochet Lace Craft

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
The Narasapur crochet lace craft, which has been a significant part of the cultural and economic fabric of the Godavari region in Andhra Pradesh, has recently been granted the prestigious Geographical Indication (GI) tag. The GI tag, registered by the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) on March 1, 2024, acknowledges that this unique craft is geographically linked to the West Godavari and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Konaseema districts in the Godavari region.
Key Details:
- Historical Background:
- The origins of the Narasapur crochet lace craft date back to 1844, when Macrae and his wife from Scotland introduced the lace-making technique to local women while they were associated with a Christian missionary in Dummugudem (now in Telangana).
- Over time, the craft became a crucial part of the region’s heritage and survived significant historical events like the Indian famine of 1899 and the Great Depression of 1929.
- Craftsmanship:
- The crochet lace is produced using thin threads and delicate crochet needles of varying sizes, resulting in intricate designs.
- The products made include doilies, pillow covers, cushion covers, bedspreads, table runners, and tablecloths, among others. These items are often exported to international markets like the US, UK, and France.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- The craft is predominantly carried out by women artisans, with over 15,000 women involved in its production. The GI tag is expected to revitalize the industry, especially after its stagnation due to the COVID-19 pandemic and competition from machine-made lace from China.
- The craft is also an important part of the Alankriti Lace Manufacturing Mahila Mutual Aided Co-operative Societies’ Federation Limited, which supports local women artisans and has revived operations at the Alankriti Lace Park in Narasapur.
- GI Tag Benefits:
- The Geographical Indication tag serves to protect the authenticity of the lace products, boost demand, and ensure better market recognition.
- It provides legal protection to the traditional craft, preventing unauthorized use of the term "Narasapur lace" by others and promoting the region's cultural heritage and economic growth.
- Future Outlook:
- With the GI tag, there is hope for increased demand for Narasapur lace products both in domestic and global markets, thus offering a fresh avenue for artisans to revive and sustain the craft.
- Alankriti Federation and other stakeholders are optimistic that the GI tag will significantly revitalize the local economy and empower women in the region.
Palparescontrarius

- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Palparescontrarius is a species of antlion that was recently spotted for the first time in Tamil Nadu, on the Madras Christian College (MCC) campus. It is notable for being a large-sized adult antlion that resembles a dragonfly but has distinct characteristics that separate it from dragonflies, such as its clubbed antennae and fluttering flight.
Key Features of Palparescontrarius:
- Appearance:
- The adult Palparescontrarius is large and resembles a dragonfly in its general body structure.
- It has lacy wings, long clubbed antennae, and a slender, grayish body.
- Its wings are typically clear, although some species of antlions have spots on their wings.
- Flight and Behavior:
- Unlike dragonflies, Palparescontrarius has a distinct fluttering flight.
- It is a weak flier and can often be spotted at night near illuminated spots.
- Habitat and Lifestyle:
- Like other antlions, Palparescontrarius is found in dry, sandy regions and is mostly active at night.
- The larvae of this species are particularly known for their predatory behavior, as they trap ants and other small insects in cone-shaped pits they dig into the sand.
- Ecological Importance:
- Antlions, including Palparescontrarius, are harmless to humans and beneficial to the environment because they feed on ants and other insects, thus helping to control pest populations.
Breakthrough in Bacterial Computing
- 25 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists at the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics in Kolkatahave successfully engineered bacteria capable of solving mathematical problems, marking a major step forward in the field of synthetic biology and biocomputing. These engineered bacteria can function like artificial neural networks, performing tasks that were traditionally reserved for humans or conventional computers.
Key Highlights:
- Bacterial Computers:
- The research team introduced genetic circuits into bacteria, turning them into computational units capable of tasks like determining whether a number is prime or identifying vowels in an alphabet.
- These bacterial "computers" mimic artificial neural networks (ANNs), where each type of engineered bacterium (called a "bactoneuron") behaves like a node in a network, processing inputs to generate outputs.
- How it Works:
- The bacteria's genetic circuits are activated by chemical inducers, which represent binary 0s and 1s (the fundamental language of computing). The presence or absence of certain chemicals determines whether a bacterium expresses a specific fluorescent protein, representing the binary states.
- For example, when asked if a number between 0-9 is prime, the bacteria can express green fluorescent proteins (1) for "yes" or red fluorescent proteins (0) for "no", providing binary outputs that solve the problem.
- Complex Tasks:
- The team advanced to more complex tasks, such as asking the bacterial computers whether adding a number (like 2 + 3) results in a prime number or if a number's square can be expressed as the sum of factorials.
- In an even more complex test, the bacteria solved an optimization problem—calculating the maximum number of pieces a pie could be cut into with a given number of straight cuts. The bacteria’s fluorescent output represented binary numbers that were converted to decimal for the correct solution.
- Technical Details:
- The researchers used Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, engineered with transcriptional genetic circuits, which recognize specific DNA sequences and trigger the expression of proteins based on the presence of chemical inducers.
- The system is similar to how ANNs work in traditional computing, where nodes (bactoneurons) take inputs, apply weights, and produce outputs based on activation functions.
- Implications and Future Prospects:
- Synthetic Biology & Biomanufacturing: This breakthrough could revolutionize industries such as pharmaceuticals and biomanufacturing by enabling biocomputers that perform specific tasks in a biological environment, potentially reducing reliance on silicon-based computers.
- Medical Applications: The ability of engineered bacteria to process data could lead to biocomputers capable of diagnosing diseases (such as cancer) at an early stage and even administering localized treatments.
- Understanding Intelligence: Bagh and his team hope to explore the biochemical nature of intelligence, pondering how intelligence could emerge from simple, single-celled organisms.
- Groundbreaking Research:
- The research, published in Nature Chemical Biology, has drawn significant attention in the synthetic biology community. Centre for Synthetic Biology highlighting the potential of bacteria programmed to solve complex problems.
This innovative work paves the way for future developments in biocomputing, where living organisms, instead of silicon chips, could be used to perform sophisticated calculations, offering new ways to think about computing, intelligence, and even the future of technology in medicine.
Chagas Disease
- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
A recent study by Texas A&M University has uncovered a concerning new risk for dogs in Texas related to Chagas disease—the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi), which causes the disease, can survive in dead kissing bugs (Triatominae). This discovery was published in the Journal of Medical Entomology in October 2024 and has raised alarms about how dead insects, which might be found in insecticide-treated dog kennels, could still pose a transmission risk for dogs.
Key Findings:
- Chagas Disease is primarily spread by kissing bugs, which carry T. cruzi in their gut. Dogs can contract the parasite by ingesting the bug's feces, especially when they lick their bite wounds.
- The study shows that even dead kissing bugs, which are often discarded in kennels, can still carry viable T. cruzi. This is particularly worrying in areas where insecticides are used to control the insects but dead bugs remain accessible to dogs.
- Researchers collected live and dead triatomines from six Texas kennels between June and October 2022, using both genetic testing and culture methods to assess whether the bugs were carrying live T. cruzi.
- 28% of the collected bugs tested positive for T. cruzi.
- A dead kissing bug (Paratriatomalecticularia) was found to still harbor live T. cruzi cultures, demonstrating that the parasite can survive even after the insect has died.
Transmission and Risks:
- Kissing bugs typically feed on the blood of animals like dogs, rodents, and raccoons, defecating near the bite site. If the dog licks the contaminated area, they can ingest the parasite-laden feces and become infected.
- The new discovery suggests that dead kissing bugs may pose a secondary transmission route for T. cruzi. Dogs that ingest these dead bugs, either in insecticide-treated areas or natural environments, could still contract the parasite.
- Researchers noted that dead bugs with intact gut contents showed a higher rate of infection than desiccated ones, which suggests that the condition of the bug after death impacts how long the parasite survives.
Implications for Management:
- The findings challenge current insecticide-based control methods. While insecticides kill the bugs, dead insects could still serve as a source of infection, necessitating new approaches for managing Chagas disease transmission in dog kennels.
- The study underscores the importance of regularly removing dead insects in kennels and reconsidering control strategies beyond just using insecticides.
About Chagas Disease:
- Chagas disease is caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite, commonly found in the feces of kissing bugs. It can cause long-term heart and digestive issues if left untreated.
- The disease is common in parts of South America, Central America, and Mexico, but it has been increasingly reported in the southern United States.
- Treatment focuses on killing the parasite in the acute phase, but once it progresses to the chronic phase, treatment is aimed at managing symptoms.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research:
- The Texas A&M team plans to explore how long T. cruzi survives in dead triatomines and whether insecticides affect the parasite’s ability to persist. They are also looking into developing integrated pest management strategies for environments with high kissing bug activity.
- The study also forms part of a broader "One Health" approach, recognizing that both human and animal health are interconnected, and research on Chagas disease in animals can help inform public health strategies.
Imperial Eagle(Aquila heliaca)

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
- A rare Imperial Eagle (Aquila heliaca) was spotted in the PulluzhiKole wetlands. This marks a significant event as the species was last reported in Kannur in 2003.
Key Highlights:
- Habitat and Migration:
- The Imperial Eagle primarily breeds in southeastern Europe, west, and central Asia.
- During the winter months, it migrates to regions including northeastern Africa, West Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Conservation Status:The IUCN Red List lists the Imperial Eagle as a vulnerable species, indicating its potential risk of extinction, underscoring the need for its conservation efforts.
- Importance of Conservation:
- The Kole fields are a Ramsar-protected area, emphasizing their critical role in preserving migratory bird habitats.
- Ongoing conservation and observation efforts in these wetlands are essential for protecting the diverse bird species that use the area.
Features of the Imperial Eagle:
- Scientific Name: Aquila heliaca
- Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Length ranges from 68 to 90 cm, with a wingspan between 1.76 to 2.2 meters.
- Color: It has a pale golden crown and nape, with a grey base extending to the tail. Its wings feature prominent white "braces" on the scapulars.
- Sexual Dimorphism: Males are typically smaller than females.
- Habitat: Prefers old forests, mountainous regions, and riverside forests.
- Feeding: It has strong legs and curved talons for capturing and killing prey, and exceptional eyesight to spot prey from high altitudes.
- Conservation Efforts: Continued monitoring and protection of the Kole wetlands and other vital habitats are crucial for the survival of this vulnerable species and other at-risk birds.
Minke Whale

- 24 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have directly measured the hearing range of minke whales for the first time, finding that they can detect high-frequency sounds up to 90 kHz.
Key Highlights:
- Implication for Ocean Noise: The study suggests that baleen whales, including minke whales, may be more affected by anthropogenic ocean noise (e.g., naval sonar) than previously recognized, as their hearing range had been underestimated.
- Research Method: A novel catch-and-release technique was used to temporarily hold adolescent minke whales in Norway for auditory evoked potential (AEP) tests to measure their hearing sensitivity.
- Findings: Contrary to the belief that baleen whales are low-frequency specialists, minke whales can detect frequencies between 45 kHz to 90 kHz.
- Impact of Findings: The results could affect future regulations on ocean noise and its impact on marine mammals, as better hearing data is now available for baleen whales.
Minke Whale Overview:
- Family: Minke whales are members of the baleen or "great" whale family and are the smallest of the rorquals.
- Species: There are two recognized species:
- Common minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata), found in various ocean basins.
- Antarctic minke whale (B. bonaerensis), found in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Subspecies:
- Dwarf minke whale: An unnamed subspecies of the common minke whale, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- North Atlantic (B. a. acutorostrata) and North Pacific (B. a. scammoni) subspecies of common minke whales.
- Distribution: Minke whales are widely spread across tropical, temperate, and polar regions (65°S to 80°N), with common minke whales in all ocean basins and dwarf minke whales mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Feeding Areas: They feed in cooler waters at higher latitudes and can be found both inshore and offshore.
- Conservation Status (IUCN):
- Common minke whale: Least Concern.
- Antarctic minke whale: Data Deficient.
Cicada

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
North American cicadas have life cycles that last for prime numbers of years, putting pressure on the idea that humans created mathematics.
What are Cicadas?
- Classification: Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Physical Features: Hemipteran insects (also known as true bugs) have piercing-sucking mouthparts and two pairs of wings.
- Life Span: Cicadas spend the majority of their life underground, feeding on plant sap. Once they emerge from the soil, they have a short adult life span of about 2 to 4 weeks.
Habitat:
- Preferred Environment: Cicadas are typically found in natural forests with large trees and are considered canopy dwellers.
- Global Distribution: Cicadas are found on every continent except Antarctica. The highest genetic diversity of cicadas is found in India and Bangladesh, followed by China.
Cicada Emergence and Life Cycle:
- Life Cycle: Cicadas have a complex life cycle, involving long periods of underground development followed by brief adult emergence.
- Periodical Cicadas: There are species of cicadas that emerge in 13-year and 17-year cycles.
- Broods: Initially, 30 broods were categorized based on geography and emergence times, but currently, only about 15 broods remain active due to some broods becoming extinct.
- Unique Phenomenon: In April 2024, a rare event is expected where a trillion cicadas from two different broods will emerge simultaneously in the Midwest and Southeast regions of the United States.
Cicada's underground Development:
- Feeding on Sap: During their underground phase, cicadas feed on the sap of plants.
- Purpose of Long Development: Researchers believe the long development period helps cicadas evade above-ground predators by keeping them hidden in the soil.
Vulnerability after Emergence:
- Emergence Behavior: Once cicadas emerge, they construct a "cicada hut" to shed their nymphal skins, then climb onto nearby trees or vegetation.
- Predator Vulnerability: Adult cicadas are vulnerable to predators such as turtles and other forest creatures because they are clumsy and defenseless, making them easy prey for predators.
Significance of the 2024 Emergence:
- The coinciding emergence of cicadas from different broods (13-year and 17-year cycles) is a rare event that highlights the complexity and mathematical precision behind the cicada life cycle.
The science of plant communication

- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
More than any organism, plants understand the significance of communication the best.
Communication Through Chemical Warning (Volatile Organic Compounds - VOCs):
- Plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when threatened, such as during herbivore grazing.
- VOCs act as distress signals, alerting neighboring plants to potential dangers.
- Neighboring plants respond by producing defensive compounds or toxins to deter herbivores.
- VOCs can travel through air and soil, enabling distant plants to prepare for threats, thereby enhancing survival across larger areas.
Wood Wide Web (Symbiotic Relationship with Mycorrhizal Fungi):
- Plants form a network with mycorrhizal fungi, connecting their roots in a symbiotic bond.
- This "Wood Wide Web" allows plants to communicate by sending chemical signals through their roots when under stress (e.g., pest attacks or drought).
- Fungi extend the root system and help share nutrients between plants, especially in times of distress.
- The network facilitates collective resilience and survival by ensuring nutrient sharing among plants.
Cooperative Behavior: Sharing Resources for Survival:
- Plants in close proximity, especially in dense forests, often share resources like water, nutrients, and light.
- When a plant detects a neighboring plant in distress, it prioritizes resource allocation to support its growth.
- This cooperative behavior promotes ecosystem stability and the overall health of forests.
- The mutual support system shows how cooperation enhances the survival of individual plants and the broader ecosystem.
Significance of Plant Communication in Ecosystem Health:
- Plants communicate through chemical signals, underground fungal networks, and cooperative behaviors.
- These interactions foster resilience, ensuring the survival of both individual plants and entire ecosystems.
- The silent communication among plants contributes to a dynamic, cooperative environment that thrives on mutual support.
Global Soil Conference 2024
- 23 Nov 2024
In News:
- Global Soil Conference (GSC) 2024 held in New Delhi.
- Focused on soil health's importance for food security, climate change mitigation, and ecosystem services.
What is the Global Soil Conference 2024?
- Organizers: Indian Society of Soil Science (ISSS) in collaboration with the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS).
- Objective: Address sustainable soil/resource management challenges and foster global dialogue.
- Theme: "Caring Soils Beyond Food Security: Climate Change Mitigation & Ecosystem Services."
Key Highlights of GSC 2024:
- Soil Health Issues:
- Soil degradation threatens productivity and global food security.
- 30% of India's soil is compromised by erosion, salinity, pollution, and organic carbon loss.
- Soil erosion is linked to SDG 15 (Sustainable Development Goal 15), aiming to protect terrestrial ecosystems.
- SDG 15:
- Goals: Promote sustainable land use, combat desertification, halt land degradation, protect biodiversity.
Concerns Regarding Soil Health in India:
- Soil Degradation:One-third of India's land faces degradation due to poor farming practices.
- Soil Erosion & Fertility Loss:
- India loses 15.35 tonnes of soil/hectare annually.
- Results in crop losses, economic damage, and environmental issues like floods and droughts.
- Soil Salinity:Reduces water infiltration, nutrient uptake, and aeration, making land infertile.
- Low Organic Content:
- Organic carbon in Indian soil is 0.54%, which hampers fertility.
- Over 70% of soils are affected by acidity or alkalinity, disrupting nutrient cycles.
- Desertification:Reduces soil fertility, increases erosion, and worsens food insecurity.
- Diversion of Fertile Land:Fertile agricultural land is diverted for non-agricultural purposes.
India's Initiatives for Soil Conservation:
- Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme:Provides farmers with soil nutrient information.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana:Focuses on efficient water use.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming & Natural Farming Mission:Promotes sustainable farming practices to protect soil health.
Guided Pinaka Weapon System

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully completed the Flight Tests of Guided Pinaka Weapon System.
Key Details of the Flight Tests:
- Conducted as part of Provisional Staff Qualitative Requirements (PSQR) Validation Trials.
- Tests Phases: Flight tests were carried out in three phases at different field firing ranges.
- Parameters Assessed:
- Ranging (the distance the weapon can accurately target).
- Accuracy (precision of hits).
- Consistency (performance over multiple trials).
- Rate of Fire (ability to fire multiple rockets simultaneously in salvo mode).
Guided Pinaka Weapon System:
- Design and Development:
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Research Centre Imarat,
- Defence Research and Development Laboratory,
- High Energy Materials Research Laboratory,
- Proof & Experimental Establishment.
- Production Agencies: Munitions India Limited, Economic Explosives Limited, Tata Advanced Systems Limited, and Larsen & Toubro.
- Developed by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in association with other DRDO labs and production agencies, including:
- Key Features:
- Pinaka: A multi-barrel rocket launcher system named after Lord Shiva’s bow.
- Mobility: Highly mobile, providing quick deployment in battlefield scenarios.
- Firepower: Capable of delivering concentrated firepower on enemy targets.
- Upgraded Version (Pinaka Mark II):
- Extended range: 70 to 80 km.
- Future range targets: 120 km and 300 km.
- Salvo Mode: Tested for the ability to launch 12 rockets simultaneously.
- Significance:
- Strategic Importance: The successful trials enhance the artillery firepower of the Indian Armed Forces.
- Completion of Pre-requisite Trials: The system has successfully completed all flight trials before its induction into the Indian Army.
Rare Leucistic Peacock

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Tamil Nadu Forest Department staff and members of a non-governmental organisation rescued a rare peacock with white feathers, caused by a genetic condition called leucism, in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
Incident Details:
- Species: Indian peacock (Pavocristatus), known for its beautiful plumage.
- Condition: The peacock was rescued due to a leg injury and its rare white plumage.
- Cause of White Plumage: The bird's white feathers are caused by leucism, a genetic condition that reduces pigmentation in feathers while leaving eye color unaffected.
Expert Insights:
- Leucism: It causes partial loss of pigmentation in animals. A leucistic animal retains normal eye color but has pale or white coloration.
- Distinction from Albinism: Unlike albinism, which results in a complete lack of melanin and often causes red or pink eyes, leucistic animals retain normal eye pigmentation.
- Identification of Leucism in Peacock: The bird’s dark eyes and pink bill and feet confirmed it as fully leucistic.
Peacock Species:
- Indian Peacock (Pavocristatus): The National Bird of India, native to India and Sri Lanka. It belongs to the Phasianidae family, which also includes pheasants, quails, and jungle fowl.
- Green Peacock (Pavomuticus): Found from Myanmar to Java.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Listed as Least Concern.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: The Indian peacock is listed under Schedule I, offering it the highest level of legal protection in India.
India’s First AI Data Bank

- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Science and Technologyrecently launched India’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) data bank that is aimed at propelling innovation and boosting the country’s national securityat the 7th Edition of the ASSOCHAM AI Leadership Meet 2024.
-
- The event theme: “AI for India: Advancing India’s AI Development – Innovation, Ethics, and Governance”.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Propel innovation and enhance national security.
- Provide access to diverse, high-quality datasets for creating scalable and inclusive AI solutions.
- Key Features of the AI Data Bank:
- Target Audience: Researchers, startups, and developers.
- Data Types: Satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- Purpose:
- To enhance national security through real-time analytics.
- Enable predictive analytics for disaster management and cybersecurity.
Strategic Importance of AI in India:
- National Security: AI to strengthen national security by providing real-time analytics from satellite, drone, and IoT data.
- AI for Development:
- AI’s role in reshaping sectors like governance, business, healthcare, education, and space exploration.
- AI as a tool for economic growth, addressing climate change, improving public service delivery, and ensuring national security.
- Ethics and Governance:
- Ensuring responsible AI use with optimal handling.
- Addressing algorithmic bias and data privacy through robust governance frameworks.
- Commitment to transparent and fair AI systems that empower people rather than replace them.
- AI in Disaster Management and Cybersecurity:
- Aligning with India’s goals to use AI for predictive analytics in disaster management.
- Enhancing cybersecurity through AI technologies.
Government’s Vision on AI:
- Empowering Citizens: AI must bridge divides and ensure equitable access to its benefits.
- AI as Backbone for Future Development: India’s focus on making AI an integral part of its future economic and technological growth.
Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- 22 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI 2025) report was released at the annual UN climate conference in Baku.
Key Highlights:
- It is published by think tanks German watch, New Climate Institute, and Climate Action Network International.It was first published in 2005.
- It tracks the progress of the world’s largest emitters in terms of emissions, renewables, and climate policy.
India's Ranking in Climate Change Performance (CCPI 2025)
- India's Rank: 10th (Dropped two places from the previous year).
- Key Factors for India's High Rank:
- Low per capita emissions: 2.9 tons of CO2 equivalent (global average: 6.6 tons).
- Rapid deployment of renewables: India is a leader in solar energy projects, including large-scale solar and rooftop solar schemes.
- Renewable energy targets: Aims for 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Energy efficiency standards: Introduced, but coverage remains inadequate.
- Electric vehicle (EV) deployment: Significant progress, especially in two-wheelers.
- Challenges for India:
- Heavy reliance on coal: India remains one of the top 10 countries with the largest developed coal reserves.
- Growth-oriented approach: Economic growth and energy demand continue to drive climate action, with limited change in climate policy expected.
- Future Pledges:
- Net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Global leadership in green energy.
CCPI 2025 Rankings Overview
Rank
Country
Key Points
1-3
Empty
No country performed well enough to achieve a "very high" rating.
4
Denmark
Leading climate actions but ranks 4th technically.
5
Netherlands
Strong climate performance, follows Denmark.
6
U.K.
Notable improvement due to coal phase-out and halting new fossil fuel licenses.
10
India
High performer, despite challenges like reliance on coal.
55
China
Largest emitter, heavily reliant on coal, ranks 55th despite promising plans.
57
U.S.
Second-largest emitter, ranks 57th with insufficient climate targets.
59
Argentina
Major climate policy setbacks, including potential exit from Paris Agreement.
64-67
Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Russia
Lowest-ranked, major oil and gas producers with weak climate policies.
General Findings of the Report
- CCPI Methodology: Assesses 63 countries (plus the EU) responsible for 90% of global emissions based on their emissions, renewable energy efforts, and climate policies.
- Global Trends:
- No country has been able to secure a "very high" rating across all categories.
- Denmark and Netherlands are among the top performers.
- The U.K. shows significant progress with its coal phase-out and fossil fuel policies.
Green World Awards 2024

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
Coal India Limited (CIL) under the aegis of the Ministry of Coal, has been conferred with the esteemed Green World Environment Award in the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) category along with the distinguished tile of Green World Ambassador.
Key Highlights:
- Reason for the Award:
- The award was granted to CIL for its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna, a CSR initiative aimed at providing permanent curative treatment for Thalassemia through Bone Marrow Transplants (BMT).
- The scheme provides financial assistance of up to ?10 lakh for BMT and has helped over 600 Thalassemia patients across India.
- Background of the Award:
- The Green Organization, an independent, non-political, non-profit environmental group, conferred the award.
- The organization has been recognizing and promoting environmental best practices and CSR initiatives globally since its establishment in 1994.
- CIL’s Role in CSR:
- CIL has been a pioneer in CSR, with its Thalassemia Bal SewaYojna being the first of its kind among public sector undertakings in India.
- The initiative partners with 17 prominent hospitals across India to provide stem cell transplants for Thalassemia patients.
- CIL’s Contribution to India's Energy Sector:
- CIL is responsible for producing over 80% of India's coal and contributes to 70% of the total coal-based power generation in the country.
- CIL accounts for 55% of India’s total power generation and meets 40% of the primary commercial energy requirements.
- Environmental Initiatives by CIL:
- CIL has adopted various measures to improve environmental sustainability, including:
- Expanding green cover over mined areas.
- Creating eco-parks and tourism spots.
- Providing mine water for domestic and agricultural use to surrounding villages.
- About Coal India Limited (CIL):
- Established: November 1975.
- Headquarters: Kolkata.
- Status: A Maharatna company and the largest coal-producing company in the world.
- Subsidiaries: CIL has seven producing subsidiaries and is a major corporate employer in India.
- About the Green Organization:
- Founded: 1994.
- Nature: Independent, non-political, non-profit organization.
- Objective: To recognize, reward, and promote environmental and CSR best practices worldwide.
- Initiatives: The Green World Awards are part of global efforts to encourage sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
- Significance of the Award:
- The Green World Environment Award highlights CIL’s commitment to social responsibility and environmental sustainability while maintaining its core role as an energy provider.
- The recognition underscores CIL’s leadership in integrating CSR initiatives with corporate operations to contribute to national development.
India’s First Indigenous Antibiotic

- 21 Nov 2024
In News:
- Nafithromycin is India's first indigenously developed antibiotic aimed at combating drug-resistant pneumonia, developed with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The drug is being marketed under the trade name "Miqnaf" by Wockhardt.
Significance in Combating Drug Resistance:
- Nafithromycin addresses Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP), a serious disease caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
- Pneumonia is responsible for over 2 million deaths globally annually, with India facing 23% of the global burden.
- The drug is 10 times more effective than current treatments like azithromycin, requiring only three doses for effective treatment, offering a safer and faster solution.
Biotechnology Sector and Public-Private Collaboration:
- BIRAC, under the Department of Biotechnology, supported the research and development of Nafithromycin.
- This achievement underscores the public-private collaboration between the government and pharmaceutical industry, demonstrating India’s capacity to develop indigenous solutions for global health challenges.
Global Health Implications:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a growing global health crisis that prolongs illnesses and raises healthcare costs.
- The new antibiotic offers a vital solution to multi-drug-resistant pathogens, contributing significantly to global health.
- India’s leadership in addressing AMR positions the country as a major player in biotechnology innovation.
Importance for Vulnerable Populations:
- Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems (e.g., diabetes, cancer patients), are particularly affected by drug-resistant pneumonia.
- Nafithromycin offers a much-needed therapeutic option for these groups.
Impact of AMR Awareness:
- The launch coincides with World AMR Awareness Week, emphasizing the urgency of tackling antimicrobial resistance.
- Public awareness, fostered by the COVID-19 pandemic, has increased the focus on biotechnology and its potential to address global health challenges.
Future Prospects:
- Nafithromycin is awaiting final approval from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) for manufacturing and public use.
- The launch is expected to lead to future breakthroughs in antibiotic development and contribute significantly to improving public health.
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- Russia reported that Ukraine fired six US-made Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles at Bryansk, Russia, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing conflict.
- This came after US President Joe Biden authorized Ukraine to use long-range missiles to strike deeper inside Russian territory, easing previous restrictions on such weapons
About the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
- Overview:
- ATACMS is a surface-to-surface artillery weapon system designed to strike targets at much greater ranges than conventional artillery, rockets, or missiles.
- Manufacturer: Produced by Lockheed Martin, a leading US defense contractor.
- First Use: It was first used during the 1991 Persian Gulf War.
- Key Features:
- Guidance: ATACMS missiles are inertially guided ballistic missiles, capable of operating in all weather conditions.
- Range: Approximately 190 miles (305 km).
- Propulsion: It uses a single-stage, solid propellant for propulsion.
- Launch Platforms: Fired from platforms like the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS) and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS).
- Payload: ATACMS missiles can carry cluster munitions, releasing hundreds of smaller bomblets over a targeted area, increasing their destructive power.
- Global Operators:Besides the US, ATACMS is also operated by countries such as Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Taiwan, and the United Arab Emirates.
SanyuktVimochan 2024

- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Army successfully conducted the Multilateral Annual Joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise, 'SanyuktVimochan 2024' at Ahmedabad and Porbandar, Gujarat.
Key Highlights:
- Conducted by: Konark Corps of Southern Command, Indian Army.
- Day 1: Tabletop Exercise (TTX)
- Theme: 'Cyclone in Coastal Region of Gujarat'.
- Focused on simulating a cyclone scenario affecting the Okha-Porbandar coastline.
- Discussed disaster relief strategies and interagency cooperation to improve response readiness.
- Attended by senior officials from NDMA, Armed Forces, State Disaster Management, and industry representatives, including delegates from nine foreign countries.
- Day 2: Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration
- Held at Chowpatty Beach, Porbandar.
- Simulated Disaster Scenario: Coordinated response to a cyclone, showcasing joint operations by:
- Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, Coast Guard, NDRF, SDRF, and other Central and State agencies.
- Key actions demonstrated:
- Requisition and Surveillance: Civil administration’s request for Armed Forces' assistance, followed by area surveillance.
- Rescue Operations: Insertion of personnel to rescue casualties.
- Casualty Evacuation: Use of resources to evacuate and assist victims.
- Resuscitation and Rehabilitation: Restoration efforts for affected citizens.
- Industrial Display &Atmanirbhar Bharat Initiative:
- Showcased indigenous HADR equipment from Indian defense industries.
- Highlighted technological advancements and self-reliance in disaster management.
- SanyuktVimochan 2024 enhanced India's disaster response capabilities, ensuring a coordinated and effective approach to humanitarian assistance.
- The exercise also bolstered India’s leadership in global disaster relief, contributing to international best practices and collaborative efforts in humanitarian assistance and disaster response.
Sickle Cell Eradication
- 20 Nov 2024
In News:
- On the occasion of Janjatiya Gaurav Diwason 15th November 2024, Hon’ble Governor of Madhya Pradesh, and Chief Minister unveiled a commemorative postage stamp dedicated to "Sickle Cell Eradication - 2047" at PG College, Dhar.
- Significance:Focuses on India’s commitment to eradicate Sickle Cell Anemia by 2047, especially in tribal communities.
Sickle Cell Anemia Overview
- What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Genetic blood disorder leading to abnormal hemoglobin.
- Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, blocking blood flow and causing pain, organ damage, and reduced life expectancy.
- Symptoms:
- Chronic anemia causing fatigue, weakness, and pallor.
- Painful episodes (sickle cell crisis) resulting in intense pain in bones, chest, and limbs.
- Delayed growth and puberty in children.
- Treatment Processes:
- Blood Transfusions: Relieve anemia and reduce pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of painful episodes.
- Gene Therapy: Includes bone marrow or stem cell transplants and methods like CRISPR for treatment.
Challenges of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India
- Tribal Population Impact:
- India has the world’s largest tribal population (~67.8 million, 8.6% of total population as per 2011 Census).
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is identified as one of the top 10 health issues for tribal communities.
- Challenges:
- Limited diagnostic and treatment facilities in remote tribal regions.
- Lack of awareness about genetic counseling and preventive care.
- High treatment costs (e.g., CRISPR therapy costs USD 2-3 million).
- Bone marrow donor availability is a challenge.
Government Initiatives for SCD Management
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023):
- Objective: Eliminate SCD as a public health issue by 2047.
- Key Features:
- Community Screening: Mass screening to identify at-risk individuals.
- Genetic Counseling: Educating families on genetic nature of SCD.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use of tools like HPLC for accurate diagnosis.
- Prenatal Testing: Partnership with organizations like Sankalp India.
- Newborn Screening: AIIMS Bhopal provides early detection.
- Technology: A mobile app and National Sickle Cell Portal for tracking data.
- Progress:Over 3.37 crore people screened, with 3.22 crore confirmed negative.
- Target Groups:Focus on children, adolescents, youth, and adults for screening, counseling, and care.
- National Health Mission (NHM) (2013):
- Emphasizes disease prevention and management, particularly for hereditary conditions like sickle cell.
- Facilitates medications like hydroxyurea for treatment.
- National Guidelines for Stem Cell Research (2017):Regulates stem cell therapies and allows Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) for SCD.
- National Guidelines for Gene Therapy (2019):Guidelines for gene therapies for inherited disorders, including CRISPR treatment for SCD.
- State Haemoglobinopathy Mission of Madhya Pradesh:Addresses screening and management challenges of SCD in the state.
Global Awareness and Observances
- World Sickle Cell Awareness Day:
- Observed on 19th June annually, with the 2024 theme: "Hope Through Progress: Advancing Sickle Cell Care Globally".
- Aimed at raising awareness about SCD struggles, improving patient care, and finding a cure.
Bharat NCX 2024

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Bharat National Cyber Security Exercise (Bharat NCX 2024), inaugurated on November 18, 2024, is a key initiative aimed at strengthening India’s cybersecurity resilience. This 12-day exercise is designed to equip cybersecurity professionals and national leadership with the skills to manage complex cyber threats, enhance incident response capabilities, and improve strategic decision-making. The event is organized by the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) in collaboration with Rashtriya Raksha University (RRU).
Key Details of Bharat NCX 2024:
- Cyber Defense and Incident Response Training
- The exercise focuses on defensive cybersecurity skills, preparing participants to defend against cyberattacks.
- Live-fire simulations will provide hands-on experience with real-time cyberattacks on IT and Operational Technology (OT) systems.
- Strategic Decision-Making Simulations
- A core component is the Strategic Decision-Making Exercise, where senior management from across sectors will simulate decision-making in a national-level cyber crisis.
- This exercise enhances their ability to respond swiftly and strategically in high-pressure scenarios.
- CISO’s Conclave
- The CISO's Conclave brings together Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) from government, public, and private sectors.
- The conclave will feature panel discussions on the latest cybersecurity trends and government initiatives, allowing professionals to exchange knowledge and collaborate.
- Bharat Cybersecurity Startup Exhibition
- An exhibition will highlight innovative cybersecurity solutions developed by Indian startups. This showcases the growing role of the private sector in strengthening India’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Leadership Engagement and Capacity Building
- Leadership engagement is a key feature, ensuring that high-level decision-makers are prepared to lead national cybersecurity efforts.
- The exercise will foster a unified approach to dealing with emerging cyber threats.
Significance for India’s Cybersecurity Strategy
- National Cybersecurity Resilience: Bharat NCX 2024 is a vital step in fortifying India’s cybersecurity defenses, preparing professionals and leadership to address the evolving cyber threat landscape.
- Collaboration and Innovation: The inclusion of industry stakeholders, startups, and leaders from various sectors underscores the importance of collaboration in developing innovative solutions to cybersecurity challenges.
- Capacity Building: The exercise aims to improve decision-making at all levels, helping India build a robust cybersecurity framework to secure its critical infrastructure and respond effectively to potential cyber crises.
Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP-IV)

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
As Delhi’s AQI worsened, the Commission for Air Quality Management issued the order to activate Stage-IV of the Graded Response Action Plan.
Restrictions Under GRAP-IV in Delhi-NCR
- Truck Movement:
- Banned except for essential goods and trucks using clean fuels (LNG, CNG, BS-VI diesel, or electric).
- Non-essential light commercial vehicles registered outside Delhi are also banned unless they are CNG or BS-VI diesel or electric vehicles (EVs).
- Delhi-registered BS-IV or older diesel vehicles (medium and heavy goods vehicles) are banned, except for those in essential services.
- Construction Activities:Suspension of all construction work, including public projects like highways, roads, flyovers, power lines, pipelines, etc.
- Schools and Work:
- Online classes for students of Classes 6 to 9 and Class 11.
- Work from home (WFH) recommendations for 50% office capacity in NCR.
- Central government employees may also be asked to work from home.
- Offline classes for Classes 10 and 12 continue, but schools for other classes must shift to online mode.
- Other Measures:
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
- Closure of colleges.
- Odd-even vehicle scheme.
- Restrictions on non-essential commercial activities.
- State governments may impose additional measures such as:
About GRAP (Graded Response Action Plan)
- Purpose: A plan to reduce air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region based on AQI levels.
- Approved By: Supreme Court in 2016 (M.C. Mehta v. Union of India).
- Notified by MoEFCC: 2017.
- Implementation Authority: CAQM (Commission for Air Quality Management).
Stages of GRAP
GRAP is an incremental system, with measures activated as air quality deteriorates:
- Stage 1: Poor AQI (201-300) – Basic pollution control measures.
- Stage 2: Very Poor AQI (301-400) – Enhanced measures.
- Stage 3: Severe AQI (401-450) – Stricter actions like shutting down industries.
- Stage 4: Severe Plus AQI (Above 450) – Most stringent restrictions, as activated on November 18, 2024.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Introduced: 2014, by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- Categories:
- Good: 0-50
- Satisfactory: 51-100
- Moderately Polluted: 101-200
- Poor: 201-300
- Very Poor: 301-400
- Severe: 401-450
- Severe Plus: 451 and above (current status in Delhi).
- Pollutants Considered: PM10, PM2.5, NO?, SO?, CO, O?, NH?, and Pb.
- Measurement: 24-hour average values for PMs, and 8-hour averages for CO and O?.
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- Established: Under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) Act, 2021.
- Mandate: To coordinate, research, and manage air quality issues in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- Composition: Includes government officials, technical experts, and NGO representatives.
- Jurisdiction: Covers Delhi and parts of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
Nepal-Bangladesh Power Transfer via India

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
Nepal starts exporting energy to Bangladesh with Indian grid support.
Significance of the Power Transfer:
- Energy Cooperation:
- A major step in regional energy cooperation among Nepal, India, and Bangladesh.
- Strengthens sub-regional connectivity in the power sector.
- Nepal’s Hydropower Potential:
- Nepal, a Himalayan nation, possesses untapped hydropower resources, and this agreement opens the door for future cross-border electricity cooperation.
- Nepal’s energy exports are a green energy initiative, supporting sustainable industrial growth in Bangladesh and regional prosperity.
- Electricity Crisis in Bangladesh:
- Bangladesh is facing an ongoing electricity shortage, worsened by the suspension of power supply from Adani’s Godda plant and the maintenance of the Payra thermal unit.
- The addition of 40 MW of Nepalese hydroelectric power aims to alleviate the energy shortfall in Bangladesh.
Tripartite Power Sales Agreement:
- Agreement Details:
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN) (India)
- Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) (Nepal)
- Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB) (Bangladesh).
- Power Export: Nepal has started exporting 40 MW of electricity, which marks a significant milestone in trilateral power cooperation.
- The agreement for power transfer was signed in October 2023 between:
Key Entities Involved:
- NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam (NVVN):
- A wholly owned subsidiary of NTPC Ltd. (National Thermal Power Corporation), created to facilitate power trading.
- NVVN is diversifying into renewables, e-mobility, and green fuel solutions.
- NTPC Ltd.:
- A Maharatna PSU under India’s Ministry of Power, established to develop power resources in India.
- Involved in large-scale power generation and clean energy initiatives
Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve in Chhattisgarh has been officially notified as India's 56th tiger reserve, marking a significant milestone in the country's conservation efforts. Here's an overview of this new reserve:
Key Details:
- Location: The tiger reserve is located across the Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, Korea, Surajpur, and Balrampur districts of Chhattisgarh.
- Area: The reserve spans 2,829.38 square kilometers and includes both core and buffer zones.
- Core/critical habitat: 2,049.2 sq. km (includes the Guru Ghasidas National Park and TamorPingla Wildlife Sanctuary).
- Buffer zone: 780.15 sq. km.
- Rank: It is the third largest tiger reserve in India, after the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (Andhra Pradesh) and Manas Tiger Reserve (Assam).
Connectivity:
The reserve forms part of a landscape complex that extends over nearly 4,500 sq. km and is interconnected with other major tiger reserves:
- Sanjay Dubri Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the north.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (Madhya Pradesh) to the west.
- Palamau Tiger Reserve (Jharkhand) to the east.
This connectivity supports greater wildlife movement, reducing the risk of inbreeding and strengthening the overall conservation efforts for the tiger population.
Biodiversity:
The Guru Ghasidas-TamorPingla Tiger Reserve is ecologically rich, harboring a wide array of species:
- 753 species have been documented, including:
- 230 bird species.
- 55 mammal species, including several threatened species such as tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and wolves.
- A variety of invertebrates, especially insects.
- The reserve's terrain includes dense forests, streams, rivers, and varied elevations, making it an ideal habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
Ecological Importance:
- Situated in the Chota Nagpur and Baghelkhand plateaus, the reserve has varied landscapes that contribute to its ecological diversity. The region's tropical climate and dense forests make it a critical habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
- The reserve's core area forms an important critical tiger habitat, providing a sanctuary for tigers to thrive with minimal human disturbance.
Conservation Impact:
With the addition of this tiger reserve, Chhattisgarh now boasts four tiger reserves, complementing the existing Udanti-Sitanadi, Achanakmar, and Indravati reserves. This bolsters the state's and the country's ongoing efforts to protect and conserve tigers, which are a keystone species in maintaining ecological balance.
Procedural Steps for Notification:
- Identification: The state government identifies a significant ecological area with potential for tiger conservation.
- NTCA Approval: After a thorough assessment, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) evaluates and approves the proposal.
- State Notification: The state government officially notifies the area as a tiger reserve under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- Implementation: The state, with NTCA support, begins implementing conservation and management strategies.
Mystery mollusk
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
- In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers have identified a new species of sea slug deep within the ocean’s midnight zone—a place that lies between 3,300 to 13,100 feet (1,000 to 4,000 meters) below the ocean's surface.
- The species, named Bathydeviuscaudactylus, is a glowing, swimming sea slug that exhibits several unique adaptations to survive in the extreme conditions of the deep ocean.
Key Features of BathydeviusCaudactylus
- Glowing Bioluminescence: One of the most striking features of this newly discovered mollusk is its ability to glow with bioluminescence. Bathydevius emits a soft, starry glow, an adaptation seen in only a few deep-sea species. The glowing feature plays a role in distracting predators and even includes the ability to detach glowing projections from its tail as a decoy.
- Unique Body Structure: Unlike most sea slugs that typically live on the seafloor, Bathydevius has evolved to thrive in the open water. It has a gelatinous, paddle-like tail and a large, bowl-shaped hood that covers its internal organs, making it appear somewhat like a “megaphone with a feathered tail.” This structure helps it capture prey, such as mysid shrimp, which it traps using its hood.
- Adaptations for Deep Sea Life: Bathydevius' transparent body, along with its ability to drift with ocean currents and flex its body to move vertically in the water column, allow it to navigate the depths of the midnight zone. Its hermaphroditic nature means it carries both male and female reproductive organs, allowing it to reproduce by attaching to the seafloor and laying eggs when needed.
Discovery and Exploration
- The unusual species was first encountered by researchers from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) during a deep-sea dive in February 2000 using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) called Tiburon. Since then, more than 150 sightings have been made of the creature in the waters off the Pacific Coast of North America, ranging from Oregon to Southern California.
- Interestingly, similar creatures have been observed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the Mariana Trench, suggesting that Bathydevius may have a wider range than initially thought. A specimen was eventually collected for further study, revealing its identity as a nudibranch, a type of soft-bodied marine mollusk.
Survival Tactics and Behavior
- Prey Capture: Unlike typical sea slugs that scrape food from the seafloor, Bathydevius uses its large hood to trap crustaceans like mysid shrimp. This allows it to thrive in the open ocean where food can be harder to obtain.
- Defensive Mechanisms: When threatened, Bathydevius can glow with bioluminescence to distract predators. This glow, which creates a starry appearance across its back, has been seen in other deep-sea species but is rare in nudibranchs. Additionally, it can detach part of its tail (a glowing projection) to confuse attackers, similar to how lizards shed their tails as a defense mechanism.
- Reproduction and Movement: As a hermaphrodite, Bathydevius has the ability to self-fertilize or mate with other individuals. During reproduction, it descends to the seafloor and uses its foot to temporarily attach, releasing eggs before returning to its swimming lifestyle. It also relies on its flexible, transparent body to blend in with the surroundings and evade predators.
India Successfully Tests Long-Range Hypersonic Missile

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
- India has made a major advancement in its defense capabilities with the successful flight test of its first long-range hypersonic missile, marking a historic moment in the country's defense technology.
- The test was conducted, by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), took place off the coast of Odisha from the Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island.
- The missile has a range of over 1,500 km and is capable of carrying various payloads for all branches of the armed forces.
Key Highlights of the Test:
- Successful Trial: The missile successfully completed its flight test with high accuracy, confirmed by the data gathered from down-range ship stations. It performed a series of terminal maneuvers, validating its precision targeting capabilities.
- Speed and Range: The missile achieved hypersonic speeds (Mach 6), or six times the speed of sound, and is designed for a range of more than 1,500 km, far exceeding the capabilities of many conventional missiles.
- Indigenous Development: This missile is a product of DRDO's indigenous efforts, developed with contributions from the Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Missile Complex in Hyderabad, as well as other DRDO laboratories and industry partners.
What are Hypersonic Missiles?
- Definition: Hypersonic missiles are defined as weapons that travel at speeds greater than Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound), or about 3,836 miles per hour (6,174 km/h). At such speeds, they are incredibly difficult to track and intercept, posing a challenge for traditional missile defense systems.
- Types:
- Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs): These are launched from rockets and glide towards their target.
- Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs): These missiles use air-breathing engines like scramjets for sustained flight at hypersonic speeds.
- Advantages: Hypersonic missiles offer several advantages, including:
- Responsive strike capability: They can target time-sensitive threats quickly and with high precision.
- Manoeuvrability: Unlike ballistic missiles, which follow a predictable parabolic trajectory, hypersonic missiles can change course mid-flight, making them harder to defend against.
- Challenges:
- Heat and air resistance: Traveling at such high speeds generates tremendous heat due to friction, presenting engineering challenges.
- Tracking and interception: Their low-altitude flight and high speeds make them harder to detect and intercept with existing missile defense systems.
- High costs: Developing and deploying hypersonic weapons comes at a higher cost than traditional missile systems.
Global Context of Hypersonic Weaponry
- Russia and China: Both Russia and China are leaders in hypersonic missile technology. Russia has already deployed the Kinzhal hypersonic missile in Ukraine, demonstrating its effectiveness in combat situations.
- United States: The U.S. is also making significant advancements, with contracts like the Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW), awarded to Lockheed Martin for continued development.
- Other Nations: Countries such as France, Germany, Australia, Japan, and Israel are also actively working on developing hypersonic missile systems.
WIPO 2024 Report

- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
India continues to make significant strides in intellectual property filings, ranking among the top 10 countries for patents, trademarks, and industrial designs.
India’s Performance in Global Intellectual Property (IP) Filings:
- Overall Growth: India continues to make significant strides in intellectual property filings, ranking among the top 10 countries for patents, trademarks, and industrial designs.
- Patent Applications: India recorded a +15.7% growth in patent applications in 2023, marking its fifth consecutive year of double-digit growth, placing it among the top contributors to global patent filings.
- Trademark Filings: India ranks 4th globally in trademark filings, reflecting the country’s growing focus on brand protection.
- Industrial Designs: India saw a 36.4% surge in industrial design applications, emphasizing creativity and design innovation.
India’s Global Patent Ranking:
- Global Rank: India ranks 6th globally for patent applications with 64,480 filings in 2023.
- Resident Filings: For the first time, over half (55.2%) of India’s patent applications were filed by residents, highlighting growing domestic innovation.
- Patent Grants: A 149.4% increase in granted patents in 2023 underscores the efficiency of India’s patent office and the rising quality of applications.
Key Metrics and Trends in Patents:
- Patent-to-GDP Ratio: India’s patent-to-GDP ratio grew from 144 in 2013 to 381 in 2023, signaling a knowledge-driven economy.
- Sectoral Diversity: India’s patent filings span diverse sectors, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, IT, and renewable energy, showcasing the broad scope of innovation.
Surge in Industrial Design Applications:
- Growth Rate: A 36.4% increase in industrial design filings in 2023, reflecting a shift towards value-added industries focused on product design and functionality.
- Leading Sectors: Key sectors driving design filings include textiles, accessories, tools, machines, and health & cosmetics.
- Manufacturing Transformation: This growth signals India’s transition from basic manufacturing to a more design-driven, innovation-focused ecosystem.
Trademark Filings:
- Global Rank: India ranks 4th globally in trademark filings with a 6.1% increase over the previous year.
- Resident Filings: Nearly 90% of trademark filings in India were made by domestic entities, highlighting a strong focus on brand protection.
- Active Trademarks: India now has over 3.2 million active trademarks, the second-largest in the world, reflecting a competitive and dynamic domestic marketplace.
Sectoral Trends in Trademarks:
- Leading Sectors: Health (21.9%), agriculture (15.3%), and clothing (12.8%) were the top sectors for trademark filings, underscoring India’s leadership in pharmaceuticals, food production, and fashion.
- Global Expansion: The rise in trademark filings also mirrors the increasing global demand for Indian products and services.
India’s Contribution to Global IP Growth:
- Global Trend: In 2023, a record 3.55 million patent applications were filed worldwide, with India contributing significantly to this surge, particularly in emerging markets.
- Local Innovation Focus: India’s rising resident filings in patents and trademarks point to a shift towards local innovation, with more Indian businesses and startups protecting their intellectual property.
Government Initiatives Fueling IP Growth:
- National IPR Policy: Launched in 2016, this policy fosters innovation, improves IP awareness, and supports domestic IP development.
- Key Measures: Modernization of IP offices, improvements in procedural requirements, and IP education initiatives.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat: Government campaigns like Atmanirbhar Bharat have supported local innovation and made Indian businesses more IP-conscious.
- Startup India & Atal Innovation Mission: These initiatives have further strengthened India’s innovation ecosystem by promoting entrepreneurship, research, and technological advancement.
- Startup India: Over 1,49,000 recognized startups as of September 2024.
- Atal Innovation Mission: More than 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs in schools and 3,500+ startups incubated across India.
Assam’s Semiconductor Plant
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
A Semiconductor Plant has been set up in Morigaon, Assam, projected for completion by mid-2025.
Overview of the Morigaon Semiconductor Plant:
- Location: Morigaon, Assam.
- Investor: Tata Semiconductor Assembly and Test Pvt Ltd (TSAT).
- Investment: ?27,000 crore.
- Production Capacity: Expected to produce 48 million semiconductor chips daily.
- Technology: Utilizes advanced packaging technologies such as flip chip and Integrated System in Package (ISIP).
- Sectors Served: Automotive, electric vehicles, telecommunications, consumer electronics.
- Completion: Projected to be completed by mid-2025.
- Job Creation: Expected to generate 15,000 direct jobs and 11,000-13,000 indirect jobs.
- Market Reach: Will serve both domestic and international markets, enhancing India's position in the global semiconductor supply chain.
India's Semiconductor Industry and Market Growth:
- Market Size (2023): Estimated at $38 billion.
- Projected Growth: Expected to grow to $109 billion by 2030.
- Government Initiatives: Several initiatives have been launched to promote domestic semiconductor manufacturing, including the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) and the Semicon India Program.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM):
- Objective: To build a self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem in India.
- Launched: 2021 with a financial outlay of ?76,000 crore.
- Scope: Covers semiconductor fabs, packaging, display manufacturing, Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Testing (OSAT), sensors, and other critical components.
- Support Schemes: Includes Modified Schemes for setting up Semiconductor and Display Fabs, as well as support for Compound Semiconductors, Silicon Photonics, and Sensors.
Key Projects in Semiconductor Industry:
- Morigaon Facility: Part of the broader government-backed initiative to enhance semiconductor production in India.
- Other Facilities: New semiconductor units by Tata Electronics (Dholera, Gujarat), CG Power (Sanand, Gujarat), and KaynesSemicon Pvt Ltd (Sanand, Gujarat).
- Modernization: The Semi-Conductor Laboratory in Mohali is being modernized, alongside initiatives like the Scheme for Promotion of Manufacturing of Electronic Components and Semiconductors (SPECS) and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
Strategic Importance of Semiconductors:
- Role in Modern Electronics: Semiconductors are critical for a wide range of devices like computers, smartphones, solar cells, LEDs, and integrated circuits.
- Global Dependence: The global semiconductor market has significant reliance on suppliers like Taiwan (44%), China (28%), and South Korea (12%).
- Global Shortage: The 2021 chip shortage highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains, prompting efforts by countries to boost domestic semiconductor production.
Government Support for Semiconductor Manufacturing:
- Financial Incentives: The government offers fiscal support for setting up semiconductor manufacturing plants:
- 50% of project cost support under the Semiconductor Fab Scheme and the Display Fab Scheme.
- Support for Compound Semiconductors and Chips to Startup (C2S) initiatives.
- Training 85,000 engineers through the C2S Programme in collaboration with academic institutions, R&D organizations, and MSMEs.
e-Tarang System
- 18 Nov 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ministry of Defence launched the AI-enabled e-Tarang System.
Key Highlights:
- Development Collaboration: Created in partnership with Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N).
- Purpose:
- Improve planning for interference-free operation of defence equipment during both wartime and peacetime.
- Enable automated, efficient planning and management of Defence Spectrum.
- Support the development of newer technologies in higher frequency bands.
- Facilitate rapid decision-making and integration of critical modern defence technologies.
BISAG-N Overview:
- Status: Autonomous Scientific Society under the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India.
- Key Roles:
- Technology development and management.
- Research and development in geo-spatial technologies.
- National and international cooperation in geo-spatial fields.
- Capacity building and entrepreneurship development in geo-spatial technology.
- Core Domains:
- Satellite Communication
- Geo-informatics
- Geo-spatial Technology
Joint Electromagnetic Board (JEMB) – Annual Meeting Highlights:
- Chairperson: Air Marshal Jeetendra Mishra, Deputy Chief of Integrated Defence Staff (Operations).
- Attendees: Senior officers from the Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, DRDO, DDP, and industry.
- Agenda: Focused on joint operations and integration in several areas:
- Electronic Warfare (EW)
- Signature Management
- Emerging Technologies
- Electromagnetic Interference/Compatibility (EMI/EMC)
- Spectrum Management
- Human Resource Management
- Key Outcome:
- Introduction of the AI-enabled e-Tarang System to enhance Defence Spectrum management.
- Release of the Technical News Letter (TNL) 2024, outlining future technologies for modern warfare.
- Development of a roadmap to enhance Spectrum Warfare capabilities and integration of EW assets across the three Services.
- Successful joint EW exercise conducted in September 2024, promoting the principle of “Victory through Jointness”.
Objective of the Meeting:
- Goal: Achieve synergy in joint electronic warfare operations across the Services.
- Focus: Establish technology development and training priorities for the future.
Exercise PoorviPrahar
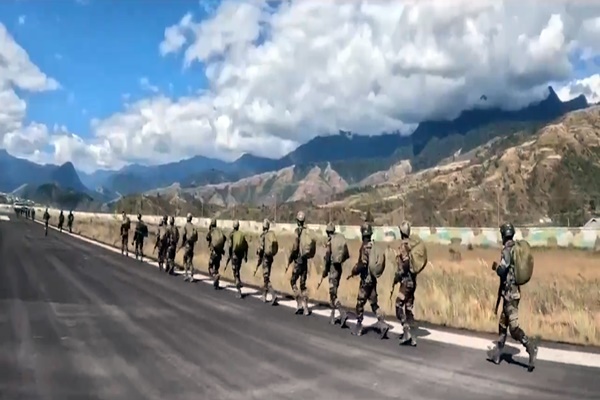

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- From November 10 to 18, 2024, the Indian Army is conducting a high-intensity tri-services exercise named PoorviPrahar in the forward areas of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The exercise aims to enhance the combat effectiveness and coordination between the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force, focusing on integrated joint operations in the challenging mountainous terrain of the region.
About Exercise PoorviPrahar
Objective: The primary goal of Exercise PoorviPrahar is to hone the combat readiness and synergy across the three branches of the Indian Armed Forces. It is designed to improve their ability to conduct integrated joint operations, especially in the difficult terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, which is crucial due to the region's strategic location along India's eastern frontier.
Key Features of the Exercise:
- Multidomain Integration:The exercise involves land, air, and sea operations, demonstrating India's capability to conduct multi-domain operations. This showcases the Indian Armed Forces' preparedness to tackle threats across all three domains simultaneously.
- Advanced Military Platforms:
- Aircraft: Advanced fighter jets, reconnaissance aircraft.
- Helicopters: Including Chinook heavy-lift helicopters and Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH Rudra).
- Artillery: The exercise makes use of the M777 Ultra-Light Howitzers, which provide mobility and precision firepower in rugged terrains.
- Swarm Drones and Loitering Munitions: These cutting-edge technologies enable precision strikes and enhanced situational awareness, contributing to more flexible and adaptive operations.
- Technological Integration:
- The exercise integrates next-generation technologies like Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and First-Person View (FPV) Drones. These tools enhance operational flexibility, improve situational awareness, and enable precision in strike capabilities, marking a significant advancement in India's military technology.
- Operational Coordination:A core component of the exercise is the development of a Common Operating Picture (COP). This system integrates real-time data from land, air, and sea operations, improving coordination and decision-making. The system relies on AI-driven analytics and satellite communications, enabling rapid information sharing and quicker response times.
- Tactical Focus on Mountain Warfare:Arunachal Pradesh, with its mountainous and rugged terrain, is the perfect setting for honing skills required for mountain warfare. The region’s proximity to India’s border with China makes it a critical area for India’s defense strategy.
Key Takeaways:
- Integrated Joint Operations: The exercise focuses on improving the coordination between the Army, Navy, and Air Force to execute seamless operations across land, air, and sea.
- Advanced Technology Integration: The exercise features the use of Swarm Drones, Loitering Munitions, and AI-driven systems to enhance precision, situational awareness, and overall operational flexibility.
- Mountain Warfare Expertise: Conducted in the mountainous terrain of Arunachal Pradesh, the exercise is crucial for preparing the Indian Armed Forces to operate effectively in such challenging landscapes.
- Strategic Posture: The exercise reaffirms India’s ability to defend its Eastern frontier and maintain a robust defense posture in the face of potential threats in the region.
Red-Headed Vulture

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Red-Headed Vulture, a critically endangered species, has been sighted for the first time in Kasaragod, Kerala, marking an important addition to the region’s avian biodiversity. This rare sighting occurred at Manhampothikunnu near Mavungal. Prior to this, the species was predominantly seen in the Wayanad region of Kerala.
- This discovery brings the total number of bird species recorded in Kasaragod to 407, showcasing the district's growing avian diversity.
About the Red-Headed Vulture:
- The Red-Headed Vulture (also known as the Asian King Vulture or Pondicherry Vulture) is one of the rarest and most critically endangered species of vultures in India. It is known for its distinctive scarlet red head and black body with a white patch on the abdomen.
- Physical Features: The bird is medium-sized, weighing around 5 kg, with a wingspan of up to 2.5 meters and a length of 80 cm. It is typically solitary, often found alone or with a mate.
- Distribution: Historically found in Central India, Nepal, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, and parts of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, the Red-Headed Vulture’s numbers have drastically declined in recent decades.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: The Red-Headed Vulture is classified as Critically Endangered.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: It is listed under Schedule 1, offering it the highest level of legal protection.
- CITES: The species is also listed in Appendix II, indicating that it requires international conservation efforts to prevent it from becoming endangered.
Threats to Vultures:
- Diclofenac Poisoning: The significant decline in vulture populations in India, including the Red-Headed Vulture, is primarily due to the widespread use of diclofenac (a veterinary drug) to treat livestock. When vultures consume the carcasses of treated animals, they ingest the toxic drug, leading to kidney failure and death.
- Other threats include pesticide contamination, lead poisoning, habitat loss, and collisions with man-made structures like power lines and wind turbines.
Conservation Efforts in India:
- India has undertaken various efforts to protect vultures, including banning diclofenac in 2006 and expanding the ban to other harmful drugs like ketoprofen and aceclofenac in 2023.
- Vulture Conservation Breeding Centres (VCBCs): These centers are focused on captive breeding and reintroduction programs for vultures, helping to increase their populations. The Jatayu Conservation and Breeding Centre in Uttar Pradesh is one of the latest initiatives, set up to protect and rehabilitate vultures.
- Vulture Safe Zones have been created across India, providing safe habitats for vulture species to recover.
- Vulture Restaurant Initiative: In some regions, safe feeding centers (such as in Jharkhand) have been established, where vultures are provided uncontaminated carcasses, reducing their exposure to toxic substances.
- Legal Protection: Several species of vultures, including the Red-Headed Vulture, are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, ensuring stringent legal measures against poaching and habitat destruction.
Global Conservation Efforts:
- India’s vulture conservation initiatives are part of a broader international effort under the SAVE (Saving Asia’s Vultures from Extinction) programme, which involves multiple regional and global organizations working to protect vulture species in South Asia.
TarunerSwapno Scheme

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee has ordered an inquiry after some intended beneficiaries of the ‘Taruner Swapna’ scheme, an initiative of the TMC government, alleged that they did not receive Rs 10,000 meant for the purchase of tablets (mobile device with a touchscreen display, rechargeable battery, and mobile operating system).
Overview:
- Aimed at bridging the digital divide by providing ?10,000 to Class 11 and 12 students in West Bengal for purchasing smartphones/tablets.
- In FY 2024-25, ?900 crore allocated for the scheme, targeting 16 lakh students.
- The main objective of the scheme is to provide scholarship to the students. So that the student can use their scholarship to buy a smartphone and tablet and can get education through online medium.
- This scheme will prove to be effective in making the future of the students bright and will also prove to be effective in strengthening them technically.
- Eligibility criteria for the scheme:
- Applicant must be a permanent resident of West Bengal State.
- The applicant should be a student.
- Students of 11th and 12th will be eligible for this scheme.
- The annual income of the family of the applicant student should not exceed Rs 2 lakh.
- Students with backlog are not eligible as this grant is for one-time only.
- This scheme will make the students technically strong and they will be able to improve their future with technology.
- Students of government/government-aided/sponsored schools and madrassas can avail assistance.
- TarunerSwapno Yojana will bridge the digital divide among students and facilitate modern education.
Europe’s Digital Euro

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The digital euro, a central bank digital currency (CBDC) being developed by the European Central Bank (ECB), aims to revolutionize Europe’s digital payment landscape. However, while the ECB has marketed it as a convenient, free, anonymous, and reliable alternative to existing cashless options like credit cards and mobile payment apps, the true purpose of the digital euro goes beyond these simplified claims.
Key Aspects of the Digital Euro
- Direct Issuance by the ECB: Unlike traditional digital payments that rely on intermediaries like banks or payment service providers, the digital euro is issued directly by the European Central Bank. This allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for third-party banks or payment gateways. It can be used for offline transactions, which is a major technical innovation that sets it apart from other digital currencies.
- A Digital Version of Cash: The digital euro is essentially a digital version of legal tender (cash), providing an alternative to cash in a world increasingly dominated by digital payments. Its key feature is direct payment between users, bypassing the traditional banking system. It aims to offer the same advantages as cash, such as anonymity, but with the convenience of digital transactions.
- Cost Reduction and Micro-Payments: The digital euro promises to lower transaction costs, especially for micro-payments that are currently prohibitively expensive using conventional bank transfers or digital services like PayPal. This cost efficiency is intended to enable new business models by lowering the friction in digital transactions, thus encouraging innovation in commerce.
The ECB’s Claims vs. the Real Motivation
While the ECB portrays the digital euro as a means to make payments easier, faster, and more secure, there is an underlying political and economic agenda that goes beyond improving consumer convenience.
- Sovereignty and Competition: One of the main drivers behind the digital euro is Europe’s desire to assert its digital sovereignty. The ECB positions the digital euro as a tool to strengthen the euro’s competitiveness against non-European payment providers, particularly those from the United States like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. The EU is concerned that foreign companies may dominate the digital payment landscape, thereby reducing Europe's ability to control its own financial systems.
- This is a defensive measure to protect European financial interests. By creating a state-backed alternative to privately controlled digital payment systems, the EU aims to ensure that Europe does not become reliant on foreign corporations for essential services.
- Not About Citizens’ Convenience Alone: While the ECB frames the digital euro as a user-friendly solution for consumers, the real concern is about the control over digital currency. The digital euro offers a more centralized alternative compared to the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The ECB aims to harness the power of the state in regulating and controlling digital transactions, thus consolidating private property and ensuring the smooth functioning of Europe’s monetary policies.
- A Tool for Strengthening the Euro: The digital euro is also seen as part of Europe’s broader ambition to establish the euro as a dominant global currency. As the first fully-regulated digital currency issued by a central bank, it could position the euro to compete against other digital currencies, including the digital yuan or the U.S. dollar. The EU sees the digital euro as a way to expand its geopolitical influence by promoting its own currency as a global standard for digital payments.
Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR)

- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) has launched the Partnerships for Accelerated Innovation and Research (PAIR) program to significantly boost research and innovation across Indian universities, especially those with limited research infrastructure. The program is designed to bring about a transformative change in India's academic research ecosystem, aligning with the broader goals of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Details:
- Launch Date: November 2024
- Ministry/Department: Department of Science and Technology (DST)
- Objective:
- To elevate research capabilities in universities that have limited resources by pairing them with well-established, top-tier institutions.
- To foster collaborations that can help these emerging universities enhance their research quality, drive innovation, and make significant, globally competitive research contributions.
- Operational Model: Hub-and-Spoke Framework
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- The top 25 institutions in the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF).
- Institutions of National Importance ranked in the top 50 NIRF.
- Spoke Institutions: These are emerging universities or institutions with limited research infrastructure. These will include:
- Central and State Public Universities ranked within the top 200 NIRF Overall.
- Top 100 NIRF University/State Public Universities.
- Select NITs and IIITs.
- Hub Institutions: These are well-established, top-tier institutions that will serve as mentors to less-researched universities. The hubs will be selected from:
- Funding:
- The program has a budget allocation of up to ?100 crore per PAIR network.
- Distribution of Funds:
- 30% for the Hub institution.
- 70% for the Spoke institutions.
- Private Institutions serving as hubs will need to contribute 25% of their allocated budget.
- Mentorship & Research Focus:
- Hubs will provide mentorship to spoke institutions, guiding them in various aspects of research such as access to resources, advanced infrastructure, and best practices.
- The collaboration is expected to enhance research capabilities, foster innovation, and encourage the development of collaborative networks across institutions.
- Regional Diversity & Inclusion:
- The program ensures regional diversity, with at least one spoke institution located outside the hub's state.
- It also allows the inclusion of one promising university from Category III institutions that may not meet the eligibility criteria but show potential for growth in research.
- Phase-wise Rollout:
- The first phase will focus on institutions ranked within the top 25 NIRF and Institutions of National Importance.
- Future phases will expand the scope, allowing more universities and institutions to participate.
- Goals Aligned with NEP 2020:
- Fostering Research Excellence: By partnering top institutions with emerging ones, PAIR seeks to improve the quality of research in India’s higher education sector.
- Promoting Regional Diversity: Ensuring a geographically diverse set of institutions participate in the research ecosystem.
- Strengthening Innovation: Helping universities in less-researched areas to compete on an international level, particularly in cutting-edge and impactful research.
- Program Implementation:
- Prospective Program Directors from eligible Hub institutions are invited to apply online for the program at ANRF PAIR Application Portal.
About ANRF:
- ANRF was established under the ANRF Act 2023 as an apex body to provide strategic direction for scientific research in India.
- With the formation of ANRF, the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), previously established under an act of Parliament in 2008, has been subsumed into ANRF.
Global Maritime Conference
- 16 Nov 2024
In News:
In a bid to enhance India’s clout in the global merchant shipping sector, the government recently hosted a two-day global maritime conference – Sagarmanthan: The Great Oceans Dialogue.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose of the Conference:
- To enhance India's maritime influence and position India as a key player in the global maritime sector, especially in merchant shipping and maritime trade.
- To showcase India's ambitions in expanding its role in global maritime trade, governance, and collaboration.
- India's Maritime Ambitions:
- Despite being the most populous nation and one of the largest global economies, India’s maritime clout has been relatively lower than expected.
- The dialogue aims to shift global attention towards India's growing role and contributions to maritime trade and shipping.
- India's Maritime Growth:
- India contributed to 16% of global maritime growth in 2023 and is on track to become the third-largest global economy within three years.
- As India’s economic and geopolitical influence expands, maritime governance will become increasingly significant, necessitating deeper international collaborations in commerce, connectivity, and trade.
- Focus Areas of the Dialogue:
- Global Maritime Trade: India's expanding role in international shipping, trade routes, and maritime security.
- International Collaborations: Promoting deeper engagement in maritime governance and policy-making ecosystems.
- Human Well-being: Highlighting the role of maritime trade in supporting human welfare, particularly in the context of sustainable development and climate change.
- Significance for India:
- The conference serves as a platform to discuss India’s aspirations, policies, and presence in global maritime affairs.
- It is an opportunity to strengthen maritime relations and address issues of global relevance such as trade routes, shipping governance, and environmental sustainability
Operation Kawach

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Delhi Police recently initiated Operation Kawach, arresting and detaining around 1,000 people in an attempt to crack down on various gangs and their operations in the wake of the recent incidents of shootings reported in the city.
Overview of Operation Kawach
- Objective: A crackdown on gang-related violence, drug trafficking, and other illegal activities like possession of firearms, banned drugs, and liquor.
- Agencies Involved:Delhi Police (Local Police, Special Cell, and Crime Branch)
- Duration: Initiated on November 12, 2024 (5 PM) and continued until November 13, 2024 (5 PM).
Key Details of the Operation
- Arrests and Detentions:
- Around 1,000 people detained.
- 486 people apprehended in Outer North Delhi (20% juveniles).
- Arrests made in Dwarka, Southwest, and North Delhi.
- Key Gangs Targeted:
- Associated with notorious gangs led by Lawrence Bishnoi, Neeraj Bawana, Kaushal Chaudhary, TilluTajpuria, Kala Jatheri, Manjeet Mahal, and Nandu gangs.
- Charges: Involvement in activities like:
- Possession of illegal firearms.
- Trafficking of liquor and banned drugs (NDPS Act).
- Theft and other criminal activities.
Significance of Operation Kawach
- Public Safety: Aimed at dismantling organized crime networks to enhance safety and reduce violence in Delhi.
- Impact on Gangs: Directly targets high-profile criminals, including those involved in gang wars and drug trafficking.
- Strategic Law Enforcement: Strengthens law enforcement capabilities, working in coordination across multiple police units.
Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)

- 15 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) retained the State Bank of India, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
Overview of D-SIBs
- Definition: D-SIBs are banks that are 'Too Big to Fail' (TBTF) and their failure could significantly disrupt essential banking services, affecting the economy.
- RBI Classification: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has designated SBI, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank as D-SIBs.
- Bucketing System: These banks are classified into different buckets based on their systemic importance.
Importance of D-SIBs
- Systemic Importance: Banks are considered systemically important due to their:
- Size
- Cross-jurisdictional activities
- Complexity
- Interconnectedness with the economy
- Impact of Failure: Failure of a D-SIB could cause significant disruption in the banking system and economy, impacting services like payments, loans, etc.
Why D-SIBs are Created
- Risk of Disruption: The failure of a large bank can disrupt essential services and lead to a broader economic crisis.
- TBTF Perception: These banks are often perceived as Too Big to Fail, leading to an expectation of government support during crises. This creates moral hazard, encouraging riskier behavior.
Assessment and Selection of D-SIBs
- Two-Step Process:
- Step 1: Selection of banks based on their size, complexity, and interconnectedness. Only banks with systemic importance are assessed (e.g., banks with assets > 2% of GDP).
- Step 2: Calculation of systemic importance score based on a range of indicators. Banks above a certain threshold are classified as D-SIBs.
- Indicators: Size (measured by Basel III Leverage Ratio Exposure Measure), interconnectedness, substitutability, and complexity are key factors.
Bucket Allocation and Capital Requirements
- D-SIBs are assigned to five buckets based on their systemic importance score:
- Bucket 1: Lowest capital surcharge (e.g., ICICI Bank).
- Bucket 5: Highest capital surcharge.
- Additional Capital Requirements:
- SBI: Additional 0.80% CET1 (Common Equity Tier 1) on Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs).
- HDFC Bank: Additional 0.40% CET1.
- ICICI Bank: Additional 0.20% CET1.
- The higher the bucket, the higher the capital surcharge.
Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs)
- Global List: Identified by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) based on data from the previous year.
- 2023 G-SIB List includes banks like JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, HSBC, etc.
- Capital Requirement for G-SIBs in India: Foreign G-SIBs with branch presence in India must meet additional CET1 requirements, proportional to their operations in India.
Key Terms
- Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs): These are used to calculate the minimum capital a bank must hold. It accounts for the risk level of a bank’s assets.
- Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1): The highest quality of capital a bank can hold, primarily made up of common stock, to absorb losses in times of distress.
Decline in African Elephant Population

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- The population of African elephants has been declining rapidly, with data showing alarming drops across the African continent.
- Survey Period: The study covers population data from 475 sites in 37 countries over 52 years (1964-2016).
- Population Decrease:
- Savannah Elephants: A 70% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Forest Elephants: A 90% decline on average across surveyed sites.
- Overall Impact: The study indicates a 77% average decline in elephant populations across both species.
Main Drivers of Decline
- Poaching: Illegal hunting for ivory and other body parts remains a major threat.
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization, agricultural expansion, and climate change are encroaching on the elephant’s natural habitats.
- Human-Elephant Conflict: Increased human settlements near elephant habitats lead to conflicts, further endangering elephant populations.
Species Overview
- Two Subspecies:
- Savannah Elephant (Loxodonta africana): Larger and more common, found in open savannas.
- Forest Elephant (Loxodonta cyclotis): Smaller and more elusive, found in dense rainforests.
- Conservation Status:
- Savannah Elephant: Endangered (IUCN).
- Forest Elephant: Critically Endangered (IUCN).
- CITES Listing: Both species are listed under CITES Appendix I, which bans international trade in endangered species.
Regional Impact
- Northern and Eastern Africa: These regions have seen drastic declines, particularly in the Sahel (Mali, Chad, Nigeria), where elephants have been extirpated (locally extinct) due to poaching and insufficient protection.
- Southern Africa: Positive Growth in some areas, particularly in Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Namibia, where elephant populations are growing due to strong conservation efforts.
Conservation Success
- Southern Africa: 42% of the surveyed sites showed increasing elephant populations, a testament to successful conservation strategies.
- Government and NGO Efforts: Successful population growth is often attributed to active management, including anti-poaching laws, protected areas, and conservation funding.
Elephant Behavior and Reproduction
- Social Structure: Elephants live in family units led by mature females, with strong social bonds.
- Low Sleep Time: Elephants sleep only 2 hours per day on average.
- Reproduction: They have a long gestation period of up to 2 years, and calves are cared for by mothers and allomothers (non-mother females).
Conservation Challenges
- Sustainability: Continued poaching and habitat destruction threaten to undo gains made in conservation.
- Fragmentation of Populations: With many elephants in isolated pockets, genetic diversity is declining, which could lead to long-term problems for species survival.
Sea Ranching Initiative off Vizhinjam Coast

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- The State Fisheries Department in Kerala launched a sea ranching project by releasing 20,000 pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fingerlings off the Vizhinjam coast as part of the artificial reef project.
- Coordinates: The fingerlings were released near artificial reef modules placed 1.5 nautical miles off the coast.
- Follow-up to Artificial Reef Project: The release of fingerlings is a follow-up to the artificial reef project aimed at replenishing marine fishery resources and promoting sustainable fishing practices.
Project Details
- Fingerling Release: The first batch of 20,000 pompano was released as part of the broader initiative to release 10 lakh fingerlings (pompano and cobia) at 10 locations along the Thiruvananthapuram coast.
- Location and Quantity: At each location, 1 lakh fingerlings will be released, where artificial reefs have already been deployed under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Reef Design: Artificial reefs consist of 150 reef modules (triangular, flower, and pipe-shaped) created at 42 locations off 33 fishing villages in the Thiruvananthapuram district.
Objective and Benefits
- Marine Resource Replenishment: The primary aim is to replenish marine fishery resources in the region by enhancing biodiversity through the introduction of fingerlings.
- Sustainable Fishing: The project aims to promote sustainable fishing practices by supporting fish populations and ensuring long-term fishery health.
- Attraction of Fish Species: The artificial reefs have already attracted a variety of fish species, including tuna, trevally, and mackerel, enhancing the fishing ecosystem.
Implementation and Funding
- Scheme: The project is being implemented under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), which focuses on sustainable fisheries development.
- Central Approval: The National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB) approved the ?3 crore funding for the initial phase in Thiruvananthapuram.
- Proposed Expansions:
- Phase II: A proposal for extending the artificial reef project to 96 villages in the districts of Kollam, Alappuzha, Ernakulam, and Thrissur with an estimated cost of ?29.76 crore.
- Phase III: A similar proposal for 96 villages in the northern districts of Malappuram, Kozhikode, Kannur, and Kasaragod with an estimated cost of ?25.82 crore.
Mission and Fingerlings Details
- Fingerlings:
- Pompano (Trachinotus blochii) and Cobia (Rachycentron canadum) fingerlings were reared at the Ayiramthengu fish farm.
- Each fingerling weighs between 8 to 10 grams.
- The release aims to stock marine areas with species that will contribute to biodiversity and fisheries sustainability.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)
- Launched: PMMSY is a Centrally funded scheme under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
- Goal: The scheme focuses on sustainable fisheries development to enhance fisheries production, boost aquaculture, and promote responsible fishing practices.
- Funding: The scheme involves both Central and State Government funding for projects related to fisheries management, infrastructure development, and resource conservation.
Mission Fingerling
- Launched: 2017 by the Union Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.
- Objective: To achieve the Blue Revolution by holistically developing and managing fisheries in India.
- Production Target: The mission aimed to increase fisheries production from 10.79 MMT (2014-15) to 15 MMT by 2020-21.
OECD Report on Indian Agricultural Policies

- 14 Nov 2024
In News:
- In 2023, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) revealed that Indian farmers faced the highest implicit taxation globally, amounting to USD 120 billion.
- Implicit Taxation: This taxation arises from government policies like export bans, duties, and price controls, aimed at lowering food prices for consumers but reducing the income of farmers.
- Export Restrictions: Key commodities affected include rice, sugar, onions, and de-oiled rice bran.
Impact on Indian Farmers
- Market Price Support (MPS):
- Negative MPS: In 2023, Indian agricultural policies resulted in a negative MPS of USD 110 billion.
- Farmers received lower prices than international market rates due to export bans and trade restrictions, impacting their income.
- Budgetary Support: Despite government subsidies and the Minimum Support Price (MSP) worth USD 10 billion, negative MPS outweighed positive support, leading to an overall loss for farmers.
- Farmer’s Share in Global Negative Support:
- India’s share of global negative price support in 2023 was 62.5%, a significant increase from 61% in 2000-02.
Global Agricultural Policy Trends
- Global Support: Total support for agriculture across 54 countries averaged USD 842 billion annually (2021-2023). However, there was a decline in support in 2022-23 from the pandemic-era peak.
- Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions (e.g., Russia-Ukraine war) and climate change are exacerbating global agricultural production and trade.
- Export Restrictions in various countries are distorting international agricultural markets.
- Farmer Protests across countries reflect the economic and social struggles of the farming community.
- Sustainability Issues: Global agricultural productivity growth is slowing, posing challenges to feeding a growing population sustainably.
India's Agricultural Policies
- Export Bans and Restrictions: These policies are intended to control domestic prices but undermine farmers’ income by lowering market prices for key agricultural products.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): MSP is meant to protect farmers, but is often set below international market rates, leading to a negative price effect.
- Regulatory Constraints: Policies like the Essential Commodities Act (1955) and APMC Act (2003), though aimed at ensuring food security, often lead to price suppression for farmers.
- Price Depressing Policies: India's agricultural policies result in lower farm-gate prices due to price controls, government-set procurement prices, and lack of market access.
Negative Market Price Support (MPS)
- Historical Trends:
- From 2014-2016, India’s Producer Support Estimate (PSE) was -6.2%, driven mainly by negative MPS (-13.1%).
- The PSE measures the annual value of transfers to farmers, both from consumers and the government.
- Inefficiencies:
- Infrastructure Gaps: Poor infrastructure and high transaction costs lower the prices farmers receive.
- Inefficient Resource Allocation: Short-term subsidies for inputs (fertilizers, irrigation) don’t address long-term agricultural challenges like climate change and market access.
Government Support Programs
- Subsidies and Schemes:
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) for organic farming.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) to promote agricultural development.
- Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP) for modernizing agricultural practices.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- The government has introduced initiatives like AgriStack and Mission Organic Value Chain Development in the North East to enhance sustainable agricultural practices and reduce the negative impacts on farmers.
Global Context and Recommendations
- Environmental Public Goods Payments (EPGP): Only 0.3% of total producer support is dedicated to environmental sustainability, despite the growing need for climate-resilient agriculture.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: The OECD advocates for governments to tie producer support to sustainable farming practices, including the use of metrics like Total Factor Productivity (TFP) and Agri-Environmental Indicators (AEIs).
- TFP measures agricultural efficiency, while AEIs assess the environmental impacts of farming.
OECD Overview
- OECD Function: Founded in 1961, the OECD is an international organization of 38 countries that promotes prosperity, equality, and well-being through economic reports, data, and policy analysis.
- India’s Role: India has been an OECD Key Partner since 2007, engaging with the OECD on various policy issues, though it is not a member.
Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI) 2024
- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
India with an abysmal score of 45.5 (out of 100) has been ranked 176th in the Global Nature Conservation Index, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- India's Ranking:
- Ranked 176th out of 180 countries in the 2024 Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI).
- India is listed among the five worst performers, along with Kiribati (180), Turkey (179), Iraq (178), and Micronesia (177).
- Score: 45.5 out of 100, indicating significant conservation challenges.
- Key Factors Contributing to Low Rank:
- Inefficient land management practices.
- Rising threats to biodiversity, exacerbated by unsustainable development and climate change.
- Four Key Markers Assessed by the NCI:
- Land Management: Ineffective management leading to significant land conversion.
- Threats to Biodiversity: Habitat loss, fragmentation, and deforestation.
- Capacity and Governance: Need for stronger political will and better enforcement of conservation laws.
- Future Trends: Growing pressure from population density, climate change, and illegal wildlife trade.
- Sustainable Land Use Concerns:
- 53% of land has been converted for urban, industrial, and agricultural purposes.
- High use of pesticides and concerns over soil pollution.
- Sustainable nitrogen index of 0.77 indicates significant risks to soil health.
- Marine Conservation Issues:
- Only 0.2% of India’s national waterways are under protected areas, with no protected areas within its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- Significant improvements needed in marine conservation despite 7.5% of terrestrial areas being protected.
- Deforestation and Habitat Loss:
- 23,300 sq. km of tree cover lost between 2001-2019 due to deforestation.
- Habitat fragmentation from agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure development.
- Impact of climate change on sensitive ecosystems like alpine regions and coral reefs.
- Biodiversity Decline:
- Despite 40% of marine species and 65% of terrestrial species being within Protected Areas (PAs), many species continue to face population decline.
- 67.5% of marine species and 46.9% of terrestrial species are still experiencing population declines.
- Illegal Wildlife Trade:
- India is the fourth-largest illegal wildlife trading nation globally, with an estimated annual trade value of £15 billion.
- The NCI emphasizes the need for stronger enforcement and international cooperation to combat wildlife trafficking.
- Ecological Wealth Under Threat:
- India’s high population density (with a population that has doubled since the late 1970s) continues to put pressure on its ecological wealth.
- The country faces significant biodiversity challenges due to overpopulation and unsustainable development.
- Recommendations and Optimism:
- The NCI stresses the need for strong political will and commitment to sustainable development.
- India can improve its rank by strengthening conservation laws, improving governance, and securing funding for environmental initiatives.
- The NCI remains optimistic about India’s potential to address its conservation challenges and achieve more sustainable outcomes in the future.
- About the Nature Conservation Index (NCI):
- Developed by: Goldman Sonnenfeldt School of Sustainability and Climate Change (Ben-Gurion University) and BioDB.com (a biodiversity database).
- Purpose: Evaluates the conservation efforts of countries, using a data-driven approach to balance conservation and development.
- Key Focus Areas: Land management, biodiversity threats, governance, and future sustainability trends.
RBI's New Framework for Reclassification of FPI to FDI
- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) directed foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) to obtain necessary approvals from the government and concurrence from the investee companies when their equity holdings go beyond the prescribed limits and they reclassify the holdings as foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Approval Requirement:
- FPIs (Foreign Portfolio Investors) must obtain necessary government approvals when reclassifying their foreign portfolio investments (FPIs) into Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- Approvals are mandatory, including those related to investments from countries sharing a land border with India.
- Investment Limits:
- According to FEMA (NDI) Rules, 2019, an FPI’s investment in an Indian company should not exceed 10% of the total paid-up equity capital (on a fully diluted basis).
- If the FPI exceeds this limit, it has 5 trading days from the settlement of trades to either divest or reclassify the excess holdings as FDI.
- Restrictions on Reclassification:
- Reclassification to FDI is not allowed in sectors where FDI is prohibited.
- FPIs must ensure compliance with FDI norms, such as entry routes, sectoral caps, investment limits, pricing guidelines, and other related conditions.
- Concurrence from Investee Companies:
- The FPI must obtain the concurrence of the investee company for reclassifying the investment into FDI.
- This ensures that the company adheres to conditions related to prohibited sectors, sectoral caps, and government approvals.
- Reclassification Procedure:
- The FPI must clearly state its intent to reclassify the investment to FDI and provide the necessary approvals and concurrence to its custodian.
- The custodian is responsible for freezing the FPI's purchase transactions in the investee company’s equity instruments until the reclassification is complete.
- Regulatory Adherence:
- The reclassification must follow the relevant provisions for FDI, including compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) and FDI guidelines.
India’s Vision of ‘Adaptive Defence’

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Shri Rajnath Singh introduced the concept of ‘Adaptive Defence’ at the inaugural Delhi Defence Dialogue (DDD).
- Adaptive Defence aims to prepare India's military for the rapidly changing landscape of modern warfare, with evolving threats and technologies shaping global security.
Key Aspects of Adaptive Defence:
- Strategic Approach:
- Adaptive Defence is an evolving strategy where military and defence systems continuously adjust to emerging threats, focusing on proactive preparedness rather than reactive responses.
- It is based on anticipating future threats, fostering flexibility, resilience, and agility in both strategic and tactical responses.
- Core Elements:
- Situational Awareness: The ability to understand and respond to dynamic, often unpredictable environments.
- Flexibility & Agility: At both the strategic and tactical levels to ensure swift and effective responses.
- Resilience: The capacity to recover and adapt quickly to unforeseen circumstances.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Emphasis on adopting cutting-edge technologies like AI, drones, and cybersecurity to stay ahead of adversaries.
The Changing Nature of Warfare:
- Grey Zone & Hybrid Warfare:
- Modern conflicts now often occur in the grey zone and involve hybrid warfare, blending traditional and non-traditional threats like cyber-attacks, terrorism, and psychological warfare.
- These new threats demand continuous adaptation in strategies, doctrines, and military operations.
- Technological Transformation:
- Drones and swarm technologies are reshaping warfare. India aspires to become a global hub for drones, leveraging these technologies for both economic and military growth.
- The increasing significance of Artificial Intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, and quantum technologies in defence highlights the need for international collaboration in research and innovation.
- Psychological Warfare:
- The rise of information overload and psychological warfare challenges traditional defence paradigms. Manipulation of information to influence public opinion and disrupt decision-making processes is now a key threat.
Government Initiatives for Adaptive Defence:
- Institutional Strengthening:
- Establishment of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) and initiatives to enhance jointness among the three armed services (Army, Navy, Air Force) to create a unified strategic force.
- Reform of training curricula and emphasis on integrated operations to ensure readiness for new-age warfare.
- Focus on Self-Reliance:
- Strengthening the indigenous defence sector through initiatives like Make in India and the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign.
- Increasing foreign direct investment (FDI) in defence and promoting defence exports, with India currently exporting to over 100 nations.
- Drone Hub Vision:
- India aims to become the world’s drone hub, supporting R&D and fostering innovation to develop reliable certification mechanisms and enhance Indian intellectual property in the drone sector.
- Programs like iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence) and ADITI are rewarding innovation and driving India's defence sector towards greater self-sufficiency.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Focus on cybersecurity, AI, and quantum technologies to develop solutions that address both national and global security challenges.
- India is also working on Theaterisation, integrating the three services into a unified force structure for enhanced coordination and joint operations.
- Defence Acquisition and Export:
- Introduction of the Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020, establishment of Defence Industrial Corridors in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, and a Positive Indigenisation List to boost self-reliance.
- India is actively increasing defence exports, aiming for Rs 50,000 crore worth of exports by 2029, with key export destinations including the USA, France, and Armenia.
Strategic Vision for the Future:
- Collaborative Approach:
- Given the interconnectedness of global security, the defence minister emphasized the importance of a collaborative approach in dealing with transnational threats.
- Cross-border issues, cyberspace threats, and the potential of quantum and nanotechnologies demand the sharing of knowledge and strategies across borders.
- Joint Military Vision:
- Jointness in defence strategy should go beyond national borders and should involve international cooperation in response to global security challenges.
- The need for interconnected solutions in the face of transnational threats underscores the importance of multilateral cooperation.
Sudden Resurgence of H5N1 in Cambodia

- 13 Nov 2024
In News:
- Cambodia saw a resurgence of H5N1 avian influenza cases after over 10 years of no human infections.
- From February 2023 to August 2024, 16 human cases were reported, with 3 deaths caused by the A/H5 clade 2.3.2.1c virus.
- Notably, 14 of these cases were caused by a novel reassortant virus, involving a mixture of clade 2.3.2.1c and clade 2.3.4.4b gene segments.
Key Points:
- Reassortment of the Virus:
- The reassortment between clades 2.3.2.1c (Southeast Asia) and 2.3.4.4b (global spread) has created a new strain.
- This reassortant virus is responsible for the second wave of infections in humans, starting in October 2023.
- Zoonotic Transmission:
- Investigations confirmed that direct contact with sick poultry or bird droppings was the primary source of human infections.
- There have been no reported cases of human-to-human transmission.
- The novel reassortant virus appears to have replaced the 2.3.2.1c strain in Cambodian poultry.
- Geographic Spread and Spillovers:
- Clade 2.3.2.1c was first reported in Cambodian poultry in March 2014. It continued to circulate in both poultry and wild birds.
- Clade 2.3.4.4b viruses began circulating in Cambodian live bird markets by 2021, co-existing with clade 2.3.2.1c.
- There were two key spillovers to humans:
- The first spillover in February 2023, associated with clade 2.3.2.1c, involved two related individuals, with one death.
- The second spillover, beginning in October 2023, involved the novel reassortant virus.
- Genetic Analysis and Mutation Concerns:
- Genetic sequencing showed significant changes in the hemagglutinin (HA) gene of viruses from human cases, indicating a shift from older local strains to newer sublineages.
- The PB2 627K mutation in the novel reassortant is concerning, as it is linked to increased mammalian adaptation and the potential for airborne transmission, particularly in mammals like ferrets.
- This mutation raises concerns about the virus’s ability to adapt to humans or other mammals.
- Environmental and Epidemiological Factors:
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- High-density poultry farming.
- Wild bird migration.
- Cross-border poultry trade in Southeast Asia.
- These factors heighten the risk of zoonotic transmission, emphasizing the need for continued vigilance in the region.
- The reassortment is believed to have been facilitated by:
- Surveillance and Response:
- One Health investigations linked human cases to infected poultry, highlighting the importance of rapid response through whole genome sequencing.
- The ongoing surveillance is critical, as the novel reassortant strain has already replaced clade 2.3.2.1c in Cambodian poultry.
- Public Health Recommendations:
- There is an urgent need to strengthen sustained surveillance of avian influenza in both poultry and wild birds, particularly in Southeast Asia.
- Public health strategies should focus on:
- Reducing human exposure to infected poultry.
- Promoting safe poultry handling practices.
- Encouraging early healthcare-seeking behavior in individuals with potential symptoms.
Nano-Coating Technology for Fertilizer Efficiency

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A mechanically stable, biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating material can enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers by tuning them for slow release, thereby limiting their interaction with the rhizosphere soil, water and microbes.
Development of Slow-Release Fertilizers:
- A biodegradable, hydrophobic nanocoating has been developed to enhance the nutrient use efficiency of chemical fertilizers.
- The nanocoating allows for slow release of nutrients, thus limiting excessive interaction with soil, water, and microbes, and optimizing fertilizer usage.
Coating Composition:
- The coating is made from nanoclay-reinforced binary carbohydrates, primarily chitosan (a biopolymer from chitin) and lignin (a plant-based polymer).
- These materials are low-cost, naturally derived, and eco-friendly, ensuring sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of fertilizer use.
Technological Innovation:
- The coating process involves using a drum rotor method to uniformly coat fertilizers, improving their efficiency.
- The tuning of hydrophobicity in the nanocoating alters the release kinetics of fertilizers, ensuring that nutrients are released in accordance with the crop’s nutrient uptake needs.
Sustainability and Biodegradability:
- The nanocoating is biodegradable, which ensures that it does not harm the environment post-application, unlike conventional chemical fertilizers that may lead to soil degradation and water pollution.
- Life cycle assessment confirms the product's long-term sustainability compared to traditional fertilizers.
Enhanced Crop Productivity:
- The slow-release coating enables a reduced fertilizer dose, while maintaining or even increasing crop yields, particularly for staple crops like rice and wheat.
- This technology facilitates higher agricultural output with fewer inputs, contributing to food security.
Industrial Viability:
- The mechanical stability of the coated fertilizers ensures they can withstand transportation and handling, making them suitable for large-scale industrial application.
- The rotary drum system used for coating ensures uniform application and superior mechanical performance, ensuring that the fertilizers are not damaged during the supply chain process.
Economic Benefits:
- The use of slow-release fertilizers can reduce overall fertilizer costs for farmers while enhancing yields, leading to improved socio-economic conditions for farmers.
- The technology holds potential for economic growth by boosting agricultural productivity and reducing the financial burden on farmers for chemical fertilizer inputs.
Global Relevance:
- The research is significant in the context of global sustainable development goals, aiming to reduce the over-reliance on conventional chemical fertilizers that contribute to soil degradation, water contamination, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Research Collaboration:
- This breakthrough was achieved by scientists from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, in collaboration with the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- The findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science: Nano, highlighting its scientific validation.
3rd Indian Space Conclave
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd Indian Space Conclave, held in New Delhi, was a significant event for India's growing role in global space exploration and strategic partnerships.
- Organized by the Indian Space Association (ISPA), the conclave brought together key stakeholders from the government, industry, academia, and space agencies to discuss India’s space ambitions and the transformative role of space technologies.
Key Highlights:
Satcom as a Transformative Force for Digital India
- Emphasis on Satellite Communication (Satcom) is more than a mere tool—it's a transformative force driving Digital India by connecting every household, village, and remote area of the country.
- Satcom has a wide array of applications that extend across essential sectors such as telecommunications, disaster management, healthcare, education, and agriculture, particularly in underserved regions.
Indo-EU Space Collaboration
- The event also showcased India’s growing space partnerships, particularly with the European Union (EU). The EU Ambassador recognized India as a dynamic space power and highlighted shared goals in Earth observation, space security, and human spaceflight.
- Proposed joint initiatives include training programs, collaborative research, and satellite missions, such as the Proba-3 satellite launch by ISRO, focusing on observing the Sun.
- India’s trustworthiness as a partner in space was underscored by its role in the successful launch of the Proba-1 and Proba-2 missions for the EU, with Proba-3 marking India’s third contribution to EU space exploration.
Space Startups and Innovation
- The rise of space-focused startups in India, spurred by the 2020 space sector reforms, was another key highlight. India now has over 300 space startups, contributing to both economic growth and innovation in the space industry.
- These reforms have helped curb brain drain, with many talented Indian professionals returning from global agencies like NASA to join the expanding Indian space ecosystem.
India’s Long-Term Space Goals
- The Indian space program has ambitious long-term goals, including:
- Gaganyaan, India’s human spaceflight mission.
- A crewed lunar landing by 2040.
- The establishment of an Indian space station by 2035.
- Plans for space tourism by 2040.
- These initiatives demonstrate India’s commitment to becoming a global leader in space exploration and technological innovation.
Space Sector Reforms (2020)
- The Space Sector Reforms 2020 were designed to increase the participation of private players in India’s space activities. The creation of agencies like the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) and the strengthening of New Space India Limited (NSIL) have been pivotal in boosting India’s global space market share.
- IN-SPACe serves as an autonomous body fostering industry, academia, and startups, while NSIL handles commercial activities and promotes high-tech space-related ventures.
India's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission
- ISRO's First Mars and Moon Analog Mission was inaugurated in Leh, Ladakh. This mission simulates the conditions of space habitats, specifically focusing on Mars and Moon environments.
- Ladakh's unique climate—high altitude, low oxygen levels, and extreme temperature fluctuations—makes it an ideal location for testing life support systems, space habitat technologies, and sustainable resource utilization.
Key Aspects of the Analog Mission:
- Life support systems like hydroponics (space farming) and standalone solar power systems to support sustainable food production and renewable energy in space habitats.
- Circadian lighting to simulate daylight cycles, maintaining astronaut health and well-being.
- The mission’s goal is to understand the psychological and operational challenges of living in isolation and extreme conditions, preparing India for future interplanetary exploration.
State of Food and Agriculture 2024Report
- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- India's annual hidden costs from agrifood systems total $1.3 trillion, the third-largest globally, after China ($1.8 trillion) and the US ($1.4 trillion).
- These costs are mainly driven by unhealthy dietary patterns leading to non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
Major Contributors to Hidden Costs:
- Unhealthy Diets: Over 73% of India’s hidden costs stem from unhealthy dietary habits, including:
- Excessive consumption of processed foods and additives ($128 billion).
- Low intake of plant-based foods, fruits, and beneficial fatty acids ($846 billion).
- These dietary risks contribute to a significant health burden, increasing the prevalence of NCDs and reducing labor productivity.
Global Context:
- Global hidden costs of agrifood systems amount to $12 trillion annually.
- 70% of these costs (~$8.1 trillion) arise from unhealthy dietary patterns, which include high intakes of sugar, salt, and processed foods, contributing to diseases and economic losses.
Health Impacts:
- The report identifies 13 dietary risk factors that contribute to NCDs, including insufficient intake of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and excessive sodium, with varying effects across different agrifood systems.
Environmental and Social Costs:
- Environmental Costs: High costs from unsustainable agricultural practices, including greenhouse gas emissions and nitrogen runoff. In some agrifood systems, environmental costs can reach up to 20% of GDP.
- Social Costs: High poverty rates among agrifood workers and undernourishment in systems like protracted crises and traditional agrifood systems contribute significantly to the hidden costs.
India’s Agrifood System Profile:
- India’s agrifood system faces significant challenges related to low wages, poor productivity, and poverty among agrifood workers, driven by distributional failures.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Issues like droughts, floods, and soil degradation threaten food security and agricultural sustainability in India.
Recommendations for Transformative Change:
- True Cost Accounting: Implementing this method can help better capture hidden costs and enable more informed decision-making for a sustainable agrifood system.
- Healthier Diets: Policies to make nutritious food more affordable and accessible to reduce health-related hidden costs.
- Sustainability Incentives: Encouraging practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, harmful land-use changes, and biodiversity loss, using labelling, certification, and industry standards.
- Consumer Empowerment: Providing accessible information about the environmental, social, and health impacts of food choices, ensuring even vulnerable households benefit from healthier options.
India’s Path Forward:
- India has several ongoing initiatives for sustainable agriculture, including:
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA).
- Eat Right Initiative.
- Digital Agriculture Mission (DAM).
- However, challenges like climate change, soil degradation, and low productivity among smallholder farmers hinder progress toward sustainable food systems.
Key Focus Areas for India’s Agrifood Systems:
- Support for Smallholder Farmers: Enhancing access to technology, markets, and financial services for marginalized farmers.
- Sustainable Practices: Adoption of water-efficient practices, soil health restoration, and environmentally friendly farming methods.
- Collaboration with International Agencies: Cooperation with FAO, WFP, and others to strengthen agricultural reforms and support smallholder farmers.
Diclipterapolymorpha

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
A new species of Dicliptera, named Diclipterapolymorpha, has been discovered in the Northern Western Ghats of India.
Habitat and Location:
- Diclipterapolymorpha was found in the grasslands of Talegaon-Dabhade, a region known for its grasslands and fodder markets.
- The species thrives in the harsh climatic conditions of the Northern Western Ghats, an area vulnerable to summer droughts and frequent human-induced fires.
Unique Characteristics:
- The species is fire-resilient (pyrophytic), exhibiting a rare dual-blooming pattern:
- First Blooming: Occurs post-monsoon, typically from November to March/April.
- Second Blooming: Triggered by grassland fires in May and June, during which the plant produces dwarf flowering shoots.
- The inflorescence structure is unique in India, with its cymules developing into spicate inflorescences, a feature more commonly found in African species.
Taxonomy:
- The species is named Diclipterapolymorpha to reflect its diverse morphological traits.
- It is taxonomically distinct within the Dicliptera genus, with no known Indian species exhibiting similar characteristics.
Conservation Implications:
- The discovery highlights the need to carefully manage grassland ecosystems, as the species is adapted to fire but still vulnerable to habitat degradation.
- Human-induced fires are essential for the species' blooming cycle but must be managed to avoid overuse and degradation of habitat.
- The species' limited habitat range underscores the need for conservation efforts to protect the delicate ecosystems of the Western Ghats.
Publication:
- A research paper detailing the discovery of Diclipterapolymorpha has been published in the prestigious Kew Bulletin.
AntarikshaAbhyas 2024

- 12 Nov 2024
In News:
- ‘AntarikshaAbhyas – 2024’ is a three-day space exercise held from November 11-13, 2024, hosted by the Defence Space Agency (DSA), Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff.
- The exercise is the first of its kind and focuses on war-gaming the growing threats to space-based assets and services.
Objective of the Exercise:
- Enhance understanding of space-based assets and their operational dependencies.
- Identify vulnerabilities in military operations in case of denial or disruption of space services.
- Integrate India's space capabilities in military operations to secure national strategic objectives.
Participants:
- Defence Space Agency (DSA) and its allied units.
- Personnel from the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Specialist agencies under Headquarters Integrated Defence Staff, including:
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCA)
- Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA)
- Strategic Forces Command (SFC)
- Representatives from ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and DRDO (Defence Research & Development Organisation).
Focus Areas:
- Space-based asset and service operational dependency.
- Securing national interests in space through technological innovation and development.
- Assessing space service vulnerabilities and impacts on military operations.
Arpactophiluspulawskii
- 11 Nov 2024
In News:
- Arpactophiluspulawskii, a new species of aphid wasp, was discovered in Nagaland (Khuzama district), marking the first record of the genus Arpactophilus outside Australasia.
- This significant discovery highlights the biodiversity of Northeastern India, a region known for its rich and unexplored fauna.
Importance of Discovery:
- The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) researchers cataloged the species, marking a major range expansion for the genus Arpactophilus, previously only found in Australasia, including regions like New Caledonia.
- The discovery expands the genus’s known distribution by thousands of kilometers, suggesting ecological connections between Nagaland and the Australasian region.
Species Characteristics:
- Arpactophiluspulawskii is distinguished by its square-shaped head, an inverted V-shaped uplifted clypeus, and rust-colored body markings.
- It features a uniquely textured thorax, setting it apart from other species in the genus.
- The wasp was collected from an altitude of over 1,800 meters, indicating Nagaland’s ecological diversity at high altitudes.
Ecological Significance:
- The Arpactophilus genus is known for its unique nesting behavior: females use silk from their abdomen to create protective cells in old termite galleries or mud nests.
- The discovery suggests that Nagaland’s ecological conditions (e.g., high altitude, diverse habitat) support the presence of such specialized fauna, making the region an important site for entomological research.
Taxonomic Contribution:
- The species is named Arpactophiluspulawskii in honor of Dr. Wojciech J. Pulawski, a distinguished expert in wasp taxonomy.
Scientific and Research Implications:
- The discovery is expected to stimulate further entomological research in Northeastern India, especially in areas like Nagaland, which are often overlooked in global biodiversity studies.
- Researchers believe that this discovery could lead to the identification of other unknown species in the region, expanding our understanding of species distribution and the ecological connectivity between regions.
Zhurong Rover

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
Chinese rover helps find evidence of ancient Martian shoreline.
Mission Overview:
- Rover: Zhurong, part of China’s Tianwen-1 Mars exploration program.
- Mission Launch: Zhurong landed in 2021 in the Utopia Planitia region of Mars' northern hemisphere.
- Key Discovery: Evidence of an ancient ocean on Mars, suggesting a habitable past for the planet.
Key Findings:
- Geological Features Indicating a Coastline:
- Data from Zhurong and orbiting spacecraft (Tianwen-1 Orbiter, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) revealed geological features such as troughs, sediment channels, and mud volcano formations, suggesting the existence of a Martian coastline.
- Features indicate both shallow and deeper marine environments, supporting the idea of a past ocean.
- Age of the Ocean:
- The ocean likely existed around 3.68 billion years ago, with its surface potentially frozen in a geologically short period.
- The ocean is thought to have disappeared by 3.42 billion years ago.
Evolutionary Scenario of Mars:
- At the time of the ocean, Mars might have already begun transitioning away from a habitable planet, losing much of its atmosphere and becoming cold and dry.
- The ocean may have formed after Mars' climate began to change, suggesting that it was once more hospitable, possibly capable of supporting microbial life.
Implications for Life on Mars:
- The presence of water, a key ingredient for life, raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in its early history.
- When Mars had a thick, warm atmosphere, conditions might have been favorable for life, as microbial life would have been more likely to exist.
Significance of Zhurong's Contribution:
- Zhurong exceeded its original mission duration of three months, operating until May 2022, helping provide key data to understand Mars' ancient water history.
- The discovery adds to ongoing efforts to study the disappearance of water on Mars and its implications for the planet's habitability.
Future Exploration:
- Other studies, including seismic data from NASA’s InSight lander, suggest that liquid water might still exist deep beneath the Martian surface, hinting at the possibility of finding water in the planet's subsurface in the future.
World’s First CO? to Methanol Plant

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- NTPC has achieved the first-ever synthesis of CO? (captured from flue gas) and hydrogen (produced via a PEM electrolyzer) into methanol at its Vindhyachal plant.
- This marks a significant step in carbon management technology, aimed at advancing sustainable fuel production.
About CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Dioxide Capture:
- CO? is captured from industrial sources, such as power plants, or directly from the atmosphere.
- Hydrogen Production:
- Renewable energy sources like solar or wind power are used to produce hydrogen through water electrolysis.
- Methanol Synthesis:
- The captured CO? is combined with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to produce methanol, typically under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Benefits of CO?-to-Methanol Conversion:
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU):
- This technology reduces the impact of CO? on the atmosphere by converting it into useful products.
- Renewable Fuel Source:
- Methanol produced through this process can be used as a fuel for transportation, power generation, or as a feedstock for chemicals.
- Energy Storage:
- Methanol offers a more practical storage and transportation option than hydrogen, making it a potential energy storage solution and aiding the transition to hydrogen-based energy systems.
- Versatile Feedstock:
- Methanol is widely used in producing chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting various industrial applications.
What is Methanol?
- Brief: Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest form of alcohol. It is a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinctive odor.
- Key Properties:
- Colorless, miscible with water, toxic if ingested, flammable.
One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) Initiative

- 10 Nov 2024
In News:
- India is in talks with Oman, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Maldives, and Singapore to establish cross-border electricity transmission lines.
- This is part of the ambitious OSOWOG initiative to create a global renewable energy grid.
Key Points:
- Proposed by the Prime Minister of India at the 2018 International Solar Alliance (ISA) Assembly.
- Aims to create a transnational electricity grid that delivers power worldwide.
- Led by India and the UK, in collaboration with ISA and the World Bank Group.
Vision of OSOWOG:
- Connect regional grids through a common infrastructure for the transfer of renewable energy, focusing on solar power.
- Harness solar and other renewable energy from regions where the sun is shining and efficiently transmit it to areas of need.
- Aim to provide power to 140 countries using clean and efficient solar energy.
Phases of OSOWOG:
- Phase 1:
- Connect the Indian grid with grids in the Middle East, South Asia, and South-East Asia.
- Share solar and other renewable energy resources.
- Phase 2:
- Expand the interconnected grid to include renewable resources from Africa.
- Phase 3:
- Achieve a global interconnection aiming for 2,600 GW by 2050.
- Integrate as many countries as possible into a single renewable energy grid.
Global Collaboration:
- Involves national governments, international organizations, legislators, power operators, and experts.
- Focus on accelerating infrastructure development for a clean energy-powered world.
Adaptation Gap Report 2024
- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Adaptation Gap Report 2024, published by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), underscores the urgent need for enhanced climate adaptation efforts, particularly through increased financial support for developing countries. The report, titled Come Hell and High Water, provides an annual assessment of global adaptation progress in planning, implementation, and financing.
Key Findings
- Adaptation Gap:
- The adaptation finance gap is estimated at $187–359 billion per year.
- Current adaptation finance falls short, with only $28 billion provided in 2022, meeting just 5% of projected needs.
- Adaptation Progress:
- International public adaptation finance to developing countries rose to $27.5 billion in 2022, up from $19 billion in 2019, reflecting progress toward the Glasgow Climate Pact's goal of doubling finance by 2025.
- Significance of Adaptation:
- Ambitious adaptation measures could reduce global climate risk by 50%.
- For instance, $16 billion annually in agriculture could prevent climate-induced hunger for 78 million people.
- Impact of Global Warming:
- According to UNEP's Emissions Gap Report 2024, global temperatures may increase by 2.6°C–3.1°C above pre-industrial levels by 2100.
- Developing countries face severe vulnerabilities, evidenced by recent floods in Nepal, Nigeria, and Chad.
- National Adaptation Plans (NAPs):
- While 171 countries have at least one adaptation policy, progress in implementation remains slow.
- 10 countries have shown no interest in developing adaptation policies.
Challenges in Adaptation Financing
- Financial Burden: Adaptation projects such as seawalls and resilient infrastructure are costly for developing nations.
- Funding Shortfalls:
- Developed nations have failed to meet financial commitments like the $100 billion goal set for 2020.
- The adaptation finance gap remains significant in non-private sector-funded areas, such as ecosystem preservation.
- High-Interest Loans: Much current funding relies on high-interest loans, increasing the debt burden for recipient countries.
Recommendations
- Adopt New Financing Goals: Establish an ambitious New Collective Quantified Goal for climate finance at COP29.
- Strategic Adaptation Financing:
- Shift from project-based to anticipatory and transformational financing.
- Invest in harder-to-finance areas like ecosystem preservation and cultural heritage.
- Alternative Financing Models: Encourage risk finance, resilience bonds, debt-for-adaptation swaps, and payments for ecosystem services.
Global and Indian Initiatives
Global Initiatives:
- Paris Agreement: Sets a global adaptation goal to enhance resilience.
- UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience: Introduced at COP28, focusing on agriculture, water, and health adaptation targets.
- Adaptation Fund: Provides project funding for developing nations under the Kyoto Protocol.
Indian Initiatives:
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): Includes eight missions, such as the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC).
- Sectoral Schemes:
- MISHTI: Mangrove initiative for shoreline protection.
- Amrit Dharohar: Enhances wetland ecosystems.
- India's adaptation spending accounted for 5.6% of GDP in 2021–2022.
Protected Planet Report 2024

- 08 Nov 2024
In News:
The Protected Planet Report 2024, released by UNEP-WCMC and IUCN, evaluates global progress toward achieving Target 3 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF). This target aims to conserve 30% of Earth's terrestrial, inland water, coastal, and marine areas by 2030.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Current Global Coverage
- Land and Inland Waters: 17.6% protected.
- Oceans and Coastal Areas: 8.4% protected.
- Progress since 2020: Minimal increase (<0.5% for both realms), equivalent to an area twice the size of Colombia.
- Remaining Challenges to Achieve Target 3 by 2030
- Land: An additional 12.4% of land area must be protected (equivalent to Brazil + Australia).
- Ocean: 21.6% more marine areas must be safeguarded (larger than the Indian Ocean).
- Key Gaps:
- Only 8.5% of protected areas on land are well-connected.
- Only one-fifth of the areas critical for biodiversity are fully protected.
- Biodiversity representation remains uneven, with some ecological regions having no protection at all.
- Governance and Effectiveness Issues
- Less than 5% of protected land and 1.3% of marine areas have management effectiveness assessments.
- Only 0.2% of protected land and 0.01% of marine areas have undergone equitable governance assessments.
- Indigenous governance covers less than 4% of protected areas despite Indigenous and traditional territories covering 13.6% of the terrestrial areas.
- Ocean Conservation Progress: Most progress is in national waters; however, areas beyond national jurisdiction (the high seas) remain underrepresented (<11% coverage).
- Data Deficiency: Insufficient data to measure biodiversity outcomes, equity, and governance in protected areas.
Importance of Target 3
- Biodiversity Benefits: Protected areas play a critical role in halting and reversing biodiversity loss.
- Ecosystem Services: These areas contribute to clean air, water, climate regulation, and food security.
- Cultural and Economic Significance: They uphold the rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities, ensuring equitable governance and sustainable resource use.
Key Recommendations
- Accelerate Conservation Efforts:
- Expand protected and conserved areas with a focus on biodiversity hotspots.
- Ensure areas are ecologically connected and effectively managed.
- Strengthen Indigenous and Local Contributions:
- Recognize and support the stewardship of Indigenous Peoples and local communities.
- Ensure their voices and knowledge systems are integrated into conservation planning.
- Improve Governance and Equity:
- Address gaps in equitable governance and include rights-based approaches.
- Global Cooperation:
- Increase international financing to developing nations for biodiversity conservation.
- Foster cross-border partnerships and support data-sharing initiatives.
- Enhance Data Availability:
- Collect and disseminate data on the effectiveness of protected areas and their biodiversity outcomes.
India’s Role and Strategy
- Commitment to KM-GBF: India updated its National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) to align with the KM-GBF goals, aiming to protect 30% of natural areas by 2030.
- Focus on Restoration: Prioritizes the restoration of forests, rivers, and other ecosystems to maintain essential resources like clean air and water.
- Indigenous Participation: India emphasizes integrating Indigenous territories into its conservation framework.
Okinawicius tekdi
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
Researchers have recently discovered a new species of jumping spider in the Baner Hill area, underscoring the region's rich biodiversity and the growing need to preserve the natural landscapes around Pune.
About Okinawicius tekdi:
- The newly identified species, named Okinawicius tekdi, is a jumping spider that contributes to the growing diversity of India's spider population, now numbering 326 species of jumping spiders.
- The name "tekdi" comes from the Marathi word for "hill," reflecting the spider's habitat.
- The last time a spider species was identified in Pune was over three decades ago.
About Jumping Spiders:
- Jumping spiders belong to the family Salticidae and are known for their distinctive eight legs and remarkable jumping ability.
- These spiders possess a segmented body, a tough exoskeleton, and jointed legs.
- In addition to their agility, they are famous for spinning webs that they use to capture their prey.
World Cities Report 2024
- 07 Nov 2024
In News:
The World Cities Report 2024, released by UN-Habitat, highlights the urgent need for cities to address climate change, both as victims and major contributors.
Key Findings of the Report
- Temperature Increases by 2040: Nearly 2 billion people living in urban areas are projected to face at least a 0.5°C rise in temperature by 2040, exposing them to heatwaves and other climate-related risks.
- Urban Vulnerability and Climate Risk:
- Cities are disproportionately affected by climate change while being major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, which exacerbates their vulnerability to events like floods, cyclones, and heatwaves.
- The urban population is facing a dual challenge: increased heat and extreme weather events such as flooding, cyclones, and erratic rainfall.
- Sea-Level Rise and Coastal Risks: Over 2,000 cities in low coastal areas, many located under 5 meters above sea level, are at heightened risk from sea-level rise and storm surges, potentially affecting more than 1.4 billion people by 2040.
- Riverine Flooding: Flood exposure in cities is growing 3.5 times faster than in rural areas, with 517 million people in urban areas projected to be exposed to riverine flooding by 2030.
- Investment Gap: Cities require between USD 4.5 trillion and USD 5.4 trillion annually to build and maintain climate-resilient systems, but current investments stand at only USD 831 billion, highlighting a massive funding shortfall.
- Decline in Urban Green Spaces: The average share of urban green spaces has dropped from 19.5% in 1990 to 13.9% in 2020, reducing cities' ability to absorb carbon, manage heat, and provide essential ecosystem services.
- Vulnerable Communities: Informal settlements and slums, often situated in environmentally sensitive areas, are disproportionately affected by climate impacts. These communities lack adequate infrastructure and are often unable to invest in necessary upgrades due to eviction fears or lack of legal recognition.
- Green Gentrification: While climate interventions like park creation can provide environmental benefits, they can also lead to green gentrification—displacing low-income households or increasing property values and rents, thus pricing vulnerable communities out.
Contributing Factors to Urban Global Warming
- Energy Consumption: Urban areas account for 71-76% of global CO? emissions from energy use, driven by dense populations, industrial activities, transportation, and high-energy demand for buildings.
- Industrial Activities: Urban industries and power plants release a variety of greenhouse gases (GHGs), including CO?, methane (CH?), and nitrous oxide (N?O).
- Land Use Changes: Urban expansion leads to deforestation and reduced carbon absorption, contributing to global warming. Urban land areas are expected to more than triple by 2050, accelerating environmental degradation.
- Waste Generation: Decomposing waste in landfills releases methane, a potent GHG, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Urban Heat Islands (UHIs) occur when cities absorb and retain more heat due to their dense infrastructure (asphalt, concrete, and buildings), increasing local temperatures and energy consumption.
Impacts of Global Warming on Cities
- Heatwaves: Cities, especially in warmer regions like India, are experiencing more severe heatwaves and rising temperatures.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: UHIs increase the intensity of heatwaves, particularly in high-density cities, where buildings and roads trap heat, exacerbating energy demands and public health risks.
- Coastal Flooding: Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities with flooding and storm surges, displacing communities and disrupting economies.
- Wildfire Seasons: Warming temperatures and prolonged droughts increase the risk of wildfires in urban areas, particularly in forest-adjacent cities.
India's Climate Initiatives for Urban Areas
- Smart Cities Mission: Focuses on developing sustainable urban infrastructure, promoting smart technologies, and enhancing resilience to climate impacts.
- AMRUT Mission: Aims to provide basic infrastructure and sustainable urban development in cities, including water supply, sewage, and green spaces.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban: Focuses on improving waste management and reducing pollution in urban areas.
- FAME India Scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles): Promotes electric vehicles to reduce urban air pollution and carbon emissions.
- Green Energy Corridor (GEC): Facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources into the national grid, encouraging clean energy use in urban centers.
Spraying Diamond Dust to cool the Earth

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
- A new study in Geophysical Research Letters suggests that diamond dust could be more effective than any other material in reflecting solar radiation.
- Objective: The goal is to reduce global temperatures by 1.6°C by spraying approximately 5 million tonnes of diamonds annually into the atmosphere.
Background of Geoengineering Solutions:
- Geoengineering refers to large-scale interventions aimed at altering Earth's natural climate system to counteract global warming.
- One proposed solution involves spraying diamond dust in the Earth's upper atmosphere to cool the planet.
- This approach is part of Solar Radiation Management (SRM), which seeks to reflect sunlight away from Earth, thereby reducing global temperatures.
- Previous Materials Considered: Sulphur, calcium, aluminium, silicon, and other compounds have been studied to perform a similar function.
Context of Geoengineering and Climate Crisis:
- Inadequate Progress: Current efforts to mitigate global warming, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, have been insufficient. Global temperatures have continued to rise, and targets like the Paris Agreement's 1.5°C are increasingly out of reach.
- Rising Global Temperatures:
- 2023: Global temperatures were approximately 1.45°C higher than pre-industrial levels.
- Projected Challenge: To meet the Paris goal, global emissions must be reduced by at least 43% by 2030. However, current actions will likely result in only a 2% reduction by 2030.
Geoengineering Technologies:
- Geoengineering Methods:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM): Reflects sunlight to cool Earth.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR): Involves capturing and storing CO?.
- SRM Techniques:
- SRM draws inspiration from natural events like volcanic eruptions, where large amounts of sulphur dioxide form particles that reflect sunlight.
- Mount Pinatubo (1991): One of the largest eruptions, which temporarily reduced global temperatures by 0.5°C due to the sulphur dioxide released.
Diamond Dust vs Other Materials:
- Study Comparison: Diamonds were found to be the most effective material compared to other compounds (sulphur, calcium, etc.) for reflecting solar radiation.
- Quantity Needed: To achieve a cooling of 1.6°C, 5 million tonnes of diamonds would need to be dispersed into the upper atmosphere each year.
Broader Geoengineering Context:
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- CCS is already in practice, where CO? emissions from industries are captured and stored underground to reduce atmospheric carbon.
- However, CCS faces high costs and scalability issues, and safe storage sites for CO? are limited.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): A more advanced method where CO? is directly removed from ambient air, but it faces even greater challenges in terms of infrastructure and cost.
VINBAX 2024 Exercise

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
The 5th Edition of Vietnam Indian Bilateral Army Exercise “VINBAX 2024” had commenced at Ambala.
Key Participants
- Indian Army: A contingent of 47 personnel from the Corps of Engineers, along with personnel from other arms and services.
- Vietnam People's Army: A similar-sized contingent representing Vietnam's military forces.
- Bi-Service Participation: For the first time, personnel from both Army and Air Force of India and Vietnam are participating.
Objectives of VINBAX 2024
- Joint Military Capability Enhancement:
- Focus on enhancing joint military capabilities of both countries, specifically in the deployment of Engineer Companies and Medical Teams.
- Peacekeeping Operations (UN Context):
- The exercise prepares both sides for United Nations Peacekeeping Operations (PKO), under Chapter VII of the UN Charter, which deals with peace enforcement actions.
- Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR):
- The exercise includes a 48-hour validation exercise with demonstrations of Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- The HADR component will include equipment displays to assess the technical standards of both contingents while executing disaster relief and humanitarian missions in peacekeeping contexts.
Key Activities & Events
- Field Training Exercise: The exercise includes a field training component, with a larger scope than previous editions, focusing on:
- Engineer Tasks.
- Medical Support.
- Disaster Relief Operations.
- Validation Exercise: A critical 48-hour validation exercise to test the preparedness of the two forces in providing HADR, including:
- Demonstrations of disaster relief operations.
- Equipment displays to showcase capabilities in managing and executing peacekeeping and humanitarian operations.
- Cultural Exchange: The exercise will also provide an opportunity for cultural exchange, where the troops will learn about the social and cultural heritage of each other.
Background of VINBAX
- Inception: VINBAX was first conducted in 2018 as part of the growing defense cooperation between India and Vietnam. The inaugural edition took place in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh.
- Alternating Locations: The exercise alternates between India and Vietnam every year.
- Previous Editions:
- 2023 Edition: Held in Vietnam.
- Current Edition: This is the 5th edition, conducted in India (Ambala and Chandimandir).
Indian Defense Engagements in Southeast Asia
- India-Indonesia Joint Special Forces Exercise (Garud Shakti 2024): Held from November 1-12, 2024, in Cijantung, Jakarta, strengthening ties with Indonesian special forces.
- Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX 2024): Held from October 23-29, 2024, in Visakhapatnam, focusing on maritime security cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
Proba-3 Mission

- 06 Nov 2024
In News:
Europe's Proba-3 mission to arrive in India for launch aboard PSLV-XL by ISRO
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The Proba-3 mission, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), aims to observe the Sun’s corona by creating an artificial solar eclipse. This will allow continuous observation of the Sun’s faint outer atmosphere, which is typically only visible during a natural solar eclipse.
- Key Features:
- Artificial Solar Eclipse: The two spacecraft will fly in formation to maintain a shadow between them, enabling the uninterrupted observation of the solar corona.
- Formation Flying: The satellites must maintain a precise formation with an accuracy of one millimetre, equivalent to the thickness of a fingernail.
Mission Details
- Launch Date: Scheduled for December 4, 2024.
- Launch Location: Satish Dhawan Space Centre near Chennai, India.
- Launch Vehicle: The PSLV-XL rocket developed by ISRO will be used for the launch.
- Spacecraft Mass: The combined mass of the two spacecraft is 550 kg.
- Orbit: The spacecraft will be placed in a highly elliptical orbit with a maximum altitude of 60,000 km to facilitate the precise formation flying.
- This high altitude minimizes Earth’s gravitational pull and reduces the amount of propellant required to maintain their positions during the mission.
Mission Significance
- Solar Observation: The primary objective is to observe the Sun’s corona, which has been challenging to study due to its faintness. The artificial eclipse will allow continuous data collection on solar activity.
- Formation Flying: This technology will allow the two satellites to maintain autonomous flight with millimetre-level precision, which is a significant advancement in satellite formation control.
- Six-Hour Observation Windows: Each formation flying session will last for up to six hours, during which the satellites will observe the Sun's corona.
Technological and Scientific Contributions
- ASPIICS Instrument: The ASPIICS (AStronomical PIcture Camera for the Intense Corona of the Sun) will be the mission's primary instrument, developed by the Royal Observatory of Belgium. It will provide crucial data on solar activity and space weather.
- International Collaboration: The mission is a collaborative effort involving 14 ESA member states and various organizations across Europe.
- Mission Control: The mission will be managed from the ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Belgium, with significant pre-launch training and preparations already underway.
ISRO's Role and Historical Context
- Launch by ISRO: The Proba-3 mission will be ISRO’s first launch for ESA since 2001, marking an important milestone in India-Europe space cooperation.
- PSLV-XL Rocket: ISRO’s PSLV-XL rocket is known for its reliability and capability in deploying satellites into precise orbits. It is well-suited to carry the 550 kg Proba-3 duo into a highly elliptical orbit for the mission.
India's Green Leap

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
India's journey toward a sustainable energy future has gained significant momentum with a series of policy reforms designed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and accelerate the shift to clean energy. The recent Asia-Pacific Climate Report from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) highlights India's remarkable progress in reforming its fossil fuel subsidy system and its efforts to foster renewable energy, positioning the country as a leader in the region's green transformation.
Key Highlights from the Report:
India's Fossil Fuel Subsidy Reform
- India has successfully reduced fossil fuel subsidies by 85%, from a peak of $25 billion in 2013 to just $3.5 billion by 2023.
- The reform strategy is built on a "remove, target, and shift" approach, which involved phasing out subsidies on petrol and diesel from 2010 to 2014, followed by incremental tax hikes on these fuels through 2017.
- These fiscal changes created space for funding renewable energy projects, such as solar parks, electric vehicle initiatives, and infrastructure improvements.
Role of Taxation in Supporting Clean Energy
- Between 2010 and 2017, India introduced a cess on coal production and imports, which contributed significantly to funding clean energy projects. Approximately 30% of the cess was directed to the National Clean Energy and Environment Fund.
- This funding supported major renewable energy initiatives, including the National Solar Mission and Green Energy Corridor project, helping reduce the cost of utility-scale solar energy and expand off-grid renewable energy solutions.
- The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017 altered the financial landscape, redirecting the cess funds to GST compensation rather than directly to clean energy.
Government Schemes and Initiatives
- India is advancing its clean energy agenda through several key government schemes:
- National Green Hydrogen Mission: Aimed at establishing India as a leader in green hydrogen production.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme: Focused on promoting solar energy among farmers, allowing them to produce renewable power.
- PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana: A program designed to provide solar energy access to rural communities, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
A Strategic Shift: From Subsidies to Clean Energy
- India’s subsidy reforms are an important part of its strategy to transition from a reliance on fossil fuels to a focus on renewable energy investments.
- These changes reflect India’s long-term goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070, as outlined in its climate action plans.
Global Significance of India’s Efforts
- The reduction in fossil fuel subsidies and the surge in clean energy investment serve as a model for other nations seeking to balance economic development with climate action.
- India’s approach demonstrates that policy reforms and innovative financing mechanisms can be used to accelerate the transition to a cleaner, greener economy while creating job opportunities and fostering economic growth.
IUCN’s First Global Tree Assessment

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
More than one in three tree species threatened with extinction, finds IUCN’s first Global Tree Assessment
Key Highlights:
Global Tree Extinction Risk:
- 38% of the world’s tree species are now facing the risk of extinction — over one in three tree species is at risk.
- This means 16,425 out of 47,282 tree speciesanalyzed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) are under threat.
- Threatened tree species outnumber all threatened birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians combined, highlighting the urgent need for conservation action.
Key Drivers of Threat:
- Deforestation: The primary threat to trees is deforestation, driven by agriculture, livestock rearing, and urban development, especially in tropical regions.
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increasingly frequent storms exacerbate the threats, particularly in tropical regions and islands.
- Invasive Species & Pests: Non-native species, pests, and diseases are adding pressure to vulnerable tree populations.
Geographic Vulnerabilities:
- Islands are particularly vulnerable, with a high proportion of threatened species due to habitat destruction and urbanization.
- South America, which boasts the highest tree diversity, faces significant threats, with 3,356 out of 13,668 species at risk, mainly due to deforestation for agriculture.
Ecological and Economic Importance of Trees:
- Trees play a fundamental role in carbon, water, and nutrient cycles, and are critical for soil formation and climate regulation.
- The loss of trees poses a growing threat to thousands of other species of plants, fungi, and animals.
- Trees are essential for local communities, providing resources such as timber, medicines, food, and fuel. Over 5,000 species of trees are used for timber and construction, while more than 2,000 species are vital for food, fuel, and medicine.
Conservation Status:
- Tree species are threatened across 192 countries.
- The assessment is the first global analysis of the conservation status of trees, enabling better-informed conservation decisions.
Positive Actions and Strategies:
- Successful community-driven conservation efforts have had positive outcomes in places like the Juan Fernández Islands, Cuba, Madagascar, and Fiji.
- Some countries, including Ghana, Colombia, Chile, and Kenya, already have national strategies for tree conservation.
- Ex-situ conservation, such as seed banks and botanical gardens, is also crucial to safeguard species that may not survive in the wild.
Urgent Call for Action:
The IUCN Global Tree Assessment underlines the urgent need for enhanced conservation efforts, including:
- Habitat protection and restoration.
- Ex-situ conservation through seed banks and botanical gardens.
- Diversified and species-focused reforestation strategies.
- Supporting community-led conservation initiatives to safeguard vulnerable tree species.
Asia-Pacific Climate Report 2024

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Climate change to put APAC GDP on thin ice with 41% melt by 2100.
Key Highlights:
- Economic Losses Due to Climate Change:
- APAC Region: High-end greenhouse gas emissions could reduce GDP by 17% by 2070 and 41% by 2100.
- India: Projected to experience a 24.7% GDP loss by 2070, with neighboring countries like Bangladesh (30.5%), Vietnam (30.2%), and Indonesia (26.8%) facing even steeper declines.
- Major Drivers of Economic Losses:
- Sea-Level Rise: Up to 300 million people at risk of coastal flooding by 2070. Annual damages could reach $3 trillion by 2070.
- Labour Productivity: The APAC region could lose 4.9% of GDP from reduced labour productivity, with India facing a sharper 11.6% loss.
- Cooling Demand: Rising temperatures could reduce regional GDP by 3.3%, but India's cooling demands could cut its GDP by 5.1%.
- Flooding and Storms: Increased rainfall and storm intensity will exacerbate flooding and landslides, particularly in mountainous regions like the India-China border, where landslides could rise by 30-70% under severe warming.
- Impact on Key Sectors:
- River Flooding: By 2070, annual riverine flooding could cause $1.3 trillion in damages across the APAC, affecting over 110 million people. India could face over $1,100 billion in flood-related damages annually.
- Forest Productivity: Climate change could reduce forest productivity by 10-30% by 2070 across APAC. India could see losses over 25%, making it one of the hardest-hit countries, alongside Vietnam and Southeast Asia.
- Climate Risks and Vulnerabilities:
- Coastal Flooding: Coastal flooding could lead to widespread economic damage, with India expected to suffer significant losses, particularly in coastal areas.
- Ecosystem Threats: Intensified storms, rainfall, and landslides will affect ecosystems, forests, and agriculture across the region.
- Climate Change and Adaptation Needs:
- Investment Requirements: Developing Asia requires $102–431 billion annually for climate adaptation, far exceeding the $34 billion tracked from 2021 to 2022.
- Private Investment: The report highlights the need for greater private climate investment and regulatory reforms to attract capital for adaptation initiatives.
- Renewable Energy: APAC is well-positioned to embrace renewable energy for a net-zero transition, and the use of carbon markets could help achieve climate goals cost-effectively.
- Regional Net-Zero Goals and Progress:
- Net-Zero Targets: 36 out of 44 Asian economies have set net-zero emissions targets, but only 4 have legally committed to these goals. India and China target 2070 and 2060, respectively, while many OECD countries aim for 2050 targets.
- Policy Gaps: Developing Asia needs clearer policies and increased financing to meet climate ambitions. Institutions like ADB are crucial in supporting these efforts.
- Action Plan for the Future:
- Urgent Climate Action: The report stresses the importance of coordinated action to address escalating climate risks.
- Enhanced Adaptation Finance: There is a need to scale up adaptation-focused finance to tackle the growing climate challenges facing the region.
India's Vulnerability and Climate Challenges:
- Labour Impact: India is expected to experience a 11.6% GDP loss due to declining labour productivity, the highest among APAC countries.
- Cooling Demands: A 5.1% reduction in GDP due to increased cooling demand.
- Flood Damage: India’s flood-related losses could surpass $1.1 trillion annually by 2070, with damages to residential and commercial properties.
Bob Khathing

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated the Major Ralengnao 'Bob' Khathing Museum of Valour in Tawang, Arunachal Pradesh, on October 31, 2023, coinciding with National Unity Day (Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel's birth anniversary).
- Significance: The museum honours Bob Khathing's contributions to India's security and the integration of Tawang into India.
Role in the Integration of Tawang:
- Tawang Expedition (1951): In January 1951, Major Bob Khathing, an officer of the Indian Frontier Administrative Service, led the expedition to peacefully integrate Tawang into India.
- Strategic Importance: At the time, there were concerns over Chinese intentions to enter Tibet and realign boundaries. Khathing's mission was crucial to prevent Chinese advances into the area.
- Expedition Details: Khathing set off with Assam Rifles troops from Charduar, Assam, and after overcoming extreme terrain and weather, he reached Tawang. On February 14, 1951, he hoisted the Indian flag, marking Tawang's official integration into India.
- Administrative Setup: Khathing established an administrative framework, including appointing Gaon Buras (village elders) to manage local governance.
Military Service and Recognition:
- World War II Service: Bob Khathing joined the Indian Army in 1939 and earned recognition for his role in the Second World War. He was awarded the Member of the British Empire (MBE) and the Military Cross (MC) for his bravery and leadership.
- Guerrilla Warfare: Khathing was part of the Victor Force, a British-led guerrilla unit tasked with countering the Japanese in Burma and India during WWII. Later, he became the adviser to SANCOL, a force set up to track Japanese forces in the region.
- Military Cross Citation: Khathing was praised for his tireless efforts in organizing local Naga support, gathering intelligence, and participating in successful ambushes, which played a critical role in defeating the Japanese.
Post-War Career and Civil Service:
- Ministerial Role in Manipur: After WWII, Khathing was demobilized and joined the interim government of Manipur, where he served as a minister in charge of the hill areas.
- Integration of Manipur: Following Manipur's merger with India in 1949, Khathing joined the Assam Rifles and served for two years before moving into civil administration.
- Key Positions: He served as Deputy Commissioner of Mokokchung (Nagaland), Development Commissioner in Sikkim, and Chief Secretary of Nagaland.
- Ambassadorship: In 1975, Khathing became India's ambassador to Burma, possibly the first person of tribal origin to hold such a position in independent India.
The Importance of His Contributions:
- Integration of Border Areas: Khathing’s role in integrating Tawang and securing India's northeastern frontier was pivotal in preventing further territorial disputes, especially with China.
- Institutional Development: He helped establish military and security institutions, including the Sashastra Seema Bal, Nagaland Armed Police, and the Naga Regiment, which played important roles in maintaining peace and security in the region.
- Heroic Leadership: Khathing's leadership, both as a soldier and civil servant, continues to be celebrated, symbolized by the Major Bob Khathing Museum of Valour.
NAMO DRONE DIDI

- 05 Nov 2024
In News:
Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare has released the Operational Guidelines of Central Sector Scheme “NAMO DRONE DIDI”
Key Highlights:
Objective:
- Empower women through Self-Help Groups (SHGs) by providing drones for agricultural rental services.
- Aim to support 14,500 SHGs from 2024 to 2026.
Scheme Overview:
- Type: Central Sector Scheme, under the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM).
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Target: Women SHGs for providing drone services in agriculture (e.g., nutrient and pesticide spraying).
Key Features:
- Financial Assistance:
- 80% subsidy (up to ?8 lakh) for SHGs to purchase drones.
- Loans for the remaining 20% via the National Agriculture Infra Financing Facility (AIF) with 3% interest subvention.
- Drone Package:
- Includes drones, spray assemblies, batteries, cameras, chargers, and measurement tools.
- Additional batteries and propellers allow up to 20 acres of coverage per day.
- Training Program:
- One SHG member will be selected for 15 days of mandatory training.
- Focus on drone operation and agricultural tasks (nutrient and pesticide spraying).
- Implementation & Oversight:
- Central Governance: Empowered Committee comprising secretaries from key ministries (Agriculture, Rural Development, Fertilizers, Civil Aviation, and Women and Child Development).
- State Level: Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs) will implement the scheme in coordination with state departments and SHG federations.
- Monitoring: IT-based Management Information System (MIS) through the Drone Portal for real-time tracking and fund disbursement.
- Financial Flexibility:
- SHGs can access loans through other Ministry of Rural Development schemes if needed.
Implementation Details:
- Governance: Central level oversight by the Empowered Committee and state-level execution by Lead Fertilizer Companies (LFCs).
- Ownership: Drones procured by LFCs will be owned by SHGs or their Cluster Level Federations (CLFs).
- Monitoring: The scheme will be tracked and managed through the Drone Portal, ensuring transparency and accountability.
LignoSat
- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
The world's first wooden satellite, LignoSat, is set to launch from the Kennedy Space Center aboard a SpaceX rocket. This pioneering satellite is a collaborative effort between Kyoto University and Sumitomo Forestry Co., marking a significant step towards exploring more sustainable materials in space exploration.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose:The primary goal of LignoSat is to test the viability of using wood in space technology, with a focus on the eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness of using renewable materials in satellite construction. The satellite will be tested aboard the International Space Station (ISS) to assess its durability, strength, and ability to withstand extreme space conditions.
- Material:The satellite is crafted from magnolia wood, chosen for its durability and adaptability. Magnolia was selected for its strength, making it a suitable candidate to endure the harsh conditions of space travel and the intense environmental factors faced in space exploration.
- Mission Details:Once launched, LignoSat will be sent to the ISS, where it will be released from the Japanese Experiment Module (Kibo). Researchers will collect data on the satellite’s performance, examining its ability to handle the challenges of space, including temperature fluctuations and physical strain.
- Environmental Benefits:One of the key advantages of wooden satellites is their environmental impact. Traditional metal satellites, when re-entering the Earth's atmosphere, can generate metal particles that contribute to air pollution. In contrast, wooden satellites like LignoSat are designed to be eco-friendly during reentry. Wood is a natural material that burns up more cleanly during reentry, reducing the potential for harmful atmospheric pollution.
First Science Result from India's Aditya-L1 Mission

- 04 Nov 2024
In News:
- The Aditya-L1 mission, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on September 2, 2023, is India's first dedicated scientific mission to study the Sun.
- Primary Payload: The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), developed by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIAp), Bengaluru, is the spacecraft's main instrument.
Key Highlights:
- First Science Outcome:The first scientific result from the mission, involving VELC, has been released. It successfully estimated the onset time of a coronal mass ejection (CME) that occurred on July 16, 2023.
- CMEs are massive solar eruptions that can disrupt electronics in satellites and communications on Earth.
- Key Findings:
- VELC's Role: The VELC payload was crucial in observing the CME close to the solar surface, providing a detailed understanding of its onset.
- CMEs are typically observed in visible light after they have traveled far from the Sun. However, VELC’s unique spectroscopic observations allowed scientists to study the CME much closer to the Sun's surface.
- Publication:The results will be published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
- Future Significance:
- As the Sun approaches the maximum phase of its current solar cycle (No. 25), CMEs are expected to become more frequent. Continuous monitoring with VELC will provide valuable data for understanding these events.
- Monitoring the thermodynamic properties of CMEs near the Sun is essential to understand their source regions and behavior.
- Mission Details:
- The spacecraft is in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point 1 (L1), about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
- Mission Lifetime: 5 years.
Kodo Millet

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Kodo millet is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections in India. It is one of the 'hardiest crops, drought tolerant with high yield potential and excellent storage properties,' according to researchers
Background on Kodo Millet:
- Kodo millet (Paspalum scrobiculatum), also known as Kodra or Varagu, is a hardy, drought-tolerant crop widely grown in India, especially in Madhya Pradesh.
- It is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections of India and is used to make various dishes like idli, dosa, and rotis.
- Kodo millet is valued for its high yield, nutritional benefits (rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants), and storage properties.
Incident in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- 10 elephants from a herd of 13 died over three days in Madhya Pradesh’s Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve.
- The cause of death was suspected to be mycotoxins associated with kodo millet, particularly Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), which is toxic to animals.
Historical Cases of Kodo Poisoning:
- The first human cases of kodo poisoning were reported in 1922 in the Indian Medical Gazette.
- Animals, including elephants, have also been affected by kodo millet consumption, with documented deaths as early as 1983.
- Cyclopiazonic Acid (CPA), a mycotoxin, was identified as the cause of kodo poisoning in the 1980s.
Why Does Kodo Millet Become Poisonous?
- Kodo millet is grown in dry and semi-arid regions and is vulnerable to fungal infections, particularly Ergot fungus, which produces CPA.
- When the crop encounters rainfall during maturing and harvesting, fungal infection can lead to "poisoned kodo," known locally as 'Matawna Kodoo' or 'Matona Kodo'.
- The mycotoxins in the infected millet are stable and resistant to standard food processing techniques.
Impact of Mycotoxins on Animals:
- Symptoms of poisoning: Vomiting, giddiness, unconsciousness, rapid pulse, cold extremities, limb tremors.
- Nervous and cardiovascular systems are primarily affected, causing liver dysfunction, heart damage, and gastrointestinal issues.
- In severe cases, consumption of infected kodo millet can cause death due to cardiovascular collapse and organ failure.
- Similar symptoms of depression and loss of mobility were observed in animal studies, including in mice.
Solution to Kodo Toxicity:
- Biocontrol agents (organisms that fight harmful pathogens) can help reduce fungal growth and mycotoxin production in kodo millet.
- Good agricultural practices: Sorting, proper storage in airtight containers, and avoiding moisture exposure during threshing can minimize contamination.
- Post-harvest management: Removing infected grains is crucial to preventing the spread of the disease.
Detection of Mycotoxins in Kodo Millet:
- Challenges: Mycotoxins are often undetectable by sight, and traditional methods like chromatography are time-consuming.
- Rapid detection tools: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), lateral flow assays (LFAs), and biosensors offer faster, on-site methods for detecting mycotoxins in kodo millet.
Centre for Science and Environment

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
Centre for Science and Environment release a report on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for Plastic Packaging
Key Findings:
- EPR Guidelines (2022) were a step towards enforcing the "polluter pays" principle, but the system faces significant issues in its implementation and registration processes.
- Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) report, released on October 29, 2024, highlights gaps in the EPR system for plastic packaging and suggests corrective actions.
EPR Guidelines Overview:
- Issued by: Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Objective: Hold producers, importers, brand owners (PIBOs), and plastic waste processors (PWPs) responsible for managing plastic packaging waste.
- Key Requirements:
- PIBOs must register on a centralized portal and set targets for collection, recycling, and reuse of plastic packaging.
- Registration involves compliance with targets on end-of-life recycling and recycled content usage.
Problems Identified in the Current EPR System:
- Low Registration and Enrollment:
- 41,577 registrations on the EPR portal, but a significant discrepancy in the type of stakeholders registered.
- 83% of registered entities are importers, 11% are producers, and only 6% are brand owners.
- Producers contribute 65% of the plastic packaging in the market but have low registration.
- Absence of Key Polluters:
- Manufacturers of virgin plastics are notably absent from the portal, despite being required to register.
- Fraudulent Practices:
- 700,000 fake certificates were generated by plastic recyclers, far exceeding the actual certificate generation capacity.
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) found that such fraudulent activities are undermining the integrity of the system.
- For example, end-of-life co-processing units (e.g., cement plants) claimed to have processed 335.4 million tonnes per annum of plastic waste, while their actual capacity is just 11.4 million tonnes per annum.
- Underreporting and Mismanagement:
- Despite 23.9 million tonnes of plastic packaging being introduced into the market, the CPCB’s estimation of plastic waste generation (4.1 MT annually) is underestimated.
- Lack of Stakeholder Representation:
- Urban local bodies and informal waste collectors—key contributors to plastic waste management—are not included in the EPR framework, which limits their incentives and support.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Incorporate the Informal Sector:
- Recognize informal waste collectors and waste management agencies in the EPR framework to improve traceability and ensure better waste management.
- Eliminate Fraudulent Practices:
- Strict actions need to be taken against fraudulent recyclers and fake certificate issuers to restore credibility to the EPR system.
- Establish Fair Pricing for EPR Certificates:
- Undertake baseline cost studies to determine the true costs of plastic waste management, ensuring fair pricing for recycling certificates and preventing undervaluation.
- Standardize Packaging:
- Focus on product standardization to ensure that packaging materials are uniform and easily recyclable.
- Strengthen Monitoring:
- Improve oversight on the registration process and ensure that all polluters (producers, importers, brand owners) comply with the system’s guidelines.
EPR and Plastic Waste Management: Context and Importance
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy approach where the responsibility of managing the entire lifecycle of plastic products (from production to disposal) lies with the producer.
- It is an essential part of India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules (2016), which mandate the recycling and proper disposal of plastic packaging waste.
Key Elements of EPR:
- Producer Accountability: Producers are responsible for the take-back, recycling, and final disposal of plastic packaging.
- Waste Minimization: Encourages reducing waste at the source by promoting sustainable packaging designs.
- Lifecycle Approach: Considers the entire lifecycle of the product, focusing on sustainability from production to disposal.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Ensures that the cost of waste management is borne by those responsible for generating the waste.
National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) 2024-2030

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The updated NBSAP was released by India at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Overview of the NBSAP (2024-30):
- Title:Updated National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plan: A Roadmap for Conservation of India’s Biodiversity.
- Objective: To provide a comprehensive roadmap for biodiversity conservation, aligning with global frameworks like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Features of the Updated NBSAP:
- Alignment with Global Frameworks:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) adopted in 2022 aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- India’s updated NBSAP aligns with KMGBF’s goals, focusing on biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource use, and ensuring fair benefit-sharing.
- 23 National Biodiversity Targets:
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Reducing threats to biodiversity
- Ensuring sustainable use of biodiversity
- Enhancing tools for biodiversity implementation
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Key Domains of Focus:
- Area-based conservation: Protecting ecosystems and habitats.
- Ecosystem resilience: Enhancing the ability of ecosystems to withstand environmental stressors.
- Recovery and conservation of threatened species.
- Conservation of agrobiodiversity: Ensuring the sustainability of agricultural biodiversity.
- Sustainable management of biodiversity.
- Enabling tools and solutions: Including financial and technical support for implementation.
- Financial Plan and Expenditure:
- Biodiversity Expenditure Review (BER) estimated an average annual expenditure of Rs 32,20,713 crore (FY 2017-2022) for biodiversity conservation.
- Future funding requirements (FY 2024-2030) estimated at Rs 81,664.88 crore annually at the central government level.
- Biodiversity Finance Plan suggests financing solutions, including public finance, corporate social responsibility (CSR), Ecological Fiscal Transfer (EFT), and Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) mechanisms.
- Capacity Building:
- The NBSAP stresses the need for capacity building across various levels—national, state, and local.
- Focus on skills acquisition for biodiversity management and enhancing knowledge to implement conservation strategies.
Implementation Framework:
- Multi-Level Governance:
- At the national level, the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) will oversee implementation with involvement from 22 other ministries.
- State-level: Involves State Biodiversity Boards and Union Territory Biodiversity Councils.
- Local level: Community-driven efforts through Biodiversity Management Committees.
- BIOFIN and Resource Mobilization:
- India is recognized as a leading country in the implementation of the Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN).
- Encouragement for private entrepreneurs, businesses, and international donors to invest in biodiversity through innovative financial instruments like:
- Green Bonds
- Green Funds
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES)
- Incentives for Financial Solutions:
- India aims to explore funding from corporate social responsibility (CSR), ecological fiscal transfers, and access and benefit sharing mechanisms to meet the financial needs for biodiversity conservation.
Challenges and Strategies:
- Challenges India Faces:
- Habitat fragmentation
- Pollution
- Illegal wildlife trade
- Adverse effects of climate change
- Strategic Responses:
- The updated NBSAP provides strategies to address these challenges, ensuring comprehensive conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB)
- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change has constituted a team to enquire into the death of ten elephants in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve of Madhya Pradesh. The team is conducting an independent enquiry in the matter.
- Incident Overview:
- Ten elephants found dead in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve, Madhya Pradesh, between October 29-31, 2024.
- Preliminary cause of death suspected to be poisoning; final cause pending postmortem and toxicological analysis.
- Government Actions:
- Union Government:
- The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) has set up a team to conduct an independent investigation into the deaths.
- Madhya Pradesh Government:
- Constituted a five-member State-level inquiry committee, headed by the Additional Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (APCCF, Wildlife).
- Committee includes members from civil society, scientists, and veterinarians.
- The State Tiger Strike Force (STSF) is conducting field investigations, combing surrounding areas for further clues.
- Other Involved Authorities:
- The Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (PCCF) and Chief Wildlife Warden of Madhya Pradesh are directly supervising the inquiry in Bandhavgarh.
- Senior officials from the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) have visited the site for discussions and investigation.
- Union Government:
About Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB):
- Mandate:
- Combats organized wildlife crime through intelligence gathering and coordination with enforcement agencies.
- Develops wildlife crime data and assists in prosecutions.
- Provides capacity building for wildlife crime enforcement agencies.
- Operations & Initiatives:
- Conducts operations like SAVE KURMA, THUNDERBIRD, WILDNET, and more to counter wildlife crimes.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
Discovery of the First "Black Hole Triple" System

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
Scientists have discovered a "black hole triple" system, which is a rare configuration in space involving one black hole and two stars.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Location: The system is located 8,000 light years away from Earth, in the constellation Cygnus.
- Key Features:
- A black hole at the center, currently consuming a star that is spiraling very close to it.
- A second, more distant star that orbits the black hole every 70,000 years, and another star that orbits it every 6.5 days.
What is a Black Hole Triple System?
- Black Hole and Two Stars: Unlike typical binary systems (comprising a black hole and one other object), this system contains a black hole surrounded by two stars, one nearby and one far away.
- V404 Cygni: The central black hole in the system is the V404 Cygni, one of the oldest known black holes, roughly 9 times the mass of the Sun.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Questions on Black Hole Formation: The discovery raises new questions about how black holes are formed. Traditionally, black holes are thought to form after the explosion of a massive star (supernova), but this system does not follow that model.
- New Formation Theory: Researchers suggest the black hole may have formed via a "direct collapse" process, where a star collapses into a black hole without undergoing a supernova explosion. This is referred to as a "failed supernova".
- In a failed supernova, the star's collapse happens too quickly for the explosive outer layers to be ejected, leading to the formation of a black hole without the typical violent explosion.
Implications for Other Binary Systems:
- The black hole’s gradual consumption of one of its stars may imply that some binary black hole systems could have originally been triple systems, with one star eventually being consumed by the black hole.
Research and Collaboration:
- Study: The discovery was made by researchers at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- Published in: The findings were published in Nature in October 2024.
Additional Context:
- Distance: The system is about 8,000 light years away, which is vast but still observable with advanced telescopes.
- Mystery of the "Failed Supernova": The concept of a failed supernova offers new insights into the life cycle of massive stars and their transformation into black holes.
ISRO's Analogue Space Mission in Ladakh

- 02 Nov 2024
In News:
In a significant leap for the country’s space exploration aspirations, India has embarked on its first analogue space mission in Leh, a landmark step that will attempt to simulate life in an interplanetary habitat to tackle the challenges of a base station beyond Earth.
Mission Overview:
- Objective: To simulate living conditions in an interplanetary habitat, addressing challenges astronauts may face during deep-space missions (e.g., Moon, Mars).
- Goal: Study long-term isolation, habitat design, resource management, and psychological effects on astronauts.
- Partners: ISRO’s Human Spaceflight Centre, AAKA Space Studio, University of Ladakh, IIT Bombay, Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council.
Rationale for Ladakh:
- Geological Similarities: Ladakh’s terrain mirrors Martian and lunar surfaces, making it ideal for testing space technologies.
- Climate: Cold, dry, high-altitude conditions simulate the extreme environments of space.
- Focus Areas: Testing habitat construction, microbial studies, and survival strategies for long-duration space travel.
What are Analogue Space Missions?
- Definition: Simulated space missions on Earth designed to replicate the conditions of space exploration.
- Purpose:
- Test technologies (e.g., life support, habitat design, in-situ resource utilization).
- Study human behavior, psychological impacts of isolation, and operational readiness for extended space travel.
- Relevance: Crucial for preparing astronauts for missions to the Moon, Mars, or asteroids.
Significance of Analogue Missions:
- Technological Testing: Analogue missions help in evaluating systems for habitat design, life support, and health monitoring.
- Human Factors: They provide insights into crew health, teamwork under pressure, and performance during isolation.
- Psychological Studies: Address the impact of confinement, isolation, and communication delays on astronauts.
- Training: Participants (analogue astronauts) are trained for real-world space missions by conducting scientific experiments and managing emergencies.
Global Examples of Analogue Missions:
- NASA’s NEEMO: An underwater mission simulating microgravity conditions to train astronauts for space tasks.
- SIRIUS Program (UAE): Focuses on the psychological impacts of long-duration space isolation, featuring international collaborations.
- Arctic Mars Analogue Svalbard Expedition (AMASE): Uses the extreme Arctic environment of Svalbard to test Mars exploration technologies and procedures.
Relation to India’s Space Aspirations:
- Gaganyaan Mission: ISRO’s human spaceflight mission aiming to send Indian astronauts into space.
- Interplanetary Exploration: The analogue mission supports India’s broader goal of advancing human space exploration and technology development for Mars and beyond.
Melanistic Tigers
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- Odisha government relocated a tigress from Maharashtra’s Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve to Similipal Tiger Reserve, Odisha, to address inbreeding issues among the tiger population.
- The tigress is part of a genetic diversification plan to remedy the increasing number of pseudo-melanistic tigers in the region.
Pseudo-melanistic Tigers:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers, often referred to as "black tigers," exhibit a darker coat with broader, more prominent stripes.
- The mutation leads to the appearance of a mostly black fur, with occasional white-orange stripes.
Genetic Basis:
- This coloration is due to a mutation in the Taqpep gene, which causes the widening and darkening of stripes on the tiger's coat.
- The mutation is linked to genetic drift and inbreeding within the isolated Similipal population.
Historical Context:
- These tigers were once considered mythical until the 1700s, with sightings only being documented in the 1990s and 2017-18.
- The first confirmed genetic evidence of the black tiger appeared when a cub was born in captivity at Oklahoma City Zoo in the 1970s.
Distribution and Prevalence:
- Pseudo-melanistic tigers are predominantly found in Similipal Tiger Reserve, with 27 out of 30 tigers in Odisha exhibiting the trait.
- Other instances of such tigers exist in captivity, such as in Nandankanan Zoological Park (Bhubaneswar) and Arignar Anna Zoological Park (Chennai), both tracing ancestry to Similipal.
Genetic Studies:
- A 2021 study by the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) linked the Taqpep gene mutation to the unique appearance of these tigers.
- The mutation causes a missense change in the gene, replacing Cytosine with Thymine (C1360T), altering the tiger’s coat pattern.
High Frequency of Mutation in Similipal:
- Genetic analyses indicate a high frequency of the Taqpep gene mutation in Similipal tigers, with a 60% chance that a tiger born there will carry the mutated gene.
- Inbreeding and genetic isolation have contributed to this phenomenon, as Similipal’s tiger population is geographically cut off from other populations.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
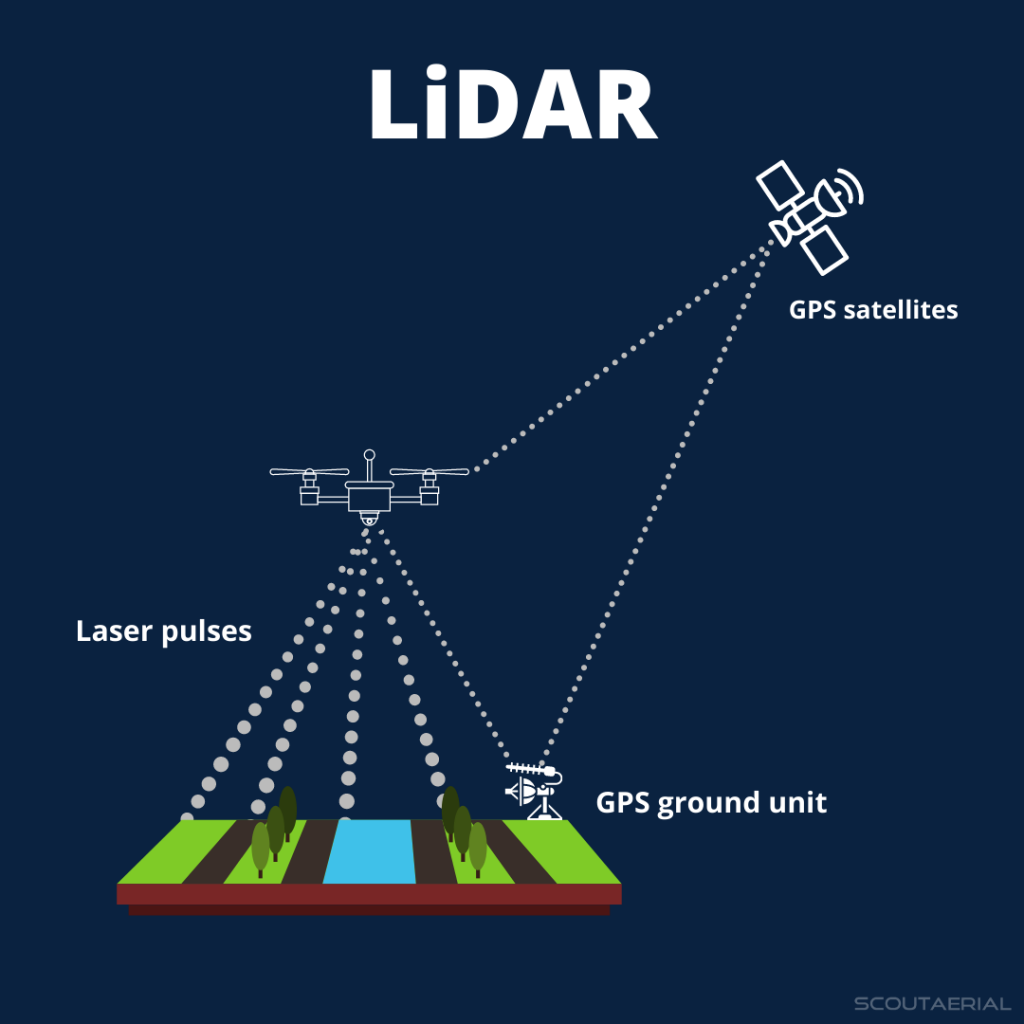
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a cutting-edge remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps of Earth's surface. This technology has recently played a crucial role in discovering a lost Mayan city hidden under the dense Mexican jungle.
What is LiDAR?
- Definition: LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and generate precise 3D models of Earth’s surface.
- Components: The system includes a laser, a scanner, and a GPS receiver. It is usually mounted on an aircraft to map large areas of terrain.
- Data Accuracy: LiDAR can create high-resolution 3D models with vertical accuracy up to 10 cm, making it highly precise for mapping ground elevation.
How LiDAR Works
- Laser Emission: LiDAR sends out rapid laser pulses toward the ground.
- Reflection: These pulses hit the Earth’s surface, reflecting off features like vegetation, buildings, and terrain.
- Measurement: The time it takes for the laser light to travel to the ground and back is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance between the sensor and the surface.
- Point Cloud Data: The reflected light data is collected as a "point cloud", representing all the surfaces it hits, including trees, buildings, and other features.
- Refinement: This point cloud can be processed into a Digital Elevation Model (DEM), stripping away vegetation and structures to reveal the “bare earth,” which highlights features like roads, buildings, and hidden settlements.
Why LiDAR is Useful for Archaeologists
- Large-Scale Surveying: Traditional archaeological methods often involve labor-intensive fieldwork, such as walking over every square meter and manually cutting through thick vegetation. LiDAR, however, allows researchers to quickly survey vast areas of land, even through dense jungle, from the comfort of a lab.
- Visibility Under Vegetation: LiDAR’s ability to penetrate dense foliage and reveal features beneath the surface is a game changer. Even thick tree canopies that obscure the ground are no match for the laser pulses, which can pass through gaps to illuminate hidden structures.
The Discovery of the Lost Mayan City
- The City of Valeriana: Using publicly available LiDAR data from a forest monitoring project in 2013, archaeologist Luke Auld-Thomas discovered a lost Mayan city in Mexico’s Campeche region. The city, named Valeriana, had been hidden for centuries by the thick jungle.
- City Features: The city has all the hallmarks of a Classic Maya political capital, including:
- Multiple enclosed plazas
- Broad causeways
- Temple pyramids
- A ball court
- A reservoir formed by damming a seasonal watercourse
- Historical Significance: Valeriana is believed to date back before 150 CE and may have been a key political and cultural center in the Maya civilization.
Applications of LiDAR Beyond Archaeology
- Geography and Mapping: LiDAR is widely used to generate precise, three-dimensional data about the Earth’s surface, helping geographers and planners.
- Environmental Monitoring: It is also used in forest monitoring, flood risk assessment, and environmental conservation.
- Urban Planning and Engineering: Engineers use LiDAR for creating highly accurate topographical maps and planning infrastructure projects.
Anti-Counterfeiting Ink developed using Luminescent Nanomaterials

- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
- A novel anti-counterfeiting ink has been developed using luminescent nanomaterials, which significantly enhances security in currency, certificates, medicines, and branded goods.
- The ink utilizes the luminescent properties of rare earth ions and bismuth, enabling excitation-dependent luminescence under different light sources, providing a robust solution to combat counterfeiting.
Key Features:
- Multi-Wavelength Luminescence:
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Vibrant blue under 365 nm UV light
- Pink under 395 nm UV light
- Orange-red under 980 nm near-infrared (NIR) light
- These varying color emissions make it difficult for counterfeiters to replicate, as traditional covert tags are visible only under UV light and can be easily duplicated.
- The ink exhibits distinct colors when exposed to various wavelengths of light:
- Enhanced Durability:
- The ink remains effective under a wide range of conditions, including varying light, temperature, and humidity, ensuring long-term usability without degradation.
- Simple Application Method:
- The luminescent nanomaterials are synthesized through a co-precipitation method at 120°C.
- The resulting nanomaterials are then mixed into commercially available PVC ink using sonication, allowing for easy dispersion of nanoparticles.
- The ink is applied using screen printing to create patterns and texts that exhibit distinct color changes under different lighting conditions.
- Security Features:
- The ink combines rare earth ions with bismuth emissions, boosting its encryption and decryption capabilities. This creates a high level of security for applications on high-value items.
Applications:
- Currency and Certificates: Enhances the authenticity of financial instruments and official documents.
- Branded Goods: Protects products from counterfeiting and fraud.
- Medicines: Helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, preventing the distribution of fake medicines.
Benefits:
- Verification: Both consumers and manufacturers can easily verify the authenticity of products, providing an accessible solution to counterfeiting.
- Practical Solution: The ink offers a practical, reliable, and non-invasive method for detecting counterfeit products, addressing a global challenge in various industries.
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change, 2024

- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
The 2024 edition of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Climate Change presents critical insights into the intersection of health and climate change.
Key Findings from the 2024 Report
- Air Pollution and Mortality in India:
- In 2021, air pollution was responsible for 1.6 million deaths in India.
- Fossil fuels (coal and liquid gas) were identified as major contributors, accounting for 38% of these deaths.
- India was ranked as the second-highest emitter of PM2.5 globally in 2022, contributing 15.8% of consumption-based and 16.9% of production-based PM2.5 emissions.
- Impact of Heat Stress:
- In 2023, India experienced 2400 hours (or 100 days) of moderate to high heat stress, particularly during light outdoor activities like walking.
- Heatwaves have become more frequent, with adults over 65 years experiencing 8.4 heatwave days per year, a 58% increase from 1990-1999.
- This increased heat exposure has led to a loss of 181 billion labor hours globally, translating into an economic loss of approximately $141 billion.
- Global and National Trends in Air Pollution:
- PM2.5 is particularly hazardous because it is fine enough to enter the lungs and bloodstream, leading to severe health risks like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO?), Sulphur Dioxide (SO?), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Ozone (O?) were identified as other pollutants contributing to poor air quality in India.
- Health Impact of Extreme Weather:
- The 2023 heatwave was one of the hottest years on record, exacerbating health risks worldwide, especially for the elderly.
- Droughts and heatwaves also contributed to a rise in food insecurity, affecting millions globally.
- Disease Transmission and Climate Change:
- Dengue transmission potential rose by 85% from 1951-1960 to 2014-2023.
- Coastal areas suitable for the spread of Vibrio pathogens, which cause cholera, expanded by 23%, affecting over 210 million people.
- Health Effects of Fossil Fuel Pollution:
- Continued reliance on fossil fuels worsens air quality, leading to health problems such as respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Government Efforts to Tackle Air Pollution in India
- National Clean Air Programme (NCAP):
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Smart City Mission
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME-II)
- NCAP is a national strategy to reduce air pollution across India, with specific action plans for 131 non-attainment cities. The initiative is supported through various central government schemes such as:
- Bharat Stage VI (BS-VI) Emission Norms:
- BS-VI standards aim to significantly reduce vehicular pollution, lowering permissible limits for NOx and particulate matter (PM) emissions from vehicles.
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR):
- SAFAR measures air quality and provides forecasts for metropolitan cities based on real-time data, helping authorities take preventive actions.
- Promotion of Renewable Energy:
- India achieved a record 11% of electricity from renewable energy in 2022. However, 71% of India’s electricity still comes from coal, underscoring the need for a faster transition to cleaner energy sources.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Union Government has decided to introduce four new components under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), aimed at promoting modern farming techniques:Hydroponics, Aquaponics, Vertical Farming&Precision Agriculture
Key Features of MIDH:
- MIDH is a Central Sponsored Scheme (CSS) aimed at the integrated development of various horticulture crops, including:
- Fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa, and bamboo.
- The scheme focuses on pre-production, production, post-harvest management, processing, and marketing activities.
Revision of Operational Guidelines and Cost Norms:
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare is revising the MIDH operational guidelines and cost norms, which were last updated in April 2014.
- The revised guidelines are expected to be released within one month.
- Cost norms are likely to increase by 20% compared to the existing rates, addressing concerns from various states about outdated guidelines.
Reason for Revision:
- Several states, including Odisha, have raised concerns over the old rates under MIDH. For example, Odisha’s Agriculture Minister highlighted that the state was still using 10-year-old rates.
- The Union Cabinet had already approved the rationalization of all CSS operating under the Ministry into two umbrella schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (PM-RKVY)
- Krishonnati Yojana (KY)
Growth in India's Horticulture Sector:
- India’s horticulture production has significantly increased in recent years:
- Total production reached 334.60 million metric tonnes in 2020-21, up from 240.53 million metric tonnes in 2010-11.
- India is now the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, surpassing food grain production.
- MIDH Annual Budget:The annual allocation for MIDH in the current financial year (2024-25) is ?2,000 crore.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Record High in 2023: World Meteorological Organization (WMO)

- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
According to the WMO, the last time the earth had a similar CO2 concentration was 3-5 million years ago, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher and sea levels were 10-20 metres higher than they are now
Key Highlights:
- Record High Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Levels:
- In 2023, annual mean carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rose by 2.3 parts per million (ppm), reaching a new record of 420 ppm.
- This marks the 12th consecutive year with an increase of over 2 ppm in CO2 levels.
- Historical Context:
- CO2 levels not seen in 3-5 million years, when temperatures were 2-3°C higher, and sea levels were 10-20 meters higher than they are today.
- Key GHGs at Record Highs:
- The globally averaged surface concentrations of CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide all reached new highs in 2023.
- Contributors to the Increase in CO2:
- Natural Variability: Natural factors such as large vegetation fires and reduced carbon absorption by forests contributed to higher CO2 levels.
- Human Activity: High fossil fuel emissions from human and industrial activities also played a major role.
- El Niño Phenomenon: The El Niño event led to higher temperatures and drier conditions, exacerbating the rise in GHG levels through increased wildfires and reduced carbon absorption by land sinks.
- Climate Feedback Loop Concerns:
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Climate change could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of GHGs.
- Wildfires could release more carbon, and warmer oceans may absorb less CO2, leading to more CO2 remaining in the atmosphere, accelerating global warming.
- The WMO warned of a vicious cycle:
- Radiative Forcing:
- Radiative forcing (the warming effect on climate) from long-lived GHGs has increased by 51.5% from 1990 to 2023, with CO2 contributing 81% of this increase.
- Methane Concerns:
- Methane saw its largest three-year increase between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase was linked to warmer temperatures and wetter land conditions during the 2020-2022 La Niña conditions, which caused an uptick in methane emissions from natural wetlands.
- Long-Term Impact of CO2:
- Given CO2's long atmospheric lifetime, even with rapid emissions reductions, the warming effect will persist for several decades.
C-295 Aircraft
- 29 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, PM Narendra Modi inaugurated the Final Assembly Line (FAL) plant in Vadodara, Gujarat, for the manufacturing of the C-295 aircraft.
- The plant is a joint venture between Tata Advanced Systems Ltd (TASL) and Airbus.
- This is the first private sector final assembly line for military aircraft in India.
Key Details:
- Manufacturing Timeline
- Contract: In September 2021, India signed a ?21,935 crore deal with Airbus Defence and Space to procure 56 C-295 aircraft to replace the IAF’s ageing Avro-748 fleet.
- Production Plan:
- The first 16 aircraft will be delivered from Airbus’s plant in Seville, Spain, between September 2023 and August 2025.
- The remaining 40 aircraft will be produced in India by TASL, with the first “Made-in-India” C-295 rolling out in September 2026.
- The entire fleet (56 aircraft) is expected to be delivered by August 2031.
- Key Features and Specifications
- Type: Tactical transport aircraft with a capacity of 5 to 10 tonnes.
- Maximum Speed: 480 km/h.
- Cabin Dimensions: 12.7 meters (41 feet 8 inches), the longest unobstructed cabin in its class.
- Passenger Capacity: Can accommodate up to 71 seats.
- Cargo Handling: Rear ramp door for quick loading/unloading and para-dropping.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from airstrips as short as 2,200 feet.
- Significance for the Indian Air Force (IAF)
- The C-295 will enhance the medium-lift tactical capability of the IAF.
- It will replace the ageing Soviet-origin AN-32 aircraft, which are nearing the end of their operational life.
- The C-295 will bridge the capability gap in troop and cargo transport over short and medium distances.
- Indigenous Content
- Indigenous Electronic Warfare Suite: All 56 aircraft will be equipped with an indigenous electronic warfare suite, developed by Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) and Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
- Made-in-India Components: 96% of the work that Airbus does in Spain will be done at the Vadodara plant, making it one of the highest-ever indigenous contributions for an aircraft in India.
- Global Operations of the C-295
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Brazilian jungles, Colombian mountains (South America)
- Deserts of Algeria and Jordan (Middle East)
- Cold climates of Poland and Finland (Europe)
- Military operations in Chad, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
- The C-295 is operational in various challenging terrains worldwide, including:
- Roles and Capabilities
- Tactical Transport: Can transport troops and supplies from main airfields to forward operating airfields.
- Short Take-off and Landing (STOL): Capable of operating from short, unprepared airstrips.
- Low-level Operations: Can conduct low-speed, low-level missions at 110 knots.
- Other Missions: Suitable for casualty evacuation, special missions, disaster relief, and maritime patrol.
ISRO’s First Electric Propulsion-Led Spacecraft (TDS-1)

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India's first home-grown electric propulsion satellite to be launched in Dec.
Key Highlights:
- Objective of TDS-1:
- Purpose: To demonstrate electric propulsion technology for satellite steering, using solar-powered ionized gas.
- Goal: Reduce reliance on chemical fuel, making satellites lighter and more efficient.
- Key Benefits of Electric Propulsion:
- Weight Reduction: The technology can significantly cut down satellite mass. For example, a satellite weighing 4 tonnes could be reduced to around 2 tonnes.
- Fuel Efficiency: By using electric propulsion, the need for chemical fuel is minimized, allowing for a more efficient journey to geostationary orbit.
- Technology Details:
- Fuel Used: Gases like Argon are ionized using solar power to create propulsion.
- Process: The ionized gas is expelled at high speeds to generate thrust, pushing the satellite towards its desired orbit.
- Historical Context:
- The technology was first used in GSAT-9 (South Asia Satellite) in 2017 but with imported Russian components.
- TDS-1 marks the first fully indigenous development of electric propulsion technology by ISRO, highlighting India’s increasing space autonomy.
- Significance for India’s Space Program:
- Self-Reliance: TDS-1 reflects ISRO’s growing capacity to develop advanced space technologies domestically.
- Future Prospects: This breakthrough is expected to lead to more efficient satellite designs, enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global space industry.
Emissions Gap Report 2024

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recently published the Emissions Gap Report 2024, in anticipation of the COP29 meeting of the UNFCCC to be held in Baku, Azerbaijan.
Key Highlights:
- Current Trajectory of Global Warming:
- If countries continue with current environmental policies, global temperatures are expected to rise by 3.1°C above pre-industrial levels.
- This is significantly higher than the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to well below 2°C, with an effort to cap it at 1.5°C.
- Paris Agreement at Risk:
- Even if all Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) are fully implemented (including both unconditional and conditional emissions reduction targets), the world would still experience 2.6°C of warming by 2030.
- This presents a major challenge to achieving the Paris Agreement’s climate goals.
- Urgent Need for Action:
- To limit global warming to 1.5°C, greenhouse gas emissions must peak before 2025 and decline by 43% by 2030.
- The report highlights the emission gap between current pledges and what is required to meet the 1.5°C goal.
- Record High Emissions:
- Global greenhouse gas emissions hit a record 57.1 gigatons of CO? equivalent in 2023.
- This represents an increase of 1.3% compared to 2022, continuing the upward trend from the previous decade.
- India’s Emissions:
- India’s greenhouse gas emissions grew by 6.1% between 2022 and 2023.
- Per capita emissions in India were 2.9 tCO?e in 2022, significantly lower than China (11 tCO?e) and the U.S. (18 tCO?e).
- G20 Countries’ Contribution:
- G20 countries, excluding the African Union, contributed 77% of global emissions in 2023.
- The six largest emitters (including China, U.S., and India) were responsible for 63% of global emissions.
- This shows a significant imbalance in emissions, with developed countries having much higher per capita emissions compared to developing nations like India and Africa.
- Necessary Emissions Cuts:
- To keep the 1.5°C target within reach, global emissions need to be cut by at least 7.5% annually until 2035.
- Cost of bridging the emissions gap: Achieving net-zero by 2050 will require USD 900 billion to USD 2.1 trillion annually, approximately 1% of global GDP.
- Emission Reduction Pathways:
- Renewable Energy: Scaling up solar and wind energy technologies could contribute up to 27% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Forest Conservation: Protecting and restoring forests could provide 20% of the required emissions reductions by 2030.
- Other crucial measures include improving energy efficiency, transitioning to electric vehicles, and focusing on fuel switching in key sectors like transport, industry, and buildings.
- Disparities in Emissions:
- Despite changes over the past two decades, large disparities remain between emissions across regions.
- Developed countries have three times higher per capita emissions compared to the global average, while India, the African Union, and least developed countries continue to have much lower emissions.
- Call to Action:
- UNEP Executive Director Inger Andersen urged countries to act now, stating: “No more hot air, please.” The urgency is to ramp up climate pledges and ensure stronger actions in the upcoming COP29 talks in Baku, Azerbaijan (November 2024), where nations must work to get on a 1.5°C pathway.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- Established: 1972, following the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm.
- Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya.
- Governing Body: The United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA), which is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on environmental matters, with 193 Member States.
- Programs & Initiatives: UNEP leads global efforts on climate action, ecosystem restoration, clean seas, and supports the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Reports: UNEP publishes crucial assessments like the Emissions Gap Report, Global Environment Outlook, and Adaptation Gap Report, influencing global environmental policies.
Hong Kong Discovers Dinosaur Fossils

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
Hong Kong discovers dinosaur fossils for the first time
Key Details:
-
- Significance: This marks the first-ever discovery of dinosaur fossils in Hong Kong.
- Time Period:The fossils date back to the Cretaceous Period, approximately 145 million to 66 million years ago.
- Fossil Details:The fossils belong to a large dinosaur, but further studies are required to determine the exact species.Initial analysis suggests the dinosaur may have been buried by sand and gravel after death, later being washed to the surface by a flood before being buried again.
- Site and Protection:Port Island, part of a geopark, is closed to the public to facilitate ongoing fossil investigations and excavation work.
- Geological and Archaeological Importance:The discovery underscores the significance of Hong Kong's geoparks and its role in preserving and showcasing natural history.This finding contributes to global understanding of prehistoric life, especially in the Cretaceous period.
2024 Global Nature Conservation Index (NCI)
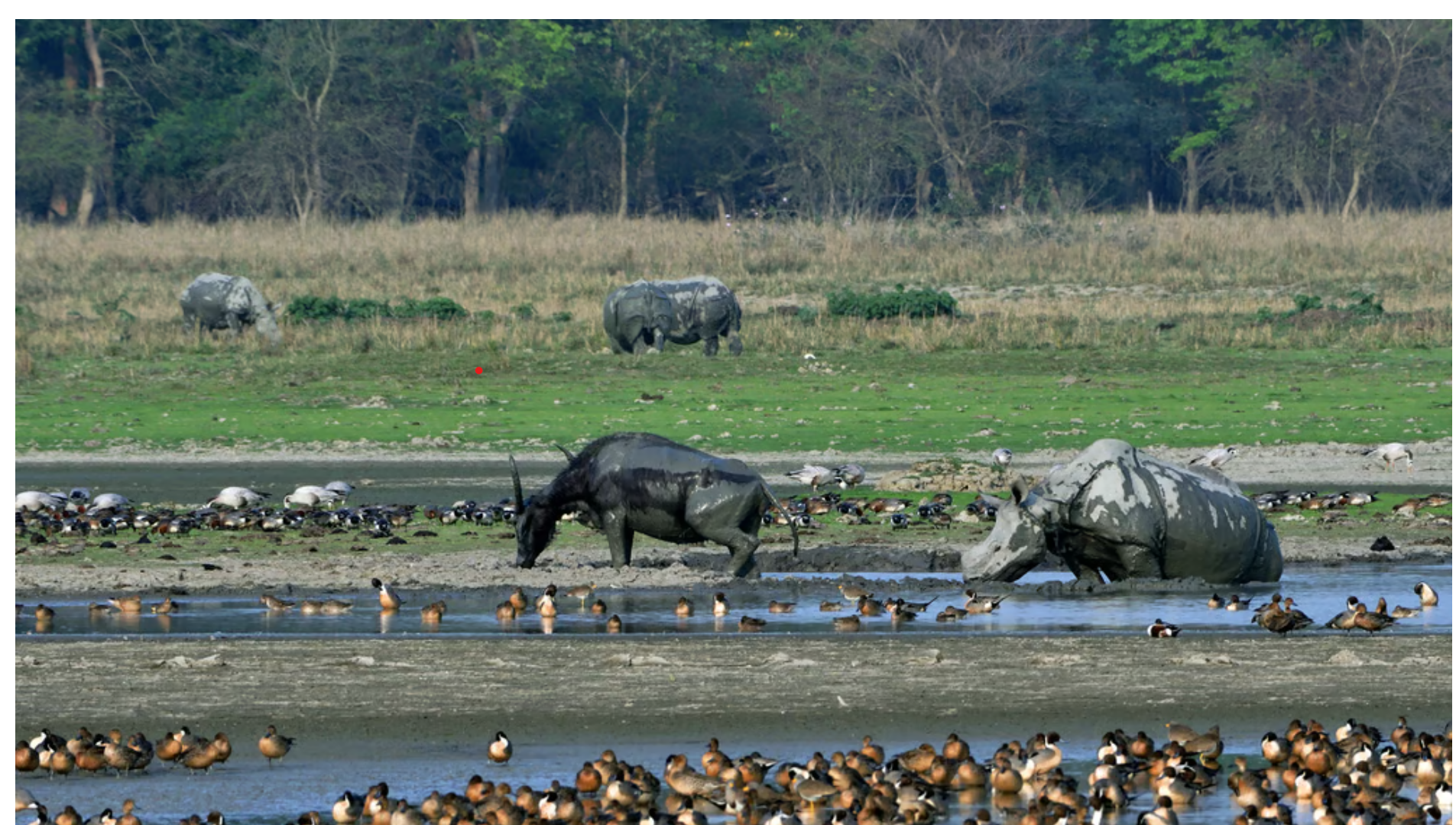

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
India with an abysmal score of 45.5 (out of 100) has been ranked 176th in the Global Nature Conservation Index, 2024.
India's Ranking and Score:
- Rank: India ranks 176th out of 180 countries.
- Score: 45.5 out of 100.
- Context: India is listed among the five "worst performers," alongside Kiribati (180), Turkey (179), Iraq (178), and Micronesia (177).
Key Factors Affecting India’s Ranking:
- Inefficient Land Management: The main contributing factor to India's low ranking.
- Threats to Biodiversity: Rising threats due to habitat loss, deforestation, climate change, and pollution.
- Deforestation: Between 2001 and 2019, India lost 23,300 sq. km of tree cover, exacerbating biodiversity loss.
Focus Areas of the Nature Conservation Index (NCI):
- Land Management: Inefficient land use practices, with 53% of land converted for urban, industrial, and agricultural purposes.
- Biodiversity Threats: Habitat loss, fragmentation, and declining populations of marine and terrestrial species.
- Governance and Capacity: Challenges in enforcement of laws and governance structures that support conservation.
- Future Trends: India faces both opportunities and challenges, given its high population density and rapid development.
Key Findings:
- Land Conversion and Urbanization: High rates of land conversion (53%) for development purposes, contributing to habitat loss.
- Soil Pollution: Issues with pesticide use and soil pollution (low nitrogen index of 0.77), affecting soil health.
- Marine Conservation: Only 0.2% of national waterways and none within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) are protected.
- Deforestation Impact: Loss of 23,300 sq. km of forest between 2001-2019.
- Biodiversity Decline: Despite 40% of marine species and 65% of terrestrial species in protected areas, biodiversity continues to decline—67.5% of marine species and 46.9% of terrestrial species face population decreases.
Marine and Terrestrial Conservation:
- Marine Areas: Need for greater investment in marine conservation, as India's marine protected areas (MPAs) are limited.
- Protected Areas: While 7.5% of India’s terrestrial area is protected, significant threats like climate change and habitat fragmentation persist.
Biodiversity and Climate Change:
- Climate Change Risks: Impacts on vulnerable ecosystems, including coral reefs and alpine regions, further threaten biodiversity.
- Population Growth: India’s rapidly growing population (one of the highest in the world) places constant pressure on natural resources and ecosystems.
Illegal Wildlife Trade:
- Global Ranking: India is the fourth-largest illegal wildlife trader globally, with an annual trade worth approximately £15 billion.
- Call for Action: Stronger enforcement of wildlife protection laws and international cooperation are crucial to combat illegal wildlife trade.
SDGs and India’s Conservation Challenges:
- SDG 14 (Life Below Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land): India faces significant challenges in meeting these Sustainable Development Goals, particularly in protecting marine life and terrestrial ecosystems.
Recommendations for Improvement:
- Stronger Political Will: Political commitment is essential for passing laws that promote sustainable development and biodiversity conservation.
- Enforcement and Funding: Increased funding for environmental initiatives and better enforcement of conservation policies are necessary to address the conservation challenges.
- Sustainable Development: Integrating sustainable land use practices and improving governance structures for conservation are key areas for focus.
New Space Missions and Developments

- 28 Oct 2024
In News:
The Space Commission also approved a joint moon mission with Japan called the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission. For LUPEX, ISRO is developing a different moon lander than the one it used for Chandrayaan-3
New Space Missions and Developments
- Chandrayaan-4 (Moon Mission):
- Type: Sample-return mission.
- Launch: Expected by 2027.
- Cost: ?2,104 crore.
- Objective: Sample collection of moon soil and rock to return to Earth.
- Mission Details: Two LVM-3 launch vehicles will launch components that will dock in Earth orbit before heading to the moon. The samples will be sent back using a bespoke canister.
- Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (LUPEX):
- Collaboration: Joint mission with Japan.
- Objective: Exploration of lunar poles with a new lander design, intended for potential crewed missions in future.
- Venus Orbiter Mission:
- Launch Window: March 2028.
- Cost: ?1,236 crore.
- Objective: Study Venus' surface and atmosphere to understand planetary evolution in the Solar System.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV):
- Development Budget: ?8,240 crore for first three development flights.
- Objective: A new launcher developed with private sector collaboration for future space missions.
Cabinet Approvals for Space Initiatives
- Human Spaceflight Programme (Gaganyaan):
- Four new missions under Gaganyaan, including an uncrewed Gaganyaan flight.
- Focus on developing technologies for India’s first space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), planned by 2028.
- Space-Based Surveillance (SBS) Missions:
- Phase 3: Approval for building 21 ISRO satellites, with 31 additional satellites by private companies.
- Total Cost: ?26,968 crore.
- Development of a Third Launch Pad:
- To support the NGLV and additional space missions at Sriharikota.
Upcoming Satellite Missions
- NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar):
- Launch: Early 2025 on a GSAT launch vehicle.
- Purpose: Earth observation using advanced radar technology.
- Issue: Protective coating added due to high temperatures during testing.
- Proba-3 (European Space Agency):
- Launch: November 29, 2024, aboard PSLV-XL.
- Objective: Study the Sun’s corona using two satellites in formation, mimicking an eclipse to capture unique solar data.
Private Sector Involvement
- Manastu Space & Dhruva Space:
- Collaboration: Testing green propulsion technology for the LEAP-3 mission.
- Technology: Hydrogen-peroxide-based green propulsion system.
- Launch: LEAP-3 mission in 2025.
- Bellatrix Aerospace:
- Project: Prototype satellite for ultra-low earth orbit at 200 km altitude.
- Ananth Technologies:
- Achievement: First private company to assemble, integrate, and test Space Docking Experiment (SpaDEx) satellites for ISRO.
Space Science and Research Updates
- Chandrayaan-3:
- Findings: The crater where Chandrayaan-3 landed is older than the South Pole-Aitken Basin (4.2-4.3 billion years old).
- Data Source: Optical High-Resolution Camera (Chandrayaan-2) and Pragyaan rover (Chandrayaan-3).
- Astrosat (India’s First Space Observatory):
- Mission Life: Expected to last two more years (originally planned for 5 years).
- Significance: Contributed to over 400 published papers based on multi-wavelength space observatory data.
ISRO-DBT Agreement for Biotechnology Experiments in Space

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have signed an agreement to conduct biotechnology experiments on the upcoming Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
- Timeline for BAS:
- The BAS is expected to be operational from 2028-2035, with the initial module launches slated for 2028 and full expansion by 2035.
- It will be located at an altitude of 400 km above Earth and will support 15–20-day missions in space.
Focus Areas of Research
- Health Impact:
- Weightlessness & Muscle Health: Studying the effects of zero-gravity on muscle loss during space missions.
- Radiation Effects: Investigating how space radiation impacts astronaut health over long durations.
- Bio-Manufacturing:
- Algae Studies: Exploring algae for potential use in nutrient-rich, long-lasting food sources and biofuel production.
- Food Preservation: Identifying algae varieties that can help preserve food for longer periods in space.
- Integration with Gaganyaan Mission:
- Experiments may also be conducted during uncrewed test flights for the Gaganyaan mission (India’s first crewed mission to space, scheduled for 2025-2026).
BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy
- Objective: The BioE3 policy aims to boost bio-manufacturing in India, which is projected to contribute $300 billion to the Indian economy by 2030.
- Key Focus Areas:
- High-Value Bio-Based Products: Promotes the development of bio-based chemicals, biopolymers, enzymes, and smart proteins.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture & Carbon Capture: Aims to strengthen agricultural practices to withstand climate change and promote carbon capture technologies.
- Healthcare & Nutrition: Focuses on advancements in biotherapeutics, functional foods, and regenerative medicine.
- Marine & Space Biotechnology: Encourages research in space and marine biotechnology for new applications.
- Innovation & Entrepreneurship: Supports R&D-driven entrepreneurship through the establishment of bio-manufacturing hubs, bio-AI centers, and biofoundries.
- Employment Growth: Aims to create skilled jobs in the growing bioeconomy, promoting green growth and sustainable industries.
Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) Overview
- Structure: The station will consist of:
- Command Module
- Habitat Module
- Propulsion Systems
- Docking Ports
- Objective: To support long-term research in space life sciences and bio-manufacturing, with a focus on human health, food sustainability, and biotechnology innovations.
21st Livestock Census

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
The Livestock Census is a crucial tool for understanding the current status of India’s livestock sector and its contribution to the economy and society.
What is the Livestock Census?
- The Livestock Census is a nationwide survey conducted every five years to assess the number, species, breed, age, sex, and ownership status of domesticated animals and poultry, including stray animals.
- Purpose: It helps in collecting comprehensive data about the livestock population and their role in the economy and society.
- First Census: The first livestock census was conducted in 1919, and this is the 21st edition.
- Next Census: The 21st Livestock Census will be conducted between October 2024 and February 2025 by approximately 87,000 enumerators across 30 crore households in India.
Animals Covered in the Census
- The census will account for 16 species of animals, including:
- Cattle, Buffalo, Mithun, Yak, Sheep, Goat, Pig, Camel, Horse, Ponies, Mule, Donkey
- Dog, Rabbit, Elephant
- Poultry: Fowl, Chicken, Duck, Turkey, Geese, Quail, Ostrich, and Emu
- The census will also collect data on 219 indigenous breeds of these species recognized by the ICAR-National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR).
Objectives of the Livestock Census
- Economic Contribution: The livestock sector contributes approximately:
- 30% of the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the agricultural sector
- 4.7% of India's overall GVA
- It plays a crucial role in rural employment, particularly in poultry and animal husbandry.
- Policy Formulation and Planning:
- The data from the census is critical for formulating and implementing policies related to livestock, ensuring sustainable growth in the sector.
- It helps in monitoring and estimating GVA from livestock.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Provides vital data for tracking the progress towards Goal 2 of SDGs (Zero Hunger) and Target 2.5, which focuses on maintaining genetic diversity in livestock, particularly addressing local breeds at risk of extinction (Indicator 2.5.2).
- Sectoral Monitoring:
- The census helps in monitoring the performance and health of India’s livestock sector, which is vital for ensuring food security, rural livelihoods, and economic growth.
Key Features of the 21st Livestock Census
- Digitization:
- Like the 2019 Census, this year’s census will be fully digitized, with data collected via a mobile application.
- Digital Monitoring: A dashboard will monitor progress at various levels, and the latitude and longitude of the data collection locations will be recorded.
- A software-based livestock census report will be generated to streamline analysis.
- New Data Points:
- For the first time, data on pastoral animals and pastoralists will be collected, focusing on their socio-economic status and livestock holdings.
- Granular Data: The census will gather information on:
- Proportions of households that rely on livestock for major income.
- Gender-based data on stray cattle.
- Extended Scope:
- In addition to animal population statistics, the census will also focus on the socio-economic contributions of the livestock sector, gender inclusion, and employment.
Significance of the Livestock Census
- A Comprehensive Livestock Profile:
- Provides a holistic view of livestock population and the interlinkages between animal husbandry, agriculture, and rural economies.
- Assists in the management and preservation of indigenous animal breeds.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Helps policymakers, researchers, and development organizations in formulating strategies for sectoral growth, genetic diversity preservation, and livelihood enhancement for rural communities.
- Monitoring Livestock Health:
- The census helps in tracking the health and sustainability of India’s livestock population, which is essential for ensuring food security and preventing animal diseases.
Findings of the 2019 Livestock Census
- Total Livestock Population: 535.78 million
- Cattle: 192.9 million
- Goats: 148.88 million
- Buffaloes: 109.85 million
- Sheep: 74.26 million
- Pigs: 9.06 million
- Other species contributed a small fraction to the total livestock population (0.23%).
Launch of 'Abhay'

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, ‘Abhay’, the seventh ship in the Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW SWC) series was launched.
Key Details:
Project Background
- Contract Details: The Ministry of Defence (MoD) signed a contract with Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, in April 2019 for the construction of eight ASW SWC ships.
- Class of Ships: The Arnala-class ships are intended to replace the older Abhay-class ASW Corvettes currently in service with the Indian Navy.
- Purpose: These ships are designed for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) operations in coastal waters and to conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO) and mine-laying activities.
Design and Features of 'Abhay'
- Dimensions:
- Length: 77 meters
- Width: 10 meters
- Speed and Endurance:
- Maximum speed: 25 knots
- Endurance: 1800 nautical miles (NM).
- Propulsion: Waterjet-propelled, offering agility and swift response in tactical situations.
- Indigenous Content: Over 80% indigenous content, supporting India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiative in defence manufacturing.
Capabilities of the ASW SWC
- Anti-Submarine Warfare:
- Designed to conduct subsurface surveillance and anti-submarine operations in coastal waters.
- Equipped with advanced sonar systems, including Hull-Mounted Sonar and Low-Frequency Variable Depth Sonar for enhanced underwater surveillance.
- Armament and Equipment:
- Torpedoes and ASW rockets for anti-submarine operations.
- Mines for mine-laying operations.
- Close-in Weapon System (CIWS): 30 mm for close-range defence against aerial and surface threats.
- 12.7 mm Stabilized Remote-Control Guns for additional defensive capability.
Strategic Importance
- Coastal Defence: The ASW SWC ships enhance the Navy’s capability to defend India’s extensive coastline and exclusive economic zone (EEZ) against submarine threats.
- Operational Role:
- In addition to anti-submarine warfare, these ships can conduct Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO), which include operations against non-traditional threats.
- Mine-laying capability to disrupt enemy naval operations.
- Advanced Detection: These ships are equipped to track both surface and underwater targets, enabling them to coordinate operations with aircraft, strengthening maritime security.
Center for Generative AI, Srijan

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
IndiaAI and Meta have announced the establishment of the Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur, along with the launch of the “YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building” in collaboration with the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), for the advancement of open source artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur:
- Focus on Generative AI (GenAI) research and innovation.
- Meta’s support for ethical and responsible development of AI technologies.
- Aim to empower researchers, students, and practitioners with the tools for responsible AI deployment.
- Focus Areas: Open science, AI policy advisory, and indigenous AI application development.
- YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building:
- Target: Empower 100,000 students and young developers (ages 18-30) with AI skills.
- Core Focus: Leveraging open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) for real-world solutions.
- Skills Development: Generative AI, open-source tools, and sector-specific AI applications (healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, mobility, and financial inclusion).
- Partnership: Collaboration with AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education).
Strategic Goals and Outcomes
- Research and Innovation:
- Strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through groundbreaking research and collaborations.
- Focus on open-source AI and indigenous AI solutions for national challenges.
- Empower India to lead in AI through ethical and responsible AI deployment.
- AI Talent Development:
- Bridge the AI talent gap by training young developers in open-source AI technologies.
- Develop AI solutions for critical sectors like healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, and financial inclusion.
- Program Components:
- GenAI Resource Hub with courses, case studies, and open datasets.
- Unleash LLM Hackathons for students to propose AI solutions for real-world challenges.
- Support for AI startups through an Innovation Accelerator.
Sectoral Focus and Impact
- Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and healthcare delivery.
- Education: AI tools for enhancing learning outcomes and personalized education.
- Agriculture: AI solutions for precision farming, pest control, and crop management.
- Smart Cities: AI in urban planning, traffic management, and public services.
- Mobility: AI applications in transportation, logistics, and urban mobility.
- Financial Inclusion: AI in fintech, digital payments, and financial services for underserved populations.
Additional Programs and Opportunities
- AICTE Collaboration: Mobilizing technical institutions across India to build AI capabilities.
- Master Training Activation Workshops: To introduce foundational AI concepts to students.
- Mentorship and Grants: Top AI solutions from hackathons will receive mentoring, seed grants, and market support.
- Student Startups: AI Innovation Accelerator will incubate 10 student-led AI startups experimenting with open-source models.
Pandemic Fund Project

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying launched the Pandemic Fund Project on "Animal Health Security Strengthening in India for Pandemic Preparedness and Response"in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Pandemic Fund Project
- Objective: Strengthening animal health security in India to enhance pandemic preparedness and response.
- Funding: $25 million initiative funded by the G20 Pandemic Fund.
- Location: New Delhi, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
Context and Importance
- Livestock Sector: Crucial for socio-economic upliftment, contributing to employment and rural development.
- Growth in Livestock Sector: Significant progress in the last 9 years through schemes like the National Animal Disease Control Program (NADCP).
- Key Diseases Targeted:
- Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD): Aimed at eradication, with over 90.87 crore vaccines administered.
- Brucellosis: Over 4.23 crore vaccines administered.
Objectives of the Pandemic Fund Project
- Enhanced Disease Surveillance: Includes genomic and environmental monitoring for early warning systems.
- Laboratory Infrastructure Development: Upgradation for better diagnosis and disease management.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships for global monitoring of zoonotic diseases.
- Integrated Monitoring System: Creation of a robust system for managing zoonotic diseases, with a focus on early detection and containment.
Documents Released for Strengthening Animal Health
- Standard Veterinary Treatment Guidelines (SVTG):
- Best practices for veterinary care to improve livestock health and productivity.
- Supports national action plans, especially for combating antimicrobial resistance.
- Crisis Management Plan (CMP) for Animal Diseases:
- Framework for effective response and containment during animal disease outbreaks.
- Ensures timely mitigation of animal disease crises.
One Health Approach
- Integration of Human, Animal, and Environmental Health: Key to preventing and managing future health crises.
- Zoonotic Risks: The project emphasizes reducing zoonotic disease transmission from animals to humans, crucial given the origins of many recent public health emergencies.
Implementation and Collaboration
- The project will be executed in collaboration with global institutions:
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- World Bank
Chanakya Defence Dialogue 2024

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Chanakya Defence Dialogue (CDD) 2024, second edition, was held at the Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi.
- Theme: "Drivers in Nation Building: Fueling Growth Through Comprehensive Security."
- Focus: Discussions on integrating national security into India's development trajectory and global strategy for a Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Key Objectives:
- The dialogue aimed to explore India’s strategic directions and development priorities by fostering discussions between policymakers, strategic thinkers, defence experts, and academia.
- Highlighted the link between national security and economic growth, stressing how security frameworks are vital for national progress.
Key Sessions and Discussions:
- Session 1: Social Cohesion and Inclusive Growth: Pillars of a Secure Nation:
- Focused on internal security, social unity, and inclusive development.
- Panelists discussed the role of community engagement, countering terrorism, and law enforcement reforms.
- Emphasized the need for integrating social progress and addressing challenges like separatism and terrorist narratives.
- Panelists called for evidence-based policies for equitable growth and stronger security frameworks to protect the country from internal threats.
- Session 2: Blurring Frontiers: The Convergence of Technology & Security:
- Addressed the intersection of technology and national security.
- Topics included AI, quantum computing, IoT, and blockchain for improving cyber resilience and data protection.
- Panelists emphasized the need to balance technological innovation with strong security measures, particularly in cybersecurity and critical infrastructure protection.
- Session 3: Ground-breakers: Shaping Land Warfare, Reflections for the Indian Army:
- Explored the integration of emerging technologies like AI, unmanned systems, and cyber warfare tools in enhancing military readiness.
- Focused on indigenous defense technologies under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, promoting self-reliance and reducing dependency on foreign technologies.
- Emphasized multi-domain operations and the challenges of adapting to evolving security threats, especially from advanced cyber and space warfare.
Strategic Insights:
- Economic Growth & Security: The dialogue highlighted that national security and economic growth are interlinked, with a strong military infrastructure crucial for sustaining development.
- Role of Technology: Technological advancements like AI, space technology, and cybersecurity are pivotal for enhancing India's defense capabilities and strategic posture in a rapidly evolving global security landscape.
- Inclusive Security: Emphasized social cohesion and inclusive growth as key components of national security, acknowledging that a unified society contributes significantly to national resilience.
- Global Diplomacy: India’s global leadership in multilateral forums, its stance on peacekeeping, and its role in promoting sustainable development were discussed as part of the country’s soft power strategy.
Precision Medicine, Biobanks, and Regulatory Challenges in India
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare. The field began to take concrete shape when scientists were wrapping up the Human Genome Project.
Introduction to Precision Medicine:
- Precision Medicine is a novel approach to healthcare that tailors treatments and preventive strategies based on an individual’s genetics, environment, and lifestyle, instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
- It leverages technologies like genomics, gene editing (CRISPR), and mRNA therapeutics to address various diseases such as cancer, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders.
- Recent breakthroughs include gene therapy for restoring vision and stem cell transplants for reversing diabetes, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Role of Biobanks in Precision Medicine:
- Biobanks are repositories storing biological samples (blood, DNA, tissues) along with associated health data. These samples are crucial for research and development of personalized treatments.
- Large and diverse biobanks are essential for ensuring that precision medicine benefits a wide demographic, as data from homogenous groups could limit the applicability of findings.
- Recent studies using biobank data have led to breakthroughs, such as identifying rare genetic disorders and developing organoid models for high-throughput drug screening.
Precision Medicine and Biobanks in India:
- Market Growth: India’s precision medicine market is growing at a CAGR of 16%, expected to surpass USD 5 billion by 2030, contributing 36% to the national bioeconomy.
- Policy Framework: The government’s BioE3 policy aims to promote biomanufacturing, with a focus on precision therapeutics and related technologies like gene editing and cancer immunotherapy.
- Biobank Initiatives:
- Genome India Programme: Completed sequencing of 10,000 genomes from 99 ethnic groups, aimed at identifying treatments for rare genetic diseases.
- Phenome India Project: Focused on collecting 10,000 samples for improving prediction models for cardio-metabolic diseases.
- Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) Mission: Aiming to identify genes that could help develop targeted therapies for genetic diseases in children.
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges in Biobanking:
- India’s biobanking regulations are inconsistent, hindering the full potential of precision medicine. Unlike countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan, which have comprehensive laws addressing issues like informed consent, data protection, and privacy, India lacks a cohesive regulatory framework.
- Informed Consent Issues: In India, participants provide samples without full knowledge of how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and for how long it will be stored. This lack of transparency undermines public trust in biobank research.
- Ethical Concerns: Without a clear regulatory framework, there is a risk of misuse of biological samples, such as non-consensual data sharing and sample mishandling.
- International Implications: The absence of robust laws allows foreign pharmaceutical companies to access Indian biobank data and samples without ensuring that the Indian population benefits from the resulting research or profits.
Global Comparison of Biobank Regulations:
- International Standards: Countries like the U.K., U.S., and Japan have established comprehensive biobank regulations, addressing:
- Informed consent for sample collection and data usage.
- Privacy protection and secure storage of genetic information.
- Withdrawal rights for participants at any stage of research.
- India’s biobank regulations lack clear provisions for data protection and participant rights, limiting the effectiveness of research and undermining public confidence in biobanks.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)

- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Financial Services Secretary stated that Microfinance institutions (MFIs) have played a crucial role in fostering financial inclusion but they should refrain from any reckless lending.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) and Financial Inclusion:
- MFIs provide small loans and financial services to low-income and marginalized groups, particularly those without access to formal banking services.
- Goal: To promote financial inclusion and empower marginalized communities, especially women, by enabling them to become self-sufficient and improve their socio-economic status.
- In India, over 168 MFIs serve around 3 crore clients across 29 states and 563 districts.
- The sector has grown significantly and is crucial for empowering Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) to access credit and other financial services.
Concerns over Reckless Lending:
- The Financial Services Secretary, emphasized that MFIs should avoid reckless lending practices that could harm both borrowers and the sector.
- Poor underwriting and irresponsible lending could lead to unsustainable debt, especially for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) with limited financial literacy.
- Key Advice: Lending practices must be responsible, careful, and should aim to empower borrowers, not exploit their limited understanding.
Government Programs Supporting MFIs:
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme: Over 77 lakh SHGs with a total loan outstanding of ?2.6 lakh crore, benefiting around 10 crore households.
- Lakhpati Didi Yojana: Aimed at empowering women, this scheme helps transform SHG members into women entrepreneurs.
Challenges Facing Microfinance Institutions:
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Many MFIs face scrutiny for high interest rates and non-compliance with borrower assessments. The RBI has urged MFIs to reassess lending practices.
- Over-Indebtedness: Many borrowers take loans from multiple MFIs, leading to unsustainable debt. As of March 2024, over 12% of borrowers had multiple loans, risking defaults.
- Low Financial Literacy: A significant challenge is low financial literacy among borrowers, which increases the risk of defaults and harms the reputation of MFIs.
RBI Guidelines on Microfinance (2022):
- Collateral-Free Loans: For households with income up to ?3 lakh, loans should be collateral-free.
- Repayment Cap: Monthly loan repayments should not exceed 50% of the borrower’s monthly income.
- Flexibility in Repayment: MFIs must offer flexible repayment options and ensure proper income assessment.
- Interest Rate Cap: The RBI has implemented guidelines to limit excessive interest rates charged by MFIs.
Government Schemes for Microfinance:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Provides financial assistance to non-corporate, non-farm small/micro enterprises.
- National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM): Promotes rural livelihoods through the formation and capacity building of Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Antyodaya Yojana: Focuses on the empowerment of rural poor through skill development and income generation.
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE): Provides guarantee cover to micro and small enterprises.
Way Forward for Microfinance Sector:
- Responsible Lending: MFIs must prioritize affordable lending practices, ensuring borrower’s repayment capacity is carefully assessed to avoid over-indebtedness.
- Enhancing Financial Literacy: MFIs should focus on financial education for borrowers, enabling them to make informed choices.
- Adherence to Regulatory Guidelines: MFIs should comply strictly with RBI regulations, including interest rate caps and borrower income assessments, to enhance sector transparency and trust.
- Malegam Committee Recommendations: Implementing suggestions like capping interest rates, tracking multiple loans, and improving transparency to prevent over-indebtedness.
- Diversifying Funding Sources: To reduce vulnerability to economic downturns, MFIs should work on diversifying their funding sources, reducing dependence on external capital.
Environmental Ship Index (ESI)
- 26 Oct 2024
In News:
- Mormugao Port Authority (MPA) has been globally recognized as an incentive provider on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) platform, acknowledged by the International Association of Ports and Harbours (IAPH).
- Mormugao is India's first port to implement Green Ship Incentives through the ESI, contributing to global efforts to reduce maritime air emissions.
‘Harit Shrey’ Scheme:
- Launched in October 2023, the ‘Harit Shrey’ scheme provides discounts on port fees based on the Environmental Ship Index (ESI) scores of commercial vessels.
- Ships with higher ESI scores (indicating better environmental performance) are rewarded with incentives to encourage eco-friendly practices in shipping.
ESI and Global Efforts for Emission Reduction:
- The Environmental Ship Index (ESI) is a global system to evaluate and reward ships based on their environmental performance, particularly their emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur oxides (SOx).
- The 2023 IMO greenhouse gas strategy aims to reduce the carbon intensity of international shipping by at least 40% by 2030.
Incentives and Benefits:
- The Harit Shrey scheme has already benefitted several vessels, promoting greenhouse gas emission reductions and contributing to sustainable maritime operations.
- The scheme aligns with global sustainability goals, particularly in reducing the carbon footprint of shipping operations.
Sustainability Recognition:
- The Mormugao Port Authority has submitted the Harit Shrey scheme for consideration in the IAPH Sustainability Awards under the World Port Sustainability Programme (WPSP), reflecting its commitment to environmental sustainability.
The Environmental Ship Index (ESI):
- ESI is a system that evaluates and rewards ships for better environmental performance than the standards set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- Ships are assessed based on their emissions of NOx and SOx, with greenhouse gas reporting also included in the evaluation.
Main Features of ESI:
- Port-Centric: Developed as a port-to-port system, where ports can offer incentives based on the ESI score.
- Voluntary Participation: Shipowners participate voluntarily to demonstrate their vessels' environmental performance.
- Automated Calculation: The ESI score is automatically calculated and updated.
- Incentives: Ships with higher ESI scores may receive benefits such as reduced port fees and priority berthing.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
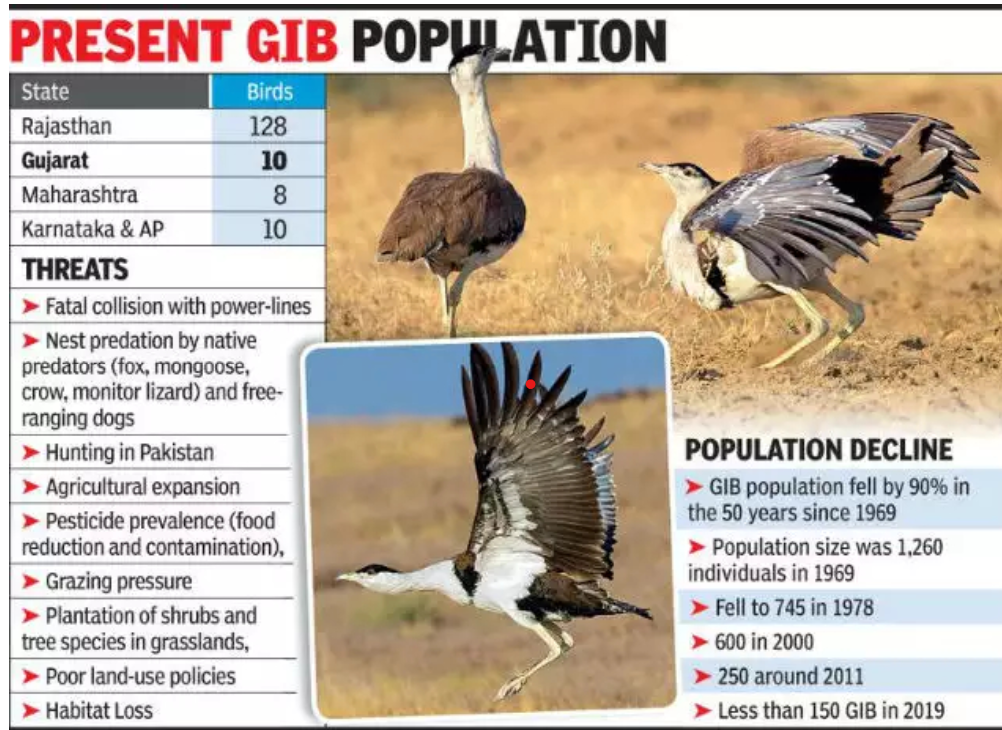
- 25 Oct 2024
A critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (GIB) chick was successfully born through artificial insemination (AI) at a breeding center in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, marking a crucial step in efforts to save the species.
Endangered Status:
- The Great Indian Bustard is classified as critically endangered with fewer than 150 individuals left in the wild in India.
- About 90% of these birds are found in the desert areas of Rajasthan, with smaller populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Main Threats to the Species:
- Habitat Loss: The primary threat is the loss of habitat, which is often perceived as wasteland and is diverted for infrastructure projects like roads and development.
- Slow Reproductive Rate: The bustard’s low reproductive rate exacerbates its risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts: Bustard Recovery Program
- In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched the Bustard Recovery Program to focus on captive breeding and creating a sustainable environment for the reintroduction of GIBs into the wild.
- A dedicated GIB breeding center was set up at the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, as part of this initiative.
- Protection Status of GIB:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- It is also the state bird of Rajasthan, emphasizing its importance in the region’s biodiversity.
Introduction to Innovative Cancer Detection Technique
- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
- Scientists have developed an ultrasound-based technique for detecting cancer, aiming to replace traditional biopsies, which are invasive and painful.
- Promising Alternative: The method uses high-energy ultrasound to release biomarkers (RNA, DNA, and proteins) from cancerous tissue into the bloodstream, allowing for early cancer detection with minimal discomfort.
- Presented at Acoustical Society Conference: The technique was discussed at the joint meeting of the Acoustical Society of America and Canadian Acoustical Association in May 2024.
Traditional Cancer Detection vs. New Ultrasound Approach
- Current Gold Standard - Biopsy: Traditionally, cancer is diagnosed using biopsies, where a tissue sample is extracted using a needle from suspected cancerous areas. Although effective, biopsies are invasive, painful, and carry some risks.
- Ultrasound as a Non-Invasive Alternative: The new method involves using high-frequency ultrasound waves to break off cancerous tissue into droplets, which are then released into the bloodstream. The biomarkers in the droplets can be analyzed for cancerous mutations.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: This ultrasound-based technique increases the levels of genetic and vesicle biomarkers in blood samples by over 100 times, enabling the detection of cancers and specific mutations that are otherwise undetectable in blood.
Key Findings of the Research
- Single Cancer Cell Detection: The technique allows for the detection of a single cancer cell in blood samples. It works by passing ultrasound waves through isolated blood samples, which break apart circulating cancer cells, releasing biomarkers into the blood.
- Cost-Effective: Traditional methods for detecting circulating cancer cells are costly (e.g., the ‘CellSearch’ test costs $10,000). In contrast, this ultrasound method can detect cancer with a much lower cost, around $100 (?8,400).
- Potential for Early Diagnosis: The research shows promise for detecting cancer at an early stage, even before symptoms appear, using blood samples.
Challenges and Next Steps
- Need for Large-Scale Clinical Trials: While the technique shows potential, large cohort studies involving diverse patient groups across different geographies and ethnicities are needed to validate the approach.
- Long-Term Study for Effectiveness: Further research is required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the technique across various cancer types and to determine the ideal biomarker thresholds for early detection.
- Regulatory Approval and Commercialization: If the clinical trials yield positive results, the method could be commercially available in approximately five years, following regulatory approval.
Understanding Cancer and Its Types
- Cancer Definition: Cancer refers to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells that can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body.
- Types of Cancer:
- Carcinoma: Cancer originating in epithelial cells (e.g., breast, lung, prostate cancer).
- Sarcoma: Affects connective tissues like bones and muscles.
- Leukemia: Affects blood-forming tissues, leading to abnormal white blood cell production.
- Lymphoma: Begins in immune cells, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Melanoma: Cancer of pigment-producing skin cells.
- Key Differences Between Normal and Cancer Cells:
- Cancer cells grow uncontrollably and evade immune detection.
- Cancerous cells accumulate chromosomal abnormalities, unlike normal cells, which follow regulated growth patterns.
National Workshop on SATHI Portal

- 25 Oct 2024
In News:
Recently, the Department of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare (DA&FW) organised a National Workshop on the SATHI (Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory) Portal in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
Purpose & Focus
- SATHI Portal: Focuses on Seed Authentication, Traceability, and Holistic Inventory to enhance seed certification, improve seed traceability, and streamline the seed supply chain.
- Primary Objective: Ensure availability of high-quality seeds to farmers through a transparent and efficient seed management system.
Key Features of the SATHI Portal
- Seed Certification: Aims to streamline seed certification processes across states for faster and more accurate seed certifications.
- Seed Traceability: Enhances transparency and traceability of seeds to ensure quality and authenticity.
- Inventory Management: The portal facilitates seed inventory management, helping farmers and stakeholders access reliable and transparent seed information.
- Technological Integration: Developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC), the portal incorporates technology-driven solutions to minimize transactional time for registrations, approvals, and certifications.
Phase-II Rollout
- Focus on seed inventory management, with the objective of offering farmers reliable access to certified seed varieties.
- It aims to integrate state-specific seed processes into the national framework for greater standardization and efficiency.
Workshops & Technical Sessions
- NIC and ICAR Presentations: Covered the core components of the SATHI Portal, including:
- Seed Law Enforcement
- DNA Fingerprinting for ensuring seed authenticity.
- Seed Laboratory Processes to uphold quality control.
- Review of Phase-I: Discussions on achievements of Phase-I, focusing on improvements in seed certification processes across states.
- State Experiences: 10 state representatives shared insights on their experiences with the portal, discussing both benefits and challenges in the implementation phase.
Role of NIC & Technology
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) is the technology partner behind the SATHI Portal, which is designed to enhance the efficiency of seed certification and inventory management.
- The portal contributes to larger digital initiatives like the Digital Agriculture Mission and Unified Farmer Service Platform (UFSP), which aim to support agricultural development through technology.
IMF's World Economic Outlook (WEO)
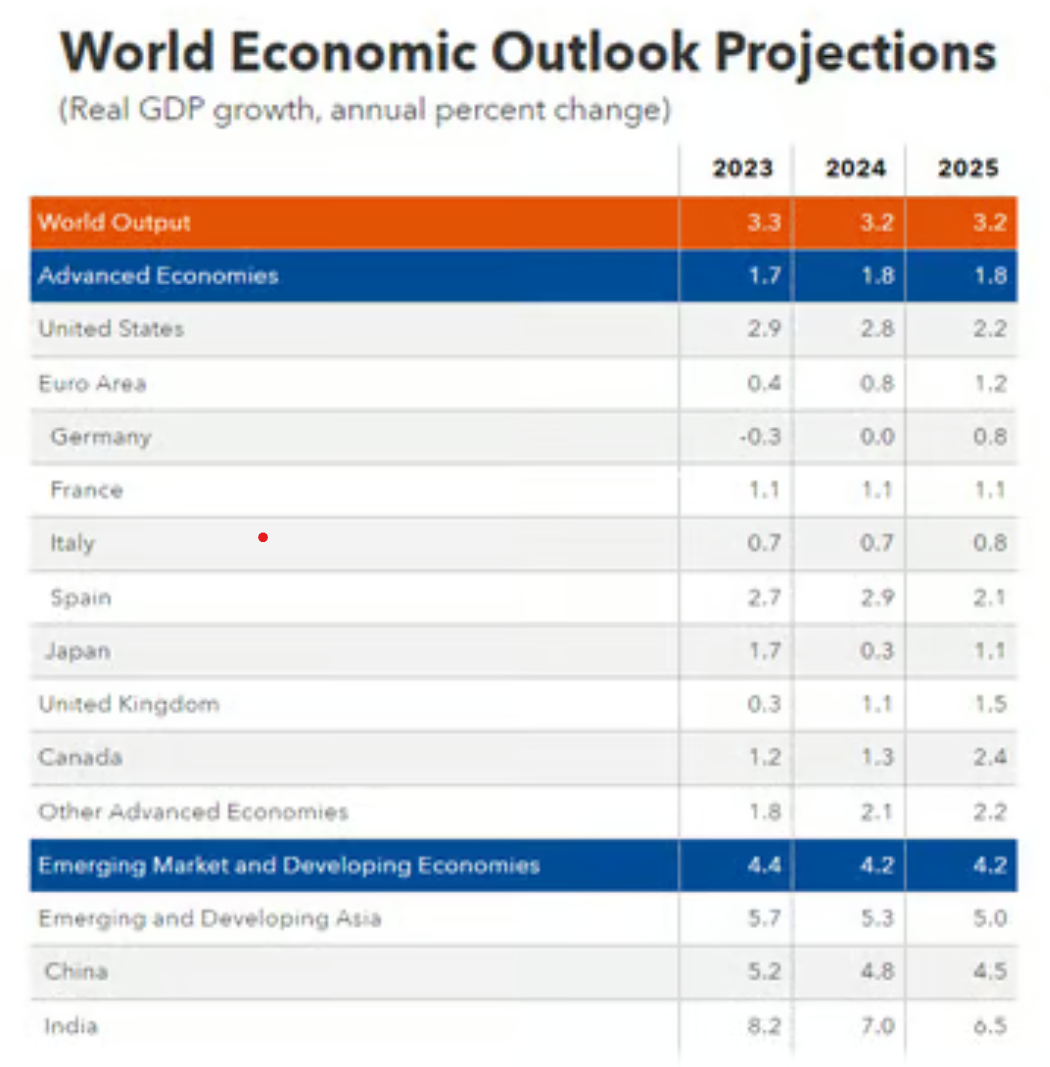
- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has maintained India’s GDP growth forecast at 7% for FY2024, marking a moderation from 8.2% in 2023.
- FY2025 Projection: Growth is expected to slow further to 6.5% in FY2025.
- India’s growth is expected to be stronger than most other large economies, yet the downward revision reflects challenges in the global economy and moderation in domestic economic momentum.
Global Economic Growth Projections:
- Global Growth (2024-2025): Global growth is projected at 3.2% in 2024 and 2025, which is stable but modest. This growth rate is largely unchanged from previous IMF forecasts.
- Long-Term Outlook: The IMF's long-term projection for global growth is 3.1%, which is considered subpar compared to pre-pandemic growth rates, signaling a potential era of low growth.
Key Risks and Uncertainties:
- The IMF highlights several downside risks to global growth, including:
-
- Monetary tightening: Central banks' high-interest rate policies to combat inflation could have long-term negative effects on economic growth and financial stability.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing conflicts, such as the Russia-Ukraine war, could disrupt global supply chains and trade, exacerbating inflation and slowing growth.
- China’s Economic Slowdown: China, the world’s second-largest economy, is facing a slower growth trajectory, especially in its real estate sector, which is dragging down its overall growth.
- Structural Challenges: The aging population and weak productivity are long-term growth inhibitors in many advanced economies, adding uncertainty to future growth prospects.
-
- Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
- 2023: Global inflation is expected to reach 6.7%.
- 2024: It is forecast to fall to 5.8%, with advanced economies expected to return to inflation targets sooner than emerging markets.
- 2025: A further decline to 4.3%.
- The primary driver of disinflation is not interest rate hikes but the unwinding of pandemic-related shocks, supply chain improvements, and the gradual return of labor supply.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks are likely to ease policies once inflation nears target levels, but risks of further commodity price spikes or geopolitical tensions could delay this.
- The IMF's inflation forecast shows global inflation cooling:
US and Europe Growth:
- Emerging Markets and Developing Economies:
- Growth Outlook: The IMF forecasts growth in emerging markets and developing economies at 4.2% for 2024 and 2025, with a slight moderation to 3.9% by 2026.
- Emerging Asia: Growth in emerging Asia (led by India and China) is expected to slow, from 5.7% in 2023 to 5% in 2025.
- India’s Relative Strength: India’s growth continues to outperform many emerging economies, though the slowdown from 8.2% in 2023 to 7% in 2024 reflects global economic headwinds.
- Income Inequality Risks:
- The IMF warns that low growth over an extended period (4+ years) could exacerbate income inequality within countries, as sluggish growth affects job creation and wage growth.
- Countries with slow economic recovery are likely to see a widening gap between rich and poor, undermining social cohesion and stability.
Cyberfraud Losses and Economic Impact

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- ?1.2 lakh crore is the projected financial loss due to cyber frauds in India over the next year (2024), according to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Union Home Ministry.
- This could amount to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Mule Accounts:
- Mule accounts are a significant contributor to cyber frauds. These accounts are used to facilitate money laundering and illegal transactions.
- On average, around 4,000 mule accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- Mule accounts typically facilitate the transfer of funds out of India, often through cryptocurrency transactions.
- Sources of Cyber Scams:
- A majority of frauds are linked to Chinese entities or China-based operations, with about half of the cybercrime complaints originating from China.
- Other major hubs for cyber frauds include Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, which house call-centre-like scam compounds.
- Azerbaijan has also been identified as a new hotspot for such scams.
- International Dimension:
- Fraudulent withdrawals have been reported from ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia using mule accounts.
- The international nature of these scams often involves routing stolen funds through various countries, using methods like cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Cybercrime and Terror Financing:
- Cyber scams have potential ramifications beyond financial losses; they can be used for terror financing and money laundering.
- Cryptocurrency is a common medium for laundering money, with an example cited of ?5.5 crore laundered through 350 transactions in a short span.
- ATM Hotspots and Fraudulent Withdrawals:
- 18 ATM hotspots have been identified across India where fraudulent withdrawals occur.
- Fraudsters exploit these locations to withdraw money, often using mule bank accounts and cross-border ATM networks.
- Government Response:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is working to combat these frauds by convening meetings with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The objective is to curb the operation of mule accounts and strengthen the banking system to prevent such frauds.
- Banks are being urged to flag unusually high-value transactions or accounts with low balances that are engaging in suspicious activity.
- Fraudulent Calls and Scam Compounds:
- Indian fraudsters, in collaboration with international scam rings, use Indian mobile phone numbers to deceive citizens.
- Countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, and Azerbaijan have been identified as hubs for investment scams involving fraudulent calls.
- Helpline and Cyber Fraud Reporting System:
- The Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (part of I4C) and the 1930 helpline provide mechanisms to report financial frauds.
- ?11,269 crore in financial frauds was reported during the first half of 2024 via these channels.
- The system also involves cooperation with over 200 financial intermediaries, including banks and wallets.
Tenkana

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- A team of arachnologists has discovered a new genus of jumping spiders, Tenkana, found across southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The discovery includes two previously known species, Tenkanamanu and Tenkanaarkavathi, and introduces a new species, Tenkanajayamangali, from Karnataka.
Name and Origin:
- The name Tenkana comes from the Kannada word for "south," reflecting the geographical region where all known species of this genus are found—southern India and northern Sri Lanka.
- The genus belongs to the Plexippina subtribe of jumping spiders, which is distinct from related genera like Hyllus and Telamonia.
Key Findings:
- Tenkanajayamangali was first discovered in Devarayanadurga reserve forest, Tumakuru district, Karnataka, at the origin of the Jayamangali river.
- The new species was identified through genetic analysis and physical examination, showing it did not match any known species.
Physical Characteristics:
- The male and female Tenkanajayamangali exhibit distinct physical differences.
- The male has pale hairs covering most of its carapace, while the female is grey with a pattern.
- The ocular area of T. jayamangali is uniformly covered with white hairs, in contrast to T. arkavathi and T. manu, which have distinctive markings.
Habitat and Distribution:
- Tenkana spiders are typically ground-dwelling and prefer dry, open habitats like short grasses, leaf litter, and rocky outcrops.
- These spiders have been observed in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and some areas in Sri Lanka.
- The male and female spiders of T. jayamangali were discovered in different regions, 2 km apart, at the hilltop and foothills of the same forest.
Ecological and Behavioral Insights:
- The Tenkana genus is considered endemic to India, with species observed in diverse regions such as Bengaluru, Yercaud (Tamil Nadu), and Bannerghatta (Karnataka).
- These spiders are found in complex microhabitats, like shaded short grasses with dry leaf litter or rocky outcrops in relatively dry habitats.
- The movement of Tenkana spiders resembles that of Stenaelurillus, another ground-dwelling spider species.
Amazon Future Engineer Program (Phase 3)

- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
- The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) launched the third phase of the Amazon Future Engineer Program in 50 Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS).
- Schools involved are spread across Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Telangana, and Tripura.
Program Focus Areas:
- Emerging Technologies: The third phase introduces tribal students to key areas like:
- Blockchain technology
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Coding and block programming
- The program is designed to equip students with skills in computer science fundamentals.
Teacher Training:
- A four-day in-person training workshop for teachers was conducted to empower them with the skills necessary to teach emerging technologies effectively.
- Teachers also participated in the EMRS Coders Expo, showcasing top student coding projects from the previous academic year.
Target Audience:
- Students: The program targets students from grades 6 to 9. Class 10 students will participate in project-based virtual sessions aligned with the CBSE AI Skills Curriculum.
- The goal is to enhance students' understanding of computer science and technology and prepare them for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) careers.
Program Expansion:
- Future Plans: The program will be rolled out in the next phase to cover a total of 410 EMRSs across India.
- Impact: Over 7,000 students in grades 6 to 8 have already benefited from the program’s introduction to computer science and block programming.
Key Goals of the Program:
- Empower Tribal Students: Provide tribal students with modern technological skills to prepare them for future STEM careers.
- Capacity Building: Equip both teachers and students with the knowledge and skills to engage with emerging technologies.
- Fostering Technological Literacy: The initiative aims to foster technological literacy and modernize education in tribal areas.
Recognition:
- During the event, Top 3 Student Coding Projects were felicitated for their creativity and innovation.
- The Top 3 IT Teachers were also recognized for their dedication in guiding students through the program.
Partnership with Amazon:
- The program is a collaboration between NESTS and Amazon, showcasing a joint effort to improve educational access and technological skill development among tribal students.
IMF retains India’s growth projection at 7% for FY25
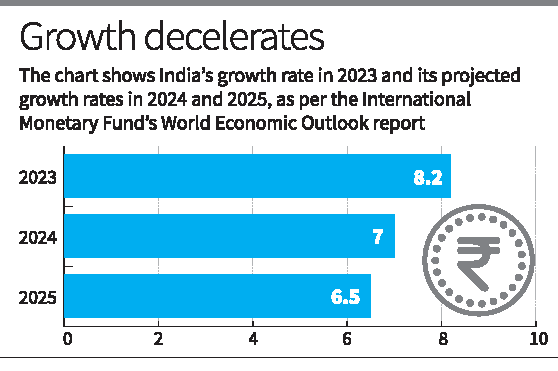
- 23 Oct 2024
In News:
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has revised India's GDP growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 7%, up by 20 basis points from its previous estimate of 6.8%.
- India’s Growth Projections:
- Current Fiscal Year (FY2024-25): India’s GDP growth is projected at 7%, unchanged from June 2024 estimates.
- Next Fiscal Year (FY2025-26): Growth expected at 6.5%.
- Growth Decline from FY2023 (8.2%): The slowdown is attributed to the exhaustion of pent-up demand post-pandemic and the economy returning to its potential.
- Global Economic Growth:
- World Output: Projected global growth at 3.2% in both 2024 and 2025.
- Advanced Economies: U.S. GDP growth revised upward to 2.8% in 2024 and 2.2% in 2025.
- Emerging Markets & Developing Economies: Growth revised upwards, largely due to stronger economic activity in Asia, with China and India being key contributors.
- Global Inflation and Monetary Policy:
- Inflation Decline: Global inflation has decreased from its peak of 9.4% in Q3 2022 to 3.5% projected by end-2025.
- Inflation Outlook: Despite reductions in inflation, price pressures persist in some regions.
- Monetary Policy Tightening: IMF acknowledges challenges due to tight monetary conditions in several economies and their potential impacts on labor markets.
- Global Risks and Challenges:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating conflicts in West Asia (e.g., Lebanon) have increased geopolitical risks, potentially affecting commodity markets.
- Protectionism: Growing protectionist policies worldwide are a risk to global trade and economic stability.
- Sovereign Debt Stress: Debt burdens in several countries could become a source of instability.
- Weak Chinese Economy: Slower-than-expected recovery in China remains a significant concern for global economic growth.
- Monetary Policy Risks: Prolonged tight monetary policies in some countries could impact labor markets and economic recovery.
- IMF’s Policy Recommendations for Medium-Term Growth:
- Monetary Policy Neutrality: Countries should adopt a neutral monetary policy stance to balance growth and inflation control.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustment: Build fiscal buffers after years of loose fiscal policy to ensure stability.
- Structural Reforms: Implement structural reforms to boost productivity and cope with challenges like aging populations, the climate transition, and the need for youth employment.
- India’s Economic Outlook - Key Drivers:
- Rural Consumption Growth: The upward revision of India's FY2024-25 GDP forecast to 7% is driven by improved consumption, especially in rural areas.
- Upward Revisions for 2023: The increased growth forecast also reflects positive carryover effects from India's 8.2% growth in 2023.
- Emerging Asia's Growth: The growth outlook for emerging Asia is supported by India and China, though long-term growth prospects for China are weaker (projected to slow to 3.3% by 2029).
- Global Economic Outlook:
- World Growth Projections: Global growth is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025.
- Diverging Growth Rates: Growth across economies is converging as output gaps close, particularly in advanced economies (e.g., U.S. labor market cooling, euro area recovery).
Z-Morh Tunnel Project in Kashmir

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
Seven people were killed in Jammu and Kashmir when suspected militants targeted the workers of infrastructure company APCO Infratech, which is constructing the Z-Morh tunnel on the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway. This is the first militant attack on a key infrastructure project in Jammu and Kashmir. In the past, militants have not targeted such infrastructure projects in the region.
What is the Z-Morh Tunnel?
- Length: 6.4 kilometers
- Connection: Links Sonamarg (a popular tourist destination) with Kangan town in central Kashmir’s Ganderbal district.
- Construction Site: Located near Gagangir village, ahead of Sonamarg.
- Naming: The tunnel gets its name from the Z-shaped road near the construction site.
Importance of the Z-Morh Tunnel
- All-Weather Connectivity: The tunnel is crucial for year-round access to Sonamarg, particularly in the winter when the road is often blocked by snow avalanches.
- Location: Situated at 8,500 feet above sea level, the tunnel provides a safe, all-weather route for tourists and locals, especially during winter months when access to Sonamarg is typically limited.
Strategic Importance
- Part of Zojila Tunnel Project:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is integral to the larger Zojila tunnel project, which aims to provide all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh.
- The Zojila Tunnel, under construction at an altitude of around 12,000 feet, will connect Sonamarg (Kashmir) to Drass (Ladakh) and is expected to be completed by December 2026.
- Military and Strategic Significance:
- The Z-Morh tunnel is crucial for rapid military mobilization between Srinagar, Kargil, Leh, and Drass regions.
- It ensures quick access for military personnel to the Ladakh border, particularly in areas of heightened security like Siachen Glacier and the Turtuk sub-sector (on the Pakistan border).
- The tunnel will reduce dependence on air transport for troop and supply movements to forward areas, leading to cost savings and extended aircraft lifespan.
The case for a nature restoration law in India

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The Nature Restoration Law (NRL), which was enacted by the European Union (EU), is an inspiring model from which India can draw points to tackle its growing environmental crises.
Background of the NRL in the EU
- The Nature Restoration Law (NRL) was enacted by the European Union (EU) to restore ecosystems and combat biodiversity loss.
- Adopted on June 17, 2024, by the EU’s Environmental Council.
- Key objectives:
- Restore 20% of EU’s land and sea areas by 2030.
- Achieve full restoration of all ecosystems by 2050.
- Part of the EU’s Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 and European Green Deal.
- Target Areas:
- Forests, agricultural lands, rivers, urban spaces.
- Restoration measures include:
- 25,000 km of free-flowing rivers.
- Planting 3 billion trees by 2030.
- Global Impact: NRL is a critical tool in reversing Europe’s biodiversity loss, where 80% of habitats are in poor condition.
Environmental Crisis in India
- Land Degradation:
- 29.7% of India’s total geographical area is affected by land degradation (as per ISRO’s Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas, 2018-19).
- 97.85 million hectares of land degraded, with a significant increase since 2003-05.
- Major desertification hotspots in Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.
- Desertification: A growing concern, affecting 83.69 million hectares in 2018-19.
- Ongoing Efforts:
- Green India Mission, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, and National Afforestation Programme have had positive effects.
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme is the second-largest watershed programme globally.
Need for a Comprehensive Nature Restoration Law in India
- The scale of India’s environmental challenges requires a comprehensive nature restoration law similar to the EU’s NRL.
- The law should have legally binding targets to restore degraded landscapes and ensure ecosystem sustainability.
Key Features of an Indian Nature Restoration Law
- Restoration Targets:
- 20% of degraded land to be restored by 2030.
- Full restoration of ecosystems (forests, wetlands, rivers, agricultural lands, urban spaces) by 2050.
- Wetland Restoration:
- Target restoring 30% of degraded wetlands by 2030.
- Priority wetlands like Sundarbans and Chilika Lake play critical roles in biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Biodiversity in Agriculture:
- Promote agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices.
- Use biodiversity indicators (e.g., butterfly or bird index) to monitor progress.
- River Restoration:
- Focus on free-flowing rivers such as the Ganga and Yamuna.
- Address pollution, obstructions, and ecosystem damage in major rivers.
- Urban Green Spaces:
- Ensure no net loss of urban green spaces.
- Promote urban forests in cities like Bengaluru and Delhi, where urban heat islands and air quality degradation are prominent.
Economic and Social Benefits of Ecosystem Restoration
- Global Economic Impact:
- Nature restoration could generate $10 trillion annually by 2030 (World Economic Forum estimate).
- Benefits for India:
- Agricultural Productivity: Restoring degraded land will enhance farm productivity.
- Water Security: Improved land restoration will contribute to better water availability.
- Job Creation: Millions of rural jobs could be created through ecosystem restoration efforts.
- Contributing to SDGs:
- The law would help India meet SDG 15 (sustainable management of forests, combating desertification).
- Climate Change Mitigation:
- Restoring ecosystems can help India enhance its carbon sinks, which is crucial for meeting Paris Agreement targets.
- Degraded lands lose their capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, contributing to global warming.
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans)
- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
The tiny nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) has played an outsized role in scientific discovery, contributing to four Nobel Prizes over the years.
Key Discoveries from C. elegans Research
- C. elegans and Cellular Processes:
- The worm has helped scientists understand programmed cell death (apoptosis), a vital process in development and disease. This work contributed to the 2002 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, addressing how cells are instructed to kill themselves and how this process goes awry in conditions like AIDS, strokes, and degenerative diseases.
- Gene Silencing and RNA Interference:
- In 2006, a Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of gene silencing via RNA interference (RNAi), a process first explored using C. elegans. This discovery led to the development of a new class of RNA-based drugs.
- Cellular Imaging Techniques:
- In 2008, C. elegans contributed to breakthroughs in cellular imaging, as its use helped invent cellular “lanterns” that allowed scientists to visualize the inner workings of cells, earning a Chemistry Nobel.
- Gary Ruvkun’s 2024 Nobel:
- Gary Ruvkun’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024 was the fourth in a series of Nobel recognitions stemming from C. elegans research, reinforcing its role in fundamental biological discoveries.
Key Facts About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans):
- Size: 1 millimeter long.
- Life Cycle: Completes in 3-5 days.
- Cell Count: 959 cells.
- Genome: First multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced in 1998.
- Sexual Reproduction: Hermaphroditic (self-fertilizing) and male.
- Scientific Role: Used to study genetics, developmental biology, neuroscience, and cell biology.
- Nobel Prize Contributions: Four Nobel Prizes, including those in Physiology, Medicine, and Chemistry, for advancements in cell death, gene silencing, and imaging.
IAEA’s 2024 Climate Change and Nuclear Power Report

- 22 Oct 2024
In News:
- The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
- The new report was launched last week on the margins of the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in Brazil.
Key Highlights:
- Nuclear Power's Role in Climate Change Mitigation:
- Nuclear energy is gaining global interest as nations seek to enhance energy security and decarbonize economies.
- To meet net-zero emissions by 2050, nuclear power is projected to play a pivotal role, with a projected capacity increase of 2.5 times the current level by mid-century in the IAEA's high case scenario.
- Investment Needs for Nuclear Expansion:
- Annual investment required to meet the IAEA's high case scenario (2050 nuclear capacity) is USD 125 billion, a significant increase from USD 50 billion annually from 2017-2023.
- If the aspirational goal to triple nuclear capacity (as pledged by over 20 countries at COP28) is to be met, USD 150 billion annually would be necessary.
- Challenges in Financing: Upfront capital for nuclear power plants is expensive, posing challenges, especially in market-driven economies and developing countries.
- Private Sector and Multilateral Support:
- The private sector will need to play a larger role in financing nuclear projects.
- The IAEA is engaging with multilateral development banks to improve financing options for developing countries to invest in nuclear energy.
- Private finance initiatives: In September 2024, 14 major financial institutions signaled readiness to help fund nuclear newbuild projects.
- Nuclear Financing at Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM):
- The IAEA report was launched during the 15th CEM in Brazil, a high-level forum for advancing clean energy technologies.
- Key stakeholders from Brazil, the IAEA, the International Energy Agency (IEA), and the U.S. discussed strategies for securing nuclear power financing, especially in the context of COP29 (2024) where clean energy financing will be a key focus.
- Nuclear Energy in the EU’s Sustainable Financing:
- The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities now includes nuclear power, facilitating the issuance of green bonds for nuclear projects in Finland and France (2023).
- EDF received €4 billion in green bonds and around €7 billion in green loans (2022-2024).
- Investment in Nuclear Power:
- To meet global climate goals, nuclear power capacity must increase by 1.8 times by 2035.
- Effective financing mechanisms are crucial to scale up nuclear power and develop the workforce and supply chains needed for the energy transition.
- Policy Reform and International Partnerships:
- The report advocates for policy reforms and international partnerships to bridge the financing gap and accelerate nuclear power deployment, particularly in emerging markets and developing economies.
- Focus on technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which could play a role in the energy transition.
- Key Areas to Support Nuclear Growth:
- Robust regulatory frameworks and new delivery models are essential to unlock investments.
- Development of skilled labor and effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the expansion of nuclear energy.
- Energy System Modelling and Planning:
- The IAEA’s energy system modelling tools assist countries like Brazil in planning nuclear power projects, including cost analyses for electricity generation and financing strategies.
Role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- Mandate: The IAEA is the leading international body for promoting the safe, secure, and peaceful use of nuclear energy and technologies.
- Functions:
- Nuclear safeguards: Ensuring nuclear activities remain peaceful and preventing the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- Assisting member states with technical support, knowledge sharing, and strengthening nuclear safety and security.
- The IAEA also supports capacity-building and emergency response in case of nuclear or radiological incidents.
- Structure:
- The IAEA General Conference is made up of all 178 member states, meeting annually to approve budgets and policies.
- The Board of Governors (35 members) meets several times a year to oversee the agency's activities and appointments.
- Headquarters: Vienna, Austria
- The IAEA is part of the United Nations family, reporting to both the UN General Assembly and the Security Council.
