Smart Cities Mission (SCM)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
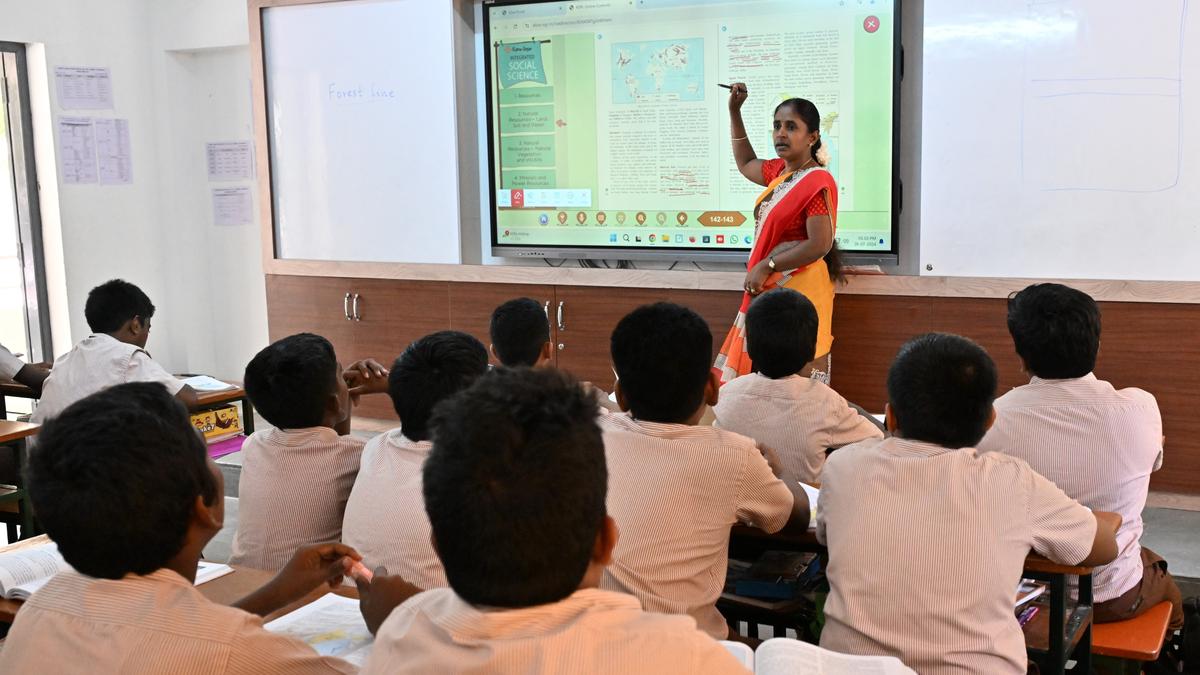
The introduction of smart classrooms as part of the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has had a significant impact on education, leading to a 22% increase in enrolment across 19 cities, according to a report from the Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B). The study covers the period from 2015-16 to 2023-24 and highlights several key benefits of this initiative, which aims to improve the overall learning environment in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Increased Enrolment: The introduction of smart classrooms has been linked to a 22% increase in student enrolment across 19 cities, suggesting that the initiative has made education more appealing and accessible.
- Smart Classroom Development: By 2023-24, 71 cities had developed 9,433 smart classrooms in 2,398 government schools. The states with the most smart classrooms are:
- Karnataka (80 classrooms)
- Rajasthan (53 classrooms)
- Tamil Nadu (23 classrooms)
- Delhi (12 classrooms)
- West Bengal has a very limited number, with just two classrooms.
- Improved Learning Experience: Teachers have expressed positive feedback, agreeing that the smart classrooms have improved learning experiences and attendance among students. Additionally, the smart classroom setup has contributed to increased comfort for teachers and higher preference for these modern facilities.
- Teacher Training: Special training provided to teachers has enhanced their comfort with using the smart classroom tools, with senior secondary teachers showing the highest comfort levels.
- Digital Libraries: The study also found that 41 cities have developed Digital Libraries with 7,809 seating capacity, offering essential resources for students. Cities like Raipur (Chhattisgarh) and Tumakuru (Karnataka) have seen positive outcomes from these libraries, particularly in supporting students preparing for competitive exams.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission aims to promote cities that offer core infrastructure, a decent quality of life, a sustainable environment, and the application of smart solutions. As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the mission have been completed.
SAAR Platform and Research
- In 2022, the Smart Cities Mission introduced the SAAR (Smart Cities and Academia towards Action and Research) platform to bridge the gap between academia and the government. Under this platform, 50 impact assessment studies have been initiated by 29 premier institutions, including six Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), and 12 specialized research institutes.
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has recently been renamed MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease), reflecting a shift in understanding of the disease's root causes and its broader implications.
Why the Name Change?
- The primary reason for renaming NAFLD to MASLD is to highlight the metabolic dysfunction as the primary cause of the disease.
- Previously, the term NAFLD focused on the absence of alcohol consumption, which inadvertently shifted attention away from the true contributors, like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- The term MASLD eliminates the stigma associated with "non-alcoholic," which may have misled people into thinking alcohol consumption was the only factor, even though metabolic issues are the central cause.
- The term MASLD shifts the focus towards metabolic dysfunction, making it easier for healthcare professionals to understand, diagnose, and treat the condition more effectively.
The Connection to Metabolic Dysfunction
- MASLD is strongly associated with metabolic issues such as abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, and high blood sugar. These metabolic problems are key contributors to liver fat accumulation.
- People with abdominal obesity are 2-3 times more likely to develop fatty liver disease. MASLD affects about 25% of the global population, and the rates increase significantly (up to 50-70%) in individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity.
- By focusing on metabolic dysfunction, MASLD encourages addressing the root causes rather than just the symptoms, offering a more effective approach to treatment and prevention.
How is MASLD Diagnosed?
Advancements in non-invasive diagnostic methods have improved the ability to diagnose MASLD more easily and accurately, including:
- FibroScan: A non-invasive, painless test to measure liver fat and stiffness, replacing the need for liver biopsy.
- MRI and Ultrasound Techniques: Reliable methods for assessing liver fat and scarring.
- Blood Tests: Common tests like ALT, AST, and GGT assess liver function. Researchers are also exploring new markers like CK-18 fragments and the ELF score (Enhanced Liver Fibrosis) to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Implications for Patient Care
The renaming of NAFLD to MASLD has important implications for patient care:
- Targeted Treatments: By focusing on the metabolic roots, treatments such as weight loss, blood sugar management, and cholesterol control can be prioritized. These interventions help reduce the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, liver failure, and cirrhosis.
- Earlier Diagnosis: MASLD encourages earlier recognition of the condition, which can lead to better management and improved long-term outcomes.
Prevention
Preventing MASLD involves avoiding foods that exacerbate liver fat buildup. Dr. Punit Singla, director at Marengo Asia Hospitals, emphasizes limiting or avoiding:
- Fast food, junk food, and processed foods
- Foods high in sugar, including red and processed meats
A healthier lifestyle with a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can significantly help prevent or manage MASLD.
61st Raising Day

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 20, 2024, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah attended the 61st Raising Day function of the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) in Siliguri, West Bengal. During the event, he e-inaugurated the Integrated Check Point (ICP) Agartala and a newly constructed residential complex for the Border Guard Force (BGF) at Petrapole. The event was attended by several dignitaries, including the Director of Intelligence Bureau (IB), Secretary of Border Management (MHA), and the Director-General of SSB.
Key Highlights from the Speech:
- Tributes to Martyrs: Shri Shah paid tributes to SSB martyrs, highlighting their sacrifices in protecting the country's borders and eliminating Left Wing Extremism in the eastern region. He acknowledged the 4 Padma Shri, 1 Kirti Chakra, and other national awards received by SSB for their exceptional service.
- Role in Connecting Borders: The Home Minister praised SSB’s role in connecting the culture, language, and heritage of border villages with mainstream India. He emphasized that the SSB has fulfilled its motto of "Service, Security, and Brotherhood" while maintaining a strong relationship with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Security and Vigilance: SSB is responsible for securing a 2,450 km border with Nepal and Bhutan. Shri Shah noted that SSB's vigilance has helped in stopping narcotics, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Additionally, the force has worked to ensure that Bihar and Jharkhand are now Naxal-free.
- Zero-Tolerance Policy: The SSB has a zero-tolerance policy on encroachments, narcotics, and smuggling. Over the last three years, the SSB successfully removed more than 1,100 encroachments from government land and seized significant amounts of narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit currency.
- Impact in Jammu & Kashmir: SSB has played a critical role in combating terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, killing more than 19 terrorists and arresting 14 through various operations.
- Humanitarian Efforts: Besides security, SSB has actively participated in disaster relief operations during floods and landslides, often at great personal risk.
- Government Schemes for CAPF Personnel: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, various welfare schemes like Ayushman Cards, CAPF e-Housing, and scholarships have been launched to support CAPF personnel and their families.
- Self-Employment Initiatives: SSB has promoted self-employment for border youth, training them in areas like beekeeping, mobile repairing, and driving. They have also contributed significantly to the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, creating awareness about drug addiction among 36,000 youth.
- Environmental Contribution: The force has planted over 6 crore trees as part of its environmental efforts.
Pegasus Spyware

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
For the first time, a court in the US has held Israel’s NSO Group liable for its intrusive spyware Pegasus, which could set up a measure of accountability for the company that it has, for long, allegedly downplayed.
Overview:
- Pegasus is a spyware developed by the Israeli company NSO Group.
- It has been used for surveillance, allegedly targeting journalists, activists, politicians, and government officials across the world, including India.
Recent Legal Developments:
- US Court Ruling (2024):
- A US court held NSO Group liable for using Pegasus to surveil 1,400 WhatsApp users, including 300 from India.
- NSO Group violated the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the California Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA).
- The ruling may revive debates on the accountability of spyware use and its implications on privacy.
Use of Pegasus in India:
- Targeted Individuals (2021):
- 300 Indian numbers allegedly targeted, including journalists, politicians, Union Ministers, and civil society members.
- High-profile targets included opposition leaders, constitutional authorities, and activists.
- Government Denial:
- The Indian government denied involvement, stating allegations lacked substance.
- In Parliament, IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw rejected claims, asserting India’s surveillance laws prevent unauthorized surveillance.
- NSO Group Response:
- NSO Group denied the allegations, calling them “false and misleading” and citing doubts about the sources.
Investigations and Legal Actions:
- Supreme Court Inquiry:
- The Supreme Court appointed a committee of technical experts in 2021 to investigate claims.
- August 2022 Report: Found no conclusive evidence of spyware use on examined devices but noted lack of cooperation from the government.
- State-Level Investigations:
- West Bengal: Set up a Commission of Inquiry into Pegasus surveillance, later halted by the Supreme Court.
- Andhra Pradesh: The issue became political, with allegations that the previous government used Pegasus to monitor opposition figures.
Pegasus Spyware Features:
- Capability: Can hack iOS and Android devices to collect data, record conversations, capture photos, and access app data.
- Exploitation Method: Uses zero-day vulnerabilities to exploit iOS and Android devices covertly.
- Invisibility: Operates without user knowledge, often only detected through signs like browser closings after phishing links are clicked.
Controversial Use of Pegasus:
- Global Use: Though intended for fighting terrorism and crime, Pegasus has been misused for spying on journalists, politicians, human rights activists, and opposition leaders.
- India Specifics:
- Pegasus Project: Targeted Indian citizens, including activists, journalists, and politicians.
- Amnesty International: Confirmed use of Pegasus to target Indian phones.
India's Legal Framework for Surveillance:
- Telecommunications Act (2023): Empowers the government to control telecom services during emergencies, but requires authorization for lawful interceptions.
- IT Act (2000): Allows the government to monitor, intercept, or decrypt information through computer resources under certain conditions.
- Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act (2023): Aims to protect personal data, including provisions on surveillance, data breaches, and rights of individuals over their data.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns:
- Impact on Fundamental Rights:
- Surveillance infringes on the right to privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Freedom of speech and expression (Article 19) may be curtailed, with surveillance being used to suppress dissent.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Surveillance often occurs without judicial or parliamentary oversight, leading to potential executive overreach.
- Inability to Seek Legal Remedies:
- Citizens targeted by surveillance cannot challenge it due to lack of awareness, undermining constitutional rights.
- Executive Overreach and Suppression of Free Expression:
- Pegasus revelations have raised concerns about surveillance targeting constitutional functionaries, suppressing free speech, and stifling open discourse.
India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind-Aus ECTA) completes two years of remarkable success, driving mutual growth and showcasing the complementarity of both economies.
Key Achievements:
- Bilateral Merchandise Trade Surge:
- Trade increased from USD 12.2 billion (2020-21) to USD 26 billion (2022-23).
- Trade moderated slightly in 2023-24 to USD 24 billion, but exports from India to Australia grew by 14%.
- From April-November 2024, bilateral trade reached USD 16.3 billion.
- Preferential Import Utilization:
- Export utilization: 79%
- Import utilization: 84%
- Sectoral Growth:
- Textiles, chemicals, and agriculture sectors have seen significant growth.
- New export products: Gold studded with diamonds, turbojets.
- India’s imports: Metalliferous ores, cotton, wood products that fuel Indian industries.
- Geopolitical Strengthening:
- Enhanced relations in forums like Quad, Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI).
Key Features of the Agreement:
- Tariff Reductions:
- Australian goods: 85% tariff-free access to India (rising to 90% by 2026).
- Indian goods: 96% tariff-free access to Australia (rising to 100% by 2026).
- Access to Key Markets:
- India: Access to Australia's fast-growing market.
- Australia: Access to India's labor-intensive sectors like gems, jewelry, textiles, leather, furniture, food, agriculture.
- Services and IT:
- 135 sub-sectors covered in services.
- India gains market access in 103 sub-sectors with Most Favoured Nation (MFN) status in 31.
- Fast-tracked approval of medicines and elimination of double taxation for India's IT sector.
- Job Creation & Skill Exchange:
- Expected creation of 1 million jobs in India.
- Opportunities for Indian yoga teachers, chefs, and 100,000 students with post-study work visas.
Future Prospects:
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA): Builds on ECTA to advance bilateral trade, with 10 formal rounds and ongoing inter-sessional discussions.
- Trade Target: Aim to reach AUD 100 billion in trade by 2030.
- Global Economic Impact: Strengthening the partnership will contribute to a more resilient and dynamic global economy, with deeper economic integration between India and Australia.
World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
India to Host World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The summit aims to bolster India's media and entertainment (M&E) industry, expand its global influence, and foster innovation and collaboration within the sector.
- Significance: First-ever global summit to cover the entire media and entertainment industry spectrum.
- Objective:
- Foster Dialogue and Trade: WAVES aims to be a premier platform for industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to engage in meaningful discussions, explore opportunities, and tackle challenges in the M&E sector.
- Promote India's M&E Industry: Attract trade and investment to India, highlighting its strengths in animation, gaming, entertainment technology, and cinema (both regional and mainstream).
- Focus Areas:
- Industry Advancements: Discussions will revolve around India’s progress in animation, visual effects, gaming, and cinema.
- Global Positioning: Establish India as a global powerhouse in the M&E sector, setting new standards for creativity, innovation, and global influence.
WAVES India - Vision and Mission:
- Vision: Position India as a Global Powerhouse: Enhance India’s standing in the dynamic M&E sector, making it a hub of creativity and innovation worldwide.
- Mission:
- Provide exclusive investment opportunities for global M&E leaders through WAVES.
- Drive India’s Creative Economy through Intellectual Property (IP) Creation for both domestic and international markets.
- Develop M&E Infrastructure: Strengthen industry infrastructure and create a skilled workforce to meet global demands.
- Adapt to New Trends: Embrace emerging technologies and transformations in the M&E landscape.
Expected Outcomes:
- Global Collaboration: Engage global M&E leaders in discussions that provoke ideas and facilitate collaborations.
- Attract Investment: Promote India as a business-friendly investment destination in the M&E sector.
- Skills and Capacity Building: Build capacity in the M&E industry and develop skilled human resources to support international needs.
PM CARES Fund Contributions and Utilization (2022-23)
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
The Prime Minister’s Citizen Assistance and Relief in Emergency Situations Fund (PM CARES Fund) received Rs 912 crore in contributions during the financial year 2022-23 as donations continued to pour in even after the Covid pandemic.
Key Highlights:
Contributions Received:
- Total contributions in 2022-23: Rs 912 crore.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 909.64 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 2.57 crore.
Interest Income:
- Total interest income for 2022-23: Rs 170.38 crore.
- From regular accounts: Rs 154 crore.
- From foreign contributions account: Rs 16.07 crore.
Refunds and Additional Inflows:
- Rs 225 crore in refunds, including:
- Rs 202 crore refund from procurement of 50,000 ventilators for government hospitals.
Disbursements:
- Total disbursed in 2022-23: Rs 439 crore:
- Rs 346 crore for PM CARES for Children.
- Rs 91.87 crore for procurement of 99,986 oxygen concentrators.
- Rs 1.51 crore for refunds.
- Rs 24,000 for legal charges, and Rs 278 for bank and SMS charges.
Cumulative Contributions (2019-23):
- Rs 13,605 crore received from 2019-20 to 2022-23.
- Voluntary contributions: Rs 13,067 crore.
- Foreign contributions: Rs 538 crore.
- Interest income over these years: Rs 565 crore.
About PM CARES Fund:
Formation and Purpose:
- Established: March 27, 2020, as a Public Charitable Trust under the Registration Act, 1908.
- Purpose: To address emergencies like COVID-19, natural disasters, and man-made calamities. It also supports healthcare infrastructure and essential facilities.
Governance and Structure:
- Chairperson: The Prime Minister (ex-officio).
- Trustees: Defence, Home, and Finance Ministers (ex-officio).
- Additional Trustees: Appointed by the PM, serving on a non-profit basis (e.g., Justice K T Thomas (retd.) and Kariya Munda).
Tax Exemptions:
- Donations are eligible for 100% tax exemption under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Donations qualify as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expenditure under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The fund is exempt under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), allowing it to receive foreign donations.
ASI Discovery at Srisailam Temple

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) uncovered ancient copper plates and gold coins at the Srisailam Temple in Andhra Pradesh, specifically in the Ghantamandapam area.
- The discovery includes 20 sets of copper plates, totaling 72 leaves, and various gold coins.
- The ASI's Epigraphy Branch in Mysore has completed the documentation of these findings, and the materials are being studied in detail.
Collaboration with Srisailam Devasthanam:
- In collaboration with the Srisailam Devasthanam, ASI plans to publish a book that will detail the findings and their historical significance.
- The book will be printed soon by Pragati Publications in Hyderabad.
Srisailam Temple Overview:
- The Srisailam Temple, also known as the Mallikarjuna Swamy Temple, is a prominent Hindu pilgrimage site in Andhra Pradesh.
- It is located in the Nallamala Hills, overlooking the Krishna River.
- The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva in the form of Mallikarjuna Swamy and Goddess Parvati as Bhramaramba Devi.
- It is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva and one of the Shakti Peethas, making it significant in both Shaivism and Shaktism.
Architectural Significance:
- The temple is built in the Dravidian style, featuring lofty towers and expansive courtyards, and is considered a prime example of Vijayanagara architecture.
- Historical references to the temple date back to the Satavahana period (2nd century AD), and the temple was further endowed by the Kakatiyas and Vijayanagara rulers.
Cultural and Religious Importance:
- The Srisailam Temple is unique for housing both a Jyotirlinga (Lord Shiva) and a Shakti Peetha (Goddess Bhramaramba), a rare combination not found at other temples.
- The great religious figure Adi Shankaracharya is believed to have visited the temple and composed the Sivananda Lahiri there.
Historical Context:
- The copper plates and inscriptions discovered are likely to provide valuable insights into the historical and cultural significance of the temple, as well as the region's ancient religious practices.
Reassessment of Conjugal Visits in Delhi Prisons

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi government is reassessing the proposal to permit conjugal visits for prisoners, following the suspension of a similar initiative in Punjab.
- Delhi Chief Minister has sought further input from the Law Department and explored if similar schemes are implemented in other states.
Conjugal Visits - Definition & Context:
- Conjugal visits involve allowing prisoners to spend private time with their legal partners or spouses, including intimate relations, within prison premises.
- No national policy exists in India for conjugal rights of prisoners, leading to varied implementations across states.
Punjab’s Pilot Project - ‘Parivar Mulakat’:
- Ludhiana Central Jail introduced the 'Parivar Mulakat' programme in September 2022, allowing face-to-face meetings with family in designated rooms.
- The initiative was suspended shortly after its launch due to security concerns, particularly difficulty in conducting thorough body checks on visitors.
Challenges in Delhi:
- Overcrowded prisons in Delhi make it challenging to manage the logistical demands of conjugal visits, especially with up to 1,200 daily visitations.
- The Home Department has received proposals but no progress has been made over the past year.
Legal Precedents on Conjugal Rights:
- Punjab and Haryana High Court (2014) ruled that prisoners have a right to conjugal visits to facilitate procreation.
- Madras High Court (2018) allowed a life convict on parole for conjugal relations, and in 2023, a judge called for similar considerations for Tamil Nadu.
Human Rights Argument:
- Advocates argue that denying conjugal visits to prisoners violates basic human rights of both prisoners and their spouses, particularly those aged 21-50, who are often in sexually active years.
- Amit Sahni, a social activist, filed a PIL highlighting that most prisoners in Delhi are denied conjugal rights despite their eligibility.
Government’s Position:
- Delhi DG (Prisons) had argued that temporary leave such as parole and furlough serve the purpose of family ties, questioning the need for conjugal visits within prison.
Need for Legal Framework:
- Legal experts suggest the creation of a law and policy framework to regulate conjugal visits, ensuring clear guidelines for their implementation.
- S.D. Singh, a Supreme Court advocate, emphasized that conjugal visits should be legally recognized as a right, requiring formal legislation for consistent implementation.
Future Considerations:
- The Delhi government’s reassessment may lead to a policy that considers both human rights and security concerns in its decision on conjugal visits.
Re-emergence of the Dodo in Kashmir’s Papier Mâché Craft
- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
Artisans in Srinagar, Kashmir, have revived the extinct dodo bird in papier mâché forms. These figurines are exported worldwide, particularly to Mauritius and Europe, ahead of the Christmas season. Over 50,000 dodo figurines have already been sent to international markets in 2024.
Key Highlights:
The Dodo:
- Scientific Name: Raphus cucullatus.
- Extinct Since: 1681, approximately 80 years after humans began interacting with them.
- Endemic to Mauritius: A flightless bird from the Indian Ocean island of Mauritius, a national symbol of the country.
- Extinction Causes: Overhunting and the introduction of invasive species like rats, pigs, and cats that preyed on their eggs.
- Physical Traits: Grey or brown plumage, about 3 feet tall, flightless and fearless.
Papier Mâché Craft in Kashmir:
- History: Practiced for over 600 years in Kashmir, introduced during the reign of King Zain-ul-Abidin (15th century).
- Techniques: Involves creating decorative objects using paper pulp, with traditional Persian motifs.
- Recent Addition of Dodo: The dodo was introduced to the papier mâché craft around two decades ago, likely by Mauritian tourists.
International Market and Demand:
- Mauritius: A significant market for the papier mâché dodo, as the bird is a national emblem of Mauritius.
- Europe: Exported to European countries during the Christmas season, contributing to the popularity of Kashmir’s handicrafts.
- Kashmir's Karkhanas: Local craft workshops in Srinagar are producing thousands of dodo figurines each season, with over 3,000 dodos produced this year.
Cultural and Economic Impact:
- Artisans' Contribution: Local artisans are helping keep the memory of the extinct dodo alive, while boosting Kashmir’s handicraft industry.
- Global Recognition: The dodo is now a sought-after item in global markets, linked to the traditional art of Kashmir.
- Kashmir Handicrafts: Several crafts from Kashmir, including papier mâché, have received Geographical Indication (GI) tags for their distinct cultural and regional significance.
Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
IIT Bombay Develops Painless Needle-Free Shock Syringes
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay, led by Viren Menezes from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, have developed a shockwave-based, needle-free syringe to deliver drugs painlessly and safely. The research was published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials and Devices.
Key Features of Shock Syringe:
- Unlike traditional syringes, the shock syringe uses high-energy shockwaves (traveling faster than the speed of sound) to deliver drugs, without the need for needles.
- The device is designed to reduce pain, tissue damage, and infection risk.
- The shock syringe aims to eliminate the discomfort and fear associated with needles.
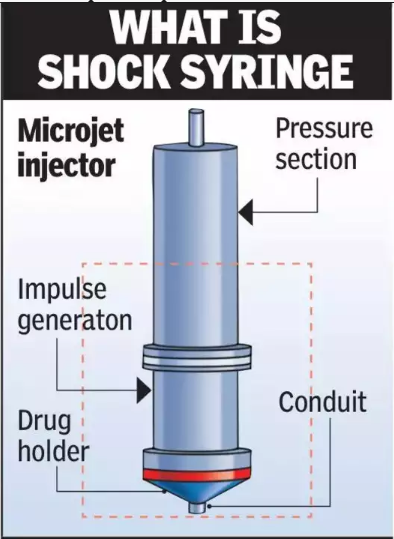
How the Shock Syringe Works:
- The shock syringe is slightly longer than a ballpoint pen and contains a micro shock tube with three sections: driver, driven, and drug holder.
- Pressurized nitrogen gas is applied to the driver section, which creates a microjet of liquid drug. The microjet travels at speeds nearly twice as fast as a commercial airplane.
- The drug is then delivered through the nozzle of the syringe, penetrating the skin rapidly and gently.
Design Considerations:
- The syringe's nozzle has an opening of 125 μm (approximately the width of a human hair), ensuring a balance between precision and speed.
- Continuous monitoring of pressure ensures safe and effective drug delivery with minimal skin damage.
Testing and Results:
- Lab tests were conducted on rats, injecting three types of drugs:
- Anaesthetics (Ketamine-Xylazine): Shock syringe produced similar results to needles in terms of effect onset and duration.
- Viscous drugs (e.g., Terbinafine): The shock syringe outperformed needles, delivering the drug more deeply into the skin layers.
- Insulin for diabetic rats: The shock syringe lowered blood sugar levels more effectively and sustained the effect for a longer period.
- The skin analysis revealed less damage and inflammation with the shock syringe compared to traditional needles.
Advantages:
- Painless drug delivery: Patients experience little to no discomfort.
- Reduced tissue damage: The shock syringe causes less skin trauma and inflammation.
- Faster healing: Wounds from the injection heal quicker compared to traditional needles.
- Better drug absorption: Especially for viscous drugs, the shock syringe delivers more efficient and deeper drug penetration.
Potential Applications:
- The shock syringe could revolutionize immunization drives, making vaccinations faster and more efficient.
- It could significantly reduce the risk of bloodborne diseases caused by needle-stick injuries.
- The device is designed to perform over 1,000 injections, ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability with minimal nozzle replacements.
Future Prospects:
- While promising, the future of shock syringes in clinical use depends on:
- Further innovation for human use.
- Obtaining regulatory approval.
- Ensuring the device’s affordability and accessibility.
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Delhi High Court has ordered the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government.
- This MoU will facilitate the implementation of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) in Delhi.
About PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- Scheme Type: Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with some Central Sector Components (CS).
- Total Outlay: Rs. 64,180 Crores for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Objective:
- To strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, focusing on:
- Building capacities in health systems at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels.
- Preparing health systems to effectively respond to current and future pandemics/disasters.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Filling critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and health research in both urban and rural areas.
- Improving healthcare delivery across the entire continuum of care.
- Central Sector Components (CS) under the Scheme:
- 12 Central Institutions: To act as training and mentoring sites with 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening NCDC: Boosting the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) and establishing 5 new regional NCDCs.
- Health Surveillance: Creation of 20 metropolitan health surveillance units and expansion of Integrated Health Information Portal across all States/UTs.
- Public Health Units: Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and strengthening 33 existing units at Points of Entry (Airports, Seaports, Land Crossings).
- Emergency Health Infrastructure: Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 mobile hospitals.
- Research and Virology Institutes: Setting up a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs under CSS Component:
- Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs):
- 17,788 rural HWCs: To be built in areas with populations of 5000 (plain) or 3000 (difficult terrain like hills, tribals, desert).
- 11,024 urban HWCs: Focus on slum and vulnerable areas with a population of 15,000-20,000.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): Establishment of 3,382 BPHUs at the block level to strengthen healthcare accessibility.
- Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs): Setting up 730 IPHLs across districts for better health monitoring.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): Establishment of 602 CCBs in districts with populations exceeding 5 lakh and referral linkages in other districts.
- Overall Goal: PM-ABHIM aims to significantly enhance healthcare infrastructure in India, making healthcare more accessible and effective, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas.
UN Approves New AU Force to Combat Al-Shabaab in Somalia
- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
- On January 19, 2024, the UN Security Council approved a new African Union (AU) force in Somalia to counter the Al-Shabaab terrorist group.
- The resolution was supported by 14 of 15 members, with the US abstaining due to concerns about funding.
- The new force will replace the African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) after its mandate ends on December 31, 2024.
New Mission - AUSSOM:
- The new mission is named African Union Support and Stabilization Mission in Somalia (AUSSOM).
- AUSSOM will continue supporting Somali forces in stabilizing the nation and combating terrorism.
- The mission's objective is to enhance security and stability in Somalia, addressing the challenges posed by Al-Shabaab and ISIL.
Mandate and Operations:
- AUSSOM allows for the deployment of up to 12,626 personnel, including 1,040 police officers, until June 2025.
- The force will focus on counterterrorism, maintaining security, and assisting the Somali government in stabilizing the country.
Financing:
- A hybrid funding approach will be used:
- 75% of the mission’s costs will be covered by the UN, and 25% will come from African Union and partner countries.
- The US raised concerns about the UN's disproportionate funding of the mission, which led to its abstention from voting.
Contributing Countries:
- Egypt has announced its participation in the new force.
- Burundi and Ethiopia will not be contributing troops to AUSSOM.
- Ethiopia has its own ongoing disputes with Somalia, particularly regarding its maritime deal with the breakaway Somaliland region.
Background on Somalia's Challenges:
- Somalia has faced decades of civil war, an insurgency by Al-Shabaab, and recurring climate disasters.
- The country is one of the poorest in the world, and its internal conflicts are exacerbated by clannism, which has fragmented its political and social structure.
Historical Context of Peace Missions in Somalia:
- Previous UN peacekeeping missions in Somalia (1992-1995) faced significant failures, notably the Battle of Mogadishu and the failure to prevent the 1993 massacre.
- The rise of Al-Shabaab in the mid-2000s has further escalated the conflict, and the mission of AUSSOM aims to address these continuing threats.
The Role of Clannism:
- Clannism has hindered the establishment of a unified government in Somalia, with clan rivalries leading to a lack of national cohesion.
- Clannism refers to the prevalence of clan-centric politics, where allegiance to clan and sub-clan interests often takes precedence over national cohesion. In Somalia, the major clans are Darod, Hawiye, Dir, and Rahanweyn.
Importance of AUSSOM:
- AUSSOM represents a strategic shift in the international approach to stabilizing Somalia, relying more on African-led initiatives for peace and security in the region.
Global Peacekeeping Operations:
- The UN peacekeeping mission has been active globally, with over 1 million personnel deployed across 70+ operations.
- Success stories like Sierra Leone (1999-2005) and Liberia (2003-2018) demonstrate the potential impact of well-executed peace missions, but past failures like in Somalia (1992-1995) and Rwanda (1994) underline the challenges faced.
India’s Contribution:
- India has contributed significantly to UN peacekeeping missions, deploying over 253,000 personnel in 49 operations since 1948.
- India’s contributions to missions in Somalia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, and Sudan reflect its active role in global peacekeeping efforts.
ASI Decodes Sanskrit Inscription Found in Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK)

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
An ancient Sanskrit inscription found in Gilgit (PoK) was decoded by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
About the Inscription:
- Location:
- Gilgit (PoK): Written in Brahmi script, dating back to 4th century CE.
- Peshawar (Pakistan): Written in Sharada script, dating to 10th century CE.
- Details of Gilgit Inscription:
- Mentions Pushpasingha, who installed a Mahesvaralinga for the merit of his guru.
- Written in Brahmi script, which was prevalent during the 4th century CE.
- Religious Context: Indicates significant religious connection, particularly with Shaivism.
- Details of Peshawar Inscription:
- Fragmentary: Engraved on a slab.
- Written in Sharada characters (10th century CE).
- Mentions Buddhist Dharini (chants), particularly referring to Da (Dha) rini in line six.
- The inscription is partially damaged, and further details are unclear.
- Earlier Discoveries:
- This is not the first Sanskrit inscription decoded from Pakistan. In the past, Sanskrit inscriptions have been found in various parts of Pakistan.
- Swat Valley: Known for numerous Buddhist rock inscriptions in Sanskrit using Nagari script, which were part of the Gupta Empire (circa 240–550 CE).
- Religious and Cultural Implications:
- The Gilgit inscription provides evidence of Shaivism as a prominent religious practice in the region during the 4th century CE.
- The Peshawar inscription suggests Buddhist influences, particularly related to Buddhist chants and rituals.
- Swat Valley's Role: The inscriptions found here highlight its importance as a center of Buddhist learning and cultural exchange.
China approves construction of World’s Largest Hydropower Dam on the Brahmaputra River

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
China approved the construction of the world's largest dam, stated to be the planet's biggest infra project, on the Brahmaputra river in Tibet close to the Indian border, raising concerns in India and Bangladesh.
Key highlights:
Overview of the Project:
- Location: Lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River (Tibetan name for Brahmaputra), where the river makes a U-turn in the Himalayan region before flowing into Arunachal Pradesh, India.
- Purpose:
- To support China’s carbon neutrality goals.
- To boost industrial growth and create jobs in Tibet.
- Expected to generate 300 billion kWh of electricity annually, over three times the capacity of the Three Gorges Dam in central China.
Significance:
- Scale: The dam is poised to be the world’s largest hydropower project, surpassing the Three Gorges Dam, and becoming the biggest infrastructure project globally, with an estimated cost of USD 137 billion.
- Engineering Challenges: The site is located in a seismic zone on the Tibetan plateau, prone to earthquakes, making construction and operational stability a major engineering challenge.
Concerns:
- Environmental Impact:
- Potential disruption to the local ecosystem and biodiversity.
- Risk of altering the river’s flow and course, which could impact agriculture and water resources downstream, particularly in India and Bangladesh.
- Geopolitical Risks:
- Water control: India and Bangladesh are concerned about China’s ability to control the water flow, with fears of China manipulating the flow to release excess water during conflicts, causing potential flooding in border areas.
- The project could also disrupt the hydrological cycle, affecting the region’s water availability, especially in Assam and Bangladesh.
Background:
- The Brahmaputra River is a trans-boundary river, flowing through China, India, and Bangladesh. Known by different names in these countries, it plays a vital role in the livelihoods of millions of people.
- China has already initiated hydropower generation on the upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo, with plans for additional projects upstream.
India-China Cooperation:
- China and India have an Expert Level Mechanism (ELM) in place since 2006 to manage trans-boundary river issues, under which China shares hydrological data with India, especially during the flood season.
- India is also constructing its own hydropower projects on the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh.
Potential Outcomes:
- Energy Generation: The dam could significantly contribute to China’s energy needs, providing a substantial amount of renewable energy.
- Regional Tensions: The dam’s construction may escalate tensions between China, India, and Bangladesh due to the control over water resources and environmental impact concerns.
Parker Solar Probe’s Closest-Ever Approach to the Sun

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA scientists announced that the Parker Solar Probe survived the closest-ever approach to the Sun. The craft was operating normally after it passed just 6.1 million km from the solar surface.
About the Parker Solar Probe:
- Launched: August 12, 2018, as part of NASA’s Living With a Star program.
- Named After: Eugene Newman Parker, a solar astrophysicist, marking the first NASA mission named after a living researcher.
- Mission Objectives:
- To study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind, investigating why the corona is hotter than the Sun’s surface.
- To explore the origins of solar winds and high-energy particles that impact space weather.
- To understand the structure and dynamics of plasma and magnetic fields around the Sun.
- To examine the mechanisms behind the acceleration and transportation of energetic particles.
Technological Feats:
- Heat Shield: Equipped with a 4.5-inch carbon-composite shield that withstands temperatures up to 1,377°C (2,500°F) while keeping the instruments cool at about 29.4°C (85°F).
- Speed: Travels at a speed of 692,000 km/h (430,000 mph), making it the fastest human-made object.
- Venus Flybys: Uses gravitational assists from Venus to gradually reduce its orbit and get closer to the Sun.
Historic Milestone:
- Closest Approach: On December 24, 2024, Parker Solar Probe reached a historic distance of 6.1 million km from the Sun's surface, the closest any human-made object has ever been.
- Comparison: If the Earth and Sun were 1 meter apart, Parker Solar Probe would be just 4 cm from the Sun.
- Temperature: At its closest, it endured temperatures up to 1,377°C.
Significance of the Mission:
- Scientific Contributions:
- Solar Wind: Helps scientists understand the origins of solar winds, which affect space weather and Earth’s technological systems.
- Corona Heating: Investigates why the Sun's corona is much hotter than its surface (a long-standing astrophysical mystery).
- Space Weather: Provides critical data for predicting space weather events that can impact satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth.
- Practical Implications:
- Improves understanding of space weather, potentially aiding in the protection of Earth’s infrastructure from solar storms.
- Technological and Engineering Marvel:
- Demonstrates advanced spacecraft technology that can withstand extreme conditions close to the Sun.
Recent Developments:
- Data Collection: As the probe passed through the Sun’s outer atmosphere (the corona), it collected valuable data expected to answer fundamental questions about solar behavior.
- Communication: Despite the extreme proximity to the Sun, the probe sent back a signal on December 26, confirming its status.
Key Dates:
- Launch: August 12, 2018.
- Closest Approach: December 24, 2024.
- Data Expected: Detailed telemetry data on January 1, 2025.
Exercise SURYA KIRAN

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian Army Contingent Departs for 18th Edition of Exercise SURYA KIRAN (India-Nepal Joint Military Exercise).
Key Highlights:
- Event Overview:
- Name: 18th Edition of Battalion-Level Joint Military Exercise SURYA KIRAN.
- Dates: 31st December 2024 to 13th January 2025.
- Location: Saljhandi, Nepal.
- Participants: Indian Army (334 personnel, led by a Battalion from the 11th Gorkha Rifles) and Nepal Army (Srijung Battalion).
- Objective of Exercise:
- Enhance interoperability in jungle warfare, counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrain, and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) under the UN Charter.
- Focus on operational preparedness, aviation training, medical aspects, and environmental conservation.
- Key Features:
- Training Focus: Improving combat skills and coordination to operate together in challenging situations.
- Exchange of Ideas: Soldiers from both nations will share best practices, enhance mutual understanding of operational procedures.
- Strengthening Bilateral Relations: Reinforces strong bonds of friendship, cultural linkages, and defense cooperation between India and Nepal.
- Significance:
- Historical Context: Exercise held alternately in India and Nepal since 2011.
- Enhances Combat Readiness: Prepares both armies to address shared security challenges and improve operational capabilities.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Fosters a productive professional environment between India and Nepal.
- Recent Developments:
- The exercise follows visits by General Upendra Dwivedi (Indian Army Chief) to Nepal and General Ashok Raj Sigdel (Nepali Army Chief) to India, strengthening military ties.
- Previous Editions:
- 17th Edition: Conducted in Pithoragarh, Uttarakhand (24th Nov - 7th Dec 2023).
Neolithic Age Grooves Discovery Near Boothapandi

- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
- Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered rock grooves created during the Neolithic age near Boothapandi village, Kanniyakumari district.
- The discovery was made by K. Hari Gopalakrishnan (Archaeological Officer, Tirunelveli and Kanniyakumari districts) and M. Faisal (Sembavalam Research Centre).
Key Highlights:
- Groove Characteristics:
- The grooves are approximately 4,000 years old, formed by Neolithic people for tool sharpening.
- Tools used for activities like hunting, ploughing, and digging were sharpened here.
- The grooves resulted from wear and tear of tools that had broken or worn out during use.
- Groove Dimensions:
- Largest groove: 15 cm in length, 4 cm in width.
- Smallest groove: 8 cm in length, 3 cm in width.
- Similar Discoveries:
- Similar grooves have been found in other parts of Tamil Nadu, including Krishnagiri, Tiruvannamalai, and Villupuram.
- Significance:
- The grooves provide evidence of Neolithic human habitation in the region.
- Ongoing excavations are expected to uncover more about Neolithic culture in the area.The Hindu
Lighthouse Tourism in India

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
Lighthouse tourism in India is rapidly emerging as an exciting and profitable segment of the country's travel and tourism industry. India's coastline, stretching over 7,500 kilometers, is home to 204 lighthouses, many of which are being transformed into vibrant tourist destinations, celebrating both India's rich maritime history and its natural beauty.
Key Highlights:
- Historical and Scenic Appeal: Lighthouses in India are often located in breathtaking coastal or island locations, offering panoramic sea views and access to surrounding natural beauty. Some of these structures are centuries old and are situated near significant cultural landmarks or UNESCO World Heritage Sites, adding cultural depth to the visitor experience.
- Economic Growth: As part of the broader Maritime India Vision (MIV) 2030 and Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, the Government of India is keen to transform these historic lighthouses into hubs of economic activity. By developing infrastructure, creating new tourism-related jobs, and fostering local entrepreneurship, lighthouse tourism aims to benefit coastal communities and boost India's tourism economy. As of 2023-24, 75 lighthouses across 10 states have been equipped with modern amenities, attracting 16 lakh visitors—a 400% increase from previous years.
- Government Initiatives:
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- The 1st Indian Lighthouse Festival, “Bharatiya Prakash Stambh Utsav”, was inaugurated on 23rd September, 2023 by the Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal and Goa Chief Minister, Shri Pramod Sawant at the historic Fort Aguada in Goa.
- The 2nd Indian Lighthouse Festival was held in Odisha. Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, was also joined by Odisha Chief Minister, Mohan Charan Majhi. Shri Sonowal dedicated two new lighthouses at Chaumuck (Balasore) and Dhamra (Bhadrak) and emphasized empowering coastal communities to preserve and promote lighthouses as part of India’s rich maritime heritage.
- Sagarmala Programme: This government initiative integrates infrastructure development with sustainable practices, ensuring that the growth of lighthouse tourism benefits local communities while preserving the environment.
- Tourism Infrastructure: The government has invested ?60 crore in enhancing these sites, providing facilities like museums, parks, amphitheaters, and more to enrich the visitor experience.
- Lighthouse Festivals: The annual Indian Lighthouse Festival, inaugurated in 2023, serves as a key event to promote lighthouse tourism and cultural heritage.
- Sustainable Development: The Indian government places a strong emphasis on eco-friendly tourism. This includes integrating lighthouses into broader coastal circuits and launching digital awareness campaigns to attract domestic and international tourists.
- Community Empowerment and Employment: Lighthouse tourism has already created direct and indirect employment, from hospitality to transportation, local handicrafts, and artisan work, with more than 500 jobs being generated. Local communities are being trained to offer skills in hospitality and tourism services.
Future Plans:
- Skill Development: Programs are being introduced to equip local people with the necessary skills to cater to the tourism industry.
- Sustainable Practices: Eco-friendly practices will continue to be emphasized to protect coastal ecosystems.
- Integration with Coastal Circuits: Lighthouses will become key points of interest in broader coastal tourism itineraries, further enhancing their appeal to tourists.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
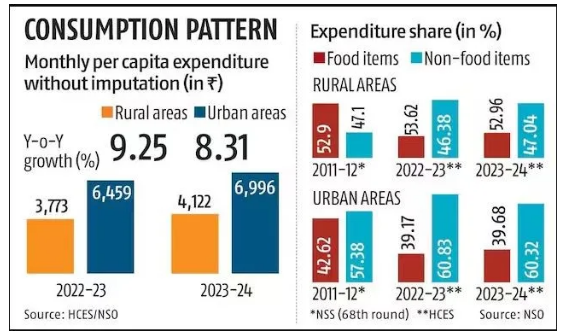
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
Operation Green Scheme

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The government’s flagship Operation Greens scheme, designed to stabilise crop prices and benefit farmers, has spent just 34 per cent of its allocated budget for 2024-25, according to a parliamentary report, even as onion farmers in Maharashtra reel from massive losses and potato shortages grip eastern states.
Key Highlights:
Overview:
- Launched: November 2018 under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana.
- Objective: Stabilize prices and improve farmers' income by enhancing the production and marketing of perishable crops, initially focusing on Tomato, Onion, and Potato (TOP).
- Expanded Scope (2021): Includes 22 perishable crops like mango, banana, ginger, apple, and shrimp.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI).
- Funding: Managed by the National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED).
Key Aims:
- Reduce price volatility in agricultural markets.
- Minimize post-harvest losses.
- Strengthen farm-to-market linkages.
- Enhance farmers’ earnings by stabilizing market prices.
- Promote value addition and food processing.
Scheme Components:
- Short-term Interventions:
- Subsidies on transportation (50%) and storage (50%) to protect farmers from distress sales.
- Price stabilization during periods of surplus or shortage.
- Long-term Interventions:
- Development of farm-gate infrastructure like cold storage and processing facilities.
- Strengthening production clusters and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Building efficient agri-logistics systems.
- Promoting food processing and value addition capacities.
Key Features:
- 50% subsidy on transportation and storage costs for eligible crops.
- Projects eligible for 50% subsidy (up to ?50 crore per project), and for FPOs, a 70% subsidy.
- Demand-driven funding based on applications, with no fixed crop or state-wise allocation.
Key Findings from Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) Report (2024):
- Underutilisation of Budget: Only 34% (?59.44 crore) of the allocated ?173.40 crore for 2024-25 spent by October 2024, leaving 65.73% unspent.
- Slow Implementation: Out of 10 targeted projects, only 3 were completed by October 2024.
- Limited Impact on Price Stabilization:
- Onion prices fell by nearly 50% in Maharashtra, despite the scheme's intent to stabilize prices.
- Potato shortages in states like Odisha and Jharkhand due to weather-induced production dips in West Bengal.
- Inconsistent Policies: Export bans and fluctuating export duties caused frustration among onion farmers, undermining the scheme’s effectiveness in ensuring fair prices.
Impact on Farmers:
- Price Stabilization: Despite the scheme’s aims, price fluctuations continue to affect farmers, especially in Maharashtra with the onion price crash.
- Post-Harvest Losses: The scheme aims to reduce wastage by building infrastructure like cold storage, but challenges remain in implementation.
- Market Linkages: Attempts to connect farmers and FPOs with retail markets have not yet yielded significant results.
Operational Challenges:
- The scheme faces challenges in fulfilling its dual mandate of ensuring fair prices for farmers while keeping consumer prices affordable.
- The slow utilization of funds and incomplete infrastructure projects raise concerns about the effectiveness of the program.
- Inconsistent policy decisions, like the export ban and imposition of export duties, have contributed to farmer discontent.
Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya Committee

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has set up an eight-member committee to create a framework for the responsible and ethical use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the financial sector.
- The committee is chaired by Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya, Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at IIT Bombay.
Key Highlights:
Committee's Objective:
- The primary goal is to develop a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI (FREE-AI) in the financial sector.
- It will guide the ethical adoption of AI in financial services to enhance operational efficiency, decision-making, and risk management.
Scope of the Committee's Work:
- Assess the current global and domestic adoption of AI in financial services.
- Identify potential risks and challenges associated with the integration of AI in the sector.
- Recommend a framework for evaluating, mitigating, and monitoring AI-related risks.
- Propose compliance requirements for various financial entities (e.g., banks, NBFCs, fintech firms).
- Suggest a governance framework for ethical AI usage.
Key Benefits of AI in Financial Services:
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, process large datasets, and enhance accuracy (e.g., loan application processing).
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive analytics in AI help forecast market trends, aiding in better financial decision-making (e.g., algorithmic trading).
- Customer Relationship Management: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer interaction, offering 24/7 support.
- Improved Risk Management: AI enables proactive fraud detection, improving security and preventing financial losses.
Concerns Associated with AI in Finance:
- Embedded Bias: AI models can replicate biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes and financial exclusion.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI poses risks to personal data security, with potential violations of privacy regulations.
- Operational Challenges: AI systems may exhibit inconsistent responses, leading to challenges in trust and effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased use of AI can heighten vulnerability to cyber-attacks and exploitation.
RBI's Role & Governance:
- The RBI aims to ensure that AI adoption in the financial sector is ethical, transparent, and aligned with global best practices.
- The committee's recommendations will influence policies to prevent misuse and safeguard consumer interests.
Rupee and Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The real effective exchange rate (REER) index of the rupee touched a record 108.14 in November, strengthening by 4.5 per cent during this calendar year, according to the latest Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data.
Key Highlights:
- Record REER Index:
- The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the rupee reached an all-time high of 108.14 in November 2024.
- This marks a 4.5% appreciation in REER during the calendar year 2024, according to RBI data.
- What is REER?
- REER is a weighted average of a country’s currency value against the currencies of its major trading partners, adjusted for inflation differentials.
- It considers 40 currencies accounting for about 88% of India's trade.
- REER Calculation:
- Nominal Exchange Rates: The exchange rate between the rupee and each partner's currency.
- Inflation Differentials: Adjusts for inflation differences between India and its trading partners.
- Trade Weights: Based on the trade share with each partner.
- Recent Trends in REER:
- In 2023, REER dropped from 105.32 in January to 99.03 in April.
- It has since been on an appreciating trend, reaching 107.20 in October and 108.14 in November 2024.
- Dollar Strengthening Impact:
- Despite the rupee weakening against the US dollar (from 83.67 to 85.19 between September and December 2024), it has appreciated against the euro, British pound, and Japanese yen.
- The dollar's strengthening was fueled by global economic factors, including inflation expectations in the US and high bond yields, which led to capital outflows from other countries, including India.
- Impact on Exports and Imports:
- Overvaluation: A REER above 100 signals overvaluation, which can harm export competitiveness (exports become costlier) while making imports cheaper.
- Undervaluation: A REER below 100 indicates a currency is undervalued, boosting exports but increasing the cost of imports.
- India's Inflation and REER:
- India's higher inflation relative to trading partners is a key factor behind the rupee’s rising REER, despite its depreciation against major currencies.
- This suggests the rupee is overvalued, which could explain why the RBI may allow the rupee to depreciate further against the dollar.
- Global Context:
- The strengthening of the US dollar, influenced by factors such as tariff policies under the Trump administration and tighter US monetary policies, plays a significant role in the depreciation of the rupee against the dollar.
- This dynamic affects India's trade balance, with potential consequences for export growth.
- Implications for India’s Economy:
- Overvalued currency (as indicated by REER above 100) can lead to a trade deficit, as imports become cheaper and exports less competitive.
- A weaker rupee, particularly against the dollar, could boost Indian exports but raise the cost of imports.
Strengthening Fisheries Extension Services

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
India possesses diverse fisheries resources that provide livelihood opportunities to approximately three crore fishers and fish farmers. The country has witnessed an 83% increase in the national fish production since 2013-14, that stands at a record 175 lakh tons in 2022-23.
Importance of Fisheries Extension Services:
- Livelihood Support: Fisheries provide livelihoods to over 3 crore fishers and fish farmers in India. The sector's growth is crucial for enhancing sustainable practices and ensuring long-term productivity.
- Growth in Fish Production: India’s fish production has seen an 83% increase since 2013-14, reaching 175 lakh tons in 2022-23, with 75% of production coming from inland fisheries. India is the second-largest fish and aquaculture producer globally.
- Role of Extension Services: Extension services bridge the gap between scientific advancements and fishers, offering guidance on:
- Species lifecycle management
- Water quality management
- Disease control
- Sustainable rearing technologies and business models.
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Fisheries Extension:
- Matsya Seva Kendras (MSKs):
- Launched under PMMSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana) in 2020, MSKs are one-stop centers providing comprehensive extension services.
- Support to Fish Farmers: MSKs offer:
- Disease testing, water, and soil analysis.
- Training on sustainable aquaculture practices.
- Technology infusion in seed/feed management.
- Focus on Inclusivity: Government assistance (up to 60%) is available for women and marginalized communities to set up MSKs.
- Examples:
- Thrissur, Kerala: Equipped with labs for water and microbial analysis.
- Maharashtra (Nasik and Sangli): Capacity-building efforts on seed/feed inputs.
- Collaborations: MSKs mobilize start-ups, cooperatives, and Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs) to share best practices, including regenerative and conservation management in the face of climate change.
- Sagar Mitras:
- Role: Deployed in coastal states and union territories, Sagar Mitras act as a vital interface between the government and marine fishers.
- Functions:
- Collection and dissemination of daily marine catch data, price fluctuations, and market insights.
- Dissemination of important information: weather forecasts, fishing zones, local regulations, and hygienic fish handling.
- Provide support on disaster preparedness and natural calamities.
Enhancing Extension Services through Digital Platforms:
- AquaBazaar: A virtual learning platform initiated by the National Fisheries Development Board to provide expert guidance on:
- Seed production and breeding of commercially important fish species.
- Practical demonstrations to improve fishers' knowledge.
- Digital Outreach: Expanding such platforms will improve access to resources for fishers, especially in rural and remote areas.
Institutional Convergence and Capacity Building:
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Fisheries extension services should be integrated with the over 700 Krishi Vigyan Kendras and state-level agricultural extension services for effective outreach.
- Formalizing the Sector: The World Bank-assisted project aims to create work-based digital identities for fishers and fish farmers, enhancing their access to extension services, training, and awareness programs.
Challenges in Fisheries Extension Services:
- Fragmented Initiatives: Multiple government schemes and programs lack institutional convergence, leading to inefficiencies in reaching the grassroots level.
- Digital Divide: Many rural and coastal areas face challenges in terms of digital literacy and internet connectivity, limiting the effectiveness of online platforms.
- Impact of Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns and resource depletion due to overfishing demand adaptive strategies and the promotion of climate-resilient practices.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
- Institutional Convergence: Combining existing extension machinery like Krishi Vigyan Kendras with fisheries extension services to leverage established networks and knowledge.
- Expand Digital Outreach: Platforms like AquaBazaar should be expanded to ensure wider access to expert knowledge, training, and best practices.
- Private Sector Collaboration: Encouraging public-private partnerships can enhance technology dissemination, capacity building, and resource mobilization in the fisheries sector.
- Focus on Sustainability: Developing climate-resilient and sustainable fisheries practices will be essential to address challenges posed by environmental changes and overfishing.
Private Aviation and Emissions

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Private aviation is releasing more than its ‘fair share’ of emissions.
Key Highlights:
- Aviation Sector's Global Emissions:
- The aviation sector contributed 2% of global CO2 emissions in 2022, around 800 Mt CO2 (International Energy Agency).
- If considered as a nation, aviation would rank among the top 10 emitters worldwide.
- Emissions from aviation have grown faster than other sectors like rail, road, or shipping in recent decades.
- Private Aviation and Its Impact:
- Private jets emit 5 to 14 times more CO2 per passenger than commercial flights and 50 times more than trains.
- Emissions from private aviation increased by 46% between 2019 and 2023.
- Each private flight contributes 3.6 tonnes of CO2 on average, intensifying global warming.
- Private aviation is responsible for significant nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and the creation of vapor trails, which further amplify environmental damage.
Trends in Private Aviation Growth:
- Global Trends:
- The number of private jets increased from 25,993 in December 2023 to 26,454 in February 2024.
- In the U.S., 69% of private aviation activity is concentrated.
- 8,500 more jets are expected to be delivered in the next 10 years globally.
- Private Aviation in India:
- 112 private planes were registered in India as of March 2024, placing it among the top 20 countries for private aircraft ownership.
- India's private aviation sector is expanding, driven by the growing billionaire and millionaire population.
- Private aircraft ownership in India stands at 1 per 1 lakh population, which is low compared to countries like Malta (46.51 per lakh) and the U.S. (5.45 per lakh).
Emission Reduction Efforts and Solutions:
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs):
- SAFs are bio-based or waste-derived fuels that can reduce carbon emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional jet fuels.
- Airlines like SpiceJet (2018) and AirAsia (2023) have tested SAFs, but large-scale adoption is hindered by high costs and limited production.
- India aims to leverage its ethanol production chain, with potential to meet 15-20% of aviation fuel demand by 2050 if only surplus sugar is used.
- Hydrogen and Electric Aviation:
- Hydrogen offers a higher energy density than kerosene and emits only water vapor, making it a clean fuel alternative. However, hydrogen faces challenges with storage, infrastructure, and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric propulsion offers zero emissions but is currently limited by battery weight, energy density, and charging infrastructure.
India’s Policy and Initiatives:
- Government Initiatives:
- UDAN Scheme (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) aims to enhance rural connectivity.
- NABH (Nextgen Airports for Bharat Nirman) seeks to increase airport capacity by five times.
- Sustainability Efforts:
- Indian airlines have tested SAFs, such as a 25% jatropha oil blend by SpiceJet in 2018.
- Ethanol for aviation fuel: India plans to use surplus sugar for ethanol, potentially fulfilling 15-20% of aviation fuel needs by 2050.
- Challenges to Decarbonisation:
- SAFs are costly and limited in availability.
- Hydrogen requires extensive infrastructure and aircraft redesign.
- Battery-electric solutions are currently unsuitable for long-haul flights due to energy limitations.
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has offered fresh insights into the timing and duration of the Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a).
What is OAE 1a?
- Definition: A period during the Cretaceous Period (~119.5 million years ago) when Earth's oceans became oxygen-depleted (anoxic), causing significant disruption in marine ecosystems.
- Cause: Triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released large amounts of CO?, leading to global warming and depletion of oxygen in oceans. This caused the formation of anoxic marine basins.
- Impact: The depletion of oxygen led to the extinction of marine species, especially plankton, and the formation of black shales (organic carbon-rich layers).
Anoxic Marine Basins:
- Characteristics: These are bodies of water with extremely low or absent oxygen, allowing certain microbes and fungi to thrive, while most aerobic organisms perish.
- Significance: Anoxic basins contribute to carbon sequestration by slowing down the decay of organic material, helping in the reduction of atmospheric CO? levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin, and Orca Basin.
Recent Study Findings (Published in Science Advances):
- Timing: OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted for about 1.1 million years, with a long recovery period for ocean ecosystems.
- Methodology: The study used isotopic analysis of volcanic tuffs from Japan's Hokkaido Island to pinpoint the timing of the event.
- Volcanic Eruptions: The study confirmed that volcanic eruptions, particularly from the Ontong Java Nui complex, released CO?, triggering oceanic oxygen depletion.
- Relevance to Modern Climate Change: The study draws parallels between past volcanic CO? emissions and current human-induced warming, warning that rapid modern warming could cause similar disruptions in marine ecosystems and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction.
Holocene Extinction:
- Definition: The ongoing Sixth Mass Extinction, primarily driven by human activities like overexploitation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
- Impact: Current extinction rates are 1,000-10,000 times higher than natural rates, with severe consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Key Mass Extinction Events:
- Permian Extinction (~250 million years ago): Linked to volcanic activity, global warming, and ocean anoxia, leading to the extinction of over 95% of species.
- Cretaceous Extinction (66 million years ago): Caused by an asteroid impact, exacerbated by volcanic eruptions, leading to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- Holocene Extinction: Caused by human activities, with long-term implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Mitigate Extinction:
- Climate Action: Limiting global warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The 30X30 Initiative, aiming to conserve 30% of lands and oceans globally by 2030.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable resource management to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On Good Governance Day, commemorating the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for various departments, launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative. This initiative is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign, which aims to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) at the grassroots level by enhancing the capacity and competence of elected representatives and officials.
Objective of the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
The initiative seeks to strengthen PRIs by providing innovative tools and frameworks for capacity building and participatory governance. It will focus on equipping local leaders and officials with the necessary knowledge and tools to make effective decisions and implement sustainable development initiatives. Piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, it uses e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to address knowledge gaps and improve service delivery at the local level. This program aligns with the government's mission to decentralize governance and promote citizen-centric and equitable development across rural India.
Other Key Initiatives Launched on Good Governance Day
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform Dashboard: A new dashboard on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, which empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators to monitor progress in capacity-building efforts. The enhanced dashboard includes customizable views, robust data filtering tools, and insights to optimize decision-making, marking the introduction of the 1600th e-learning course. This development is part of the Mission Karmayogi initiative to strengthen the civil service through continuous learning.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: The CPGRAMS Annual Report provided a review of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS). This platform has been instrumental in resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually, leveraging advanced technologies and multilingual support. The report also highlighted the implementation of the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI), which has improved transparency, accountability, and the efficiency of public service delivery.
- Single Simplified Pension Application Form: A new digital pension system was launched, combining nine separate pension forms into a single, streamlined application. This digital transformation integrates e-HRMS with Bhavishya, reducing processing time and ensuring timely pension disbursement with real-time tracking and Aadhaar-based e-signatures. This system enhances the user experience for pensioners, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Compendium of Pension Related Instructions 2024: Dr. Singh introduced a comprehensive Compendium of updated rules, procedures, and guidelines related to pensions. This document serves as a reference for pensioners and administrative personnel, ensuring clarity in the pension process and aligning with the government's vision of simplifying and streamlining pension systems.
Good Governance Day 2024 (Sushasan Diwas)
- Observed on: December 25 annually, marking the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1924–2018).
- Introduced in 2014: By the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Purpose: To honor Vajpayee's contribution and promote good governance practices in India.
- Objective of Good Governance Day:
- Promote Government Accountability: Ensuring government actions and services are transparent and citizens benefit equally.
- Instill Good Governance Values: Encourages civil servants to practice effective and responsible governance.
- Bridge the Gap: Between citizens and the government through active participation.
- Theme for 2024: "India’s Path to a Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens through Good Governance and Digitalisation."
Cephalopods

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Octopuses and their relatives are a new animal welfare frontier
- Cephalopods are highly intelligent, marine invertebrates that include species such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish.
- They are members of the class Cephalopoda in the phylum Mollusca, which is known for its diversity and complex morphology.
- Cephalopods are often considered one of the most behaviorally and morphologically complex classes within this phylum.
Key Features and Anatomy
Cephalopods exhibit several distinctive features:
- Body Structure: They have a head-foot structure, where the head is merged with the foot, and arms/tentacles surround the head. The arms and tentacles are derivatives of the foot, with some species possessing additional appendages for grasping or movement.
- Tentacles and Beak: Cephalopods possess tentacles, often with suction cups or hooks for capturing prey. They also have beak-like jaws, which are used to break down food.
- Eyes and Vision: Their unique W-shaped pupils enhance their vision. Most cephalopods are believed to be colorblind, but they exhibit remarkable visual camouflage through chromatophores (pigment cells) and reflectors beneath their skin, which can produce a wide range of colors and patterns.
- Movement: Cephalopods use jet propulsion to move. By expelling water from their mantle cavity, they can quickly travel through the water. Some species, like octopuses, also "walk" using their arms, while squids and cuttlefish employ fins for propulsion.
- Circulatory System: They have three hearts. Two hearts pump deoxygenated blood, while the third pumps oxygenated blood. Their blood is blue due to the presence of copper-based hemocyanin, which is effective in cold, low-oxygen environments.
- Neural Systems: Cephalopods are known for their advanced nervous systems. A significant portion of the neurons, especially in octopuses, are not located in the central brain but are distributed across the arms in “mini-brains” or ganglia, which helps coordinate movement and sensory functions independently.
Cognitive Abilities
Cephalopods have garnered significant attention due to their impressive cognitive abilities. Their intelligence is demonstrated in several areas:
- Problem-Solving: They are capable of using tools and strategies to solve complex tasks, such as escaping enclosures or catching prey.
- Learning and Memory: Cephalopods exhibit sophisticated learning behaviors, including associative learning and memory. Some species are known to delay gratification, choosing more preferred food items over immediate but less desirable ones. They also show evidence of "reversal learning," where they can adjust their behavior in response to changing environmental cues.
- Camouflage and Communication: Cephalopods can manipulate their skin's color and texture for camouflage, aiding in hunting and predator avoidance. For example, the Australian giant cuttlefish uses its chromatophores to communicate with potential mates or warn off competitors.
Species Diversity
Cephalopods are classified into three primary superorders:
- Octopodiforms: Includes octopuses (e.g., Octopus vulgaris), which are known for their intelligence and ability to solve problems.
- Decapodiforms: Includes squids and cuttlefish (e.g., Sepia officinalis, Architeuthis dux), which possess unique locomotion and hunting strategies.
- Nautiloids: Includes the chambered nautilus, the only cephalopod with an external shell, which is considered more primitive compared to other cephalopods.
Ethical and Conservation Concerns
Due to their intelligence and advanced nervous systems, cephalopods are becoming a focus of ethical debates regarding their treatment. Recently, California and Washington have enacted bans on octopus farming, and Hawaii is considering similar measures. These decisions are driven by the growing understanding of cephalopods' cognitive abilities and their capacity for suffering. As a result, there are increasing calls for humane treatment regulations similar to those for vertebrates.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Cephalopods play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. As carnivorous predators, they help maintain the balance of marine food chains by hunting smaller prey. Some species, such as the cuttlefish, also play important roles in communicating and signaling within their species through visual displays.
Kilauea Volcano
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Kilauea volcano erupts on Hawaii's Big Island.
Location:
- Kilauea is located on the southeastern shore of Hawaii’s Big Island, within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park.
Type of Volcano:
- Active Shield Volcano – Kilauea is a shield volcano, meaning it has broad, gentle slopes due to the eruption of fluid lava, which flows easily across large areas. Its eruptions tend to be less explosive than those of other types of volcanoes, creating a relatively safe environment for research and tourism compared to more volatile volcanoes.
Key Features:
- Summit Caldera: Kilauea has a large caldera at its summit, Halema'uma'u, which is a major volcanic feature. The caldera formed from the partial collapse of the volcano after the eruption of large amounts of magma. The caldera spans around 3 miles in length and 2 miles in width, covering an area of over 4 square miles.
- Rift Zones: Kilauea has two active rift zones stretching to the east and southwest, which are areas where lava can erupt and spread across the island. These rift zones are responsible for much of the volcanic activity.
- Lava Flows: Over the last 1,000 years, Kilauea has covered 90% of its surface with lava flows, making it one of the most active volcanoes in the world. It is known for producing highly fluid lava, which allows the lava to travel long distances from the eruption site.
- Historical Activity: Kilauea has had near-continuous eruptions in modern history, particularly between 1983 and 2018, with 34 eruptions since 1952. The volcano has remained active with frequent eruptions, and its lava lake was visible at the summit until 1924.
- Mythological Significance: The volcano is considered the home of Pele, the Hawaiian goddess of fire, lightning, and volcanoes. The Halema'uma'u crater is especially sacred, as it is believed to be the goddess's dwelling place.
Why is Kilauea Significant?
- Active and Young: Kilauea is one of the youngest volcanic products of the Hawaiian hotspot, a series of volcanic islands formed by the movement of the Pacific plate over a stationary plume of hot material beneath the Earth’s crust.
- Continuous Eruptions: It has been erupting regularly, with the exception of a quiet period between 1924 and 1952. Its eruptions are a significant natural phenomenon that scientists and visitors closely monitor.
- Proximity to Mauna Loa: Kilauea is located near Mauna Loa, another active shield volcano. Together, these two volcanoes form a large volcanic region, and their slopes merge seamlessly, making this area home to two of the world's most active volcanoes.
Shield Volcanoes and Kilauea
- Shield Volcanoes: A shield volcano is characterized by its broad, gentle slopes. These slopes are formed by repeated eruptions of fluid basalt lava, which spreads easily over large areas. Unlike composite volcanoes, which have steep, conical shapes, shield volcanoes like Kilauea have a much wider, dome-like appearance.
- Low Explosivity: Eruptions from shield volcanoes are generally low in explosivity, and lava flows are typically slow-moving. However, explosive events can occur if water interacts with lava, but this is relatively rare in Kilauea's eruptions.
Kilauea's Current Activity
In December 2024, Kilauea began erupting again, continuing its pattern as one of the most active volcanoes in the world. This eruption has once again drawn attention to the ongoing volcanic activity on the Big Island of Hawaii, as the volcano regularly contributes to the reshaping of the island and its landscape.
Other Volcanoes in India:
While Kilauea is known for its active status, India also has volcanic features, although most are dormant or extinct:
- Barren Island (Andaman Islands) – India’s only active volcano.
- Narcondam (Andaman Islands) – A dormant volcano.
- Baratang (Andaman Islands) – Known for mud volcanoes.
- Deccan Traps (Maharashtra) – A vast volcanic plateau formed by ancient eruptions.
- Dhinodhar Hills (Gujarat) – Extinct volcano.
- Dhosi Hill (Haryana) – An ancient volcanic site with historical significance.
GenCast AI
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
Google’s GenCast AI is an advanced weather forecasting model developed by DeepMind that uses machine learning techniques to provide more accurate and longer-term weather predictions compared to traditional forecasting methods.
How GenCast Works:
- Training on Reanalysis Data:
- GenCast is trained on 40 years of reanalysis data (from 1979 to 2019). This data combines historical weather observations with modern weather forecasts, providing a comprehensive picture of past weather and climate conditions.
- Ensemble Forecasting with AI:
- Unlike traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models, which run simulations based on physical laws and initial conditions, GenCast uses an ensemble forecasting approach where multiple predictions are generated by an AI model, not an NWP model.
- It produces a range of possible weather scenarios, each with different starting conditions, to reflect the uncertainty in weather forecasts.
- Neural Network and Diffusion Model:
- GenCast uses a neural network architecture with 41,162 nodes and 240,000 edges that process weather data. Each node accepts data, manipulates it, and passes it to another node, helping to refine and improve predictions.
- It uses a diffusion model, a type of AI model commonly used in generative AI. The model takes noisy input data, processes it through 30 refinement steps, and gradually produces a clearer forecast (de-noising the data).
- The result is a probabilistic forecast, such as "there's a 25% chance of rain in Chennai on December 25," rather than a deterministic forecast, which would provide exact quantities like "5 mm of rain."
- Faster Processing:
- The entire forecast process is incredibly efficient. GenCast can generate 50 ensemble forecasts at once with a spatial resolution of 0.25° x 0.25° (latitude-longitude) and temporal resolution of 12 hours.
- Using Google's TPU v5 units, it can produce these forecasts in just 8 minutes—far faster than traditional supercomputers, which can take several hours to run NWP simulations.
Key Features of GenCast:
- Better Performance on Extreme Weather: GenCast has shown superior accuracy in predicting extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones, compared to traditional NWP models like those from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF).
- Probabilistic Forecasting: GenCast produces probabilistic forecasts, offering predictions like the likelihood of rain rather than precise measures, which helps with better preparation, especially for extreme weather events.
- Long-Term Forecasting: GenCast can generate forecasts for up to 15 days, which is longer than most traditional models, and is particularly useful for anticipating events like wind power generation and tropical cyclone tracking.
- Efficiency: GenCast's speed and resource efficiency set it apart from traditional NWP models, reducing forecast times dramatically.
Comparison with Traditional Weather Models:
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP): Traditional NWP models rely on solving complex physical equations to simulate the atmosphere and provide deterministic forecasts. These models require significant computational power and are typically limited to weather predictions for about a week.
- GenCast's Probabilistic Forecasts: In contrast, GenCast offers probabilistic predictions, making it better suited for providing early warnings about extreme weather, with better lead times for disaster preparation.
Future Developments:
While GenCast is impressive, Google acknowledges the importance of traditional NWP models for both supplying initial conditions and providing the foundational data needed to train AI models like GenCast. Ongoing collaboration with weather agencies is crucial to enhancing AI-based methods for weather prediction.
Overall, GenCast represents a significant leap forward in the use of AI for weather forecasting, with potential for greater accuracy, efficiency, and longer-term predictions compared to current methods.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)

- 24 Dec 2024
In News
Justice V. Ramasubramanian, a retired Supreme Court judge, has been appointed as the new chairperson of the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC). This decision was made by President Droupadi Murmu, and it comes following the completion of Justice Arun Kumar Mishra's tenure as NHRC chairperson in June 2023. After Justice Mishra's retirement, Vijaya Bharathi Sayani served as the acting chairperson. Alongside Justice Ramasubramanian, Priyank Kanoongo and Dr. Justice Bidyut Ranjan Sarangi (Retd.) have also been appointed as members of the commission.
Justice Ramasubramanian had been appointed a judge of the Supreme Court in September 2019 and retired in June 2023. His appointment to the NHRC is seen as a significant development for human rights advocacy and protection in India.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
Establishment and Legal Framework
- Formation Date: The NHRC was established on October 12, 1993, under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- Paris Principles: It was created in alignment with the Paris Principles (1991), which were endorsed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, aimed at setting standards for national human rights institutions.
- Statutory Body: NHRC is a statutory body, meaning it is established by law, with a primary function to safeguard human rights in India.
Objectives
The NHRC's primary objective is to promote and protect human rights as defined in Section 2(1)(d) of the PHRA, which include fundamental rights such as:
- Right to Life
- Right to Liberty
- Right to Equality
- Right to Dignity
These rights are guaranteed by the Indian Constitution and are essential to the protection of individuals' freedoms and welfare.
Composition of NHRC
- Chairperson: A former Chief Justice of India or a former Supreme Court judge serves as the chairperson.
- Members:
- One former or sitting Supreme Court judge.
- One former or sitting Chief Justice of a High Court.
- Three members, with at least one woman, who have experience in human rights matters.
- Ex-Officio Members: The chairpersons of various National Commissions (e.g., SC/ST, Women, Minorities) and the Chief Commissioner for Persons with Disabilities are also part of the NHRC.
Functions and Powers
The NHRC has several crucial functions and powers to ensure the protection and promotion of human rights:
- Inquiry into Human Rights Violations: The commission can inquire into violations of human rights by public servants or negligence in protecting rights.
- Recommendations: It can make recommendations on how to protect, promote, and effectively implement human rights within India.
- Review of Laws: NHRC assesses various laws, treaties, and international instruments related to human rights.
- Research and Awareness: It promotes research, publications, and awareness about human rights issues, including educating the public about their rights and safeguards.
- Inspection of Institutions: NHRC has the authority to visit and inspect institutions such as jails, detention centers, and other places of confinement to ensure the humane treatment of individuals.
The ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Its Evolution

- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The ‘no-detention’ policy was a significant part of India’s education reforms under the Right to Education (RTE) Act of 2009. This policy aimed to prevent the detention or expulsion of students until the completion of elementary education (Classes 1-8), with a focus on reducing dropout rates and ensuring every child receives at least basic education. However, the policy has been contentious, with arguments both for and against its implementation.
What was the ‘No-Detention’ Policy and Why Was It Introduced?
The RTE Act (2009) made education free and compulsory for children aged 6 to 14, under Article 21A of the Constitution. Section 16 of the Act specifically prohibited the detention or expulsion of students in elementary education (Classes 1-8). The rationale was to prevent the demotivation and fear of failure that might cause children to drop out of school, especially those from marginalized backgrounds. By promoting automatic progression through grades, the policy aimed to ensure that no child was left behind due to academic struggles.
Key to this system was Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE), which assessed students on a holistic basis, beyond just formal exams, encouraging learning through regular feedback and assessments.
Amendments to the RTE Act (2017 and 2019)
In 2017, a Bill was introduced to amend the RTE Act, following concerns about the effectiveness of the ‘no-detention’ policy. The amended policy allowed for regular exams in Classes 5 and 8. If students failed, they would be given a re-examination within two months. If they still did not meet promotion criteria, detention could be enforced. This amendment empowered the Centre and states to decide whether to detain students in these grades.
The amendment came after criticism of the original policy for promoting students without sufficient learning progress. States like Madhya Pradesh and Punjab argued that no-detention was leading to poor academic performance, and called for a return to the traditional system of promoting students based on examination results.
Arguments for and Against the No-Detention Policy
Arguments for No-Detention:
- Reduced Dropout Rates: The policy helped ensure students, especially from disadvantaged backgrounds, continued in school without the fear of failure, leading to a drop in dropout rates.
- Holistic Development: It encouraged a child-centric learning approach where students were assessed on their overall development rather than just exam performance.
- Social Inclusivity: By promoting students regardless of performance, it was hoped that education would be more inclusive, preventing marginalization of students from lower socio-economic backgrounds.
Arguments Against No-Detention:
- Decline in Learning Outcomes: The policy led to a lack of motivation for students to perform academically. Without the accountability of exams, many students became less serious about their studies.
- Low Teacher Accountability: With automatic promotion, teachers had less incentive to ensure quality learning, leading to an overall dip in teaching standards.
- Impact on Educational Standards: Data indicated a decline in learning levels in government schools, as students were passed through the system without mastering the required skills.
In 2015, the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE) conducted a study suggesting that more flexibility was needed in the policy, allowing schools to retain students who were significantly behind. However, there were differing views within the committee. Some members argued that detention had no proven benefits, and that the real issue was the poor quality of the education system itself.
In 2016, the TSR Subramanian Committee on the New Education Policy suggested continuing the no-detention policy until Class 5, citing evidence of reduced dropout rates and increased enrollment. However, other states pushed for scrapping it due to concerns over declining educational standards.
The Shift Toward Scrapping the No-Detention Policy
By 2019, the RTE Act was amended to give states the discretion to hold back students in Classes 5 and 8, if they failed to meet the promotion criteria. This change came after state feedback that the no-detention policy was having adverse effects on learning outcomes and teacher accountability.
In 2024, the Ministry of Education took further steps to formalize this shift by introducing new rules under the RTE Act Amendment. Students failing to meet the promotion criteria in Classes 5 and 8 will be given additional instruction and an opportunity for a re-examination. If they still fail, they can be detained, with specialized guidance provided to help them catch up.
Which States Continue or Scrapped the No-Detention Policy?
The decision to maintain or scrap the policy varies across states and union territories:
- States Retaining No-Detention Policy: Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Odisha, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, among others, continue to implement the no-detention policy, citing its role in minimizing dropouts and promoting inclusivity.
- States That Have Scrapped the Policy: Delhi, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, West Bengal, and Gujarat have already discarded the policy, opting for examinations and re-examinations in Classes 5 and 8 to ensure better academic accountability.
Why the Controversy?
The debate over the no-detention policy hinges on balancing academic accountability with social inclusivity. Supporters argue that it ensures children from marginalized communities receive their full elementary education, while opponents point to the decline in learning standards, especially in government schools, as a major issue.
In summary, while the no-detention policy was introduced with the noble aim of reducing school dropouts and ensuring every child completed at least elementary education, its effectiveness has been questioned due to concerns over declining learning outcomes. The recent changes represent a shift towards better accountability and quality in education, while still ensuring that children receive additional support before being detained.
Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) Mission
- 24 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is set to launch its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) mission, a key milestone in India’s space capabilities. The mission will deploy two 220-kg satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), into a 740 km orbit using the PSLV-C60 rocket. SpaDeX aims to demonstrate the technology for satellite docking, a critical component for future space missions such as lunar exploration and the development of India's own space station, Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS).
Key Objectives of SpaDeX Mission:
- Primary Objective: To demonstrate the rendezvous, docking, and undocking of two small spacecraft (SDX01 and SDX02) autonomously.
- Secondary Objectives: Include testing electric power transfer between the docked spacecraft, composite spacecraft control, and post-docking payload operations.
The mission will see the two spacecraft gradually approach each other, performing a series of maneuvers, starting at a 20 km distance and closing to millimeter-scale distances before docking. Once docked, they will execute secondary tasks, such as scientific payload operations, using advanced technologies including high-resolution cameras, multi-spectral payloads, and radiation monitors.
Technological Innovations:
- Docking Mechanism: An indigenous, motor-driven, low-impact, androgynous docking system with capture, extension/retraction, and rigidization mechanisms. Both spacecraft are equipped with identical docking systems to simplify operations.
- Advanced Sensors: The spacecraft will use a Laser Range Finder (LRF), Proximity & Docking Sensors (PDS), and Rendezvous Sensors for precise distance measurement and to guide the docking process.
- Inter-Satellite Communication: The spacecraft will employ autonomous inter-satellite links (ISL) for real-time communication and data sharing.
- RODP Processor: This system, based on GNSS, ensures accurate position and velocity determination for the spacecraft during the docking procedure.
Significance of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Technological Milestone: SpaDeX positions India as the fourth country, after the US, Russia, and China, to develop space docking technology.
- Space Exploration: The successful demonstration will facilitate future space exploration, including Chandrayaan-4 and interplanetary missions.
- Modular Space Infrastructure: Space docking is essential for building multi-modular space stations, which allows the construction of large structures in space and enhances flexibility for future missions.
- Satellite Servicing: Docking enables satellite servicing, including repairs, refueling, and upgrades, which increases the operational lifespan of satellites.
SpaDeX Mission for India’s Space Station:
The SpaDeX mission is a crucial step towards India’s plans for the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). This will be India’s first modular space station, designed to conduct advanced scientific research, including in life sciences and medicine. BAS is expected to begin operations by 2035, and the development of docking technology is pivotal for its assembly and operation.
Mission Launch Details:
The PSLV-C60 rocket is set to launch the SpaDeX mission from Sriharikota. The mission is a demonstration of India's growing space capabilities and its indigenous technologies, including the Bharatiya Docking System (BDS).
Challenges and Technological Requirements:
The docking process requires extremely precise maneuvering, as the two spacecraft will be traveling at speeds of 28,800 km/h and must reduce their relative velocity to just 0.036 km/h before docking. This level of precision is crucial for future missions involving spacecraft servicing, crew transfers, and the construction of space infrastructure like BAS.
In addition to the docking demonstration, SpaDeX will carry 24 academic and startup payloads aboard the PSLV’s fourth stage, POEM (PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-4), offering a valuable platform for microgravity research.
Future Prospects:
The success of SpaDeX will pave the way for more complex missions, such as India’s lunar and Mars exploration programs, the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and international collaborations in satellite servicing and space infrastructure.
72nd North Eastern Council (NEC) Plenary Session

- 23 Dec 2024
Overview:
The 72nd Plenary of the North Eastern Council (NEC), concluded in Agartala, Tripura, marking the second time the city hosted this significant event since 2008. The plenary featured a series of high-level discussions focused on accelerating development and addressing the socio-economic challenges of the North Eastern Region (NER), which includes Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, and Tripura.
Key Highlights:
- Pre-Plenary Technical Sessions: Central ministries presented their developmental agendas for the NER, charting a path forward for the region's growth and addressing key challenges.
- Main Plenary:
- Presiding Officers: The session was chaired by the Union Home Minister and NEC Chairman, Shri Amit Shah, along with DoNER Minister, Shri Jyotiraditya M. Scindia, and Minister of State, Dr. Sukanta Majumdar.
- Participants: Governors, Chief Ministers, Chief Secretaries, Planning Secretaries, and high-ranking officials from all eight northeastern states will engage in strategic discussions to foster regional development.
- Agartala as Host:
- Agartala's selection as the venue signifies the evolving role of the city in regional development, as plenary sessions are usually held in Shillong and Guwahati.
- Significance of the NEC:
- The North Eastern Council (NEC), established in 1971, plays a pivotal role in the socio-economic development of the region. It was initially an advisory body but has evolved into a regional planning agency with a larger mandate.
- The NEC has contributed significantly to the development of critical infrastructure in the region, such as over 11,500 kilometers of roads, power generation through NEEPCO, and educational institutions like RIMS.
- Prime Minister's Vision for the NER:
- The Prime Minister’s vision for the region revolves around recognizing it as 'Ashta Lakshmi'—symbolizing immense potential and cultural richness. The NEC is central to realizing this vision through initiatives like the PM-DevINE scheme.
Key Achievements of the NEC:
- Over 11,500 kilometers of road construction, improving regional connectivity.
- Increased power generation capacity via projects managed by NEEPCO.
- Established institutions like the Regional Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) and others that cater to regional educational and technical needs.
Recent Focus and Shift in Governance:
- In the 72nd Plenary, the Union Home Minister highlighted a shift in the focus of police forces in northeastern states, urging them to focus not just on insurgency control but on ensuring the constitutional rights of citizens, reflecting a new governance phase in the region.
RBI's Report on State Finances (2024-25)

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) report titled "State Finances – A Study of Budgets of 2024-25" provides a comprehensive analysis of the fiscal position of Indian states.
Key Highlights
- States' Performance Post-Pandemic
- Improved Tax Revenue: The average tax buoyancy has increased significantly from 0.86 (2013-2020) to 1.4 (2021-2025), reflecting enhanced tax collection efficiency.
- Capital Expenditure: There is a consistent rise in capital expenditure, which increased from 2.4% of GDP in 2021-22 to 2.8% in 2023-24 and is budgeted at 3.1% in 2024-25. This indicates a growing focus on investment in infrastructure like highways and bridges.
- Fiscal Discipline and Debt Levels
- Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD): The gross fiscal deficit is projected at 3.2% of GDP in 2024-25, a slight increase from 2.9% in 2023-24.
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio: While states' debt-to-GDP ratio decreased from 31.0% in March 2021 to 28.5% in March 2024, it remains higher than the pre-pandemic level of 25.3% in 2019.
- Increased Borrowing and Debt Pressure
- Market Borrowings: States' reliance on market borrowings has increased, accounting for 79% of the GFD in FY25. Gross market borrowings surged by 32.8%, totaling Rs 10.07 trillion in FY23-24.
- Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs): Continued losses in DISCOMs, accumulating Rs 6.5 lakh crore by 2022-23 (2.4% of India's GDP), continue to strain state finances.
- Rising Subsidy Burden
- Many states are offering subsidies and loan waivers, such as farm loan waivers and free services (electricity, transport, etc.), which risk diverting funds away from critical infrastructure projects. This includes significant subsidies for income transfers to farmers, women, and youth.
- Fiscal Transparency Concerns
- Revenue Generation Issues: Revenue growth from non-tax sources and central grants is slowing. The pace of State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) growth has also slowed down, which impacts overall state revenues.
- Lack of Fiscal Transparency: Inadequate reporting of off-budget liabilities obfuscates the true fiscal position, leading to a lack of clarity and accountability in state finances.
Recommendations by the RBI
- Debt Consolidation: States are encouraged to create clear and transparent debt reduction paths, with consistent reporting of off-budget liabilities to improve fiscal accountability.
- Expenditure Efficiency: Focus on outcome-based budgeting, ensuring funds are directed towards productive and sustainable investments, particularly in climate-sensitive areas.
- Subsidy Rationalization: States should contain and optimize subsidies to ensure they don't overshadow essential growth-promoting expenditure.
- Efficient Borrowings: Reduce over-reliance on market borrowings to control fiscal deficits and minimize financial risks.
- Revenue Generation: Improve collection mechanisms for SGST, strengthen non-tax revenue sources, and increase grants to reduce dependence on borrowings.
Balancing Subsidies and Fiscal Discipline
- Importance of Subsidies: Welfare programs like subsidies for healthcare, food security (e.g., Public Distribution System), and LPG connections (e.g., Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana) play a crucial role in human development and economic equality by supporting vulnerable populations.
- Importance of Fiscal Discipline: Excessive welfare spending without corresponding revenue generation can lead to high deficits and public debt, threatening long-term fiscal stability. Maintaining fiscal discipline ensures sustainable public finances, promotes investor confidence, and supports economic growth.
Green fixed deposits

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
Green fixed deposits (FDs) are a type of investment scheme offered by banks and financial companies, aimed at environmentally-conscious investors. They function similarly to traditional fixed deposits, where funds are locked in with a bank for a fixed tenure. The primary distinction between green and regular deposits lies in the allocation of funds. While regular deposits are pooled into a common fund, the funds from green deposits are exclusively allocated to projects that promote environmental sustainability.
Key Features of Green Fixed Deposits:
- Investment Purpose: The funds raised through green FDs are directed towards environmentally beneficial projects, such as renewable energy initiatives (solar and wind power), clean technology, organic farming, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Eligibility: Green deposits are available to various entities, including individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), societies, clubs, non-profit organizations, and sole proprietorships.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on green deposits may or may not differ from regular deposits, depending on the policies set by the lending institution. Some banks and financial institutions, like IndusInd Bank, Federal Bank, DBS Bank India, and HDFC Ltd., offer green deposits, with Bank of Baroda recently launching the BOB Earth Green Term Deposit with an interest rate of up to 7.15% per annum.
- Safety: Like regular fixed deposits, green deposits are insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) under the provisions of the DICGC Act, 1961, ensuring the safety of the investment.
- Overdraft Facility: Banks may offer overdraft facilities against green deposits, providing more flexibility to investors.
- Premature Withdrawal: If the investor chooses to withdraw the deposit before the agreed tenure (after six months), the green FD will be converted into a regular fixed deposit.
- Denomination: Green deposits are denominated in Indian Rupees only.
Centenary of Belgaum session

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Belagavi Session of 1924, marking its centenary in December 2024, holds significant historical and cultural value in India's freedom struggle. This session, the 39th All-India Congress session, was presided over by Mahatma Gandhi, the only instance he served as the Congress president. It took place in Belagavi, Karnataka, from December 26-27, 1924, amidst a growing momentum for India’s fight against British colonial rule.
Key Aspects of the Belagavi Session:
- Gandhi's Leadership: This was the only Congress session Gandhiji chaired, marking a pivotal moment in the freedom movement. His leadership emphasized non-violence, self-reliance, and unity among diverse groups, setting the stage for future movements like the Salt March and Quit India Movement.
- Focus on Social Change: Gandhi used the session to push for social reforms, including the abolition of untouchability, promotion of khadi (hand-spun cloth), and supporting village industries. These initiatives aimed to make Congress a movement for both political freedom and social upliftment.
- Promoting Hindu-Muslim Unity: Gandhi strongly advocated for Hindu-Muslim unity, recognizing its critical importance in the larger struggle for independence. His stance emphasized communal harmony during a time of social and political divisions.
- Cultural Impact: The session also featured musical performances, including contributions from Hindustani maestros like Vishnu Digambar Paluskar and Gangubai Hangal. The Kannada song “Udayavagali Namma Chaluva Kannada Nadu” became an anthem for the region's unification movement.
- Legacy: The session had a lasting impact, with initiatives such as promoting khadi, reducing Congress membership fees, and creating new avenues for peasant participation in the freedom movement. The Pampa Sarovara well, dug during the event, continues to provide water to parts of Belagavi.
Centenary Celebrations:
The centenary of the Belagavi Session is being celebrated with a range of events, including:
- A Congress Working Committee (CWC) meeting on December 26, 2024.
- A public rally with the theme “Jai Bapu, Jai Bhim, Jai Samvidhan.”
- Cultural events and exhibitions are also planned, including competitions, tableaux, and charkha marathons.
National Farmers' Day

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
National Farmers' Day, also known as Kisan Diwas, is celebrated annually on December 23rd to honor the vital contributions of Indian farmers and commemorate the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, India's fifth Prime Minister. A passionate advocate for rural development and farmers' welfare, Charan Singh's policies laid the foundation for several reforms aimed at uplifting the agrarian economy. His contributions continue to inspire government initiatives that prioritize the welfare of farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural growth and ensuring food security for the nation.
The Legacy of Chaudhary Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh was born on December 23, 1902, in Noorpur, Uttar Pradesh. His deep understanding of rural issues and commitment to improving farmers’ lives earned him the title of "Kisan Leader". Throughout his political career, he championed reforms such as the Debt Redemption Bill (1939), which alleviated the financial burdens of farmers, and the Land Holding Act (1960), which promoted fair distribution of agricultural land. He also advocated for Minimum Support Price (MSP), and his policies laid the groundwork for NABARD and other farmer-centric institutions.
Significance of Kisan Diwas
Kisan Diwas highlights the importance of agriculture in India’s economy and employment, with farmers constituting nearly 50% of the workforce. The day emphasizes the need for policies that address farmers' challenges such as climate change, financial constraints, and technological adoption. It also serves as a reminder of the necessity to empower farmers through innovative solutions, financial security, and sustainable farming practices.
Key Government Initiatives for Farmer Welfare
The Indian government has launched several schemes to address the challenges faced by farmers and support their socio-economic upliftment:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to mitigate financial risks due to crop loss.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY): A pension scheme for farmers to ensure long-term social security.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient fertilizer use and soil health by providing farmers with personalized soil health reports.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): These entities help farmers collectively access markets, reduce costs, and improve bargaining power.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Provides affordable credit to farmers, especially for agriculture-related activities.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Helps farmers access timely credit for agricultural purposes at concessional rates.
Significant Budget Allocations and New Schemes
The government has drastically increased its budget allocation to the agriculture sector. From Rs. 21,933.50 crore in 2013-14, the budget has risen to Rs. 1,22,528.77 crore for 2024-25, underlining the government's commitment to farmer welfare and sustainable agricultural development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme: This initiative, aimed at empowering Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs), supports the use of drones for agricultural purposes, including fertilizer and pesticide application, with 80% financial assistance.
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP): Enhances the quality and productivity of horticulture crops by ensuring disease-free planting material.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to modernize farming with digital infrastructure, including crop estimation surveys and e-agriculture platforms.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Encourages chemical-free, sustainable farming practices.
Farmers' Role in Nation-Building
India’s agricultural sector not only sustains the livelihoods of millions but also contributes significantly to the country's GDP. In FY 2023-24, agriculture contributed 17.7% to the Gross Value Added (GVA). With over 54% of the country's land dedicated to agriculture, farmers are critical to food security and rural development.
In 2023-24, India achieved a record foodgrain production of 332.2 million tonnes, illustrating the resilience of Indian farmers in ensuring food availability despite challenges like climate change.
IPBES Nexus Report

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The IPBES Nexus Report, formally titled The Assessment Report on the Interlinkages Among Biodiversity, Water, Food, and Health, was released to address the interconnected global challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, food insecurity, water scarcity, and health risks. The report stresses that these challenges are deeply intertwined and cannot be solved separately; doing so would lead to ineffective or even counterproductive results.
Key Highlights of the Nexus Report
- Interconnections Between Global Challenges: The report emphasizes the strong interlinkages between the five major global challenges:
- Biodiversity Loss
- Water Scarcity
- Food Insecurity
- Health Risks
- Climate Change
It argues that efforts to address these challenges independently are ineffective and often exacerbate the problems. For example, scaling up food production to combat hunger can put more pressure on land, water, and biodiversity.
- Economic Cost of Biodiversity Loss:
- Global GDP Dependency: Over half of the global GDP (approximately $58 trillion annually) depends on nature. Biodiversity degradation significantly undermines productivity and economic output.
- Unaccounted Costs: The neglect of biodiversity in economic activities contributes to a loss of $10-25 trillion annually.
- Delayed Action: Delaying action on biodiversity conservation could double the costs within the next decade, potentially incurring $500 billion per year in additional costs.
- Synergistic Approach: The report identifies over 70 response options that promote synergistic outcomes across the five challenges. These include:
- Restoring Carbon-Rich Ecosystems: Such as forests, soils, and mangroves to address climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Managing Biodiversity to Prevent Disease Transmission: Effective biodiversity management reduces risks of diseases passing from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases).
- Sustainable Diets: Promoting diets that are both healthy and environmentally sustainable.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implementing solutions that rely on natural processes to mitigate challenges like water scarcity and climate change.
- Inequality and Vulnerability: The report highlights how inequality exacerbates the challenges. Vulnerable populations, especially those living in areas where biodiversity has sharply declined, face increased health risks, malnutrition, and economic instability. 41% of people live in regions where biodiversity loss has been particularly severe, and 9% face high health burdens due to these declines.
- Principles for Transformative Change: The report outlines principles for achieving transformative change:
- Equity and Justice: Ensuring fair distribution of resources and opportunities for all.
- Pluralism and Inclusion: Embracing diverse perspectives and voices in policy-making.
- Respectful Human-Nature Relationships: Recognizing and nurturing reciprocal relationships between humans and nature.
- Adaptive Learning and Action: Continuously evolving policies and strategies based on feedback and new evidence.
- Urgency for Immediate Action: The report stresses that immediate action is critical. If the world continues to neglect biodiversity, it will face not only environmental collapse but also a missed opportunity for economic growth. Immediate implementation of nature-positive strategies could unlock $10 trillion in business opportunities and create 400 million jobs by 2030.
The IPBES Transformative Change Assessment Report
- This report builds upon the 2019 IPBES Global Assessment Report and advocates for transformative change to halt biodiversity loss and achieve global development goals. It defines transformative change as a system-wide shift in:
- Views: Changing how we think about nature and its value.
- Structures: Reforming systems of governance and organization.
- Practices: Changing behaviors and practices that harm nature.
Key Challenges to Transformative Change:
- Disconnection from Nature: Human societies' disconnection from nature, often rooted in historical domination, is a major cause of biodiversity loss.
- Economic Inequality: The concentration of power and wealth exacerbates environmental degradation.
- Unsustainable Consumption: Unsustainable patterns of consumption and production are significant drivers of environmental harm.
Synergistic Strategies for Transformation:
- Conserve and Regenerate: Restore ecosystems that have both ecological and cultural value.
- Mainstream Biodiversity: Integrate biodiversity considerations into sectors like agriculture, forestry, and infrastructure development.
- Transform Economic Systems: Adopt policies such as true cost accounting and sustainability-based tax principles to internalize the environmental costs of economic activities.
- Inclusive Governance: Promote governance systems that involve all stakeholders, especially local communities, in decision-making.
SAMARTH UDYOG BHARAT 4.0 INITIATIVE

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative, launched by the Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI), aims to enhance the competitiveness of the Indian capital goods sector by promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. This initiative is part of the Scheme for Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
Key Features of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
- Establishment of Smart Manufacturing Hubs: Under this initiative, four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres have been set up across India:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab, Pune
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing, IIT Delhi
- I-4.0 India @ IISc, Bengaluru
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell, CMTI, Bengaluru
- Cluster Industry 4.0 Experience Centres: In addition to the above centres, 10 cluster Industry 4.0 experience centres have been approved. These will be established under a Hub and Spoke model, managed by the C4i4 Lab in Pune, and spread across India.
- Key Achievements:
- Model Factories: Development of an Industry 4.0 enabled Model Factory at C4i4, Pune, and a smart production-based factory at CMTI Bengaluru.
- Industry 4.0 Solutions: More than 50 use-cases for Industry 4.0 solutions were compiled to support implementation.
- Maturity Assessment Tool: Creation of the Industry 4.0 Maturity Model (I4MM), specifically designed to assess the readiness of Indian manufacturing companies for Industry 4.0.
- Online Assessment Tool: Launch of a free online assessment tool by C4i4 Lab, Pune, to help MSMEs evaluate their maturity in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Training and Awareness:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular awareness seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events are organized to educate industries about Industry 4.0.
- Workforce Training: The SAMARTH Centres have trained over 5000 professionals on smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Consultancy Services: The centres offer consultancy in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics, along with incubation support for start-ups and MSMEs.
- Impact on MSMEs:
- Digital Maturity Assessments: Over 100 digital maturity assessments have been completed for the auto industry, and more than 500 improvement initiatives have been identified.
- Training and Capacity Building: Over 500 digital champions have been trained on Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Focus on MSMEs: While no direct financial assistance is provided to industries, including MSMEs, under this initiative, the SAMARTH Centres play a key role in helping them adopt Industry 4.0 technologies and build their capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative seeks to increase the global competitiveness of India's capital goods and manufacturing sectors.
- It leverages Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, automation, data analytics, and AI to modernize manufacturing processes.
- The initiative involves setting up 4 major Smart Manufacturing Hubs and 10 regional experience centres across the country to facilitate awareness, training, and adoption of Industry 4.0 among manufacturers, especially MSMEs.
- While it does not provide financial aid, it helps industries improve their digital maturity, trains workforce, and guides them through consultancy and workshops.
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)

- 22 Dec 2024
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav inaugurated two groundbreaking facilities at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun: the Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification and the Next Generation DNA Sequencing (NGS) Facility. These facilities are designed to enhance India’s capabilities in wildlife conservation and support the growth of traditional crafts like Pashmina weaving.
Key Highlights
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)
The NGS facility is a cutting-edge research tool that enables the high-throughput analysis of entire genomes. This technology is pivotal in studying wildlife genetics and biodiversity by decoding millions of DNA sequences at once.
Applications in Wildlife Conservation:
- Genetic Diversity and Health: NGS helps assess the genetic diversity of species and their population health.
- Evolutionary Relationships: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history and unique adaptations of species.
- Disease Surveillance: The technology supports studying pathogen-host interactions and monitoring diseases affecting wildlife.
- Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade: NGS can help detect illegal wildlife trade and the movement of endangered species.
- Impact of Climate Change: It is crucial for studying how climate change affects genetic diversity and species survival.
This facility positions WII as a leading hub for molecular research, enabling more precise conservation efforts and studies on endangered species like tigers, elephants, and riverine dolphins.
Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification
Launched under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model between WII and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), the Pashmina Certification Centre (PCC) has been significantly upgraded. The facility now includes a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) for advanced wool testing and certification.
Key Features of the Upgraded Facility:
- Fiber Analysis: The SEM-EDS technology ensures accurate identification and certification of Pashmina fibers, free from any prohibited materials.
- Unique ID and E-certificates: Each certified product is tagged with a unique ID and e-certificate, enhancing traceability and authenticity.
- Global Trade Facilitation: The certification process eliminates delays at exit points, ensuring smoother international trade for certified Pashmina products.
The PCC has already certified over 15,000 Pashmina shawls and plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of artisans and weavers in Jammu & Kashmir. By ensuring the authenticity of Pashmina, the facility also helps combat the illegal trade of Shahtoosh wool, which is harmful to the Tibetan antelope (Chiru).
Significance for Artisans and Conservation:
- Support for Artisans: The upgraded facility helps increase the credibility of Pashmina products in global markets, benefiting local artisans and weavers.
- Conservation Impact: By certifying genuine Pashmina products, the initiative indirectly contributes to the conservation of the Tibetan antelope by reducing illegal poaching and trade.
- Sustainability: The PCC is a self-sustaining model that not only supports conservation but also generates revenue and creates job opportunities.
Overview of the Genome India Project
The Genome India Project is a gene mapping initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology, aiming to create a comprehensive database of genetic variations across the Indian population. The project focuses on understanding genetic diversity and its implications for health, agriculture, and biodiversity conservation in India.
Goals:
- Comprehensive Gene Mapping: The project seeks to map the genetic variations found within India’s diverse population, enabling better healthcare and disease management.
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Insights from the project will also aid in wildlife conservation by understanding the genetic health of endangered species and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
This initiative is aligned with India’s broader goals of using advanced technologies to address modern conservation challenges and foster a sustainable future.
India State of Forest Report 2023

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), assesses the forest and tree resources of the country based on satellite data and field-based inventories. The ISFR 2023 is the 18th edition of this report, with the first published in 1987.
Key Findings
- Total Forest and Tree Cover:
- Area: 827,357 sq km (25.17% of India's geographical area)
- Breakdown:
- Forest cover: 715,343 sq km (21.76%)
- Tree cover: 112,014 sq km (3.41%)
- Increase from 2021: An increase of 1,445 sq km, including:
- Forest cover: +156 sq km
- Tree cover: +1,289 sq km
- State-wise Forest and Tree Cover:
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Madhya Pradesh (85,724 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (67,083 sq km)
- Maharashtra (65,383 sq km)
- Top 3 States by Forest Cover:
- Madhya Pradesh (77,073 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (65,882 sq km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,812 sq km)
- States with Maximum Increase in Forest and Tree Cover:
- Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan
- Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha showed the most significant increase in forest cover.
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Forest Cover Percentage (as a proportion of total geographical area):
- Lakshadweep: 91.33% (Highest)
- Mizoram: 85.34%
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 81.62%
- 19 States/UTs have over 33% forest cover, with 8 states having more than 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- Total Mangrove Cover: 4,992 sq km (a decrease of 7.43 sq km from 2021).
- Notable Changes: Gujarat saw the largest loss of mangroves, whereas Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra reported increases.
- Carbon Stock and Climate Targets:
- Total Carbon Stock: 7,285.5 million tonnes (an increase of 81.5 million tonnes from the previous assessment).
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India’s carbon stock has reached 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Achieved an additional 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink compared to the 2005 baseline, towards the 2030 target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes.
- Bamboo and Timber Production:
- Bamboo Bearing Area: Estimated at 154,670 sq km, an increase of 5,227 sq km since 2021.
- Timber Potential: Estimated annual potential production of 91.51 million cubic meters from trees outside forests.
Achievements:
- There has been a notable increase in the forest and tree cover, particularly in states like Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- The carbon stock in forests has increased, helping India make significant progress in its climate change mitigation goals.
- The bamboo bearing area has also expanded, promoting biodiversity and economic benefits through bamboo cultivation.
Concerns:
- Mangrove Loss: Gujarat experienced a notable decrease in mangrove area, highlighting the need for focused conservation efforts in coastal regions.
Forest Survey of India (FSI) Overview
- Established: 1981, under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mission: To assess, monitor, and research forest resources across India, providing data for sustainable management, national planning, and conservation.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
72% Decline in Bird Species at Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary, Assam

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study has revealed a dramatic decline in the number of bird species at Assam's Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary (BBBS). The sanctuary, once home to a rich diversity of avian species, has experienced a 72% decline in bird species over the past 27 years. The study, published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa, highlights the severe biodiversity crisis facing the sanctuary.
Key Findings:
- Bird Species Count Decline:
- In 1997, the sanctuary recorded 167 bird species.
- Recent surveys (2022-2024) have only recorded 47 species, marking a 71.85% decline in species count.
- Surveys:
- 2011 Survey: Recorded 133 species (86 resident, 23 migratory, 24 local migrants).
- 2017-2018 Survey: Found 120 species, along with a variety of other biodiversity, including macrophytes, fish, and aquatic ferns.
- Impact on Migratory Birds:
- Migratory species like Brown Shrike, Citrine Wagtail, and White Wagtail (winter migrants), and the Lesser Kestrel (summer migrant) were recorded recently.
- Main Causes of Decline:
- Anthropogenic Activities: Overfishing, poaching, excessive harvesting of aquatic plants, and egg collection.
- Land Use Changes: Habitat degradation due to agriculture, machinery noise, and land being used as pasture areas.
- Disruption of Food Chain: Habitat loss and changes in foraging and breeding grounds for both migratory and resident birds.
- Species of Concern:
- Poached Birds: Lesser whistling duck, Fulvous whistling duck, White-breasted waterhen, Indian pond heron, Eastern spotted dove, and Yellow-footed green pigeon.
- Threatened Species: The sanctuary is home to globally threatened species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant.
About Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated between Dhemaji and Lakhimpur districts in Assam, the sanctuary spans 11.25 sq. km at an altitude of 90-95 meters above sea level.
- History: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1996, it was originally part of the Subansiri River which has now shifted 7 km from the wetland.
- Climate & Vegetation:
- Moist tropical climate with an average annual rainfall of around 2,000 mm.
- The vegetation includes flooded valley grasslands and wetland plants, providing crucial habitat for migratory birds.
- Significance for Avian Species:
- Hosts a variety of migratory waterfowl, especially during the winter.
- Home to globally threatened bird species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant, along with resident birds such as the Indian Pond Heron and Fulvous Whistling Duck.
Conservation Efforts:
- The decline in bird species at the sanctuary has raised alarm about the degradation of wetland habitats.
- The study emphasizes that habitat loss can disrupt the food chain, water table, and nutrient cycle, which in turn harms both the ecosystem and human communities.
- The authors of the study advocate for intense conservation efforts to restore and protect the sanctuary’s biodiversity.
Assam's Biodiversity:
- Assam is one of India's most biodiverse states, with around 950 bird species, including 17 endemic species.
- The state also hosts 55 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBA), which are vital hotspots for avian species.
New Undersea Cables to Boost India’s Digital Connectivity

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
India is expanding its digital infrastructure with the launch of two major undersea cable systems aimed at enhancing its Internet connectivity with Asia and Europe. The India Asia Xpress (IAX) and India Europe Xpress (IEX) are set to provide additional data links between India and these regions, supporting the growing demand for data usage. This also marks India’s increasing involvement in submarine cable resilience and security discussions.
Key Points:
- New Cable Systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
- Total Length: Both cables, together spanning over 15,000 kilometers, will expand India’s undersea cable network.
- Ownership and Investment:
- Both cable systems are owned by Reliance Jio, with a strategic investment from China Mobile.
- Geopolitical Impact:
- These expansions are a response to growing Internet traffic, as well as India's rising geopolitical ambitions. They help bolster India’s defense strategy, improving cable resilience against disruptions from cyberattacks or physical damages.
- India’s active role in maritime cable network security is being closely watched, especially in key regions like the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea.
- Past Cable Disruptions:
- In March, three cables connecting India to West Asia and Europe were disrupted, impacting Internet traffic. However, India’s alternate routing systems and data centers ensured services remained operational, highlighting the country’s resilience.
- International Role:
- India’s role in submarine cable resilience is growing. Telecom Secretary Neeraj Mittal is part of the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Impact on India’s Connectivity:
- Bangladesh's Role:
- Plans to sell bandwidth from Bangladesh to Northeast India were recently put on hold. However, this does not significantly impact India as Northeast India already benefits from substantial fiber-optic connectivity through Power Grid Corporation of India’s transmission lines.
About Underwater Cables:
- What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber-optic cables laid under the ocean to transmit data across vast distances at high speeds.
- New Cable Systems:
- IAX: Connects India to Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia).
- IEX: Connects India to Europe (France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Djibouti).
- How They Work:
- Fiber-optic technology uses laser beams through thin glass fibers to transmit data.
- The cables are protected by multiple layers of insulation, plastic, and steel wires and are buried near shores or laid directly on the ocean floor in deep sea regions.
- Cable Features:
- Data Capacity: New cables can carry up to 224 Tbps (Terabits per second).
- Durability: Designed to avoid damage from fault zones, fishing areas, or anchors.
- Speed: Faster and more cost-efficient than satellite communications for large-scale data transfer.
Why Undersea Cables Over Satellites?
- Higher Capacity: Submarine cables handle far more data than satellites.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable for high-volume data transfers.
- Reliability: Cables provide more stable connections, especially for large-scale data, compared to satellites.
Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program

- 21 Dec 2024
On December 20, 2024, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $350 million policy-based loan aimed at expanding India's manufacturing sector and improving the resilience of its supply chains. This loan is part of the Strengthening Multimodal and Integrated Logistics Ecosystem (SMILE) program.
Key Points:
- Loan Agreement Signatories:
- Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), Ministry of Finance, Government of India
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- SMILE Program:
- Goal: Strengthen the logistics ecosystem to enhance India's manufacturing sector and improve supply chain resilience.
- Structure: The program includes two subprograms focusing on strategic reforms in logistics and infrastructure development.
- Key Features of the SMILE Program:
- Strengthening Multimodal Infrastructure: Enhances logistics infrastructure at the national, state, and city levels.
- Standardization: Improves warehousing and other logistics assets to attract private sector investment.
- External Trade Logistics: Enhances efficiencies in external trade logistics.
- Smart Systems: Adopts systems for efficient, low-emission logistics to promote sustainability.
- Expected Outcomes:
- Cost Reduction & Efficiency: Strategic reforms will reduce logistics costs and improve efficiency.
- Job Creation: Infrastructure development and reforms are expected to generate substantial employment opportunities.
- Gender Inclusion: The program promotes gender inclusion through economic growth initiatives.
- Impact on India’s Economy:
- The transformation of India’s logistics sector will enhance the competitiveness of the manufacturing sector and drive sustainable economic growth.
About the Asian Development Bank (ADB):
- Headquarters: Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines.
- Established: December 19, 1966.
- Members: 69 countries, including both regional (e.g., India, China) and non-regional (e.g., USA, Japan) members.
- Function: ADB promotes social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific, providing loans, grants, and technical assistance for development projects.
- Key Shareholders:
- Japan: 15.57%
- USA: 15.57%
- India: 6.32%
- China: 6.43%
- Australia: 5.77%
2023 National Tansen Samman

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
- The prestigious National Tansen Samman for 2023 was conferred upon Pt. Swapan Choudhary, a renowned tabla maestro from Kolkata, at the National Tansen Festival held in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Highlights:
- Tansen Festival: This festival, renowned for its celebration of classical music, is organized annually in Gwalior, which is considered the music capital of Madhya Pradesh.
- Prize Details: As part of the honor, Pt. Swapan Choudhary was presented with an honorarium of five lakh rupees, a citation plaque, and a shawl-shriphal.
- About the Award:
- The National Tansen Samman was established in 1980 by the Madhya Pradesh government to recognize exceptional contributions to Indian classical music.
- It is named after Tansen, one of India's most celebrated classical musicians.
- The award is the highest national honor in the field of Indian classical music.
- Additional Award:
- Raja Mansingh Tomar Samman for 2023 was awarded to Sanand Nyas, an institution from Indore. This institution has been active for 35 years in the promotion of classical music, drama, and cultural festivals.
- Pt. Swapan Choudhary’s Remark: In response to receiving the honor, Pt. Choudhary expressed his gratitude and pride in joining the ranks of distinguished artists awarded the National Tansen Samman.
About Tansen: The Iconic Musician
- Legacy: Tansen, also known as Miyan Tansen, was a prominent Indian classical musician, composer, and vocalist. He is credited with popularizing several ragas and revolutionizing the Indian classical music tradition.
- Role at Akbar’s Court: Tansen was one of the Navaratnas (nine jewels) in the court of Mughal Emperor Akbar. He held the title of Mian, meaning "learned man," bestowed upon him by Akbar.
- Contributions:
- Tansen is famous for his compositions, including the introduction of notable ragas such as Miyan ki Malhar, Miyan ki Todi, and Darbari.
- He also improved the plucked rabab, which is of Central Asian origin, enhancing its role in Indian classical music.
- Historical Influence: Tansen's life and work are surrounded by extensive legend, and his contributions remain deeply influential in the development of Indian classical music today.
Specialised Investment Fund (SIF)
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
SEBI has introduced a new asset class called Specialised Investment Fund (SIF), designed to bridge the gap between Mutual Funds (MFs) and Portfolio Management Services (PMS). This new asset class is targeted at informed investors who are willing to take on higher risks.
SIFs offer a blend of the flexibility seen in PMS and the regulatory framework governing MFs, making them suitable for investors seeking more customized and riskier investment strategies.
Key Features of SIF:
- Minimum Investment: The minimum investment threshold for SIFs is Rs. 10 lakh. However, accredited investors (who meet specific eligibility criteria) can invest with lower amounts.
- Expense Structure: SIFs will follow the same expense structure as mutual funds. For equity schemes up to Rs 500 crore in size, the maximum allowable fee is 2.25% of assets under management (AUM), with the cap decreasing as the fund size grows. This ensures transparency and keeps management fees in line with existing mutual fund norms.
- Investment Strategies: SIFs can offer a mix of open-ended, close-ended, and interval investment strategies. Specific details on permissible strategies will be released by SEBI in the future.
- Investment Restrictions:
- For debt instruments, a single issuer's exposure is capped at 20% of the total AUM. However, this can be raised to 25% with approval from the Asset Management Company (AMC)’s trustees and board of directors. Government securities are exempt from this limit.
- For equities, the exposure is capped at 10% of the total AUM, in line with the norms for mutual funds.
- Ownership in Companies: The maximum permissible ownership in any company is raised to 15%, including the MF exposure.
- REITs and InvITs: SIFs can invest a maximum of 20% of their AUM in Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs). However, the exposure to a single issuer in these areas is limited to 10%.
- Branding and Marketing: SEBI mandates AMCs to distinguish SIFs clearly from MFs through distinct branding, advertising, and website presence. This helps in creating a clear differentiation between the two products for investors.
- Risk Management and Compliance: AMCs managing SIFs are required to have robust risk management systems, internal control systems, and expertise to handle the investments effectively. Trustees are responsible for ensuring that the AMC complies with all risk management, investor protection, and disclosure norms.
Regulatory Context:
- The regulations on SIFs are similar to those governing mutual funds, including taxation and other compliance requirements.
- SEBI also introduced the Mutual Fund Lite regulations to encourage the growth of passively managed funds, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and index funds. These regulations are designed to reduce compliance burdens and lower the barriers to entry for new players in the mutual fund industry.
Significance of SIFs:
- Targeted Audience: SIFs cater to investors who are knowledgeable and willing to take on riskier investments, thereby filling a gap between traditional MFs (which are more conservative) and PMS (which offer highly customized solutions).
- Higher Flexibility: While SIFs maintain some regulations of MFs, they offer more flexibility in investment choices, allowing AMCs to explore more dynamic strategies.
- Investor Protection: By maintaining the same expense structure as mutual funds and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks, SEBI aims to protect investor interests while allowing for higher returns that come with riskier investments.
Parliamentary Standing Committee on Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (PSC) and MGNREGA
- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) on Rural Development and Panchayati Raj highlighted several issues within the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS). The committee recommended reforms to address these challenges, especially concerning wage rates, workdays, payment systems, and infrastructure.
Key Challenges in MGNREGS Implementation:
- Wages Not Aligned with Inflation:
- MGNREGA wage rates have failed to keep pace with inflation, diminishing the purchasing power of rural workers. This discourages workers from completing the full 100 workdays.
- The wage guarantee of 100 days per household often falls short, especially during times of natural calamities or post-pandemic recovery.
- Revision of Permissible Works:
- The list of allowable work under MGNREGA is outdated and doesn't cover all rural needs, such as flood protection or land erosion management. Delayed revisions limit its effectiveness in addressing region-specific challenges.
- Delayed Payment of Wages:
- Issues like Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) glitches, inactive Aadhaar details, or frozen bank accounts often lead to delayed wage payments.
- The delay in wages undermines the scheme's goal of providing livelihood support.
- Unemployment Allowance:
- Those who apply for work but are not provided employment within 15 days are entitled to a daily unemployment allowance. However, this allowance is rarely paid, and when it is, the amounts are insufficient.
- Weak Social Audits:
- Social audits are a vital mechanism to ensure transparency and accountability. However, in the 2020-21 fiscal year, only 29,611 Gram Panchayats out of a total were audited, pointing to the weak social audit system.
- Lack of Ombudsman:
- Despite the provision for 715 ombudsmen, only 263 have been appointed. This reduces the oversight and accountability of the scheme.
Recommendations for MGNREGS Reform by the PSC:
- Revision of Wage Rates:
- Link MGNREGA wages to an inflation index, ensuring wages reflect the rising cost of living in rural areas.
- The base year (2009-2010) should be updated to align with current inflation trends.
- Increase Days of Work:
- The PSC recommended increasing the guaranteed workdays from 100 to 150 days. This will provide better livelihood security, especially in times of economic distress.
- Improvement in Payment Mechanisms:
- The committee recommended maintaining alternative payment systems alongside ABPS to prevent wage delays.
- A streamlined process should be put in place to ensure timely wage disbursement, reducing bureaucratic hurdles.
- National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS):
- The committee stressed the importance of training programs to help beneficiaries effectively use the NMMS.
- It also suggested retaining alternative attendance methods to avoid exclusion due to technological barriers. NMMS helps enhance transparency and accountability by tracking attendance and work progress.
- Sufficient Fund Allocation:
- The committee emphasized the need for adequate financial allocations for MGNREGS to make it more effective in providing livelihood security to rural households.
Additional Context and Statistics:
- In 2024-25, the average wage increase under MGNREGA was just Rs 28/day.
- The MGNREGA wage increase for 2023-24 ranged from 2%-10%.
- The Consumer Price Index for Agricultural Labour (CPI-AL) is used to determine wage rates, although Dr. Nagesh Singh Committee (2017) recommended using the CPI Rural instead.
About the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (PSC):
- Established: August 5, 2004.
- Jurisdiction: The committee oversees the Ministry of Rural Development and the Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- Composition: 31 members – 21 from Lok Sabha and 10 from Rajya Sabha.
- Functions:
- Reviews Demands for Grants and reports.
- Examines Bills referred by the Speaker or Chairman.
- Reviews the annual reports of relevant ministries.
- Considers national policy documents.
About MGNREGA:
- Launched: 2005 by the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Objective: Provides 100 days of unskilled manual work at minimum wages for rural households annually.
- Key Features:
- Legal Guarantee: Work must be provided within 15 days of request.
- Unemployment Allowance: If work isn't provided within 15 days, beneficiaries are entitled to a daily allowance.
- Women-Focused: At least one-third of beneficiaries are women.
- Social Audits: Mandated by the Gram Sabha for all projects under the scheme.
Masali Village in Gujarat

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
In Gujarat, Masali village in Banaskantha district has become country’s first solar border village.
Key Highlights:
Location:
Masali village is located in Banaskantha district, Gujarat, approximately 40 kilometers from the Pakistan border. The village, with a population of around 800 people, has recently achieved a significant milestone by becoming India’s first fully solar-powered border village.
Solarization Initiative:
Under the PM Suryaghar Yojana, the village has installed solar rooftops on 119 houses. These solar installations collectively generate over 225 kilowatts of electricity, which is more than sufficient to meet the village’s energy needs. This initiative marks a step forward in solarizing border areas of India, promoting sustainability and reducing dependency on conventional energy sources.
Significance of the Initiative:
- India's First Solar-Powered Border Village: Masali village is the first of its kind in India, making it a model for other border regions to adopt renewable energy solutions.
- Promotes Renewable Energy: The transition to solar power encourages sustainability, reduces dependence on traditional fossil fuels, and supports India's renewable energy goals.
- Part of the Border Development Project: Masali is part of a broader government plan that aims to solarize 11 villages in Vav taluka and 6 villages in Suigam taluka, strengthening energy access in these strategically vital areas.
- Energy Security: By harnessing solar energy, the village enhances its energy reliability and self-sufficiency, especially in remote areas with limited access to the national grid.
PM Suryaghar Yojana: Launched in 2024, the PM Suryaghar Yojana aims to provide free electricity to eligible Indian households by subsidizing the installation of rooftop solar panels. Key features of the scheme include:
- A subsidy covering up to 40% of the installation cost of solar panels.
- Eligible families receive 300 free electricity units per month, saving up to Rs. 18,000 annually.
- The scheme is expected to save the government approximately Rs. 75,000 crore annually on electricity costs.
- It encourages the use of renewable energy, lowers carbon emissions, and reduces the electricity expenses for the government.
Eligibility for the Scheme:
- Indian citizens who own a house with a suitable roof for installing solar panels.
- Households must have a valid electricity connection and should not have received any prior subsidy for solar panels.
Broader Implications:
The successful solarization of Masali village is not just an energy achievement but also a significant step toward promoting renewable energy usage, enhancing energy security, and fostering sustainable development in India’s border regions. It is expected that other regions in Gujarat and across the country will follow this example, improving both local living conditions and national energy resilience.
Reimposition of Protected Area Permit (PAP) in Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of the Government of India has recently reinstated the Protected Area Regime (PAR) for the states of Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland, which are strategically located along the international border with Myanmar. This move comes amid growing security concerns, particularly the influx of migrants from Myanmar, which has been cited as a significant factor in the ongoing conflicts in the region.
What is Protected Area Permit (PAP)?
A Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permission required for foreign nationals to visit certain areas of India deemed sensitive due to their proximity to international borders or other security-related concerns. The regulations governing the PAP are laid down under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958, which restricts the entry of foreigners to designated regions within India.
Purpose of PAP:
The PAP regime serves multiple critical objectives:
- National Security: It ensures the monitoring and regulation of foreign nationals in sensitive border areas.
- Preservation of Local Communities: The regime safeguards indigenous populations and their unique cultural heritage.
- Environmental Conservation: The permit helps minimize ecological disturbances in fragile regions, ensuring sustainable tourism and development.
Key Features of PAP Regime:
- Eligibility: All foreign nationals, excluding Bhutanese citizens, must obtain a PAP to enter these designated areas. The permit can be granted for specific regions, routes, and time periods.
- Validity: The PAP is typically valid for 10 days with the possibility of extension.
- Restricted Areas: Certain foreign nationals, particularly those from Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, require prior approval from the MHA to enter these regions.
- Tourism and Other Permits: While foreign nationals can visit these regions for tourism purposes under the PAP, non-touristic visits require special permission from the MHA.
- Registration: Foreigners must register with the Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) within 24 hours of arrival in the protected area.
Historical Context and Reimposition:
The PAP regime was lifted for Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland in 2011, as part of efforts to boost tourism in the region. However, due to rising security concerns related to illegal immigration and ethnic tensions, the MHA reimposed the PAP in 2025. The government’s move aligns with its broader national security strategy to better control foreign movements in sensitive border regions, particularly those with Myanmar, where the Free Movement Regime (FMR) had previously allowed easier cross-border travel.
Background on Security Concerns:
The influx of individuals from Myanmar, particularly members of the Chin community, which shares ethnic ties with the Kuki-Zomi communities in India, has been a source of tension. The Manipur government has repeatedly emphasized that uncontrolled migration has contributed to the unrest in the state. Additionally, the decision to end the FMR between India and Myanmar has further intensified the debate over border security and migration.
Impact on Tourism and Local Communities:
While the reimposition of the PAP is seen as a measure to strengthen security, it has raised concerns in states like Mizoram and Nagaland, which have been actively promoting tourism. For example, Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival recently attracted over 200,000 visitors, including foreign nationals. The reintroduced restrictions may dampen tourism in these states, which were previously exempt from the PAP to encourage foreign visits.
Key Legal Provisions Under the PAP Regime:
- Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958: This order mandates the requirement of a PAP for foreigners visiting areas close to international borders.
- Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963: This order covers areas that require a Restricted Area Permit (RAP) for foreign nationals, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
States Affected by the PAP Regime:
The PAP regime affects regions close to India’s international borders, including the entire states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand.
Dark Comets

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
Dark comets are a newly identified class of celestial objects that challenge our traditional understanding of comets and asteroids. Unlike regular comets, these objects exhibit characteristics that blur the lines between comets and asteroids, leading astronomers to closely study their nature, origin, and significance.
Discovery and Background
The first hint of dark comets appeared in 2016, when asteroid 2003 RM exhibited strange orbital deviations that suggested it might be a comet in disguise. NASA further fueled this interest in 2017 when it discovered ‘Oumuamua, an interstellar object that entered our Solar System. Though initially classified as an asteroid, its erratic motion and lack of a visible tail led scientists to consider it a dark comet. Since then, several more objects with similar characteristics have been discovered, and astronomers now identify these objects as a new class—dark comets.
Characteristics of Dark Comets
- Appearance: Dark comets do not exhibit the brilliant, glowing tails typically associated with comets. Instead, they resemble asteroids, appearing as faint points of light in space. Unlike bright comets, they do not have a visible coma (a cloud of gas and dust) or a tail, making them much harder to detect.
- Size: Dark comets are typically small, ranging from a few meters to a few hundred meters in diameter. Due to their small size, there is less surface area for material to escape, preventing the formation of the iconic tails seen in traditional comets.
- Orbital Path: These objects follow elongated, elliptical orbits. While some of them travel close to the Sun, they can also venture to the outer reaches of the Solar System, far beyond Pluto, and even into the Oort Cloud—the distant region where long-period comets are believed to originate.
- Spin and Gas Dispersion: Dark comets often rotate rapidly, dispersing gas and dust in all directions. This rapid spin contributes to their invisibility, as the gas and dust are scattered evenly, making it more difficult for astronomers to detect their presence.
- Composition: The composition of dark comets may also play a role in their lack of visibility. Over time, the materials that form the bright tails of comets may be depleted, especially for older objects. As a result, dark comets may not release enough gas to produce a visible coma or tail.
Types of Dark Comets
There are two main categories of dark comets:
- Inner Dark Comets: These are smaller objects that reside closer to the Sun and typically travel in nearly circular orbits. They are often just a few meters in size, with less surface area for gas and dust to escape.
- Outer Dark Comets: These larger objects, measuring over 100 meters in diameter, travel in highly eccentric orbits, similar to Jupiter-family comets. These dark comets follow elliptical paths that bring them close to the Sun and then send them back toward the outer reaches of the Solar System.
Importance of Studying Dark Comets
Dark comets may hold critical clues about the early Solar System and the formation of Earth. Studying these objects can provide insights into the origins of water on Earth, as well as the ingredients necessary for life. Their unique composition and orbits also offer potential for understanding the processes that led to the formation of planets.
Recent Discoveries and Advancements
Astronomers recently discovered 10 new dark comets with the help of the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) on a large telescope in Chile. The DECam, designed to study distant galaxies and stars, has enabled researchers to detect these faint objects by analyzing images of the night sky. Further progress is expected with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory, which will feature the largest digital camera ever built. This new instrument will allow astronomers to capture more detailed images of the night sky and detect fainter objects, potentially doubling or even tripling the number of known dark comets in the next decade.
Key Facts:
- Dark comets lack the characteristic glowing tails of typical comets, instead resembling asteroids.
- They exhibit erratic motions and follow elliptical orbits, often extending beyond Pluto and into the Oort Cloud.
- They are typically small (a few meters to hundreds of meters wide) and spin rapidly.
- The first dark comet was identified in 2016, with more discoveries made in the years since.
- The Dark Energy Camera (DECam) in Chile has been instrumental in detecting these elusive objects, with a new Vera C. Rubin Observatory expected to further enhance detection in the future.
- Studies suggest that between 0.5% and 60% of Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) could be dark comets, many originating from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
India's First-Ever Ganges River Dolphin Tagging in Assam

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
India conducts the first-ever satellite tagging of the Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica) in Assam, a key step in wildlife conservation.
Key Highlights:
Objective of Tagging: The tagging aims to understand:
- Migratory patterns
- Range and distribution
- Habitat utilization, especially in fragmented river systems.
Key Participants:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
- Assam Forest Department
- Aaranyak (NGO)
- Funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
Significance of the Tagging:
- Technology Used: Lightweight satellite tags compatible with Argos systems were employed, minimizing interference with the dolphin’s movement despite its limited surfacing time (5-30 seconds).
- Insight into Dolphin Ecology: Helps fill knowledge gaps regarding habitat needs and seasonal migration, especially in disturbed river ecosystems.
Ganges River Dolphin – India's National Aquatic Animal:
- Endemic to India with around 90% of the population in India.
- Known for being nearly blind and using echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Plays a crucial role as an apex predator and indicator species for river ecosystem health.
Project Dolphin:
- Launched by PM Narendra Modi in 2020, modeled after Project Tiger.
- Focuses on conservation of riverine and marine dolphins.
- A 10-year initiative funded by MoEFCC to safeguard dolphin populations and address ecosystem challenges.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Endangered.
- Protection: Included in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and CITES Appendix I.
- Major Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, bycatch, and water abstraction, compounded by damming and sand mining.
Broader Impact:
- The tagging initiative contributes to evidence-based conservation strategies for Ganges River Dolphins.
- Will aid in the development of a comprehensive conservation action plan for the species.
- Expands the understanding of critical habitats within river ecosystems, benefiting both biodiversity and the communities dependent on these resources.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
In mid-2024, India surpassed China as the largest importer of Russian oil. This milestone has been accompanied by the operationalization of a new maritime route, the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC), which connects Chennai in India to Vladivostok in Russia. The new sea route is significantly reducing both shipping times and costs, facilitating smoother commodity trade between the two countries, particularly crude oil shipments.
The Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC)
The EMC, covering a distance of about 5,600 nautical miles, has reduced the shipping time between India and Russia’s Far East by up to 16 days. The Chennai-Vladivostok route now takes just 24 days, compared to over 40 days using the traditional St. Petersburg-Mumbai route. This reduction in transit time makes it a highly efficient route for transporting goods such as crude oil, coal, LNG, fertilizers, and other commodities. Additionally, this new corridor supports India’s maritime sector and aligns with the country’s broader vision for maritime growth and regional strategic engagement.
Key Features of the EMC:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: The route cuts shipping time and distance, reducing costs associated with longer transit periods. For example, a ship traveling between Vladivostok and Chennai now takes only about 12 days at cruising speed, compared to the traditional route's 40+ days.
- Strategic Importance: Vladivostok is Russia’s largest Pacific port, and the corridor strengthens India's strategic presence in the region. This maritime route bypasses traditional chokepoints like the Suez Canal, offering faster, more direct access to key markets.
- Diversification of Trade: Besides crude oil, the EMC facilitates the transportation of coal, LNG, fertilizers, and metals, diversifying India's trade portfolio with Russia. It also helps maintain supply chains for essential goods.
- Boosting India’s Maritime Sector: The corridor supports India’s Maritime Vision 2030, which aims to enhance the efficiency and reach of India's maritime trade, a sector responsible for over 70% of the country’s trade value.
Economic and Strategic Impact:
- The new Eastern Maritime Corridor is particularly significant for India’s energy needs. As the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, India imports over 85% of its crude oil demand. The growing imports of Russian crude, especially the Urals grade, are crucial for securing India’s energy future. Additionally, Russia’s competitive pricing on crude, coupled with the savings on shipping costs through the EMC, makes Russian oil even more attractive.
- Beyond the economic benefits, the EMC also supports India’s broader strategic goals, including strengthening ties with Russia, a key partner in defense, nuclear cooperation, and regional geopolitics. The closer maritime links also help counterbalance China's growing dominance in the Pacific region, aligning with India's Act Far East Policy and enhancing trade and diplomatic engagement with East Asia and Russia.
Other Key Maritime Corridors Relevant to India:
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC): A 7,200 km multimodal route linking the Indian Ocean with Russia, offering alternative trade routes to Europe and Central Asia.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A recent project announced at the G20 Summit, which connects India, the Middle East, and Europe via rail, road, and maritime links, fostering greater regional integration.
- Northern Sea Route (NSR): A 5,600 km Arctic route offering shorter transit times between the Barents and Kara Seas and the Bering Strait, gaining importance due to growing imports of Russian energy resources.
In conclusion, the Eastern Maritime Corridor is reshaping India-Russia trade dynamics, boosting economic ties and strategic cooperation between the two nations. By facilitating faster and cheaper transportation, the EMC is not only beneficial for trade in crude oil but also for a range of other commodities, positioning India as a key player in the evolving global trade network.
One Nation, One Election
- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The government has recently taken steps to implement "One Nation, One Election" by presenting two Constitution Amendment Bills in the Lok Sabha: the One Nation One Election – The Constitution 129th Amendment Bill 2024 and the Union Territories Laws Amendment Bill 2024.
Introduction to the Concept:
- Objective: Proposes synchronizing elections for Lok Sabha (national) and State Legislative Assemblies to be held on the same day.
- Purpose: Aims to reduce costs, minimize logistical challenges, and address governance disruptions caused by frequent elections.
- 2024 Report: The High-Level Committee Report on Simultaneous Elections, released in December 2024, outlines a roadmap for implementing this reform.
Historical Background:
- Previous Practice: From 1951 to 1967, Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections were conducted together.
- Disruptions: The practice was interrupted due to premature dissolutions and emergencies, leading to staggered elections across India.
High-Level Committee on Simultaneous Elections:
- Committee Formation: Headed by former President Ram Nath Kovind, formed on 2nd September 2023.
- Public Response: Over 21,500 responses, with 80% in favor.
- Political Party Responses: 32 political parties supported the idea, while 15 raised concerns about regional party marginalization.
- Expert Consultations: Majority of experts supported the reform, emphasizing resource optimization and reduced disruptions.
Committee Recommendations:
- Constitutional Amendments: Proposals to amend Articles 82A and 324A to enable simultaneous elections.
- Two-Phase Implementation:
- Phase 1: Synchronize elections for Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Include Municipalities and Panchayats within 100 days.
- Single Electoral Roll: Creation of a unified electoral roll and EPIC for all levels of elections, reducing duplication and errors.
Rationale for Simultaneous Elections:
- Governance Consistency: Reduces focus on election preparation, allowing more attention to developmental work.
- Prevents Policy Paralysis: Mitigates disruptions caused by the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) during frequent elections.
- Resource Optimization: Reduces the need for personnel and resources for election duties, allowing better allocation to governance tasks.
- Preserves Regional Party Relevance: Local issues remain prioritized, ensuring regional parties' concerns are heard.
- Equitable Political Opportunities: Encourages diversification and inclusivity within political parties.
- Financial Benefits: Reduces the financial burden of conducting multiple elections, enhancing economic efficiency.
Conclusion:
- The concept of "One Nation, One Election" is a significant reform aimed at streamlining India's electoral processes. With broad public and political support, it promises improved governance, cost savings, and better resource management in the future.
Wroughton’s Free-Tailed Bat

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
Wroughton’s free-tailed bat, a highly rare species of molossus bat, has been spotted at the Delhi Development Authority (DDA)’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park, marking a unique sighting.
Key Highlights:
- Species Overview: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni) is a rare species of molossus bat, notable for its powerful flight and ecological importance in controlling insect populations and assisting in pollination.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Listed as "Data Deficient".
- Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily found in the Western Ghats, with a single known breeding colony.
- Small colonies in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and a solitary individual sighted in Cambodia.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Large in size, with huge ears extending beyond the muzzle.
- Bicoloured velvet fur.
- Noted for powerful flying capabilities, enabling long-distance foraging.
- Ecological Role:
- Regulates insect populations.
- Known for assisting in pollination.
- Habitat:
- Roosts in caves, or dark, damp, and slightly warm places, typically in moderate-sized colonies.
- Significance of the Delhi Sighting:
- The sighting at Yamuna Biodiversity Park is significant for Delhi, marking a rare occurrence in the region.
- Delhi's bat species: The city is home to about 14 bat species, with four species, including the Indian false vampire and Egyptian free-tailed bat, considered locally extinct.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Two decades of ecological restoration have created specialized niches in the area, aiding species rewilding and ecological balance.
- The Aravalli Biodiversity Park in Gurugram now serves as the only known roosting site for the Blyth’s horseshoe bat in Delhi NCR.
- Additional Notes:
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat was considered critically endangered until 2000 due to its limited known population. However, the discovery of populations in other regions has led to a reclassification to "Data Deficient".
- Despite being discovered over a century ago, much about the bat's feeding ecology remains unknown.
Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Report 2024

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Report 2024 was released by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI). The report focuses on the theme “Poverty Amid Conflict”, examining the interplay between violent conflict and multidimensional poverty.
Key Findings:
- Global Poverty Levels:
- 1.1 billion people (~18% of the global population) live in acute multidimensional poverty across 112 countries.
- India has the largest number of people living in multidimensional poverty, with 234 million people.
- Multidimensional Poverty Indicators:
- The MPI assesses poverty across three key dimensions:
- Health: Child mortality, malnutrition.
- Education: Years of schooling, school attendance.
- Living Standards: Access to clean water, sanitation, electricity, cooking fuel, housing quality, and ownership of basic assets.
- A person is considered MPI poor if they are deprived in one-third or more of the weighted indicators.
- The MPI assesses poverty across three key dimensions:
- Impact of Conflict:
- Countries experiencing violent conflict exhibit higher deprivations across all 10 MPI indicators when compared to non-conflict nations.
- 40% (455 million people) of those living in poverty are in conflict-affected regions. These regions include active war zones, fragile states, and areas with low peace.
- Child Poverty:
- 584 million children (27.9% of all children globally) are living in extreme poverty, highlighting the disproportionate impact on the younger population.
- In contrast, 13.5% of adults are living in extreme poverty.
- Regional Distribution:
- The regions with the highest poverty rates are Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, which together account for 83.2% of the global poor.
- Rural Poverty: A majority of the poor (83.7%, or 962 million people) live in rural areas, with 70.7% of the poor concentrated in rural parts of Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
- Countries with the Highest Poverty:
- India: 234 million people.
- Pakistan: 93 million people.
- Ethiopia: 86 million people.
- Nigeria: 74 million people.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo: 66 million people. These five countries account for 48.1% of the global poor.
- Poverty Amid Conflict:
- The report underscores that 2023 witnessed the highest number of conflicts since World War II, leading to the displacement of 117 million people due to violent conflicts and other factors like natural disasters.
- Conflict zones continue to experience higher poverty, as nearly 40% of the world's poorest people live in these areas.
India's Poverty Situation:
- India's Poor Performance:
- India has 234 million people living in multidimensional poverty, making it the country with the largest share of the global poor.
- Regional Disparities: Poverty rates in rural areas remain high due to poor infrastructure, limited economic opportunities, and underdeveloped services outside of agriculture.
- Poor Nutrition: Malnutrition, especially among children, is a significant concern.
- Education: The quality of education remains subpar, especially in government-run schools, affecting learning outcomes.
- Water and Sanitation: Inadequate access to clean drinking water and sanitation is prevalent, especially in rural areas.
- Economic Setbacks: The COVID-19 pandemic worsened the economic situation, leading to job losses and reduced incomes.
Government Initiatives for Poverty Alleviation:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): Provides subsidized food grains to 67% of India's population, targeting rural areas (75%) and urban areas (50%).
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY): Aims to provide LPG connections to women from Below Poverty Line (BPL) families.
- Ayushman Bharat: Health insurance coverage up to ?5 lakh per family, designed to protect against catastrophic healthcare costs.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan: Focuses on reducing malnutrition, particularly among children, adolescent girls, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- Right to Education Act (RTE): Guarantees free and compulsory education for children between 6 and 14 years.
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Works to ensure universal sanitation coverage, including the construction of toilets and promoting cleanliness.
Schengen Zone Membership

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the European Union (EU) cleared Bulgaria and Romania for full membership in the Schengen Zone, effective January 1, 2025. This marks the end of a 13-year wait for these Eastern European nations, which joined the EU in 2007.
Key Highlights:
- Schengen Integration: Until now, Bulgaria and Romania were partially integrated into the Schengen Zone, with air and sea travel without border checks since March 2024. However, land border controls were still in place due to Austria's objections, mainly due to concerns over migration and border security.
- Austria's Shift: Austria had blocked full entry for years but finally lifted its veto on December 9, 2024, after a border protection package was agreed upon. This package includes joint border guard deployment at the Bulgarian-Turkish border and temporary land border controls for six months.
Schengen Zone Details:
- What is the Schengen Zone?
- Created by the Schengen Agreement (1985) and the Schengen Convention (1990), it is the world’s largest area without internal border controls, allowing free movement across most EU countries and some non-EU countries. It currently includes 29 countries (25 EU states and 4 non-EU countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland).
- Key Features:
- Free Movement: Over 425 million people can travel freely within the zone without border checks.
- Uniform Visa Policy: Short-term stays of up to 90 days are allowed for tourists and business travelers from outside the Schengen Area.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: The Schengen Information System (SIS) facilitates security and border management by sharing critical data between countries.
- Temporary Border Controls: Countries can temporarily reintroduce border controls for security reasons, after notifying other member states and the European Commission.
Bulgaria and Romania
- Bulgaria:
- Capital: Sofia
- Location: Southeastern Europe, bordered by the Black Sea, Romania, Turkey, Greece, North Macedonia, and Serbia.
- Political System: Parliamentary Republic
- Romania:
- Capital: Bucharest
- Location: Bounded by Ukraine, Moldova, Black Sea, Bulgaria, Serbia, and Hungary.
- Political System: Semi-Presidential Republic
Implications of Full Schengen Membership:
- Security and Unity: Romania and Bulgaria's full integration into the Schengen Zone is seen as a boost to both EU security and unity. It solidifies the EU's commitment to free movement while enhancing border security across Europe.
- Impact on Migration: With Bulgaria and Romania’s full membership, the EU’s border management system will be more integrated, helping to address ongoing migration challenges.
World Bank Report on Poverty in India

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
The World Bank has set a clear mission: ending extreme poverty and boosting shared prosperity on a livable planet. This new edition of the biennial series, previously titled Poverty and Shared Prosperity, assesses the three components of the mission and emphasizes that reducing poverty and increasing shared prosperity must be achieved without high costs to the environment.
Extreme Poverty in India:
- Current Poverty Status (2024):
- 129 million Indians are living in extreme poverty, defined as earning less than $2.15 (?181) per day.
- This marks a significant improvement from 431 million in 1990, demonstrating progress in poverty alleviation.
- Poverty Trends:
- In 2021, there was a reduction of 38 million people in extreme poverty, bringing the total to 167.49 million.
- However, higher poverty standards (set at $6.85 (?576) per day) now show more Indians below the poverty line than in 1990, mainly due to population growth.
- Survey Methodology:
- The 2022-23 Household Consumption and Expenditure Survey (HCES) in India used the Modified Mixed Reference Period (MMRP) method to improve data accuracy.
- The report suggests the need for careful analysis of the survey data, which may impact future poverty estimates.
Global Poverty Trends:
- Slowdown in Poverty Reduction:
- Global poverty reduction has slowed considerably, with 700 million people (8.5% of the global population) living in extreme poverty in 2024.
- The slowdown is attributed to factors like low economic growth, the COVID-19 pandemic, and increased fragility.
- Challenges in Achieving Targets:
- The global extreme poverty rate is expected to be 7.3% in 2030, which is double the World Bank's target of 3%.
- At current rates, extreme poverty eradication by 2030 is unlikely. It could take decades to eradicate extreme poverty, and over a century to lift people above the $6.85/day threshold.
- Impact of Polycrisis:
- Polycrisis refers to the confluence of multiple crises—slow growth, climate risks, and increased uncertainty—making global poverty reduction more challenging.
- Global prosperity has also been impacted, with slower income growth, particularly after the pandemic.
India's Role in Global Poverty Reduction:
- Contribution to Global Poverty:
- India’s contribution to global extreme poverty is expected to decline significantly over the next decade. However, even if India eradicates its extreme poverty by 2030, the global extreme poverty rate would only fall from 7.31% to 6.72%, still above the UN SDG target of 3%.
Proposed Pathways for Addressing Poverty:
- Faster and Inclusive Growth:
- Focus on increasing labor productivity, income, and employment to boost economic growth inclusively.
- Climate Resilience:
- Strengthen risk management and mitigation efforts to protect vulnerable populations from climate shocks, ensuring that growth does not worsen environmental degradation.
Global Priorities:
- Low-Income Countries: Prioritize poverty reduction through investments in human, physical, and financial capital to foster growth.
- Middle-Income Countries: Focus on inclusive income growth that reduces vulnerability, and seek synergies such as cutting air pollution alongside poverty reduction.
- High-Income Countries: Accelerate climate mitigation efforts while managing the transition costs involved.
Cyclone Chido
- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Cyclone Chido makes landfall in Mozambique after leaving trail of destruction in French-administered Mayotte.
About Cyclone Chido:
- Location and Impact:
- Cyclone Chido struck Mayotte, a French overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, in December 2024.
- It is the strongest storm to hit Mayotte in at least 90 years.
- Cyclone Characteristics:
- Wind speeds exceeded 200 km/h (124 mph), with gusts surpassing 225 km/h (140 mph).
- The cyclone caused significant devastation to the region, prompting expressions of condolences from global leaders.
- Cyclone Classification:
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), cyclones are classified based on wind speed:
- Depression: 31–49 km/h
- Deep Depression: 50–61 km/h
- Cyclonic Storm: 62–88 km/h
- Severe Cyclonic Storm: 89–117 km/h
- Very Severe Cyclonic Storm: 118–166 km/h
- Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm: 167–221 km/h
- Super Cyclonic Storm: Above 222 km/h
- Cyclone Chido was classified as a Super Cyclonic Storm, based on its wind speeds exceeding 222 km/h.
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), cyclones are classified based on wind speed:
About Mayotte:
- Geography:
- Mayotte is an archipelago in the Mozambique Channel, between Madagascar and the coast of Mozambique.
- It consists of two main islands: Grande Terre (the larger main island) and Petite Terre (the smaller island of Pamandzi).
- Political and Economic Context:
- Mayotte is an overseas department of France, and it is the poorest territory in both France and the European Union.
- France colonized Mayotte in 1843 and annexed the entire Comoros archipelago in 1904.
- A 1974 referendum showed that 95% of Comoros voters favored independence, but 63% of Mayotte's population voted to remain part of France. Subsequently, Grande Comore, Anjouan, and Moheli declared independence in 1975.
- Mayotte remains administratively under French governance.
- Biodiversity:
- Mayotte is renowned for its rich biodiversity, particularly for having one of the world’s largest enclosed lagoons.
Cyclones
- What is a Cyclone?
- A cyclone is a large-scale, rotating system of air that forms around a low-pressure area, bringing violent storms and extreme weather conditions.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, cyclones rotate anticlockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they rotate clockwise due to the Coriolis effect.
- Tropical Cyclone Characteristics:
- Calm Centre (Eye): The cyclone’s center, or "eye," experiences relatively calm weather with low air pressure.
- High Wind Speed: Cyclones generally have average wind speeds around 120 km/h.
- Closed Isobars: Isobars (lines of equal atmospheric pressure) are tightly packed, leading to high wind velocities.
- Formation Over Oceans: Cyclones typically form over warm ocean waters.
- East-to-West Movement: Influenced by trade winds, cyclones usually move from east to west.
- Seasonal Nature: Cyclones occur during specific seasons based on regional climatic conditions.
Kisan Kavach

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Scientists develop ‘kisan kavach’ to shield farmers from pesticide sprays.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The Kisan Kavach is designed to shield farm labourers from harmful pesticide exposure. Pesticides, often neurotoxins, can be detrimental to health, causing symptoms like dizziness, headaches, vomiting, and even death with high exposure.
- Development:
- Developed by Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem), Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Launched by Union Minister of State for Science and Technology.
- Fabric Technology:
- The suit uses oxime fabric, which chemically breaks down common pesticides on contact, preventing them from penetrating the skin.
- Mechanism: The fabric works through nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis, deactivating pesticides upon contact and preventing pesticide-induced toxicity and lethality.
- Components of the Kit:
- Consists of a trouser, pullover, and face-cover.
- Washable and reusable: The suit retains its protective properties even after 150 washes, in a wide temperature range, and under UV light exposure.
- Affordability:
- Priced at ?4,000 per kit, with efforts underway to reduce costs through increased production.
- Field Testing and Efficacy:
- Animal studies: Rodent tests showed that animals exposed to pesticides and covered with ordinary cotton cloth died within four days, while those with the activated fabric remained safe.
- Human trials are still pending.
- Health Implications:
- Pesticides are linked to chronic health issues, including cancer, as per studies by the National Institute of Nutrition (Indian Council of Medical Research).
- Global Context:
- In 2020, India used 61,000 tonnes of pesticides, despite producing much more (2,58,130 tonnes in 2022-2023).
- Pesticide-related health issues are a major concern, with 60% of India’s adult workforce engaged in agriculture.
- Impact:
- The suit aims to protect farm labourers from pesticide exposure and promote sustainable agriculture.
- It could help reduce health complications and improve working conditions for farmers, who often lack proper protective gear.
- Future Plans:
- Awareness campaigns will be conducted to inform farmers about this protective technology.
- Efforts are underway to make the kit more affordable as demand increases.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF), launched by Union Minister Pralhad Joshi aims to support farmers by facilitating post-harvest finance using electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to minimize distress selling and ensure financial security for farmers, particularly small and marginalized ones.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Total Corpus: ?1,000 crore for post-harvest finance.
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?75 lakh.
- Non-agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled and cooperative banks.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- Small and marginal farmers/Women/SC/ST/PwD: 85% for loans up to ?3 lakh, and 80% for loans between ?3 lakh to ?75 lakh.
- Other borrowers: 75% coverage for loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Risks Covered: Both credit risk and warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Fees: 0.4% per annum for farmers, and 1% per annum for non-farmers.
Objectives:
- Minimize distress selling: By providing easy access to loans post-harvest, the scheme helps farmers avoid selling produce at low prices due to cash crunches.
- Instill confidence in banks: The scheme provides a guarantee cover to lenders, encouraging them to offer loans against e-NWRs.
- Encourage warehouse registration: The scheme emphasizes the need for more warehouses, particularly those closer to farmland, to improve accessibility for farmers.
About e-NWRs:
- e-NWRs are digital versions of traditional warehouse receipts that enable farmers to pledge stored commodities as collateral for loans.
- These receipts are governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007, and since 2017, e-NWRs have been mandated for use in transactions related to agricultural produce stored in WDRA-accredited warehouses.
Expected Impact:
- This scheme is expected to boost post-harvest lending, with a target of increasing lending to ?5.5 lakh crore in the next decade.
- It will improve farmers’ income, reduce dependence on informal credit sources, and foster better financial inclusion.
- Additionally, it will create a more reliable supply chain for agricultural produce, enhancing food security.
Future Targets:
- Increase the number of registered warehouses under the WDRA to 40,000 in the next 1–2 years.
- Use platforms like e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi to streamline the lending process and avoid repeated visits to banks.
How La Niña Affects India's Climate?
- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
La Niña, a phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), occurs when the Pacific Ocean region between Indonesia and South America is cooler than usual. This phenomenon influences global weather patterns, including those in India. Here’s how La Niña specifically affects India’s climate:
Monsoon Rainfall:
- La Niña typically results in normal to above-normal rainfall during the monsoon season in India. This is due to the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the central Pacific, which affects atmospheric circulation and strengthens the monsoon winds.
- In contrast, El Niño usually brings below-average rainfall and droughts to India, leading to agricultural stress.
- Recent La Niña years (2020-2022) saw above-normal monsoon rains, which benefited agricultural productivity, while the El Niño year of 2023 resulted in below-normal rains, impacting water availability and agriculture.
Winter Temperatures:
- During La Niña, winter temperatures in India are generally colder in the north, with cooler nights but relatively warmer days compared to El Niño winters. The planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) tends to be lower, trapping pollutants close to the surface. However, higher wind speeds during La Niña help to disperse air pollution, improving air quality.
- South India may experience colder-than-usual winters during La Niña, but current meteorological data suggests the ongoing winter in India is not strongly influenced by La Niña, as its expected onset has been delayed.
Impact on Summer Heat:
- La Niña generally provides relief from extreme summer heat, as it reduces the frequency and intensity of heatwaves. In contrast, El Niño summers are typically hotter and bring record-breaking heat waves.
- For example, April 2023 saw intense heatwaves across India, attributed to the El Niño phase, but if a La Niña forms and persists into the summer of 2025, it could help moderate the extreme heat.
The "Triple Dip" La Niña Phenomenon:
- A Triple Dip La Niña refers to a rare occurrence where three consecutive La Niña events happen, as was the case from 2020 to 2022. This is significant because these prolonged events can lead to stronger climatic impacts. In contrast, the current El Niño (2023) follows this period, potentially contributing to an irregular transition between La Niña and El Niño phases, which may intensify extreme weather patterns.
Global Climate Changes and La Niña:
- Climate change is believed to be increasing the frequency and intensity of both La Niña and El Niño events. Rising sea and land temperatures are disrupting the balance of the Pacific Ocean and could exacerbate extreme La Niña events, which might lead to harsher winters in India and other regions.
Forecast for 2024-2025:
- As of December 2024, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and global meteorological bodies predict a weak La Niña event to emerge by late 2024 or early 2025. This could lead to colder winters and above-normal rainfall in the 2025 monsoon season, offering some relief from the heatwaves and dry conditions of the previous years.
Conclusion:
If a La Niña forms by the end of 2024, it is likely to bring cooler winters, a relief from extreme summer heat, and above-normal monsoon rainfall in 2025. Given the delayed onset and weakening of the current La Niña, the overall impact on India’s climate in the immediate future might be milder compared to previous La Niña years, but it still holds potential for more favorable conditions for agriculture and air quality.
Vijay Diwas 2024

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 16, 2024, India commemorated Vijay Diwas, marking the 53rd anniversary of its victory in the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War. This day honors the bravery and sacrifices of Indian soldiers and the Mukti Bahini, whose collective efforts led to the creation of Bangladesh as an independent nation. On this occasion, leaders across India, paid heartfelt tributes to the fallen heroes who contributed to the victory, and to the enduring India-Bangladesh friendship.
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War culminated in the surrender of over 90,000 Pakistani soldiers, and India’s victory is celebrated as a defining moment in South Asian history.
The War’s Historical Context:
The 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War was a pivotal conflict between East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) and West Pakistan (now Pakistan), leading to Bangladesh’s independence. It was a direct result of decades of social, political, and economic discrimination faced by East Pakistan, despite its larger population and contribution to Pakistan’s economy. Major events leading to the war included:
- Cultural and linguistic marginalization, with East Pakistan's Bengali language and identity being suppressed by the West.
- The 1970 elections that saw the Awami League, led by Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, win a decisive victory in East Pakistan, but their demand for greater autonomy was rejected by West Pakistan.
- The violent crackdown by the Pakistani military in Operation Searchlight in March 1971, leading to widespread atrocities and a mass exodus of refugees into India.
India’s Role in the War:
India’s involvement in the conflict was initially cautious, but the refugee crisis—with over 10 million people fleeing to India—forced India to take action. India provided humanitarian aid and supported the Mukti Bahini, a guerrilla force of Bangladeshi fighters. On December 3, 1971, Pakistan’s preemptive airstrike on Indian military bases led to India's retaliation and full-scale military involvement, including air and naval operations.
India’s military, with assistance from the Mukti Bahini, launched a decisive campaign, ultimately leading to Pakistan’s surrender on December 16, 1971, and the creation of Bangladesh.
Vijay Diwas Observances:
- The 53rd Vijay Diwas celebrations at Fort William, Kolkata, saw a Bangladeshi delegation—including Mukti Joddhas (freedom fighters)—reflect on their memories of the war, highlighting India's crucial role in the liberation of Bangladesh.
- The event also featured a wreath-laying ceremony, military tattoo, and a salute to the shared sacrifice and friendship between India and Bangladesh.
The 1971 Surrender Painting and New Symbolism:
In an interesting development, the iconic 1971 surrender painting, depicting the surrender of Pakistani forces in Dhaka, was moved from the Army Chief’s lounge to the Manekshaw Centre. The painting was replaced by Karam Kshetra–Field of Deeds, a new artwork symbolizing India’s strategic and cultural heritage. This new piece incorporates elements like Lord Krishna’s chariot, Chanakya, and modern military assets, reflecting India’s military prowess and heritage.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan agreement to enhance horticulture crop productivity by improving plant health management. This initiative is part of India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to provide farmers with access to certified disease-free planting materials to improve yields, quality, and resilience, particularly against climate change impacts.
Key Highlights of the Loan Agreement
- Objective: Improve access to certified, disease-free planting materials for horticulture crops.
- Implementation: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Focus: The initiative will enhance farmers’ productivity, resilience to climate change, and pest/disease management through the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP).
About the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
The Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme aims to tackle critical challenges in horticulture by ensuring farmers have access to high-quality, virus-free planting materials. The program is designed to:
- Enhance crop yields and quality.
- Promote climate-resilient varieties to help farmers adapt to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Safeguard the environment by controlling plant diseases and pests proactively.
Key Components of the CPP
- Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): Establishment of nine world-class CPCs across India, equipped with advanced diagnostic labs and tissue culture facilities to maintain disease-free foundation planting materials.
- Certification Framework: A robust certification system will be introduced to ensure accountability in planting material production, including accreditation for private nurseries.
- Climate Resilience: Focus on developing and disseminating climate-resilient plant varieties, addressing the growing concerns over extreme weather events and changing pest behavior due to climate change.
Significance of the Loan Agreement
- Climate Adaptation: The project will help farmers mitigate the effects of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns and altered pest/disease behaviors.
- Economic Impact: The initiative aligns with India's vision of self-reliance in horticulture (Atmanirbhar Bharat), boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Long-term Benefits: Improved farm productivity, sustainability, and economic well-being for farmers, especially in the face of climate change.
Global Horticulture Significance
- India’s Position: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, contributing 33% to the agricultural GDP.
- Land Coverage: Horticulture occupies 18% of India’s agricultural land, yet its production surpasses that of food grains.
Implementation and Impact
- Implementation Period: The project will be executed from 2024 to 2030, with 50% financial assistance from ADB.
- Institutional Strengthening: The initiative will bolster India’s ability to manage plant health, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques and capacity-building for horticulture professionals.
Exercise Agni Warrior

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The 13th edition of Exercise Agni Warrior (XAW-2024), a joint military drill between the Indian Army and the Singapore Armed Forces (SAF), concluded successfully at the Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra. The exercise focused on enhancing mutual understanding and interoperability between the two nations’ artillery units.
Key Facts:
- Participating Nations: India and Singapore
- Location: Field Firing Ranges, Devlali, Maharashtra
- Participants:
- 182 personnel from the Singapore Artillery
- 114 personnel from the Indian Army's Regiment of Artillery
- Objective: To maximize mutual understanding of drills and procedures for joint operations under the UN Charter, particularly in firepower planning and execution, utilizing advanced artillery technologies.
- Historical Context: The exercise began in 2004 under a bilateral agreement between India and Singapore and has evolved over the years, now marking 20 years of cooperation.
Purpose and Highlights:
The exercise aimed to reinforce the long-standing defense relationship between India and Singapore, focusing on:
- Joint Firepower Planning and Execution: Both forces demonstrated the use of New Generation Artillery Equipment, enhancing their firepower coordination.
- Enhancing Interoperability: The exercise emphasized seamless coordination between the two armies to operate as a multinational force under the UN Charter, addressing global security challenges.
- Knowledge Sharing: Personnel from both armies exchanged expertise on advanced artillery tactics, fostering a deeper understanding of each other's military capabilities.
- Technological Integration: Both sides integrated cutting-edge technologies, allowing the exchange of best practices in the use of artillery systems.
Key Objectives of XAW-2024:
- Enhanced Interoperability: To ensure smooth coordination in joint operations, fostering the ability to respond to regional security threats.
- Firepower and Coordination Techniques: Sharing expertise on artillery planning, coordination, and execution.
- Advanced Equipment Use: Testing and demonstrating modern artillery systems in joint operations, ensuring both forces are prepared for contemporary warfare.
Structure and Execution:
The exercise was structured to include pre-exercise training, field operations, and a post-exercise evaluation:
- Pre-Exercise: Both armies engaged in interactive sessions to familiarize themselves with each other's artillery tactics and advanced systems.
- Field Operations: Simulated combat scenarios tested joint firepower execution, emphasizing real-time problem-solving and decision-making under pressure.
- Post-Exercise Review: A thorough analysis identified areas for improving joint operations and coordination.
Strategic Significance:
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Agni Warrior reinforces the defense partnership, facilitating joint operations that support regional security.
- Regional Stability: The exercise underscores the commitment of both nations to peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Capacity Building: Both Indian and Singaporean forces gained exposure to sophisticated firepower planning and gained operational readiness for future deployments.
Little Bunting

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Little Bunting recently spotted in Mount Abu, Rajasthan, a sighting previously unseen in the region.
About the Little Bunting:
- Scientific Name: Emberiza pusilla
- Family: Bunting family (Emberizidae)
- IUCN Red List Status: Least Concern
Distribution:
- Breeding Range: Far northeast Europe and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East (taiga region).
- Migratory Pattern: Migrates to the subtropics during winter, with sightings in northern India, southern China, and northern Southeast Asia.
Physical Features:
- Size: Small bird, measuring 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inches).
- Coloration:
- White underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides.
- Chestnut face with a white malar stripe, black crown stripes, and a white eye-ring.
- Fine dark border behind chestnut cheeks.
- Similarity: Resembles a small female reed bunting but with distinct black crown stripes.
Call and Song:
- Call: Distinctive "zik".
- Song: A rolling "siroo-sir-sir-siroo".
Habitat and Behavior:
- Typically found in agricultural areas, feeding on grains.
- Migration: Avoids extreme cold conditions, possibly due to climate change influencing its movement into Rajasthan.
Recent Sightings in India: Spotted in Gurugram, Chandigarh, northern Punjab, and now Rajasthan.
Conservation Significance: The sighting underscores the need to preserve forest areas and wetlands for migratory species like the Little Bunting.
Search and Rescue Aid Tool (SARAT)

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS), under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, has developed SARAT Version 2 to aid Indian Search and Rescue (SAR) agencies like the Indian Coast Guard.
Key Highlights:
Purpose: SARAT is designed to assist in locating missing objects or individuals at sea by simulating the probable search area, considering factors like wind, currents, and waves.
Improvements in Version 2:
- The search area now starts from the last known position of the object, improving the accuracy of the search.
- Enhanced visualizations for better judgment of probable search areas, including colour coding of regions and markers to identify the last known position.
- Optimized search: Reduces the vast search area to a few high-probability regions, allowing for better utilization of limited search resources.
Technical Aspects:
- The tool uses model currents from the Regional Ocean Modelling System run on high-performance computers at INCOIS.
- It accounts for uncertainties in the initial location and the last known time of the missing object using model ensembling.
- Users can select from 60 types of missing objects based on shape and buoyancy.
Interactive Map & Multi-language Support:
- Results are shown on an interactive map, providing the probable search area.
- The tool also sends results as text messages to emails and mobile phones in languages of coastal states, enabling local fishermen to use it effectively during distress situations.
Launched in 2016, Updated in 2024: SARAT was launched in 2016 and the updated version (SARAT Version 2) has been designed with feedback from the Indian Coast Guard and other stakeholders involved in marine search operations.
Access: The updated SARAT Version 2 can be accessed at: https://sarat.incois.gov.in/sarat/home.jsp.
African Swine Fever

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
African Swine Fever has been reported at two pig farms in Koottickal and Vazhoor grama panchayats in Kottayam district.
Action Taken:
- Culling of Pigs: All pigs in the affected farms and within a 1 km radius will be culled and disposed of according to Central Government guidelines.
- Infected Zone: A 1 km radius around the affected farms has been declared an infected zone.
- Surveillance Zone: A 10 km radius around the infected area has been designated a surveillance zone.
About African Swine Fever (ASF)
- African swine fever (ASF) is a highly contagious and hemorrhagic viral disease of domestic and wild pigs. It is a notifiable disease and its outbreak should be immediately reported to the higher authorities.
- ASF causes destructive effect on piggery due to high morbidity and mortality (up to 90-100 %). In India it was first confirmed in Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in February-March 2020.
- Currently, there is no effective vaccine available against ASF, so prevention by adopting strict biosecurity measures is the only way to prevent ASF.
CLINICAL SIGNS
- High fever (106-1080 F), lethargy and loss of appetite
- Increased respiration rate
- Blue-purple discoloration of skin of ears, abdomen and rear legs
- Discharge from the eyes and nose; bloody froth from the nose/mouth
- Constipation or bloody diarrhea
- Abortion
- Death of pigs in 6-15 days
Diagnosis: Confirmatory diagnosis in gov. laboratories
Zakir Hussain

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Ustad Zakir Hussain, the legendary tabla virtuoso, passed away at the age of 73 due to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF).
Key Highlights:
- Career Highlights:
- Born on March 9, 1951, to Ustad Alla Rakha, a renowned tabla maestro.
- Began tabla training at age 7, with early guidance from his father.
- Co-founded Shakti in 1973 with John McLaughlin, blending Indian classical music with Western influences, pioneering world music.
- Worked with global artists, including George Harrison, John McLaughlin, and Mickey Hart.
- Awarded four Grammy Awards, including three at the 66th Grammy Awards (2024), and honored with the Padma Vibhushan in 2023.
- A visiting professor at Stanford and Princeton universities.
- Musical Style:
- Transformed the tabla from a background instrument into a dynamic, expressive solo performance.
- Known for his complex rhythms and spontaneous performances, making tabla accessible and glamorous.
- Emphasized the concept of "hazri" (attendance) in the court of music, seeing his music as an offering to a higher power.
- Cultural Influence:
- His music was a bridge between traditional Indian classical and contemporary global sounds, impacting audiences worldwide.
- Played a pivotal role in the cultural exchange of Indian classical music, gaining fans and respect across the globe.
- Participated in projects such as the Taj Mahal tea commercials and "Desh Raag", symbolizing unity and diversity in India.
What is Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)?
- IPF is a chronic lung disease causing scarring of the lung tissue, leading to difficulty in breathing.
- Cause: The exact cause is unknown, hence termed "idiopathic" (unexplained).
- Risk Factors: Most common in older adults (over 50), men, and those with a history of smoking or viral infections.
About the Tabla:
- Structure: Composed of two drums—Tabla (right) and Bayan (left)—used primarily in Hindustani classical music.
- Material: Tabla has a wooden body, while Bayan can be made of clay or metal, both covered with animal skin and syahi paste.
- Role: Primarily accompanies vocal and instrumental performances, and is essential in various classical dance forms in northern India.
- Historical Note: Believed to have been invented by Amir Khusrau.
Prominent Tabla Players:
- Ustad Alla Rakha (father of Zakir Hussain).
- Zakir Hussain (himself).
- Shafat Ahmed and Samta Prasad.
India Maritime Heritage Conclave 2024

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The 1st India Maritime Heritage Conclave (IMHC 2024), a landmark event organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) was recently held.
Key Highlights:
Event Overview:
- Organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), held on December 11-12, 2024.
- Theme: "Towards Understanding India's Position in Global Maritime History."
- Celebrated India’s maritime legacy and future vision as a maritime powerhouse.
India’s Maritime Heritage:
- Deeply rooted in ancient traditions; references in Rig Veda, mythology, literature, and archaeology.
- Modern India boasts a 7,500 km coastline, 13 major ports, 200 non-major ports, handling 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Ports handle 1,200 million tonnes of cargo annually, vital for economic growth.
Key Features of IMHC 2024:
- International Participation: Dignitaries from 11 countries, including Greece, Italy, UK.
- Exhibition: Showcased ancient shipbuilding techniques, navigation systems, historical trade routes.
- Cultural Program: Celebrated coastal traditions with performances and festivities.
- Key Focus: Sustainable maritime innovation, skill development, youth engagement, and cultural preservation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC):
- Location: Lothal, Gujarat – an ancient Harappan site (2600 BCE).
- Significance: Home to the world’s oldest dry-dock (2400 BCE).
- Future Vision: NMHC to showcase maritime history with 14 galleries, open aquatic gallery, lighthouses, and a research institute.
Modern Maritime Significance:
- India’s Global Maritime Ranking: 16th largest globally, 3rd largest in ship recycling.
- Trade Backbone: 95% of India's trade by volume, 70% by value handled by maritime sector.
- Port Performance: India ranks 22nd in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (2023).
Future Maritime Vision:
- Sustainable Blue Economy: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices, green shipping, and maritime tourism.
- Skill Development: Training programs to empower local communities and boost maritime workforce.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading ports and shipping infrastructure under the Sagar Mala Program.
- Policy Framework: Integrated policies for maritime heritage preservation and economic development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Maritime India Vision 2030: Focus on increasing maritime capacity and sustainability.
- SAGAR: Security and Growth for All in the Region initiative.
- Ship Repair & Recycling Mission: Promote India as a global leader in ship recycling.
- Green Hydrogen Hubs: Development of eco-friendly maritime infrastructure.
Santa Ana Winds

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The ongoing Franklin Fire in Malibu, California, has burned over 4,000 acres and affected around 22,000 people. Although the exact cause of the fire is still under investigation, experts point to two key factors contributing to the intensity of the blaze: Santa Ana winds and climate change.
Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds are powerful, dry winds that typically occur in Southern California from October to January.
- They are caused when high-pressure systems over the Great Basin (the area between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada) push air toward low-pressure areas over California’s coast.
- As the air moves downhill through mountain passes, it compresses and heats up, which significantly lowers the humidity—sometimes to levels below 10%—creating dry conditions. This extremely low moisture content dehydrates vegetation, making it highly susceptible to combustion.
- These winds have been a natural feature of California's weather, contributing to wildfires for years. However, when combined with other factors like climate change, their impact has become more severe.
The Role of Climate Change
While Santa Ana winds have long played a role in California's wildfires, climate change has exacerbated the situation in recent years. The state's wildfire season has lengthened due to rising global temperatures, which have led to:
- Warmer springs and summers.
- Earlier snowmelt in spring, which leaves vegetation drier for longer periods.
- Longer and more intense dry seasons, which cause increased moisture stress on vegetation.
As a result, forests and brushlands are now more vulnerable to fires. Climate change has also contributed to more extreme weather events, including heatwaves, which further dry out vegetation and create favorable conditions for wildfires.
Intensification of Wildfire Seasons
Recent studies have shown that California's wildfire season has grown longer over the past two decades. For example, a 2021 study in Nature Scientific Reports found that the state's annual burn season has shifted, with the peak fire season now occurring earlier in the year, from August to July. Additionally, research published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) in 2023 indicated that the largest wildfires in California history have occurred in the past 20 years, with five of the top 10 largest fires taking place in 2020 alone.
Looking Ahead
The situation is expected to worsen as climate change continues. If global temperatures rise by more than 3°C by the end of the century, as predicted by the United Nations, California’s wildfire risk will likely intensify. The combination of Santa Ana winds and increasingly dry conditions will continue to make areas like Malibu, and much of California, more prone to destructive wildfires.
In conclusion, while Santa Ana winds remain a natural contributor to California's wildfires, the influence of climate change has significantly lengthened the wildfire season, making wildfires more frequent, intense, and harder to control. The continued rise in global temperatures only accelerates these trends, posing a growing challenge for fire management and public safety in California.
'Jalvahak' Scheme for Inland Waterways Promotion

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
Govt Unveils ‘Jalvahak’ To Boost Inland Waterways, Cargo Movement Incentivised on NW1, NW2 & NW16
Key Highlights:
- Launch of 'Jalvahak' Scheme:
- Launched by: Union Minister for Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, on December 15, 2024.
- Objective: The scheme aims to promote the use of inland waterways for long-haul cargo transportation, reduce logistics costs, and alleviate congestion in road and rail networks.
- Targeted Waterways:
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- NW 1: River Ganga
- NW 2: River Brahmaputra
- NW 16: River Barak
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- Incentives:
- The scheme offers up to 35% reimbursement on operating expenses for cargo transported over 300 km via these waterways, particularly using the Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route (IBPR).
- Encouraging Private Operators: The scheme also incentivizes the hiring of vessels owned by private operators to promote competition and efficiency.
- Scheduled Cargo Service:
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Kolkata - Patna - Varanasi - Patna - Kolkata (for NW 1)
- Kolkata - Pandu (Guwahati) (for NW 2 via IBPR)
- Transit Times: Predefined and fixed for efficiency:
- Kolkata to Patna: 7 days
- Patna to Varanasi: 5 days
- Kolkata to Varanasi: 14 days
- Kolkata to Pandu: 18 days
- Pandu to Kolkata: 15 days
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Economic and Environmental Impact:
- Cargo Shift Target: The initiative aims to shift 800 million tonne-kilometres of cargo by 2027.
- Growth Projections:
- 200 million tonnes of cargo by 2030.
- 500 million tonnes by 2047, supporting the Blue Economy and Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- The move to waterways aims to reduce the pressure on India's roads and rail systems, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective logistics system.
- Strategic Goals:
- Modal Shift: The scheme seeks to achieve a shift of 800 million tonne-kilometres by 2027 with an investment of ?95.4 crores.
- Sustainability: Inland waterways are considered an environmentally friendly, efficient, and low-cost transportation mode, with a focus on sustainability.
- Logistics Optimization: This initiative is expected to help optimize supply chains for major shipping companies, freight forwarders, and trade bodies involved in bulk and containerized cargo.
- Implementation Agencies:
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI): The main body responsible for the development and regulation of inland waterways.
- Inland & Coastal Shipping Limited (ICSL): A subsidiary of the Shipping Corporation of India, responsible for the operation of vessels.
- Broader Impact:
- Economic Growth: The scheme is expected to foster economic growth by improving logistics efficiency.
- Decongestion: The initiative aims to decongest the road and rail transport systems, facilitating smoother movement of cargo.
- Regional Connectivity: Enhances connectivity, particularly in eastern India, benefiting areas along the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Barak rivers.
- About the National Waterways:
- India has 14,500 km of navigable inland waterways, which include rivers, canals, and backwaters. These waterways are significantly under-utilized compared to other countries.
- The National Waterways Act, 2016 declared 111 waterways (including both existing and newly identified ones) for navigation.
- The Jalvahak scheme is part of India's broader strategy to unlock the potential of its inland waterways, offering an efficient, economical, and environmentally sustainable alternative for cargo transport.
Rajmarg Saathi - Upgraded Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPV) by NHAI
- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
With an aim to enhance road safety and strengthen highway patrolling, NHAI plans to implement the upgraded and forward-looking Incident Management Services. The guidelines on the subject include updated specifications for new Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs) named ‘Rajmarg Saathi’ and outlines design, functions, technology, components and manpower specifications for the RPVs.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Rajmarg Saathi:
- Initiative by: National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- Objective: Enhance highway safety, emergency response, and road maintenance efficiency across India.
- Launched in: December 2024.
What is Rajmarg Saathi?
- Definition: An upgraded version of Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs), designed for effective highway patrolling and incident management.
- Main Aim: Improve highway safety and ensure smooth traffic flow through advanced technology and quick emergency responses.
Key Features:
- Advanced Design:
- Closed Cabinets: For organized storage and easy access to emergency tools and inventory, replacing earlier models with open storage space.
- AI-Powered Technology:
- Dashboard Cameras: Equipped with AI-enabled cameras to capture and analyze road conditions like cracks, potholes, and other distresses.
- Road Monitoring: The system also monitors vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, and other infrastructure elements.
- Integration with NHAI One: Data collected by AI systems is integrated into NHAI’s centralized application for efficient road maintenance.
- Emergency Preparedness: The RPVs are fully equipped with modern communication and safety tools, designed to minimize traffic disruptions during emergencies.
Data Collection and Maintenance:
- Weekly Analytics: The system will collect and analyze road condition data weekly to streamline maintenance activities and monitor highway safety.
Vehicle Usage and Replacement:
- Replacement Guidelines: RPVs will be replaced after 3 years of operation or 3,00,000 km to ensure they remain functional and service-ready.
Visibility and Branding:
- External Branding: RPVs are designed to be highly visible with enhanced branding for easy recognition as highway patrol vehicles.
- Uniform for Personnel: The patrolling personnel will wear updated uniforms, including bright blue colors and reflective jackets with authority logos for better identification.
Role in Incident Management:
- RPVs will play a crucial role in managing traffic incidents, ensuring smooth traffic flow, and enhancing road safety by addressing emergencies quickly.
Commitment to Road Safety:
- NHAI remains committed to improving road safety standards and ensuring a smooth, hassle-free travel experience for all users across the national highway network.
About NHAI:
- Establishment: NHAI was established under the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988, and became operational in 1995.
- Responsibilities: It is responsible for developing, maintaining, and managing national highways in India.
- Objectives:
- Promote transparency in awarding contracts.
- Maintain high standards of project implementation.
- Ensure comfort and convenience for users of the national highway system.
India's Road Network:
- Size: India has the 2nd-largest road network in the world, spanning approximately 63.32 lakh km, which includes national highways, expressways, state highways, and rural roads.
India-Australia CCEA

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The 3-day stocktake meeting took place in New Delhi, marking a significant step in strengthening the India-Australia trade and strategic partnership.
Key Highlights:
- Key Discussion Areas:
- Trade in goods and services.
- Mobility, agri-tech cooperation, and market access.
- Focus on ensuring the CECA delivers balanced benefits for both nations.
- Food security concerns and market access modalities aligned with India’s goals.
- Background on Negotiations:
- The discussions in New Delhi were a continuation of the 10th round of negotiations held in Sydney (August 2024).
- Both sides aimed to outline a path forward for the early conclusion of the CECA.
- Importance of CECA:
- CECA is a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) aimed at eliminating tariffs and liberalizing services sectors to enhance business opportunities and cooperation.
- It addresses five key areas: Goods, Services, Digital trade, Government procurement & **Rules of Origin/Product Specific Rules
- New areas under discussion include: Competition policy, MSMEs, Gender, Innovation, Agri-tech, Critical minerals & Sports
- Historical Context:
- CECA negotiations began in May 2011, were suspended in 2016, and resumed in September 2021.
- The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) was signed in 2022, serving as a foundational agreement and a precursor to CECA.
- Trade Statistics (2023-24):
- India's imports from Australia: $16.2 billion.
- India's exports to Australia: $8 billion.
- Trade has grown significantly, with India being Australia’s 5th-largest trading partner.
- Regional Cooperation Initiatives:
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)
- Trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) with Japan.
- India and Australia are partners in several regional initiatives:
- India's CECA with Other Countries:
- India has similar CECA agreements with several nations, including: Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand & New Zealand
- Future Prospects:
- The stocktake discussions have paved the way for further cooperation in areas such as agricultural innovation, market access, and supply chain resilience.
- Both nations are optimistic about the early conclusion of the CECA and the broader economic partnership.
This recent stocktake visit represents a significant step in the ongoing efforts to solidify trade ties and deepen economic cooperation between India and Australia under the framework of the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement.
100-Day Intensified Nationwide TB Campaign

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
- Union Health Minister Shri JP Nadda launched a 100-day intensified TB campaign in Panchkula, Haryana, aimed at reducing TB incidence and mortality. The campaign will focus on 347 high-risk districts across India.
Key Highlights:
- Campaign Goals:
- Find and treat missing TB cases, especially in high-risk groups.
- Significantly reduce TB-related deaths.
- Focus Areas:
- The campaign is part of India’s larger goal to eliminate TB before the 2030 SDG deadline.
- Strategies include early detection and rapid treatment of TB patients.
- Historical Context:
- TB was once seen as a "slow death" and patients were isolated.
- In 2018, the Prime Minister set the vision to end TB before 2030.
- Recent Government Initiatives:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs network of 1.7 lakh centers helps in early TB detection.
- Increased diagnostic infrastructure: Laboratories increased from 120 in 2014 to 8,293 today.
- Introduction of new drug regimens: Shorter and more effective treatments have increased the treatment success rate to 87%.
- Ni-kshay Support: Rs 3,338 crore transferred to 1.17 crore TB patients via direct benefit transfer.
- Key Achievements:
- TB decline rate in India has increased from 8.3% (2015) to 17.7% today, surpassing the global average.
- TB-related deaths have dropped by 21.4% over the past decade.
- Private Sector Involvement:
- Mandatory notification of TB patients by private practitioners has led to an 8-fold increase in TB case notifications.
- 4Ts Approach for TB Elimination: Test, Track, Treat, and Technology (use of advanced tools for diagnosis and treatment).
- New Initiatives:
- Ni-kshay Vahaan: Mobile vans to detect and treat TB patients in remote areas.
- Launch of national guidelines for a new drug-resistant TB regimen (BPaLM), which is a 4-drug combination therapy for multi-drug-resistant TB.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana:
- Increase in nutritional support: Monthly support raised from Rs 500 to Rs 1000 per TB patient.
- The initiative also includes energy boosters for enhanced patient care.
- Mobile Diagnostics:
- Deployment of AI-enabled portable X-ray units and molecular tests to bring diagnostics closer to people, especially in remote areas.
- Monitoring and Data: Intensified data tracking via the Ni-kshay portal to provide timely updates to TB patients.
- Background of the Campaign:
- Part of the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP).
- The 347 districts were selected based on indicators like death rates, presumptive TB examination rates, and incidence rates.
- Campaign Materials:
- Unveiling of Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) resources in regional languages.
- Honoring TB Champions and Ni-kshay Mitras during the event.
- Government’s Strategic Framework:
- India’s National Strategic Plan (NSP) for TB elimination (2017-2025).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign and Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- Tuberculosis (TB) Overview:
- TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and primarily affects the lungs, spreading through the air.
- Mortality rate has decreased from 28 per lakh (2015) to 23 per lakh (2022).
Desert Knight Air Combat Exercise

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
India, France and UAE recently kicked off a major air combat exercise called “Desert Knight” over the Arabian Sea, strengthening trilateral defence cooperation and enhancing military interoperability amid the ongoing geopolitical churn.
Key Highlights:
- What It Is: A trilateral air combat exercise aimed at improving military interoperability and enhancing combat readiness among the participating nations.
- Nations Involved: India, France, and the UAE.
- Location: Conducted over the Arabian Sea, approximately 350-400 km southwest of Karachi.
- Aim of the Exercise:
- To strengthen trilateral defence cooperation among the three nations.
- To enhance combat skills and military interoperability of the air forces involved.
- Details of the Exercise:
- Duration: The exercise lasts for three days.
- The exercise involves large force engagement and intensive combat maneuvers in a realistic operational environment.
- Aircraft Involved:
- India: Deployed Sukhoi-30MKIs, Jaguars, IL-78 mid-air refuellers, and AEW&C (Airborne Early Warning and Control) aircraft from bases like Jamnagar.
- France: Deployed Rafale jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
- UAE: Deployed F-16 jets and other aircraft from Al Dhafra airbase.
Strategic Significance:
- The exercise is part of India’s efforts to build military interoperability with nations in the Persian Gulf region and strengthen defence ties with France and the UAE.
- Enhances combat readiness and strengthens cooperation against both traditional and non-traditional threats.
- Reflects the geopolitical shift and growing military cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, especially in the context of China’s expansionist activities.
- Trilateral Framework: India, France, and the UAE launched a trilateral framework in 2022, focusing on areas like defence, technology, energy, and environment.
- Previous Exercises: In addition to Desert Knight, the countries also conducted their first trilateral maritime exercise in June 2023 to enhance cooperation in maritime security.
Broader Defence Relations:
- India-France: Long-standing strategic partnership with regular joint exercises like Shakti (army), Varuna (navy), and Garuda (air force).
- India-UAE: The defence relationship has grown significantly in recent years, with regular professional exchanges, combat exercises, and staff talks. India participates in the Desert Flag exercise at Al Dhafra airbase annually.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
Switzerland Suspends MFN Clause in Tax Treaty with India

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
Switzerland scraps MFN status to India, dividend income to face higher tax
Key Highlights:
- Reason for Suspension:
- The suspension follows a 2023 Supreme Court ruling in India, which clarified that the MFN clause in tax treaties is not automatically triggered when a country joins the OECD if the tax treaty with that country was signed before its OECD membership.
- The Court ruled that the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) cannot be enforced unless it is notified under the Income-Tax Act, 1961.
- Details of the Suspension:
- Starting January 1, 2025, Switzerland will suspend the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) clause in its DTAA with India.
- The MFN clause was part of the India-Switzerland DTAA signed in 1994.
Impact of the Suspension:
- Higher Tax Liabilities for Indian Companies: Withholding tax on dividends from Switzerland will increase from 5% to 10% for Indian companies.
- Effects on Swiss Investments in India: Swiss companies will continue to face a 10% withholding tax on dividends from India, as per the India-Switzerland DTAA.
- Potential Re-evaluation of MFN Clauses by Other Countries: Other countries may reconsider how the MFN clause is applied in their tax treaties with India, following this development.
- No Change for Other Benefits: Other DTAA benefits and investments related to the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) will remain unaffected.
Most Favoured Nation (MFN) Clause Overview:
- Definition: The MFN principle ensures that favorable trading terms given by one WTO member country to another are extended to all other WTO members, promoting non-discrimination.
- Purpose: To ensure equal treatment among trading nations by preventing discrimination, and to promote fair trade and equitable market access.
- Key Features:
- Equal treatment in tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers.
- Members must extend the best terms to all other WTO members.
- Origin: The MFN principle was established after World War II as a cornerstone of the multilateral trading system under the WTO.
- Exceptions:
- Bilateral or regional trade agreements.
- Special access granted to developing countries.
- Non-WTO members (e.g., Iran, North Korea) are not bound by MFN rules.
- Removal of MFN:
- There is no formal procedure under the WTO to suspend MFN status.
- Countries are not obligated to notify the WTO when suspending or removing MFN treatment.
Recent Development:
- From January 1, 2025, Indian companies will face higher withholding tax (10%) on income sourced from Switzerland, as a result of the MFN clause suspension.
Empowering ASHA Workers

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
ASHAs (Accredited Social Health Activists) are critical to India's healthcare system, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Since the program's launch in 2005, ASHAs have been integral in improving maternal health, increasing immunization rates, and promoting family planning and sanitation awareness. The network of ASHAs has grown to nearly 1 million members, making it one of the largest community health worker programs in the world.
Role of ASHAs: ASHAs work as community health activists, beyond basic healthcare delivery, by:
- Promoting health awareness.
- Mobilizing local participation in health programs.
- Increasing the utilization of existing health services.
They play a central role in improving maternal and child health, and their efforts have led to increased institutional deliveries and improved immunization rates in rural India.
Challenges Faced by ASHAs: Despite their essential role, ASHAs face several challenges:
- Inadequate compensation and delayed payments, which undermine motivation.
- Heavy workloads with insufficient support and resources.
- Social and economic marginalization, often leading to a lack of recognition and respect.
- Punitive systems that emphasize compliance and record-keeping, hindering autonomy.
This environment limits ASHAs' capacity to act as independent change agents, reducing their effectiveness in driving long-term health improvements.
Psychological Empowerment of ASHAs: To address these challenges, it's essential to empower ASHAs not just financially, but psychologically. Research in motivation theory, particularly Self-Determination Theory (SDT), provides a framework to achieve this. SDT emphasizes the importance of three key psychological needs:
- Autonomy: The need for ownership over one's work.
- Competence: The need to feel capable and effective in performing tasks.
- Relatedness: The need for social connection and recognition.
By fostering these three needs, ASHAs can become more intrinsically motivated and empowered to take ownership of their roles.
Strategies for Empowerment:
- Autonomy: Giving ASHAs more control over their work and decision-making can improve their engagement and efficacy. This can be achieved by reducing rigid monitoring and compliance systems.
- Competence: Providing continuous, quality training and resources will help ASHAs build the skills and confidence needed to perform their roles effectively. Digital tools and modern training programs can be used to enhance their capabilities.
- Relatedness: ASHAs should receive direct feedback from the communities they serve, fostering a sense of connection and accomplishment. Encouraging networks among ASHAs will also help combat isolation and provide peer support.
Government Efforts and Initiatives: The Indian government has recognized the need to support ASHAs through several initiatives:
- Increased remuneration and performance-based incentives.
- Insurance coverage under schemes like Ayushman Bharat.
- Training programs for skill development under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- Village Health Mapping and digital engagement platforms to enhance outreach and feedback mechanisms.
Moving Forward:
To further empower ASHAs, several key steps should be taken:
- Formalizing employment status: Transitioning ASHAs from volunteers to formal workers with benefits can ensure more stability and recognition.
- Improving compensation: Ensuring timely and adequate payments along with performance bonuses will incentivize ASHAs and increase job satisfaction.
- Enhancing infrastructure: Ensuring ASHAs have access to the necessary tools, medical supplies, and transportation to perform their tasks effectively.
- Digital integration: Expanding digital tools for data collection and communication can streamline their work and improve coordination with healthcare systems.
Under the Sal Tree Theatre Festival

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
“Under the Sal Tree” Theatre Festival, held annually in Rampur, Assam, promotes eco-friendly and sustainable practices in theatre while showcasing rich cultural diversity.
Overview:
- Location: Rampur village, Goalpara district, Assam
- Organizer: Badungduppa Kalakendra, a social and cultural organization
- Founded: 1998 by Sukracharjya Rabha
- Festival Focus: Eco-friendly theatre practices, cultural diversity, and sustainability
Key Features
- Unique Setting: Open-air festival under Sal trees, with no artificial lighting or electric sound systems.
- Sustainability:
- No use of plastic.
- Carbon-neutral, with eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, straw, and cane.
- Performances in natural daylight, avoiding electric lights.
- International Participation: Theatre groups from countries like Poland, South Korea, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, North Korea, Bolivia, and Holland have performed.
- Cultural Celebration: Highlights indigenous art forms, languages, and traditions, e.g., Rabha and Bodo plays.
Festival Activities
- Performances:
- Includes plays like “Dadan Raja” (Rabha language play), “Kindhan Charithiram” (Tamil), and “Kisan Raj” (Hindi).
- Focus on themes such as societal change and resilience of farmers.
- Workshops & Community Projects: For performing artists, promoting artistic innovation and social impact.
- Anniversary Celebrations:
- 25th anniversary celebrated with special events and book releases, e.g., “Resonance: Echoing the Spirit of Badungduppa” and “Sukracharjya Rabha on the Back Stage”.
Impact & Legacy
- Theatre Movement: Celebrates art amidst nature, breaking geographical barriers despite the remote location.
- Founder’s Vision: Sukracharjya Rabha believed in the synergy between art and nature, aiming to bring social change through theatre.
- Local Involvement:
- 20 resident artists contribute to the festival’s success.
- Festival has become a major cultural attraction in Assam, drawing thousands of theatre enthusiasts.
One Nation, One Election Bill
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The One Nation, One Election Bill has made significant progress in India, passing the Lok Sabha with 269 votes in favor and 198 votes against. The bill proposes the synchronization of elections for the Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and local bodies (Panchayats and Municipalities), aiming to streamline the electoral process, reduce costs, and enhance governance.
Key Updates:
- The bill has been approved by the Union Cabinet and will be reviewed by a Joint Parliamentary Committee (JPC), whose report will be presented for further approval and discussion in Parliament.
- The process will unfold in two phases:
- Phase 1: Simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Phase 2: Synchronizing local body elections (Panchayats and Municipalities) within 100 days of the general elections.
Historical Context:
- 1951-1967: India previously conducted simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies until disruptions, such as premature dissolutions of assemblies, led to staggered elections after 1967.
- The One Nation One Election concept has been revived to address inefficiencies in the current system, especially the high cost of conducting frequent elections.
Advantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Cost Reduction: Synchronizing elections can significantly lower the financial burden by eliminating the need for multiple election cycles, reducing the deployment of resources like security personnel and election staff.
- Long-Term Governance Focus: Politicians can prioritize governance and policy implementation rather than election campaigning, fostering long-term stability.
- Increased Voter Turnout: Voter fatigue, caused by frequent elections, may reduce, leading to higher turnout as elections occur less often.
- Fairer Political Competition: Smaller regional parties could have a better chance to compete with larger national parties by reducing election-related costs.
- Efficient Use of Resources: Security forces and administrative resources can be deployed more effectively, avoiding the redundancy caused by multiple election cycles.
Disadvantages of the One Nation, One Election Bill:
- Synchronization Challenges: Aligning elections across a vast and diverse country like India, especially in states with unstable political situations, may prove difficult.
- Federalism Concerns: The implementation may require constitutional changes that could impact India's federal structure, potentially limiting the autonomy of states in election matters.
- Impact on Regional Issues: National issues could overshadow regional concerns, diluting the focus on state-specific matters.
- Challenges for Regional Parties: Larger national parties may dominate the electoral landscape, reducing the influence of regional parties and undermining the federal nature of the political system.
- Accountability Risks: Fixed terms without frequent elections might reduce public scrutiny of elected officials, affecting their accountability.
Constitutional Amendments Required:
The implementation of One Nation, One Election requires amendments to several key constitutional provisions:
- Article 83: Regarding the duration of the Lok Sabha, amendments are needed to synchronize the timing of dissolution.
- Article 85: Deals with the sessions and dissolution of Parliament, which needs to be aligned with the new system.
- Article 172: Pertains to the duration of State Legislatures, requiring amendments for synchronization.
- Article 174: Similar to Article 85, it governs the sessions and dissolution of State Legislatures, needing standardization.
Implementation Challenges:
- Logistical Complexity: Conducting simultaneous elections would require immense logistical coordination, including vast numbers of electronic voting machines and trained personnel.
- Political Accountability: Fixed terms may reduce the accountability that frequent elections bring, potentially leading to governance stagnation.
- Impact on Federalism: Amendments to the Constitution regarding state legislatures might face resistance from states concerned about their autonomy.
International Mountain Day 2024
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
On 11th December 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in collaboration with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment (NIHE), hosted an event titled ‘Youth for the Himalaya: Innovate, Inspire, Impact’ to mark International Mountain Day.
Event Overview:
- The event was themed “Mountain Solutions for a Sustainable Future – Innovation, Adaptation, and Youth.”
- It emphasized the critical role of young people in addressing the environmental challenges faced by the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
- The aim was to showcase youth-driven innovations contributing to the region's sustainability, catalyzing active youth participation in environmental actions. This initiative aligns with the Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, which encourages sustainable practices and collective environmental responsibility.
Key Highlights:
- Young changemakers, innovators, and stakeholders from across the country participated, including students, youth representatives, and members of the private sector, civil society, and government.
- The event highlighted discussions on sustainable solutions for the Himalayan region, integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements in areas like eco-tourism, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience.
- Short films and videos produced by NIHE and IUCN, such as "Promoting Conservation of Threatened Plant Species in the Western Himalayas" and "Himalayan Futures: Voices from the Ground," were also showcased.
International Mountain Day
- International Mountain Day, observed every year on December 11th since 2003, was established by the United Nations to raise awareness about the sustainable development of mountain regions.
- Mountains cover about one-fifth of the Earth's surface and provide essential freshwater to half of humanity, supporting agriculture, clean energy, and health.
Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The IHR spans 13 Indian states and union territories, stretching approximately 2,500 kilometers from west to east. It is a biodiversity hotspot with significant ecological and cultural value. However, it faces challenges such as unsustainable development, climate change impacts, cultural erosion, and rising tourism.
Key Concerns for IHR:
- Unsustainable Development: Infrastructure projects and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Glacial melting and rising temperatures affect water resources and increase flood risks.
- Cultural Erosion: Modernization threatens traditional practices of indigenous communities.
- Tourism Pressure: Waste generation due to growing tourism puts immense pressure on the region's fragile ecology.
Measures for Protection:
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting eco-tourism and enforcing capacity limits to minimize environmental impact.
- Water Management: Capturing glacial meltwater for agriculture and ecosystem support.
- Disaster Preparedness: Developing disaster management strategies and early warning systems for events like landslides and floods.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation: Protecting both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices through designated zones.
- Integrated Development: Establishing a "Himalayan Authority" for coordinated development in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Journey Hits $1 Trillion Milestone
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
India has reached a historic milestone, surpassing $1 trillion in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows since April 2000. This achievement highlights India’s growing status as a major global investment hub and is further validated by a 26% increase in FDI inflows, which reached $42.1 billion during the first half of FY 2024-25.
Key Highlights of India’s FDI Growth:
- $1 Trillion Milestone: India has attracted a total of $1 trillion in FDI from April 2000 to September 2024. This figure includes equity, reinvested earnings, and other capital inflows.
- 26% Growth in FDI: FDI inflows surged by 26% in the first half of FY 2024-25, totaling $42.1 billion.
- Top Investors: Major investors include Mauritius (25%), Singapore (24%), and the United States (10%). These countries benefit from favorable tax treaties with India, boosting investment.
- Dominant Sectors: FDI has flowed into sectors like services, manufacturing, technology, and telecommunications, with significant investments also in pharmaceuticals, automobile, and construction development.
Factors Behind India’s FDI Success:
- Policy Reforms: India’s liberalized FDI policies, such as allowing 100% FDI in most sectors under the automatic route, have attracted foreign capital. Key reforms like abolishing angel tax and reducing corporate tax rates in the Income Tax Act of 2024 have also enhanced investor confidence.
- Business Environment: India’s rise in global competitiveness is evident in its improvement in rankings. It moved from 43rd to 40th in the World Competitiveness Index 2024 and climbed to 40th in the Global Innovation Index 2023, up from 81st in 2015.
- Investor Confidence: The government’s efforts, including initiatives like "Make in India", Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sector-specific incentives, have fostered a conducive environment for investment.
- Global Investment Standing: India has been the third-largest recipient of greenfield projects globally and saw a 64% increase in international project finance deals.
Contribution of Mauritius and Singapore:
- Mauritius and Singapore lead as the primary sources of FDI into India. Their favorable tax treaties with India make them attractive gateways for foreign investments. Mauritius accounted for 25%, and Singapore for 24% of the total FDI inflows.
Key Sectors Attracting FDI:
- Services Sector: Significant growth in services, especially financial services, has attracted substantial foreign investments.
- Manufacturing and Technology: These sectors have benefited from policies like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, which encourage foreign investments in high-tech manufacturing.
- Telecommunications and Pharmaceuticals: India’s growing digital ecosystem and strong pharmaceutical industry continue to attract international investments.
Importance of FDI for India:
- Infrastructure Development: FDI plays a crucial role in financing infrastructure projects, helping meet the country’s significant infrastructure needs.
- Balance of Payments: FDI helps bridge India’s current account deficit, ensuring stable foreign exchange reserves.
- Technology Transfer and Employment: Foreign investments bring advanced technology and create jobs, boosting productivity across sectors.
- Currency Stability: FDI supports the Indian Rupee in global markets by injecting foreign capital.
Challenges:
Despite the positive trends, India faces challenges such as geopolitical tensions, regulatory issues, global economic uncertainty, and infrastructure bottlenecks that can affect investor sentiment and capital inflows.
Way Ahead:
- Focus on Infrastructure: Continued investment in infrastructure development, including public-private partnerships (PPPs), will be crucial for sustained economic growth.
- Workforce Skilling: Collaborative efforts to upskill the workforce will ensure that India can meet the evolving demands of industries.
- Research and Development: Strengthening R&D and innovation will enhance India’s productivity and global competitiveness.
2024 World Chess Championship

- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
D. Gukesh became the youngest world chess champion after defeating Ding Liren of China in the final game of their match.
Key Facts about the 2024 World Chess Championship:
- Held At: Singapore, from November 25 to December 12, 2024.
- Players: Reigning champion Ding Liren (China) vs. Challenger D. Gukesh (India).
- Significance: This was the first-ever World Championship match contested by two Asian players. Gukesh became the third Asian to win the World Championship after Viswanathan Anand (India) and Ding Liren (China).
- Historical Context: The World Chess Championship was first established in 1886 with Wilhelm Steinitz as the first official World Champion.
- Governing Body: Organized by FIDE (Fédération Internationale des Échecs), which has been responsible for the event since 1948.
- Selection Process: Gukesh earned his spot through his victory in the 2024 Candidates Tournament in Toronto, while Ding Liren was the reigning champion after Magnus Carlsen declined to defend his title.
D. Gukesh: Key Details
- Birth: May 29, 2006, in Chennai, India.
- Grandmaster Title: Achieved at age 12 years, 7 months, and 17 days, making him the third-youngest Grandmaster in history.
- Chess Rating: He is the youngest player to reach a 2750 FIDE rating.
- Significant Wins:
- Gold medals in both team and individual events at the 2024 Chess Olympiad.
- Bronze medal in team events at the 2024 Asian Games.
- Remarkable Fact: Gukesh is four years younger than Garry Kasparov was when he won the World Championship in 1985.
FIDE World Chess Championship Overview:
- Founded: 1924 in Paris; headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland.
- Governing Body: The International Chess Federation (FIDE) is recognized by the International Olympic Committee and governs global chess competitions. FIDE has 201 member countries.
Indian Chess Achievements:
- Viswanathan Anand: First Indian to win the World Chess Championship (5-time World Champion).
- D. Gukesh: Second Indian to win the World Chess Championship.
Disease X
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent outbreak reported in the first week of December 2024 in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which has claimed over 400 lives and remains unclassified, has raised concerns that it could be an instance of Disease X.
What is Disease X?
- Definition: Disease X is a hypothetical, unidentified pathogen that has the potential to cause a global health crisis, either as an epidemic or pandemic.
- Origins: Could arise from zoonotic spillover (animal-to-human transmission), antimicrobial resistance, bioterrorism, or lab accidents.
- Severity: Predicted to be 20 times more lethal than SARS-CoV-2, with rapid transmission and significant mortality.
- Features: Represents unknown threats, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, or prions.
- Emergence Factors: Driven by deforestation, urbanization, climate change, and human-wildlife interactions.
Historical Context
- Conceptualization: The term was coined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2018, post the 2014–2016 Ebola outbreak, which revealed gaps in global health responses.
- Zoonotic Origins: Around 70% of emerging diseases since 1940 have zoonotic origins, linked to human encroachment on wildlife habitats.
WHO’s Priority Pathogen List
- Purpose: To focus global resources and attention on diseases with high epidemic or pandemic potential but lacking sufficient vaccines or treatments.
- Pathogens Listed: Includes Ebola, Marburg, Lassa fever, Nipah virus, Rift Valley fever, Zika virus, and Disease X.
- Criteria: These diseases have high mortality rates, potential for rapid spread, and inadequate preventive or therapeutic options.
Why Disease X is a Concern
- Unpredictability: Its emergence, transmission, and impact remain uncertain, making preparedness challenging.
- Globalization: Increased global travel and trade facilitate rapid spread of diseases across borders.
- Environmental Drivers: Climate change, urbanization, and deforestation disrupt ecosystems, bringing humans into closer contact with wildlife and pathogens.
Patterns in Emerging Diseases
- Zoonotic Spillover: The majority of emerging diseases originate from animals, with over 1.7 million undiscovered viruses in wildlife that could infect humans.
- Increased Outbreaks: Since the mid-20th century, the frequency of new diseases has risen, reflecting environmental, demographic, and global factors.
Challenges in Predicting Disease X
- Uncertainty: The vast pool of potential pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc.) makes it difficult to predict the exact nature, origin, or timing of Disease X.
- Environmental and Climatic Changes: Climate change reshapes disease transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases like malaria and dengue.
- Technological and Knowledge Gaps: Many pathogens that could cause pandemics are still unidentified. Genomic sequencing and AI are advancing but cannot fully predict Disease X.
Global Preparedness Initiatives
- WHO's Role: WHO’s priority pathogen list and Pandemic Treaty aim to ensure coordinated, global responses to future outbreaks.
- Pandemic Fund: Supports strengthening health systems, especially in low-income countries.
- mRNA Vaccine Hubs: Enhance vaccine production capacity, particularly in developing countries.
- Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI): Works on "prototype pathogen" platforms to create vaccines within 100 days of identifying a new disease.
Indian Initiatives for Disease Surveillance and Preparedness
- Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP): Tracks outbreaks, monitors trends, and strengthens the country’s epidemic preparedness.
- National Institute of Virology (NIV): Focuses on researching viral pathogens and zoonotic diseases.
- Biotech Initiatives: Indigenous vaccine development and diagnostic tools are crucial for combating future outbreaks.
- Emergency Response Fund: Allocates resources to support immediate pandemic response efforts.
Key Challenges in Tackling Disease X
- Prediction Complexity: The interactions between humans, animals, and the environment are too complex to predict the exact nature of Disease X.
- Health Disparities: Low- and middle-income countries often lack the infrastructure to effectively combat pandemics, making them more vulnerable.
- Climate Change: Alters transmission dynamics, expanding the range of diseases carried by vectors like mosquitoes.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Surveillance: Implementing real-time genomic sequencing and AI-driven tools for early outbreak detection.
- Global Cooperation: Promoting equitable sharing of vaccines, diagnostics, and treatments to ensure timely and efficient responses.
- Public Health Infrastructure: Invest in strengthening healthcare systems, especially in high-risk regions like the Congo Basin.
- Research and Development: Focus on universal vaccines, diagnostic tools, and prototype pathogen platforms that can be quickly adapted to new diseases.
Indian Scientists Develop Novel Gene Therapy for Haemophilia
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
Indian scientists have developed a successful gene therapy treatment for severe haemophilia A, a rare inherited blood disorder causing spontaneous, potentially fatal bleeding episodes.
Key Highlights:
Trial Success:
- The trial, conducted at Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore, involved five patients from Tamil Nadu.
- Results: None of the five patients reported bleeding episodes for over a year after receiving the treatment. The follow-up period averaged 14 months.
- This marks a significant improvement, as haemophilia patients typically experience frequent bleeding episodes requiring regular treatment.
Gene Therapy as a One-Time Solution:
- Traditional treatments involve frequent injections of clotting factors to prevent bleeding.
- The new gene therapy offers a one-time solution, teaching the body to produce enough clotting factor to prevent hemorrhages.
Haemophilia A - Overview:
- Caused by the absence of Factor VIII, a critical blood-clotting protein.
- Hemophilia A primarily affects males (since it's an X-linked disorder), though some females with two defective X chromosomes can also develop the condition.
- Symptoms include prolonged bleeding from minor injuries or internal bleeding in joints and muscles.
Current Treatment Challenges:
- Haemophilia treatments can be expensive and require lifelong care, costing up to ?2.54 crore over a 10-year period.
- The therapy requires repeated infusions of clotting factors or synthetic alternatives, which can be burdensome.
Gene Therapy Details:
- The gene therapy used in this trial involves fusing stem cells with the gene for Factor VIII using a lentivirus vector (safer than other vectors like adenovirus).
- This therapy eliminates the need for repeated Factor VIII infusions, providing a more cost-effective and sustainable solution.
Global Context:
- India has one of the world’s largest haemophilia populations, with an estimated 40,000 to 100,000 patients.
- The success of this gene therapy in India could lead to localized production, reducing treatment costs and increasing accessibility to gene therapy in resource-constrained settings.
Comparison with Roctavian:
- Roctavian, the only FDA-approved gene therapy for haemophilia A, also uses gene delivery to produce Factor VIII, but requires immunosuppressive therapy and is not approved for children.
- In contrast, the Vellore trial's lentivirus-based approach is considered safer, especially for children, with the potential for broader application.
Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The Railways (Amendment) Bill, 2024 was passed in the Lok Sabha on December 20, 2024, aiming to enhance the functioning and autonomy of Indian Railways.
Key Provisions:
- Repeal of the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905: The Bill repeals the 1905 Act and incorporates its provisions into the Railways Act, 1989, simplifying the legal framework by reducing the need to refer to two separate laws.
- Statutory Backing for Railway Board: The Bill provides statutory backing to the Railway Board, which previously lacked such a legal mandate. It grants the Union government the authority to determine the number of members, their qualifications, terms, and conditions of service.
- Decentralization of Power: The Bill aims to decentralize decision-making, granting greater autonomy to regional railway zones. This shift will allow more independence in budgeting, infrastructure projects, and recruitment, addressing long-standing calls for improved regional empowerment.
- Independent Regulator: The Bill proposes the creation of an independent regulator for overseeing tariffs, safety, and private sector participation. This idea has been supported by previous expert committees to encourage greater competition and transparency in the sector.
- Fast-Tracking Infrastructure and Services: The Bill will streamline approvals for new train services and infrastructure projects, helping meet demands from underserved regions, particularly in states like Bihar.
Objectives:
- Modernization of the Legal Framework: By incorporating the provisions of the 1905 Act into the 1989 Act, the Bill aims to simplify and modernize the legal architecture governing the railways.
- Empowerment of Railway Zones: Autonomy for railway zones is seen as a key step towards improving efficiency and accountability in operations.
- Private Sector Participation: The establishment of an independent regulator is expected to promote private participation in the railway sector, aligning with international standards.
Historical Context:
- The Indian Railways Act, 1890 established the foundations for Indian Railways as a government entity, which was further refined with the Indian Railway Board Act, 1905.
- This Bill aligns with recommendations from previous committees, including the Sreedharan Committee (2014) and the Committee on Restructuring Railways (2015), which have called for greater decentralization and autonomy for railway zones, as well as an independent regulatory body.
Challenges and Proposed Reforms:
- Financial Sustainability: The railways face challenges such as high operating costs, particularly from salaries and pensions, and losses in the passenger segment. Suggestions to improve finances include rationalizing passenger fares, enhancing freight revenue, and attracting private investment in infrastructure.
- Efficient Freight Operations: The Bill also addresses concerns about network congestion, especially for freight operations, and aims to increase the competitiveness of freight transport by improving infrastructure and reducing cross-subsidies from passenger fares.
Recommendations of various Committees on reforming the Railways
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
Regulatory Structure for Railway Sector
- Set up independent regulator to fix tariffs, promote competition, and protect consumer interests
Organisational structure of Indian Railways
- Corporatisation of Indian Railways
- Reorganise Railway Board to reflect a corporate business structure
- Envision the Railway Board as a policymaker alone
- Provide zones with full financial autonomy
Operations
- Separate core and non-core business (hospitals, schools, catering and security) of the Railways
- Permit private participation in some railway operations
Finances
- Clearly define social obligations and commercial business roles
- Restructure accounting procedure to reflect zone and route-wise profit and loss statements6,7,9
- Develop PPP models to attract private participation in: (i) developing and maintaining stations/ terminals, (ii) leasing of wagons, (iii) freight train operations, (iv) manufacturing of rolling stock, and (v) running non-core business operations
- Monetise railway assets
- Rationalise passenger tariffs
World Malaria Report 2024

- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The World Malaria Report 2024 released by the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights significant progress in malaria control, particularly in India, but underscores the continued burden of malaria in Southeast Asia, where India accounts for half of all malaria cases.
About Malaria:
- Cause: Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, primarily P. falciparum and P. vivax, transmitted through bites from infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- Transmission: Non-contagious; transmitted via mosquito bites.
- Symptoms: Fever, chills, and headaches appear 10–15 days after the mosquito bite. In some individuals, the symptoms may be mild.
- Prevention: Includes vector control strategies like insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor spraying. Malaria is treatable with early diagnosis and prompt medication.
India’s Malaria Status:
- Progress:
- India has made significant strides in reducing malaria, with cases decreasing from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023, a reduction of 82.4%.
- Similarly, malaria-related deaths dropped by 82.9%, from 35,000 in 2000 to 6,000 in 2023.
- Exit from High-Burden-High-Impact (HBHI) Group:
- India exited this group in 2024, signaling its success in reducing malaria burden.
- Cases dropped by 69% (from 6.4 million in 2017 to 2 million in 2023), and deaths fell by 68% (from 11,100 to 3,500 in the same period).
Key Strategies Behind India's Success:
- Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapy (ACT): Used to treat malaria effectively.
- Long-Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLIN): Widely deployed to control mosquito populations.
- Targeted Interventions: Focused on forested and tribal areas where malaria transmission is higher, particularly in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, and the North-East.
- Effective Monitoring: Ensures proper implementation of strategies and interventions.
WHO's Global Malaria Report 2024 Highlights:
- Global Burden: In 2023, there were 263 million malaria cases globally and 597,000 deaths. The African region remains the hardest hit, accounting for 95% of malaria deaths.
- Progress Since 2000: Malaria incidence and deaths have significantly decreased. The global number of malaria cases and deaths dropped substantially, with over 2.2 billion cases and 12.7 million deaths averted.
- Malaria-Free Countries: As of November 2024, 44 countries and one territory, including Egypt, have been certified malaria-free.
- Emerging Threats: Drug resistance (especially to Artemisinin) and insecticide resistance are growing concerns, affecting control efforts.
India and Southeast Asia:
- India contributes nearly half of the malaria cases in Southeast Asia, while Indonesia accounts for about one-third. Despite progress, India and Indonesia together accounted for 88% of malaria deaths in the region.
- South-East Asia Progress: The region reduced malaria cases by 82.4% from 22.8 million in 2000 to 4 million in 2023. Timor-Leste and Bhutan reported zero indigenous malaria cases in 2023.
Global Recommendations:
- WHO stresses the need for continued investment, innovative strategies, and targeted actions, especially in high-burden areas like Africa, to sustain progress and tackle remaining challenges, such as drug resistance, insecticide resistance, and new vector species like Anopheles stephensi, which thrives in urban areas.
Smuggling in India Report 2023-24
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
The annual ‘Smuggling in India - Report 2023-24’ report, which highlights DRI’s performance and experience over the last financial year as well as trends in the field of anti-smuggling and commercial fraud, will be released during the celebration.
Major Narcotics Hubs and Routes:
- Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan (The Death Crescent):
- Primary source of heroin trafficked into India.
- Routes via Africa, the Gulf, and India-Pakistan border.
- Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand (The Death Triangle):
- Significant source of synthetic drugs and heroin.
- Drugs often enter India through porous northeastern borders (e.g., Assam, Mizoram).
- Vulnerable regions: Moreh, Churachandpur, Zokhawthar.
- Maritime Routes:
- India’s vast coastline provides opportunities for drug trafficking, often through concealed shipping containers and fishing vessels.
- Air Routes:
- Increased trafficking due to international air traffic.
- Smuggled drugs often concealed in luggage, courier packages, or ingested by mules.
Major Narcotics Trends and Seizures (FY24):
- Cocaine:
- Significant increase in trafficking, particularly from South America and Africa.
- 47 seizures, up from 21 in the previous year.
- Seized quantity: 107 kg.
- Methamphetamine:
- Spiked in northeastern states like Assam and Mizoram.
- Seized quantity in FY24: 136 kg; increased in the first half of FY25 with 123 kg.
- Hydroponic Marijuana:
- Increasing smuggling from the US, Thailand, and other countries.
- Black Cocaine:
- New form of cocaine coated with substances like charcoal or iron oxide to evade detection.
- Contraband Cigarettes:
- Smuggling through sea routes, especially from Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
- Seizures increased by 19% in FY25, reaching 3.95 crore sticks.
- Illicit Gold:
- Significant destination for gold smuggling from West Asia (UAE, Saudi Arabia).
- Seized quantity fell slightly (1,319 kg in FY24), with land and air routes being primary methods.
- Wildlife Smuggling:
- Seizures included 53.5 kg of elephant tusks, leopard skins, live pangolins, and more.
Challenges and Issues:
- Porous Borders:
- Smuggling across eastern borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal remains a significant challenge.
- Difficult terrain in these regions aids traffickers.
- Air and Sea Routes:
- Growing use of air and maritime routes due to faster movement of goods.
- Technology and Detection:
- Emergence of “black cocaine” challenges traditional detection methods.
Anti-Smuggling and Drug Control Efforts:
- International Cooperation:
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) and the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) lead global efforts.
- Paris Pact Initiative targets Afghan opiate trafficking.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (1985) provides legal framework.
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) and Anti-Narcotics Task Force (ANTF) work together for enforcement.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan focus on awareness and rehabilitation.
ABOUT DRI
- The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is the premier intelligence and enforcement agency on anti-smuggling matters under the aegis of Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC), Government of India.
- It came into existence on 4th December 1957.
- With its Headquarters at New Delhi, 12 Zonal Units, 35 Regional Units and 15 Sub-Regional Units, DRI has been carrying out its mandate of preventing and detecting cases of smuggling of narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances, gold, diamonds, precious metals, wildlife products, cigarettes, arms, ammunitions & explosives, counterfeit currency notes, foreign currency, SCOMET Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) items, hazardous & environmentally sensitive materials, antiques etc. and taking punitive action against the organised crime groups engaged therein.
- DRI is also engaged in unearthing commercial frauds and instances of customs duty evasion.
Hyperloop Technology
- 12 Dec 2024
In News:
India’s first hyperloop test track (410 meters) completed by Indian Railways, IIT-Madras’Avishkar Hyperloop team and TuTr (incubated startup) at IIT-M discovery campus, Thaiyur in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
India’s First Hyperloop Test Track:
- Location: IIT Madras’ Discovery Campus, Chennai.
- Collaboration: Indian Railways, IIT-Madras' Avishkar Hyperloop team, and TuTr Hyperloop (startup).
- Track Length: 410 meters.
- Test Speed: Initial successful test at 100 km/h; plans for 600 km/h in the next phase.
- Passenger Capacity: 40–100 passengers per pod, depending on design.
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Concept: A high-speed transport system using pods in low-pressure vacuum tubes, designed to achieve speeds similar to aircraft (up to 1,100 km/h).
- Working:
- Magnetic Levitation (Maglev): Pods float on magnets, eliminating friction.
- Vacuum Tubes: Reduces air resistance for high-speed travel.
- Propulsion: Linear induction motors propel pods.
- Energy: Solar-powered, designed for zero emissions.
India’s Hyperloop Projects:
- Current Status:
- Successful testing of a 410-meter test track at IIT Madras.
- Ongoing feasibility studies for routes like Chennai Airport–Parandur, Mumbai–Pune, and Amritsar–Chandigarh.
- Phase 1 & 2: First phase involves a 11.5-kilometer track; future expansion to 100 km.
- Mumbai–Pune Corridor: Planned as India’s first full-scale Hyperloop system, aiming to reduce travel time from 3–4 hours to 25 minutes.
Benefits of Hyperloop:
- Speed: Capable of reaching speeds up to 1,100 km/h (operational speed around 360 km/h).
- Efficiency: Reduces travel time, energy-efficient with reduced air resistance and friction.
- Sustainability: Powered by renewable energy (e.g., solar power), offering zero emissions.
- Point-to-Point Travel: No intermediate stops, making it more time-efficient.
Challenges:
- Infrastructure Costs: Expensive to build the vacuum tubes, stations, and supporting systems.
- Land Acquisition: Difficulty in acquiring land, especially in densely populated areas.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of a specific regulatory framework for such advanced transport systems.
- Technological Barriers: Complex engineering challenges, including development of maglev systems and vacuum seals.
Global Context:
- Origin: Concept proposed by Elon Musk in 2013.
- Worldwide Adoption: Hyperloop is being explored globally, with projects in the U.S., UAE, and Europe.
GG Tau A System

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
GG Tau A System: Located about 489 light-years from Earth, this system is a triple-star setup that is between 1 to 5 million years old. This makes it an ideal system for studying the early stages of planetary formation.
Findings from the Discovery:
- Protoplanetary Disk: The system features a protoplanetary disk made of gas and dust, where new planets are forming. Researchers from NISER (National Institute of Science Education and Research), Odisha detected emissions from key molecules in the disk.
- Chemical Molecules: The molecules are frozen on tiny dust particles in the coldest regions of the disk (temperatures between 12 K and 16 K). These frozen molecules could serve as the building blocks for new planets.
Significance of the Discovery:
- Triple-Star Configuration: GG Tau A’s triple-star system is rare, and it has complex gravitational interactions among the three stars. This complicates how the gas and dust disk behaves and provides unique insights into planetary formation in multi-star systems.
- Study of Planet Formation: Traditionally, planets form around single stars or in binary systems. However, multi-star systems like GG Tau A present challenges for planet formation. Studying this system helps scientists understand how planets can form in more complex environments.
- Cold Conditions for Planet Formation: The study found that icy conditions in the disk are essential for the accumulation of materials that form planets. These low temperatures (below the freezing point of carbon monoxide) allow dust and gas particles to clump together, creating the foundation for exoplanets.
Broader Implications:
- Exoplanet Diversity: This research enhances our understanding of how planets form in different types of star systems, contributing to the study of exoplanets and their potential diversity across the universe.
- Astrophysics and Planetary Science: This discovery plays a crucial role in improving our knowledge of the early stages of planet formation, especially in complicated star systems like triple-star setups, which are rare but can provide valuable insights into how planetary systems evolve under unique conditions.
Research Tools:
- The team used advanced radio telescopes located in the Atacama Desert (Chile) to observe the emissions from the disk, highlighting the role of cutting-edge technology in space exploration and astronomical research.
Champions of the Earth Award

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Madhav Gadgil, an Indian ecologist, received the UN Environment Programme (UNEP)'s Champions of the Earth Award in 2024.
- The Champions of the Earth Award is UNEP’s highest environmental honor, recognizing individuals, organizations, and governments for significant contributions to environmental protection and sustainable development.
Contributions of Madhav Gadgil:
- Work in Western Ghats:
- Gadgil is recognized for his seminal work in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive region in India, which is a global biodiversity hotspot.
- He chaired the Western Ghats Ecology Expert Panel (WGEEP), formed by the Indian government to assess the impacts of population pressure, climate change, and development on the region.
- Recommendations by WGEEP:
- Ecologically Sensitive Area (ESA): Recommended declaring the entire Western Ghats range as an ESA.
- The WGEEP suggested dividing the Western Ghats into three Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZ) based on environmental sensitivity.
- Development Restrictions: Proposed a ban on activities like mining, quarrying, thermal power plants, and large-scale hydropower projects in the most sensitive zones (ESZ-1).
- Governance Recommendations: Suggested a bottom-to-top governance approach, beginning with Gram Sabhas, and the creation of a Western Ghats Ecology Authority (WGEA) for effective management.
- Impact of Gadgil’s Work:
- His research and recommendations have played a crucial role in shaping environmental policy and public opinion in India.
- The UNESCO World Heritage status for the Western Ghats in 2012 was a significant step in global recognition of the region’s ecological importance.
About the Champions of the Earth Award:
- History & Significance:
- Established in 2005, the award recognizes trailblazers working towards addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- Since its inception, it has honored 122 laureates who have shown outstanding leadership in environmental conservation.
- 2024 Awardees:
- Madhav Gadgil (India) – for his work on the Western Ghats.
- Sonia Guajajara (Brazil) – for advocacy for Indigenous rights and environmental protection.
- Amy Bowers Cordalis (USA) – for her work in Indigenous rights and ecosystem restoration.
- Gabriel Paun (Romania) – for defending Europe’s old growth forests from illegal logging.
- Lu Qi (China) – for contributions to afforestation and combating desertification.
- SEKEM (Egypt) – for advancing sustainable agriculture.
Key Facts about UNEP:
- UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- Established in 1972, UNEP is a leading global authority on environmental issues.
- UNEP aims to address climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution through scientific research, policy support, and public advocacy.
- UNEP is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya and works closely with 193 Member States to tackle the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges.
Ayush Visa

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- Recently, the government introduced a separate category of Ayush Visa for foreigners seeking treatment under the Ayush systems of medicine (Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy).
- The Ayush Visa is available in four sub-categories:
- Ayush Visa: For foreigners visiting India for therapeutic care and wellness treatment in accredited hospitals/wellness centers.
- Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients seeking Ayush treatment.
- e-Ayush Visa: An electronic version of the Ayush Visa for convenience.
- e-Ayush Attendant Visa: For attendants accompanying patients on an e-Ayush Visa.
- Visa Statistics (as of December 4, 2024):
- 123 regular Ayush visas have been issued.
- 221 e-Ayush visas issued.
- 17 e-Ayush attendant visas issued.
- Advantage Healthcare India Portal:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the Advantage Healthcare India portal, an official platform for Medical Value Travel (MVT).
- The portal facilitates information for international patients seeking medical treatment and wellness services in India.
- The website for accessing the portal is www.healinindia.gov.in.
- Government's Objectives: The government aims to sensitize stakeholders involved in MVT, including Ayush facility providers, to ensure smooth services for international patients.
Human Rights Day 2024

- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
Human Rights Day 2024 celebrated every year on 10th December is dedicated to promote protection of fundamental rights and freedom of all individuals.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: Promote and protect human rights and freedoms worldwide.
- Theme (2024): “Our Rights, Our Future, Right Now” – highlights the importance of immediate action to protect and uphold human rights globally.
Historical Significance:
- Commemorates: The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
- UN Resolution: Established by UN Resolution 423 (V) in 1950.
- First Observance: December 10, 1950.
- Father of Human Rights Day: Eleanor Roosevelt, for her pivotal role in drafting the UDHR.
Key Highlights:
- The UDHR:
- Adopted in 1948, it defines fundamental human rights for all individuals.
- Comprises 30 articles, addressing rights such as freedom, equality, and access to education, healthcare, and fair employment.
- Role of the UN: UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC): A body under the UN responsible for monitoring and promoting human rights worldwide, comprising 47 member states.
- Human Rights Day Focus in 2024:
- Emphasizes human rights education, particularly among the youth.
- Addresses emerging challenges like cybercrimes, AI impacts, and climate change.
- Reaffirms the importance of safeguarding human dignity globally.
Human Rights Declared by UDHR:
- Right to freedom and equality
- Right to life, liberty, and security
- Freedom from slavery and torture
- Right to recognition before the law
- Equal protection under the law
- Right to a fair trial
- Right to privacy and protection from attacks
- Right to work and fair employment
- Right to rest and leisure
- Right to education
- Right to an adequate standard of living
- Right to participate in government and cultural activities
AgeXtend
- 11 Dec 2024
In News:
- AgeXtend is developed by researchers at Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology – Delhi (IIIT-Delhi) to rapidly identify age-defying compounds, known as geroprotectors, to promote healthy aging.
Key Features of AgeXtend:
- What is AgeXtend?
- An AI-based platform designed to discover compounds with geroprotective (anti-aging) properties.
- Objective: To accelerate the identification of molecules promoting longevity by reducing the time and effort compared to conventional research methods.
- Development: Developed by researchers from the Indraprastha Institute of Information Technology (IIIT), Delhi.
- Working Mechanism:
- Scans over 1.1 billion compounds to predict, analyze, and validate molecules with anti-aging potential.
- Utilizes machine learning to determine efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action.
- Experimental validation conducted using yeast, worms (C. elegans), and human cell models.
- Significance:
- The largest study on longevity, including compounds from commercial drugs, FDA-approved drugs, Ayurvedic, and Chinese medicine.
- Provides a scientific rationale for identifying geroprotective compounds, aiding targeted research.
- Open-source code and data promote collaboration and allow commercial exploration.
Platform Capabilities:
- AI Analysis:
- Uses bioactivity data from existing geroprotectors to predict new compounds with similar properties.
- Evaluates geroprotective potential, toxicity, and identifies target proteins and mechanisms of action for accuracy and safety.
- Unique Feature: Explains why a compound is considered geroprotective, revealing underlying mechanisms.
- Example Validation: Successfully identified benefits of metformin and taurine without prior knowledge, confirming the platform’s predictive power.
- Study Scale: The study involved scanning over 1.1 billion molecules, making it the largest study on longevity to date.
Open-Source and Commercial Use:
- Availability:
- The code and data are available as open-source for researchers and students. Commercial access is available for a fee.
- A Python package for AgeXtend is available via pip on pypi.org.
- Further Collaboration: The researchers have reached out to pharma companies to further investigate promising compounds.
- Exploring Natural Compounds: AgeXtend also explores natural compounds from the human microbiome, investigating their role in controlling cell aging.
Sora Turbo

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
OpenAI officially launched Sora Turbo, its advanced text-to-video artificial intelligence (AI) tool, marking a significant development in the field of visual AI generation. This follows Google’s recent expansion of its video-generative AI tool, Veo, for Vertex AI customers. However, hours after Sora Turbo’s release, OpenAI temporarily disabled sign-ups due to overwhelming demand.
Key Features of Sora Turbo:
- Text-to-Video Generation: Users can input text prompts, and Sora Turbo will generate videos based on the provided descriptions. This makes it one of the first widely accessible AI-powered video generation models.
- Video Quality & Formats: Sora Turbo can generate videos in 1080p resolution, lasting up to 20 seconds. It supports both vertical and horizontal formats.
- Remix Options: Users can remix the AI-generated videos with their own assets, allowing for customization and extension of the content.
- Speed & Interface: The tool has been optimized for faster video generation compared to its previous version, with a new user interface designed to make the process more intuitive.
- Subscription Plans:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): Users get up to 50 videos at 480p resolution per month or fewer videos at 720p resolution.
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Offers 10 times more usage, with higher resolution and longer durations.
User Access and Availability:
- Access Requirements: To use Sora Turbo, individuals need to subscribe to either the ChatGPT Plus or ChatGPT Pro plans. The tool is included in these subscriptions without additional charges.
- Geographic Limitations: As of now, Sora Turbo is unavailable in the European Union, United Kingdom, and Switzerland.
Metadata & Safety Features:
- Transparency: All videos generated by Sora Turbo will include C2PA metadata for content provenance and authenticity, along with a visual watermark.
- Abuse Prevention: OpenAI has implemented safeguards to block the generation of harmful content, including child sexual abuse materials and sexual deepfakes.
Future Developments:
OpenAI has plans to offer tailored pricing for different users starting in early 2025. Additionally, Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Sora as a groundbreaking product, comparing it to the early days of GPT technology, and emphasized its potential for co-creation and innovative visual content generation.
INS Tushil Commissioned into the Indian Navy in Russia

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy officially commissioned INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, at Kaliningrad, Russia. This marks a significant milestone in India-Russia defense cooperation and strengthens India’s maritime capabilities.
About INS Tushil:
- Class & Design: INS Tushil is the seventh ship in the Krivak III class (Project 1135.6) of frigates. It is part of an upgraded series, following the Talwar-class and Teg-class frigates, and was built at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia.
- Development & Contract: The construction was initiated under a 2016 contract between the Indian Government, JSC Rosoboronexport (a Russian defense company), and the Indian Navy. The ship incorporates 26% indigenous technology, highlighting growing cooperation between Indian and Russian industries.
- Key Features:
- Stealth Design: With advanced radar-absorbing features, it is less detectable by enemy radar.
- Weaponry: Equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles, anti-submarine torpedoes, electronic warfare systems, and more.
- Versatility: Designed for blue-water operations, the ship can engage in air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic warfare.
- Helicopter Deck: Supports operations of upgraded Kamov 28 and Kamov 31 helicopters.
- Speed: Capable of exceeding 30 knots.
Significance:
- Enhanced Naval Capabilities: The commissioning of INS Tushil boosts India’s defense strength in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a vital area for global maritime trade and security.
- Maritime Security: INS Tushil is designed to support India’s vision of maintaining stability in the IOR and to act as a deterrent against piracy and other maritime threats.
- Defense Cooperation: This commissioning exemplifies the growing defense ties between India and Russia, underscored by joint development, technology transfer, and shared expertise. The ship reflects a major step in India's self-reliance in defense, in line with the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
- Strategic Role in Global Defense: The ship is a key asset in the Indian Navy's efforts to secure maritime trade routes, enhance regional security, and provide humanitarian assistance in times of need.
Key Events & Facts:
- Construction Timeline: The keel of INS Tushil was laid in 2013, and it launched in 2021. After completing extensive sea and weapon trials in 2024, it was formally commissioned into the Navy.
- Collaborative Effort: The ship is a product of collaborative efforts between Indian and Russian industries, marking a significant achievement in joint defense manufacturing.
Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India announced the appointment of Sanjay Malhotra as the 26th Governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). He replaces Shaktikanta Das, whose six-year tenure ends on December 10, 2024.
Background of Sanjay Malhotra:
- Education & Early Career: Sanjay Malhotra is a 1990-batch IAS officer from the Rajasthan cadre. He holds a degree in Computer Science Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur and a Master’s in Public Policy from Princeton University.
- Professional Experience: Malhotra has over 33 years of experience in various sectors including power, finance, taxation, information technology, and mines. He is currently serving as the Revenue Secretary in the Ministry of Finance, a position he has held since October 2022. Prior to this, he was Secretary of the Department of Financial Services.
- Monetary Policy and Challenges: As RBI Governor, Malhotra will inherit the responsibility of steering India's monetary policy, especially as inflation has been a persistent issue and economic growth has slowed. His first monetary policy review is expected in February 2025.
About the Appointment Process:
RBI Governors are appointed by the Government of India, and the appointment process involves the Financial Sector Regulatory Appointment Search Committee, which includes the Cabinet Secretary, the current RBI Governor, the Financial Services Secretary, and two independent members. The committee prepares a list of eligible candidates, interviews them, and the final decision is made by the Cabinet Committee on Appointments, chaired by the Prime Minister.
RBI Governors Eligibility Criteria
- The RBI Act, 1934 does not mention any specific qualification for the governor. People with different educational backgrounds were selected to head the institution. However, the governor traditionally is either a civil services personnel or an economist.
- Candidates should have prior experience in areas such as:
- Working with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or World Bank.
- Serving as Chairman or General Manager of a bank.
- Holding significant positions in reputable financial or banking organizations.
- Working in the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India.
- The candidate must be an Indian citizen aged 35 years or older.
- The candidate cannot be a member of Parliament, State Legislature, or hold any other office for profit
Key Responsibilities of the RBI Governor:
- Monetary Policy: The RBI Governor chairs the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), which is responsible for setting benchmark interest rates and managing inflation.
- Regulation of Financial Institutions: The Governor oversees the regulation of banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions.
- Currency Management: The Governor ensures the proper issuance of currency and the withdrawal of unfit notes.
- Crisis Management and Policy Execution: The Governor is pivotal in managing financial crises and ensuring the execution of policies related to foreign exchange and financial inclusion.
National Panchayat Awards 2024

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 celebrated the remarkable contributions of 45 Panchayats from across India for their role in driving sustainable and inclusive development in rural areas. The awards were presented on 11th December 2024 at Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi, with President Smt. Droupadi Murmu and Union Minister of Panchayati Raj Shri Rajiv Ranjan Singh (Lalan Singh) presiding over the event.
Key Highlights:
- Categories of Awards: The awards focus on rural governance, social inclusion, environmental sustainability, and the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through Localization of SDGs (LSDGs).
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar (DDUPSVP): Recognizes top-performing Gram Panchayats across 9 thematic areas like health, water, sanitation, and governance.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Sarvottam Panchayat Satat Vikas Puraskar: Awarded to the best Panchayats based on overall excellence across all LSDG themes.
- Gram Urja Swaraj Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Honors Panchayats for contributions to renewable energy.
- Carbon Neutral Vishesh Panchayat Puraskar: Awarded to Panchayats achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
- Panchayat Kshamta Nirmaan Sarvottam Sansthan Puraskar: Recognizes institutions supporting Panchayats in implementing LSDGs.
- Notable Achievements:
- Women’s Leadership: 42% of the award-winning Panchayats were led by women.
- States with Top Performers: States like Tripura, Odisha, and Maharashtra were prominently recognized for their achievements, especially in sustainability efforts like carbon neutrality and renewable energy adoption.
- Prize Distribution: A total of ?46 crore was awarded to the 45 winners, with funds directly transferred to their accounts.
Objectives:
The National Panchayat Awards aim to:
- Promote rural development through effective Panchayat governance.
- Encourage competition among Panchayats for improving public services and infrastructure.
- Recognize excellence in implementing sustainable development practices.
Key Themes of the Awards:
The awards are aligned with 9 LSDG themes that contribute to achieving 17 SDGs:
- Poverty-Free and Enhanced Livelihoods
- Healthy Panchayat
- Child-Friendly Panchayat
- Water-Sufficient Panchayat
- Clean and Green Panchayat
- Self-Sufficient Infrastructure
- Socially Just and Secured Panchayat
- Panchayat with Good Governance
- Women-Friendly Panchayat
The National Panchayat Awards 2024 underscore the significant role of Panchayats in shaping rural India by focusing on inclusive and sustainable development. The awards also promote the importance of localized governance in achieving SDGs, encouraging other Panchayats to adopt best practices and contribute to India's overall development goals.
Reforms in Merchant Shipping

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
The Government is preparing to introduce several significant bills aimed at driving much-needed reforms in the shipping industry. Key among them are the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 and the Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024, both of which promise to bring transformative changes to boost the sector.
Context and Need for Reforms:
- Outdated Framework: The Merchant Shipping Act, 1958, and the Coasting Vessels Act, 1838, fail to address the current needs of the shipping sector, particularly offshore vessels.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate regulation of offshore vessels, maritime training institutions, and welfare provisions for seafarers on foreign-flagged ships.
- Global Alignment: Need to align with international maritime conventions and modernize administration for competitiveness and better governance.
- Investment and Growth: Outdated laws hinder foreign investment and ease of doing business, necessitating a regulatory overhaul.
Key Features of the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Ease of Vessel Registration:
- Reduces ownership threshold for Indian entities from 100% to 51%, enabling NRIs, OCIs, and foreign entities to invest.
- Facilitates registration of vessels chartered by Indian entities under the "bareboat charter-cum-demise" system, promoting capital-deficient entrepreneurs.
- Temporary registration provisions for vessels destined for demolition, boosting India's ship recycling industry.
- Expansion of Vessel Scope:
- Broadens the definition of "vessel" to include all types of mechanized and non-mechanized crafts, such as submersibles, hydrofoils, and Mobile Offshore Units (MOUs).
- Ensures comprehensive regulatory oversight, particularly in the offshore sector, enhancing transparency and safety.
- Coastal Security:
- Strengthens coastal security by empowering authorities to issue instructions to all types of vessels, addressing vulnerabilities highlighted by incidents like the 26/11 Mumbai attacks.
- Marine Pollution Measures:
- Incorporates global standards like the MARPOL convention to address marine pollution.
- Introduces measures such as reducing sulphur content in marine fuel and banning single-use plastics on Indian ships.
- Launch of the ‘Swachh Sagar’ portal to ensure proper disposal of ship-generated waste.
- Seafarer Welfare:
- Expands welfare provisions to include Indian seafarers working on foreign-flagged ships, offering protections under the Maritime Labour Convention (MLC).
- Ensures better working conditions and safety standards for a growing workforce of Indian seafarers abroad.
- Maritime Training Regulations:
- Establishes a legal framework to regulate maritime training institutions, addressing the rise of unauthorized institutes post-liberalization.
- Ensures standardized, high-quality education and eliminates fraudulent practices.
Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024:
- Focus on Commercial Utilization of Coastal Waters:
- Distinguishes between the technical regulation of ships and the commercial utilization of Indian coastal waters.
- Aims to streamline licensing, operations, and coastal planning, enhancing the integration of inland and coastal shipping.
- Alignment with ‘Sagarmala’ Program: Supports the promotion of coastal shipping through better infrastructure and connectivity, in line with the government's ‘Sagarmala’ initiative, which boosts port connectivity and coastal trade.
International Conventions India Has Ratified:
- MARPOL: Focuses on preventing ship-based pollution.
- Maritime Labour Convention (MLC): Protects seafarers' rights and ensures fair working conditions.
- Bunker Convention: Addresses liability for oil pollution damage.
- Wreck Removal Convention: Mandates safe removal of shipwrecks.
- Civil Liability Convention: Establishes liability for oil pollution incidents.
Significance of the Reforms:
- Modernized Framework: Aligns India’s maritime laws with global standards for enhanced competitiveness.
- Economic Growth: Encourages foreign investment and entry into the shipping sector by removing regulatory barriers.
- Environmental Sustainability: Focus on combating marine pollution and ensuring sustainable shipping practices.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Strengthens coastal security and ensures stringent safety regulations for vessels.
- Seafarers’ Welfare: Extends benefits and protections to Indian seafarers working globally, ensuring better working conditions.
- Maritime Education: Provides a robust regulatory framework to ensure high-quality, standardized maritime training.
Turner Prize

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
Jasleen Kaur, a 38-year-old Indian-origin Scottish artist, has won the prestigious Turner Prize 2024 for her exhibition "Alter Altar". This win highlights Kaur’s unique ability to weave together personal, political, and spiritual elements into a cohesive artistic expression. The exhibition explores themes such as plurality, migration, and cultural identity, drawing from Kaur’s own family history and experiences.
Exhibition Overview:
"Alter Altar," which was first showcased in Glasgow, features an array of everyday objects and cultural symbols, including:
- A vintage red Ford Escort covered in a large crocheted doily, symbolizing her father’s migrant aspirations.
- Worship bells, Irn-Bru orange resin, an Axminster carpet, and family photographs.
- Soundtracks, including music from Nusrat Fateh Ali Khan and Bob Marley, which reflect Kaur’s multicultural upbringing.
The exhibition blends these elements to examine migration, identity, and belonging. The jury, chaired by Alex Farquharson, Director of Tate Britain, praised Kaur’s ability to combine different voices through unexpected and playful material combinations, creating a visual and aural experience that evokes both solidarity and joy.
Personal and Political Reflection:
Kaur’s work reflects on the Sikh concept of Miri Piri, which represents the balance between the political and the spiritual. This duality is central to her exploration of cultural practices and the effects of violence, colonialism, and empire on these traditions. In her acceptance speech, Kaur also addressed political issues, calling for a ceasefire in Gaza and an end to institutional complicity in Israel's actions.
About the Turner Prize:
The Turner Prize, established in 1984, is one of the most prestigious awards in contemporary British art. It aims to recognize recent developments in British art. Kaur’s win is particularly significant as it marks the 40th anniversary of the award. Previous winners include renowned Indian-origin artists such as Anish Kapoor (1991).
Black holes in Webb data allay threat to cosmology’s standard model

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched almost three years ago, has provided unprecedented insights into the early universe. Astronomers were surprised to find large, fully-developed galaxies when the universe was only 400-650 million years old, a timeframe previously thought to be too early for such structures.
The Challenge to the Standard Model:
- Cosmological Expectations: According to the standard model of cosmology, the first stars formed around 100-200 million years after the Big Bang, and galaxies began to form within the first billion years.
- Unexpected Findings: JWST observations seemed to show that galaxies were already large and well-formed much earlier than expected, raising questions about the timeline of galaxy formation.
New Study's Contribution:
- The Study: A study published in the Astrophysical Journal in August 2024, examined JWST data from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science (CEERS) Survey. They focused on galaxies from 650 to 1,500 million years after the Big Bang.
- Key Findings: One explanation for the unexpected size and number of early galaxies is that these galaxies formed stars much more efficiently than those in the modern universe. This could account for the larger-than-expected galaxies.
The Role of Black Holes:
- Impact of Black Holes: The study also explored the presence of black holes at the centers of early galaxies. These black holes, which emit significant light, were previously unaccounted for in the star mass estimations of galaxies. When the researchers removed the light from black holes (referred to as "little red dots"), they found that the galaxies were not as massive as initially thought.
- Correction to Previous Estimates: This adjustment in calculations helped align the data with the standard model of cosmology, sparing it from a major revision.
Implications for the Standard Model:
- Star Formation Efficiency: The study suggests that extreme conditions in the early universe, including abundant gas and less disruptive stellar events, could explain the higher efficiency of star formation.
- Cosmology's Stability: Despite earlier challenges to the standard model, the new findings support its predictions, showing that more efficient star formation and the role of black holes could explain the rapid growth of galaxies in the early universe.
Future Research Directions:
- Expanding Data Sets: The team plans to incorporate more data from JWST to study even earlier galaxies, which could help refine our understanding of galaxy formation in the early universe.
- Further Observations: As the team continues to explore galaxies from even earlier periods (around 400 million years after the Big Bang), they aim to strengthen their findings and provide further evidence to either support or challenge the current cosmological models.
Moths' Reproductive Choices Based on Plant Acoustic Emissions

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
A new study, "Female Moths Incorporate Plant Acoustic Emissions into Their Oviposition Decision-Making Process," published last month, explores how female moths use sounds emitted by plants to choose where to lay their eggs.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Plant Emitted Sounds:
- Background: Last year, it was discovered that plants emit ultrasonic clicks or pops when stressed (e.g., dehydration). These sounds, although inaudible to humans, can be detected by animals, including insects.
- Moths’ Sensitivity: Moths, particularly the Egyptian cotton leafworm, are shown to be sensitive to these plant sounds, which they use as cues for laying eggs on plants.
Methodology:
- Experimental Setup: Researchers placed a hydrated tomato plant in an experimental arena with another hydrated plant that emitted distress sounds. They observed the behavior of female Egyptian cotton leafworms to understand how these sounds influenced their oviposition choices.
- Initial Finding: Moths typically choose healthy, thriving plants to lay eggs, as they provide better food sources for the larvae.
Study Findings:
- Moths’ Response to Sounds: The moths preferred to lay eggs on the “silent” plant rather than the one emitting distress sounds. This indicates that moths can not only detect the presence of a plant but also interpret acoustic signals to inform their egg-laying decisions.
- Implications: This behavior suggests that moths use a complex set of sensory inputs, including plant-emitted sounds, to select the most suitable plant for offspring development.
Broader Ecological Context:
- Moths as Insects: Moths belong to the order Lepidoptera and are found in diverse environments globally, except polar regions. With around 160,000 species, they are highly adapted and often nocturnal, though some species are diurnal.
- Impact on Agriculture: Certain moth species, especially during their caterpillar stage, are major agricultural pests (e.g., corn borers, bollworms), making understanding their behavior crucial for pest management strategies.
- Climate Change Considerations: Moths, like other species, are impacted by climate change, which can alter the timing and growth of plants they depend on, potentially influencing their reproductive strategies.
Conclusion:
- Innovative Findings: The study reveals a previously unknown aspect of moth behavior, showing that they incorporate plant acoustic emissions into their oviposition decisions.
- Future Implications: This discovery opens avenues for further studies on how environmental signals, like sound, affect the behavior of insects, and how these behaviors could be impacted by changing environmental conditions.
RBI's Stance on De-dollarisation and Risk Diversification

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
- Governor Shaktikanta Das clarified that India is not pursuing "de-dollarisation," but rather aiming to diversify risk in trade. Measures like local currency trade agreements and Vostro accounts are intended to reduce reliance on the US dollar without eliminating it entirely.
- Objective: The goal is to de-risk India's trade, not to fully replace the dollar, especially amidst rising geopolitical tensions.
Key Highlights:
Vostro Accounts and Local Currency Trade:
- Vostro Accounts: These accounts, held by foreign banks in Indian rupees, facilitate transactions in local currencies, helping mitigate the risks of dollar dependency.
- International Currency Trade: By promoting trade in local currencies, the RBI seeks to reduce exposure to fluctuations in the dollar's value. However, these efforts have faced challenges due to India’s limited international presence in goods and services trade.
Gold Purchases by Central Banks:
- Surge in Gold Purchases: Global central banks, including the RBI, have significantly increased gold holdings. India added 27 tonnes in October 2024 alone, the largest increase among central banks.
- Motivations for Gold: The surge in gold buying reflects growing concerns about geopolitical risks, including the Ukraine war, and the potential for secondary sanctions. Gold is seen as a safe haven asset that diversifies reserves away from the US dollar.
Decline in Dollar Dominance:
- Global Shift: The share of the US dollar in global reserves has been gradually declining, partly due to the rise of the Chinese yuan. Central banks are increasingly turning to gold and alternative currencies as part of a diversification strategy.
- Impact on Emerging Markets: Countries like India are particularly motivated to reduce reliance on the dollar due to geopolitical tensions and economic vulnerabilities linked to the dollar’s dominance.
India’s Domestic Currency Trade Initiatives:
- Trade with Russia and UAE: India is actively exploring trade in domestic currencies with countries like Russia and the UAE to reduce dependence on the dollar. However, these efforts have faced slow uptake due to India’s trade deficit with most countries except the US.
- Challenges in Adoption: Despite efforts to internationalize the rupee, high transaction costs and lack of sufficient demand for rupee-based trade are significant barriers.
BRICS and Shared Currency Discussions:
- Geopolitical Complexity: BRICS nations, due to their geographical and economic diversity, have discussed the possibility of a shared currency, but no consensus has been reached.
- Reluctance Toward Yuan: India has resisted using the Chinese yuan for transactions, particularly for Russian oil imports, despite the yuan’s growing acceptance. This reflects India’s desire to maintain economic sovereignty and avoid over-reliance on a single currency.
Regional Implications of Dollar Volatility:
- Neighbourhood Impact: Countries like Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Pakistan have experienced significant financial distress due to declining dollar reserves and surging oil prices, exacerbated by the Ukraine war.
- India’s Resilience: India’s strong dollar reserves have helped it maintain economic stability, but the country remains cautious of dollar volatility, particularly as oil prices rise.
Conclusion:
- Strategic Balance: India’s approach reflects a strategic balance of mitigating risks while ensuring global trade stability. The RBI’s emphasis on gold accumulation and pushing for rupee-based trade demonstrates a desire to reduce exposure to the dollar, but challenges like trade deficits and high transaction costs still hinder the full realization of these goals.
- Economic Sovereignty: Through these measures, India seeks to safeguard its economic sovereignty and financial stability in an increasingly unpredictable global economy.
Oilfields Amendment Bill, 2024

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
To encourage domestic production of petroleum and other mineral oils, along with private investment in these sectors to reduce import dependence, the Rajya Sabha passed the Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Amendment Bill, 2024.
Key Details:
- Objective:
- Encourage domestic petroleum production.
- Reduce import dependence by promoting private investment in the oil sector.
- Key Amendments:
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- The Bill separates petroleum and mineral oil production from mining activities.
- The Oilfields (Regulation and Development) Act, 1948, is amended to focus on mineral oils, distinct from the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Expanded Definition of Mineral Oils:
- Includes hydrocarbons in various forms (natural gas, crude oil, petroleum, coal bed methane, and shale gas/oil).
- Excludes coal, lignite, and helium from the definition (falling under the Mines and Minerals Act).
- Petroleum Lease:
- Replaces the term "mining lease" with "petroleum lease."
- Covers activities such as exploration, development, production, and transportation of mineral oils.
- Private Investment:
- Provisions to attract private investment by clarifying rules for petroleum leases.
- Current mining leases remain valid without altering terms to the lessee's disadvantage.
- Decriminalization and Penalties:
- Replaces criminal punishment with financial penalties.
- Fines can go up to Rs. 25 Lakh, with additional penalties for ongoing violations.
- Rule-making Power of Central Government:
- Expands the Centre's authority over petroleum lease regulations, conservation, royalties, mergers, facility sharing, environmental protection, and dispute resolution.
- Delinking petroleum from mining:
- Significance of the Bill:
- Energy Access and Security: Ensures energy security by boosting domestic production.
- Attracting Investment: Creates a conducive environment for private sector investment.
- Environmental Safeguards: Provisions to control carbon emissions and promote renewable energy in oilfields.
- Opposition Criticism:
- State Rights on Mining: Concerns raised by opposition parties, particularly the DMK, about the reduction of state control over resource taxation (taxing mineral rights).
- Impact on Federal Balance: States traditionally manage mining rights under the Constitution’s State List (Entry 50). The Bill may shift control to the Union List (Entry 53), creating constitutional concerns.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Opposition figures like P.P. Suneer (CPI) argue for prioritizing public companies like ONGC, fearing privatization may worsen environmental governance.
- Adjudication of Disputes:
- Appeals against penalty decisions will be handled by the Appellate Tribunal, as per the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Broader Significance:
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on fuel imports, fostering energy security and economic stability.
- Regulation: Strengthens the enforcement mechanism for petroleum operations while encouraging private participation.
Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB):
- Formation: Established under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Functions: Regulates refining, transportation, distribution, storage, marketing, and sale of petroleum products and natural gas.
- Role in the Bill: Ensures competitive markets for gas and handles appeals regarding regulatory decisions.
Markhor Spotted in North Kashmir's Baramulla
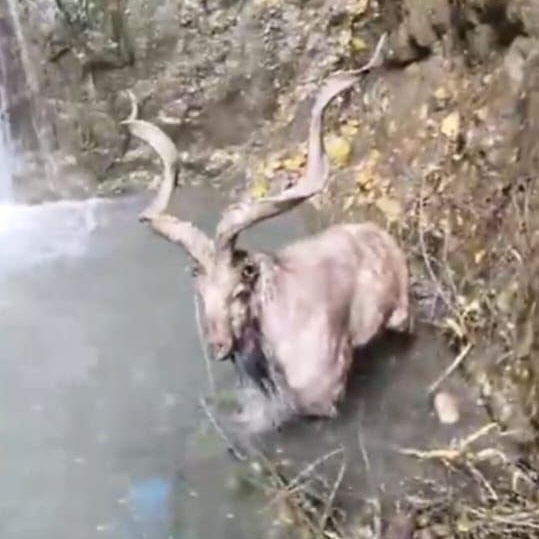

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, a Markhor, a rare wild goat with spiral-shaped horns, was spotted in Noorkha village of Boniyar in Baramulla district, North Kashmir.The animal was seen near a waterfall in Noorkha, prompting locals to alert the authorities.
Key Highlights:
- The Markhor (Capra falconeri) is a large, wild goat species native to mountainous regions in Central and South Asia, including countries such as Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, and others.
- The species is considered endangered and is listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- The Markhor population in India is concentrated in areas like Shopian, Banihal Pass, Shamsbari, and Kazinag in Jammu and Kashmir.An estimated 300 Markhors live in Kashmir's dense pine and birch forests.
- Threats and Conservation Status:
- The Markhor faces threats due to human activities and natural factors, leading to a decline in its population.
- It is classified as 'Near Threatened' on the IUCN Red List and protected under the Indian Wildlife Protection Act and the Jammu and Kashmir Wildlife Protection Act.
- Significance of the Sighting:The sighting of the Markhor has excited both villagers and wildlife enthusiasts, as these animals are not typically found outside their natural habitats, particularly near human settlements.
Kawasaki Disease
- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Comedian Munawar Faruqui recently opened up about a tough time in his life when his young son was diagnosed with Kawasaki disease.
What is Kawasaki Disease?
- Kawasaki disease is a rare condition that primarily affects children under the age of five.
- It causes inflammation in the blood vessels, including those that supply blood to the heart.
- With early treatment, most children recover without long-term health issues.
Possible Causes:
- The exact cause of Kawasaki disease is not well understood.
- Experts believe it may be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including certain infections.
Symptoms: Kawasaki disease symptoms typically appear in two phases and may last for several weeks. Common symptoms include:
- High fever lasting more than five days.
- Red eyes without discharge.
- A rash on the body, particularly in the chest and groin area.
- Swollen hands and feet, sometimes accompanied by redness.
- Red, cracked lips and a swollen, red tongue.
- Swollen lymph nodes, particularly on one side of the neck.
Detection & Treatment:
- There’s no test that can directly detect Kawasaki disease. But healthcare providers can do tests that support a diagnosis of Kawasaki disease or rule out other possible illnesses.
- Treatment for Kawasaki disease includes:Immune globulin (IVIG), or human blood proteins you receive by IV. About 10% of children may not respond to the first dose of IVIG and will need a second dose or other medications.
Community and Individual Forest Rights in Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR)

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Coimbatore District Collector, granted community and individual forest rights under the Forest Rights Act, 2006, to tribal settlements in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) on December 6, 2024.These rights were handed over to three tribal settlements and 14 families at a function in Coimbatore.
Key Highlights:
- Community Forest Rights:
- Three tribal settlements in ATR—Nagaroothu I, Nagaroothu II, and Chinnarpathi—were granted community rights.
- These rights allow the settlements to collect forest produce excluding timber, such as mango, amla, honey, tamarind, and grass for making brooms.
- Individual Forest Rights:
- Individual rights were granted to 14 families from the Old Sarkarpathy tribal settlement.
- The families had requested these rights for traditional cultivation practices passed down by their ancestors.
- The individual rights were approved after the recommendation of a sub-divisional committee and scrutiny by a district-level committee.
- About the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- Purpose: The FRA was enacted to address historical injustices faced by forest-dwelling communities and ensure their livelihood and food security.
- Key Provisions:
- Individual Rights: Self-cultivation, habitation, and in-situ rehabilitation.
- Community Rights: Access to grazing, fishing, water bodies in forests, and protection of traditional knowledge and customary rights.
- Eligibility: Rights can be claimed by any community or individual who has lived in the forest for at least three generations (75 years) before December 13, 2005.
- Critical Wildlife Habitats: The Act mandates that critical wildlife habitats in national parks and sanctuaries remain inviolate for wildlife conservation.
- Authorities Involved in Vesting Forest Rights:
- Gram Sabha: Initiates the process for determining the nature and extent of rights.
- Sub-Divisional Level Committee: Examines resolutions passed by the Gram Sabha.
- District Level Committee: Grants final approval for forest rights.
- Challenges with Forest Rights Implementation:
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- Arbitrary rejection of claims.
- Lack of deadlines for claims processing.
- Unaddressed rights of communities displaced by development projects.
- The Xaxa Committee pointed out several challenges in the implementation of the FRA, such as:
- About Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Located in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, at an altitude of 1,400 meters.
- Established as a tiger reserve in 2007, it is surrounded by multiple protected areas like the Parambikulam Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and Eravikulam National Park.
- Biodiversity in Anamalai Tiger Reserve:
- Habitats: The reserve contains wet evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, and unique habitats like montane grasslands and marshy grasslands.
- Flora: The reserve is home to around 2,500 species of angiosperms, including species like balsam, orchids, and wild relatives of cultivated crops such as mango, jackfruit, cardamom, and pepper.
- Fauna: It supports various wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, sambars, spotted deer, leopards, jackals, and jungle cats.
Sacred Groves

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Preserving India’s sacred groves can help country achieve its conservation & climate goals.
Sacred Groves in India:
- Sacred groves are forest patches that are culturally and spiritually important for various communities.
- They are known by different names across India: sarnas in Jharkhand, devgudis in Chhattisgarh, and orans in Rajasthan.
- Groves vary in size from small clusters of trees to expansive forests covering several acres.
Threats to Sacred Groves:
- Sacred groves are increasingly under threat due to deforestation, mining, and development activities.
- Many sacred groves are being displaced or degraded, putting biodiversity and cultural practices at risk.
Ecological and Cultural Importance:
- Sacred groves are rich in biodiversity and serve as important carbon sinks, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- They have been maintained by indigenous communities for centuries, creating a deep connection between people and nature.
- Sacred groves also play a crucial role in preserving indigenous spiritual practices and cultural heritage.
Contribution to Climate and Conservation Goals:
- India’s climate commitment of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 requires the protection of forests, including sacred groves.
- Sacred groves, when properly managed, can help in carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation.
- Preserving these groves can support forest conservation and foster coexistence with wildlife, ensuring a balance between development and environmental preservation.
Role of Indigenous Communities:
- Indigenous communities have long used sacred groves to regulate the use of forest resources and ensure environmental sustainability.
- Before modern ecological concepts, sacred groves were seen as natural conservation practices guided by spiritual beliefs.
- This traditional wisdom can be leveraged to enhance conservation efforts in India.
Examples of Successful Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Waghoba Grove in Maharashtra:
- Located in Chinchwadi village, the Taata chi Vanrai grove is dedicated to Waghoba, the tiger deity, and covers eight acres.
- Local communities, including the Thakars, have successfully resisted illegal timber extraction and helped conserve the grove, witnessing the return of wildlife like leopards.
- Worship of Waghoba has played a significant role in preserving forest patches and fostering human-animal coexistence.
- Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve:
- Sacred groves around the Tadoba Reserve, dedicated to Waghoba, are important in reducing human-wildlife conflicts by promoting spiritual ties with the forest.
Government and Community Efforts:
- The Jharkhand government introduced the concept of gherabandi (boundary walls) in 2019 to conserve sacred groves.
- In Chhattisgarh, the renovation of sacred groves has been undertaken to protect and restore these areas.
- Despite these efforts, challenges remain in involving local communities and integrating sacred groves into broader conservation policies.
The Role of OECMs in Sacred Grove Conservation:
- Sacred groves are considered part of Other Effective Area-Based Conservation Measures (OECMs), which are areas conserved for biodiversity outside protected regions.
- OECMs recognize the cultural, spiritual, and socio-economic value of these areas and promote sustainable conservation practices that benefit both biodiversity and local communities.
- Sacred groves play an essential role in achieving long-term biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services.
World’s Oldest Wild Bird Lays Egg at 74 in Hawaii

- 08 Dec 2024
In News:
Wisdom, the world’s oldest known wild bird, a Laysan albatross, has laid her estimated 60th egg at the age of 74. This remarkable event occurred at the Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge in the Pacific Ocean, part of the Hawaiian Archipelago.
Background on Wisdom and Laysan Albatrosses
Wisdom, first banded as an adult in 1956, has been a part of the albatross population in the Pacific for decades. Laysan albatrosses are known for their strong migratory habits and lifelong pair bonding.
The Life Cycle of the Laysan Albatross
The egg incubation process for Laysan albatrosses is shared between both parents and lasts around seven months. Once the chick hatches, it takes five to six months to develop before it is ready to take its first flight over the ocean. These seabirds, which predominantly feed on squid and fish eggs, spend the majority of their lives soaring across the open seas.
Wisdom’s longevity and success in raising up to 30 chicks over her lifetime have been notable achievements. While Laysan albatrosses typically live up to 68 years, Wisdom’s age surpasses this average by several years.
About the Laysan Albatross
The Laysan albatross (Phoebastriaimmutabilis) is a large seabird found across the North Pacific. The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands host nearly the entire population of Laysan albatrosses, with most breeding pairs found on islands like Laysan and Midway Atoll. These birds are known for their long-distance soaring capabilities, with some covering hundreds of miles a day without flapping their wings.
Laysan albatrosses have blackish-brown upper wings and backs, with flashes of white in their primary feathers. They are monogamous, forming lifelong bonds with a single mate. Despite their impressive flying ability and vast range, their population is currently listed as "Near Threatened" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Development Initiatives for North East Region (NER)

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) was announced as a new Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding in the Union Budget 2022-23 with initial outlay of Rs.1500 crore.
PM-DevINE Scheme:
- Launched in 2022 as a Central Sector scheme, with 100% Central funding.
- Initial outlay: Rs. 1500 crore in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- Total outlay: Rs. 6600 crore for the period from FY 2022-23 to FY 2025-2026, approved by the Union Cabinet on 12 October 2022.
- Objectives:
- Fund infrastructure projects in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti.
- Support social development projects tailored to the felt needs of the NER.
- Enable livelihood opportunities for youth and women.
- Address development gaps in various sectors.
- 35 projects worth Rs. 4857.11 crore have been sanctioned under the scheme up to 30 November 2024, including 7 projects from the Union Budget 2022-23.
Industrialization Initiatives:
- North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS):
- Launched on 1 April 2017, ended on 31 March 2022.
- Aimed at promoting industrialization in the NER.
- UNNATI Scheme:
- Launched on 9 March 2024 for enhancing regional infrastructure and promoting industrial growth.
- Provides specific incentives to industries, including:
- Capital Investment Incentive.
- Capital Interest Subvention.
- Manufacturing & Services Linked Incentive.
Budgetary Allocation for NER Development:
- Non-exempt Union Ministries/Departments are mandated to allocate at least 10% of their annual Gross Budgetary Allocation towards NER development.
- Between 2019-20 and 2023-24, these Ministries/Departments have incurred Rs. 3,53,412 crore towards the development of NER.
Role of State Governments and Central Support:The Government of India supplements state efforts with various schemes to promote industrialization and infrastructure development in the NER.
The PM-DevINE scheme, along with initiatives like UNNATI and the allocation of substantial funds by the central government, aims to accelerate the holistic development of NER. These efforts focus on infrastructure, social development, and industrialization, with specific emphasis on youth and women empowerment, ensuring long-term growth and prosperity for the region.
China Plus OneStrategy

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
India had ‘limited success’ in capturing ‘China Plus One’ opportunity.
Limited Success in ‘China Plus One’ Strategy:
- India has had limited success in attracting multinational companies looking to diversify their supply chains under the ‘China Plus One’ strategy, aimed at reducing dependence on China.
- Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Malaysia have been more successful in benefiting from this shift due to factors like lower labor costs, simplified tax laws, and proactive Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
Geopolitical Context - US-China Trade Conflict:
- The fresh US-China trade conflict involves tit-for-tat restrictions, with the US imposing export controls on Chinese high-tech goods and China retaliating by banning key materials.
- India's Position: As a "connecting economy" not directly aligned with the US or China, India stands to benefit from trade diversions arising from this conflict.
Opportunities for India Amid Trade Diversion:
- NITI Aayog CEO BVR Subrahmanyam highlighted opportunities arising from trade diversion, particularly due to US trade policies under President-elect Donald Trump, which could potentially create an economic boom for India.
- India has opportunities to capture a larger share of the global trade, especially in sectors where it currently holds a small market share (less than 1% of world trade in many areas).
Trade Policy Challenges:
- Steel Import Duty Proposal: NITI Aayog Vice Chairperson cautioned against imposing high duties on steel imports, arguing that it could reduce India’s competitiveness and lead to negative consequences for domestic industries reliant on steel.
- The global steel market has been affected by oversupply from China, with India’s iron and steel exports experiencing a sharp decline in Q1 FY25 due to weak domestic demand.
Impact of US Tariffs:
- A general 10% tariff on all imports by the US would not have a major negative impact on India.
- However, a 60% tariff on China could open significant opportunities for India, especially in sectors where it competes directly with China. There might be short-term shocks but long-term benefits.
Ongoing Trade Fragmentation:
- The report noted that trade fragmentation is driven by strict export controls on Chinese goods, implemented by the US to curb China’s growth, particularly in high-tech sectors.
Sectoral Competitiveness:
- While China remains India's key competitor across most export sectors, countries like Brazil, Indonesia, and South Africa generally lag behind India.
- Malaysia and Thailand outperform India in select sectors such as electrical machinery.
Challenges in the EU Market - Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- Iron and steel industry facehigh exposure under the CBAM for EU exports, with tariffs potentially rising by 20-35% due to carbon emissions-related regulations.
- Indian firms could experience higher compliance costs due to the requirement for detailed emissions reporting, impacting competitiveness in the European market.
‘Anna Chakra’ and SCAN Portal

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and New & Renewable Energy, launched ‘Anna Chakra’, the Public Distribution System (PDS) Supply chain optimisation tool and SCAN (Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA) portal a significant step towards modernizing the Public Distribution System and subsidy claim mechanisms of the States.
Anna Chakra: PDS Supply Chain Optimization Tool
- Purpose: A tool developed to enhance the efficiency of PDS logistics across India, optimizing food grain transportation.
- Collaboration: Developed by the Department of Food and Public Distribution, in collaboration with the World Food Programme (WFP) and IIT-Delhi’s Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT).
- Functionality: Uses advanced algorithms to identify optimal transportation routes for food grains.
- Key Features:
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: Achieves annual savings of Rs 250 crores by reducing fuel consumption, time, and logistics costs.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces transportation-related emissions by cutting transportation distance by 15-50%, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
- Wide Coverage: Impacts 30 states, 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops (FPS), and 6,700 warehouses in the PDS supply chain.
- Technology Integration: Linked with the Freight Operations Information System (FOIS) of Railways and PM Gati Shakti platform, enabling geo-location mapping of FPS and warehouses.
SCAN Portal: Subsidy Claim Application for NFSA
- Objective: To streamline the subsidy claim process under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) 2013, ensuring better utilization of funds.
- Functionality: Provides a unified platform for states to submit food subsidy claims, reducing administrative complexity and delays.
- Key Features:
- Single Window Submission: Simplifies subsidy claim submission for states, enhancing coordination.
- Automated Workflow: End-to-end automation ensures efficiency, transparency, and faster settlements.
- Rule-Based Processing: Claims are scrutinized and approved through a rule-based system, speeding up the approval process.
Public Distribution System (PDS) Overview
- Purpose: Ensures food security by providing subsidized food grains to vulnerable populations under the NFSA, benefitting nearly 80 crore people.
- Management: A joint effort between the Central and State/UT Governments. The Food Corporation of India (FCI) handles procurement and transportation, while state governments manage local distribution.
- Commodities: Primarily wheat, rice, sugar, and kerosene, with some states also distributing pulses and edible oils.
Initiatives to Reform PDS in India
- One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC):
- Goal: To allow portability of ration cards, benefiting migrant workers and seasonal laborers.
- Features: Biometric authentication, digital payments, and enhanced inclusivity.
- SMART-PDS Scheme (2023-2026):
- Objective: To upgrade technology in PDS, including computerized FPS, point-of-sale (POS) machines, and GPS tracking for transparency and fraud reduction.
- Aadhaar and Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- Purpose: Ensures proper beneficiary identification and cash transfers, allowing beneficiaries to purchase grains from the open market.
- Technology and Transparency Enhancements:
- GPS and SMS Monitoring: Ensures the proper delivery of food grains to FPS and provides citizens with updates via SMS.
PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
Union Minister for Education, launched the PMeVIDYA DTH 24x7 Channel No. 31 dedicated to Indian Sign Language (ISL) on December 6, 2024, in New Delhi.
Channel Purpose and Vision:
- Objective: To bridge the communication gap between the hearing-impaired and hearing populations by promoting ISL.
- Significance: Channel 31 aims to unlock talent and ensure equal opportunities for all, making society more inclusive and progressive.
- ISL's Role: Pradhan emphasized the importance of alternative communication methods like ISL, which ensures that individuals with hearing impairments have equal access to education, employment, and societal participation.
Government's Focus on Inclusivity:
- Legal Framework: Pradhan highlighted the expansion of recognized disabilities from 7 to 21, making the legal framework more comprehensive.
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The policy focuses on inclusive education, with particular attention to Children with Special Needs (CwSN). The NEP promotes the standardization of ISL and its inclusion in educational curricula.
- Employment and Cultural Expression: ISL is not only essential for communication but also contributes to cultural expressions like dance and drama. Pradhan emphasized that learning ISL would open employment opportunities and allow individuals to express themselves fully.
Importance of Channel 31:
- The launch of Channel 31 aligns with India’s commitment to ensuring equal rights and access to education, as enshrined in the Constitution.
- Pradhan urged for widespread adoption of ISL, ensuring that more people learn the language to better support the hearing-impaired community.
PM e-Vidya Initiative:
- Launch Date: PM e-Vidya was launched as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan on May 17, 2020, to bridge the digital divide and ensure inclusive education.
- Key Components:
- DIKSHA: A national platform providing e-content for all grades.
- DTH TV Channels: Initially started with 12 channels, now expanded to 200, offering supplementary education in multiple languages.
- SWAYAM: A platform for online courses and MOOCs for both school and higher education.
- Community Radio & Podcasts: These platforms are used for wider educational outreach, especially in rural and remote areas.
- e-Content for Teachers: Interactive videos and resources aimed at enhancing teacher education.
Channel Content:
- Channel 31 will provide 24x7 educational content for children with hearing impairments, teachers, and other stakeholders.
- The content will include school curricula, career guidance, skill training, mental health support, and promotion of ISL as a subject.
- The content will be available on YouTube, increasing its reach and accessibility.
RBI Cuts CRR, Keeps Repo Rate Unchanged

- 07 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently made significant monetary policy decisions that could have a broad impact on the economy.
Key Highlights:
Cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- CRR Reduction: The RBI has reduced the CRR by 50 basis points (bps), from 4.5% to 4%.
- Impact on Banks: This move will free up ?1.16 lakh crore in liquidity, which banks can use to lend, boosting the credit flow in the economy.
- Objective: The CRR cut is aimed at easing the liquidity stress in the financial system, which has been tightening due to RBI's foreign exchange interventions.
- Bank Benefits: Banks will benefit as they don’t earn interest on the CRR, and the extra liquidity may help them reduce deposit rates. Additionally, it may encourage banks to pass on benefits to borrowers, particularly in terms of lending rates.
Repo Rate Kept Unchanged at 6.5%
- Decision: The MPC decided to keep the key policy rate, the Repo rate, unchanged at 6.5%, continuing its stance for the 11th consecutive meeting.
- Reasons for Keeping Repo Rate Steady:
- Persistent inflation, particularly food prices, is a key concern. Despite strong growth in sectors like rural consumption, inflation remains high and continues to affect disposable income.
- RBI Governor emphasized that durable price stability is essential for strong, sustained economic growth.
Impact on Borrowers
- Borrowing Costs: With the Repo rate unchanged, external benchmark lending rates (EBLR) linked to the Repo rate will not rise, providing relief to borrowers by keeping Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) stable.
- Deposit Rates: However, the CRR cut may lead to a marginal reduction in deposit rates due to increased liquidity in the system.
Economic Growth Forecast Adjusted
- Reduced GDP Growth Estimate: The RBI has downgraded the GDP growth forecast for FY25 to 6.6%, down from the earlier estimate of 7.2%. This revision comes after the economy showed signs of slowdown in the second quarter of FY25.
- Growth Outlook: Despite the downgrade, the RBI remains cautiously optimistic about recovery driven by festive demand and rural consumption. Governor Das indicated that the slowdown had likely bottomed out and the economy is set to recover in the coming quarters.
Inflation Forecast Raised
- Inflation Outlook: The inflation estimate for FY25 has been revised upward to 4.8%, compared to the earlier forecast of 4.5%. This is largely due to rising food prices, which surged to a 14-month high of 6.21% in October.
- Inflationary Pressures: The MPC noted that inflation has remained above the RBI’s target of 4%, primarily driven by food inflation. As inflation impacts consumption, the RBI aims to balance growth support with inflation management.
Monetary Policy Stance
- Neutral Stance Retained: The RBI has maintained a ‘neutral’ stance, meaning it is neither tightening nor easing monetary policy drastically, focusing instead on bringing inflation closer to its target of 4%.
- Inflation Control: While the RBI is aware of the economic slowdown, it continues to prioritize inflation control to ensure price stability and support sustainable growth.
Global and Domestic Economic Context
- Global Factors: The RBI has also been cautious about global developments, including capital outflows and the impact of U.S. monetary policy on the Indian economy. A rate cut could have further weakened the rupee by narrowing the interest rate differential with the U.S.
- Domestic Concerns: Domestically, the economy faces challenges such as weak manufacturing growth and high inflation. The GDP growth in Q2 FY25 dropped to 5.4%, a seven-quarter low, highlighting concerns over demand and inflationary pressures.
BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
In a significant move, the Indian Parliament passed the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024 on December 5, 2024, bringing much-needed reforms to the aviation sector. The Bill, which replaces the Aircraft Act of 1934, aims to streamline aviation regulations and improve the ease of doing business in the industry.
Key Highlights of the BharatiyaVayuyanVidheyak Bill, 2024:
- Single-Window Clearance for Aviation Personnel: One of the major changes is the transfer of responsibility for the Radio Telephone Operator Restricted (RTR) certification from the Department of Telecom (DoT) to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA). This move consolidates the certification process under a single authority, making it easier for aviation personnel like pilots, engineers, and flight dispatchers to obtain their licenses.
- Regulation of Aircraft Design: The Bill not only retains provisions for regulating aircraft manufacturing, maintenance, and repair, but also introduces new provisions to regulate aircraft design and the places where aircraft are designed.
- Enhanced Penalties for Violations: The Bill specifies severe penalties for violations, such as dangerous flying, carrying prohibited items (like arms or explosives), or littering near airports. Offenders may face imprisonment up to three years, fines up to ?1 crore, or both.
- Introduction of Second Appeal Mechanism: For the first time, the Bill introduces a second appeal process against decisions of regulatory bodies like the DGCA and BCAS, ensuring further scrutiny of decisions related to penalties.
- Improved Licensing Process: The shift of the RTR certification process from the DoT to DGCA aims to curb allegations of corruption associated with the previous system, where candidates often had to pay bribes to clear exams.
Organizational Setup and Authorities:
The Bill outlines the establishment of three key authorities under the Ministry of Civil Aviation:
- DGCA: Responsible for civil aviation safety, licensing, and ensuring compliance with international standards.
- BCAS: Ensures aviation security and develops relevant security measures.
- AAIB: Investigates aviation accidents and incidents.
The central government retains supervision over these bodies, with the power to modify or review their orders.
Criticisms and Concerns:
- Lack of Autonomy for DGCA: The DGCA, unlike independent regulators in other sectors (such as telecom or insurance), operates under direct government supervision. The lack of clear qualifications, selection process, and tenure for the DGCA Director General has raised concerns about the regulator's independence.
- Unilateral Appointment of Arbitrators: The Bill empowers the government to unilaterally appoint an arbitrator in certain cases, which has been criticized for potentially violating the right to equality under Article 14 of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has previously ruled that such unilateral appointments may be unconstitutional.
- Discretionary Criminal Penalties: The central government is granted the discretion to impose criminal penalties for rule violations, which some argue could undermine the principle of separation of powers, as it is the legislature's role to define criminal offenses and penalties.
- Exclusionary Hindi Title: Some critics argue that the Hindi title of the Bill may alienate non-Hindi-speaking populations, which make up a significant portion of India’s demographic.
Hornbill Festival

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The Hornbill Festival, a vibrant celebration of Nagaland's culture and tourism, is an annual event that takes place from December 1 to 10.
About the Hornbill Festival:
- Origin: First held in the year 2000.
- Purpose: The festival aims to foster inter-tribal communication, preserve the cultural heritage of Nagaland, and showcase the harmonious blending of traditional and modern elements.
- Significance: Referred to as the “festival of festivals,” it has become an essential part of the state’s cultural calendar.
- Organizers: It is organized by the Tourism and Art & Culture Departments of the Government of Nagaland.
- Location: The festival takes place annually at the Naga Heritage Village in Kisama, located about 12 kilometers from Kohima.
- Cultural Showcase: Over the years, it has evolved into a significant celebration that highlights the vibrant and diverse cultural traditions of the various tribes in Nagaland.
- Name Origin: The festival is named after the Hornbill bird, which holds cultural importance among the Naga tribes.
- Theme of the 2024 Hornbill Festival:The 2024 edition is themed “Cultural Connect,” celebrating the rich heritage and cultural diversity of Nagaland. The festival continues to merge modernity and tradition through a variety of activities, including Naga wrestling, traditional archery, food stalls, fashion shows, beauty contests, and musical performances. Additionally, the Archives Branch is presenting a special exhibition titled “Naga-Land & People in Archival Mirror” in partnership with the National Archives of India, offering a deeper look at the region's history and cultural practices.
- Recent Milestone:This year marks the 25th anniversary of the Hornbill Festival.
Festival Highlights:
- Annual Event: Held each year since its inception in 2000, it serves as a major cultural event for Nagaland.
- Symbolism: Named after the Hornbill bird, which represents boldness and grandeur in Naga folklore.
- Location: The festival is hosted at Kisama Heritage Village, a cultural center that preserves Naga traditions with 17 indigenous houses (Morungs) that represent each of the tribes.
- Cultural Diversity: Nagaland, known as the “Land of Festivals,” is home to 17 major tribes, each with its distinct festivals and cultural practices. The Hornbill Festival promotes inter-tribal interaction and celebrates the state’s rich heritage.
- National Significance: Reflecting India’s unity in diversity, the festival serves as a platform for different cultural practices to coexist, strengthening the nation’s collective identity.
India and Slovenia Announce Five-Year Collaboration Plan
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
India and Slovenia have announced a five-year scientific collaboration plan (2024-2029) to deepen ties in research and technology. The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) was finalized during a meeting between Dr. Jitendra Singh (Indian Minister for Science and Technology) and Dr. Igor Papi? (Slovenian Minister for Higher Education, Science, and Innovation) on December 5, 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Joint Research Focus: The collaboration will focus on hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, AI, renewable energy, and smart cities.
- Over 20 Successful Projects: More than 20 joint initiatives in sectors like health, AI, and energy have already been implemented.
- Future Areas of Collaboration: New research projects will be launched, further strengthening academic exchanges and scientific networks between the countries.
- Hydrogen Technologies: Both ministers emphasized hydrogen's role in global energy sustainability, marking it as a critical area for future research.
- Historical Partnership: This builds on a partnership dating back to a 1995 agreement, with initiatives like the Joint Working Group on Scientific and Technological Cooperation.
What is the Programme of Cooperation (PoC)?
- The Programme of Cooperation (PoC) is a formal agreement between two countries designed to enhance collaboration in specific sectors, such as science, technology, and innovation.
- In the case of India and Slovenia, the PoC for the period 2024–2029 aims to promote joint research efforts, academic exchanges, and partnerships in emerging fields like hydrogen technologies, sustainable innovation, and other transformative areas.
- The PoC serves as a structured framework for long-term cooperation, enabling both nations to develop networks among scientists and researchers while addressing global challenges through collaborative innovation.
PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana

- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, the world’s largest domestic rooftop solar initiative, is transforming India’s energy landscape with a bold vision to supply solar power to one crore households by March 2027.
Key Details:
Targeted Installations:
- 10 lakh installations by March 2025.
- 1 crore installations by March 2027.
Subsidy and Financing:
- Offers up to 40% subsidy for rooftop solar installations based on household electricity consumption.
- Collateral-free loans available for up to 3 kW solar systems at a 7% interest rate.
Key Benefits:
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana offers several significant benefits to participating households:
- Free Electricity for Households: The scheme provides households with free electricity through the installation of subsidized rooftop solar panels, significantly reducing their energy costs.
- Reduced Electricity Costs for the Government: By promoting the widespread use of solar power, the scheme is expected to save the government an estimated ?75,000 crore annually in electricity costs.
- Increased Use of Renewable Energy: The scheme encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy mix in India.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: The transition to solar energy under this scheme will help lower carbon emissions, supporting India's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Eligibility Criteria:
1. The applicant must be an Indian citizen.
2. Must own a house with a roof that is suitable for installing solar panels.
3. The household must have a valid electricity connection.
4. The household must not have availed of any other subsidy for solar panels.
Impact
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana is expected to have far-reaching outcomes, both for individual households and the nation as a whole:
- Household Savings and Income Generation: Households will benefit from significant savings on their electricity bills. Additionally, they will have the opportunity to earn extra income by selling surplus power generated by their rooftop solar systems to DISCOMs. For instance, a 3-kW system can generate over 300 units per month on average, providing a reliable source of energy and potential revenue.
- Expansion of Solar Capacity: The scheme is projected to add 30 GW of solar capacity through rooftop installations in the residential sector, significantly contributing to India's renewable energy goals.
- Environmental Benefits: Over the 25-year lifetime of these rooftop systems, it is estimated that the scheme will generate 1000 BUs of electricity while reducing CO2 emissions by 720 million tonnes, making a substantial positive impact on the environment.
- Job Creation: The scheme is also expected to create approximately 17 lakh direct jobs across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, supply chain, sales, installation, operations and maintenance (O&M), and other services, thereby boosting employment and economic growth in the country.
Model Solar Village
- Under the "Model Solar Village" component of the scheme, the focus is on establishing one Model Solar Village per district throughout India.
- This initiative aims to promote solar energy adoption and empower village communities to achieve energy self-reliance.
- An allocation of ?800 crore has been designated for this component, with ?1 crore provided to each selected Model Solar Village.
- To qualify as a candidate village, it must be a revenue village with a population of over 5,000 (or 2,000 in special category states). Villages are selected through a competitive process, evaluated on their overall distributed renewable energy (RE) capacity six months after being identified by the District Level Committee (DLC).
- The village in each district with the highest RE capacity will receive a central financial assistance grant of ?1 crore.
- The State/UT Renewable Energy Development Agency, under the supervision of the DLC, will oversee the implementation, ensuring these model villages successfully transition to solar energy and set a benchmark for others across the country.
RangeenMachli App
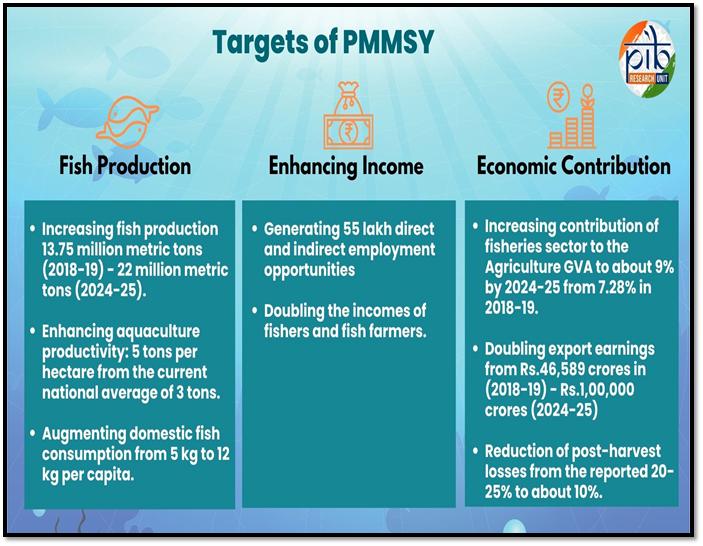
- 06 Dec 2024
In News:
The app was developed by the ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA) with support from the Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY) under the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India.
Key Highlights:
- Target Audience: The app caters to hobbyists, farmers, and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Multilingual Support: The app offers content in eight Indian languages, making it accessible to a broad and diverse audience.
- Main Objectives:
- Provide information on popular ornamental fish species and their care.
- Promote local aquarium businesses through dynamic directories.
- Enhance knowledge of ornamental aquaculture techniques for fish farmers and shop owners.
- Serve as an educational tool for newcomers and professionals in the ornamental fish industry.
- Salient Features:
- Multilingual Content: Ensures broader reach and user accessibility.
- Comprehensive Fish Information: Offers detailed guidance on fish care, breeding, and maintenance.
- Find Aquarium Shops Tool: A directory updated by shop owners, helping users find reliable local aquarium shops and promoting local businesses.
- Educational Modules:
- Basics of Aquarium Care: Covers key aspects like aquarium types, filtration, lighting, feeding, and maintenance.
- Ornamental Aquaculture: Focuses on breeding and rearing ornamental fish, particularly for farmers.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Promoting Local Businesses: The app encourages economic growth by increasing visibility for local aquarium shops and creating opportunities for business owners.
- Authenticity and Reliability: Users can access verified information, reducing the reliance on unverified sources and promoting healthier aquariums.
- Sustainability and Growth: The app’s features are designed to foster sustainability and growth in the ornamental fish trade by providing reliable information and empowering users.
Pradhan Mantri MatsyaSampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- Objective: Aimed at transforming the fisheries sector, improving fish production, productivity, quality, technology, infrastructure, and management, while strengthening the value chain and promoting the welfare of fishers.
- Launch: The scheme was launched in 2020 with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores for a 5-year period (2020-21 to 2024-25).
- Focus Areas:
- Inland fisheries and aquaculture.
- Fisheries management and regulatory framework.
- Infrastructure and post-harvest management.
- Doubling fishers' and fish farmers' incomes.
- Components:
- Central Sector Scheme (CS): Fully funded by the central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS): Partially funded by the central government and implemented by states.
- Sub-Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri MatsyaKisanSamridhiSah-Yojana (PM-MKSSY): Launched under PMMSY to formalize the fisheries sector and support micro and small enterprises with over Rs. 6,000 crore investment (FY 2023-24 to 2026-27).
- Beneficiaries: Includes fishers, farmers, fish vendors, fisheries cooperatives, SC/STs, women, differently-abled persons, state and central entities, and private firms.
Fisheries Sector Contribution:
- Supports around 30 million people.
- India is the 3rd largest fish producer globally, with a fish production of 175.45 lakh tons in FY 2022-23.
- Contributes 1.09% to the Gross Value Added (GVA) of India and 6.72% to agricultural GVA.
Related Schemes:
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF): Launched with a fund of Rs. 7,522.48 crore.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Extended to fishers and farmers from FY 2018-19.
- Sustainable fisheries development.
- Doubling income and job creation in the sector.
- Boosting exports and agricultural GVA.
- Social and economic security for fishers.
Trade Watch Quarterly
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
NITI Aayog released its first quarterly report, Trade Watch Quarterly (TWQ), on December 4, 2024, focusing on India's trade developments during Q1 FY2024 (April-June).
Overview:
- Purpose: The publication aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of India’s trade performance, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Target: To leverage insights for evidence-based policy interventions and foster informed decision-making, contributing to sustainable growth in India’s trade.
Trade Performance Highlights (Q1 FY24):
- Total Trade: $576 billion (5.45% YoY growth).
- Merchandise Exports: Growth was restrained due to declines in iron & steel, and pearls.
- Imports: Driven by high-value goods, including aircraft, spacecraft, mineral fuels, and vegetable oils.
- Services Exports: Displayed a surplus, particularly in IT services.
- Growth in Services Exports: A positive trend, rising by 10.09% YoY, particularly in IT services and business solutions.
Key Challenges for India’s Trade:
- Limited Success in China-Plus-One Strategy:Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia have gained more from this strategy, benefitting from cheaper labor, simplified tax laws, and lower tariffs.
- CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism):Starting in 2026, CBAM will impose carbon taxes on imports like cement, steel, and fertilizers. India’s iron and steel industry could face significant risks due to this.
- Declining Share in Labor-Intensive Sectors:India’s global market share in labor-intensive sectors (e.g., textiles, leather) has declined despite a strong workforce.
- Geopolitical Instability (West Asia):
- Oil price hikes could increase India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD) and fuel inflation.
- Declining agricultural exports to markets like Iran further add to the challenges.
Strategic Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges:
- Infrastructure Modernization:
- Expansion of digital platforms like Trade Connect e-Platform to streamline processes and support exporters.
- Strengthening logistics via the National Logistics Policy.
- Export Incentives:Continuation of schemes like RoDTEP (Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products) to maintain export competitiveness.
- Technological Integration:Leveraging digital trade to tap into high-growth sectors and foster innovation in trade.
- Strengthening FTAs (Free Trade Agreements):Focus on negotiating strategic FTAs with global partners (e.g., the UK and the EU) to reduce trade barriers and enhance global market access.
Geopolitical and Environmental Risks:
- U.S.-China Trade Tensions:Offers opportunities for India to diversify its supply chains, but also poses challenges in terms of overdependence on certain countries.
- Impact of CBAM:Risk to carbon-intensive Indian exports like steel and aluminium, which will face tariffs starting in 2026.
Sectoral Performance:
- Growing Sectors:
- IT Services: India’s market share of IT services reached 10.2%, continuing to be a strong contributor.
- Pharmaceuticals, Electrical Machinery, and Mineral Fuels: Significant contributors to export growth.
- Declining Sectors:Labor-Intensive Goods: Declines in global market share for textiles, pearls, and leather.
Pathway to $2 Trillion Exports by 2030:
- India's Export Aspirations:To achieve the target of $2 trillion in exports by 2030, India must address structural inefficiencies, diversify exports, and reduce trade barriers.
- Vision 2047:Aligning with India’s broader vision to become a developed nation, the report stresses the importance of strengthening trade, technology, and infrastructure to realize these ambitions.
- Trade's Role in Economic Growth:
- Trade is vital to India’s economic trajectory, contributing significantly to GDP growth.
- Through evidence-based policymaking, infrastructure modernization, and strategic global partnerships, India can achieve sustained growth in trade, leading to the realization of a Viksit Bharat (Developed India) by 2047.
Heat Shock Protein 70
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
JNU scientists make big discovery that could change malaria, Covid-19 treatment.
Overview of the Discovery:
- Institution: Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU), Special Centre for Molecular Medicine.
- Key Discovery: Identification of human protein Hsp70 as a critical factor in the spread of malaria and COVID-19.
- Research Collaboration: Involvement of Indian and Russian researchers.
- Outcome: Development of a small molecule inhibitor of Hsp70 that could act as a broad-spectrum treatment for multiple infections.
About Heat Shock Protein 70 (Hsp70):
- Definition: Hsp70 is a type of molecular chaperone protein.
- Function:
- Helps other proteins fold into their proper shapes.
- Prevents protein misfolding.
- Regulates protein synthesis and protects proteins from stress.
- Elevates during cellular stress to shield cells from damage.
- Role in Cellular Processes:
- Prevents protein aggregation and assists in protein transport across membranes.
- Plays a critical role in protein homeostasis and cell survival during stress conditions.
Hsp70's Role in Disease Spread:
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Interaction:
- Hsp70 interacts with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and human ACE2 receptors.
- Facilitates viral entry into human cells by stabilizing this interaction during fever (when Hsp70 levels rise).
- Malaria:Pathogens like malaria parasites rely on the host's machinery for survival, including Hsp70.
Research Findings and Implications:
- Published in: International Journal for Biological Macromolecules.
- Inhibition of Hsp70:
- Targeting Hsp70 can disrupt viral replication.
- In lab tests, Hsp70 inhibitor (PES-Cl) blocked SARS-CoV-2 replication at low doses.
- Potential for Broad-Spectrum Treatment:
- Hsp70 could be a target for treating multiple infections, not limited to COVID-19 or malaria.
- Prevention of Drug Resistance:
- Host-targeting antivirals are less prone to resistance as the virus cannot mutate the host protein (Hsp70).
- This approach could be especially beneficial for combating rapidly evolving viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (e.g., Omicron).
Host-Targeting Approach vs. Traditional Drugs:
- Host-Targeting: Targets the host cell machinery (e.g., Hsp70) rather than the virus itself.
- Reduces the likelihood of viral mutation-induced resistance.
- Traditional Drugs: Target the virus directly, which can lead to resistance, especially with rapidly mutating viruses.
Global Health and Pandemic Preparedness:
- Universal Tool for Infectious Diseases: The discovery could serve as a universal tool for managing infections during health emergencies.
- Collaboration and Importance: Highlights the significance of international collaboration in addressing global health challenges (e.g., Dr. Pramod Garg of AIIMS, Ph.D. scholar Prerna Joshi).
- Future Implications:Preparation for future pandemics, as the world must remain vigilant even post-COVID-19.
Donald Trump's Threat on BRICS and US Dollar

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
- US President-elect Donald Trump threatens BRICS countries (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) with 100% import tariffs if they create a new currency or support an alternative to the US dollar as the global reserve currency.
- Trump emphasizes that attempts to undermine the US dollar’s dominance will face economic retaliation, asserting the US economy won’t tolerate such moves.
Background
- Weaponization of the Dollar: The US has increasingly used its financial influence to impose sanctions (e.g., Russia, Iran) and cut off countries from systems like SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication).
- Concerns: Countries are concerned about their vulnerability to US monetary policies, which can have global impacts (e.g., rising US interest rates causing economic instability in other countries).
Efforts to Reduce Dependence on the US Dollar
- BRICS Countries’ Initiatives:
- Russian President Putin criticizes the weaponization of the dollar.
- Brazil's President Lula advocates for a new BRICS currency to increase payment options and reduce vulnerabilities.
- India's Steps:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows invoicing and payments in Indian rupees for international trade (since 2022), particularly with Russia.
- Prime Minister Modi supports increasing financial integration and cross-border trade in local currencies within BRICS.
- External Affairs Minister Jaishankar emphasizes the importance of mutual trade settlements in national currencies.
- China-Russia Trade: Over 90% of trade between Russia and China is settled in rubles and yuan due to their more balanced trade relations.
Internationalization of the Indian Rupee
- RBI's Role:
- In July 2022, RBI allowed export/import settlements in rupees, starting with Russia in December 2022.
- More than 19 countries, including the UK and UAE, have agreed to settle trade in rupees.
- Challenges:
- The Indian rupee currently accounts for only 1.6% of global forex turnover.
- India’s trade imbalance with Russia limits the effective use of rupee reserves.
- Indian banks are cautious due to the risk of US sanctions.
Global Trends in Currency Diversification
- Multipolarity in Finance: Emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil are advocating for a more decentralized financial system, moving away from US dominance.
- Declining Dollar Share: The US dollar’s share of global reserves is gradually decreasing, with non-traditional currencies like the Chinese yuan gaining ground.
Risks of Moving Away from the US Dollar
- Chinese Dominance: Concerns about increasing Chinese economic influence, especially within BRICS, as China pushes for more use of the yuan in trade.
- Liquidity and Volatility Issues: Alternatives to the dollar may face challenges like lower liquidity and increased exchange rate volatility.
- Implementation Challenges: Countries, especially those with trade imbalances, find it difficult to adopt local currencies for international trade.
Potential Impact of 100% US Tariff on BRICS Imports
- Global Trade Dynamics: A blanket tariff would likely encourage deeper intra-BRICS trade and accelerate the move towards de-dollarization.
- Impact on the US: Higher import costs for American consumers and potential trade diversification to third countries could hurt the US economy without revitalizing domestic manufacturing.
- Retaliation: BRICS countries might retaliate with tariffs on US goods, escalating trade tensions.
India’s Strategic Approach
- Diplomatic Engagement: India should clarify to the US that diversifying trade mechanisms is not anti-American but seeks financial stability and multipolarity.
- Leadership Role in BRICS: India should support financial reforms within BRICS that align with its interests while maintaining strong ties with the US.
- Promotion of Digital Currency: India should accelerate its Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and strengthen international platforms like UPI to enhance its global financial presence.
International Debt Report 2024
- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently released, World Bank’s "International Debt Report 2024" highlights a worsening debt crisis for developing nations, with 2023 marking the highest debt servicing levels in two decades, driven by rising interest rates and economic challenges.
Key Highlights:
Rising Debt Levels:
- Total external debt of low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) reached $8.8 trillion by the end of 2023, an 8% increase since 2020.
- For IDA-eligible countries (those receiving concessional loans from the World Bank), external debt rose by 18%, reaching $1.1 trillion.
Debt Servicing Costs:
- Developing nations paid a record $1.4 trillion in debt servicing costs (principal and interest) in 2023.
- Interest payments surged by 33%, totaling $406 billion, putting immense pressure on national budgets, especially in critical sectors like health, education, and environmental sustainability.
Interest Rate Increases:
- Interest rates on loans from official creditors doubled to 4% in 2023.
- Rates from private creditors rose to 6%, the highest in 15 years, exacerbating the financial burden on developing countries.
Impact on IDA-Eligible Countries:
- IDA countries faced severe financial strain, paying $96.2 billion in debt servicing, including $34.6 billion in record-high interest costs (four times higher than a decade ago).
- On average, 6% of their export earnings were allocated to debt payments, with some countries dedicating up to 38%.
Role of Creditors:
- Private creditors reduced lending, leading to more debt-servicing payments than new loans.
- In contrast, multilateral lenders like the World Bank provided additional support, with the World Bank contributing $28.1 billion.
- Multilateral institutions have emerged as crucial support systems, becoming "lenders of last resort" for poor economies.
Debt Data Transparency:
- Efforts to improve debt transparency led to nearly 70% of IDA-eligible economies publishing accessible public-debt data in 2023, a 20-point increase since 2020.
- Accurate debt data can reduce corruption and promote sustainable investment.
Global Financial Reforms:
- There is a growing call for global financial reforms to address the systemic challenges of developing nations facing rising debt burdens.
- Proposed measures include increased concessional financing, improved restructuring mechanisms, and the establishment of a Global Debt Authority for better debt management.
Impact on Climate and Development Goals:
- Debt servicing has become a larger financial burden than climate initiatives in many countries, with developing nations spending more on debt servicing than climate goals (2.4% of GDP vs. 2.1% for climate investments).
- To meet climate commitments under the Paris Agreement, climate investments would need to rise to 6.9% of GDP by 2030.
Debt Relief Initiatives:
- Programs like the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative and the Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative (MDRI) provide debt relief to the world’s poorest nations, helping them meet Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- For instance, Somalia saved $4.5 billion in debt service after completing the HIPC program in December 2023.
Global Sovereign Debt Roundtable (GSDR):
- The GSDR brings together debtor nations and creditors (both official and private) to improve debt sustainability and address restructuring challenges.
- Co-chaired by the IMF, World Bank, and G20, the forum aims to find coordinated solutions for sovereign debt issues.
Overview of Global Plastic Treaty Negotiations

- 05 Dec 2024
In News:
The recent negotiations for a global treaty aimed at curbing plastic pollution, held in Busan, South Korea, concluded without reaching a legally binding agreement. This marked the fifth round of discussions since the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) initiated the process in March 2022, with the goal of finalizing a treaty by the end of 2024. The failure to adopt a treaty was primarily due to disagreements over production cap goals and the elimination of specific plastic chemicals and products.
Key Points of Dispute
- Production Cap Goals: A coalition of over 100 countries, including many from Africa, Latin America, and the European Union, pushed for clear production cap goals in the treaty. They argued that such measures are essential for effective regulation of plastic pollution.
- Opposition from Oil-Producing Nations: Conversely, a group of “like-minded countries” such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Russia, and Iran opposed these provisions. They contended that regulating production cuts exceeded the original mandate set by UNEA and could lead to trade restrictions disguised as environmental measures. India and China aligned with this coalition, emphasizing their concerns regarding economic impacts.
Draft Treaty Highlights
Despite the failure to finalize an agreement, discussions produced a draft text that included both consensus points and contentious issues:
- Consensus Points:
- Proposals for banning open dumping and burning of plastics.
- Definitions for various plastic types were suggested but lacked clarity on contentious terms like microplastics.
- Contentious Issues:
-
- The draft did not adequately address definitions for microplastics or recycling standards.
- References to single-use plastics were included but faced pushback from certain nations.
India’s Position
India articulated its stance focusing on several key areas:
- Development Rights: Emphasized the need for recognizing varying responsibilities among countries in managing plastic pollution while considering their developmental rights.
- Technical and Financial Support: Advocated for provisions ensuring technical assistance and financial support for developing nations to manage plastic waste effectively.
- Opposition to Production Caps: India opposed any articles that would impose caps on polymer production, arguing that such measures were not directly linked to reducing plastic pollution.
Future Steps
The negotiations will continue with plans to reconvene in 2025. In the meantime, global plastic production is projected to rise significantly, potentially tripling by 2050 if no urgent action is taken. The ongoing dialogue will need to address both environmental concerns and developmental needs to create a balanced approach toward managing plastic pollution globally.
Global Context and Initiatives
The need for a global treaty is underscored by alarming statistics:
- Over 462 million tons of plastic are produced annually, with a significant portion contributing to pollution.
- Microplastics have infiltrated ecosystems worldwide, affecting biodiversity and human health.
Countries like Rwanda and Austria have implemented successful measures to reduce plastic waste, serving as models for global efforts. Initiatives such as the UNDP Plastic Waste Management Program in India aim to enhance waste management practices while addressing environmental impacts.
SheSTEM 2024

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), under the NITI Aayog and the Office of Science & Innovation, at the Embassy of Sweden, in partnership with Nordic collaborators - Innovation Norway, Innovation Centre Denmark, and Business Finland, announced the successful conclusion of SheSTEM 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: To inspire youth, especially women, to explore careers in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) and promote innovative solutions for sustainability.
- Theme: Focus on Battery Technology and Energy Storage Systems (BEST), part of the India-Nordic BEST project, aimed at fostering sustainability through advanced energy solutions.
Key Features of the Challenge:
- Target Audience: Students from grades 6–12 across India.
- Participation: Over 1,000 submissions showcasing innovative energy storage solutions.
- Format: Students presented prototypes or concepts via a 2-minute video format.
- Focus Areas: Sustainability, energy storage, and innovative solutions to global challenges.
Significance of SheSTEM 2024:
- Youth Empowerment: Provides a platform for young innovators to showcase their ideas and contribute to global sustainability.
- Global Impact: Encourages collaboration between India and Nordic countries in academia, business, and government to explore energy storage and sustainable technologies.
- Women in STEM: Highlights the importance of gender inclusivity in STEM fields, particularly in sustainability and technology.
Key Facts about AIM (Atal Innovation Mission):
- Established: 2016 by NITI Aayog to foster innovation and entrepreneurship across India.
- Core Functions:
- Promote Entrepreneurship: Financial support, mentorship, and nurturing innovative startups.
- Promote Innovation: Creating platforms for idea generation and collaboration.
- Key Programs: Atal Tinkering Labs, Atal Incubation Centres, Atal New India Challenges, and Mentor India.
- Monitoring: Systematic monitoring of initiatives using real-time MIS systems and dashboards.
ICJ Hearing on Landmark Climate Change Case

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has begun hearings on a landmark climate change case, seeking an advisory opinion on the obligations of countries under international law regarding climate change.
- The case stems from a UN General Assembly (UNGA) resolution initiated by Vanuatu in March 2023, co-sponsored by 132 countries.
Background:
- Vanuatu, a small island nation, faces existential threats from rising sea levels.
- The resolution was passed to clarify climate obligations in light of international laws, including the UNFCCC, Paris Agreement, and other legal instruments like the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas, and the Universal Declaration on Human Rights.
Global Impact of the Case:
- The outcome of the case could influence global climate governance, particularly in the context of climate negotiations.
- It may broaden the legal basis for climate obligations and underscore the legal consequences for non-compliance.
India’s Position:
- India has voiced concerns about the judicial process being the best approach to tackle climate issues, advocating for diplomatic efforts.
- India is scheduled to make its submission on December 5, highlighting its preference for a collaborative, non-top-down approach in climate discussions.
Implications for Developed and Developing Countries:
- The case highlights the historical responsibility of developed countries for climate change due to their higher emissions.
- The ICJ's advisory opinion could reinforce the argument that developed countries' obligations extend beyond the UNFCCC and Paris Agreement, incorporating broader international legal frameworks.
Climate Litigation and Precedent:
- The ICJ ruling could set a precedent for climate litigation, potentially influencing over 2,600 ongoing climate lawsuits globally.
- Notable rulings include the European Court of Human Rights, which held Switzerland accountable for failing to meet emissions targets, and India's Supreme Court recognizing the right to be free from adverse climate impacts in 2023.
Record Participation and Importance of the Case:
- The ICJ has received over 90 written submissions, with 97 countries and 12 international organizations participating in the hearings.
- The case is significant for the growing number of climate-related lawsuits and the evolving nature of international climate law.
Future Prospects:
- The ICJ’s advisory opinion, though non-binding, could significantly impact future climate negotiations, particularly in terms of responsibility sharing and climate finance.
- The outcome could also influence calls for compensation for climate damages, especially from vulnerable states like small island nations.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
The Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, is once again in focus, albeit in a context in which its objectives are being ignored. Civil suits questioning the religious character of mosques at Varanasi and Mathura are progressing apace. These developments show that legislation freezing the status of places of worship is inadequate to stop Hindu claimants from making determined legal efforts to achieve their goal of replacing them with temples.
Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991:
- Objective: To preserve the religious character of places of worship as they existed on August 15, 1947, and prevent changes in religious identity.
- Key Provisions:
- Section 3: Prohibits conversion of a place of worship from one religion to another.
- Section 4(1): Ensures the religious character remains unchanged from August 15, 1947.
- Section 4(2): Terminates ongoing or future legal proceedings seeking to alter the religious character of a place of worship.
- Exemptions:
- Ayodhya dispute: Exempted, allowing ongoing litigation.
- Ancient monuments & archaeological sites: Not covered by the Act.
- Already settled disputes or those agreed upon before the Act came into force.
- Penalties: Violators can face up to 3 years of imprisonment or fines.
- Criticism: The Act has been challenged for limiting judicial review, imposing a retrospective cutoff date, and restricting religious rights.
Recent Legal Disputes:
- Gyanvapi Mosque (Varanasi):
- Claim: Hindu worshippers assert the right to worship deities (e.g., Ma Sringar Gauri, Lord Vishweshwar) within the mosque premises.
- Legal Basis: Claim that the mosque was built over an ancient Hindu temple.
- Court's Ruling: The court allows the case to proceed, stating that the aim is to assert worship rights, not change the mosque’s status.
- Archaeological Survey: ASI report confirms the existence of a temple before the mosque’s construction.
- Key Legal Outcome: The Places of Worship Act does not bar these suits as they aim to ascertain the religious character of the site, not alter it.
- Shahi Idgah Mosque (Mathura):
- Claim: Hindu groups assert the mosque was built over Lord Krishna’s birthplace.
- Historical Context: The dispute was settled by a compromise in 1968, which was implemented in 1974, where part of the land was given to the mosque.
- Current Legal Dispute: New suits challenge the 1968 agreement as ‘fraudulent’ and seek the entire land to be transferred to the deity.
- Court's Ruling: The Act is not applicable as the 1968 agreement predates the 1991 Act, and the dispute pertains to the compromise, not the religious character.
- Shahi Jama Masjid (Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh):
- Claim: Allegation that the mosque was built over a Hindu temple (Hari Har Mandir).
- Survey Request: Petitioners seek a survey to verify the site’s historical and religious character.
- Legal Context: The mosque is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904.
Key Legal Interpretations:
- Court’s Role: Courts have ruled that the Places of Worship Act does not prohibit suits related to the religious character of a site if they are aimed at determining, not altering, that character.
- Interpretation of ‘Religious Character’: The Allahabad High Court stated that a structure can’t have dual religious character (both Hindu and Muslim), and the religious character of a place must be determined through evidence.
Political and Social Implications:
- Ongoing Controversy: The Gyanvapi and Mathura mosque disputes continue to fuel political and religious debates, as Hindu organizations seek to assert their claims, while mosque committees and Muslim groups resist changes.
- Public and Legal Attention: The legal and political landscape surrounding the Places of Worship Act remains contentious, with several legal suits challenging its applicability.
1984 Bhopal disaster

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
Forty years after the Bhopal disaster on December 2-3, 1984, several hundred tonnes of toxic waste still remain around the ill-fated Union Carbide plant.
Overview of the incident:
The 1984 Bhopal disaster, one of the world’s worst industrial accidents, was caused by the release of methyl isocyanate (MIC) gas, which was a key component in the production of pesticides at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) plant. However, the toxic legacy of the disaster extends far beyond MIC, with a range of other harmful substances lingering in the environment. These include:
- Methyl Isocyanate (MIC):Primary toxic agent: MIC is a highly toxic, volatile compound. Exposure can cause severe respiratory distress, eye irritation, pulmonary edema, and even death.
- Heavy Metals:The site of the plant is contaminated with various heavy metals, including:
- Mercury: Known to accumulate in the body and affect the nervous system, kidneys, and liver. Even small doses over time can lead to chronic health problems.
- Chromium: Exposure to high levels of chromium, particularly hexavalent chromium, is associated with lung cancer and damage to the respiratory system.
- Lead: A potent neurotoxin, lead can cause developmental delays, memory problems, and damage to the kidneys.
- Nickel: Can cause respiratory and lung cancers when inhaled in significant quantities.
- Copper: High levels of copper exposure can damage the liver and kidneys.
- Organic Compounds:Several organic chemicals were found at the site, including:
- Hexachlorobutadiene: A suspected carcinogen that can cause liver damage, kidney damage, and neurological issues upon exposure.
- Chloroform (Trichloromethane): Known for its effects on the central nervous system, exposure can lead to dizziness, loss of consciousness, and even death at high concentrations. It is also a possible carcinogen.
- Carbon Tetrachloride: A potent liver toxin, exposure can result in liver damage, cancer, and nervous system toxicity.
- Trichlorobenzene: These compounds are volatile and can spread through air and water, accumulating in fatty tissues and causing damage to organs like the liver and kidneys.
- Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs):Some of the contaminants, particularly the organic compounds, are classified as persistent organic pollutants, which do not degrade easily in the environment. These can lead to:
- Cancer: Several of these compounds are carcinogenic.
- Neurological damage: Prolonged exposure can affect both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Reproductive and developmental disorders: Exposure has been linked to adverse effects on fertility and developmental health in humans.
- Environmental and Long-term Health Effects:
- Even decades later, contamination continues to affect the health of people living around the site, with high rates of cancers, birth defects, respiratory diseases, and other health issues. Water sources in the region remain unsafe due to heavy contamination with toxic chemicals. Persistent organic pollutants have been identified in local communities, indicating that the contamination continues to spread.
Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training (RESET) Programme

- 04 Dec 2024
In News:
At an event celebrating the National Sports Day, The Minister for Youth Affairs & Sports and Labour& Employment launched “Retired Sportsperson Empowerment Training” (RESET) Programme.
Key Highlights:
- Objective:
- Empower retired athletes through career development.
- Provide tailored education, internships, and skill enhancement.
- Address the human resource gap in the sports sector.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Retired athletes aged 20-50 years.
- Winners of international medals or participants in international events.
- National/state-level medalists or participants in recognized competitions (e.g., National Sports Federations, Indian Olympic Association).
- Courses Offered (16 Courses):
-
- Strength & Conditioning Trainer
- Sports Nutritionist
- Sports Event Management
- Corporate Wellness Trainer
- Sports Masseur
- Sports Entrepreneurship
- Store Manager
- Fitness Centre Manager
- Physical Education Trainer
- Fitness Trainer
- Yoga Trainer
- Venue Supervisor
- Self-Defence Trainer
- Community Sports Trainer
- Camping & Trekking Guide
- Facility Caretaker
- Program Structure:
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Class 12 and above
- Class 11 and below
- Hybrid learning mode:
- Self-paced learning via a dedicated portal.
- On-ground training and internships.
- Two levels based on educational qualifications:
- Internship and Placement:
- Internships offered in sports organizations, competitions, training camps, and leagues.
- Post-course placement assistance and entrepreneurial guidance.
- Implementing Agency:Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE) for the pilot phase.
- Importance:
- Provides sustainable career pathways for retired athletes.
- Utilizes the experience and skills of retired athletes to benefit future generations of athletes.
- Contributes to the growth of sports and nation-building.
- National Sports Day (29th August):
- Celebrated in honor of Major Dhyan Chand's birth anniversary.
- Promotes sports and physical fitness in India.
- Awards like Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna presented to honor excellence in sports.
26 Rafale-Marine Jets

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- Deal for 26 Rafale-M jets nearing completion, with final formalities expected to be completed by January 2025.
- These jets are designed for naval operations and will be deployed on INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
- Rafale-M Features: Multi-role, advanced avionics, AESA radar, and armaments like Meteor, MICA, SCALP, EXOCET.
- Three Scorpene Submarines: Additional three Scorpene-class submarines to be procured from France.
- These are part of a repeat order to Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), with five of the earlier six already inducted into service.
Nuclear Capabilities:
- INS Arighaat: Successfully fired a Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), marking a significant milestone for India's nuclear deterrence.
- Indigenous Nuclear Attack Submarine (SSN): India’s first indigenous SSN expected by 2036-37.
Strategic Maritime Engagement:
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR): Active monitoring of maritime activities, especially of China's PLA Navy and Chinese research vessels.
- Pakistan Navy Expansion: Acknowledged Pakistan’s efforts to become a 50-ship Navy, including the acquisition of 8 Chinese submarines. Indian Navy is adapting its plans to address this.
Nuclear Submarine Program (SSBN):
- INS Arihant: Conducted multiple deterrence patrols.
- INS Arighaat: Ongoing trials including the recent K4 SLBM test, with a range of 3,500 km.
Naval Vision 2047:
- Navy Chief released Vision 2047 document, outlining the future direction and growth of the Indian Navy.
Bilateral and Multilateral Engagements:
- Participation in various bilateral and multilateral exercises, including RIMPAC 2024 (Hawaii) and Russian Federation Navy’s Raising Day (St. Petersburg).
Notre-Dame Cathedral

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
The Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, a landmark symbol of French Gothic architecture, is set to reopen on after undergoing extensive renovations following a devastating fire in April 2019.
Historical and Architectural Significance:
- Location: Situated on Île de la Cité in the Seine River, Paris.
- Construction: Began in 1163 under Bishop Maurice de Sully and completed in 1260, showcasing a blend of early Gothic to Rayonnant Gothic styles.
- Key Features: The cathedral is renowned for its rib vaults, flying buttresses, stained-glass windows, and sculpted gargoyles.
- Cultural Importance: It has been a stage for significant historical events, including Napoleon Bonaparte's coronation in 1804. It also houses the Holy Crown of Thorns and relics from the crucifixion of Jesus.
- Literary Legacy: Featured in Victor Hugo's "The Hunchback of Notre-Dame" (1831), which drew attention to its architectural and historical significance.
Modern History and Renovation:
- The cathedral endured historical events such as the French Revolution, World War II, and attacks during the Protestant Reformation.
- In April 2019, a fire severely damaged the roof and spire, sparking an international outpouring of support for its restoration.
- Renovation efforts began soon after, involving more than 1,000 craftspeople, with President Emmanuel Macron calling it “the project of the century.”
Construction and Modifications Over Centuries:
- The Notre-Dame was a model for early Gothic architecture and has undergone multiple renovations, including the addition of flying buttresses and other structural changes during the 13th and 14th centuries.
- Modifications continued through the Renaissance and Classical periods, reflecting changing artistic styles and the political moods of the time.
Significance in French History:
- Witness to History: The cathedral has been central to 800 years of French history, serving as a backdrop for both brilliant and tumultuous events.
- Religious and Political Symbolism: It was the heart of Paris' religious and political life, acting as a symbol of the intertwined relationship between the church and the monarchy.
Madhya Pradesh’s 8th Tiger Reserve: Ratapani

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh was officially declared a Tiger Reserve, making it the 8th such reserve in the state. This declaration follows approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Key Details:
- Core Area: 763.8 sq. km
- Buffer Area: 507.6 sq. km
- Total Area: 1,271.4 sq. km
- Ratapani Tiger Reserve is located in the Raisen and Sehore districts, within the Vindhya hills, and is home to approximately 90 tigers.
- It also forms a crucial part of Madhya Pradesh’s tiger habitat and serves as a migration corridor from the Satpura ranges.
Economic and Ecotourism Benefits:
- The designation will boost ecotourism, generating employment and improving livelihoods for local communities.
- Eco-development programs will support residents, providing new opportunities and addressing the balance between conservation and human interests.
Wildlife Conservation and Management:
- The reserve will focus on habitat management, wildlife protection, and community engagement.
- The core area has been recognized as a critical tiger habitat under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- Efforts will include strengthening anti-poaching measures, improving surveillance, and enhancing prey base restoration.
Significance for Madhya Pradesh:
- This move places Madhya Pradesh as the "Tiger State of India", with significant conservation focus on the Ratapani and Madhav National Park (also in the process of becoming a tiger reserve).
- Madhya Pradesh now hosts 8 tiger reserves, contributing significantly to the country's overall tiger conservation efforts.
MahaKumbh Mela 2025

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- On December 1, 2024, the Uttar Pradesh government declared the MahaKumbh Mela area as a temporary district for four months.
- The new district will be known as the MahaKumbh Mela District, to streamline management for the 2025 MahaKumbh.
- Over 5,000 hectares of land will be part of this district, including 66 revenue villages from four tehsils: Sadar, Sorav, Phulpur, and Karchana.
Key Administrative Changes:
- Mela Adhikari (Kumbh Mela Officer) will act as the District Magistrate (DM) and will hold powers of Executive Magistrate, District Magistrate, and Additional District Magistrate.
- The Mela Adhikari will have authority under the Indian Civil Defense Code, 2023, and the Uttar Pradesh Revenue Code, 2006.
- The Mela Adhikari can appoint an Additional Collector for the district.
MahaKumbh Mela Overview:
- The Kumbh Mela is recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims, with participants bathing in sacred rivers at locations including Prayagraj, Haridwar, Ujjain, and Nashik.
- The PrayagrajKumbh takes place at the Sangam, the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati rivers.
- The event spans over a month and includes religious, cultural, and social activities, along with massive infrastructural setup including tented townships, civic facilities, and security measures.
International Day of Persons with Disabilities 2024

- 03 Dec 2024
In News:
- The International Day of Persons with Disabilities (IDPD), observed annually on December 3, celebrates the resilience, contributions, and leadership of persons with disabilities (PwDs) worldwide.
- Theme: “Amplifying the leadership of persons with disabilities for an inclusive and sustainable future”
History
- Proclamation: Established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1992 to promote the rights and well-being of persons with disabilities (PwDs).
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD): Adopted in 2006, further advanced the rights and well-being of PwDs and supports the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Initiatives
Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities
- In order to give focused attention to policy issues and meaningful thrust to the activities aimed at the welfare and empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), a separate Department of Disability Affairs was carved out of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment on May 12, 2012.
- The Department was renamed the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities on December 8, 2014.
- The Department acts as a nodal agency for matters pertaining to disability and persons with disabilities, including effecting closer coordination among different stakeholders: related Central Ministries, State/UT Governments, NGOs, etc., in matters pertaining to disability.
Accessible India Campaign
- The Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan), launched on December 3, 2015 aims to achieve universal accessibility for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs) across India.
- The key focus areas include improving Built Environment Accessibility in public spaces, enhancing Transportation Accessibility for independent mobility, creating an accessible Information and Communication ecosystem, and expanding Sign Language Access through interpreter training and better media support.
Deendayal Divyangjan Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS)
- DDRS is a central sector scheme to provide grant-in-aid to non-governmental organizations (NGOs) for projects relating to the rehabilitation of persons with disabilities aimed at enabling persons with disabilities to reach and maintain their optimal, physical, sensory, intellectual, psychiatric, or socio-functional levels.
District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC)
- The District Disability Rehabilitation Centre (DDRC) aims to address the needs of persons with disabilities through a multifaceted approach.
- Its objectives include early identification and intervention, raising awareness, and assessing the need for assistive devices along with their provision and fitment, arrangement of loans for self-employment and more. Additionally, it acts as an outreach center for services provided by National Institutes and works to promote a barrier-free environment for individuals with disabilities.
Assistance to Persons with Disabilities for Purchase/Fitting of Aids/ Appliances (ADIP) Scheme.
- The main objective of the Scheme is to provide grants-in-aid to the various implementing agencies (National Institutes/Composite Regional Centers/Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India.
Schemes For Implementation Of Rights of Persons With Disabilities Act 2016 (SIPDA)
- The Scheme for Implementation of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 (SIPDA) is a comprehensive "Central Sector Scheme" that encompasses 10 sub-schemes following its revision during the Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC) meeting on 11th August 2021.
- This revised scheme, approved by the Hon'ble Finance Minister, is designed to operate from 2021–22 to 2025–26.
Divya Kala Mela
- The Divya Kala Mela is a national-level fair dedicated to Divyangjan and represents a significant milestone in India’s journey toward inclusivity and empowerment of the Divyangjan, or differently-abled individuals.
PM-DAKSH
- PM-DAKSH (Pradhan Mantri DakshtaAurKushaltaSampannHitgrahi) Yojana is a one-stop destination for Persons with Disabilities (PwDs), skill training organizations, and employers across India to be a part of the National Action Plan for Skill Development of Persons with Disabilities implemented by the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD). Under this portal, there are two modules:
- Divyangjan Kaushal Vikas: Skill training is conducted for PwDs through the portal across the country.
- Divyangjan Rozgar Setu: The platform aims to act as a bridge between PwDs and employers having jobs for PwDs. The platform provides geo-tagged based information on employment/earning opportunities within private companies as well as PwDs across India.
Network Readiness Index 2024

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India has climbed 11 positions to secure 49th rank in the Network Readiness Index (NRI) 2024, compared to 60th in NRI 2023.
- This improvement reflects India’s significant progress in the digital and telecommunication sectors.
NRI 2024 Overview:
- The NRI 2024 report assesses the network readiness of 133 economies based on four pillars: Technology, People, Governance, and Impact, using 54 variables.
- Published by the Portulans Institute, Washington DC.
India's Leading Indicators:
- Top rankings:
- 1st Rank: ‘AI scientific publications’, ‘AI talent concentration’, and ‘ICT services exports’.
- 2nd Rank: ‘FTTH/Building Internet subscriptions’, ‘Mobile broadband internet traffic’, and ‘International Internet bandwidth’.
- 3rd Rank: ‘Domestic market scale’.
- 4th Rank: ‘Annual investment in telecommunication services’.
Digital Progress:
- India has demonstrated remarkable digital transformation, especially in technological innovation and digital infrastructure.
Economic Grouping:
- India ranks 2nd in the lower-middle-income countries group, following Vietnam.
Telecommunication Achievements:
- Tele-density has increased from 75.2% to 84.69% in the past decade, with 119 crore wireless connections.
- Internet subscribers have surged from 25.1 crore to 94.4 crore, aided by Digital India initiatives and rural broadband expansion.
- 5G Launch: In 2022, India launched 5G services, significantly boosting global mobile broadband speed rankings from 118th to 15th.
Future Vision:
- India’s Bharat 6G Vision aims to position the country as a leader in future telecom technologies, backed by strong infrastructure and investments in emerging technologies.
Telecom Reforms:
- Spectrum management, ease of doing business, and consumer protection reforms have strengthened India’s telecom sector, contributing to its improved network readiness ranking.
World AIDS Day 2024
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
World AIDS Day is observed annually on December 1 since 1988 to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS and demonstrate solidarity with affected individuals. It commemorates lives lost to AIDS and highlights progress and ongoing challenges in prevention, treatment, and care.
Key Highlights:
- 2024 Theme: "Take the Rights Path: My Health, My Right!"
- Focuses on healthcare access, human rights, and addressing systemic inequalities in HIV prevention and treatment services.
- Aims to empower individuals to manage their health and reduce stigma.
- Advocates for inclusivity and global cooperation to eradicate AIDS.
Global and National Perspective on HIV/AIDS
- Global Progress:
- According to UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2023, significant strides have been made globally in reducing new HIV infections and improving treatment access.
- India has been acknowledged for its robust legal framework and financial investments in HIV control.
- India's HIV Statistics:
- Over 2.5 million people live with HIV in India.
- Annual new infections: 66,400, a 44% reduction since 2010.
- HIV prevalence among adults is 0.2%.
- Free lifelong treatment is provided to over 16 lakh people at 725 ART centers (as of 2023).
India’s Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Response
- Early Initiatives:
- India’s response to HIV/AIDS began in 1985 with sero-surveillance and blood safety measures.
- The National AIDS and STD Control Programme (NACP) was launched in 1992, evolving into one of the world’s largest HIV/AIDS control programs.
- Evolution of NACP:
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focused on awareness and blood safety.
- Phase II (1999-2007): Introduced direct interventions in prevention, detection, and treatment.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Expanded decentralized management at the district level.
- Phase IV (2012-2017): Increased funding and sustainability of interventions.
- Phase IV Extended (2017-2021): Passage of the HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017; introduction of the ‘Test and Treat’ policy; and response to the COVID-19 pandemic with IT innovations.
- NACP Phase V (2021-2026):
- Central Sector Scheme with an outlay of Rs. 15,471.94 crore.
- Goals: Reduce new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2025-26 from 2010 levels.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis, reduce stigma, and ensure universal access to STI/RTI services for vulnerable populations.
- Key strategies include community-centered approaches, technology integration, gender-sensitive responses, and public-private sector partnerships.
Key Objectives of NACP Phase V
- Prevention & Control:
- Ensure 95% of high-risk individuals access prevention services.
- Achieve the 95-95-95 targets: 95% of HIV-positive individuals know their status, are on treatment, and achieve viral suppression.
- Eliminate vertical transmission of HIV and syphilis.
- Reduce stigma and discrimination to less than 10%.
- STI/RTI Prevention:
- Universal access to high-quality services for at-risk populations.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users' Conference (AOMSUC-14)was held in New Delhi, India, hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under the Ministry of Earth Sciences. This annual event brings together meteorologists, earth scientists, and satellite data users to discuss advancements in satellite technology for weather and climate monitoring.
Key Facts:
- Objective:
- Promote Satellite Observations: Highlight the importance of satellite data for meteorology and climatology.
- Advance Remote Sensing Science: Foster advancements in satellite technology and its application in weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
- Encourage Collaboration: Facilitate dialogue between satellite operators and users to enhance the use of satellite data across the Asia-Oceania region.
- Discuss Future Plans: Update on the current status and future plans of international space programs.
- Engage Young Scientists: Encourage the involvement of young researchers in satellite science and meteorology.
- Participants:
- Around 150 participants from various countries, including key international space organizations like WMO, NASA, ESA, JAXA, and other meteorological and space entities.
- The conference will feature oral presentations, poster sessions, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on satellite data application.
- Significance of the Conference:
- Regional Cooperation: AOMSUC promotes stronger cooperation between countries in the Asia-Oceania region, addressing shared challenges in meteorology and satellite data usage.
- Improved Forecasting: Enhances satellite data utilization for more accurate weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and climate monitoring.
- Disaster Risk Management: Strengthens early warning systems for extreme weather events, improving disaster preparedness and response.
- Capacity Building: Offers training and workshops for local meteorologists, boosting the capacity of countries to use satellite data effectively for weather forecasting and climate services.
- Data Sharing: Encourages collaboration in satellite data sharing, facilitating better access to meteorological data across national borders.
- History of AOMSUC:The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China in 2010. Since then, the conference has been held annually in various Asia-Oceania locations and has become a leading event for the meteorological community.
KisanPehchaan Patra
- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
The Indian government is actively promoting the creation of digital identities for farmers through the KisanPehchaan Patra (Farmer ID). The initiative is an essential part of the Digital Agriculture Mission under the AgriStack initiative.
Key Details:
Objective:
- The main goal is to provide digital IDs linked to Aadhaar for farmers, capturing comprehensive agricultural data including land records, crop information, and ownership details.
- These digital identities are designed to enhance farmers' access to government schemes and digital agriculture services.
Farmer ID Creation Timeline:
- The government plans to create digital IDs for 11 crore farmers in phases:
- 6 crore farmers in FY 2024-25.
- 3 crore farmers in FY 2025-26.
- 2 crore farmers in FY 2026-27.
AgriStack Initiative:
- The AgriStack initiative aims to build a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for the agriculture sector, which includes:
- Farmers' Registry.
- Geo-referenced village maps.
- Crop Sown Registry.
Implementation Strategy:
- Camp-mode approach: States have been instructed to organize field-level camps to ensure faster and inclusive registration of farmers.
- Financial Incentives:
- States will receive ?15,000 per camp for organizing these camps.
- Additionally, ?10 per Farmer ID issued.
- Funding is provided through the Pradhan Mantri KisanSamman Nidhi (PM-Kisan) scheme.
Benefits of Digital Farmer ID:
- Targeted Delivery of Benefits: Ensures subsidies and benefits reach legitimate farmers and eliminates duplication.
- Precision Agriculture: Supports data-driven policies for better crop planning, insurance, and market linkages.
- Financial Inclusion: Facilitates easy access to credit, loans, and crop insurance, empowering farmers financially.
- Better Monitoring: Helps in tracking the actual implementation of schemes and ensures that only eligible farmers benefit.
Progress in States:
- Advanced States: Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttar Pradesh have made significant progress in issuing digital Farmer IDs.
- Testing Phase: States like Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha are still in the field-testing phase.
- Special Assistance Scheme: The Finance Ministry allocated ?5,000 crore in August 2024 to assist states in creating the Farmers' Registry, with funds available until March 2025.
Linkage with Land Records and Crop Data:
- The Farmer ID integrates with state land records and crop data, creating a dynamic and accurate database known as the Farmer’s Registry.
- This data helps in the development of better agricultural policies and decision-making.
Digital Agriculture Mission:
- The government approved a substantial outlay of ?2,817 crore for the Digital Agriculture Mission, which is intended to modernize agricultural practices and build robust digital infrastructure.
- The mission also includes the launch of the Digital Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), which will help in crop estimation and better resource allocation.
National Policy on Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP)

- 02 Dec 2024
In News:
- India is working on a national policy to enhance female labour force participation (FLFP), focusing on creating a supportive care economy structure.
- The policy is being developed by an inter-ministerial team involving the Ministries of Skill Development, Labour, Rural Development, and Women and Child Development.
- Goal: To reduce barriers for women, especially related to caregiving responsibilities, and increase their participation in the workforce.
Key Focus Areas:
- Care Economy: Involves both paid and unpaid caregiving services, such as childcare, eldercare, domestic work, and health services.
- The policy aims to formalize care work, addressing its undervaluation and encouraging women's workforce participation.
- Proposes a core skilling package for caregivers, particularly for childcare in rural and informal sectors.
- Childcare Facilities: Targeting women working under schemes like MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme).
Current Challenges:
- Post-marriage employment drop: Women face a significant decline in workforce participation after marriage, often due to caregiving roles.
- In India, 53% of women are outside the labour force, mostly due to unpaid domestic work, unlike only 1.1% of men.
- The gender divide in caregiving is stark: Women spend over 5 hours daily on unpaid domestic work (81% of females), compared to 12.4% of males.
Key Initiatives:
- Palna Scheme: Provides daycare through Anganwadi-cum-Crèche facilities for working parents, benefiting children aged 6 months to 6 years. 1,000 crèches are operational.
- Women’s Employment Data:
- In rural India, 36.6% of women participate in the workforce, compared to 23.8% in urban areas.
- Post-marriage, female employment drops by 12 percentage points, even without children.
- Improving Female Labour Force Participation (FLFP): Key to India's growth, as matching women’s workforce participation with men could boost GDP by 27% (IMF).
Barriers to Women’s Workforce Inclusion:
- Unpaid Care Work: Women's disproportionate share of household duties limits paid employment opportunities.
- Cultural Norms: Gender expectations restrict women’s access to employment, especially in rural areas.
- Educational Barriers: Limited access to education for girls restricts skill development, lowering job prospects.
- Health & Safety Issues: Health challenges and safety concerns at workplaces hinder women's workforce participation.
- Lack of Supportive Policies: Absence of parental leave and flexible work arrangements for women, especially in the informal sector.
Government Initiatives for Women’s Employment:
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao: Promotes girl child education and empowerment.
- National Education Policy (NEP): Ensures gender equity in education.
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Extends paid maternity leave to 26 weeks and mandates crèche facilities in large establishments.
- Labour Codes (2019-2020): Codifies labor laws to provide a framework for improving women’s workplace safety and employment opportunities.
Global Examples & Inspiration:
- Japan’s Womenomics: Aimed at increasing female participation, Japan's womenomics reforms have grown women’s labour force participation from 64.9% to 75.2% (2013-2023).
- Flexible Work Models: Countries like Netherlands encourage part-time and remote work, offering flexibility to manage work-life balance.
- Sweden’s Investment in ECCE: Investing 1% of GDP in Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) has significantly reduced women’s workforce exclusion.
Way Forward:
- National Women’s Urban Employment Guarantee Act (WUEGA): Promotes gender-balanced work environments and childcare facilities at work sites.
- Flexible Work Options: Encouraging remote work, parental leave, and childcare support will empower more women to balance caregiving and employment.
- Investment in the Care Economy: To reduce the care burden on women, substantial investment in ECCE and related sectors is essential to increase women’s participation and economic independence.
Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The controversy surrounding the Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, has intensified following claims that the mosque, built during the Mughal Emperor Babur's reign (1526–1530), was constructed over a Hindu temple, the Hari Har Mandir. This claim has led to legal battles and violent clashes, making it part of a broader series of disputes involving mosques built during the Mughal era, such as the Gyanvapi mosque in Varanasi and the Eidgah Masjid in Mathura.
Background and Legal Context:
The dispute began when a petition was filed in Sambhal's district court on November 19, 2024, claiming the Jama Masjid was built on the site of an ancient temple. The petitioners, led by Hari Shanker Jain, demanded a survey to ascertain the religious character of the site. This petition follows a pattern seen in similar cases in Varanasi, Mathura, and Dhar, where Hindu groups have raised similar claims about mosque sites. The court ordered a photographic and videographic survey of the mosque, which, initially carried out peacefully, later sparked violence on November 24 when the survey was accompanied by chanting crowds. This led to protests, stone pelting, and allegations of police firing, resulting in several deaths.
The Jama Masjid is a protected monument under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904, and is listed as a Monument of National Importance by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). This gives the case legal and cultural sensitivity, as it involves both national heritage and religious sentiments.
Historical and Architectural Context:
The Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal was constructed by Mir Hindu Beg, a general under Babur, in the early 16th century. It is one of three mosques commissioned by Babur, alongside those in Panipat and Ayodhya. The mosque is noted for its architectural style, which includes a large square mihrab hall, a dome, and arches, constructed using stone masonry and plaster. Some historians argue that the mosque might be a Tughlaq-era structure modified during Babur's reign. Locally, Hindu tradition holds that the mosque incorporates elements of a Vishnu temple, believed to be the site of Kalki, the tenth avatar of Vishnu.
The Places of Worship Act, 1991:
The dispute has reignited debates about the Places of Worship (Special Provisions) Act, 1991, which mandates that the religious character of any place of worship as it existed on August 15, 1947, should be maintained, with the exception of the ongoing Babri Masjid dispute. The Act aims to prevent any further contests regarding religious sites, and Section 3 of the Act explicitly prohibits converting a place of worship into a site of a different religious denomination.
The petition filed in Sambhal seeks to alter the religious character of the mosque, directly contravening the Places of Worship Act. The petitioners have cited remarks by Supreme Court Justice D.Y. Chandrachud in 2022, suggesting that a survey to ascertain the religious character of a place might not violate the Act. This has led to petitions challenging the Act in the Supreme Court, including cases from Varanasi, Mathura, Dhar, and now Sambhal.
The Legal and Social Implications:
The ongoing dispute over the Shahi Jama Masjid highlights the tension between historical narratives, legal frameworks, and communal harmony. The Supreme Court has intervened in the matter, temporarily halting further proceedings in the trial court, urging that the mosque's management committee approach the Allahabad High Court. The Court emphasized the importance of maintaining peace and harmony and cautioned against any actions that could escalate tensions.
The case underscores the challenges of balancing India's rich historical heritage with its diverse religious communities. As the legal process unfolds, the outcome of the Sambhal dispute could set significant precedents for how similar cases are handled in the future.
Conclusion:
The Sambhal mosque dispute, much like the Gyanvapi and Ayodhya cases, brings to the forefront the complex intersections of history, religion, and law. It also raises critical questions about the application of the Places of Worship Act and its implications for preserving India's pluralistic society. The outcome of this case, alongside the pending petitions in other states, will be crucial in shaping the future of religious site disputes in India.
India-Cambodia Joint Military Exercise CINBAX

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
The first edition of CINBAX (Counter-Terrorism Counter-Bio-Terrorism and Intelligence Operations Exercise) was launched on December 1, 2024, at the Foreign Training Node, Pune.
Key Details:
- Participants: 20 personnel from each side – the Indian Army and the Cambodian Army – focusing on enhancing cooperation for UN peacekeeping operations.
- Objective:
- Enhancing Trust and Interoperability: CINBAX aims to foster mutual trust, build camaraderie, and improve operational efficiency between the two armies in conducting peacekeeping operations under UN guidelines.
- Focus Areas: Joint Counter-Terrorism (CT) operations, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), cyber warfare, logistics, casualty management, and disaster relief operations.
- Phases of the Exercise:
- Phase I: Orientation for Counter-Terrorism operations in the context of UN peacekeeping missions.
- Phase II: Conduct of tabletop exercises to simulate and plan response scenarios.
- Phase III: Finalization of plans and review of lessons learned, focusing on operational strategies and tactical decision-making.
- Key Topics Covered:
- Discussions on setting up a Joint Training Task Force for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance.
- Exploring cyber warfare, hybrid warfare, and unconventional tactics.
- Strategies for managing logistics, casualties, and coordination during Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
- Promotion of Indigenous Defence Equipment:
- The exercise will showcase Indian-made weapons and defence equipment, supporting India’s commitment to Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliance in defence production).
- Objective: To highlight India's advanced military technology and indigenous defence capabilities.
- Significance for India-Cambodia Relations:
- The exercise strengthens military ties between India and Cambodia, contributing to improved cooperation in regional peacekeeping efforts.
- CINBAX marks a significant milestone in India-Cambodiadefence collaboration and sets the stage for future joint operations.
India-Cambodia Bilateral Relations
- Historical Context:
- India and Cambodia share strong religious, cultural, and linguistic ties, with Hindu rituals influencing Cambodian culture and Sanskrit and Khmer sharing common words.
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1952, even before Cambodia's independence from France.
- Key Developments:
- 1954: Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru visited Cambodia, initiating strong diplomatic ties, particularly during the Non-Aligned Movement.
- Post-1970s: India played a pivotal role in Cambodia's recovery from the Khmer Rouge regime. India was the first democratic country to recognize the Heng Samrin regime in 1981 and contributed to Cambodia's political reconciliation.
- 1980s: India facilitated dialogue for the Paris Peace Accord and contributed to the success of UNTAC elections in 1993.
- Strategic and Economic Cooperation:
- Defence: Enhanced cooperation in defence capacity building, military training, and infrastructure development.
- Trade: India exports pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, automobiles, and leather products to Cambodia. In return, Cambodia exports organic chemicals, apparel, and footwear to India.
- Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC): Established in 2000, MGC includes Cambodia and aims to enhance cooperation in sectors like trade, education, tourism, and cultural exchanges.
- Recent Collaboration:
- India has extended financial assistance for infrastructure projects in Cambodia, especially in restoring and conserving cultural heritage sites like Angkor Wat.
- MoUs signed in bilateral cooperation, cultural exchanges, and development projects highlight the growing India-Cambodia strategic partnership.
Key Highlights on India’s Horticulture and Plant Health Management Initiatives

- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Government of India and ADB sign $98 million loan to promote plant health management in India’s horticulture.
Key Highlights:
$98 Million Loan Agreement with ADB:
- India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan to enhance horticulture productivity and resilience.
- Objective: Improve farmers' access to certified, disease-free planting materials, which will increase crop yield, quality, and climate resilience.
- Focus Areas: The project aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to strengthen plant health management in horticulture.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP):
- Implemented under MIDH: The Clean Plant Programme is part of the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- Goal: To provide virus-free, high-quality planting materials to farmers, boosting horticultural crop yields and promoting climate-resilient varieties.
- Implementation Period: 2024-2030, with 50% financial support from ADB.
- Key Components:
- Establishment of 9 Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) with state-of-the-art diagnostic, therapeutic, and tissue culture laboratories.
- Certification Framework: Developing a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966 to certify clean plants.
- Support to Nurseries: Infrastructure development for large-scale nurseries.
- Significance: The programme strengthens India's self-reliance in horticulture and enhances adaptability to climate change impacts.
Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH):
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Focus: Holistic development of the horticulture sector, including fruits, vegetables, mushrooms, spices, and more.
- Funding Pattern:
- General States: 60% by Government of India (GoI), 40% by State Governments.
- North-Eastern and Himalayan States: 90% by GoI.
Horticulture Sector at a Glance:
- Contribution to Agricultural GDP: Accounts for 33% of the gross value.
- Land Coverage: Occupies 18% of agricultural land in India.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally.
- Surpassing Food Grains: Horticulture production exceeds food grain production, occupying much less land (25.66 million hectares vs. 127.6 million hectares for food grains).
Key Benefits of the CPP:
- Climate Resilience: Promotes climate-resilient plant varieties and helps farmers adapt to climate change.
- Innovation: Encourages the use of advanced testing techniques and builds institutional capacity.
- Long-term Impact: Expected to improve sustainability, productivity, and the economic well-being of farmers.
Additional Horticulture Initiatives:
- CHAMAN (Horticulture Assessment using Geo-informatics): A programme to estimate area and production of horticultural crops using scientific methods.
- Kisan Rail Services: Facilitates transportation of perishable horticultural products like fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme: By the National Horticulture Board to support the sector’s growth.
Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI) 2023
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
- It was launched by Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology, Earth Sciences, PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy, and Space, along with Shri V. Srinivas, the Secretary of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- This initiative, conceptualized by DARPG, aims to evaluate and rank central Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal mechanisms.
Key Aspects of GRAI 2023:
- Objective: GRAI 2023 was designed to provide a comparative assessment of Ministries and Departments based on their grievance redressal systems. It was created based on recommendations from the Parliamentary Standing Committee of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances, and Pensions.
- Assessment Method: The index evaluates 89 Central Ministries and Departments across four dimensions:efficiency, feedback, domain&organisational Commitment
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Group A: Ministries/Departments with more than 10,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Group B: Ministries/Departments with 2,000 to 9,999 grievances (33 Ministries/Departments)
- Group C: Ministries/Departments with fewer than 2,000 grievances (28 Ministries/Departments)
- Top Performers:
- Group A: The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare topped the rankings.
- Group B: The Office of the Comptroller & Auditor General of India led.
- Group C: The Department of Investment & Public Asset Management ranked first.
- It is calculated using data from the Centralised Public Grievance Redressal and Management System (CPGRAMS) from January to December 2023. Ministries are grouped into three categories based on the number of grievances received in 2023:
- Analysis: GRAI 2023 includes an in-depth analysis of the root causes of effective grievance redressal for each Ministry/Department, presented in a color-coded, easily understandable format.
- Advancements: The report outlines a roadmap for improving grievance redressal, emphasizing:
- Utilization of advanced technologies such as AI and Machine Learning (ML) for predictive analytics and data analysis.
- The introduction of features like IGMS 2.0 and TreeDashboard within CPGRAMS.
- Improved training for Grievance Redressal Officers (GROs) and more rigorous audits to increase accountability.
- Expansion of CPGRAMS integration to local governments, enhancing the grievance redressal system across all levels of governance.
Commonwealth Secretariat recognized CPGRAMS as a best practice in grievance redressal at its meeting in April 2024.
SASCI Scheme for Tourism Development
- 01 Dec 2024
In News:
Centre clears scheme for development of 40 tourist destinations across 23 States at a cost of ?3,295 crore.
Key Details:
- Focus Areas: The scheme encourages the development of lesser-known destinations such as Bateshwar (Uttar Pradesh), Ponda (Goa), Gandikota (Andhra Pradesh), and Porbandar (Gujarat) to reduce overcrowding at popular sites.
- Implementation Timeline: Projects must be completed within two years, with funding released in stages until March 2026.
- Key Features:
- Long-term interest-free loans for 50 years.
- States responsible for project execution and maintenance, often through public-private partnerships (PPP).
- The Ministry of Tourism will monitor progress, and 66% of the funds have already been released.
- Emphasis on sustainability and boosting local economies by creating jobs through tourism.
- States must provide land at no cost and ensure proper infrastructure like safety, connectivity, and utilities.
Selection Criteria for Projects:
- Consultation Process: Detailed regional consultations led to the selection of 40 projects from 87 proposals received by the Ministry of Tourism. West Bengal was the only state not submitting proposals.
- Evaluation Criteria: Projects were evaluated based on:
- Connectivity, tourism potential, and ecosystem.
- Financial viability and sustainability.
- Impact on local economy and job creation.
- Funding Pattern:
- A maximum of ?100 crore for each project, with higher funding considered for exceptional projects.
- Total funding capped at ?250 crore per state, allocated on a first-come, first-served basis.
Importance of the Scheme:
- Economic Growth & Employment: Projects are designed to stimulate local economies, create employment, and promote sustainable tourism.
- Global Branding: The scheme aims to brand and market tourist destinations on a global scale.
- Tourism Infrastructure Growth: It aims to improve the entire tourism value chain, including transportation, accommodation, activities, and services.
Tourism Sector Overview:
- Current Status:
- India ranks 39th among 119 countries in the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) increased by 47.9% in 2023, with 9.52 million tourists.
- Tourism contributed 5% to India’s GDP in 2022-23 and created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs.
- India earned ?2.3 lakh crore in foreign exchange in 2023 through tourism.
- Projected revenue from tourism to exceed $59 billion by 2028.
- Initiatives for Promotion:
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme: To develop theme-based circuits.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2020): Promotes domestic tourism.
- PRASHAD & HRIDAY Schemes: Focus on pilgrimage and heritage city development.
MGNREGA Job Card Deletions Issue:
- Context: A significant surge in deletions of job cards under MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) raised concerns over transparency and workers’ rights.
- Reasons for Deletion:
- Permanent migration, duplicate cards, forged documents, and refusal to work.
- Aadhaar-based payment system (ABPS) implementation led to deletions for non-linked cards.
- Implications:
- Violation of workers’ legal right to employment, especially when deletions were made without due process.
- The "Not willing to work" designation undermines livelihood opportunities, especially in high unemployment rural areas.
- Recommendations for Reform:
- Strengthening verification processes and ensuring deletions follow due procedure.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas to review and approve deletions.
- Regular audits and better grievance redressal mechanisms.
Other Government Initiatives in Tourism:
- National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD): For holistic and sustainable development of pilgrimage tourism.
- Incredible India & E-Visa Initiatives: To attract more foreign tourists.
- Regional Connectivity Scheme (UDAN): Enhances air connectivity to remote tourist destinations.
- National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): Preserves and rejuvenates heritage sites.
