Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
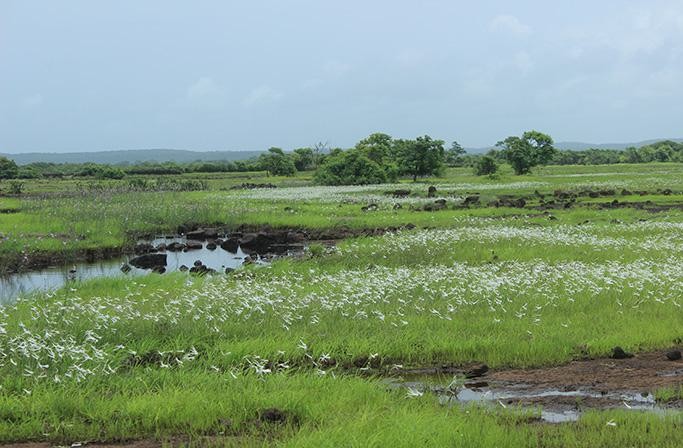
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
Stellaria bengalensis

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
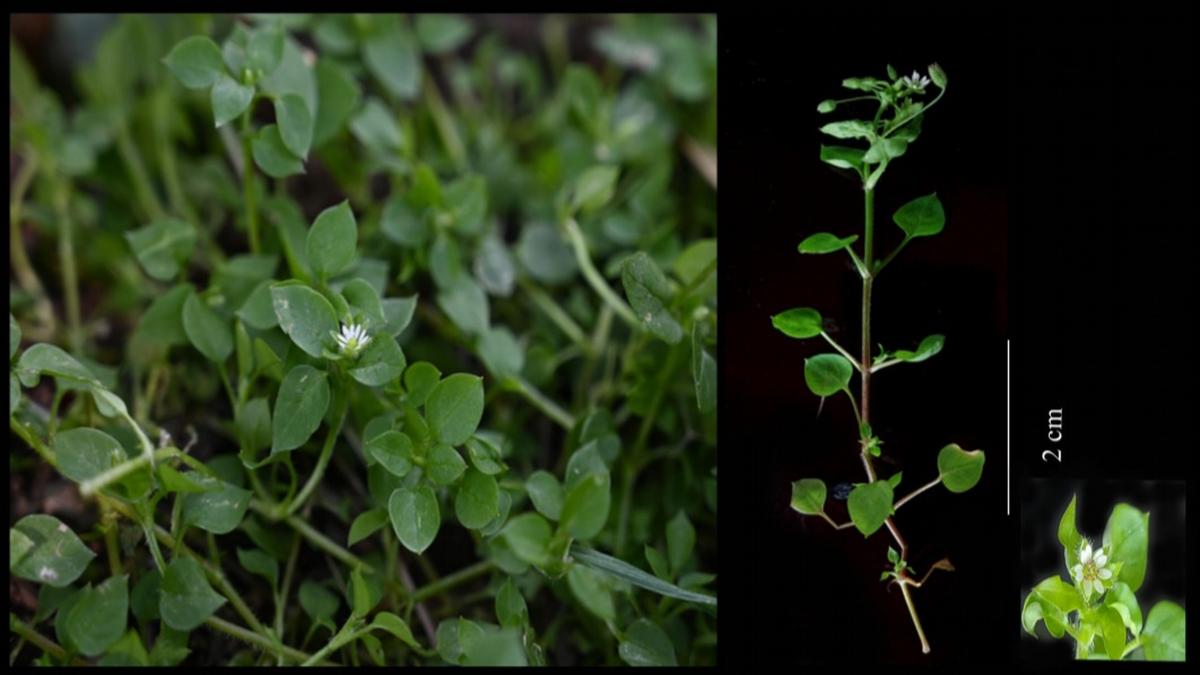
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP) 2024-2030

- 03 Nov 2024
In News:
The updated NBSAP was released by India at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Overview of the NBSAP (2024-30):
- Title:Updated National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plan: A Roadmap for Conservation of India’s Biodiversity.
- Objective: To provide a comprehensive roadmap for biodiversity conservation, aligning with global frameworks like the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF).
Key Features of the Updated NBSAP:
- Alignment with Global Frameworks:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) adopted in 2022 aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- India’s updated NBSAP aligns with KMGBF’s goals, focusing on biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource use, and ensuring fair benefit-sharing.
- 23 National Biodiversity Targets:
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Reducing threats to biodiversity
- Ensuring sustainable use of biodiversity
- Enhancing tools for biodiversity implementation
- The targets are focused on three key themes:
- Key Domains of Focus:
- Area-based conservation: Protecting ecosystems and habitats.
- Ecosystem resilience: Enhancing the ability of ecosystems to withstand environmental stressors.
- Recovery and conservation of threatened species.
- Conservation of agrobiodiversity: Ensuring the sustainability of agricultural biodiversity.
- Sustainable management of biodiversity.
- Enabling tools and solutions: Including financial and technical support for implementation.
- Financial Plan and Expenditure:
- Biodiversity Expenditure Review (BER) estimated an average annual expenditure of Rs 32,20,713 crore (FY 2017-2022) for biodiversity conservation.
- Future funding requirements (FY 2024-2030) estimated at Rs 81,664.88 crore annually at the central government level.
- Biodiversity Finance Plan suggests financing solutions, including public finance, corporate social responsibility (CSR), Ecological Fiscal Transfer (EFT), and Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) mechanisms.
- Capacity Building:
- The NBSAP stresses the need for capacity building across various levels—national, state, and local.
- Focus on skills acquisition for biodiversity management and enhancing knowledge to implement conservation strategies.
Implementation Framework:
- Multi-Level Governance:
- At the national level, the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) will oversee implementation with involvement from 22 other ministries.
- State-level: Involves State Biodiversity Boards and Union Territory Biodiversity Councils.
- Local level: Community-driven efforts through Biodiversity Management Committees.
- BIOFIN and Resource Mobilization:
- India is recognized as a leading country in the implementation of the Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN).
- Encouragement for private entrepreneurs, businesses, and international donors to invest in biodiversity through innovative financial instruments like:
- Green Bonds
- Green Funds
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES)
- Incentives for Financial Solutions:
- India aims to explore funding from corporate social responsibility (CSR), ecological fiscal transfers, and access and benefit sharing mechanisms to meet the financial needs for biodiversity conservation.
Challenges and Strategies:
- Challenges India Faces:
- Habitat fragmentation
- Pollution
- Illegal wildlife trade
- Adverse effects of climate change
- Strategic Responses:
- The updated NBSAP provides strategies to address these challenges, ensuring comprehensive conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
Great Indian Bustard (GIB)
- 25 Oct 2024
A critically endangered Great Indian Bustard (GIB) chick was successfully born through artificial insemination (AI) at a breeding center in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, marking a crucial step in efforts to save the species.
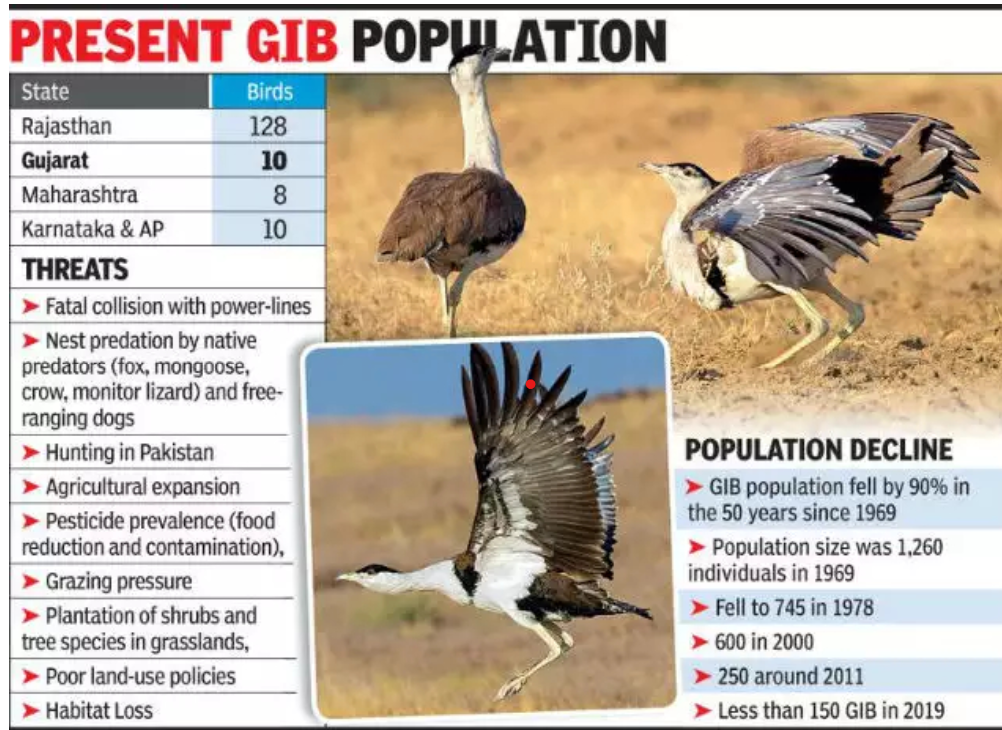
Endangered Status:
- The Great Indian Bustard is classified as critically endangered with fewer than 150 individuals left in the wild in India.
- About 90% of these birds are found in the desert areas of Rajasthan, with smaller populations in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
Main Threats to the Species:
- Habitat Loss: The primary threat is the loss of habitat, which is often perceived as wasteland and is diverted for infrastructure projects like roads and development.
- Slow Reproductive Rate: The bustard’s low reproductive rate exacerbates its risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts: Bustard Recovery Program
- In 2016, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change launched the Bustard Recovery Program to focus on captive breeding and creating a sustainable environment for the reintroduction of GIBs into the wild.
- A dedicated GIB breeding center was set up at the Desert National Park in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, as part of this initiative.
- Protection Status of GIB:
- IUCN: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix 1
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- It is also the state bird of Rajasthan, emphasizing its importance in the region’s biodiversity.
Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) SKILLS Platform

- 24 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
In response to the escalating biodiversity crisis, the Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) is designed to support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
About GSAP SKILLS Platform:
- The Global Species Action Plan (GSAP) SKILLS platform, standing for (Species Conservation Knowledge, Information, Learning, Leverage, and Sharing), brings the GSAP’s content online and enables real-time updates of technical tools and resources.
- This platform aims to facilitate global collaboration and partnership by connecting decision-makers, species conservation practitioners, and experts at all levels.
- It ensures accessibility and relevance by providing real-time updates on technical tools and resources.
- Each target within the Global Biodiversity Framework is accompanied by a summary and rationale for species conservation interventions, actions, and sub-actions, along with the actors involved and the technical tools and resources required, facilitating the scaling-up of implementation efforts.
- Managed proactively by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the platform meets the needs of governments and stakeholders to take decisive action for species conservation.
- The development of the GSAP SKILLS platform has been principally supported by the Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea, with additional resources from the Tech4Nature Initiative, launched by IUCN and Huawei in 2020.
What is the Global Species Action Plan?
- It has been developed to support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) and to address the increasing biodiversity loss worldwide.
- It outlines strategic interventions and actions to conserve and sustainably manage species while ensuring equitable benefits.
About Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) is an outcome of the 2022 United Nations Biodiversity Conference.
- Its tentative title had been the "Post-2020 Global Biodiversity Framework".
- The GBF was adopted by the 15th Conference of Parties (COP15) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) on 19 December 2022.
- It has been promoted as a "Paris Agreement for Nature".
- It is one of a handful of agreements under the auspices of the CBD, and it is the most significant to date.
- It has been hailed as a "huge, historic moment" and a "major win for our planet and for all of humanity."
- UN Secretary-General António Guterres speaking at the 2022 biodiversity conference in Montreal which led to this treaty
- The Framework is named after two cities, Kunming, which was scheduled to be the host city for COP15 in October 2020 but postponed and subsequently relinquished the hosting duties due to China's COVID policy, and Montreal, which is the seat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Secretariat and stepped in to host COP15 after Kunming's cancellation.
Odisha’s Gupteswar Forest Is Now A Biodiversity Heritage Site (TOI)
- 13 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Gupteswar forest in the Koraput district of Odisha has been officially declared the fourth biodiversity heritage site (BHS) in the state.
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS)?
- A Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) is a unique ecosystem with rich biodiversity that is designated for special protection and conservation.
- These sites are typically declared by individual states or local bodies under the provisions of the Biological Diversity Act, of 2002, in India.
Who can Declare BHS?
- Under Section 37 of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 the State Government in consultation with local bodies may notify areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS).
- The ‘Biodiversity Heritage Sites’ (BHS) are unique ecosystems having rich biodiversity comprising of any one or more of the following components:
- The richness of wild as well as domesticated species or intra-specific categories.
- High endemism.
- Presence of rare and threatened species, keystone species, and species of evolutionary significance.
- Wild ancestors of domestic/cultivated species or their varieties.
- Past pre-eminence of biological components represented by fossil beds and having significant cultural, ethical or aesthetic values are important for the maintenance of cultural diversity, with or without a long history of human association with them.
- “The creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them.
- The purpose of declaring BHS is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation of such sites.”
The main objectives of declaring an area as a BHS are:
- To conserve biological diversity, including genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and species diversity.
- To protect habitats of rare, endemic, and threatened species.
- To promote sustainable use of biodiversity.
- To maintain cultural diversity and traditional knowledge associated with biodiversity.
- To raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation.
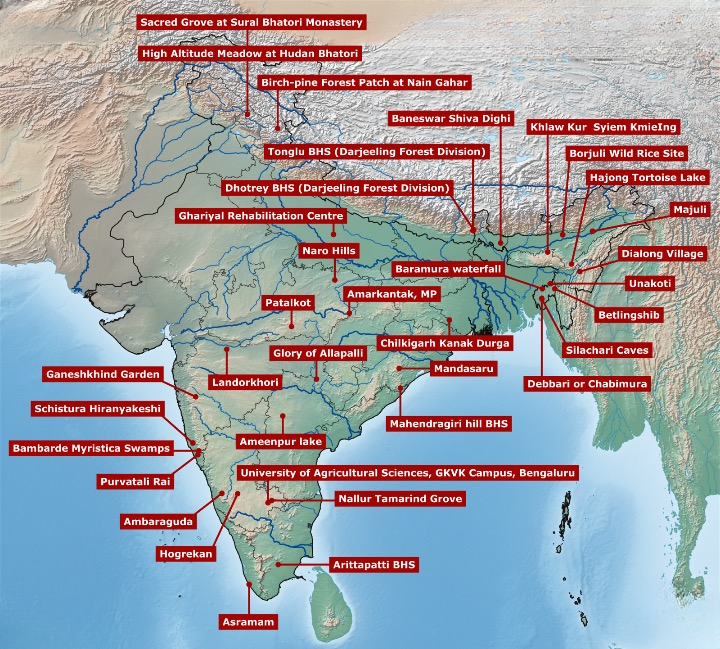
Biodiversity Heritage Sites (BHS) of India:
The Nagoya Protocol (Down To Earth)

- 07 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News
Cameroon, a central African country recently adopted the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing.
About the Nagoya Protocol:
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilisation (the Protocol) is a globally binding agreement designed to fulfill the access and benefit-sharing obligations outlined in the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- Adopted in Nagoya, Japan, in October 2010, the Protocol came into effect on October 12, 2014, following the deposit of the fiftieth instrument of ratification.
- It establishes a transparent legal framework to ensure the fair and equitable distribution of benefits derived from the use of genetic resources, a key objective of the CBD.
Benefits of the Protocol:
- It provides researchers with a structured framework to access genetic resources for biotechnological research and development while ensuring a fair share of benefits derived from their utilization.
- Indigenous and local communities stand to benefit from the recognition and protection of traditional knowledge associated with genetic resources.
Scope of the Protocol:
- The Protocol covers genetic resources within the scope of the CBD and addresses the benefits arising from their utilization.
- Additionally, it encompasses traditional knowledge linked to genetic resources covered by the CBD and the benefits derived from its utilization.
Key Facts about the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- With 196 contracting parties, the CBD is the most comprehensive binding international agreement for conserving nature and sustainably managing natural resources.
- Opened for signing at the UN Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, the CBD aims to conserve biological diversity, ensure its sustainable use, and promote the fair and equitable sharing of benefits.
- The CBD covers biodiversity across ecosystems, species, and genetic resources.
- The Conference of the Parties (COP) serves as the highest decision-making body of the Convention, with the Secretariat based in Montreal, Canada.
- To further CBD objectives, two internationally binding agreements were adopted: the Cartagena Protocol in 2000, regulating the transboundary movement of living modified organisms, and the Nagoya Protocol in 2010, facilitating access to genetic resources and the equitable sharing of benefits.
