Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan

- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan initiative, launched by Defence Minister coinciding with the 77th Army Day celebrations, is a collaborative effort between the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Tourism.
Key Highlights:
- This initiative is designed to promote battlefield and border tourism by providing citizens with access to historically significant battlefields and military sites.
Objectives
- Promote Battlefield and Border Tourism: Encourage citizens and tourists to explore India's military history.
- Enhance Awareness: Educate visitors about India’s historic battles and military valor.
- Socio-Economic Development: Boost infrastructure, connectivity, and local economies in border regions.
Features of Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan
- Virtual Tours and Interactive Content: The platform offers historical narratives, virtual tours, and interactive multimedia to provide a detailed account of each battlefield.
- Travel Planning Assistance: Visitors can access information regarding permits, travel routes, and accommodations.
- Integration with the Incredible India Campaign: The initiative is part of the government’s broader tourism strategy, ensuring widespread promotion.
- Collaborative Infrastructure Development: The Indian Army is working with local civil authorities to facilitate safe tourism without compromising operational preparedness.
Key Locations Covered
- Galwan Valley (Ladakh): Site of the 2020 India-China clash.
- Doklam: A tri-junction between India, Bhutan, and China.
- Line of Control (LoC) and Line of Actual Control (LAC) Sites:
- Nathu La Pass (Sikkim): Significant in the 1967 Indo-China clashes.
- Longewala (Rajasthan): Site of a key battle during the 1971 Indo-Pak war.
- Other Sites: Locations of the 1962 war with China and various Indo-Pak conflicts.
Significance
- Historical and Patriotic Engagement: Provides citizens firsthand insights into the challenges faced by soldiers in remote, strategic locations.
- Tourism Development in Border Areas: Previously restricted areas now open for visitors, leading to economic benefits for local communities.
- National Security Awareness: Encourages greater appreciation of India's defense forces and their contributions.
Implementation
The first phase of the Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan project includes key battlefields and border sites across seven major regions. Future phases will expand coverage to additional historical military locations.
Global Economic Prospects (GEP) Report 2025
- 17 Jan 2025
In News:
The World Bank has released its Global Economic Prospects (GEP) report for 2025, a flagship biannual publication analyzing trends and projections in the global economy, with a focus on emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs). The report highlights economic growth forecasts, trade dynamics, and the challenges and opportunities shaping the global economic landscape.
Global Economic Outlook
- The world economy is projected to expand at a steady yet subdued rate of 2.7% in both 2025 and 2026, maintaining the pace of 2024.
- Inflation, which peaked above 8% in recent years, is expected to stabilize at an average rate of 2.7% in 2025 and 2026, aligning with central bank targets.
- Despite growth, the global economy remains 0.4 percentage points below the 2010-2019 average, raising concerns about its ability to tackle poverty effectively.
Challenges and Risks
- Trade Restrictions: New trade restrictions imposed in 2024 were five times higher than the 2010-19 average, contributing to a slowdown in global trade and economic growth.
- Rising Protectionism: Increased fragmentation in global trade policies is limiting exports and hampering economic integration.
- Policy Uncertainty: Adverse policy shifts, sluggish progress in reducing inflation, and weaker performance in major economies pose downside risks to global recovery.
- Debt and Investment Concerns: Developing economies are experiencing sluggish investment growth and high debt levels, exacerbated by climate change-related costs.
Emerging Markets and Developing Economies (EMDEs)
- EMDEs have significantly evolved since 2000, now contributing about 45% of global GDP, compared to 25% at the start of the century.
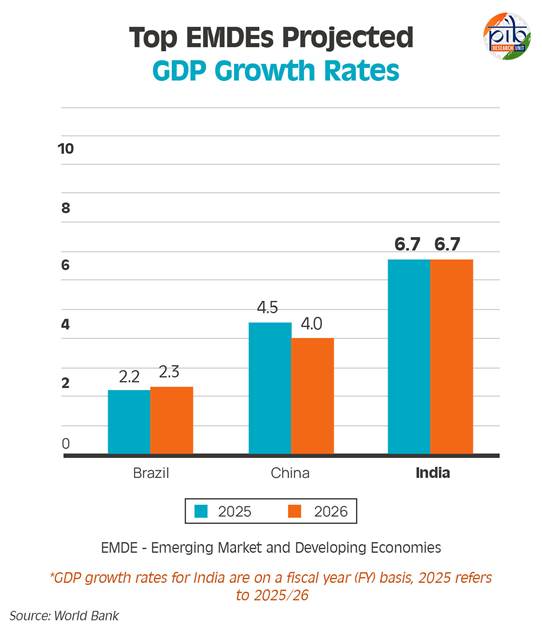
- The three largest EMDEs—India, China, and Brazil—have accounted for approximately 60% of annual global growth over the past two decades.
- Growth in low- and middle-income developing countries is expected at 4.1% in 2025 and 4% in 2026, with a notable slowdown compared to the early 2000s.
- Low-income countries are projected to rebound to 5.7% in 2025 and 5.9% in 2026, aided by easing conflicts in some regions.
- The world's poorest nations, with annual per capita incomes below USD 1,145, recorded growth of 3.6% in 2024, impacted by conflicts in regions like Gaza and Sudan, alongside lingering effects of COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions.
India-Specific Highlights
- Fastest-Growing Major Economy: India is expected to maintain its position as the world’s fastest-growing major economy, with a projected growth rate of 6.7% in both 2025 and 2026.
- Sectoral Growth: The services sector will remain robust, while manufacturing activity is expected to strengthen.
- Investment Growth: Supported by rising private investment, improved corporate balance sheets, and favorable financing conditions, investment growth in India is expected to remain steady.
- Key Growth Drivers:
- Infrastructure development under the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- Innovation-driven initiatives like Startup India and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
- Expansion of the digital economy and financial inclusion efforts.
- Rural Demand and Consumption: Growth in rural demand and a recovery in farm production have bolstered consumer spending, although urban consumption remains affected by inflation and slow credit growth.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
January is Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, and the focus on this month underscores the critical importance of preventing cervical cancer, a disease responsible for significant mortality among women in India. At the heart of this prevention is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, which is recognized as the most effective measure to prevent cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers. Despite its potential, the HPV vaccine remains out of reach for many due to its high cost and the need for greater awareness.
HPV and its Impact in India
HPV is responsible for 99.7% of cervical cancers worldwide, making it one of the primary causes of cancer in women. In India, cervical cancer is the third most common cancer among women, accounting for about 6-29% of all cancers in women. As of GLOBOCAN 2020, India alone has 20% of the global burden of cervical cancer, with over 123,000 cases and a 9.1% mortality rate.
Additionally, HPV can lead to several other cancers, including anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, and throat cancers, making its vaccination vital for overall cancer prevention.
The HPV Vaccine: A Game-Changer
The HPV vaccine is the most effective tool to prevent infections caused by the virus and reduce the incidence of associated cancers. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies that neutralize the virus before it can cause damage. There are different types of vaccines authorized in India, including:
- Gardasil (protects against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18)
- Cervarix (a bivalent vaccine targeting HPV 16 and 18)
- Cervavac (India's first HPV vaccine, developed by the Serum Institute of India)
The vaccine is recommended for both males and females between 9 and 26 years, with a special focus on children aged 12 to 13 years, as the vaccine is most effective when administered before exposure to the virus. It’s also suitable for people who are immunocompromised or HIV-infected.
Challenges to HPV Vaccination in India
Despite the obvious benefits, the uptake of the HPV vaccine in India faces several barriers:
- High Costs: The price of the vaccine remains prohibitively high. For example:
- Gardasil 9 costs ?10,850 per dose.
- Gardasil 4 is priced between ?2,000 to ?4,000 per dose.
- Cervavac, the Indian-made vaccine, costs around ?2,000 per dose, which is more affordable but still out of reach for many.
- Awareness and Cultural Perceptions: There is a lack of awareness about HPV and its link to cervical cancer. Cultural factors, particularly around reproductive health, can also create reluctance to vaccinate, especially in rural or conservative areas.
- Limited Access: Currently, the vaccine is available through private practitioners and is not part of the National Immunisation Programme (NIP), limiting access to the broader population.
The Way Forward: National Immunisation and Awareness Campaigns
The National Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (NTAGI) has recommended that the HPV vaccine be included in India’s National Immunisation Programme (NIP). This would enable broader access and affordability, especially for girls aged 9–14 years and ensure that a routine vaccination schedule is implemented at the age of 9 years. Some states like Punjab and Sikkim have already taken steps to introduce the vaccine in their state-level immunization programs.
Additionally, a nationwide HPV vaccination campaign could raise awareness about the vaccine and its benefits, helping to overcome the challenges of cost, safety concerns, and cultural perceptions. Regular cervical cancer screenings (such as Pap smears and HPV tests) should also be encouraged to identify precancerous changes early.
Does ‘Blood Money’ Have a Legal Standing?

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
The concept of ‘blood money’ has come under scrutiny recently, especially in the context of the death sentence awarded to Indian nurse Nimisha Priya from Kerala in Yemen. This case, where the focus is on monetary compensation paid to the victim’s family, has sparked renewed discussions on the practice of blood money.
What is ‘Blood Money’?
‘Blood money’ or diya is a term used in Islamic Sharia law and refers to a sum of money that the perpetrator of a crime must pay to the victim or the victim’s family, typically in cases of unintentional murder or homicide. The custom is designed to offer compensation to the family for the loss of income and alleviate their suffering, rather than placing a price on human life. This practice allows the victim’s family to forgive the accused and avoid retribution, called qisas, under the Sharia.
However, even when blood money is paid, the community or state retains the authority to impose a penalty or punishment, which could include imprisonment or other penalties, based on the seriousness of the crime.
How Does Blood Money Figure in Islamic Sharia Law?
In Islamic law, the amount of blood money varies based on several factors such as the victim’s gender, religion, and nationality. The following examples demonstrate the application of blood money in different Islamic countries:
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, blood money is part of traffic regulations, where the perpetrator must pay compensation to the heirs of victims who die in road accidents. While a Sharia court determines the amount of compensation, the police handle the determination of the guilty party. In workplace accidents, a special committee sets the amount. Saudi Arabia has considered reforming its laws to ensure equal compensation for men and women, Muslims and non-Muslims. However, efforts to amend the laws have not yet been fully implemented.
- Iran: In Iran, blood money differs based on the gender and religion of the victim. A woman’s compensation is typically set at half of that of a man’s. While the Supreme Court of Iran upheld a law to equalize compensation for all individuals in 2019, full implementation of the law has yet to be realized.
- Pakistan: Pakistan has incorporated provisions for diya and qisas in its legal system through the Criminal Laws (Amendment) Ordinance, 1991, aligning its practices with those of Islamic law.
- Yemen: In Yemen, parties involved can negotiate compensation, with judicial oversight ensuring fairness.
India’s Stand on ‘Diya’ and Blood Money
India does not include the provision for blood money in its formal legal framework. However, a similar concept exists in the form of plea bargaining, which allows the accused to negotiate with the prosecution in exchange for a reduced sentence or charge. Plea bargaining involves the defendant pleading guilty to a lesser offense in return for a concession, either in terms of the charges or the sentence.
Plea Bargaining in India:
Introduced under the Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2005, plea bargaining was added to the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973. While it bears some resemblance to blood money in that it allows for compensation to the victim, it has significant limitations:
- It can only be applied to crimes punishable by imprisonment of less than seven years.
- It is not applicable to heinous crimes such as murder or rape, or offenses involving women or children under 14.
- The accused must voluntarily agree to plead guilty, with no coercion involved.
While plea bargaining may include compensation under Section 265E of the Code, discussions continue to refine this provision to make it more inclusive, similar to the reforms seen in Islamic countries regarding blood money.
Historical Practices Similar to Blood Money
Throughout history, various cultures have had practices similar to blood money. These include:
- Brehon Law (Ireland): In the 7th century, Brehon law established the concept of Éraic (body price) and Log nEnech (honor price). These were compensation systems that allowed for the amicable resolution of crimes, avoiding capital punishment.
- Galanas (Wales): Galanas in Welsh law determined compensation based on the victim's social status, where a blood fine was required in cases of murder, unless the killing was justified.
- Wergeld (Germany): The Wergeld system in early medieval Germany required compensation for homicide or grave offenses, often in monetary terms.
- Other Medieval States: Several medieval states established a standard payment for the victims’ families in the event of homicide or serious crimes, much like blood money.
Cases of Indians Pardoned with Blood Money
India has witnessed instances where blood money has been invoked for Indian nationals facing death sentences abroad:
- Arjunan Athimuthu (Kuwait, 2019): Arjunan’s death sentence was commuted to life imprisonment after his family paid ?30 lakh in blood money.
- Abdul Rahim (Saudi Arabia): Abdul Rahim, convicted for the murder of a Saudi boy in 2006, was pardoned after ?34 crore in blood money was paid. However, he has not been released from prison yet.
- UAE Cases:
- In 2017, 10 Indians were pardoned after paying 200,000 dirhams as blood money.
In 2009, 17 Indians on death row for the murder of a Pakistani national were pardoned after a blood money amount of nearly ?4 crore was paid.
Nine Years of Startup India

- 16 Jan 2025
In News:
On January 16, 2025, India marks nine years of Startup India, a transformative journey that began in 2016. Designated as National Startup Day, this occasion celebrates the nation’s strides in fostering a robust and inclusive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Current Status (as of Jan 2025)
Over 1.59 lakh startups recognized by DPIIT, making India the 3rd largest startup ecosystem globally.
- More than 100 unicorns (startups valued over $1 billion).
- Key hubs: Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Mumbai, Delhi-NCR; growing contribution from smaller cities.
Key Sectors
- Major sectors: Fintech, Edtech, Health-tech, E-commerce.
- Notable companies: Zomato, Nykaa, Ola exemplify India's shift from job seekers to job creators.
Key Milestones (2016–2025)
- Startups grew from around 500 in 2016 to 1.59 lakh in 2025.
- 73,151 startups with at least one-woman director as of 2024, showcasing rise in women entrepreneurship.
- Over 16.6 lakh jobs created by DPIIT-recognized startups by 2024.
Core Features of Startup India
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplified compliance, self-certification, and single-window clearances.
- Tax Benefits: Three-year tax exemptions for eligible startups.
- Funding Support: ?10,000 crore Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) supports early-stage funding.
- Sector-Specific Policies: Policies focusing on sectors like biotechnology, agriculture, and renewable energy.
Industry-wise Jobs Created
- IT Services: 2.04 lakh jobs.
- Healthcare & Lifesciences: 1.47 lakh jobs.
- Professional & Commercial Services: 94,000 jobs.
- Total direct jobs created: 16.6 lakh (as of Oct 2024).
Flagship Schemes
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS).
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme.
Other Key Initiatives
- Capacity Building & Handholding: Workshops for regional ecosystems, especially in non-metro cities.
- Outreach & Awareness: Initiatives to facilitate funding, incubation, and mentorship opportunities.
- Ecosystem Development: National-level events like Startup Mahakumbh to bring together key stakeholders.
- International Linkages: India’s G20 Presidency institutionalized Startup20 to enhance global collaborations.
BHASKAR Platform (Launched in Sept 2024)
- Objective: Centralize and streamline interactions within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
- Key Features:
- Networking: Connects startups, investors, mentors, and government bodies.
- Resources: Provides quick access to essential tools and knowledge for scaling startups.
- Global Outreach: Promotes India as a global innovation hub.
Startup Mahakumbh
- 2024 Edition: Hosted 1,300 exhibitors, 48,000 visitors, and 392 speakers, including unicorn founders and policymakers.
- 2025 Edition (3-5 April, New Delhi): Theme - “Startup India @ 2047 – Unfolding the Bharat Story.”
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)

- 15 Jan 2025
In News:
Odisha has become the 34th state to implement the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY). The National Health Authority (NHA) of the Union Ministry of Health signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Department of Health and Family Welfare, Government of Odisha to onboard the state under the scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The scheme will be implemented alongside the existing Gopabandhu Jan Arogya Yojana in Odisha.
- It provides health coverage of Rs. 5 lakh per family per annum, with an additional Rs. 5 lakh for women members.
- Approximately 1.03 crore families will be covered under the scheme.
- Shri JP Nadda, Union Health Minister, emphasized that the scheme is the world’s largest and fastest-growing health coverage initiative.
- Shri Mohan Charan Majhi, Chief Minister of Odisha, highlighted that people will now have access to cashless treatment in over 29,000 empaneled hospitals.
About Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY:
- Launched in 2018 under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoH&FW).
- Targets 12 crore families (~55 crore beneficiaries).
- Provides cashless hospital coverage for secondary and tertiary care.
- Fully funded by the government, with cost-sharing between the Centre and states.
- Covers nearly 2,000 medical procedures, including major surgeries.
Since its inception, over 8.19 crore hospital admissions have been recorded, with ?1.13 lakh crore spent on healthcare for marginalized sections.
Cyclone Dikeledi
- 15 Jan 2025
Cyclone Dikeledi struck Mayotte, a French overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, located in the Mozambique Channel. The cyclone caused severe flooding and damage, following closely after Cyclone Chido, which had hit the region in December 2024.
About Mayotte:
- Comprises two islands from the Comoros archipelago: Mayotte (Grande Terre) and Pamandzi (Petite Terre).
- It is the poorest region in both France and the European Union.
- Colonized by France in 1843 and annexed along with the Comoros in 1904.
- In a 1974 referendum, while 95% of Comoros opted for independence, 63% of Mayotte voted to remain French.
- While Comoros declared independence in 1975, Mayotte continues to be governed by France.
Cyclone Chido, which struck in December 2024, was recorded as the most severe storm to hit Mayotte in 90 years.
Purulia Observatory

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
New observatory at remote Purulia district West Bengal is expected to contribute significantly to Astrophysics.
Key Highlights:
Location and Significance:
- Established by: S.N. Bose Centre for Basic Sciences (SNBCBS), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
- Location: The observatory is situated at Panchet Hill, in the Garpanchakot area of Purulia district, West Bengal, at an elevation of 600 meters above ground level.
- Longitude Gap: Positioned at a longitude of approximately 86° E, this observatory fills a critical longitudinal gap in global astronomical observation networks. There are very few observatories along this longitude, making it strategically important for observing transient astronomical phenomena that last from minutes to hours.
- Global Impact: This location will allow for unique contributions to global astrophysical research, especially in observing transient events, which require observatories spread across all global longitudes.
Technological and Educational Role:
- The observatory is equipped with a 14-inch telescope for scientific observations.
- It will serve as a training ground for students and researchers, helping them to handle telescopes, record astronomical data, and engage in research.
- The observatory aims to foster national and international collaborations in astronomical research, furthering India’s contributions to the field.
Collaborations and Ecosystem Development:
- MOU with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University: The observatory will be run jointly with Sidhu Kanu Birsa University, sharing resources and responsibilities. The collaboration promises to bring scientific and educational advancements to Purulia, a district traditionally considered backward.
- The establishment of the observatory is expected to boost the local ecosystem, creating a space for scientific engagement and inspiring students in the region.
Research and Contributions:
- The research team, from the Department of Astrophysics at SNBCBS, contributed to the conceptualization, site characterization, and installation of the telescope.
- Their efforts ensure the observatory will be capable of high-quality scientific observations, especially with regard to weather parameters and astronomical seeing conditions.
Future Prospects:
- Scientists emphasized that the observatory will significantly contribute to the global body of knowledge in observational astronomy.
- Also highlighted the potential of the observatory to create a scientific ecosystem in the region.
- The observatory will also serve as a source of inspiration for students in Purulia and provide a much-needed boost to local education in the fields of science and astrophysics.
Konkan Region’s Sada and Biodiversity

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
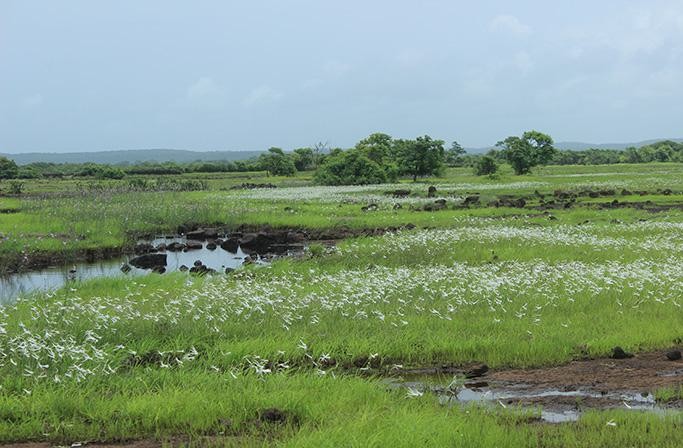
A Konkan secret, the flat-top sada is a freshwater paradise.
Key Highlights:
Geography of Sada:
- The Konkan region lies between the Arabian Sea and the Western Ghats.
- Sada refers to flat-topped hills, formed by centuries of erosion, and is a prominent feature in the Ratnagiri district.
- These areas are typically barren except during the monsoon season when they come alive with flora and fauna.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- A biodiversity survey between 2022-2024 recorded 459 plant species, with 105 being endemic to the Konkan region.
- The survey also identified 31 species of reptiles, 13 species of amphibians, 169 species of birds, and 41 species of mammals.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in water conservation. The lateritic soil layer atop the Sada acts as a catchment for rainwater, recharging the groundwater and providing freshwater to local communities year-round.
Traditional Land Use and Agriculture:
- Local Farming: During monsoons, the Sada is used by locals for growing traditional crops like rice and millets (e.g., nanchani), using sustainable farming practices without pesticides or chemical fertilizers.
- Water Management: The locals rely on open wells, springs, and perennial streams for freshwater, which are carefully maintained through cultural rituals and community hygiene practices.
Conservation and Cultural Importance:
- The region is home to geoglyphs, ancient artworks estimated to be 10,000 years old, adding to its cultural and historical significance.
- Waterbodies on the Sada serve as habitats for species like the Indian flapshell turtle (Lissemys punctata) and provide water for other wildlife, including leopards, jackals, hyenas, barking deer, and migratory birds.
Environmental Threats:
- Land-use Change: Increasing conversion of open land and croplands into orchards and residential areas, along with various developmental projects, threatens the region's biodiversity.
- Mining: Extraction of laterite stones for construction purposes is another environmental risk.
- Wasteland Classification: The region is often classified as a ‘wasteland’ in the Wasteland Atlas, further complicating conservation efforts.
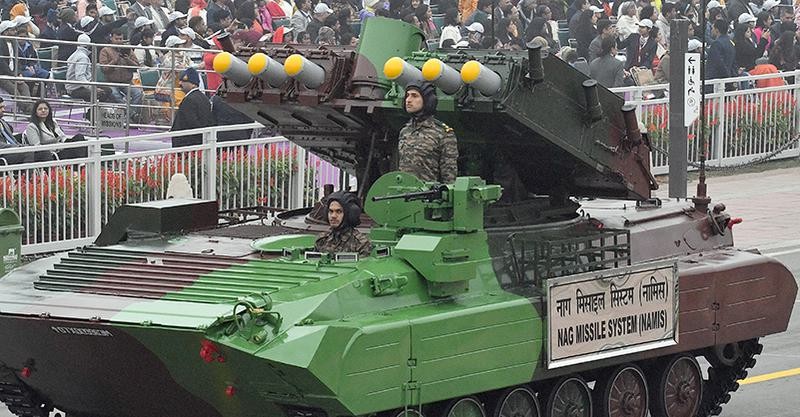
Nag Mark-2

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted field evaluation trials of India's indigenous Anti-Tank Missile - Nag Mark 2 at the Pokhran Field Range in Rajasthan.
Overview of Nag Mk-2:
- Type: Third-generation, fire-and-forget anti-tank guided missile (ATGM).
- Development: Indigenous development by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- Functionality: Designed to neutralize modern armored threats, including those with Explosive Reactive Armour (ERA), using advanced fire-and-forget technology.
Technological Features:
- Fire-and-Forget Technology: Operators lock onto targets before launch, allowing the missile to autonomously track and engage targets, ensuring precision strikes.
- Lock-on After Launch: The missile can lock onto the target post-launch, providing flexibility in complex battlefield environments.
- Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with Imaging Infrared (IIR) seekers for enhanced accuracy, both during the day and at night.
Performance and Range:
- Effective Range: The missile has a range of 7 to 10 kilometers, a significant improvement over its predecessor, Nag Mk-1, which had a range of only 4 kilometers.
- Test Trials: Successfully destroyed all targets at both maximum and minimum ranges during the field evaluation trials at Pokhran Field Range, Rajasthan.
- Attack Mode: Includes a top-attack capability to target the vulnerable upper surfaces of armored vehicles, enhancing its effectiveness.
Platform and Integration:
- Launch Platform: The missile is launched from the NAMICA (Nag Missile Carrier) Version 2, a tank destroyer vehicle used by the Indian Army to launch anti-tank missiles.
- Versatility: Designed for integration with multiple platforms, enhancing operational flexibility in different combat scenarios.
Strategic and Operational Significance:
- Indigenous Defence Capability: Reduces India's dependence on foreign weapons systems, strengthening self-reliance in defense technology.
- Enhanced Battlefield Readiness: Provides the Indian Army with a cutting-edge weapon to counter modern armored vehicles, improving tactical advantages.
- Operational Effectiveness: The missile’s precision and ability to neutralize targets with minimal collateral damage make it an essential tool in modern warfare.
- Strategic Deterrence: Demonstrates India’s technological advancements in missile systems, signaling strength and deterrence to adversaries.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform

- 14 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Minister of Commerce & Industry Shri Piyush Goyal launches Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform.
Bharat Cleantech Manufacturing Platform:
- Objective: Strengthen India's cleantech value chains, especially in solar, wind, hydrogen, and battery storage sectors.
- Platform Features:
- Aims to promote collaboration, co-innovation, and knowledge-sharing among Indian firms.
- Focus on scaling up manufacturing, sharing ideas, technologies, and resources.
- Acts as a financing platform for the cleantech sector.
- Designed to position India as a global leader in sustainability and cleantech innovation.
India's Clean Energy Commitment:
- Target: 500 GW of clean energy capacity by 2030.
- India has been a front-runner in fulfilling its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement and UNFCCC.
- Early Achievement: India achieved its 2022 renewable energy target of 200 GW, 8 years ahead of schedule.
- Largest Interconnected Grid: India boasts the world’s largest interconnected power grid, enhancing its renewable energy distribution capacity.
- Gujarat is a pioneer in solar power adoption in India.
Union Minister Shri Piyush Goyal's Views:
- On Product-Linked Incentives (PLIs):
- PLIs and subsidies are seen as short-term aids; long-term growth of the clean energy sector depends on it becoming self-sustaining.
- Urged Indian firms to innovate and scale up manufacturing within the country.
- On Clean Energy and Sustainability:
- Stressed the importance of innovation and collaboration to achieve sustainability goals.
- India aims to attract international investors by creating a compelling business case for cleantech investments.
- 3S Approach (Speed, Scale, and Skill): Key to implementing India's renewable energy program, emphasizing rapid deployment, large-scale adoption, and skill development in the sector.
Bharat Climate Forum 2025:
- Event Objective: A platform for policymakers, industry leaders, and stakeholders to discuss climate action, clean energy, and India’s role in global climate goals.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Aligning India’s clean energy initiatives with global climate goals (UNFCCC, Paris Agreement).
- Emphasizing India’s early achievements in clean energy adoption.
- Promoting sustainable development and clean energy solutions.
India's Performance in Renewable Energy:
- India’s progress has been commendable in meeting its climate targets and setting up clean energy capacity ahead of schedule.
- The government’s initiatives, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, have made solar power affordable and scalable through transparency in auctions, competitive bidding, and speed in project implementation.
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals
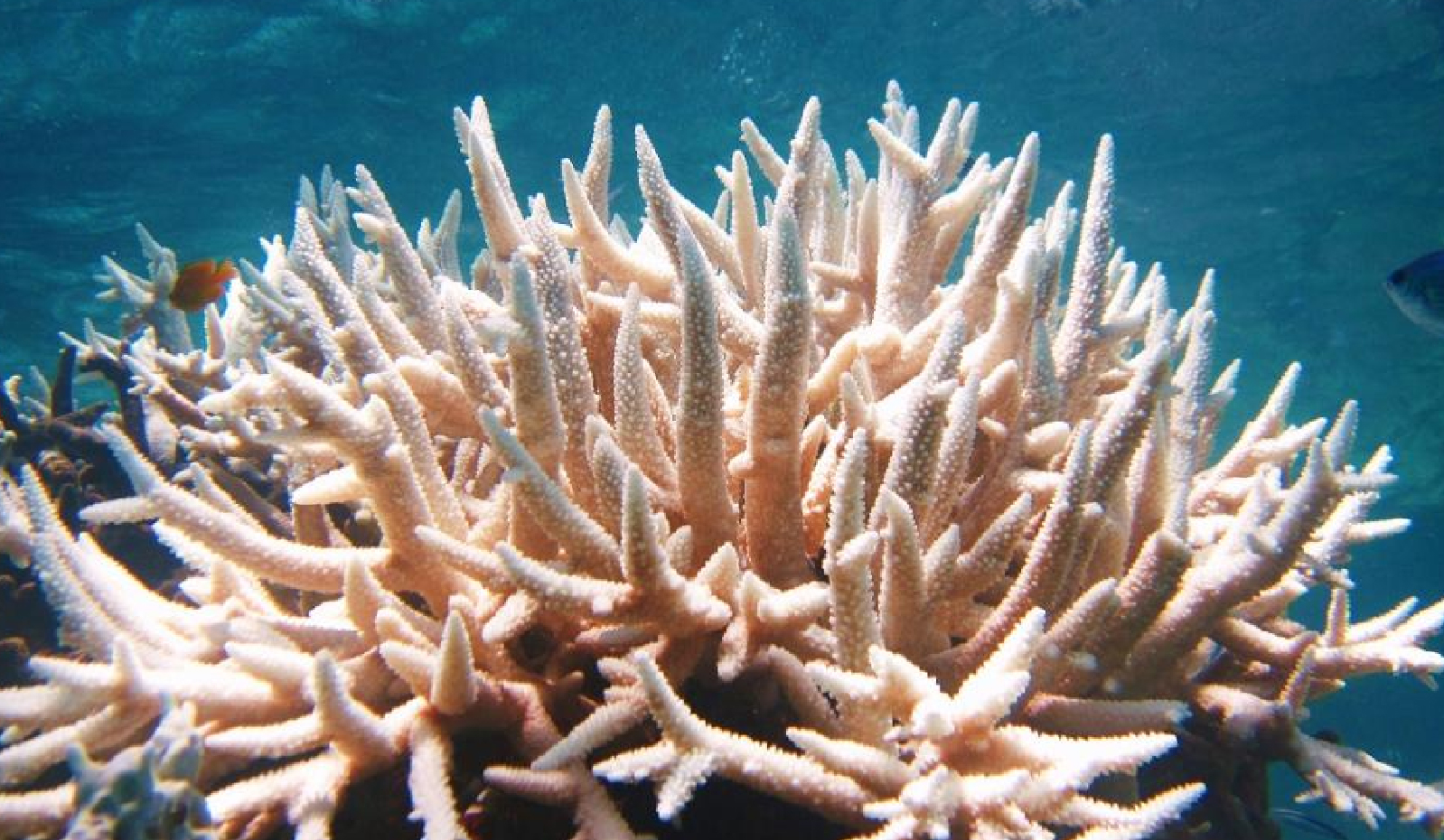

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
World’s First Cryo-Born Baby Corals Successfully Settled on the Great Barrier Reef.
Introduction to Cryo-Born Corals
- Cryo-born corals are created using cryopreservation techniques, which involve freezing coral cells and tissues at very low temperatures.
- The process preserves coral cells by preventing the formation of ice crystals that would otherwise damage them.
- Cryopreservation involves adding cryoprotectants to remove water from cells, enabling their survival during freezing and thawing.
Significance of the Breakthrough
- Climate Change Resilience: The initiative aims to create heat-tolerant corals, which are crucial in combating the impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Selective Breeding Advantage: Cryopreservation allows for controlled breeding and bypasses the limitations of natural coral spawning, which occurs only once a year. This enables multiple reproduction cycles without disturbing wild populations.
The Process of Cryo-Born Coral Production
- Sperm Collection: During coral spawning events, sperm from various coral species is collected and frozen at -196°C using liquid nitrogen, halting metabolic processes.
- Coral Egg Fertilization: Cryopreserved sperm is used to fertilize fresh coral eggs, which are grown in a specialized research facility called the National Sea Simulator.
- Coral Cradles: After growth, the cryo-born corals are carefully transported and settled into specially designed "coral cradles" placed in the Great Barrier Reef, where their growth is monitored during their critical first year.
Importance of Cryo-Born Corals in Reef Restoration
- The primary aim is to introduce millions of heat-tolerant corals annually to restore reefs affected by climate change.
- The Taronga CryoDiversity Bank houses the world’s largest frozen coral sperm collection from 32 coral species, collected annually since 2011, providing a resource for future restoration efforts.
Coral Reefs: An Overview
- Corals are marine invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are built by colonies of coral polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Coral reefs are typically found in shallow, sunlit waters with a temperature range of 16-32°C and depths less than 50 meters.
Global and Indian Coral Conservation Efforts
- India:
- The National Committee on Wetlands, Mangroves, and Coral Reefs (1986) advises on conservation measures.
- The Environment (Protection) Act (1986) prohibits the use of coral and sand in construction.
- Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) uses Biorock technology for coral restoration.
- Global Efforts:
- CITES lists coral species in Appendix II, regulating coral trade.
- The World Heritage Convention designates coral reefs as protected sites.
Global Impact and Future Directions
- The innovative work by Australian scientists opens the door for large-scale restoration efforts by allowing more controlled breeding and genetic diversity, making corals more resilient to climate change.
- This breakthrough could revolutionize coral restoration, scaling up efforts to introduce millions of resilient corals to reefs worldwide, building long-term resilience against climate change.
Sovereign Artificial Intelligence

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been remarkable in recent years. In 2018, a 340-million-parameter AI model was considered large, whereas models like ChatGPT now have 1.8 trillion parameters.
- As part of its ambition to make the digital economy worth USD 1 trillion by 2028, India is focusing on AI sovereignty and investing in semiconductors and AI technologies to achieve this goal.
What is Sovereign AI?
Definition
- Sovereign AI refers to a nation’s ability to develop, control, and deploy AI using its own resources, including infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This involves not just developing AI models but also creating infrastructure and nurturing homegrown talent to lead AI advancements within the country.
Key Aspects of Sovereign AI
- National Control: Ensures AI technologies align with a country's laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Data Sovereignty: Emphasizes control of data within the country’s borders, protecting privacy, security, and national interests.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is transforming industries, markets, and governance, with AI-powered tools assisting professionals and governments.
- Ethical Considerations: Countries define security protocols and ethical frameworks to govern the use of AI technologies.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reduces reliance on foreign technologies, encouraging domestic development in AI to achieve strategic independence.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is crucial for industrial innovation. Without it, nations risk falling behind in the global economy.
Growth and Importance of AI
Evolution of AI Models
- In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered a significant achievement.
- Today, ChatGPT uses 1.8 trillion parameters, and Google’s Gemini uses 1.5 trillion parameters. In comparison, China’s DeepSeek has a model with 240 billion parameters.
- Parameters are the internal variables of AI models, adjusted during training to improve their performance and accuracy.
Strategic Applications
- Sovereign AI plays a pivotal role in critical sectors such as:
- Defense
- Healthcare
- Transportation
- Governance
- It helps redefine industries, boost innovation, and streamline operations across various sectors.
India’s Position in Sovereign AI
AI Infrastructure Development
- Tata Group and Reliance are building AI infrastructure in India, including the development of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- India has allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project under the IndiaAI Mission, which includes creating an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips.
Government Initiatives
- The IndiaAI Mission is designed to boost India’s AI capabilities by building infrastructure, fostering talent, and supporting innovation within the country.
Global AI Compact
- A Global AI Compact has been proposed to ensure equitable access to AI technologies across nations.
- The compact advocates for sharing AI resources globally while promoting cooperation and addressing challenges associated with AI governance.
Pink Fire Retardant

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
As wildfires continue to rage across Southern California, authorities are deploying pink fire retardant from aircraft to help combat the blazes. Despite its widespread use, concerns over its effectiveness and environmental risks have surfaced in recent years.
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- Fire retardant is a chemical mixture designed to slow down or extinguish wildfires. The most commonly used product in the U.S. is Phos-Chek, a brand of retardant.
- Phos-Chek primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry (salts like ammonium polyphosphate), which helps the retardant stay longer and resist evaporation, unlike water.
Purpose and Visibility
- Fire retardants are sprayed ahead of fires to coat vegetation, reducing oxygen and preventing flames from spreading.
- Color is added to the fire retardant, often bright pink, to improve visibility. This ensures firefighters can track its spread and create effective fire lines, helping protect lives and property.
Manufacturer
- Perimeter Solutions manufactures Phos-Chek, which is used for aerial fire suppression efforts.
Effectiveness of Pink Fire Retardant
Limited Effectiveness
- The use of fire retardants like Phos-Chek is not always effective across different wildfire conditions.
- Aerial retardants depend on environmental conditions like terrain, slope, and weather for optimal effectiveness.
- Researchers, including Forest Service scientists, suggest that retardant effectiveness is more limited under changing climate conditions.
- Climate change is narrowing the window of opportunity for using aerial retardants, reducing their impact.
Uncertainty in Impact
- The effectiveness of fire retardants is hard to quantify. Multiple firefighting methods are used simultaneously, making it difficult to attribute wildfire suppression success solely to the retardant.
Environmental Concerns of Pink Fire Retardant
Toxicity and Pollution
- Phos-Chek contains toxic metals such as chromium and cadmium, both of which are harmful to humans and the environment.
- Chromium and cadmium are linked to serious health issues, including cancer and liver/kidney diseases.
- Aquatic life is particularly vulnerable to these toxins, as the chemicals can enter waterways, causing extensive damage to ecosystems.
Impact on Rivers and Streams
- The use of pink fire retardant has raised concerns regarding the contamination of rivers and streams.
- A study by the University of Southern California (USC) in 2024 estimated that 850,000 pounds of toxic chemicals have been released into the environment since 2009 due to fire retardant use.
Growing Use and Pollution
- From 2009 to 2021, over 440 million gallons of retardant were applied across U.S. lands.
- During this period, an estimated 400 tons of heavy metals were introduced into the environment, further exacerbating the pollution levels.
Financial and Practical Concerns
High Cost and Inefficiency
- The cost of deploying fire retardant is significant. Aerial firefighting operations require substantial resources, including planes, helicopters, and large quantities of retardant.
- Environmental experts argue that using fire retardant from planes is ineffective and expensive, especially in light of the growing environmental concerns.
India Joins the UN-CEBD

- 13 Jan 2025
In News:
- India has recently joined the United Nations Committee of Experts on Big Data and Data Science for Official Statistics (UN-CEBD), marking a significant step in strengthening its role in global statistical frameworks.
- The inclusion is a result of India's recent membership in the United Nations Statistical Council (UNSC), signaling the nation's growing influence in global data governance.
Key Highlights
- India's Growing Influence: India’s entry into the UN-CEBD highlights its growing stature in the international statistical community, emphasizing its commitment to utilizing big data and data science for informed decision-making.
- Strategic Opportunity: This membership allows India to contribute to shaping global standards in leveraging big data for official statistical purposes, especially in tracking Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What is UN-CEBD?
- UN-CEBD is a specialized body under the United Nations, formed in 2014 to explore the benefits and challenges of using big data and data science to strengthen global statistical systems.
- It was established under the United Nations Statistical Commission (UNSC).
- Members: The committee consists of 31 member states (including India) and 16 international organizations.
Key Objectives
- Monitor SDGs: Use big data to track progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Address Data Challenges: Overcome challenges in utilizing non-traditional data sources, such as satellite imagery, Internet of Things (IoT), and private sector data.
- Promote Big Data Use: Encourage practical applications of big data across borders while addressing associated challenges.
Governance and Functions
- Advisory Board: Provides strategic direction, convening four times a year.
- UN Bureau: Manages day-to-day operations.
- Key Functions:
- Strategic Coordination: Vision and direction for utilizing big data in global official statistics.
- Capacity Building: Enhance capabilities through training, technical assistance, and knowledge sharing.
- Public Trust: Establish confidence in using big data for official statistics.
Big Data: Definition and Importance
What is Big Data?
- Big data refers to vast, complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional data management systems.
- It enables enhanced decision-making and improved processes for policy formulation, product development, and governance.
India's Big Data Initiatives
- National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP): Facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Big Data Management Policy: Defines strategies for managing large datasets within government agencies.
- National Data Warehouse on Official Statistics: Centralizes official data for better access and analysis.
The 6Vs of Big Data
- Volume: Large amounts of data.
- Velocity: Speed of data generation and processing.
- Variety: Different types of data.
- Veracity: Accuracy of data.
- Value: Significance of the data.
- Variability: Fluctuations in data.
India’s Role in the UN-CEBD
Contribution to Global Standards
- India's initiatives such as the Data Innovation Lab and the use of satellite imagery and machine learning will be shared with other members, fostering global collaboration in statistical innovations.
- India will contribute to shaping international standards for the use of big data in monitoring SDGs.
Enhancing Statistical Processes
- Modernization of Data: India aims to modernize its statistical processes by incorporating IoT, satellite data, and private-sector data.
- Real-time Insights: Providing policymakers with timely and accurate data to address key socio-economic issues.
- Improving Estimates: Using big data to enhance the accuracy of official statistics, improving governance and policymaking.
Strategic Goals of India's Engagement
- Streamline Statistical Production: Innovation in data collection, processing, and analysis to reduce delays in data availability.
- Improve Decision-Making: Provide real-time, evidence-based insights to policymakers.
- Foster International Collaboration: Share India’s expertise and learn from global best practices to build future-ready statistical systems.
GEAPP and ISA Sign $100 Million Agreement for Solar Projects

- 12 Jan 2025
In News:
The Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet (GEAPP) signed a Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF) agreement with the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to mobilize $100 million for funding high-impact solar energy projects. This collaboration is part of a wider effort to accelerate India's clean energy transition, bridge financing gaps, and enhance the country's energy systems. Along with this agreement, two other key initiatives were announced:
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition)
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge)
These programs aim to address energy transition challenges by fostering scalable, cost-efficient solutions, digitalizing utilities, and supporting innovations for sustainable energy.
Key Features:
- Multi-Donor Trust Fund (MDTF):
- The MDTF aims to raise and deploy $100 million to finance impactful solar energy projects, with ISA driving the strategic direction.
- GEAPP’s Project Management Unit will provide governance, fundraising, and technical expertise to ensure project success.
- The collaboration emphasizes the importance of solar energy in achieving India's clean energy goals.
- DUET (Digitalization of Utilities for Energy Transition):
- Focuses on transforming grid systems by digitalizing grid assets and integrating them with smart sensors.
- Real-time data will help reduce transmission losses and facilitate Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) deployment, assisting in the integration of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) into the grid.
- ENTICE 2.0 (Energy Transitions Innovation Challenge):
- A platform for identifying and scaling innovative solutions to accelerate the clean energy transition, especially within India's growing startup ecosystem.
- Focuses on supporting investable opportunities for energy transition solutions, building on the earlier success of ENTICE 1.0.
Global Impact of GEAPP:
GEAPP, launched with an initial commitment of $464 million, has already funded 130 projects across 40 countries. These projects have impacted over 50 million people, helping reduce 43 million tons of CO2 emissions. The collaboration with ISA is expected to deepen GEAPP's efforts in mobilizing capital to foster clean energy access and tackle climate change.
India’s Clean Energy Transition:
India has already extended electricity access to over 800 million people, but about 2.5% of households still remain unelectrified. Distributed renewable energy, especially solar energy, will play a pivotal role in reaching these underserved populations. India aims for 47 GW of battery energy storage systems by 2032, which will support grid stability and energy access.
Additional Initiatives and Impact:
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS):
- GEAPP has also supported India’s first commercial standalone BESS project, which will provide 24/7 power to over 12,000 low-income customers.
- The project is set to lower electricity tariffs by 55%, benefiting economically disadvantaged communities.
- Strategic Alliances:
- The partnership with ISA and the strategic initiatives like DUET and ENTICE 2.0 aim to further India’s climate and energy goals, bringing renewable energy solutions to underserved regions, and supporting the country's energy security.
Role of GEAPP and ISA:
- GEAPP works to mobilize financing, provide technical expertise, and ensure effective implementation of renewable energy projects globally.
- ISA focuses on solar energy solutions, and with this agreement, it seeks to enhance the solar energy capacity in its member countries, aligning with climate targets.
About GEAPP:
GEAPP is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, philanthropy, technology partners, and financial institutions. Its goal is to transition developing economies to clean energy while enhancing economic growth. It aims to:
- Reduce 4 gigatons of carbon emissions.
- Provide clean energy access to 1 billion people.
- Create 150 million new jobs globally.
UJALA Scheme

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
UJALA scheme completes 10 years, saves ?19,153 crore annually
UJALA Scheme (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch Date: 5th January 2015 by PM Narendra Modi
- Objective:
- To promote energy-efficient LED lighting across India
- To reduce energy consumption, lower electricity bills, and decrease carbon emissions
- Implementing Body: Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), Ministry of Power
- Scheme Relevance: Aims to provide affordable LED bulbs, tube lights, and fans to every household
- Global Recognition: World’s largest zero-subsidy domestic lighting scheme
Key Features:
- Affordability: Subsidized LED bulbs (?70-80), reducing the cost of electricity for households
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs, 50% less than CFLs
- Environmental Impact: Significant reduction in CO? emissions by avoiding millions of tonnes annually
- Market Transformation: Over 36.87 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving approximately ?19,153 crore on electricity bills each year
- Consumer Benefit:
- On-Bill Financing: LED bulbs available for purchase through deferred payment via electricity bills
- Targeted low-income communities through Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
Achievements:
- Energy Savings: 47.9 billion kWh annually
- Cost Savings: ?19,153 crore saved on electricity bills
- Carbon Emission Reduction: 38.7 million tonnes of CO? avoided per year
- Peak Demand Reduction: 9,586 MW reduction in peak electricity demand
- Street Lighting: Over 1.34 crore LED streetlights installed, saving 9,001 million units annually
Key Initiatives:
- GRAM UJALA Scheme (March 2021): Aimed at rural households, providing LED bulbs at ?10 each
- Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP): Aimed at reducing public lighting costs with energy-efficient streetlights
- Encouraging Domestic Manufacturing: Stimulated local LED production, aligning with the "Make in India" mission
- E-Procurement Transparency: Real-time procurement ensuring price reductions and maintaining quality
Impact on Environment:
- Energy Savings & Carbon Footprint: The scheme significantly reduced the carbon footprint by promoting energy-efficient appliances
- Reduction in Household Consumption: Consumers benefit from reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills
New Method to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
A recent breakthrough in agricultural research offers a promising solution to improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) in crops, particularly in rice and Arabidopsis, by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants. This innovative approach provides an environmentally sustainable way to enhance crop yields while minimizing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which have significant ecological and economic drawbacks.
Key Findings and Research Overview:
- Reducing NO Levels: The study, conducted by researchers at the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), demonstrated that by reducing nitric oxide (NO) levels in plants, nitrogen uptake could be significantly improved. This leads to a better NUE, a crucial factor for enhancing crop yield sustainably.
- NUE and Its Importance: NUE refers to the efficiency with which plants use nitrogen for biomass production. Improving NUE allows for higher crop yields with less fertilizer input, reducing costs and minimizing nitrogen-related environmental pollution.
- Traditional Approaches and Their Limitations: Current techniques to improve NUE primarily rely on the use of inorganic nitrogen fertilizers. These methods, though effective, have several downsides:
- They involve high operational costs for farmers.
- Excessive fertilizer use contributes to the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and other pollutants.
- The production of these fertilizers also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the new study proposes a genetic and pharmacological manipulation of NO levels, offering a sustainable alternative to these traditional, resource-heavy methods.
Study Methodology:
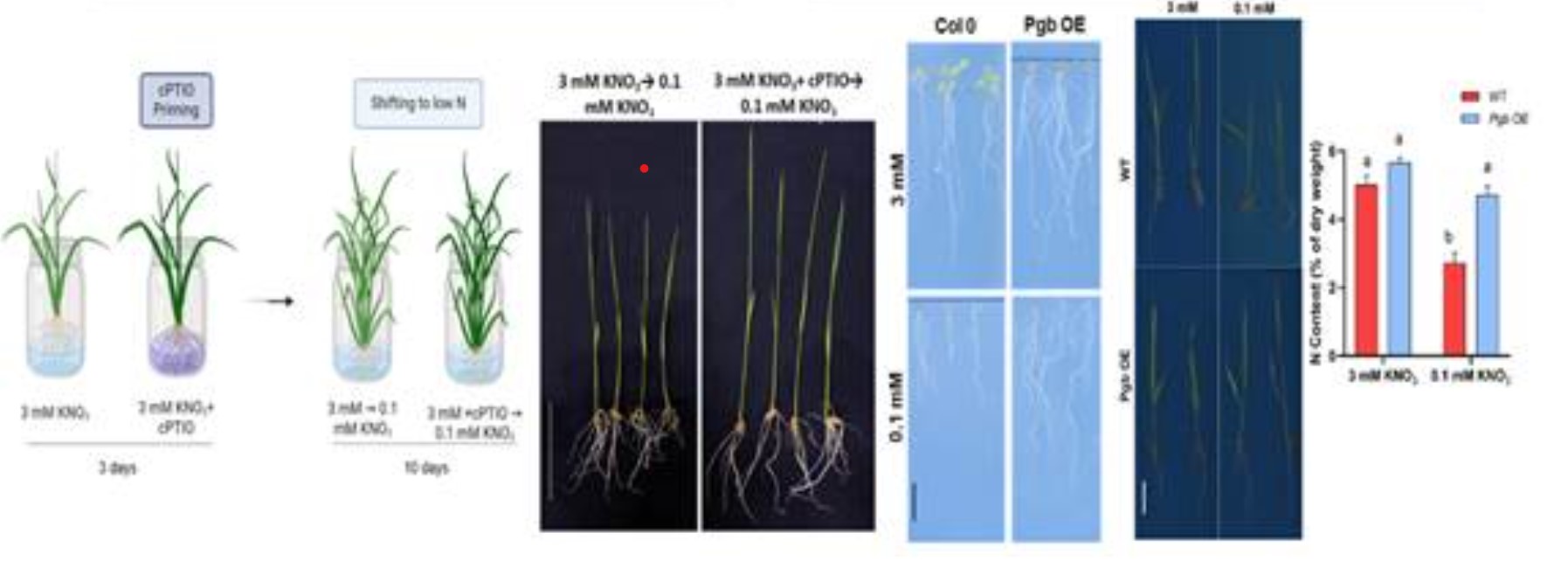
The research team employed both genetic and pharmacological approaches to regulate NO levels in plants:
- Phytoglobin Overexpression: By overexpressing phytoglobin (a natural NO scavenger), the researchers increased the expression of high-affinity nitrate transporters (HATs) like NRT2.1 and NRT2.4. These transporters are essential for efficient nitrogen uptake.
- NO Donor and Scavenger Treatments: Plants were treated with NO donor (SNAP) and NO scavenger (cPTIO) to monitor the effects on NUE.
- Results: The treatment led to more efficient nitrogen uptake, especially under low NO conditions, by enhancing the expression of HATs. This method could increase plant growth and nitrogen utilization without relying on excessive fertilizer use.
Significance and Impact:
This research provides a pathway to enhance crop yield sustainably by addressing one of the most critical challenges in modern agriculture—reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. By modulating NO levels to regulate nitrogen uptake, this approach offers:
- Reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering farmers' operational costs.
- Minimized environmental impact, including lower nitrogen oxide emissions and less nitrogen runoff.
- Improved nitrogen uptake efficiency, ensuring better crop yields, especially under conditions with limited nitrogen availability.
Broader Implications:
- Global Nitrogen Challenges:
- The overuse of nitrogen fertilizers has been a major driver of nitrogen pollution, leading to issues like eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and climate change.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), excessive nitrogen use has worsened environmental conditions globally, while many regions, particularly in low-income countries, suffer from nitrogen depletion, which reduces crop productivity.
- Health and Environmental Risks:
- Nitrogen pollution contributes to health issues like methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) and various long-term diseases.
- Nitrogen compounds also play a role in greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change.
- Future Directions for Sustainable Agriculture:
- This study highlights the need for innovative nitrogen management strategies, integrating both biological and genetic approaches to optimize nitrogen use.
- Research is underway to develop NO scavenging formulations and identify bacteria that could be used in soil to enhance NUE in plants.
- Policy Recommendations:
- Governments should focus on reducing the environmental and health impacts of nitrogen fertilizer production and usage by promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Encouraging biological nitrogen fixation through crops like soybeans and alfalfa, and investing in low-emission fertilizers, can help mitigate nitrogen pollution.
Dr. V. Narayanan Takes Over as ISRO Chairman

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
Dr. V. Narayanan has been appointed as the new Chairman of ISRO and Secretary of the Department of Space (DoS), effective from January 14, 2025, succeeding Dr. S. Somanath.
Background and Career of Dr. V. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan, currently the Director of Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in Thiruvananthapuram, has been a key figure in ISRO since joining in 1984. With a focus on cryogenic propulsion, he has played an instrumental role in developing critical technologies for ISRO's launch vehicles. Notably, his work has contributed to India becoming the sixth country globally capable of building and operationalizing cryogenic engines.
Dr. Narayanan’s career highlights include:
- Cryogenic Technology: Leading the development of cryogenic engines for LVM3 (India's heaviest launch vehicle) and PSLV, which are central to missions like Chandrayaan and Gaganyaan.
- Chandrayaan-2 & Chandrayaan-3: As part of ISRO’s missions to the moon, his contributions were pivotal in rectifying the propulsion system issues post-Chandrayaan-2's hard landing, leading to the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 in August 2023.
- Gaganyaan Mission: Overseeing the development of the propulsion systems for crew and service modules, critical for India’s ambitious human spaceflight program.
Dr. S. Somanath's Legacy:
Dr. S. Somanath, who served as ISRO Chairman and DoS Secretary spearheaded multiple landmark missions, including:
- Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1, and INSAT missions.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Re-usable Launch Vehicle (RLV-LEX), and Gaganyaan abort missions.
- National Space Policy 2023 and fostering partnerships between ISRO and private ventures.
Dr. Somanath’s tenure significantly elevated India’s space capabilities, with Chandrayaan-3 marking a historic milestone in India’s lunar exploration.
Dr. Narayanan’s Role in Upcoming ISRO Missions:
As ISRO Chairman, Dr. Narayanan will oversee several ambitious space missions, including:
- NVS-02: The launch of India's navigation satellite as part of the IRNSS constellation.
- Unmanned Gaganyaan Mission: Leading the uncrewed G-1 flight, a precursor to India's first human spaceflight.
- Indo-US NISAR Satellite: A significant collaborative launch with NASA for earth observation.
Additionally, high-profile projects such as Chandrayaan-4, India’s own space station, and future missions to Mars and Venus are in the pipeline, although not all may occur during his tenure.
Vision for ISRO Under Dr. Narayanan:
Dr. Narayanan aims to expand India’s presence in space, targeting increased global market share, particularly in the space economy, which currently holds 2% of the global space sector. His leadership will focus on:
- Increasing Satellite Capacity: Expanding India’s satellite fleet, which currently stands at 53, to meet growing demands for communication, navigation, and earth observation.
- Private Sector Involvement: Leveraging space sector reforms and collaborating with private players to drive innovation and meet burgeoning satellite needs.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening ties with other space agencies, as ISRO continues to build respect on the global stage.
Upcoming Space Missions and ISRO's Agenda for 2025:
Under Dr. Narayanan's leadership, ISRO has a packed agenda for 2025:
- GSLV Mk-II/IRNSS-1K Mission
- Gaganyaan G-1 Mission (uncrewed flight)
- Chandrayaan-4, Bharatiya Antariksha Station, and Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) preparations.
Dr. Narayanan’s vision aligns with India's broader goals of becoming a dominant player in the global space economy, aspiring to increase its space market share from 2% to 10%.
Flamingo Festival 2025

- 10 Jan 2025
In News:
The Flamingo Festival 2025 took place at Sullurpeta, in Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. It celebrates the arrival of migratory birds, with a focus on flamingos, to the region's key bird habitats, including Pulicat Lake and Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary.
Key Highlights:
- Birdwatching: Over 200 bird species, including flamingos, are expected to flock to the region during this festival.
- Locations: The event spans across five locations:
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary
- B.V. Palem (Pulicat Lake)
- Atakanithippa
- Sri City
- Sullurpeta (site for cultural programs and stalls)
- Collaborations: In association with organizations like the Bombay Natural History Society.
- Focus on Local Community: Local residents of the eco-sensitive zone will be prioritized and supported.
Key Facts on Local Wildlife and Significance:
- Pulicat Lake:
- Location: On the Andhra Pradesh-Tamil Nadu border, with 96% of the lake in Andhra Pradesh.
- Significance: The second-largest brackish water lake in India (after Chilika Lake in Odisha).
- Biodiversity: Critical habitat for migratory birds, including flamingos, and home to diverse flora and fauna.
- Economic Importance: Supports local fisheries and provides livelihood to nearby communities.
- Nelapattu Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: 20 km north of Pulicat Lake.
- Ecological Role: Largest breeding site in Southeast Asia for spot-billed pelicans.
- Biodiversity: 189 bird species, including painted storks and glossy ibises.
- Flora and Fauna: Features Barringtonia swamp forests and southern dry evergreen scrub, critical for biodiversity conservation.
- Symbiotic Relationship with Locals: Guano (bird droppings) from pelicans serves as a natural fertilizer for local agriculture, benefiting the farmers.
Flamingo Facts:
- Species: India hosts two flamingo species:
- Greater Flamingo (larger size, pale pink)
- Lesser Flamingo (smaller size, bright pink)
- Behavior: Nomadic and social birds, found in large flocks.
- Coloration: Flamingos' pink color comes from carotenoids in their diet, which are broken down and absorbed into their bodies.
Environmental & Economic Impact: The festival, apart from being a celebration of migratory birds, plays a vital role in:
- Eco-tourism development
- Biodiversity conservation
Local community engagement by highlighting sustainable tourism practices and supporting local livelihoods through eco-friendly initiatives like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
Bharatpol

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated the ‘Bharatpol’ portal, which aims to streamline international cooperation for law investigating agencies.
Key Highlights:
Bharatpol is a newly launched portal developed by the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India to facilitate faster and more efficient international cooperation between Indian law enforcement agencies and Interpol. It was inaugurated by Union Home Minister Amit Shah, to streamline the process of sharing criminal intelligence and coordinating efforts in transnational crimes like cybercrime, human trafficking, drug trafficking, financial fraud, and organized crime.
The portal aims to address the current challenges in international collaboration, which previously relied on slower communication methods such as letters, emails, and faxes, often leading to delays in investigations.
Key Features and Functions of Bharatpol:
- Unified Platform: Bharatpol integrates CBI as the National Central Bureau (NCB-New Delhi) with all Indian law enforcement agencies, from state police forces to higher authorities. This allows better coordination and quicker access to international resources.
- Simplified Request Mechanism: The portal provides a standardized method for frontline police officers to request international assistance from Interpol member countries, using templates for efficiency.
- Rapid Information Dissemination: Bharatpol enables the CBI to quickly share criminal intelligence and other pertinent information with law enforcement agencies across India, helping to tackle international criminal activities in real-time.
- Increase in Utilization of Interpol Notices: The portal makes it easier for Indian law enforcement agencies to issue and manage Red Corner Notices and other Interpol notices, which are essential tools in tracking criminals globally.
- Capacity Building and Training: Bharatpol includes resources for training law enforcement personnel, improving their ability to conduct investigations abroad and seek foreign assistance via Interpol.
How Bharatpol Works:
- Key Modules of Bharatpol:
- Connect: Facilitates the integration of Indian agencies with the Interpol NCB-New Delhi, creating a seamless communication channel.
- INTERPOL Notices: Supports the rapid issuance and processing of Interpol Notices like Red Corner Notices to locate criminals globally.
- References: Enables Indian agencies to seek and offer international assistance for investigations.
- Broadcast: Ensures quick availability of assistance requests from Interpol member countries, facilitating faster responses.
- Resources: Manages document exchanges and training materials to support the capacity-building efforts of law enforcement agencies.
Potential Benefits of Bharatpol:
- Enhanced Coordination: Bharatpol facilitates better collaboration between central, state, and Union Territory agencies, allowing for a more structured and efficient approach to international crime investigations.
- Faster Investigation: Real-time sharing of information and the use of Interpol notices will help in tracking criminals and criminal activities both in India and abroad.
- Simplified Extradition Process: By streamlining international communication, Bharatpol will assist in expediting the extradition of criminals to India for prosecution.
- Support for Transnational Crime Prevention: It will help address growing threats such as cybercrime, human trafficking, and organized crime by improving the ability of Indian law enforcement to collaborate globally.
National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)

- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
- Union Minister Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan urges states to accelerate efforts under the National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) to enhance domestic production of edible oils and reduce reliance on imports.
Key Facts Regarding the NMEO-OP Scheme:
About the Scheme:
- Objective: Enhance domestic production of crude palm oil (CPO) and reduce India's dependence on edible oil imports.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Focuses on expanding oil palm cultivation in India.
Key Targets:
- Area Expansion: Aim to cover an additional 6.5 lakh hectares by 2025-26, reaching a total of 10 lakh hectares.
- Production Increase: CPO production is targeted to rise from 0.27 lakh tonnes (2019-20) to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26, and further to 28 lakh tonnes by 2029-30.
- Per-Capita Consumption: Maintain a consumption level of 19 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
Focus Regions:
- Special Focus: North-Eastern States and Andaman & Nicobar Islands for oil palm cultivation and CPO production.
Key Features:
- Viability Price (VP) Mechanism: Aims to protect farmers from market volatility by providing price assurance. Payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- Increased Assistance:
- Assistance for planting material increased from Rs 12,000/ha to Rs 29,000/ha.
- Special assistance of Rs 250 per plant for rejuvenating old gardens.
- Regional Support:
- For North-East and Andaman, an additional 2% of the CPO price is borne by the government to ensure fair payments to farmers.
- Special provisions for half-moon terrace cultivation, bio-fencing, and land clearance for integrated farming.
Oil Palm Cultivation:
- Origin: Native to the tropical rainforests of West Africa, oil palm is a new crop in India with high oil-yielding potential.
- Oil Yield: Oil palm produces five times the yield of traditional oilseeds per hectare.
- Types of Oil Produced:
- Palm Oil: Extracted from the mesocarp (fruit's fleshy part), containing 45-55% oil.
- Palm Kernel Oil: Derived from the kernel, used in lauric oils.
- Major States for Cultivation: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala (98% of total production).
- Other Key States: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Nagaland.
India's Oil Palm Potential:
- Cultivated Area: India currently has 3.70 lakh hectares under oil palm cultivation.
- Total Potential Area: Around 28 lakh hectares.
- Imports: India is the world's largest palm oil importer, with imports of 9.2 million tonnes in 2023-24, accounting for 60% of total edible oil imports. The country primarily imports from Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Z-Morh Tunnel
- 11 Jan 2025
In News:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Z-Morh Tunnel at Sonamarg, which has now been renamed the Sonamarg Tunnel.
Key Takeaways:
- A 6.4-km bi-directional tunnel with an approach road of 5.6 km, Z-Morh connects the Sonamarg health resort with Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- The tunnel has acquired its name for the Z-shaped road stretch that was previously at the place where the tunnel is being constructed.
- The Z-Morh project was initiated by the Border Roads Organisation in 2012. Although the BRO awarded the construction contract to Tunnelway Ltd, the project was subsequently taken over by National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
Significance
Strategic Importance
- Connectivity: Provides all-weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh, ensuring year-round access.
- Military Significance:
- Critical for rapid deployment of Indian Armed Forces to Ladakh’s border areas, particularly in the context of tensions with Pakistan and China.
- Reduces dependence on air transport, lowering costs and increasing the longevity of the Indian Air Force’s aircraft.
- Adjacent Projects:
- Zojila Tunnel: An even more crucial project connecting Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion by December 2026 (extended to 2030). This will bypass the avalanche-prone Zojila Pass.
- Srinagar-Leh Highway: The Z-Morh Tunnel supports the key Srinagar-Leh route, which is important for defence logistics and trade.
Economic Significance
- Tourism:
- Sonamarg, known as the "Meadow of Gold," will benefit from year-round accessibility, boosting tourism.
- Local businesses that rely on seasonal tourist traffic will have consistent revenue flow.
- Trade and Agriculture:
- Reduced travel time and improved road safety will benefit farmers and traders, especially for those transporting goods between Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Facilitates increased investment and economic growth in the region.
Broader Infrastructure Projects in Jammu & Kashmir
Several key infrastructure projects are contributing to regional development:
- Zojila Tunnel
- Cost: ?6,800 crore
- Length: 13 km tunnel, bypassing Zojila Pass.
- Completion: Expected by 2030.
- Strategic Importance: Provides all-weather connectivity to Ladakh.
- Srinagar Semi-Ring Road
- Cost: ?2,919 crore
- Objective: Relieve traffic congestion in five districts, including Srinagar.
- Delay: New completion date is June 2025.
- Hydroelectric Power Projects:
- Ratle HE Project: 850 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar district.
- Kwar HE Project: 540 MW, in Kishtwar.
- Pakal Dul HE Project: 1,000 MW, on the Marusudar River, Kishtwar.
- Kiru HE Project: 624 MW, on Chenab River, Kishtwar.
- Strategic Relevance: These projects will enhance energy security and contribute to the region’s power grid.
Bhashini Initiative
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
e-Shram Portal, which aims to provide social security benefits to unorganised workers, has been upgraded with multilingual functionality for all 22 scheduled languages of India. This development, supported by the Bhashini Initiative, ensures that unorganised workers from diverse linguistic backgrounds can access the portal more easily and benefit from government welfare schemes.
About Bhashini Initiative:
- Launched in: July 2022
- Developed by: Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
- Aim: To eliminate language barriers in accessing digital services by making AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools publicly available.
Key Features:
- Local Language Translation: Bhashini offers AI-powered translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages to ensure that digital platforms like e-Shram are accessible to everyone in their native languages.
- Open AI and NLP Resources: These tools are made available to Indian MSMEs, startups, and innovators to create a more inclusive digital ecosystem.
- Crowdsourcing Platform (Bhashadaan): A platform for people to contribute to building linguistic datasets through initiatives like Suno India, Likho India, Bolo India, and Dekho India, furthering language diversity in digital services.
- National Digital Public Platform: Aimed at providing universal access to digital content in all Indian languages, facilitating smoother communication across regions.
e-Shram Portal: A One-Stop Solution for Unorganised Workers
- Purpose: The e-Shram portal was created to provide unorganised workers with access to social security benefits and welfare schemes.
Recent Upgrade:
- Multilingual Functionality: The portal has now been upgraded to support 22 scheduled languages, making it more inclusive and user-friendly for workers who speak various regional languages.
- Previous Version: Previously, the portal was only available in English, Hindi, Kannada, and Marathi. The integration of 22 languages is a significant improvement, enabling broader participation.
Importance of the e-Shram Portal for Unorganised Workers:
- Welfare Access: The portal provides access to government schemes designed for the welfare, livelihood, and well-being of unorganised workers, including gig and platform workers and building and construction workers.
- Integration of Social Security Schemes:
- As of now, the portal facilitates access to 12 government schemes, with plans to integrate even more, including state-level programs.
- Future plans include launching a mobile app, a single application form, and the integration of payment gateways for faster disbursement of benefits.
AI-Driven Inclusive Development and Economic Transformation

- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
IndiaAI, under the Digital India Corporation, has partnered with Microsoft to advance AI adoption in India for inclusive development and economic transformation. The collaboration focuses on skilling, innovation, AI safety, and responsible AI development, with a goal of fostering AI innovation across India, particularly in underserved rural and urban areas.
Key Highlights:
- Training 500,000 Individuals by 2026:
- Target Audience: Students, educators, developers, government officials, and women entrepreneurs.
- Goal: Empower these groups with foundational and advanced AI skills for economic opportunities and digital transformation.
- AI Catalysts (Centers of Excellence):
- Establishment of AI hubs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities to foster rural AI innovation.
- Objective to equip 100,000 AI innovators and developers through hackathons, community building, and creating an AI marketplace.
- AI Productivity Labs:
- Set up in 20 National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across 10 states.
- Focus on training 20,000 educators and providing AI education to 100,000 students in 200 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- Support for Startups:
- Microsoft’s Founders Hub program will provide Azure credits, business resources, and mentorship to 1,000 AI startups in India, boosting innovation and growth in the Indian startup ecosystem.
- Development of Indic Language Models:
- Work on creating foundational AI models with support for Indic languages to address India’s linguistic diversity and cultural needs.
- AI Safety Institute:
- Focus on building frameworks, standards, and evaluation metrics for responsible AI development.
- Support for the creation of an AI Safety Institute in India to promote ethical and safe AI practices.
- Infrastructure & Research:
- Microsoft will also focus on enhancing cloud infrastructure and support for AI research through Microsoft Research India.
- AI-driven solutions will be developed for critical sectors like healthcare, education, and agriculture.
Investment and Strategic Goals:
- $3 Billion Investment:
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- Building scalable infrastructure for AI applications.
- Enhancing cloud services and AI capabilities.
- Establishing new data centers across India, supporting the AI-first agenda.
- Microsoft has pledged $3 billion to expand AI and cloud infrastructure in India over the next 2 years. This investment will focus on:
- AI Skill Development:
- 10 million people will be trained over the next five years in AI skills, empowering the Indian workforce to adapt to AI technologies, driving job creation and economic growth.
- AI in India’s Economy:
- India aims to become a global leader in AI, with AI-powered solutions contributing to diverse sectors like finance, e-commerce, and manufacturing.
- Focus on economic growth through AI-powered industries and fostering entrepreneurship in underserved communities.
AI Technologies and Applications:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves machines performing tasks that require human intelligence like decision-making, problem-solving, and learning from data.
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems improve through data without being explicitly programmed.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI systems understand and respond to human language.
- Computer Vision: AI systems analyze and interpret visual information.
- Robotics: AI powers automated tasks through robots in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Cloud Infrastructure enables the scaling of AI systems:
- Cloud Computing provides on-demand access to computing power, essential for AI tasks requiring large amounts of data and processing power.
- Data Centers host AI models and data, and cloud services such as Microsoft Azure will support AI startups and businesses.
Expected Impact and Benefits:
- Inclusive AI Development: Focus on empowering women, students, and rural innovators to bridge the digital divide and promote economic empowerment.
- Startup Ecosystem: The collaboration will foster a robust AI startup ecosystem, promoting innovation and entrepreneurship through AI tools, Azure credits, and mentorship.
- Skill Development & Education: AI-driven skill training initiatives will prepare millions of individuals for the jobs of the future, particularly in the AI-driven economy, and support education reform.
- AI for Critical Sectors: Development of AI-enabled solutions to address challenges in sectors such as healthcare, education, and agriculture, driving social impact and economic growth.
Miyawaki Technique
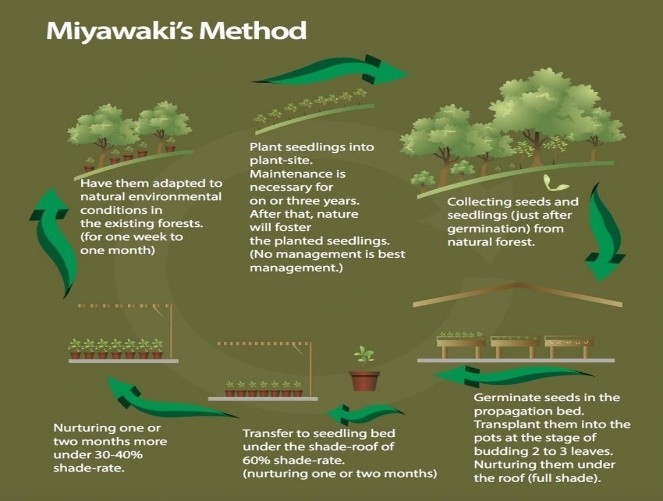
- 09 Jan 2025
In News:
- Prayagraj Municipal Corporation has successfully transformed over 56,000 square meters of garbage dumps and barren lands into lush green forests using the Miyawaki Technique over the past two years, as part of environmental conservation efforts in preparation for Mahakumbh 2025.
About Miyawaki Technique:
- Origin: Developed by Akira Miyawaki, a Japanese botanist, in the 1970s to create dense and fast-growing forests.
- Key Features:
- Dense Planting: Trees and shrubs are planted close together, often using native species.
- Accelerated Growth: Trees grow 10 times faster than in traditional forests.
- Soil Restoration: Improves soil fertility and promotes natural regeneration.
- Biodiversity Boost: Supports a variety of flora and fauna by mimicking natural ecosystems.
- Significance:
- Urban Reforestation: Converts barren or polluted lands into green spaces.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduces air and water pollution.
- Absorbs carbon and helps combat climate change.
- Lowers temperatures by 4-7°C.
- Sustainability: Prevents soil erosion and promotes long-term ecological balance.
Miyawaki Forests in Prayagraj:
- Achievements:
- Over 56,000 square meters of land converted into dense forests using the Miyawaki technique over the last two years.
- The project aims to create oxygen banks in preparation for the Mahakumbh 2025 and enhance air quality for millions of expected visitors.
- Plantations:
- 55,800 square meters of area developed across 10+ locations in Prayagraj.
- Largest plantation: 1.2 lakh trees in Naini industrial area.
- 27,000 trees planted in Baswar after cleaning the city's largest garbage dump.
- Environmental Impact:
- The plantations are helping to reduce dust, dirt, and foul odors, thus improving air quality.
- Temperature regulation: The dense forests can lower temperatures by 4 to 7 degrees Celsius.
- Biodiversity and Soil Fertility: Accelerated growth of trees boosts biodiversity and improves soil fertility.
- Tree Species Planted:
- Mango, Mahua, Neem, Peepal, Tamarind, Arjuna, Teak, Amla.
- Ornamental and medicinal plants like Hibiscus, Kadamba, Gulmohar, etc.
- Other species include Sheesham, Bamboo, Lemon, Drumstick (Sahjan), and Tecoma.
Benefits of Miyawaki Forests:
- Air and Water Pollution Reduction: Trees absorb carbon, purify air, and improve water quality.
- Temperature Control: The forests help in reducing urban heat islands, lowering the temperature during hot months.
- Soil Conservation: The dense forests prevent soil erosion and promote the regeneration of the natural ecosystem.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: The technique supports a rich variety of species, improving ecological balance.
Anji Khad Bridge

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
The Indian Railways has unveiled a monumental engineering achievement with the completion of the Anji Khad Bridge, India’s first cable-stayed rail bridge.
Overview:
- The Anji Khad Bridge is India's first cable-stayed rail bridge, located in Jammu and Kashmir’s Reasi district.
- It is a key part of the Udhampur-Srinagar-Baramulla Rail Link (USBRL) project aimed at enhancing connectivity between Jammu and Kashmir and the rest of India.
- The bridge crosses the Anji River, a tributary of the Chenab River, and is expected to transform regional transport, boost tourism, and promote economic growth.
Key Features:
- Dimensions:
- Total length: 725.5 meters.
- Main Pylon Height: 193 meters from the foundation, standing 331 meters above the riverbed.
- The bridge is designed for train speeds of up to 100 km/h and can withstand wind speeds of up to 213 km/h.
- Structure and Design:
- Asymmetrical cable-stayed design supported by 96 cables with varying lengths (82 to 295 meters).
- The structure includes:
- A 120-meter approach viaduct on the Reasi side.
- A 38-meter approach bridge on the Katra side.
- A 473.25-meter cable-stayed portion crossing the valley.
- A 94.25-meter central embankment linking the main bridge to the approach viaduct.
- Construction Techniques:
- Used advanced construction techniques such as DOKA Jump Form Shuttering, Pump Concreting, and Tower Crane Technique to enhance safety and reduce construction time by 30%.
- A 40-ton tower crane imported from Spain was employed for operations at great heights.
- The project utilized site-specific investigations by IIT Roorkee and IIT Delhi due to the region’s complex geological and seismic conditions.
- Engineering Challenges:
- The bridge had to be constructed in the difficult Himalayan terrain, with fragile geological features such as faults and thrusts.
- Seismic activity in the region required additional precautions in the design and construction process.
- Safety and Monitoring:
- Equipped with an integrated monitoring system that includes multiple sensors to ensure the structural health of the bridge during operation.
Importance and Impact:
- Connectivity: The bridge will significantly improve connectivity between Katra and Reasi, ensuring faster rail travel and linking the Kashmir Valley with the rest of India.
- Tourism and Economic Growth: Expected to boost tourism and economic development by improving access to the region, attracting visitors, and facilitating smoother transportation of goods and services.
- Sustainability: The bridge's design ensures it remains safe under extreme weather conditions, offering long-term reliability for the Indian Railways network.
Collaboration and International Expertise:
- The design and supervision were handled by ITALFERR (Italy), with proof-checking conducted by COWI (UK).
- The project combines Indian engineering codes with Eurocodes, adhering to international standards for structural integrity.
Section 479 of the BNSS 2023

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
Centre urges states, UTs to ensure undertrial prisoner relief in jails.
Key Highlights:
- Objective: The MHA has urged states and Union Territories (UTs) to implement provisions of Section 479 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) 2023 to provide relief to undertrial prisoners (UTPs) in jails. This initiative aims to address issues such as long detention and overcrowding in prisons.
Key Provisions of Section 479 of BNSS, 2023
- Purpose: To offer relief to undertrial prisoners by mandating their release on bail or bond under specific conditions.
- Key Provisions:
- Subsection (1):
- Release on Bail: UTPs who have served half the maximum sentence for their offense (except offenses punishable by death or life imprisonment) are eligible for release on bail.
- Release on Bond for First-Time Offenders: First-time offenders, who have served one-third of the maximum sentence, are eligible for release on bond by the court.
- Subsection (3):
- Mandatory Application: It is the responsibility of the prison superintendent to apply to the concerned court for the release of eligible prisoners on bail or bond.
- Subsection (1):
- Superintendent’s Role:
- Prison superintendents are mandated to ensure timely applications for bail or bond are filed for eligible UTPs.
Implementation and Reporting
- MHA’s Advisory:
- On January 1, the MHA issued a letter to the Chief Secretaries, Director Generals, and Inspectors General of prisons in all states and UTs to ensure compliance with the provisions of Section 479 of BNSS.
- States and UTs were instructed to report the status of implementation in a prescribed format starting from January 1, 2025.
- Data to be Reported:
- First-Time UTPs: Number of first-time UTPs who have served one-third of their maximum sentence.
- Court Applications: Number of applications for bail filed by jail superintendents.
- Release on Bail: Number of UTPs released on bond or bail after meeting the eligibility criteria.
- Other UTPs: Number of UTPs who have completed half of their sentence, and the number of applications filed for their release.
- MHA’s Campaign:
- Launched on Constitution Day (November 26), this campaign encouraged states and UTs to identify eligible prisoners and file their bail applications, thus helping to reduce overcrowding in prisons and mitigate long-term detention.
Background and Context
- Why Section 479?
- Section 479 aims to reduce the prolonged detention of undertrials, some of whom may have already served significant portions of their maximum sentences. This will not only alleviate overcrowding in prisons but also expedite justice for prisoners who have spent extended periods in jail awaiting trial.
- Earlier MHA Initiatives:
- Prior to this directive, the MHA had issued an advisory on October 16, 2024, encouraging states and UTs to implement Section 479. A special push was also made during Constitution Day to move applications for the release of eligible prisoners.
- Expected Outcome:
- The measures are expected to significantly ease the challenges of overcrowded jails and provide timely relief to undertrials, especially first-time offenders. By enforcing these provisions, the government seeks to improve the judicial process for UTPs and contribute to a more effective and humane criminal justice system.
Sonobuoys

- 08 Jan 2025
In News:
India and the U.S. have announced cooperation on the co-production of U.S. sonobuoys to enhance Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA) for the Indian Navy. This technology is vital for tracking submarines and strengthening defense capabilities, particularly in the Indian Ocean region amidst growing Chinese naval presence.
This partnership is a key step in deepening defense cooperation under the U.S.-India Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), launched in May 2022, and will contribute to strengthening both countries’ defense industrial bases.
About Sonobuoys
- What They Are:
- Sonobuoys are expendable sonar devices used for anti-submarine warfare and underwater acoustic research.
- Typically, small (13 cm in diameter and 91 cm in length), they are designed for deployment from aircraft or ships to detect submarines in deep waters.
- Working Principles:
- Deployment: Dropped from aircraft or ships, they activate upon water impact.
- Surface Float: Equipped with inflatable floats and radio transmitters to communicate with tracking platforms on the surface.
- Sensors: Hydrophones descend to selected depths, capturing underwater acoustic signals.
- Data Communication: Transmit acoustic data via Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF) radios to operators on aircraft or ships.
- Types of Sonobuoys:
- Active Sonobuoys: Emit sound energy and receive echoes, transmitting the data back to operators.
- Passive Sonobuoys: Only listen for underwater sounds from submarines or ships and relay the information back.
- Special Purpose Sonobuoys: Measure environmental data like water temperature and ambient noise.
- Other Applications:
- Beyond anti-submarine warfare, sonobuoys are used for environmental research, including studying marine life such as whales.
Co-production of Sonobuoys: India-U.S. Collaboration
- Manufacturing Agreement:
- Ultra Maritime (U.S.) and Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL) have entered into discussions to co-produce U.S. sonobuoys, in line with India’s "Make in India" initiative.
- The production will follow U.S. Navy standards, with manufacturing split between the U.S. and India.
- The focus will also be on developing bespoke technologies to optimize sonobuoy performance in the unique acoustic environment of the Indian Ocean.
- Interoperability:
- The sonobuoys co-produced in India will be interoperable between U.S. Navy, Indian Navy, and allied aircraft such as P-8, MH-60R, and MQ-9B Sea Guardian.
- This ensures seamless integration and compatibility with naval assets from the U.S., India, Japan, and Australia, especially given the Quad's strategic naval exercises like Malabar.
- Production Location:
- The sonobuoys will be manufactured at BDL's facilities in Visakhapatnam, with a focus on meeting the Indian Navy’s operational demands.
Strategic and Defense Context
- U.S. and Indian Naval Cooperation:
- India has increasingly acquired military platforms from the U.S., such as the P-8I maritime patrol aircraft, MH-60R helicopters, and MQ-9 drones. These assets are also used by other Quad nations like Australia and Japan, highlighting the importance of interoperability and shared defense capabilities in the region.
- Enhanced Maritime Domain Awareness:
- With China’s growing naval presence in the Indian Ocean, the cooperation on sonobuoys aligns with India’s strategic priority of enhancing maritime domain awareness (MDA) and Undersea Domain Awareness (UDA), which are critical for national security.
- Future Plans:
- India has also signed a $3.5 billion contract for 31 MQ-9B drones, enhancing its surveillance capabilities for maritime and other defense applications. Deliveries of these drones will begin in 2029, further boosting India’s defense readiness in the region.
ISRO's Cowpea Seed Germination Experiment in Space
- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
ISRO successfully germinated cowpea seeds (Vigna unguiculata) in microgravity conditions during the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission. This experiment, conducted using the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS), marks a significant advancement in space-based agricultural research.
Details of the Experiment:
- Mission Overview:
- The experiment took place aboard the PSLV-C60 POEM-4 mission, which included 24 sophisticated payloads.
- The CROPS payload, developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), is an automated system designed to study seed germination and plant survival in microgravity environments.
- Methodology:
- Eight cowpea seeds were placed in a controlled, closed-box system, equipped with temperature regulation and advanced monitoring tools.
- The system tracked plant development using high-definition cameras, sensors for oxygen, carbon dioxide, humidity, temperature, and soil moisture levels.
- Significance:
- The cowpea seeds successfully germinated within four days, with leaf development expected soon.
- This breakthrough in space agriculture is vital for the development of sustainable farming techniques in space, especially for long-term space missions and human settlements on other celestial bodies.
Broader Implications:
- Space Agriculture:
- The successful germination of cowpea seeds sets the foundation for growing crops in space, essential for self-sufficient habitats in space.
- This experiment is a significant step towards sustainable space agriculture, reducing the need for Earth-based resources in extraterrestrial environments.
- Future Missions:
- The experiment's success is pivotal for future missions aimed at Moon or Mars exploration, where space-grown crops will be necessary to support human life.
- ISRO’s achievement reinforces its growing expertise in space research and highlights the potential for international collaboration in space exploration and agricultural science.
About Cowpea Seeds:
- Cowpea (also known as lobia in Hindi) is a robust, nutrient-rich legume, ideal for agricultural research due to its adaptability and resilience in varied environments.
- The successful experiment with cowpea seeds holds promise for future extraterrestrial agriculture, ensuring food security for astronauts on long-duration missions.
NCC Republic Day Camp 2025

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar’s Address at NCC Republic Day Camp 2025.
Key Highlights
- PanchPran as the Foundation of India’s Transformation:
- PanchPran (Five Resolutions) were outlined by Vice-President Jagdeep Dhankhar as the guiding principles for India’s future development.
- These principles are fundamental to India’s national progress, ensuring a balanced approach to development and societal transformation.
The Five Principles of PanchPran:
- Social Harmony:
- Aims to strengthen unity by leveraging India’s diverse cultures and traditions as sources of national strength.
- Promotes inclusiveness and national integration.
- Family Enlightenment:
- Emphasizes the importance of families in nurturing patriotic and moral values.
- Acts as a foundation for creating a cohesive, enlightened society that respects traditions.
- Environmental Consciousness:
- Advocates for sustainable development and conservation of nature.
- Focuses on protecting natural resources for future generations.
- Swadeshi (Self-reliance):
- Encourages promoting indigenous products as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Strengthens India’s self-reliance by focusing on domestic production and consumption.
- Civic Duties:
- Instills responsibility among citizens to actively contribute to the nation’s growth.
- Encourages participation in community and national development activities.
National Cadet Corps (NCC)
- The National Cadet Corps (NCC) is the youth wing of the Indian Armed Forces, established in 1948.
- It is open to school and college students on a voluntary basis and is a Tri-Services organization, comprising the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Purpose and Training:
- Cadets undergo basic military training in small arms and drills.
- Officers and cadets have no obligation for active military service after completing their courses.
- Historical Background:
- Traces its origins back to the ‘University Corps’ formed under the Indian Defence Act of 1917 to address shortages in Army personnel.
- Structure and Leadership:
- The NCC is headed by a Director General (DG), a senior officer with a 3-star rank.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Disposal of Toxic Waste from Union Carbide Factory (Bhopal)

- 07 Jan 2025
In News:
The Madhya Pradesh government has begun disposing of the 337 tonnes of toxic waste from the premises of Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) in Bhopal, 40 years after the gas tragedy.
Key Highlights:
- Packing and Transportation:
- Waste is packed in airtight containers under the supervision of the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board (MPPCB).
- 12 specially designed airtight containers are being used for packing, and each container will be loaded onto trucks for transport.
- The waste movement will be escorted with a green corridor of about 250 kilometers.
- Incineration Process:
- The waste will undergo incineration in Pithampur, with residue stored in a two-layer membrane landfill to prevent contamination.
- A trial incineration of 10 tonnes of the waste was done in 2015 with no harmful effects, and results were submitted to the High Court.
Bhopal Gas Tragedy: A Historical Overview
- About the Tragedy:
- In 1984, a chemical leak at the Union Carbide pesticide plant released methyl isocyanate (MIC), leading to one of the worst industrial disasters in history.
- The leak was caused by a failed maintenance attempt and malfunctioning safety systems.
- Immediate effects included respiratory issues, eye problems, and abdominal pain, while long-term effects included chronic lung conditions, genetic abnormalities, and higher infant mortality rates.
- Legal and Government Response:
- In 1985, the Indian government passed the Bhopal Gas Leak Disaster Act to represent victims in legal claims.
- UCIL initially offered USD 5 million, while the Indian government demanded USD 3.3 billion. The case was settled in 1989 for USD 470 million.
- In 2010, seven Indian nationals were convicted for causing death by negligence, but were released on bail.
Hazardous Waste Management in India
- Definition and Types:
- Hazardous waste refers to waste that poses significant risks due to toxicity, reactivity, or corrosiveness.
- Common sources include chemical production, outdated technologies, and wastewater treatment.
- Regulations and Disposal Methods:
- The Environment Protection Act (1986) and the Basel Convention (1992) govern hazardous waste management in India.
- India generates about 7.66 million tonnes of hazardous waste annually, with the majority being landfillable (44.3%) and recyclable (47.2%).
- Disposal methods include incineration, co-processing in cement plants, and material/energy recovery.
- Challenges in Hazardous Waste Management:
- Inadequate treatment technologies, especially in small and medium industries.
- The need for stricter compliance with waste management laws and more efficient remediation of hazardous sites like Bhopal.
Great Nicobar Island Development Project
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
An international cruise terminal to facilitate a “global” port-led city, “high-end” tourism infrastructure, and a ship-breaking yard are among the new additions to the ?72,000 crore mega-infrastructure project in Great Nicobar Island proposed by the Union Shipping Ministry.
Overview of the Project:
- The Great Nicobar Island Development Project is a ?72,000-crore initiative to transform the southernmost island of India into a hub for defense, logistics, commerce, eco-tourism, and infrastructure development.
- It is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Ltd (ANIIDCO) over 16,610 hectares of land.
- The project includes multiple components like an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), an international airport, greenfield cities, a mass rapid transport system, and a free trade zone.
Key Proposed Developments:
- International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT): To make Great Nicobar a key player in global maritime trade.
- Greenfield International Airport: To improve connectivity and serve as a strategic airport.
- Greenfield Cities: New urban settlements to support the infrastructure.
- Coastal Mass Rapid Transport System: An advanced transportation network along the coast.
- Free Trade Zone: To facilitate international trade activities.
- International Cruise Terminal (new addition): To attract global tourists and facilitate cruise tourism.
- Ship Breaking Yard (new addition): To establish a facility for ship building and breaking.
Geographical and Ecological Context:
- Great Nicobar Island is the largest island in the Nicobar group, located at the southern tip of India. It is covered in rainforests and hosts diverse species, including endangered ones like the leatherback turtle and the Nicobar megapode.
- The island's ecosystem is rich in biodiversity, with extensive mangroves, coral reefs, and rainforests.
Significance of the Project:
- Geo-strategic Importance: The island’s location near the Malacca Strait offers a strategic maritime advantage, enhancing India’s global maritime presence.
- National Security: With increasing Chinese influence in the region, the project aims to strengthen India's maritime security.
- Economic Growth: The ICTT and other infrastructure will boost economic activities, making the region a vital trade hub.
- Job Creation: The development will lead to numerous job opportunities for locals, especially in sectors like tourism, ports, and transport.
- Tourism Development: With eco-tourism at its core, the project is expected to generate substantial income through tourism, improving the local economy.
- Social Infrastructure: It will lead to improvements in healthcare, education, and digital services through initiatives like telemedicine and tele-education.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
Five years after the COVID pandemic, China is experiencing a surge in HMPV cases, particularly in children under 14 years of age
Key Highlights:
- What is HMPV?
- A respiratory virus from the Pneumoviridae family, discovered in 2001.
- Causes both upper and lower respiratory tract infections, similar to the common cold or flu.
- Origin and Discovery:
- Identified in the Netherlands in 2001 through genomic sequencing of respiratory samples.
- Risk Groups:
- Children under 5 years, especially infants.
- Elderly individuals (65+).
- Immunocompromised persons and those with chronic respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma).
- Symptoms:
- Common: Cough, runny nose, fever, sore throat.
- Severe: Wheezing, shortness of breath, potentially leading to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Incubation Period: 3-6 days.
- Transmission:
- Spread via droplets from coughing or sneezing.
- Close contact (e.g., handshakes, hugs).
- Contaminated surfaces, touching face after contact.
- Treatment:
- No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine available.
- Symptom management: hydration, rest, OTC medications for fever and congestion.
- Severe cases may require hospitalization (oxygen therapy, IV fluids).
- Diagnosis:
- NAATs (Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests): Detect viral genetic material.
- Antigen-based immunoassays: For severe cases or outbreaks.
- Complications:
- Can lead to bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, asthma, or COPD flare-ups.
- Risk of ear infections (otitis media) in some cases.
- Prevention:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing, covering coughs/sneezes, maintaining personal hygiene.
- Physical Distancing: Avoid close contact, wear masks in crowded settings.
- Caution for Vulnerable Groups: Extra care for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Global Situation:
- China: Experiencing a rise in HMPV cases, particularly among children under 14 years.
- India: No reported cases yet, but monitoring the situation closely.
Key Facts:
- HMPV is a winter virus commonly seen in colder months (winter and early spring).
- Estimated 10%-12% of respiratory illnesses in children are caused by HMPV.
- The virus is part of the Pneumoviridae family, alongside respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), measles, and mumps.
No specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV; antibiotics are ineffective.
National Sports Awards 2024
- 06 Jan 2025
In News:
The National Sports Awards 2024 were recently announced by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports to celebrate excellence in Indian sports.
Key Highlights:
Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award
- This is India's highest sporting honor, renamed in 2021 after hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.
- It’s awarded for exceptional performance in sports over a four-year period.
- 2024 Winners:
- Gukesh D (Chess)
- Harmanpreet Singh (Hockey)
- Praveen Kumar (Para-Athletics)
- Manu Bhaker (Shooting)
- The award includes a cash prize of Rs 25 lakh.
Arjuna Award
- Recognizes outstanding performance in sports over the previous four years and attributes like leadership, discipline, and sportsmanship.
- 2024 Winners: Various athletes across multiple disciplines received this honor.
Arjuna Award (Lifetime)
- Given to retired athletes who have not only excelled during their careers but also contributed to the promotion of sports post-retirement.
- 2024 Winners:
- Shri Sucha Singh (Athletics)
- Shri Murlikant Rajaram Petkar (Para-Swimming)
Dronacharya Award
- Given to coaches who have made a consistent and significant contribution by guiding sportspersons to excel at international events.
- The award includes a bronze statue of Dronacharya, a certificate, and a cash prize.
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (MAKA) Trophy
- Awarded to the top-performing university in the Khelo India University Games.
- 2024 Winner: Chandigarh University.
Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puruskar
- Recognizes individuals or organizations for their contribution to the promotion and development of sports.
- 2024 Winner: Physical Education Foundation of India.
These awards were selected by a committee led by Justice (Retd.) V. Ramasubramanian and include eminent sportspersons, journalists, and sports administrators. The winners will receive their awards from the President of India, marking a prestigious moment in Indian sports.
Year of Artificial Intelligence

- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has declared 2025 as the "Year of Artificial Intelligence" (AI), aiming to empower over 14,000 AICTE-approved colleges and benefit 40 million students. This initiative aligns with the Prime Minister’s vision to make India a global leader in AI and technology.
Key Objectives and Features of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- Positioning India as a Global AI Leader:
- Empowering students with AI skills to drive innovation and lead in the emerging AI-driven economy.
- Preparing India’s workforce for the technological advancements of the future.
- Core Elements of the AICTE AI Initiative:
- AI Affirmation Pledge: Institutions will adopt and display an AI Affirmation Pledge, focusing on innovation, ethics, and education in AI.
- Comprehensive AI Integration:
- Introducing interdisciplinary AI courses and research programs.
- Setting up AI labs in collaboration with industries to meet global standards.
- Promoting ethical AI practices with societal benefits in focus.
- AI Awareness Campaign:
- “AI for All: The Future Begins Here” campaign includes workshops, hackathons, and guest lectures.
- Formation of student-driven AI chapters to foster innovation and research.
- Faculty Development & Industry Partnerships:
- Workshops and certification programs for faculty to improve AI teaching.
- Collaboration with companies like Adobe, CISCO, and IBM for student exposure through internships and mentorships.
- Recognition of Excellence: Institutions excelling in AI integration will be recognized, serving as role models for others.
- Action Plan for Institutions:
- All institutions are required to submit AI Implementation Plans by December 31, 2024. These plans will be evaluated by the AICTE Approval Bureau and exemplary submissions will be highlighted as benchmarks.
- Shaping India as a Global AI Leader:
- AICTE aims to revolutionize India’s education system and enhance its position in the global AI race, focusing on building a self-reliant workforce.
Additional Context on AICTE and its Role:
- AICTE Overview:
- A statutory body and national-level council under the Ministry of Education.
- Established in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body for technical education in India.
Government Initiatives to Support AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI and Consumer Protection:
- AI-driven tools launched to enhance consumer protection, such as the National Consumer Helpline, e-MAAP Portal, and Jago Grahak Jago mobile application.
- New guidelines for regulating deceptive marketing in e-commerce to ensure consumer confidence in the digital market.
- Tools like the e-Daakhil Portal for online complaint filing.
Impact:
- This initiative will have a far-reaching impact, involving more than 14,000 institutions and 40 million students nationwide, preparing them for leadership roles in AI and technology, and helping India secure its future in the global AI-driven economy.
Translocation of Tigers from Madhya Pradesh
- 05 Jan 2025
In News:
Madhya Pradesh to translocate 15 Tigers to Rajasthan, Odisha and Chhattisgarh.
Key Highlights of the Translocation:
- Scale of Translocation: Largest relocation of big cats from a single state in India.
- Approval: NTCA has approved the translocation of 15 tigers from Madhya Pradesh to Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
- Source Reserves:
- Bandhavgarh, Panna, Kanha, and Pench Tiger Reserves in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distribution Plan:
- Rajasthan: 4 tigresses.
- Chhattisgarh: 2 male tigers and 6 tigresses.
- Odisha: 1 male tiger and 2 tigresses.
- Funding: States receiving tigers will bear all expenses related to translocation.
Objectives of the Translocation:
- Enhance Tiger Conservation: Reintroduce and bolster tiger populations in recipient states.
- Population Management: Relocate tigers to areas with suitable habitats to alleviate territorial disputes in overpopulated reserves.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new individuals to isolated tiger groups to prevent inbreeding and support long-term species survival.
About Kanha, Bandhavgarh, and Pench Tiger Reserves:
- Kanha Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Maikal range of the Satpura Mountains.
- Significance: Largest national park in Madhya Pradesh.
- Distinct Feature: First tiger reserve in India with an official mascot, ‘Bhoorsingh the Barasingha’.
- Flora and Fauna: Rich biodiversity with Royal Bengal Tigers, leopards, and the IUCN Vulnerable species, Barasingha.
- Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Between Vindhyan and Satpura ranges in Umaria district, Madhya Pradesh.
- Significance: Known for one of the highest densities of Royal Bengal Tigers in India.
- Historical Link: The ancient Bandhavgarh Fort, linked to the legend of Lord Rama and Lakshmana.
- Pench Tiger Reserve:
- Location: Spans Seoni and Chhindwara districts in Madhya Pradesh, extends into Maharashtra.
- Significance: Inspiration for Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book.
- Flora and Fauna: Includes teak, saag, mahua forests; tigers, leopards, wild dogs, and gaur are key species.
Tiger Translocation Project Overview:
- First Project:
- Initiated in 2018, two tigers relocated from Kanha and Bandhavgarh to Satkosia Tiger Reserve in Odisha.
- Main Objectives:
- Reintroduce Tigers: In areas where they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Alleviate Territorial Disputes: Overpopulated reserves need additional tigers to reduce human-animal conflict.
Benefits of Translocation:
- Ecological Balance: Restores predator-prey dynamics in underpopulated reserves.
- Human-Animal Conflict Mitigation: Reduces conflict in overcrowded reserves.
- Rewilding Landscapes: Revives areas where tigers were locally extinct.
Concerns Associated with Translocation:
- Local Community Protests: Villagers fear tigers will pose a threat to their safety.
- Territorial Disputes: New tigers may face conflict with resident tigers.
- Poor Forest Management: Inadequate prey augmentation and habitat management may hinder success.
Madhya Pradesh’s Role in Tiger Conservation:
- Largest Tiger Population: Madhya Pradesh hosts the largest number of tigers in India, with 785 tigers as per NTCA’s 2022 report.
- Tiger Reserves: The state is home to nine tiger reserves, including the newly notified Madhav Tiger Reserve in Shivpuri.
- Translocation Strategy: Madhya Pradesh’s involvement helps reduce local tiger population pressure and contributes to broader conservation efforts across India.
Inter-State Tiger Translocation Goals:
- Reinforcement and Reintroduction: Introduce tigers into areas historically part of their range but from which they have been extirpated or extinct.
- Genetic Diversity: Introduce new tigers to isolated populations to maintain long-term population health.
Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS)

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- The CPPS aims to enhance pension accessibility and simplify the disbursement process for over 7.85 million pensioners in India.
- Key Benefit: Pensioners can now receive their pension from any bank or branch across India, eliminating the need for physical verifications and providing seamless nationwide pension disbursement.
Key Highlights:
- Key Features:
- No need for physical verification: Pensioners do not have to visit the bank for verification at the time of pension commencement.
- Seamless pension disbursement: Upon release, the pension amount is credited immediately.
- Nationwide access: Pensioners can withdraw their pension from any bank or branch, without needing to transfer Pension Payment Orders (PPO) when relocating or changing banks.
- Significance:
- Eliminates the decentralised pension system, where each regional office maintained separate agreements with a few banks.
- Ensures pension portability, especially for pensioners who move or change banks.
Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO):
- Overview:
- EPFO is a statutory body under the Employees' Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Act, 1952, and works under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- Structure:
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Government (Central & State)
- Employers
- Employees
- The Central Board of Trustees is chaired by the Union Minister of Labour and Employment.
- Administered by a tripartite board called the Central Board of Trustees, consisting of representatives from:
- Key Schemes Operated by EPFO:
- Employees’ Provident Funds Scheme, 1952 (EPF): A savings scheme for workers.
- Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 (EPS): A pension scheme for employees after retirement.
- Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance Scheme, 1976 (EDLI): Provides life insurance coverage to workers.
- Global Coverage: EPFO is also the nodal agency for implementing Bilateral Social Security Agreements with other countries, offering reciprocal social security benefits to international workers from countries with such agreements.
- Impact: The EPFO schemes cover Indian workers and international workers from countries with which EPFO has signed bilateral agreements.
Key Facts:
- CPPS improves the convenience and accessibility of pension services for millions of pensioners across India by simplifying the pension disbursement process and providing nationwide access without the need for physical verifications.
- EPFO, a statutory body under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, plays a crucial role in managing provident funds, pensions, and insurance schemes for both domestic and international workers, fostering social security across India.
Project VISTAAR

- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
IIT Madras has partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare on Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources). MoU signed between the Ministry and IIT Madras to integrate information about agricultural start-ups into the VISTAAR platform.
Key Highlights:
Project Objectives:
- Digitalisation of Agricultural Extension: To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the agricultural extension system through digital platforms.
- Access to Start-Up Innovations: Provide farmers easy access to over 12,000 start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors, connecting them to technological solutions and innovations.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Focus on making farming more sustainable and climate-resilient by promoting adoption of innovative technologies.
Key Features of VISTAAR:
- Integration of start-up data via IIT Madras' startup information platform and its incubatee, YNOS Venture Engine.
- Advisory services covering:
- Crop production
- Marketing
- Value addition
- Supply chain management
- Information on government schemes for agriculture, allied sectors, and rural development.
- Real-time, contextual, and accurate information to enhance decision-making and improve farming practices.
Significance of the Project:
- The platform will expand the outreach of agricultural extension services, providing support to farmers across India.
- It will ensure farmers access high-quality advisory services that are critical for improving productivity and income.
- Integration of start-up-driven innovations will aid in the adoption of climate-resilient farming practices.
- Timely and accurate information will empower farmers to make informed decisions and improve the efficiency of agricultural processes.
Impact on Farmers:
- Digitalisation will provide farmers with easier access to expert advice and resources, enhancing productivity.
- Improved access to government schemes ensures farmers can avail themselves of financial and technical support for development.
- The project aligns with national objectives of enhancing agriculture’s contribution to India’s economy and ensuring food security.
Air India In-Flight Wi-Fi Connectivity
- 04 Jan 2025
In News:
- Tata Group’s Air India launched free Wi-Fi connectivity on select domestic and international flights.
- First Indian airline to offer Internet connectivity on domestic flights.
- The service is free for a limited introductory period on select domestic flights.
- Gradual expansion of Wi-Fi availability to more aircraft in the fleet.
Key Highlights:
Aircraft with Wi-Fi:
- Available on Airbus A350, Boeing 787-9, and select Airbus A321neo aircraft.
- Aircraft equipped with special hardware for Internet connectivity.
- Some aircraft, previously operated by Vistara, now part of Air India after the merger in November.
Technology Partner:
- Vistara’s in-flight Wi-Fi was facilitated by Tata Group’s Nelco, in collaboration with Panasonic Avionics.
- This service is now extended to select Air India domestic flights.
How to Access Wi-Fi:
- Passengers enable Wi-Fi on their devices and connect to the "Air India Wi-Fi" network.
- Redirected to an Air India portal where they enter details (PNR and last name) for access.
Connectivity Technologies:
- Air-to-Ground (ATG) Technology:
- Uses ground-based cellular towers to provide internet.
- Antenna on the aircraft’s belly picks up signals from nearby towers.
- Limited by tower availability, works best over land with dense coverage.
- Satellite-Based Connectivity:
- Uses satellites to provide internet by transmitting signals from ground stations to the aircraft.
- Provides wider coverage, particularly effective over oceans and sparsely populated areas.
In-Flight Wi-Fi Operation:
- Multiple in-cabin antennas collect signals from passengers’ devices.
- Signals are sent to an onboard server.
- For satellite-based systems, signals are transmitted via an antenna to satellites and then relayed to ground stations.
- For ATG systems, signals are sent directly to ground towers.
- In-flight Wi-Fi is slower compared to ground-based internet, though newer technologies are improving speed.
Cost Considerations:
- Airlines incur high initial costs for equipping aircraft with Wi-Fi technology (antennas and hardware).
- Air India is investing in a $400 million retrofit program for its fleet, which could include installing internet connectivity.
- Some airlines install Wi-Fi on new planes, while others retro-fit older models.
Revenue Model:
- Airlines often charge for Wi-Fi after offering a small volume of free internet.
- Some airlines provide free Wi-Fi for loyalty program members or premium passengers (business/first class).
- Air India is offering free Wi-Fi for now, but plans to introduce charges at a later date.
Future Outlook:
- In-flight internet is expected to become a significant source of ancillary revenue.
- Complimentary Wi-Fi for economy class passengers is unlikely in the near-to-medium term due to high costs involved in installation and operation.
Global Context:
- In-flight connectivity is becoming standard on major full-service carriers (FSCs) worldwide.
- Air India's move aligns with global trends, as it aims to be among the world’s leading airlines.
CGWB Report on Groundwater Contamination
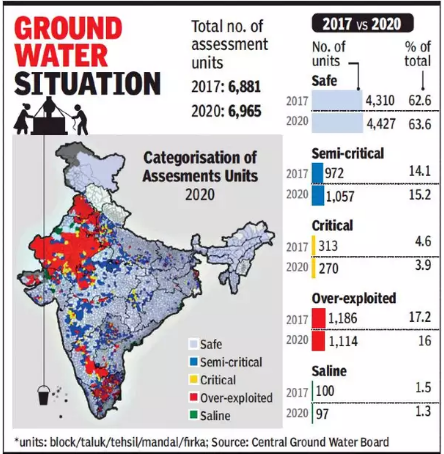
- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) report on groundwater quality reveals alarming levels of contamination in India's groundwater, with a focus on nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and uranium. The report highlights the impact of agricultural practices, poor waste management, and urbanisation on water quality.
Key Highlights:
Nitrate Contamination:
- 440 districts in India report excessive nitrate levels in groundwater, with 20% of samples exceeding the permissible nitrate limit of 45 mg/L (WHO and BIS standards).
- High-risk regions: Rajasthan (49%), Karnataka (48%), and Tamil Nadu (37%) are the top states with high nitrate levels. Other affected states include Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Causes: Nitrate contamination is mainly due to excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, over-irrigation, and poor management of animal waste. Urbanisation and improper sewage systems exacerbate the problem.
Other Groundwater Contaminants:
- Fluoride contamination: A significant concern in Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Arsenic contamination: Elevated arsenic levels found in several states, especially in floodplains of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers (West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur).
- Uranium contamination: 42% of uranium-contaminated samples are from Rajasthan, and 30% from Punjab. Chronic exposure to uranium leads to kidney damage.
Groundwater Extraction and Availability:
- 60.4% of groundwater is being extracted across India.
- 73% of groundwater blocks are classified as in the ‘safe’ zone, an improvement from 67.4% in 2022.
Monsoon Impact:
- Nitrate contamination increases post-monsoon, with 32.66% of samples exceeding safe limits during the rainy season.
Health Implications:
- High nitrate levels, particularly dangerous for infants, can cause blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia).
- Long-term exposure to contaminants like fluoride and arsenic can lead to fluorosis and increase the risk of cancers and skin lesions.
Sources of Contamination:
- Agricultural practices: Excessive use of fertilizers, pesticides, and improper irrigation.
- Waste disposal: Leaking septic systems, sewage, and hazardous waste sites contribute to contamination.
- Urbanisation: Increased wastewater and sewage, along with poor waste management, worsen the issue.
Measures to Address Contamination:
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) and Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABHY) aim to conserve and manage groundwater resources.
- National Aquifer Mapping and Management Program (NAQUIM) to assess and map aquifer systems.
- Pollution control programs: Under the Water (Prevention & Control) Act, 1974, and initiatives like sewage treatment plants and effluent treatment plants to manage wastewater.
- Public awareness: Campaigns like Swachh Bharat Mission and Catch the Rain educate communities on the importance of groundwater conservation.
Key Statistics:
- 56% of districts in India report groundwater nitrate levels exceeding the safe limit of 45 mg/L.
- Monsoon effects: Post-monsoon data shows a significant increase in contamination levels (32.66% vs. 30.77% pre-monsoon).
National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) Scheme 2025

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
- The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG) has issued the guidelines for the 28th National e-Governance Awards (NAeG) 2025.
- Nominations for the awards can be submitted online via the official portal: www.nceg.gov.in.
Key Highlights:
- Award Categories: Nominations for the awards can be submitted under the following six categories:
- Government Process Re-engineering: Digital transformation through the use of technology to improve government processes.
- Innovation by Use of AI and New Age Technologies: Fostering citizen-centric services via artificial intelligence and other modern technologies.
- Best e-Gov Practices in Cyber Security: Recognizing excellence in e-Governance practices focused on cybersecurity.
- Grassroot Level Initiatives: Initiatives at the Districts, ULBs (Urban Local Bodies), or Gram Panchayats that deepen service delivery.
- Replication and Scaling Up of Successful Projects: Projects awarded in the past (such as NAeG or Prime Minister’s Awards) that have been successfully replicated or scaled.
- Digital Transformation using Data Analytics: Projects that leverage data analytics on digital platforms for enhancing governance.
- Eligibility: The awards are open to Central Ministries/Departments, State Governments, District Collectors, Research Institutions, and other relevant entities.
- Award Details:
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- 10 Gold Awards.
- 6 Silver Awards.
- The NAeG 2025 will feature 16 awards:
- Incentives:
- Gold Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 10 lakh.
- Silver Award winners will receive a Trophy, Certificate, and an incentive of Rs 5 lakh.
- The incentive will be used for further implementation of the awarded projects or bridging resource gaps in public welfare.
- Objective: The goal of the National Awards for e-Governance is to recognize and promote excellence in the implementation of e-Governance initiatives and digital transformation efforts across India.
Tinnitus

- 03 Jan 2025
In News:
Researchers at IIT Bombay have created an affordable device to diagnose and manage tinnitus, a condition involving persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears. The device offers personalized treatment solutions and a comprehensive approach to managing tinnitus.
What is Tinnitus?
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the absence of external noise, meaning only the affected individual hears it. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system problems.
- It affects over 740 million adults globally, with 120 million experiencing severe symptoms (JAMA Neurology, 2022).
- Common symptoms include sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, irritability, and significant impacts on mental health and social life.
- Treatment may include: Hearing aids, sound-masking devices, medications, and coping techniques to manage the noise.
Device Features:
- Precise Tinnitus Matching: Identifies the exact nature and frequency of sounds experienced by the patient.
- Customizable Treatment: Provides a tailored, multimodal approach to treatment, ensuring each patient gets a unique experience.
- Tracking Progress: Includes tools to monitor disease progression and patient improvement over time.
Affordability and Accessibility:
- The device is cost-effective, addressing the issue of high costs associated with current tinnitus management solutions.
- This breakthrough is especially beneficial for low-income regions, where access to expensive tinnitus treatment is limited.
Impact on Healthcare:
- The device empowers doctors with precise diagnostic tools, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and the efficacy of treatment.
- It aims to enhance patient quality of life by offering an affordable and accessible solution to tinnitus management.
Funding and Development:
- The project has received funding from Tata Centre for Technology and Design (TCTD), IIT Bombay, and Wadhwani Research Centre for Bioengineering (WRCB).
Significance:
- This development represents a technological advancement in tinnitus care, with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of the condition and improve the well-being of affected individuals worldwide.
Stellaria bengalensis

- 02 Jan 2025
In News:
After a plant species of the genus Stellaria (family Caryophyllaceae) was reported from Kerala earlier this year, researchers have identified another member of the same genus at Kalimpong district in West Bengal.
Key Highlights:
Discovery and Identification:
- Published: The discovery was published in Phytotaxa.
- Location: Found in Kalimpong district, West Bengal, at altitudes of 2,245-2,450 metres in the Sangser forest.
- Named: The species is named Stellaria bengalensis after the state of West Bengal.
Taxonomy and Characteristics:
- Family: Caryophyllaceae.
- Type: Annual herb.
- Size: Grows to a height of 8 to 10.5 cm.
- Flowers: White in color, with shorter petals, often included within the sepal, and absence of bracts.
- Seeds: Sharp and pointed.
- Flowering and Fruiting: Occurs from May to September.
Distribution:
- Region: Primarily found in the Himalayan region.
- Similar Species: Stellaria mcclintockiae, identified earlier in Kerala (Nelliyampathy Hills).
- Both species grow in muddy soil slopes and are annuals.
Conservation Status:
- Under IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) criteria, the species is assessed as "data deficient", pending further studies.
- Potential Habitat: There is a possibility of finding more populations in the western Himalayas.
Significance:
- Stellaria bengalensis is the second Stellaria species reported in India in 2025.
- India is home to about 22 Stellaria species, predominantly found in the Himalayan region.
- The discovery adds to biodiversity knowledge in India and underscores the importance of studying plant species in the region.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
The introduction of smart classrooms as part of the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) has had a significant impact on education, leading to a 22% increase in enrolment across 19 cities, according to a report from the Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIM-B). The study covers the period from 2015-16 to 2023-24 and highlights several key benefits of this initiative, which aims to improve the overall learning environment in government schools.
Key Findings:
- Increased Enrolment: The introduction of smart classrooms has been linked to a 22% increase in student enrolment across 19 cities, suggesting that the initiative has made education more appealing and accessible.
- Smart Classroom Development: By 2023-24, 71 cities had developed 9,433 smart classrooms in 2,398 government schools. The states with the most smart classrooms are:
- Karnataka (80 classrooms)
- Rajasthan (53 classrooms)
- Tamil Nadu (23 classrooms)
- Delhi (12 classrooms)
- West Bengal has a very limited number, with just two classrooms.
- Improved Learning Experience: Teachers have expressed positive feedback, agreeing that the smart classrooms have improved learning experiences and attendance among students. Additionally, the smart classroom setup has contributed to increased comfort for teachers and higher preference for these modern facilities.
- Teacher Training: Special training provided to teachers has enhanced their comfort with using the smart classroom tools, with senior secondary teachers showing the highest comfort levels.
- Digital Libraries: The study also found that 41 cities have developed Digital Libraries with 7,809 seating capacity, offering essential resources for students. Cities like Raipur (Chhattisgarh) and Tumakuru (Karnataka) have seen positive outcomes from these libraries, particularly in supporting students preparing for competitive exams.
Smart Cities Mission (SCM)
- Launched in June 2015, the Smart Cities Mission aims to promote cities that offer core infrastructure, a decent quality of life, a sustainable environment, and the application of smart solutions. As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the mission have been completed.
SAAR Platform and Research
- In 2022, the Smart Cities Mission introduced the SAAR (Smart Cities and Academia towards Action and Research) platform to bridge the gap between academia and the government. Under this platform, 50 impact assessment studies have been initiated by 29 premier institutions, including six Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), eight Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), and 12 specialized research institutes.
61st Raising Day

- 31 Dec 2024
In News:
On December 20, 2024, Union Home Minister Shri Amit Shah attended the 61st Raising Day function of the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) in Siliguri, West Bengal. During the event, he e-inaugurated the Integrated Check Point (ICP) Agartala and a newly constructed residential complex for the Border Guard Force (BGF) at Petrapole. The event was attended by several dignitaries, including the Director of Intelligence Bureau (IB), Secretary of Border Management (MHA), and the Director-General of SSB.
Key Highlights from the Speech:
- Tributes to Martyrs: Shri Shah paid tributes to SSB martyrs, highlighting their sacrifices in protecting the country's borders and eliminating Left Wing Extremism in the eastern region. He acknowledged the 4 Padma Shri, 1 Kirti Chakra, and other national awards received by SSB for their exceptional service.
- Role in Connecting Borders: The Home Minister praised SSB’s role in connecting the culture, language, and heritage of border villages with mainstream India. He emphasized that the SSB has fulfilled its motto of "Service, Security, and Brotherhood" while maintaining a strong relationship with Nepal and Bhutan.
- Security and Vigilance: SSB is responsible for securing a 2,450 km border with Nepal and Bhutan. Shri Shah noted that SSB's vigilance has helped in stopping narcotics, arms smuggling, and human trafficking. Additionally, the force has worked to ensure that Bihar and Jharkhand are now Naxal-free.
- Zero-Tolerance Policy: The SSB has a zero-tolerance policy on encroachments, narcotics, and smuggling. Over the last three years, the SSB successfully removed more than 1,100 encroachments from government land and seized significant amounts of narcotics, weapons, and counterfeit currency.
- Impact in Jammu & Kashmir: SSB has played a critical role in combating terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, killing more than 19 terrorists and arresting 14 through various operations.
- Humanitarian Efforts: Besides security, SSB has actively participated in disaster relief operations during floods and landslides, often at great personal risk.
- Government Schemes for CAPF Personnel: Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, various welfare schemes like Ayushman Cards, CAPF e-Housing, and scholarships have been launched to support CAPF personnel and their families.
- Self-Employment Initiatives: SSB has promoted self-employment for border youth, training them in areas like beekeeping, mobile repairing, and driving. They have also contributed significantly to the Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, creating awareness about drug addiction among 36,000 youth.
- Environmental Contribution: The force has planted over 6 crore trees as part of its environmental efforts.
World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025

- 30 Dec 2024
In News:
India to Host World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit (WAVES) 2025.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The summit aims to bolster India's media and entertainment (M&E) industry, expand its global influence, and foster innovation and collaboration within the sector.
- Significance: First-ever global summit to cover the entire media and entertainment industry spectrum.
- Objective:
- Foster Dialogue and Trade: WAVES aims to be a premier platform for industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to engage in meaningful discussions, explore opportunities, and tackle challenges in the M&E sector.
- Promote India's M&E Industry: Attract trade and investment to India, highlighting its strengths in animation, gaming, entertainment technology, and cinema (both regional and mainstream).
- Focus Areas:
- Industry Advancements: Discussions will revolve around India’s progress in animation, visual effects, gaming, and cinema.
- Global Positioning: Establish India as a global powerhouse in the M&E sector, setting new standards for creativity, innovation, and global influence.
WAVES India - Vision and Mission:
- Vision: Position India as a Global Powerhouse: Enhance India’s standing in the dynamic M&E sector, making it a hub of creativity and innovation worldwide.
- Mission:
- Provide exclusive investment opportunities for global M&E leaders through WAVES.
- Drive India’s Creative Economy through Intellectual Property (IP) Creation for both domestic and international markets.
- Develop M&E Infrastructure: Strengthen industry infrastructure and create a skilled workforce to meet global demands.
- Adapt to New Trends: Embrace emerging technologies and transformations in the M&E landscape.
Expected Outcomes:
- Global Collaboration: Engage global M&E leaders in discussions that provoke ideas and facilitate collaborations.
- Attract Investment: Promote India as a business-friendly investment destination in the M&E sector.
- Skills and Capacity Building: Build capacity in the M&E industry and develop skilled human resources to support international needs.
Sambar Deer

- 29 Dec 2024
In News:
Three poachers were arrested for killing a sambar deer in the Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS), East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
Action Taken:
- Poachers Arrested: The poachers were booked under the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 and Arms Act 1959. The seized articles were handed over to the police, and a FIR was registered.
- Sanctuary Protection Efforts: The Divisional Forest Officer (DFO) emphasized the need for intensified surveillance to prevent further hunting incidents. Public cooperation was urged to report such incidents for prompt action.
About Sambar Deer:
- Scientific Name: Rusa unicolor.
- Native Regions: Found across the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
- Other Names: Known as Jarao in Nepal and Four-eyed deer in China.
- IUCN Red List: Listed as Vulnerable.
Key Features:
- Size: Stands between 1.2–1.4 meters at the shoulder.
- Weight: Can reach up to 550 kg, making it the largest oriental deer.
- Coat: Dark brown with a ruff around the neck, and unspotted.
- Antlers: Male sambar bears long, rugged antlers with three points (tines).
- Behavior: Elusive, most active at dusk and night.
Habitat:
- Water Dependency: Always found near water sources.
- Habitat Range: Dry deciduous forests, rainforests, and mixed forests.
- Social Structure: Often found alone or in small groups.
About Daying Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary (DEMWS):
- Location: Situated in East Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Established: Originally established as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary in 1976, renamed Daying Ering Memorial in 1986.
- Climate: Tropical, receiving both north-east and south-west monsoons.
- Waterways: Home to the Siang River, one of Arunachal's major rivers.
Flora:
- Vegetation: Composed mainly of riverine plains with a variety of thatch and grasses.
- Trees: Includes scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
Fauna:
- Mammals: Includes Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant.
- Birds: Over 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey: 2023-24
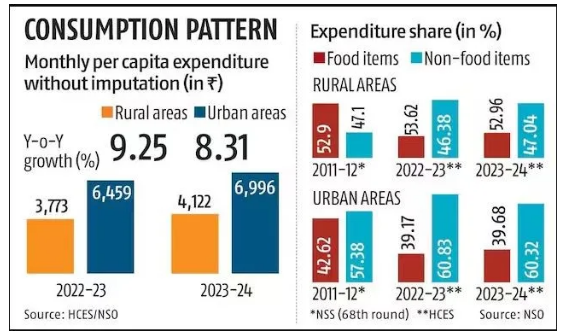
- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The latest Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) for 2023-24 reveals notable trends in consumption patterns in rural and urban India, reflecting economic shifts post-pandemic.
Key Highlights:
- Food Spending Increase: The share of food expenditure in household budgets has increased both in rural and urban areas, likely due to rising food prices.
- Rural households allocated 47.04% of their expenditure to food in 2023-24, up from 46.38% in 2022-23.
- Urban households spent 39.68% of their budgets on food, slightly up from 39.17% last year.
- Narrowing Urban-Rural Gap: The gap in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) between rural and urban households has steadily reduced over the past decade.
- In 2023-24, rural consumption spending was 69.7% of urban consumption, an improvement from 71.2% in 2022-23 and 83.9% in 2011-12.
- Increased Rural Spending: Rural India has seen significant increases in spending. The average monthly spending per person in rural areas rose by 9.3% to Rs 4,122 in 2023-24, surpassing the 8.3% rise to Rs 6,996 in urban areas.
- This suggests a growing momentum in rural consumption, which has outpaced urban consumption growth in the last year.
- Spending Trends Across Income Groups: While the top 5% of both rural and urban populations saw a decrease in their consumption spending, every other income group, including the bottom 5%, registered an increase in spending.
- The bottom 20% in both rural and urban areas saw the highest growth in expenditure, signaling rising economic activity among lower-income groups.
- Non-Food Expenditure Dominates: Non-food items make up a larger share of household spending, particularly in urban areas, where they account for 60.32% of total expenditure compared to 52.96% in rural areas.
- In rural India, major non-food expenses include medical, conveyance, and clothing, while urban households allocate more to entertainment, education, and miscellaneous goods.
- Regional Consumption Patterns: Consumption expenditure varied significantly across states, with western and northern states like Maharashtra, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu spending more than the national average.
- In contrast, eastern and central states, including West Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha, spent less. Sikkim reported the highest per capita expenditure in both rural (Rs 9,377) and urban (Rs 13,927) areas, while Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest.
- Declining Consumption Inequality: The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has declined in both rural and urban areas.
- This reflects reduced disparity in spending, indicating a trend toward more equitable economic growth across regions.
- Food Expenditure Trends: Food categories like beverages, processed foods, and cereals continued to see rising shares in total expenditure. The rise in spending on food items was particularly notable in rural areas for eggs, fish, and meat.
Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya Committee

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has set up an eight-member committee to create a framework for the responsible and ethical use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the financial sector.
- The committee is chaired by Dr. Pushpak Bhattacharyya, Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at IIT Bombay.
Key Highlights:
Committee's Objective:
- The primary goal is to develop a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI (FREE-AI) in the financial sector.
- It will guide the ethical adoption of AI in financial services to enhance operational efficiency, decision-making, and risk management.
Scope of the Committee's Work:
- Assess the current global and domestic adoption of AI in financial services.
- Identify potential risks and challenges associated with the integration of AI in the sector.
- Recommend a framework for evaluating, mitigating, and monitoring AI-related risks.
- Propose compliance requirements for various financial entities (e.g., banks, NBFCs, fintech firms).
- Suggest a governance framework for ethical AI usage.
Key Benefits of AI in Financial Services:
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, process large datasets, and enhance accuracy (e.g., loan application processing).
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive analytics in AI help forecast market trends, aiding in better financial decision-making (e.g., algorithmic trading).
- Customer Relationship Management: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer interaction, offering 24/7 support.
- Improved Risk Management: AI enables proactive fraud detection, improving security and preventing financial losses.
Concerns Associated with AI in Finance:
- Embedded Bias: AI models can replicate biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes and financial exclusion.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI poses risks to personal data security, with potential violations of privacy regulations.
- Operational Challenges: AI systems may exhibit inconsistent responses, leading to challenges in trust and effectiveness.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased use of AI can heighten vulnerability to cyber-attacks and exploitation.
RBI's Role & Governance:
- The RBI aims to ensure that AI adoption in the financial sector is ethical, transparent, and aligned with global best practices.
- The committee's recommendations will influence policies to prevent misuse and safeguard consumer interests.
Rupee and Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)

- 27 Dec 2024
In News:
The real effective exchange rate (REER) index of the rupee touched a record 108.14 in November, strengthening by 4.5 per cent during this calendar year, according to the latest Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data.
Key Highlights:
- Record REER Index:
- The Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the rupee reached an all-time high of 108.14 in November 2024.
- This marks a 4.5% appreciation in REER during the calendar year 2024, according to RBI data.
- What is REER?
- REER is a weighted average of a country’s currency value against the currencies of its major trading partners, adjusted for inflation differentials.
- It considers 40 currencies accounting for about 88% of India's trade.
- REER Calculation:
- Nominal Exchange Rates: The exchange rate between the rupee and each partner's currency.
- Inflation Differentials: Adjusts for inflation differences between India and its trading partners.
- Trade Weights: Based on the trade share with each partner.
- Recent Trends in REER:
- In 2023, REER dropped from 105.32 in January to 99.03 in April.
- It has since been on an appreciating trend, reaching 107.20 in October and 108.14 in November 2024.
- Dollar Strengthening Impact:
- Despite the rupee weakening against the US dollar (from 83.67 to 85.19 between September and December 2024), it has appreciated against the euro, British pound, and Japanese yen.
- The dollar's strengthening was fueled by global economic factors, including inflation expectations in the US and high bond yields, which led to capital outflows from other countries, including India.
- Impact on Exports and Imports:
- Overvaluation: A REER above 100 signals overvaluation, which can harm export competitiveness (exports become costlier) while making imports cheaper.
- Undervaluation: A REER below 100 indicates a currency is undervalued, boosting exports but increasing the cost of imports.
- India's Inflation and REER:
- India's higher inflation relative to trading partners is a key factor behind the rupee’s rising REER, despite its depreciation against major currencies.
- This suggests the rupee is overvalued, which could explain why the RBI may allow the rupee to depreciate further against the dollar.
- Global Context:
- The strengthening of the US dollar, influenced by factors such as tariff policies under the Trump administration and tighter US monetary policies, plays a significant role in the depreciation of the rupee against the dollar.
- This dynamic affects India's trade balance, with potential consequences for export growth.
- Implications for India’s Economy:
- Overvalued currency (as indicated by REER above 100) can lead to a trade deficit, as imports become cheaper and exports less competitive.
- A weaker rupee, particularly against the dollar, could boost Indian exports but raise the cost of imports.
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
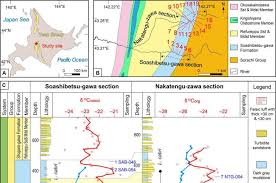
- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study published in Science Advances has offered fresh insights into the timing and duration of the Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a).
What is OAE 1a?
- Definition: A period during the Cretaceous Period (~119.5 million years ago) when Earth's oceans became oxygen-depleted (anoxic), causing significant disruption in marine ecosystems.
- Cause: Triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released large amounts of CO?, leading to global warming and depletion of oxygen in oceans. This caused the formation of anoxic marine basins.
- Impact: The depletion of oxygen led to the extinction of marine species, especially plankton, and the formation of black shales (organic carbon-rich layers).
Anoxic Marine Basins:
- Characteristics: These are bodies of water with extremely low or absent oxygen, allowing certain microbes and fungi to thrive, while most aerobic organisms perish.
- Significance: Anoxic basins contribute to carbon sequestration by slowing down the decay of organic material, helping in the reduction of atmospheric CO? levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin, and Orca Basin.
Recent Study Findings (Published in Science Advances):
- Timing: OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted for about 1.1 million years, with a long recovery period for ocean ecosystems.
- Methodology: The study used isotopic analysis of volcanic tuffs from Japan's Hokkaido Island to pinpoint the timing of the event.
- Volcanic Eruptions: The study confirmed that volcanic eruptions, particularly from the Ontong Java Nui complex, released CO?, triggering oceanic oxygen depletion.
- Relevance to Modern Climate Change: The study draws parallels between past volcanic CO? emissions and current human-induced warming, warning that rapid modern warming could cause similar disruptions in marine ecosystems and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction.
Holocene Extinction:
- Definition: The ongoing Sixth Mass Extinction, primarily driven by human activities like overexploitation, habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and invasive species.
- Impact: Current extinction rates are 1,000-10,000 times higher than natural rates, with severe consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Key Mass Extinction Events:
- Permian Extinction (~250 million years ago): Linked to volcanic activity, global warming, and ocean anoxia, leading to the extinction of over 95% of species.
- Cretaceous Extinction (66 million years ago): Caused by an asteroid impact, exacerbated by volcanic eruptions, leading to the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs.
- Holocene Extinction: Caused by human activities, with long-term implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Mitigate Extinction:
- Climate Action: Limiting global warming to 1.5°C as per the Paris Agreement.
- Biodiversity Conservation: The 30X30 Initiative, aiming to conserve 30% of lands and oceans globally by 2030.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable resource management to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation.
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
On Good Governance Day, commemorating the 100th birth anniversary of former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Dr. Jitendra Singh, the Union Minister of State for various departments, launched the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative. This initiative is part of the broader ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign, which aims to empower Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) at the grassroots level by enhancing the capacity and competence of elected representatives and officials.
Objective of the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ Initiative
The initiative seeks to strengthen PRIs by providing innovative tools and frameworks for capacity building and participatory governance. It will focus on equipping local leaders and officials with the necessary knowledge and tools to make effective decisions and implement sustainable development initiatives. Piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, it uses e-learning platforms, AI-powered chatbots, and mobile apps to address knowledge gaps and improve service delivery at the local level. This program aligns with the government's mission to decentralize governance and promote citizen-centric and equitable development across rural India.
Other Key Initiatives Launched on Good Governance Day
- iGOT Karmayogi Platform Dashboard: A new dashboard on the iGOT Karmayogi platform, which empowers ministries, departments, and state administrators to monitor progress in capacity-building efforts. The enhanced dashboard includes customizable views, robust data filtering tools, and insights to optimize decision-making, marking the introduction of the 1600th e-learning course. This development is part of the Mission Karmayogi initiative to strengthen the civil service through continuous learning.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: The CPGRAMS Annual Report provided a review of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS). This platform has been instrumental in resolving over 25 lakh grievances annually, leveraging advanced technologies and multilingual support. The report also highlighted the implementation of the Grievance Redressal Assessment and Index (GRAI), which has improved transparency, accountability, and the efficiency of public service delivery.
- Single Simplified Pension Application Form: A new digital pension system was launched, combining nine separate pension forms into a single, streamlined application. This digital transformation integrates e-HRMS with Bhavishya, reducing processing time and ensuring timely pension disbursement with real-time tracking and Aadhaar-based e-signatures. This system enhances the user experience for pensioners, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Compendium of Pension Related Instructions 2024: Dr. Singh introduced a comprehensive Compendium of updated rules, procedures, and guidelines related to pensions. This document serves as a reference for pensioners and administrative personnel, ensuring clarity in the pension process and aligning with the government's vision of simplifying and streamlining pension systems.
Good Governance Day 2024 (Sushasan Diwas)
- Observed on: December 25 annually, marking the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee (1924–2018).
- Introduced in 2014: By the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government under Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Purpose: To honor Vajpayee's contribution and promote good governance practices in India.
- Objective of Good Governance Day:
- Promote Government Accountability: Ensuring government actions and services are transparent and citizens benefit equally.
- Instill Good Governance Values: Encourages civil servants to practice effective and responsible governance.
- Bridge the Gap: Between citizens and the government through active participation.
- Theme for 2024: "India’s Path to a Viksit Bharat: Empowering Citizens through Good Governance and Digitalisation."
Cephalopods

- 26 Dec 2024
In News:
Octopuses and their relatives are a new animal welfare frontier
- Cephalopods are highly intelligent, marine invertebrates that include species such as octopuses, squids, and cuttlefish.
- They are members of the class Cephalopoda in the phylum Mollusca, which is known for its diversity and complex morphology.
- Cephalopods are often considered one of the most behaviorally and morphologically complex classes within this phylum.
Key Features and Anatomy
Cephalopods exhibit several distinctive features:
- Body Structure: They have a head-foot structure, where the head is merged with the foot, and arms/tentacles surround the head. The arms and tentacles are derivatives of the foot, with some species possessing additional appendages for grasping or movement.
- Tentacles and Beak: Cephalopods possess tentacles, often with suction cups or hooks for capturing prey. They also have beak-like jaws, which are used to break down food.
- Eyes and Vision: Their unique W-shaped pupils enhance their vision. Most cephalopods are believed to be colorblind, but they exhibit remarkable visual camouflage through chromatophores (pigment cells) and reflectors beneath their skin, which can produce a wide range of colors and patterns.
- Movement: Cephalopods use jet propulsion to move. By expelling water from their mantle cavity, they can quickly travel through the water. Some species, like octopuses, also "walk" using their arms, while squids and cuttlefish employ fins for propulsion.
- Circulatory System: They have three hearts. Two hearts pump deoxygenated blood, while the third pumps oxygenated blood. Their blood is blue due to the presence of copper-based hemocyanin, which is effective in cold, low-oxygen environments.
- Neural Systems: Cephalopods are known for their advanced nervous systems. A significant portion of the neurons, especially in octopuses, are not located in the central brain but are distributed across the arms in “mini-brains” or ganglia, which helps coordinate movement and sensory functions independently.
Cognitive Abilities
Cephalopods have garnered significant attention due to their impressive cognitive abilities. Their intelligence is demonstrated in several areas:
- Problem-Solving: They are capable of using tools and strategies to solve complex tasks, such as escaping enclosures or catching prey.
- Learning and Memory: Cephalopods exhibit sophisticated learning behaviors, including associative learning and memory. Some species are known to delay gratification, choosing more preferred food items over immediate but less desirable ones. They also show evidence of "reversal learning," where they can adjust their behavior in response to changing environmental cues.
- Camouflage and Communication: Cephalopods can manipulate their skin's color and texture for camouflage, aiding in hunting and predator avoidance. For example, the Australian giant cuttlefish uses its chromatophores to communicate with potential mates or warn off competitors.
Species Diversity
Cephalopods are classified into three primary superorders:
- Octopodiforms: Includes octopuses (e.g., Octopus vulgaris), which are known for their intelligence and ability to solve problems.
- Decapodiforms: Includes squids and cuttlefish (e.g., Sepia officinalis, Architeuthis dux), which possess unique locomotion and hunting strategies.
- Nautiloids: Includes the chambered nautilus, the only cephalopod with an external shell, which is considered more primitive compared to other cephalopods.
Ethical and Conservation Concerns
Due to their intelligence and advanced nervous systems, cephalopods are becoming a focus of ethical debates regarding their treatment. Recently, California and Washington have enacted bans on octopus farming, and Hawaii is considering similar measures. These decisions are driven by the growing understanding of cephalopods' cognitive abilities and their capacity for suffering. As a result, there are increasing calls for humane treatment regulations similar to those for vertebrates.
Environmental and Ecological Role
Cephalopods play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. As carnivorous predators, they help maintain the balance of marine food chains by hunting smaller prey. Some species, such as the cuttlefish, also play important roles in communicating and signaling within their species through visual displays.
RBI's Report on State Finances (2024-25)

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) report titled "State Finances – A Study of Budgets of 2024-25" provides a comprehensive analysis of the fiscal position of Indian states.
Key Highlights
- States' Performance Post-Pandemic
- Improved Tax Revenue: The average tax buoyancy has increased significantly from 0.86 (2013-2020) to 1.4 (2021-2025), reflecting enhanced tax collection efficiency.
- Capital Expenditure: There is a consistent rise in capital expenditure, which increased from 2.4% of GDP in 2021-22 to 2.8% in 2023-24 and is budgeted at 3.1% in 2024-25. This indicates a growing focus on investment in infrastructure like highways and bridges.
- Fiscal Discipline and Debt Levels
- Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD): The gross fiscal deficit is projected at 3.2% of GDP in 2024-25, a slight increase from 2.9% in 2023-24.
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio: While states' debt-to-GDP ratio decreased from 31.0% in March 2021 to 28.5% in March 2024, it remains higher than the pre-pandemic level of 25.3% in 2019.
- Increased Borrowing and Debt Pressure
- Market Borrowings: States' reliance on market borrowings has increased, accounting for 79% of the GFD in FY25. Gross market borrowings surged by 32.8%, totaling Rs 10.07 trillion in FY23-24.
- Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs): Continued losses in DISCOMs, accumulating Rs 6.5 lakh crore by 2022-23 (2.4% of India's GDP), continue to strain state finances.
- Rising Subsidy Burden
- Many states are offering subsidies and loan waivers, such as farm loan waivers and free services (electricity, transport, etc.), which risk diverting funds away from critical infrastructure projects. This includes significant subsidies for income transfers to farmers, women, and youth.
- Fiscal Transparency Concerns
- Revenue Generation Issues: Revenue growth from non-tax sources and central grants is slowing. The pace of State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) growth has also slowed down, which impacts overall state revenues.
- Lack of Fiscal Transparency: Inadequate reporting of off-budget liabilities obfuscates the true fiscal position, leading to a lack of clarity and accountability in state finances.
Recommendations by the RBI
- Debt Consolidation: States are encouraged to create clear and transparent debt reduction paths, with consistent reporting of off-budget liabilities to improve fiscal accountability.
- Expenditure Efficiency: Focus on outcome-based budgeting, ensuring funds are directed towards productive and sustainable investments, particularly in climate-sensitive areas.
- Subsidy Rationalization: States should contain and optimize subsidies to ensure they don't overshadow essential growth-promoting expenditure.
- Efficient Borrowings: Reduce over-reliance on market borrowings to control fiscal deficits and minimize financial risks.
- Revenue Generation: Improve collection mechanisms for SGST, strengthen non-tax revenue sources, and increase grants to reduce dependence on borrowings.
Balancing Subsidies and Fiscal Discipline
- Importance of Subsidies: Welfare programs like subsidies for healthcare, food security (e.g., Public Distribution System), and LPG connections (e.g., Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana) play a crucial role in human development and economic equality by supporting vulnerable populations.
- Importance of Fiscal Discipline: Excessive welfare spending without corresponding revenue generation can lead to high deficits and public debt, threatening long-term fiscal stability. Maintaining fiscal discipline ensures sustainable public finances, promotes investor confidence, and supports economic growth.
Green fixed deposits

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
Green fixed deposits (FDs) are a type of investment scheme offered by banks and financial companies, aimed at environmentally-conscious investors. They function similarly to traditional fixed deposits, where funds are locked in with a bank for a fixed tenure. The primary distinction between green and regular deposits lies in the allocation of funds. While regular deposits are pooled into a common fund, the funds from green deposits are exclusively allocated to projects that promote environmental sustainability.
Key Features of Green Fixed Deposits:
- Investment Purpose: The funds raised through green FDs are directed towards environmentally beneficial projects, such as renewable energy initiatives (solar and wind power), clean technology, organic farming, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Eligibility: Green deposits are available to various entities, including individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), societies, clubs, non-profit organizations, and sole proprietorships.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on green deposits may or may not differ from regular deposits, depending on the policies set by the lending institution. Some banks and financial institutions, like IndusInd Bank, Federal Bank, DBS Bank India, and HDFC Ltd., offer green deposits, with Bank of Baroda recently launching the BOB Earth Green Term Deposit with an interest rate of up to 7.15% per annum.
- Safety: Like regular fixed deposits, green deposits are insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) under the provisions of the DICGC Act, 1961, ensuring the safety of the investment.
- Overdraft Facility: Banks may offer overdraft facilities against green deposits, providing more flexibility to investors.
- Premature Withdrawal: If the investor chooses to withdraw the deposit before the agreed tenure (after six months), the green FD will be converted into a regular fixed deposit.
- Denomination: Green deposits are denominated in Indian Rupees only.
National Farmers' Day

- 23 Dec 2024
In News:
National Farmers' Day, also known as Kisan Diwas, is celebrated annually on December 23rd to honor the vital contributions of Indian farmers and commemorate the birth anniversary of Chaudhary Charan Singh, India's fifth Prime Minister. A passionate advocate for rural development and farmers' welfare, Charan Singh's policies laid the foundation for several reforms aimed at uplifting the agrarian economy. His contributions continue to inspire government initiatives that prioritize the welfare of farmers, fostering sustainable agricultural growth and ensuring food security for the nation.
The Legacy of Chaudhary Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh was born on December 23, 1902, in Noorpur, Uttar Pradesh. His deep understanding of rural issues and commitment to improving farmers’ lives earned him the title of "Kisan Leader". Throughout his political career, he championed reforms such as the Debt Redemption Bill (1939), which alleviated the financial burdens of farmers, and the Land Holding Act (1960), which promoted fair distribution of agricultural land. He also advocated for Minimum Support Price (MSP), and his policies laid the groundwork for NABARD and other farmer-centric institutions.
Significance of Kisan Diwas
Kisan Diwas highlights the importance of agriculture in India’s economy and employment, with farmers constituting nearly 50% of the workforce. The day emphasizes the need for policies that address farmers' challenges such as climate change, financial constraints, and technological adoption. It also serves as a reminder of the necessity to empower farmers through innovative solutions, financial security, and sustainable farming practices.
Key Government Initiatives for Farmer Welfare
The Indian government has launched several schemes to address the challenges faced by farmers and support their socio-economic upliftment:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): Provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): Offers crop insurance to mitigate financial risks due to crop loss.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PM-KMY): A pension scheme for farmers to ensure long-term social security.
- Soil Health Card Scheme: Promotes efficient fertilizer use and soil health by providing farmers with personalized soil health reports.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): These entities help farmers collectively access markets, reduce costs, and improve bargaining power.
- Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS): Provides affordable credit to farmers, especially for agriculture-related activities.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Helps farmers access timely credit for agricultural purposes at concessional rates.
Significant Budget Allocations and New Schemes
The government has drastically increased its budget allocation to the agriculture sector. From Rs. 21,933.50 crore in 2013-14, the budget has risen to Rs. 1,22,528.77 crore for 2024-25, underlining the government's commitment to farmer welfare and sustainable agricultural development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Namo Drone Didi Scheme: This initiative, aimed at empowering Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs), supports the use of drones for agricultural purposes, including fertilizer and pesticide application, with 80% financial assistance.
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP): Enhances the quality and productivity of horticulture crops by ensuring disease-free planting material.
- Digital Agriculture Mission: Aims to modernize farming with digital infrastructure, including crop estimation surveys and e-agriculture platforms.
- National Mission on Natural Farming (NMNF): Encourages chemical-free, sustainable farming practices.
Farmers' Role in Nation-Building
India’s agricultural sector not only sustains the livelihoods of millions but also contributes significantly to the country's GDP. In FY 2023-24, agriculture contributed 17.7% to the Gross Value Added (GVA). With over 54% of the country's land dedicated to agriculture, farmers are critical to food security and rural development.
In 2023-24, India achieved a record foodgrain production of 332.2 million tonnes, illustrating the resilience of Indian farmers in ensuring food availability despite challenges like climate change.
IPBES Nexus Report

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The IPBES Nexus Report, formally titled The Assessment Report on the Interlinkages Among Biodiversity, Water, Food, and Health, was released to address the interconnected global challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, food insecurity, water scarcity, and health risks. The report stresses that these challenges are deeply intertwined and cannot be solved separately; doing so would lead to ineffective or even counterproductive results.
Key Highlights of the Nexus Report
- Interconnections Between Global Challenges: The report emphasizes the strong interlinkages between the five major global challenges:
- Biodiversity Loss
- Water Scarcity
- Food Insecurity
- Health Risks
- Climate Change
It argues that efforts to address these challenges independently are ineffective and often exacerbate the problems. For example, scaling up food production to combat hunger can put more pressure on land, water, and biodiversity.
- Economic Cost of Biodiversity Loss:
- Global GDP Dependency: Over half of the global GDP (approximately $58 trillion annually) depends on nature. Biodiversity degradation significantly undermines productivity and economic output.
- Unaccounted Costs: The neglect of biodiversity in economic activities contributes to a loss of $10-25 trillion annually.
- Delayed Action: Delaying action on biodiversity conservation could double the costs within the next decade, potentially incurring $500 billion per year in additional costs.
- Synergistic Approach: The report identifies over 70 response options that promote synergistic outcomes across the five challenges. These include:
- Restoring Carbon-Rich Ecosystems: Such as forests, soils, and mangroves to address climate change and biodiversity loss.
- Managing Biodiversity to Prevent Disease Transmission: Effective biodiversity management reduces risks of diseases passing from animals to humans (zoonotic diseases).
- Sustainable Diets: Promoting diets that are both healthy and environmentally sustainable.
- Nature-Based Solutions: Implementing solutions that rely on natural processes to mitigate challenges like water scarcity and climate change.
- Inequality and Vulnerability: The report highlights how inequality exacerbates the challenges. Vulnerable populations, especially those living in areas where biodiversity has sharply declined, face increased health risks, malnutrition, and economic instability. 41% of people live in regions where biodiversity loss has been particularly severe, and 9% face high health burdens due to these declines.
- Principles for Transformative Change: The report outlines principles for achieving transformative change:
- Equity and Justice: Ensuring fair distribution of resources and opportunities for all.
- Pluralism and Inclusion: Embracing diverse perspectives and voices in policy-making.
- Respectful Human-Nature Relationships: Recognizing and nurturing reciprocal relationships between humans and nature.
- Adaptive Learning and Action: Continuously evolving policies and strategies based on feedback and new evidence.
- Urgency for Immediate Action: The report stresses that immediate action is critical. If the world continues to neglect biodiversity, it will face not only environmental collapse but also a missed opportunity for economic growth. Immediate implementation of nature-positive strategies could unlock $10 trillion in business opportunities and create 400 million jobs by 2030.
The IPBES Transformative Change Assessment Report
- This report builds upon the 2019 IPBES Global Assessment Report and advocates for transformative change to halt biodiversity loss and achieve global development goals. It defines transformative change as a system-wide shift in:
- Views: Changing how we think about nature and its value.
- Structures: Reforming systems of governance and organization.
- Practices: Changing behaviors and practices that harm nature.
Key Challenges to Transformative Change:
- Disconnection from Nature: Human societies' disconnection from nature, often rooted in historical domination, is a major cause of biodiversity loss.
- Economic Inequality: The concentration of power and wealth exacerbates environmental degradation.
- Unsustainable Consumption: Unsustainable patterns of consumption and production are significant drivers of environmental harm.
Synergistic Strategies for Transformation:
- Conserve and Regenerate: Restore ecosystems that have both ecological and cultural value.
- Mainstream Biodiversity: Integrate biodiversity considerations into sectors like agriculture, forestry, and infrastructure development.
- Transform Economic Systems: Adopt policies such as true cost accounting and sustainability-based tax principles to internalize the environmental costs of economic activities.
- Inclusive Governance: Promote governance systems that involve all stakeholders, especially local communities, in decision-making.
SAMARTH UDYOG BHARAT 4.0 INITIATIVE

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative, launched by the Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI), aims to enhance the competitiveness of the Indian capital goods sector by promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. This initiative is part of the Scheme for Enhancement of Competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
Key Features of SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
- Establishment of Smart Manufacturing Hubs: Under this initiative, four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres have been set up across India:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab, Pune
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing, IIT Delhi
- I-4.0 India @ IISc, Bengaluru
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell, CMTI, Bengaluru
- Cluster Industry 4.0 Experience Centres: In addition to the above centres, 10 cluster Industry 4.0 experience centres have been approved. These will be established under a Hub and Spoke model, managed by the C4i4 Lab in Pune, and spread across India.
- Key Achievements:
- Model Factories: Development of an Industry 4.0 enabled Model Factory at C4i4, Pune, and a smart production-based factory at CMTI Bengaluru.
- Industry 4.0 Solutions: More than 50 use-cases for Industry 4.0 solutions were compiled to support implementation.
- Maturity Assessment Tool: Creation of the Industry 4.0 Maturity Model (I4MM), specifically designed to assess the readiness of Indian manufacturing companies for Industry 4.0.
- Online Assessment Tool: Launch of a free online assessment tool by C4i4 Lab, Pune, to help MSMEs evaluate their maturity in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Training and Awareness:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular awareness seminars, workshops, and knowledge-sharing events are organized to educate industries about Industry 4.0.
- Workforce Training: The SAMARTH Centres have trained over 5000 professionals on smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Consultancy Services: The centres offer consultancy in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics, along with incubation support for start-ups and MSMEs.
- Impact on MSMEs:
- Digital Maturity Assessments: Over 100 digital maturity assessments have been completed for the auto industry, and more than 500 improvement initiatives have been identified.
- Training and Capacity Building: Over 500 digital champions have been trained on Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Focus on MSMEs: While no direct financial assistance is provided to industries, including MSMEs, under this initiative, the SAMARTH Centres play a key role in helping them adopt Industry 4.0 technologies and build their capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative seeks to increase the global competitiveness of India's capital goods and manufacturing sectors.
- It leverages Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, automation, data analytics, and AI to modernize manufacturing processes.
- The initiative involves setting up 4 major Smart Manufacturing Hubs and 10 regional experience centres across the country to facilitate awareness, training, and adoption of Industry 4.0 among manufacturers, especially MSMEs.
- While it does not provide financial aid, it helps industries improve their digital maturity, trains workforce, and guides them through consultancy and workshops.
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)

- 22 Dec 2024
Recently, the Union Minister Shri Bhupender Yadav inaugurated two groundbreaking facilities at the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun: the Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification and the Next Generation DNA Sequencing (NGS) Facility. These facilities are designed to enhance India’s capabilities in wildlife conservation and support the growth of traditional crafts like Pashmina weaving.
Key Highlights
Next Generation DNA Sequencing Facility (NGS)
The NGS facility is a cutting-edge research tool that enables the high-throughput analysis of entire genomes. This technology is pivotal in studying wildlife genetics and biodiversity by decoding millions of DNA sequences at once.
Applications in Wildlife Conservation:
- Genetic Diversity and Health: NGS helps assess the genetic diversity of species and their population health.
- Evolutionary Relationships: It aids in understanding the evolutionary history and unique adaptations of species.
- Disease Surveillance: The technology supports studying pathogen-host interactions and monitoring diseases affecting wildlife.
- Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade: NGS can help detect illegal wildlife trade and the movement of endangered species.
- Impact of Climate Change: It is crucial for studying how climate change affects genetic diversity and species survival.
This facility positions WII as a leading hub for molecular research, enabling more precise conservation efforts and studies on endangered species like tigers, elephants, and riverine dolphins.
Advanced Facility for Pashmina Certification
Launched under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model between WII and the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH), the Pashmina Certification Centre (PCC) has been significantly upgraded. The facility now includes a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) for advanced wool testing and certification.
Key Features of the Upgraded Facility:
- Fiber Analysis: The SEM-EDS technology ensures accurate identification and certification of Pashmina fibers, free from any prohibited materials.
- Unique ID and E-certificates: Each certified product is tagged with a unique ID and e-certificate, enhancing traceability and authenticity.
- Global Trade Facilitation: The certification process eliminates delays at exit points, ensuring smoother international trade for certified Pashmina products.
The PCC has already certified over 15,000 Pashmina shawls and plays a crucial role in supporting the livelihoods of artisans and weavers in Jammu & Kashmir. By ensuring the authenticity of Pashmina, the facility also helps combat the illegal trade of Shahtoosh wool, which is harmful to the Tibetan antelope (Chiru).
Significance for Artisans and Conservation:
- Support for Artisans: The upgraded facility helps increase the credibility of Pashmina products in global markets, benefiting local artisans and weavers.
- Conservation Impact: By certifying genuine Pashmina products, the initiative indirectly contributes to the conservation of the Tibetan antelope by reducing illegal poaching and trade.
- Sustainability: The PCC is a self-sustaining model that not only supports conservation but also generates revenue and creates job opportunities.
Overview of the Genome India Project
The Genome India Project is a gene mapping initiative launched by the Department of Biotechnology, aiming to create a comprehensive database of genetic variations across the Indian population. The project focuses on understanding genetic diversity and its implications for health, agriculture, and biodiversity conservation in India.
Goals:
- Comprehensive Gene Mapping: The project seeks to map the genetic variations found within India’s diverse population, enabling better healthcare and disease management.
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Insights from the project will also aid in wildlife conservation by understanding the genetic health of endangered species and their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
This initiative is aligned with India’s broader goals of using advanced technologies to address modern conservation challenges and foster a sustainable future.
India State of Forest Report 2023

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), assesses the forest and tree resources of the country based on satellite data and field-based inventories. The ISFR 2023 is the 18th edition of this report, with the first published in 1987.
Key Findings
- Total Forest and Tree Cover:
- Area: 827,357 sq km (25.17% of India's geographical area)
- Breakdown:
- Forest cover: 715,343 sq km (21.76%)
- Tree cover: 112,014 sq km (3.41%)
- Increase from 2021: An increase of 1,445 sq km, including:
- Forest cover: +156 sq km
- Tree cover: +1,289 sq km
- State-wise Forest and Tree Cover:
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Madhya Pradesh (85,724 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (67,083 sq km)
- Maharashtra (65,383 sq km)
- Top 3 States by Forest Cover:
- Madhya Pradesh (77,073 sq km)
- Arunachal Pradesh (65,882 sq km)
- Chhattisgarh (55,812 sq km)
- States with Maximum Increase in Forest and Tree Cover:
- Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan
- Mizoram, Gujarat, and Odisha showed the most significant increase in forest cover.
- Top 3 States by Total Forest and Tree Cover Area:
- Forest Cover Percentage (as a proportion of total geographical area):
- Lakshadweep: 91.33% (Highest)
- Mizoram: 85.34%
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands: 81.62%
- 19 States/UTs have over 33% forest cover, with 8 states having more than 75%.
- Mangrove Cover:
- Total Mangrove Cover: 4,992 sq km (a decrease of 7.43 sq km from 2021).
- Notable Changes: Gujarat saw the largest loss of mangroves, whereas Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra reported increases.
- Carbon Stock and Climate Targets:
- Total Carbon Stock: 7,285.5 million tonnes (an increase of 81.5 million tonnes from the previous assessment).
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India’s carbon stock has reached 30.43 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent.
- Achieved an additional 2.29 billion tonnes of carbon sink compared to the 2005 baseline, towards the 2030 target of 2.5-3.0 billion tonnes.
- Bamboo and Timber Production:
- Bamboo Bearing Area: Estimated at 154,670 sq km, an increase of 5,227 sq km since 2021.
- Timber Potential: Estimated annual potential production of 91.51 million cubic meters from trees outside forests.
Achievements:
- There has been a notable increase in the forest and tree cover, particularly in states like Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- The carbon stock in forests has increased, helping India make significant progress in its climate change mitigation goals.
- The bamboo bearing area has also expanded, promoting biodiversity and economic benefits through bamboo cultivation.
Concerns:
- Mangrove Loss: Gujarat experienced a notable decrease in mangrove area, highlighting the need for focused conservation efforts in coastal regions.
Forest Survey of India (FSI) Overview
- Established: 1981, under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Mission: To assess, monitor, and research forest resources across India, providing data for sustainable management, national planning, and conservation.
- Headquarters: Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
India’s National Quantum Mission

- 22 Dec 2024
In News:
India is preparing to launch its first quantum satellite within 2-3 years as part of its National Quantum Mission (NQM), a significant initiative aimed at positioning India as a global leader in quantum technologies. This satellite will play a pivotal role in enhancing the security of communications, particularly in the face of the potential threat posed by quantum computers to existing cryptographic systems.
What is a Quantum Satellite?
A quantum satellite is a type of communication satellite that uses quantum physics principles to secure data transmission. Unlike conventional satellites that rely on classical encryption, quantum satellites leverage quantum mechanics to achieve unbreakable encryption through Quantum Key Distribution (QKD).
Key Features:
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): Ensures secure key sharing, revealing any attempts of eavesdropping.
- Security Advantage: Provides "unconditional security" by detecting any interference during the transmission process.
- Data Transmission: Unlike conventional satellites that encode data in classical bits, quantum satellites encode information in quantum states or qubits.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure communications. The most widely used method is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), which ensures that the keys used to encrypt and decrypt messages remain secret and unbreakable.
Key Mechanisms:
- Quantum Measurement: Any attempt to measure the quantum state (such as a photon carrying information) changes its state, alerting the sender and receiver to potential eavesdropping.
- Quantum Entanglement: When two quantum particles (photons) are entangled, a change in one will instantaneously affect the other, ensuring that the key remains secure.
Why is Quantum Satellite Important?
The advent of quantum computing threatens the cryptographic methods that secure current digital communications. Quantum computers, with their vast computational power, could potentially crack encryption codes that are currently deemed secure. Quantum satellites aim to counteract this threat by using quantum cryptography to make communications tamper-proof.
Security in the Quantum Era:
- Classical Encryption: Relies on mathematical problems that are difficult to solve without the decryption key.
- Quantum Encryption: Uses quantum properties, such as superposition and entanglement, to offer superior security.
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
The National Quantum Mission (NQM) was approved by the Union Cabinet in April 2023 with a budget of ?6,000 crore for implementation over eight years (2023-2031). The mission aims to accelerate the development and application of quantum technologies, with a focus on quantum communication, quantum computing, quantum sensing, and quantum metrology.
Key Objectives:
- Development of Quantum Computers: Building intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits.
- Quantum Communication: Establishing secure, satellite-based quantum communication systems within India and internationally.
- Research and Innovation: Fostering quantum technologies and creating a self-reliant ecosystem.
India’s Advancements in Quantum Technology
India is making significant progress in quantum research and communication. The Raman Research Institute in Bengaluru has identified Hanle, Ladakh as an ideal location for quantum communication experiments due to its optimal atmospheric conditions.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has already demonstrated successful free-space quantum communication over short distances (300 meters). The upcoming quantum satellite will build upon this progress to create secure quantum communication networks within India and internationally.
Global Context: Micius Satellite and China’s Lead
China is a global leader in quantum communications, having launched the world’s first quantum satellite, Micius, in 2016. Micius demonstrated the feasibility of secure quantum communication by generating pairs of entangled photons. India’s quantum satellite will build on this technology to create robust, long-range quantum communication networks.
Limitations of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
Despite its promise, QKD faces several limitations:
- Technological Maturity: The technology is still in the experimental phase, and large-scale commercial implementation is not yet feasible.
- Authentication Issues: QKD lacks reliable methods to authenticate the transmission source, leaving it vulnerable to impersonation attacks.
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining QKD networks requires specialized hardware, leading to higher costs.
- Denial-of-Service Risks: Eavesdroppers can trigger the abort mechanism, leading to transmission interruptions.
- Signal Loss: Atmospheric and distance-related attenuation can degrade the quality of quantum signals.
National Quantum Mission and Sectoral Impact
The NQM aligns with India's national priorities, including Digital India, Make in India, and Start-up India. The mission’s outcomes are expected to impact various sectors, such as:
- Healthcare: Quantum computing for drug design and medical research.
- Space Exploration: Enhancing communication security for space missions.
- Banking and Financial Services: Strengthening data security and transaction integrity.
- Energy: Improving energy systems and smart grids through advanced sensing technologies.
IRIS²: The European Union's Ambitious Satellite Network

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
The European Union (EU) has announced the launch of IRIS² (Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity, and Security by Satellite), a highly ambitious space program that aims to enhance satellite connectivity, security, and resilience for both governmental and civilian applications. The initiative is set to rival major global satellite systems, such as Elon Musk's Starlink, and aims to provide secure, high-speed broadband connectivity, particularly in underserved regions.
Key Features of IRIS²:
- Satellite Constellation: The system will consist of 290 satellites, including 264 in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 18 in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
- First Launch: The first satellite for the program is scheduled for launch in 2029.
- Secure Connectivity: IRIS² is designed to provide secure, high-speed broadband services, particularly for European regions that lack reliable connectivity.
- Collaboration: The project is a collaboration between the EU, the European Space Agency (ESA), and private sector partners, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus.
- Funding: The program is funded through a €10.6 billion (~$11 billion) investment, with a 12-year concession for its implementation.
Applications of IRIS²:
- Governmental Use:
- Border Surveillance: Enhanced monitoring for national security.
- Crisis Management: Reliable communication during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Infrastructure Security: Safeguarding key national infrastructure.
- Defense: Boosting military communication resilience.
- Civilian Use:
- Broadband Access: Providing internet access in rural and underserved areas.
- Smart Energy: Supporting management of energy grids and related technologies.
- Transportation: Ensuring reliable communication and navigation in aviation, maritime, and automotive sectors.
- Remote Healthcare: Improving healthcare access in remote locations.
Significance of IRIS²:
- Strategic Asset: The program will strengthen EU sovereignty in space technology and improve its technological independence, reducing reliance on non-European satellite systems.
- Cyber and Communication Resilience: IRIS² is designed to enhance resilience against cyber threats and communication disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service for both public and private sectors.
- Commercial Benefits: The satellite network will provide high-speed connectivity for businesses across Europe, offering a boost to commercial activities in remote and underserved areas.
- Complementary to Existing EU Programs: IRIS² complements other EU space initiatives, such as Copernicus (Earth observation) and Galileo (satellite navigation), enhancing the EU's capabilities in the space sector.
Overview of the IRIS² Satellite Network:
- Deployment in LEO and MEO:
- 264 satellites in LEO will provide low-latency communication for a wide range of applications.
- 18 satellites in MEO will offer broader coverage and support for global connectivity.
- Funding and Partners: The program is funded by the EU, ESA, and private firms, including SES, Eutelsat, and Airbus, ensuring both public and private sector involvement in the project.
- Applications:
- The network will provide secure satellite services for critical government functions, including surveillance, defense, and crisis management.
- It will also support civilian uses, such as broadband, smart grids, and transportation, and will facilitate cloud-based services.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance:
- Boost to European Competitiveness: By developing its own satellite system, the EU will enhance its competitive position in the global space sector.
- Security and Autonomy: IRIS² will help Europe maintain control over its communication infrastructure, strengthening its autonomy and reducing dependence on external players for critical services.
- Resilience in Crisis Situations: In times of disruption (e.g., natural disasters, cyberattacks), IRIS² will ensure that Europe can maintain secure, reliable connectivity.
72% Decline in Bird Species at Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary, Assam

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
A recent study has revealed a dramatic decline in the number of bird species at Assam's Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary (BBBS). The sanctuary, once home to a rich diversity of avian species, has experienced a 72% decline in bird species over the past 27 years. The study, published in the Journal of Threatened Taxa, highlights the severe biodiversity crisis facing the sanctuary.
Key Findings:
- Bird Species Count Decline:
- In 1997, the sanctuary recorded 167 bird species.
- Recent surveys (2022-2024) have only recorded 47 species, marking a 71.85% decline in species count.
- Surveys:
- 2011 Survey: Recorded 133 species (86 resident, 23 migratory, 24 local migrants).
- 2017-2018 Survey: Found 120 species, along with a variety of other biodiversity, including macrophytes, fish, and aquatic ferns.
- Impact on Migratory Birds:
- Migratory species like Brown Shrike, Citrine Wagtail, and White Wagtail (winter migrants), and the Lesser Kestrel (summer migrant) were recorded recently.
- Main Causes of Decline:
- Anthropogenic Activities: Overfishing, poaching, excessive harvesting of aquatic plants, and egg collection.
- Land Use Changes: Habitat degradation due to agriculture, machinery noise, and land being used as pasture areas.
- Disruption of Food Chain: Habitat loss and changes in foraging and breeding grounds for both migratory and resident birds.
- Species of Concern:
- Poached Birds: Lesser whistling duck, Fulvous whistling duck, White-breasted waterhen, Indian pond heron, Eastern spotted dove, and Yellow-footed green pigeon.
- Threatened Species: The sanctuary is home to globally threatened species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant.
About Bordoibam-Bilmukh Bird Sanctuary:
- Location: Situated between Dhemaji and Lakhimpur districts in Assam, the sanctuary spans 11.25 sq. km at an altitude of 90-95 meters above sea level.
- History: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1996, it was originally part of the Subansiri River which has now shifted 7 km from the wetland.
- Climate & Vegetation:
- Moist tropical climate with an average annual rainfall of around 2,000 mm.
- The vegetation includes flooded valley grasslands and wetland plants, providing crucial habitat for migratory birds.
- Significance for Avian Species:
- Hosts a variety of migratory waterfowl, especially during the winter.
- Home to globally threatened bird species like the Spot-billed Pelican and Lesser Adjutant, along with resident birds such as the Indian Pond Heron and Fulvous Whistling Duck.
Conservation Efforts:
- The decline in bird species at the sanctuary has raised alarm about the degradation of wetland habitats.
- The study emphasizes that habitat loss can disrupt the food chain, water table, and nutrient cycle, which in turn harms both the ecosystem and human communities.
- The authors of the study advocate for intense conservation efforts to restore and protect the sanctuary’s biodiversity.
Assam's Biodiversity:
- Assam is one of India's most biodiverse states, with around 950 bird species, including 17 endemic species.
- The state also hosts 55 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBA), which are vital hotspots for avian species.
New Undersea Cables to Boost India’s Digital Connectivity

- 21 Dec 2024
In News:
India is expanding its digital infrastructure with the launch of two major undersea cable systems aimed at enhancing its Internet connectivity with Asia and Europe. The India Asia Xpress (IAX) and India Europe Xpress (IEX) are set to provide additional data links between India and these regions, supporting the growing demand for data usage. This also marks India’s increasing involvement in submarine cable resilience and security discussions.
Key Points:
- New Cable Systems:
- India Asia Xpress (IAX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia.
- India Europe Xpress (IEX): Connects Chennai and Mumbai with France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Djibouti.
- Total Length: Both cables, together spanning over 15,000 kilometers, will expand India’s undersea cable network.
- Ownership and Investment:
- Both cable systems are owned by Reliance Jio, with a strategic investment from China Mobile.
- Geopolitical Impact:
- These expansions are a response to growing Internet traffic, as well as India's rising geopolitical ambitions. They help bolster India’s defense strategy, improving cable resilience against disruptions from cyberattacks or physical damages.
- India’s active role in maritime cable network security is being closely watched, especially in key regions like the Bay of Bengal and the South China Sea.
- Past Cable Disruptions:
- In March, three cables connecting India to West Asia and Europe were disrupted, impacting Internet traffic. However, India’s alternate routing systems and data centers ensured services remained operational, highlighting the country’s resilience.
- International Role:
- India’s role in submarine cable resilience is growing. Telecom Secretary Neeraj Mittal is part of the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Impact on India’s Connectivity:
- Bangladesh's Role:
- Plans to sell bandwidth from Bangladesh to Northeast India were recently put on hold. However, this does not significantly impact India as Northeast India already benefits from substantial fiber-optic connectivity through Power Grid Corporation of India’s transmission lines.
About Underwater Cables:
- What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables are fiber-optic cables laid under the ocean to transmit data across vast distances at high speeds.
- New Cable Systems:
- IAX: Connects India to Asia (Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia).
- IEX: Connects India to Europe (France, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Djibouti).
- How They Work:
- Fiber-optic technology uses laser beams through thin glass fibers to transmit data.
- The cables are protected by multiple layers of insulation, plastic, and steel wires and are buried near shores or laid directly on the ocean floor in deep sea regions.
- Cable Features:
- Data Capacity: New cables can carry up to 224 Tbps (Terabits per second).
- Durability: Designed to avoid damage from fault zones, fishing areas, or anchors.
- Speed: Faster and more cost-efficient than satellite communications for large-scale data transfer.
Why Undersea Cables Over Satellites?
- Higher Capacity: Submarine cables handle far more data than satellites.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable for high-volume data transfers.
- Reliability: Cables provide more stable connections, especially for large-scale data, compared to satellites.
Reimposition of Protected Area Permit (PAP) in Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland

- 20 Dec 2024
In News:
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of the Government of India has recently reinstated the Protected Area Regime (PAR) for the states of Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland, which are strategically located along the international border with Myanmar. This move comes amid growing security concerns, particularly the influx of migrants from Myanmar, which has been cited as a significant factor in the ongoing conflicts in the region.
What is Protected Area Permit (PAP)?
A Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permission required for foreign nationals to visit certain areas of India deemed sensitive due to their proximity to international borders or other security-related concerns. The regulations governing the PAP are laid down under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958, which restricts the entry of foreigners to designated regions within India.
Purpose of PAP:
The PAP regime serves multiple critical objectives:
- National Security: It ensures the monitoring and regulation of foreign nationals in sensitive border areas.
- Preservation of Local Communities: The regime safeguards indigenous populations and their unique cultural heritage.
- Environmental Conservation: The permit helps minimize ecological disturbances in fragile regions, ensuring sustainable tourism and development.
Key Features of PAP Regime:
- Eligibility: All foreign nationals, excluding Bhutanese citizens, must obtain a PAP to enter these designated areas. The permit can be granted for specific regions, routes, and time periods.
- Validity: The PAP is typically valid for 10 days with the possibility of extension.
- Restricted Areas: Certain foreign nationals, particularly those from Afghanistan, China, and Pakistan, require prior approval from the MHA to enter these regions.
- Tourism and Other Permits: While foreign nationals can visit these regions for tourism purposes under the PAP, non-touristic visits require special permission from the MHA.
- Registration: Foreigners must register with the Foreigners Registration Officer (FRO) within 24 hours of arrival in the protected area.
Historical Context and Reimposition:
The PAP regime was lifted for Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland in 2011, as part of efforts to boost tourism in the region. However, due to rising security concerns related to illegal immigration and ethnic tensions, the MHA reimposed the PAP in 2025. The government’s move aligns with its broader national security strategy to better control foreign movements in sensitive border regions, particularly those with Myanmar, where the Free Movement Regime (FMR) had previously allowed easier cross-border travel.
Background on Security Concerns:
The influx of individuals from Myanmar, particularly members of the Chin community, which shares ethnic ties with the Kuki-Zomi communities in India, has been a source of tension. The Manipur government has repeatedly emphasized that uncontrolled migration has contributed to the unrest in the state. Additionally, the decision to end the FMR between India and Myanmar has further intensified the debate over border security and migration.
Impact on Tourism and Local Communities:
While the reimposition of the PAP is seen as a measure to strengthen security, it has raised concerns in states like Mizoram and Nagaland, which have been actively promoting tourism. For example, Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival recently attracted over 200,000 visitors, including foreign nationals. The reintroduced restrictions may dampen tourism in these states, which were previously exempt from the PAP to encourage foreign visits.
Key Legal Provisions Under the PAP Regime:
- Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958: This order mandates the requirement of a PAP for foreigners visiting areas close to international borders.
- Foreigners (Restricted Areas) Order, 1963: This order covers areas that require a Restricted Area Permit (RAP) for foreign nationals, such as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
States Affected by the PAP Regime:
The PAP regime affects regions close to India’s international borders, including the entire states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand.
India's First-Ever Ganges River Dolphin Tagging in Assam

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
India conducts the first-ever satellite tagging of the Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista gangetica) in Assam, a key step in wildlife conservation.
Key Highlights:
Objective of Tagging: The tagging aims to understand:
- Migratory patterns
- Range and distribution
- Habitat utilization, especially in fragmented river systems.
Key Participants:
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
- Assam Forest Department
- Aaranyak (NGO)
- Funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
Significance of the Tagging:
- Technology Used: Lightweight satellite tags compatible with Argos systems were employed, minimizing interference with the dolphin’s movement despite its limited surfacing time (5-30 seconds).
- Insight into Dolphin Ecology: Helps fill knowledge gaps regarding habitat needs and seasonal migration, especially in disturbed river ecosystems.
Ganges River Dolphin – India's National Aquatic Animal:
- Endemic to India with around 90% of the population in India.
- Known for being nearly blind and using echolocation for navigation and hunting.
- Plays a crucial role as an apex predator and indicator species for river ecosystem health.
Project Dolphin:
- Launched by PM Narendra Modi in 2020, modeled after Project Tiger.
- Focuses on conservation of riverine and marine dolphins.
- A 10-year initiative funded by MoEFCC to safeguard dolphin populations and address ecosystem challenges.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Endangered.
- Protection: Included in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act (1972) and CITES Appendix I.
- Major Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, bycatch, and water abstraction, compounded by damming and sand mining.
Broader Impact:
- The tagging initiative contributes to evidence-based conservation strategies for Ganges River Dolphins.
- Will aid in the development of a comprehensive conservation action plan for the species.
- Expands the understanding of critical habitats within river ecosystems, benefiting both biodiversity and the communities dependent on these resources.
National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP)

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
The Central Zoo Authority, under the aegis of the Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) has taken up the development of the ‘National Wildlife Health Policy in consultative workshop held in Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Organized by: Central Zoo Authority (CZA), under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
- Event: Consultative workshop held at Indira Prayavaran Bhawan, New Delhi, on the development of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP).
- Purpose: To address health threats to wildlife and integrate wildlife health management with public and animal health.
Goals of the National Wildlife Health Policy (NWHP):
- One Health Approach: Integrates human, animal, and environmental health, recognizing their interdependence.
- Focus Areas:
- Prevent and control zoonotic diseases.
- Improve disease surveillance and early detection, especially in protected areas.
- Promote biosecurity measures and epidemic preparedness.
- Enhance research and development in wildlife health management.
- Advocate for community awareness on wildlife health and conservation.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Wildlife Health Management Unit (WHMU): Proposed unit to oversee the policy's implementation.
- Collaboration: Involves coordination with various stakeholders including government ministries, NGOs, academic institutions, and veterinary universities.
- Disease Surveillance: Establish protocols for monitoring and controlling wildlife diseases, especially in protected areas.
- Capacity Building: Training programs for professionals involved in wildlife conservation and health management.
- Biosecurity Protocols: Strengthen measures to reduce disease transmission risks.
Supporting Institutions:
- GISE Hub, IIT Bombay and Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India are providing support in policy development.
Challenges Addressed:
- Wildlife in India faces various health challenges including:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., Canine Distemper Virus).
- Habitat loss and climate change impacts.
- Illegal wildlife trade and other anthropogenic pressures.
- India has over 91,000 wildlife species and more than 1,000 protected areas, making comprehensive health management crucial.
Expected Outcomes:
- Comprehensive Framework: A science-based framework for wildlife health, integrating ecological, human, and animal health.
- Disease Outbreak Response: Structured mechanisms for disease management, surveillance, and legal frameworks.
- Public Health Integration: Safeguard wildlife health, which directly impacts balanced ecosystems and biodiversity.
Policy’s Strategic Alignment:
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31): The policy complements the action plan’s 103 conservation actions and 250 projects, including disease surveillance protocols in tiger reserves and other protected areas.
- Research & Development: Encourages the development of strategies to manage wildlife health and prevent disease outbreaks.
Wroughton’s Free-Tailed Bat

- 19 Dec 2024
In News:
Wroughton’s free-tailed bat, a highly rare species of molossus bat, has been spotted at the Delhi Development Authority (DDA)’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park, marking a unique sighting.
Key Highlights:
- Species Overview: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat (Otomops wroughtoni) is a rare species of molossus bat, notable for its powerful flight and ecological importance in controlling insect populations and assisting in pollination.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Listed as "Data Deficient".
- Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Geographical Distribution:
- Primarily found in the Western Ghats, with a single known breeding colony.
- Small colonies in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and a solitary individual sighted in Cambodia.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Large in size, with huge ears extending beyond the muzzle.
- Bicoloured velvet fur.
- Noted for powerful flying capabilities, enabling long-distance foraging.
- Ecological Role:
- Regulates insect populations.
- Known for assisting in pollination.
- Habitat:
- Roosts in caves, or dark, damp, and slightly warm places, typically in moderate-sized colonies.
- Significance of the Delhi Sighting:
- The sighting at Yamuna Biodiversity Park is significant for Delhi, marking a rare occurrence in the region.
- Delhi's bat species: The city is home to about 14 bat species, with four species, including the Indian false vampire and Egyptian free-tailed bat, considered locally extinct.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Two decades of ecological restoration have created specialized niches in the area, aiding species rewilding and ecological balance.
- The Aravalli Biodiversity Park in Gurugram now serves as the only known roosting site for the Blyth’s horseshoe bat in Delhi NCR.
- Additional Notes:
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat was considered critically endangered until 2000 due to its limited known population. However, the discovery of populations in other regions has led to a reclassification to "Data Deficient".
- Despite being discovered over a century ago, much about the bat's feeding ecology remains unknown.
Kisan Kavach

- 18 Dec 2024
In News:
Scientists develop ‘kisan kavach’ to shield farmers from pesticide sprays.
Key Highlights:
- Purpose: The Kisan Kavach is designed to shield farm labourers from harmful pesticide exposure. Pesticides, often neurotoxins, can be detrimental to health, causing symptoms like dizziness, headaches, vomiting, and even death with high exposure.
- Development:
- Developed by Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem), Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
- Launched by Union Minister of State for Science and Technology.
- Fabric Technology:
- The suit uses oxime fabric, which chemically breaks down common pesticides on contact, preventing them from penetrating the skin.
- Mechanism: The fabric works through nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis, deactivating pesticides upon contact and preventing pesticide-induced toxicity and lethality.
- Components of the Kit:
- Consists of a trouser, pullover, and face-cover.
- Washable and reusable: The suit retains its protective properties even after 150 washes, in a wide temperature range, and under UV light exposure.
- Affordability:
- Priced at ?4,000 per kit, with efforts underway to reduce costs through increased production.
- Field Testing and Efficacy:
- Animal studies: Rodent tests showed that animals exposed to pesticides and covered with ordinary cotton cloth died within four days, while those with the activated fabric remained safe.
- Human trials are still pending.
- Health Implications:
- Pesticides are linked to chronic health issues, including cancer, as per studies by the National Institute of Nutrition (Indian Council of Medical Research).
- Global Context:
- In 2020, India used 61,000 tonnes of pesticides, despite producing much more (2,58,130 tonnes in 2022-2023).
- Pesticide-related health issues are a major concern, with 60% of India’s adult workforce engaged in agriculture.
- Impact:
- The suit aims to protect farm labourers from pesticide exposure and promote sustainable agriculture.
- It could help reduce health complications and improve working conditions for farmers, who often lack proper protective gear.
- Future Plans:
- Awareness campaigns will be conducted to inform farmers about this protective technology.
- Efforts are underway to make the kit more affordable as demand increases.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF)

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF), launched by Union Minister Pralhad Joshi aims to support farmers by facilitating post-harvest finance using electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to minimize distress selling and ensure financial security for farmers, particularly small and marginalized ones.
Key Features of the Scheme:
- Total Corpus: ?1,000 crore for post-harvest finance.
- Loan Coverage:
- Agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?75 lakh.
- Non-agricultural purposes: Loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled and cooperative banks.
- Guarantee Coverage:
- Small and marginal farmers/Women/SC/ST/PwD: 85% for loans up to ?3 lakh, and 80% for loans between ?3 lakh to ?75 lakh.
- Other borrowers: 75% coverage for loans up to ?200 lakh.
- Risks Covered: Both credit risk and warehouseman risk.
- Guarantee Fees: 0.4% per annum for farmers, and 1% per annum for non-farmers.
Objectives:
- Minimize distress selling: By providing easy access to loans post-harvest, the scheme helps farmers avoid selling produce at low prices due to cash crunches.
- Instill confidence in banks: The scheme provides a guarantee cover to lenders, encouraging them to offer loans against e-NWRs.
- Encourage warehouse registration: The scheme emphasizes the need for more warehouses, particularly those closer to farmland, to improve accessibility for farmers.
About e-NWRs:
- e-NWRs are digital versions of traditional warehouse receipts that enable farmers to pledge stored commodities as collateral for loans.
- These receipts are governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007, and since 2017, e-NWRs have been mandated for use in transactions related to agricultural produce stored in WDRA-accredited warehouses.
Expected Impact:
- This scheme is expected to boost post-harvest lending, with a target of increasing lending to ?5.5 lakh crore in the next decade.
- It will improve farmers’ income, reduce dependence on informal credit sources, and foster better financial inclusion.
- Additionally, it will create a more reliable supply chain for agricultural produce, enhancing food security.
Future Targets:
- Increase the number of registered warehouses under the WDRA to 40,000 in the next 1–2 years.
- Use platforms like e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi to streamline the lending process and avoid repeated visits to banks.
How La Niña Affects India's Climate?
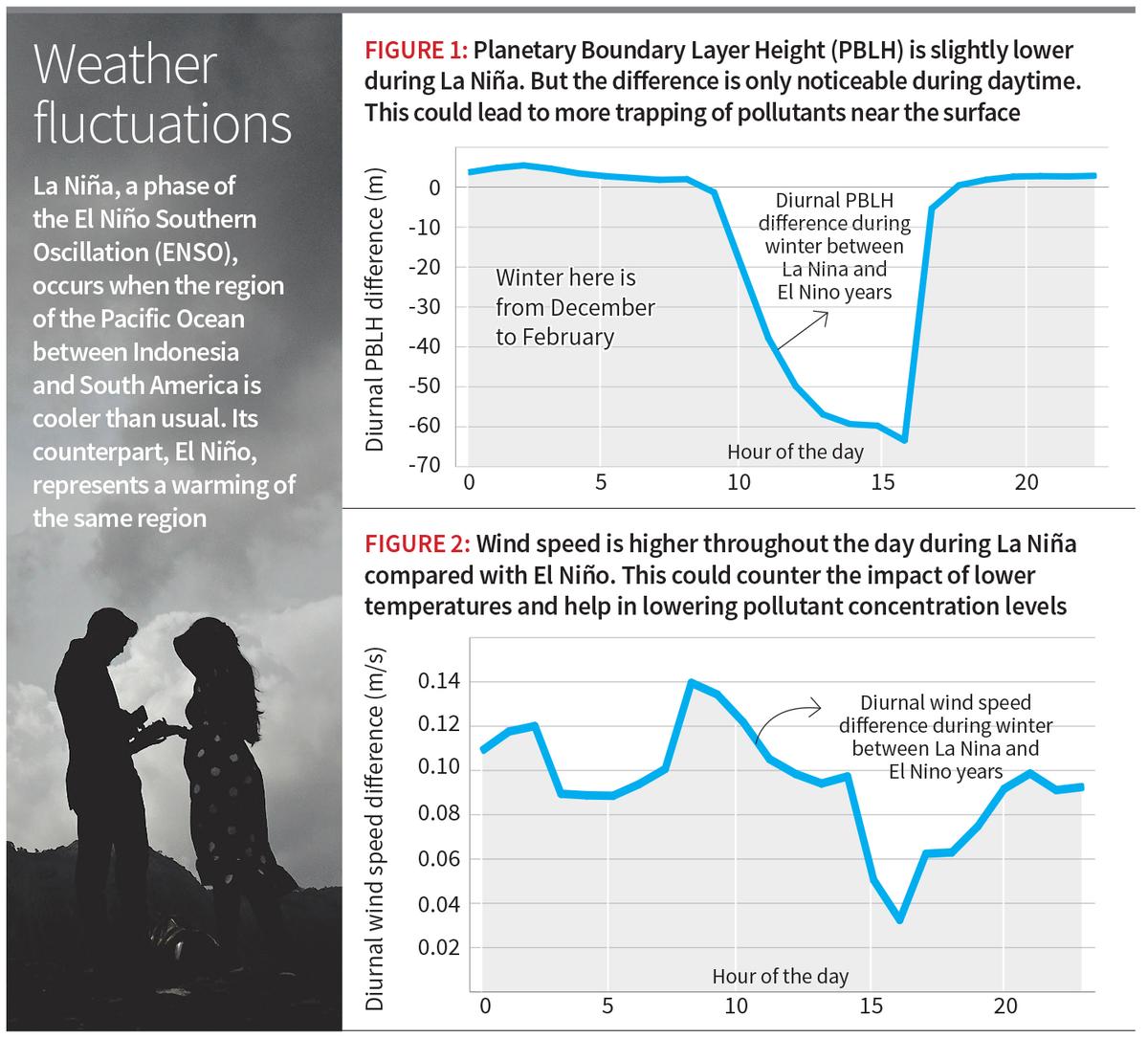
- 28 Dec 2024
In News:
La Niña, a phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), occurs when the Pacific Ocean region between Indonesia and South America is cooler than usual. This phenomenon influences global weather patterns, including those in India. Here’s how La Niña specifically affects India’s climate:
Monsoon Rainfall:
- La Niña typically results in normal to above-normal rainfall during the monsoon season in India. This is due to the cooling of sea surface temperatures in the central Pacific, which affects atmospheric circulation and strengthens the monsoon winds.
- In contrast, El Niño usually brings below-average rainfall and droughts to India, leading to agricultural stress.
- Recent La Niña years (2020-2022) saw above-normal monsoon rains, which benefited agricultural productivity, while the El Niño year of 2023 resulted in below-normal rains, impacting water availability and agriculture.
Winter Temperatures:
- During La Niña, winter temperatures in India are generally colder in the north, with cooler nights but relatively warmer days compared to El Niño winters. The planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) tends to be lower, trapping pollutants close to the surface. However, higher wind speeds during La Niña help to disperse air pollution, improving air quality.
- South India may experience colder-than-usual winters during La Niña, but current meteorological data suggests the ongoing winter in India is not strongly influenced by La Niña, as its expected onset has been delayed.
Impact on Summer Heat:
- La Niña generally provides relief from extreme summer heat, as it reduces the frequency and intensity of heatwaves. In contrast, El Niño summers are typically hotter and bring record-breaking heat waves.
- For example, April 2023 saw intense heatwaves across India, attributed to the El Niño phase, but if a La Niña forms and persists into the summer of 2025, it could help moderate the extreme heat.
The "Triple Dip" La Niña Phenomenon:
- A Triple Dip La Niña refers to a rare occurrence where three consecutive La Niña events happen, as was the case from 2020 to 2022. This is significant because these prolonged events can lead to stronger climatic impacts. In contrast, the current El Niño (2023) follows this period, potentially contributing to an irregular transition between La Niña and El Niño phases, which may intensify extreme weather patterns.
Global Climate Changes and La Niña:
- Climate change is believed to be increasing the frequency and intensity of both La Niña and El Niño events. Rising sea and land temperatures are disrupting the balance of the Pacific Ocean and could exacerbate extreme La Niña events, which might lead to harsher winters in India and other regions.
Forecast for 2024-2025:
- As of December 2024, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and global meteorological bodies predict a weak La Niña event to emerge by late 2024 or early 2025. This could lead to colder winters and above-normal rainfall in the 2025 monsoon season, offering some relief from the heatwaves and dry conditions of the previous years.
Conclusion:
If a La Niña forms by the end of 2024, it is likely to bring cooler winters, a relief from extreme summer heat, and above-normal monsoon rainfall in 2025. Given the delayed onset and weakening of the current La Niña, the overall impact on India’s climate in the immediate future might be milder compared to previous La Niña years, but it still holds potential for more favorable conditions for agriculture and air quality.
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme

- 17 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $98 million loan agreement to enhance horticulture crop productivity by improving plant health management. This initiative is part of India’s Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP), aiming to provide farmers with access to certified disease-free planting materials to improve yields, quality, and resilience, particularly against climate change impacts.
Key Highlights of the Loan Agreement
- Objective: Improve access to certified, disease-free planting materials for horticulture crops.
- Implementation: The project will be implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- Focus: The initiative will enhance farmers’ productivity, resilience to climate change, and pest/disease management through the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP).
About the Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
The Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme aims to tackle critical challenges in horticulture by ensuring farmers have access to high-quality, virus-free planting materials. The program is designed to:
- Enhance crop yields and quality.
- Promote climate-resilient varieties to help farmers adapt to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
- Safeguard the environment by controlling plant diseases and pests proactively.
Key Components of the CPP
- Clean Plant Centers (CPCs): Establishment of nine world-class CPCs across India, equipped with advanced diagnostic labs and tissue culture facilities to maintain disease-free foundation planting materials.
- Certification Framework: A robust certification system will be introduced to ensure accountability in planting material production, including accreditation for private nurseries.
- Climate Resilience: Focus on developing and disseminating climate-resilient plant varieties, addressing the growing concerns over extreme weather events and changing pest behavior due to climate change.
Significance of the Loan Agreement
- Climate Adaptation: The project will help farmers mitigate the effects of climate change, including unpredictable weather patterns and altered pest/disease behaviors.
- Economic Impact: The initiative aligns with India's vision of self-reliance in horticulture (Atmanirbhar Bharat), boosting agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- Long-term Benefits: Improved farm productivity, sustainability, and economic well-being for farmers, especially in the face of climate change.
Global Horticulture Significance
- India’s Position: India is the second-largest producer of fruits and vegetables globally, contributing 33% to the agricultural GDP.
- Land Coverage: Horticulture occupies 18% of India’s agricultural land, yet its production surpasses that of food grains.
Implementation and Impact
- Implementation Period: The project will be executed from 2024 to 2030, with 50% financial assistance from ADB.
- Institutional Strengthening: The initiative will bolster India’s ability to manage plant health, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques and capacity-building for horticulture professionals.
Little Bunting

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
Little Bunting recently spotted in Mount Abu, Rajasthan, a sighting previously unseen in the region.
About the Little Bunting:
- Scientific Name: Emberiza pusilla
- Family: Bunting family (Emberizidae)
- IUCN Red List Status: Least Concern
Distribution:
- Breeding Range: Far northeast Europe and northern Eurosiberia to the Russian Far East (taiga region).
- Migratory Pattern: Migrates to the subtropics during winter, with sightings in northern India, southern China, and northern Southeast Asia.
Physical Features:
- Size: Small bird, measuring 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inches).
- Coloration:
- White underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides.
- Chestnut face with a white malar stripe, black crown stripes, and a white eye-ring.
- Fine dark border behind chestnut cheeks.
- Similarity: Resembles a small female reed bunting but with distinct black crown stripes.
Call and Song:
- Call: Distinctive "zik".
- Song: A rolling "siroo-sir-sir-siroo".
Habitat and Behavior:
- Typically found in agricultural areas, feeding on grains.
- Migration: Avoids extreme cold conditions, possibly due to climate change influencing its movement into Rajasthan.
Recent Sightings in India: Spotted in Gurugram, Chandigarh, northern Punjab, and now Rajasthan.
Conservation Significance: The sighting underscores the need to preserve forest areas and wetlands for migratory species like the Little Bunting.
India Maritime Heritage Conclave 2024

- 16 Dec 2024
In News:
The 1st India Maritime Heritage Conclave (IMHC 2024), a landmark event organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) was recently held.
Key Highlights:
Event Overview:
- Organized by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways (MoPSW), held on December 11-12, 2024.
- Theme: "Towards Understanding India's Position in Global Maritime History."
- Celebrated India’s maritime legacy and future vision as a maritime powerhouse.
India’s Maritime Heritage:
- Deeply rooted in ancient traditions; references in Rig Veda, mythology, literature, and archaeology.
- Modern India boasts a 7,500 km coastline, 13 major ports, 200 non-major ports, handling 95% of trade by volume and 70% by value.
- Ports handle 1,200 million tonnes of cargo annually, vital for economic growth.
Key Features of IMHC 2024:
- International Participation: Dignitaries from 11 countries, including Greece, Italy, UK.
- Exhibition: Showcased ancient shipbuilding techniques, navigation systems, historical trade routes.
- Cultural Program: Celebrated coastal traditions with performances and festivities.
- Key Focus: Sustainable maritime innovation, skill development, youth engagement, and cultural preservation.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC):
- Location: Lothal, Gujarat – an ancient Harappan site (2600 BCE).
- Significance: Home to the world’s oldest dry-dock (2400 BCE).
- Future Vision: NMHC to showcase maritime history with 14 galleries, open aquatic gallery, lighthouses, and a research institute.
Modern Maritime Significance:
- India’s Global Maritime Ranking: 16th largest globally, 3rd largest in ship recycling.
- Trade Backbone: 95% of India's trade by volume, 70% by value handled by maritime sector.
- Port Performance: India ranks 22nd in the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (2023).
Future Maritime Vision:
- Sustainable Blue Economy: Emphasis on eco-friendly practices, green shipping, and maritime tourism.
- Skill Development: Training programs to empower local communities and boost maritime workforce.
- Infrastructure Development: Upgrading ports and shipping infrastructure under the Sagar Mala Program.
- Policy Framework: Integrated policies for maritime heritage preservation and economic development.
Notable Initiatives:
- Maritime India Vision 2030: Focus on increasing maritime capacity and sustainability.
- SAGAR: Security and Growth for All in the Region initiative.
- Ship Repair & Recycling Mission: Promote India as a global leader in ship recycling.
- Green Hydrogen Hubs: Development of eco-friendly maritime infrastructure.
Santa Ana Winds

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
The ongoing Franklin Fire in Malibu, California, has burned over 4,000 acres and affected around 22,000 people. Although the exact cause of the fire is still under investigation, experts point to two key factors contributing to the intensity of the blaze: Santa Ana winds and climate change.
Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds are powerful, dry winds that typically occur in Southern California from October to January.
- They are caused when high-pressure systems over the Great Basin (the area between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Nevada) push air toward low-pressure areas over California’s coast.
- As the air moves downhill through mountain passes, it compresses and heats up, which significantly lowers the humidity—sometimes to levels below 10%—creating dry conditions. This extremely low moisture content dehydrates vegetation, making it highly susceptible to combustion.
- These winds have been a natural feature of California's weather, contributing to wildfires for years. However, when combined with other factors like climate change, their impact has become more severe.
The Role of Climate Change
While Santa Ana winds have long played a role in California's wildfires, climate change has exacerbated the situation in recent years. The state's wildfire season has lengthened due to rising global temperatures, which have led to:
- Warmer springs and summers.
- Earlier snowmelt in spring, which leaves vegetation drier for longer periods.
- Longer and more intense dry seasons, which cause increased moisture stress on vegetation.
As a result, forests and brushlands are now more vulnerable to fires. Climate change has also contributed to more extreme weather events, including heatwaves, which further dry out vegetation and create favorable conditions for wildfires.
Intensification of Wildfire Seasons
Recent studies have shown that California's wildfire season has grown longer over the past two decades. For example, a 2021 study in Nature Scientific Reports found that the state's annual burn season has shifted, with the peak fire season now occurring earlier in the year, from August to July. Additionally, research published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) in 2023 indicated that the largest wildfires in California history have occurred in the past 20 years, with five of the top 10 largest fires taking place in 2020 alone.
Looking Ahead
The situation is expected to worsen as climate change continues. If global temperatures rise by more than 3°C by the end of the century, as predicted by the United Nations, California’s wildfire risk will likely intensify. The combination of Santa Ana winds and increasingly dry conditions will continue to make areas like Malibu, and much of California, more prone to destructive wildfires.
In conclusion, while Santa Ana winds remain a natural contributor to California's wildfires, the influence of climate change has significantly lengthened the wildfire season, making wildfires more frequent, intense, and harder to control. The continued rise in global temperatures only accelerates these trends, posing a growing challenge for fire management and public safety in California.
'Jalvahak' Scheme for Inland Waterways Promotion

- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
Govt Unveils ‘Jalvahak’ To Boost Inland Waterways, Cargo Movement Incentivised on NW1, NW2 & NW16
Key Highlights:
- Launch of 'Jalvahak' Scheme:
- Launched by: Union Minister for Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Shri Sarbananda Sonowal, on December 15, 2024.
- Objective: The scheme aims to promote the use of inland waterways for long-haul cargo transportation, reduce logistics costs, and alleviate congestion in road and rail networks.
- Targeted Waterways:
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- NW 1: River Ganga
- NW 2: River Brahmaputra
- NW 16: River Barak
- The scheme focuses on three major National Waterways (NWs):
- Incentives:
- The scheme offers up to 35% reimbursement on operating expenses for cargo transported over 300 km via these waterways, particularly using the Indo-Bangladesh Protocol Route (IBPR).
- Encouraging Private Operators: The scheme also incentivizes the hiring of vessels owned by private operators to promote competition and efficiency.
- Scheduled Cargo Service:
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Kolkata - Patna - Varanasi - Patna - Kolkata (for NW 1)
- Kolkata - Pandu (Guwahati) (for NW 2 via IBPR)
- Transit Times: Predefined and fixed for efficiency:
- Kolkata to Patna: 7 days
- Patna to Varanasi: 5 days
- Kolkata to Varanasi: 14 days
- Kolkata to Pandu: 18 days
- Pandu to Kolkata: 15 days
- Service Launch: Fixed, scheduled cargo vessel services have been introduced, running between key locations:
- Economic and Environmental Impact:
- Cargo Shift Target: The initiative aims to shift 800 million tonne-kilometres of cargo by 2027.
- Growth Projections:
- 200 million tonnes of cargo by 2030.
- 500 million tonnes by 2047, supporting the Blue Economy and Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiatives.
- The move to waterways aims to reduce the pressure on India's roads and rail systems, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective logistics system.
- Strategic Goals:
- Modal Shift: The scheme seeks to achieve a shift of 800 million tonne-kilometres by 2027 with an investment of ?95.4 crores.
- Sustainability: Inland waterways are considered an environmentally friendly, efficient, and low-cost transportation mode, with a focus on sustainability.
- Logistics Optimization: This initiative is expected to help optimize supply chains for major shipping companies, freight forwarders, and trade bodies involved in bulk and containerized cargo.
- Implementation Agencies:
- Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI): The main body responsible for the development and regulation of inland waterways.
- Inland & Coastal Shipping Limited (ICSL): A subsidiary of the Shipping Corporation of India, responsible for the operation of vessels.
- Broader Impact:
- Economic Growth: The scheme is expected to foster economic growth by improving logistics efficiency.
- Decongestion: The initiative aims to decongest the road and rail transport systems, facilitating smoother movement of cargo.
- Regional Connectivity: Enhances connectivity, particularly in eastern India, benefiting areas along the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Barak rivers.
- About the National Waterways:
- India has 14,500 km of navigable inland waterways, which include rivers, canals, and backwaters. These waterways are significantly under-utilized compared to other countries.
- The National Waterways Act, 2016 declared 111 waterways (including both existing and newly identified ones) for navigation.
- The Jalvahak scheme is part of India's broader strategy to unlock the potential of its inland waterways, offering an efficient, economical, and environmentally sustainable alternative for cargo transport.
Rajmarg Saathi - Upgraded Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPV) by NHAI
- 15 Dec 2024
In News:
With an aim to enhance road safety and strengthen highway patrolling, NHAI plans to implement the upgraded and forward-looking Incident Management Services. The guidelines on the subject include updated specifications for new Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs) named ‘Rajmarg Saathi’ and outlines design, functions, technology, components and manpower specifications for the RPVs.
Key Highlights:
Launch of Rajmarg Saathi:
- Initiative by: National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- Objective: Enhance highway safety, emergency response, and road maintenance efficiency across India.
- Launched in: December 2024.
What is Rajmarg Saathi?
- Definition: An upgraded version of Route Patrolling Vehicles (RPVs), designed for effective highway patrolling and incident management.
- Main Aim: Improve highway safety and ensure smooth traffic flow through advanced technology and quick emergency responses.
Key Features:
- Advanced Design:
- Closed Cabinets: For organized storage and easy access to emergency tools and inventory, replacing earlier models with open storage space.
- AI-Powered Technology:
- Dashboard Cameras: Equipped with AI-enabled cameras to capture and analyze road conditions like cracks, potholes, and other distresses.
- Road Monitoring: The system also monitors vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, and other infrastructure elements.
- Integration with NHAI One: Data collected by AI systems is integrated into NHAI’s centralized application for efficient road maintenance.
- Emergency Preparedness: The RPVs are fully equipped with modern communication and safety tools, designed to minimize traffic disruptions during emergencies.
Data Collection and Maintenance:
- Weekly Analytics: The system will collect and analyze road condition data weekly to streamline maintenance activities and monitor highway safety.
Vehicle Usage and Replacement:
- Replacement Guidelines: RPVs will be replaced after 3 years of operation or 3,00,000 km to ensure they remain functional and service-ready.
Visibility and Branding:
- External Branding: RPVs are designed to be highly visible with enhanced branding for easy recognition as highway patrol vehicles.
- Uniform for Personnel: The patrolling personnel will wear updated uniforms, including bright blue colors and reflective jackets with authority logos for better identification.
Role in Incident Management:
- RPVs will play a crucial role in managing traffic incidents, ensuring smooth traffic flow, and enhancing road safety by addressing emergencies quickly.
Commitment to Road Safety:
- NHAI remains committed to improving road safety standards and ensuring a smooth, hassle-free travel experience for all users across the national highway network.
About NHAI:
- Establishment: NHAI was established under the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988, and became operational in 1995.
- Responsibilities: It is responsible for developing, maintaining, and managing national highways in India.
- Objectives:
- Promote transparency in awarding contracts.
- Maintain high standards of project implementation.
- Ensure comfort and convenience for users of the national highway system.
India's Road Network:
- Size: India has the 2nd-largest road network in the world, spanning approximately 63.32 lakh km, which includes national highways, expressways, state highways, and rural roads.
NASA Captures Active Volcano Erupting on Jupiter's Moon Io

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
NASA has revealed new details about Io, Jupiter’s third-largest moon and the most volcanic world in our solar system.
Overview:
- NASA’s Juno mission has revealed new insights about Io, Jupiter's third-largest moon, known as the most volcanic world in the solar system.
- Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which send plumes and lava flows into space, creating its unique, fiery surface.
Recent Discoveries and Observations:
- Fiery Heart of Io:
- NASA's Juno mission has helped solve a 44-year-old mystery regarding Io’s volcanic activity, revealing that its volcanoes are likely powered by separate magma chambers rather than a single large magma ocean.
- This discovery was made during Juno’s close flybys in late 2023 and early 2024, using Doppler measurements and precise gravity data to understand the moon’s interior.
- Volcanic Activity:
- Io's volcanoes constantly erupt, spewing lava and plumes that shape its surface. The volcanic activity was first observed by NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979.
- Tidal Flexing: Io experiences constant squeezing due to its elliptical orbit around Jupiter, which generates immense internal heat and causes frequent eruptions.
- Scientific Insights:
- The research suggests that tidal forces from Jupiter do not create a global magma ocean inside Io, as previously thought, but instead lead to localized magma chambers that fuel its volcanoes.
- Tidal flexing is the primary cause of the immense internal energy on Io, which melts portions of the moon's interior and drives volcanic activity.
- Broader Implications:
- Understanding Other Moons and Exoplanets: Juno's findings have broader implications for understanding the interiors of other moons like Enceladus and Europa, and even exoplanets and super-Earths.
- Future Missions:
- Juno will continue its mission, with the next close approach to Jupiter scheduled for December 27, 2024, bringing it 2,175 miles above Jupiter's cloud tops. Since entering Jupiter’s orbit in 2016, Juno has traveled over 645 million miles.
Empowering ASHA Workers

- 14 Dec 2024
In News:
ASHAs (Accredited Social Health Activists) are critical to India's healthcare system, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Since the program's launch in 2005, ASHAs have been integral in improving maternal health, increasing immunization rates, and promoting family planning and sanitation awareness. The network of ASHAs has grown to nearly 1 million members, making it one of the largest community health worker programs in the world.
Role of ASHAs: ASHAs work as community health activists, beyond basic healthcare delivery, by:
- Promoting health awareness.
- Mobilizing local participation in health programs.
- Increasing the utilization of existing health services.
They play a central role in improving maternal and child health, and their efforts have led to increased institutional deliveries and improved immunization rates in rural India.
Challenges Faced by ASHAs: Despite their essential role, ASHAs face several challenges:
- Inadequate compensation and delayed payments, which undermine motivation.
- Heavy workloads with insufficient support and resources.
- Social and economic marginalization, often leading to a lack of recognition and respect.
- Punitive systems that emphasize compliance and record-keeping, hindering autonomy.
This environment limits ASHAs' capacity to act as independent change agents, reducing their effectiveness in driving long-term health improvements.
Psychological Empowerment of ASHAs: To address these challenges, it's essential to empower ASHAs not just financially, but psychologically. Research in motivation theory, particularly Self-Determination Theory (SDT), provides a framework to achieve this. SDT emphasizes the importance of three key psychological needs:
- Autonomy: The need for ownership over one's work.
- Competence: The need to feel capable and effective in performing tasks.
- Relatedness: The need for social connection and recognition.
By fostering these three needs, ASHAs can become more intrinsically motivated and empowered to take ownership of their roles.
Strategies for Empowerment:
- Autonomy: Giving ASHAs more control over their work and decision-making can improve their engagement and efficacy. This can be achieved by reducing rigid monitoring and compliance systems.
- Competence: Providing continuous, quality training and resources will help ASHAs build the skills and confidence needed to perform their roles effectively. Digital tools and modern training programs can be used to enhance their capabilities.
- Relatedness: ASHAs should receive direct feedback from the communities they serve, fostering a sense of connection and accomplishment. Encouraging networks among ASHAs will also help combat isolation and provide peer support.
Government Efforts and Initiatives: The Indian government has recognized the need to support ASHAs through several initiatives:
- Increased remuneration and performance-based incentives.
- Insurance coverage under schemes like Ayushman Bharat.
- Training programs for skill development under the National Health Mission (NHM).
- Village Health Mapping and digital engagement platforms to enhance outreach and feedback mechanisms.
Moving Forward:
To further empower ASHAs, several key steps should be taken:
- Formalizing employment status: Transitioning ASHAs from volunteers to formal workers with benefits can ensure more stability and recognition.
- Improving compensation: Ensuring timely and adequate payments along with performance bonuses will incentivize ASHAs and increase job satisfaction.
- Enhancing infrastructure: Ensuring ASHAs have access to the necessary tools, medical supplies, and transportation to perform their tasks effectively.
- Digital integration: Expanding digital tools for data collection and communication can streamline their work and improve coordination with healthcare systems.
International Mountain Day 2024
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
On 11th December 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in collaboration with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment (NIHE), hosted an event titled ‘Youth for the Himalaya: Innovate, Inspire, Impact’ to mark International Mountain Day.
Event Overview:
- The event was themed “Mountain Solutions for a Sustainable Future – Innovation, Adaptation, and Youth.”
- It emphasized the critical role of young people in addressing the environmental challenges faced by the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
- The aim was to showcase youth-driven innovations contributing to the region's sustainability, catalyzing active youth participation in environmental actions. This initiative aligns with the Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, which encourages sustainable practices and collective environmental responsibility.
Key Highlights:
- Young changemakers, innovators, and stakeholders from across the country participated, including students, youth representatives, and members of the private sector, civil society, and government.
- The event highlighted discussions on sustainable solutions for the Himalayan region, integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements in areas like eco-tourism, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience.
- Short films and videos produced by NIHE and IUCN, such as "Promoting Conservation of Threatened Plant Species in the Western Himalayas" and "Himalayan Futures: Voices from the Ground," were also showcased.
International Mountain Day
- International Mountain Day, observed every year on December 11th since 2003, was established by the United Nations to raise awareness about the sustainable development of mountain regions.
- Mountains cover about one-fifth of the Earth's surface and provide essential freshwater to half of humanity, supporting agriculture, clean energy, and health.
Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The IHR spans 13 Indian states and union territories, stretching approximately 2,500 kilometers from west to east. It is a biodiversity hotspot with significant ecological and cultural value. However, it faces challenges such as unsustainable development, climate change impacts, cultural erosion, and rising tourism.
Key Concerns for IHR:
- Unsustainable Development: Infrastructure projects and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Glacial melting and rising temperatures affect water resources and increase flood risks.
- Cultural Erosion: Modernization threatens traditional practices of indigenous communities.
- Tourism Pressure: Waste generation due to growing tourism puts immense pressure on the region's fragile ecology.
Measures for Protection:
- Sustainable Tourism: Promoting eco-tourism and enforcing capacity limits to minimize environmental impact.
- Water Management: Capturing glacial meltwater for agriculture and ecosystem support.
- Disaster Preparedness: Developing disaster management strategies and early warning systems for events like landslides and floods.
- Bio-Cultural Conservation: Protecting both natural biodiversity and indigenous cultural practices through designated zones.
- Integrated Development: Establishing a "Himalayan Authority" for coordinated development in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Journey Hits $1 Trillion Milestone
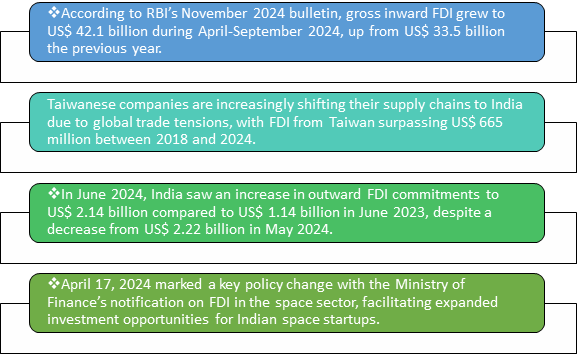
- 13 Dec 2024
In News:
India has reached a historic milestone, surpassing $1 trillion in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows since April 2000. This achievement highlights India’s growing status as a major global investment hub and is further validated by a 26% increase in FDI inflows, which reached $42.1 billion during the first half of FY 2024-25.
Key Highlights of India’s FDI Growth:
- $1 Trillion Milestone: India has attracted a total of $1 trillion in FDI from April 2000 to September 2024. This figure includes equity, reinvested earnings, and other capital inflows.
- 26% Growth in FDI: FDI inflows surged by 26% in the first half of FY 2024-25, totaling $42.1 billion.
- Top Investors: Major investors include Mauritius (25%), Singapore (24%), and the United States (10%). These countries benefit from favorable tax treaties with India, boosting investment.
- Dominant Sectors: FDI has flowed into sectors like services, manufacturing, technology, and telecommunications, with significant investments also in pharmaceuticals, automobile, and construction development.
Factors Behind India’s FDI Success:
- Policy Reforms: India’s liberalized FDI policies, such as allowing 100% FDI in most sectors under the automatic route, have attracted foreign capital. Key reforms like abolishing angel tax and reducing corporate tax rates in the Income Tax Act of 2024 have also enhanced investor confidence.
- Business Environment: India’s rise in global competitiveness is evident in its improvement in rankings. It moved from 43rd to 40th in the World Competitiveness Index 2024 and climbed to 40th in the Global Innovation Index 2023, up from 81st in 2015.
- Investor Confidence: The government’s efforts, including initiatives like "Make in India", Goods and Services Tax (GST), and sector-specific incentives, have fostered a conducive environment for investment.
- Global Investment Standing: India has been the third-largest recipient of greenfield projects globally and saw a 64% increase in international project finance deals.
Contribution of Mauritius and Singapore:
- Mauritius and Singapore lead as the primary sources of FDI into India. Their favorable tax treaties with India make them attractive gateways for foreign investments. Mauritius accounted for 25%, and Singapore for 24% of the total FDI inflows.
Key Sectors Attracting FDI:
- Services Sector: Significant growth in services, especially financial services, has attracted substantial foreign investments.
- Manufacturing and Technology: These sectors have benefited from policies like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, which encourage foreign investments in high-tech manufacturing.
- Telecommunications and Pharmaceuticals: India’s growing digital ecosystem and strong pharmaceutical industry continue to attract international investments.
Importance of FDI for India:
- Infrastructure Development: FDI plays a crucial role in financing infrastructure projects, helping meet the country’s significant infrastructure needs.
- Balance of Payments: FDI helps bridge India’s current account deficit, ensuring stable foreign exchange reserves.
- Technology Transfer and Employment: Foreign investments bring advanced technology and create jobs, boosting productivity across sectors.
- Currency Stability: FDI supports the Indian Rupee in global markets by injecting foreign capital.
Challenges:
Despite the positive trends, India faces challenges such as geopolitical tensions, regulatory issues, global economic uncertainty, and infrastructure bottlenecks that can affect investor sentiment and capital inflows.
Way Ahead:
- Focus on Infrastructure: Continued investment in infrastructure development, including public-private partnerships (PPPs), will be crucial for sustained economic growth.
- Workforce Skilling: Collaborative efforts to upskill the workforce will ensure that India can meet the evolving demands of industries.
- Research and Development: Strengthening R&D and innovation will enhance India’s productivity and global competitiveness.
INS Tushil Commissioned into the Indian Navy in Russia

- 10 Dec 2024
In News:
Recently, the Indian Navy officially commissioned INS Tushil, a multi-role stealth guided missile frigate, at Kaliningrad, Russia. This marks a significant milestone in India-Russia defense cooperation and strengthens India’s maritime capabilities.
About INS Tushil:
- Class & Design: INS Tushil is the seventh ship in the Krivak III class (Project 1135.6) of frigates. It is part of an upgraded series, following the Talwar-class and Teg-class frigates, and was built at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia.
- Development & Contract: The construction was initiated under a 2016 contract between the Indian Government, JSC Rosoboronexport (a Russian defense company), and the Indian Navy. The ship incorporates 26% indigenous technology, highlighting growing cooperation between Indian and Russian industries.
- Key Features:
- Stealth Design: With advanced radar-absorbing features, it is less detectable by enemy radar.
- Weaponry: Equipped with BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, Shtil Surface-to-Air Missiles, anti-submarine torpedoes, electronic warfare systems, and more.
- Versatility: Designed for blue-water operations, the ship can engage in air, surface, underwater, and electromagnetic warfare.
- Helicopter Deck: Supports operations of upgraded Kamov 28 and Kamov 31 helicopters.
- Speed: Capable of exceeding 30 knots.
Significance:
- Enhanced Naval Capabilities: The commissioning of INS Tushil boosts India’s defense strength in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), a vital area for global maritime trade and security.
- Maritime Security: INS Tushil is designed to support India’s vision of maintaining stability in the IOR and to act as a deterrent against piracy and other maritime threats.
- Defense Cooperation: This commissioning exemplifies the growing defense ties between India and Russia, underscored by joint development, technology transfer, and shared expertise. The ship reflects a major step in India's self-reliance in defense, in line with the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative.
- Strategic Role in Global Defense: The ship is a key asset in the Indian Navy's efforts to secure maritime trade routes, enhance regional security, and provide humanitarian assistance in times of need.
Key Events & Facts:
- Construction Timeline: The keel of INS Tushil was laid in 2013, and it launched in 2021. After completing extensive sea and weapon trials in 2024, it was formally commissioned into the Navy.
- Collaborative Effort: The ship is a product of collaborative efforts between Indian and Russian industries, marking a significant achievement in joint defense manufacturing.
Moths' Reproductive Choices Based on Plant Acoustic Emissions

- 09 Dec 2024
In News:
A new study, "Female Moths Incorporate Plant Acoustic Emissions into Their Oviposition Decision-Making Process," published last month, explores how female moths use sounds emitted by plants to choose where to lay their eggs.
Key Highlights:
Significance of Plant Emitted Sounds:
- Background: Last year, it was discovered that plants emit ultrasonic clicks or pops when stressed (e.g., dehydration). These sounds, although inaudible to humans, can be detected by animals, including insects.
- Moths’ Sensitivity: Moths, particularly the Egyptian cotton leafworm, are shown to be sensitive to these plant sounds, which they use as cues for laying eggs on plants.
Methodology:
- Experimental Setup: Researchers placed a hydrated tomato plant in an experimental arena with another hydrated plant that emitted distress sounds. They observed the behavior of female Egyptian cotton leafworms to understand how these sounds influenced their oviposition choices.
- Initial Finding: Moths typically choose healthy, thriving plants to lay eggs, as they provide better food sources for the larvae.
Study Findings:
- Moths’ Response to Sounds: The moths preferred to lay eggs on the “silent” plant rather than the one emitting distress sounds. This indicates that moths can not only detect the presence of a plant but also interpret acoustic signals to inform their egg-laying decisions.
- Implications: This behavior suggests that moths use a complex set of sensory inputs, including plant-emitted sounds, to select the most suitable plant for offspring development.
Broader Ecological Context:
- Moths as Insects: Moths belong to the order Lepidoptera and are found in diverse environments globally, except polar regions. With around 160,000 species, they are highly adapted and often nocturnal, though some species are diurnal.
- Impact on Agriculture: Certain moth species, especially during their caterpillar stage, are major agricultural pests (e.g., corn borers, bollworms), making understanding their behavior crucial for pest management strategies.
- Climate Change Considerations: Moths, like other species, are impacted by climate change, which can alter the timing and growth of plants they depend on, potentially influencing their reproductive strategies.
Conclusion:
- Innovative Findings: The study reveals a previously unknown aspect of moth behavior, showing that they incorporate plant acoustic emissions into their oviposition decisions.
- Future Implications: This discovery opens avenues for further studies on how environmental signals, like sound, affect the behavior of insects, and how these behaviors could be impacted by changing environmental conditions.
MhadeiWildlife Sanctuary
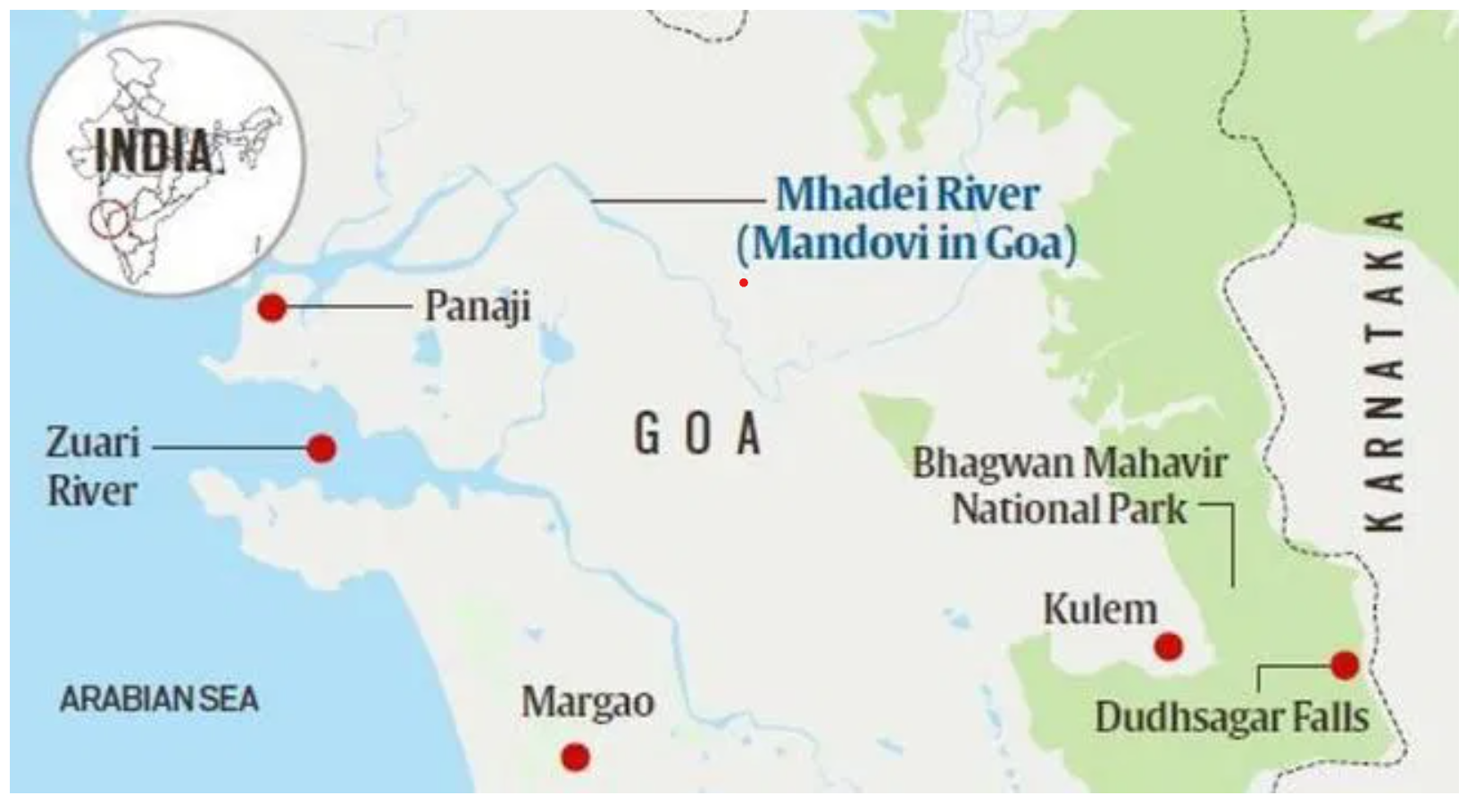
- 01 Nov 2024
In News:
An adult tigress and three cubs have been spotted in the Mhadei wildlife sanctuary in Goa marking the first time evidence of the species has been recorded in the forests bordering the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka since 2020.
Key Highlights:
Location and Geography:
- It is located near Chorla Ghat, between North Goa and Belgavi, and borders Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The sanctuary is traversed by the Mhadei River, which meets the sea at Panaji, Goa.
Ecological Significance:
- It is part of the Western Ghats, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and shares this ecosystem with Mollem National Park and other protected areas in Goa.
- The sanctuary is integral to wildlife corridors connecting the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), critical for tiger conservation.
Flora and Fauna:
- It is home to diverse wildlife, including the critically endangered Long-billed vultures that nest at Vazra Falls.
- The region supports a variety of flora and fauna due to its biodiversity-rich Western Ghats ecosystem.
Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa is the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a key area.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended that Mhadei WLS be designated as a tiger reserve to enhance protection efforts.
- The sanctuary is a potential candidate for inclusion under Project Tiger.
- In 2020, a Royal Bengal tigress and her cubs were tragically poisoned due to human-animal conflict.
Mahadayi Water Dispute:
- The Mahadayi (Madei, Mandovi) River is a source of dispute between Karnataka and Goa regarding water sharing.
- Karnataka seeks to divert water from the river to the Malaprabha River basin for drinking water supply in several districts, through the Kalasa-Banduri Nala project.
- The matter is currently being heard in the Supreme Court.
Center for Generative AI, Srijan

- 27 Oct 2024
In News:
IndiaAI and Meta have announced the establishment of the Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur, along with the launch of the “YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building” in collaboration with the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), for the advancement of open source artificial intelligence (AI) in India.
Key Initiatives Launched
- Center for Generative AI, Srijan (????) at IIT Jodhpur:
- Focus on Generative AI (GenAI) research and innovation.
- Meta’s support for ethical and responsible development of AI technologies.
- Aim to empower researchers, students, and practitioners with the tools for responsible AI deployment.
- Focus Areas: Open science, AI policy advisory, and indigenous AI application development.
- YuvAi Initiative for Skilling and Capacity Building:
- Target: Empower 100,000 students and young developers (ages 18-30) with AI skills.
- Core Focus: Leveraging open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) for real-world solutions.
- Skills Development: Generative AI, open-source tools, and sector-specific AI applications (healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, mobility, and financial inclusion).
- Partnership: Collaboration with AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education).
Strategic Goals and Outcomes
- Research and Innovation:
- Strengthen India’s AI ecosystem through groundbreaking research and collaborations.
- Focus on open-source AI and indigenous AI solutions for national challenges.
- Empower India to lead in AI through ethical and responsible AI deployment.
- AI Talent Development:
- Bridge the AI talent gap by training young developers in open-source AI technologies.
- Develop AI solutions for critical sectors like healthcare, education, agriculture, smart cities, and financial inclusion.
- Program Components:
- GenAI Resource Hub with courses, case studies, and open datasets.
- Unleash LLM Hackathons for students to propose AI solutions for real-world challenges.
- Support for AI startups through an Innovation Accelerator.
Sectoral Focus and Impact
- Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, personalized medicine, and healthcare delivery.
- Education: AI tools for enhancing learning outcomes and personalized education.
- Agriculture: AI solutions for precision farming, pest control, and crop management.
- Smart Cities: AI in urban planning, traffic management, and public services.
- Mobility: AI applications in transportation, logistics, and urban mobility.
- Financial Inclusion: AI in fintech, digital payments, and financial services for underserved populations.
Additional Programs and Opportunities
- AICTE Collaboration: Mobilizing technical institutions across India to build AI capabilities.
- Master Training Activation Workshops: To introduce foundational AI concepts to students.
- Mentorship and Grants: Top AI solutions from hackathons will receive mentoring, seed grants, and market support.
- Student Startups: AI Innovation Accelerator will incubate 10 student-led AI startups experimenting with open-source models.
Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD)
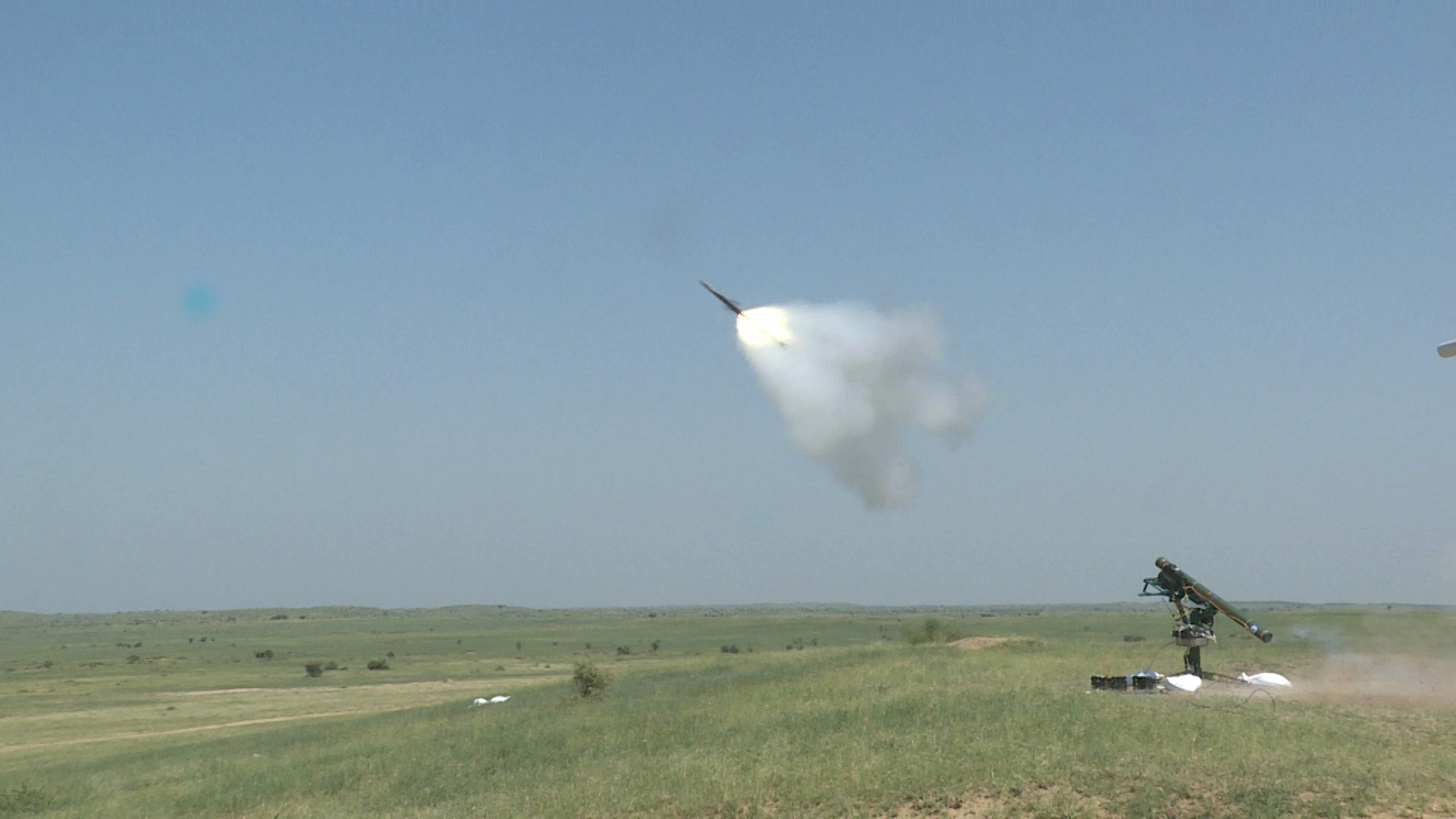

- 06 Oct 2024
In News:
DRDO completed development trials of the 4th Generation miniaturised Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORAD).
Key Details:
- Trial Location: Conducted at Pokhran Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
- Importance: VSHORAD addresses the Indian Army's need to replace legacy Igla systems, with past efforts making little progress.
- Recent Procurement: Army acquired small volumes of Igla-S through emergency procurement.
- Production Collaboration: Two production agencies involved in Development cum Production Partner (DcPP) mode for VSHORAD missiles.
- Trial Dates: Successful tests held on October 3 and 4, 2024.
Key Performance Metrics:
- Maximum Range and Altitude: Interception against high-speed aerial targets.
- Hit-to-Kill Capability: Demonstrated success in engaging targets in various scenarios (approaching, receding, crossing).
System Overview:
- Type: Fourth generation man-portable air defence system (MANPADS).
- Developer: Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in collaboration with other DRDO labs and industry partners.
Capabilities:
- Designed to neutralise low altitude aerial threats at short ranges.
- Features include Dual-band IIR Seeker, miniaturised Reaction Control System, and integrated avionics.
- More portable and lightweight than existing missile systems in the Army's arsenal.
USCIRF Report on India: Key Highlights

- 04 Oct 2024
In News:
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF), a Washington DC-based bipartisan U.S. federal government agency, has released a country update on India, flagging “collapsing religious freedom conditions”.
- Agency Overview:
- The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is an independent, bipartisan U.S. federal commission established under the 1998 International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA).
- Its primary functions include reviewing global religious freedom violations, providing policy recommendations to U.S. leaders, and publishing annual reports.
- Current Concerns:
- USCIRF's latest report indicates a “collapse” in religious freedom conditions in India, particularly worsening throughout 2024, especially around national elections.
- Legal and Policy Changes:
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- State-level anti-conversion and anti-terrorism laws.
- Implementation rules for the 2019 Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA).
- Passage of a State-level Uniform Civil Code (UCC) Bill in Uttarakhand.
- Strengthening of discriminatory legislation, including:
- Violations and Incidents:
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Authorities have facilitated the construction of Hindu temples on former mosque sites.
- Increased attacks on religious minorities, particularly following the consecration of the Ayodhya temple in January 2024.
- Targeting of Religious Minorities:
- Arrests of Christians accused of forced conversions under anti-conversion laws.
- Anti-cow slaughter laws exploited by vigilante groups to target Muslims, Christians, and Dalits, often with little to no legal repercussions for perpetrators.
- Expropriation of Places of Worship:
- Recommendations:
- USCIRF urges the U.S. State Department to designate India as a “Country of Particular Concern” due to severe violations of religious freedom.
About USCIRF
- Composition: Comprised of nine commissioners appointed by the U.S. President or Congressional leaders, supported by non-partisan staff.
- Objective: To monitor and recommend actions on religious freedom violations aligned with international human rights standards.
PM E-DRIVE Scheme

- 03 Oct 2024
In News:
The Union Cabinet approved the PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-DRIVE) Scheme to promote electric mobility in the country.
Objective:
- Accelerate electric vehicle (EV) adoption
- Establish essential charging infrastructure
- Promote cleaner and sustainable transportation
Key Highlights
- Significant Occasion: Launched on the eve of Mahatma Gandhi's 155th Birth Anniversary, aligning with the vision of ‘Swachh Bharat’ and ‘Swachh Vahan’.
- Financial Commitment: Union Cabinet approved a financial outlay of ?10,900 crore for the scheme over two years (approved on September 11, 2024).
Key Features of the PM E-DRIVE Scheme
- Subsidies/Demand Incentives:
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- 24.79 lakh electric two-wheelers (e-2Ws)
- 3.16 lakh electric three-wheelers (e-3Ws)
- 14,028 electric buses (e-buses)
- Total of ?3,679 crore allocated for:
- E-Voucher Introduction:
- Aadhaar-authenticated e-vouchers for EV customers
- Simplifies access to incentives, with real-time generation for dealers.
- E-Ambulances:
- ?500 crore allocated for deployment
- Standards to be developed with relevant ministries.
- E-Buses:
- ?4,391 crore for 14,028 e-buses in nine major cities
- Focus on replacing scrapped state transport unit buses.
- E-Trucks:
- ?500 crore for incentivizing electric trucks
- Scrapping certificates required for incentives.
- Public Charging Stations:
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- 22,100 fast chargers for electric four-wheelers (e-4Ws)
- 1,800 for e-buses
- 48,400 for e-2Ws/3Ws
- ?2,000 crore to install:
- Test Agency Modernization:
- ?780 crore for upgrading Ministry of Heavy Industries test agencies to accommodate new EV technologies.
La Nina and North India’s pollution
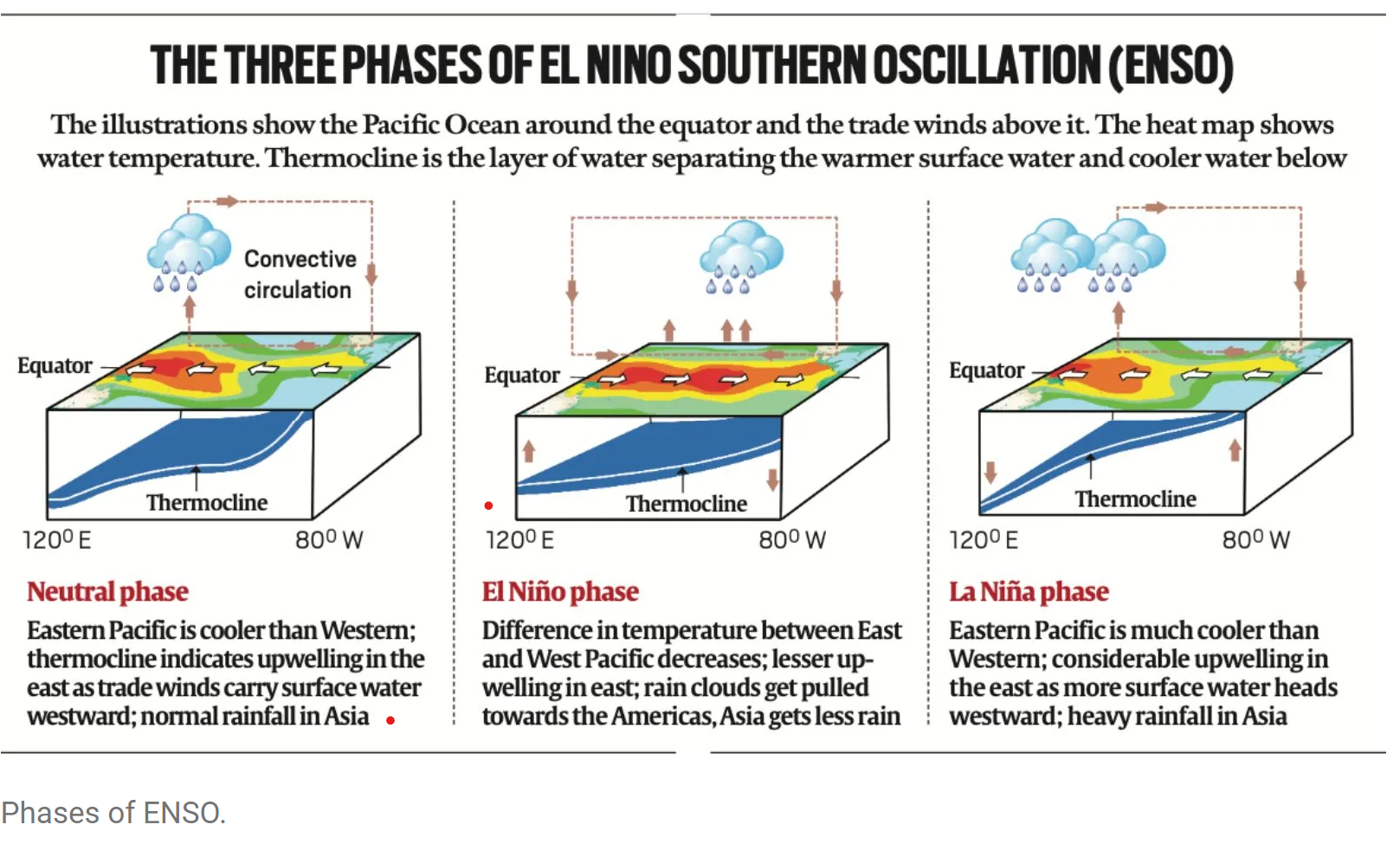
- 01 Oct 2024
In News:
Recent research by scientists at the National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) has underlined the links between climate change, La Niña and air quality.
Key Points on Air Quality Outlook for Delhi and North India
- Delayed La Niña & Monsoon Retreat:
- Erosion of optimism for improved air quality this winter in Delhi.
- Significant pollution challenges anticipated in early winter months.
- Possible relief in December and January, contingent on La Niña strengthening.
- Impact of Stubble Burning:
- If stubble burning occurs at half the intensity of previous years, November air quality may deteriorate.
- Research Insights:
- Study by National Institute of Advanced Science (NIAS) links climate change, La Niña, and air quality.
- Notable air quality improvement in winter 2022-23 was linked to La Niña conditions.
- Late onset of La Niña contributes to air quality uncertainty.
- Changing Pollution Dynamics:
- Shift from local emission-centric views to broader climatological factors is necessary.
- Air quality in Delhi worsens during winter due to high humidity, calm winds, and poor pollutant dispersion.
- La Niña Delays:
- Delayed La Niña onset means weak winds and stagnant conditions, worsening pollution.
- Expected development between September and November 2024.
- Effects of Stubble Burning:
- North-north-westerly winds could carry pollution from stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana into Delhi.
- Potential Outcomes of Late La Niña Onset:
- If La Niña develops in December or January, may improve air quality slightly.
- However, a longer, severe winter could exacerbate pollution issues due to lower inversion layers.
- NIAS-SAFAR Model Predictions:
- Early La Niña could have worsened air quality in the peninsular region.
- Early onset might have improved northern air quality.
- Link to Climate Change:
- Evidence suggests extreme air pollution correlates with climate change.
- Emphasizes the need for rigorous mitigation efforts and broader airshed management.
- Call for Rethinking Air Quality Strategies:
- Focus on integrating larger climatic factors into air quality policies.
- Prioritize health-centric measures through collaborative efforts with scientific bodies.
What is La Niña?
- La Niña (or ‘The Little Girl’ in Spanish) is a phase of what climatologists refer to as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a phenomenon that is a key driver of global natural climate variability.
- ENSO is characterised by changes in sea temperatures along the tropical Pacific Ocean due to atmospheric fluctuations overhead. These changes alter and interfere with the global atmospheric circulation, and influence weather worldwide.
- Occurring in irregular cycles of anywhere between two to seven years, ENSO has three phases — warm (El Niño or ‘The Little Boy’ in Spanish), cool (La Niña), and neutral.
- During the neutral phase, the eastern Pacific (off the northwestern coast of South America) is cooler than the western Pacific (around Philippines and Indonesia). This is because prevailing trade winds — caused by Earth’s rotation, between 30 degrees north and south of the equator — move east to west, sweeping warmer surface water along with them. The relatively cool waters from below rise to the surface to replace the displaced water.
- These wind systems weaken in the El Niño phase, leading to lesser displacement of warmer waters off the American coasts. Consequently, the eastern Pacific becomes warmer than usual. The opposite happens in the La Niña phase i.e. trade winds become stronger than usual and push larger quantities of water to the western Pacific.
Digital Agriculture Mission

- 03 Sep 2024
Introduction
India's digital revolution has significantly transformed governance and service delivery in recent years by creating digital identities, secured payments and transactions. This progress has paved the way for a thriving digital ecosystem across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, education, and retail, positioning India as a leader in citizen-centric digital solutions.
For a similar transformation of the Agriculture Sector, the Union Cabinet Committee, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi approved the 'Digital Agriculture Mission' with a substantial financial outlay of Rs. 2,817 Crore, including a central government share of Rs. 1,940 Crore, on September 2, 2024.
The Digital Agriculture Mission is designed as an umbrella scheme to support various digital agriculture initiatives. These include creating Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), implementing the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES), and supporting IT initiatives by the Central Government, State Governments, and Academic and Research Institutions.
The scheme is built on two foundational pillars:
- Agri Stack
- Krishi Decision Support System.
Additionally, the mission includes ‘Soil Profile Mapping’ and aims to enable farmer-centric digital services to provide timely and reliable information for the agriculture sector.
AgriStack: Kisan ki Pehchaan
AgriStack is designed as a farmer-centric Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to streamline services and scheme delivery to farmers. It comprises three key components:
1. Farmers' Registry
2. Geo-referenced village maps
3. Crop Sown Registry
- A crucial feature of AgriStack is the introduction of a 'Farmer ID', similar to Aadhaar card, serving as a trusted digital identity for farmers.
- These IDs, created and maintained by the State Governments/ Union Territories, will be linked to various farmer-related data, including land records, livestock ownership, crops sown, and benefits availed.
- The implementation of AgriStack is progressing through partnerships between the Central and State Governments, with 19 states having signed MoUs with the Ministry of Agriculture. Pilot projects have been conducted in six states to test the creation of Farmer IDs and the Digital Crop Survey.
- The six states include Uttar Pradesh (Farrukhabad), Gujarat (Gandhinagar), Maharashtra (Beed), Haryana (Yamuna Nagar), Punjab (Fatehgarh Sahib), and Tamil Nadu (Virudhnagar).
Key targets include:
- Creating digital identities for 11 crore farmers over three years (6 crore in FY 2024-25, 3 crore in FY 2025-26, and 2 crore in FY 2026-27)
- Launching the Digital Crop Survey nationwide within two years, covering 400 districts in FY 2024-25 and all districts in FY 2025-26
2. Krishi Decision Support System
- The Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) will integrate remote sensing data on crops, soil, weather, and water resources into a comprehensive geospatial system.
3. Soil Profile Mapping
Under the mission, detailed soil profile maps on a 1:10,000 scale for approximately 142 million hectares of agricultural land have been envisaged, with 29 million hectares of soil profile inventory already being mapped.
- Further under the Digital Agriculture Mission, the Digital General Crop Estimation Survey (DGCES) will be used for crop-cutting experiments to provide precise yield estimates, enhancing agricultural production accuracy.
- The mission is expected to create direct and indirect employment in agriculture, providing opportunities for around 2,50,000 trained local youth and Krishi Sakhis.
- By leveraging modern technologies like data analytics, AI, and remote sensing, the mission will improve service delivery for farmers, including streamlined access to government schemes, crop loans, and real-time advisories.
Key Components of the Mission
The Digital Agriculture Mission focuses on grassroots implementation, targeting farmers as the primary beneficiaries. Some of the key benefits of the mission include:
- Digital authentication for accessing services and benefits, reducing paperwork and the need for physical visits.
- Enhanced efficiency and transparency in government schemes, crop insurance, and loan systems through accurate data on crop area and yield.
- Crop map generation and monitoring for better disaster response and insurance claims.
- Development of digital infrastructure to optimize value chains and provide tailored advisory services for crop planning, health, pest management, and irrigation.
Digital Public Infrastructure for Agriculture
- Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 that the Government, in partnership with states, will implement Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agriculture over the next three years.
- This initiative will cover farmers and their lands, with a digital crop survey for Kharif planned for 400 districts this year. The goal is to update registries with details of 6 crore farmers and their lands.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 had previously introduced the DPI for agriculture, which aims to provide comprehensive data on farmers, including demographic details, land holdings, and crops sown. The DPI will integrate with state and central digital infrastructures to offer a range of farmer-centric services, including information on livestock, fisheries, soil health, and available benefits.
Conclusion
- The Union Cabinet also approved six major schemes alongside the Digital Agriculture Mission, with a total outlay of Rs 14,235.30 crore.
- These initiatives include Rs 3,979 crore for Crop Science aimed at ensuring food security and climate resilience by 2047, and Rs 2,291 crore for strengthening Agricultural Education, Management, and Social Sciences to support students and researchers. Rs 1,702 crore is allocated for Sustainable Livestock Health and Production to boost incomes from livestock and dairy, while Rs 1,129.30 crore is designated for Sustainable Development of Horticulture to increase income from horticulture. Additionally, Rs 1,202 crore will be invested in strengthening Krishi Vigyan Kendra, and Rs 1,115 crore towards Natural Resource Management.
- These comprehensive approaches leverage digital technologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in India's agricultural sector, potentially transforming the lives of millions of farmers across the country. By extending the digital revolution to agriculture, India aims to further solidify its position as a global leader in innovative, technology-driven solutions for critical sectors of the economy.
Recent Announcement on Dark Matter Research

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
Recently two representatives from the LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) experiment, working 1.5 km underground at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota, announced that they had placed the tightest restrictions yet on the identities of dark matter particles, resulting in a null finding that clarified which identities these particles could not have, leading to a sense of resignation rather than disappointment among the physics community, as similar experiments like XENON-nT in Italy and PandaX-4T in China have yielded empty results for decades despite significant efforts.
Background on Dark Matter
- Definition: Dark matter makes up most of the universe's mass, contributing to its structure.
- Composition: Likely consists of previously unknown particles that:
- Do not interact with photons.
- Remain stable over billions of years.
- Key Question: Can dark matter interact with atomic nuclei and electrons?
Experimental Strategies
- Proposed Method:
- Introduced by physicists Mark Goodman and Ed Witten in 1985.
- Concept: Use a “sail” (a chunk of metal) deep underground to detect dark matter interactions.
- Objective: Measure unknown mass and interaction rate (cross-section) of dark matter particles.
Scattering Cross-Section
- Concept:
- Similar to light interaction with different media (vacuum, glass, rock).
- Cross-sections indicate how readily a particle can scatter.
- Previous Limits: Proposed limits as small as 10−38cm210^{-38} text{cm}^210−38cm2.
- Current Achievements: Recent experiments have ruled out cross-sections as small as 10−44cm210^{-44} text{cm}^210−44cm2.
Challenges Ahead
- Neutrino Interference:
- As detectors increase in size, they also detect more noise from neutrinos, complicating dark matter detection.
- Both PandaX-4T and XENONnT report issues with neutrino signals.
- Resignation in Community:
- Scientists had hoped for clearer results before facing the challenge of distinguishing dark matter from neutrinos.
Alternative Research Avenues
- Focus on Lighter Particles:
- Exploring dark particles lighter than atomic nuclei for easier detection.
- Technological Development:
- Advancing technologies to measure minimal energy transfers using special materials.
Conclusion
- Ongoing Effort: The search for dark matter continues to unite scientific disciplines and require innovative approaches.
- Human Ingenuity: The pursuit reflects a broader effort to understand the universe, drawing on collective expertise and creativity.
NAMASTE programme

- 30 Sep 2024
In News:
A recent government survey has shed light on the demographics of workers engaged in the hazardous cleaning of urban sewers and septic tanks across India. This initiative, part of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment's NAMASTE programme, highlights significant disparities within this labor sector.
Key Findings
- Community Representation: An overwhelming 91.9% of the 38,000 workers profiled belong to marginalized communities:
- Scheduled Castes (SC): 68.9%
- Other Backward Classes (OBC): 14.7%
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): 8.3%
- General Category: 8%
- Mortality Rates: Between 2019 and 2023, at least 377 individuals died while performing hazardous cleaning tasks, underscoring the dangers associated with this work.
The NAMASTE Programme
- Objective: The NAMASTE programme aims to mechanize sewer work to prevent fatalities linked to manual cleaning. It seeks to transition workers into safer, more sustainable roles as "sanipreneurs" by providing safety training, equipment, and capital subsidies.
- Background: This programme replaces the earlier Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS), focusing on the more technical aspects of hazardous cleaning rather than manual scavenging.
- Namaste is a Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) as a joint initiative of the MoSJE and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- The Scheme has been approved with an outlay of Rs. 360 crore for four years from 2022-23 to 2025-26.
- NAMASTE aims to achieve the following outcomes:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India
- All sanitation work is performed by skilled workers
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter
- Sanitation workers are collectivized into SHGs and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises
- All Sewer and Septic tank sanitation workers (SSWs) have access to alternative livelihoods
- Strengthened supervisory and monitoring systems at national, state and ULB levels to ensure enforcement and monitoring of safe sanitation work
- Increased awareness amongst sanitation services seekers (individuals and institutions) to seek services from registered and skilled sanitation workers
Progress and Coverage
- Implementation: Since the scheme's inception, 3,326 urban local bodies (ULBs) have begun profiling workers, with many reporting minimal or no workers engaged in hazardous cleaning.
- Data Collection: The government is gathering data from over 3,000 ULBs across 29 states and union territories to better understand the scope and risks associated with this labor.
ETURNAGARAM WILDLIFE SANCTUARY

- 29 Sep 2024
In News:
A rare collision of two cyclones has led to significant environmental impact, including the flattening of thousands of trees within the sanctuary.
Key Details:
- Location: Situated in the Mulugu district of Telangana, near the borders of Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh. Approximately 100 km from Warangal and 250 km from Hyderabad.
- Establishment: Declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1952 by the Nizam government of Hyderabad.
- Area: Covers around 806 square kilometers.
Geographic Features
Rivers:
- Dayyam Vagu: A significant water source that divides the sanctuary into two parts.
- Godavari River: Flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
Flora
- Vegetation: Dense tropical dry deciduous forest.
- Key Species: Includes teak, bamboo, madhuca, and terminalia trees, creating a lush habitat.
Fauna
- Wildlife: Home to diverse species such as:
- Mammals: Tiger, leopard, panther, wolf, wild dogs, jackals, sloth bear, chousingha, blackbuck, nilgai, sambar, spotted deer, and four-horned antelope.
- Reptiles: Notable for its population of mugger crocodiles and snakes, including cobras, pythons, and kraits.
Cultural Significance
- Temple: The famous Sammakka-Saralamma Temple is located within the sanctuary.
INDIA WATER WEEK (IWW) 2024

- 27 Sep 2024
In News:
- The 8th edition of India Water Week (IWW) 2024 was held from September 17-20, 2024, at the Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
- Organized by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, this prestigious international event has established itself as a key platform for collaboration in water resource management.
- With participation from global water experts, government leaders, and private-sector representatives, the event aimed to address the critical challenges of water management, foster innovation, and promote sustainable water practices.
Theme and Focus
The theme for India Water Week 2024 was "Partnerships and Cooperation for Inclusive Water Development and Management." This theme underscored the importance of cross-sectoral and international collaboration to address the 21st-century's growing water challenges and the need for integrated efforts in water conservation, management, and equitable access to water resources.
India Water Week: An International Forum
- Since its inception in 2012, India Water Week has grown into a pivotal event in global water diplomacy, offering a platform for dialogue, innovation, and knowledge sharing.
- Each edition focuses on a specific water-related issue, providing policymakers, experts, and industry leaders the opportunity to present solutions and explore cooperative strategies.
International WASH Conference
- A key highlight of IWW 2024 was the International WASH Conference, organized by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- This conference focused on global collaboration in Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH), aiming to address pressing sanitation challenges and promote hygiene standards.
- The conference was held between 17th-19th September 2024, in New Delhi. This three-day gathering, centered on the theme ‘Sustaining Rural Water Supply’, offered a platform for knowledge exchange, showcasing innovations, and sharing best practices aimed at addressing global WASH challenges, with a special focus on achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6).
Key Takeaways from India Water Week 2024
The India Water Week 2024 concluded with several important takeaways:
- Collaboration and Cooperation: Water security can only be achieved through partnerships across sectors and borders.
- Innovation in Water Management: Startups and technological innovations are key to addressing the future challenges of water resource management.
- Community Participation: Local communities play a crucial role in water conservation efforts, and their involvement is vital to achieving sustainable development.
- Policy Recommendations: The event produced several policy recommendations for sustainable water governance, addressing challenges in climate resilience, infrastructure development, and groundwater management.
Conclusion
India Water Week 2024 was a landmark event that brought together a diverse group of stakeholders to address the complexities of water management in the 21st century. The event paved the way for a more sustainable and inclusive approach to water development through partnership, cooperation, and innovation, ensuring equitable access to water resources for all.
INDIA'S BIOE3 POLICY AND SMART PROTEINS

- 26 Sep 2024
In News:
The Indian government recently approved the Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment (Bioe3) Policy, which prioritizes the production of "smart proteins". This initiative aligns with broader national goals of achieving a sustainable, circular bioeconomy and a Net Zero carbon economy.
What Are Smart Proteins?
Smart proteins are alternative proteins derived from unconventional sources such as:
- Algae
- Fungi
- Insects
- Fermentation processes
- Lab-grown cells
This category also includes plant-based proteins, designed to replicate the taste and nutritional value of animal products without the need for livestock farming.
Environmental Benefits
The production of smart proteins offers significant environmental advantages:
- Water Use: 72-99% less water compared to conventional meat.
- Land Use: 47-99% less land required.
- Water Pollution: 51-91% reduction in pollution.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: 30-90% fewer emissions.
Health and Safety
With rising incomes, India's protein consumption has increased, from 9.7% of calories in 1991 to 11% in 2021. Smart proteins:
- Enhance food safety by reducing the risk of zoonotic diseases.
- Foster ethical consumption and align with traditional Indian dietary preferences.
Objectives of the BioE3 Policy
The Bioe3 Policy aims to:
- Foster high-performance biomanufacturing.
- Promote sustainable growth and innovation in biotechnology.
- Support the transition towards a Net Zero carbon economy.
By emphasizing the development of smart proteins, the Bioe3 Policy represents a strategic move towards a more sustainable and resilient food system in India.
ACHIEVING GLOBAL NUCLEAR DISARMAMENT

- 26 Sep 2024
Overview
Global nuclear disarmament remains a top priority for the United Nations, initially emphasized in the General Assembly’s first resolution in 1946. Despite historical efforts, approximately 12,100 nuclear weapons still exist today, with ongoing modernization plans in many countries.
Key Historical Milestones
- 1945: Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing an estimated 213,000 people.
- 1946: First UN resolution identifies nuclear disarmament as a key goal.
- 1959: General Assembly endorses the goal of general and complete disarmament.
- 1963: Opening of the Partial Test Ban Treaty.
- 1978: First Special Session of the General Assembly dedicated to disarmament.
- 1996: Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty opens for signature.
- 2017: Adoption of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Recent Developments
- 2019: U.S. withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty.
- 2023: Russia suspends participation in the New START Treaty, raising concerns over arms control.
The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons
- Established: December 2013, following a high-level meeting on nuclear disarmament.
- Observed: Annually on September 26.
- Purpose: Raise awareness about the dangers of nuclear weapons and promote their total elimination.
Goals of the International Day
- Enhance public education on the humanitarian risks associated with nuclear weapons.
- Mobilize international efforts towards a nuclear-weapon-free world.
Continuing Challenges
- The doctrine of nuclear deterrence remains central to the security policies of nuclear-armed states and their allies.
- No nuclear weapons have been destroyed under a treaty framework, and current disarmament negotiations are stagnant.
- Growing frustration among UN Member States over the slow progress in nuclear disarmament.
SWACHH BHARAT MISSION 2.0

- 24 Sep 2024
Mission Overview:
- Launched on October 1, 2021, as the second phase of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Aims for "Garbage-Free Status" in all urban areas by 2026.
- Focuses on 100% source segregation, door-to-door waste collection, and scientific waste management.
Legacy Waste Issues:
- Legacy waste consists of improperly collected and stored solid waste, often found in landfills and abandoned sites.
- Approximately 15,000 acres of prime land are buried under nearly 16 crore tonnes of legacy waste in India.
- The mission seeks to convert legacy dumpsites into green zones and establish scientific landfills to manage untreated waste.
Current Progress:
- Of 2,424 identified dumpsites (each with over 1,000 tonnes of waste), only 470 have been fully remediated (16% reclaimed).
- 1,224 sites are under ongoing remediation, while 730 remain untouched.
- Out of 28,460 acres of affected land, 4,552 acres have been reclaimed, with 23,908 acres still to be addressed.
State Performance:
- Tamil Nadu: 837 acres reclaimed (42% of its total dumpsite area).
- Gujarat: Leads in percentage, reclaiming 75% of its landfill area (698 out of 938 acres).
Financial Aspects:
- Central assistance of ?3,226 crore has been approved for remediation efforts.
- States and Union Territories must provide a matching share to access these funds.
Challenges:
- Legacy waste management involves complexities such as radiological characterization, leachate management, and fire control.
- Current municipal solid waste generation in India is around 150,000 tonnes per day.
Historical Context:
- The original Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-U 1.0) launched on October 2, 2014, focused on making urban areas Open Defecation Free (ODF).
GREENLAND LANDSLIDE AND GLOBAL SEISMIC WAVES

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
Massive Greenland landslide sent seismic waves around earth for 9 days. One year ago, roughly 25 million cubic metres of ice and rock splashed into the Dickson Fjord in Greenland and displaced the water enough to give rise to a 200-metre high mega-tsunami; in this way, a melting glacier led to a planet-wide tremor, and researchers warn that it may not be the last
Seismic Observations
- Detection: Unusual seismic signals recorded by stations worldwide, characterized by a single frequency, unlike typical earthquake vibrations.
- Classification: Initially termed a "USO" (unidentified seismic object) due to its atypical properties.
- Duration: Waves persisted for nine days, unlike typical aftershock patterns.
Investigation Efforts
- Collaboration: Involved over 68 researchers from 40 universities across 15 countries.
- Data Sources: Combined seismic data, satellite imagery, water level monitors, and a classified bathymetric map from the Danish Navy.
- Conclusion: The seismic waves resulted from a massive landslide caused by the collapse of Hvide Støvhorn peak, which triggered a series of events leading to the tsunami.
Mega-Tsunami and Seiche
- Tsunami Details:
- Created by the avalanche crashing into the fjord, displacing water significantly.
- Resulted in waves that reflected off fjord walls, reaching heights of nearly 110 meters due to the fjord's unique shape.
- Seiche Phenomenon:
- Oscillations in the fjord persisted for over nine days, reflecting the energy from the landslide.
- Maximum amplitude of the seiche recorded at 7.4 meters, with a frequency of 11.45 MHz.
Climate Context
- Global Warming Impact: Thinning glaciers contributed to instability in the region, making such landslides more likely.
- Future Predictions: Researchers warn of increased frequency and scale of similar events as climate change continues to affect Arctic and subarctic regions.
Key Takeaways
- The Greenland landslide serves as a reminder of the unpredictable consequences of climate change, including massive geological events.
- The incident highlights the interconnectedness of natural systems and the potential for localized events to have global repercussions.
ROBOTIC MULES AND HIGH-ALTITUDE INNOVATIONS IN THE ARMY

- 24 Sep 2024
In News:
The Army has inducted 100 robotic mules, known as Multi-Utility Legged Equipment (MULE), under the fourth tranche of emergency procurements (EP).
- Purpose: These robotic mules are designed for surveillance and transporting light loads across challenging terrains, especially in high-altitude areas.
- Specifications:
- Endurance: Capable of operating for up to three years.
- Temperature Range: Functions effectively in extreme temperatures from -40°C to +55°C.
- Payload Capacity: Can carry up to 15 kg.
- Mobility: Can climb stairs, steep hills, and traverse obstacles; waterproof and able to cross rivers.
- Sensing Abilities: Equipped with electro-optics and infrared capabilities for object recognition.
- Control Mechanisms: Operable via an easy-to-use remote control, Wi-Fi, or Long-Term Evolution (LTE) connections.
- Mission Programming: Can be programmed for specific missions using waypoints or pre-recorded tasks.
- Combat Integration: Capable of integration with small arms for military applications.
- Logistics Drones: Logistics drones are currently undergoing trials to enhance support and movement in forward areas, particularly in high-altitude conditions.
- High-Altitude Habitat Evaluation: A new tent designed for extreme cold environments (operating at temperatures down to -40°C) is under evaluation. This tent, called Peak Pods, is intended for use in sub-zero conditions.
- Evaluation Locations: The tent has been tested in three high-altitude sites:
- Leh (11,500 feet)
- Daulat Beg Oldie (16,700 feet)
- Durbuk (12,500 feet)
- Significance: These advancements reflect the Army's focus on technological innovations to enhance operational capabilities in high-altitude areas, especially following the 2020 stand-off with China in Eastern Ladakh.
- Funding and Timelines: The EP process allows contracts up to ?300 crore, with a requirement for delivery within one year.
AMUR FALCONS

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
An order issued by the District Magistrate directed the owners of air guns to deposit their hunting weapons at the offices of respective village authorities.
Amur Falcons: An Overview
Scientific Classification:
- Common Name: Amur Falcon
- Scientific Name: Falco amurensis
- Family: Falconidae
Physical Characteristics:
- Size: Small raptors, approximately 28-30 cm in length.
- Distinctive Features: Dark plumage with white wing linings; reddish-orange eyes and feet.
Migration Patterns:
- Breeding Grounds: Southeastern Russia and northern China.
- Migratory Route: They leave their breeding areas in autumn, traveling south to round the Himalayas, stopping in Nagaland, and then heading towards the Western Ghats before crossing the Indian Ocean to reach South Africa.
- Distance: These falcons undertake an incredible journey of around 22,000 kilometers annually, making them one of the most remarkable long-distance migrants among raptors.
Diet:
- Primarily insectivorous, they also consume small vertebrates when available.
Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
- Legal Protection:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule IV
- Convention on Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix II
Recent Conservation Efforts:
- Ban in Manipur: The Tamenglong district administration has imposed a ban on hunting, catching, killing, and selling Amur falcons in preparation for their migratory arrival.
- Tagging Program: In 2016, radio transmitters were used to monitor their migration routes.
- Awareness Initiatives: An annual ‘Amur Falcon Festival’ in Tamenglong district promotes awareness and celebrates these migratory birds.
Threats:
- Amur falcons face various threats including habitat loss, hunting, and illegal trapping.
Cultural Significance:
- Locally known as ‘Kahuaipuina’ in Manipur and ‘Molulem’ in Nagaland, these birds hold ecological and cultural significance, particularly in regions that serve as critical stopover points during migration.
Summary
The Amur falcon is a small but remarkable migratory raptor known for its long-distance travels from its breeding grounds in Asia to Africa. Conservation efforts in India, particularly in the Tamenglong district of Manipur, aim to protect these birds from hunting and habitat loss, ensuring their continued survival and highlighting their importance in the ecosystem.
QUAD GROUPING

- 22 Sep 2024
In News:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi arrived in the United States, where he will participate in the fourth Quad Leaders Summit in Wilmington, Delaware.
What is the Quad Grouping?
The Quad, or Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, is an informal strategic alliance comprising India, the United States, Japan, and Australia. Originally formed in response to the Indian Ocean tsunami in 2004, the Quad aims to foster collaboration in various areas, but its primary focus has become countering the influence of China in the Indo-Pacific region.
Historical Background
- 2004: The Quad began as a response to the Indian Ocean tsunami, facilitating disaster relief.
- 2007: Japanese PM Shinzo Abe formalized the alliance.
- 2017: Amid rising Chinese assertiveness, the Quad was revitalized, expanding its objectives beyond maritime security.
Structure and Characteristics
- The Quad is not a formal organization; it lacks a secretariat or permanent decision-making body like the EU or UN.
- It focuses on strengthening bilateral and multilateral ties among member nations.
- Unlike NATO, the Quad does not include collective defense provisions but conducts joint military exercises to demonstrate unity.
Key Developments
- In 2020, the Malabar naval exercises expanded to include Australia, marking the first joint military exercises of the Quad since its resurgence.
- The first in-person summit took place in Washington, D.C. in 2021.
Objectives of the Quad
The Quad has outlined several primary objectives:
- Maritime Security: Ensuring safe and open sea routes in the Indo-Pacific.
- Climate Change: Addressing environmental challenges collaboratively.
- Investment Ecosystem: Creating opportunities for economic investment in the region.
- Technological Innovation: Promoting advancements and cooperation in technology.
- Public Health: Collaborating on initiatives like vaccine diplomacy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Expansion and Future Directions
The Quad members have discussed expanding the partnership to include countries like South Korea, New Zealand, and Vietnam. In a joint statement, they reaffirmed their commitment to a free, open, resilient, and inclusive Indo-Pacific governed by international law.
Challenges and Opposition
China views the Quad as an effort to encircle and contain its influence. Beijing has criticized the grouping, labeling it as a strategy that incites discord among Asian nations.
EUROPA CLIPPER MISSION

- 21 Sep 2024
In news:
NASA is preparing to launch the Europa Clipper mission, which aims to investigate Jupiter's icy moon, Europa.
Key Details:
- Objective: This mission will place a spacecraft in orbit around Jupiter to conduct a thorough study of Europa, focusing on its potential habitability.
- Significance: Europa Clipper will be NASA's first mission specifically designed to explore an ocean world beyond Earth. Europa is believed to have a subsurface ocean beneath its icy surface, which raises the possibility of supporting life.
- Spacecraft Specifications:
- The spacecraft measures 100 feet (30.5 meters) from end to end and 58 feet (17.6 meters) across, making it the largest NASA spacecraft ever built for a planetary mission.
- Mission Plan:
- Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and conduct 49 close flybys of Europa to gather critical data regarding its environment and potential habitability.
- Instrumentation:
- Equipped with nine scientific instruments and a gravity experiment that leverages its telecommunications system, the spacecraft will maximize data collection by operating all instruments simultaneously during each flyby. This approach will allow scientists to compile comprehensive data layers, creating an in-depth understanding of Europa.
- Power Source:
- The spacecraft is outfitted with large solar arrays to harness sunlight for its energy needs while operating in the challenging environment of the Jupiter system.
Solar Array
A solar array is a collection of solar panels interconnected to generate electrical power. When combined with other components like an inverter and battery, it forms a complete solar energy system.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
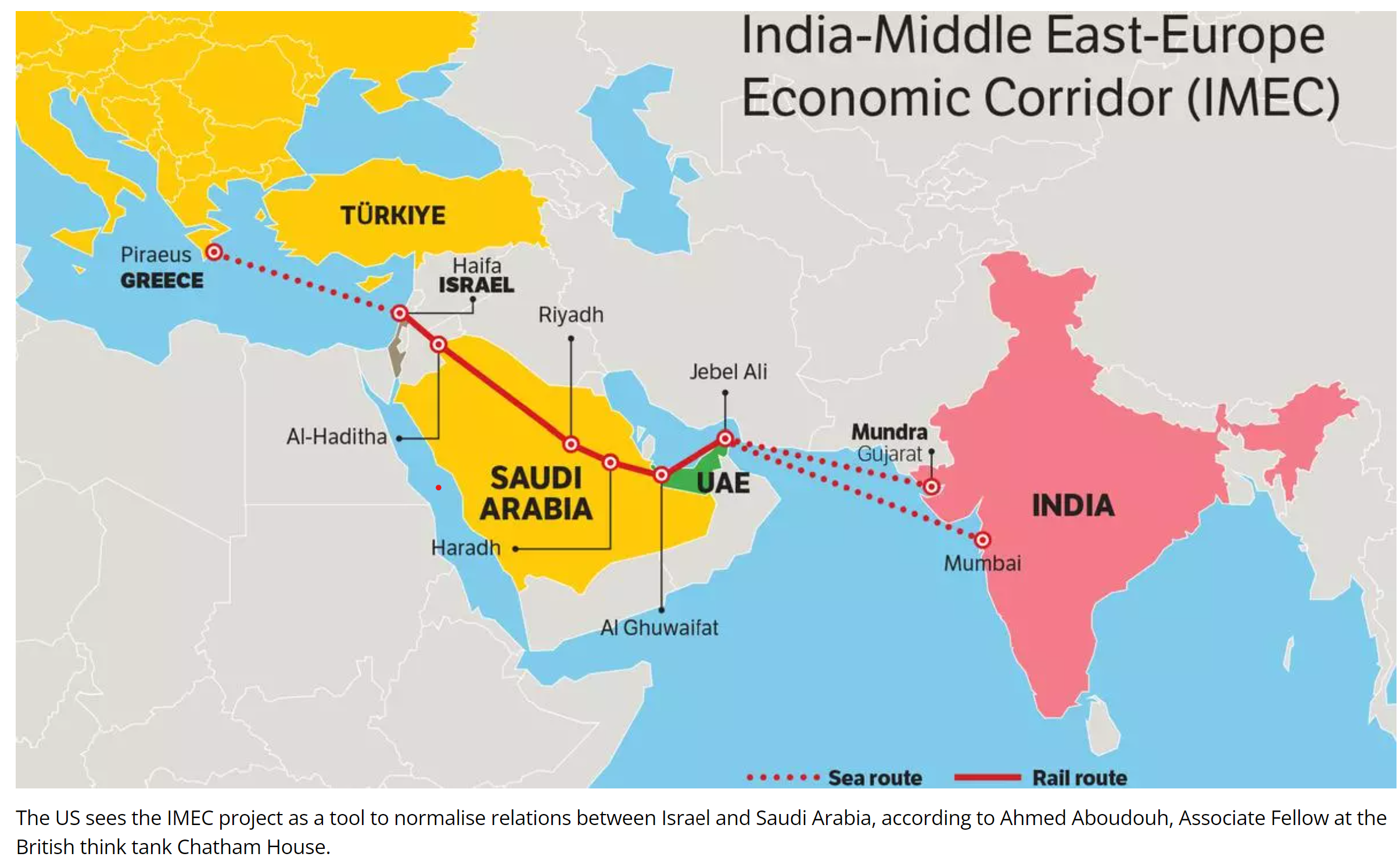
- 07 Sep 2024
In News:
IMEC is an important initiative that can add to India's maritime security and faster movement of goods between Europe and Asia, said Union Minister of Commerce & Industry at the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) India-Mediterranean Business Conclave 2024 in New Delhi.
Key Details:
- Corridors:
- East Corridor: Connects India to the Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Links the Gulf to Europe.
- Components:
- Railroad: Provides a reliable and cost-effective cross-border ship-to-rail transit network.
- Ship-to-Rail Networks: Integrates road, sea, and rail transport routes.
- Road Transport: Complements the overall transport infrastructure.
- Expected Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Enhances transit efficiency and reduces costs.
- Economic Unity: Promotes economic integration and job creation.
- Environmental Impact: Lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transformative Integration: Connects Asia, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Additional Features:
- Infrastructure: Includes laying cables for electricity and digital connectivity, and pipes for clean hydrogen export.
- Implementation:
- MoU Commitments: Participants will collaboratively address technical design, financing, legal, and regulatory aspects.
- Action Plan: A meeting is planned within 60 days to develop an action plan with specific timetables.
Geoeconomic Perspective
- Economic Integration and Interdependence:
- Prosperity Through Integration: IMEC aims to foster trade and investment among India, the Middle East, and Europe, potentially leading to mutual prosperity and regional stability.
- Building Bridges: Aligns with the liberal international order by promoting economic interdependence to reduce tensions and create shared interests.
- Support from Major Powers: Backed by the US, Europe, and India, signaling a strong commitment to economic ties and regional stability.
- Economic Potential:
- Infrastructure and Trade Routes: Enhances infrastructure and trade routes, boosting economic activity, trade volumes, and investment opportunities.
- Regional Development: Promotes job creation and development in economically disadvantaged areas along the corridor.
Geopolitical Perspective
- Strategic Rivalry with China:
- Countering the BRI: IMEC is seen as a strategic counterbalance to China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), offering an alternative aligned with US, European, and Indian interests.
- Regional Influence: Aims to limit China’s influence in the Middle East and South Asia by establishing a competing corridor.
- Geopolitical Alliances:
- Aligning Interests: Involves strategic partnerships among the US, Europe, and India, reflecting concerns about China’s global strategy and shifting power dynamics.
- Rivalry and Competition: The IMEC could be viewed as a global positioning move, responding to China’s growing influence and securing strategic interests.
Reasons for Joining the IMEC
- Economic Enhancement:
- Boosts Indo-Gulf Relations: Enhances trade and economic ties with the Arab Gulf, addressing infrastructure gaps.
- Regional Connectivity: Links India with key partners like Israel and Jordan, boosting economic opportunities.
- Strategic Trade Routes:
- Alternative Routes: Complements existing routes like Chabahar Port and INSTC, connecting India to southern Eurasia.
- Bypassing Choke Points: Offers a shorter route to Eastern Mediterranean and Western Europe, avoiding strategic choke points.
- Energy and Trade Opportunities:
- Access to Resources: Provides potential access to Eastern Mediterranean gas fields.
- Trade Bloc Connectivity: Links India with the EU and GCC, opening up growth opportunities.
- Geopolitical Aspirations:
- Global Power Ambitions: Supports India’s goal to enhance global influence and integrate with eastern and western neighbors.
- Economic Growth: Leverages economic integration to support development and influence.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Economic Integration: Facilitates infrastructure creation for increased trade volumes and regional stability.
AgriSURE Fund and Krishi Nivesh Portal

- 04 Sep 2024
In News:
- Recently, the Union agriculture minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan launched two initiatives — a fund aimed at boosting farm-sector startups, and a single-window portal to process investments — as part of a slew of measures being taken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led government in its third term to bolster the farm economy.
Key Details:
- AgriSure is a ?750-crore fund established to support agricultural startups.
- Krishi Nivesh Nidhi is a portal designed to expedite the clearance of project proposals.
- Both initiatives aim to enhance farm incomes.
Awards for Credit Disbursal:
- Scheduled banks were recognized for their credit disbursals under the government’s agriculture infrastructure fund.
- First prize: State Bank of India (SBI).
- Second prize: HDFC Bank.
- Third prize: Canara Bank.
Significance of Agriculture Sector:
- Agriculture contributes 16% to India’s GDP.
- Farmers play a crucial role as both producers and consumers in the economy.
PM Modi’s Strategy to Double Farmers’ Incomes:
- The strategy includes:
- Increasing output.
- Reducing input costs.
- Ensuring profitable prices.
- Promoting crop diversification.
- Supporting natural farming.
- Enhancing value addition to crops.
Details of AgriSure Fund:
- Blended capital fund with a total corpus of ?750 crore:
- ?250 crore each from the Department of Agriculture and NABARD.
- ?250 crore to be raised from financial institutions.
- Managed by NabVentures, a subsidiary of NABARD.
- Provides both equity and debt support to startups and agripreneurs.
- Focuses on high-risk, high-impact activities within the agriculture value chain.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund:
- Mobilized projects worth ?78,000 crore with ?45,000 crore in financing so far.
- Expanded areas of coverage approved by the Union Cabinet on August 28.
- Aims to create durable farm assets, such as warehouses and processing plants.
- Can be used by agricultural produce marketing committees (APMCs) for market facility improvements.
Funding and Loan Details:
- Part of the ?20-lakh crore stimulus package introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Total funding of ?1 lakh crore over four years:
- ?10,000 crore for 2020-21.
- ?30,000 crore each for the subsequent three financial years.
- Provides medium-to-long term debt financing for rural projects.
- Interest subvention of 3% per annum on loans up to ?2 crore for seven years, with the government covering part of the interest.
Planetary Alignment

- 23 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Next month, on June 3, there will be a planetary alignment that may actually allow you to witness six planets align in the sky.
What is a Planetary Alignment?
- Planetary alignment is a term used to describe the positioning of planets in the solar system such that they appear to be in a straight line or close to one when viewed from a specific vantage point, for us that's Earth.
- It is an astronomical event that happens when, by coincidence, the orbits of several of the planets of the Solar System bring them to roughly the same side of the Sun at the same time.
- This phenomenon is more an illusion of perspective rather than the planets being in a perfect line in space.
- It’s important to emphasise that the planets aren’t forming a straight line in space – that’s a much rarer astronomical event called a syzygy.
- However, because all the planets, including the Earth, orbit around the Sun in roughly the same orientation (moving in which we call the “Plane of the Ecliptic”), when they’re on the same side of the Sun as each other, they appear to form a line in the sky when we view them from Earth.”
- Planetary alignments are rather common within themselves, especially when two, three, or even four planets align in the sky.
- Five or more planets aligning, however, is less common.
- April 8, 2024, was the last time the planets were all in alignment.
Which planets will align?
- Mercury, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune will form a near-straight line, offering an extraordinary opportunity to witness this cosmic phenomenon.
Which planets will be visible?
- While six planets align, not all of them will be visible to the naked eye, due to their vast distance from Earth.
- Meanwhile, the Moon will also play a spoilsport as it distorts the visibility.
- Mercury and Jupiter will be tricky to see in the sky due to their proximity to the Sun in their orbit.
- However, Mars and Saturn will be visible to the naked eye, though very dim.
- Meanwhile, keen observers will need telescopes or high-powered binoculars to spot the distant planets Uranus and Neptune.
Nucleosynthesis
- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the process by which stars forge elements inside their cores.
What is Nucleosynthesis?
- Nucleosynthesis is the process by which atomic nuclei undergo nuclear reactions and decay to form new nuclei.
- It is responsible for the production of new elements in the universe.
- Nucleosynthesis occurs in various environments, such as during the Big Bang, in the cores of stars through nuclear fusion, and in black hole accretion disks through nuclear burning.
- The process is temperature-dependent, and the rates of nuclear reactions are influenced by the temperature of the environment.
- The Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (BBN) model is a fundamental theory that explains the evolution of the early universe and predicts the abundance of light elements.
- Nucleosynthesis plays a crucial role in understanding the composition of the universe and can provide insights into physics beyond the standard model.
Types of nucleosynthesis:
- Nucleosynthesis occurs in several different environments and phases of the universe's evolution, including:
- Stellar Nucleosynthesis: This occurs within stars and is responsible for producing most of the chemical elements heavier than hydrogen and helium.
- As stars age and undergo various stages of nuclear fusion, they synthesize elements up to iron in their cores, and heavier elements during supernova explosions at the end of their life cycles.
- Big Bang Nucleosynthesis: This took place during the early moments of the universe's existence, shortly after the Big Bang.
- t primarily produced the lightest elements, hydrogen, and helium, along with trace amounts of lithium, beryllium, and boron.
- Cosmic Ray Spallation: High-energy cosmic rays interacting with interstellar matter can cause fragmentation of atomic nuclei, resulting in the production of lighter elements and isotopes.
Project Astra

- 20 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, during the company's annual developer conference, Google unveiled an early version of Project Astra.
What is Project Astra?
- Project Astra is an experimental “multimodal” AI assistant developed by Google DeepMind.
- It's designed to be a versatile tool that can understand and respond to information from the real world through various means, like text, voice, images, and even videos.
- This makes it different from current AI assistants that mostly rely on internet searches and user input.
- Building on Google’s Gemini language model, Astra has multimodal capabilities to perceive visuals, sounds, and other real-world inputs.
- The aim is to create a universal AI helper that seamlessly assists us in daily life by comprehending the actual environment through sight and sound, not just text.
- Astra represents Google’s vision for next-gen AI assistants.
Key Features of Google's Project Astra:
- Visual Understanding: Astra can interpret and analyze visual input from its camera feed.
- It identifies objects, reads text, and describes scenes and environments in detail, allowing users to show Astra something and ask questions about it.
- Voice Interaction: Astra supports natural conversation without the need to repeatedly use wake words.
- It comprehends context and facilitates back-and-forth dialogue, even allowing users to interrupt its responses.
- Remembering Context: Astra retains memory of previous conversation parts, objects it has seen, and information provided by the user.
- This contextual awareness enhances the fluidity of interactions.
- Multimodal Integration: Astra integrates visual and auditory inputs to form a comprehensive understanding of the current situation, correlating what it sees and hears to fully grasp the context.
- Real-Time Assistance: Astra delivers real-time assistance by rapidly processing sensor data and queries, ensuring a responsive and interactive user experience.
What are Multimodal AI Models?
- Multimodal AI models are advanced artificial intelligence systems that process and integrate multiple types of data inputs, such as text, images, audio, and video, to develop a comprehensive understanding of context.
- By combining these different modalities, these models enhance their ability to interpret complex scenarios more accurately than unimodal systems.
- For instance, in autonomous vehicles, multimodal AI uses data from cameras, lidar, radar, and GPS for better navigation.
- In healthcare, these models integrate medical images with patient history for improved diagnostics.
- Applications also include virtual assistants, which understand and respond to spoken commands while recognizing objects in images, and educational tools that combine text, video, and interactive content for richer learning experiences.
- Multimodal AI models are often implemented using deep learning techniques, which allow the model to learn complex representations of the different data modalities and their interactions.
- As a result, these models can capture the rich, diverse information present in real-world scenarios, where data often comes in multiple forms.
Plunging Region of a Black Hole

- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the first time, astronomers have observed the area right at the edge of a black hole where matter stops orbiting and plunges straight in at near-light speed.
What is the Plunging Region of a Black Hole?
- The plunging region of a black hole is an area where matter ceases to orbit the celestial object and instead falls directly into its incalculable depths.
- This phenomenon was initially predicted by Albert Einstein's groundbreaking theory of general relativity, which continues to shape our understanding of the cosmos.
- As matter approaches a black hole, it is torn apart and forms a rotating ring known as an accretion disc.
- According to general relativity, there exists an inner boundary within this disc, beyond which nothing can maintain its orbit around the black hole.
- Instead, the material is drawn towards the black hole at nearly the speed of light, marking the beginning of the plunging region.
- This region, situated just outside the event horizon, represents the point of no return for matter falling into a black hole.
- Despite the challenges posed by studying these enigmatic structures, researchers believe that investigating plunging regions could unveil new insights into the formation and evolution of black holes.
- Additionally, these studies may offer valuable information about the fundamental properties of space-time, potentially transforming our understanding of the universe and its most mysterious inhabitants.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a celestial phenomenon that arises from the remnants of a massive star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel and undergone gravitational collapse.
- It is characterized by an unfathomably dense core, known as a singularity, which is enveloped by a boundary called the event horizon.
- The event horizon serves as a point of no return; any matter or light that crosses this boundary is irrevocably drawn towards the singularity, making it impossible to escape the immense gravitational pull.
Black holes are classified into three categories based on their size and formation process:
- Stellar-mass black holes: These form when a massive star collapses at the end of its life cycle. They typically have masses ranging from approximately five to several dozen times that of our Sun.
- Supermassive black holes: Found at the centre of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way, these colossal structures boast masses that can reach billions of times the mass of the Sun.
- Intermediate-mass black holes: With masses between those of stellar mass and supermassive black holes, these entities are thought to form through the merger of smaller black holes or the collapse of dense clusters of stars.
- Due to their extreme nature, black holes have been the subject of extensive research and fascination in the scientific community.
- The study of these enigmatic structures continues to yield invaluable insights into the fundamental principles governing our universe.
Mitogenome
- 18 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
New research has found South African leopards originated from two unique clades in southern and central Africa approximately 0.8 million years ago.
What is a Mitogenome?
- DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and also in the mitochondrial genome, or mitogenome.
- Mitogenomes are DNA molecules that float around outside the nucleus of a cell.
- They store their own set of genetic information and are maternally inherited, which means they are only passed on from mother to offspring.
- Mitogenomes are a “genomic by-catch” when sequencing the whole genome.
- They are so abundant in cells that it is very easy to extract them.
- Studying mitogenomes is a reliable way to track the ancestry of a species.
- This is because genes mutate (change) at a regular rate over time.
- The changes in the mitogenome provide a picture of any species' evolution over hundreds of thousands of years.
What is DNA?
- DNA or Deoxyribonucleic Acid is the genetic material that codes the information for all the different processes that make an organism living like growth, replication, metabolism, etc.
- DNA is present in each cell (except for some viral species, RBCs, sieve cells, etc.) and is passed down from parents to their offspring. DNA is comprised of units called nucleotides.
- DNA is self-replicating, a long stretch of nucleotides.
- DNA is a form of nucleic acid and is one of the four major macromolecules that make up the living system.
- In eukaryotic cells, it is found in the nucleus of the cell whereas in prokaryotes it is found free-floating in the cell cytoplasm.
- Other than the nucleus DNA is also found in mitochondria, chloroplast, and in smaller forms called plasmid in certain bacterial species.
Synchrotron

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
China's latest scientific achievement, the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS), is poised to become Asia's first fourth-generation synchrotron light source which is scheduled to commence operations by the end of this year.
What is a Synchrotron?
- A synchrotron is a type of circular particle accelerator where particles travel in a loop.
- It functions by accelerating charged particles, typically electrons, through sequences of magnets until they approach the speed of light.
How Does It Work?
- Acceleration: Charged particles are accelerated through magnets.
- Production of Light: These high-speed electrons generate extremely bright light, known as synchrotron light.
- This light, predominantly in the X-ray region, is millions of times brighter than conventional sources and 10 billion times brighter than the sun.
- Beamlines and Workstations: The intense light is directed down beamlines to experimental workstations for research purposes.
Applications:
- Research: Scientists use synchrotron light to study tiny matter such as atoms and molecules.
- By examining how a sample scatters, diffracts, absorbs, or reemits the synchrotron light, they can uncover details about its structure and chemical composition.
Global Presence:
- There are approximately 70 synchrotrons worldwide in various stages of development.
- They have varying technical specifications and uses, ranging from practical applications to fundamental theoretical research.
In India:
- India has a synchrotron facility known as the "Indus Synchrotron."
- It is located at the Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology (RRCAT) in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- The Indus Synchrotron is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source that is used for various research applications in fields such as materials science, biology, and environmental science.
What is the High Energy Photon Source (HEPS)?
- HEPS (High Energy Photon Source) is recognized as the brightest synchrotron X-ray source in Asia.
- Location: The HEPS facility is situated in Huairou, China, approximately 50 kilometres from Beijing.
- Acceleration Capabilities: HEPS is designed to accelerate electrons up to energies of 6 gigaelectron volts within its 36-kilometer circumference storage ring, producing high-energy X-rays for research purposes.
- Nanoscale Investigations: The high-energy X-rays generated by HEPS can penetrate deep into samples, allowing researchers to study intricate details at the nanometer scale.
- Diverse Research Applications: HEPS will cater to various research fields, including energy, condensed matter physics, materials innovation, and biomedicine, by providing access to 14 specialized beamlines.
- Superiority to Existing Synchrotrons: Compared to China's current most advanced synchrotron, the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (with a circumference of 432 meters), HEPS will offer a time resolution 10,000 times better.
PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) Mission

- 17 May 2024
Why is it in the News?
NASA is set to launch the two small satellites of the PREFIRE mission from New Zealand on May 22 aimed at filling in critical gaps in data from Earth's polar regions.
What is the PREFIRE Mission?
- PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) is a NASA mission that involves sending two tiny twin spacecraft, known as CubeSats, to the Earth's polar regions to gather data on the heat energy radiated out to space and its impact on our climate.
- PREFIRE consists of two, 6U CubeSats with a baseline mission length of 10 months.
- These shoebox-sized satellites will orbit at altitudes between 292 and 403 miles, crossing paths in the atmosphere.
Objectives:
- The mission will help close a gap in understanding how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space, especially from the Arctic and Antarctica.
- Analysis of PREFIRE’s measurements will inform climate and ice models, providing better projections of how a warming world will affect sea ice loss, ice sheet melt, and sea level rise.
- Improving climate models can ultimately help to provide more accurate projections on the impacts of storm severity and frequency, as well as coastal erosion and flooding.
- By studying the far-infrared radiation emitted from these regions, PREFIRE will help improve the accuracy of climate models, enhancing our understanding of phenomena such as Arctic warming, sea ice loss, and ice-sheet melting.
The mission will help in:
- Uncover the reasons behind the Arctic warming more than 2½ times faster than the global average since the 1970s.
- Provide scientists with a clearer understanding of how efficiently far-infrared heat is emitted by materials such as snow and sea ice, and how clouds affect the amount of far-infrared radiation that escapes to space.
- Enhance predictions about future changes in the heat exchange between Earth and space, and how these changes will impact phenomena like ice sheet melting, atmospheric temperatures, and global weather patterns.
How will the Satellites Work?
- The mission with cube satellites about the size of a shoebox will be launched aboard an Electron launch vehicle.
- It is equipped with technology proven on Mars and will measure a “little-studied portion” of the radiant energy emitted by Earth.
- Two satellites carrying a thermal infrared spectrometer will be in asynchronous near-polar orbits and will be passing over a given spot on Earth at different times. To maximize coverage, they will be overlapping every few hours near the poles.
- The instruments weighing less than 6 pounds (3 kilograms) each will make readings using a device called a thermocouple, similar to the sensors found in many household thermostats.
Why is it Important to Study the Polar Regions?
- According to NASA, Earth's climate balance hinges on the equilibrium between the heat energy the planet receives from the Sun and the amount it radiates back into space.
- The difference between incoming and outgoing energy determines Earth's temperature and climate.
- The polar regions are crucial in this balance.
- Changes in the polar regions can significantly impact global weather patterns.
- Extreme storms, flooding, coastal erosion – all of these phenomena are influenced by what’s happening in the Arctic and Antarctic.
- This underscores the importance of understanding polar dynamics to predict and mitigate global climate effects.
C-Dome Defense System

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Israel for the first time used a seaborne missile defense system to shoot down a drone approaching from the Red Sea that had set off sirens in the port city of Eilat.
What is the C-Dome Defense System?
- The C-Dome is a naval version of Israel's Iron Dome air defense system, designed to protect against rocket and missile attacks.
- Drawing from Iron Dome's technology, C-Dome shares its 90% effectiveness rate and utilizes radars to detect and destroy short-range rockets with its missiles.
Operational Deployment and Integration:
- First unveiled in 2014 and declared operational in 2022, the C-Dome is mounted on Sa'ar 6-class corvettes and German-made warships.
- It employs the same interceptor as the Iron Dome but differs in its integration with the ship's radar for target detection, ensuring full-circular vessel protection.
Combatting Modern Threats:
- C-Dome's primary objective is to counter a wide range of modern maritime and coastal threats with high kill probability.
- Its successful deployment and performance underscore its pivotal role in safeguarding Israel's naval interests and assets against evolving security challenges.
About Iron Dome:
- Developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Israel Aerospace Industries, the Iron Dome is a cutting-edge air missile defense system that offers protection against short-range rockets by intercepting them above Israeli territory.
- With its multi-rocket handling capacity, Iron Dome became operational in 2011 and features:
- All-weather capabilities for day and night functionality
- Launching versatility with various interceptor missiles
- A range of approximately 40 miles
- Portable design for deployment on ships or land
- Adaptive defense through reloadable interceptors
Iron Dome consists of three key elements:
-
- Radar system for detecting incoming rockets
- Command-and-control mechanism to evaluate threat levels
- Interceptors are designed to neutralize incoming rockets before impact
- These components work in tandem to provide Israel with a robust and reliable defense against aerial threats.
India Imposed Import Restrictions on Solar PV Cells

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recent government orders on attempts to increase local sourcing of solar modules to support India’s renewables manufacturing ecosystem have been widely reported in the media as ‘import restrictions’.
What is the Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) List?
- The Approved List of Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic Modules (ALMM) comprises government-approved manufacturers eligible for use in government projects, government-assisted projects, and schemes.
- ALMM aims to boost the domestic solar industry and reduce dependence on imports, particularly from China.
ALMM's Suspension and Reinstatement:
- The ALMM was kept in abeyance for two years to address concerns raised by renewable energy producers with pre-existing government contracts.
- During this period, India's domestic solar industry struggled to compete with cheap Chinese imports.
- To support local manufacturers, the government launched initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme under the Atmanirbhar Bharat ('Self-Reliant India') Programme.
- With the PLI scheme enhancing the competitiveness of Indian manufacturers, the ALMM was reinstated in March 2024.
- The government believes that domestic companies can now meet India's solar equipment demand, making the ALMM an essential tool for promoting import substitution and self-reliance in the renewable energy sector.
Solar PV Imports:
- India heavily relies on solar cell and module imports, with China and Vietnam being the primary suppliers.
- Government data reveals that India imported approximately $11.17 billion worth of solar cells and modules over the past five years.
- As of 2023-24, China accounted for 53% of solar cell imports and 63% of solar PV modules.
China's Competitive Edge:
- Several factors contribute to China's dominance in solar PV exports:
- Cost-effective manufacturing due to lower power costs
- Government policies prioritizing the solar PV sector
- Economies of scale and continuous innovation driven by growing domestic demand
- These advantages have made China the most cost-competitive location for producing solar PV components, making it challenging for other countries to match their production capabilities.
What is the Scope of Solar Energy in India?
- India's solar sector holds immense potential, driven by the government's target of achieving 500 GW of installed non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
- Moreover, the country's rapid growth in electricity demand, fueled by economic activities and climate adaptation measures, positions solar power as a critical resource.
- Solar energy accounted for one-third of renewable energy generation from April 2023 to February 2024, showcasing its significance in India's energy mix.
- Despite an estimated solar power potential of 748.99 GW, the country has yet to fully exploit this resource.
- To harness this potential, the government is implementing various schemes and programs, paving the way for a sustainable and prosperous solar future.
Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)

- 10 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the US White House has officially instructed NASA to create a lunar time standard for international and private sector coordination on the Moon.
What is Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC)?
- Coordinated Lunar Time (LTC) is a lunar-based time system being developed by NASA in collaboration with other government agencies to establish a standardized time zone for the Moon.
- LTC aims to provide a precise timekeeping benchmark for lunar spacecraft and satellites, synchronizing communication between astronauts, bases, and Earth.
Importance of LTC:
- As lunar exploration and commerce expand, a unified time standard becomes essential for managing operations, ensuring transaction reliability, and coordinating logistics.
- Furthermore, LTC addresses the discrepancy in timekeeping between Earth and the Moon due to differences in gravity, as time ticks faster on the Moon, causing Earth-based clocks to lose an average of 58.7 microseconds per day.
- Establishing LTC will prevent potential problems in spacecraft docking, data transfer, communication, and navigation.
How Will a Lunar Time Standard Be Established?
- Like on Earth, atomic clocks can be deployed on the lunar surface to set a time standard.
- These clocks have to be placed on the Moon at different locations since the Moon’s rotation and even local lumps of mass, called mascons, beneath the crust of the Moon affect the flow of time ever so slightly.
- Mascons or mass concentrations are so dense that they alter the Moon’s local gravity field.
- These effects are minor but the output from these clocks can be synthesized to give the Moon its own independent time, which can be tied back to UTC for seamless operations from Earth as well.
How Does Earth’s Time Standard Work?
- Most of the clocks and time zones of the world are based on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), set by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in Paris, France.
- UTC is essentially an internationally agreed-upon standard for world time.
- It is tracked by a weighted average of more than 400 atomic clocks placed in different parts of the globe.
- Atomic clocks measure time in terms of the resonant frequencies — the natural frequency of an object where it tends to vibrate at a higher amplitude — of atoms such as cesium-133.
- In atomic time, a second is defined as the period in which a cesium atom vibrates 9,192,631,770 times.
- As the vibration rates at which atoms absorb energy are highly stable and ultra-accurate, atomic clocks make for an excellent device for gauging the passage of time.
- To obtain their local time, countries must subtract or add a certain number of hours from UTC depending on how many time zones they are away from 0 degree longitude meridian, also known as the Greenwich meridian.
- If a country lies on the west of the Greenwich meridian, it has to subtract from the UTC, and if a country is located on the east of the meridian, it has to add.
Imposition of Anti-Dumping Duty on Sodium Cyanide

- 09 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) has now recommended the imposition of anti-dumping duty on sodium cyanide (NaCN) imported from China, the European Union, Japan, and Korea.
Key Facts About Sodium Cyanide:
- Sodium cyanide (NaCN) is a highly toxic, inorganic compound with a white, crystalline appearance.
- It is a solid at room temperature and has a high affinity for metals, making it useful in various industrial processes.
- Due to its toxic nature, proper handling and safety protocols must be followed when working with sodium cyanide.
Applications of Sodium Cyanide:
- Mining and Metallurgy: Sodium cyanide is widely used in the extraction of gold and silver from ores. It is employed in a technique called "cyanide heap leaching," where a dilute sodium cyanide solution is sprayed onto crushed ore.
- The cyanide forms a water-soluble complex with the precious metals, enabling their recovery from the ore.
- Electroplating: NaCN is utilized as an electrolyte in electroplating processes, particularly for the deposition of silver, gold, and other metals on various surfaces to improve their appearance, durability, or conductivity.
- Synthetic Fiber Production: Sodium cyanide is used in the manufacturing of synthetic fibers such as acrylic and nylon.
- It serves as a catalyst in the polymerization process, promoting the formation of long-chain polymers that make up the fibers.
- Pesticides: Due to its toxicity, sodium cyanide has been used as a fumigant to control pests and rodents.
- However, its use in this field has been largely phased out in many countries due to safety concerns and the development of safer alternatives.
- Dye and Pigment Production: NaCN can be used in the production of certain dyes and pigments, particularly those containing nitrogen.
- It acts as a precursor for the synthesis of these compounds.
What is Anti-Dumping Duty?
- An anti-dumping duty is a tariff imposed by a domestic government on foreign imports suspected of being sold at prices lower than those in the exporter's domestic market.
- This measure aims to prevent these products from undercutting local businesses and harming the local economy.
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) oversees a framework of international trade rules governing anti-dumping measures.
- Under this agreement, governments are permitted to address dumping practices if they pose a threat of significant harm to a domestic industry.
Calculation of Anti-Dumping Duty:
- The calculation of anti-dumping duty involves determining the difference between the normal value and the export value of the product.
- The normal value represents the market value of the product in the exporter's domestic market, while the export value denotes the price at which the product is sold when exported to India.
- The anti-dumping duty is levied to neutralize this price disparity and safeguard the domestic industry from the adverse effects of inexpensive imports.
Anti-Dumping Mechanism in India:
- India's anti-dumping mechanism is overseen by the Directorate General of Anti-Dumping and Allied Duties (DGAD) under the Ministry of Finance.
- The legal framework for anti-dumping in India is established by the Customs Tariff Act of 1975 and the Customs Tariff Rules of 1995.
- The DGAD conducts investigations to assess whether a surge in below-cost imports has negatively impacted the domestic industry.
Presence of Ozone on Jupiter's Moon Callisto

- 02 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
An international team of scientists, including from India, has discovered strong evidence indicating the presence of ozone on Jupiter’s moon Callisto, shedding light on the complex chemical processes taking place on icy celestial bodies in the Solar System.
Study on the Formation of Ozone in Callisto's Icy Environment:
- A recent study examined the chemical evolution of sulfur dioxide (SO2)-rich astrochemical ice found on Callisto's surface when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
- The investigation revealed a unique signature indicating the formation of ozone, which could have implications for the potential habitability of the Jovian moon.
- Callisto is Jupiter's second-largest moon and the third-largest moon in our solar system.
- It has a relatively stable surface, which could play a vital role in preserving subsurface oceans or potential habitats beneath its icy crust.
- The study analyzed UV absorption spectra data from ice samples containing SO2, a primary component of Callisto's surface ice, and observed the generation of ozone under UV irradiation.
- Ozone formation on Callisto could have implications for the moon's astrobiological potential, as ozone can protect the surface from harmful radiation.
- Further research is needed to better understand the implications of this discovery on Callisto's habitability and the potential for future exploration missions.
Callisto's Distinctive Environment:
- Following Saturn, Jupiter boasts the second-highest number of moons in the Solar System, with Callisto ranking among its largest moons and holding the position of the third-largest moon overall, after Ganymede and Titan.
- Comprised predominantly of water ice, rocky elements, sulfur dioxide, and traces of organic compounds, Callisto presents a compelling potential for harboring life beyond Earth within the Solar System.
- The moon's extensively cratered surface bears witness to a lengthy history of impacts from asteroids and comets.
Importance of the Research:
- The identification of ozone on Callisto hints at the existence of oxygen, a crucial component essential for the development of intricate molecules vital for life, including amino acids, thus prompting inquiries into the moon's potential for sustaining life.
- This finding also has implications for other icy moons within our Solar System, offering insights that could broaden our comprehension of habitable environments beyond Earth.
Significance of Ozone:
- Consisting of three oxygen atoms bonded together, the ozone molecule plays a pivotal role in shielding life on Earth.
- Situated in the lower region of the Earth's stratosphere, approximately 15-35 kilometers above the surface, the ozone layer acts as a protective barrier.
- Without this layer, ultraviolet radiation would intensify, posing significant threats to various species and disrupting ecosystems.
- Ultraviolet-B and ultraviolet-C, with wavelengths ranging from 290 to 320 nanometers and 100 to 280 nanometers respectively, can cause DNA damage, and mutations, and elevate the risk of skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
- Furthermore, ultraviolet light can impede plant growth and adversely affect diverse organisms.
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KOSO)
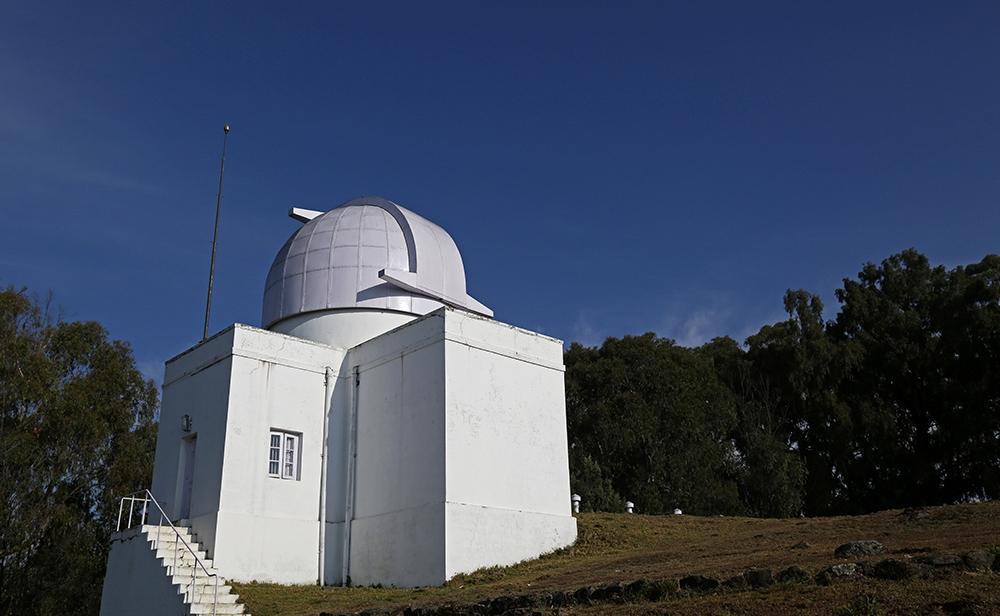

- 01 Apr 2024
Why is it in the News?
Since ancient times, seafarers, mathematicians, astronomers, and physicists have all diligently studied and tracked the Sun and its phenomena, with the establishment of the Madras Observatory by the British East India Company in 1792 marking a pioneering effort in this region.
About Kodaikanal Solar Observatory:
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory is a solar observatory owned and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru.
- It is on the southern tip of the Palani Hills 4 kilometers from Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu).
- The Government of India separated Astrophysics from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) in April 1971.
- From solar data recorded on basic photographic plates or films, the 125-year-old KoSO boasts a mammoth digital repository containing 1.48 lakh digitized solar images of 10 terabytes.
- These include 33,500 white-light images (showing sunspots) and thousands of other images of the Sun recorded every day since the start of the 20th century.
- KoSO is the only observatory offering high-resolution digitized images for such a long period (with coverage of more than 75 percent).
- Today, it houses a spectrum of advanced instruments like the H-alpha telescope to perform full disc imaging, a White light Active Region Monitor (WARM) with calcium and sodium filters to make full disc simultaneous observations of the photosphere and chromosphere layers of the Sun, a solar tunnel telescope and more.
Links to the Great Drought:
- Scanty rainfall over south India during the winter monsoon of 1875 triggered one of the worst droughts the country had experienced till then.
- Multiple failed crops over the famine-stricken peninsular India killed 12.2 to 29.3 million people across the Madras and Mysore Provinces during 1875-1877.
- India, along with China, Egypt, Morocco, Ethiopia, southern Africa, Brazil, Columbia, and Venezuela, suffered concurrent multi-year droughts during 1876-1878, later named the Great Drought, and an associated global famine that killed nearly 50 million.
- The drought was thought to be due to multiple reasons:
- Solar activity
- Cool Pacific Ocean conditions followed by a record-breaking El Nino (1877-1878)
- Strong Indian Ocean Dipole and
- Warm North Atlantic Ocean conditions.
Solar Physics Observatory in Palani Hills:
- Established in response to the British Raj's acknowledgment of solar activity's link to India's weather patterns, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory, also known as the Indian Solar Observatory, was founded to conduct systematic studies on solar phenomena and their correlation with Indian meteorology.
- Located in Kodaikanal, selected for its favorable atmospheric conditions after careful consideration by Charles Michie Smith (a Professor of Physics at the Madras Christian College), the observatory was officially sanctioned by the Government of India in August 1893 and inaugurated by Lord Wenlock (the then Governor of Madras) in 1895.
- Commencing systematic observations in 1901, it merged with the Madras Observatory, enriching its instrumentation.
- Notable discoveries ensued, including the identification of the Evershed Effect.
- Over time, the observatory expanded its research domains to encompass cosmic rays, radio astronomy, and ionospheric physics, among others, solidifying its status as a pioneering institution in the field of astrophysics.
- Notably, it initiated solar radio observations in 1952, marking a significant milestone in Indian solar research.
- Despite the closure of contemporaneous observatories, the Palani Hills Solar Physics Observatory has endured, continuing to contribute to our understanding of the Sun and its effects on Earth's climate and space weather.
Why Study the Sun?
- Being the primary source of energy, life on Earth is supported by the Sun.
- Any change on the solar surface or its periphery could significantly affect the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Powerful solar storms and solar flares can be potentially harmful to Earth’s satellite-based operations, power grids, and navigational networks.
- The KoSO (Kodaikanal Solar Observatory), which has been imaging the Sun for over a century now, has a rich repository of data.
- This is extremely useful not only to reconstruct the Sun’s historic past but also to link its behavioral changes to better understand and predict its future and its impact on life on Earth and Space weather.
X-Class Solar Flares

- 30 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently the Earth was hit by an X-class solar flare that was strong enough to ionize part of the planet's atmosphere.
What are Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are large explosions from the surface of the sun that emit intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation.
- The intensity of the explosion determines what classification the flare belongs to.
- The most powerful are X-class flares, followed by M-, C-, and B-class; A-class flares are the smallest.
- These flares can be visible as bright flashes in a particular region of the sun and can last several minutes.
- Solar flares occur when magnetic energy builds up in the solar atmosphere and is released suddenly.
- These outbursts are intrinsically linked to the solar cycle — an approximately 11-year cycle of solar activity driven by the sun's magnetic field.
What Causes Solar Flares?
- The sun's surface is a magnetically mixed-up place.
- Magnetic fields are created from electrically charged gases generating electrical currents that act as a magnetic dynamo inside the sun.
- These magnetic fields twist, tangle, and reorganize themselves due to the turbulent nature of the gases that create them.
- This unsettled magnetic field behavior — also known as solar activity — can trigger solar flare eruptions from the surface that release vast amounts of electromagnetic radiation — a form of energy that includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays, gamma rays, and visible light.
- Solar flares tend to originate from regions of the solar surface that contain sunspots — darker, cooler portions of the solar surface where magnetic fields are particularly strong.
- As such, the number of sunspots can indicate the likelihood of a solar flare eruption.
- Solar activity follows an approximately 11-year cycle with the peak of sunspot activity coinciding with the solar maximum and a sunspot hiatus coinciding with the solar minimum.
- During periods of low solar activity when no sunspots are present, it is unlikely that a solar flare will occur.
What are X-Class Solar Flares?
- Solar flares are categorized into five classes based on the intensity of emitted X-rays, with each class letter denoting a 10-fold increase in energy output, akin to the Richter scale for earthquake strength assessment.
- X-class flares are the most powerful solar flares.
- Then there are M-class flares that are 10 times smaller than X-class flares, then C-class, B-class, and finally A-class flares which are too weak to significantly affect Earth.
- Within each letter class, a finer scale from 1 to 9 gives the flare assessment greater precision with larger numbers representing more powerful flares within the class.
- However, X-class flares can break this nine-point rating mold with higher ratings, since there is no class more powerful than X-class.
- Fortunately, X-class flares occur on average about 10 times per year.
How do Solar Flares Affect the Earth?
- Disruption of Satellite Communications: Solar flares can interfere with satellite communications, GPS signals, and radio transmissions, causing disruptions or blackouts in telecommunications and navigation systems.
- Auroral Displays: Intense solar flares can trigger colorful auroras, or Northern and Southern Lights, as charged particles interact with Earth's magnetic field, creating stunning light displays in the polar regions.
- Power Grid Disturbances: Severe solar flares have the potential to induce geomagnetic storms that can overload power grids, leading to widespread power outages and damage to electrical infrastructure.
- Radiation Hazards: Solar flares emit harmful radiation, particularly in the form of ultraviolet and X-rays, which can pose risks to astronauts in space and airline passengers at high altitudes.
- Impact on Electronics: The influx of charged particles during solar flares can induce currents in electrical circuits, potentially damaging or disrupting sensitive electronic devices, such as computers, satellites, and spacecraft.
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- 28 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, NASA's Soho mission, which is tasked with observing the Sun, has captured its 5000th comet as it dives around the star in our Solar System.
About Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
- SOHO was built as a general solar observatory, with twelve suites of scientific instruments to track all of these properties of the Sun.
- During its operations, it has provided important insights, including:
- Details about the interior of the Sun,
- What sunspots look like beneath the surface,
- Measurements of the speed of the solar wind,
- The charged particles that escape from the corona,
- Mapping the magnetic field behavior over the Sun’s surface; and
- Revealing new phenomena such as “solar tornadoes”.
- Built in Europe, SOHO is operated jointly by ESA and NASA, with contributions from a large number of scientists, engineers, and other staff around the world.
- The spacecraft was launched in 1995 with a planned two-year mission.
- Its work was successful enough to justify keeping the observatory going, and it’s still operating more than 20 years later.
- The probe orbits the Sun at a place where the gravity of the Sun and Earth balance each other out, known as the first Lagrange point (L1).
- Center for Astrophysics (CfA) scientists and engineers provided SOHO’s Ultraviolet Coronagraph Spectrometer (UVCS), which operated until 2013 and measured the ultraviolet spectrum of the hot solar atmosphere.
- UVCS provided the insight that the corona is too hot to be produced by ordinary thermal transfer, where particles collide and pass energy to each other.
- Instead, the corona and solar wind must be accelerated by the magnetic field interactions in some way.
- Other SOHO instruments measure the speed and composition of the solar wind; the seismic waves that travel across the Sun’s surface; the fluctuations in the temperature, composition, and density of different parts of the corona; and the motion of matter upward from the Sun’s interior to its surface.
Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP)

- 26 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Kerala's shift towards an alternative approach for the implementation of smart electricity meters, sidelining the Central government's Rs 3 lakh crore project, poses a challenge to the Union Government's initiative of replacing 250 million traditional meters with smart meters in all households by March 2025.
About the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP):
- The Indian government has initiated the Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) to revolutionize the country's energy sector through the implementation of smart meters.
- By replacing 25 crore conventional meters, the SMNP aims to enhance the operational efficiency and revenue management of distribution companies (DISCOMs).
- Under the leadership of Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL), a joint venture of four National Public Sector Enterprises, the scheme is set to make waves in the energy sector.
- EESL, comprised of NTPC Limited, PFC, REC, and POWERGRID, operates under the Ministry of Power and is committed to undertaking the necessary capital and operational expenditures with zero upfront investment from states and utilities.
- The Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) model facilitates the recovery of smart meter costs via the monetization of energy savings resulting from improved billing accuracy, reduced meter reading costs, and increased efficiency.
- In accordance with guidelines set forth by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), the strategic deployment of these smart meters adheres to industry standards.
Smart meters offer a multitude of advantages:
-
- Consumers can monitor their electricity usage and make informed decisions to reduce their bills.
- Utilities benefit from enhanced operational efficiency, enabling better power demand management.
- Web-based Monitoring: The interconnected smart meter network can mitigate utilities' commercial losses, enhance revenue generation, and propel power sector reforms.
- The Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP) paves the way for a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape in India, revolutionizing the way utilities operate and consumers engage with their electricity usage.
What are Smart Meters?
- A smart meter serves as an advanced tool for recording electricity consumption and voltage levels, offering a significant upgrade over traditional metering systems.
- While conventional meters simply measure power usage, smart meters take it a step further by transmitting real-time data to utility providers at intervals of 15 minutes or hourly.
- Smart meters truly live up to their name by utilizing internet connectivity to facilitate two-way communication.
- On one hand, they empower consumers with up-to-date information on energy usage patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions and manage consumption more efficiently.
- On the other hand, utility providers gain valuable insights for monitoring purposes and ensuring accurate billing.
- In essence, smart meters pave the way for improved energy management, increased transparency, and enhanced efficiency, catering to the evolving needs of both consumers and utility providers in today's digital era.
ISRO’s Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 Landing Experiment
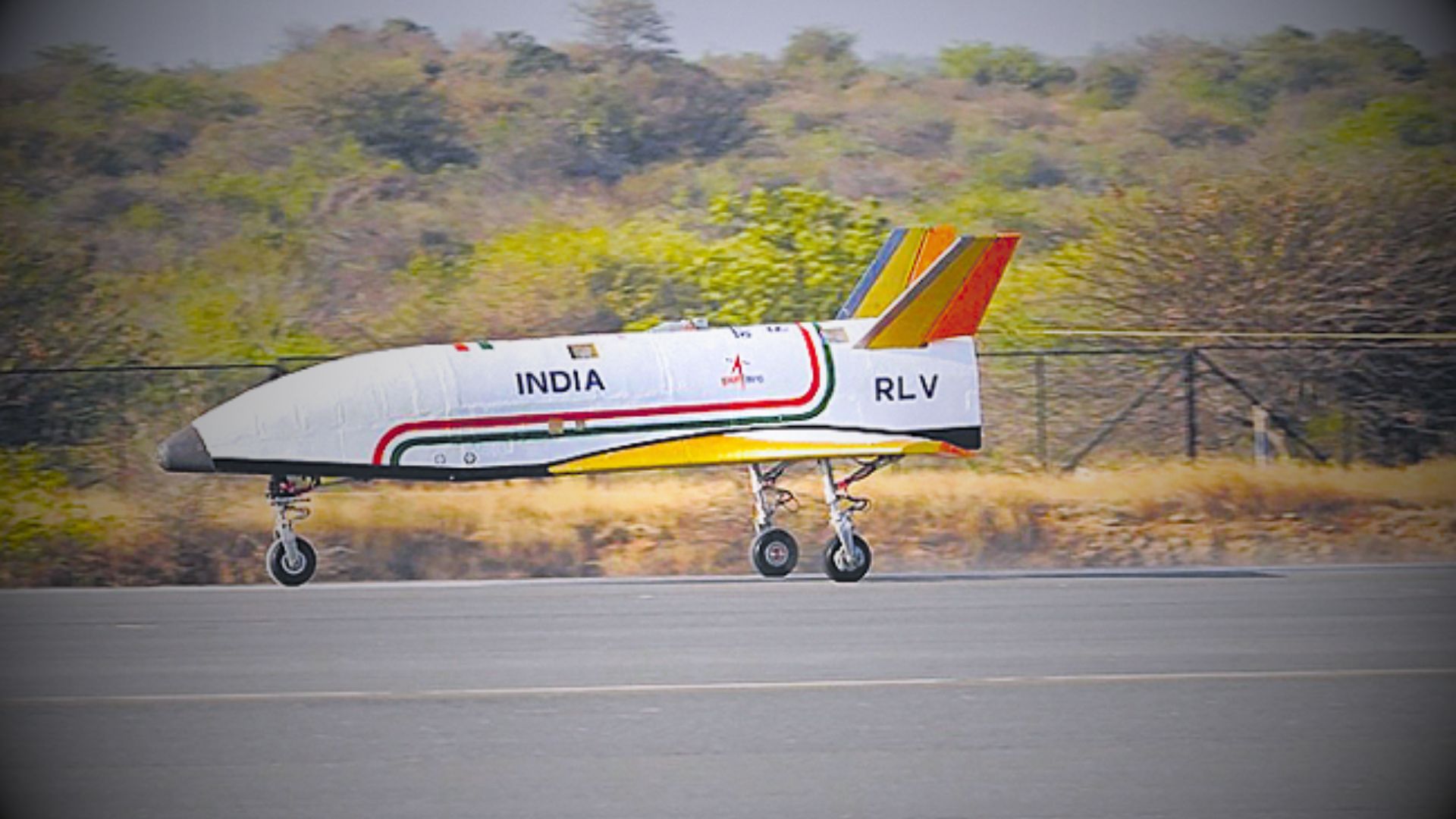

- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully conducted the Pushpak Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02 landing experiment at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga recently.
What is a Reusable Landing Vehicle (RLV) LEX 02?
- Continuing our exploration into reusable landing vehicles, RLV-LEX-02 marks the second mission in our series conducted at the Aeronautical Test Range.
- Following the success of RLV-LEX-01 last year, this latest endeavor showcases the remarkable autonomous landing capability of our reusable launch vehicle (RLV).
- Notably, RLV-LEX-02 demonstrates the vehicle's ability to navigate and safely land from off-nominal initial conditions immediately upon release from a helicopter.
Methodology of the Experiment:
- The RLV LEX-02 mission showcased the autonomous landing prowess of our reusable launch vehicle under demanding circumstances following its release from a helicopter.
- Dubbed 'Pushpak', this winged vehicle was airlifted by an Indian Air Force Chinook helicopter and released from a height of 4.5 km.
- Navigating autonomously, it adeptly approached the runway, making precise cross-range corrections before executing a flawless landing.
- Utilizing a combination of its brake parachute, landing gear brakes, and nose wheel steering system, it safely came to a stop.
- Notably, the winged body and all flight systems previously employed in RLV-LEX-01 were repurposed for RLV-LEX-02 after undergoing necessary certification and clearances.
- This remarkable mission was executed collaboratively by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Liquid Propulsion System Centre (LPSC), and the ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU).
What is the Reusable Launch Vehicle?
- The reusable launch vehicle represents a pioneering space plane design characterized by a low lift-to-drag ratio, which mandates high glide angles during approach and consequently requires landing at velocities reaching 350 kmph.
- Integral to its innovation are a multitude of indigenous systems developed meticulously. These encompass sophisticated navigation systems, leveraging pseudolite technology for precise localization, as well as instrumentation and sensor arrays, among other advancements, all spearheaded by ISRO.
Hepatitis B
- 23 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Public knowledge and awareness about Hepatitis B, a deadly disease that can cause end-stage liver cirrhosis and liver cancer, is dismal in India, according to a new study conducted by Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi.
What is Hepatitis B?
- It is a severe liver infection that can lead to liver damage, cancer, and death.
- The virus spreads through contact with an infected person's blood or bodily fluids.
- One can get hepatitis B through sexual contact, sharing needles or other drug-injection equipment, or from mother to child during childbirth.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is a severe viral infection of the liver that can cause inflammation and scarring.
- Symptoms include fatigue, fever, abdominal pain, dark urine, joint pain, and jaundice.
Causes of Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- HBV is found in the blood and body fluids of an infected person. It can spread through contact with fluids, such as:
- Blood, through needle sharing or accidental needle sticks
- Contact with body fluids, such as saliva, etc.
- Sexual contact with someone who has HBV
- From a mother to a child through childbirth
- Hepatitis B can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as:
- Sharing personal items like toothbrushes or razors with someone who has HBV
- Getting a tattoo or body piercing with contaminated equipment
Types of Hepatitis B:
- There are three main types of hepatitis B: acute, chronic, and carriers.
- Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after exposure to the virus. It is the most common type of hepatitis B in children.
- Chronic hepatitis B is a long-term illness that can lead to serious health problems, including liver failure and liver cancer.
- Carriers of hepatitis B have the virus in their blood but do not show any symptoms.
Treatment for Hepatitis B
- Several medications can help treat hepatitis B.
- These include antiviral drugs, which can help reduce the amount of virus in the body, and immunomodulators, which can help boost the immune system to better fight the virus.
- If the liver is damaged, one may also need medication to help protect it from further damage.
- HBIG (Hepatitis B Immuno Globulin) is one of the best ways to treat hepatitis B.
- Adults who have been exposed to hepatitis should get HBIG and vaccination as soon as possible, preferably within 24 hours but not later than 14 days after the exposure.
Prevention of Hepatitis B:
- The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated.
- The vaccine is given as a series of shots.
- The first shot is usually given at birth; the rest at 1–2 months old, 6–18 months old, and 4–6 years old.
- If one was not vaccinated as a child, they can receive the vaccines as an adult.
PIB Fact Check Unit (FCU)

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Supreme Court stayed the Centre’s notification of the Fact Check Unit (FCU) under the Press Information Bureau (PIB) until the Bombay High Court arrives at a final decision on the challenge to the amended Information Technology (IT) Rules.
Background:
- Under the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules, 1961, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) is entrusted with the responsibility of disseminating information about government policies, schemes, and programs through various mediums of communication.
- In fulfilling its role, the Ministry publicizes the policies, initiatives, schemes, and programs of the Government of India through press releases, press conferences, webinars, publication of books, etc.
- To carry out this crucial function, the Ministry has several attached and subordinate offices, including the Press Information Bureau (PIB).
- A significant aspect of the responsibility of facilitating public information about the functioning of the Government of India involves countering the dissemination of fake, false, and misleading information.
- The PIB has been carrying out this function for a long through a wide distribution of accurate and reliable information, issuing rebuttals, etc.
- In the age of social media where information spreads rapidly, the spread of fake and manipulated information, especially related to the functioning of a democratically elected Government, is dangerous to society as it has the potential to intensify social, economic, and political conflicts, weaken public trust in democratic institutions, and even endanger the life of the citizens.
What is the PIB Fact Check Unit (FCU)?
- The Press Information Bureau has been at the forefront of taking proactive measures to combat fake news related to the Government of India.
- In November 2019, PIB established a Fact Check Unit (FCU) to tackle the issue of fake news about the Government of India, its various ministries, Departments, Public Sector Undertakings, and other Central Government organizations.
- The unit verifies claims about government policies, regulations, announcements, and measures.
- Through an established rigorous fact-checking procedure, the PIB Fact Check Unit helps dispel myths, rumors, and false claims and provides accurate and reliable information to the public.
Organization
- The PIB Fact Check Unit is headed by a senior DG/ADG level officer of the Indian Information Service (IIS).
- The day-to-day operations of the Unit are handled by IIS officers at various levels. The Unit reports to the Principal Director General, PIB who functions as the Principal Spokesperson of the Government of India.
Fact-Check Mechanism
- Users send requests over WhatsApp, email, or a web portal. Each such request received is considered a ‘Query’.
- Queries are segregated by the Unit based on their relevance to matters about the Government of India.
- Only queries about the Government of India are considered and taken up as Actionable Queries, while others are deemed not relevant for action.
- The information in question is checked rigorously through multiple layers of cross-checking through Government Open-source information, use of technological tools, and verification from the concerned Government of India organization.
- Should the Unit come across a piece of information that the Unit ascertains must be busted publicly for the larger benefit of the people of India, after investigation and verification from official & authoritative sources, it publishes a 'Fact Check' on its social media platforms.
- Often a single fact check can be a result of multiple queries.
Fact-checked content can be segregated into the following three categories:
- Fake: any factually incorrect news, content, or, piece of information related to the Government of India, spread intentionally or unintentionally, that can deceive or manipulate the audience, with or without the intention to cause potential harm, can be flagged as Fake
- Misleading: any information presented, either partially true or with selective presentation of facts or figures or with distortion of facts or figures and to deceive or mislead the recipient of the information.
- True: any information that is found to be factually correct after investigation
Usha Mehta

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
A recent film has been launched, depicting the inspiring life story of Indian freedom fighter Usha Mehta.
About Usha Mehta:
- Born in 1920 in the village of Saras, near Surat in Gujarat, Usha Mehta, affectionately known as Ushaben, embodied the Gandhian principles of non-violence and civil disobedience from a young age.
Early Activism:
- At the tender age of eight in 1928, she participated in a protest march against the Simon Commission, demonstrating her early commitment to India's independence struggle.
- The Secret Congress Radio: In 1942, amidst the fervor of the Quit India Movement, Usha Mehta and her colleagues boldly established the Secret Congress Radio.
- This clandestine radio station played a pivotal role in connecting freedom movement leaders with the masses, ensuring the dissemination of crucial information, and maintaining the spirit of resistance against colonial rule.
Establishing an Underground Radio Station:
- With the outbreak of the War in 1939, the British government imposed stringent measures, including the suspension of all amateur radio licenses throughout the Empire.
- Operators were mandated to surrender their equipment to the authorities, under threat of severe repercussions for non-compliance.
Key Figures in the Operation:
- Usha Mehta, alongside Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, and Chandrakant Jhaveri, played instrumental roles in orchestrating the Congress Radio initiative, defying the ban on amateur radio broadcasting.
The Congress Radio Trial:
- The trial of the five accused individuals—Usha Mehta, Babubhai Khakar, Vithalbhai Jhaveri, Chandrakant Jhaveri, and Nanak Gainchand Motwane, who facilitated crucial equipment—captivated public attention in Bombay.
- While Vithalbhai and Motwane were acquitted, Mehta, Babubhai, and Chandrakant faced severe sentences for their involvement.
Usha Mehta's Legacy:
- Following her release from Pune's Yerawada Jail in March 1946, Usha Mehta was lauded in nationalist circles as "Radio-ben," symbolizing her courageous defiance and commitment to the freedom struggle through underground broadcasting.
Independence, PhD, & Padma Vibhushan
- When India finally achieved independence in 1947, the British had divided the country into two parts – India and Pakistan, sending the region into chaos.
- The divide results in massive bloodshed with more than 10 million Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs seeking to find their home.
- Mehta was torn. “In a way, I was very happy, but sad at the same time because of partition.
- It was an independent India but a divided India,” she was quoted as saying in the book Freedom Fighters Remembered.
- She was away from active politics in independent India due to her ill health but continued to remain a staunch Gandhian till the very end.
- She penned the script for a documentary on Gandhi produced by her colleague at the radio station, and earned a PhD in Gandhian thought at the University of Bombay.
- She taught political science and ran the politics department at the university.
- She also taught at Wilson College for 30 years.
- She was also the president of the Gandhi Peace Foundation.
- In 1998, she was awarded India’s highest civilian honor, the Padma Vibhushan.
- She lived a simple life and never married or had children.
- She died on 11 August 2000 at the age of 80.
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Dr. Neeraj Mittal's unanimously elected as co-chair of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)'s digital innovation board recently.
About the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- Established in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, the ITU has evolved into the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies (ICT).
- Recognized as a vital intergovernmental organization, the ITU facilitates collaboration between governments and private sector entities to advance global telecommunication and ICT services.
Key Points:
- Status: Designated as a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1947.
- Membership: Boasting a diverse membership of 193 countries and over 1000 companies, universities, and international and regional organizations.
Functions:
- Allocation of global radio spectrum and satellite orbits.
- Coordination and establishment of technical standards about telecommunication/ICT.
- Initiatives to enhance ICT accessibility in underserved communities worldwide.
- India's Engagement: India has maintained an active presence within the ITU since 1869, consistently participating in its endeavors.
- Notably, India has been a regular member of the ITU Council since 1952.
- Headquarters: Located in Geneva, Switzerland, the ITU serves as the global epicenter for fostering collaboration and innovation in the realm of ICT.
What is the Digital Innovation Board?
- The Digital Innovation Board is a pivotal component of the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development, aimed at addressing pressing needs within the realm of innovation as outlined in the Kigali Action Plan, which was adopted at the World Telecommunication Development Conference 2022.
- Comprised of Ministers and Vice Ministers of Telecom/ICT from 23 Member Countries of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), spanning across Asia, Europe, Africa, and North, and South America, this board serves as a strategic advisory body.
- ITU initiated the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Alliance for Digital Development to tackle significant challenges and opportunities in innovation.
- This alliance operates through three key mechanisms:
- The Digital Transformation Lab
- The Network of Acceleration Centers, and
- The Digital Innovation Board.
- The Digital Innovation Board's primary objective is to offer strategic guidance, expertise, and advocacy in promoting local capacity building, fostering innovation, and encouraging entrepreneurship in digital development.
- Its overarching mission is to cultivate a more inclusive and equitable digital future for all stakeholders.
Enforcement Directorate (ED) Arrests Delhi Chief Minister

- 22 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal was recently arrested in the Delhi excise policy case, in which he had been issued multiple summons by the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
About the Enforcement Directorate (ED):
- Established in 1956 as the 'Enforcement Unit' under the Department of Economic Affairs, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) underwent a name change in 1957.
- Presently, ED operates under the Department of Revenue (Ministry of Finance) administrative control for operational purposes.
Roles and Responsibilities:
- ED is responsible for enforcing the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) and certain provisions of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
- In case of FEMA violations, ED has the authority to attach the assets of offenders.
- ED is also empowered to conduct searches, seizures, arrests, prosecutions, and surveys against PMLA offenses.
Appointment Process for ED Director:
- The Central Government appoints the ED Director based on the recommendations of a committee, which comprises:
Chairperson: Central Vigilance Commissioner
Members: Vigilance Commissioners, Home Secretary, Secretary DOPT, and Revenue Secretary.
What is the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22?
- The Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22, also known as the new liquor policy, was introduced on November 17, 2021, to transform liquor sales in the city.
- This policy marked a significant departure from the traditional model by privatizing liquor shops and aiming to enhance customer experience while curbing black market activities.
- However, amidst controversy and allegations of procedural irregularities, Delhi ultimately reverted to its previous excise regime.
Key Features:
- The new policy divided Delhi into 32 zones, each open for bidding by firms, departing from individual licenses to zone-based bidding.
- 849 retail vend licenses were auctioned by the Excise department.
- Notably, the policy allowed for discounts to retail customers and reduced dry days to three from 21.
- It proposed innovative measures such as home delivery of liquor and lowering the drinking age from 25 to 21, although these were not implemented.
Controversy:
- Before implementation, the policy underwent scrutiny by the Chief Secretary, who alleged procedural lapses and irregularities.
- The report implicated the Deputy CM for making unilateral decisions, leading to financial losses and allegations of kickbacks.
- These kickbacks were purportedly used to influence elections in other states, leading to a CBI investigation and subsequent arrest of the Deputy CM and others.
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) also initiated investigations into alleged money laundering, with claims of substantial proceeds of crime and kickbacks reaching prominent political figures.
- In essence, the Delhi Excise Policy 2021-22, while aiming for modernization and improved governance in liquor sales, was marred by controversy and allegations of corruption, prompting a thorough investigation into its implementation and aftermath.
Project GR00T

- 21 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
AI chip leader Nvidia on Tuesday (March 19) announced Project GR00T or Generalist Robot 00 Technology, which promises to revolutionize the evolution of humanoid robots.
What is Project GR00T?
- Project GR00T stands for Generalist Robot 00 Technology.
- It is essentially a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots.
- This ambitious project aims to create a general-purpose foundation model for humanoid robots, enabling them to understand natural language, learn new skills from observing humans, and solve various tasks in real-time.
- Robots built on this platform are designed to understand natural language and emulate movements by observing human actions, such as instantly learning coordination, dexterity, and other skills.
- This can help the robots navigate and engage with the real world around them.
- The goal of Project GR00T is to advance the field of embodied artificial general intelligence (AGI) and drive breakthroughs in robotics.
- NVIDIA intends to leverage its expertise in AI and its technological resources to develop this foundational model, which would provide humanoid robots with human-like abilities, such as emotion, reaction, and movement.
The Potential Consequences of Project GR00T and Humanoid Robots in the Workforce:
- As humanoid robots, such as those envisioned by NVIDIA's Project GR00T, become more advanced and capable of handling various hazardous or repetitive tasks, concerns arise over potential job displacement.
- For instance, Nvidia's partnership with Hippocratic AI to develop AI-powered healthcare agents may lead to a reduction in the demand for nurses.
- However, proponents argue that these robots can serve as valuable aids for humans, enhancing their quality of life and complementing their skills rather than supplanting them entirely.
- Consequently, the impact of humanoid robots on the workforce may ultimately depend on their successful integration into existing labor structures, as well as the willingness and ability of society to adapt to this transformative technology.
Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG)

- 20 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's largest gas utility GAIL (India) Ltd commissioned the country's first SSLNG unit at its Vijaipur complex in Madhya Pradesh recently.
India Unveils Its First Small-Scale LNG Plant:
- In a significant step towards a cleaner energy mix, GAIL (India) Ltd. has commissioned India's first Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) plant in Vijaipur, Madhya Pradesh.
- This plant will produce 36 tonnes of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) daily, utilizing cutting-edge technology like treatment skids and liquefaction skids to convert natural gas into LNG.
- As part of India's commitment to increasing the proportion of natural gas in its primary energy mix from 6% to 15% by 2030, the SSLNG plant will play a pivotal role in reducing pollution emissions while catering to the nation's growing energy demands.
- This milestone achievement paves the way for a greener future and positions India as a significant player in the global LNG landscape.
What is Small-Scale LNG?
- Small-scale LNG (SSLNG) is an emerging industry that offers a novel approach to natural gas distribution.
- While there is no standard international definition, SSLNG typically involves the liquefaction and transportation of natural gas in smaller quantities using specialized trucks and vessels.
- This allows for the supply of LNG to industrial and commercial consumers in regions without pipeline connectivity.
- SSLNG can be sourced from existing large-scale LNG import terminals or small liquefaction plants in gas-rich locations.
- End-users regasify the LNG using small vaporizers for traditional use cases like supplying Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles and piped gas for households and industries.
- Alternatively, LNG can be supplied in its liquid form for direct use.
Benefits of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG):
- Expanded Accessibility: SSLNG overcomes the constraints of traditional pipeline infrastructure, enabling natural gas delivery to regions previously lacking access.
- This opens new avenues for cleaner fuel alternatives and widespread energy availability.
- Operational Flexibility: SSLNG's modular design allows for rapid deployment in response to local demand fluctuations, making it an ideal solution for remote locations, industrial environments, and diverse transportation requirements.
- Sustainability Promotion: By fostering the adoption of cleaner fuels, SSLNG significantly reduces emissions in various transportation sectors, including trucks, buses, and marine vessels. This contributes to a greener future and combats climate change.
- Strengthened Energy Security: Decentralized SSLNG distribution systems diversify fuel sources and bolster energy security, ensuring reliable and stable energy supply amid global fluctuations and uncertainties.
Challenges of Small-Scale LNG (SSLNG) Implementation:
- Vehicle Availability Constraints: Limited options for LNG-powered vehicles impede the widespread adoption of LNG as a fuel source, underscoring the need for increased production and diversification of vehicle models.
- Insufficient Retail Infrastructure: The lack of a well-established LNG retail network hinders convenient consumer access to LNG fuel, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure expansion and enhancement.
- Higher Upfront Investment: The comparatively higher initial costs of LNG vehicles compared to traditional diesel options may deter potential buyers, necessitating innovative financial solutions and incentives.
- Financing Barriers: The absence of dedicated financing options for LNG vehicles poses obstacles for interested buyers, requiring tailored financial instruments to support SSLNG uptake.
- Restricted Pipeline Coverage: SSLNG faces logistical challenges in areas without existing natural gas pipeline networks, highlighting the need for infrastructure development to extend its reach to remote regions.
- Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles: SSLNG projects may encounter regulatory and permitting setbacks, including environmental and safety concerns, potentially prolonging project timelines and inflating costs.
- Addressing these challenges is essential for expediting SSLNG implementation and fostering its growth.
SAKHI App To Assist Gaganyaan Crew

- 19 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) facility at Thumba in Thiruvananthapuram, has developed a multi-purpose app that will help astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission carry out a range of tasks such as looking up vital technical information or communicating with one another.
About SAKHI App:
- The Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), an ISRO facility in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, has created the versatile 'SAKHI' app for astronauts on the Gaganyaan space flight mission.
- SAKHI stands for 'Space-borne Assistant and Knowledge Hub for Crew Interaction'.
Purpose:
- During the mission, the app will assist Gaganyaan crew members in various tasks such as accessing vital technical information and communicating with each other.
Utility:
- Health Monitoring: It will monitor key health parameters like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, providing crucial insights into the crew's physical condition during the mission.
- Additionally, it will remind them of hydration, dietary schedules, and sleep patterns.
- Connectivity:
- Astronauts can use the app to maintain mission logs in various formats, including voice recordings, texts, and images.
- It will ensure seamless communication between the crew, the onboard computer, and ground-based stations.
- Current Status: An engineering model of the custom-built hand-held smart device featuring SAKHI has been tested, with the development of a flight model underway.
About the Gaganyaan Mission:
- The primary objective of the mission is to demonstrate the capability to launch and safely return three crew members to low Earth orbit.
- The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3) is designated as the launch vehicle for the Gaganyaan mission.
- Crew Escape System (CES): A vital component of the mission, CES is powered by quick-acting, high-burn rate solid motors.
- It ensures the safe evacuation of the Crew Module and crew in case of emergencies during launch or ascent.
- Orbital Module: Comprising the Crew Module (CM) and Service Module (SM), the Orbital Module orbits the Earth, providing safety and support throughout the mission phases.
- Crew Module (CM): Designed to offer a habitable space with Earth-like conditions for the crew during their time in space.
- Service Module (SM): This module supports the CM during orbit, containing essential systems such as thermal, propulsion, power, avionics, and deployment mechanisms.
- This will mark ISRO's inaugural manned spaceflight mission, joining the ranks of the US, Russia, and China, which have previously conducted human spaceflights.
Revenue-Based Financing

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Revenue-based financing (RBF) is increasingly popular among startups and digital SMEs due to a lack of venture capital and limited access to traditional credit options.
What Is Revenue-Based Financing?
- Revenue-based financing is a method of raising capital for a business from investors who receive a percentage of the enterprise's ongoing gross revenues in exchange for the money they invested.
- In a revenue-based financing investment, investors receive a regular share of the business's income until a predetermined amount has been paid.
- Typically, this predetermined amount is a multiple of the principal investment and usually ranges between three to five times the original amount invested.
How Revenue-Based Financing Works?
- Capital investment: An investor or a group of investors provides capital to a company (but not as a traditional loan nor in exchange for equity in the company).
- Revenue percentage agreement: In return for the capital, the company agrees to give the investor a fixed percentage of its gross revenues each month.
- Repayment structure: The company repays the invested capital through payments based on monthly or annual revenue.
- The amount paid each month varies as it is directly tied to the company’s revenue for that month.
- Repayment cap or term: There is usually a cap on the total amount to be repaid, often set as a multiple of the original investment (e.g., 1.5x or 2x the initial amount).
- Alternatively, the repayment might continue until a specific term is reached, such as a number of years.
Comparing Revenue-based Financing to Debt and Equity-based Models:
- While revenue-based financing shares similarities with debt financing in terms of regular investor repayments, it differs notably as it doesn't involve interest payments.
- Instead, repayments are based on a predetermined multiple, yielding returns higher than the initial investment.
- Moreover, unlike traditional debt arrangements, revenue-based financing doesn't necessitate collateral.
- Additionally, unlike equity-based models, it doesn't entail transferring ownership stakes in the company to investors.
Chausath Khamba

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Characterized by its marble pillars and intricate latticework, Chausath Khamba (64 pillars) stands adjacent to the Nizamuddin dargah, a 14th-century shrine erected in honor of the revered Sufi saint Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
About the Chausath Khamba:
- Chausath Khamba was built in AD 1623 - 24 to serve as a tomb for Mirza Aziz Koka, the foster brother of Mughal Emperor Akbar.
- It is so called on account of the 64 (chausath) monolithic marble pillars (khamba) and stands close to his father, Atgah Khan’s tomb, at the edge of the Dargah of Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya.
- The tomb enclosure is entered through a lofty arched gateway and has a large sunken forecourt.
- The mausoleum is unique on account of it being built entirely of marble, with 25 marble domes supporting the flat roof of the structure.
- The plan for Chausath Khamba could have been inspired by the wooden garden pavilions from Persia - such as the Chihil Sutun, and in turn, the Chausath Khamba seems to have inspired the architectural design for Emperor Shahjahan’s Diwan-i-Aam, Hall of Audience.
- Each facade of the square structure has five marble arches inset with marble jaallis or lattice screens and a doorway in the central arch providing access to the tomb.
- The column capitals are intricately carved with simple yet striking pendentives bridging the square floor plan to the circular dome above.
- The structure also finds mention in Sir Gordon Risley Hearn’s book The Seven Cities of Delhi.
- As per author and historian Sam Dalrymple, the edifice embodies the architectural style of Gujarat and Ahmedabad within Delhi, serving as the Urs Mahal for hosting festivities during the commemoration of Nizamuddin's passing.
- This illustrates the historical dissemination of regional architectural influences across India over centuries.
Predictive AI: Its Applications and Advantages

- 18 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Predictive AI is revolutionizing data analysis, decision-making, and industry leadership, offering businesses unprecedented insights and strategic advantages.
What is Predictive Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Predictive artificial intelligence (AI) utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze historical data and forecast future events, distinguishing it from traditional AI focused solely on retrospective analysis.
- This cutting-edge technology employs advanced algorithms and machine learning models to sift through extensive datasets, identifying subtle patterns and trends.
- Unlike conventional approaches, Predictive AI doesn't just analyze data; it transforms it into actionable insights, enabling organizations to:
- Anticipate future outcomes,
- Predict market shifts, and
- Make strategic decisions with unprecedented foresight.
- By continuously learning from past data and adapting to changing trends, Predictive AI becomes an invaluable tool, guiding businesses through uncertain landscapes.
How Predictive AI Work?
- Leveraging Big Data: Predictive AI relies on access to extensive datasets, often referred to as "big data," as larger datasets typically lead to more accurate analyses.
- Utilizing Machine Learning (ML): As a subset of AI, ML involves training computer programs to analyze data autonomously, without human intervention.
- In the realm of predictive AI, ML algorithms are applied to vast datasets to extract valuable insights.
- Autonomous Processing: Predictive AI models are capable of autonomously processing massive datasets, eliminating the need for human oversight.
- Pattern Recognition: Through ML techniques, predictive AI learns to recognize patterns within datasets, associating specific data points or occurrences with potential future events.
- By examining numerous factors, predictive AI can identify intricate patterns indicative of recurring events, enabling organizations to anticipate future outcomes effectively.
Difference Between Predictive AI and Generative AI:
- Predictive AI and generative AI both employ machine learning techniques and leverage extensive datasets to generate their outputs.
- However, while predictive AI utilizes machine learning to forecast future outcomes, generative AI employs machine learning to produce original content.
- For instance, a predictive AI model may inform fishermen about impending storms, whereas a generative AI model may craft a fictional narrative depicting various scenarios involving weather and fishing expeditions.
- While both types of AI rely on statistical analysis to discern patterns, their objectives, machine learning methodologies, and applications differ significantly.
Various Applications of Predictive AI:
- Assessing the Impact of Natural Disasters: With the recent eruption of a volcano in Iceland, the potential repercussions on air travel echo concerns from a similar event in 2010, which disrupted flights across Europe.
- Predictive AI leverages data analysis to identify patterns and anticipate the impact of such extreme weather events on air travel. Platforms like Yandex offer interactive maps for real-time monitoring of ash clouds post-eruption.
- Enhancing Oil and Gas Exploration: In the realm of oil and gas exploration, companies possess extensive historical geological data that can inform predictive AI systems.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- For instance, Saudi Aramco utilizes its meta-brain generative AI to optimize drilling plans, analyze geological data, and forecast drilling outcomes accurately.
- By analyzing past drilling successes, these systems can predict optimal locations for new oil wells.
- Inventory and Supply chain management: Predictive AI aids in inventory and supply chain management by identifying peak consumer demand periods, facilitating proactive stock adjustments, and optimizing resource allocation to address fluctuations in road congestion and meet increased user demands.
- Marketing campaigns: Just as predictive AI can anticipate user or customer behavior, it can help prognosticate what kinds of content or products prospective customers may be interested in.
- Advancing Medical Research: Predictive AI plays a pivotal role in drug discovery, a cornerstone of contemporary medical research.
- Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly collaborating to leverage predictive AI models for analyzing vast datasets and identifying potential drug candidates. Initiatives like the 'MELLODDY Project', supported by the EU Innovative
- Medicines Initiative and multiple pharmaceutical firms, exemplify this collaborative effort in pooling data and leveraging predictive AI for drug discovery.
First Drug to Treat Common, Lethal Liver Disease Gets US Nod
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals Inc.’s drug Rezdiffra gained the first US approval to treat a potentially deadly liver disease that affects millions worldwide, succeeding in an area where some bigger rivals have failed.
What is Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)?
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver.
- NASH (or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) is a type of NAFLD that can damage the liver.
- NASH occurs when the fat buildup in the liver leads to inflammation (hepatitis) and scarring.
- NASH can be life-threatening, as it can cause liver scarring (called cirrhosis) or liver cancer.
- It is estimated that 3% to 5% of the global population is affected by NASH, though the disease is considered to be underdiagnosed.
Who gets NASH?
- The condition may be hereditary.
- If a person has family members who have had NASH or NAFLD, they are at risk.
- Additionally, having certain health conditions may increase a person’s risk of developing NASH. These include:
- Being overweight or obese.
- Having high cholesterol or high triglyceride levels.
- Having type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or prediabetes.
What are the signs and symptoms of NASH?
- NASH is known as a “silent” disease because many people present with few or no symptoms.
- However, some people will experience tiredness, pain, and discomfort in the upper right part of the abdomen.
How is NASH diagnosed?
- Diagnosing NASH can be challenging because symptoms may not be noticeable until the disease progresses.
- Healthcare providers typically suspect NASH based on abnormal blood or liver test results or imaging showing liver fat.
- Confirmation requires a liver biopsy, an invasive procedure with risks and expenses, involving taking a small liver sample for microscopic examination.
How is NASH treated?
- To manage NASH, losing weight is often recommended as it can reduce liver fat, inflammation, and scarring.
- This involves losing around 3% to 5% of body weight by limiting fats and sugars in the diet.
- Heavy alcohol use should also be avoided to prevent further liver damage.
- If NASH progresses to cirrhosis, treatment may involve medications, medical procedures, or even a liver transplant.
- Currently, there are no approved medications specifically for treating NASH, but ongoing research aims to develop new treatments.
Tesla’s India entry gets boost as government approves new EV policy
- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government announced a new electric vehicle (EV) policy recently that is expected to provide a major boost to Tesla's plans to start operations in India.
What is the Revised EV Policy Offering Tax Incentives?
- The Government of India has sanctioned a new initiative aimed at positioning India as a premier manufacturing hub, fostering the production of cutting-edge electric vehicles (EVs) within the nation.
- Crafted to entice investments from renowned global EV manufacturers, this policy seeks to provide Indian consumers access to state-of-the-art EV technology while bolstering the Make in India campaign.
- By cultivating a competitive environment among EV players, the policy endeavors to fortify the EV ecosystem, stimulating innovation and efficiency.
- Furthermore, it is anticipated to stimulate substantial production rates, capitalize on economies of scale, and drive down production costs, consequently curbing crude oil imports, narrowing trade imbalances, and mitigating urban air pollution, thereby fostering a healthier environment for all.
Key Features of the Policy:
- Minimum Investment Requirement: Companies are mandated to invest a minimum of Rs 4,150 Crores.
- Investment Ceiling: There is no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Manufacturing Timeline: Companies must establish manufacturing facilities in India within 3 years and commence commercial production of e-vehicles.
- Within 5 years, they should achieve 50% domestic value addition.
- Domestic Value Addition (DVA): Localization levels of 25% by the 3rd year and 50% by the 5th year are mandatory during manufacturing.
- Customs Duty: A customs duty of 15%, applicable to Completely Knocked Down (CKD) units, will be enforced for 5 years.
- Import Limits: Import of at most 8,000 EVs annually is permitted under this scheme, with provisions for carrying forward unutilized import quotas.
- Bank Guarantee Requirement: Investment commitments necessitate bank guarantees to cover the forgone customs duty.
EV Adoption in India:
- In 2023, electric vehicle sales in India surged by 49.25% year-on-year, surpassing 15 lakh units, as the Federation of Automobile Dealers' Association (FADA) reported.
- This notable increase follows a total sale of approximately 10 lakh units recorded in 2022, indicating a rapid growth trajectory.
- Factors contributing to this surge include improved product availability, escalating fuel prices, state subsidies, and incentives provided under the FAME-II Initiative.
What is the FAME-II Scheme?
- The FAME India scheme, initiated in 2015, serves as an incentive program aimed at accelerating the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, with its acronym standing for "Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles in India."
- In 2019, the Central government sanctioned Phase II of the FAME Scheme with a budgetary allocation of 10,000 Crore over three years, extending until March 31, 2024.
- The primary objective of Phase II is to stimulate demand by facilitating the deployment of 7000 e-Buses, 5 lakh e-3 Wheelers, 55,000 e-4 Wheeler Passenger Cars (including Strong Hybrid), and 10 lakh e-2 Wheelers, thereby fostering the growth of the electric vehicle ecosystem.
- Under the FAME-II scheme, nearly 2 lakh vehicles have received support, signifying a significant stride towards electric vehicle adoption in the country.
Government Initiatives to Promote EV Usage:
- Battery Swapping Policy: The Battery Swapping Policy offers an alternative approach wherein discharged batteries are exchanged for charged ones, enabling efficient charging without vehicle downtime.
- NITI Aayog has recently unveiled a draft battery-swapping policy, prioritizing metropolitan cities with populations exceeding 40 lakh for the establishment of battery-swapping networks in the initial phase.
- Switching to EVs: Central and State governments extend upfront subsidies to mitigate the overall costs associated with electric vehicles, incentivizing consumers to transition towards cleaner mobility options.
- E-AMRIT Portal: The e-AMRIT portal serves as a comprehensive platform, furnishing resources and support to facilitate the seamless transition to electric vehicles, thereby bolstering the nation's electrification agenda.
'ETHANOL 100' hits the road at 183 Indian Oil stations in five states

- 16 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a strategic advance towards cleaner fuel alternatives, India commenced the sale of ETHANOL 100 across 183 Indian Oil outlets in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, New Delhi, and Tamil Nadu.
What is ETHANOL 100 Fuel?
- ETHANOL 100 fuel represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, offering a high-octane rating ranging from 100 to 105.
- This elevated octane level is particularly advantageous for high-performance engines, delivering improved efficiency and power output while simultaneously reducing environmental impact.
- One of the key features of ETHANOL 100 is its remarkable versatility, making it suitable for a diverse range of vehicles, including flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) designed to accommodate various fuel types such as gasoline, ethanol, or any blend thereof.
- This adaptability ensures that ETHANOL 100 can seamlessly integrate into existing automotive fleets without requiring extensive modifications or infrastructure upgrades.
- The composition of ETHANOL 100 consists of approximately 93 to 93.5 percent ethanol blended with 5 percent petrol and 1.5 percent co-solvent acting as a binder.
- This well-balanced formulation not only enhances fuel performance but also contributes to its practicality as a mainstream fuel option.
- In addition to its performance benefits, ETHANOL 100 stands out as a cleaner and greener alternative to traditional gasoline.
- By emitting lower levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and particulate matter, ETHANOL 100 plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and improving air quality in our communities.
- With the right infrastructure and support mechanisms in place, ETHANOL 100 has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry by offering a sustainable and eco-friendly fuel solution that aligns with the global efforts to combat environmental degradation and promote sustainable development.
What are Flex-fuel Vehicles?
- Flex-fuel vehicles are engineered to operate on a diverse range of fuels, offering consumers the flexibility to choose between petrol, ethanol, or methanol at the point of refueling.
- Equipped with an internal combustion engine (ICE), these vehicles can seamlessly switch between different fuel types, providing versatility and convenience to drivers.
- While possessing similarities to conventional petrol-only cars, flex-fuel vehicles undergo minor modifications to accommodate the use of alternative fuels, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance across various fuel options.
Devin AI, an AI software engineer, can handle coding projects end-to-end

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a US-based startup Cognition has unveiled an AI-powered tool, Devin, which it calls the “world’s first fully autonomous AI software engineer”.
What is Devin?
- Devin is a super-smart computer program created by a company called Cognition.
- It's like having a clever assistant for software engineering tasks.
- With just a simple instruction, Devin can write code, build websites, and make software all on its own.
- But Devin isn't trying to replace human engineers, instead, it's meant to work together with them to make their jobs easier.
- The special feature of Devin is its ability to think ahead and solve tricky problems.
- It can learn from its mistakes and keep getting better over time.
- Plus, it has all the tools that a human engineer needs, like a way to write code and browse the internet.
- Devin has been tested against other AI programs, and it did way better, solving almost 14 out of 100 problems compared to just under 2 for others.
- So, in simple terms, Devin is like a super-smart assistant that helps engineers do their work faster and better, without taking their jobs away.
How does Devin work?
- Devin works by using advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to understand and execute tasks related to software engineering.
- When given a prompt or instruction, Devin analyzes the request and uses its vast database of knowledge and problem-solving techniques to generate code, design websites, or develop software.
- One of Devin's key features is its ability to think ahead and plan complex tasks.
- It can make thousands of decisions based on the given task and learn from its mistakes to improve its performance over time.
- Devin also has access to essential tools like a code editor and web browser, enabling him to complete tasks from start to finish.
- It can learn new technologies, tackle a wide range of engineering challenges, and even train its own AI models.
- Additionally, Devin can collaborate with human engineers in real time, providing updates, accepting feedback, and contributing to design choices.
- Overall, Devin works by harnessing the power of AI to automate routine tasks, streamline workflows, and empower engineers to focus on more complex problems.
- By combining human expertise with machine intelligence, Devin represents a significant advancement in software engineering technology.
Conservationists to propose Kazhuveli watershed region in T.N. for nomination to World Monuments Fund Watch 2025

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Eri (tank) network in the Kazhuveli watershed region in the Villupuram district which comprises an incredible network of tanks created thousands of years ago is to be proposed for nomination to the World Monuments Fund Watch 2025 program.
About the World Monuments Fund (WMF)?
- The World Monuments Fund (WMF) is a non-profit organization headquartered in New York, committed to safeguarding and conserving endangered ancient and historic sites worldwide.
- Collaborating with local partners globally, the WMF offers financial and technical assistance to support preservation efforts.
- With a track record of raising over $300 million and securing an additional $400 million from other entities, the WMF has successfully preserved over 700 sites and championed the protection of more than 800 cherished landmarks since its establishment.
World Monuments Watch:
- The World Monuments Watch, initiated in 1996, is a program centered on nominations, fostering a link between local heritage conservation and international engagement.
- Through this initiative, the WMF has allocated over $110 million towards projects at over 300 Watch sites, enabling communities to utilize the platform's visibility to secure an additional $300 million from various funding sources.
World Monuments Fund in India:
In India, the World Monuments Fund (WMF) has focused on conserving significant cultural and ecological sites, including:
- The Kazhuveli Watershed Region: Renowned for its ancient 'Eri' network, an intricate system of tanks dating back thousands of years.
- Situated in the Villupuram district of Tamil Nadu, spanning from Gingee to Marakkanam and extending to the Auroville plateau.
- Proposed pilot projects in Munnur village aim to develop a heritage toolkit applicable across the watershed and beyond if the nomination is successful.
- Suranga Bawadi: An ancient water management system located on the Deccan Plateau in Karnataka.
- Included in the World Monument Watch list for 2020, highlighting its significance for preservation efforts.
Vision for Edible Oil Self-Reliance takes root in the North-East

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has reiterated the Government’s commitment to move towards self-sufficiency in edible oils production and harped on the importance of oil palm cultivation in the northeast region.
About the National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP):
- The National Mission for Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) is an initiative launched by the Government of India in August 2021 to significantly enhance oil palm cultivation and crude palm oil production.
- This centrally sponsored scheme prioritizes the North East region and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, aiming to boost the area and productivity of oilseeds and Oil Palm.
- The targets of NMEO-OP include expanding the oil palm area to 10 lakh hectares by 2025-26, a substantial increase from 3.5 lakh hectares in 2019-20, along with elevating Crude Palm Oil production to 11.20 lakh tonnes by 2025-26 from 0.27 lakh tonnes in 2019-20.
- Furthermore, the mission seeks to enhance consumer awareness to maintain a consumption level of 19.00 kg/person/annum until 2025-26.
- Implementation of NMEO-Oil Palm involves various stakeholders such as the State Departments of Agriculture and Horticulture, Central University, ICAR-Institutions, CDDs, SAUs, KVKs, Central Agencies/Cooperatives, Oil palm processors/ Associations, DD Kisan, AIR, DD, TV channels.
- The salient features of NMEO-OP encompass assistance for planting material, inputs for intercropping up to a gestation period of 4 years, the establishment of seed gardens and nurseries, micro-irrigation, bore well/pump set/water harvesting structure, vermicompost units, solar pumps, harvesting tools, custom hiring center cum harvester groups, farmers and officers training, and replanting of old oil palm gardens, among others.
Oil Palm Production in India:
- Originating in West Africa, Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis) is a relatively recent crop in India known for its high vegetable oil yield per hectare.
- It yields two main oils, palm oil, and palm kernel oil, utilized in both culinary and industrial applications.
- The primary oil palm-growing states in India include Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Kerala, which collectively contribute to 98% of the total production.
- Additionally, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Mizoram also have significant areas dedicated to oil palm cultivation.
Honoring, the Architect of Mumbai (Bombay)

- 15 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Maharashtra cabinet recently decided to ask the Ministry of Railways to rename Mumbai Central Station after Nana Jagannath Shankarseth.
Who was Nana Jagannath Shankarseth?
- Nana Jagannath Shankarseth was a social reformer, educationist, and philanthropist and often described as the “architect” of Mumbai (then Bombay).
- He made extremely valuable contributions in terms of both ideas and money to multiple sectors, to lay a strong foundation for the city.
- Shankarseth was greatly inspired by the legendary merchant and philanthropist Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy.
- As a social reformer and community leader, Shankarseth earned the goodwill of both Indians and the British.
- He became the first Indian to be nominated to the Legislative Council of Bombay.
Shankarseth’s Most Significant Contributions:
- Education: Shankarseth was deeply committed to the growth and spread of education in Bombay, and donated land owned by his family for educational institutions.
- Like many social reformers of his age, he believed that Indians could progress through education.
- He also worked for the education of girls and women.
- Shankarseth founded the Native School of Bombay, which was renamed first as the Bombay Native Institution, and then as the Board of Education.
- Finally, this institution evolved into the prestigious Elphinstone College.
- Museum, Temples: Shankarseth was among the wealthy donors who helped promote Dr Bhau Daji Lad Museum in Byculla, which was designed by a famous London-based architect.
- The Bhawani Shankar Temple near Nana Chowk was Shankarseth’s tribute to his late mother Bhawanibai Murkute.
- He also built a Ram temple.
- Railways: The first train in India ran between Boribunder and Thane on April 16, 1853.
- The 34-km project was undertaken by the Great Indian Peninsular Railway Company.
- The committee that gave the project impetus included Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy and Nana Shankarseth.
News-sharing service by Prasar Bharati launched, content to be ‘free of copyright’

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Ahead of the Lok Sabha polls, public broadcaster Prasar Bharati launched a news-wire-like service to offer free content across mediums, which will be free of copyright or credit obligations.
What is PB-SHABD?
- PB-SHABD, an acronym for Prasar Bharti - Shared Audio Visuals for Broadcast and Dissemination, is a comprehensive platform designed to deliver daily news feeds encompassing video, audio, text, photos, and other formats to media subscribers.
- Leveraging the expansive network of Prasar Bharati reporters, correspondents, and stringers, the service offers up-to-the-minute news coverage spanning various regions of the country.
- Functioning as a centralized hub for news content, SHABD serves as a valuable resource for organizations, offering a wide array of news stories across fifty categories in all major Indian languages.
- Furthermore, the shared feeds facilitate tailored storytelling across diverse platforms, catering to the specific needs of newspapers, TV channels, and digital portals.
- In an inaugural gesture, the service is provided free of charge for the initial year, extending invaluable support to smaller media outlets and contributing to enhanced accessibility to news content.
About Prasar Bharti:
- Prasar Bharti functions as the nation's Public Service Broadcaster, operating under the Prasar Bharati Act established in 1997 as a statutory autonomous body.
- Its primary objective is to deliver public broadcasting services aimed at informing and entertaining the public.
- Comprising the former media units of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, namely the Doordarshan Television Network and All India Radio, Prasar Bharti plays a vital role in disseminating news and entertainment content.
- Headquartered in New Delhi, Prasar Bharti serves as a cornerstone of India's media landscape, dedicated to fulfilling its mandate of public service broadcasting.
Lab to monitor seawater quality and testbed to track monsoon systems inaugurated
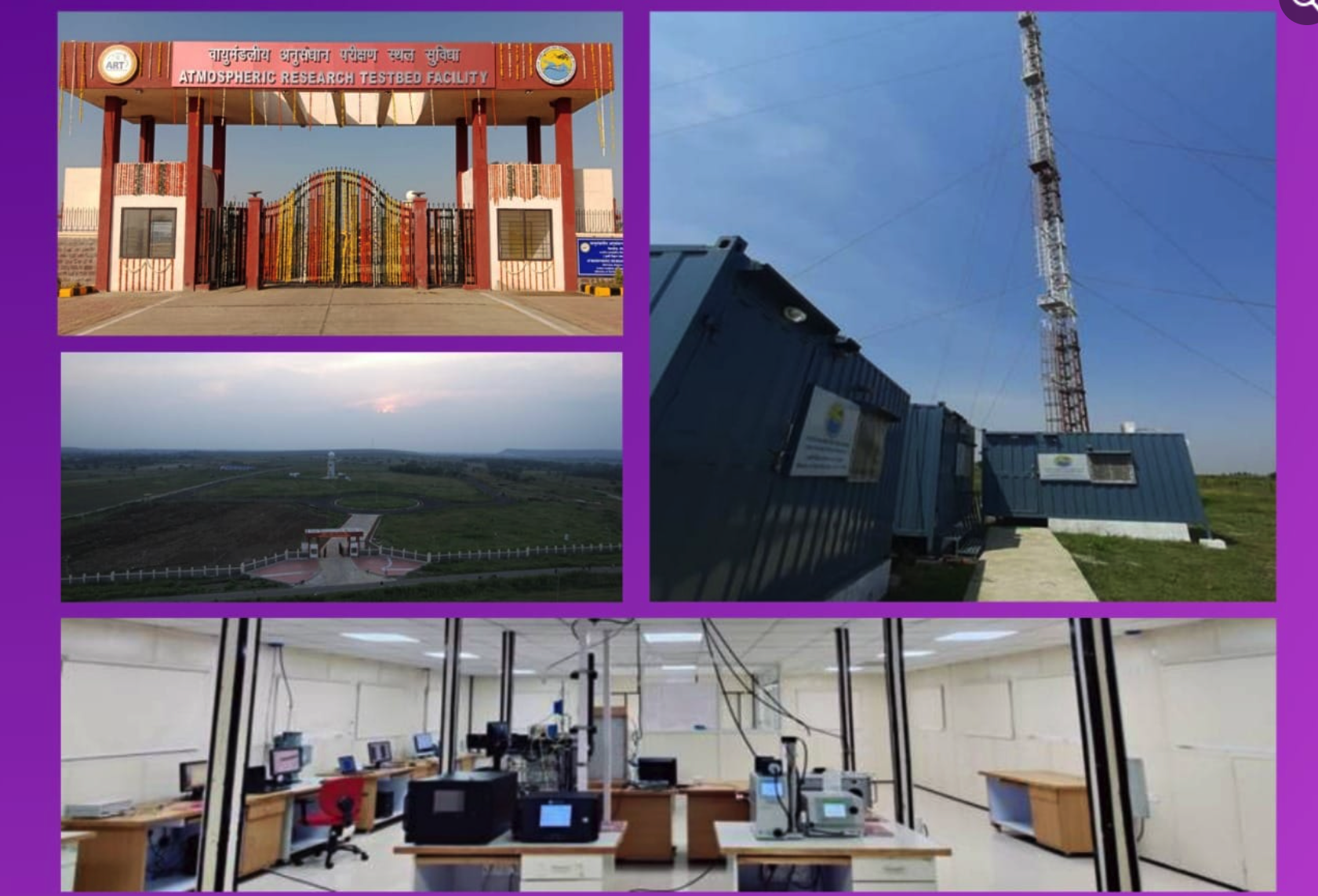

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently India commissioned the atmospheric testbed facility near Bhopal, equipped with high-end instruments to record vital parameters for enhancing weather models and conducting advanced studies on the Indian monsoons, with construction commencing in early 2018.
What is the Atmospheric Research Testbed (ART)?
- The ART is an open-field, focused observational and analytical research programme at Silkheda.
- The facility aims to conduct ground-based observations of weather parameters like temperature, wind speeds, etc., and in-situ (on-site) observations of the transient synoptic systems – like low-pressure areas and depressions that form in the Bay of Bengal – during the southwest monsoon season from June to September.
- Studying these systems and their associated cloud parameters will be used to generate high volumes of data over a long period.
- It can then be compared with the existing weather models so that improvements can be made to obtain accurate rainfall predictions.
- The setup at ART will also be used for calibrating and validating various satellite-based observations, part of weather predictions and forecasting.
- Spread over 100 acres, the ART has been developed by the Ministry of Earth Sciences for Rs 125 crore.
- The Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, is in charge of the operations.
- Under the first phase, remote sensing-based and in-situ measurements using 25 meteorological instruments have commenced.
- In the second phase, ART will deploy instruments such as a radar wind profiler and balloon-bound radiosonde, and soil moisture and temperature measuring equipment.
What instruments are ART equipped with?
- To obtain continuous observations of convection, clouds, and precipitation, and monitor the major modes of variabilities, the ART is equipped with over two dozen high-end instruments, radars, and more.
- At 72 meters, ART will house India’s tallest meteorological tower.
- Some of the instruments deployed are an aethalometer for performing aerosol studies, a cloud condensation nuclei counter, a laser ceilometer to measure cloud sizes, a micro rain radar to calculate raindrop size and its distribution, and a Ka-band cloud radar and a C-band Doppler weather radar to help track the movement of rain-bearing systems over this zone.
Why is having an Atmospheric Research Testbed important?
- At present, 45% of India’s labor force is employed in the agriculture sector and much of Indian agriculture is rain-fed.
- Cultivation along the Monsoon Core Zone (MCZ), which spans the central India region from Gujarat to West Bengal, is primarily rainfall-fed.
- The southwest monsoon season accounts for 70 percent of the country’s annual average rainfall (880mm).
- Throughout India, the majority of Kharif cultivation is undertaken between July and August, which see an average monthly rainfall of 280.4mm and 254.9mm (1971–2020 average), respectively.
- During this four-month-long season, several rain-bearing synoptic systems, namely the low pressures or depressions, develop in the Bay of Bengal.
- Inherently, these systems move westwards/northwestwards over to the Indian mainland and pass through the MCZ, causing bountiful rainfall.
Why is it important to have data about monsoons over central India?
- Studies have correlated the all-India rainfall performance to the rainfall received over the central India region, highlighting its importance.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) issues rainfall forecasts for the country’s four homogeneous regions – north, west, east, and south peninsular India.
- In addition, it issues a special rainfall forecast for the MCZ, which is considered India’s food bowl.
- However, there is still limited understanding of the role of these synoptic systems, their associated cloud physics, cloud properties, and their overall role in enhancing the monsoon rainfall.
- Central India, therefore, acts as a natural laboratory for scientists and meteorologists to perform a hands-on study of the Indian monsoons.
- They can record data and make observations about the allied systems, clouds, and other associated physical and atmospheric parameters.
- Additionally, climate change is driving erratic rainfall patterns in tropical regions, like India.
- It has also strengthened the low-pressure systems, which are aided by high temperatures.
- This results in very heavy rainfall recorded along their trajectory during the monsoons.
- Now, with ART, scientists will be able to generate and obtain long-term observations on cloud microphysics, precipitation, convection, and land-surface properties, among a host of other parameters.
- This information will be assimilated and fed into the numerical weather models to enhance forecast output, especially the rainfall forecasts.
- More accurate forecasts will ultimately help the farming community plan their activities better.
Why Madhya Pradesh?
- The ART has been established at Silkheda, a location that falls directly in line with the path of major rain-bearing synoptic systems.
- This will facilitate direct monitoring and tracking.
- Besides, the locality is pristine and free of anthropogenic and other pollutants, making it the best site in central India for setting up sensitive, high-end meteorological instruments and observatories for recording data.
NITI Aayog launches 'vocal for local' initiative to promote grassroots-level entrepreneurship

- 14 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
NITI Aayog on Wednesday launched the 'Vocal for Local' initiative under its Aspirational Blocks Programme to bolster local economies and foster grassroots-level entrepreneurship, an official statement said.
What is the ‘Vocal for Local’ Initiative?
- The 'Vocal for Local' initiative, led by NITI Aayog through its Aspirational Blocks Programme, aims to foster self-reliance and sustainable development.
- Under this initiative, products from 500 aspirational blocks have been curated and unified under the Aakanksha brand.
- Aakanksha is an overarching brand, with potential extensions into various sub-brands to tap into global markets.
- A dedicated section has been established on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal under the Aakanksha brand to promote these products.
- Additionally, partners in the initiative offer support in areas such as e-commerce facilitation, establishing market linkages, financial and digital literacy, documentation and certification, and skill enhancement.
About Aspirational Blocks Programme:
- Inspired by the Aspirational District Programme launched in 2018, the Aspirational Blocks Programme extends its reach to 112 districts nationwide.
- This new initiative targets the enhancement of underperforming blocks across various development indicators.
- It aims to foster comprehensive growth in regions requiring additional support.
- Initially encompassing 500 districts across 31 States and Union Territories, the programme focuses on blocks in six key states: Uttar Pradesh (68 blocks), Bihar (61), Madhya Pradesh (42), Jharkhand (34), Odisha (29), and West Bengal (29).
What is the Government e-Marketplace (GeM)?
- Established in 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) serves as an online platform for public procurement.
- GeM acts as a centralized portal, streamlining the procurement process for common-use Goods & Services required by various Government Departments, Organizations, and PSUs.
- Purchases made through GeM by Government users are mandated by the Ministry of Finance under the General Financial Rules, 2017.
- GeM is operated by GeM SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle), a 100% Government-owned, non-profit company operating under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
On Dandi March anniversary, PM Modi launches master plan for Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Describing various initiatives of his government as “a way of its dedication towards Mahatma Gandhi”, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a master plan for the Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project in Ahmedabad recently, on the anniversary of the historic Dandi March.
About Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project:
- On the anniversary of the historic Dandi March, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a master plan for the Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram redevelopment project in Ahmedabad.
- This joint initiative by the central government and the Gujarat government, known as the Gandhi Ashram Memorial and Precinct Development Project, is set to cost around Rs 1,200 crore.
- During the inauguration, PM Modi emphasized the importance of conserving heritage sites, stating that "a country which cannot conserve its heritage also loses its future."
- He highlighted the collective responsibility of all Indians to preserve this globally renowned site, which holds immense historical and cultural significance.
- The government's commitment to restoring old buildings to their original form, with the aim of eliminating the need for new constructions, was outlined by PM Modi.
- This approach aligns with the principle of preserving the authenticity and integrity of heritage sites, ensuring that future generations can experience and appreciate their true essence.
- The Sabarmati Gandhi Ashram, established by Mahatma Gandhi in 1917, played a pivotal role in India's struggle for independence.
- By undertaking this redevelopment project, the government seeks to honor the legacy of the father of the nation and create a space that inspires future generations to learn from his life and teachings.
About Dandi March:
- The Dandi March, also known as the Salt March or Salt Satyagraha, was a significant non-violent protest action led by Mahatma Gandhi in March-April 1930.
- This landmark event marked the beginning of a larger civil disobedience campaign that Gandhi waged against British rule in India, which extended into early 1931.
- The Dandi March garnered widespread support for Gandhi among the Indian populace and drew considerable international attention.
- The motivations behind the Dandi March were rooted in the British monopoly over salt production and distribution in India.
- A series of laws prohibited Indians from producing or selling salt independently, forcing them to purchase heavily taxed salt that was often imported.
- This affected the majority of Indians, who were poor and could not afford the high cost of salt. Indian protests against the salt tax had begun in the 19th century and remained a major point of contention throughout British rule.
- By undertaking the Dandi March and defying the salt laws, Gandhi sought to mobilize the Indian populace against British oppression and galvanize support for the Indian independence movement.
- The march, which covered over 240 miles from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi, symbolized the spirit of nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience that would come to characterize India's struggle for freedom.
Impact of Dandi March:
- The Dandi March had a profound impact on the Indian independence movement and left an indelible mark on the country's history.
- The mass civil disobedience that ensued after Gandhi's iconic march led to millions of Indians breaking the salt laws by making or buying illegal salt.
- Gandhi's unwavering commitment to satyagraha against the salt tax inspired countless others to join the movement, including prominent leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Thousands were arrested and imprisoned, including Gandhi himself, but the spirit of resistance only grew stronger.
- News of Gandhi's detention galvanized tens of thousands more to join the satyagraha, and the march on the Dharasana salt works went ahead as planned in May 1931.
- Despite facing violent opposition from the police, the peaceful marchers, led by the poet Sarojini Naidu, persisted in their nonviolent resistance.
- Gandhi's release from custody in January 1931 marked a turning point, as he began negotiations with Lord Irwin aimed at ending the satyagraha campaign.
- These efforts culminated in the Gandhi-Irwin Pact, signed on March 5, 1931, which formalized a truce between the Indian independence movement and the British government.
- The Dandi March, therefore, served as a catalyst for change, uniting Indians from all walks of life in a shared struggle for freedom and justice.
- The events of the Salt Satyagraha remain an enduring symbol of the power of nonviolent resistance and the indomitable spirit of the Indian people in their quest for self-determination.
Khelo India Rising Talent Identification will take sports to the doorstep of aspiring champions

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports, Shri Anurag Singh Thakur inaugurated the unique Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) programme amidst much enthusiasm at the Sector 7 sports complex, in Chandigarh recently.
About the KIRTI Programme:
- The KIRTI Programme is an ambitious nationwide initiative aimed at school children between the ages of nine and 18.
- With a dual focus, the scheme strives to uncover hidden talent from every corner of the country while simultaneously utilizing sports as a powerful tool to combat addiction to drugs and digital distractions.
Primary Objectives of KIRTI's Programme:
- Identifying and nurturing talented young athletes from across India, ensuring that no potential goes unnoticed.
- Leveraging sports as a means to steer youth away from harmful addictions and encourage a healthier, more active lifestyle.
- To achieve these goals, KIRTI plans to conduct 20 lakh assessments throughout the year at designated Talent Assessment Centres across the nation.
- The programme launched with a strong start at 50 centers in India, assessing 50,000 applicants in the first phase across 10 sports such as athletics, boxing, wrestling, hockey, and football.
- KIRTI's athlete-centric approach is characterized by its transparent selection methodology, which is grounded in Information Technology.
- The programme employs data analytics based on Artificial Intelligence to predict sporting potential in aspiring athletes, ensuring that talent identification is both objective and data-driven.
- By channeling India's youth towards sports and providing them with the necessary support, KIRTI aims to foster a new generation of athletes and promote a healthier, more active society.
About Khelo India Scheme:
- The Khelo India Scheme is the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Government of India.
- This Central Sector Scheme is designed to instill a sports culture and achieve sporting excellence in the country by leveraging the transformative power of sports and its cross-cutting influence.
- The Khelo India Scheme encompasses multiple verticals, with "Sports Competitions and Talent Development" being a key focus area.
- Within this vertical, the "Talent Identification and Development" component plays a crucial role in identifying and nurturing athletes at both the grassroots and elite levels.
- The primary objective is to strengthen the sports ecosystem in India by cultivating talent and providing athletes with the necessary resources and support to excel in their respective disciplines.
- Through the Khelo India Scheme, the government aims to promote sports as a way of life, encouraging greater participation and creating a robust platform for athletes to showcase their skills.
- By investing in sports infrastructure, training, and competition opportunities, the scheme seeks to establish India as a global sporting powerhouse and inspire future generations to embrace the spirit of sportsmanship and athletic achievement.
Govt's new code bars unethical marketing of drugs by pharma firms

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The government has notified a new legal code to curb the unethical marketing of drugs and banning medical representatives from using “inducement” to access healthcare professionals
About the Uniform Code of Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (UCPMP) 2024:
- The UCPMP 2024 has been implemented to regulate unethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, with a focus on promoting transparency and ethical conduct.
- The updated guidelines encompass various aspects, including drug endorsement, promotion, ethical behavior for medical representatives, and the maintenance of professional relationships with healthcare professionals.
Key provisions of the UCPMP 2024 include:
- Prohibiting the offering of gifts and travel facilities to healthcare professionals or their family members by pharmaceutical companies.
- Mandating that medical representatives should not use any form of inducement or subterfuge to gain interviews with healthcare professionals, nor should they provide payment for access under any guise.
- Holding pharmaceutical companies responsible for the actions of their medical representatives.
- Banning the supply of free drug samples to individuals who are not qualified to prescribe such products.
- Requiring each pharmaceutical company to maintain detailed records of free samples provided to healthcare practitioners, with the total value of distributed samples not exceeding two percent of the company's domestic sales per year.
- Compulsory constitution of an Ethics Committee for Pharmaceutical Marketing Practices (ECPMP) by all pharmaceutical associations, along with the establishment of a dedicated UCPMP portal on their websites for implementation and monitoring purposes.
- Detailed guidelines on how drugs should be promoted in textual and audio-visual marketing materials, ensuring that information is balanced, up-to-date, verifiable, and non-misleading.
- Restrictions on making unverified claims and comparisons about a drug's usefulness, as well as using terms like "safe" and "new" without proper qualification.
- Assigning responsibility for adherence to the UCPMP 2024 to the Chief Executive Officers of pharmaceutical companies.
- Outlining penalties for violating the code and establishing a clear process for handling complaints, ensuring accountability and effective oversight.
- The UCPMP 2024 serves as a comprehensive framework for promoting ethical practices within the pharmaceutical industry, aiming to protect the interests of patients, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders while fostering an environment of transparency and integrity.
India world’s top arms importer between 2019-23: SIPRI

- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India was the world’s top arms importer for the period 2019-23 with imports having gone up by 4.7% compared to the period 2014-18, according to the SIPRI.
Highlights from the SIPRI Report 2023:
- The report highlights that India continues as the world’s largest arms importer, maintaining this position despite ongoing efforts to enhance its defense-industrial base, accounting for a significant 9.8% of global arms imports between 2019 and 2023.
- There has been a steady increase in India's arms imports, with a 4.7% rise observed between 2014-18 and 2019-23, attributed in part to emergency procurements prompted by the prolonged military standoff with China.
- The dynamics of arms suppliers are changing, with Russia historically serving as India's primary weapons supplier, still accounting for 36% of its arms imports, although there is a shift towards diversification, with India increasingly turning to Western countries and domestic manufacturers.
- Notably, between 2019-23, Russian deliveries constituted less than half of India's arms imports for the first time since 1960-64.
- Western suppliers like France and the United States are emerging as key players, collectively accounting for 46% of India's arms imports, with significant contracts in progress, such as India's procurement of 31 armed MQ-9B Sky Guardian drones from the US and 26 Rafale-M fighters from France.
- In the global arms trade landscape, India ranks as the top importer, followed by Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Ukraine, Pakistan, Japan, Egypt, Australia, South Korea, and China, while the United States leads among exporters with a 42% share, followed by France and Russia.
- India's role as a major arms customer is underscored by its position as the largest arms customer for France, Russia, and Israel, highlighting its significance in global arms procurement.
- Meanwhile, China remains a dominant supplier to Pakistan, accounting for 61% of its exports, and also exports 11% of its arms to Bangladesh, consolidating its influence in the region.
Challenges Encountered by India in Indigenous Production of Defense Equipment:
- Efforts to promote indigenous defense production, exemplified by initiatives like 'Make in India', have encountered persistent challenges, notably the failure to materialize any projects under the Strategic Partnership (SP) model, which was introduced to foster collaboration between the public and private sectors within the defense industry.
- The SP model, designed to facilitate joint endeavors between government-owned defense entities and private companies, has yet to yield tangible results, necessitating a thorough review of the policy framework.
- Key areas for improvement include a reevaluation of pricing methodologies, ensuring long-term orders to sustain production, and addressing bottlenecks that impede project implementation.
- Furthermore, India's defense sector has seen minimal Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), amounting to only Rs 5,077 crore since the sector was opened to private companies in 2001.
- Despite efforts to liberalize FDI regulations, such as allowing up to 74% through the automatic route and up to 100% through the government route in 2020, investment inflows remain disproportionately low.
About Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI):
- The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) is a renowned independent international institute committed to investigating various aspects of conflict, armaments, arms control, and disarmament.
- Founded in 1966 and headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, SIPRI consistently ranks among the world's most respected think tanks.
SIPRI's mission is multi-faceted and encompasses the following key objectives:
- Conducting in-depth research and activities related to security, conflict, and peace, with the aim of developing a deeper understanding of the complex factors that influence global stability.
- Providing insightful policy analysis and recommendations to policymakers, international organizations, and civil society actors, helping them make informed decisions and develop strategies to address security challenges.
- Facilitating dialogue and building capacities among various stakeholders, including governments, academia, and non-governmental organizations, to foster cooperation and promote mutual understanding on peace and security issues.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in the field of international security by maintaining comprehensive databases on arms transfers, military expenditure, and other relevant data, which contribute to a more accurate assessment of global security trends.
- By adhering to these core principles and objectives, SIPRI plays a vital role in advancing the global discourse on peace and security, while supporting efforts to mitigate conflict and promote stability worldwide.
Decoding the Trillion-Dollar Impact of GPUs on the AI Industry
- 13 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
As the global demand for the latest AI technologies surges, one unexpected item has emerged as a highly sought-after commodity: the graphics processing unit (GPU).
What is a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)?
- A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a specialized computer chip designed to efficiently render graphics and images by performing rapid mathematical calculations.
- Widely used in both professional and personal computing, GPUs were initially developed to handle the rendering of 2D and 3D images, animations, and video content.
- Similar to a Central Processing Unit (CPU), a GPU is an integral component of computing devices.
- However, the primary distinction lies in the GPU's specialized design to handle and accelerate graphics workloads and display graphics content on devices like PCs or smartphones.
- While a typical modern CPU consists of between 8 and 16 "cores" that process complex tasks sequentially, GPUs contain thousands of smaller cores.
- These cores are engineered to work simultaneously ("in parallel") to achieve fast overall processing, making GPUs ideal for tasks involving numerous simple operations that can be executed concurrently.
- GPUs operate using a technique called parallel processing, where multiple processors manage separate parts of a single task.
- They also possess their own dedicated RAM to store and process large amounts of data for graphics-intensive applications.
- In graphics applications, the CPU sends instructions to the GPU for drawing graphics content on the screen.
- The GPU then executes these instructions in parallel at high speeds, displaying the content on the device—a process known as the graphics or rendering pipeline.
- They also possess their own dedicated RAM to store and process large amounts of data for graphics-intensive applications.
- Modern GPUs have expanded beyond their traditional role in graphics rendering and are now employed in various applications such as creative content production, video editing, high-performance computing (HPC), and artificial intelligence (AI).
- By offloading graphics-related tasks from the CPU, GPUs enable fast and smooth rendering of content on computer screens.
- As technology continues to advance, the applications of GPUs will likely expand even further, solidifying their position as an essential component in the computing landscape.
Mission Divyastra: India's Agni-V missile makes maiden flight with MIRV

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India on Monday announced the successful testing of an Agni missile capable of carrying multiple warheads meant to hit multiple targets simultaneously.
What are Agni-5 Missiles?
- Agni is a long-range missile developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation, DRDO.
- The family of Agni missiles has been in the arsenal of the Indian armed forces since the early 1990s.
- This latest variant of the missile is equipped with what is known as MIRV (Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle) technology, first developed at least five decades ago but in possession of only a handful of countries.
Salient Features of Agni-5:
- Powered by a three-stage solid-fuel engine, Agni-5 boasts a range exceeding 5,000km.
- The Agni series encompasses medium to Intercontinental variants, spanning Agni-1 to Agni-5, with ranges varying from 700 km to over 5,000 km.
- DRDO’s successful June 2021 test of Agni P, a canisterized missile, demonstrated a range capability ranging between 1,000 and 2,000 km.
- With its ability to be launched from both road and rail platforms, Agni-5 ensures ease of deployment and swift launch capabilities.
What is MIRV Technology?
- The MIRV have revolutionized the concept of ballistic missile payloads by enabling a single missile to carry multiple warheads, each capable of targeting enemies at different locations.
- The technology was first introduced in the US with the successful test of the Minuteman III in 1968, which brought the technology into actual use in the 1970.
- The Soviet Union developed their own MIRV-enabled ICBM and SLBM technology by the end of the 1970s.
- The strategic shift started by MIRV has enabled many nations to greater target damage and reduce the effectiveness of enemy missile systems, altering the landscape of global nuclear deterrence.
- The warheads on MIRVs can be launched at different speeds and in different directions.
- Some MIRVed missiles can hit targets as far as 1,500 km apart.
- The technology requires a delicate combination of large missiles, small warheads, precise guidance, and a complex mechanism for releasing warheads sequentially during flight.
How does MIRV Work?
- The MIRV-equipped missile follows a trajectory into space similar to other ballistic missiles.
- After the boost phase, the missile’s upper stage, known as ‘bus’, reaches suborbital spaceflight, and aligns itself based on designated targets.
- The ‘bus’ sequentially deploys multiple warheads along with decoys and countermeasures.
- Each warhead can be assigned a different target or trajectory.
- After the deployment, the warheads re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere and proceed to their respective targets.
What are the Challenges?
- The MIRV technology enhances first-strike proficiency and complicates the calculus of mutual assured destruction.
- With the ability to deploy multiple warheads from a single missile, nations can achieve a broader spread of targets, making the defense system less effective and more costly.
- Although MIRVs were not initially made to defeat ballistic missile defenses, they are much more difficult to defend against than traditional missiles.
- Possession of MIRV technology not only exhibits a country’s nuclear prowess but plays a crucial role in shaping international security and nuclear deterrence strategies.
STPI launches 24th Centre of Entrepreneurship FinGlobe in Gandhinagar to nurture startups in fintech & banking services

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) recently launched its 24th Center of Entrepreneurship (CoE) - "FinGlobe," dedicated to fostering innovation and growth in the financial technology sector, at STPI-Gandhinagar, GIFT City.
About Software Technology Parks of India (STPI):
- Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) was set up in 1991 as an autonomous society under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- STPI’s main objective has been the promotion of software exports from the country. STPI acts as ‘single-window in providing services to the software exporters.
- The services rendered by STPI for the software exporting community have been statutory services, data communications services, incubation facilities, training and value-added services.
- STPI has played a key developmental role in the promotion of software exports with a special focus on SMEs and start-up units.
Services of STPI:
- Main services of STPI include Statutory services, Incubation and Data communication services to the IT/ITES/ESDM sector.
- Statutory services: STPI has been implementing the Software Technology Park (STP) scheme and the Electronics Hardware Technology Park (EHTP) scheme for the promotion of the IT/ITES industry.
- STP Scheme is a unique scheme, designed to promote the software industry and growth of start-ups and SMEs without any locational constraints.
- Incubation services: STPI is offering ultra-modern office facilities to small units and entrepreneurs.
- Plug-n-Play facilities for start-ups enable a short gestation period.
- This has encouraged many entrepreneurs to start their own operations and grow in a competitive environment.
Objectives of STPI:
- Promotion of software and software services development and exports, including IT Enabled Services (ITES)/Bio-IT.
- Provision of statutory and promotional services to exporters through the implementation of schemes like Software Technology Park/Electronics and Hardware Technology Park, among others.
- Offering data communication services, along with value-added services, to industries related to IT/ITES.
- Encouraging micro, small, and medium entrepreneurs by fostering an entrepreneurial environment in the IT/ITES sector.
. India ‘one of the worst autocratisers’: V-Dem report on democracy

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India, which was downgraded to the status of an “electoral autocracy” in 2018, has declined even further on multiple metrics to emerge as “one of the worst autocratizers”, according to the ‘Democracy Report 2024’ released by the Gothenburg-based V-Dem Institute that tracks democratic freedoms worldwide.
About V-Dem (Varieties of Democracy):
- The V-Dem Institute, established in 2014 by Swedish political scientist Staffan Lindberg, is a research institution dedicated to studying the various forms of democratic governance around the world.
- Headquartered at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden, V-Dem produces several high-profile datasets that assess the qualities of different governments based on hundreds of indicator variables.
- These datasets are widely used by political scientists due to their comprehensive coverage of various aspects of government and are freely available to the public.
- V-Dem's annual publications provide valuable insights into the functioning of governments worldwide, promoting transparency and understanding of democratic institutions.
About The Democracy Report:
- The Democracy Report presents a comprehensive analysis of the state of democracy worldwide, with a particular focus on the trends of democratization and autocratization.
- The report classifies countries into four distinct regime types based on their performance on the Liberal Democracy Index (LDI): Liberal Democracy, Electoral Democracy, Electoral Autocracy, and Closed Autocracy.
- The LDI is a composite index that encompasses both liberal and electoral dimensions of democracy.
- It is based on 71 indicators, which are grouped into the Liberal Component Index (LCI) and the Electoral Democracy Index (EDI).
- The LCI assesses various aspects of individual and minority rights, as well as legislative constraints on the executive.
- The EDI evaluates the extent to which elections are free and fair, considering factors such as freedom of expression and association.
- In addition to the LCI and EDI, the LDI also incorporates three other component indices:
- The Egalitarian Component Index (measuring social group equality)
- The Participatory Component Index (assessing the vibrancy of citizen groups and civil society organizations), and
- The Deliberative Component Index (evaluating whether political decisions are based on public reasoning or emotional appeals, solidarity attachments, and coercion).
- The Democracy Report, along with the underlying dataset, scientific articles, and working papers, is publicly available for download on the V-Dem Institute's website.
- The website also offers interactive graphic tools to facilitate the exploration and visualization of the data.
Key Insights from the Democracy Report 2024:
- The Democracy Report 2024, a collaborative effort involving 4,200 scholars from 180 countries, draws from 31 million datasets spanning 202 countries from 1789 to 2023.
Global Trends:
- In 2023, 42 countries (home to 35% of the world’s population) experienced autocratization.
- Autocracies now encompass 71% of the world's population, up from 48% a decade ago.
- The overall level of democracy has regressed to 1985 levels for the average global citizen.
- Eastern Europe, South, and Central Asia witnessed the most significant decline in democracy.
- Freedom of expression, clean elections, and civil society engagement were the most affected aspects in autocratizing nations.
Focus on 2024 Elections:
- Of the 60 countries holding elections in 2024, 31 are experiencing democratic backsliding.
India's Situation:
- India, classified as an electoral autocracy since 2018, has further deteriorated, earning the title of "one of the worst autocratizers."
- The report notes that India's level of liberal democracy has plummeted to levels comparable to those during the 1975 emergency declared by Indira Gandhi.
- Under the V-Dem classification, a liberal democracy requires robust mechanisms for judicial independence, checks on executive power, and strong protection of civil liberties and equality under the law.
- India currently falls into the category of electoral autocracy, characterized by multiparty elections but lacking adequate freedom of expression and fair electoral processes.
India launches revamped scheme to help advance pharma industry's tech capabilities

- 12 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's Department of Pharmaceuticals recently unveiled the Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (RPTUAS) to help advance the technological capabilities of India's pharmaceutical industry and align it with global standards.
What is the Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme?
- In an effort to support pharma companies aligned with global quality standards, the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP) has announced a revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme.
- It has been incorporated as a sub-scheme under the Scheme - Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry (SPI), which was launched in July 2022.
Objective:
- To facilitate Micro, Small and Medium Pharma Enterprises (MSME) of proven track record to upgrade their technology to meet WHO-GMP or Schedule M standards.
Intended Beneficiaries:
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises of the pharma sector.
Key Features of the Revised Scheme:
- Broadened Eligibility Criteria: Reflecting a more inclusive approach, eligibility for the PTUAS has been expanded beyond Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to include any pharmaceutical manufacturing unit with a turnover of less than 500 crores that requires technology and quality upgradation.
- Preference remains for MSMEs, supporting smaller players in achieving high-quality manufacturing standards.
- Flexible Financing Options: The scheme introduces more flexible financing options, emphasizing subsidies on reimbursement basis, over traditional credit-linked approaches.
- Comprehensive Support for Compliance with New Standards: In alignment with revised Schedule-M and WHO- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, the scheme now supports a broader range of technological upgrades.
- Eligible activities include improvements such as HVAC systems, water and steam utilities, testing laboratories etc.
- State Government Scheme Integration: The revised scheme allows integration with state government schemes, enabling units to benefit from additional top-up assistance. This collaborative approach aims to maximize support for the pharmaceutical industry in their technology upgradation efforts.
- The new benefit limit is based on turnover of the company. Units with less than Rs 5 crore turnover will get an incentive of 20 percent of investment under eligible activities.
- The units with turnover ranging from Rs 50 crore to less than Rs 250 crore will get an incentive of 15 percent of investment, while for those with turnover ranging from Rs 250 crore to less than Rs 500 crore, it will be 10 percent of investment under eligible expenses.
NHAI to start rolling out satellite-based tolling on national highways soon

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari said in Parliament in February that the government plans to implement a new highway toll collection system based on the global navigation satellite system before the model code of conduct for the 2024 election kicks in.
What is the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)?
- GNSS refers to a constellation of satellites providing signals from space that transmit positioning and timing data to GNSS receivers.
- The receivers then use this data to determine location.
- Examples of GNSS include Europe’s Galileo, the USA’s GPS, Russia’s GLONASS and China’s BeiDou
How will the GNSS-Based Toll System work?
- The system will use an automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) system through cameras installed on highways and deduct tolls based on the distance traveled by a vehicle.
- The device monitors the movements while driving, accurately marking the entry and exit points on tolled segments. By analyzing travel distance, it computes the charges accordingly.
- This eliminates the uniformity of fixed tolls at booths, ensuring fairness for drivers traversing shorter distances.
Difference between FASTags and ANPR technology:
- FASTags streamline electronic toll payments at toll plazas equipped with scanners, enabling vehicles to pass through without stopping.
- Conversely, GNSS-based systems utilize ANPR technology to deduct tolls based on distance traveled, rendering traditional toll plazas unnecessary.
What are the Challenges?
- Detection of Non-Compliance: Without physical barriers, detecting non-compliant vehicles, such as those without an On-Board Unit (OBU) or engaging in fraudulent activities, poses a challenge.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying gantry-mounted Automatic Number-Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems along highways is essential for capturing violations and enforcing toll payments.
- License Plate Quality: The effectiveness of ANPR systems relies on the quality of license plates; subpar plates hinder accurate recognition and enforcement efforts.
- Data Privacy and Security: GNSS-based toll systems entail collecting and processing sensitive location data, necessitating robust privacy and security measures.
Inflection AI rolls out new large language model to its Pi chatbot

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Inflection AI launched its latest LLM, Inflection 2.5, an upgrade to its model that powers its friendly chatbot Pi personal assistant.
About Inflection 2.5:
- Inflection-2.5 is an “upgraded in-house model that is competitive with all the world’s leading LLMs like GPT-4 and Gemini.
- The newly upgraded LLM comes with its signature personality and uniquely empathetic fine-tuning.
- Its latest model achieved GPT-4’s performance with only 40 per cent of the OpenAI model’s computation power for training.
- Besides, it seems Inflection 2.5 has made some stellar strides in areas of IQ such as coding and mathematics.
- This means that the model has made substantial improvements on key benchmarks.
- With the new upgrade, Pi has now been endowed with world-class real-time web search capabilities to ensure that users get access to high-quality and up-to-date information in real-time.
What is the Pi chatbot?
- Pi is an advanced chatbot powered by Inflection AI's cutting-edge language model, Inflection 2.5 which allows one to have deep and meaningful conversations.
- To access the chatbot, one needs to log on to Inflection.AI, click on Meet Pi, and simply start talking to the chatbot right away.
- Pi is more humane and has been promoted as a chatbot that has a personality.
- In other words, Inflection AI dubbed it as a chatbot that is “supportive, smart, and there for you anytime”.
- Pi is more like a companion to humans and is free to use.
- The chatbot comes with a voice, in six distinct voices, to choose from adding life to conversations.
Pi chatbot boasts a number of impressive features that make it stand out from other conversational AI systems:
- Real-time web search capabilities: Pi can access and present up-to-date information on a wide range of topics, ensuring that users always have access to accurate and relevant information.
- Empathetic personality: Pi's unique empathetic fine-tuning allows it to understand and respond to the emotional nuances of human communication, making it a more engaging and personable conversational partner.
- Versatile conversation topics: Whether you're discussing current events, asking for local recommendations, studying for an exam, drafting a business plan, coding, or just talking about hobbies, Pi is equipped to handle a wide range of conversational topics.
- User-friendly interface: Designed with accessibility in mind, Pi's intuitive interface makes it easy for users of all technical abilities to engage with the chatbot and get the most out of their conversations.
Health ministers of 11 African countries commit to end malaria deaths

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a historic gathering in Cameroon’s capital Yaoundé, African health ministers, global malaria partners, funding agencies, scientists, civil society organizations and other principal malaria stakeholders pledged to end malaria deaths, especially given the tools and systems available.
What is the Yaounde Declaration?
- The Yaounde Declaration was endorsed by health ministers from 11 African nations with the highest malaria burden, aiming to expedite efforts to eliminate malaria-related deaths.
- Signed during the Yaoundé conference, co-hosted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of Cameroon, the declaration underscores a collective commitment to combat malaria.
- The signatory countries include Burkina Faso, Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania, together accounting for approximately 70% of the global malaria burden.
- Commitments entail stronger leadership and increased domestic funding for malaria control programs, leveraging data technology, adhering to updated technical guidance, and intensifying efforts at national and sub-national levels.
- Ministers pledged augmented health sector investments to fortify infrastructure, personnel, and program implementation, fostering multi-sectoral collaboration, and cultivating partnerships for funding, research, and innovation.
- Signatories affirmed their resolute dedication to hasten malaria mortality reduction and to ensure mutual accountability for the declaration's outlined commitments.
Current Status of Malaria:
- Between 2019 and 2022, global malaria cases increased from 233 million to 249 million, with Africa experiencing a substantial rise from 218 million to 233 million cases, highlighting the continent as the epicenter of the malaria crisis.
- The 11 African countries represented at the conference bear the highest burden of malaria infections and deaths.
Progress and Challenges:
- Despite some progress, malaria incidence has only declined by 7.6% and mortality by 11.3%, falling short of the African Union’s interim goals.
- Only seven out of 46 member states have achieved a 40% reduction in malaria incidence or mortality.
- Urgent action is imperative to bridge a financial gap of $1.5 billion to sustain basic malaria services, especially for vector control.
- Additional funding of $5.2 billion annually for progress towards elimination and $11 billion for climate adaptation in the health sector is crucial to avert significant surges in cases and deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations like children and pregnant women.
UGC notifies framework for private universities to set up off-campus centers

- 11 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
In line with the “future academic vision” instead of “commercial interests”, the UGC has notified modalities on March 6 for state private universities to set up off campus centers within their respective states.
News Summary:
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) recently permitted private universities to establish off-campus centers and outlined regulations for the same.
- Previously, private universities in the country were restricted from opening off-campus centers in other states.
- In a meeting held on March 5, the UGC decided to authorize state private universities to establish off-campus centers across the country, provided they meet specific criteria.
- Criteria include a minimum of five years of establishment and accreditation from the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), without requiring an A or B grade.
- Universities seeking to establish off-campus centers must meet staff, infrastructure, and financial requirements mandated by the commission and obtain approvals from statutory and regulatory bodies.
- These universities must ensure the provision of infrastructure, faculty, and courses offered at the main campus to students at their off-campus centers.
- A one-time establishment fee of Rs 10 lakh is required to be paid to the UGC by the universities.
- The UGC reserves the right to conduct inspections and take punitive actions against universities in case of irregularities or complaints.
- Additionally, the UGC may order the closure of a university’s off-campus center for violations, with the university responsible for relocating affected students to the main campus.
About University Grants Commission (UGC):
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) of India operates as a statutory body established under the UGC Act, 1956.
- Its primary mandate encompasses coordinating, determining, and upholding standards within higher education institutions across India.
- UGC holds the authority to grant recognition to universities and colleges within the country and allocates funds to these recognized institutions.
- Nodal Ministry: Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education.
Mandate of UGC:
- Facilitating and coordinating university education initiatives.
- Establishing and maintaining standards in teaching, examination, and research activities within universities.
- Formulating regulations to define minimum education standards.
- Monitoring advancements in collegiate and university education while disbursing grants to these institutions.
- Serving as a crucial intermediary between the Union and State governments and higher education institutions.
- Providing advisory services to the Central and State governments concerning measures aimed at enhancing university education standards.
Conclusion
Academic experts said that this decision may prove beneficial for students as they will get more options to choose from. However, it also means that the 16 government-run universities in the state will face more competition. More students may shift to these centers, leaving a large number of approved seats in the public universities vacant every year.
India’s indigenous fifth-gen fighter jet AMCA

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) this week cleared a Rs 15,000 crore project to design and develop the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India’s fifth-generation fighter multirole fighter jet.
About Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA)?
- The AMCA will be India’s indigenous fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas is a 4.5-generation single-engine multirole aircraft.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) will be the nodal agency for executing the programme and designing the aircraft.
- It will be manufactured by state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft will put India in a select group of nations that have their own fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- Discussions for developing the AMCA started in 2007.
- The initial plan was to jointly develop the aircraft with Russia under a Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) programme.
- However, India withdrew from the FGFA project in 2018.
Features of AMCA:
- Stealth: The 25-tonne twin-engine aircraft, which will be bigger that other fighters in the Indian Air Force inventory, will have advanced stealth features to avoid detection by enemy radar.
- With stealth features, this aircraft (AMCA) would be able to compete with other stealth fighters in the world.
- Fuel & Weapons: The aircraft will have a large, concealed internal fuel tank of 6.5-tonne capacity, and an internal weapons bay for a range of weapons, including indigenous weapons, to be buried in its belly.
- Engine: The AMCA Mk1 variant will have the US-built GE414 engine of the 90 kilonewton (kN) class, while the more advanced AMCA Mk2 will fly on the more powerful 110kN engine, which will be developed indigenously by DRDO’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) in collaboration with a foreign defense major.
- India has been talking with Safran SA of France, one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aircraft engines and related equipment, in order to finalize the roadmap for the development of the combat aircraft engine
- Another important aspect would be to ensure a higher utilization time and smaller serviceability or maintenance periods for the aircraft.
- This will be aided by the inclusion of a comprehensive Integrated Vehicle Health Management (IVHM) system to keep track of multiple structural components, and to assess the condition of the aircraft in real time.
- Other features such as a diverterless supersonic inlet for controlling air flow into the engines, and a serpentine air intake duct to shield the engines from radar emissions, are likely to be part of the AMCA.
Other Fifth-generation Fighters:
- Only a few countries have built a fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft.
- The list of the aircraft currently in service includes:
- The F-22 Raptor and F-35A Lightning II of the US
- The Chinese J-20 Mighty Dragon, and
- The Russian Sukhoi Su-57.
India to restart Penicillin G manufacture
- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India will start manufacturing the common antibiotic Penicillin G later this year, three decades after the country’s last plant shut down, Union health minister Mansukh Mandaviya announced last week.
What is Penicillin G?
- Penicillin G serves as a key active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) utilized in the production of various common antibiotics.
- Its molecular formula is C16H18N2O4S.
- Penicillin G (potassium or sodium) is an FDA-approved antibacterial medication primarily indicated for treating severe bacterial infections like pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, syphilis, among others.
- This natural penicillin antibiotic is typically administered intravenously or intramuscularly due to limited oral absorption.
- Additionally, Penicillin G may be employed in certain instances as prophylaxis against susceptible organisms.
Why did Penicillin Manufacturing Stopped in India?
- The discontinuation of Penicillin G production in India, along with numerous other active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), resulted from the influx of cheaper Chinese products driven by subsidies.
- Torrent Pharma in Ahmedabad was the final plant to halt Penicillin G production, with at least five companies, including Torrent, manufacturing the antibiotic in the country during the 1990s.
- In the early 1990s, India boasted nearly 2,000 API manufacturers, while approximately 10,000 units produced formulations. However, the allure of cheaper Chinese alternatives grew, particularly with the relaxation of customs rules during the country's economic liberalization.
- The Drug Prices Control Order, which imposed price caps on essential medicines, further incentivized companies to opt for cheaper imported products.
- While India previously sold Penicillin G for around Rs 800 per kg, China drastically reduced prices to nearly Rs 400 per kg, rendering domestic manufacturing economically unviable.
Why the Delay in Restarting Production?
- Lack of Urgency: Despite awareness within the industry and government about the decline in API production in India due to the availability of cheaper alternatives globally, there was limited emphasis on restarting domestic production.
- The supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic highlighted the need for self-reliance, prompting the government to launch initiatives like the PLI scheme to bolster domestic manufacturing.
- High Initial Investment: API manufacturing, particularly for fermented compounds like Penicillin G, entails significant upfront costs.
- Establishing a production facility requires substantial capital investment, with companies often needing several years to break even.
- Dominance of China: China has emerged as a dominant supplier, significantly expanding its manufacturing capacity over the past three decades.
- Competing with Chinese prices would necessitate substantial investments in larger facilities.
What's the Impact of PLI Schemes?
- Reduction in API Imports: Since the implementation of the PLI scheme, there has been a notable decrease in API imports.
- For instance, the import dependency for paracetamol, which was previously two-thirds of the required volume, has now halved.
- Incentive Structure: The PLI scheme offers incentives structured as follows:
- 20% support for the first four years, gradually reducing to 15% in the fifth year and 5% in the sixth year for eligible sales of fermentation-based bulk drugs like antibiotics, enzymes, and hormones such as insulin.
- Chemically synthesized drugs receive a 10% incentive for six years on eligible sales.
The ‘Architecture Nobel’: Why Pritzker laureate Riken Yamamoto’s work stands out

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Japanese architect Riken Yamamoto was this week declared winner of the 2024 Pritzker Architecture Prize, the highest international award in the field, which is sometimes referred to as the “Architecture Nobel”.
About Pritzker Architecture Prize:
- The Pritzker Architecture Prize is an international prize awarded each year to a living architect or a group of architects for significant achievements.
- It was established by the Pritzker family of Chicago in 1979 through their Hyatt Foundation, which until today is responsible for the prestigious award.
- The idea behind the Pritzker Prize is to honor contemporary architects “whose built work demonstrates a combination of those qualities of talent, vision, and commitment, which has produced consistent and significant contributions to humanity and the built environment through the art of architecture.”
- The award consists of a bronze medallion and a prize money of 100,000 USD.
- It is conferred during a ceremony held at an architecturally significant site throughout the world.
- The prize, which is also known as the Nobel Prize of architecture, is awarded “irrespective of nationality, race, creed, or ideology”.
- Nominations come from a range of architects, academics, and critics and the jury consists of five to nine experts.
History of the Prize:
- The idea for the Pritzker Prize came from Jay and Cindy Pritzker, who wanted to encourage and stimulate a greater public awareness of architecture, while also inspiring more creativity in the profession.
- The name Pritzker comes from the family who are based in Chicago and own the Hyatt Hotels.
Riken Yamamoto's Notable Works:
- Yamamoto, the ninth laureate from Japan, is known for his iconic architectural designs, such as the Hiroshima Nishi Fire Station (2000), featuring a transparent façade with glass walls and floors, offering passersby a glimpse inside.
- His design of the Koyasu Elementary School (2018) incorporates spacious, open terraces that facilitate arts education in dance, music, and painting while fostering student interaction.
Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay, the unsung feminist freedom fighter in the history of India

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Post-Independence, the revival of the crafts sector began with Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay who strongly championed the handicrafts movement for the role it could play in social and economic upliftment.
About Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay:
- Kamaladevi was born in April 1903 in a liberal Chitrapur Saraswat Brahmin family in Mangalore (now Mangaluru).
- She completed her primary education at the local St Ann’s Convent.
- Growing up in a land with a rich cultural heritage, especially of the music and dance form Yakshagana, she developed a taste for traditional art forms.
- After her father’s untimely death, Kamaladevi moved to her maternal uncle’s house.
- There, she met renowned freedom fighters, including Gopalkrishna Gokhale, Srinivasa Shastri, Ramabai Ranade and Annie Besant.
- Kamaladevi was married off at the age of 14 and widowed two years later.
- Unperturbed by these life events, she joined Queen Mary’s College in Madras (now Chennai) for higher studies.
- There, she met Sarojini (Chattopadhyay) Naidu’s brother Harindranath Chattopadhyay which led to their wedlock.
- However, their marriage ended over incompatibility issues and this, too, created history – Kamaladevi was the first legal divorce granted through an Indian court of law.
- Kamaladevi played a prominent role in political reforms and India’s freedom struggle.
- She was the first woman to contest the Madras provincial elections.
- Though she lost by a narrow margin, she got recognition and was appointed secretary of the All-India Women’s Conference.
- She joined Indian National Congress in 1927 and was elected to the All-India Congress Committee within a year.
- During the Salt March to Dandi, she convinced Gandhi to give women equal opportunity to be in the forefront of the march.
- Later, she joined Seva Dal and trained women activists.
- However, the British government banned Seva Dal and threw Kamaladevi into jail.
- There, she contracted jaundice. Having experienced the pathetic condition of the prison hospital, she built a hospital for inmates upon release.
- Kamaladevi got attracted to socialism and took up the problems of laborers and peasants.
- During World War II, she visited America and met several political activists, mostly blacks, and shared with them India’s non-violent approach to freedom struggle.
- The British got wind of her activism and banned her from returning to India.
- Unmoved, Kamaladevi continued on her journey, visiting South Africa, China, Japan and Vietnam.
- Kamaladevi was inarguably the embodiment of women’s empowerment.
- She was an advocate of female sexual freedom and birth control.
- Her remarriage after widowhood and legal divorce from her second marriage were symbolic of her self-empowerment.
- She acted in many films (a Kannada film, too) when the film industry was not considered a respectable place for women.
- Indeed, Kamaladevi’s immense travel and experiences shaped her as a secular, socialist world citizen.
- Such were her ideals that led to her building the city of Faridabad to rehabilitate some 50,000 craftsmen who moved to India from Pakistan during Partition.
- Post-independence, she helped revive Indian handicrafts and built institutions for a ‘New India’-- to name a few, the National School of Drama, Bharatiya Natya Sangha, Lady Irwin College, Sangeet Natak Academy, Central Cottage Industries Emporium, World Craft Council, Craft Council of India, and the Delhi Craft Council.
- Kamaladevi was a prolific writer, too and wrote 18 books altogether, touching upon women’s issues, Indian handicrafts and her foreign visits.
- She published her autobiography, “Inner Recesses, Outer Spaces: Memoir” (1986).
- She received several awards in recognition of her public service, like Padma Bhushan and Padma Vibhushan, the Ramon Magsaysay Award and the UNESCO Award.
- She died in Mumbai on October 29, 1988, aged 85.
Every village to have agricultural credit societies by 2027

- 09 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah Friday said that the Centre has decided to ensure formation of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027.
Context:
- Union Cooperation Minister Amit Shah recently announced the Centre's commitment to establishing Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) in every village by 2027, introducing 20 new activities to enhance their profitability.
- Emphasizing the significance of computerization in PACS, Shah highlighted its role in fostering development opportunities.
- He also inaugurated the National Cooperative Database and unveiled the 'National Cooperative Database 2023: A Report' to bridge existing gaps through comprehensive analysis.
- The database initiative progressed through three phases, including mapping approximately 2.64 lakh societies across agriculture, dairy, and fisheries sectors in the first phase.
- Subsequent phases involved data collection from various federations, banks, and mapping of the remaining 8 lakh primary cooperative societies in other sectors.
- The unveiling revealed over 8 lakh registered societies in the country, connecting more than 30 crore citizens.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)?
- PACS are grassroots cooperative credit societies, constituting the final tier in a three-tier cooperative credit system led by State Cooperative Banks (SCBs) at the state level.
- SCBs channel credit to District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) operating at the district level, which collaborate with PACS, directly serving farmers.
- PACS operate as cooperative entities, with individual farmers as members and elected office-bearers from within the community. Villages may host multiple PACS.
- These societies extend short-term and medium-term agricultural loans to farmers for various farming activities.
Number of PACS in India:
- Established since 1904, India currently boasts over 1,00,000 PACS nationwide, engaging a significant member base exceeding 13 crore farmers.
- However, operational PACS stand at only 63,000, indicating the need for enhanced functionality and outreach.
Why are PACS Appealing?
- PACS offer crucial last-mile connectivity, ensuring farmers have access to capital at the onset of agricultural activities.
- They streamline credit extension processes, providing farmers with timely financial support with minimal paperwork, unlike traditional banks known for cumbersome procedures.
- PACS simplify paperwork and administrative tasks, offering farmers collective strength and assistance from PACS office-bearers.
- Unlike individual interactions required with commercial banks, PACS enable farmers to navigate loan processes collectively, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Challenges Faced by PACS:
- Political influences often overshadow financial prudence within PACS, impacting loan recovery.
- Various committees have highlighted systemic issues within the cooperative system, including low member participation, lack of professionalism, inadequate governance, bureaucratic hurdles, and a workforce with aging and disengaged employees.
Union Cabinet approves India AI Mission with 10,372 cr outlay

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
India has made its first move to address a key shortcoming it currently has in unlocking opportunities around generative artificial intelligence (AI) – that of computing hardware.
What is IndiaAI Mission?
- India's AI Mission entails the launch of an artificial intelligence (AI) initiative, announced by the Prime Minister at the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit 2023 in New Delhi, with implementation overseen by the 'IndiaAI' Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC).
- Led by the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY), the mission aims to establish a computing capacity exceeding 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) and develop foundational models trained on datasets encompassing major Indian languages, focusing on priority sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Additionally, the mission will involve the establishment of AI Curation Units (ACUs) in 50-line ministries and the creation of an AI marketplace to provide AI services and pre-trained models to AI application developers.
- Implementation of the AI computer infrastructure will follow a public-private partnership model, with 50% viability gap funding, with Rs 4,564 crore allocated from the total outlay of Rs 10,372 crore for building computing infrastructure.
Key Features of the IndiaAI Mission:
- IndiaAI Compute Capacity: Establishing a scalable AI computing ecosystem to meet the growing demands of India's burgeoning AI start-ups and research community.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre: Focusing on the development and deployment of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and domain-specific foundational models in critical sectors.
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: Streamlining access to high-quality non-personal datasets to fuel AI innovation.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative: Promoting the adoption of AI applications in critical sectors, addressing problem statements sourced from Central Ministries, State Departments, and other entities.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: Mitigating barriers to entry into AI programs by expanding AI courses at undergraduate, master's, and Ph.D. levels.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Supporting and accelerating deep-tech AI startups by providing streamlined access to funding for futuristic AI projects.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Ensuring the responsible implementation of AI projects through the development of indigenous tools and frameworks to foster trust and safety in AI applications.
The Significance of the IndiaAI Mission:
- The IndiaAI Mission aligns with the vision of fostering indigenous AI development and leveraging AI technology for the benefit of India.
- It aims to demonstrate to the international community the positive impact of AI technology on society, thereby enhancing India's global competitiveness.
- By establishing a comprehensive ecosystem for AI innovation through strategic partnerships across public and private sectors, the mission will catalyze AI-driven advancements.
- It will foster creativity and bolster internal capabilities, ensuring India's technological sovereignty.
- Furthermore, the mission is poised to create employment opportunities that demand advanced skills, leveraging India's demographic advantage.
After 10 years struggle, Mendha gets separate Panchayat status under Gramdan Act

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Maharashtra government recently notified Mendha, a village deep inside the forests of the state’s Gadchiroli district, as a separate Gram Panchayat under The Maharashtra Gramdan Act, 1964.
What is Gramdan?
- Gramdan is an expansion of the Bhoodan Movement started in 1951 by Aacharya Vinoba Bhave.
- ‘Bhoodan’ meant redistribution of land from bigger landowners to the landless.
- Under Gramdan, the entire village will put its land under a common trust.
- This way, the land will not be sold outside the village or to one who has not joined Gramdan in the village.
- But the landowners can continue to cultivate it and reap the benefits.
- The Movement paved the way for the protection of natural resources by giving equal rights and responsibilities to everyone in the community and empowering communities to move towards self-governance.
- Under the Act, at least 75 percent of landowners in the village should surrender land ownership to the village community for it to be declared as ‘gramdan’.
- Such land should at least be 60 percent of the village land. Five per cent of the surrendered land is distributed to the landless in the village for cultivation.
- Recipients of such land cannot transfer the same without the permission of the community.
- The rest remains with the donors.
- They and their descendants can work on it and reap the benefits.
- But they cannot sell it outside the village or to a village resident who has not joined Gramdan.
- Today, seven states in India have 3,660 Gramdan villages, the highest being in Odisha (1,309).
- The states are Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh.
- In September 2022, the Assam government repealed the Assam Gramdan Act, 1961 and Assam Bhoodan Act, 1965, bypassing The Assam Land and Revenue Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
- This, it said, was done to counter encroachment on donated lands in the state.
- Till that time, Assam had 312 Gramdan villages.
About Mendha’s Village Struggle:
- The village, comprising around 500 Gond Adivasis, has fought for its forests for years.
- It is popular as the first village in India to secure community forest rights (CFR), following the passing of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006.
- Some 80 per cent of the area in the village is covered with dense forest.
- People here believe that land is not a private property but a collective resource that provides food and livelihood and should be saved and passed on to the next generation.
- All villagers in Mendha have surrendered their land, which is unique. In all other villages, only about 75-80 per cent of landowners had agreed to do so.
- The village fulfilled these conditions of the Act in 2013 and notified the district collector about its decision to implement the Act.
Amit Shah launches National Cooperative Database, to help in policy making
- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
Cooperation Minister Amit Shah on Friday launched the National Cooperative Database and stressed that it would help in policy making.
About National Cooperative Database (NCD):
- The National Cooperative Database (NCD) is an initiative spearheaded by the Ministry of Cooperation, responding to the pressing need for a robust database to effectively capture essential information concerning India's extensive cooperative sector.
- Developed collaboratively with State Governments, National Federations, and stakeholders, the NCD is designed to promote a cooperative-centric economic model, offering a web-based digital dashboard for seamless data management.
- Acting as a centralized repository, the NCD aggregates data from cooperative societies, including National/State Federations, with information entered and authenticated by nodal officials at RCS/DRCS offices for cooperative societies and provided by various national/state federations for federations.
- The collected data encompasses diverse parameters, such as registered names, locations, membership numbers, sectoral details, operational areas, financial statements, audit statuses, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the cooperative landscape.
- Serving as a vital communication tool, the NCD facilitates efficient interaction between the Central Ministry, States/UTs, and Cooperative Societies, fostering collaboration and synergy within the cooperative sector.
- Key features and benefits of the NCD include single-point access, comprehensive and updated data, user-friendly interface, vertical and horizontal linkages, query-based reports and graphs, Management Information System (MIS) reports, data analytics, and geographical mapping capabilities.
Kerala declares man-animal conflict a state-specific disaster

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Amid repeated deaths from animal attacks and rising anger over them, Kerala recently declared man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, becoming the first state in the country to do so.
What is Man-animal Conflict?
- Man-animal conflict refers to the interaction between wild animals and humans, resulting in adverse outcomes for both people and wildlife, as well as their habitats.
- Escalating Conflict: In states across India, human-wildlife conflict has intensified, leading to a significant rise in human casualties.
- For instance, in Maharashtra, the conflict resulted in 86 in 2021 and 105 deaths in 2022, marking a sharp increase compared to previous decades.
Causes:
- Factors contributing to this conflict include the encroachment of grodeathswing human and animal populations into each other's territories, habitat fragmentation due to legal and illegal land use changes, alterations in cropping patterns attracting wildlife to agriculture, and habitat destruction from invasive alien species.
- Despite having over 700 protected areas, a substantial portion of elephant, lion, and tiger ranges lie outside these protected zones, exacerbating the conflict.
Ecologist Perspective:
- Ecologist Madhav Gadgil highlights that the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 has inadvertently facilitated an environment where wild animals can invade human habitats with impunity.
- He cites the optimal foraging theory in ecology, which underscores animals' efforts to maximize nutrient intake while minimizing time, effort, and risks.
Solutions:
- Addressing the issue requires robust enforcement and pragmatic policies to mitigate conflict incidences.
- Engaging local communities, as suggested by the Future for All Report 2021 (by WWF and UNEP), fosters coexistence between humans and wildlife, acknowledging that complete elimination of conflicts is impractical.
- Additionally, awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about man-animal conflict and skill development initiatives for communities living near forests can alleviate pressures on agricultural and forest lands.
Kerala's Decision to Declare Man-Animal Conflict as a State-Specific Disaster:
- Implications of the Decision: Currently, the management of man-animal conflict falls under the jurisdiction of the forest department, operating in accordance with the Wildlife Protection Act.
- By designating man-animal conflict as a state-specific disaster, the responsibility for addressing it shifts to the state disaster management authority, empowered by the Disaster Management Act, enabling swifter and more decisive action.
- Rationale for the Decision: Instances of loss of life due to man-animal conflict have prompted calls to tranquilize, capture, or eliminate the responsible animals.
- Presently, the chief wildlife warden, holding the sole authority in the state, makes decisions regarding wild animals causing disturbances in human settlements.
- Past decisions to tranquilize aggressive animals, like wild elephants, have faced legal challenges.
- Under the disaster management authority, actions can be taken that supersede other regulations, including those outlined in the Wildlife Protection Act.
- According to the Disaster Management Act, except for the Supreme Court or a High Court, no court has jurisdiction to entertain suits or proceedings regarding actions taken by relevant authorities in line with the Act.
- Additionally, the Act stipulates that its provisions hold precedence over any other law during the specific period of a declared disaster.
Kerala's Success in Managing Man-Animal Conflict:
- Kerala, with approximately 5,700 wild elephants in 2017, comprising 19% of the nationwide population of 30,000, witnessed a significantly lower incidence of human fatalities caused by elephants, accounting for only 81 (4%) of the 2,036 deaths recorded in India between 2018 and 2021.
- Factors Contributing to Kerala's Effective Management of Man-Animal Conflict:
- Maintenance of Unchanged Wilderness Boundaries: Kerala has largely preserved the boundaries between wilderness and civilization in recent years, contributing to the mitigation of man-animal conflicts.
- Evolution of Agricultural Practices: Changes in agricultural practices, such as the cultivation of crops like coffee, pepper, and tea, which hold less appeal for elephants, have helped reduce conflicts between humans and elephants.
- Unique Elephant Characteristics: Individual elephants are identified and named based on their distinct characteristics, such as Kabali, an elephant residing in the Athirapally jungle in Thrissur district, known for its tendency to attack or chase automobiles.
- These factors collectively contribute to Kerala's successful management of man-animal conflict, resulting in relatively fewer human fatalities caused by elephants compared to other regions in India.
Countries hope to bring BBNJ or High Seas treaty into force by 2025

- 08 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News
The Blue Leaders High-Level Event on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction was held in Belgium on March 7, 2024, to urge nations to ratify a new treaty to protect the high seas from pollution, climate change and overfishing.
What is the BBNJ Treaty?
- The BBNJ Treaty, also referred to as the Treaty of the High Seas, is an international agreement aimed at conserving and sustainably managing marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, operating within the framework of the UNCLOS.
- These areas encompass the high seas beyond exclusive economic zones or national waters.
- It represents nearly half of the Earth's surface and is characterized by minimal regulation and understanding of their biodiversity, with only 1% currently under protection.
- Launched at the One Ocean Summit in February 2022, the High Ambition Coalition on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction seeks to unite various delegations involved in BBNJ negotiations toward a comprehensive and ambitious outcome.
- The negotiations focus on key elements agreed upon in 2015, including the conservation and sustainable use of marine genetic resources, area-based management tools such as marine protected areas, environmental impact assessments, and initiatives for capacity-building and technology transfer in marine science and management.
- India is yet to sign the treaty. However, it called on efforts for entry into force and implementation of the treaty at the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration held in September 2023.
The Importance of a Legally Binding Instrument for BBNJ:
- Biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction is crucial for ocean health, coastal communities' welfare, and global sustainability, constituting 95% of the ocean and offering essential ecological, economic, social, cultural, scientific, and food-security benefits.
- Despite their significance, these areas face escalating threats such as pollution, overexploitation, and the impacts of climate change, compounded by the anticipated rise in demand for marine resources in the future.
- Even the deep seafloors, considered one of the most inhospitable habitats, are experiencing the onset of extinction processes, with alarming statistics showing that 62% of assessed mollusc species are threatened, including critically endangered, endangered, and vulnerable species, while the International Seabed Authority permits deep sea mining contracts.
- It is imperative to establish a legally binding framework for managing and regulating biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction, as over 60% of this resource in the global seas remains unmanaged and unprotected, necessitating comprehensive conservation measures.
ISRO’s second rocket launchport in Tamil Nadu’s Kulasekarapattinam

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of the second rocket launchport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) at Kulasekarapattinam on February 28.
Why does India need a new launchport?
- With the Union government’s recent policy announcing the opening of the space sector to private players, a sharp rise in the number of commercial launches is certain.
- To ensure that ISRO’s first launchport, the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR in Sriharikota, is not overburdened with a high number of launches, the space agency has decided to build another facility.
- While SHAR will be only used for launching bigger and heavy-lift-off missions, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport will be used to launch smaller payloads.
- SHAR will also be available for India’s big ticket missions to the Moon, Venus, and much touted human-flight mission, the Gaganyaan.
- Private players could develop space-qualified sub-systems, build satellites, and even launch vehicles using the new launchport.
- It will also facilitate dedicated launch infrastructure for all the on-demand commercial launches.
Why is the new ISRO launchport located in Tamil Nadu?
- Geographically, scientifically, and strategically, the Kulasekarapattinam launchport provides a natural advantage to ISRO’s future launches pertaining to the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
- Allowing a direct southward and smaller launch trajectory for the light weight SSLVs carrying less fuel, the Kulasekarapattinam facility will boost ISRO’s attempts to enhance payload capacities.
- Currently, the trajectory followed by all launches from SHAR are longer as they follow a path which requires the vehicle to skirt eastwards around Sri Lanka before taking the actual southward flight.
- This consumes additional fuel. However, the same would not be required for future launches from Kulasekarapattinam, which is geographically located several kilometers to the west of Colombo, thereby allowing a straight southward flight and simultaneously saving the already limited fuel available onboard SSLV.
- Notably, both the launch ports are located in Southern India, near the equator.
- For a launch site close to equator the magnitude of the velocity imparted due to Earth’s rotation is about 450 m/s, which can lead to substantial increase in the payload for a given launch vehicle.
- Geostationary satellites must necessarily be in the equatorial plane.
- So, for such satellites, the closer the launch site is to the equator the better it is.
What are SSLVs?
- SSLV is the new small satellite launch vehicle developed by ISRO to cater for the launch of small satellites.
- It has a three-stage launch vehicle, having a lift-off weight of about 120 tonnes and is 34 meters in length and 2 meters in diameter.
- SSLV is designed with a three-stage solid propulsion and a liquid propulsion stage, which is the terminal stage.
- The SSLV missions are useful to launch small-sized satellites weighing anywhere between 10 to 500kg into the Low Earth Orbit.
- Going by their size and weight, these are typically referred to as mini, micro or nano satellites.
- They are low on cost and intended satellite insertion into orbits takes a shorter flight time.
- SSLV are best suited for commercial and on-demand launches.
- Previously, satellite projects built by college students and private players involved in the space sector have benefitted from SSLV missions.
What are the features of SHAR?
- SHAR is situated along the east coast of Andhra Pradesh and is located 80 km off Chennai.
- It currently provides launch infrastructure to all ISRO missions.
- It is equipped with a solid propellant processing setup, static testing, and launch vehicle integration facilities, telemetry services — tracking and command network to oversee the launch — and a mission control center.
- SHAR has two launch complexes that are routinely used to launch the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), the Geosynchronous Space Launch Vehicles (GSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III, now renamed as LVM3.
Haiper, the text-to-video model created by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni

- 07 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, a company founded by former members of Google DeepMind, TikTok, and top labs from research academia — introduced an eponymous new text-to-video model Haiper.
What is Haiper?
- Haiper is an all-in-one visual foundation model that allows everyone, with or without technical training, to generate high-quality video content with ease.
- The founders claim that Haiper brings forward cutting-edge machine learning with the belief that creativity should be “fun, surprising, and shareable”.
- The company has built Haiper as a powerful, industry-agnostic creativity tool.
- It was released by Google DeepMind and Tiktok alumni.
What does Haiper do?
- Haiper offers tools such as text-to-video, animated static images, video repainting tools, etc.
- Users can go on to the website, log in with their email addresses, and start generating videos for free by typing in text prompts.
- At present, users can only generate HD video spanning 2 seconds, and a slightly lower-quality video could go up to four seconds.
Strengths and limitations:
- While the short length is a limitation, the company is working towards extending the video outputs.
- Presently, the tool is free to use, with an aim to build a community.
- While OpenAI’s Sora is still not available for the public, Haiper is offering users to try its tool for free on its website.
Exclusive-World on brink of fourth mass coral reef bleaching event- NOAA

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world stands on the brink of witnessing its fourth mass coral bleaching event, a phenomenon that threatens to hit vast expanses of tropical reefs, including significant portions of Australia's iconic Great Barrier Reef.
Key Findings from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
- Impending Fourth Mass Coral Bleaching Event: The world is on the brink of a fourth mass coral bleaching event, following those in 1998, 2010, and 2014.
- To classify as global, widespread bleaching must occur across three ocean basins: the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian.
- Impact of Previous Events: The last global mass coral bleaching event occurred from 2014 to 2017, resulting in the loss of nearly a third of the Great Barrier Reef's corals.
- Preliminary data indicates that approximately 15% of the world's reefs experienced significant coral die-offs during this event.
- Current Situation: This year is witnessing even more severe bleaching events, with the Caribbean experiencing its worst coral bleaching on record following the Northern Hemisphere summer last year.
- Link to Climate Phenomena: Coral bleaching is often associated with the naturally occurring El Niño climate phenomenon, which leads to warmer ocean waters.
- Climate Change Impact: The world recently experienced its first 12-month period with an average temperature exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- A temperature rise of 1.5°C is considered the tipping point for mass coral die-offs, with scientists estimating that 90% of the world's corals could be lost as a result.
About the Corals and Coral Reefs:
- Corals: Corals are animals known as polyps, which engage in a symbiotic relationship with tiny algae called zooxanthellae.
- These algae provide corals with food and oxygen, while corals offer them a safe habitat.
- Coral Reefs: Coral reefs are limestone structures formed by thousands of tiny coral animals and are predominantly found in tropical climates.
Coral Bleaching and Its Concerns:
- Coral bleaching occurs when corals are exposed to stressful conditions like high temperatures, pollution, or changes in water chemistry, leading them to expel the zooxanthellae.
- Without these algae, corals lose their color and turn white, hence the term 'bleaching,' and cannot survive for long in this state.
- Recovery Potential: Despite its severity, coral bleaching doesn't necessarily mean the end of the reef; timely removal of stressors can facilitate the return of zooxanthellae and coral recovery.
- Ecological Importance: Coral reefs serve as habitats and food sources for numerous fish and marine species.
- They also offer coastal protection from erosion and storms and play a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
- Cultural and Aesthetic Value: Beyond their ecological functions, coral reefs represent stunning biodiversity and natural beauty, making their loss a tragic prospect for future generations.
- Impacts: When coral reefs suffer, so do the ecosystems and communities reliant on them, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of coral degradation.
Google-backed satellite to track global oil industry methane emissions
- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
MethaneSAT — a satellite which will track and measure methane emissions at a global scale — was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California recently.
What is MethaneSAT?
- MethaneSAT will orbit the Earth 15 times a day, monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- It will create a large amount of data, which will tell “how much methane is coming from where, who’s responsible, and are those emissions going up or down over time”.
- The data collected by MethaneSAT will be made public for free in near real-time.
- This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Institutions involved in the development:
- The entity behind MethaneSAT is the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) — a US-based nonprofit environmental advocacy group.
- To develop the satellite, EDF partnered with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency.
Features of MethaneSAT:
- Historically, tracking the source of methane emissions and measuring them has been quite challenging.
- ?While some satellites can provide high-resolution data, they can only scan specific, pre-targeted sites.
- Others can examine larger areas and detect large emitting events, but cannot scan “smaller sources that account for the majority of emissions in many, if not most, regions,” the EDF statement added.
- Due to this discrepancy, according to an International Energy Agency (IEA) report, global methane emissions are about 70 per cent higher than levels reported by national governments.
- MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Equipped with a high-resolution infrared sensor and a spectrometer, the satellite will fill critical data gaps.
- It can track differences in methane concentrations as small as three parts per billion in the atmosphere, which enables it to pick up smaller emissions sources than the previous satellites.
- MethaneSAT also has a wide-camera view — of about 200 km by 200 km — allowing it to identify larger emitters so-called “super emitters”.
Significance of MethaneSAT:
- Advancing the Goals of the Global Methane Pledge 2021: The Global Methane Pledge, signed by over 150 countries in 2021, aims to reduce collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- During the previous year's COP, over 50 companies pledged to significantly reduce methane emissions and routine flaring.
- MethaneSAT will play a crucial role in helping these entities achieve their targets.
- Enhancing Transparency: The satellite will usher in a new era of transparency by providing publicly available data accessible to anyone worldwide.
- This data will enable monitoring of methane commitments made by governments and corporations, promoting accountability and transparency in emission reduction efforts."
Why Do We Need to Track and Measure Methane Emission?
- Methane is an invisible but strong greenhouse gas, and the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide, responsible for 30 percent of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- According to the United Nations Environment Programme, over a period of 20 years, methane is 80 times more potent at warming than carbon dioxide.
- The gas also contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone — a colorless and highly irritating gas that forms just above the Earth’s surface.
- According to a 2022 report, exposure to ground-level ozone could be contributing to one million premature deaths every year.
- Therefore, it is crucial to cut methane emissions and the main culprit, fossil fuel operations, which account for about 40 percent of all human-caused methane emissions.
- The objective of MethaneSAT is to help achieve this goal.
Holistic Progress Card: How NCERT is planning to change student assessment

- 06 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The New Education Policy (NEP), established in 2020, proposed redesigning the assessment system of school students in India recently.
About the Holistic Progress Card (HPC):
- It Is Developed by Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development (PARAKH), a standard-setting body under the NCERT.
- The Holistic Progress Card (HPC) marks a significant departure from traditional assessment methods for students in the foundational stage (Classes 1 and 2), preparatory stage (Classes 3 to 5), and middle stage (Classes 6 to 8), aligning with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Features:
- Incorporates feedback from parents, classmates, and self-evaluation by students.
- Aims to provide a comprehensive view of students' academic performance, cognitive abilities, socio-emotional skills, and creativity during class activities.
- Aligns with the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCFSE) to prioritize learner-centric evaluation.
- Emphasizes a shift from numerical grades to a 360-degree evaluation, focusing on students' active engagement in class activities and the demonstration of diverse skills and competencies.
- Enables teachers to identify students' strengths and weaknesses, fostering personalized support and intervention.
- Encourages students to reflect on their progress and set academic and personal goals, fostering self-awareness and accountability.
- Involves parents in the learning process, integrating their insights on homework, classroom engagement, and extracurricular activities.
- Includes peer evaluation, allowing students to assess their classmates' contributions to activities.
Benefits:
- Goes beyond numerical grades, providing descriptive and analytical evaluations that encompass academic achievements and critical skill development.
- Promotes a shift from summative to formative assessment, fostering competency-based evaluation and holistic growth.
India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s legal gender gap index

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
India's ranked improved to 113 out of 190 countries in the World Bank’s Women, Business and Law index, according to the 10th edition of the report released Monday.
About Women, Business and Law Index:
- The "Women, Business and the Law (WBL)" index is a project of the World Bank Group, specifically designed to measure the legal environment for women's economic opportunities across 190 economies.
- It's distinct from a general "Gender Equality Index" as it focuses specifically on legal frameworks and their impact on women's involvement in business and professional life.
What does it Measure?
- The WBL index assesses legal frameworks across eight indicators:
- Mobility (freedom of movement)
- Workplace (discrimination, maternity leave, etc.)
- Pay (equal pay for equal work)
- Marriage (property rights, domestic violence)
- Parenthood (parental leave, child custody)
- Entrepreneurship (starting and running a business)
- Assets (ownership and inheritance)
- Pension (access to and benefits)
- Scoring: Each indicator is scored on a scale of 0 to 100, with 100 representing the highest level of legal rights and protections for women.
- The overall score for a country is the average of these eight indicators.
- Latest version: The latest edition is "Women, Business and the Law 2024", released in October 2023.
- This version also introduces two new indicators:
- Safety (addressing violence against women)
- Childcare (availability, affordability, and quality)
Highlights of the Report:
- Women spend an average of 2.4 more hours a day on unpaid care work than men—much of it on the care of children.
- Only 62 economies—fewer than a third—have quality standards governing childcare services, which has an adverse impact on the employment opportunity of women as mothers with young children have their battles to pick.
- Women face hindrances in areas such as entrepreneurship as just one in every five economies mandate gender-sensitive criteria for public procurement processes, meaning women are deprived of significant economic opportunities.
About India:
- According to the 10th edition of the Women, Business and Law index, India ranks 113 out of 190 countries in the Index.
- The addition of Safety and childcare as indicators in the new index is believed to have improved India’s ranking slightly.
- The index shows that in India, women enjoy 60% of the legal rights compared to men, which is lower than the global average of 64.2%, but much higher than the 45.9% of the legal protections compared to men.
- Over the years, India’s score has remained constant at 74.4%, whereas a total of 14 countries around the world, including Denmark, Canada, and Finland, score a perfect 100 in the legal framework score.
- Some of the less developed countries like Ethiopia, Namibia, and even Burundi have better scores than India.
- India’s performance is much lower in providing supportive frameworks, such as programs, services, budgets, procedures, inspections, and sanctions for non-compliance with quality standards.
- Only 54.2% of the supportive frameworks needed were established in the country.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi witnessed the start of the process of core-loading the indigenous prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR) at the Madras Atomic Power Station in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
What is the PFBR?
- The PFBR, or Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor, is a nuclear reactor designed to produce more nuclear fuel than it consumes.
- In nuclear fission, the nucleus of an atom absorbs a neutron, becomes unstable, and splits into two, releasing energy.
- If the unstable nucleus releases additional neutrons, the reactor’s facilities can utilize them to initiate more fission reactions.
How does the PFBR work?
- PHWRs use natural or low-enriched U-238 as the fissile material and produce Pu-239 as a byproduct.
- This Pu-239 is combined with more U-238 into a mixed oxide and loaded into the core of a new reactor together with a blanket.
- This is a material the fission products in the core react with to produce more Pu-239.
- A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor that produces more fissile material than it consumes.
- In a ‘fast’ breeder reactor, the neutrons aren’t slowed, allowing them to trigger specific fission reactions.
- The PFBR is designed to produce more Pu-239 than it consumes.
- It uses liquid sodium, a highly reactive substance, as coolant in two circuits. Coolant in the first circuit enters the reactor and leaves with (heat) energy and radioactivity.
- Via heat-exchangers, it transfers only the heat to the coolant in a secondary circuit.
- The latter transfers the heat to generators to produce electricity.
DoT launches Digital Intelligence Portal, ‘Chakshu’ facility to curb cyber crimes, financial frauds

- 05 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) recently launched its ‘Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP)’ to curb the misuse of telecom resources in cybercrimes and financial frauds, and the ‘Chakshu’ facility on the Sanchar Saathi portal to enable citizens to report suspected fraud communication.
About Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP):
- Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP) is developed by the Department of Telecommunications.
- It is a secure and integrated platform for real time intelligence sharing, information exchange and coordination among the stakeholders i.e. Telecom Service Providers (TSPs), law enforcement agencies (LEAs), banks and financial institutions (FIs), social media platforms, identity document issuing authorities etc.
- The portal also contains information regarding the cases detected as misuse of telecom resources. The shared information could be useful to the stakeholders in their respective domains.
- It also works as a backend repository for the citizen-initiated requests on the Sanchar Saathi portal for action by the stakeholders.
- The DIP is accessible to the stakeholders over secure connectivity and the relevant information is shared based on their respective roles.
- The said platform is not accessible to citizens.
What is the Chakshu Facility?
- Chakshu is the latest addition to the citizen centric facilities already available on the Sanchar Saathi portal of DoT.
- It facilitates citizens to report suspected fraud communication received over call, SMS or WhatsApp with the intention of defrauding like KYC expiry or update of bank account / payment wallet / SIM / gas connection / electricity connection, sextortion, impersonation as government official / relative for sending money, disconnection of all mobile numbers by Department of Telecommunications etc.
- In case, a citizen is already a victim of cyber-crime or financial fraud, it is advised to report at cyber-crime helpline number 1930 or website https://www.cybercrime.gov.in of Government of India.
Grey-zone Warfare Latest Entry in Lexicon of Warfare

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
On the last day of the 2024 Raisina Dialogue (February 24), India’s Chief of Defence Staff General Anil Chauhan said that “grey zone warfare” is the latest in informal warfare.
What is the Grey Zone Warfare?
- Grey zone warfare refers to a strategic approach where a nation seeks to gain advantages over others without engaging in overt conflict.
- It involves a series of tactics, including cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and economic pressures, aimed at subtly undermining or destabilizing adversaries.
- China has notably employed this strategy against India and neighboring countries.
What are the China's Grey Zone Tactics Against India?
- South China Sea Activities: China asserts its dominance in the South China Sea using naval and civilian vessels, raising tensions with neighboring countries like India.
- Infrastructure Near Borders: China constructs infrastructure and settlements near India's borders, bolstering territorial claims and strategic positioning.
- Digital Investments: China invests in Indian digital platforms and media, influencing public narratives and perceptions.
India's Counter-Measures:
- Inter-Agency Collaboration: India promotes collaboration among defense, intelligence, and law enforcement agencies to devise comprehensive strategies to counter grey zone threats.
- Enhanced Vigilance: India increases surveillance and presence in border areas and strategic locations to detect and respond to covert Chinese activities.
- Regulating Foreign Investments: India scrutinizes foreign investments in critical sectors, particularly technology, to safeguard national security interests.
Long-Term Implications for India:
- Information Warfare: Grey zone conflicts often involve digital misinformation, influencing public opinion and perceptions.
- Economic Leverage: Dependency on foreign investments poses vulnerabilities if used as leverage by investing nations.
- Technology Dependency: Heavy reliance on foreign technology exposes India to risks, emphasizing the need to bolster indigenous technological capabilities.
Conclusion
Grey zone warfare encompasses a multifaceted strategic landscape, blending digital, economic, and geopolitical tactics. India recognizes these challenges and is actively devising strategies to navigate this complex terrain.
Several OPEC+ nations extend oil cuts to boost prices

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Moscow, Riyadh, and several other OPEC+ members announced extensions to oil production cuts first announced in 2023 as part of an agreement among oil producers to boost prices following economic uncertainty.
What is the OPEC+ Oil Alliance?
- OPEC+ is a coalition of oil-exporting nations that convenes regularly to determine the quantity of crude oil to offer on the global market.
- Origin: This alliance was established in late 2016 to formalize a framework for collaboration between OPEC and non-OPEC oil-producing nations on a consistent and sustainable basis.
- The primary objective of these nations is to collaborate on regulating crude oil production to stabilize the oil market.
- OPEC+ collectively controls approximately 40% of global oil supplies and holds over 80% of proven oil reserves.
- At its core, OPEC+ consists of OPEC member states, predominantly comprising nations from the Middle East and Africa.
- Membership: It includes OPEC member states along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Russia, Mexico, Malaysia, South Sudan, Sudan, and Oman.
About the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC):
- OPEC, short for the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, is a permanent intergovernmental organization comprised of oil-exporting nations.
Mission:
- To coordinate and harmonize the petroleum policies of its member countries.
- To ensure the stability of oil prices in global oil markets, aiming to eliminate detrimental and unnecessary fluctuations.
- Formation: Founded in 1960 by the five original members - Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Presently, it consists of 13 member countries, which include Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Headquarters: Located in Vienna, Austria.
India halts Pakistan-bound ship suspected of carrying CNC machines from China

- 04 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Indian security agencies have intercepted a Pakistan-bound ship from China at Mumbai's Nhava Sheva port.
What are CNC Machines and Wassenaar Arrangements?
- CNC machines are controlled by a computer and offer efficiency, consistency, and accuracy not possible manually.
- These machines have been included in the Wassenaar Arrangement since 1996.
- This international arms control regime aims to stop the proliferation of equipment with both civilian and military uses, with India being among the 42 member countries exchanging information on transfers of conventional weapons and dual-use goods and technologies.
About the Wassenaar Arrangement:
- The Wassenaar Arrangement is a voluntary export control framework established in July 1996.
- Comprising 42 member nations, it facilitates the exchange of information regarding transfers of conventional weaponry and dual-use goods and technologies.
- Dual-use items possess the capacity for both civilian and military applications.
- The arrangement's secretariat is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
Membership:
- The arrangement boasts 42 member states, predominantly consisting of NATO and EU nations.
- Members are obligated to report arms transfers and dual-use goods and technology transfers or denials to destinations beyond the arrangement biannually.
- India became a member of the Arrangement in 2017.
Objectives:
- Central to its operation is the continual exchange of technology-related information, encompassing both conventional and nuclear-capable technologies, among member states.
- This information exchange involves the maintenance and refinement of comprehensive lists of materials, technologies, processes, and products deemed militarily significant.
- The primary goal is to regulate the movement of technology, materials, or components to entities or nations that could jeopardize global security and stability.
Wassenaar Arrangement Plenary:
- The WA Plenary is the decision-making and governing body of the Arrangement.
- It is composed of representatives of all Participating States who normally meet once a year, usually in December.
- Chairmanship of the Plenary is subject to annual rotation among Participating States.
- In 2018, the United Kingdom held the Plenary Chair, while Greece assumed the position in 2019.
- Decisions within the Plenary are made through consensus.
How India’s first semiconductor fabrication plant can help plug into the global value chain

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently approved the country's first semiconductor fab to be made by the Tata Group in collaboration with Powerchip Taiwan.
What is Semiconductor Fabrication?
- The semiconductor fabrication process is a complex and highly specialized series of steps that transform raw materials into functional electronic components.
- This process involves a multitude of techniques and technologies, with each stage requiring precise control and attention to detail.
- A semiconductor fab -- short for fabrication -- is a manufacturing plant in which raw silicon wafers are turned into integrated circuits (ICs).
- A fab lab features a clean room where ICs are etched onto wafers.
- The completed chips are sent to a back-end assembly and test facility before they are packaged and sold.
- A semiconductor fab facility always includes a clean room -- so known because its environment is carefully controlled to eliminate dust and vibrations and to keep the temperature and humidity within a specific narrow range.
- Contamination can enter the fab environment through external sources, resulting in damage to products that can affect overall yield.
- To minimize the losses, all potential sources of contamination are thoroughly analysed and cleaned.
- For example, the tools used in the chip manufacturing process have low levels of particulates and fibres.
- The goal is to ensure that extraneous contamination is not introduced into the semiconductor fab to ensure the highest quality of the final products.
Technology Used in Semiconductor Fab Labs:
- Photolithography: Photolithography is a crucial optical process in the fabrication process, as it is used to create intricate circuit patterns on a single wafer's surface.
- This is achieved by coating the wafer with a photosensitive material, called a photoresist, and then exposing it to high-wavelength deep ultraviolet (DUV) or extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light through a mask containing the desired pattern.
- The exposed photoresist undergoes a chemical change, which allows it to be selectively removed.
- It leaves behind a patterned layer that serves as a protective layer for subsequent processing steps, such as etching and deposition.
Minimum age to cast postal ballots hiked to 85 years

- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
For the upcoming Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections, senior citizens who are 85 years and older will be able to opt for postal ballots as the government recently amended the rule to increase the eligibility from the current limit of 80 years and above.
News Summary:
- The government, in collaboration with the Election Commission, has introduced amendments to the Conduct of Election Rules (1961), specifically targeting the eligibility criteria for voting by postal ballot.
- Notably, the minimum age for senior citizens eligible for postal voting has been increased from 80 years to 85 years.
- Previously, Rule 27A of the Conduct of Election Rules had extended the postal ballot facility to senior citizens above 80 years, persons with disabilities, poll officers, and individuals diagnosed with COVID-19.
- This provision was first implemented during the 2020 Bihar assembly polls, coinciding with the onset of the pandemic.
- Despite the initial extension of postal voting rights to senior citizens aged 80 and above, a subsequent review by the Election Commission revealed that only a small fraction, approximately 2-3%, of eligible voters in this age group opted for postal ballots.
- The majority preferred to physically visit polling stations to cast their votes.
- Considering the statistics indicating that the total number of senior citizens above 80 years stands at 1.75 crore, with 98 lakh falling within the age range of 80-85 years, the government deemed it necessary to amend the existing rule.
- This adjustment reflects a nuanced approach aimed at ensuring efficient electoral processes while addressing the preferences and needs of elderly voters.
What is Postal Voting?
- Postal voting is only available to a specific group of voters.
- By retyping her choices on the ballot paper and returning it to the inspection officer before counting, a voter can remotely cast her ballot using this feature.
Who Can Avail This?
- Armed forces members such as those in the Army, Navy, and Air Force, armed police officers serving outside their home states, government workers stationed outside of India, and their wives are only eligible to vote by mail.
Features:
- Voters may use this service from any location outside of the designated constituency.
- This system makes it easier to create voter electoral roll data for services.
- It has two layers of security, making it a secure system:
- 1. Downloading the encrypted electronically transmitted postal ballot (ETPB) file requires an OTP (one-time password).
- 2. To decrypt, print, and deliver ETPB, a PIN is necessary.
- By sending postal ballots electronically to eligible service voters, this system addresses the time constraint associated with mailing postal ballots.
- The specific quick response code ensures confidentiality and prevents the duplication of cast ETPB.
Concerned Raised by Political Parties:
- Parties argue that allowing voters 65 and older to cast postal ballots violates voting confidentiality since many of the population lacks education and may ask for help from others at various points, ultimately identifying their chosen candidate.
- Their exposure to "administrative influence or influence by the government or the ruling party" also results from this.
How the development of Agaléga figures in India’s vision for its maritime neighbourhood
- 02 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Prime Ministers Narendra Modi and Pravind Jugnauth jointly inaugurated an airstrip and the St James Jetty on North Agaléga Island in the Indian Ocean.
About Agalega Islands:
- Agaléga Island comprises two islets, a long and thin northern island and a shorter, round southern island.
- It is slightly over 3,000 kilometres from the nearest mainland Indian coast, deep in the Indian Ocean near Madagascar.
- Despite its pristine appeal, Agaléga remains largely undiscovered by tourists and there are no hotels, water bungalows, or bustling tourist shops.
- Instead, approximately 300 islanders sustain themselves through coconut cultivation and fishing, maintaining a way of life passed down through generations.
Importance of Agalega Islands:
- The development of the Agalega Islands holds significant socio-economic and national security implications for Mauritius, aligning closely with India's maritime vision.
- Despite being a dependency of Mauritius, the islands have long remained underdeveloped, posing challenges to the sustainability and well-being of their inhabitants.
- Necessities often required referral to Mauritius due to the lack of infrastructure.
- Moreover, the absence of an official government or security presence posed a serious vulnerability, necessitating urgent attention.
- Recognizing the potential to transform this vulnerability into a strategic asset, Mauritius prioritized the development of the islands and the establishment of facilities capable of accommodating ships and aircraft.
- In this regard, the construction of a jetty and an airstrip emerged as imperative steps to bolster the islands' infrastructure.
- Given the shared interests and cooperation between Mauritius and India, the government of Mauritius selected India as its preferred development partner for this ambitious initiative.
Why did Mauritians Choose India?
- Ties between India and Mauritius go back to 1948, 20 years before the country’s independence from Britain.
- Seventy percent of the inhabitants of Mauritius are of Indian origin, and the two countries share deep historical, social, and cultural bonds.
- The consistent feature in the history of bilateral relations has been friendship and trust at all levels — the political leadership, the diplomatic and military communities, as well as between the peoples of the two countries.
- The development of these strategically located islands required trust more than anything else. India was the obvious choice.
Significance for India:
- The goodwill and trust between the two countries will be further enhanced. India will welcome opportunities to further develop these islands in collaboration with Mauritius as the latter deems appropriate.
- The joint development of Agaléga underscores India’s commitment to the vision of Security And Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), and its willingness to assist smaller maritime nations in building capacity and developing capability.
- It will indicate to other maritime neighbours that India is a benign and friendly country that respects the sovereignty of independent nations.
- India would like to emerge as the preferred development and security partner in the Indian Ocean Region.
Doomsday Glacier has lost 50 billion tons of ice, melting began 80 years ago

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Antarctica's Doomsday Glacier, the world's widest glacier, has lost over 50 billion tons of ice and the melting rate is on the rise as the continent gets warmer.
What is Doomsday Glacier?
- The Thwaites Glacier (also known as Doomsday Glacier), a massive and world’s widest glacier is located in West Antarctica.
- The Doomsday nickname reflects the potential for catastrophic flooding if the glacier were to collapse completely.
- Scientists are particularly concerned about Thwaites Glacier because of its size and location.
- If it were to collapse or significantly retreat, it could lead to a more rapid flow of ice from the interior of West Antarctica into the ocean, contributing to rising sea levels.
- The collapse could lead to a 65 cm rise in global sea level.
- The ice loss in the region has been observed to be accelerating since the 1970s, however, so far it remained unclear as to when this retreat began.
- The significant glacial retreat began in the 1940s and the findings coincide with previous work that studied retreat on Pine Island Glacier and found glacial retreat began in the ‘40s as well.
- This change is not random nor specific to one glacier but It is part of a larger context of a changing climate.
Why Did the Melting Begin?
- The meeting was kicked off by an extreme El Nino climate pattern that warmed the west Antarctic, and since then the glacier has not been able to recover from the damage.
- It is significant that El Niño only lasted a couple of years, but the two glaciers, Thwaites and Pine Island remain in significant retreat.
- Once the system is kicked out of balance, the retreat is ongoing.
- The Doomsday Glacier's melting remains one of the most crucial events triggered and accelerated by climate change and could lead to the submergence of several coastal regions of the world.
ZSI names a newly discovered head-shield sea slug after President Droupadi Murmu
- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Zoological Survey of India named a new marine species of head-shield sea slug with ruby red spot which was discovered from West Bengal and Odisha coast after President of India Droupadi Murmu.
About Melanochlamys Droupadi:
- Melanochlamys Droupadi is a newly discovered marine species of head-shield sea slug distinguished by its striking ruby red spot.
- This species, belonging to the Melanochlamys genus, was first identified along the coasts of Digha in West Bengal and Udaipur in Odisha.
Key Features:
- This small invertebrate typically measures up to 7 mm in length.
- It primarily inhabits wet and soft sandy beaches.
- Adorned in brownish-black hues, it features a distinctive ruby-red spot towards its hind end.
- Melanochlamys Droupadi exhibits hermaphroditic characteristics, possessing both male and female reproductive organs. However, it requires another sea slug for successful reproduction.
- Internally, it possesses a shell and a posterior segment comprising 61 per cent of its body length.
- To safeguard against sand infiltration, it continuously secretes transparent mucus, forming a protective sheath around its body.
- When in motion, it burrows beneath smooth sand, creating a moving capsule where its body remains mostly concealed, akin to a turtle, leaving behind a discernible trail.
What are Sea Slugs?
- Sea slugs are a diverse group of molluscs inhabiting marine environments, characterized by their slug-like appearance.
- They occupy a wide range of habitats, spanning from shallow intertidal zones to the depths of the ocean, and from polar regions to tropical waters.
- As agile predators, sea slugs prey on mobile organisms such as other shelled and unshelled sea slugs, roundworms, marine worms, and small fish.
- Currently, researchers have identified 18 species of sea slugs worldwide.
- While sea slugs predominantly inhabit temperate regions within the Indo-Pacific Oceanic realm, three species exhibit truly tropical distributions: Melanochlamys papillata from the Gulf of Thailand, Melanochlamys bengalensis from the West Bengal and Odisha coast, and the newly discovered species.
World's First Vedic Clock to be Unveiled by PM Modi in Ujjain
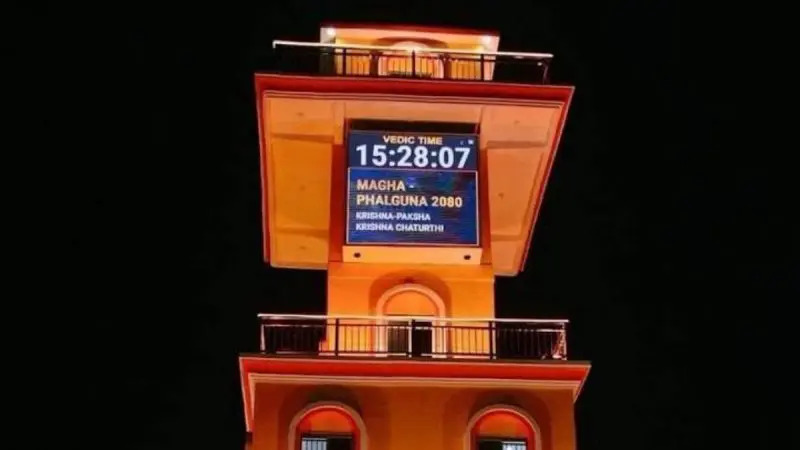

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the Vedic Clock in Ujjain as part of the 'Vikramotsav' celebration in Madhya Pradesh.
Features of the Vikramaditya Vedic Clock:
- This is the world's first 'Vedic Clock', designed to display time according to the ancient Indian traditional Panchang (time calculation system).
- The clock is installed on an 85-foot high tower constructed at Jantar Mantar in Ujjain, adjacent to the Government Jiwaji Observatory.
- It will display 30 Muhurats, tithi, and all other time calculations of Vedic Hindu panchang.
- Additionally, Samvat, Mas, moon position, Parva, Shubhshubh Muhurat, Ghati, Nakshatra, solar eclipse, and lunar eclipse, among other things
- It will be the world’s first clock in which Indian time calculation will be displayed.
- The Vedic clock installed in Ujjain as the city has been considered the centre of time calculation.
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through Ujjain.
Time calculation:
- The unique timepiece calculates time-based on Vedic Hindu Panchang, planetary positions, Muhurat, astrological calculations, solar eclipse, and lunar eclipse, among other things, and also indicates the Indian Standard Time (IST) and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- The period from one sunrise to the next is used to calculate time.
- The clock will calculate time from one sunrise to another.
- The time period between the two sunrises will be divided into 30 parts, with each hour consisting of 48 minutes according to ISD.
- The reading will start from 0.00 with the sunrise functions for 30 hours (an hour of 48 minutes).
- Also, there will be a dedicated mobile application for the readings of the Vedic Clock, and citizens will be able to use it on their smartphones, computers, televisions, and other devices.
Why It is Located in Ujjain?
- The standard time of the world was determined from Ujjain 300 years ago.
- Throughout the world, the time prescribed and transmitted from Ujjayini (Ujjain) has been followed.
- The shortest fraction of time is included in Indian time calculations based on the Indian astronomical theory and the motions of planetary constellations.
- Ujjain was previously thought to be India’s central meridian, and the city determined the nation’s time zones and time differences, according to Hindu astronomical belief.
- The city of Lord Mahakal is situated exactly where the Tropic of Cancer and Zero Meridians meet.
- Additionally, it is situated in the oldest observatory in India, which Sawai Jai Singh II of Jaipur constructed in the early 1700s.
- Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh, which is located at 82°30’ East longitude, is the location of the zero meridians on the Prime Meridian, or IST, four hours ahead of GMT, according to the 1884 convention on meridians.
India to set up International Big Cat Alliance

- 01 Mar 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Environment Ministry plans to set up and coordinate an International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), along the lines of the International Solar Alliance, an India-headquartered initiative to promote solar installations globally.
About the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA):
- The idea of the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) was first given by Prime Minister Modi during his speech on the occasion of Global Tiger Day in 2019.
- He called for developing an alliance of global leaders to curb poaching in Asia.
- The alliance was formally announced on April 9, 202, in Mysuru, as India commemorated the completion of 50 years of Project Tiger.
- The alliance will focus on the conservation of seven big cats, which include Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar, and Cheetah. Out of these, five are found in India.
- Membership to the IBCA is open to 97 'range' countries, encompassing the natural habitats of these big cats, as well as other interested nations and international organizations.
- The alliance aims to facilitate cooperation among countries to advance the conservation agenda for mutual benefit.
- Operating with a multifaceted approach, the IBCA endeavours to establish robust linkages across various domains, including knowledge sharing, capacity building, networking, advocacy, financial and resource support, research, technical assistance, education, and awareness.
- Governance of the alliance consists of a General Assembly comprising all member countries, a Council comprised of seven to fifteen member countries elected by the General Assembly for a five-year term, and a Secretariat.
- The IBCA Secretary General, appointed by the General Assembly upon the Council's recommendation, serves a specific term.
- To support its initiatives, the IBCA has secured initial funding of Rs. 150 crore from the Government of India for the period spanning from 2023-24 to 2027-28.
RBI tweaks norms related to the Regulatory Sandbox scheme

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Reserve Bank recently tweaked guidelines for the Regulatory Sandbox (RS) scheme under which participating entities will have to comply with digital personal data protection norms.
About the Regulatory Sandbox Scheme:
- The Regulatory Sandbox scheme denotes a controlled regulatory environment where new products or services can undergo live testing.
- Functioning as a "safe space" for businesses, regulators may offer certain relaxations for testing purposes within this environment.
- It serves as a structured platform for regulators to engage with the industry and develop regulations that foster innovation and enable the delivery of cost-effective financial products.
- The scheme holds potential as a tool for creating dynamic regulatory environments that adapt to emerging technologies through evidence-based learning.
Objectives:
- Offering innovative technology-led entities an opportunity for limited-scale testing of new products or services, potentially involving regulatory relaxations before broader implementation.
- At its core, the Regulatory Sandbox is a formal program allowing market participants to test new products, services, or business models in live settings, under appropriate oversight.
- Proposed financial services under the scheme should leverage new or emerging technology to address consumer needs or offer benefits.
- The overarching goal is to promote responsible innovation in financial services, enhance efficiency, and deliver consumer benefits.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the 'Enabling Framework for Regulatory Sandbox' in August 2019 after extensive consultations.
- The updated framework mandates compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act of 2023 for sandbox entities.
- Furthermore, the timeline for various stages of the Regulatory Sandbox process has been extended from seven to nine months.
- Fintech companies, including startups, banks, financial institutions, and other entities providing support to financial services businesses, are among the target applicants for entry into the Regulatory Sandbox.
PM Modi lays stone for India’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam
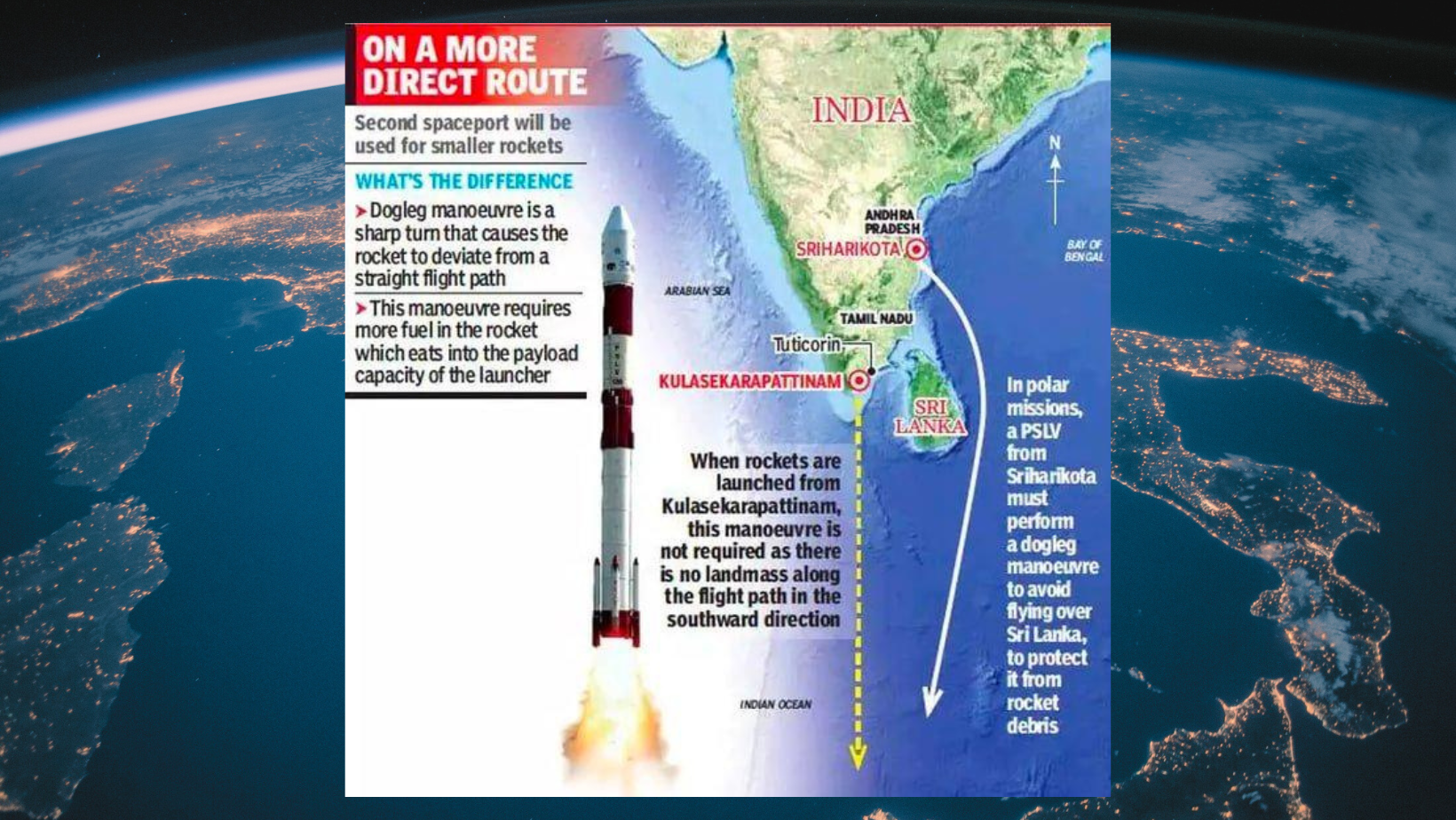
- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone for the country’s second spaceport at Kulasekarapattinam in Tuticorin district recently.
About Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport:
- The Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport is a forthcoming space launch facility located in Kulasekarapattinam, a coastal village near the temple town of Tiruchendur in Thoothukudi district, southern Tamil Nadu.
- It will become the second operational spaceport in India after the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, established in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, in 1971, and will feature two launch pads.
- The primary focus of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport will be to facilitate the commercial launch of Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs).
- Spanning 2,350 acres, the spaceport will comprise 35 essential facilities, including a launch pad, rocket integration facilities, ground range and checkout facilities, and a mobile launch structure (MLS) equipped with checkout computers.
- With the capability to launch up to 24 satellites annually using a mobile launch structure, it offers a strategic advantage by enabling direct southward launches over the Indian Ocean, thus conserving fuel for small rocket launches.
- This stands in contrast to the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, where launching into a polar orbit necessitates additional fuel due to the curved trajectory required to avoid crossing landmasses, particularly Sri Lanka.
- The estimated cost of the Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport project is Rs. 986 crore.
About the Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs):
- The SSLV, or Small Satellite Launch Vehicle, is a three-stage launch vehicle characterized by three solid propulsion stages and a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) serving as a terminal stage.
- Measuring 2 meters in diameter and 34 meters in length, the SSLV boasts a lift-off weight of 120 tonnes.
- Designed for versatility, the SSLV can effectively launch a 500kg satellite into a 500 km planar orbit.
- Notable features of the SSLV include its cost-effectiveness, rapid turnaround time, ability to accommodate multiple satellites, feasibility for launch-on-demand, and minimal infrastructure requirements.
New waste management technology could improve life in rural India

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A new waste management technology that allows pyrolysis at a community level could help rural Indians cut indoor air pollution, improve soil health, and generate clean power, a recent study has claimed.
What is BioTRIG?
- BioTRIG represents a novel waste management technology centered around pyrolysis, poised to mitigate indoor air pollution, enhance soil quality, and foster clean energy generation across rural India.
- This community-oriented pyrolysis system is ingeniously crafted to utilize locally generated waste, offering a sustainable solution tailored to village environments.
- The innovative process yields three valuable by-products: bio-oil, syngas, and biochar fertilizer, presenting multifaceted benefits for rural communities, from cleaner energy sources to enhanced agricultural productivity.
- Moreover, the self-sustaining nature of BioTRIG enables the utilization of syngas and bio-oil to fuel subsequent pyrolysis cycles, with excess electricity catering to local energy needs, fostering self-reliance and sustainability.
- By harnessing the clean-burning properties of bio-oil and the soil-enriching qualities of biochar, BioTRIG empowers rural households to transition away from traditional cooking fuels while concurrently enhancing agricultural resilience and carbon sequestration efforts.
Significance:
- Computer simulations indicate that the BioTRIG system holds the potential to significantly mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from communities, potentially reducing them by nearly 350 kg of CO2-eq per capita per year.
- This projection underscores a noteworthy positive influence on both climate emissions and public health.
- The BioTRIG technology could mark a paradigm shift in waste management practices and energy generation methods within rural India, promising transformative benefits for communities.
What is Pyrolysis?
- Pyrolysis is a transformative chemical recycling method that disassembles residual organic matter into its fundamental molecular components.
- This innovative process entails confining the waste within an oxygen-deprived enclosure and subjecting it to temperatures exceeding 400 degrees Celsius.
Education Minister launches SWAYAM Plus platform

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Union Minister of Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Dharmendra Pradhan recently launched the ‘SWAYAM Plus’ platform to offer courses developed collaboratively with the industry.
About the SWAYAM Plus Platform:
- SWAYAM is a Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platform providing educational opportunities by bringing the best teaching and learning resources to everyone.
- Operated by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)-Madras, this platform aims to extend educational opportunities to both traditional students and working professionals, aligning with the provisions of the NEP 2020 for flexible entry and exit points in education.
- By enabling individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, SWAYAM Plus empowers them to enhance their skills and career prospects, thus contributing to India's knowledge economy.
Objectives and features:
- SWAYAM Plus primarily focuses on achieving the following:
- Building an ecosystem for all stakeholders in professional and career development, including learners, course providers, industry, academia, and strategic partners;
- Enabling a mechanism that provides credit recognition for high?quality certifications and courses offered by the best industry and academia partners;
- Reaching a large learner base by catering to learning across the country, with a focus on reaching learners from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas and Offering employment-focused courses, based on learner needs – across chosen disciplines with options to learn through resources in vernacular languages.
- Enhanced employability: SWAYAM Plus empowers individuals to balance work and studies through online courses, enhancing skills and career prospects.
- Industry partnerships: Courses are tailored to industry requirements in collaboration with industry leaders.
Key features:
- Multilingual content, AI guidance, credit recognition, and pathways to employment are prominent features.
Implementation and reach:
- SWAYAM Plus aims to offer high-quality courses with credit recognition, reaching learners nationwide, especially from tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas.
Value-added services:
- Value-added services like mentorship, scholarships, and job placements will be provided, creating a digital ecosystem for upskilling and reskilling at all education levels.
- SWAYAM, launched in 2017, had enrolled 72 lakh learners by 2023.
- Now, in line with the NEP 2020, SWAYAM Plus will incorporate courses tailored to industry requirements, developed in collaboration with industry leaders like L&T, Microsoft, and CISCO.
European Parliament adopts nature restoration law

- 29 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The European Parliament recently adopted the first European Union (EU) law to restore degraded ecosystems across the 27-nation political and economic bloc.
About the Nature Restoration Law:
- The Nature Restoration Law is hailed as a significant stride toward rejuvenating Europe’s natural habitats, with a staggering 81% currently classified as being in poor health.
- It sets a pioneering example for global emulation, emphasizing the criticality of safeguarding and revitalizing our natural environment for the welfare of forthcoming generations.
Objectives:
- This legislation aims to rejuvenate ecosystems, habitats, and species across the European Union's (EU) terrestrial and marine domains, fostering the enduring recuperation of diverse and robust nature.
- Additionally, it endeavors to contribute to the EU's climate mitigation and adaptation objectives while fulfilling international commitments.
- These directives aspire to encompass a minimum of 20% of the EU's land and marine territories by 2030, with the ultimate goal of restoring all ecosystems in need by 2050.
Specific Targets:
- Wetlands, forests, grasslands, rivers, lakes, heath & scrub, rocky habitats, and dunes: The objective is to enhance and restore biodiverse habitats on a large scale, fostering the recovery of species populations through habitat improvement and expansion.
- Pollinating Insects: The target is to reverse the decline of pollinator populations by 2030, aiming for a positive trajectory in pollinator numbers.
- Forest Ecosystems: The aim is to promote an upward trend in standing and fallen deadwood, varied aged forests, forest connectivity, common forest bird populations, and organic carbon reserves.
- Urban Ecosystems: The objective is to achieve zero net loss of green urban spaces by 2030 and expand the total area covered by green urban spaces by 2040 and 2050.
- Agricultural Ecosystems: The goal is to bolster grassland butterfly and farmland bird populations, increase organic carbon reserves in cropland mineral soils, and augment the proportion of agricultural land featuring diverse landscape characteristics.
About the European Union (EU):
- The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 European countries that collaborate on various issues, including trade, security, and environmental protection.
- Founded after World War II to promote peace and economic cooperation, the EU has evolved into a complex organization with its own institutions, laws, and currency (the euro).
- It operates on the principles of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, with the European Commission, European Parliament, and European Council among its key decision-making bodies.
- The EU's single market allows for the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people across member states, fostering economic growth and prosperity.
- Additionally, the EU plays a prominent role in global affairs, advocating for multilateralism, sustainable development, and climate action.
Scientists are closer to creating a reference genome for Indians; 10,000 samples sequenced already

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Government’s ambitious Genome India initiative achieved a significant milestone Tuesday as researchers completed sequencing 10,000 healthy genomes from different regions of the country, representing 99 distinct populations.
News Summary:
- The Department of Biotechnology has announced the successful completion of India's '10,000 genome' project, aimed at establishing a comprehensive reference database of whole-genome sequences within the country.
- This milestone marks the creation of a detailed genetic map of India, offering significant potential for both clinicians and researchers in diverse fields.
- With India emerging as the largest genetic laboratory globally, this rich dataset is poised to catalyze advancements in the country's biology sector.
- Notably, India's bio-economy has witnessed remarkable growth, expanding from $10 billion in 2014 to over $130 billion in 2024, signaling a promising trajectory for future development.
- The entirety of the genomic dataset will be housed at the Indian Biological Data Centre (IBDC), serving as a valuable digital resource for research purposes.
- Established in 2022, the IBDC represents India's sole indigenous databank, eliminating the need for Indian researchers to rely on foreign servers for hosting biological datasets.
What is Genome Sequencing?
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the exact order of the building blocks (nucleotides) that make up an organism's entire DNA, or genome.
- It's like reading the complete instruction manual for life, containing the information needed to create and maintain an organism.
Applications of Genome Sequencing:
- Healthcare: Doctors can diagnose diseases with greater accuracy, personalize treatments, and uncover the causes of rare conditions.
- Agriculture: Scientists can engineer crops with desired traits like disease resistance and improved yield, while breeders select animals with specific characteristics.
- Forensics: DNA profiling aids criminal investigations and paternity testing.
- Conservation: Studying the genetic diversity of endangered species helps with conservation efforts while analyzing invasive species' origins aids in controlling their spread.
What is the Human Genome Project (HGP)?
- Initiated in 1990, the Human Genome Project aimed to elucidate the entire sequence of the human genome.
- In 2023, the project culminated in the release of the latest version of the complete human genome, boasting a mere 0.3% error margin.
- Enabled by the Human Genome Project, whole-genome sequencing facilitates the examination of an individual's genome to uncover deviations from the average human genome.
- These deviations, or mutations, offer insights into an individual's susceptibility to diseases, their responsiveness to specific stimuli, and other pertinent genetic attributes.
About the Genome India Project:
- The Genome India Project stands as a pioneering initiative approved by the Department of Biotechnology, geared towards gene mapping.
- This project sets out with the ambitious objective of compiling an exhaustive repository documenting genetic diversity across the Indian populace.
- At its core, the endeavor seeks to conduct genome sequencing for more than 10,000 individuals spanning various geographic and ethnic backgrounds within India, ultimately laying the groundwork for a standardized reference genome specific to the Indian demographic.
Significance of the Genome India Project:
- Unveiling Unique Genetic Variants: The Genome India Project holds the key to unraveling genetic variants exclusive to India’s diverse population, enabling tailored drug formulations and therapeutic interventions.
- For instance, mutations like MYBPC3, linked to premature cardiac arrest and prevalent in 4.5% of Indians, underscore the necessity of region-specific genetic insights, contrasting with global rarity.
- Similarly, the discovery of the LAMB3 mutation, causing a severe skin disorder and impacting nearly 4% of the population around Madurai, emphasizes the localized genetic complexities absent in global databases.
- Comprehensive Database for India's Population: With a colossal population exceeding 1.3 billion, India boasts a mosaic of over 4,600 distinct population groups, many practicing endogamy.
- This vast demographic diversity underscores the need for a comprehensive genetic database tailored to India's populace, crucial for identifying and addressing disease-causing mutations prevalent within specific groups.
- Unlike extrapolating findings from global datasets, the Genome India Project provides precise genetic insights essential for Indian-centric healthcare strategies.
Google unveils Genie AI which can create video games from text and image prompts

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, Google DeepMind unveiled Genie, a novel model capable of creating interactive video games based solely on textual or image prompts.
What is Genie AI?
- Genie is a foundation world model that is trained on videos sourced from the Internet.
- The model can “generate an endless variety of playable (action-controllable) worlds from synthetic images, photographs, and even sketches.”
- It is the first generative interactive environment that has been trained in an unsupervised manner from unlabelled internet videos.
- When it comes to size, Genie stands at 11B parameters and consists of a spatiotemporal video tokenizer, an autoregressive dynamics model, and a simple and scalable latent action model.
- These technical specifications let Genie act in generated environments on a frame-by-frame basis even in the absence of training, labels, or any other domain-specific requirements.
What does Genie do?
- Genie is a new kind of generative AI that enables anyone – even children – to dream up and step into generated worlds similar to human-designed simulated environments.
- It can be prompted to generate a diverse set of interactive and controllable environments although it is trained on video-only data.
- It is a breakthrough as it makes playable environments from a single image prompt.
- According to Google DeepMind, Genie can be prompted with images it has never seen.
- This includes real-world photographs, and sketches, allowing people to interact with their imagined virtual worlds.
- When it comes to training, they focus more on videos of 2D platformer games and robotics.
- Genie is trained on a general method, allowing it to function on any type of domain, and it is scalable to even larger Internet datasets.
Why is it Important?
- The standout aspect of Genie is its ability to learn and reproduce controls for in-game characters exclusively from internet videos.
- This is noteworthy because internet videos do not have labels about the action that is performed in the video, or even which part of the image should be controlled.
- It allows you to create an entirely new interactive environment from a single image.
- This opens up many possibilities, especially new ways to create and step into virtual worlds.
- With Genie, anyone will be able to create their own entirely imagined virtual worlds.
Ex-SC Judge Justice AM Khanwilkar Appointed As Lokpal Chairperson

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Nearly 19 months after he retired as a Supreme Court judge, Justice A M Khanwilkar was appointed the chairperson of the anti-corruption ombudsman Lokpal on Tuesday. The post fell vacant nearly two years ago.
Who is AM Khanwilkar?
- Justice Ajay Manikrao Khanwilkar was a Supreme Court judge between May 2016 and July 2022.
- He has also served as chief justice of the Madhya Pradesh High Court and the Himachal Pradesh High Court and as a judge of the Bombay High Court.
- Recently appointed as the Chairperson of the anti-corruption ombudsman Lokpal on Tuesday.
- The appointment came nearly two years after the post fell vacant.
- Khanwilkar was elected for the post following discussions by a high-level committee, which included:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi
- Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud
- Leader of the Opposition in Lok Sabha, Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury
- The Lokpal has been functioning without its permanent chief since the conclusion of Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose's term on May 27, 2022.
About Lokpal:
- The Lokpal is a statutory body established under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act of 2013.
- Its primary mandate is to investigate allegations of corruption against certain public officials and handle related matters.
- The organizational structure of Lokpal includes a chairperson and a maximum of eight members.
- The chairperson must be a former Chief Justice of India, a former Judge of the Supreme Court, or an eminent individual meeting specified eligibility criteria.
- Half of the maximum eight members are judicial members, who must be former Judges of the Supreme Court or former Chief Justices of High Courts.
- Additionally, a minimum of fifty percent of the members are drawn from SC/ST/OBC/minority backgrounds and include women.
How are Members Appointed?
- The President of India appoints the Chairperson and Members based on recommendations from a selection committee.
- This committee comprises the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Speaker of Lok Sabha, the Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, the Chief Justice of India or a nominated Judge, and one eminent jurist.
- Members serve a term of five years or until they reach 70 years of age, whichever comes first, starting from the date they assume office.
- The Chairperson receives salary, allowances, and other benefits equivalent to those of the Chief Justice of India.
- Similarly, Members receive salary, allowances, and other benefits equivalent to those of a Judge of the Supreme Court.
Jurisdiction:
- The Lokpal has the authority to investigate allegations of corruption against current or former Prime Ministers, Union Ministers, Members of Parliament, and officials from various levels of the Union Government categorized under Groups A, B, C, and D.
- Its jurisdiction extends to include chairpersons, members, officers, and directors of entities established by parliamentary acts or financed by the Union or State government, as well as any organization receiving foreign contributions exceeding Rs 10 lakh.
- However, there are exceptions regarding the Prime Minister's jurisdiction. The Lokpal cannot investigate allegations related to international relations, external/internal security, public order, atomic energy, and space. Moreover, complaints against the PM require approval from at least two-thirds of the Lokpal's members before initiation of an inquiry.
Powers of Lokpal:
- The Lokpal possesses the authority to oversee and issue directives to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
- Once the Lokpal has referred a case to the CBI, the investigating officer cannot be transferred without the Lokpal's approval.
- It holds the power to authorize the CBI to conduct search and seizure operations related to these cases.
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal is endowed with powers akin to those of a civil court.
- In specific circumstances, the Lokpal can confiscate assets, proceeds, receipts, and benefits obtained through corrupt means.
- It is empowered to recommend the transfer or suspension of public servants implicated in corruption allegations.
- The Lokpal can issue directives to prevent the destruction of records during the preliminary inquiry phase.
- As per Section 48 of the Act, the Lokpal is mandated to submit an annual report on its activities to the President, which is subsequently laid before both Houses of Parliament.
First Pey Jal Survekshan Awards to be conferred by President on 5th March

- 28 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
President Droupadi Murmu will present the first Pey Jal Survekshan Awards on the 5th of next month in New Delhi.
About the Pey Jal Survekshan Awards:
- The Pey Jal Survekshan Awards feature a prestigious lineup of 130 accolades, spotlighting outstanding contributions in the realm of water management.
- The awards span various categories, including the Pey Jal Gold, Silver, and Bronze City Awards, with each tier symbolizing excellence in specific population segments (ranging from 1 to 10 Lakh, 10 to 40 Lakh, and more than 40 Lakh).
- In addition to these, commendations are also extended for commendable efforts in areas such as Best Water Body, Sustainability Champion, Reuse Champion, Water Quality, City Saturation, and the prestigious AMRUT 2.0 Rotating Trophy of the Year.
Comprehensive Evaluation Parameters:
- Embracing a multifaceted approach, the evaluation criteria encompass a wide array of parameters, including accessibility, coverage, water quality maintenance at treatment facilities and household levels, sustainability practices ensuring the health of water bodies, adoption of SCADA/flowmeters, and efficient reuse of treated wastewater.
- Cities are meticulously graded using a star rating system, ranging from 5 stars to No star, meticulously reflecting their performance across these pivotal benchmarks.
- Ensuring Water Purity and Transparency: The Pey Jal Survekshan reinforces the assurance of clean water through rigorous independent NABL lab testing at both the source and consumer ends.
- Leveraging advanced technological tools such as GIS-enabled web portals, geo-tagging, and infrastructure mapping, the survey captures precise and transparent data, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Enhancing Urban Governance and Citizen Engagement: Anticipated to serve as a catalyst for urban local body (ULB) decision-making processes, the outcomes of the Pey Jal Survekshan are poised to elevate service delivery standards while fostering active citizen participation.
- By nurturing a sense of ownership and disseminating knowledge on water conservation and optimal utilization, the awards endeavor to empower communities toward sustainable water management practices.
What is the AMRUT Mitra initiative?
- The AMRUT Mitra initiative is geared towards active engagement of women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in urban water management, recognizing women as pivotal stakeholders and highlighting their vital role in household water governance.
- Tasked with executing AMRUT 2.0 projects, the Mitras will undertake various responsibilities, including billing, collection, leak detection, plumbing, water quality monitoring, and infrastructure upkeep.
- At its core, AMRUT Mitra seeks to cultivate a sense of ownership among women, fostering inclusivity and diversity in traditionally male-dominated domains while ensuring equitable access to safe drinking water and addressing gender disparities.
- Expected outcomes encompass the empowerment of women SHGs, socio-economic upliftment, alignment with AMRUT 2.0 objectives, heightened community awareness, and the establishment of a blueprint for future endeavors.
An initiative to improve nutrition in adolescent girls using Ayurveda under Mission Utkarsh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The project for anemia control under Mission Utkarsh will be a joint public health initiative by the Ministries of Ayush and Women and Child Development and will be launched in five aspirational districts first as a pilot project.
About Mission Utkarsh:
- Mission Utkarsh was launched in January 2022, a new initiative of “rapid improvement of selected Districts” to improve.
- Under this mission, 15 central ministries and departments are working to bring select key performance indicators in bottom districts to the state and national average.
- Over 94,000 adolescent girls between the age group of 14-18 years registered under Poshan Tracker at approximately 10,000 Anganwadi Centres will benefit in 12 12-month periods of the program.
- The coordinating agency for the project will be the Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences (CCRAS).
- Classical Ayurveda medicines (Drakshavaleha and Punarnavadi mandoor) for better nutrition to improve the health of the anemic adolescent girls will be provided for a period of 3 months.
- These five districts are Dhubri in Assam, Bastar in Chhattisgarh, Paschimi Singhbhum in Jharkhand, Gadchiroli in Maharashtra, and Dholpur in Rajasthan.
- Building research capacity through training, conferences, workshops, and seminars with the active participation of researchers of integrative healthcare would be enhanced.
What is Anaemia?
- According to WHO, anemia occurs when there is a lower-than-normal count of red blood cells or a reduced hemoglobin concentration within them, crucial for oxygen transport throughout the body.
Symptoms
- This condition leads to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and shortness of breath due to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common nutritional cause, although deficiencies in folate, vitamins B12 and A can also contribute.
- Chronic diseases like kidney or liver disease, cancer, and genetic conditions such as sickle cell anemia further exacerbate anemia.
Significance:
- Anaemia has significant implications, particularly affecting vulnerable populations like pregnant women and children under five, impacting reproductive health and reducing work capacity, thus posing an economic burden.
Anaemia in India:
- India faces a substantial anemia burden, with recent surveys indicating alarming prevalence rates among women aged 15-49 and children aged six months to five years, highlighting the urgent need for public health interventions.
RBI Allows Lending And Borrowing Govt Securities

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a bid to deepen the bond market, the Reserve Bank of India on Wednesday issued guidelines for lending and borrowing in government securities.
What are Government Securities?
- Government securities, also known as G-Secs, refer to the debt instruments issued by the government to finance its fiscal requirements.
- These securities are backed by the government’s guarantee of repayment and are considered risk-free investments.
- They are an integral part of the fixed-income market and are traded on the government securities market.
- Government securities serve as a means for the government to raise funds from the public to meet its expenditure needs, bridge budget deficits, and fund developmental projects.
- Investors who purchase these securities lend money to the government in return for regular interest payments and the principal amount at maturity.
- These securities come in mainly two categories:
- Short-Term: Often known as “Treasury Bills,” these have initial maturities of less than a year.
- Long-Term: Typically referred to as Government Bonds or Dated Securities, these have an original maturity of one year or more.
- In India, the Central Government issues both treasury bills and bonds or dated securities while the State Governments issue only bonds or dated securities, which are called State Development Loans (SDLs).
Treasury Bills (Short-Term G-Secs)
- Treasury Bills, commonly known as T-Bills, are short-term government securities with a maturity period of less than one year.
- They are issued at a discount to their face value and are highly liquid instruments.
- T-Bills serve as a mechanism for the government to efficiently manage its short-term funding requirements.
Dated Securities (Long-Term G-Secs)
- Dated Securities are long-term government securities with a fixed maturity period, typically 5 to 40 years.
- They pay regular interest to investors, known as coupon payments, and return the principal amount at maturity.
- Dated Securities are vital for financing long-term projects and meeting government borrowing needs.
Centre approves interest-free loans to FCV tobacco growers in Andhra Pradesh

- 27 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Central Government has approved a 10 thousand rupees interest-free Loan to the Flue Cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco growers in Andhra Pradesh.
What is Flue Cured Tobacco?
- There are three types of tobacco curing methods traditionally used: Air-Cured, Fire-Cured, and Flue-Cured.
- Each of the different curing methods results in a tobacco product that is distinguishable by both its nicotine content and its aroma.
Flue-Cured:
- Flue-curing tobacco is raised with a low level of nitrogen and harvested by priming method.
- Harvested leaves are strung on sticks which are then stacked into to flue curing barn.
- The barn is artificially heated.
- Green leaves should be loaded in the upper half of the barn and the lighter ones in the lower half.
- The three steps are Yellowing, Fixing the color, and Drying.
Grading:
- After curing, leaves are graded by sorting leaves into uniform lots according to body, color, and degree of blemish or damage.
- The most important elements of quality in FCV tobacco are color, texture, size, blemish, strength, even burning with white ash, and agreeable flavor.
Why is Tobacco Cured?
- To create smoking tobacco, the tobacco leaves need to be cured, or dried out.
- The wet, green tobacco leaves of a tobacco plant initially contain too much moisture to catch fire.
- They also have a higher chlorophyll content.
- By releasing a certain amount of chlorophyll from the leaves during the drying-out process, the natural tannins come out giving the smoked tobacco its flavor and scent.
- The curing process makes the leaf dry enough to smoke while increasing the sugar and natural tannins found in each leaf to create the sweetly aromatic and mild taste tobacco is known for.
Key Characteristics of Flue-cured Tobacco:
-
- Produces primarily cigarette tobacco
- Contains a high sugar content
- Contains medium to high levels of nicotine
- Rich in natural tannins which creates its distinct mild and slightly sweet flavor and aroma
- FCV tobacco is mainly produced in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka in India.
PM Modi Inaugurates 'Sudarshan Setu', India's Longest Cable-Stayed Bridge

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
PM Modi recently inaugurated the Sudarshan Setu, a four-lane cable-stayed bridge connecting Okha to Beyt Dwarka island in Gujarat.
About the Sudarshan Setu:
- 'Sudarshan Setu' is the country's longest cable-stayed bridge 2.32 km on the Arabian Sea connecting Beyt Dwarka island to mainland Okha in Gujarat's Devbhumi Dwarka district.
- It boasts a unique design, featuring a footpath adorned with verses from the Bhagavad Gita and images of Lord Krishna on both sides.
- It also has solar panels installed on the upper portions of the footpath, generating one megawatt of electricity.
- The 2.32 km bridge, including 900 metres of a central double-span cable-stayed portion and a 2.45 km long approach road, has been constructed at a cost of Rs 979 crore.
About Beyt Dwarka:
- Bet/Beyt (pronounced ‘Bait’ Dwarka also known as Shankhodara, is an island located near the shores of Okha which is situated around 30 km from Dwarka, in the Gulf of Kutch.
- It said that Lord Krishna resided here while Dwarka was his constitutional seat.
History:
- Bet Dwarka derived its name from the word ‘bet’ which translates to ‘gift’ and is believed that Lord Krishna received it from his friend Sudama.
- In the ancient epic, Mahabharata, Bet Dwarka is known by the name of ‘Antardvipa’ to which people of the Yadava clan needed to travel by boat.
- Explorations and excavations carried out under the sea have revealed the presence of settlements whose age can be traced back to the era of the Harappan civilisation and that of the Mauryan rule.
- In the later years, the region was under the administration of the Gaekwad clan of the state of Baroda.
- During the revolt of 1857, Vaghers attacked the region and captured it, but had to concede defeat in two years and return the region back to the Gaekwads.
Ladakh: Centre agrees to examine demand for statehood, inclusion in Sixth Schedule of Constitution

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the Centre has agreed to examine whether the provisions of the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution can be implemented in Ladakh.
What is the Sixth Schedule?
- The Sixth Schedule under Article 244 provides for the formation of autonomous administrative divisions — Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) — that have some legislative, judicial, and administrative autonomy within a state.
- ADCs have up to 30 members with a term of 5 years and can make laws, rules and regulations with regard to land, forest, water, agriculture, village councils, health, sanitation, village- and town-level policing, inheritance, marriage and divorce, social customs and mining, etc.
- The Bodoland Territorial Council in Assam is an exception with more than 40 members and the right to make laws on 39 issues.
- The Sixth Schedule applies to the Northeastern states of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram (three Councils each), and Tripura (one Council).
Why does Ladakh want to be part of the Sixth Schedule?
- There was much enthusiasm initially, mostly in Leh, after the August 5, 2019 decisions that created two new Union Territories.
- The Buddhist-dominated Leh district had long demanded UT status because it felt neglected by the erstwhile state government, which was dominated by politicians from Kashmir and Jammu.
- This development has sparked concerns among locals regarding potential challenges related to identity preservation, resource allocation, and administrative oversight.
- Also, the changed domicile policy in Jammu and Kashmir has raised fears in the region about its own land, employment, demography, and cultural identity.
- The UT has two Hill councils in Leh and Kargil, but neither is under the Sixth Schedule.
- Their powers are limited to the collection of some local taxes such as parking fees and allotment and use of land vested by the Centre.
- The Sixth Schedule empowers the Governor of the State to designate specific areas as administrative units within the Autonomous Districts and Autonomous Regions.
Can Ladakh be included in the Sixth Schedule?
- In September 2019, the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes recommended the inclusion of Ladakh under the Sixth Schedule, noting that the new UT was predominantly tribal (more than 97%), people from other parts of the country had been restricted from purchasing or acquiring land there, and its distinct cultural heritage needed preservation.
- Notably, no region outside the Northeast has been included in the Sixth Schedule.
- In fact, even in Manipur, which has predominantly tribal populations in some places, the autonomous councils are not included in the Sixth Schedule.
- Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh, which are totally tribal, are also not in the Sixth Schedule.
- “Ladakh’s inclusion in the Sixth Schedule would be difficult.
- The Constitution is very clear, the Sixth Schedule is for the Northeast.
- For tribal areas in the rest of the country, there is the Fifth Schedule.
- However, it remains the prerogative of the government — it can, if it so decides, bring a Bill to amend the Constitution for this purpose.
G-33 calls for progress on agricultural trade ahead of WTO Ministerial Conference

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The G-33 group of countries recently expressed serious concern over the lack of progress in agriculture trade negotiations and urged the members of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) to work on a permanent solution to the issue of public stockholding of grains for food security purposes.
Key Highlights of the G33 Trade Ministers Meeting in Abu Dhabi:
- Special Safeguard Mechanism: The G33 group emphasized the importance of the Special Safeguard Mechanism (SSM) as a crucial instrument against significant import surges or sudden price declines.
- They called for WTO members to reach an agreement and adopt a decision on SSM by the 14th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC).
- Permanent Solution for Public Stockholding: The G33 nations sought a permanent solution during the 13th Ministerial Conference, which commenced in Abu Dhabi recently.
- The MC serves as the highest decision-making body of the WTO.
- Critical Importance of Public Stockholding: The G33 statement highlighted the critical significance of public stockholding for food security in developing countries.
- It enables governments to procure crops from farmers at the minimum support price (MSP) and store and distribute food grains to the poor.
- This program supports low-income or resource-poor producers and contributes to rural development.
- The 13th WTO Ministerial Conference provides a crucial platform for WTO members to engage in constructive discussions and work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
What is G 33?
- The G33 is a forum of developing countries including India, Brazil, South Africa etc. formed during the Cancun ministerial conference of the WTO (2003), to protect the interest of the developing countries in agricultural trade negotiations.
- It was created to help group countries which were all facing similar problems.
- The G33 has proposed special rules for developing countries at WTO negotiations, like allowing them to continue to restrict access to their agricultural markets.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
- The group has advocated the creation of a "special products" exemption, which would allow developing countries to exempt certain products from tariff exemptions, and also a "special safeguard mechanism" which would permit tariff increases in response to import surges.
Analysis of Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23 Report

- 26 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The per capita monthly household expenditure more than doubled in 2022-23 as compared to 2011-12, according to the latest study by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO).
Context:
- As per the 2022-23 report, rising inequality between the top and bottom of the pyramid.
- Urban and rural households register higher expenditure, spending less on food items.
- New methodology and questionnaire used in Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2022-23.
About the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO):
- The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) comes under the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation headed by a Director General.
- It is responsible for the conduct of large-scale sample surveys in diverse fields on an All-India basis.
- Primarily data are collected through nationwide household surveys on various socio-economic subjects, Annual Survey of Industries (ASI), etc.
- Besides these surveys, NSSO collects data on rural and urban prices and plays a significant role in the improvement of crop statistics through supervision of the area enumeration and crop estimation surveys of the State agencies.
- It also maintains a frame of urban area units for use in sample surveys in urban areas.
The NSSO has four Divisions:
- Survey Design and Research Division (SDRD): This Division, located at Kolkata, is responsible for the technical planning of surveys, formulation of concepts and definitions, sampling design, designing of inquiry schedules, drawing up of tabulation plans, and analysis and presentation of survey results.
- Field Operations Division (FOD): The Division, with its headquarters at Delhi/Faridabad, is responsible for the collection of primary data for the surveys undertaken by NSS.
- Data Processing Division (DPD): The Division, with its headquarters at Kolkata is responsible for sample selection, software development, processing, validation and tabulation of the data collected through surveys.
- Survey Coordination Division (SCD): This Division, located in New Delhi, coordinates all the activities of different Divisions of NSS.
- It also brings out the bi-annual journal of NSS, titled “Sarvekshana”, and organizes National Seminars on the results of various Socio-economic surveys undertaken by NSS.
Key Insights From the 2022-23 Survey:
- Evolution of Food Expenditure: Over the past two decades, there has been a notable shift in spending patterns on food in India.
- Between 1999-2000 and 2022-23, both urban and rural households witnessed a gradual decline in the share of expenditure allocated to food.
- This period marks the first instance where food expenditure has dropped to below 50% in rural India and below 40% in urban India.
- Changing Dietary Preferences: The composition of food consumption has also undergone significant changes.
- Cereals and pulses have seen a reduction in their share of overall food consumption expenditure, while spending on milk has surged, surpassing that on cereals and pulses combined.
- In a noteworthy shift, the average Indian now spends more on fruits and vegetables than on food grains.
- Furthermore, expenditure on animal proteins like eggs, fish, and meat has shown a growing trend, indicating a preference for animal-based proteins over plant-based ones.
- Rise in Processed Food Consumption: There has been an observed increase in the share of expenditure allocated to processed foods, beverages, and purchased cooked meals.
- This trend aligns with the Engel Curve hypothesis, suggesting that as incomes rise, households allocate a smaller proportion of their spending to food and tend to prefer superior items over inferior ones.
- Closing Rural-Urban Consumption Gap: Consumption growth in rural areas has outpaced that in urban areas, leading to a narrowing of the rural-urban consumption divide.
- If this trend continues, it could potentially lead to parity in urban and rural incomes and consumption patterns in the future.
- Challenges in Inflation Calculation: The findings of the latest Household Consumption Expenditure (HCE) Survey underscore the need to review the inflation basket.
- The current Consumer Price Index (CPI)-based inflation calculation, established in 2012, may not accurately reflect contemporary consumption patterns.
- For instance, the disparity between the weightage assigned to cereals in the CPI basket and actual expenditure on cereals by rural households highlights the need for recalibration.
- Insights on Poverty Reduction: According to NITI Aayog CEO B V R Subrahmanyam, the latest survey indicates a reduction in poverty to five per cent nationwide.
- Both rural and urban areas are witnessing increased prosperity, as evidenced by rising per capita monthly expenditure.
- Demand for Legal Guarantee to MSP: While there is a demand for a legal guarantee to Minimum Support Price (MSP) for 23 crops, including food grains and sugarcane, the survey data suggests that the growth in the farm sector is being primarily driven by livestock, fisheries, and horticulture crops.
- This poses a pertinent question regarding the promotion of production: should the focus be on crops outside the MSP purview, such as milk, fish, poultry products, fruits, and vegetables, given their growing consumption trends?
BharatGPT Unveils Hanooman, a New Suite of Indic Generative AI Models

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Recently, the BharatGPT group, led by IIT Bombay along with seven other elite Indian engineering institutes announced that it would launch its first ChatGPT-like service next month.
What is Hanooman?
- Hanooman is a series of large language models (LLMs) that can respond in 11 Indian languages like Hindi, Tamil, and Marathi, with plans to expand to more than 20 languages.
- It is unveiled by Seetha Mahalaxmi Healthcare (SML) in partnership with the IIT Bombay-led BharatGPT ecosystem.
- The BharatGPT group, which is backed by Reliance Industries.
- Hanooman has been designed to work in four fields, including health care, governance, financial services, and education.
- According to BharatGPT, the series isn’t just a chatbot but It is a multimodal AI tool, which can generate text, speech, videos and more in multiple Indian languages.
- One of the first customised versions is VizzhyGPT, an AI model fine-tuned for healthcare using reams of medical data.
- The size of these AI models ranges from 1.5 billion to a whopping 40 billion parameters.
Are There Any Other Indian Language Models?
- Apart from BharatGPT, a host of different startups like Sarvam and Krutrim, backed by prominent VC investors such as Lightspeed Venture Partners and billionaire Vinod Khosla’s fund, are also building AI models customised for India
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
- Large language models use deep learning techniques to process large amounts of text.
- They work by processing vast amounts of text, understanding the structure and meaning, and learning from it.
- LLMs are ‘trained’ to identify meanings and relationships between words.
- The greater the amount of training data a model is fed, the smarter it gets at understanding and producing text.
- The training data is usually large datasets, such as Wikipedia, OpenWebText, and the Common Crawl Corpus.
- These contain large amounts of text data, which the models use to understand and generate natural language.
First moon-landing by private company
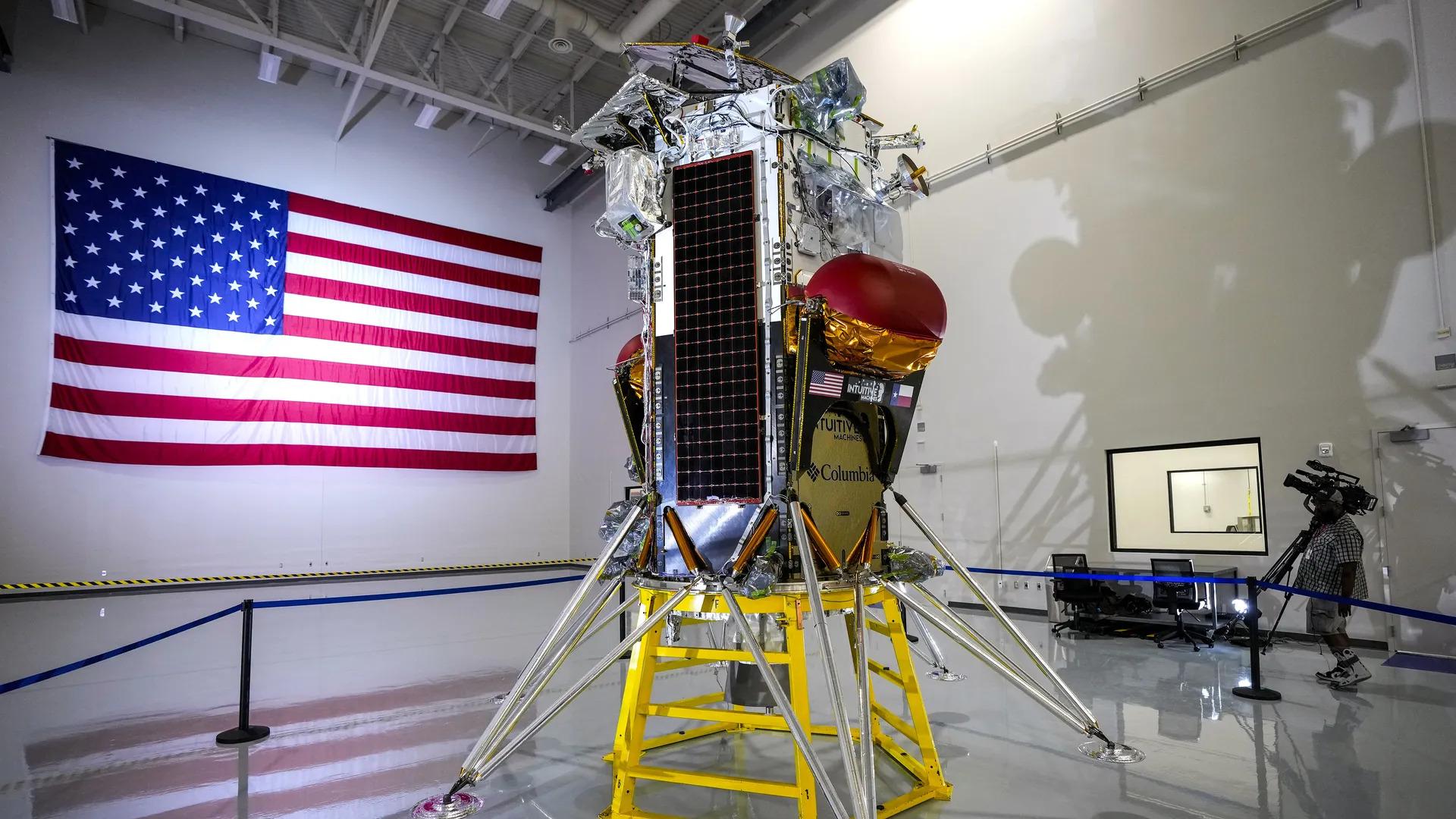

- 24 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Fifty-two years after the last successful Apollo mission, a US-made spacecraft landed on the Moon recently which also marks the arrival of private space companies on the lunar surface.
What is Odysseus Lunar Exploration?
- Odysseus is a spacecraft built by Intuitive Machines, embarked on its journey from Earth aboard a Falcon 9 rocket by SpaceX recently.
- Intuitive Machines, headquartered in Houston, USA, boasts a decade-long legacy in space exploration endeavours.
- Loaded with six NASA payloads, Odysseus set its course for the Moon.
- Its lander module, Nova-C, achieved the milestone of landing in the Moon's south pole region, following Chandrayaan-3's similar feat last year.
- This marks the third successful moon-landing event in under a year, alongside Chandrayaan-3 and Japan's SLIM (Smart Lander for Investigating Moon).
Mission Objectives:
- The primary aim of the lunar lander is to assess the environmental conditions at the Moon's south pole.
- This assessment holds significant importance as NASA gears up for a crewed mission in September 2026 with Artemis III.
- Before sending astronauts to this area, NASA seeks to gather crucial data, including insights into water presence and accessibility, to inform mission planning.
Funding:
- Under the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, NASA allocated $118 million to Intuitive Machines for this mission.
- CLPS has engaged at least 14 private companies to ferry NASA payloads to the Moon, fostering a collaborative environment aimed at nurturing the private space industry's capabilities in lunar exploration technology and science.
The Significance of Odysseus:
- Advancing Long-Term Lunar Presence: Odysseus' successful landing heralds a transformative phase in lunar exploration, aiming to establish infrastructure and a technological ecosystem capable of sustaining extended human presence.
- Diverging from Past Lunar Missions: In contrast to the moon landings of the 1960s and 1970s spearheaded by the US and the Soviet Union, Odysseus' mission focuses on leveraging lunar resources for sustained exploration.
- While historic moon landings were remarkable feats, technological limitations of the time hindered the immediate utilisation of lunar resources such as mining.
- Supporting US Commitment to Moon Exploration via Artemis Program: Odysseus' touchdown aligns with the US commitment to rekindle lunar exploration through the ambitious Artemis program.
- This endeavour transcends mere lunar landing missions, aiming to establish essential infrastructure and a thriving lunar economy conducive to comprehensive exploration.
- Unlocking Lunar Potential as a Gateway to Deep Space: By laying the groundwork for lunar infrastructure and economic activity, missions like Odysseus pave the way for leveraging the Moon as a springboard for deeper space exploration, offering nations unprecedented opportunities for cosmic discovery.
Kiru Hydropower Corruption Case: CBI Searches J&K Ex-Governor Satya Pal Malik’s Premises

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The CBI conducted searches at the premises of former Jammu and Kashmir governor Satya Pal Malik and 29 other locations recently in connection with alleged corruption in the Rs 2,200-crore Kiru Hydropower project.
What are the Corruption Allegations Surrounding the Kiru Hydel Project?
- During his tenure as the governor of Jammu and Kashmir from August 23, 2018, to October 30, 2019, Satya Pal Malik claimed that he was offered a Rs 300-crore bribe to approve two files, one of which pertained to the project.
- In 2022, the J&K government requested a CBI investigation into alleged misconduct, previously highlighted by Satya Pal Malik, in the awarding of two government contracts.
- Concerns have been raised regarding the award of civil works, particularly to Patel Engineering Ltd, a prominent infrastructure and construction company established in 1949.
- The CBI has initiated action against the former CVPPPL chairman, MD, and Directors, as well as Patel Engineering.
- According to the FIR, an inquiry by the J&K Anti-Corruption Bureau and the Power Department had been conducted.
- The FIR alleges non-compliance with e-tendering guidelines in the awarding of civil works for the project.
- Additionally, accusations of substandard work and failure to employ local youth have been levelled against the hydel project.
What is the Kiru Hydel Power Project?
- The 624MW Kiru hydroelectric project is being developed as a run-of-river scheme in the Kishtwar district of Jammu and Kashmir, a union territory in India.
- Location of the Kiru project: The Kiru hydropower project is being built along the Chenab River near the villages of Patharnakki and Kiru, approximately 42 km from Kishtwar.
- It will be located between the Kirthai II hydroelectric project to its upstream and the Kwar hydroelectric project to its downstream.
- The project is being developed by the Chenab Valley Power Projects (CVPPPL) joint venture (JV) between:
- National Hydroelectric Power (NHPC, 49%)
- Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development (JKSPDC, 49%) and
- The Power Trading Corporation (PTC, 2%)
- The Ministry of Environment Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) awarded environmental clearance for the hydroelectric project in 2016 while the foundation stone was laid in February 2019.
- The project is being constructed at an estimated cost of Rs 4,287 crore and is expected to start commercial operations in July 2025.
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the investment in the project in March 2019.
- Apart from helping address the energy demand across northern India and the state’s rural areas, it could aid small-scale and cottage industries.
Advantages of the Kiru Hydroelectric Power Project:
- This project aims to alleviate the energy shortage in Northern India while also enhancing the transportation, education, healthcare, and road infrastructure in the area.
- By bringing electricity to rural communities, the project will lessen the reliance of residents on alternative energy sources.
- The heightened power availability will foster the growth of small-scale and cottage industries, generating employment opportunities and revenue for the local populace.
What is a Run-of-river Project?
- Run-of-river hydropower is a facility that channels flowing water from a river through a canal or penstock to spin a turbine.
- Typically a run-of-river project will have little or no storage facility.
- Run-of-river provides a continuous supply of electricity (base load), with some flexibility of operation for daily fluctuations in demand through water flow that is regulated by the facility.
Race to the global eradication of Guinea worm disease nears the finish line
- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The world is on the brink of a public health triumph as it closes in on eradicating Guinea worm disease. There were more than 3.5 million cases of this disease in the 1980s, but according to the WHO, they dwindled to 14 cases in 2021, 13 in 2022, and just six in 2023.
What is Guinea Worm Disease?
- Dracunculiasis is also called guinea worm disease (GWD).
- It is an infection caused by a parasite called Dracunculus medinensis (guinea worm).
- This parasite is an organism that survives by deriving nutrients and feeding off another organism.
- GWD spreads through drinking contaminated water.
- It is presently eradicated in most parts of the world but is still seen in remote parts of Africa and some remote rural areas in the world where there is no access to clean drinking water.
- GWD is considered endemic in three African countries, Sudan, Ethiopia, and Mali.
- In recent years, a few cases of GWD in animals, especially dogs, have been reported in developed countries as well.
- GWD is a serious condition, that causes debilitating pain and complications, affecting the quality of life
Symptoms:
- People infected with Guinea worm don’t typically have any symptoms until about a year after they're first infected.
- It’s not until the worm is about to erupt from the skin that people start to feel sick.
- What that happens, the symptoms of Guinea worm disease can include Fever, Nausea and vomiting, Diarrhoea, Shortness of breath, Burning, itching, pain, and swelling where the worm is in the body (often the legs and feet) and Blister where the worm breaks through the skin.
Impact:
- Guinea worm disease isn’t often deadly, but it can cause serious complications, lifelong disabilities, and financial hardship for those involved.
- The pain involved is often so intense that it’s difficult for people to work, go to school, or care for themselves or others.
- This lasts an average of 8.5 weeks, though lifelong disability is common.
Dracunculiasis Treatment:
- There is no vaccine or drug developed to prevent or treat this disease.
- The only means available is the management of the disease which is removing the whole worm and caring for the wound caused by it and avoiding infection in the process or exposure to the guinea worm larvae at all costs, especially by avoiding contaminated drinking water and stagnant water sources.
- Without proper treatment, wounds caused by the worm can become infected by bacteria, leading to sepsis, septic arthritis, and contractures (when joints lock and deform).
- In some cases, these infections become life-threatening.
Earth’s early evolution: Fresh insights from rocks formed 3.5 billion years ago

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
Exploring ancient cratons such as the Singhbhum Craton in India, alongside similar formations in South Africa and Australia, provides unparalleled insights into the early stages of our planet's development, reaching back approximately 3.5 billion years.
What is Singhbhum Craton?
- The Singhbhum Craton encompasses a vast expanse of rugged terrain, primarily spanning regions in Jharkhand and Odisha, situated between the Chhota Nagpur plateau and the Eastern Ghats.
- Dating back approximately 3.5 billion years, this ancient segment of the Earth's crust offers valuable insights into early geological processes.
- Its oldest rock formations consist predominantly of volcanic and sedimentary rocks, referred to as greenstone successions.
- Greenstones are characterised by submarine volcanic rocks with minor sedimentary components.
- Geologically akin to greenstone belts in South Africa's Barberton and Nondweni regions and the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia, these areas experienced extensive submarine mafic volcanic activity, rich in magnesium oxide, between 3.5 and 3.3 billion years ago, with preserved features like pillowed lava and komatiites.
Significance:
- The Singhbhum Craton sheds light on early tectonic activities during the Archaean era, enhancing our understanding of the Earth's formative stages.
- Its distinctive geological characteristics, particularly the presence of greenstone belts, yield invaluable data on surface and atmospheric processes crucial for theorising about early habitable conditions and the emergence of life on Earth.
What are Cratons?
- A craton is a stable and ancient part of Earth's lithosphere that has experienced long-term tectonic and geomorphic stability.
- It is considered to be the nucleus of a continent and is characterised by its thick and cold lithosphere.
- Cratons can undergo destruction, which is defined as a geological process resulting in the loss of craton stability due to changes in its physical and chemical properties.
- The mechanisms responsible for craton destruction include oceanic plate subduction, rollback and retreat of subducting plates, stagnation and dehydration of subducting plates in the mantle transition zone, melting of the mantle caused by dehydration of stagnant slabs, non-steady flow in the upper mantle induced by melting, and changes like the lithospheric mantle.
- Craton destruction can lead to crustal thinning, surface uplift, and the concentration of mineral deposits.
Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY)

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
The Department of Social Justice and Empowerment, being the Nodal Department for the welfare of senior citizens, develops and implements programmes and policies for these groups in close collaboration with State Governments, Non-Governmental Organisations and civil society.
About the Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme to improve the quality of life of the Senior Citizens.
- The project is implemented by the Department of Social Justice and Empowerment.
Aims and Objectives:
- The main objective of the Scheme is to improve the quality of life of Senior Citizens by providing basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care and entertainment opportunities and by encouraging productive and active ageing through providing support for capacity building of State/ UT Governments/Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs)/Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) / local bodies and the community at large.
The components of the AVYAY Scheme are as under:-
-
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC)
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC)
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY)
- Elderline – National Helpline for Senior Citizens
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE)
- Geriatric Caregivers Training
Components of the AVYAY Scheme:
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC): Grant aid is provided to Non-Governmental/ Voluntary Organizations for running and maintenance of Senior Citizens' Homes (old age homes), continuous care homes, etc.
- Facilities like shelter, nutrition, medicare and entertainment are provided free of cost to indigent senior citizens.
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC): Grant in aid is released to States/ UTs for the creation of a pool of trained Geriatric Caregivers for senior citizens, for carrying a special drive for Cataract Surgeries for Senior Citizens and State Specific Activities for the welfare of senior citizens, especially who are indigent in the States/UTs.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY): To provide for senior citizens, suffering from any age-related disability/infirmity such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth and loco-motor disabilities.
- The eligible senior citizens under this component are those who are in the BPL Category or have monthly income up to Rs.15000/.
- Generic and non-generic devices are distributed to the senior citizens through the camps.
- Elderline: National Helpline for Senior Citizens (14567): The Ministry has set up the National Helpline for Senior Citizens to provide free information, Guidance, Emotional Support and field intervention in cases of abuse and rescues.
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE): To promote out-of-the-box and innovative solutions for commonly faced problems, innovative start-ups are identified and encouraged to develop products, processes and services for the welfare of the elderly under this initiative.
- The initiative is implemented through IFCI Venture Capital Funds Ltd. (Investment Manager).
- Geriatric Caregivers Training: To bridge the gap in supply and increasing demand in the field of geriatric caregivers and also to create a cadre of professional caregivers in the field of geriatrics.
- The component is implemented through the National Institute of Social Defence and at present 3,180 geriatric caregivers have been trained.
In a first, CERN scientists carry out laser cooling of Positronium

- 23 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In a first, an international team of physicists from the Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved a breakthrough by demonstrating the laser cooling of Positronium.
About Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS):
- AEgIS is an experiment at the Antiproton Decelerator facility at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research).
- It is a collaboration of physicists from a number of countries in Europe and from India.
- In 2018, AEgIS demonstrated the first pulsed production of antihydrogen atoms, by interacting pulse-produced positronium (an atom consisting of only an electron and a positron) with cold, trapped antiprotons.
- The primary scientific goal of the Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) is the direct measurement of the Earth's gravitational acceleration, g, on antihydrogen.
What is Positronium?
- Positronium is a bound state system of a positron and an electron, similar to the hydrogen atom, where an electron orbits around a proton.
- In the case of positronium, the positron and the electron orbit around their common centre of mass.
- The system is unstable, and the two particles eventually annihilate each other, releasing two or more gamma ray photons.
- Positronium has two possible states:
- The singlet state (para-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are antiparallel and the system has a shorter lifetime, and
- The triplet state (ortho-positronium), in which the electron and the positron spins are parallel, and the system has a longer lifetime.
- Positronium has been studied extensively in experimental and theoretical physics because it provides a simple system for testing quantum electrodynamics (QED) and for studying the properties of matter and antimatter.
- It also has potential applications in fields such as material science, plasma physics, and astrophysics.
What is Antimatter?
- Antimatter shares similarities with ordinary matter, except for its opposite electric charge.
- Often referred to as "mirror" matter, antimatter pairs with ordinary matter particles.
- For example, while an electron possesses a negative charge, its antimatter counterpart is a positron, which carries a positive charge and has the same mass as an electron.
- Positrons, antiprotons, and antineutrons are the antimatter counterparts of electrons, protons, and neutrons, respectively, collectively known as antiparticles.
- These antiparticles can combine to form anti-atoms and theoretically could lead to the formation of antimatter regions within our universe.
- However, the coexistence of matter and antimatter is short-lived due to their tendency to annihilate upon contact, resulting in the release of substantial energy in the form of gamma rays or elementary particles.
- Antimatter, like matter, emerged during the Big Bang.
- Scientists have produced antimatter particles through high-speed collisions in large particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider operated by CERN outside Geneva.
- Additionally, antiparticles are sporadically generated throughout the universe through natural processes.
Hundred years ago, Satyendra Nath Bose changed physics forever
- 20 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
In 2024, we commemorate the centenary of Bose's pivotal discovery of the precise equations governing the behaviour of collections of photons, fundamental particles of light.
About Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Satyendra Nath Bose (1894-1974) was an eminent Indian physicist renowned for his pioneering contributions to theoretical physics, notably in the realms of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics.
- His groundbreaking research laid the groundwork for Bose-Einstein statistics and the theoretical elucidation of Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Bose's profound insights not only advanced the understanding of fundamental physics but also played a pivotal role in refining the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
- His visionary work eventually paved the way for significant discoveries in particle physics, including the identification of the Higgs Boson, colloquially referred to as the "God Particle."
Major Contributions of Satyendra Nath Bose:
- Foundation of Bose-Einstein Statistics and Bosons: In 1924, Bose formulated a revolutionary explanation for Planck's law of black-body radiation using quantum mechanics principles, introducing the concept of "Bose-Einstein statistics."
- This theory delineates the behaviour of particles known as "bosons," characterized by integer spin.
- Bose-Einstein statistics elucidate how bosons, such as photons and atoms, preferentially occupy the same quantum state, a behaviour distinct from fermions governed by the Pauli exclusion principle.
- This groundbreaking work laid the groundwork for understanding particle behaviour at low temperatures and foretold the existence of the Bose-Einstein condensate, a novel state of matter.
- Prediction of Bose-Einstein Condensate: Bose's collaboration with Einstein in statistical mechanics led to the theoretical prediction of the Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC), a revolutionary concept in quantum physics.
- According to Bose-Einstein statistics, at ultra-low temperatures approaching absolute zero, bosons can congregate in the lowest energy state, forming a condensed state.
- Often dubbed the "fifth state of matter," BEC occurs when bosons lose sufficient energy to coalesce into a single quantum state, creating a cohesive "super-particle" cloud.
- Experimental confirmation of Bose-Einstein condensation in 1995, decades after Bose's theoretical proposal, garnered Eric Cornell, Carl Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001.
- Together with Meghnad Saha, he published the first English translation of Einstein’s papers on general relativity.
- His dedication to research and scientific integrity earned him numerous accolades, including the Padma Vibhushan and the Fellowship of the Royal Society.
Bird flu outbreak in Andhra: Could H5N1 spark the next pandemic?

- 19 Feb 2024
Why is it in the News?
A bird flu outbreak in poultry in Andhra Pradesh’s Nellore district was reported recently. Laboratory tests by the National Institute of High-Security Animal Diseases in Bhopal confirmed that it was caused by the type A strain of the H5N1 variant of the avian influenza virus.
What is Bird Flu/Avian Influenza?
- Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a viral respiratory illness primarily affecting birds.
- It's caused by specific strains of the Influenza A virus.
- Bird flu spreads between both wild and domesticated birds.
- It has also been passed from birds to humans who are in close contact with poultry or other birds.
- There is no clear evidence that the virus can be transmitted from human to human.
- However, this may have happened in rare cases, where a person has become ill after caring for a sick family member.
- While most types don't infect humans, certain strains like H5N1, H7N9, and H5N6 have caused concern due to their ability to transmit to humans in rare cases.
- Transmission:
- Birds: Spreads easily between birds through bodily fluids (saliva, faeces, nasal discharge) and contaminated environments.
- Humans: Primarily occurs through direct contact with infected birds or surfaces, inhaling infected droplets, or consuming undercooked poultry meat from infected birds.
- Symptoms:
- The symptoms of bird flu in humans are similar to those of regular influenza and include:
- Can range from mild (fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches) to severe (pneumonia, respiratory failure, multi-organ failure, death).
- Symptoms usually appear within 3-7 days of exposure.
- Treatment: Antiviral medications like Tamiflu have proven effective in managing human infections caused by avian influenza viruses, reducing both the severity of symptoms and the likelihood of fatalities.
Avian Influenza in India:
- Initial Incidence: The first instance of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) H5N1 in India occurred in 2006 in Navapur, Maharashtra, marking the onset of recurrent annual outbreaks.
- The emergence of H5N8 was documented in India in November 2016, primarily affecting wild birds in five states, with Kerala reporting the highest number of cases.
- This disease has been identified in 24 states and union territories, prompting the culling of over 9 million birds to curb its spread.
- Corresponding Strategy: India's strategy for managing Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) revolves around a "detect and cull" approach, as delineated in the National Action Plan for Prevention, Control, and Containment of Avian Influenza (revised - 2021).
Indian Immunologicals rolls out indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine (Financial Express)
- 22 Jan 2024
Why is it in the News?
Indian Immunologicals Ltd (IIL), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) recently announced that it has launched India’s first indigenously developed Hepatitis A vaccine, Havisure.
About Havisure Vaccine:
- The vaccine is effective in preventing the disease and is recommended for children in routine immunization.
- It is a two-dose vaccine wherein the first dose is administered at above 12 months of age and the second dose is given at least after 6 months of the first dose.
- The vaccine is also recommended for individuals who are at risk of exposure or travel to the regions with high hepatitis A prevalence.
- In addition to this people with occupational risk of infection and suffering from chronic liver diseases also need Hepatitis A vaccination.
Key Facts About Hepatitis A:
- Hepatitis A is an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV).
- The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected (and unvaccinated) person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the faeces of an infected person.
- The disease is closely associated with unsafe water or food, inadequate sanitation, poor personal hygiene and unprotected sex.
- Unlike hepatitis B and C, hepatitis A does not cause chronic liver disease but it can cause debilitating symptoms and rarely fulminant hepatitis (acute liver failure), which is often fatal.
- Hepatitis A occurs sporadically and in epidemics worldwide, with a tendency for cyclic recurrences.
- Epidemics related to contaminated food or water can erupt explosively, such as the epidemic in Shanghai in 1988 that affected about 300,000 people.
- They can also be prolonged, affecting communities for months through person-to-person transmission.
- Hepatitis A viruses persist in the environment and can withstand food production processes routinely used to inactivate or control bacterial pathogens.
- Geographical distribution: Infection is common in low- and middle-income countries with poor sanitary conditions and hygienic practices, and most children (90%) have been infected with the hepatitis A virus before the age of 10 years, most often without symptoms.
- Transmission: The hepatitis A virus is transmitted primarily by the fecal-oral route; that is when an uninfected person ingests food or water that has been contaminated with the feces of an infected person.
- In families, this may happen through dirty hands when an infected person prepares food for family members.
- Waterborne outbreaks, though infrequent, are usually associated with sewage-contaminated or inadequately treated water.
- Symptoms: Symptoms of hepatitis A range from mild to severe and can include fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark-coloured urine and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin).
- Not everyone who is infected will have all the symptoms.
- Treatment: There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A.
- Recovery from symptoms following infection may be slow and can take several weeks or months.
- Prevention: Improved sanitation, food safety and immunization are the most effective ways to combat hepatitis A.
Rating agencies too subjective, loaded against India, need reform: CEA (Indian Express)

- 22 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Credit rating agencies need to reform their sovereign rating process to correctly reflect the default risk of developing economies, saving billions in funding costs, the government’s chief economic adviser, V Anantha Nageswaran, said recently.
What is a Sovereign Credit Rating?
- A Sovereign Credit Rating serves as an assessment of a government's ability to meet its debt obligations, with a lower rating reflecting higher credit risk.
- Rating agencies typically consider multiple factors such as growth rate, inflation, government debt, short-term external debt as a percentage of GDP, and political stability.
- A positive credit rating not only boosts credibility but also indicates a history of timely loan repayments, aiding banks and investors in evaluating loan applications and determining appropriate interest rates.
- The global credit rating industry is dominated by three major agencies: Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch.
- Despite India's ascent from the 12th to the 5th largest economy globally in 2023, with the second-highest growth rate among comparable economies, its credit ratings from S&P and Fitch stand at BBB, while Moody's rates it at Baa3—indicating the lowest investment-grade level.
Concerns Regarding Credit Rating Methodology:
- A quantitative examination revealed that more than 50% of credit ratings rely on qualitative components.
- Institutional Quality, predominantly gauged through the World Bank’s Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGIs), emerges as the primary factor influencing the credit rating of a developing economy.
- This poses a challenge as these metrics are often non-transparent, perception-driven, and derived from a limited group of experts, making them inadequate in representing the sovereign's willingness to meet its financial obligations.
- The non-trivial impact of these indicators on ratings implies that developing economies must exhibit progress along subjective indicators to secure a credit rating upgrade.
CEA's Suggestions for Credit Rating Reform:
- The Chief Economic Advisor (CEA) proposed a shift towards primarily considering a country's historical debt repayment record as a key determinant of its 'willingness to pay,' in contrast to relying on potentially suboptimal qualitative information.
- Embracing such a model would significantly enhance the credibility of Credit Rating Agencies (CRAs).
- The use of qualitative information and judgment should only be a last resort when genuine, verifiable data options are unavailable.
- If governance indicators are to be employed, they should be grounded in clear, well-defined, and measurable principles, steering away from subjective assessments by CRAs.
- CRAs possess a comprehensive database of global best practices, influencing their judgments.
- Sharing this knowledge with the countries they assess would empower sovereigns to take targeted actions to enhance their creditworthiness.
Cops lose Rs 12 crore in chit fund scheme, probe on (TOI)

- 20 Dec 2023
Why is it in the News?
Around 70 persons belonging to AP special police have lost nearly Rs 12 crore in a chit fund scheme in Mangalagiri, said the police. Mangalagiri police registered a case and launched an public sector investigation.
What are Chit Funds?
- Chit funds, also known as Kuri and Chitty, serve as versatile financial instruments encompassing both borrowing and saving components.
- In this financial arrangement, a group of individuals collectively contributes a fixed sum at regular intervals, with the understanding that one member will receive the total pooled amount during each interval.
- This process repeats until every member has received their share.
- Typically managed by a chit-fund company, this financial instrument operates by having a group of contributors make regular contributions toward the chit value for a duration equivalent to the total number of subscribers.
- The recipient of the pooled money is determined through an auction or lucky draw, employing a reverse auction system where the individual willing to accept the lowest amount is chosen.
- The sum forfeited by the winning bidder is distributed among other bidders, deducting a foreman's charges and commission.
- The share each bidder receives is termed a dividend. Interestingly, a winning bidder can continue to invest in subsequent intervals, even after claiming their sum.
Types of Chit Funds:
Chit funds can be categorized into three types:
- Chit Funds Run by State Governments:
- Managed and regulated by state governments.
- Public sector undertakings (PSUs) also fall under this category.
- These funds are considered safe, with limited chances of loss. Business processes are transparent and well-regulated.
- Private Registered Chit Funds:
- Registered under the Chit Funds Act of 1982.
- Typically initiated by well-established financial institutions or business entities.
- While participation in these funds may not be as secure as state-run or public-sector funds, the calculated risk is manageable due to their association with reputable private-sector entities.
- Unregistered Chit Funds:
- These chit-funds lack legal recognition, and participation involves a higher risk.
- Commonly found throughout India, they are often formed by a close-knit group of associates.
- Participation in unregistered chit funds is discouraged due to the potential for disputes, which rely heavily on the integrity and honesty of the members involved.
What is Saradha Chit Fund Scam?
- The Saradha scam, also known as the Saradha Group financial scandal, was a major financial scam that surfaced in 2013.
The Saradha scheme:
- The scheme, run by Saradha Group (an umbrella company with 200 private players), was launched in the early 2000s by businessman Sudipto Sen.
- Aimed at small investors, the scheme became popular in a very short time as it promised high returns.
- The money was collected through a wide network of agents, who were paid commissions of over 25 per cent.
- The Saradha Group raised about Rs 2,500 crore in a few years time.
- The company used varied marketing means to build its brand.
- Apart from popular marketing techniques like celebrity endorsements, the company used to sponsor cultural events such as Durga Puja and invest in popular football clubs to attract more investors.
- The scheme soon expanded to Odisha, Assam, and Tripura, and the number of investors reached close to 1.7 million.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) (TOI)

- 04 Aug 2023
Why in the News?
The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) has reported that three private sector satellite manufacturers plan to launch their earth observation satellites during this fiscal year.
About Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe):
- IN-SPACe serves as a single-window, independent, and autonomous agency within the Department of Space (DOS).
- It was established as part of the Space sector reforms to encourage and facilitate the active involvement of private players in the space industry.
- IN-SPACe's responsibilities include promoting, enabling, authorizing, and supervising various space activities of non-governmental entities, such as manufacturing launch vehicles and satellites, providing space-based services, and utilizing space infrastructure and facilities.
- Acting as an intermediary between ISRO and Non-Governmental Entities (NGEs), the agency assesses opportunities for leveraging India's space resources effectively and enhancing space-based initiatives.
- Also, IN-SPACe addresses the specific needs and demands of private players, including educational and research institutions, while working in collaboration with ISRO.
- The headquarters of IN-SPACe is located in Bopal, (Ahmedabad).
Green Rising initiative launched at RewirEd summit to empower Youth-Led climate solutions (DD News)

- 09 Dec 2023
What is the Green Rising Initiative?
- The "Green Rising" initiative focuses on engaging youth for impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level, aligning with the global effort to address the severe impacts of climate change.
- This initiative encompasses both the global "Green Rising" initiative and the "Green Rising India Alliance," a collaborative endeavor that brings together UNICEF, Generation Unlimited, and a diverse network of public, private, and youth partners.
- The primary objective is to mobilize millions of young individuals globally, encouraging their active engagement in green initiatives aimed at addressing and adapting to the profound impacts of climate change within their communities.
- In India, this effort is channelled through the YuWaah campaign, which specifically focuses on harnessing the energy and commitment of the youth to drive impactful environmental actions at the grassroots level.
About UNICEF:
UNICEF, or the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, is a specialized agency of the United Nations committed to promoting the well-being and rights of every child globally.
- Foundation and Establishment: Established in 1946 by the United Nations General Assembly, UNICEF was originally designed to provide emergency food and healthcare to children in countries devastated by World War II.
- Over time, UNICEF's scope evolved to include long-term developmental programs, focusing on education, healthcare, nutrition, clean water, sanitation, and protection for children in need.
- UNICEF is governed by an Executive Board consisting of 36 members who are elected to terms of three years by the United Nations Economic and Social Council.
- Universal Presence: UNICEF operates in over 190 countries and territories worldwide, making it one of the most extensive and widely recognized humanitarian organizations globally.
- Child Rights Advocacy: UNICEF is a leading advocate for children's rights, working to ensure that every child has the right to survive, thrive, and reach their full potential, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Emergency Response: In times of crises, including natural disasters, conflicts, and pandemics, UNICEF plays a crucial role in providing immediate and life-saving assistance to affected children and communities.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: UNICEF collaborates with governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), other UN agencies, and the private sector to implement its programs and maximize its impact.
- Funding Mechanism: UNICEF is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from governments, private donors, businesses, and the general public. It relies on these funds to carry out its programs and respond to emergencies.
- Focus on Equality and Inclusion: UNICEF emphasizes the importance of equality and inclusion, working to address disparities and ensure that the most vulnerable children, including those with disabilities or from marginalized communities, are not left behind.
- Global Campaigns: UNICEF spearheads global campaigns to address critical issues affecting children, such as vaccination drives, education initiatives, and efforts to eliminate child labour and violence against children. These campaigns aim to rally public support and create awareness about the challenges faced by children worldwide.
- It was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1965 for the “promotion of brotherhood among the nations”.
- Headquarters: New York City
