Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) (NewsOnAir)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Health Authority (NHA) has recently declared the extension of its Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS) until the 31st of December 2023.
About Digital Health Incentives Scheme (DHIS):
- Launched in December 2022, the DHIS became effective from 1st January 2023.
- The scheme is implemented by the National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Its primary objectives include giving a further impetus to digital health transactions across the country through the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM).
Salient Features of DHIS:
- The scheme offers incentives of up to four crore rupees, determined by the number of digital health records created and linked to patients' Ayushman Bharat Health Account numbers.
- Incentives are extended to hospitals, diagnostic labs, and providers of digital health solutions, including Hospital/Health Management Information Systems (HMIS) and Laboratory Management Information Systems (LMIS).
- Health facilities (hospitals and diagnostic labs) registered with the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission's Health Facility Registry (HFR) and meeting the specified eligibility criteria can avail of the incentives.
Benefits of DHIS:
- Incentives for Digitization: Healthcare facilities and Digital Solution Companies participating in the scheme can earn incentives to cover expenses related to digitization.
- Enhanced Efficiency in Healthcare Delivery: DHIS streamlines the healthcare process, eliminating hassles in registration, appointment scheduling, consultations, IPD admission, discharge, and more.
- Robust Digital Health Ecosystem: The scheme contributes to the development of a strong digital health ecosystem, encompassing various levels of healthcare facilities.
- Improved Quality of Care: DHIS facilitates evidence-based, accessible, and high-quality healthcare services, leading to better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missiles (TOI)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Israel's Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) anti-tank guided missiles were recently delivered to the Indian Air Force.
About the Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missile:
- The Spike Non-Line of Sight (NLOS) Anti-tank Guided Missile (ATGM) is a sophisticated fire-and-forget missile designed for anti-tank and anti-personnel purposes.
- It features a tandem-charge high-explosive warhead.
- Developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, an Israeli defense technology company, the Spike NLOS ATGM comes in man-portable, vehicle-launched, and helicopter-launched variants.
- The missile is currently in use by the defense forces of Israel and 38 other countries, including India, Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Peru, Spain, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, the UK, Philippines, and Singapore.
- Key features of the Spike NLOS ATGM:
- Striking range of up to 30 kilometers
- Weight of 71 kg, and
- An electro-optical seeker that offers superior target visibility compared to radar or infrared-guided missiles.
- The missile's seeker is equipped with a datalink, enabling the launch operator to maintain control over the missile during flight.
- This capability allows for precise targeting, including attacking different parts of a tank or engaging an alternative target, or aborting the strike if necessary.
- The Spike NLOS ATGM can be armed with various types of warheads, making it versatile for destroying tanks, and air defense systems, or for use in urban combat scenarios.
Perucetus colossus (Indian Express)
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
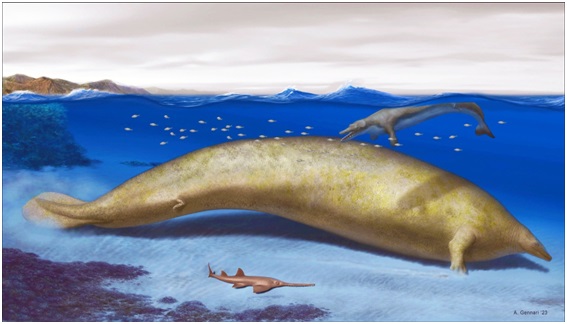
Perucetus colossus, whose fossils were discovered in Peru, maybe the heaviest discovered animal ever, even heavier than the blue whale.
About Perucetus colossus:
- The whale species Perucetus colossus is known from a recently described fossil dating back over 38 million years.
- Despite potentially being shorter in length, scientists believe that this ancient whale species might have been heavier than the modern blue whale.
- Researchers estimate that the weight of the Perucetus colossus could have ranged from 85 to an astonishing 340 tonnes.
- The fossilized bones of this species exhibited an unusual combination of large volume and extreme density, a characteristic known as pachyosteosclerosis.
- Pachyosteosclerosis is not observed in living whales, dolphins, and porpoises, but it is present in sirenians, a marine mammal group that includes sea cows.
- Unlike deep-diving whales, Perucetus colossus likely lived in shallow coastal areas, suggesting that it might have dived with air in its lungs.
- However, diving with air in the lungs would make it challenging to stay near the seafloor.
- The heavy bones of the Perucetus colossus might have played a crucial role in enabling it to do so.
- The skeletal mass of the Perucetus colossus is estimated to have been between five and eight tons, double that of a modern blue whale.
Study in India (SII) portal (Indian Express)

- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Study In India (SII) portal was recently introduced by the Education Ministry, aiming to promote Indian education among international students.
About the Study in India (SII) portal:
- The Study in India (SII) portal serves as a dedicated website offering comprehensive information about higher education institutions (HEIs) in India.
- The main objective of the portal is to establish India as a global education hub and attract students from diverse backgrounds.
- The portal showcases a wide range of academic programs available in the HEIs, including undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral courses, along with courses related to the Indian Knowledge System (IKS), such as Yoga, Ayurveda, and classical arts.
- Detailed information about the academic facilities, research support, and other related offerings in the institutes is provided on the portal.
- It acts as a convenient one-stop platform for students, enabling them to register, apply for a visa, select desired courses, and receive offer letters from their chosen institutes.
- The portal allows students to apply to multiple institutes or courses of their preference, simplifying the application process.
- Study in India (SII) offers a streamlined and well-organized application process, providing international students with easy access to higher education opportunities in India.
What is Study in India (SII) Programme?
- The Study in India (SII) program is a prominent initiative initiated by the education ministry in 2018 with the aim of positioning India as a premier education destination for international students.
- The program seeks to attract foreign students to pursue higher education in India, providing them with valuable educational opportunities offered by renowned Indian universities.
Great Nicobar Island Project (DownToEarth)
- 05 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
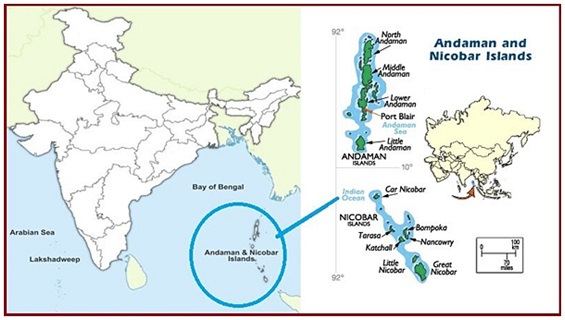
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change's statement in the Rajya Sabha, approximately 964,000 trees are expected to be cut down for the implementation of the Great Nicobar Island Project.
About Great Nicobar Island Project:
- Ministry:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Implementing Agency:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- The project is a massive undertaking with a budget of ?72,000 crore and is spearheaded by NITI Aayog, known as NITI Aayog's Project for Great Nicobar Island.
- Objective:
- The primary goal of the project is to achieve holistic development for the Great Nicobar Island (GNI).
- The project's vision is to transform the Great Nicobar Island, situated in the Bay of Bengal, into a modern, sustainable, and self-sufficient territory, thus facilitating the comprehensive development of Great Nicobar.
The plan comprises four key components:
- A transshipment port at Galathea Bay with an investment of ?35,000 crore.
- Development of a dual-use military-civil international airport.
- Establishment of a power plant.
- Creation of a township to support the overall project.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) (TOI)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) has reported that three private sector satellite manufacturers plan to launch their earth observation satellites during this fiscal year.
About Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe):
- IN-SPACe serves as a single-window, independent, and autonomous agency within the Department of Space (DOS).
- It was established as part of the Space sector reforms to encourage and facilitate the active involvement of private players in the space industry.
- IN-SPACe's responsibilities include promoting, enabling, authorizing, and supervising various space activities of non-governmental entities, such as manufacturing launch vehicles and satellites, providing space-based services, and utilizing space infrastructure and facilities.
- Acting as an intermediary between ISRO and Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs), the agency assesses opportunities for leveraging India's space resources effectively and enhancing space-based initiatives.
- Also, IN-SPACe addresses the specific needs and demands of private players, including educational and research institutions, while working in collaboration with ISRO.
- The headquarters of IN-SPACe is located in Bopal, (Ahmedabad).
Samudrayaan (IndiaToday)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
India's ambitious Samudrayaan project, aimed at exploring the deep ocean and its resources, is set to send three personnel to a depth of 6000 meters in a submersible vehicle.
About Samudrayaan Project:
- India's inaugural manned mission to delve into the depths of the ocean for exploration.
- Its primary objectives include studying deep ocean resources and conducting biodiversity assessments.
- The mission is designed to ensure minimal disturbance to the ecosystem, focusing solely on exploration.
- Part of the comprehensive Deep Ocean Mission aligned with the Central Government's Blue Economy policy.
- The Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) leads the implementation of this ambitious, multi-institutional endeavor.
What is the Blue Economy?
- Blue economy refers to the sustainable use of marine resources for exploration, economic growth, improved livelihoods, and transport while preserving the health of marine and coastal ecosystems.
- In India, the blue economy encompasses a wide range of sectors, including shipping, tourism, fisheries, and offshore oil and gas exploration.
Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana (PIB)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
In the Lok Sabha, the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas provided details about the Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN scheme.
About Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana:
- The scheme was officially notified in March 2019.
- Its main objective is to extend financial support to integrated bio-ethanol projects, facilitating the establishment of Second Generation (2G) ethanol projects using lignocellulosic biomass and other renewable feedstocks.
- It has a financial outlay of Rs. 1969.50 crore, spanning the period from 2018-19 to 2023-24.
- Financial assistance of Rs. 150 crore is offered per project for commercial projects, while demonstration projects receive Rs. 15 crore per project.
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas serves as the nodal ministry for this scheme.
What is Lignocellulosic Biomass?
- Abundant Source: It is found in agricultural and forestry residues, as well as dedicated energy crops.
- Biofuels and Bio-based Products: Lignocellulosic biomass holds promise as a sustainable feedstock for producing biofuels like second-generation ethanol and various bio-based products.
- Challenges: Efficiently breaking down its complex structure to release sugars for fermentation or chemical conversion is a key challenge.
- Innovative Technologies: Researchers are exploring enzymatic hydrolysis and thermochemical treatments to unlock its energy potential.
- Green and Sustainable Future: Utilizing lignocellulosic biomass can reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and mitigate environmental impacts linked to conventional energy production.
Himalayan vulture bred (The Hindu)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The first-ever instance of captive breeding of the Himalayan vulture in India has been successfully recorded at the Assam State Zoo in Guwahati by researchers.
About Himalayan Vulture:
- Scientific Name: Gyps himalayensis
- It is a rare and the largest bird species native to the Himalayas.
- Habitat:
- The Himalayan vulture primarily inhabits higher regions of the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau, typically found at elevations above 1500 meters.
- This species has a distribution range that extends from western China, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to the eastern part of the Himalayan mountain range, including India, Nepal, and Bhutan, and further to central China and Mongolia.
- Description:
- This vulture is impressively large, featuring a sandy brown plumage with a pale, featherless head. In flight, it displays black primaries and a distinctive small-headed, squared-winged appearance.
- Himalayan vultures are usually spotted alone or in small groups, but they gather in large flocks when feeding on a carcass.
- Conservation status:
- The Himalayan vulture is categorized as "Near Threatened" on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
- To ensure its preservation, the species is covered under the Multi-species Action Plan (MsAP) for the conservation of African-Eurasian vultures and is also included in national Action Plans in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Cambodia.
- Threats:
- The most significant potential threat to this vulture species is believed to be mortality resulting from the ingestion of diclofenac and other vulture-toxic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), commonly used in livestock, particularly in South Asia.
CHD1L gene (DownToEarth)
- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A new study indicates that some individuals of African descent have a CHD1L gene variant that may be involved in controlling the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
What is the CHD1L gene?
- The CHD1L gene encodes proteins that aid in repairing DNA damage within the body.
- A specific variant of the CHD1L gene is found predominantly in the African population and has been associated with a decreased viral load (amount of HIV in the blood) of HIV-1, the most common and severe type of HIV compared to HIV-2.
- Through the analysis of DNA from nearly 4,000 people of African descent living with HIV-1, researchers identified the presence of a gene variant of CHD1L located on chromosome 1.
- Individuals carrying this particular gene variant exhibited a low viral load, reducing their risk of transmitting the virus and slowing the progression of their own HIV-related illness.
- The study suggests that between 4% and 13% of people with African origins could be carrying this specific CHD1L gene variant.
Lunar Codex (The Guardian)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Lunar Codex program has the potential to bestow immortality upon an assorted collection of human-created art.
About Lunar Codex:
- The Lunar Codex is a remarkable collection of art curated by artists worldwide, intended to endure on the lunar surface as a timeless testament to human creativity, even amid tumultuous times like wars, pandemics, and economic crises.
- At the helm of this endeavor is Samuel Peralta, a semi-retired physicist and art enthusiast from Canada.
- Comprising diverse forms of digitized art, the Lunar Codex will be dispatched to the moon to serve as a permanent record of human ingenuity. Memory cards and NanoFiche, an updated 21st-century version of film-based microfiche, guarantee the safe arrival of these artistic expressions to the lunar surface.
- Carefully assembled from contributions by 30,000 artists, writers, filmmakers, and musicians representing 157 countries, the collection spans an array of art forms, including images, magazines, books, podcasts, movies, and music.
- The art is divided into four capsules:
- The first capsule, the Orion collection, has already encircled the moon after being launched aboard NASA's Artemis 1 mission via the Orion spacecraft last year.
- In the months ahead, multiple lunar landers will transport the Lunar Codex capsules to distinct locations, including craters at the moon's South Pole and the lunar plain known as Sinus Viscositatis, ensuring the enduring legacy of human creativity on Earth's celestial neighbor.
JALDOST airboat (The Hindu)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) recently revealed its latest creation, the JALDOST airboat.
What is JALDOST?
- JALDOST is an innovative airboat specifically designed for water operation, aimed at effectively removing excess aquatic weed and floating waste from various water bodies.
- The airboat features a closed, airtight pontoon-type hull, ensuring its inherent unsinkability.
- Notably, the JALDOST incorporates a hybrid propulsion system, combining air propulsion and paddle wheel propulsion, making it versatile and efficient in its movements.
- Operating through weed with ease, JALDOST serves as an ideal platform for collecting and transporting these undesirable aquatic plants to the shore.
- It achieves this through a steel mesh belt conveyor system situated at the front, which gathers the waste and deposits it on the horizontal deck conveyor.
- Upon reaching the shore, the collected waste is efficiently unloaded using a rear conveyor system, facilitating easy transfer to trucks or tractors.
- The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has introduced two versions of the airboat, namely JALDOST Mark-1 and an upgraded version, JALDOST Mark-2, further enhancing its capabilities.
Iberian wolf (DownToEarth)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
As per the regional government, the Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus) has been declared extinct in the historical region of Andalusia, located in the southernmost part of Iberia, since the year 2020.
About the Iberian Wolf:
- The Iberian wolf is a subspecies of the Grey wolf, distinguished by its prolonged isolation from other wolf populations for over a century.
- With the largest wolf population in Western Europe, this magnificent species is native to the Iberian Peninsula, encompassing Spain and Portugal.
- Thriving in diverse habitats, Iberian wolves inhabit forests, inland wetlands, shrublands, grasslands, pastures, and mountainous areas.
- These wolves lead a social lifestyle, living, hunting, and traveling in small packs.
- Each pack includes the alpha male and female, along with their young and older offspring.
- The alphas serve as the pack leaders, responsible for establishing territory, selecting den sites, tracking down, and hunting prey.
- Primarily carnivorous, the Iberian wolf's diet comprises various animal species.
- With regard to conservation, the Iberian wolf holds the status of "Vulnerable" according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Schemer (Indian Express)

- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry has recently announced a fresh target for its PM SVANidhi scheme, focusing on empowering street vendors.
About PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme:
- Launched on June 01, 2020, by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, the PM SVANidhi Scheme aims to assist street vendors affected by the Covid-19 lockdown in reviving their livelihoods.
- As a micro-credit initiative, it provides street vendors with a collateral-free loan of Rs. 10,000 at a low-interest rate (below 12%) for one year, facilitating their financial recovery.
- Originally scheduled until March 2022, the scheme has now been extended till December 2024 with a focus on expanding the affordable loan corpus, encouraging digital transactions, and promoting holistic socio-economic development for street vendors and their families.
- Eligibility for the loan requires street vendors who were vending on or before March 24, 2020, and hold a certificate of vending issued by the Town Vending Committees (comprising local authorities and vendors) after conducting a survey.
- The scheme offers several benefits, including an interest subsidy of 7% per annum on timely loan repayment, no penalty on early repayment, cash back incentives up to Rs. 100 per month to promote digital transactions, and the possibility of credit limit escalation for prompt loan repayment.
- The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) serves as the implementation agency for the scheme, ensuring efficient delivery and monitoring of financial support to street vendors across the country.
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) (Indian Express)
- 03 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
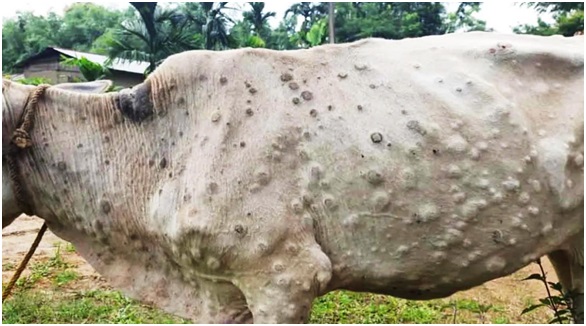
The Telangana High Court's division bench recently conveyed its discontentment over the absence of specific information regarding measures taken to manage the outbreak of Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) in cattle.
What is Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD):
- Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a highly infectious viral disease that affects cattle, ranging from acute to chronic in nature.
- It is caused by the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV), belonging to the genus Capripoxvirus within the poxviridae family (related to smallpox and monkeypox viruses), but it is not zoonotic, meaning it does not spread to humans.
- Symptoms of LSD include the enlargement of lymph nodes, resulting in lumps on the cattle's skin, primarily appearing on the head, neck, limbs, udder, genitalia, and perineum.
- The cutaneous nodules, usually 2–5 cm in diameter, may develop into ulcers and scabs over time.
- Other signs of infection include high fever, reduced milk yield, nasal and ocular discharge, salivation, loss of appetite, depression, damaged hides, emaciation, infertility, and abortions.
- Transmission occurs through blood-feeding insects such as certain flies, mosquitoes, and ticks, as well as the movement of affected animals and contaminated equipment.
- Direct animal-to-animal transmission can also occur in some cases.
- While no direct antiviral treatment is available for LSD, supportive care is provided to infected animals, including the use of antibiotics, painkillers, and wound care sprays to alleviate symptoms.
- Vaccines are used to control disease transmission, as there is no specific cure.
- LSD is economically significant as it can lead to temporary reductions in milk production, temporary or permanent sterility in bulls, hide damage, and, in some instances, fatalities among the affected cattle population.
ZARTH App (The Hindu)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Center for Data-Driven Discovery at the California Institute of Technology has recently unveiled the ZARTH app, enabling smartphone users to actively search for transients.
What is ZARTH App?
ZARTH (ZTF Augmented Reality Transient Hunter) combines the excitement of an augmented reality mobile game with serious scientific pursuits. This innovative app empowers users to engage in real science while enjoying a gaming experience.
Key Features:
- Leveraging the open-source Sky Map, the ZARTH app integrates daily data from the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) at California's Palomar Observatory.
- The Palomar Observatory houses the prestigious 200-inch Hale reflector, one of the world's oldest and most powerful telescopes.
- The ZTF conducts bi-daily scans of the entire northern sky, generating crucial large-area sky maps with applications in tracking near-earth asteroids and studying supernovae.
- Each day, the ZARTH app receives real-time data on transients detected by the ZTF, including flaring stars, white dwarf binaries, active galactic nuclei, and other intriguing types.
- Transients are ranked based on rarity and significance, fostering a competitive environment among players who strive to earn points and daily credits displayed on leaderboards.
Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023 (Indian Express)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023, has been successfully passed by the Lok Sabha.
The Offshore Areas Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
It seeks to amend the existing Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002, to regulate mining activities in India's maritime zones.
The key highlights of the Bill include:
- Reservation of Offshore Areas: The government is empowered to reserve offshore areas not under any operating rights.
- Composite Licence and Production Lease: The administering authority can grant composite licenses or production leases to the government or a government company.
- Fixed Production Lease Period: The provision for renewal of production leases is removed, and a fixed period of fifty years, akin to the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act 1957, is introduced.
- Auction-Based Allocation: Private sector entities can acquire production leases through auction by competitive bidding.
- Operating Rights for Government Entities: Operating rights without competitive bidding can be granted to government or government companies or corporations in mineral-bearing areas reserved by the central government.
- Atomic Minerals: For atomic minerals, exploration licenses or production leases can only be granted to the government or government corporations.
- Production Commencement Timeline: A four-year timeline for production commencement and dispatch after the execution of composite licenses or production leases is introduced, with a two-year timeline (extendable by one year) for re-commencement of production and dispatch after discontinuation.
- Framing Rules for Conservation and Environment: The central government is enabled to establish rules for mineral conservation and systematic development in offshore areas, along with measures to protect the environment and control pollution resulting from exploration or production operations.
eSanjeevani (India's Integrated Telemedicine Solution ) (Indian Express)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Union Health Minister revealed to the Rajya Sabha that the eSanjeevani telemedicine application, introduced by the Centre, has successfully conducted a remarkable 14,17,81,384 teleconsultations.
About eSanjeevani:
- eSanjeevani is an integrated telemedicine solution, hosted on the cloud, developed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- This telemedicine app facilitates seamless communication between doctors and patients as well as doctor-to-doctor interactions.
- The Centre for Development and Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Mohali, is responsible for the design, development, deployment, and maintenance of this platform.
- The eSanjeevani system consists of two essential modules:
- eSanjeevani AB-HWC:
- This module serves as a doctor-to-doctor telemedicine platform, strategically implemented across all Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) in the country under the Ayushman Bharat Scheme.
- It operates on a Hub-and-Spoke model, with zonal hubs comprising MBBS/Specialty/Super-Specialty doctors connected to state-level Ayushman Bharat-Health and Wellness Centers.
- eSanjeevani OPD:
- Rolled out in 2020 during the initial Covid-19 lockdown when outpatient departments (OPDs) were closed, this module enables patient-to-doctor remote consultations.
- People can access outpatient services from the comfort of their homes, ensuring healthcare accessibility during challenging times.
- eSanjeevani represents a significant step towards enhancing healthcare accessibility and digital healthcare services across India.
Infrastructure investment trust (InvIT) (Business Standard)

- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The government is actively developing a proposal to introduce a new Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) dedicated to national highways. This initiative aims to enable domestic retail investors to own units of the trust, expanding opportunities for individual investors to participate in highway infrastructure projects.
What is Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT)?
- An Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) functions as a Collective Investment Scheme, offering a pathway for both individual and institutional investors to directly invest in diverse infrastructure projects.
- Operating akin to mutual funds, InvITs are established as trusts and undergo registration with Sebi (Securities and Exchange Board of India).
- InvITs involve four key parties:
- the Trustee, Sponsor(s), Investment Manager, and Project Manager. The Sebi-certified Trustee assumes the crucial role of overseeing the InvIT's performance. Meanwhile, the Sponsor(s) act as the company's promoters responsible for creating and setting up the InvIT.
- Overall, InvITs present an attractive investment option, as they allow investors to participate in the development of vital infrastructure projects while enjoying the benefits of a collective investment structure similar to mutual funds.
What is NHAI InvIT?
- NHAI InvIT is an infrastructure investment trust proudly sponsored by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) to bolster the government's National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) initiative.
- This Trust has been established by NHAI in accordance with the Indian Trusts Act, of 1882, and adheres to the regulations set forth by SEBI (Security and Exchange Board of India).
- The NHAI InvIT plays a vital role in supporting the nation's infrastructure development by providing a platform for investors to participate in highway projects' growth and monetization.
- Through this innovative investment vehicle, NHAI aims to tap into private and institutional investments to enhance the funding and execution of critical infrastructure projects across the country, ultimately contributing to India's overall economic progress.
TransLunar Injection (TLI) (The Hindu)
- 02 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The TransLunar Injection (TLI) was performed successfully from ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru recently.
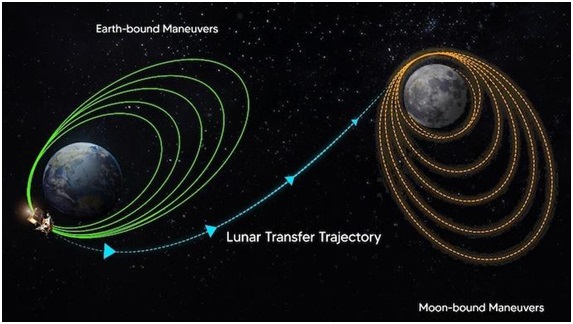
What is the TransLunar Injection (TLI)?
- TransLunar Injection (TLI) is a crucial space mission maneuver, propelling spacecraft from Earth's orbit to a trajectory aimed at reaching the Moon.
- An essential step in lunar missions, TLI allows spacecraft to break free from Earth's gravity and commence their journey toward the Moon.
- TLI is executed when the spacecraft reaches the perigee, the closest point to Earth in its orbit.
- During TLI, the spacecraft's propulsion system ignites its engines, accelerating the craft and providing the necessary speed to escape Earth's gravitational pull.
- The thrust and duration of the TLI burn are determined by factors like spacecraft mass, Earth's orbital velocity, and specific mission objectives.
- Following a successful TLI, the spacecraft is directed onto a lunar trajectory, continuing its autonomous journey to the Moon without further reliance on Earth's propulsion.
- Subsequent to TLI, the spacecraft enters a transfer orbit, an elliptical path that intersects with the Moon's orbit.
- The spacecraft traverses this highly eccentric orbit until it reaches the lunar surface.
- As the spacecraft approaches the Moon, additional maneuvers like lunar orbit insertion (LOI) may be executed to enter lunar orbit or facilitate landing, based on the mission's objectives.
- TLI has been effectively utilized in numerous Moon missions, including Apollo, Chang'e, and Artemis missions.
National Digital Nagrik Forum (Indian Express)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The forum by the Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT) aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and help build the capacities of citizens to engage with innovation via expert sessions and instructional materials.
About the National Digital Nagrik Forum:
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum is an online platform with the primary goal of advancing the rights of traders, consumers, and various sections of society, while also influencing policy to foster the growth of the digital trade economy.
- Through expert sessions and instructional materials, the forum aims to raise awareness about digital regulations and empower citizens to engage with innovation effectively.
- The main objective is to shape policy discourse around the digital economy trade in India, aligning with the Government of India's vision of establishing a trillion-dollar digital economy.
- Simultaneously, it seeks to maintain an open, safe, trusted, and accountable Internet ecosystem.
- The forum will conduct awareness camps, digital and physical dialogues, and training sessions.
- It will also engage in targeted outreach to stakeholders from the government, private sector, and civil society.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum will concentrate on five core themes:
- The first pillar focuses on consumer protection and online safety, with a central emphasis on efficient grievance redressal mechanisms.
- The second pillar addresses the challenges of digital cartelization, advocating for a level-playing field to discourage discriminatory and anti-competitive practices in the online world.
- The third pillar explores the potential of Indian digital technologies to transform retail and industrial trade, while also contributing to employment growth and expanding investment opportunities.
- The fourth pillar advocates for a first principles-based taxation policy that fosters certainty and productivity, especially for sectors with high growth potential. It simultaneously works to prevent illegal activities like tax evasion and money laundering.
- The fifth pillar conducts research on emerging technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence to assess their impact on retail trade and ensure the protection of consumers' interests.
- The National Digital Nagrik Forum aims to make significant contributions towards shaping a vibrant digital economy in India, fostering fair trade practices, and safeguarding the interests of both consumers and traders.
Room-temperature Superconductor (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Korean researchers claim to have developed a superconductor that can operate at room temperature and ambient pressure.
What have the researchers developed?
- The researchers assert that they have created a superconductor named LK-99, which operates at room temperature and under ambient pressure.
- LK-99 is a combination of powdered compounds containing lead, oxygen, sulphur, and phosphorus.
- Upon heating at extremely high temperatures, it transforms into a dark grey solid.
- The potential significance of this discovery is immense, provided other laboratories can replicate these results.
- Nevertheless, some researchers remain skeptical as this study has not undergone peer review, and the results must be independently reproduced by other scientific groups.
What is a Superconductor?
- A superconductor is a material that exhibits superconductivity, a unique state of matter characterized by the absence of electrical resistance and the exclusion of magnetic fields.
- In a superconductor, an electric current can flow indefinitely without any hindrance.
- Superconductors have significant practical applications in our everyday lives.
- In 1933, Walther Meissner and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered that superconductors act as perfect diamagnets, repelling magnetic fields, a phenomenon known as the Meissner effect.
- This property makes them ideal for applications like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- However, achieving superconductivity typically requires extremely low temperatures.
- Currently, researchers are actively exploring and developing superconductors that can operate at room temperature, a groundbreaking advancement that would revolutionize various technologies and industries.
How will the room-temperature superconductors help?
- The use of room-temperature superconductors can offer significant benefits in various applications.
- Typically, the critical temperature of conventional superconductors is below 10 Kelvin (-263 degrees Celsius), whereas room temperature is around 20-22°C.
- By having superconductors that function at room temperature, the cost of electricity grids, computer chips, magnets for maglev trains, energy-storage devices, and fusion reactors can be reduced significantly.
- This is achieved through electricity and cost savings on coolants, as the need for extreme cooling methods is eliminated.
- The widespread adoption of room-temperature superconductors holds the potential to revolutionize multiple industries, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA) (The Hindu)

- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
During the Man ki Baat program, the Prime Minister announced that India achieved a remarkable feat by destroying 10 lakh kilograms of drugs worth ?12,000 crore in the previous year.
What is Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA)?
- Launched on: The NMBA was launched on 15th August 2020.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment oversees the implementation of NMBA.
- Aim: The primary objective of NMBA is to raise awareness about the harmful consequences of substance abuse, with a special focus on youth, women, and children.
- It aims to reach out to higher education institutes, university campuses, schools, and the broader community, encouraging community involvement and ownership of the initiative.
- Implementation: NMBA is implemented in 372 vulnerable districts, identified based on the findings of the first Comprehensive National Survey and inputs from the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- Significance:
- NMBA targets and engages various stakeholders directly or indirectly affected by substance abuse, as well as those vulnerable to it.
- The major beneficiaries of NMBA include youth, women, children, educational institutions, civil society, and the community at large.
- This approach emphasizes community involvement rather than just organizational participation in addressing the issue of substance abuse.
Cell-free DNA (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
Over the past two decades, as genome sequencing technologies have become increasingly accessible, scientists have made significant strides in understanding the applications of Cell-free DNA.
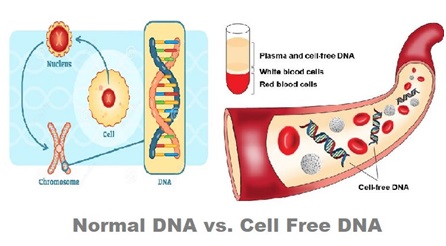
Regarding Cell-free DNA:
- In the human body, a significant portion of the DNA in the genome is safely enclosed within cells, safeguarded by specific proteins to prevent degradation.
- However, in various circumstances, certain DNA fragments are liberated from their confines and can be found outside the cells, circulating in body fluids.
- These minute fragments of nucleic acids are commonly referred to as cell-free DNA (cfDNA).
How Cell-free DNA is generated/released?
- The generation and release of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can occur through various mechanisms.
- One such process is when a cell undergoes cell death, leading to the degradation of nucleic acids and subsequent release of cfDNA.
- The degradation of cfDNA is influenced by a diverse set of processes, resulting in variations in the amount, size, and origin of cfDNA.
- Furthermore, this release of cfDNA can be associated with different biological processes, including those essential for normal development, the progression of certain cancers, and various other diseases.
- The generation and release of cfDNA can be triggered by a range of situations and processes, making it a versatile biomarker with potential implications in various health conditions.
Applications of Cell-free DNA (cfDNA):
- One of the most prevalent uses of cfDNA is in non-invasive prenatal testing, where it aids in screening fetuses for specific chromosomal abnormalities.
- Also, cfDNA serves as a valuable tool for comprehending human diseases and leveraging this knowledge to enhance diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis.
- cfDNA plays a crucial role in understanding the rejection of transplanted organs by the body.
- It shows promise as a potential biomarker for various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, neuronal tumors, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.
Cocos (Keeling) Islands (The Hindu)
- 01 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
A maritime patrol aircraft from the Indian Navy and a transport aircraft from the Indian Air Force (IAF) made a visit to Australia's Cocos (Keeling) Islands (CKI) recently.
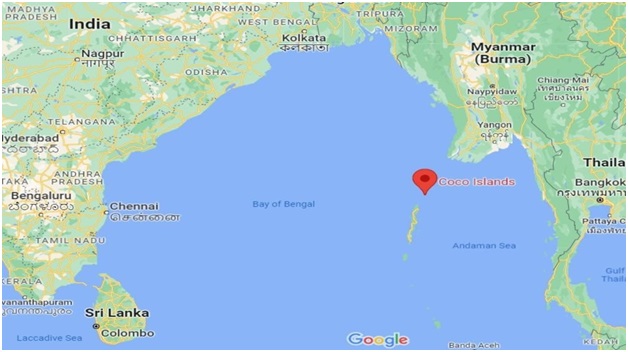
About Cocos (Keeling) Islands:
- Location:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are situated in the eastern Indian Ocean, approximately 2,900 kilometers (1,800 miles) northwest of the Australian city of Perth.
- Geography:
- Comprising coral atolls and islands, the archipelago includes North Keeling Island and the South Keeling Islands.
- Administrative Headquarters:
- The territory's administrative headquarters are located on West Island, situated in the southern atoll.
- Climate:
- The islands experience a warm and humid climate.
- Vegetation:
- The predominant vegetation consists of coconut palms, which were previously cultivated for copra on plantations.
- On North Keeling and Horsburgh islands, coarse grass serves as the primary ground cover.
- National Park:
- The northern atoll is home to Australia's most remote Commonwealth National Park, known as the Pulu Keeling National Park.
- Inhabitants:
- The population of the islands mainly comprises descendants of the original plantation workers, predominantly of Malay origin.
- Administration:
- The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are governed by an administrator appointed by the Australian governor-general. The islands became an Australian territory under the Cocos (Keeling) Islands Act 1955.
US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (Indian Express)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform under the US – India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
Facts About:
In August 2023, the U.S.-India Renewable Energy Technology Action Platform (RETAP) was launched under the Strategic Clean Energy Partnership.
RETAP was established to take bilateral collaboration further with a result-oriented, time-bound technology focus.
It is intended to advance new and emerging renewable technologies with a view toward deployment and scaling.
RETAP’s initial focus is to be on green/clean hydrogen, wind energy, long long-duration energy storage, and to explore geothermal energy, ocean/tidal energy and other emerging technologies as mutually determined in the future.
The initial work plan is guided by the following five themes:
- Research & Development
- Piloting & Testing of Innovative Technologies
- Advanced Training & Skill Development
- Policy and Planning for Advancing RET and Enabling Technologies
- Investment, Incubation and Outreach programmes
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1940523
Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) report (Economic Times)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Annual update of the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI) 2023 has been released.
Facts About:
India ranked second among the countries worst hit by air pollution with Bangladesh topping the list.
- Nepal ranked third followed by Pakistan and Mongolia.
PMI in South Asia: Particulate pollution has increased9.7 percent from 2013 to 2021 in South Asia.
- In India, PM2.5 levels rose 9.5 percent; in Pakistan 8.8 percent; and in Bangladesh, levels rose by 12.4 percent over this same time interval.
Life Expectancy: An average Indian citizen loses around 5.3 years of life expectancy due to air pollution.
- While an average citizen in Bangladesh loses 6.8 years of their life to air pollution
- An average Chinese citizen has seen an improvement — from 4.7 years of life expectancy being lost in 2013 to 2.5 now, an improvement of 2.2 years,
Pollution in India: Pollution in India has increased from 56.2 µg/m3 in 2020 to 58.7 µg/m3 in 2021.
- This is more than 10 times the WHO guideline of 5 µg/m3.
Health Risk: Pollution is biggest threat to human health in India in terms of lowering life expectancy, beating cardiovascular diseases and child and maternal malnutrition.
- While particulate pollution takes 5.3 years off the life of the average Indian, cardiovascular diseases reduce life expectancy by about 4.5 years, and child and maternal malnutrition reduces life expectancy by 1.8 years.
Poor AIr in Delhi: It is the most polluted city in the world.
- Delhi’s annual average PM2.5 level in 2021 was found to be 126.5 µg/m3, which is more than 25 times the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 µg/m3.
- Delhi residents are on track to lose 11.9 years of life expectancy on average relative to the WHO limit and 8.5 years relative to the national guideline if the current pollution levels persist.
About Air Quality Life Index (AQLI)
- AQLI measures the impact of particulate pollution on life expectancy.
- It is released by Energy Policy Institute at University of Chicago (EPIC).
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/your-life-is-getting-short-by-5-years-due-to-air-pollution-chicago-university-report-reavels-scary-numbers/articleshow/103198930.cms?from=mdr
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World-2023 (FAO)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A recently published report, ‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023, shows that the cost of a healthy diet has increased in India in recent years, but it is still lowest among the BRICS countries (including the newly added six countries) and India’s neighbours.
Facts About:
- The ‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023 report prepared by FAO and United States agencies has been released with the theme of “Urbanisation, agrifood systems transformation, and healthy diets across the rural-urban continuum”.
- According to a UN agency report 74% of people in India can’t afford a healthy diet because of increasing costs.
‘State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World’ (SOFI) 2023 :-
The report is published by the partnership of Food and Agriculture Organisation(FAO) of the United Nations with the United States agencies i.e International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), World Food Programme (WFP) and World Health Organisation (WHO).
The aim of the report is
- ending hunger
- achieving food security
- improving nutrition
- to provide an in-depth analysis for achieving this goal in the context of the SDG.
FAO:-Each year, FAO’s most deeply scrutinised report presents the leading numbers of undernourished people worldwide, while advocating for strategies against hunger and malnutrition.
SOFI 2023 related to India:-
PPP report:-
- The concept of PPP is 1ppp dollar in the United States should be able to buy the same amount of goods in either India or Brazil or in other countries.
- xPPP dollar per day means how much would it cost to buy a very simple healthy diet in every country.
- According to this data India compared to its other countries or other regional countries of the world itself has the lowest PPP dollar for a healthy diet.
According to another data which shows the share of the population that is unable to afford a healthy diet in 2021, for instance 74% of the Indian population cannot afford a healthy diet and the fourth highest share in the country itself .
So when it comes to afford a healthy diet, India comes fourth.
Because of stagnation, poor income levels, General stagnation, people of India are not able to afford the cheapest healthy diet in the world.
According to Above two report
- India doesn’t have to spend too much to get a healthy diet.
- 74% of our population cannot afford a healthy diet.
Conclusion:-
The share of people able to afford such a healthy diet is still low: India is at the bottom of that list because income levels are stagnant or going down.
- For example, while in mumbai the cost of meals have risen by 65% in last 5 years wages and salaries have only risen by 28% to 37% , so it shows that prices are rising but our incomes are not rising therefore though India have the cheapest food in the world there is most of people of india can’t afford it.It is not about the can’t afford food it’s a about a nutritional healthy diet divided by FAO and the UN.
Source: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc3017en
Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh’s Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases (Times now)
- 31 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister presented Meghalaya Shawl and Chhattisgarh Dhokra Art and Telangana Bidri Art vases to Greek President and Prime Minister.
Facts About:
Meghalaya shawls
Meghalaya shawls were originally woven for Khasi and Jaintia royalty who considered them a symbol of their power and status.
Shawls were worn at formal events and festivals, and their intricate designs and vibrant colors reflected the wealth and prestige of the royal family.
The designs used in Meghalaya shawls were very symbolic.
- For example, the use of animal motifs such as tigers and elephants was a symbol of strength and power, while the use of floral motifs was a symbol of beauty and grace.
- The weavers, mostly women, spend hours weaving intricate designs and patterns using traditional weaving techniques.
- The shawls are made from local wool and natural colors.
- Shawls are highly valued for their fine workmanship and intricate designs.
Dhokra Art of Chhattisgarh
One of the earliest manifestations of this ancient art is the dancing girl object found in the excavations at Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa.
Traditionally, the Gadwads, Gonds and Dhurwas tribes of Chhattisgarh practice the art of Dhokra using the lost wax technique or hollow casting.
It is named after the Dhokar Damar, an Indian tribe in the central and eastern part of the country.
Common themes in Dhokra art revolve around Hindu gods and goddesses and various animal figures.
Dhokra Art is a non-ferrous metal casting art that uses wax casting technology.
This type of metal casting has been used in India for over 4000 years and is still used today.
There are two main processes involved in lost wax casting: solid casting and hollow casting.
Bidri Art vases
It originated from the city of Bidar in Karnataka in the 14th century.
Bidar in Karnataka and Hyderabad in Telangana are the most active centers of the art form.
Bidri Work handicraft is the art of inlaying metal alloys.
The soil of Bidar Fort magically gives black color to the base metals and the art form has been given the prestigious GI status.
Technique: For smelting, a new mold must be made, into which molten metal, an alloy of zinc and copper, is poured.
- Patterns are drawn on them and carved with a chisel and hammer.
- The engravings are attached with silver wire.
- This contrast of shiny silver with black metal is unique in Bidri art.
Source: https://www.timesnownews.com/india/meghalaya-shawl-to-telangana-vase-what-pm-modi-gifted-to-his-greek-counterpart-article-103065689
Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary (The Hindu)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, scientists suggested rerouting the railway track running through the Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary.
Facts About:
The Hoollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary was renamed on 25 May 2004, formerly known as the Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary or Hollongapar Reserve Forest.
It is an isolated protected area of evergreen forest located in the Jorhat district of Assam.
Vegetation: The upper canopy of the forest is dominated by the Hollong tree, while the Nahar dominates the middle canopy. The lower canopy consists of evergreen shrubs and herbs.
Fauna:
- The sanctuary has a rich biodiversity and is home to the only apes in India, the western Hoolock, as well as the only nocturnal primate found in the northeast Indian states, the Bengal slow loris.
- Also it is home to Stump-tailed macaque, northern pig-tailed macaque, eastern Assamese macaque, rhesus macaque, and capped langur etc
Key facts about Hoolock Gibbon
It is the only ape found in India.
It is native to eastern Bangladesh, Northeast India, Myanmar, and Southwest China.
Gibbons, the smallest and fastest of all apes, live in tropical and subtropical forests in the southeastern part of Asia.
The Hoolock gibbon, unique to India’s northeast, is one of 20 species of gibbons on Earth.
It is categorised into Western Hoolock Gibbon and Eastern Hoolock Gibbon.
Like all apes, they are extremely intelligent, with distinct personalities and strong family bonds.
Western Hoolock Gibbon
- It has a much wider range, as it is found in all the states of the northeast, restricted between the south of the Brahmaputra River and east of the Dibang River.
- It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Eastern Hoolock gibbon
- It inhabits specific pockets of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in India, and southern China and northeast Myanmar.
- It is listed as Vulnerable in the IUCN Red list.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/reroute-railway-track-running-through-assam-gibbon-sanctuary-suggest-scientists/article67247555.ece
Cauvery Water dispute (Indian Express)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Cauvery Water Authority fixes quantum to be released by Karnataka.
Facts About:
- The current outflow rate into the river is 4,398 cubic feet per second (cusecs), whereas the inflow stands at 2,300 cusecs as of Wednesday.
- The outflow rate was 2,292 cusecs on Tuesday at 8 p.m. but was increased after 11 p.m.
- The Kabini Reservoir in Mysuru district also contributes to the outflow, currently standing at 2,000 cusecs.
- Cumulatively, both reservoirs will release around 6,398 cusecs of water.
Cauvery Water Sharing Dispute: Historical Background
- 1892 Onset: The water dispute originates from 1892 between British-ruled Madras Presidency and the princely state of Mysore (now Karnataka).
- 1924 Agreement: A 50-year agreement mediated by the British aimed to ease tensions but set the stage for future conflicts.
- Post-Independence Battles: Karnataka’s dam constructions in the 1960s-80s triggered Tamil Nadu’s Supreme Court appeal, leading to the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT).
- Interim Measures: The Cauvery River Authority (CRA) implemented interim orders in 1998. Contentious issues persisted despite CWDT’s 2013 award.
- Final Award: CWDT’s 2013 award allocated water quantities for Tamil Nadu (419 TMC), Karnataka (270 TMC), Kerala (30 TMC), and Puducherry (7 TMC).
Water Sharing Criteria
- Monthly Schedule: Karnataka, the upper riparian state, must provide Tamil Nadu a specified monthly water quantity.
- Annual Allocation: In a “normal” year, Karnataka provides 177.25 TMC to Tamil Nadu, with 123.14 TMC during the southwest monsoon.
- Challenges: Monsoon disagreements arise due to varying rainfall during this period.
Constitutional Provisions for Water Sharing
- Article 262: Empowers Parliament to address inter-State river disputes; IRWD Act, 1956 enacted under this article.
- Seventh Schedule: Defines legislative authority over water resources in Entry 17 (State List) and Entry 56 (Union List).
Resolving Cauvery Water Sharing
(A) Supreme Court’s 2018 Verdict:
- Cauvery as National Asset: The Supreme Court declared Cauvery a “national asset,” upholding inter-State river water equality.
- Allocation Adjustments: The Court noted deficiencies in CWDT’s assessment, resulting in marginal relief for Karnataka and reduced allocation for Tamil Nadu.
- Formation of CMB: The Court directed the establishment of the Cauvery Management Board (CMB) for effective implementation.
(B) Cauvery Water Management Scheme:
- CWMA Establishment: Formed to regulate water releases with CWRC’s assistance.
- Permanent and Technical Bodies: CWMA oversees regulation, while CWRC ensures data collection and award implementation.
Current Status and Future Implications:
- Ongoing Challenge: The Cauvery water dispute remains a historical and legal challenge.
- Resource Management: CWMA and CWRC aim to address the dispute through effective water management.
- Continued Struggle: The dispute underscores the complexity of water sharing in a federal system and the need for equitable solutions.
Tamil Nadu’s Contention
- CWMA’s Decision: CWMA sought 10,000 cusecs for 15 days from Karnataka, but Karnataka proposed 8,000 cusecs up to August 22.
- Previous Agreement: Karnataka’s refusal to adhere to the earlier agreement of 15,000 cusecs for 15 days at the CWRC meeting angered Tamil Nadu.
- Distress-sharing Formula: Tamil Nadu supports distress-sharing, but Karnataka hasn’t embraced it.
Karnataka’s Perspective
- Rainfall Deficit: Karnataka claims lower rainfall in Cauvery’s catchment areas, including Kerala, leading to reduced inflow.
- Challenging Situation: Karnataka cites reduced reservoir inflow as the reason for not releasing water this year.
- Lack of Consistency: Despite endorsing distress-sharing, Karnataka declined to accept the formula.
Future Scenario
- Tamil Nadu’s Concerns: Mettur reservoir’s critically low storage affects farmers and upcoming kuruvai crop.
- Water Shortage: Current water availability may last only 10 days, considering dead storage and drinking water needs.
- Awaiting Supreme Court: The case’s outcome depends on the Supreme Court’s interpretation and decision.
- Need for Resolution: The need for a mutually acceptable distress-sharing formula is evident.
Ongoing Challenges and Factors Prolonging the Dispute:
- Erratic Water Levels: Flood-drought cycles, pollution, and groundwater depletion cause unpredictable water levels.
- Idealistic Calculations: SC’s verdict relies on favorable conditions often misaligned with reality.
- Dependency and Population: Both states heavily rely on the river, causing conflicting urban and agricultural water needs.
- Inefficient Water Use: Inefficient irrigation methods lead to low crop productivity per unit of water used.
- Hydropolitics and Delays: Water disputes are used for political mobilization. Prolonged tribunal processes contribute to delays.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/bangalore/cauvery-water-dispute-siddaramaiah-says-tn-causing-unnecessary-nuisance-8934747/
Kampala Declaration (Down to Earth)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A total of 48 African countries have now agreed to adopt the Kampala Ministerial Declarationon Migration, Environment and Climate Change (KDMECC) to address the nexus of human mobility and climate change in the continent.
Facts About:
Background: KDMECC was originally signed and agreed upon by 15 African states in Kampala, Uganda in July 2022.
The Declaration is the first comprehensive, action-oriented framework led by Member States to address climate-induced mobility in a practical and effective manner.
The KDMECC-AFRICA is expected to be signed by Member States during the Africa Climate Summit in Nairobi on September 4, 2023.
Need:
- Africa is one of the world's most vulnerable continents to the impacts of climate change.
- Climate change, which leads to an increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, has a direct impact on migration.
Significance:
- The Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment and Climate Change gives us the unprecedented opportunity to support Member State priorities in addressing the challenges while also leveraging migration for sustainable development.
- It will ensure that all voices, including those of youth, women and persons in vulnerable situations are the priority of the expanded declaration.
Linkage between Climate change and Human Rights:
- Climate change has indisputable long-term consequences on the environment, which, in turn, seriously undermine the enjoyment of human rights.
- The African continent is projected to be one of the hardest hit by the negative effects of climate change.
- The consequences of climate change are not only disproportionately felt by the most vulnerable and poorest populations; there are also disparities along gender lines.
- The connections between climate change, gender equality, and women’s rightsare complicated and multidimensional.
- In contrast, most existing studies on gender and climate change action offer a narrow conception of what gender equality and women’s rights mean in the context of climate change action.
Other similar declarations:
The Maputo Convention on the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources: This Convention shall apply;
- To all areas which are within the limits of national jurisdiction of any Party; and
- To the activities carried out under the jurisdiction or control of any Partywithin the area of its national jurisdiction or beyond the limits of its national jurisdiction.
The Parties shall adopt and implement all measures necessary to achieve the objectives of this Convention, in particular through preventive measures and the application of the precautionary principle, and with due regard to ethical and traditional values as well as scientific knowledge in the interest of present and future generations.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/climate-change/kampala-declaration-on-climate-change-human-mobility-now-has-48-african-countries-as-members-91393
Sequencing the Y Chromosome (The Hindu)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Scientists have fully sequenced the Y chromosome for the first time, uncovering information that could have implications for the study of male infertility and other health problems.
Facts About:
- In the nucleus of a human cell, each DNA molecule is packaged into a long thread like structure called chromosome.
- Most human cells contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. One half of each pair of chromosomes from one parent, while other half comes from other parent.
- The 23rd pair are X and Y chromosomes, often called as sex chromosomes. The other 22 pairs called as autosomes.
- Females have a pair of X chromosomes, whereas males have X and Y chromosome.
- The Y chromosome is male-determining because it bears a gene called SRY, which directs the development of a ridge of cells into a testis in the embryo.
- The embryonic testes make male hormones, and these hormones direct the development of male features in a baby boy.
What is the difficulty in sequencing Y chromosome?
- Repetition - The Y chromosome was a particularly hard nut to crack because it is unusually repetitive.
- While all human chromosomes contain repeats, more than 30 million letters of the Y chromosome — out of 62.5 million — are repetitive sequences, sometimes called satellite DNA or junk DNA.
- Repetitive DNA complicates the assembling of data from genetic sequencing.
- Palindromes - The Y chromosome also contains palindromes — sequences of letters that are the same backward and forward, like radar.
- Degeneration of Proto- Y - The proto-Y is degenerating at a faster pace, losing about 10 active genes per million years, reducing the number from its original 1,000 to just 27.
- There has been great debate about whether this degradation continues, because at this rate the whole human Y would disappear in a few million years
How the scientists unravelled the complex Y chromosome?
- Sequencing - Advanced "long-read" sequencing technology and computational methods enabled researchers to achieve a complete reading of the Y chromosome.
- This accomplishment added over 30 million repetitive base pairs to the human reference genome.
- The new technology has allowed sequencing of bases along individual long DNA molecules, producing long-reads of thousands of bases.
- It effectively dealt with repetitive sequences and transformed raw sequencing data into a usable resource.
- These longer reads are easier to distinguish and can therefore be assembled more easily.
- Findings- Overall, the combined research determined that the Y chromosome has 106 protein-coding genes.
- 42 were found that were new, but many still appear to be repeats.
What is the importance of the study?
- Advanced diagnostics- The study empowers future sequencing endeavours to explore into health and disease aspects through comprehensive Y chromosome inclusion.
- To study whether loss of the Y chromosome is a biomarker of biological aging or has a direct effect on the health of men.
- Infertility- It will help to study conditions and disorders linked to the chromosome, such as lack of sperm production that leads to infertility.
- Health- Genes have been identified on the Y chromosomes that have been shown to be required for the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease.
- Dark matter- It represents the ‘dark matter’ of the genome. This analysis will allow us to better understand the regions of the Y chromosome that have regulatory functions and may encode mRNA and proteins.
- Human evolution- Assembling complete sequences of Y chromosomes across space and time not only helps to investigate sex chromosome evolution but also human evolution.
- Gene therapy- It will open up avenues to treat diseases that may linked to Y chromosomes.
- Future studies- The findings provide a solid base to explore how genes for sex and sperm work, how the Y chromosome evolved, and whether as predicted will disappear in a few million years.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/y-male-chromosome-gene-sequencing-sry-gene-sequencing-evolution/article67230274.ece
Food Inflation & Challenges of Malnutrition (Down to Earth)
- 30 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent data, the cost of meals rose by 65% in five years, wages by just 37% in the last five years.
Facts About:
- In Mumbai, the cost of a vegetarian thali surged 65% in five years, while income for laborers and salaried workers in urban Maharashtra increased only 37% and 28%, respectively. This discrepancy is making essential food items unaffordable, leading to compromised meals.
What is Thalinomics?
- Thalinomics is a term coined by an Indian economist and former Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India, Arvind Subramanian.
- It refers to a concept that involves analyzing changes in the cost of a vegetarian thali (a meal consisting of a variety of dishes served on a single plate) to gain insights into the trends and dynamics of food inflation and affordability.
- It involves tracking the prices of key ingredients that constitute a thali, such as cereals, pulses, vegetables, and other essential items.
- This concept is particularly relevant in countries like India, where food affordability and inflation are significant concerns for a large population.
Key insights: A case study of Mumbai and urban Maharashtra
- Rising Cost of Thali: The cost of preparing a home-cooked vegetarian thali in Mumbai has increased significantly by 65% over the past five years. This increase is attributed to rising prices of essential ingredients like rice, dal, vegetables, and other items that constitute a thali.
- Income Growth: Over the same five-year period, the average wage earned by casual laborers in urban Maharashtra increased by 37%, while the average salary of regular salaried workers increased by 28%. These income growth rates reflect the changes in earnings for these two categories of workers.
- Disparity Between Costs and Income: While the cost of a thali increased by 65%, income growth for casual laborers and salaried workers was significantly lower, at 37% and 28%, respectively.
- Affordability Challenge: The disparity between rising costs and income growth has resulted in essential food items becoming increasingly unaffordable for households. This affordability challenge can lead to reduced portion sizes or a compromise in the variety and nutritional quality of meals.
- Impact on Budget Share: The study also analyzes the portion of monthly wages or salaries required to afford two thalis every day for a month. This share increased from 22.5% of a casual laborer’s monthly earnings in 2018 to 27.2% in 2023. For salaried employees, it increased from 9.9% to 12.8% over the same period.
- Incomplete Data: Data limitations, particularly regarding the absence of certain ingredients like spices and ghee in the analysis, This suggests that the actual cost of making a thali could be even higher than the calculated figures.
Key aspects of the relationship between thali prices and inflation
- Inflation and Ingredient Prices: The prices of ingredients like rice, dal, vegetables, and oil can be affected by inflation. If the prices of these essential ingredients rise due to inflationary pressures, the overall cost of preparing a thali would increase.
- Food Inflation: The cost of a thali, which is composed of various food items, is directly influenced by food inflation. If there’s high food inflation, it can significantly impact the affordability of thalis and other meals.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: Inflation can be driven by supply and demand imbalances. If there’s a shortage of certain ingredients due to supply disruptions (e.g., poor harvests or transportation issues), prices can rise. Similarly, changes in consumer demand patterns can affect the prices of specific ingredients, further impacting thali costs.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks often use monetary policy tools to control inflation. Interest rate adjustments, money supply regulation, and other measures can impact inflation rates. High inflation rates can lead to increased production costs for farmers and manufacturers, which may trickle down to the prices of thali ingredients.
- Income Effects: Inflation can impact consumers’ purchasing power. When inflation outpaces income growth, households might need to allocate a larger portion of their income to cover basic expenses like food. This can particularly affect lower-income households, leading to affordability challenges for items like thalis.
- Regional Variation: Inflation rates can vary regionally and even locally. Different regions might experience different rates of inflation due to factors like supply chain disruptions, local economic conditions, and government policies.
- Government Policies: Government policies such as subsidies, import/export regulations, and agricultural policies can influence ingredient prices and, consequently, the cost of preparing a thali. These policies can impact the supply and availability of key ingredients.
Implications of the higher cost of a thali
- Nutritional Impact: The rising cost of thali ingredients can lead to compromised nutritional intake as households might cut back on certain items to manage expenses. This can result in inadequate diets and potential health implications.
- Affordability Strain: As thali prices escalate, households may face financial strain by allocating a larger portion of their income to food expenses. This can limit their ability to save, invest, and engage in non-essential expenditures.
- Dietary Diversity: Increased thali costs can potentially lead to reduced dietary diversity as households might opt for cheaper, less nutritious alternatives, affecting overall dietary quality.
- Balanced Meals: Higher thali costs might lead to smaller portions or fewer items in the thali, disrupting the balance of a typical meal and potentially impacting satiety and nutritional completeness.
- Quality of Life: Reduced dietary quality due to affordability challenges can have broader implications for individuals’ quality of life, health, and overall well-being.
- Economic Struggles: For households with limited disposable income, the burden of increased thali costs can exacerbate economic struggles and hinder progress.
Way forward
- Policy Interventions: Implement policies to address the widening gap between thali costs and income growth, ensuring that essential food remains affordable.
- Income Enhancement: Focus on raising wages for casual laborers and salaried workers to match the rising cost of thalis.
- Affordability Measures: Establish measures to mitigate the impact of expensive thalis on households, considering subsidies or targeted assistance.
- Nutrition Awareness: Launch campaigns to educate households about maintaining nutritious diets even when faced with affordability challenges.
- Gender-Inclusive Approach: Address gender disparities by formulating policies that empower women economically.
- Data-Driven Approach: Base policies on accurate and up-to-date data on food prices, wages, and consumption patterns.
- Food Security Initiatives: Strengthen food security programs to ensure access to nutritious food despite thali cost increases.
- Policy Evaluation: Continuously assess the effectiveness of policies in addressing thali affordability and overall well-being.
Conclusion
- The shifting dynamics between escalating costs and relatively stagnant income pose a serious challenge to maintaining a nutritionally balanced diet. As prices continue to rise, a more comprehensive approach is crucial to ensuring that affordable nutrition remains within reach for all strata of society.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/price-of-food-inflation-42483
Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23 (PIB)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Air Force (IAF) contingent departed to participate in Exercise BRIGHT STAR-23, scheduled to be held at Cairo (West) Air Base, Egypt, from 27 August to 16 September 2023.
Facts About:
- It is a biennial multilateral tri-service exercise.
- This multinational exercise was launched in 1980 as part of the US-brokered peace treaty between Egypt and Israel.
- This is the first time that IAF is participating in Ex BRIGHT STAR-23.
- Participating countries: United States of America, Saudi Arabia, Greece and Qatar.
- The Indian Air Force contingent will consist of five MiG-29, two IL-78, two C-130 and two C-17 aircraft.
- Personnel from the IAF's Garud Special Forces, as well as those from the Numbers 28, 77, 78 and 81 Squadrons, will be participating in the exercise.
- Objective: To practice planning and execution of joint operations. Besides leading to the formation of bonding across borders, such interactions also provide a means to further strategic relations between participating nations.
- India and Egypt have had an exceptional relationship and deep cooperation wherein the two jointly undertook the development of aero-engine and aircraft in the 1960s, and training of Egyptian pilots was done by Indian counterparts.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1955399
LK-99 (The Hindu)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Independent scientists have found that LK-99 is not a superconductor.
Facts About:
- LK-99 has been claimed by South Korean scientists as a superconductor at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. However, currently scientists have discarded their claims.
What are the reasons behind discarding LK-99 as a superconductor?
- First, when superconductors get cold, they push away magnets, causing repulsion below their transition temperature. The South Korean video showed LK-99 partly repelling a magnet. However, independent researchers found that the material was an insulator whose impurities could be magnetized.
- Second, the South Korean scientists saw less resistance in LK-99 around 104°C, which could mean it’s a superconductor. However, researchers found that this drop occurred due to the copper sulphide impurities present in the material.
- Hence, as per the scientists, no formal confirmation aligns with the initial declarationthat this material can conduct electricity without resistance in regular conditions.
What lies ahead?
- The LK-99 case raises concerns over misunderstandings caused in the open science competition. However, this misunderstanding shouldn’t stop open collaboration.
- Moreover, now, the burden lies on South Korean group to show evidence for their claim
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/lk-99-room-temperature-superconductor-hype/article67233834.ece
Moody’s Report on Demographic Dividend (Economic Times)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Alongwith the population growth, strong education and quality infrastructure are key to reap economic gains in India: Moody
Facts About:
Relation between population growth and economic growth:
Population Growth as a Driver of Economic Growth (Early Stages)
- A larger population means a larger labor force, which can lead to increased production, consumption, and innovation. This phenomenon is often referred to as the demographic dividend. When the ratio of working-age individuals to dependents (children and elderly) is high, it can create a favorable environment for economic expansion.
Labor Force and Human Capital:
- A growing population can provide a larger labor force, which, if properly educated and skilled, can contribute to higher productivity and economic growth. However, for population growth to positively impact economic growth, there must be adequate investments in education, healthcare, and skill development to ensure that the workforce is productive and capable of contributing to economic activities.
Consumption and Demand:
- A larger population can lead to increased consumption and demand for goods and services, which can stimulate economic growth. Businesses may expand to meet this increased demand, leading to higher levels of investment and production.
Urbanization and Productivity:
- Population growth often leads to urbanization, as people move from rural areas to cities in search of better opportunities. Urbanization can lead to increased productivity due to factors like economies of scale, improved infrastructure, and better access to markets and resources.
Resource Constraints and Negative Impacts:
- Rapid population growth without corresponding economic development and resource management can lead to resource constraints, environmental degradation, and increased competition for limited resources. This can have negative effects on economic growth in the long run.
Demographic Transition:
- As economies develop and standards of living improve, birth rates tend to decline. This results in a shift from high population growth rates to lower ones. During this demographic transition, countries can experience a period of accelerated economic growth due to a relatively smaller dependent population.
Aging Population:
- In more advanced economies, declining birth rates and increased life expectancy can lead to an aging population. While this may result in a decline in the working-age population, it can also create opportunities for innovation and growth in industries related to healthcare, elderly care, and technology.
Quality of Institutions and Policies:
- The relationship between population growth and economic growth is influenced by the quality of institutions and policies in place. Good governance, effective healthcare systems, education policies, and infrastructure development play a crucial role in determining how population growth impacts economic growth.
In summary, the relationship between population growth and economic growth is not deterministic, and its effects can vary widely based on numerous factors. While a growing population can potentially provide a demographic dividend and contribute to economic growth, this positive outcome depends on factors such as investments in human capital, infrastructure, and sound governance.
Additionally, as countries progress in their development, the relationship often becomes more nuanced, with demographic transitions and changingpopulation structures influencing economic dynamics.
Factors responsible for India’s population growth
- Falling mortality: The IMR has decreased from 40.7 in 2015-16 to 35.3 in 2019-21.
- Increasing Life expectancy at birth: It reached to 69.7 years in the 2015-19 period from 31 in 1947.
- Unintended pregnancies: 1 in every 7 unintended pregnancies of world occur in India.
- Lack of female education, child marriage and early marriages, etc.
Challenges caused by growing population
- Pressure on resources: As India has only 2.45% of the global surface area and 4% of the water resources.
- Pandemic outbreaks: Due to increasing urbanization and expansion of humans in wild habitats.
- Disruption and Conflicts: Due to rise in struggle for finite resource.
- Decline in social indicators: Due to suboptimal public expenditures on health and education may not be possible.
- Pressure on economy: Due to low skilled workforce, stagnant economy, unemployment, etc.
- Widening gender gap: If expenditure on health and education decline, women would suffer the most.
Way ahead to harness the benefits of population growth
- Supporting Reproductive Justice: Provisions of safe and effective methods of family planning and freedom to make the best reproductive choice.
- Education for all: Educational attainment, particularly of girls, enhances intergenerational formation of human capital and has a positive impact on demographic behaviour with respect to nuptiality, fertility, health, etc.
- Foster Inclusive Growth developing democratic institutions to facilitate equity in the society.
- Facilitate migration to bridge the demand and supply of the workforce.
- Investment in green technology and social innovations to adapt to and mitigate climate and environmental changes.
- Better geriatric care, health insurance and pension facilities for 65+ age category.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/india-must-focus-on-education-and-infra-for-growth-moodys-report/articleshow/103147127.cms?from=mdr
Care Protocol for Babies in India (The Hindu)
- 29 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
British nurse was sentenced to life in prison after being found guilty in the worst child serial killer case in the history of the U.K.
Facts About:
What are patient safety provisions in India?
National Patient safety Implementation Framework - It was launched for the period 2018-25 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Patient safety - It is the fundamental element of public healthcare, defined as the freedom for a patient from unnecessary harm.
Hippocratic Oath - It is an oath of ethics historically taken by physician which is one of the most widely known of Greek medical texts.
Consumer Protection Act,1986 - It deals with medical negligence and deficiency of services
Clinical Establishment Act, 2010 - It sets out the legal rights of the patients.
Institutional Mechanism - To see the patients’ rights in terms of medication and devices are protected and that they are not overcharged.
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority
- Drugs Controller General of India
Charter of patients’ rights - It is adopted by the National Human Rights Commission.
It act as a guidance document for the Union Government and State Governments to formulate concrete mechanisms for Patients’ Rights.
Charter of Patients’ Rights and Responsibilities - It is approved by National Council for Clinical Establishments.
Responsibilities of Patients’ -
- Provide all health related information.
- Cooperate with Doctors during examination and treatment.
- Pay hospitals agreed fees on time.
- Respect dignity of doctors and other hospital staff.
- Never resort to violence
How is neonatal safety maintained?
- Rules - There are no exclusive rules for neonatal care and safety, or protection against external harm in Indian hospitals.
- However, there are provisions and checks against issues like inadvertent mix-up of babies at birth and abduction.
- Training - The healthcare staff is also trained to counsel parents and provide emotional support, contributing to the safety and development of neonates.
- Adequate manpower - Trained healthcare is fostered by adequate staffing which can closely monitor each baby’s condition and respond swiftly to any concerns.
- Equipment - Neonates are typically kept in controlled environments to avoid exposure to external infections and temperature fluctuations.
What lies ahead?
- Regular training and continuing medical education for healthcare staff are essential to maintain high-quality neonatal care and uphold safety standards.
- The global organisation has also advised families that prompt medical care should be sought in case of danger signs.
- These include feeding problems, reduced activity, difficult breathing, fever, fits or convulsions, jaundice in the first 24 hours after birth.
- Families are also required to register the birth and bring the baby for timely vaccination, according to national schedules.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/explained-what-is-the-care-protocol-for-babies-in-india/article67239285.ece
Seethakali folk art (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 20-member group is going to perform Seethakali folk art, outside Kerala for the first time as to revive one of the fading dance forms of Kerala.
Facts About:
- In the early times, Seethakali was performed as part of the harvest festival Onam.
- From Atham star till the 28th day after Onam, the performers who belong to the subaltern communities go from one house to another performing this art.
Key Features of Seethakali:
- Folk Dance Drama: Seethakali is a traditional folk dance drama that was once performed during the festival days in erstwhile Desinganad (Kollam, Kerala), primarily during the Onam festivities.
- Dalit Artists: The performance was carried out by Dalit artists belonging to the Veda and Pulaya communities, focusing on presenting episodes from the Ramayana from Sita’s perspective.
- Vanayatra to Andardhanam: Seethakali portrays the journey from “vanayatra” (exile to the forest) to “andardhanam” (descend into the earth) of Sita, featuring a blend of songs, storytelling, and fast movements.
- Instruments: The dance drama is accompanied by instruments such as ganjira, manikatta, chiratta, and kaimani.
- Narrative through Songs: Seethakali’s story is conveyed through songs, with 28 collected over three years, featuring a folk style influenced by Vallappaattu, Kuthirappaattu, and Rakshasappattu.
- Oral Tradition: Seethakali songs were orally transmitted from one generation to the next, which led to a pause in the tradition.
- Basic Movements: The dance involves basic steps, striving to preserve the original essence of the art form.
- Character Ensemble: The performance includes key characters such as Sita, Ram, Lakshman, Ravan, and Hanuman.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/artistes-breathe-a-new-life-into-seethakali-folk-art/article67234768.ece
Terai-Arc Landscape (TAL) (Times of India)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the poop of tigers has helped a team of scientists at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) understand the prey selection patterns of the striped feline in the Indian part of the Terai-Arc Landscape.
Facts About:
- It is an 810km stretch between the river Yamuna in the west and the river Bhagmati in the east.
- It comprises the Shivalik hills, the adjoining bhabhar areas and the Terai flood plains.
- It is spread across the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and the low-lying hills of Nepal.
- About 22% of the wild tiger population in India is found across the TAL, living amidst some of the highest human and livestock densities on the subcontinent.
- The landscape boasts of some of India’s most well-known Tiger Reserves and Protected Areas, such as Corbett Tiger Reserve, Rajaji National Park, Dudhwa Tiger Reserve, Valmiki Tiger Reserve and Nepal’s Bardia Wildlife Sanctuary, Chitwan National Park, Sukhla Phanta Wildlife Sanctuary.
- These forests are home to three flagship species: the Bengal tiger(Panthera tigris), the greater one-hornedrhino (Rhinoceros unicornis) and the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus).
Key Facts about the Wildlife Institute of India
- It is an autonomous Institution of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India.
- It was established in 1982.
- It offers training programs, academic courses and advisory in wildlife research and management.
- The Institute is actively engaged in research across the breadth of the country on biodiversity-related issues.
Source: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/dehradun/10-tiger-corridors-across-india-need-attention-experts/articleshow/95518729.cms
The State of India’s Birds Report (The Hindu)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The State of India’s Birds Report has been released recently.
Facts About:
- The State of India’s Birds (SoIB) report based on data collected from approximately 30,000 birdwatchers has unveiled concerning trends regarding India’s bird population.
- The study highlights a substantial decline in numerous bird species, attributing this decline to a range of factors.
About SoIB Report
- The SoIB report aims to evaluate the conservation status of a wide range of species regularly present in India.
- It is published by a partnership involving 13 governmental and non-governmental organizations, including SACON, WII, and ZSI.
- The report extensively employs data from over 30 million observations on eBird by more than 30,000 birdwatchers.
- The report assesses distribution range size, abundance trends over the long term and since 2015, and information from the IUCN Red List to categorize Indian species into Low, Moderate, and High Conservation Priority tiers.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Widespread Decline: Among the species analyzed, 60% of those assessed for long-term trends show decline, while 40% exhibit a decline in current annual trends.
- Raptors and Vultures: Birds consuming vertebrates and carrion, including raptors and vultures, have significantly declined, possibly due to pollutants or prey availability reduction.
- Endemics and Biodiversity Hotspots: Endemic species in the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka biodiversity hotspot have experienced rapid declines over the past decades.
- Positive Outlook: Certain generalist species, exemplified by the Indian peafowl, demonstrate remarkable increases in abundance, with a 150% rise observed over the past decades.
- Conservation Priority: The report classifies species into High, Moderate, and Low Conservation Priority, with 178 species as High Priority, 323 as Moderate, and 441 as Low Priority. Noteworthy species include the Ruddy shelduck, Indian courser, Narcondam hornbill, and Nicobar megapode.
Identified Threats to Bird Species
- The report underscores threats encompassing forest degradation, urbanization, energy infrastructure.
- Birds are highly impacted by environmental pollutants like Nimesulide affecting vulture populations, climate change’s impacts on migratory species, avian diseases, and illegal hunting and trade.
Actions and Research Implications
- Targeted Conservation: The report advocates for the conservation of specific groups, such as grassland specialists that have suffered a more than 50% decline, highlighting the importance of protecting and preserving grassland ecosystems.
- Long-Term Monitoring: The significance of continuous, systematic bird population monitoring is emphasized to comprehend subtle fluctuations in bird numbers.
- In-Depth Research: Further research is needed to understand the causes behind both declines and increases in bird populations.
- Synergy among Policies: The report calls for the harmonization of policies related to river, water, and wasteland development, recognizing the multifaceted role of abundant, widespread bird species.
- Citizen Participation: Citizen Engagement plays a pivotal role in biodiversity conservation, warranting an essential role in the action plan for bird population and habitat preservation.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/kerala/state-of-indias-birds-report-lists-20-species-of-highest-conservation-priority-for-kerala/article67241741.ece
RIGHT TO REPAIR (Indian Express)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In recent years, several states in the U.S. have enacted ‘right to repair’ laws.
Facts About:
- It refers to government measures that forbid manufacturers to impose barriers that deny consumers the ability to repair consumer products.
- The sectors identified for the right to repair include farming equipment, mobile phones/tablets, consumer durables, and automobiles/automobile equipment.
- Government has launched a unified portal, https://righttorepairindia.gov.in, to onboard leading brands and reliable third-party technicians to provide easy access to overhauling services.
- The portal has on boarded leading brands such as Apple, Samsung, Honda, Kent RO Systems, Havells, Hewlett Packard, and Hero MotoCorp.
- The portal seeks to streamline trade between original equipment manufacturers and third-party sellers.
- The right to repair has been recognized in many countries across the globe, including the USA, UK, and European Union.
Significance of Right to repair for India:
- Lowering costs for consumers: By providing access to third-party technicians, the right to repair can reduce costs for consumers who may not be able to afford expensive repairs or replacement devices.
- Reducing electronic waste: India is one of the largest generators of electronic waste in the world, and the right to repair can help reduce e-waste by extending the lifespan of electronic devices and appliances.
- Supporting small businesses: The right to repair can also support small businesses that provide repair services, by creating a level playing field with manufacturers who may have previously had a monopoly on repairs.
- Empowering consumers: By giving consumers the ability to repair their own devices or choose where to have them repaired, the right to repair empowers consumers to make informed choices and take control of their own devices.
- Promoting transparency and collaboration: The right to repair framework aims to build a consumer-centric ecosystem that promotes transparency and collaboration between manufacturers, sellers, and consumers.
Challenges associated with implementing right to repair in India
- Limited Access to Information: Many manufacturers do not provide adequate information to consumers about repair options or how to repair devices, which can make it difficult for consumers to exercise their right to repair.
- Lack of Awareness: Consumers lack awareness about their rights to repair and the benefits of repairing their devices leading to a lack of demand for repair services, limiting the growth of the repair industry.
- Opposition from manufacturers: Some manufacturers may oppose the right to repair, arguing that it could compromise their intellectual property rights or lead to safety concerns making it difficult to pass legislation or regulations to support the right to repair.
- Limited availability of spare parts: The availability of spare parts is often limited in India, particularly for older or less common models of devices makes it difficult for repair technicians to perform repairs or for consumers to find reliable repair services.
- Lack of regulatory mechanism: Currently, there is no comprehensive regulation in India that governs the right to repair which can lead to confusion among consumers and repair technicians about their rights and responsibilities, and may limit the growth of the repair industry.
Way Forward:
Many countries around the world have been attempting to pass effective ‘right to repair’ laws. But the movement has faced tremendous resistance from tech giants such as Apple and Microsoft over the years.
The New York legislation is a reminder that it is time to not only acknowledge the right to repair of consumers but also respond to the corresponding rights of the manufacturers. This warrants some expedited policy changes to recognise the ‘right to repair’, be it through amendments in the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 or through a separate law.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-what-is-the-right-to-repair-movement-7400287/
Scholarship Schemes for Religious Minorities (PIB)
- 28 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
There is a shift in Centre’s policy towards minority education in the past few years. It has discontinued two key educational schemes for religious minorities and gradually cut down on the expenditure incurred on the programmes of the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
Facts About:
Minority Educational Schemes: Overview
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme: Initially covering classes 1 to 10, now limited to classes 9 and 10.
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme: Supports class 11 and above students, with increased funding this fiscal year.
- Merit-cum-Means based Scholarship Scheme: Aided professional and technical courses, underwent significant funding reduction.
- Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF): Provided financial assistance for research scholars but discontinued in 2022.
- Padho Pardesh: Discontinued interest subsidy scheme for higher education abroad.
- Begum Hazrat Mahal National Scholarship: Scholarship for meritorious girls discontinued.
Policy Shift and Consequences
- Change in Focus: Despite acknowledging the importance of education for religious minorities and inclusive growth, the government has discontinued two key educational schemes, narrowed the scope of another, and reduced expenditure on multiple programs by the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
- Beneficiary Drop: Between 2019 and 2022, the number of beneficiaries under six educational schemes for religious minorities decreased by 7%, while government spending on these programs declined by around 12.5%.
- Budget Cuts: The Ministry of Minority Affairs faced a budgetary reduction of 38.3% for the fiscal year 2023-24, from Rs 5,020.5 crore in 2022-23 to Rs 3,097 crore. Additionally, a significant portion of funds allocated in the previous year went unutilized.
Importance of Strengthening Educational Aid
- Diverse Religious Minorities: India encompasses over 30 crore people from religious minority communities, including Muslims (14.2%), Christians (2.3%), Sikhs (1.7%), Buddhists (0.7%), Jains (0.4%), and Zoroastrians.
- Challenges Faced by Muslims: Muslims, the largest religious minority, confront challenges in areas like economics, health, and education. Their participation in formal employment remains low, with many working in the informal sector under poor conditions.
- Sachar Committee Report: The Sachar Committee highlighted the deprivation and neglect faced by Muslims across various development dimensions, underscoring the need for affirmative action.
- Formation of Ministry of Minority Affairs: Responding to these challenges, the UPA government established this Ministry in 2006 to ensure focused attention on the issues affecting minority communities.
Challenges and Impact
- Reduction in beneficiaries and funding has impacted the implementation of schemes, resulting in a widening gap in education and economic parameters.
- Poor coverage of beneficiaries and unchanged low unit costs remain hurdles in scheme implementation.
- Muslim students’ enrolment in higher education is lagging behind other communities, worsening the existing disparities.
Way Forward
- Strengthen educational aid through enhancing scholarships, such as pre-matric, post-matric, merit-cum-means, and national overseas scholarships.
- Implement targeted schemes based on the 15-Point Programme to address development gaps in minority-concentrated localities.
- Make scholarships demand-driven and provide additional financial resources to improve unit costs.
- Increase the total budget allocation for the Ministry of Minority Affairs to address the deprivation in educational attainment for minorities.
Source: https://static.pib.gov.in/WriteReadData/specificdocs/documents/2022/mar/doc202231626301.pdf
G20 ministers agree to map global value chains, link MSMEs (Indian Express)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations agreed recently to map global value chains, integrate small businesses with them and ease trade documentation.
Facts About:
What are important parts of outcome document from Trade and Investment Ministers of G20 nations?
- Comprehensive framework within the G20 context for the purpose of mapping out global value chains is suggested.
The objective is to comprehend the existing issues and identify the necessary actions to enhance the inclusivity, sustainability, and resilience of these value chains.
- It focuses on MSMEs. The declaration from Jaipur emphasizes the imperative of reinforcing the capabilities of MSMEs.
Due to their small scale, MSMEs face limitations in accessing critical information, financial resources, and market-related data points.
A worldwide trade assistance platform, overseen by theInternational Trade Centre, will be consistently upgraded through consultation with UNCTAD and the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
This evolution aims to make the platform more inclusive and to offer comprehensive data to MSMEs.
- The principles associated with the digitization of trade documents is important part of outcome document. The aim is to minimize the reliance on paper documents and remove obstacles that hinder the seamless movement of goods and services.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/g20-trade-meet-ends-ministers-priority-areas-value-chains-msmes-8909647/
China-Bhutan boundary dispute and its impacts on India (The Hindu)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The 13th Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on the China-Bhutan boundary issues was held recently.
Facts About:
- A joint press release from Beijing and Thimphu said the 13th Expert Group Meeting (EGM) was held in Beijing
- It described as an “important outcome” the setting up of a Joint Technical Team on the Delimitation of the China-Bhutan Boundary, which held its first meeting along the sidelines of the EGM.
- The two sides had talks on
- continuously implementing the MOU on the Three-Step Road Map for Expediting the China-Bhutan Boundary Negotiations
- agreed to expedite and take simultaneous steps to implement the Three-Step Road Map
- agreed upon keeping the positive momentum of frequent Expert Group Meetings
- holding the 14th Expert Group Meeting on the China-Bhutan Boundary Issues as soon as possible
- maintaining communication on holding the 25th Round of China-Bhutan Boundary Talk
- It did not, however, announce a date for the already much delayed 25th round of boundary talks, which have not been held since 2016.
- In recent months, both sides have portrayed the long-running talks as picking up speed and nearing a possible solution, which would have ramifications for India.
- While there was a two-year gap between the 10th round of the EGM held in April 2021 and the 11th round of the EGM held in January 2023, the last two rounds have been held in relatively quick succession.
Impact on India
- Experts in India have said any deal between Beijing and Thimphu that accedes to a “swap arrangement” between areas to the North (Jamparlung and Pasamlung valleys) with Doklam to the West would be of concern to India, given the proximity to India’s narrow “Siliguri corridor” that connects northeastern States with the rest of India.
- India and China were involved in a stand-off in Doklam near the India-China-Bhutan trijunction in 2017.
- In March, the Bhutanese Prime Minister said in an interview that the process of “demarcating territories” and “drawing a line” could be completed “after one or two more meetings”.
Conclusion
The boundary talks between Bhutan and China began in 1984, and the 24th round was held in 2016.
The talks have largely focused on disputed areas to Bhutan’s north, and to its west, abutting the Doklam plateau.
However, these have been stalled since 2016, especially after the 2017 Doklam stand-off.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/interview/post-covid-necessary-for-neighbours-to-work-together-bhutan-fm-on-china-bhutan-boundary-talks/article65646740.ece
7th Global Environment Facility (GEF) Assembly (Down to Earth)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
As per the chief executive of the Global Environment Facility (GEF) in a plenary session, it will likely to work more closely with civil society organisations in the future.
Facts About:
About: Environmental leaders from 185 countries will gather in Vancouver, Canada for the Seventh Assembly of the Global Environment Facility from August 22-26, 2023.
Global Environment Facility (GEF): The GEF Assembly, which meets every 4 years, is the global body that coordinates financing for international efforts to address climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, and factors inhibiting land and ocean health.
Points of discussion:
- Building on recent diplomatic breakthroughs on biodiversity loss, toxic chemicals, and the high seas, the GEF Assembly will be a critical stocktaking for 2030 goals to end pollution and nature loss, combat climate change, and propel inclusive, locally-led conservation.
- GEF would work directly with non-governmental organisations that work at the convention level.
- It is set to include the launch of the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund, a new source of funding for protecting species and ecosystems globally.
- The fund will open new avenues for private sector and philanthropic support to enable rapid implementation of the historic Global Biodiversity Framework agreed at COP15 in Montreal, December 2022, and of the high seas treaty adopted in New York City, in June 2023.
Need of such an initiative:
- Biodiversity funding needs differ between recipient countries, for example between countries with key areas for biodiversity (often large emerging countries such as Brazil and Indonesia) and the least developed countries (LDCs) or Small Island Developing States (SIDS), for which it is more difficult to access funds.
Global Biodiversity Framework:
- It contains goals to be achieved by 2050 focus on ecosystem and specieshealth including;
- To halt human-induced species extinction,
- The sustainable use of biodiversity,
- Equitable sharing of benefits, and
- On implementation and finance to include closing the biodiversity finance gap of $700 billion per year.
Source: https://update-mac.com/?tid=103&tag_id=1528a5df-4f9e-4046-9232-3361bc5f2c12&cnv_id=e891de8lpg6sc0b4c&placement=20427977&sub1=726006&clickcost=0
India-Iran drop Foreign Arbitration clause in Chabahar Port Issue (The Hindu)
- 26 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India and Iran have agreed to pursue arbitration under rules framed by the UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) and will not go for commercial arbitration in foreign courts.
Facts About:
UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL):
It is a subsidiary body of the UN General Assembly, established in 1966.
Mandate: To further the progressive harmonisation and unification of the law of international trade.
Membership:
- The Commission is composed of 60 member States elected by the General Assembly.
- The 60 member States include 14 African States, 14 Asian States, 8 Eastern European States, 10 Latin American and Caribbean States and 14 Western European and other States.
- The General Assembly elects members for terms of six years; every three years, the terms of half of the members expire.
- India is a founding member of this organisation.
Key facts about Chabahar Port
- It is a seaport in the Sistan-Balochistan province of Iran, on the Gulf of Oman, at the mouth of the Strait of Hormuz.
- It is a deep-water port with direct access to the Indian Ocean that is outside the Hormuz Strait.
- Its geographic proximity to countries such as Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India, as well as its status as a key transit centre on the burgeoning International North-South Transport Corridor.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-and-iran-drop-foreign-court-arbitration-for-chabahar-port/article67234071.ece
Insurance Surety Bonds (PIB)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)is advocating for the adoption of surety bond insurance products for highway projects
Facts About:
These bonds can be defined in their simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act.
These are instruments where insurance companies act as ‘Surety’ and provide the financial guarantee that the contractor will fulfil its obligation as per the agreed terms.
Surety is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement.
The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal: The party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety: The insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee: The party who requires and often receives the benefit of the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organisation.
What are the advantages?
- It will act as a security arrangement for infrastructure projects and will insulate the contractor as well as the principal.
- The product will cater to the requirements of a diversified group of contractors, many of whom are operating in today’s increasingly volatile environment.
- The product gives the principal a contract of guarantee that contractual terms and other business deals will be concluded in accordance with the mutually agreed terms.
- In case the contractor doesn’t fulfil the contractual terms, the Principal can raise a claim on the surety bond and recover the losses they have incurred.
- Unlike a bank guarantee, the Surety Bond Insurance does not require large collateral from the contractor, thus freeing up significant funds for the contractor, which they can utilise for the growth of the business.
- The product will also help in reducing the contractors’ debts to a large extent, thus addressing their financial worries.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1951715
National Medical Commission (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has put on hold the regulations that make it mandatory for doctors to prescribe generic drugs.
Facts About:
- In light of the criticism received by the Indian Medical Association (IMA) as well as the as the Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance (IPA), the National Medical Commission put on hold the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023.
- Even the country’s apex drug regulator, the Central Drugs Standard Drug Control Organisation (CDSCO), questioned the language in the notification.
- The participating bodies suggested that the guidelines be kept in abeyance until the WHO’s good manufacturing practices are implemented.
- The participants said that prescribing only generic drugs will prompt pharmacies to sell generic drugs at high-profit margins, disincentivising firms that manufacture quality branded generics
National Medical Commission:
- The National Medical Commission is a statutory body established under the National Medical Commission Act, 2019.
- The NMC replaced the erstwhile Medical Council of India (MCI) which was established in 1934.
Objectives of NMC –
- Improve access to quality and affordable medical education;
- Ensure availability of adequate and high-quality medical professionals in all parts of the country;
- Promote equitable and universal healthcare that encourages community health perspective and makes services of medical professionals accessible to all the citizens;
- Encourages medical professionals to adopt latest medical research in their work and to contribute to research;
- Objectively assess medical institutions periodically in a transparent manner;
- Maintain a medical register for India;
- Enforce high ethical standards in all aspects of medical services;
- Have an effective grievance redressal mechanism.
Composition of NMC –
- NMC is a 25-member body, majority of them being nominated by the Central government.
- Tenure of NMC members is four years (except for part-time members whose tenure is two years).
- The NMC has 11 part-time members representing states or state medical councils.
- The NMC chairpersons and other members, nominated by the Central government, cannot be renominated.
- Any decision requires approval of the majority (minimum 13 out of 25) of the Commission.
Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023:
- On August 2nd, the National Medical Commission had published the Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations, 2023 aimed at reshaping prescription practices.
- It mandated that registered medical practitioners prescribe medications using “generic”, “non-proprietary”, or “pharmacological” names.
- The guidelines define a generic drug as a “drug product that is comparable to brand/reference listed product in dosage form, strength, route of administration, quality and performance characteristics, and intended use.”
- It says branded generic drug is one which has come off patent and is manufactured by drug companies and sold under different companies’ brand names.
- The guidelines say, “Every RMP (Registered Medical Practitioner) should prescribe drugs using generic names written legibly and prescribe drugs rationally, avoiding unnecessary medications and irrational fixed-dose combination tablets.”
- The guidelines have also talked about punitive measures against those violating the directive.
- Besides the instructions on generic drugs, the NMC guidelines included directives on issues ranging from continued medical education, usage of social media platforms and maintaining a dynamic register of doctors.
- It also barred doctors from attending events sponsored by pharmaceutical companies.
- However, the NMC guidelines have not gone down well with the Indian Medical Association (IMA).
Issued Raised by the Indian Medical Association (IMA):
- The IMA issued a statement in response to the regulations introduced by the NMC.
- The IMA says the biggest impediment to generic drugs is the uncertainty about its quality.
- IMA said that the quality control in the nation being very weak, there’s practically no guarantee of the quality of drugs and prescribing drugs without assured quality would be detrimental to patient health.
- The statement added that less than 0.1% of the drugs manufactured in India are tested for quality.
- The IMA said that step should be deferred till the Government can assure the quality of all the drugs released into the market.
- The statement says patient care and safety are not negotiable.
- The IMA says it has been demanding for long that only good quality drugs should be made available in the country and prices should be uniform and affordable.
- It urges the Government to have ‘one drug, one quality, one price’ system whereby all brands should either be sold at the same price or banned and only generics allowed while ensuring highest quality of these drugs.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/india/nmc-hold-regulations-mandating-doctors-prescribe-generic-drugs-bar-them-endorsing-drug-brand-8907964/
Gene-Edited Mustard (Indian Express)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Indian scientists have developed the first ever low-pungent mustard that is pest and disease-resistant. It is based on CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing.
Facts About:
- Among India’s domestically grown oilseeds, rapeseed-mustard stands out.
- However, its pungent oil and unpalatable meal have posed challenges for both consumers and livestock.
- Scientists have undertaken breeding efforts to create Canola-quality (white) mustard with reduced pungency and improved meal quality.
About Rapeseed-Mustard
- Rapeseed-Mustard: India’s significant oilseed is rapeseed-mustard, contributing significantly to vegetable oil production and meal availability.
- Pungency: Mustard seeds contain glucosinolates, compounds that give the oil and meal their pungent flavor and odor.
Quest for Canola-Quality Mustard
- Canola-Quality Pursuit: Scientists aimed to breed mustard lines with low glucosinolate content similar to Canola.
- Reducing Pungency: Efforts to create low-pungency oil and meal have faced challenges due to the necessity of glucosinolates in plant defense.
- Vulnerability to Pests and Diseases: Canola-quality mustard lines have not been cultivated extensively due to their susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Role of Gene Editing
- Innovative Research: Gene editing emerges as a solution to balance glucosinolate levels for improved quality and plant defence.
- CRISPR/Cas9 Approach: Researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing tool to target and modify 10 out of 12 GTR genes in Indian mustard.
- Achieving Desired Changes: Editing GTR genes led to lower glucosinolate content in seeds while preserving higher levels in leaves and pod walls.
Benefits of GE Mustard
- Easy Synthesis: Glucosinolates are synthesized in mustard leaves and pod walls before translocation to seeds.
- Dual Benefit of Glucosinolates: The study revealed that edited mustard lines with low-seed glucosinolates exhibited improved defence against pests and diseases.
Distinction between GE and GM
- GE Mustard: The new mustard lines are genome-edited (GE), not genetically modified (GM).
- Transgene-Free Solution: Unlike GM crops with foreign genes, GE lines have no foreign DNA and no residual gene-editing tools.
Regulatory Considerations and Future Prospects
- Regulation Changes: India’s regulatory environment is shifting, exempting GE plants free of exogenous introduced DNA from stringent approval requirements.
- Potential Field Trials: Scientists are preparing for open field trials of GE mustard, with expectations to conduct them in the upcoming planting season.
- Importance of Self-Reliance: With massive edible oil imports, domestic oilseed production through breeding advancements like GE mustard becomes vital for self-reliance.
Economic Implications and Self-Sufficiency
- Importance of Oilseeds: India’s substantial edible oil imports highlight the need for boosting domestic oilseed production.
- Mustard’s Role: Mustard’s high oil content and protein-rich meal position it as a significant oilseed crop.
- Potential Benefits: Both GE mustard and GM hybrid mustard have the potential to reduce dependence on imported vegetable oils.
Conclusion
- The journey of rapeseed mustard from its pungent state to a potentially improved, self-sufficient crop demonstrates the power of innovative breeding techniques.
- The breakthrough in gene editing opens doors to balancing quality and plant defence.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/gene-edited-mustard-less-pungent-more-useful-8901549/
India and the Northern Sea Route (NSR) (The Hindu)
- 25 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Murmansk, the beginning point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), is witnessing the rising trend of Indian involvement in cargo traffic.
Facts About:
What is Northern Sea Route?
- It is the shortest shipping route for freight transportation between Europe and countries of the Asia-Pacific region, straddles four seas of the Arctic Ocean.
- Coverage- It runs around 5,600 km, the Route begins at the boundary between the Barents and the Kara seas (Kara Strait) and ends in the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
- Save distance- Distance savings along the NSR can be as high as 50% compared to the currently used shipping lanes via Suez or Panama.
- The traditional Suez Canal route is 8000 km longer than Northern Sea passage.
- 2021 blockage- The 2021 blockage of the Suez Canal, which forms part of the widely-used maritime route involving Europe and Asia, has led to greater attention on the NSR.
- Navigability- Arctic Ocean remain icebound during most of the year, the icebreaking assistance is organised to ensure safe navigation along the NSR.
What are the advantages of Northern Sea Route?
- Profitable-It is a strategically important transport artery; it is economically profitable when comapared with Suez Canal.
- Save fuel- It will save fuel due to reduced distance.
- Cost effective- The shorter distance reduces the cost of staff labor and chartering vessels.
- The route does not charge payments for the passage unlike Suez Canal.
- Time saving-There are no queues (unlike, for example, the Suez Canal);
- Safety- There is no risk of a pirate attack.
Why Arctic region is so significant for India?
- Impact on India-The vulnerability of the Arctic region leads to unprecedented changes in the climate.
- This may have an impact on India in terms of economic security, water security and sustainabilit
- Svalbard Treaty- India’s engagement with the Arctic can be traced to the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in 1920.
- Conduct studies: Indian conducts studies regarding atmospheric, biological, marine, hydrological, glaciological events.
- Arctic Council- Arctic Council addresses the issues faced by governments in the region and the indigenous people of the Arctic.
- India is an observer state in Arctic Council including China.
- Himadri research station- India's first permanent Arctic research station located at Spitsbergen, Svalbard, Norway.
- It is located at the International Arctic Research base, Ny-Alesund.
- Infrastructural base-
- Multi-sensor moored observatory was inaugurated in 2014
- Northernmost atmospheric lab was launched in 2016
- Successful expeditions- India conducted around 13 successful expeditions to Arctic till 2022.
- Arctic Policy of 2022- It mentions that the country’s approach to economic development of the region is guided by UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- Potential for minerals- The region constitutes the largest unexplored prospective area for hydrocarbons remaining on the earth.
- There may be significant reserves of coal, zinc, and silver.
- Institutional support- In 2018 India renamed National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research to National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research.
- It shows India’s refocusing priorities in Arctic region.
What are the driving factors for India to participate in the NSR development?
- Growth in cargo traffic- India engagement in NSR is on the constant rise and during 2018-2022, the growth rate was around 73%.
- Last year, the volume of cargo traffic was 34.117 million tonnes.
- India-Russia trade- India increasingly imports crude oil and coal from Russia in recent years.
- The record supplies of energy resources for the Indian economy are possible due to such a reliable and safe transport artery as the NSR.
- Transit route- NSR assumes importance, given India’s geographical position and the major share of its trade associated with sea transportation.
- East meets East- In 2019 India and Russia signed Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC) project.
- It is signed as one linking with another organise international container transit through the NSR.
- Reduce travel time-The 10,500 km-long CVMC, passing through the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea and Malacca Strait, will bring down transport time to 12 days.
- This is almost a third of what is taken under the existing St. Petersburg-Mumbai route of 16,000 km.
- Chennai Port Trust study- Fuel and fertilisers are some of the cargo that can be imported from Russia to India through CVMC.
What lies ahead?
- NSR development plan- It is approved until 2035 by Russia, this sets the cargo traffic target as 80 million tonnes and 150 million tonnes for 2024 and 2030.
- The plan approval took place amid economic sanctions imposed by the West against Russia following the latter’s war with Ukraine.
- Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor project-Workshop featuring stakeholders from the two countries, is expected to be held in the second half of October.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/explained-india-and-the-northern-sea-route/article67230900.ece
ASTRA air-to-air Missile (PIB)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Light Combat Aircraft(LCA) Tejas successfully test-fired an ASTRA beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile off the coast of Goa.
Facts About:
- The ASTRA BVR missile is designed to engage and destroy highly maneuvering supersonic aerial targets. It has a range of over 100 kilometers.
BVR missiles are capable of engaging beyond the range of 20 nautical miles or 37 kilometres.
- This missile has all weather day and night capability. The system is being developed to meet specific requirements.
- It is jointly designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), Research Centre Imarat (RCI) and other laboratories of DRDO.
- ASTRA missile would significantly enhance the combat prowess of Tejas and reduce the dependency on imported weapons.
Tejas is a single-engine multi-role fighter aircraft capable of operating in high-threat air environments. It has been designed to undertake the air defence, maritime reconnaissance and strike roles.
- The ASTRA Mk-I Weapon System integrated with SU-30 Mk-I aircraft is being inducted into the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Fujiwhara Effect (Indian Express)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, powerful winds tormented the Bay Area and other parts of Central and Southern California, uprooting trees and disrupting the power supply due to Fujiwhara effect.
Facts About:
- It was identified by a Japanese meteorologist Sakuhei Fujiwhara.
- It was observed for the first time over the western Pacific Ocean, when typhoons Marie and Kathy merged in 1964.
What is it?
- When two hurricanes (or cyclones, depending on where you live), spinning in the same direction, are brought close together, they begin ‘an intense dance around their common center’ – this interaction between two cyclones is called the Fujiwhara effect.
When it Occur?
- If one hurricane’s intensity overpowers the other, then the smaller one will orbit it and eventually crash into its vortex to be absorbed.
- On the other hand, if two storms of similar strengths pass by each other, they may gravitate towards each other until they reach a common center and merge, or merely spin each other around for a while before shooting off on their own paths.
- In rare instances, the two ‘dancing’ cyclones, if they are intense enough, may merge with one another, leading to the formation of a mega cyclone capable of wreaking havoc along coastlines.
Experts have noted the rising frequency of this unusual effect, attributing it to a rapidly warming world and the subsequent heating of ocean waters.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwia1b_gj6OBAxXpSmwGHVb_DTQQFnoECBUQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Findianexpress.com%2Farticle%2Fexplained%2Fexplained-climate%2Ffujiwhara-effect-cyclones-dance-8905398%2F&usg=AOvVaw0_moE3dRI3IZbhz8XqmBkl&opi=89978449
CHANDRAYAAN 3 MAKES SOFT LANDING (The Hindu)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Launched on 14 July 2023, Chandrayaan-3 etched its place in history when the lander and rover touched down near the lunar south pole region on 23 August 2023 at 18:02 IST.
Facts About:
- Chandrayaan-3, part of the Indian Space Research Organisation's (ISRO) Chandrayaan program, signifies a remarkable feat in lunar exploration.
- Comprising a lander named Vikram and a rover named Pragyan, akin to the Chandrayaan-2 mission, this mission focuses on achieving a controlled landing and rover mobility on the lunar surface.
- With the propulsion module transporting the lander-rover configuration to lunar orbit, a powered descent by the lander was the critical phase of the operation.
- The mission encompasses a Lander and Rover configuration, propelled by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota. The propulsion module carries the Lander and Rover until the lunar orbit's 100 km mark.
Origins and Progression: Chandrayaan-2's Influence
- Chandrayaan-2's launch in July 2019, which featured an orbiter, lander, and rover, set the stage for Chandrayaan-3.
- While the initial lander's trajectory went awry during a landing attempt in September 2019, ISRO's spirit remained unbroken, leading to the conception of Chandrayaan-3 and other future lunar missions.
Global Collaboration: ESA's Involvement
- The European Space Tracking network (ESTRACK), operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), provided support for the mission.
- A mutual support agreement emerged, where ESA's tracking assistance for ISRO missions, including Gaganyaan (India's human spaceflight program) and the Aditya-L1 solar research mission, was reciprocated by ISRO's support for future ESA missions.
- This collaboration underlines the global nature of space exploration.
Mission Aims
- ISRO laid out three primary objectives for Chandrayaan-3:
- Achieve a safe and soft lunar landing.
- Demonstrate the rover's mobility capabilities.
- Conduct experiments on lunar surface materials to enhance understanding of lunar composition.
Spacecraft Configuration
Propulsion Module
- Carries the lander-rover to a 100 km lunar orbit.
- Features a solar panel and mounting structure for the lander.
Lander (Vikram)
- Executes the soft landing on the Moon.
- It had four landing legs and four landing thrusters capable of producing 800 newtons of thrust each
- Accommodates the rover and scientific instruments.
Rover (Pragyan)
- A six-wheeled, 26 kg vehicle.
- Conducts diverse measurements, contributing to lunar research.
- Investigates lunar surface composition, presence of water ice, lunar impact history, and atmosphere evolution.
Payloads
Lander Payloads
Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE)
- Objective: Measure thermal conductivity and temperature of the lunar surface.
- Information gleaned aids in comprehending lunar surface properties near polar regions.
Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA)
- Objective: Measure seismic activity around the landing site, revealing the lunar crust and mantle's structure.
Langmuir Probe (LP)
- Objective: Estimate plasma density variations in the vicinity of the landing site.
- Langmuir probe plays a crucial role in studying ionosphere and atmospheric phenomena.
Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA)
- Objective: Passive experiment for lunar laser ranging studies.
- LRA aids in comprehending the dynamics of the Moon system.
Additional Payload: Collaboration with NASA
- Passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA contributes to lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover Payloads
Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS)
- Objective: Determine elemental composition (e.g., Mg, Al, Si, K, Ca, Ti, Fe) of lunar soil and rocks around the landing site.
- APXS provides insights into the chemical makeup of lunar materials.
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS)
- Objective: Conduct qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis.
- LIBS aids in deciphering chemical and mineralogical composition for a deeper understanding of the lunar surface.
Propulsion Module Payload
Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE)
- Objective: To make future discoveries of smaller planets through reflected light, potentially identifying habitable exoplanets.
- SHAPE payload enhances India's contribution to the study of exoplanets.
Mission Progress
The mission progressed through several stages, including launch, Earth and lunar orbit maneuvers, and descent. Notable milestones include:
- Launch on 14 July 2023.
- Lunar orbit insertion on 5 August 2023.
- Lander separation from the propulsion module on 17 August 2023.
- Successful soft landing on 23 August 2023, making India the fourth nation to land on the Moon.
Technological Innovations
- Advanced Altimeters: Laser and RF-based altimeters for precise altitude measurements.
- Velocimeters: Laser Doppler Velocimeter and Lander Horizontal Velocity Camera for speed monitoring.
- Inertial Measurement: Laser Gyro-based Inertial referencing and Accelerometer package for navigation.
- Navigation, Guidance & Control (NGC): Software elements for powered descent trajectory design.
- Hazard Detection and Avoidance: Lander Hazard Detection & Avoidance Camera and Processing Algorithm.
- Landing Leg Mechanism: Enhanced landing leg design for secure touchdown.
Mission Life
- Propulsion Module: Carried lander and rover to lunar orbit, with operation of experimental payload for up to 6 months.
- Lander Module: 1 Lunar Day (14 Earth Days).
- Rover Module: 1 Lunar Day (14 Earth Days).
Key Team Members and Funding:
- ISRO Chairperson: Somanath.
- Mission Director: Mohanakumar.
- Associate Mission Director: Narayanan.
- Project Director: Veeramuthuvel.
- Deputy Project Director: K.
- Vehicle Director: Biju C. Thomas.
- Estimated cost: Around ?615 crore.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/isro-chandrayaan-3-vikram-lander-touch-down-live-updates/article67219323.ece
National Curriculum Framework for school Education 2023 (PIB)
- 24 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the final National Curriculum Framework (NCF) has been released by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
Facts About:
- Framed by: The NCF was drafted by the National steering committee headed by former Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), K. Kasturirangan.
- Key points:
- For languages:
- From now, Students in Classes 9 and 10 will need to learn three languages, of which at least two will be native to India.
- Classes 11 and 12, students will learn two languages, including one of Indian origin.
- Board Exams: The NCF states that all students will be allowed to take Board exams on at least two occasions during any given school year, with only the best score being retained.
- New Text books: It follows the lead of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, and gives assent for formulating new textbooks from Grades 3 to 12 under the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
- Number of Subjects: For students from Classes 9 to 12 has to study five mandatory subjects, with an option of adding one more subject.
- Now, the number of mandatory subjects for Classes 9 and 10 is seven and six for Classes 11 and 12.
- Optional subjects have been grouped in three parts in the NCF.
- The first optional group includes art education, physical education and vocational education.
- The second group includes Social Science, the Humanities, and interdisciplinary areas.
- The third group includes Science, Mathematics, and computational thinking.
- Shift to semester-based term: The NCF has recommended that in the long term, all Boards should change to semester or term-based systems.
- Now, there is no hard separation between academic and vocational subjects, or between Science, Social Science, Art, and Physical Education.
- For languages:
NCF from NEP 2020:
The NCF brings the aims and commitments of the NEP:
- This includes the full range of human capacities, values and dispositions that are aimed to be developed in school education.
- Pedagogy, practices, and culture must work in tandem to develop these, and move away from an overemphasis on memorization and content accumulation; in fact, content reduction is required to create space for such development.
- The 5+3+3+4 Curricular and Pedagogical structure of school education is reflected in the learning standards, the content, the pedagogy, and the assessment approaches.
- It is integrative and holistic with equal status to all subjects and learning domains from Math to Sports.
- It integrates vocational education in all schools, and there is integration across subjects while developing rigorous subject understanding and capacities.
National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT):
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an autonomous organisation set up in 1961 by the Government of India to assist and advise the Central and State Governments on policies and programmes for qualitative improvement in school education.
- The major objectives of NCERT and its constituent units are to:
- Undertake, promote and coordinate research in areas related to school education
- Prepare and publish model textbooks, supplementary material, newsletters, and journals and develops educational kits, multimedia digital materials, etc.
- organize pre-service and in-service training of teachers
- develop and disseminate innovative educational techniques and practices
- Collaborate and network with state educational departments, universities, NGOs and other educational institutions
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1951485
Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North East Region (PM-DevINE) (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The revised guidelines were issued for the Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for the North East Region (PM-DevINE).
Facts About:
- PM-DevINE, was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 to address development gaps in the North Eastern Region (NER).It was approved by the Cabinet for the remaining four years of the 15th Finance Commission from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The new Scheme is a Central Sector Scheme and will be implemented by the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER).
- The PM-DevINE Scheme will have an outlay of Rs.6,600 crore for the four year period from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- An Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC) will be established, tasked with various functions under the scheme.
Objectives of PM-DevINE
- Fund infrastructure convergently, in the spirit of PM Gati Shakti;
- Support social development projects based on felt needs of the NER;
- Enable livelihood activities for youth and women;
- Fill the development gaps in various sectors.
Functions of Empowered Inter-Ministerial Committee (EIMC)
- It assesses initial project proposals based on quality, viability, and socio-economic impact, working alongside representatives from relevant Indian Government Ministries/Departments and State Governments.It then recommends project selection from among these proposals.
- The EIMC proposes effective monitoring and evaluation methods, which may involve on-site inspections through third-party agencies.
- The committee also devises mechanisms for the operation and maintenance of PM-DevINEprojects, aiming to ensure their sustainability.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=194206
Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap (Indian Express)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, a new report ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’, was published by the anti-debt campaigners Debt Justice and partners.
Facts About:
Key Takeaways from ‘The Debt-Fossil Fuel Trap’ report:
- Debt-Reliant Economies and Fossil Fuel Dependence:Poor countries burdened with heavy debts are compelled to rely on fossil fuel revenue to repay loans borrowed from wealthier nations, multilateral creditors like the World Bank and IMF, or private lenders.
For Example: Argentina has been supporting fracking projects in the Vaca Muerta oil and gas field in Northern Patagonia to generate revenues to ease the country’s debt crisis. Notably, the IMF has also backed these projects.
- Surging External Debt Payments in Global South:The external debt payments of Global South countries have surged by 150% between 2011 and 2023, reaching the highest levels in 25 years.
- Debt Crisis and Constrained Public Spending:Around 54 countries are facing a debt crisis, resulting in reduced public spending during the pandemic to meet loan repayment obligations.
- Climate Challenges Amplify Borrowing in Global South:Many of these indebted countries lack adequate resources for climate adaptation, mitigation, and addressing loss and damage, forcing them to borrow more money.
- Natural Disasters Escalate Debt-to-GDP Ratio:After events like natural disasters, countries can see their debt as a percentage of GDP rise significantly, such as Dominica’s experience after Hurricane Maria in 2017.
- Unfulfilled Pledges: Despite promises to discontinue investing in fossil fuels in Global South countries, richer nations and lenders continue to finance fossil fuel projects through loans, perpetuating fossil fuel production.
- Resource Backed Loans (RBLs):Resource backed loans (RBLs) are a mechanism through which repayment is tied to natural resources or future income streams derived from those resources.
Recommendations for a Sustainable Path Forward:
- Implementing ambitious debt cancellation for countries in need without economic conditions
- Rejecting repayments from fossil fuel projects.
- Aligning bilateral and multilateral finance with a 1.5-degree warming scenario while avoiding fossil fuel financing.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/rich-countries-force-poor-nations-rely-fossil-fuels-8904371/
20th ASEAN India Economic Ministers’ Meeting (PIB)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India participated in the 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting.
Facts About:
- The 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ meeting was held in Semarang, Indonesia.
- The Economic Ministers or their representatives from all the 10 ASEAN countries viz. Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam participated in the meeting.
- The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste also joined the Meeting as an observer.
- The Ministers reviewed the bilateral trade and investment relations between India and ASEAN and underscored their commitment to strengthen and enhance the economic partnership between India and ASEAN to ensure that the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership delivers meaningful benefits for both sides, particularly in the post-pandemic era.
- The Ministers also interacted with the ASEAN-India Business Council (AIBC).
- The main agenda of this year’s meeting was the timely review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) which was signed in 2009.
- India and ASEAN registered a bilateral trade of USD 131.5 billion in 2022-23. The trade with ASEAN accounted for 11.3% of India’s global trade in 2022-23.
ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA):
- AITIGA is a trade deal between the ten member states of ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN and India signed the Agreement at the 7th ASEAN Economic Ministers-India Consultations in Bangkok, Thailand in 2009. The Agreement, which came into effect in 2010, is sometimes referred to as the ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement.
- The Agreement has led to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India since its signing.
- The Agreement originated out of the Framework Agreement on Comprehensive Economic Cooperation between India and ASEAN created in 2003.
- It covers trade in physical goods and products and not services trade.
ASEAN and India signed a separate ASEAN-India Trade in Services Agreement in 2014.
Along with the ASEAN-India Investment Agreement, the three agreements collectively form the ASEAN-India Free Trade Area.
- Under the Agreement, ASEAN and India have committed to progressively eliminating duties on 76.4 percent of goods and to liberalize tariffs on over 90 percent of goods.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1950902#:~:text=Shri%20Rajesh%20Agrawal%2C%20Additional%20Secretary,%2C%20Minister%20of%20Trade%2C%20Indonesia.
Strong case to restore Section 8(4) of the RP Act (The Hindu)
- 23 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The recent disqualification of Rahul Gandhi, based on his conviction and imprisonment in a defamation case, has brought attention to the legal complexities and implications associated with the disqualification of sitting legislators in India. The focus is on the Supreme Court's decision to strike down Section 8(4) of the Representation of People Act 1951.
Facts About:
Disqualification and Legal Framework:
- Instant Disqualification and Lily Thomas Case: The disqualification of Rahul Gandhi based on his conviction in a defamation case raised questions about the legal basis of instant disqualification for sitting legislators. The Supreme Court's judgment in Lily Thomas vs Union of India (2013) invalidated Section 8(4) of the Representation of People Act 1951, removing the three-month appeal window before disqualification took effect.
- Section 8(3) and Disqualification: With the removal of Section 8(4), only Section 8(3) remains, which stipulates that a person convicted and sentenced to imprisonment for at least two years shall be disqualified from the date of conviction. The wording does not explicitly indicate an immediate disqualification upon the court's pronouncement of guilt.
- Disqualification Authority and Presidential Role: The authority to declare a sitting legislator disqualified might lie with the President of India under Article 103. While the Supreme Court rejected this proposition in Lily Thomas, the Consumer Education & Research ... vs Union Of India & Ors (2009) held that the President's declaration is necessary for disqualification.
Legal Implications and Challenges:
- Staying of Sentence and Conviction: The question arises whether the stay of only sentence or the stay of conviction itself is required to lift the disqualification. Different High Courts have held differing views on this issue, adding complexity to the interpretation of disqualification.
- Quantum of Sentence and Disqualification: Disqualification hinges on the imprisonment term being two years or more. The recent case of Rahul Gandhi emphasized this connection, highlighting that the disqualification's trigger is the sentence length, not just the conviction itself.
- Career Impact and Urgent Attention: Instant disqualification can significantly affect legislators' careers, especially given the slow pace of appeals and legal proceedings. There's a need to address this issue urgently to ensure the stability of legislators' careers and prevent abrupt disqualifications.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/a-strong-case-to-restore-section-84-of-the-rp-act/article67224103.ece
New Scheme Guidelines for North Eastern Region (PIB)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (MDoNER) releases new Scheme Guidelines for implementing Cabinet-approved Schemes during 15th Finance Commission's balance period (2022-2026).
Facts About:
- The Cabinet approved Continuation of the North East Special Infrastructure Development Scheme (NESIDS) with an outlay of Rs.8139.50 crore for the period from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- The scheme is a central sector scheme.It has two components viz. NESIDS-Road and NESIDS-Other Than Road Infrastructure (OTRI).
- The objective of the NESIDS is to support infrastructure development in identified sectors including connectivity in the North Eastern States.
- The Union Cabinet had also approved continuation of the ‘Schemes of North Eastern Council (NEC)’ for the period from 2022-23 to 2025-26 with a total outlay of Rs.3202.7 crore.
- The MDoNER Schemes help provide gap-filling support to the eight North Eastern States as per their felt needs, by taking up projects – e.g., for developing infrastructure to mitigate connectivity and social sector deficits and enhancing livelihood and employment opportunities in the region.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=195088
ICMR study on post COVID mortality (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) study reported that 17.1% of those hospitalized since September 2020 experience post-Covid conditions.
Facts About:
What were the main findings of the ICMR study?
- The study, encompassing 14,419 Covid-19 patients hospitalized since September 2020, revealed a 6.5% mortality rate within a year after hospitalization. Around 17.1% experienced post-Covid-19 conditions. It also highlighted the increased mortality risk associated with comorbidities, age, and gender.
How did the study define “post-Covid-19 conditions”?
- The study defined “post-Covid-19 conditions” as the persistence or new onset of fatigue, breathlessness, or cognitive abnormalities, due to the lack of established definitions from organizations like the World Health Organization or the CDC during patient enrollment.
What impact did a single vaccine dose have on mortality?
- The study indicated that a single vaccine dose prior to Covid-19 infection reduced one-year mortality by 60%, emphasizing the importance of vaccination even before exposure.
Who faced a higher risk of mortality according to the study?
- The study revealed that individuals with comorbid conditions were at the highest risk of mortality, being more than 9 times likely to die within a year. Men were 1.3 times more likely to die, while those above 60 years were 2.6 times more likely.
What risk did children face in terms of mortality?
- Children between 0 and 18 years had a 5.6-fold higher risk of death in the year following infection, with a 1.7-fold increase in the immediate four weeks post-hospitalization. Severe comorbidities among admitted children were hypothesized as a reason for the higher odds of death.
Can mild Covid-19 variants lead to long Covid?
- The long Covid might occur even in individuals with mild Covid-19. While symptoms improve with therapy, over-diagnosis of long Covid may be occurring, warranting consideration of alternative causes for reported symptoms.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/explained-the-debate-over-indias-smartphone-manufacturing-dreams/article67220769.ece
PLI Scheme for Smartphone Manufacturing Industry & Its Effectiveness (The Hindu)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Over the last few months, former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan and the Minister of State for Electronics Rajeev Chandrasekhar have sparred over how well a Central government scheme to boost electronics manufacturing has been faring.
Facts About:
- Former RBI governor Raghuram Rajan, along with two other economists, had released a brief discussion paper arguing that the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) programme isn’t really pushing India towards becoming a self-sufficient manufacturing powerhouse.
- They argued that the government is using taxpayer money to create an ecosystem of low-level assembly jobs that will still depend heavily on imports.
What is the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Programme?
- Around five years ago, the Government of India decided it wanted more companies to make things in India.
- Manufacturing is a key ingredient to economic growth and also comes with what economists call a multiplier effect — every job created and every rupee invested in manufacturing has a positive cascading effect on other sectors in the economy.
- To boost manufacturing in India, the Government introduced the production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme.
- Under PLI, the government gives money to foreign or domestic companies that manufacture goods here.
- The annual pay-out is based on a percentage of revenue generated for up to five years.
PLI Programme for Smartphone Manufacturing Industry:
- The industry that has shown the most enthusiasm for the scheme is smartphone manufacturing.
- Companies like Micromax, Samsung, and Foxconn (which makes phones for Apple) can get up to 6% of their incremental sales income through the PLI programme.
- With the scheme, mobile phone exports jumped from $300 million in FY2018 to an astounding $11 billion in FY23.
- Imports – while India imported mobile phones worth $3.6 billion in FY2018, it dropped to $1.6 billion in FY23.
- Central government Ministers, including Mr. Chandrasekhar, have regularly cited this data as proof of the PLI’s scheme’s success.
Former RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan’s Argument:
- In his paper, the former Central bank governor argued that while imports of fully put-together mobile phones have come down, the imports of mobile phone components — including display screens, cameras, batteries, printed circuit boards — shot up between FY21 and FY23.
- Incidentally, these are the same two years when mobile phone exports jumped the most.
- He said that manufacturers aren’t really making mobile phones in India in the traditional sense which would involve their supply chain also moving to India and making most of the components here as well.
- All that the companies are doing is importing all of the necessary parts and assembling them in India to create a ‘Made in India’ product.
- Another criticism is that low-level assembly work doesn’t produce well-paying jobs and doesn’t nearly have anywhere the same multiplier effect that actual manufacturing might provide.
Union Government’s Response:
- Minister of State for Electronics Rajeev Chandrasekhar’s argument is two-fold.
- First, he said, Mr. Rajan wrongly assumed that all imports of screens, batteries, etc. are used to make mobile phones.
- It is possible these items are used also for computer monitors, DSLR cameras, electric vehicles etc.
- He also argued that not all mobile phone production in India is supported by the PLI scheme, only around 22% so far.
- The Minister’s overarching point is that the import dependency isn’t as bad as Mr. Rajan says it is.
Conclusion:
- Former RBI Governor argued that even if only 60% of imports are used for production, India’s net exports will still be negative.
- That is, even if only 60% of screens, batteries, etc. are used to make mobile phones, the final import tally would still beat the final export tally.
- The main divide is over whether the PLI programme will be able to create long-lasting jobs and firmly establish India as a manufacturing and supply hub that adds value to the production process.
- The Union Government believes that it will take time for the PLI Scheme’s results to show.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/business/Industry/explained-the-debate-over-indias-smartphone-manufacturing-dreams/article67220769.ece
Marine Heat Waves (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Extreme Heat waves are harming marine life in the Mediterranean Sea.
Facts About:
Why are high sea temperatures a problem?
- Lesser dissolution of gases: Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolve better at colder temperatures, so that means the warmer the water; the less oxygen is available to breathe.
- Higher rate of respiration in marine organism: Higher temperatures also cause an increase in metabolism, which in turn means animals have to breathe even more than usual.
- The rise in temperature accelerates metabolism, and the organisms need more food to maintain this metabolic rate.
- More Algal blooms: They are more common in hotter waters. Such blooms can further deplete oxygen levels and produce toxins harmful for fish, marine mammals and birds.
What species and ecosystems are worst hit by marine heat waves?
- High water temperatures are most harmful for animals living at the bottom of oceans, lakes or rivers.
- These benthic species include corals, mussels, sponges, starfish and plants like sea grasses, and are often attached to rock or solid ground.
- Scientists observed mass deaths of benthic species along thousands of kilometers of Mediterranean coastline between 2015 and 2019.
What does extreme heat in the Mediterranean mean for people?
- Affecting fishing activities in the area: Fishermen are catching fewer familiar species and instead are finding more invasive fish which they have difficulty selling.
- Increase in invasive fishes: Some are even poisonous, like the puffer fish migration is seen in the region.
- Habitat loss: It could also lead to an overall decline in fish populations, while disappearing seagrass.
What is the phenomenon behind heat trap in oceans?
- Ocean Heat Content (OHC): It is the amount of energy absorbed by and stored in the oceans. It is measured in joules.
- When sunlight reaches the earth, oceans absorb this energy and store it as heat.
- While the heat is first absorbed at the surface of the water body, some of it is eventually disbursed throughout.
- Water has a higher heat capacity than air, which means that it can store much larger amounts of heat.
- GHG emissions - These gases trap heat in a blanket around the earth, not allowing it to escape, thus raising the temperature of the earth’s surface and leading to global warming.
Why Mediterranean Sea is significant for global temperatures?
The Mediterranean Sea has significant implications for global temperatures due to its role as a "climate amplifier." This phenomenon is referred to as the "Mediterranean Effect" or "Mediterranean Climate Amplification." Here are the reasons:
- Heat Absorption and Release: The Mediterranean Sea has a lower heat capacity compared to the vast oceans, such as the Atlantic or Pacific.
- As a result, it heats up and cools down more quickly. During the summer months, the Mediterranean Sea absorbs heat from the sun, leading to warming of the surrounding land areas.
- In winter, it releases the stored heat, moderating temperatures in nearby regions.
- Warm and Dry Summers: The Mediterranean region experiences warm and dry summers, which are conducive to high evaporation rates from the sea's surface.
- This process results in the release of latent heat into the atmosphere, contributing to the warming of the air.
- Atmospheric Circulation: The temperature contrast between the relatively warm Mediterranean Sea and the cooler landmasses during summer leads to the development of low-pressure systems over land.
- This creates a pressure gradient that drives winds from the sea to the land, bringing warm, moist air with it. This warm air can further increase temperatures over land areas.
- Feedback Loops: The warming effect of the Mediterranean Sea can lead to feedback loops. Warmer land areas result in higher evaporation rates, which in turn contribute to the amplification of temperature rise.
- This cycle of heat absorption, release, and evaporation intensifies the Mediterranean Climate Amplification.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/extreme-heatwaves-mediterranean-sea-8901948/
Vegetated Canopies (Indian Express)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
In a recent development in Spain, tensioned sail-like vegetated awnings or canopies known as “Greenshades” have been strategically installed on the facades of buildings.
Facts About:
- Vegetated canopies are innovative structures designed to reintroduce greenery into urban landscapes.
- Inspired by the natural canopies found in forests and diverse plant ecosystems, these canopies play a crucial role in mitigating the urban heat island effect and enhancing the overall environmental quality of urban areas.
- This installation approach not only adds an aesthetic dimension to the urban architecture but also serves as a practical solution for reintroducing green elements in areas where traditional planting is challenging.
Emulating Nature’s Canopies:
- Mimicking the canopy formations observed in forest ecosystems, these vegetated awnings recreate a semblance of natural green cover.
- By doing so, they provide shade, reduce direct sunlight exposure, and create a more pleasant atmosphere in commercial streets and public spaces.
- This is particularly valuable in areas where the presence of trees and vegetation is limited.
Hydroponic Growth System:
- The vegetation integrated within these awnings grows using a hydroponic growth system.
- This method utilises a water supply point to provide the plants with the necessary moisture and nutrients. Additionally, a water outlet is incorporated into the design to facilitate efficient drainage.
- This innovative approach ensures that the greenery thrives even in non-traditional planting environments.
BENEFITS OF VEGETATED CANOPIES
Cooling Effects via Evapotranspiration
- Singular Green’s innovative canopy design efficiently reduces temperatures in both immediate areas and beneath the awnings.
- Achieved through evapotranspiration, where plants transfer water to the atmosphere, this cooling process enhances comfort.
Air Quality Improvement through Plant Selection
- Carefully chosen plants possess a special ability to absorb gases, including pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide.
- This contributes to better urban air quality and healthier living conditions.
Noise Reduction with Sound Wave Absorption
- Vegetated canopies excel at absorbing sound waves, minimising noise pollution and creating a more serene urban environment.
- Incorporating sound-absorbing substrates enhances the auditory experience.
Oxygen Generation and Gas Filtration
- Surprisingly, a single square metre of these canopies produces a year’s worth of oxygen for an individual.
- Moreover, they serve as natural filters, removing harmful gases from the air and thus improving overall air quality.
Efficient Water and Lighting Integration
- Beyond their green benefits, these canopies facilitate centralised water and lighting installations.
- Integrated lights equipped with motion sensors respond to real-time needs, promoting energy-efficient urban infrastructure.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
- Introducing these canopies into urban spaces fosters biodiversity by creating habitats for diverse wildlife.
- This initiative aligns with the vision of sustainable, nature-friendly cities, nurturing a harmonious urban ecosystem.
In the face of climate change-induced challenges, our response must be proactive, multifaceted, and holistic. The success of vegetated canopies as a means to combat extreme heat waves demonstrates that nature-inspired solutions have the power to transform urban environments into havens of sustainability, resilience, and well-being. By embracing such strategies and embarking on a collective journey, we can build cities that thrive in harmony with the planet.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/vegetated-canopies-green-spaces-urban-spain-8893918/
Concerns about Drilling in the North Sea (The Hindu)
- 22 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Prime Minister of the U.K. recently backed plans for new fossil fuel drilling off Britain’s coast.
Facts About:
Evolution of North Sea Drilling
- Origins and Legislation: The North Sea drilling history dates back to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the Continental Shelf, which set the stage for exploration in the region.
- Continental Shelf Act: The U.K. Parliament’s enactment of the Continental Shelf Act in 1964 established the country’s jurisdiction over oil and gas resources beneath its seabed.
Milestones and Concerns in Drilling
- Early Exploration and Challenges: British Petroleum (BP) was granted the first exploration license in 1964, leading to natural gas discovery the following year.
- Forties Field Discovery: BP’s breakthrough commercial oil discovery in the Forties Field in 1970 marked a significant milestone.
- Expanding Operations and Safety Revamp: The following years witnessed increased exploration activities and installation of oil platforms. The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 prompted crucial safety reforms.
Rationale and Concerns
- Government’s Position: In an official statement, the government justified the move as a strategy to enhance Britain’s energy independence.
- Environmental Alarm: However, environmental experts express apprehension, especially given the global push towards averting irreversible climate change.
North Sea Transition Authority and Offshore Licensing
- NTSA’s Role: The North Sea Transition Authority (NTSA) is responsible for regulating the oil, gas, and carbon storage sectors.
- Offshore Licensing Round: The NTSA is currently conducting the 33rd offshore oil and gas licensing round, aiming to award more than 100 licenses.
- Timing and Awards: The first licenses are expected to be granted in the autumn, furthering the expansion of drilling operations.
Shaping Geopolitical Energy Dependence
- Energy Security Concerns: The Prime Minister emphasized the necessity of domestic oil and gas sources, even as the country aims to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Strategic Implications: The decision is portrayed as an effort to reduce reliance on oil and gas imports, which could originate from potentially unfavourable sources.
Ecological Concerns and Climate Impact
- Adverse Environmental Effects: Offshore drilling poses risks to workers, marine ecosystems, and climate health. It contributes to ocean warming, rising sea levels, and threatens marine biodiversity.
- Carbon Pollution Impact: Carbon pollution settling into oceans contributes to acidification, endangering coral reefs and shellfish.
Evaluating UK’s Climate Commitments
- Climate Change Committee Report: The Climate Change Committee (CCC) pointed out deficiencies in the U.K.’s preparations for climate change under the National Adaptation Programme.
- Adaptation Implementation: The CCC’s assessment highlighted a lack of substantial implementation of adaptation measures to address climate risks.
- Inconsistent with Paris Agreement: The Climate Action Tracker assesses the U.K.’s climate action as not fully aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Long-Term Targets: The U.K.’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and long-term targets do not reflect a fair share of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Incompatibility with Limits: Licensing new oil and gas extraction plans contradicts the 1.5°C temperature rise limit set by the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
- The UK’s endorsement of offshore drilling reflects a complex balancing act between energy security, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship.
- As the world grapples with the imperative of combating climate change, the decisions made today hold the potential to shape the course of a sustainable future.
Evolution of North Sea Drilling
- Origins and Legislation: The North Sea drilling history dates back to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the Continental Shelf, which set the stage for exploration in the region.
- Continental Shelf Act: The U.K. Parliament’s enactment of the Continental Shelf Act in 1964 established the country’s jurisdiction over oil and gas resources beneath its seabed.
Milestones and Concerns in Drilling
- Early Exploration and Challenges: British Petroleum (BP) was granted the first exploration license in 1964, leading to natural gas discovery the following year.
- Forties Field Discovery: BP’s breakthrough commercial oil discovery in the Forties Field in 1970 marked a significant milestone.
- Expanding Operations and Safety Revamp: The following years witnessed increased exploration activities and installation of oil platforms. The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 prompted crucial safety reforms.
Rationale and Concerns
- Government’s Position: In an official statement, the government justified the move as a strategy to enhance Britain’s energy independence.
- Environmental Alarm: However, environmental experts express apprehension, especially given the global push towards averting irreversible climate change.
North Sea Transition Authority and Offshore Licensing
- NTSA’s Role: The North Sea Transition Authority (NTSA) is responsible for regulating the oil, gas, and carbon storage sectors.
- Offshore Licensing Round: The NTSA is currently conducting the 33rd offshore oil and gas licensing round, aiming to award more than 100 licenses.
- Timing and Awards: The first licenses are expected to be granted in the autumn, furthering the expansion of drilling operations.
Shaping Geopolitical Energy Dependence
- Energy Security Concerns: The Prime Minister emphasized the necessity of domestic oil and gas sources, even as the country aims to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Strategic Implications: The decision is portrayed as an effort to reduce reliance on oil and gas imports, which could originate from potentially unfavourable sources.
Ecological Concerns and Climate Impact
- Adverse Environmental Effects: Offshore drilling poses risks to workers, marine ecosystems, and climate health. It contributes to ocean warming, rising sea levels, and threatens marine biodiversity.
- Carbon Pollution Impact: Carbon pollution settling into oceans contributes to acidification, endangering coral reefs and shellfish.
Evaluating UK’s Climate Commitments
- Climate Change Committee Report: The Climate Change Committee (CCC) pointed out deficiencies in the U.K.’s preparations for climate change under the National Adaptation Programme.
- Adaptation Implementation: The CCC’s assessment highlighted a lack of substantial implementation of adaptation measures to address climate risks.
- Inconsistent with Paris Agreement: The Climate Action Tracker assesses the U.K.’s climate action as not fully aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Long-Term Targets: The U.K.’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and long-term targets do not reflect a fair share of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Incompatibility with Limits: Licensing new oil and gas extraction plans contradicts the 1.5°C temperature rise limit set by the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
- The UK’s endorsement of offshore drilling reflects a complex balancing act between energy security, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship.
- As the world grapples with the imperative of combating climate change, the decisions made today hold the potential to shape the course of a sustainable future.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/explained-drilling-in-the-north-sea-history-and-environmental-concerns/article67204792.ece
Turmeric Supplements (The Hindu)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) issued a medical advisory warning Australians of the risk of liver injury from using medicines and herbal supplements containing turmeric or its active ingredient, curcumin.
Facts About:
Health benefits of turmeric:
- The risk of liver injury did not appear to relate to curcuma longa consumed in typical dietary amounts as a food.
- As a staple ingredient in South and South East Asian cuisine, turmeric is also used in Ayurvedic and Chinese-medicine concoctions.
- Several studies report it to have anti-oxidant properties that can help with inflammation.
- These include arthritis and infections.
- A research have reported that curcumin used along with the drug Artemisininwas effective in treating malaria when tested on mice.
- There have also been studies investigating the drug as an adjuvant in chemotherapy based on results in mice and animal studies.
- However, their effect in human trials have been inconclusive.
Adverse effects of turmeric:
- The French Agency for Food reported various adverse effects, including reports of hepatitis, potentially related to the consumption of food supplements containing turmeric or curcumin.
- The ANSES report underlines that turmeric has “choleretic” properties, which means it stimulates the secretion of bile to improve digestion, and therefore, it is advisable that those with bile duct disease should avoidturmeric.
- Curcumin could also interact with medications such as anticoagulants, cancer drugs and immunosuppressants, reducing their safety and effectiveness.
Why is curcumin being used in supplements?
- One of the challenges of turmeric and by extension curcumin is that very little of it is absorbed, or made ‘bioavailable’, by the body.
- To improve its bioavailability, a popular approach is to use piperine, the major active component of black pepper, which improves bioavailability by 2000.
- However, whether increasing the bioavailability of curcumin and packaging them in supplements makes them effective and safe for use in medicines is still being debated with no conclusive evidence emerging from trials.
Safe limit on consumption of turmeric:
- The European Food Safety Authority has set an acceptable daily intake of 180 mg of curcumin per day for a 60 kg adult as the safe level of consumption.
- A World Health Organization/Food and Agricultural Organisationadvisoryrecommends 3 mg/kg of body weight.
- India’s Food Safety and Standards Authority of India has standards that packaged turmeric must comply with but nothing on the recommended dietary allowance.
- Statistically, on an average about 200 to 500mgs is consumed on a daily basis in Indian households.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/explained-are-turmeric-supplements-advisable/article67214093.ece
Expansion of BRICS (Indian Express)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently there have been internal conflicts about the nature and scope of the potential expansion of BRICS.
Facts About:
- BRICS is an acronym for five regional economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- The first four were initially grouped as “BRIC” in 2001 by an economist Jim O’Neill, who coined the term to describe fast-growing economies that would collectively dominate the global economy by 2050.
- Summits: The governments of the BRICS states have met annually at formal summits since 2009.
- India hosted the 13th BRICS summit in 2021 virtually.
- China hosted the 14th BRICS summit in 2022.
- South Africa will host the 15th summit 2023.
- BRICS is an important grouping bringing together the major emerging economies from the world, comprising:
- 41% of the world population,
- 24% of the world GDP
- Over 16% share in world trade.
- Total combined area of 29.3% of the total land surface of the world
- Over a period of time, BRICS countries have come together to deliberate on important issues under the three pillars of:
- political and security,
- economic and financial and
- Cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
- New Development Bank and BRICS: Formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states.
- The Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments.
The need for BRICS expansion
- Economic strength: The economic strength of the five members of the grouping is not as promising as it was when the platform was first announced in 2009.
- Though the BRICS nations certainly represent 43% of the world’s population and around 30% of the global economy, their economic weaknesses are certain.
- China’s anti-western orientation: China is focused on a quick expansion of BRICS with the aim of giving the platform a distinctly anti-western orientation.
- Prevailing Anti-Western sentiment: Many realize that the doors of other groupings are closed to them.
- The clamour reflects prevailing anti-western sentiments and a pervasive desire to create a sizeable forum of the Global South.
- Global challenges: Russia is being marginalised in the global economy, while China is facing a difficult economic environment with the west turning against it.
Challenges with expanding BRICS grouping:
- An increase in membership is likely to weigh the group in favour of Chinabecause some countries waiting to join are also part of the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative.
- This raise concerns that an expanded BRICS could be seen as a Chinese-led anti-American bloc.
- India, which has been strengthening its bilateral relationship with the US, has been concerned about expansion.
- India views China’s role in driving these countries for membership of BRICS along with the support of Russia.
- India also raised its concern in last year’s BRICS that any addition of new members must follow the carefully thought-out objective criteria for membership.
- This should be mutually discussed among the present members, so that all are of the same view regarding expansion.
- Further, at the BRICS foreign ministers’ meeting last month, India’s External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar emphasized the need to consider the ways in which existing BRICS countries collaborate with each other and engages with non-BRICS countries.
Way Forward:
The 15th BRICS summit holds multifaceted importance for India, offering a platform for addressing geopolitical concerns, facilitating bilateral talks, and advancing economic collaborations. As the global landscape continues to evolve, BRICS remains a critical forum for emerging economies to engage and collaborate on key global challenges. The outcomes of this summit will not only affect the member nations but also shape the broader trajectory of international relations and cooperation.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/brics-expansion-significance-for-india-8907925/
Megalithic Site In Kerala (The Hindu)
- 21 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A large number of megalithic hat stones were found during a recent archaeological salvage excavation conducted by the Kerala Archaeology Department at Nagaparamba in Kuttippuram village, near Tirunavaya.
Facts About:
- Hat stones, popularly called Thoppikkallu in Malayalam, are hemispherical laterite stones used as lid on burial urns during the megalithic period.
What is Salvage excavation?
- Salvage excavation also known as rescue archaeology or emergency archaeology, refers to a type of archaeological excavation that is conducted in response to a situation where archaeological remains are threatened by construction, development, or other activities
Megaliths
- Megaliths were constructed either as burial sites or commemorative (non-sepulchral) memorials.
- Origin: As megalithic societies were preliterate, the racial or ethnic origins of the megalithic people are thus difficult to pin down.
- Significance: Megaliths were not built for commoners. They signify the emergence of a ruling class or elite who presided over a surplus economy.
- Time – Period: In India, archaeologists trace the majority of the megaliths to the Iron Age (1500 BC to 500 BC), though some sites precede the Iron Age, extending up to 2000 BC.
Geographical Spread: Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent, though the bulk of them are found in peninsular India, concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Even today, a living megalithic culture endures among some tribes such as the Gonds of central India and the Khasis of Meghalaya.
- Different Types of Megalithic Structure include: Stone Circles, Dolmen, Cist, Monolith and Capstone style.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/hat-stones-in-abundance-at-archaeology-site-near-tirunavaya/article67210231.ece
RBI allows switch from ‘floating to fixed rate’ regime (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) asked all regulated entities (REs), including banks and NBFCs, to give personal loan borrowers an option to switch over from a floating rate to a fixed rate regime at the time of resetting interest rates.
Facts About:
- When a customer takes a loan, the interest rate reset clause in the loan agreement allows the lender to review the interest rate after a certain period, as per the occurrence of a scheduled reset date of the loan.
- The reset rate is the new interest rate that a borrower must pay effective from the scheduled reset date.
- EMI of a floating rate loan changes with periodical changes in reset interest rates.
- These rates and the calculation are not uniform for all the banks as the cost of funds differs from banks.
Changes made by RBI:
The RBI asked banks to implement the following regulations:
- For Regulated entities (RE) :
- At the time of sanction, REs will have to clearly communicate to the borrowers about the possible impact of a change in benchmark interest rate on the loan leading to changes in EMI and/or tenor or both.
- Any increase in the EMI/ tenor or both will have to be communicated to the borrower immediately through appropriate channels.
- At the time of reset of interest rates, REs will have to give the option to borrowers to switch over to a fixed rate as per their board-approved policy.
- The policy will also specify the number of times a borrower will be allowed to switch during the tenor of the loan.
- REs will have to disclose all applicable charges for switching loans from floating to fixed rate and any other service charges/ administrative costs in the sanction letter and also at the time of revision of charges or costs from time to time.
- For EMI or Elongation of tenor:
- The borrowers will also be given the choice to opt for enhancement in EMI or elongation of tenor or for a combination of both options, and to prepay, either in part or in full, at any point during the tenor of the loan, with foreclosure charges.
- The RBI said REs will have to ensure that these instructions are extended to the existing as well as new loans by December 31, 2023.
Why has RBI issued new regulations?
- RBI's Supervisory Reviews: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has conducted supervisory reviews and received feedback from the public.
- Unreasonable Tenor Elongation: Instances of banks significantly extending tenors of floating rate loans without proper borrower consent and communication have been identified.
- Interest Rate Changes: Banks can alter interest rates by adjusting the internal benchmark rate and spread during the loan term, potentially harming borrowers' interests and monetary transmission.
- Arbitrary EMI Resets: Borrowers complain of banks arbitrarily resetting Equated Monthly Installments (EMIs) and extending tenors without adequate notification.
- Hidden Foreclosure Charges: Borrowers are often unaware of foreclosure charges, adding to borrower dissatisfaction.
- Stress Concealment: RBI notes that prolonged tenor elongation may obscure underlying stress in banks' financial health.
- Refinancing Challenges: While theoretically possible, refinancing floating rate loans across different banks with distinct internal benchmarks is complex due to varying benchmark adjustment methods.
- Limited Borrower Options: Borrowers might feel compelled to stay with their original bank, paying higher charges, as refinancing is often impractical due to benchmark disparities.
Possible impacts:
- Interest rate of borrowers: Banks can change the interest rate by changing the internal benchmark rate and the spread during the term of the loan which could harm the interest of the borrower and also impair monetary transmission.
Benefits of Fixed rate regime:
- For borrowers:
- Protection from Rate Hikes: Shifting to a fixed rate provides protection against potential future increases in interest rates. This can be particularly beneficial if interest rates are expected to rise in the near future.
- Budgeting and Financial Planning: Fixed payments make it easier for borrowers to budget and plan their finances since they know exactly how much they need to allocate for their loan payments.
- Potential Cost: Fixed interest rates tend to be initially higher than prevailing floating rates. Borrowers opting for a fixed rate might end up paying more initially compared to what they would have paid with a floating rate if rates remain relatively stable or decrease.
- For lenders:
- Interest Rate Risk Mitigation: Lenders are less exposed to interest rate risks when borrowers opt for fixed rates. They can better manage their own interest rate risk since they know the interest income they'll receive remains constant.
- Lending Profitability: Fixed-rate loans typically come with higher initial interest rates compared to floating-rate loans. This can lead to increased lending profitability for lenders, especially if rates remain stable or decline.
- Potential Lower Loan Demand: Higher initial fixed rates might deter some potential borrowers who are attracted to lower initial payments offered by floating rates.
- Limited Flexibility: Lenders might have less flexibility in adjusting loan terms for borrowers with fixed-rate loans, as the interest rate remains constant regardless of market conditions.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/rbi-fixed-rate-regime-personal-loan-8898445/
Bio-Trace Minerals Project (PIB)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Technology Development Board under Department of Science and Technology (TDB-DST) collaborated with M/s Chemlife Innovations pvt ltd. for innovation in the Bio-Trace Minerals Project.
Facts About:
How does the collaboration between TDB and Chemlife Innovations align with India’s strategic framework for livestock development?
- The collaboration between TDB and Chemlife Innovations aligns with India’s strategic framework, including the National Livestock Mission, which seeks to enhance livestock productivity, optimize feed resources, and infuse technology into livestock management. By developing bio-trace minerals for animal feed, the project addresses crucial aspects of animal nutrition, aligning seamlessly with the mission’s objectives.
What innovative technology does Chemlife Innovations employ in their project, and how does it contribute to sustainability?
- Chemlife Innovations employs the “Accelerated Natural Bio Transformation” (ANBioT) technology, which facilitates chelation reactions using a proprietary nutrient medium. This technology operates under milder conditions and is eco-friendly, aligning with principles of sustainability by reducing environmental impact and resource consumption.
How does the use of pupa proteins contribute to the project’s eco-friendly approach?
- Pupa proteins, rich in hydroxy amino acids, are utilized in the project as an alternative to imported ligands. This economical alternative not only enhances the project’s economic viability but also aligns with India’s goal of self-sufficiency, reducing reliance on imported resources and promoting sustainable practices.
What certifications does Chemlife Innovations hold, and how do they attest to the company’s commitment to quality?
- Chemlife Innovations holds Global Certification for Animal Feed Additive Quality and Feed Safety, as well as the esteemed FAMI-QS certification. These certifications validate the company’s commitment to producing high-quality and safe products, maintaining global standards in their operations.
How does the project contribute to the circular economy, and what role does repurposing silk worm pupae meal play?
- The project contributes to the circular economy by repurposing silk worm pupae meal, reducing waste generated by the silk industry. By using locally available by-products, the project aligns with principles of sustainability, economic viability, and import substitution goals.
How does the project’s innovative product “MinBioZen” address livestock health and sustainability?
- “MinBioZen” is an innovative bio-trace mineral product developed by Chemlife Innovations. It integrates bioavailability and stability, optimizing livestock health and growth. This product showcases the company’s dedication to innovation and environmental stewardship, aligning with the goals of sustainable resource utilization.
Source: https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjUsaL43aGBAxVEwjgGHU5XAs8QFnoECBQQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fpib.gov.in%2FPressReleaseIframePage.aspx%3FPRID%3D1950125&usg=AOvVaw16iXZ25GRw2ND9aklzZ5ri&opi=89978449
Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket (Economic Times)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Chennai-based start-up AgniKul Cosmos, has commenced the process of integrating its cutting-edge Agnibaan SOrTeD rocket at its private Launchpad in Sriharikota.
Facts About:
- The integration process was initiated on Independence Day on August 15, 2023.
- A successful launch would make AgniKul the second Indian space tech start-up to send its launch vehicle into space after Skyroot Aerospace.
- AgniKul: Established in 2017, by aerospace engineers Srinath Ravichandran and Moin SPM, along with IIT-Madras faculty member Prof. Sathyanarayan R Chakravarthy.
About Agnibaan SOrTeD (SubOrbital Technological Demonstrator):-
Type: single-stage launch vehicle.
Powered by: AgniKul’s patented Agnilet engine.
- Agnilet engine: It is the world’s sole single-piece 3D-printed engine.
- It is a single-piece, 6 kilonewton (kN) semi-cryogenic engine.
- Initial trial: early 2021.
- Verified at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) in Thiruvananthapuram.
- 3D printing: uses materials such as plastics and metals to convert products envisaged on computer-aided design to real three-dimensional items.
Payloads: up to 100 kg.
Altitude: 700 km
- It can carry payloads in five different configurations. (LVM3-M2 rocket)
Stages: It is a customizable launch vehicle that could be launched in one or two stages.
Unique feature: unlike traditional sounding rockets that launch from guide rails, it will lift off vertically and follow a predetermined trajectory to perform a precisely orchestrated set of maneuvers during flight.
The rocket’s first stage could have up to seven Agnilet engines, depending on the mission, which are powered by Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene.
The rocket is also designed for launch from more than 10 different launch ports.
To ensure its compatibility with multiple launch ports, AgniKul has built a launch pedestal named ‘Dhanush’.
- It will support the rocket’s mobility across all its configurations.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/science/chennai-based-agnikul-prepares-for-maiden-sub-orbital-flight-of-agnibaan-rocket/articleshow/102805834.cms?from=mdr
3D Printing (The Hindu)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India’s first 3D printed Post Office was inaugurated in Bengaluru’s Cambridge Layout.
Facts About:
- India’s pioneering 3D-printed post office located in Bengaluru’s Cambridge Layout was recently inaugurated.
3D Printed Post Office
- Swift Build: The 3D-printed post office was constructed in just 43 days, surpassing the original deadline by two days.
- Construction Team: Larsen & Toubro Limited undertook the project in collaboration with IIT Madras.
Technological Process
- Spatial Dimension: The post office covers an area of 1,021 square feet and was created using advanced 3D concrete printing.
- Automated Procedure: Robotic printers used an automated process to layer concrete according to the approved design.
- Strong Bonding: A specially formulated quick-hardening concrete ensured strong bonding between layers.
- Rapid Construction: With robotic precision and pre-embedded designs, the project was completed in just 43 days, far shorter than the conventional 6 to 8 months.
Advantages of 3D Printing
- Cost-Effective: The project cost ?23 lakhs, indicating a 30-40% cost reduction compared to traditional methods.
- Showcasing Technology: The project highlighted concrete 3D printing technology using indigenous machinery and robots, showcasing its scalability.
Distinctive Features
- Continuous Perimeter: The project boasted continuous perimeter construction without vertical joints.
- Flexibility: The 3D printing accommodated curved surfaces and different site dimensions, overcoming flat wall limitations.
- Structural Innovation: Continuous reinforced concrete footing and three-layer walls were created, enhancing structural integrity.
- Reduced Timeline: The innovative technique drastically reduced the construction timeline to 43 days, minimizing material wastage.
Source: https://www.google.co.in/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwi88OSW3aGBAxVDTWwGHafnBzMQFnoECB8QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.thehindu.com%2Fnews%2Fcities%2Fbangalore%2Findia-first-3d-printed-post-office-is-now-open-for-business-in-bengaluru%2Farticle67208897.ece&usg=AOvVaw1xcvOgM9Z66xFGFeSZ-7W_&opi=89978449
Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas (Indian Express)
- 19 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
New data from the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of World Resources Institute (WRI) has been released.
Facts About:
What does it mean for a country to be exposed to extreme water stress?
- Extreme water stress signifies that a country uses more than 80% of its renewable water supply for activities such as irrigation, livestock, industry, and domestic needs. This reliance makes them vulnerable to water scarcity during periods of drought.
How does the WRI define the term ‘water stress’?
- A region is deemed ‘water stressed’ when the demand for water surpasses the available volume or when water quality limitations restrict its use for various purposes.
Which regions and countries are the most water-stressed according to the report?
- The most water-stressed regions are West Asia, North Africa, and South Asia. Notable water-stressed countries include Bahrain, Cyprus, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, and others.
How is global water demand projected to change by 2050?
- Global water demand is estimated to increase by 20-25% by 2050. Additionally, watersheds facing unpredictable water supplies are expected to rise by 19%. This could result in 100% of West Asia and North Africa’s population facing extreme water stress by 2050.
What are the implications of high water stress beyond immediate concerns?
- The report emphasizes that extreme water stress affects not only consumers and industries but also has far-reaching political implications. Water stress can impact political stability, making it a critical issue to address for global leaders.
What are the economic implications of solving global water challenges?
- According to WRI’s findings, addressing global water challenges would cost around 1% of the global GDP or 29 cents per person per day from 2015 to 2030. Despite the costs, the potential economic benefits and stability improvements make it a worthwhile investment.
Source: https://chinawaterrisk.org/useful-links/aquaduct-water-risk-atlas/
INS Vindhyagiri' (PIB)
- 18 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
President Droupadi Murmu launched the 'INS Vindhyagiri' in Kolkata at Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE).
Facts About:
- Project 17A – Vindhyagiri, named after the mountain range in Karnataka, is the sixth ship of the Project 17A program, as per PTI reports.
- Vindhyagiri, a technologically advanced Frigate, and a tribute to the erstwhile INS Vindhyagiri, the Leander Class ASW Frigate.
- Old Vindhyagiri – It is nearly 31 years of service from July 1981 to June 2012, had witnessed various challenging operations and multinational exercises.
- Under the Project 17A program, a total of 4 ships by Mazagon Dock Ltd (MDL) and 3 ships by GRSE are under construction.
- The project's first 5 ships have been launched by the MDL and GRSE between 2019 and 2022.
- Project 17A ships have been designed in-house by the Indian Navy's Warship Design Bureau, the pioneer organization for all warship design activities.
- A substantial 75% of the orders for equipment and systems of Project 17A ships are from indigenous firms.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1949974
Artificial Intelligence Index 2023 (Indian Express)
- 18 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India ranked fifth in Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based investments according to Stanford University’s annual AI Index report 2023.
Facts About:
- AI Index is an independent project at Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI).
Purpose:
- The annual report compiles, analyzes, and visually presents AI-related data to empower responsible and ethical AI advancements in collaboration with human interests
Global AI Investment Rankings
- United States
- China
- United Kingdom
- Israel
- India
India's Remarkable Growth
- India secured the fifth position in AI investments received by startups worldwide in 2022.
- AI startups in India attracted $3.24 billion in funding, surpassing countries like South Korea, Germany, Canada, and Australia.
Investment Revival amidst Recession
- Despite a global AI investment dip since 2021 due to economic challenges, a resurgence in Venture Capital (VC) funding is anticipated this year.
- Enterprises and consumers' heightened interest in generative AI products like Open AI's ChatGPT is expected to drive this revival.
Global Contribution to LLM Development
- 54% of researchers involved in advancing large language models (LLMs) hail from American institutions.
- Significant progress observed as researchers from Canada, Germany, and India joined the LLM development landscape in the past year.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/artificial-intelligence/key-takeaways-from-stanford-ai-index-report-2023-8539812/
PM Vishwakarma (Economic Times)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved a new Scheme named “PM Vishwakarma”
Facts About:
Type: Central Sector Scheme
Aim: To strengthen and nurture the Guru-Shishyaparampara or family-based practice of traditional skills by artisans and craftspeople working with their hands and tools.
– To improve the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftspeople and to ensure that the Vishwakarmas are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
Coverage: The scheme will provide support to artisans and craftspeople of rural and urban areas across India.
– Eighteen traditional trades will be covered under the scheme. These include carpenter, boat maker, armourer, blacksmith, hammer and tool kit maker, locksmith, goldsmith, potter, sculptor, stone breaker, cobbler, mason, basket/mat/broom maker/coir weaver, traditional doll and toy maker, barber, garland maker, washerman, tailor and fishing net maker.
Duration of the scheme: Five years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).
Key Features of the scheme: Artisans and craftspeople will be provided a recognition through PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
– The scheme has a provision of credit support of up to ?1 lakh (first tranche) and ?2 lakh (second tranche) with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
– It also has a provision to provide skill upgradation, incentive for toolkit as well as digital transactions and marketing support.
– Skilling programmes will take place at both basic and advanced types. Participants will get a stipend of ?500 per day while undergoing training.
– Beneficiaries will also receive up to ?15,000 to buy modern tools.
Source: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/pms-vishwakarma-scheme-launch-on-sept-17-70-ministers-to-attend-event-at-70-locations/articleshow/103559849.cms?from=mdr
The first-ever Global Summit on Traditional Medicine (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The first WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit will take place in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Facts About:
First WHO Traditional Medicine Global Summit:
Organized by: World Health Organization (WHO) and co-hosted by the Ministry of Ayush.
Aim: To bring together various stakeholders, such as traditional medicine practitioners, policymakers, academics, and others on a common platform to share best practices, evidence and innovation related to how traditional medicine contributes to health and sustainable development.
Significance: Traditional and complementary medicine has been vital for health in communities for centuries and has influenced modern medical knowledge.
– About 40% of today’s medicines have natural origins, including well-known drugs like aspirin and artemisinin.
– Currently, 170 countries have informed WHO about their use of traditional medicine, seeking evidence and data to guide safe, cost-effective, and fair policies and regulations.
About WHO Global Centre for Traditional Medicine:
In 2022, WHO with the support of the Government of India established the Global Centre for Traditional Medicine in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
Mandate: The centre provides leadership on all global health matters related to traditional medicine as well as extending support to member countries in shaping various policies related to traditional medicine research, practices and public health.
Significance: It is the first and only global outpost for traditional medicine across the globe.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/who-director-general-to-inaugurate-first-ever-global-summit-on-traditional-medicine/article67193778.ece
Removing gender stereotypes from the law (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Supreme Court has recently launched a ‘Handbook on Combating Gender Stereotypes’.
Facts About:
What is the significance?
- Combats Gender Stereotypes: It aims to combat gender stereotypes in language used within the judiciary and legal community.
- For instance, terms like "career woman," "fallen woman," "faithful or obedient wife," "eve-teasing," and "hermaphrodite" have been identified as gender-unjust terms.
- The Supreme Court suggests using more neutral and respectful terms like "woman," "wife," "street sexual harassment," and "intersex" instead.
- Promoting Equity and Justice: Promoting a more just and equitable society. He mentioned that relying on predetermined stereotypes in judicial decision-making goes against the duty of judges to decide cases impartially, based on their merits.
- Addresses false assumptions: The handbook addresses false assumptions about women's characteristics, such as the stereotype that women are overly emotional, illogical, and unable to make rational decisions.
- It emphasizes that a person's gender should not determine their capacity for rational thought.
- Addresses Prejudices: The handbook discusses assumptions made about a woman's character based on her clothing choices and sexual history.
- These assumptions can influence how the court assesses her actions, particularly in cases involving sexual violence, and may undermine the importance of consent in such cases.
- Significance of language: The Chief Justice pointed out that language used by judges reflects not only their interpretation of the law but also their perception of society.
- The example of changing the term "pauper" to "indigent" in the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 was cited to demonstrate how language can impact the dignity and humanity attributed to individuals.
- The handbook aims to raise awareness about the role of language in perpetuating gender stereotypes within the legal system and provides guidance on using more respectful and neutral terms to promote fairness and equality.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/to-remove-gender-stereotypes-from-the-law-a-new-supreme-court-handbook/article67201169.ece
Legalising Cannabis : Good or Bad for India (The Hindu)
- 17 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Himachal Pradesh CM has announced that the state government is considering legalizing the cultivation of cannabis.
Facts About:
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant used primarily for medical or recreational purposes.
- The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD).
- It is used by smoking, vaporizing, within the food, or as an extract.
Prospects of legalizing Marijuana
(1) Health benefits
- The cannabinoids found in Cannabis is a great healer and has found mentioned in Ayurveda.
- It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions like multiple sclerosis, arthritis, epilepsy, insomnia, HIV/AIDS treatment, and cancer.
(2) Ecological benefits
- The cannabis plant and seeds apart from being labelled a ‘super-foods’ as per studies is also a super-industrial carbon-negative raw material.
- Each part of the plant can be used for some industry. Hemp currently is also being used to make bio-fuel, bio-plastics and even construction material in certain countries. The cosmetic industry has also embraced Hemp seeds.
(3) Marijuana is addiction-free
- An epidemiological study showed that only 9% of those who use marijuana end up being clinically dependent on it.
- The ‘comparable rates’ for tobacco, alcohol and cocaine stood at 32%, 15% and 16% respectively.
(4) Good source of Revenue
- By legalizing and taxing marijuana, the government will stand to earn huge amounts of revenue that will otherwise go to the Italian and Israeli drug cartels.
- In an open letter to US President George Bush, around 500 economists, led by Nobel Prize winner Milton Friedman, called for marijuana to be “legal but taxed and regulated like other goods”.
(5) A potential cash crop
- The cannabis plant is something natural to India, especially the northern hilly regions. It has the potential of becoming a cash crop for poor marginal farmers.
- If proper research is done and the cultivation of marijuana encouraged at an official level, it can gradually become a source of income for poor people with small landholdings.
(6) Prohibition was ineffective
- In India, the consumption of synthetic drugs like cocaine has increased since marijuana was banned, while it has decreased in the US since it was legalized in certain states.
- Moreover, these days, it is pretty easy to buy marijuana in India and its consumption is widespread among the youth. So it is fair to say that prohibition has failed to curb the ‘problem’.
(7) Marijuana is less harmful
- Marijuana consumption was never regarded as a socially deviant behaviour any more than drinking alcohol was. In fact, keeping it legal was considered as an ‘enlightened view’.
- It is now medically proven that marijuana is less harmful than alcohol.
Risks of Legalizing Cannabis
(1) Health risks continue to persist
- There are many misconceptions about cannabis. First, it is not accurate that cannabis is harmless.
- Its immediate effects include impairments in memory and in mental processes, including ones that are critical for driving.
- Long-term use of cannabis may lead to the development of addiction of the substance, persistent cognitive deficits, and of mental health problems like schizophrenia, depression and anxiety.
- Exposure to cannabis in adolescence can alter brain development.
(2) A new ‘tobacco’ under casualization
- A second myth is that if cannabis is legalized and regulated, its harms can be minimized.
- With legalization comes commercialization. Cannabis is often incorrectly advertised as being “natural” and “healthier than alcohol and tobacco”.
- Tobacco, too, was initially touted as a natural and harmless plant that had been “safely” used in religious ceremonies for centuries.
(3) Unconvincing Advocacy
- Advocates for legalization rarely make a convincing case. To hear some supporters tell it, the drug cures all diseases while promoting creativity, open-mindedness, moral progression.
- Too much trivialization of Cannabis use could lead to its mass cultivation and a silent economy wreaking havoc through a new culture of substance abuse in India.
Legalization status elsewhere in India
- Several states in India have already legalized cannabis cultivation, including neighboring Uttarakhand, which became the first state in the country to do so in 2017.
- Controlled cultivation is being done in some districts of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh.
Legal Framework for Cannabis Cultivation
- Definition of Cannabis: The Parliament has defined cannabis in the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS), 1985.
- Ban on extracting resin and flowers: While a complete ban has been imposed on extracting the resin and flowers of the cannabis plant, the law determines the method and extent of cultivation of cannabis for medicinal and scientific purposes.
- Authorities to States: Section 10 (a) (iii) of the Act empowers States to make rules regarding the cultivation of any cannabis plant, production, possession, transport, consumption, use, purchase, sale, and consumption of cannabis (except charas).
- Cultivation of hemp: States are also empowered to permit, by general or special order, the cultivation of hemp, only for obtaining fibber or seeds or for horticultural purposes.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-risks-of-legalising-cannabis/article29216035.ece
Talwar-class Stealth Frigates (PIB)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
- Two Krivak- or Talwar-class stealth frigates are now expected to be delivered by May and October in 2024
- The ship is in the final stages of development; in two months time, it will go for sea trials.
Facts About:
The Talwar class of frigates of the Indian Navy have been built in Russia under an Indo-Russian joint production.
The Talwar class guided missile frigates are modifiedKrivak III class frigates from Russia.
- In October 2016, India and Russia signed an Inter-Governmental Agreement for four stealth frigates, after which a $1-billion deal was signed for direct purchase.
The Talwar Class has a displacement of 4,000 tons and speed of 30 knots and is capable of accomplishing a wide variety of naval missions, primarily, finding and eliminating enemy submarines and large surface ships.
Due to the use of stealth technologies and a special hull design, the resulting frigate features reduced radar cross section (RCS) as well as electromagnetic, acoustic and infrared signatures.
Source: https://swarajyamag.com/defence/russia-delays-advanced-talwar-class-stealth-frigates-delivery-yet-again-now-projected-to-join-navy-by-may-and-october-2024
Graphene-Aurora program (PIB)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) Secretary launched the ‘Graphene-Aurora program’ at a function in Maker Village Kochi, Kerala.
Facts About:
- The program shall be implemented by Digital University Kerala with joint funding from Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), and Government of Kerala and Industry partners, Carborundum PvtLimitedjoined as one of the main industry partners.
- It shall nurture the deep/emerging Graphene technology & innovation ecosystem that can guide, develop, implement, and support SMEs and startups to commercialize developed graphene technologies for scale adoption.
- Creation of a commercialization eco-system for graphene as an emerging technology would help India take a pole position in the world’s new material market.
Key facts about Graphene
- Graphene is a material that is extracted from graphite and is made up of pure carbon.
- It is one of the most important elements in nature which we find in daily objects like the lead of a pencil.
- It is the world’s thinnest, strongest, and most conductive material of both electricity and heat.
- It conducts electricity better than copper.
- It is 200 times stronger than steel but six times lighter.
- It is almost perfectly transparent as it absorbs only 2% of light.
- It is impermeable to gases, even those as light as hydrogen and helium.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1948661
Deemed Forest (The Hindu)
- 16 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Odisha has no ‘deemed forest’ as per the amended Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980.
Facts About:
What are deemed forests?
Deemed forest refers to land that resembles forests but has not been recognized as such by either the Union or the States.
They account for about 1% of the total forest land in the country.
In 1996, the Supreme Court expanded the remit of the Van (SanrakshanEvamSamvardhan) Act to areas that weren’t notified as forests but conformed to the “dictionary” definition of forests i.e. deemed forests.
- The Godavarman verdict stated that the states must identify and categorize such land.
- The SC directed the states to establish Expert committees to determine deemed forests in order to clarify the area that may be protected under the Forest (Conservation) Act.
According to the Forest Act, land cannot be diverted without the consent of the Centre as well as gram panchayats in the regions.
- It serves as a deterrent to deforestation by directing the parties responsible for diverting forest land to grow trees on a plot of land equivalent to twice the razed area and imposing a significant monetary penalty.
What does the Odisha government directive mention?
All district collectors must ensure that the diversion of forest land for infrastructure projects, particularly state development projects, should follow provisions of the new law.
Any survey or exploration will also not be treated as a non-forestry activity.
Expert Committees
Although all the states were expected to form expert committees to identify deemed forests, not all States submitted their reports.
- This has left states with enough leeway in defining or omitting large parcels of land as forests.
According to the Union Ministry of Environment, the amendments to the 1980 Act were necessary to remove ambiguities and clarify the application of the laws.
According to the amended act, the Forest Conservation Act would not apply to notified forest land that was legally diverted for non-forest uses between 1980 and 1996.
- As a result, forest land that was not specifically notified as such would cease to be protected under the provisions of the Act.
The Union Environment Ministry had earlier stated that deemed forests would continue to be protected.
- The amendments made to the FCA recognized deemed forest lands, which had been identified by the Expert Committee of the State. Therefore the provisions of the Act will be applicable in such lands also.
Future unclear
According to the latest Forest Survey of India, Odisha has approximately 52,156 square km or 130 lakh acres of forest coverage.
- This amounts to 33.50% of the State’s geographical area, which is much higher than the national level of forest cover - 21.71%.
Since 1996, around 66 lakh acres have been identified as deemed forests in Odisha.
- However, a majority of this land has not been officially notified in the government records.
This amounts to about 40-50% of Odisha’s forest land.
In addition, there are several community forests that are managed by tribal and forest-dependent groups while several have land title rights under the provisions of the separate Forest Rights Act.
- The decision of the Odisha government that deemed forests have ceased to exist means that these will face an uncertain future.
One consequence of the new amendments is that there will be no check on forest diversion, making it easier to divert forest land.
- According to data from the Union Coal and Mining Ministry, of the 19,200 hectares of forest land that have been diverted nationally for mining between 2017-2022, around 8,000 hectares was from Odisha.
The reality on the ground is that most of the forest officer bureaucracy isn’t too keen on protecting forest rights
Impact
The Adivasi communities of Odisha depend on the deemed forests for their livelihood.
- These include some of the community-protected forests and bio-cultural habitats of vulnerable tribal groups such as the Dongria Kondhs in Niyamgiri.
- The removal of deemed forest areas from the Act could adversely affect the statutory rights of these communities which have claimed community forest rights and habitat rights on such forests
Around 46% of Odisha’s geographical area is notified as fifth schedule area under the Constitution, where thePanchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas (PESA) Act applies.
Boundary disputes: In Karnataka, people have alleged that large amounts of agriculture and non-forest land are “unscientifically” classified as deemed forest land.
- This was found to have caused undue hardship to farmers in the region and restricted industrial development.
Criticism
Deemed forests already identified as forests in records ‘held’ by any department or administration should be considered as ‘forest’ even by the new amendment.
- However, the directive of the Odisha government violates this.
It is uncertain if the amendment is yet to be considered to be law as the date of enforcement is yet to be notified.
- The government has temporarily withdrawn the notification until the Union Government establishes the rules and guidelines of the new act.
The amendment narrows down the definition of forests.
- As a result, vast tracts of forests are excluded which leaves them vulnerable to destruction.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/other-states/no-more-deemed-forests-says-odisha-government/article67198187.ece
Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA) (PIB)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
14 States and Union Territories are yet to sign a crucial Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Union Education Ministry.
Facts About:
Higher education Institutions (HEIs) in India
Statistics
As per the AISHE report 2020-21, there are 1,113 Universities, 43,796 Colleges, and 11,296 Stand Alone Institutions.
- There are 422 State Public Universities that have 41,836 affiliated colleges.
- 446 Universities are privately managed and 475 Universities are located in rural areas, 17 are women-centric universities.
Total enrolment in higher education has been estimated to be 4.13 crores with 2.12 crores boys and 2.01 crores females.
- Females constitute 48.7% of the total enrolment.
There are 2,255 students enrolled in Integrated Ph.D. in addition to 2.11 lakh students enrolled in Ph.D. Level.
Major problems currently faced by the higher education system in India – As identified by National Education Policy 2020:
- A severely fragmented higher educational ecosystem; less emphasis on the development of cognitive skills and learning outcomes;
- A rigid separation of disciplines, early specialization, and streaming of students into narrow areas of study;
- Limited access particularly in socio-economically disadvantaged areas, with few HEIs that teach in local languages;
- Limited teacher and institutional autonomy;
- Inadequate mechanisms for merit-based career management and progression of faculty and institutional leaders;
- Lesser emphasis on research at most universities and colleges, and lack of competitive peer-reviewed research funding across disciplines;
- Suboptimal governance and leadership of HEIs;
- An ineffective regulatory system; and large affiliating universities result in low standards of undergraduate education.
- PM-USHA aims to address the key gaps and issues identified by NEP 2020.
What is Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA)?
Background
- Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA) was a Centrally Sponsored Scheme to fund States/UTs institutions.
- It was launched with the vision to attain higher levels of access, equity, and excellence in the State higher education system with greater efficiency, transparency, accountability, and responsiveness.
- The first phase of the scheme was launched in 2013 and the second phase was launched in 2018.
- Now, in the light of the National Education Policy, RUSA scheme has been launched as Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (PM-USHA).
About
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme of the Government of India executed through the Ministry of Education.
- The scheme aims to work with over 300 HEIs including the state universities, its affiliated colleges to raise the quality of education.
Key Objectives of Pradhan Mantri Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan
The key objectives of PM-USHA are to improve access, equity and quality in higher education through planned development of higher education at the state level.
The objectives also include:
- creating new academic institutions,
- expanding and upgrading the existing ones,
- developing institutions that are self-reliant in terms of quality education, professionally managed, and characterized by greater inclination towards research.
Funding
- The PM-USHA aims at providing strategic funding to eligible state higher educational institutions.
- The central funding is based on norms and is outcome dependent.
- Funds flow from the central ministry through the state governments/union territories before reaching the identified institutions.
- Funding to states is made on the basis of the critical appraisal of State Higher Education Plans, which enlist each state’s strategy to address issues of equity, access and excellence in higher education.
Source: https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/upload_document/pm-usha_guidelines.pdf
National Medical Commission’s New Guidelines (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to the National Medical Commission’s Registered Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations or NMC RMP Regulations 2023, doctors can now refuse treatment to the unruly and violent patients.
Facts About:
The National Medical Commission Act, 2019:
- It was introduced to address various issues and challenges in the medical field, including improving the quality of medical education, enhancing access to healthcare services, and ensuring ethical and transparent practices.
- Key Provisions include:
- Ethical and Professional Conduct: The Act emphasizes maintaining ethical and professional conduct among medical practitioners and includes provisions to address any deviations from these standards.
- Community Health Providers: The Act introduces the concept of Community Health Providers who are allowed to practice limited medicine in underserved rural areas to address the shortage of doctors.
- Formation of the National Medical Commission (NMC): NMC is an regulatory body which regulates medical education and medical professionals.
- Establishment of Medical Advisory Council.
- Reforms in Medical Education.
Refusing treatment is a complex issue that involves various stakeholders viz. doctors and healthcare professionals, patients and their families, healthcare institutions, medical associations and regulatory bodies, legal authorities, ethics committees, public opinion and media, religious and cultural communities, etc.
Arguments in Favour of the Regulation:
- Unruly Behaviour
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- For example, a 21-year-old patient attacked a doctor with a knife during consultation at Delhi’s Sir Ganga Ram Hospital.
- Dignity and Integrity: Unruly behaviour can sometimes cross ethical boundaries, leading to disrespectful or abusive treatment of healthcare staff. Doctors have a right to work in an environment that respects their dignity and professional integrity.
- For example, a 40-year-old doctor on duty in a hospital in Faridabad was assaulted by attendants of a patient as the doctor was attending to another patient, he could not immediately attend to the patient.
- Brings Deterrence: Allowing unruly behaviour to go unchecked might enable a cycle of disruptive or non-compliant behaviour, which could negatively impact the patient’s overall health outcomes. By refusing treatment, the doctor may communicate that certain standards of behaviour are expected for a therapeutic relationship to proceed.
- Right to Freedom to practise any profession: The regulations give the doctors the right to choose whom they will serve, except in case of a life-threatening emergency.
- Justice: If an unruly patient’s behaviour poses a threat to their own safety, the safety of healthcare staff, or the safety of other patients, refusing treatment might be justified as a means to mitigate these risks.
- Financial Constraints
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- If a patient cannot afford the treatment, the doctor might argue that proceeding with treatment without full financial transparency could undermine the patient’s autonomy and informed consent.
- In extreme cases, relatives of patients have been known to hold doctors or hospital staff hostage, demanding treatment.
- Professional Boundaries: Some proponents of this perspective argue that doctors have a professional duty to provide medical care and expertise, but they are not obligated to address broader societal issues such as patients’ financial difficulties.
- Autonomy and Consent: Doctors are ethically obligated to provide patients with accurate information about their treatment options,including potential costs.
- Ethical Boundaries: Doctors have ethical responsibilities not only toward their patients but also toward themselves, their families and the healthcare community.
- For example, potential threats and violence have long-lasting impacts which manifests in the degradation of personal and professional relations.
- Objectivity: Taking decisions which are free from subjectivity caused by emotions, perceptions and individual bias is necessary for long term sustainability.
- For example, Free medical care for a desperate patient may be ethical, but providing it to many patients may not be feasible for one provider.
- Selfless Duty: Medical practitioners often prioritize the well-being of their patients above their own comfort, personal time and space. However, the job can be thankless at times.
- For example, During COVID-19 despite their selfless dedication, medical professionals were subjected to regular assaults and verbal abuse throughout the country.
Arguments against the Regulation
- Dedication and the Duty of Care: Dedication is the sense of deep rooted commitment to devote oneself to a cause.. This includes a duty to provide care to those in need, regardless of their financial status.
-
- In India, out-of-pocket health expenditure accounts for more than half of total health expenditure pushing many households into poverty. This shows the dire need for empathy and compassion towards those in need.For example, Dr Ramanand Singh has been treating his patients for just Rs 50 for the past 35 years in Bihar. He even waives off his fees in cases where the patients cannot afford medical treatment.
- Justice and Equity: The principle of justice requires that healthcare be distributed fairly and equitably.Denying treatment to a patient solely based on their inability to pay could be seen as unjust, perpetuating disparities in healthcare access.
- Hippocratic Oath: Physicians pledge to do what is in the best interest of their patients and to avoid causing harm.
- Physicians promise to treat all patients fairly, regardless of their background, and to provide care to the best of their abilities without bias.
- Unholy Nexuses: Many doctors form nexuses with drugmakers to prescribe specific drugs from their brand instead of generic drugs leads to considerable rise in treatment costs for patients.
- For example, freebies given to doctors including travel expenses, gifts etc. by drugmakers is a common practice.Beneficence: It means kindness or generosity and this principle refers to the moral obligation to act in a manner that will benefit others.The principle of beneficence obligates doctors to act in the best interests of their patients and to promote their well-being.
- Compassion: It is the desire to end someone’s suffering which forms the core principle of a medical practitioner. Refusing treatment to individuals on certain grounds could lead to the possibility of crisis of conscience among several practitioners.
- Loss of Trust and Credibility: The medical profession relies on public trust, and denying treatment to those in need could erode that trust and damage the reputation of the medical community.
- Responsibility: Some argue that healthcare professionals have a broader social responsibility to address systemic issues in healthcare, including affordability and access. Refusing treatment might be seen as abdicating this responsibility.
- Undermining Right to Life: Providing a legal caveat for the registered physicians to refuse treatment is against the fundamental right guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Further, there is no specific definition of “abusive” in law as it is purely a subjective interpretation that may depend on the personal opinion of any individual.
- Subjective interpretation may further lead to exclusion on the basis of race, religion, caste, sex etc.
What Should be Done?
- Persuasion: Influencing patients to follow prescribed norms for behaviour and ensuring smooth functioning.
- For example, during COVID-19 pandemic, voice messages were circulated using caller tune to make people aware of the importance of vaccination and prevent attacks on health workers.
- Emotional Intelligence: Equipping and training medical personnel with necessary skills so that they can manage their emotions and try to avoid escalation of situation and providing practical solutions to the given problems.
- Transparent Approaches: Consider alternative approaches before refusing treatment. This might involve social workers, mental health professionals, or conflict resolution experts to address the underlying issues contributing to the unruly behaviour.
- For example, Doctors in San Diego (USA)refer patients to low-cost family health centersthat provide caring, affordable, high-quality health care and supportive services to everyone.
- Ethical Principles Balancing: Weigh the principles of patient autonomy, duty of care, patient safety, and respect for healthcare personnel’s well-being. Consider how refusing treatment aligns with these principles and what potential consequences might arise from the decision.
- For example, Doctors Without Borders is a Nobel Peace Prize receiver charity that provides humanitarian medical care in conflict zones to all those in need of medical care, irrespective of the role played by them in the conflict.
- Tolerance: Accepting actions and practices which may be considered to be incorrect but still tolerable to some extent that they should not be prohibited or penalised heavily.
- For example, a significant number of the cases of unruly behaviour arises in situations which may not be considered as “common” and even the most well-behaved might behave in a way which is not acceptable in society due to the shock or intensity of the moment which one may not be able to handle.
- Consent: Communicating the decision clearly to the patient, and explaining the reasons behind it thus ensuring that the patient understands the potential consequences of their behaviour on their health and the doctor-patient relationship.
- Offering Continuity of Care: If possible, provide recommendations for alternative sources of care, whether within your healthcare institution or elsewhere. Ensure the patient’s ongoing health needs are addressed.
Conclusion
We must protect those who heal. Ethical decisions in healthcare are rarely black and white. It’s important to approach each situation with sensitivity, professionalism, and a commitment to upholding the well-being of patients, healthcare staff, and the broader community. Consulting with colleagues, supervisors, and ethics committees can provide valuable guidance in making these difficult decisions
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/doctors-new-national-medical-commission-guidelines-8890632/#:~:text=The%20guidelines%20say%20that%20doctors,but%20at%20least%20three%20credits.
Urea Gold (Indian Express)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi officially launched Urea Gold fertiliser.
Facts About:
- In a significant development, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled Urea Gold, a novel fertiliser product, created by Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF), a state-owned entity. This pioneering formulation involves enhancing urea with sulphur to address crucial agricultural challenges.
What is Urea Gold?
- Traditional urea primarily consists of 46% nitrogen (N). Urea Gold represents a leap forward by combining 37% nitrogen and 17% sulphur.
- This innovative composition serves two primary purposes: bolstering soil quality and boosting nitrogen utilization efficiency.
Soil Deficiencies Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE)
- Soil Deficiencies in India
- Indian soils suffer from deficiencies, particularly in key nutrients like sulphur (S).
- This deficiency is particularly crucial for certain crops such as oilseeds and pulses, which play a significant role in India’s agricultural output. These crops require adequate sulphur for healthy growth and optimal yield.
- The deficiency in sulphur can hinder their productivity and affect the overall agricultural landscape.
- Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency (NUE) Challenge
- NUE refers to the proportion of applied nitrogen fertilisers that is effectively taken up by crops for growth and yield production.
- Only about 35% of the nitrogen from urea, a commonly used fertiliser, is utilized by crops in India.
- The rest, roughly 65%, is lost through various processes, including ammonia volatilisation into the atmosphere and leaching into the ground as nitrate.
Challenges in Urea Consumption in India
- Import Dependency: India heavily relies on imported urea due to insufficient domestic production. Around 7.6 million tonnes of urea were imported out of the total 35.7 million tonnes sold last fiscal year.
- Feedstock Dependency: The feedstock for domestic urea production, natural gas, is predominantly imported. This adds to the overall import dependence for the fertiliser.
- High Consumption: Urea is India’s most widely used fertiliser, with consumption rising from 26.7 million tonnes to 35.7 million tonnes between 2009-10 and 2022-23.
- Environmental Impact: Excessive urea usage contributes to environmental problems such as air and water pollution. Ammonia emissions and nitrate leaching are associated with these environmental challenges.
- Higher Input Costs: Inefficient fertiliser use due to low NUE leads to higher input costs for farmers. They need to apply more fertiliser to achieve desired yields.
Significance of Urea Gold
- Nutrient Enrichment: Urea Gold is a novel fertiliser fortified with sulphur (S). It contains 37% nitrogen (N) and 17% sulphur, addressing soil deficiencies that are critical for crops like oilseeds and pulses.
- Targeted Improvement: The sulphur content in Urea Gold addresses the specific nutrient requirements of oilseeds and pulses, which are crucial components of Indian agriculture and are significantly import-dependent.
- Packaging and Pricing Shift: Urea Gold’s introduction might entail packaging in 40-kg bags, adapting to the preferences of farmers.While exact pricing remains undisclosed, market trends suggest Urea Gold could be priced between Rs 400 to Rs 500 per 40-kg bag.
- Enhanced NUE: The sulphur-coated urea granules in Urea Gold facilitate a controlled and gradual release of nitrogen. This extended nutrient availability improves NUE, leading to reduced fertiliser application frequency and better crop health.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Urea Gold’s dual focus on addressing soil deficiencies and improving NUE contributes to more sustainable agricultural practices. It reduces excessive fertiliser use and associated environmental impact.
- Economic Benefit: The improved NUE offered by Urea Gold has the potential to reduce input costs for farmers, as they can achieve similar or better yields with lower fertiliser quantities.
- Potential Yield Boost: The sustained nitrogen release mechanism of Urea Gold can potentially lead to increased crop yields due to longer periods of vibrant foliage and enhanced nutrient availability.
Potential Hurdles
- Pricing Uncertainty: Lack of clear pricing details for Urea Gold could impact its adoption among farmers.
- Subsidy Disparity: The current additional rates offered by the government may not sufficiently incentivize companies to promote fortified fertilisers like Urea Gold.
- Limited Farmer Incentives: Farmers might perceive fortified fertilisers as more expensive compared to traditional options, leading to reluctance in adoption.
- Distribution Challenges: Ensuring uniform distribution and application of fortified fertilisers presents logistical complexities.
- Regulatory Influence: Regulatory aspects, such as pricing controls and subsidy structures, can affect the feasibility of fortified fertiliser products.
- Awareness Gap: Limited farmer awareness regarding the benefits and correct usage of fortified fertilisers might hinder their willingness to switch.
- Production Scalability: Scaling up fortified fertiliser production to meet demand and ensure availability poses a significant hurdle.
Way Forward
- Price Rationalization: The government could consider revisiting subsidy rates to make fortified fertilisers economically attractive for both companies and farmers. This would encourage the adoption of innovative products like Urea Gold.
- Subsidy Structure: Tailoring subsidies to reflect the enhanced benefits of fortified fertilisers, such as improved NUE and reduced environmental impact, could encourage their adoption.
- Education Campaigns: Launching awareness campaigns about the advantages of fortified fertilisers, like Urea Gold, can educate farmers and dispel misconceptions about their higher costs.
- Field Demonstrations: Organizing on-field demonstrations of the benefits of fortified fertilisers could provide tangible evidence to farmers, boosting their confidence in making the switch.
- Long-Term Perspective: Encouraging farmers to consider the long-term economic and environmental benefits of fortified fertilisers could shift their focus from initial cost concerns.
- Market Diversification: Exploring partnerships with private sector players and agribusinesses to promote fortified fertilisers could enhance market penetration.
- Gradual Transition: Gradually phasing in fortified fertilisers while continuing to offer traditional options at subsidized rates can ease farmers into adopting the new products.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/how-to-make-urea-more-efficient-as-a-fertiliser-and-why-thats-needed-8891183/
Indian judicial data on bail appeals (The Hindu)
- 14 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The number of bail appeals filed in India’s High Courts surged post 2020, according to the ‘High Court dashboard’ by DAKSH, a think-tank focussed on law and justice system reforms.
Facts About:
- Bail appeals went up from around 3.2 lakh to 3.5 lakh each year before 2020, to 4 lakh to 4.3 lakh thereafter.
- Consequently, the number of pending bail appeals in High Courts also surged from around 50,000 to 65,000 to between 1.25 lakh to 1.3 lakh.
Reasons for rise in bail appeals post 2020
- One possible reason could be the sharp increase in cases related to the flouting of COVID-19-related lockdown norms during the pandemic.
- At the same time, pending bail cases piled up as the functioning of the courts was compromised during this time.
- The DAKSH ‘High Court dashboard’ explains that in 77% of regular bail cases, it was not possible to ascertain the Act under which the person seeking bail was imprisoned.
- It was not mentioned in the e-courts data of various High Courts. An analysis of 23% of cases in which the Act was mentioned shows that the Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897, was ranked fourth, hinting at the possibility of cases surging under this Act as the reason for more bail appeals.
- The database also reveals that the median number of days taken from the filing date to the decision date for regular bail applications was 23. However, for some High Courts, the median days taken for disposal were much higher.
Conclusion
- Delays in resolution have the same effect as denying bail as the accused remains in prison for the duration of their trial,” the DAKSH database argues.
- Finally, data regarding the outcome of bail appeals in High Courts were also missing in many cases. In close to 80% of the disposed bail cases in all High Courts, the outcome of the bail appeal — whether it was granted or rejected — was either unclear, or the outcome was missing.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/data/data-indian-judicial-data-hides-more-than-it-reveals-in-bail-cases/article67198313.ece
What is Luna-25? (The Hindu)
- 12 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Russia is set to launch its first lunar landing spacecraft in nearly half a century on August 11
Facts About:
- It is also designated as the Luna-Glob-Lander which is a Russian lunar lander mission.
- It is targeted to the south polar region of the Moon.
- There are two primary scientific objectives of the mission: to study composition of the polar regolith, and to study the plasma and dust components of the lunar polar exosphere.
- It will take off from the Vostochny cosmodrome.
- Lander structure:
- Luna 25's lander features a four-legged base housing landing rockets and propellant tanks.
- An upper compartment contains solar panels, communication equipment, onboard computers, and scientific instruments.
- Payloads:
- It carries eight science instruments, including gamma-ray and neutron spectrometers, infrared spectrometers, mass spectrometers, and imaging systems.
- Landing Site:
- The primary landing site for Luna 25 is near the lunar south pole, with a reserve site located southwest of the Manzini crater.
- Mission duration:
- It is expected to operate on the lunar surface, studying regolith and exospheric dust and particles, for approximately one year.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/luna-25-failure-roscosmos-implications-moon-base-china/article67218643.ece
MALABAR-2023 (PIB)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Indian Navy's indigenous frontline warships INS Sahyadri and INS Kolkata will participate in Exercise MALABAR 2023.
Facts About:
- The MALABAR series of maritime exercises commenced in 1992 as a bilateral exercise between the Indian Navy and US Navy.
- Japan joined the Naval Exercises in 2015. Malabar 2020 saw the participation of the Australian Navy.
- This year marks the 27th edition of MALABAR which is being hosted by Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and will see participation from the US Navy (USN), Japan Maritime Self Defence Force (JMSDF) and the Royal Australian Navy (RAN).
- INS Sahyadri is the third ship of the indigenously designed and built Project-17 class multi-role stealth frigates.
- INS Kolkata is the first ship of the indigenously designed and built Project-15A class destroyers.
- Both ships have been built at Mazagon Dock Ltd, Mumbai and are fitted with a state-of-the-art array of weapons and sensors to detect and neutralise threats in surface, air and underwater domains.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947436
China’s economy slides into deflation (Economic Times)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Facts About:
China’s recent bout of deflation, marked by a decline in consumer prices for the first time in over two years, has sparked debates about its implications and causes.
- This article delves into the intricacies of deflation, its potential impact on economic growth, and the unique circumstances driving deflation in China.
Understanding Deflation
- Deflation Defined: Deflation refers to a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services within an economy.
- Historical Context: Historically, the terms “inflation” and “deflation” were linked to changes in the money supply, with “inflation” representing a rise and “deflation” a fall in money supply.
Concerns Associated with Deflation
- Economic Slowdown: Many economists view deflation as an indicator of dwindling demand for goods and services, potentially leading to an economic slowdown.
- Demand-Supply Dynamics: Falling prices may prompt consumers to delay purchases, hampering demand and triggering a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Resource Utilization: A certain level of inflation is deemed necessary for optimal resource utilization, ensuring full economic potential is realized.
Varied Perspectives on Deflation
- Positive Instances: Some economies have experienced deflation during periods of robust growth. Japan witnessed increased real income levels despite persistent deflation.
- Economic Crises: Deflation can arise during economic crises when cautious spending and resource reallocation occur.
- Consumer Demand and Prices: Some economists argue that consumer demand dictates prices, rather than the other way around.
China’s Deflation Scenario
- Policy Measures: China’s central bank maintained low interest rates to stimulate demand amid the post-pandemic recovery.
- Property Sector Turmoil: China’s pre-pandemic property sector challenges, affecting GDP contribution, may be a root cause of the current deflationary trend.
- Complex Factors: While liquidity may not be the core issue, comprehensive analysis of money supply and monetary transmission is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Repercussions of Chinese Deflation
[A] Positive Impacts:
- Cheaper Imports: If Chinese goods become cheaper due to deflation, it could lead to lower import costs for India, benefiting consumers and businesses that rely on Chinese imports.
- Lower Input Costs: Reduced prices for raw materials and intermediate goods from China could lower production costs for Indian industries that depend on these inputs.
- Global Supply Chains: If Chinese deflation reduces the cost of production within global supply chains, Indian businesses integrated into these chains might experience cost savings.
- Improved Trade Balance: Cheaper Chinese imports can contribute to a more favorable trade balance for India, especially if it leads to reduced import bills.
[B] Negative Impacts:
- Export Competition: Cheaper Chinese exports due to deflation could increase competition for Indian exports in international markets, potentially affecting certain Indian industries.
- Import Dumping: A flood of cheap Chinese goods into the Indian market could harm domestic producers, leading to job losses and economic strain.
- Investment Flows: A slowdown in China’s economy caused by deflation might lead to reduced investor confidence and affect foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to India.
- Currency Effects: If China’s central bank devalues its currency to boost exports in response to deflation, it could lead to a stronger Indian rupee, impacting India’s export competitiveness.
- Commodity Prices: Reduced demand for commodities from China due to deflation could lead to lower global commodity prices, affecting Indian exporters of raw materials.
Conclusion
- China’s encounter with deflation amidst efforts to boost demand and stabilize its economy presents a multi-faceted challenge.
- Understanding the nuances of deflation, its interaction with demand dynamics, and China’s unique economic landscape are vital.
- As China navigates its path forward, policymakers must consider the interplay of factors, including the property sector’s impact and broader economic goals.
Source: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwidya2w1qGBAxVcd2wGHTEWAzQQFnoECC0QAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fm.economictimes.com%2Fopinion%2Fet-editorial%2Fwhy-chinas-economy-is-down-not-out%2Farticleshow%2F102731901.cms&usg=AOvVaw1udWdqudtF2oR3qve57xGB&opi=89978449
NavIC to link to Aadhaar enrolment devices (The Hindu)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Department of Space (DoS) has told the Parliamentary Committee of Science and Technology that the Navigation with Indian Constellation or (NavIC) is going to be integrated into Aadhaar enrolment devices.
Facts About:
About the merger:
- Need: Currently the Aadhaar enrolment kits that are used to collect and verify personal details are linked to Global Positioning system (GPS).
- The DoS has conducted successful field trials and is providing technical expertise for the finalisation of procurement specifications for the devices.
- Overall, the integration of NavIC into Aadhaar enrolment devices will enhance navigation accuracy and provide better disaster management capabilities.
- Significance:
- NavIC’s integration will enhance the accuracy and reliability of these devices.
Aadhaar authentication process:
- The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has been created, with the mandate of providing a Unique Identity (Aadhaar) to all Indian residents.
- The UIDAI provides online authentication using demographic and biometric data.
- Aadhaar authentication is the process involves Aadhaar Number, along with other attributes, including biometrics, is submitted online to the Aadhaar system for its verification on the basis of information or data or documents available with it.
- During the authentication transaction, the resident’s record is first selected using the Aadhaar Number and then the demographic/biometric inputs are matched against the stored data which was provided by the resident during enrolment/update process.
How NavIC will ensure data protection?
- NavIC offers two services:
- Standard Position Service (SPS) for civilian users and;
- Restricted Service (RS) for strategic users.
- These two services are provided in both L5 (1176.45 MHz) and S band (2498.028 MHz).
- NavIC coverage area includes India and a region up to 1,500 km beyond the Indian boundary.
- Newer satellites will have an additional band called L1 that will be compatible with civilian use.
Present NavIC uses:
- The National Disaster Management Agency (NDMA) was already utilising NavIC as an alert dissemination system for major natural disasters like landslips, earthquakes, floods, and avalanches.
- The Indian National Centre for Ocean Information System (INCOIS) relies on NavIC to broadcast cyclones, high waves, and tsunamis alert messages to fishermen venturing into the deep sea.
Organizations working with NavIC data:
- NavIC standards were set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Telecom Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI), Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC), Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), and Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM), International Electrotechnical Committee (IEC), and International Standards Organisation (ISO).
Concerns with GPS or other global systems:
- Threat to data security and sovereignty: System like GPS and GLONASS are operated by defence agencies of the respective nations.
- Breach of personal information: It is possible that the civilian service can be degraded or denied.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/technology/indian-gps-navic-to-link-to-aadhaar-enrolment-devices/article67181022.ece
India, Japan to restart trilateral cooperation with Sri Lanka (The Hindu)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Sri Lanka, India and Japan are studying ways of restarting trilateral cooperation on the East Container Terminal (ECT) project in Colombo.
Facts About:
Exploring New Avenues of Collaboration
- Shared Vision for Indo-Pacific Stability: India and Japan share a vision of a Free Open and Inclusive Indo-Pacific (FOIIP), which they believe benefits all nations in the region. This common vision has provided a basis for renewed cooperation and joint initiatives.
- Potential Areas for Collaboration: The Pathfinder Foundation's paper highlights potential areas of collaboration, including renewable energy projects, grid connectivity, development of Trincomalee as an oil pipeline hub, and people-centric initiatives like tourism and education.
- Joint Economic Vision Statement: Leaders from India and Sri Lanka have issued a Joint Economic Vision Statement, setting the stage for collaborative efforts to catalyze economic growth.
- While governments will play a role in kickstarting projects, they intend to involve the private sector in investment and execution.
- Debt restructuring process:India, Japan, and France's collaborative effort in co-chairing a committee for Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process demonstrates the commitment to stabilizing the country's financial situation. This initiative aims to address debt-related challenges and foster economic recovery.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- Balancing Interests and Lessons from the Past: Officials acknowledge the challenges faced in executing joint projects, given past setbacks. The need to align interests and strategies between India, Japan, and Sri Lanka remains a crucial factor in determining the success of future collaborations.
- Toward a Resilient Indo-Pacific Partnership: Japan underscores the significance of Japan's partnership with India and Sri Lanka in realizing a Free and Open Indo-Pacific.
- Japan emphasizes creditor parity, transparency, and debt sustainability in Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process.
- Role of China: China's involvement in Sri Lanka's infrastructure projects and its status as the country's largest bilateral lender add complexity to the trilateral dynamics. China's investments in Sri Lanka have prompted concerns about debt sustainability and transparency.
- While India and Japan aim to include China in the creditors' platform for Sri Lanka's debt restructuring process, China's decision to remain an observer highlights the complexities of fostering inclusive cooperation.
Conclusion
The revival of trilateral cooperation marks a crucial step toward promoting stability and development in the Indo-Pacific region. By overcoming challenges and leveraging their collective strengths, India, Japan, and Sri Lanka have the potential to contribute to a more interconnected and prosperous future for the region.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-japan-look-to-restart-trilateral-cooperation-with-sri-lanka-but-with-caution/article67180586.ece
Uniform Civil Code (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Kerala Legislative Assembly has unanimously adopted a resolution expressing its concern over the Union Government move to impose a Uniform civil code (UCC).
Facts About:
- The Kerala Assembly resolution essentially strikes a cautious note that a proposed “UCC could harm the secular nature of the country. “
- The resolution also talks about federalism – that the Centre could make a unilateral move on the contentious issue without consulting states.
- The resolution also argued that, it is critical to note that the Uniform Civil Code was limited to Directive Principles.
What does Constitution say about UCC?
- The Constitution refers to civil code only in its Directive Principles.
- Implementation of Directive Principles is not mandatory.
- The court may order to enforce Fundamental rights. But the Directive Principles of Article 44 of the Constitution cannot be enforced even by the courts.
Can the state legislate on UCC?
- Article 162 of the Constitution:
- The issue of personal laws falls in List III —the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution.
- While subjects in the Union lists fall within the purview of the Parliament, states can legislate on subjects in the State List.
- For entries in the ‘Concurrent List’, Article 162 of the Constitution gives state governments the power to legislate on subjects where a central law does not occupy the field.
- If there is a central law, it automatically gains precedence over the state law on the subject.
- Entry 5 of Concurrent List:
- Also the Entry 5 of the Concurrent lists “Marriage and divorce; infants and minors; adoption; wills, intestacy and succession; joint family and partition; all matters in respect of which parties in judicial proceedings were immediately before the commencement of this Constitution subject to their personal law.
- This allows states the power to legislate on the subject but only in the absence of a central law.
Do states can bring their own personal laws again?
The answer to it is NO, due to following cases;
- State laws on the issues mentioned in Entry 5 of the Concurrent List will not have precedence over central legislation.
- On specific areas not covered by central legislation, states can legislate.
- But central legislation already covers all aspects of marriage, divorce, inheritance and succession.
Supreme Court’s stand:
- The Court mentioned that Article 162 of the Constitution indicates that the executive power of a State extends to matters with respect to which the Legislature of the State has power to make laws.
- In view of the provisions of Entry 5 of the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule, the constitution of a Committee per se cannot be challenged as ultra vires.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/kerala-assembly-resolution-against-uniform-civil-code-8885558/#:~:text=The%20Kerala%20Legislative%20Assembly%20on,a%20common%20personal%20law%20code.
Bill on Election Commission members’ Appointments (Indian Express)
- 11 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A Bill is set to be introduced in the Rajya Sabha with the view of overturning the effect of the Supreme Court’s (SC) verdict on the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and Election Commissioners (ECs).
Facts About:
- The Bill seeks to establish a committee of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Cabinet Minister nominated by the PM for selecting members of the Election Commission of India (ECI).
- Current Procedure: Currently, the Law Minister suggests a pool of suitable candidates to the Prime Minister for consideration.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the PM.
- As per the Bill, a Search Committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary and comprising two other members, not below the rank of Secretary to the government, having knowledge and experience in matters relating to elections, shall prepare a panel of five persons who can be considered for appointment.
- Then, as per the Bill, a Selection Committee consisting of the Prime Minister, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister will appoint the CEC and other ECs.
Present structure to appoint CEC and ECs:
- Under Article 324 (2), the President appoints the CEC and other ECs.
- The President makes the appointment on the advice of the Union Council of Ministers headed by the Prime Minister.
- The Constitution does not prescribe any qualifications, academic or otherwise, for appointment to these offices.
- Tenure:
- The tenure of office and the conditions of service of all the commissioners is determined by the President.
- The tenure of commissioners is 6 years or up to the age of 65, whichever is earlier.
- The CEC and the two other ECs have the same powers and emoluments, including salaries, which are the same as a Supreme Court judge.
- All three commissioners have the same right of taking a decision. In case of a difference of opinion amongst the three members, the matter is decided by the Commission by a majority.
Process of removal:
- Article 324 of the Constitution of India mentions the provisions to safeguard and ensure the independent and impartial functioning of the Election Commission.
- The CEC is provided with security of tenure. He cannot be removed from his office except in the same manner and on the same grounds as a judge of the Supreme Court.
- Any other election commissioner or a regional commissioner cannot be removed from office except on the recommendation of the CEC.
Supreme Courts’ Judgment:
- On March 2, a five-judge bench of the Supreme Court unanimously ruled that a high-power committee consisting of the Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India must pick the CEC and ECs.
- The judgement by a bench came in 2015, challenging the constitutional validity of the practice of the Centre-appointed members of the Election Commission.
- According to the judgement, the SC has now given the Opposition and the judiciary a say in the matter, ruling that the CEC and ECs must be appointed by the President on the advice of a committee comprising the PM, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India.
- Also, in 2018, a two-judge bench of the SC referred the case to a larger bench since it required a close examination of Article 324 of the Constitution, which deals with the role of a Chief Election Commissioner.
Debate around appointment of CEC and ECs:
- Article 324(2) reads that “The Election Commission shall consist of the Chief Election Commissioner and such number of other Election Commissioners, if any, as the President may from time-to-time fix and the appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners shall, subject to the provisions of any law made in that behalf by Parliament, be made by the President.”
- The Parliament has the power to nullify the effect of a Court ruling by addressing the concerns flagged in the judgment.
- In this case, the arrangement prescribed by the Supreme Court was specifically because the Court noted that there was a “legislative vacuum.” Filling that vacuum is well within the purview of the Parliament.
- However, the idea of an independent body that conducts elections permeates through the judgement.
- The Court repeatedly stated that to be the objective of the framers of the Constitution.
- The composition of the Selection Committee in the Bill raises questions on whether the process is now independent or still rigged in favour of the Executive.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-law/bill-election-commission-members-appointment-process-explained-8885676/#:~:text=The%20Centre%27s%20Bill%20seeks%20to,Commission%20of%20India%20(ECI).
Consultative Committees (PIB)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, the government was asked about the constitution of consultative committees for the year 2023-24.
Facts About:
Consultative Committees.
- These committees are constituted by the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs. Consultative Committees of different ministries are not constituted year wise.
- As per Guidelines on Constitution, Functions and Procedures of Consultative Committees, Consultative Committees shall be constituted upon constitution of each Lok Sabha.
- For 17th Lok Sabha, 40 Consultative Committees have so far been constituted.
- The maximum membership of a Consultative Committee should be limited to forty. In addition, a maximum of four Members from both Houses can also be nominated as Permanent Special Invitees. The minimum membership of the Consultative Committee shall be ten.
- There is no requirement of presence of a minimum number of Members to constitute the quorum for holding meetings of Consultative Committees.
- The Minister concerned with each Ministry/Department shall preside over the meeting of the Consultative Committee attached to his/her Ministry.
- Functions: Consultative committees provide a forum for informal discussions between the ministers and the members of Parliament on policies and programmes of the government and the manner of their implementation
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947060
Small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs) (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The recent increase in coal consumption, despite the increase in solar and wind power, suggests that reliable and low-carbon electricity resources are critical to ensure the deep decarbonisation of power generation, along with grid stability and energy security.
Small modular reactors – a type of nuclear reactor – can be helpful to India in this regard.
Facts About:
Sources of Energy Production:
- India’s Energy sector is one of the most diversified in the world. Sources of power generation range from conventional sources such as coal, lignite, natural gas, oil, hydro and nuclear power, to viable non-conventional sources such as wind, solar, agricultural and domestic waste.
- India was ranked fourth in wind power, fifth in solar power and fourth in renewable power installed capacity, as of 2020.
- Near-universal household access to electricity was achieved in 2019, meaning that over 900 million citizens have gained an electrical connection in less than two decades.
- But, the per capita electricity consumption in India is only one-third of the global average, even though the demand for energy has doubled.
- So, to catch up with the increasing demand for energy, there is a need to make arrangements for a secure and sustainable form of self-reliance in the energy sector.
What are Small Modular Nuclear reactors (SMRs)?
- Small modular reactors (SMRs) are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW (e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- SMRs, which can produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity using:
- Small– physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular – making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors – harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
Conventional Nuclear power plants vs. Small modular reactors:
- Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs) are efficient users of land and their grid integration costs are lower than those associated with variable renewable energy (VRE) sources because NPPs generate power 24x7 in all kinds of weather.
- As an alternative, several countries are developing small modular reactors (SMRs) – nuclear reactors with a maximum capacity of 300 MW – to complement conventional NPPs.
- SMRs can be installed in decommissioned thermal power plant sites by repurposing existing infrastructure, thus sparing countries from having to acquire more land and/or displace people beyond the existing site boundary.
- SMRs can be safely installed and operated at several brownfield sites that may not meet the more stringent zoning requirements for conventional NPPs.
Need for SMRs:
- According to the International Energy Agency, the demand for critical minerals like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements, required for clean-energy production technologies, is likely to increase by up to 3.5x by 2030.
- This jump poses several global challenges, including the large capital investments to develop new mines and processing facilities.
- The environmental and social impacts of developing several new mines and plants in China, Indonesia, Africa, and South America within a short time span, coupled with the fact that the top three mineral-producing and -processing nations control 50-100% of the current global extraction and processing capacities, pose geopolitical and other risks.
Advantages of SMRs:
- SMRs are designed with a smaller core damage frequency (the likelihood that an accident will damage the nuclear fuel) and source term (a measure of radioactive contamination) compared to conventional NPPs.
- They also include enhanced seismic isolation for more safety.
- SMR designs are also simpler than those of conventional NPPs and include several passive safety features, resulting in a lower potential for the uncontrolled release of radioactive materials into the environment.
How nuclear reactors can lead to sustainable energy generation?
- Accelerating the deployment of SMRs under appropriate international safeguards, by implementing a coal-to-nuclear transition at existing thermal power-plant sites, will take India closer to net-zero and improve energy security because uranium resources are not as concentrated as reserves of critical minerals.
- Most land-based SMR designs require low-enriched uranium, which can be supplied by all countries that possess uranium mines and facilities for such enrichment if the recipient facility is operating according to international standards.
- Further, serial manufacture of SMRs can reduce costs by simplifying plant design to facilitate more efficient regulatory approvals and experiential learning with serial manufacturing.
What are the initiatives to Achieve Self-reliance in the Energy Sector?
- Gas Based Economy
- Blending of Ethanol in Petrol
- Prime Minister UjjwalaYojana
- Renewable Energy Initiatives
- National Hydrogen Mission
Way forward:
- The aspects like investment, infrastructure development, private-public partnership, green financing, policy framework need to be strengthened both at the national level and regional level to cater to inclusiveness in the development process.
- Green energy has tremendous potential in contributing to income, employment, and entrepreneurship and undoubtedly fosters sustainable development.
- In addition to job and income generation, it opens up opportunities/avenues for investment and markets for new products and services. So, India should focus on achieving green energy and self-reliance in the Energy Sector together.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/small-modular-reactors-india-nuclear-power-net-zero/article67175626.ece
Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The number of elephants in Karnataka has increased according to an interim report on Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates, 2023.
Facts About:
- It was reported by “Asian Elephant Population and Demography Estimates, 2023”.
- The population range for elephants in Karnataka is estimated to bebetween (5,914 - 6,877).
- The report was officially released by Karnataka’s Forest Minister, ahead of World Elephant Day, which is observed on August 12 to raise awareness about the importance of protecting these endangered animals.
- The report was the result of a synchronised elephant census conducted from May 17 to 19, involving the Forest Department of Karnataka and neighbouring states including Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Goa.
- Among the different regions, the Bandipur Tiger Reserve stands out with the highest elephant density of 1,116 elephants and a density of 0.96 elephants per square kilometre.
The Nagarahole Tiger Reserve follows closely with 831 elephants and a density of 0.93 elephants per square kilometre.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/karnataka/number-of-elephants-in-state-goes-up-by-364-from-last-census-touching-6395/article67176333.ece
Belem Declaration (Down to Earth)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The eight countries that make up the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) signed the Belém Declaration during the Amazon Summit.
Facts About:
- The leaders focused on initiating a dialogue about the sustainability of mining and fossil fuel-related activities but failed to commit to stopping oil drilling in the region.
- This lack of consensus has implications for global biodiversity goals, including those set under the Convention on Biological Diversity’s Global Biodiversity Framework in 2022, where countries agreed to protect 30% of land and sea by 2030.
About Belem Declaration:
The Belem Declaration is a statement released during the Amazon Summit, involving leaders from Amazon countries.
- It emphasizes the importance of Indigenous knowledge for biodiversity conservation and calls for Indigenous Peoples’ participation in decision-making.
- The declaration promotes sustainable forest use and diverse economic solutions, addressing concerns about deforestation and degradation in the Amazon region.
- It also underlines the need to protect land rights to prevent deforestation and preserve biodiversity within Indigenous territories.
Source: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/forests/belem-declaration-amazon-countries-fail-to-agree-on-protection-goals-91095
Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (The Hindu)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India is all set to get its own car crash safety star rating from Oct 1, 2023
Facts About:
What is Bharat NCAP?
- Bharat NCAP is a new car safety assessment programme which proposes a mechanism of awarding ‘Star Ratings’ to automobiles based upon their performance in crash tests.
- BNCAP standard is aligned with global benchmarks and it is beyond minimum regulatory requirements.
- The proposed Bharat NCAP assessment will allocate Star Ratings from 1 to 5 stars.
- The testing of vehicles for this programme will be carried out at testing agencies, with the necessary infrastructure.
Its implementation
- BNCAP will be rolled out from April 1, 2023.
- It will be applicable on type-approved motor vehicles of category M1 with gross vehicle weight less than 3.5 tonnes, manufactured or imported in the country.
- M1 category motor vehicles are used for the carriage of passengers, comprising eight seats, in addition to driver’s seat.
Significance of Bharat NCAP
- BNCAP rating will provide consumers an indication of the level of protection offered to occupants by evaluating the vehicle in the areas of:
- Adult occupant protection
- Child occupant protection
- Safety assist technologies
- It will serve as a consumer-centric platform, allowing customers to opt for safer cars based upon their Star-Ratings.
- It will also promote a healthy competition among original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in India to manufacture safer vehicles.
- It will ensure structural and passenger safety in cars, along with increasing the export-worthiness of Indian automobiles.
- It will prove to be a critical instrument in making our automobile industry Aatmanirbhar.
Why does India need to crash-test vehicles?
- Indian vehicles have historically not been crash-tested in the country.
- Despite being home to only 1% of the world’s vehicles, India shoulders 11% of the global road crash fatality burden.
What about existing testing standards?
- India’s Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR) mandate a safety and performance assessment, including a basic conformity crash test by agencies like the ARAI and ICAT when vehicles go in for type approvals.
- However, this does not involve a crash test rating.
- Many international automakers have been found to sell products in India which score much lower on safety and structural performance parameters.
- This is done to reduce costs in the price-sensitive Indian market.
- However, safety is moving up nowadays the list of key purchase criteria in India as well.
How will a homegrown NCAP help?
- Global NCAP (GNCAP) crash tests for many best-selling Indian vehicles have dismal ratings, many of them rated zero in a bias.
- The government hopes that by facilitating these tests by in-house agencies, more automakers will voluntarily undergo safety assessments and build vehicles that hold up to global standards.
How will it compare with GNCAP?
- The government wants the two tests to be in congruence with each other.
- It intends to design the?BNCAP?to?resemble?the GNCAP, the global gold standard, as closely as possible, including the speed for crash testing at 64kmph.
- Central Motor Vehicle rules encompass standards with?respect?to pedestrian protection and seat belt reminders among others and will be retained in the testing under the BNCAP.
- The government hopes the move will increase the export-worthiness of Indian automobiles.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/explained-what-is-the-bharat-new-car-assessment-programme/article67228536.ece
India takes first step to remove animals from Drug-testing (Indian Express)
- 10 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, an amendment to the New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules (2023) passed by the Government of India, aims to replace the use of animals in research, especially in drug testing.
Facts About:
What is the reason behind shifting to Alternative testing modes?
- The drug development journey involves rigorous testing to assess the efficacy and unintended effects.
- The first step of this process has been to test the candidate molecule in at least two animal species: a rodent (mouse or rat) and a non-rodent, such as canines and primates
- Lack of accuracy: Human response is influenced by factors like genetics and diet, leading to a significant mismatch between animal models and human responses.
- This mismatch contributes to the high failure rate during human clinical trials, highlighting the need for more accurate testing methods.
- Animals cannot consent to their own participation in research.
- Welfare of animals: Critics argue that animal testing can cause suffering and harm to animals. Animals are held in sterile, isolated cages, forced to suffer disease and injury, and typically euthanized at the end of each study.
What are Alternative testing modes?
- Organoids: These technologies encompass three-dimensional cellular structures, known as "organoids" or "mini-organs," which closely replicate the functions of specific body organs at a miniature scale.
- Organ-on-a-chip: The "organ-on-a-chip" technology employs small chips with human cells and microchannels to simulate physiological processes.
- organ-on-a-chip are AA-battery-sized chips lined with human cells connected to microchannels, to mimic blood flow inside the body.
- Additive manufacturing: 3D bioprinters use human cells as 'bio-ink' to build tissues. This could help make personalized drug tests and change how we create drugs.
What are Global regulatory frameworks that have adopted non-animal methods to test the effect and potential side-effects of new drug candidates?
- European Union: In 2021, the European Union adopted a resolution for an action plan promoting non-animal technologies in research, regulatory testing, and education.
- USA: The U.S. passed the FDA Modernization Act 2.0 in December 2022, permitting the use of these methods for drug safety and efficacy testing.
- South Korea: South Korea introduced a Bill for advancing alternatives to animal testing in December 2022.
- Canada: In June 2023, Canada amended its Environmental Protection Act to minimize vertebrate animal use in toxicity testing.
India
- In March 2023, the Indian government incorporated non-animal alternatives for drug testing and development into the drug development process by modifying the New Drugs and Clinical Trials Rules 2019.
- This step followed public input and consultation with the Drug Technical Advisory Board, which advises governments on drug-related technical issues at both the Central and State levels.
What are the challenges with these alternate methods?
- Multidisciplinary: Developing an organ-on-a-chip system requires multidisciplinary knowledge in the fields of cell biology, materials science, fluid dynamics, electronics, engineering, and pharmacology/toxicology to accurately replicate organ behavior and assess drug effects.
- At present there is a lack of focused training and expertise in India.
- Dependence of Imports: Most of the reagents, cell-culture related materials, and instruments for these technologies are currently imported from the U.S., Europe, and Japan.
- Managing Complexity: Researchers simplify recreating human tissues in the lab by minimizing components for disease simulation.
- No universal approach due to disease-specific variations; for example, a liver-on-a-chip won't fit all liver diseases.
- Variability arises from differences in lab protocols, expertise, and specific research goals. Regulators express concerns about data consistency due to these variations.
Suggestions
- Establishment of specialized institutes: Recently, a meeting organized by the Centre for Predictive Human Model Systems and Humane Society International India called for the need of specialized institutes similar to the Wyss Institute.
- WyssInsitute in Boston is a dedicated center that focuses on innovations that emulate human biology.
- The dedicated institute will facilitate effective communication and collaboration across various fields.
- Promoting innovation: Developing a comprehensive and self-sustaining ecosystem in India to address this gap in the fields of cell culture, material science, and electronics.
- Guidelines: Urgent need for guidelines establishing minimal quality criteria and standards for these systems.
- Existing guidelines on animal testing requirements need re-evaluation and updating to accommodate advancements in cell-based and gene-editing therapies.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/animal-trials-drug-development-india-amendment-2019-rules/article67019288.ece
ECOWAS and Niger Coup: Challenges and Potential Responses (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Context: Recently there was apprehension of intervention by the ECOWAS( Economic Community of West African States) in Niger following a military coup in the country.
Facts About:
- The recent coup in Niger has brought the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) into the spotlight as it grapples with responding to the political crisis in the region.
- As Niger faces economic hardships and military intervention by regional players looms, the role of ECOWAS is under scrutiny.
Understanding ECOWAS
- Formation and Membership: Established in 1975, ECOWAS aims to foster economic integration among its 15 member countries, including Benin, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Nigeria, and more.
- Objective: The organization envisions a borderless region based on democratic principles and good governance.
- Economic Goals: ECOWAS seeks to create a unified trading bloc, single currency, and enhanced cooperation in sectors such as industry, energy, and telecommunications.
ECOWAS in Conflict Resolution
- Regional Peacekeeping: ECOWAS has played a role in resolving conflicts by deploying peacekeeping missions. Notable examples include ECOMOG’s involvement in Liberia and Sierra Leone during the 1990s and early 2000s.
- Gambia Crisis: In 2017, ECOWAS intervened in Gambia, ensuring the peaceful transfer of power after then-President Yahya Jammeh refused to step down following an election defeat.
- Challenges and Successes: While ECOWAS has effectively resolved conflicts in some cases, it faces challenges due to differing interests among member countries and evolving security threats.
ECOWAS’s Response to Niger Coup
- Potential Military Intervention: ECOWAS has hinted at possible military intervention in Niger. However, regional challenges, including shared borders with other military-led nations, could complicate intervention plans.
- Support for Coups: Some military coups in West Africa have been justified by leaders citing terrorism and security challenges, accusing civilian governments of inadequacy.
- Security Situation: The ECOWAS Commission President reported a significant rise in terrorist attacks in the region, with a substantial death toll and refugees fleeing the violence.
Economic Measures and Sanctions
- Economic Sanctions: ECOWAS has previously imposed economic sanctions on countries undergoing political turmoil. However, the efficacy of these measures is questionable, especially when nations are grappling with economic difficulties.
- France’s Role: France’s historical ties to Niger and the presence of foreign troops have fueled local sentiments against foreign involvement, creating complexities for potential interventions.
Challenges and Dilemmas
- Leadership Dynamics: The current chairman of ECOWAS, Nigerian President Bola Ahmed Tinubu, advocates for military intervention in Niger. However, internal opposition and conflicting interests within ECOWAS member states complicate decision-making.
- Complexity of the Situation: The unique circumstances of each nation undergoing turmoil require tailored responses. The Niger coup’s leader, Gen. Abdourahmane Tchiani, has a history with ECOWAS peacekeeping missions.
Conclusion
- ECOWAS’s response to the Niger coup underscores the complexity of regional dynamics, the challenges of military intervention, and the delicate balance between security and democratic governance.
- As the organization grapples with finding an effective solution, its role as a mediator and peacekeeping force in West Africa continues to evolve in response to the changing geopolitical landscape.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/ecowas-west-africa-niger-coup-explained-8882492/
State of Elementary Education in Rural India Report (Indian Express)
- 09 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan launched the first State of Elementary Education in Rural India report.
Facts About:
Key Highlight of the Report:
Pan-India survey was conducted by the Development Intelligence Unit (DIU), across 6,229 rural households in 20 states, focussing on 6 to 16-year-old children in rural communities.
Equality Among Gender: Parents from rural communities believe that a child’s gender, whether a boy or a girl, should not hinder their educational aspirations.
- Total of 78 percent of parents of girls and 82 per cent of parents of boys wanted to educate their children to graduation and above.
Parental participation: About 84 percent of parentsregularly attend parent-teacher meetings, demonstrating their active involvement in their children’s education.
Role of Parents: Majority of children (62.5 per cent) are under the supervision of their mothers when it comes to their studies, while 49 per cent are supervised by their fathers.
- Over 38 per cent of parents opt for private tutors to further enhance their children’s education.
- About 26 per cent of the children study under the supervision of a private tutor.
Drop Outs: Out of the total dropped-out children, around one-fourth of male children discontinued their education during primary schooling, due tolack of interest in studies.
- Dropout rate for female children is high at 35 per cent, due to the need to contribute to the family’s earnings.
- A higher proportion of both boys and girls dropped out of school after completing the primary school education (75 per cent for boys and 65 per cent for girls).
Increased access to smartphones: Nearly half, 49.3 percent of students in rural India have access to smartphones.
- 76.7 percent of these students primarily use their phones for entertainment purposes, such as playing video games and watching movies.
- Only 34 percent of smartphone-accessible students use their devices for study-related downloads, while 18 percent access online learning through tutorials.
Learning Environment at Home: 40 percent of parents have age-appropriate reading materials available at home, beyond school books.
- Only 40 percent of parents engage in daily conversations with their children about their school learning, while 32 percent have such discussions a few days a week.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/education/78-parents-in-rural-india-want-their-daughters-to-study-till-graduation-and-beyond-report-8885528/#:~:text=in%20family's%20earnings.- ,According%20to%20the%20survey%2C%20one%2Dfourth%20of%20male%20children%20dropped,after%20completing%20primary%20school%20education.
Gita Mittal Committee (The Hindu)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Supreme Court panel flags reconstruction of lost essential documents of victims as the first healing step in Manipur.
Facts About:
The Committee
- The committee was constituted to supervise, intervene and monitor relief and rehabilitation, restoration of homesteads, religious places of worships, better relief work, etc. in Manipur.
- The committee is led by former Jammu & Kashmir High Court Chief Justice Gita Mittal, the committee includes Justices (retd) Shalini P Joshi and Asha Menon.
- This move aims to oversee various aspects beyond the investigation, such as relief, rehabilitation, and compensation for those affected by the violence.
- The committee's role extends beyond investigation, encompassing vital aspects of recovery and rebuilding.
- The primary goal behind the committee is to restore public confidence, reinforce faith in the rule of law, and rebuild trust within the affected community.
- The committee has filed three separate reports in the Supreme Court after meeting stakeholders on August 19.
The Reports
- First report – The first of the three reports submitted by the committee highlights the loss of essential documentation of the residents of Manipur who have been dis-housed.
- The committee suggests the appointment of a nodal officer to take charge of the reconstruction of these documents.
- Second report – The committee’s second report raised concerns on the Manipur Victim Compensation Scheme (MVCS).
- The committee says the MVCS needs to be substantially improved.
- The MVCS should be in the same league as the schemes framed by the National Legal Services Authority (NLSA).
- Third Report – The committee submitted a proposal for appointment of domain experts to facilitate its work.
Manipur Victim Compensation Scheme (MVCS)
- Victim Compensation Scheme (VCS) – Compensation to persons groundlessly arrested is under Section-358.
- The Government introduced the Central Victim Compensation Fund (CVCF) Scheme to enable support to victims of rape, acid attacks, human trafficking, women killed or injured in cross border firing.
- The Manipur scheme – It provides that if a victim of violence has received benefits under any other scheme, then they would not receive any compensation under the state victim compensation scheme.
- NALSA scheme – The benefit received under other schemes would be taken into consideration while determining the extent of benefits that would be additionally provided to the victims of violence.
Source:
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/manipur-violence-supreme-court-to-pass-orders-on-august-25-to-facilitate-proper-functioning-of-justice-mittal-panel/article67218800.ece#:~:text=A%20Supreme%20Court%2Dappointed%20committee,taken%20to%20nurse%20the%20Stat
Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023 (PIB)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Rajya Sabha approved the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation Amendment) Bill, 2023 which seeks larger participation of the private sector in mineral exploration and production, including that for sought-after lithium.
Facts About:
Key-highlights of the Bill
The Bill amends the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957. The Act regulates the mining sector.
Out of restrictions: The reform initiative in the Bill brings lithium out from the list of restrictive atomic minerals where permission to mine could only be granted by the Centre to government companies.
Welcomed private players: The change would allow auction of this critical mineral, used extensively for making batteries for electric vehicles, by the private sector.
Forestry clearance process: The amendment Bill will also dispense with the cumbersome forestry clearance process for mine reconnaissance and prospecting operations, making it easier for the private sector to participate in exploration of the country’s mineral resources.
Auction power: The Bill empowers the central government to exclusively auction mining lease and composite exploration licence for certain critical high value minerals such as gold, silver, platinum and copper.
Exploration licence: One of the major reforms proposed in the Bill is to introduce exploration licence for deep-seated and critical minerals. The exploration licence granted through auction will allow the licencee from private sectors to undertake “reconnaissance” and prospecting operations for critical and deep-seated minerals.
Composite mineral licence: The reform proposals in the amendment legislation also include allowing states to grant composite mineral licence without having to get central nod.
Fixing mineral-wise maximum area: It will also raise and fix mineral-wise maximum area limits for mineral concessions to provide larger and economically viable mines to investors.
- For prime minerals such as iron ore, the maximum area for prospecting licence and mining lease has been doubled to 50 sq. km and 20 sq. km respectively.
- This would allow private entries to get same land area for mining as was earlier being given to government companies and that also by the state governments itself without any need for central approval.
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical minerals are elements that are the building blocks of essential modern-day technologies, and are at risk of supply chain disruptions.
- These minerals are now used everywhere from making mobile phones, computers to batteries, electric vehicles and green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines.
- Based on their individual needs and strategic considerations, different countries create their own lists.
Recent government interventions
Mineral Security Partnership (MSP): India joined Mineral Security Partnership (MSP),a US-led collaboration that aims to catalyse public and private investment in critical mineral supply chains globally.
- The MSP includes Australia, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, UK, the European Commission, Italy, and now India.
Identification of critical minerals: Recently, the Centre has identified ‘30 critical minerals’, which are essential for the country’s economic development and national security.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947213
The Coastal Aquaculture Authority (Amendment) Bill 2023 (PIB)
- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Government has recently introduced the Coastal Aquaculture Authority (Amendment) Bill 2023 to promote ease of doing business.
Facts About:
What is Coastal Aquaculture?
- Coastal aquaculture refers to culturing or cultivating, under controlled conditions in ponds, pens and enclosures or in coastal areas of shrimp, prawn, fish or any other aquatic life in saline or brackish water.
- Coastal aquaculture does not include freshwater aquaculture.
What is the Coastal Aquaculture Authority Act 2005?
- Coastal Aquaculture Authority - The Act introduced the Coastal Aquaculture Authority (CAA).
- The main objective of the Authority is to regulate coastal aquaculture activities in coastal areas in order to endure sustainable development without causing damage to the coastal environment.
- The authority consists of a Chairperson who is a current or former HC judge being an expert in coastal aquaculture.
- The members will be nominated by the
- Central Department of Ocean Development
- Ministry of Environment and Forests
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Commerce
- 4 members representing coastal States on a rotation basis and one member secretary.
- Coastal area - It refers to the area declared as the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ), and includes such other area as the Central Government may notify under Environment Protection Act 1986.
What are the new provisions of the amendment bill 2023?
- Definition - It broadens the definition of coastal to include rearing and cultivation of any life stages of fish including crustacean, mollusc, finfish, seaweed or any other aquatic life.
- Environment friendly - It encourages environment friendly aquaculture such as cage culture, seaweed culture, bi-valve culture, marine ornamental fish culture and pearl oyster culture.
- It has the potential for creating employment opportunitiesfor coastal fisher communities especially fisherwomen.
- Brood stocks - It encourages the establishment of facilities in areas having direct access to seawater to produce genetically improved and disease-free brood stocks and seeds for use in coastal aquaculture.
- Brood stock or brood fish are a group of mature individuals used in aquaculture for breeding purposes.
- Brood Stock Multiplication Centre - The center will be used to rear marine organisms under strict biosecurity and disease surveillance.
- Usage of antibiotics - The Bill seeks to prevent the use of antibiotics and pharmacologically active substances which are harmful to human health in coastal aquaculture.
- Biosecurity - It introduces measures for analyzing and preventing the risk of introducing or spreading harmful organisms like viruses and bacteria within the coastal aquaculture unit.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1947213
Mediation Bill, 2023 (Live law)

- 08 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
The Parliament has passed the Mediation Bill 2023 to reduce pendency of court cases.
Facts About:
The Mediation Bill, 2021
- It was introduced in the Rajya Sabha in December, 2021, with the Parliamentary Standing Committee being tasked with a review of the Bill.
- The Bill aims at institutionalising mediation and establishing the Mediation Council of India.
Key Features of the Bill
Pre-litigation mediation
- Parties must attempt to settle civil or commercial disputes by mediation before approaching any court or certain tribunals.
- Even if they fail to reach a settlement through pre-litigation mediation, the court or tribunal may at any stage refer the parties to mediation if they request for the same.
Disputes not fit for mediation
- The Bill contains a list of disputes which are not fit for mediation.
- These include disputesrelating to claims against minors or persons of unsound mind, involving criminal prosecution, and affecting the rights of third parties. The central government may amend this list.
Applicability
- The Bill will apply to mediations conducted in India:
involving only domestic parties
involving at least one foreign party and relating to a commercial dispute (i.e., international mediation)
if the mediation agreement states that mediation will be as per this Bill.
- If the central or state government is a party, the Bill will apply to commercial disputes, and other disputes as notified.
Mediation process
- Mediation proceedings will be confidential, and must be completed within 180 days (may be extended by 180 days by the parties).
- A party may withdraw from mediation after two sessions.
- Court annexed mediation must be conducted as per the rules framed by the Supreme Court or High Courts.
Mediators
- Mediators may be appointed bythe parties by agreement, a mediation service provider (an institution administering mediation).
- They must disclose any conflict of interest that may raise doubts on their independence.
- Parties may then choose to replace the mediator.
Concerns Highlighted by the Parliamentary Standing Committee
Pre-Litigation
- The panel highlighted many key issues including mandatory and coercive nature of pre-litigation mediation.
- Making pre-litigation mediation necessary may result in case delays and provide another instrument in the hands of truant litigants to prolong case disposition.
Clause 26: The panel was against Clause 26of the draft which gives power to the SC or the High court to make laws of pre-litigation according to them.
Non-Applicability to Non-Commercial Disputes: The members questioned the non-applicability of the provisions of the Bill to disputes/matters of non-commercial nature involving the Government and its agencies.
Appointments: The panel had discussions about the qualifications and appointment of the Chairperson and Members of the proposed Mediation Council.
Recommendations Accepted by the Union Cabinet
Reducing the Time for Concluding a Mediation
- The Union cabinet has accepted the recommendations of the standing committee by reducing the time for concluding a mediation from 180 to 90 days.
Making Pre-Litigation Mediation Voluntary
- The recommendation for making pre-litigation mediation voluntary instead of mandatory was also much needed as voluntariness is an essential principle of mediation.
Recognition and Enforcement of Agreements
- Recognition and enforcement of settlement agreements arising out of mediation is a welcome move.
- This is also in line with India’s commitment as a signatory to the United Nations Convention on International Settlement Agreements Resulting from Mediation (Singapore Convention).
Provisions of the Final Bill that Require a Relook
Limited Grounds to Challenge a Settlement Agreement
- The limited grounds listed to challenge the enforcement of a settlement agreement and the fact that a period of 90 days is given to raise the challenge need a relook.
- The fact that a settlement agreement is essentially a contract between the parties; there are several instances where grounds for challenge such as fraud and impersonation are detected at a later stage.
Technical Flaws in Clause 8
- Clause 8 of the Bill entitles a party to move the Court before the commencement or during mediation for interim relief but only in “exceptional circumstances”.
- The term “exceptional circumstances”is not only undefined in the Bill but is also abnormal to the settled principles of seeking interim relief before the civil courts.
- Moreover, there is no remedy of appeal available against an order passed under this proposed section.
The Concept of Online and Community Mediation
- A recent Niti Aayog report reveals that only 55 per cent of India have access to the internet and only 27 per cent possess compatible devices.
- For online mediation to be a success, the government will have to scale the bandwidth accessibility to remote parts of the country.
- As for community mediation, the Bill makes it mandatory to have a panel of three mediators.This requirement is unnecessary and impinges on the flexibility that mediation brings.
Restricting the Government’s Participation in Mediation to only Commercial Disputes
- The real issue is that the government is the biggest litigant in the country.
- Restricting the ability of the government to participate in mediation proceedings arising only out of commercial disputes goes against the objective of enacting the legislation.
Way Forward
Legal Aid Setup: Setting up legal aid or access to justice clinics with adequate IT infrastructure could address the issue of online mediation.
Inclusion of Government Related Disputes in the Bill
- The standing committee had also recommended that government-related disputes be included in the Bill.
- The common litigant sees the government as an adversary before the court of law. The Bill provided a golden opportunity to the government to change that perception.
- This will inspire confidence amongst all stakeholders but would also help in reducing pendency backlog.
Conclusion
Mediation should be promoted as a preferred and voluntary mode of securing justice.
Although the legislature may have intended to lighten the load on the judiciary, the law needs to be improved because it may cause a delay in the administration of justice and raise the cost of litigation.
Source: https://www.livelaw.in/news-updates/parliament-passes-mediation-bill-234671
River Devika Rejuvenation Project (PIB)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently, Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Science & Technology sheds light on the progress of the River Rejuvenation Project, Devika. This initiative, inspired by the Namami Ganga campaign, aims to safeguard the sacred Devika River’s purity and health.
Facts About:
Comprehensive Waste Management:
- Focus on Liquid Waste Management.
- Creation of a network of pipes and manholes connecting households.
- Objective: Efficient disposal of liquid waste, preventing pollution, and preserving the sanctity of the river.
Complementary Solid Waste Management:
- Encompasses responsible collection, disposal, and management of solid waste.
- Essential to prevent environmental degradation and maintain river and surrounding health.
Financial Allocation Breakdown:
- Project investment exceeds Rs 190 crores.
- Allocation shared between Central and Union Territory (UT) at a 90:10 ratio.
Empowering Communities through PRIs:
- Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) pivotal for grassroots project success.
- PRIs’ involvement enhances community engagement, fosters ownership, and promotes sustainable development practices.
Devika River:
- Originates from Suddha Mahadev temple in Jammu and Kashmir’s Udhampur district.
- Flows through western Punjab (now Pakistan) where it merges with the Ravi River.
Cultural Significance:
- Revered by Hindus as sister of the Ganga River.
- Devika River believed to be a manifestation of Goddess Parwati, benefiting the people of MaderDesha (areas between river Ravi and Chenab).
Source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1946187
Revised manufacturing rules for drug firms (Indian Express)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
Recently the center government directed all pharmaceutical companies in the country to implement the revised Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Facts About:
Directions by the Government:
- Larger companies with a turnover of over Rs 250 crore have been asked to implement the changes within six months.
- The medium and small-scale enterprises with turnover of less than Rs 250 crore have been asked to do so within a year.
About Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP):
- Quality Management: It is a set of guidelines and quality management principles which ensure pharmaceutical products, as well as other products in the food and healthcare industries, are consistently produced and controlled to meet quality standards appropriate for their intended use.
- Aspects Include: It covers all aspects of the manufacturing process, including the premises, equipment, personnel, materials, production, quality control, documentation, and storage of finished products.
Need for the Improved Standards:
- To match up with the Global Standards: Implementation of the new norms will bring the Indian industry on par with global standards.
- Only 2,000 of the 10,500 drug manufacturing units in the country at present meet global standards, being WHO-GMP certified.
- The improved standards will ensure that pharmaceutical companies follow standard processes, quality control measures, and do not cut corners, improving the quality of medicines available in India as well as sold in the global market.
- To improve Indian Products Image: There have been a string of incidents where other countries have reported alleged contamination in India-manufactured syrups, eye-drops, and eye ointments.
- The deaths of 70 children in the Gambia, 18 children in Uzbekistan, three persons in the United States, and six deaths in Cameroon have been linked to these products.
- To rectify the Deficiencies: A risk-based inspection of 162 manufacturing units by the government found several deficiencies — incoming raw materials not being tested before use, product quality not being reviewed , absence of quality failure investigation, infrastructure deficiency to prevent cross-contamination, faulty design of manufacturing and testing areas, missing qualified professionals, and poor documentation.
- To Provide a Structure to the Draft: Implementation of the revised good manufacturing practices (GMP) as listed in the 2018 draft schedule M of the drugs and cosmetics rules.
Major Changes & Significance:
- Standard & Reliable Quality: The revised GMP guidelines focus on quality control measures, proper documentation, and IT backing to maintain quality of medicines produced.
- Review & Validation: It introduces pharmaceutical quality systems, quality risk management, product quality review and validation of equipment.
- Thorough Investigation: Carrying regular quality reviews of all its products, verify consistency of the quality and the processes, thorough investigation of any deviation or suspected defect and implementation of any preventive actions.
- Evaluation of Changes: It also suggests a change control system to evaluate all changes that may affect the production or quality of the product.
- Maintenance of Stability & Required Conditions:The companies will also be needed to mandatorily maintain the drugs in a stability chamber, set the proper temperature and humidity, and carry out an accelerated stability test as well.
- Data Safety & Security: The guidelines also state that companies should have GMP-related computerized systems, which ensure that there is no tampering of data related to the processes.
- In case sensitive data is entered manually to the system, there will be additional checks to validate the accuracy of the data. Backups would also be created to ensure there is no loss of data.
Conclusion:
The step taken is a required and desirable one. Instituting the same quality across the industry will give confidence to regulators from other countries and will improve the quality of drugs in the domestic markets.
Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-health/revised-manufacturing-rules-for-drug-firms-what-changes-and-why-8879305/
5% of birds in India are endemic (The Hindu)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
A publication, titled ‘75 Endemic Birds of India’, which was released on the 108th foundation day of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), points out that about 5% of birds found in the country are endemic and are not reported in other parts of the world.
Facts About:
India’s bird species:
- India is home to 1,353 bird species, which represents approximately 40% of global bird diversity.
- Of these 1,353 bird species, 78 species, which is around 5%, are endemic to the country.
About the Publication:
- The publication highlights the importance of endemic bird species in the country.
- The details of endemic bird species contained in the publication include etymology (meanings of scientific names) and their historical relevance along with vital facts such as subspecies’ differences, distinguishing traits, preferred habitats, breeding habits, and food preferences.
- Objective: The publication is aimed at making information about endemic birds of the country available to everyone, and highlighting the efforts to conserve species that are found only in restricted areas.
Highlights from the Publication:
- Around 75 bird species belong to 11 different orders, 31 families, and 55 genera, and exhibit remarkable distribution patterns across various regions in India.
- The highest number of endemic species has been recorded in the Western Ghats, with 28 bird species.
- Some of the rare species recorded in the country’s bio-geographic hotspot are;
- The Malabar Grey Hornbill (Ocycerosgriseus)
- Malabar Parakeet (Psittaculacolumboides
- Ashambu Laughing Thrush (Montecinclameridionalis)
- The White-bellied Sholakili (Sholicolaalbiventris)
- Amongst them 25 bird species are endemic to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Bird species which are only found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands are;
- Nicobar Megapode (Megapodiusnicobariensis);
- Nicobar Serpent Eagle (Spilornisklossi);
- Andaman Crake (Rallinacanningi); and
- Andaman Barn Owl (Tytoderoepstorffi).
- Four species of birds are endemic to the Eastern Himalayas, and one each to the Southern Deccan plateau and central Indian forest.
- Of the 78 endemic species, 25 are classified as ‘Threatened’ by the IUCN.
- Three species are listed as ‘Critically Endangered’.
- Five of the endemic birds in India are categorised as ‘Endangered’, and
- 17 as ‘Vulnerable’,
- While 11 are categorised as ‘Near Threatened’ on the IUCN Red List.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/5-of-birds-in-india-are-endemic-reveals-zoological-survey-of-india-publication/article67162268.ece#:~:text=India%20is%20home%20to%201%2C353,are%20endemic%20to%20the%20country
India's Sugar Surplus and its Impact on Agriculture (The Hindu)

- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
India became the world’s top sugar producer in 2021-2022, surpassing Brazil, but the extensive use of resources in sugar production is depleting rapidly, leading to a potential crisis in the future.
Facts About:
The Factors Behind Excessive Sugar Production
- The phenomenon of India's excess sugar production can be attributed to a confluence of factors, including government policies and measures aimed at promoting sugarcane cultivation. At the heart of this lies the fair and remunerative price (FRP) scheme, a government initiative ensuring that sugar mills pay sugarcane farmers a minimum price, thereby ensuring their fair profits
- State governments have further incentivized sugarcane cultivation through substantial subsidies, which some critics argue are aimed at securing the votes of farmers in politically influential rural regions.
- The repercussions of these policies have led to a significant sugar surplus, driving up exports to record levels. However, this expansionary approach has not escaped global scrutiny. Brazil, Australia, and Guatemala raised objections with the World Trade Organization (WTO), alleging that India's excessive export subsidies and domestic support violate international trade rules. The subsequent ruling against India by the WTO underscored the global ramifications of this sugar surplus.
Addressing the Excess Sugar Production: Ethanol as a Solution
- To mitigate the challenges posed by surplus sugar production, the Indian government has explored alternative avenues, with a focus on diverting excess sugar to ethanol production. Ethanol, a versatile organic compound derived from fermenting sugarcane molasses or sugar, has a range of applications in various industries, from alcoholic beverages to chemicals and cosmetics.
- In the realm of transportation, ethanol-blended petrol (EBP) has emerged as an effective strategy to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles, contributing to reduced crude oil imports and greenhouse gas emissions.
- The government's Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program, initiated in 2003, has made significant strides, aiming to achieve a blending rate of 20% by 2025. Reductions in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on ethanol have further supported this transition.
- Efforts to channel a substantial portion of sugar towards ethanol production have yielded positive results, highlighting a potential solution to the problem of excess sugar.
Groundwater Depletion and Environmental Consequences
- While India's EBP program has succeeded in reducing certain imports and emissions, it has also unearthed environmental concerns associated with sugarcane cultivation. The intensive water requirements of sugarcane, coupled with over-cultivation, have significantly impacted groundwater resources. This trend is particularly pronounced in India's top sugarcane-growing states, which rely heavily on groundwater for irrigation.
- With sugarcane demanding approximately 3,000 mm of rainfall for optimal growth, regions that typically receive 1,000-1,200 mm of rainfall resort to excessive groundwater extraction from confined aquifers. A startling statistic emerges – the cultivation of 100 kg of sugar necessitates a staggering two lakh liters of groundwater for irrigation. This alarming scenario has escalated concerns, particularly in drought-prone and groundwater-stressed areas, threatening the availability of this vital resource.
Sustainable Solutions and the Path Forward
- To safeguard India's agricultural sector from a looming crisis and ensure its long-term sustainability, a multifaceted approach is imperative. While the allure of financial gains from sugar surplus and exports is undeniable, a shift towards balanced and sustainable agricultural practices is essential.
Diversified Subsidy Schemes
- A crucial step involves reevaluating incentive structures that disproportionately favor sugarcane cultivation over other crops. By introducing comprehensive and fair subsidy schemes for a variety of crops, farmers can be encouraged to diversify their cultivation practices. Such measures can prevent monocultures, promote equitable income distribution, and contribute to more efficient resource utilization.
Environmentally Responsible Cultivation
- The adoption of environmentally conscious cultivation practices holds the key to mitigating the groundwater depletion crisis. Implementing methods such as drip irrigation, which directs water directly to the roots of sugarcane plants, can significantly reduce water consumption compared to traditional flood irrigation techniques. Government support through subsidies for setting up drip irrigation systems can accelerate this transition.
Integrated Water Management
- India's agricultural landscape requires a comprehensive approach to water management, encompassing rainwater harvesting, wastewater treatment, and improved canal irrigation networks. By minimising stress on groundwater reservoirs and exploring alternative water sources for irrigation, the strain on vital resources can be alleviated.
Investment in Research
- Despite significant strides, gaps remain in understanding groundwater availability and distribution. Investing in comprehensive groundwater research and data collection is essential for informed decision-making and sustainable resource management.
Conclusion:
As India assumes a prominent role in the global agricultural arena, the imperative for sustainability becomes increasingly apparent. While the achievements in sugar production are commendable, the nation must navigate the delicate balance between economic gains and environmental responsibility. By reassessing subsidy structures, promoting diversified cultivation practices, and embracing environmentally conscious techniques, India can pave the way for a resilient agricultural sector that not only based on the article: meets domestic demands but also ensures the well-being of future generations.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/india-excess-sugar-production-guzzling-groundwater/article67157121.ece
Organ shortage continues to cost lives (The Hindu)
- 07 Aug 2023
What is the News ?
According to recent data, around three lakh patients wait for organ donation in the country.
About:
- the number of donors (including cadavers) grew from 6,916 in 2014 to only 16,041 in 2022.
- The country registered 1,589 kidney, 761 liver and 250 heart transplants in the deceased category that year.
- Kidney and pancreas transplants grew from 3 in 2014 to 22 in 2022.
- In contrast, living donor kidney transplants rose from 4,884 in 2014 to 9,834 in 2022.
- Liver transplants in this category grew from 1,002 to 2,957
- one person is added to the waitlist every 10 minutes in the country
Ministry’s steps to enhance organ donations
- doing away with the domicile rule
- removal of age bar for registration of recipients
- removal of fee for registration for transplant
- easing rules on withdrawal of life support (passive euthanasia)
- facilitation of organ transport across the country
- giving special casual leave for employed organ donors
The annual need for 2,00,000 kidney transplants highlights the pressing urgency of the situation.
- However, a mere 10,000 transplants are performed each year, revealing a staggering gap.
- The demand for deceased donors is substantial because many families lack suitable living donors.
- Therefore, relying on deceased donors can help partially meet this demand
- statistics indicate around 70%-75% of donors are women. Wives, mothers, and sisters have emerged as the most prevalent sources of donatio
Organ donation pledges in India need to translate into actual donations and for that, medical staff need to be educated.
- They must be able to recognise, identify, inform, and counsel familiesabout brain death and the importance of organ donation.
- The gap between demand and supply continues to be tremendous. So, there is a need to equip our ICU staff with knowledge and awareness, the sooner the gap will close.
Greater awareness will improve in following way
- One cadaver can save up to eight lives.
- Two donated kidneys can free two patients from dialysis treatment.
- One donated liver can be split among two patients on the waitlist.
- Two donated lungs mean two other patients are given a second chance, and a donated pancreas and donated heart translate to two more patients receiving the gift of life.
- One tissue donor — someone who can donate bone, tendons, cartilage, connective tissue, skin, corneas, sclera, and heart valves and vessels — can save the lives of as many as 75 people.
Source: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/health/indias-poor-organ-donation-record-continues-to-cost-lives/article67161978.ece#:~:text=Three%20lakh%20patients%20wait%20for,donor%20can%20save%20several%20lives
