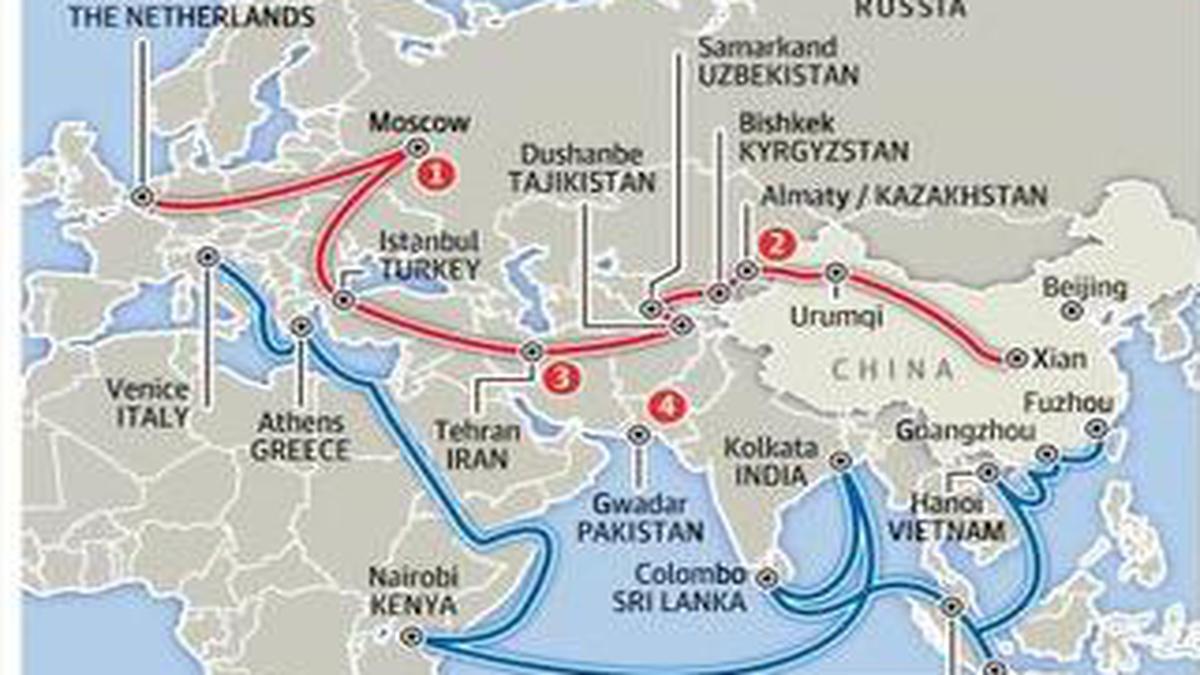
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- 30 Oct 2024
In News:
- Brazilhas opted not to join China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), becoming the second BRICS country after India to reject the multi-billion-dollar infrastructure project.
- Brazil prefers to explore alternative ways to collaborate with Chinese investors without signing a formal treaty, aiming to avoid the perceived risks of the BRI.
BRICS and India’s Role:
- Brazil’s decision follows India’s long-standing opposition to the BRI, particularly due to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passing through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which India views as a violation of its sovereignty.
- India has consistently argued that BRI projects should adhere to international norms, good governance, and transparency, emphasizing that such initiatives should be financially sustainable and not lead to debt traps.
Brazil’s Broader Economic Strategy:
- Brazil aims to balance its relationship with China, which is a major economic partner, but without being bound by the BRI. This decision reflects broader concerns within Brazil about the long-term financial sustainability of BRI projects, especially after witnessing debt crises in other countries like Sri Lanka.
Global Context and the BRI's Impact:
- The BRI, launched by China in 2013, spans several infrastructure sectors and has expanded globally, but it has faced criticism for its potential to trap smaller nations in unsustainable debt.
- India and Brazil’s resistance to the BRI highlights growing skepticism among emerging economies about the long-term implications of joining China's flagship project.
