Exercise Agni Warrior
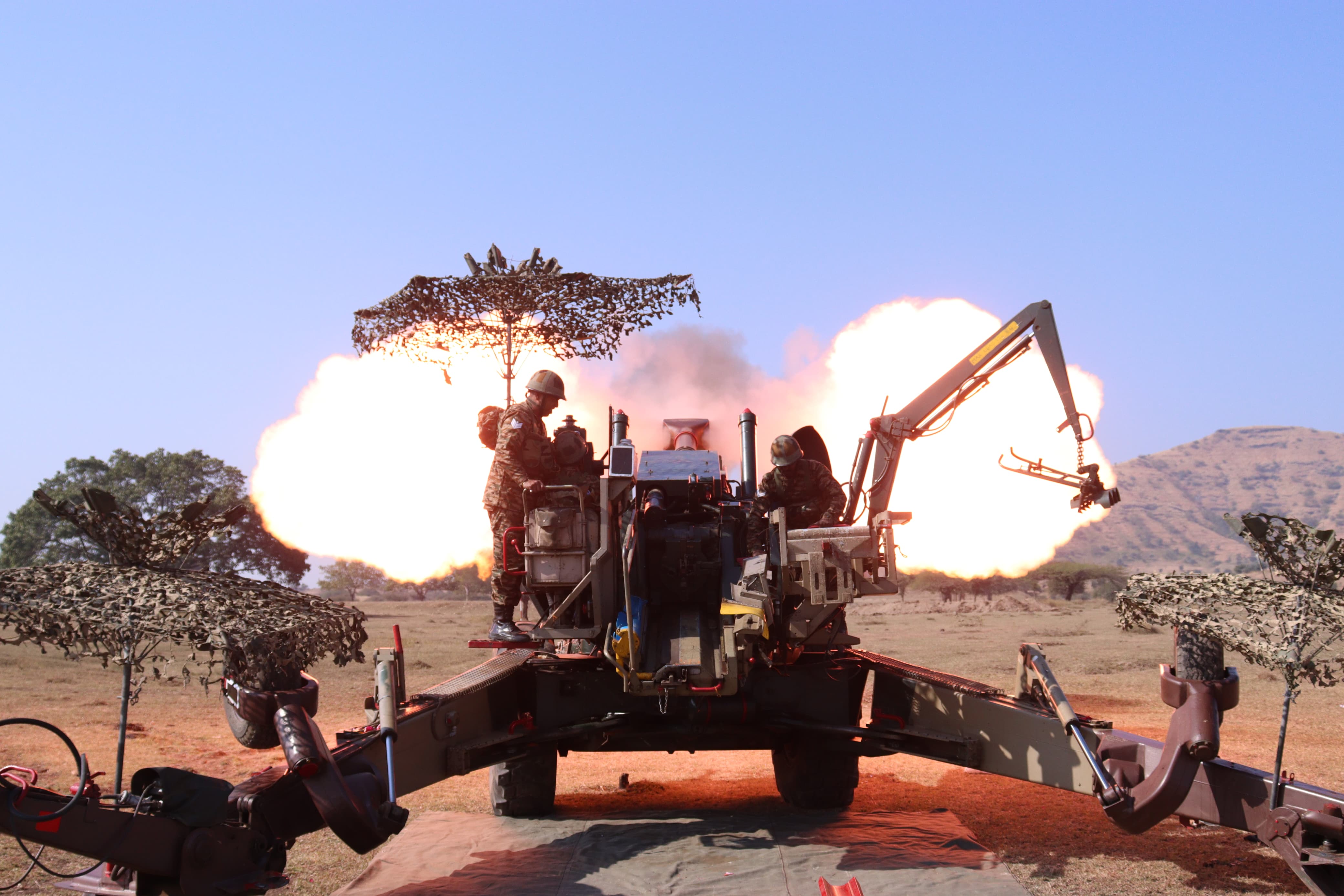

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Agni Warrior (XAW-2024), a joint military drill between the Indian Army and the Singapore Armed Forces (SAF), concluded successfully at the Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra. The exercise focused on enhancing mutual understanding and interoperability between the two nations’ artillery units.
Key Facts:
- Participating Nations: India and Singapore
- Location: Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra
- Participants:
- 182 personnel from the Singapore Artillery
- 114 personnel from the Indian Army's Regiment of Artillery
- Objective: To maximize mutual understanding of drills and procedures for joint operations under the UN Charter, particularly in firepower planning and execution, utilizing advanced artillery technologies.
- Historical Context: The exercise began in 2004 under a bilateral agreement between India and Singapore and has evolved over the years, now marking 20 years of cooperation.
Purpose and Highlights:
The exercise aimed to reinforce the long-standing defense relationship between India and Singapore, focusing on:
- Joint Firepower Planning and Execution: Both forces demonstrated the use of New Generation Artillery Equipment, enhancing their firepower coordination.
- Enhancing Interoperability: The exercise emphasized seamless coordination between the two armies to operate as a multinational force under the UN Charter, addressing global security challenges.
- Knowledge Sharing: Personnel from both armies exchanged expertise on advanced artillery tactics, fostering a deeper understanding of each other's military capabilities.
- Technological Integration: Both sides integrated cutting-edge technologies, allowing the exchange of best practices in the use of artillery systems.
Key Objectives of XAW-2024:
- Enhanced Interoperability: To ensure smooth coordination in joint operations, fostering the ability to respond to regional security threats.
- Firepower and Coordination Techniques: Sharing expertise on artillery planning, coordination, and execution.
- Advanced Equipment Use: Testing and demonstrating modern artillery systems in joint operations, ensuring both forces are prepared for contemporary warfare.
Structure and Execution:
The exercise was structured to include pre-exercise training, field operations, and a post-exercise evaluation:
- Pre-Exercise: Both armies engaged in interactive sessions to familiarize themselves with each other's artillery tactics and advanced systems.
- Field Operations: Simulated combat scenarios tested joint firepower execution, emphasizing real-time problem-solving and decision-making under pressure.
- Post-Exercise Review: A thorough analysis identified areas for improving joint operations and coordination.
Strategic Significance:
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Agni Warrior reinforces the defense partnership, facilitating joint operations that support regional security.
- Regional Stability: The exercise underscores the commitment of both nations to peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Capacity Building: Both Indian and Singaporean forces gained exposure to sophisticated firepower planning and gained operational readiness for future deployments.
PyPIM platform
- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Israeli researchers from the Israel Institute of Technology have developed the PyPIM platform, which allows computers to process data directly in memory, eliminating the need for a central processing unit (CPU). This breakthrough aims to address key challenges in modern computing, particularly in terms of energy consumption and processing efficiency.
Key Features of the PyPIM Platform:
- Integration with Python and PIM Technology:
- The PyPIM platform merges Python programming with digital processing-in-memory (PIM) technology, facilitating in-memory computing where computations occur directly within memory instead of transferring data to and from the CPU.
- Functionality and Innovations:
- Direct In-Memory Computations: PyPIM uses specialized instructions that enable computations to take place directly in memory, reducing the need for data movement between the CPU and memory.
- Developer-Friendly: It allows developers to use familiar languages like Python to write software for in-memory computing systems.
- Solving the "Memory Wall" Issue:
- The platform addresses the memory wall problem, where the speed of the CPU and memory exceeds the data transfer rates, creating bottlenecks that lead to inefficiencies.
- By performing calculations directly in memory, PyPIM reduces time and energy spent on data transfer, optimizing performance.
- Performance Improvements:
- Energy and Time Efficiency: By minimizing energy-intensive data transfers, PyPIM leads to significant energy and time savings.
- Simulation Tools: The platform includes tools that allow developers to simulate potential performance improvements from in-memory processing.
- Real-World Benefits:
- Faster Processing: Tasks performed using PyPIM have demonstrated faster processing speeds, with minimal code changes, particularly in mathematical and algorithmic tasks.
- The platform delivers a significant performance boost in areas like data analysis and algorithmic operations.
The PyPIM platform marks a pivotal advancement in computing architecture, providing a more energy-efficient and faster alternative to traditional CPU-dependent systems by reducing reliance on external memory processing and cutting down on data transfer delays.
AUSTRAHIND 2024
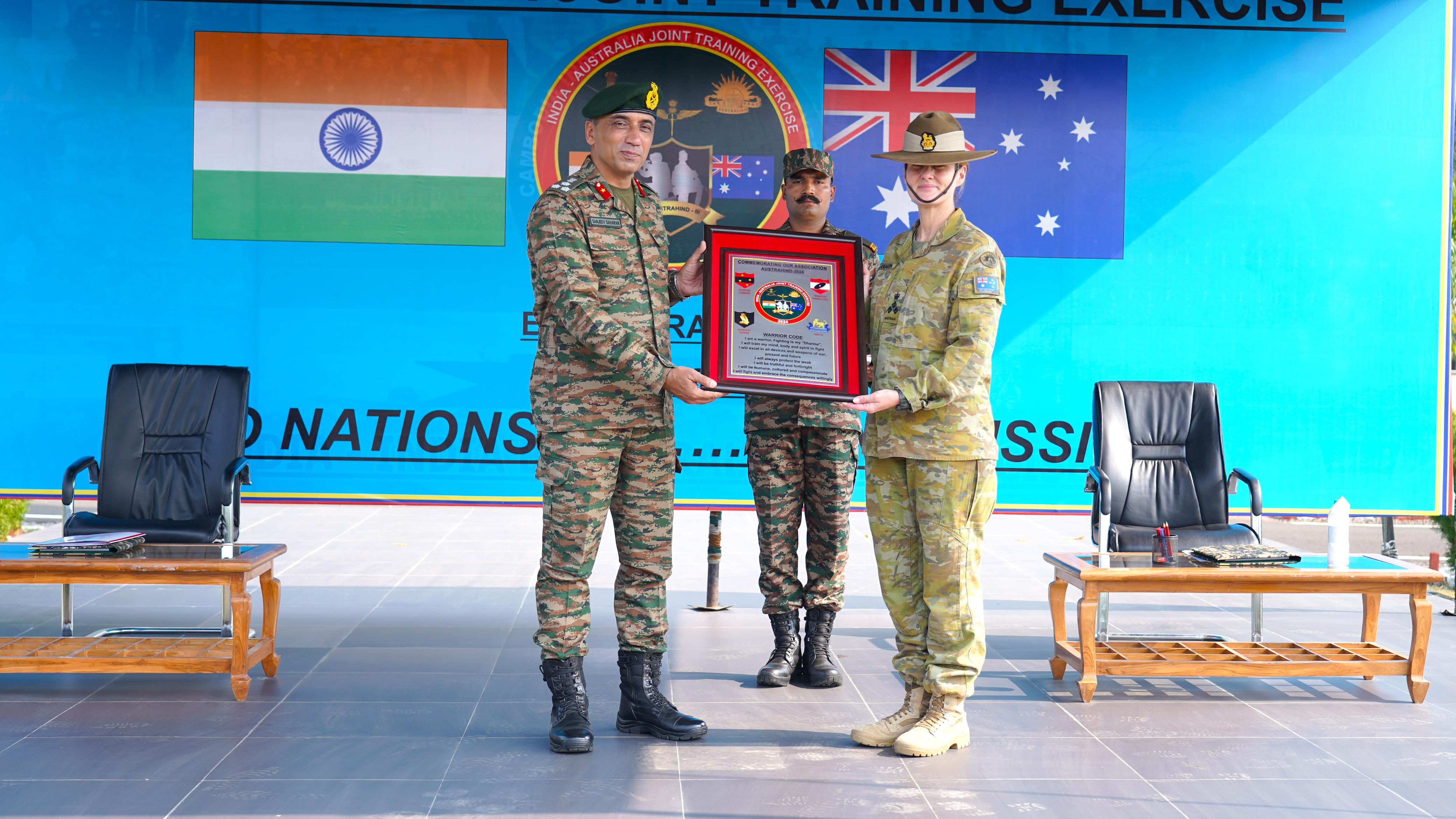

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- The 3rd edition of Exercise AUSTRAHIND started on 8th November 2024 at the Foreign Training Node in Pune, Maharashtra. The exercise will run until 21st November 2024.
Participating Forces:
- Indian Contingent: 140 personnel, primarily from the DOGRA Regiment and Indian Air Force (14 personnel).
- Australian Contingent: 120 personnel from the 13th Light Horse Regiment of the 10th Brigade of the 2nd Division.
Purpose of the Exercise:
- Enhance Military Cooperation between India and Australia.
- Promote Interoperability in conducting joint sub-conventional operations in semi-urban and semi-desert terrain.
- Focus on operations under Chapter VII of the UN mandate.
Key Objectives:
- Joint Tactical Drills and Planning to improve coordination between the forces.
- Training in counter-terrorism operations, special heli-borne operations, and drone countermeasures.
Phases of the Exercise:
Combat Conditioning and Tactical Training Phase:
- Includes drills such as terrorist response, territory capture, and Raid and Search & Destroy Missions.
- Establishment of Joint Operations Centre and securing critical infrastructure like helipads.
- Training on drone operations and counter-drone measures.
Validation Phase: Practical application and testing of skills learned in the previous phase.
Significance:
Best Practices Sharing: Both sides will exchange tactics, techniques, and procedures for conducting effective tactical operations.
Camaraderie Building: The exercise will foster a strong bond between soldiers from both countries.
Background: AUSTRAHIND is an annual exercise held alternately in India and Australia. The last edition took place in Australia in December 2023.
Digital Population Clock

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Bengaluru's first digital population clock was inaugurated at the Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC) on November 8, 2024.
- The initiative is collaboration between ISEC and the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
Purpose:
- The clock provides real-time population estimates for Karnataka and India.
- It aims to enhance awareness about population dynamics and provide accurate demographic data for research and policy analysis.
Key Features:
- Real-time Updates:
- Karnataka’s population is updated every 1 minute and 10 seconds.
- India’s population updates every 2 seconds.
- Precision:
- The clock operates with satellite connections for real-time, accurate data updates.
- It functions autonomously with integrated components, ensuring continuous and precise tracking.
- Location: The clock is prominently displayed at the entrance of ISEC.
- National Expansion: Similar digital population clocks are being installed in 18 Population Research Centres across India by MoHFW.
Significance:
- Awareness: The clock serves as a visual tool to highlight the rapid pace of population growth and its implications for sustainable development.
- Research and Analysis: The clock is part of a broader effort to improve demographic studies and inform policy-making.
- Census Data Research Workstation:
- ISEC has introduced a new research workstation, supported by MoHFW, for in-depth demographic analysis.
- The facility is equipped with advanced software for studying population trends and supporting academic research.
RNA Editing

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
Wave Life Sciences became the first biotechnology company to treat a genetic condition by editing RNA at the clinical level.
- What is RNA Editing?
- Definition: RNA editing is the modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) after it’s synthesized from DNA but before it is translated into proteins.
- Process: mRNA consists of exons (coding regions) and introns (non-coding regions). Exons code for proteins, while introns are removed before protein synthesis.
- Types of RNA Modifications:
- Addition: Insertion of a nucleotide.
- Deletion: Removal of a nucleotide.
- Substitution: Replacement of one nucleotide with another.
- Mechanism of RNA Editing:
- Involves Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA (ADAR) enzymes.
- ADAR enzymes modify adenosine to inosine, which is recognized as guanosine, allowing mRNA to be corrected.
- Guide RNA (gRNA) directs ADAR enzymes to the specific mRNA region for editing.
- Clinical Use of RNA Editing:
- Wave Life Sciences used RNA editing to treat α-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), a genetic disorder.
- Other potential applications include treating diseases such as Huntington’s disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Parkinson’s disease, obesity, and neurological disorders.
- Challenges in RNA Editing:
- Temporary Effects: RNA editing provides temporary changes, requiring repeated treatments for sustained effects.
- Delivery Issues: Current delivery methods, like lipid nanoparticles and adeno-associated virus vectors, have limitations in carrying large molecules.
- Specificity: ADARs may cause unintended changes in non-target regions of mRNA, leading to potential side effects.
- Comparison: RNA Editing vs. DNA Editing:
- Safety: RNA editing causes temporary changes and presents fewer risks than DNA editing, which makes permanent alterations to the genome.
- Immune Response: RNA editing uses enzymes naturally found in the body (ADAR), which reduces the risk of immune reactions, unlike DNA editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 that can trigger immune responses.
- Significance of RNA:
- Structure: RNA is a nucleic acid, similar to DNA but typically single-stranded. It consists of a backbone of ribose sugars and phosphate groups, with bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- Types of RNA:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the core of the ribosome and catalyzes protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Regulatory RNAs: Regulate gene expression.
- α-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD):
- A genetic disorder where the protein α-1 antitrypsin accumulates in the liver, damaging both the liver and lungs.
- Treatments include weekly intravenous therapy or, in severe cases, liver transplants.
- RNA editing offers a potential new treatment approach.
- Global Impact:
- RNA editing is still in its early stages but shows promise for treating a wide range of genetic and chronic conditions.
- Ongoing research and clinical trials suggest RNA editing could become a key part of future gene-editing therapies.
Global Education Monitoring Report 2024

- 09 Nov 2024
In News:
- Released at the Global Education Meeting, hosted in Fortaleza by Brazil, the G20 President.
- Highlights progress and challenges in global education, with a focus on leadership, financing, and access.
Key Observations:
Leaders as Agents of Change:
- Education leadership is defined as social influence towards achieving common educational goals.
- Education leaders must:
- Define clear purposes and influence change.
- Balance learning outcomes with equity, quality, and inclusion.
Funding Deficits:
- 4 out of 10 countries spend less than 4% of their GDP on education.
Out-of-School Children:
- 251 million children and youth globally remain out of school, with only a 1% reduction since 2015.
Regional Disparities in Education Access:
- Central and Southern Asia show significant progress, but countries like Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan still have large out-of-school populations.
Recommendations:
- Leadership Development: Empower school principals with the autonomy to manage schools effectively.
- Capacity Building for System Leaders: Strengthen the ability of education officials to act as system leaders.
- Climate Change Education: Introduce climate change topics in early education across subjects, not limited to science.
India’s Educational Initiatives:
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: Focuses on developing school leadership through training and workshops for principals.
- NISHTHA Program: Aims to improve leadership and management competencies of school heads and teachers.
Current Educational Landscape:
- Since 2015, 110 million children have entered school, and 40 million more complete secondary education.
- However, 33% of children in low-income countries remain out of school, compared to only 3% in high-income countries.
- Sub-Saharan Africa houses more than half of the global out-of-school youth.
Challenges in Education Financing:
- UNESCO–World Bank report highlights that 40% of countries allocate less than 15% of their public expenditure to education.
- Countries investing less than 4% of GDP in education face significant resource shortages.
- Low-income countries spend an average of $55 per learner, while high-income countries spend $8,543 per learner.
Need for Innovative Financing Mechanisms:
- Debt-for-Education Swaps: Proposes converting unsustainable debt into funding for education, leveraging past successful initiatives.
- Multilateral Platforms: Suggested to facilitate global negotiations for converting debt into educational investments, involving entities like UNESCO and the G20.
International Cooperation and Solidarity:
- Decline in Education Assistance: Official development assistance for education has decreased from 9.3% in 2019 to 7.6% in 2022.
- Strengthening Partnerships: The need for enhanced global cooperation to fill the educational financing gap and ensure equitable access to quality education.
