Pig-Butchering Scam
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
In its annual report, the Union Home Ministry has warned the public against getting trapped in organised 'pig-butchering scams'.
Key Highlights:
- What is it?
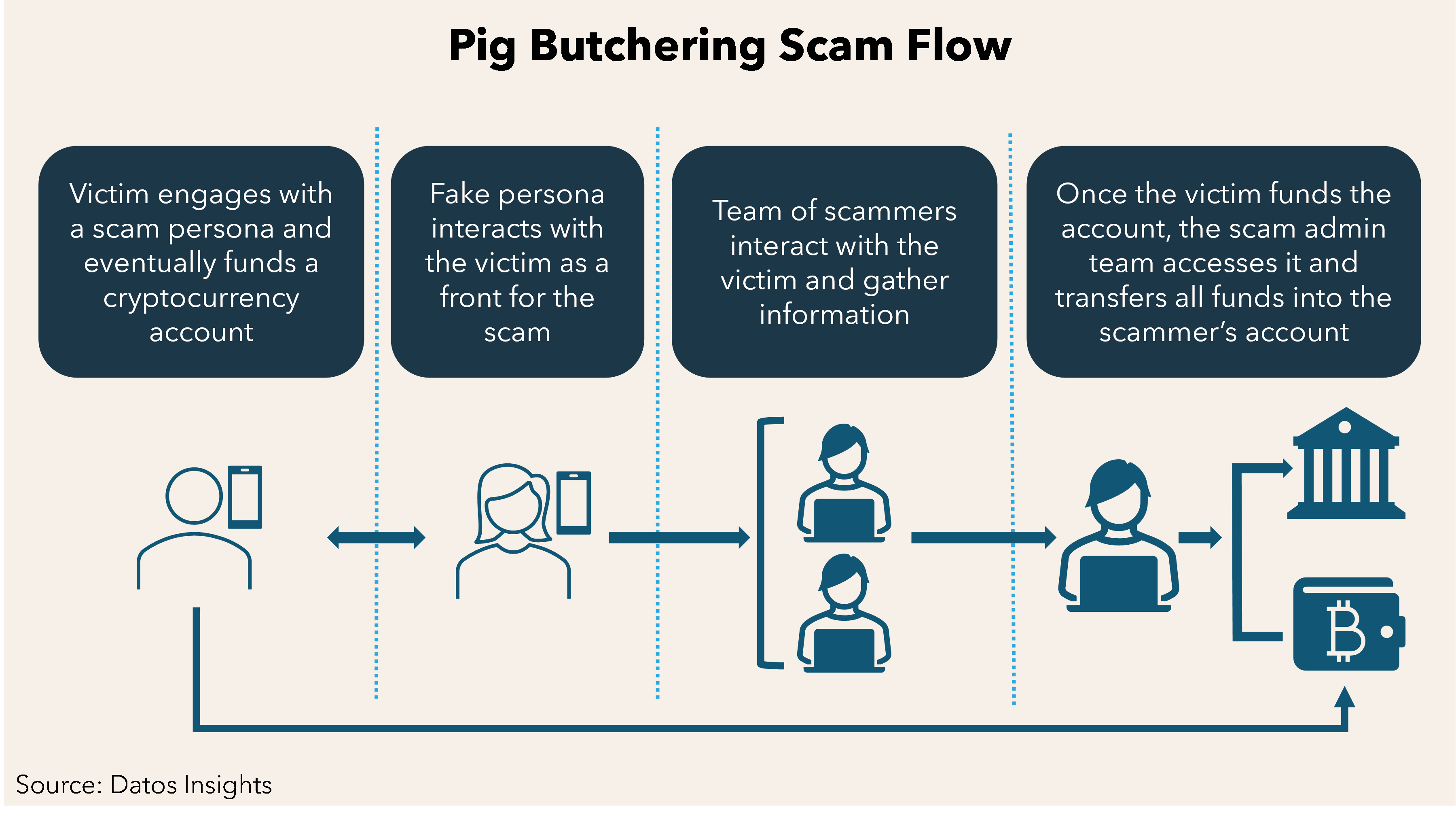
- The Pig-Butchering Scam is a sophisticated form of cybercrime in which fraudsters deceive victims into investing in fake online trading platforms. The term "pig-butchering" is derived from the analogy of "fattening up" victims before stealing their money, much like preparing a pig for slaughter.
- How it works:
- Initial Contact: Scammers typically reach out to victims through social media platforms, dating apps, or deceptive ads on websites like Google and Facebook.
- Building Trust: Fraudsters create false friendships, using these connections to lure victims into investing in fake online trading apps. Cryptocurrency investments are often involved due to the ambiguity in the crypto market.
- The Scam: Victims are shown fabricated profits to encourage further investment. However, when they try to withdraw their funds, the money is stolen, and they realize the trading platform was fake.
- Features of the Scam:
- Use of fraudulent online trading platforms
- Fabricated blockchain transactions, making fund recovery nearly impossible
- Reliance on victims’ desire for quick financial gains
- Linked to money laundering and cyber slavery in some cases
- Origin of the Scam:
- The scam first appeared in China in 2016, where it was referred to as “sha zhu pan” (translated as "killing pig game").
- It is a form of Ponzi scheme, wherein organized scammers exploit victims by using fake online identities and offering false investment opportunities.
- How Cybercriminals Lure Victims:
- The scammer (host) contacts potential victims via social media, dating apps, or deceptive online advertisements.
- They build trust with the victim, enticing them into exploring online investments and cryptocurrency trading, often capitalizing on the lack of clarity in the crypto space.
- The victim is then persuaded to invest larger amounts in fake trades, believing they are making real profits.
- How the Scam is Executed:
- The scammer uses fake online trading platforms to create the illusion of profit.
- After building the victim’s confidence, the fraudster encourages larger investments.
- When victims try to withdraw their funds, they realize their money is gone, often with blockchain transactions making it nearly impossible to trace or recover the funds.
- Statistics on Cybercrime in India:
- In March 2024, the National Cybercrime Threat Analytical Unit recorded over 37,500 complaints related to cybercrime.
- The highest number of complaints (42%) were associated with WhatsApp (14,746), followed by Telegram (7,651), Instagram (7,152), Facebook (7,051), and YouTube (1,135).
- Union Home Ministry’s Response:
- The MHA has flagged pig-butchering scams as a global phenomenon that could involve large-scale money laundering and cyber slavery.
- The Ministry is collaborating with Google for intelligence sharing to flag suspicious digital lending apps and other forms of fraud.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre is working on capacity building to combat such scams and improve the response to cybercrimes.
Bharat NCX 2024

- 19 Nov 2024
In News:
The Bharat National Cyber Security Exercise (Bharat NCX 2024), inaugurated on November 18, 2024, is a key initiative aimed at strengthening India’s cybersecurity resilience. This 12-day exercise is designed to equip cybersecurity professionals and national leadership with the skills to manage complex cyber threats, enhance incident response capabilities, and improve strategic decision-making. The event is organized by the National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) in collaboration with Rashtriya Raksha University (RRU).
Key Details of Bharat NCX 2024:
- Cyber Defense and Incident Response Training
- The exercise focuses on defensive cybersecurity skills, preparing participants to defend against cyberattacks.
- Live-fire simulations will provide hands-on experience with real-time cyberattacks on IT and Operational Technology (OT) systems.
- Strategic Decision-Making Simulations
- A core component is the Strategic Decision-Making Exercise, where senior management from across sectors will simulate decision-making in a national-level cyber crisis.
- This exercise enhances their ability to respond swiftly and strategically in high-pressure scenarios.
- CISO’s Conclave
- The CISO's Conclave brings together Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) from government, public, and private sectors.
- The conclave will feature panel discussions on the latest cybersecurity trends and government initiatives, allowing professionals to exchange knowledge and collaborate.
- Bharat Cybersecurity Startup Exhibition
- An exhibition will highlight innovative cybersecurity solutions developed by Indian startups. This showcases the growing role of the private sector in strengthening India’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Leadership Engagement and Capacity Building
- Leadership engagement is a key feature, ensuring that high-level decision-makers are prepared to lead national cybersecurity efforts.
- The exercise will foster a unified approach to dealing with emerging cyber threats.
Significance for India’s Cybersecurity Strategy
- National Cybersecurity Resilience: Bharat NCX 2024 is a vital step in fortifying India’s cybersecurity defenses, preparing professionals and leadership to address the evolving cyber threat landscape.
- Collaboration and Innovation: The inclusion of industry stakeholders, startups, and leaders from various sectors underscores the importance of collaboration in developing innovative solutions to cybersecurity challenges.
- Capacity Building: The exercise aims to improve decision-making at all levels, helping India build a robust cybersecurity framework to secure its critical infrastructure and respond effectively to potential cyber crises.
TarunerSwapno Scheme

- 17 Nov 2024
In News:
Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee has ordered an inquiry after some intended beneficiaries of the ‘Taruner Swapna’ scheme, an initiative of the TMC government, alleged that they did not receive Rs 10,000 meant for the purchase of tablets (mobile device with a touchscreen display, rechargeable battery, and mobile operating system).
Overview:
- Aimed at bridging the digital divide by providing ?10,000 to Class 11 and 12 students in West Bengal for purchasing smartphones/tablets.
- In FY 2024-25, ?900 crore allocated for the scheme, targeting 16 lakh students.
- The main objective of the scheme is to provide scholarship to the students. So that the student can use their scholarship to buy a smartphone and tablet and can get education through online medium.
- This scheme will prove to be effective in making the future of the students bright and will also prove to be effective in strengthening them technically.
- Eligibility criteria for the scheme:
- Applicant must be a permanent resident of West Bengal State.
- The applicant should be a student.
- Students of 11th and 12th will be eligible for this scheme.
- The annual income of the family of the applicant student should not exceed Rs 2 lakh.
- Students with backlog are not eligible as this grant is for one-time only.
- This scheme will make the students technically strong and they will be able to improve their future with technology.
- Students of government/government-aided/sponsored schools and madrassas can avail assistance.
- TarunerSwapno Yojana will bridge the digital divide among students and facilitate modern education.
Cyberfraud Losses and Economic Impact

- 24 Oct 2024
In News:
- ?1.2 lakh crore is the projected financial loss due to cyber frauds in India over the next year (2024), according to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Union Home Ministry.
- This could amount to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Mule Accounts:
- Mule accounts are a significant contributor to cyber frauds. These accounts are used to facilitate money laundering and illegal transactions.
- On average, around 4,000 mule accounts are identified daily by I4C.
- Mule accounts typically facilitate the transfer of funds out of India, often through cryptocurrency transactions.
- Sources of Cyber Scams:
- A majority of frauds are linked to Chinese entities or China-based operations, with about half of the cybercrime complaints originating from China.
- Other major hubs for cyber frauds include Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, which house call-centre-like scam compounds.
- Azerbaijan has also been identified as a new hotspot for such scams.
- International Dimension:
- Fraudulent withdrawals have been reported from ATMs in Dubai, Hong Kong, Bangkok, and Russia using mule accounts.
- The international nature of these scams often involves routing stolen funds through various countries, using methods like cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Cybercrime and Terror Financing:
- Cyber scams have potential ramifications beyond financial losses; they can be used for terror financing and money laundering.
- Cryptocurrency is a common medium for laundering money, with an example cited of ?5.5 crore laundered through 350 transactions in a short span.
- ATM Hotspots and Fraudulent Withdrawals:
- 18 ATM hotspots have been identified across India where fraudulent withdrawals occur.
- Fraudsters exploit these locations to withdraw money, often using mule bank accounts and cross-border ATM networks.
- Government Response:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is working to combat these frauds by convening meetings with the Union Finance Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The objective is to curb the operation of mule accounts and strengthen the banking system to prevent such frauds.
- Banks are being urged to flag unusually high-value transactions or accounts with low balances that are engaging in suspicious activity.
- Fraudulent Calls and Scam Compounds:
- Indian fraudsters, in collaboration with international scam rings, use Indian mobile phone numbers to deceive citizens.
- Countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, and Azerbaijan have been identified as hubs for investment scams involving fraudulent calls.
- Helpline and Cyber Fraud Reporting System:
- The Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System (part of I4C) and the 1930 helpline provide mechanisms to report financial frauds.
- ?11,269 crore in financial frauds was reported during the first half of 2024 via these channels.
- The system also involves cooperation with over 200 financial intermediaries, including banks and wallets.
GLOBAL CYBERSECURITY INDEX 2024

- 21 Sep 2024
In News:
- India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024, published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), with an impressive score of 98.49 out of 100.
Role-Modeling Country: This accomplishment places India among ‘role-modeling’ countries, reflecting a strong commitment to cybersecurity practices globally.
Assessment Criteria: The GCI 2024 evaluates national efforts based on five pillars:
-
- Legal Measures
- Technical Measures
- Organizational Measures
- Capacity Development
- Cooperation
- Evaluation Methodology: The index utilized a comprehensive questionnaire comprising 83 questions, which cover 20 indicators, 64 sub-indicators, and 28 micro-indicators, ensuring a thorough assessment of each country's cybersecurity landscape.
- Tier Classification: The GCI 2024 report categorized 46 countries in Tier 1, the highest tier, indicating a strong commitment across all five cybersecurity pillars. Most countries fall into lower tiers, either “establishing” (Tier 3) or “evolving” (Tier 4) their cybersecurity frameworks.
Key Achievements
- Global Standing: India ranks at the top level of global cybersecurity rankings, showcasing its dedication to enhancing cyber resilience and securing its digital infrastructure.
- Government Initiatives:
- Robust Frameworks: Establishment of comprehensive frameworks for cybersecurity and cybercrime laws.
- Sectoral Support: Implementation of Sectoral Computer Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs) that provide technical support and incident reporting across various industries.
- Educational Integration: Cybersecurity has been integrated into primary and secondary education curricula to foster informed digital citizens.
- Public Awareness: Targeted campaigns have promoted secure online practices across multiple sectors, including private industry and academia.
- Skill Development and Innovation: The government has provided incentives and grants to enhance skill development and promote research within the cybersecurity sector.
- International Collaborations: India has engaged in numerous bilateral and multilateral partnerships to strengthen its capacity-building and information-sharing efforts.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Overview: Established in 1865, the ITU is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies, becoming a UN agency in 1947.
- Membership: ITU has 193 member countries and over 1,000 associated organizations, including companies and universities.
- Functions: ITU coordinates global radio spectrum allocation, sets technical standards for telecommunication, and works to improve ICT access in underserved communities.
- India's Involvement: India has been an active ITU member since 1869 and a regular participant in the ITU Council since 1952.
